
VHF FM TRANSCEIVER
TK -6 11 0
SERVICE MANUAL
Microphone
(T91-0621-05)
Cabinet
(A01-2170-03)
© 2000-6 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8519-00 (N) 1113
Knob (VOL)
(K29-5389-03)
CONTENTS
GENERAL ................................................................. 2
SYSTEM SET-UP ..................................................... 3
OPERATING FEATURES ......................................... 4
REALIGNMENT........................................................ 8
INSTALLATION...................................................... 10
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION......................................... 13
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA..................................... 18
DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENTS ....................... 20
PARTS LIST ............................................................ 22
EXPLODED VIEW .................................................. 31
Key top
(K29-5388-02)
PACKING ................................................................ 32
ADJUSTMENT ....................................................... 33
TERMINAL FUNCTION ......................................... 40
PC BOARD VIEWS
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6100-XX) (A/3, C/3) ........... 41
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6100-XX) (B/3).................... 47
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................ 51
BLOCK DIAGRAM................................................... 57
SPECIFICATIONS................................................... 59
Panel assy
(A62-0761-13)

TK-6110
GENERAL
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians familiar with similar types of commercial grade communications equipment. It contains all required service information for the equipment and is current as of the publication data. Changes which may occur after publication are
covered by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions.
These are issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment information, the full part identification number should be included.
This applies to all parts : components, kits, or chassis. If the
part number is not known, include the chassis or kit number
of which it is a part, and a sufficient description of the required component for proper identification.
PERSONNEL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personnel safety :
• DO NOT transmit if someone is within two feet (0.6
meter) of the antenna.
• DO NOT transmit until all RF connectors are verified se-
cure and any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF and DO NOT operate this equipment near
electrical blasting caps or in an explosive atmosphere.
• All equipment should be properly grounded before
power-up for safe operation.
• This equipment should be serviced by a qualified techni-
cian only.
3. PRE-INSTALLATION CHECKOUT
3-1. Introduction
Each radio is adjusted and tested before shipment. However, it is recommended that receiver and transmitter operation be checked for proper operation before installation.
3-2. Testing
The radio should be tested complete with all cabling and
accessories as they will be connected in the final installation. Transmitter frequency, deviation, and power output
should be checked, as should receiver sensitivity, squelch
operation, and audio output. Signalling equipment operation
should be verified.
4. PLANNING THE INSTALLATION
4-1. General
Inspect the vehicle and determine how and where the
radio antenna and accessories will be mounted.
Plan cable runs for protection against pinching or crushing wiring, and radio installation to prevent overheating.
4-2. Antenna
The favored location for an antenna is in the center of a
large, flat conductive area, usually at the roof center. The
trunk lid is preferred, bond the trunk lid and vehicle chassis
using ground straps to ensure the lid is at chassis ground.
4-3. Radio
The universal mount bracket allows the radio to be
mounted in a variety of ways. Be sure the mounting surface
is adequate to support the radio’s weight. Allow sufficient
space around the radio for air cooling. Position the radio
close enough to the vehicle operator to permit easy access
to the controls when driving.
PRE-INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS
1. UNPACKING
Unpack the radio from its shipping container and check
for accessory items. If any item is missing, please contact
KENWOOD immediately.
2. LICENSING REQUIREMENTS
Federal regulations require a station license for each radio installation (mobile or base) be obtained by the equipment owner. The licensee is responsible for ensuring transmitter power, frequency, and deviation are within the limits
permitted by the station license.
Transmitter adjustments may be performed only by a licensed technician holding an FCC first, second or general
class commercial radiotelephone operator’s license. There
is no license required to install or operate the radio.
2
4-4. DC Power and wiring
1. This radio may be installed in negative ground electrical
systems only. Reverse polarity will cause the cable fuse
to blow. Check the vehicle ground polarity before installation to prevent wasted time and effort.
2. Connect the positive power lead directly to the vehicle
battery positive terminal. Connecting the Positive lead to
any other positive voltage source in the vehicle is not recommended.
3. The cable provided with the radio is sufficient to handle
the maximum radio current demand. If the cable must be
extended, be sure the additional wire is sufficient for the
current to be carried and length of the added lead.
GENERAL / SYSTEM SET-UP
TK-6110
5. INSTALLATION PLANNING – CONTROL STATIONS
5-1. Antenna system
Control station. The antenna system selection depends
on many factors and is beyond the scope of this manual.
Your KENWOOD dealer can help you select an antenna system that will best serve your particular needs.
5-2. Radio location
Select a convenient location for your control station radio
which is as close as practical to the antenna cable entry
point. Secondly, use your system’s power supply (which
supplies the voltage and current required for your system).
Make sure sufficient air can flow around the radio and
power supply to allow adequate cooling.
SYSTEM SET-UP
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and alignment procedures contained in this manual.
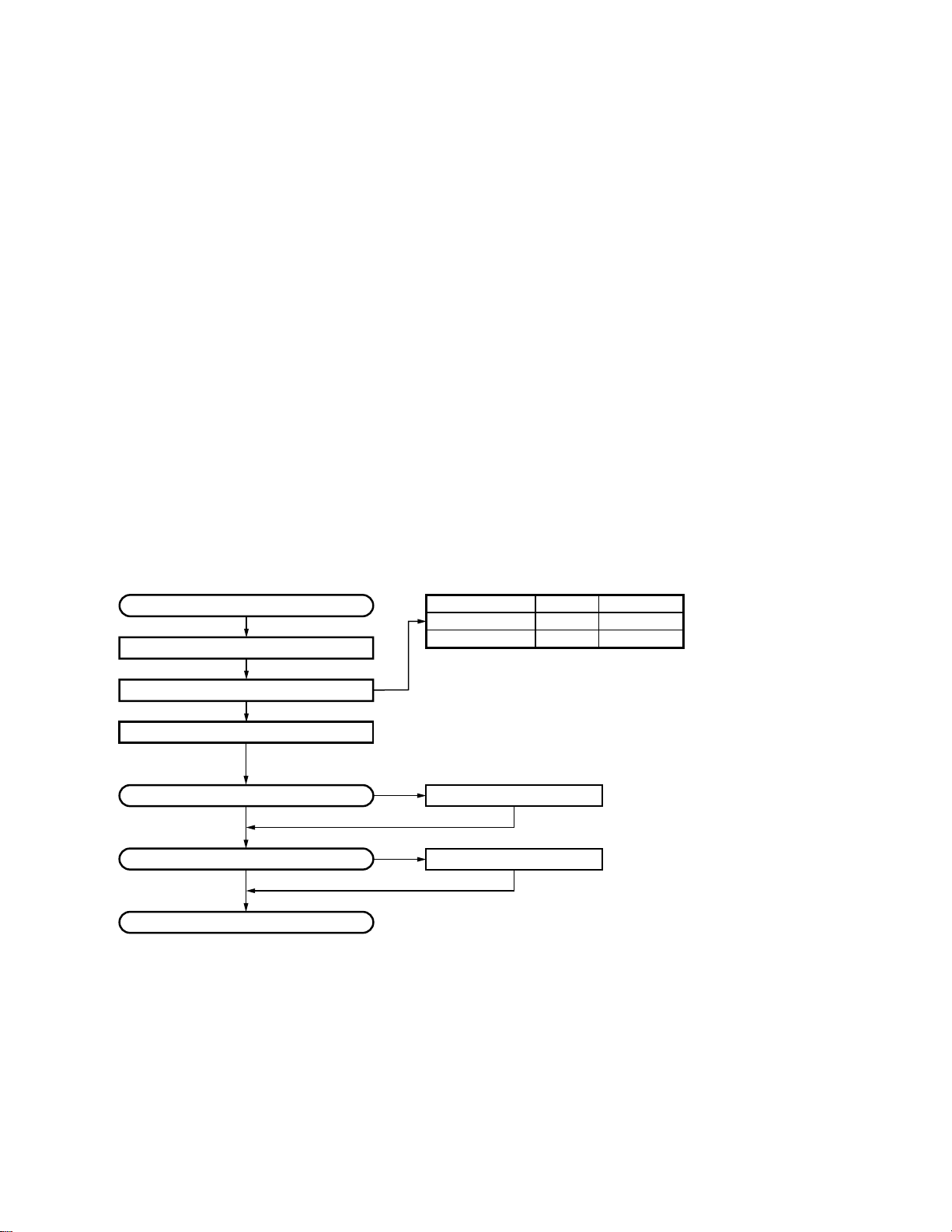
Merchandise received
License and frequency allocated by FCC
Choose the type of transceiver
Transceiver programming
Are you using the external speaker?
NO
Are you using the ignition sense cable?
NO
Delivery
Frequency range
29.7~37MHz
35~50MHz
See page 8
A personal computer (IBM PC or compatible), programming interface (KPG-46),
and programming software (KPG-59D) are required for programming.
(The frequency and signalling data are programmed for the transceiver.)
YES
YES
KES-4 (EXT. SP)
RF power
70W
70W
KCT-18
Type
TK-6110 K
TK-6110 K2
See page 12
See page 12
3
TK-6110
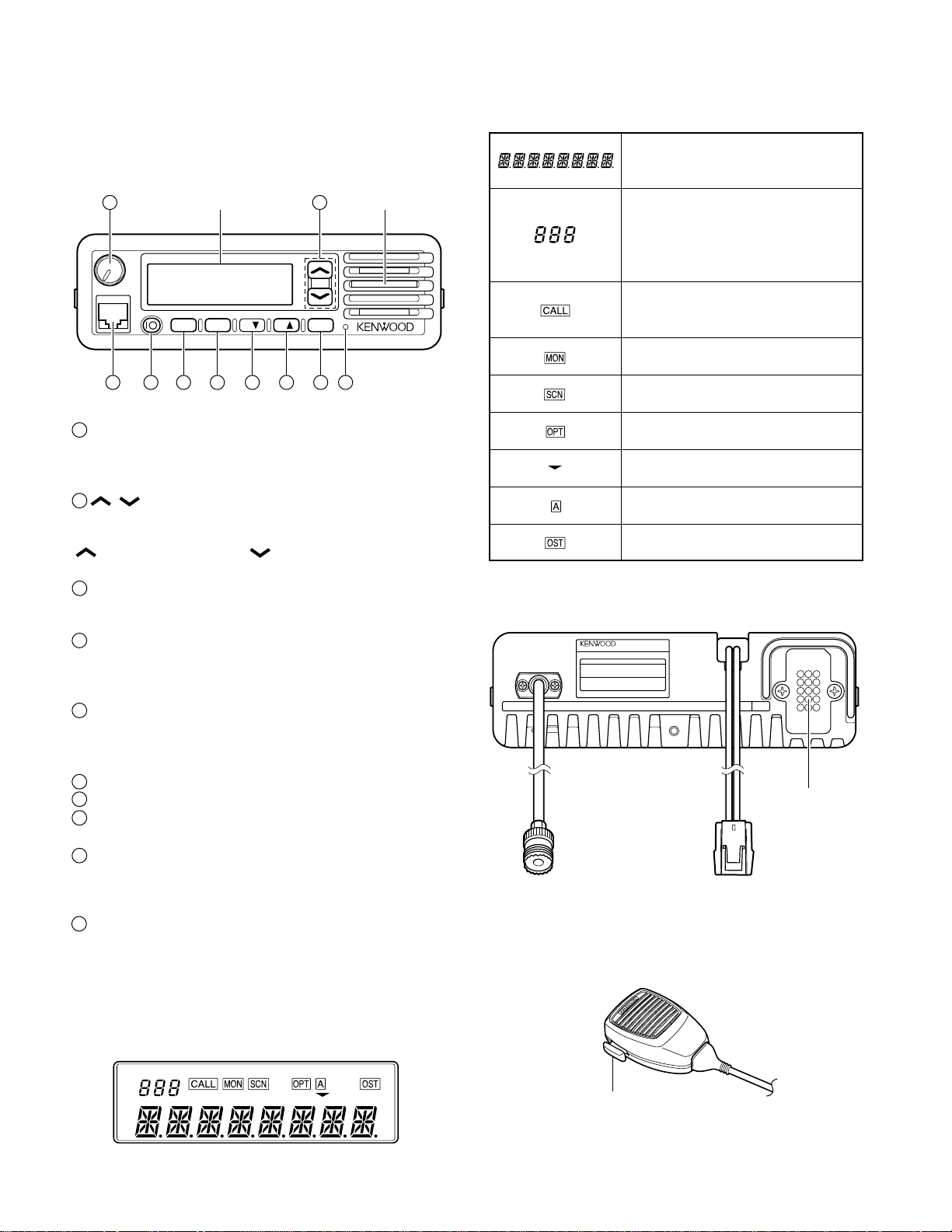
TK-6110
Antenna
connector
Power input
connector
15 pin connector
(for accessories)
PTT (Push To Talk) switch
Press and hold to transmit,
then speak into the microphone.
Release to receive.
OPERATING FEATURES
1. Controls and Functions
1-1. Front Panel
1
3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1
Volume control
Turn clockwise to increase the volume. Turn counter-
clockwise to decrease the volume.
2
/ keys
Press these keys to activate their programmable functions. The default settings of these keys are “Channel Up”
(
) and “Channel Down” ( ).
3
Microphone jack
Insert the microphone plug into this jack.
Display
MON A B C SCN
Speaker
2
10
Displays the operating Channel number,
the Channel name, and the transceiver
status.
Displays the operating channel number
and the channel status:
P indicates a Priority channel
HC indicates a Home Channel
tA indicates Talk Around mode
Flashes when a call is received by DTMF
or 2-Tone signaling. Appears during and
after transmitting if set by the dealer.
Appears when signaling squelch is
turned OFF.
Appears while scanning is in progress.
Appears when the optional scrambler
board is enabled.
Appears when the selected channel is in
the scanning sequence.
Appears when Aux is ON.
Appears when Operator Selectable Tone
is enabled.
1-3. Rear Panel
4
IO (Power) switch
Press to switch the power ON. Press and hold for approximately 1 second to switch the power OFF.
5
MON key
Press MON to activate its programmable function. The
default setting of this key is “Monitor”.
A key
6
7
B▼ key
8
C▲ key
SCN key
9
Press SCN to activate its programmable function. The
default setting of this key is “Scan”.
10
LED
Lights red while transmitting. Lights green while the selected channel is busy. Blinks orange when you receive a
call by 2-Tone or DTMF.
Press these PF (programmable function)
keys to activate their programmable func-
tions. The default setting of these keys is
“No Function”.
1-2. Display
1-4. Microphone
4

OPERATING FEATURES
TK-6110
2. Scanning
2-1. Start Scanning
You can start scanning when 1 priority channel and at
least 1 ADD channel, or 2 or more ADD channels are selected. The transceiver must be in the normal receiving
mode (releasing PTT).
Press the key programmed to the scan, the scan starts.
The “SCN” (scan) icon appears on the main display and
“SCAN” or revert channel appears on the 8-digit alphanumeric display.
2-2. Stop Scanning
The scan stops temporarily if the following conditions are
satisfied.
1) A carrier is detected, then signalling matches on channel
for which receive the signalling is set by the program-
ming software.
2) A carrier is detected on the channel for which receiving
signalling is not set by the programming software or
when the monitor (signalling cancel) function is activated.
2-3. Types of Scan Channel
1) Priority channel is the most important channel for the
scan, and always detects a signal during scan and when
the scan stops temporarily.
2) Non-priority channels detects a signal during scan and
when scan stops temporarily.
2-4. Setting Priority Channel
Priority channel can be set as follows with the programming software (KPG-59D).
1) Specify priority channel as fixed priority channel.
2) Make selected channels, priority channels.
2-5. Scan Type Depending on the Priority Channel
1) When no priority channels are set : Only the non-priority
channels are scanned.
If the transceiver stops on a non-priority channel, priority
channel is still checked for signals at the specified time
intervals.
If the transceiver detects a signal on a priority channel, it
pauses at the priority channel and starts receiving the
calls.
2) When priority channel is set : Either priority channel is
scanned.
If a priority channel stops temporarily, it stops until there
is no signal on the priority channel.
2-6. Revert Channel
The revert channel is used to transmit during scanning
and set by the programming software (KPG-59D).
1) Last called channel
The transceiver reverts to the last called channel during
the scan.
2) Last used channel
The transceiver reverts to the last used (transmitted)
channel during scan. “Last used” revert channel in-
cludes talkback function.
3) Selected with talkback
The transceiver reverts to the channel before scanning or
the channel that you changed during scan.
4) Selected channel
The transceiver reverts to the channel before scanning or
the channel that you changed during scan.
While the transceiver pauses scanning, the revert channel becomes the channel you selected with [CH UP], [CH
DW], [CH1] to [CH5] in the last step.
5) Priority with talkback
The transceiver reverts to the priority channel.
If you press PTT during a resume timer (dropout delay
time, TX dwell time) or calling, you can transmit on current channel to answer to the call however revert channel
is set to priority channel.
After resume time, scan re-starts and transmission channel is return to priority channel.
6) Priority
The transceiver reverts to the priority channel.
2-7. Scan End
When you press the key once again, programmed to the
scan function during scan mode, the scan ends.
The scan icon “SCN” and “SCAN” or revert channel (pro-
grammable) display goes off.
2-8. Temporarily Delete/Add
It is possible to delete or add channel temporarily during
scan. When scan stops on unnecessary channel for example by interference of the other party, activate the delete/
add function (for example press the key), then that channel
is deleted temporarily and scan re-start immediately.
When you would like to add the deleted channel tempo-
rarily to scan sequence, select the desired (deleted) channel
during scan, activate the delete/add function (for example
press the key) before scan re-start.
That channel is added temporarily to scan sequence. The
temporary deleted or added channels are returns to pre-set
delete/add, when the transceiver exits from scan mode.
3. Optional Features
You can use these features using the programming soft-
ware (KPG-59D).
3-1. Beep Tones
The beep tones (power on tone, control tone, warning
tone, alert tone) are individually programmable to the fixed
level 0 to 31 or follow the mechanical volume position.
3-2. Minimum Volume
The minimum volume is programmable (0 to 31). The
transceiver remains the minimum volume level however the
mechanical volume position is set to zero.
3-3. BCL (Busy Channel Lockout) Override
You can transmit in spite of Busy Channel Lockout situa-
tion. For example : To make an emergency voice call.
To transmit under busy channel lockout situation, press
PTT once more within approx. 500ms after the PTT release.
5

TK-6110
ABCDEFGH I
JKLMNOPQR
STUVWXYZ
123456789
0-
All on
OPERATING FEATURES
3-4. Sub LCD Display
You can use 3-digit 7-segment the display to display the
channel number. It is useful when the main (8-digit 13-segment) display indicates channel name.
3-5. Emergency Channel Display
The transceiver can be programmed to display “EMERGENCY” channel name when it is in emergency mode.
If you set to “off” by KPG-59D the transceiver shows
selected group/channel/status before entering to the emergency mode however the transceiver is in an emergency
mode.
3-6. Clear to Transpond
The transceiver waits the transpond of 2-Tone/DTMF if
channel is busy until channel open. This feature replies to
the transpond signal when the caller returns to receive.
3-7. Mode (Enable/Disable)
The transceiver has many special modes mainly for maintenance.
· Panel Test mode
· Clone mode
· Main programming mode
It is possible to set enable/disable for each mode. We
recommend to set these mode to Disable after set up to
save contents.
3-8. ID
The transceiver is capable to have ID. The format is
DTMF. The timing that the transceiver sends ID is programmable.
Begin of TX : Connect ID is send on beginning of trans-
mission.
End of TX : Disconnect ID is send on end of transmission.
Both : Connect ID is send on beginning of transmission
and disconnect ID is send on end of transmission.
Off : Sending ID function is disabled.
There is also “PTT ID” setting for each channel. Refer
“PTT ID” of channel feature.
3-9. OST (Operator Selectable Tone)
The transceiver is capable to have “OST” function and 16
tone pair (QT/DQT) with max 8-digit name for each tone pair.
3-11. “TOT” Pre-Alert
The transceiver has “TOT” pre-alert timer. This parameter selects the time at which the transceiver generates
“TOT” pre-alert tone before “TOT” is expired.
“TOT” will be expired when the selected time passes
from a TOT pre-alert tone.
3-12. “TOT” Re-Key Time
The transceiver has “TOT” re-key timer. This timer is the
time you can not transmit after “TOT” exceeded. After
“TOT” re-key time expired you can transmit again.
3-13. “TOT” Reset Time
The transceiver has “TOT” reset timer. This timer is the
minimum wait time allowed during a transmission that will
reset the “TOT” count.
“TOT” reset time causes the “TOT” to continue even
after PTT is released unless the “TOT” reset timer has expired.
3-14. Signalling
Signalling “AND/OR” sets the audio unmute condition
for any channel programmed with the option signalling (2Tone/ DTMF).
AND : “AND” requires both the valid option signalling
and the programmed QT/DQT to be received for audio to
unmute (and initiate an option signalling decode alert).
OR : “OR” requires either the valid option signalling or
the programmed QT/DQT to be received for audio to
unmute (an option signalling decode alert is only initiated
if the proper option signalling is decoded).
4. Channel Features
You can use these features using the programming software (KPG-59D).
4-1. Alphanumeric Display (Channel Name)
The programming software (KPG-59D) enables you to set
the alphanumeric display for channel name. The total text
size of channel name are 8-digits.
The characters can be used as shown in Figure 1.
•“OST” Back Up
The transceiver is programmable the selected “OST”
code is memorized or not. If you set to Disable (no memorized), the “OST” function always starts at “off”.
3-10. “TOT” (Time-Out Timer)
The transceiver has the “TOT”. This parameter selects
the period of time users can continuously transmit.
When the selected period passes, the transceiver generates an warning tone and stops the transmission.
6
Fig. 1

OPERATING FEATURES
TK-6110
4-2. Option Signalling
The transceiver is programmable to the option signalling
(2-Tone decode program 1, 2-Tone decode program 2, 2Tone decode program 3, DTMF decode) to each channel. It
is useful to receive an individual call.
Receive format is selectable “AND” or “OR” with QT/
DQT. The radio response of option signalling is programmable call Alert and “Transpond” for each option signalling
(2-Tone decode program 1, 2-Tone decode program 2, 2Tone decode program 3, DTMF).
4-3. PTT ID
PTT ID provides a DTMF ANI to be sent with every time
PTT (connect ID at beginning of transmission, disconnect ID
at end of transmission, or both).
You can program PTT ID “on” or “off” for each channel.
The contents of ID are programmed for each transceiver.
4-4. Busy Channel Lockout
Transmission is inhibited when the channel is busy. It is
able to set this feature “Yes” or “No” for each channel.
4-5. Scan Delete/Add
Scanning “delete/add” is programmable for each channel. Set the currently selected channel required to include in
the scan sequence to “add”.
The operator can change the “delete/add” information
using the key programmed to “delete/add” function.
5. Key Functions
5-1. No Function
Sounds error operation beep, and no action will occur.
Use this function when the transceiver is required to be
more simple operated.
5-2. AUX.
The AUX function can be programmed for push key.
If this key is pressed, the “A” icon lights on the LCD and
the AUX port which is contained in 15-pin connector located
at the rear of the transceiver goes to low level.
If pressed again, the “A” icon goes off and the AUX port
goes to Open-collector.
5-3. Channel Down
If this key is pressed once, the channel number decreases by one step. If this key is hold down, the channel
number decreases continuously.
5-4. Channel Up
If this key is pressed once, the channel number increases
by one step. If this key is hold down, channel number increases continuously.
5-6. Delete/Add
This key switches the currently displayed channel be-
tween “Delete” and “Add”.
The “Add” channel contained in the scan sequence, and
“Delete” channel is not contained. In the scan mode, this
key switches the channel delete or add temporarily.
5-7. Home Channel
Press this key once, the channel switches to the pre-programmed home channel. Press this key again, the channel
goes back to the previous channel.
5-8. Monitor
Monitor the channel before a transmission. Press this
key once, “MON” appears and unmutes speaker if a carrier
is present, regardless of the specified signalling (including
option signalling). Press this key again, “MON” disappears
and mutes speaker.
Press this key after the Option Signalling is matched, the
Option Signaling is reset. DBD (Dead Beat Disable) mode is
not reset by this operation.
Press and hold the Monitor key for 2 seconds to disable
the squelch.
5-9. Operator Selectable Tone
When this key is pressed, the “OST” icon lights and Encode/Decode QT/DQT is switched to the OST Tone pair. If
pressed again, the “OST” icon goes off and Encode/Decode
QT/DQT returns to KPG-59D pre-set.
When this key is held down for 1 second, the transceiver
enters “OST Select Mode”. In this mode, the display
shows OST No. or OST Name which is set to the channel
and operator can select one of OST Tone pair using UP key
and DW key.
If pressed this key again, the displayed OST code is
memorized to the channel, the transceiver exits from the
OST Select Mode, returns to normal channel display and
“OST” icon lights.
16 kinds of tone pair for OST can be programmed by
KPG-59D. OST is useful to access the repeater with same
radio frequency and different tone (QT/DQT).
5-10. Scan
Press this key starts scanning. Pressing this key stops
scanning.
5-11. Squelch Level
The preset squelch level is varied in user mode (0 to 15).
Press the key programmed to “squelch level”, the transceiver enters to “squelch level adjust mode”.
The squelch level can be adjusted by
key programmed to “squelch level” again, the adjusted
level is memorized and returns to the normal user mode.
/ . Press the
5-5. Channel Name
This key switches the LCD display between the current
channel number and programmed channel name.
5-12. Talk Around
Press this key, the transceiver uses the receive frequency and the tone for transmission.
The operator can call the other party directory (without
repeater). Press this key again, the talk around function
goes off.
7
TK-6110
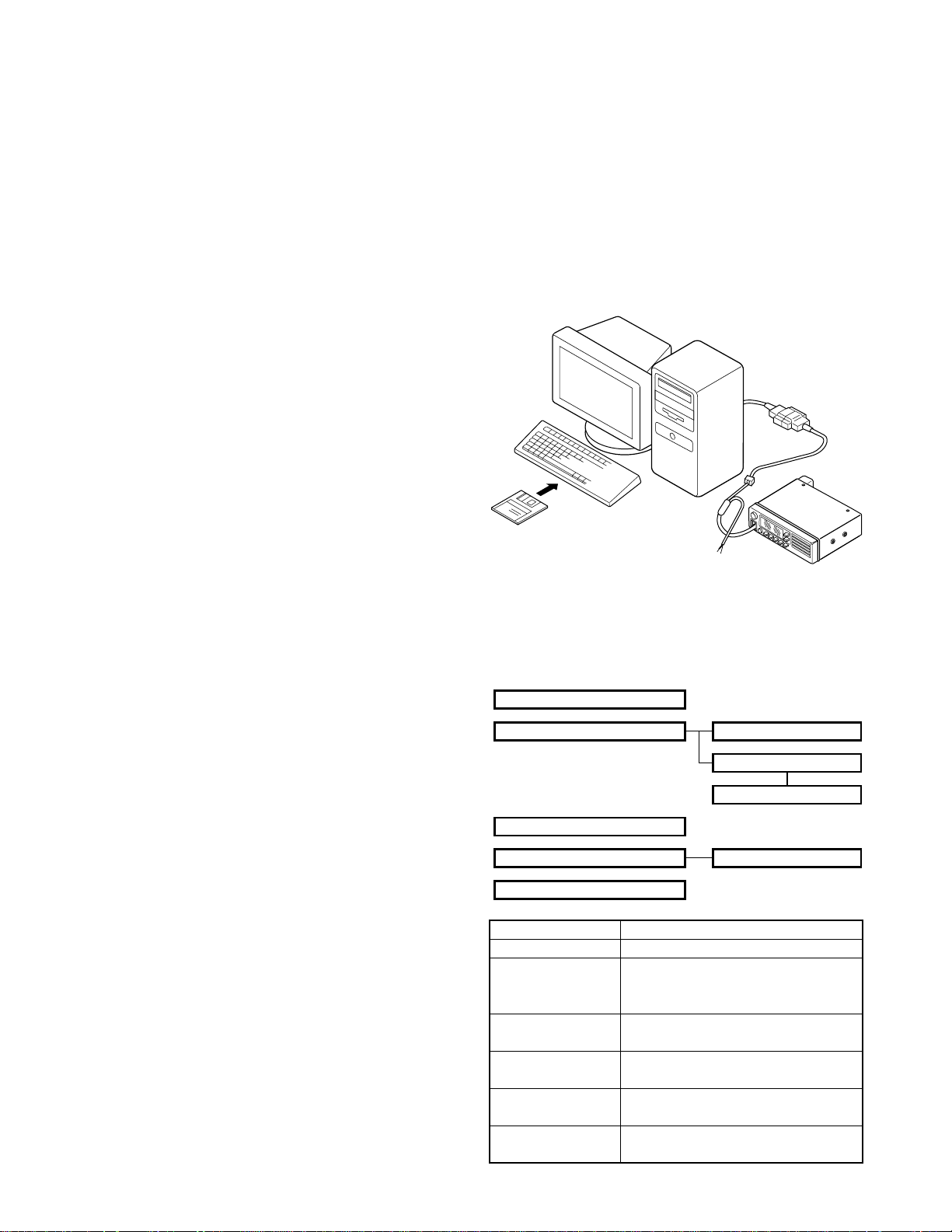
User mode
PC mode
PC programming mode
PC test mode
PC tuning mode
Panel test mode
Panel tuning mode
Clone mode
Main programming mode
OPERATING FEATURES / REALIGNMENT
5-13. Emergency Call
When the Emergency function (key) is activated, the ra-
dio enters the “Emergency Mode”.
In this mode, the radio automatically switches to the programmed “Emergency Channel” and starts transmission
with the Emergency ID Code programmed in an installed
ANI Board (dependent on ANI board capabilities and programming). The LCD display (Emergency Text) and the TX
LED operation are dependent on the “Emergency CH Display” settings.
6. 2-Tone
2-Tone signalling opens the squelch only when the RADIO receives a proper 2-Tone code that is the same as the
pre-programmed 2-Tone for the channel. When the RADIO
receives a 2-Tone code, the CALL icon flashes.
If Transpond has been programmed, the RADIO will return an acknowledgment signal automatically after receiving
the 2-Tone code.
If Alert Tone has been programmed, an Alert Tone
sounds after receiving a 2-Tone code. Unmute condition is
canceled and the CALL icon goes off when ; (1) pressing the
[MON] Key, (2) hanging the microphone on its hook, (3) muting continues for 10 seconds. (If “Auto Reset” has been
programmed)
7. DTMF
DTMF Signalling opens the squelch only when the RADIO receives a proper DTMF code that is the same as the
pre-programmed “Primary Code (Individual ; 1~7digits)” or
“Secondary Code (Group ; 1~7digits)”. When the RADIO receives a correct code, the CALL icon flashes.
If Transpond has been programmed, the RADIO will return an acknowledgment signal automatically after receiving
the DTMF code.
If Alert Tone has been programmed, an Alert Tone
sounds after receiving a DTMF code. Unmute condition is
canceled and the CALL icon goes off when ; (1) pressing the
[MON] Key, (2) hanging the microphone on its hook, (3) muting continues for 10 seconds (If “Auto Reset” has been programmed), and (4) receiving reset code. (Primary code +
“#” or secondary code + “#”)
8-3. Programming Software KPG-59D Description
KPG-59D is the programming software for TK-6110 supplied on two 3.5" floppy disks. This software runs under MSDOS version 3.1 or later, and Windows MS-DOS prompt on
an IBM-PC or compatible machine.
The data can be input to or read from TK-6110 and edited
on the screen. The programmed or edited data can be
printed out. It is also possible to tune the transceiver.
We recommend that install KPG-59D for example to
harddisk first then use it.
KPG-46
IBM-PC
KPG-59D
TK-6110
Fig. 2
REALIGNMENT
1. Mode
8. Data Programming (PC Mode)
8-1. Preparation and Connection
The TK-6110 transceiver is programmed by using a personal computer, programming interface cable KPG-46, and
programming software KPG-59D.
The programming software can be used with an IBM-PC
or compatible machine. Figure 2 shows the setup for programming.
8-2. Programming Interface Cable KPG-46 Description
The KPG-46 is required to interface the transceiver with
the computer. It has a circuit in its D-sub 25pin connector
case that converts RS-232C logic level to TTL level.
KPG-46 is used to connect between transceiver microphone connector and RS-232C serial port of computer.
8
Mode Function
User mode Customer use this mode
PC mode Communication between the radio and
PC (IBM compatible).
It requires the KPG-59D.
PC programming Frequency, signalling and features write
mode to the radio and read from the radio.
PC test mode Check the radio using the PC.
This feature is included in the FPU.
Panel test mode Dealer uses to check the fundamental
(Refer to ADJUSTMENT)
Main programming Re-write to firmware of the flash ROM.
mode
characteristics.
REALIGNMENT
TK-6110
2. How to Enter Each Mode
Mode Operation
User mode Power on
PC mode Turn on the transceiver.
Then, set the transceiver to PC mode from
the menu in KPG-59D.
Panel test mode Hold down the [MON] key, turn the radio
power on.
Main programming
mode
Hold down the [A] key, turn the radio
power on.
3. Clone Mode
1. Turn the master side transceiver power on with the
[SCN] key held down. The master side transceiver displays “CLONE”.
2. Set the power switch on the slave side transceiver to
ON.
3. Connect the cloning cable (E30-3382-05) between the
master side transceiver (source) and slave side transceiver (clone).
4. Press the [SCN] key on the master side transceiver to
start cloning.
5. The TX LED on the master side transceiver flashes when
cloning starts and an “END” message appears when
cloning ends.
6. The BUSY LED on the slave side transceiver flashes.
7. When a problem occurs during cloning, an “ERROR”
message appears on the slave side transceiver.
8. Pressing the [SCN] key sets clone mode again.
4-3. Programming
1. Set the transceiver to Main Programming Mode.
2. Connect the KPG-46 to the transceiver.
3. Start up the programming software (KPG-59D), select
“firmware program” in the “Program” item, and press
the Return key on the personal computer. This starts up
the firmware programmer.
4. The top screen is displayed. Press any key to advance
to the next screen.
5. Set the communications speed (normally, 115,200bps)
and communications port in the Setup item.
6. Set the firmware to be updated by File select.
7. Held down the [A] key. Turn the transceiver power on.
Until the display change to “PROG1152”
8. Check the connection between the transceiver and the
personal computer, and make sure that the transceiver
is in the Main Programming Mode.
9. Press F10 on the personal computer. A window opens
on the display to indicate progress of writing. When the
transceiver starts to receive data, “PG” is appeared on
2 digit sub display.
10. If writing ends successfully, the TX LED on the transceiver lights and the checksum is displayed.
11. If you want to continue programming other transceivers, repeat steps 5 to 8.
Notes :
• To start the Firmware Programmer from KPG-59D, the
Fpro path must be set up by KPG-59D setup.
• This mode cannot be entered if the Main Programming
mode is set to Disable in the Programming software
(KPG-59D).
[SCN]
[SCN]
STARTCLONE
[SCN]
END
4. Main Programming Mode
4-1. Preface
Flash memory is mounted on the transceiver. This allows the transceiver to be upgraded when new features are
released in the future. (For details on how to obtain the firmware, contact Customer Service.)
4-2. Connection Procedure
Connect the transceiver to the personal computer (IBM
PC or compatible) with the interface cable (KPG-46). (Connection is the same as in the PC Mode.)
4-4. Function
1. If you press the [SCN] key while “PROG1152” is displayed, the checksum is displayed. If you press the [C]
key while the checksum is displayed, “PROG1152” is
redisplayed.
2. A transmission speed can be selected by pressing the [C]
key while “PROG1152” is displayed.
115200bps : PROG1152
19200bps : PROG 192
38400bps : PROG 384
57600bps : PROG 576
Note :
Normally, write in the high-speed mode.
5. Panel Test Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
9
TK-6110
1. Optional Voice Scrambler Function
The optional voice scrambler function can be used by two
methods.
1. Assign this function to any programmable keys by using
the programming software (KPG-59D).
When the programmed key is pressed, the
appears and optional scrambler function is enabled.
When the programmed key is pressed again, the
cator disappears and the function is disabled.
2. Assign the optional scrambler function to each channel
by using the programming software (KPG-59D). The optional scrambler function can be used without pressing
the programmed key.
1-1. Scrambler Code Setting
The code can be configured by two methods.
1. Hold down the programmed OPT key to enter the code
setting mode.
Select a new code by pressing [
change.
When the programmed key is pressed again, the new
code is stored and exit the code setting mode.
2. Set a code for each channel by using the programming
software (KPG-59D).
] or [ ] key to
INSTALLATION
indicator
indi-
TX-RX unit
Component side
A
D
B
E
C
F
K
G
H
J
S
X
N
L
T
Y
P
M
W
Z
R
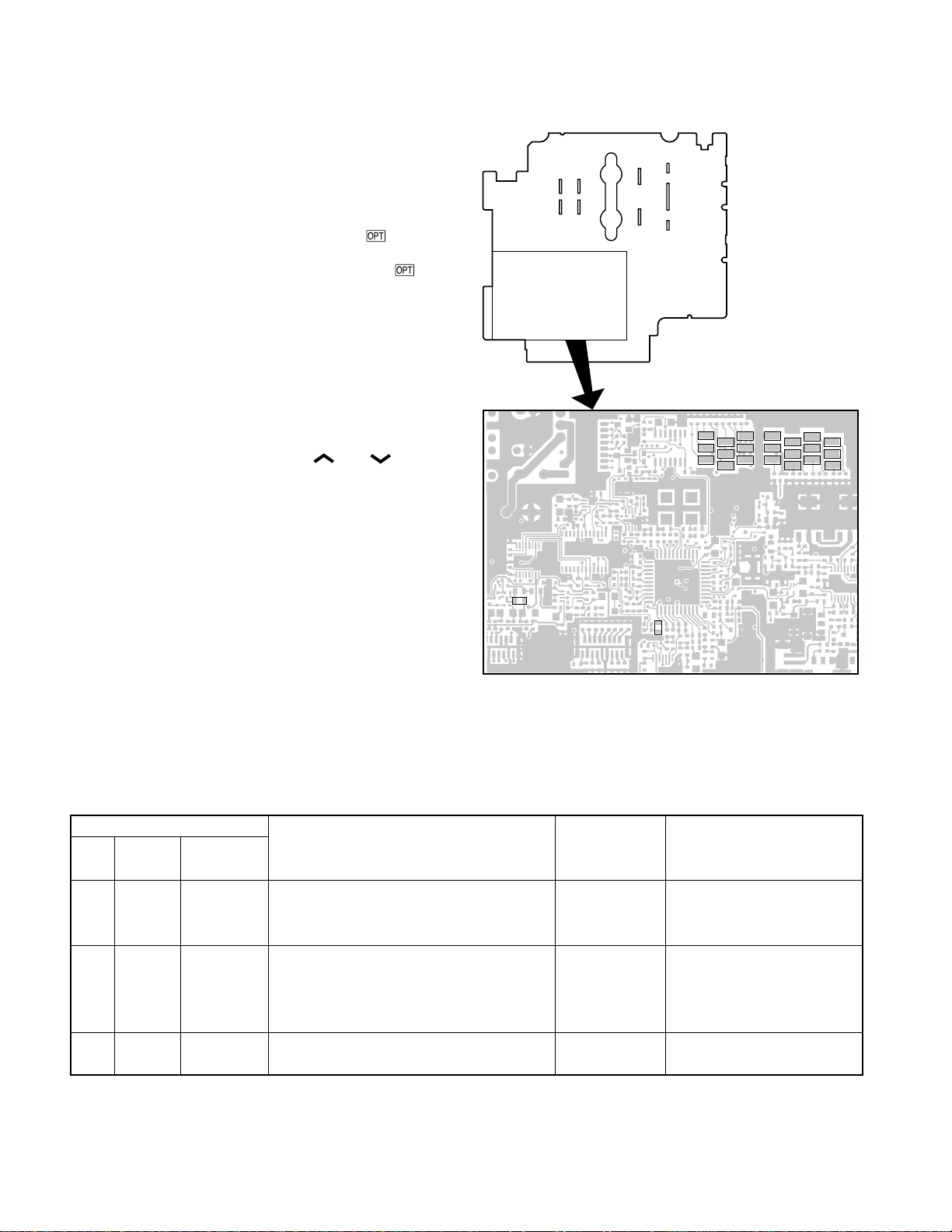
2.Option Board Terminal
R725
Terminals for mounting the option board are provided at
the center of the TX-RX unit. The table shows the correspondence between the board and terminals. Disconnect
R778
R725 and R778 in TX-RX unit when the voice scrambler
board is attached.
Connect the option board to the connection terminals of
the TX-RX unit.
Fig. 1
2-1. Option Port 1 (For ANI board etc.)
Port name
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
(PCB)
(Schematic diagram)
B RX IN Data in Board data input. Connected to Reference
T DATA Data out Board data output. Connected to Reference
OUT ANI board → the circuit 1kHz/150mVrms →
Z TCONT T control Audio amplifier power control → CPU input L : Audio amp on
Name Description Connection Note
Transceiver (Receiver demodulaion circuit) → the circuit 1kHz STD DEV →
ANI board 250~350mVrms
Transceiver (Transmitter modulation circuit) 2.5~3.5kHz (Wide),
1.25~1.75kHz (Narrow)
TX-RX unit microprocessor H : Audio amp off
10
TK-6110
INSTALLATION
Port name
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
(PCB)
(Schematic diagram)
X STONE Side tone Beep during PTT ID Connected to
R AUDI IH Audio inhibit Microphone muting during PTT ID Connected to
K GND Ground Ground Ground
W AUX Aux Emergency channel request → CPU input L : EMG CH request
J PTTO PTT Microprocessor PTT logic → ANI board CPU output L : TX, H : RX
P EMERG Emergency Microprocessor emergency channel logic → CPU output L :
N BUSY
Y KEY
L +8V Board power Switched B Power supply
Name Description Connection Note
the circuit
the circuit
TX-RX unit microprocessor H : No EMG CH request
Emergency operation request
ANI board H :
Channel busy
(Transmission)
Key TX-RX unit microprocessor H : No transmission request
supply
Microprocessor busy logic → ANI board CPU output L : Busy, H : Not busy
Transmission start control GE-star → CPU input L : Transmission request
No emergency operation request
2-2. Option Port 2 (For voice scrambler etc.)
Port name
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
(PCB)
(Schematic diagram)
G CODE 1
D CODE 2
E CODE 3
F CODE 4
A TXOUT TX out Board → Connected to Reference
M RXOUT RX out Board → Transceiver (Audio amp) Connected to
K GND Ground Ground Ground
J PTTO Scrambler modulation/demodulation control CPU output L : TX, H : RX
H CLRC Clear/Code Specifies whether to scramble CPU output L : Scramble, H : Normal
B RXIN RX in Transceiver (Microphone circuit) → Board Connected to Reference
C TXIN TX in transceiver (Microphone circuit) → Board Connected to
L +8V Board power Switched B Power supply
Name Description Connection Note
Scrambler code 1
Scrambler code 2
Scrambler code 3
Scrambler code 4
supply
First of four bits of scrambler code CPU output Board code selection
Second of four bits of scrambler code (Logic by binary code)
Third of four bits of scrambler code
Fourth of four bits of scrambler code
Transceiver (Transmitter modulation circuit) the circuit 1kHz/15mVrms →
2.5~3.5kHz (Wide),
1.25~1.75kHz (Narrow)
the ciircuit
the circuit 1kHz STD DEV →
250~350mVrms
the circuit
11
TK-6110
INSTALLATION
3. Ignition Sense Cable (KCT-18)
The KCT-18 is an optional cable to use the following func-
tions:
3-1. Ignition function
The ignition function allows you to turn the transceiver’s
power on and off with the ignition key of your car. When
you are driving with the ignition key on, the horn alert function is disabled.
3-2. Timed power off function
The timed power off function turns the transceiver’s
power off the time specified with the programming software (KPG-59D) after the ignition key is turned off. When
you are driving with the ignition key on, the horn alert function is disabled.
The ignition sense function and the timed power off func-
tion can be used at the same time.
3-3. Modification
1. Remove the short plug from the accessory connector (15
pins) on the back of the transceiver.
2. Insert the KCT-18 into pin 3 (IGN).
1
3
13
15
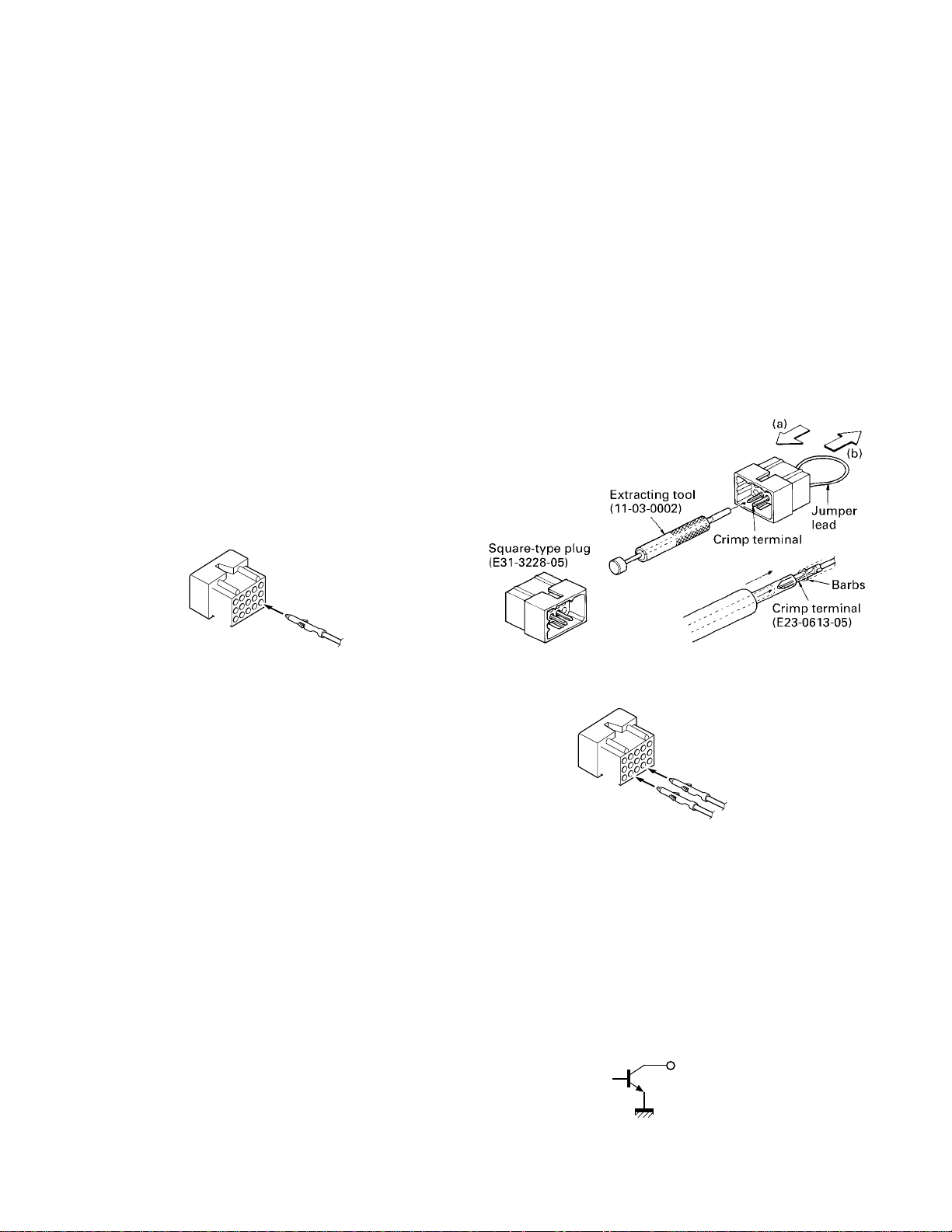
Contact
2. Remove the terminals with the jumper from the connector housing holes number 9 and 12 using the extracting
tool.
Removing the jumper lead (Fig. 3-2)
1) Insert the extracting tool (11-03-0002) into the connector while pushing the jumper lead in the direction
of (a).
2) Push the extracting tool into collapse the barbs of the
crimp terminal.
3) Pull out the lead while continuing to push the extracting tool in the direction (b).
3. Reinsert the terminal with the black and white stripe lead
into hole number 6, and the terminal with the black lead
into hole number 12 (Fig. 3-3).
4. Attach the connector to the external speaker connector
on the radio.
KCT-18
Fig. 2
4. External Speaker (KES-4)
1. The external speaker output from the accessory connector (15 pins) on the back of the transceiver is 10W/4
ohms. Use the KES-4.
4-1. Connection for the KES-4 with the TK-6110
• When taking the AF output from the accessory
connector (15-pin) on the rear of the radio
The following tools are required for changing the connec-
tor.
Extracting tool
the following extracting tool is recommended :
Molex Inc. Order No. : 11-03-0002
1. Remove the connector with jumper from the external
speaker connector on the rear panel of the radio (Fig. 3-
1).
Note : Save the jumper, which is required when the radio
is used without the external speaker.
Fig. 3-1 Fig. 3-2
1
12
3
6
Black lead
Black/White lead
13
15
Fig. 3-3
5. Horn Alert Function
The HR pin of the accessory connector (15-pin) on the
rear of the transceiver is an open collector and the maximum current is 100mA. The maximum available current can
be increased to 1A by installing a relay.
Program the Horn Alert Function, using KPG-59D.
HR (Pin 10)
12
Fig. 4
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-6110
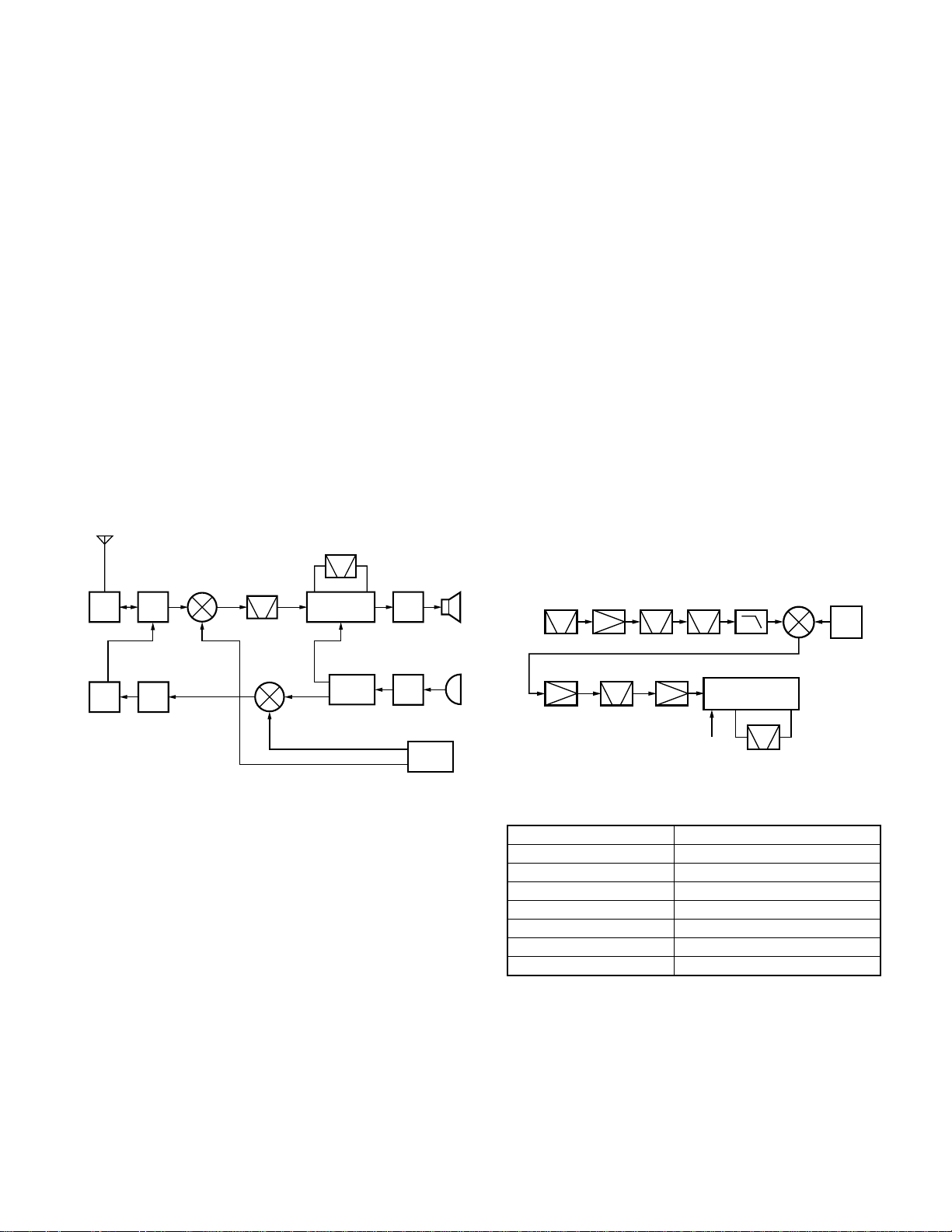
1. Overview
The KENWOOD model TK-6110 is a VHF/FM transceiver
designed to operate in the frequency range of 29.7 to
37MHz (K), 35.0 to 50.0MHz (K2), the unit consists of a receiver, a transmitter, a phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency
synthesizer, power supply circuits, a control unit.
2. Circuit Configuration by Frequency
The receiver is a double-conversion superheterodyne
with a first intermediate frequency (IF) of 128.55MHz and a
second IF of 455kHz. Incoming a signals from the antenna
are mixed with the local signal from the PLL1 to produce the
first IF of 128.55MHz.
This is then mixed with the 129.005MHz seconds local
oscillator output to produce the 455kHz second IF. This is
detected to give the demodulated signal.
The transmit signal is modulated PLL2-VCO2 (129.005
MHz) from the microphone. The transmit signal frequency
is down-conversion with PLL2 and PLL1. It is then amplified
and sent to the antenna.
ANT
TX/RX
29.7~37.0MHz : K
35.0~50.0MHz : K2
LPF
AMP
ANT
SW
PA
AMP
29.7~
37.0MHz : K
35.0~
50.0MHz : K2
TX
1st MIX
MCF
128.55MHz
TX MIX
129.005
MHz
158.705~166.005MHz : K
164.005~179.005MHz : K2
158.25~165.55MHz : K
163.55~178.55MHz : K2
CF
455kHz
FM IF
SYSTEM
129.005
MHz
PLL2
VCO2
AF
AMP
MIC
AMP
PLL1
VCO1
3. Receiver System
3-1. Front-End RF Amplifier
An incoming signal from the antenna is applied to a bandpass filter (L202) after going through a low-pass filter and an
antenna switch (K1). The signal is then amplified by the RF
amplifier (Q201) and again filtered by another band-pass filter (L203, L206 and L207).
3-2. First Mixer
The signal from the band-pass filter is heterodyned with
the first local oscillator signal from the PLL frequency synthesizer circuit at the first mixer (IC201) to become a
128.55MHz first intermediate frequency (IF) signal.
The first IF signal is fed through two monolithic crystal
filters (XF201) to further remove spurious signals.
3-3. IF Amplifier
The first IF signal is amplified by Q202 and Q205, and
then enters IC202 (FM processing IC). The signal is heterodyned again with a second local oscillator signal
(129.005MHz) with in IC202 to become a 455kHz second IF
signal. The second IF signal is fed through a 455kHz ceramic filter, CF201 and CF202 to further eliminate unwanted
signals before it is amplified and FM detected in IC202.
IC201
1st MIX
SP
MIC
BPF
Q202
IF AMP
Q201
RF AMP
128.55MHz
BPF BPF LPF
MCF
XF201
IF AMP
Q205
FM IF SYSTEM
129.005MHz
Fig. 2 Receiver section
IC202
D502
T/R
SW
CF201,202
455kHz
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 128.55MHz
Pass bandwidth ±7.5kHz or more at 3dB
Attenuation bandwidth ± 35kHz or less at 40dB
Ripple 1.0dB or less
Insertion loss 5dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 70dB or more at fo±910kHz
Terminating impedance 1000Ω
Table 1 Crystal filter (L71-0560-05)
(TX-RX unit XF201)
13
TK-6110
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
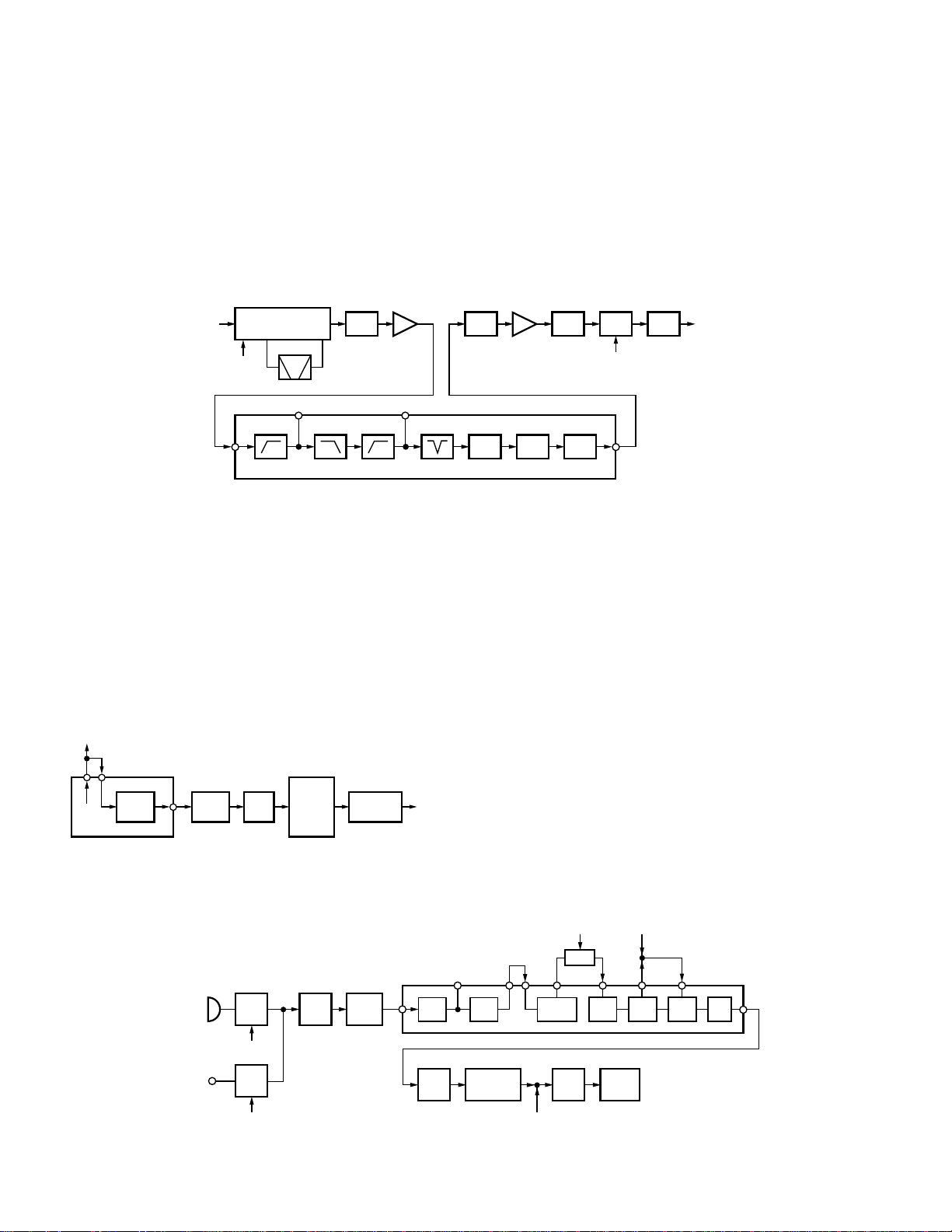
3-4. Audio Amplifier Circuit
The recovered audio signal obtained from IC202 is amplified by IC709, IC713, low-pass filtered by IC713 high-pass
filtered by IC713 and band-eliminate filtered by IC713.
The audio signals then passed through a de-emphasized
by IC713. The processed audio signal passes through an
audio volume control and is amplified to a sufficient level to
drive a loudspeaker by an audio power amplifier BTL
(IC102).
IC203
SW
CF201,202
455kHz
2
FM IF SYSTEM
129.005
MHz
IC713
HPF
5
IC202
IC709 (2/2)
AF AMP
1
HPFLPF BEF
IC710
VOL
DE-
EMP
IC711 (2/2)
AF AMP
EXP
IC710
VOL
MUTE
IC105
MUTE
AM1
41
IC102
AF
AMP
ES2
Fig. 3 Audio amplifier circuit
3-5. Squelch Circuit
The output signal from IC202 enters FM IC again, then
passed through a band-pass filter. The noise component
output from IC202 is amplified by Q206 and rectified by
D205 to produce a DC 0 voltage corresponding to the noise
level. The DC voltage is sent to the analog port of the CPU
(IC604).
And IC202 outputs a DC voltage (RSSI) corresponding to
the input of the IF amplifier.
AF OUT
IC604
CPU
31
SQL
Output
expander
Mute
circuit
9
DET
OUT
8
Noise
amp
IC202
7
Q206 D206
Noise
amp
DET
Fig. 4 squelch circuit
SW
IC714 (2/2)
AMPMIC1
D711
LIMIT
12
IC713
HPF
4. Transmitter System
4-1. Microphone Amplifier
The signal from the microphone is high-pass filtered by
IC713, passed through microphone mute and microphone
amplifier circuit (Q703 and IC714), limited and pre-emphasized by IC713 and D711.
4-2. Modulator Circuit
The output of Audio-processor (IC703) is passed to the D/
A converter (IC710) for maximum deviation adjustment and
the summing amplifier (IC711) before being applied to a
varactor diode in the voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) located in the frequency synthesizer section.
4-3. Down-Mixer
At Q503, a modulated VCO2 signal is mixed with 2nd local oscillator signal, 129.005MHz. The difference of the two
signals is used for the transmission signal 29.7~37MHz (K),
35.0~50.0MHz (K2). The output was filtered through a lowpass filter.
ALC
15
16
COMP
MM
Q708
SW
18 19
TONE
98
LPF HPF IDC
PRE
EMP
6
14
MIC2
(External
input)
MC1
SW
MC2
IC711 (1/2)
O4
LSD
SW
IC710IC712
D/A
I4
Fig. 5 Microphone circuit
SUM
AMP
L517
VCO
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
PDAT,PCLK,LE
TCXO
LPF
LPF
VCO2
VCO1
BUFF
BUFF
BUFF SW
BUFF
CPU
SW
16.8MHz
UL
Dual PLL
8TB/8R
8TB/8R
TX
local 1
RX
local 1
TX
local 2
RX
local 2
MOD/TONE
TK-6110
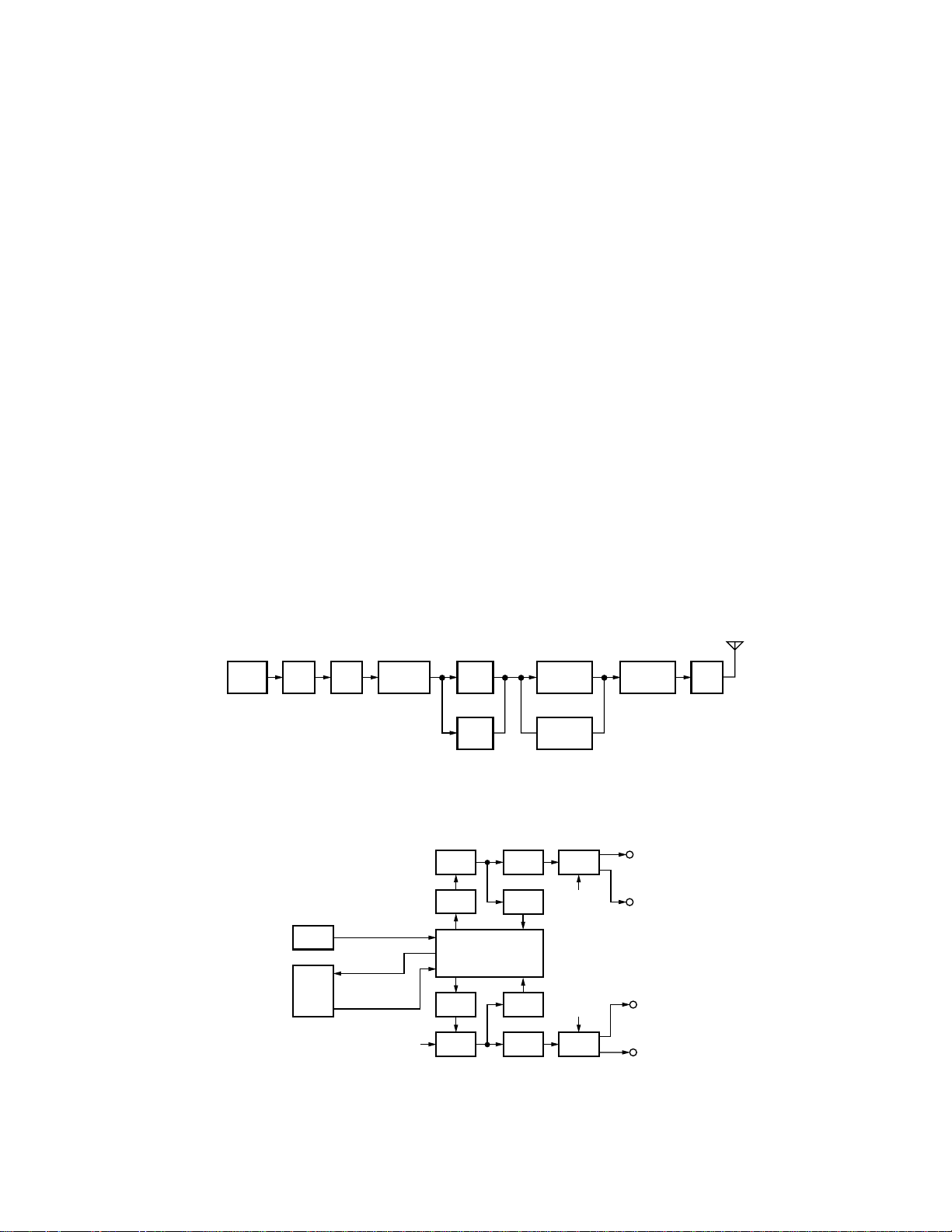
4-4. Driver and Final Power amplifier Circuits
The transmit signal is generated by the TX mixer (Q503).
The transmit signal obtained from the buffer amplifier Q1
and Q2, is amplified by Q3 to approximately 30dBm. This
amplified signal is amplified by Q4 and Q5 to approximately
8W, and this signal is passed to the final stage.
The RF power amplifier consists of transistor (Q6 and Q7)
and is capable of roducing up to 70W of RF power.
4-5. Transmit/Receive Switching Circuit
The final output signal is passed through a transmit/receive switching circuit (K1) before it is passed to the antenna terminal.
4-6. Automatic Power Control, Circuit and Transmitter
The APC circuit consists of an RF level detector, an exciter control section and a temperature sensing circuit. The
RF level detector senses the forward and reflected power.
The transmitter output power is kept constant by the exciter
control circuit which monitors the forward power and regulates the supply voltage applied to the exciter section.
If the antenna load becomes abnormal, the reflected
power increases, causing the exciter control circuit to reduce the supply voltage to the exciter. In case of an abnormal temperature rise in the power amplifier section, the
temperature sensing circuit detects this condition and send
the information to the APC circuit. These actions reduce the
transmitter output power to a safe operating level.
5. PLL Frequency Synthesizer
The frequency synthesizer consists of the VCXO (X501),
VCO (L517), PLL IC (IC501) and buffer amplifiers.
The VCXO generates 16.8MHz reference frequency. The
frequency stability is within ±5.0ppm (temperature range of
–30 to +60°C). The output of the VCXO is applied to pin 8 of
the PLL IC.
VCO (L517) has 2 internal VCOs. One for the 1st local
oscillator (K : 158.25~166.005MHz, K2 : 163.55~179.005
MHz) and another one for the 2nd local oscillator
(129.005MHz). Each output is connected to a dual PLL IC
(IC501).
VCO1 oscillates at K : 158.705~166.005MHz, K2 :
164.005~179.005MHz during transmission and it oscillates
at K : 158.25~165.55MHz, K2 : 163.55~178.55MHz during
reception.
VCO2 oscillates at 129.005MHz during both reception
and transmission. However, the oscillated signal is modulated during transmission. Each PLL circuit has LPFs and
buffer amplifiers.
The output of VCO1 goes through the buffer amplifier,
then the output is switched either for the 1st local oscillator
circuit of the receiver or TX mixer.
The output of VCO2 goes through the buffer amplifier,
then the output is switched either for the 2nd local oscillator
circuit of the receiver or TX mixer.
Q503
TX
mixer
Q1
RF
amp
Q2
RF
amp
Q3
Predrive
amp
Q4
Drive
amp
Q5
Drive
amp
Fig. 6 Drive and final amplifier
Fig. 7 PLL block diagram
Q6
RF power
amp
Q7
RF power
amp
K1
TX/RX
ANT SW
ANT
LPF
15
 Loading...
Loading...