Page 1

Model 2308 Portable Device
Battery/Charger Simulator
User’s Manual
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
www.keithley.com
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 2

.
Page 3

WARRANTY
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of
one (1) year from date of shipment.
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables,
software, rechargeable batteries, diskettes, and documentation.
During the warranty period, Keithley Instruments will, at its option, either repair or replace any product that proves
to be defective.
To exercise this warranty, write or call your local Keithley Instruments representative, or contact
Keithley Instruments headquarters in Cleveland, Ohio. You will be given prompt assistance and return instructions.
Send the product, transportation prepaid, to the indicated service facility. Repairs will be made and the product
returned, transportation prepaid. Repaired or replaced products are warranted for the balance of the original
warranty period, or at least 90 days.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
This warranty does not apply to defects resulting from product modification without Keithley Instruments’ express
written consent, or misuse of any product or part. This warranty also does not apply to fuses, software,
non-rechargeable batteries, damage from battery leakage, or problems arising from normal wear or failure to follow
instructions.
THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR USE. THE REMEDIES
PROVIDED HEREIN ARE BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES.
NEITHER KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. NOR ANY OF ITS EMPLOYEES SHALL BE LIABLE FOR ANY
DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE
OF ITS INSTRUMENTS AND SOFTWARE, EVEN IF KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. HAS BEEN ADVISED IN
ADVANCE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. SUCH EXCLUDED DAMAGES SHALL INCLUDE, BUT
ARE NOT LIMITED TO: COST OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION, LOSSES SUSTAINED AS THE RESULT OF
INJURY TO ANY PERSON, OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY.
A G R E A T E R M E A S U R E O F C O N F I D E N C E
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Corporate Headquarters • 28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, Ohio 44139
440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168 • 1-888-KEITHLEY (1-888-534-8453) • www.keithley.com
3/07
Page 4

Model 2308 Portable Device
Battery/Charger Simulator
User’s Manual
©2008, Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Any unauthorized reproduction, photocopy, or use the information herein, in whole or in part, without the prior written
approval of Keithley Instruments, Inc. is strictly prohibited.
TSP, TSP-Link, and TSP-Net are trademarks of Keithley Instruments, Inc. All other brand names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A.
Document Number:
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 5

The following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some
instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions may
be present.
This product is intended for use by qualified personnel who recognize shock hazards and are familiar with the safety precautions required
to avoid possible injury. Read and follow all installation, operation, and maintenance information carefully before using the product. Refer
to the user documentation for complete product specifications.
If the product is used in a manner not specified, the protection provided by the product warranty may be impaired.
The types of product users are:
Responsible body is the individual or group responsible for the use and maintenance of equipment, for ensuring that the equipment is
operated within its specifications and operating limits, and for ensuring that operators are adequately trained.
Operators use the product for its intended function. They must be trained in electrical safety procedures and proper use of the instrument.
They must be protected from electric shock and contact with hazardous live circuits.
Maintenance personnel perform routine procedures on the product to keep it operating properly, for example, setting the line voltage or
replacing consumable materials. Maintenance procedures are described in the user documentation. The procedures explicitly state if the
operator may perform them. Otherwise, they should be performed only by service personnel.
Safety Precautions
Service personnel are trained to work on live circuits, perform safe installations, and repair products. Only properly trained service
personnel may perform installation and service procedures.
Keithley Instruments products are designed for use with electrical signals that are rated Measurement Category I and Measurement
Category II, as described in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standard IEC 60664. Most measurement, control, and
data I/O signals are Measurement Category I and must not be directly connected to mains voltage or to voltage sources with high transient
over-voltages. Measurement Category II connections require protection for high transient over-voltages often associated with local AC
mains connections. Assume all measurement, control, and data I/O connections are for connection to Category I sources unless otherwise
marked or described in the user documentation.
Exercise extreme caution when a shock hazard is present. Lethal voltage may be present on cable connector jacks or test fixtures. The
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) states that a shock hazard exists when voltage levels greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak,
or 60VDC are present. A good safety practice is to expect that hazardous voltage is present in any unknown circuit before measuring.
Operators of this product must be protected from electric shock at all times. The responsible body must ensure that operators are
prevented access and/or insulated from every connection point. In some cases, connections must be exposed to potential human contact.
Product operators in these circumstances must be trained to protect themselves from the risk of electric shock. If the circuit is capable of
operating at or above 1000V, no conductive part of the circuit may be exposed.
Do not connect switching cards directly to unlimited power circuits. They are intended to be used with impedance-limited sources. NEVER
connect switching cards directly to AC mains. When connecting sources to switching cards, install protective devices to limit fault current
and voltage to the card.
Before operating an instrument, ensure that the line cord is connected to a properly-grounded power receptacle. Inspect the connecting
cables, test leads, and jumpers for possible wear, cracks, or breaks before each use.
11/ 07
Page 6

When installing equipment where access to the main power cord is restricted, such as rack mounting, a separate main input power
!
disconnect device must be provided in close proximity to the equipment and within easy reach of the operator.
For maximum safety, do not touch the product, test cables, or any other instruments while power is applied to the circuit under test.
ALWAYS remove power from the entire test system and discharge any capacitors before: connecting or disconnecting cables or jumpers,
installing or removing switching cards, or making internal changes, such as installing or removing jumpers.
Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the common side of the circuit under test or power line (earth) ground. Always
make measurements with dry hands while standing on a dry, insulated surface capable of withstanding the voltage being measured.
The instrument and accessories must be used in accordance with its specifications and operating instructions, or the safety of the
equipment may be impaired.
Do not exceed the maximum signal levels of the instruments and accessories, as defined in the specifications and operating information,
and as shown on the instrument or test fixture panels, or switching card.
When fuses are used in a product, replace with the same type and rating for continued protection against fire hazard.
Chassis connections must only be used as shield connections for measuring circuits, NOT as safety earth ground connections.
If you are using a test fixture, keep the lid closed while power is applied to the device under test. Safe operation requires the use of a lid
interlock.
If a screw is present, connect it to safety earth ground using the wire recommended in the user documentation.
The symbol on an instrument indicates that the user should refer to the operating instructions located in the user documentation.
The symbol on an instrument shows that it can source or measure 1000V or more, including the combined effect of normal and
common mode voltages. Use standard safety precautions to avoid personal contact with these voltages.
The symbol on an instrument shows that the surface may be hot. Avoid personal contact to prevent burns.
The symbol indicates a connection terminal to the equipment frame.
If this symbol is on a product, it indicates that mercury is present in the display lamp. Please note that the lamp must be properly
disposed of according to federal, state, and local laws.
The WARNING heading in the user documentation explains dangers that might result in personal injury or death. Always read the
associated information very carefully before performing the indicated procedure.
The CAUTION heading in the user documentation explains hazards that could damage the instrument. Such damage may invalidate the
warranty.
Instrumentation and accessories shall not be connected to humans.
Before performing any maintenance, disconnect the line cord and all test cables.
To maintain protection from electric shock and fire, replacement components in mains circuits - including the power transformer, test leads,
and input jacks - must be purchased from Keithley Instruments. Standard fuses with applicable national safety approvals may be used if
the rating and type are the same. Other components that are not safety-related may be purchased from other suppliers as long as they
are equivalent to the original component (note that selected parts should be purchased only through Keithley Instruments to maintain
accuracy and functionality of the product). If you are unsure about the applicability of a replacement component, call a Keithley Instruments
office for information.
To clean an instrument, use a damp cloth or mild, water-based cleaner. Clean the exterior of the instrument only. Do not apply cleaner
directly to the instrument or allow liquids to enter or spill on the instrument. Products that consist of a circuit board with no case or chassis
(e.g., a data acquisition board for installation into a computer) should never require cleaning if handled according to instructions. If the
board becomes contaminated and operation is affected, the board should be returned to the factory for proper cleaning/servicing.
Page 7

Table of Contents
Section Topic Page
1 Getting Started ....................................................................................... 1-1
Overview..................................................................................................... 1-2
Applications ................................................................................................ 1-2
Performance features ................................................................................. 1-2
Warranty information .................................................................................. 1-2
Contact information..................................................................................... 1-2
Specifications.............................................................................................. 1-3
Inspection ................................................................................................... 1-3
Options and accessories ............................................................................ 1-3
Power supply overview............................................................................... 1-3
Remote display option ................................................................................ 1-5
Power-up .................................................................................................... 1-7
Line power connection ......................................................................... 1-7
Power-up sequence ............................................................................. 1-7
Fuse replacement ................................................................................ 1-8
Display modes ............................................................................................ 1-8
Default settings ......................................................................................... 1-11
Setups - Save, Power-on, and Recall ................................................ 1-12
Menu......................................................................................................... 1-12
Getting around the MENU ........................................................................ 1-14
SCPI programming ................................................................................... 1-15
2 Basic Power Supply Operation .......................................................... 2-1
Test connections ........................................................................................ 2-2
Remote sense ...................................................................................... 2-5
Local sense .......................................................................................... 2-5
RFI considerations ............................................................................... 2-6
Outputting voltage and current ................................................................... 2-6
Setting voltage protection value ........................................................... 2-6
Selecting proper current range............................................................. 2-8
Selecting current limit mode................................................................. 2-8
Editing output voltage and current limit values..................................... 2-9
Using the OPERATE key.................................................................... 2-11
Output bandwidth...................................................................................... 2-11
Output impedance .................................................................................... 2-12
Changing the battery channel’s output impedance ............................ 2-12
SCPI programming - outputting voltage and current ................................ 2-13
Command notes (outputting voltage and current).............................. 2-14
Reading back V and I ............................................................................... 2-16
V and I display modes (Single or Dual)............................................. 2-16
Measurement configuration................................................................ 2-16
SCPI programming — measure V and I, and DVM input ......................... 2-17
Command notes (measure V and I, and DVM input) ......................... 2-18
Independent voltage measurements (DVM) ............................................. 2-18
DVM input display mode .................................................................... 2-18
Measurement configuration................................................................ 2-19
SCPI programming - DVM........................................................................ 2-19
Sink operation........................................................................................... 2-19
Page 8

Table of Contents Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Section Topic Page
Programming examples ............................................................................ 2-21
Outputting and reading back V and I .................................................. 2-21
DVM measurements ........................................................................... 2-21
Analog output............................................................................................ 2-22
3 Pulse Current Measurements.............................................................. 3-1
Overview ..................................................................................................... 3-2
Trigger level.......................................................................................... 3-2
Trigger delay......................................................................................... 3-3
Integration times ................................................................................... 3-3
Average readings count........................................................................ 3-4
Measurement configuration......................................................................... 3-4
Current range ....................................................................................... 3-5
Integration times ................................................................................... 3-5
Average readings count........................................................................ 3-5
Trigger delay and trigger level .............................................................. 3-6
Pulse current display mode .................................................................. 3-7
Pulse current measurement procedure....................................................... 3-7
No pulses detected ............................................................................... 3-8
Determining correct trigger level (pulse current)................................... 3-9
TRIG NOT DETECTED message....................................................... 3-11
SCPI programming - pulse current measurements................................... 3-12
Command notes (pulse current measurements) ................................ 3-14
Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect..................................................... 3-16
Pulse current digitization ........................................................................... 3-19
Pulse current step method ........................................................................ 3-20
TLEV steps ......................................................................................... 3-21
Timeout setting ................................................................................... 3-25
Integration time ................................................................................... 3-25
Range with pulse current step ............................................................ 3-26
Programming examples ............................................................................ 3-26
Pulse current measurements.............................................................. 3-26
Pulse current digitization .................................................................... 3-27
Pulse current STEP method (battery channel only)............................ 3-27
4 Long Integration Measurements ........................................................ 4-1
Overview ..................................................................................................... 4-2
Integration time ..................................................................................... 4-3
Trigger edge ......................................................................................... 4-3
Trigger level.......................................................................................... 4-3
Pulse timeout........................................................................................ 4-4
Measurement configuration......................................................................... 4-6
Current range ....................................................................................... 4-6
Integration time ..................................................................................... 4-6
Pulse timeout........................................................................................ 4-7
Trigger edge and trigger level............................................................... 4-7
Long integration display mode.............................................................. 4-8
Long integration measurement procedure.................................................. 4-8
General notes ....................................................................................... 4-9
Determining correct trigger level (long integration)............................... 4-9
SCPI programming.................................................................................... 4-11
Command notes (long integration measurements)............................. 4-12
Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect..................................................... 4-12
Programming examples ............................................................................ 4-16
5 Relay Control .......................................................................................... 5-1
Overview ..................................................................................................... 5-2
Connections ................................................................................................ 5-3
Controlling relays ........................................................................................ 5-4
SCPI programming...................................................................................... 5-5
ii 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 9

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Table of Contents
Section Topic Page
6 GPIB Operation....................................................................................... 6-1
Introduction ................................................................................................. 6-2
GPIB bus connections................................................................................. 6-2
Primary address .......................................................................................... 6-3
Setting the GPIB timeout for responses...................................................... 6-4
Long integration readings ..................................................................... 6-4
Pulse current readings.......................................................................... 6-4
MAV (Message Available Bit) ............................................................... 6-4
General bus commands .............................................................................. 6-5
REN (remote enable)............................................................................ 6-5
IFC (interface clear).............................................................................. 6-6
LLO (local lockout)................................................................................ 6-6
GTL (go to local) ................................................................................... 6-6
DCL (device clear) ................................................................................ 6-6
SDC (selective device clear)................................................................. 6-6
GET (group execute trigger)................................................................. 6-6
SPE, SPD (serial polling)...................................................................... 6-6
Front panel aspects of GPIB operation ....................................................... 6-6
Remote indicator and LOCAL key ........................................................ 6-7
Error and status messages................................................................... 6-7
Programming syntax ................................................................................... 6-7
Command words................................................................................... 6-7
Program messages............................................................................... 6-9
Response messages .......................................................................... 6-11
Message exchange protocol............................................................... 6-12
7 Status Structure...................................................................................... 7-1
Overview ..................................................................................................... 7-2
Status byte and SRQ ............................................................................ 7-2
Status register sets ............................................................................... 7-2
Queues ................................................................................................. 7-2
Clearing registers and queues .................................................................... 7-3
Programming and reading registers............................................................ 7-4
Programming enable registers.............................................................. 7-4
Reading registers.................................................................................. 7-5
Status byte and service request (SRQ)....................................................... 7-5
Status byte register ............................................................................... 7-6
Service request enable register............................................................ 7-7
Serial polling and SRQ ......................................................................... 7-7
Status byte and service request commands ......................................... 7-8
Status register sets...................................................................................... 7-8
Register bit descriptions ....................................................................... 7-8
Condition registers .................................................................................... 7-12
Event registers.................................................................................... 7-12
Event enable registers........................................................................ 7-13
Queues...................................................................................................... 7-14
Output queue...................................................................................... 7-15
Error queue......................................................................................... 7-15
Programming example - read error queue.......................................... 7-16
8 Common Commands ............................................................................ 8-1
Overview ..................................................................................................... 8-2
IEEE-488.2 common commands and queries............................................. 8-2
*IDN? .................................................................................................... 8-2
*OPC..................................................................................................... 8-3
*SAV <NRf> and RCL <NRf> ............................................................... 8-3
*RST ..................................................................................................... 8-4
*TRG..................................................................................................... 8-4
*TST?.................................................................................................... 8-4
*WAI...................................................................................................... 8-4
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 iii
Page 10

Table of Contents Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Section Topic Page
9 Measurement Commands and
Optimizing Measurement Speed ........................................................ 9-1
Overview ..................................................................................................... 9-2
Command notes: Signal-oriented measurement commands
and queries........................................................................................... 9-3
Optimizing measurement speed ................................................................. 9-5
Auto Zero State..................................................................................... 9-5
Programming examples........................................................................ 9-6
GPIB 488.1 protocol.................................................................................... 9-7
Selecting the 488.1 protocol ................................................................. 9-7
Protocol differences.............................................................................. 9-8
Trigger on talk both channels ...................................................................... 9-9
Bus commands................................................................................... 9-10
Command notes ................................................................................. 9-10
Trigger continuous mode........................................................................... 9-10
Bus commands................................................................................... 9-10
Command notes ................................................................................. 9-11
Using trigger continuous mode........................................................... 9-11
Programming sequence example....................................................... 9-11
10 DISPlay and FORMat ........................................................................... 10-1
DISPlay subsystem ................................................................................... 10-2
Command notes (SCPI commands - display)..................................... 10-2
FORMat subsystem .................................................................................. 10-4
Command notes (SCPI commands - data format).............................. 10-5
11 SCPI Tables............................................................................................ 11 -1
SCPI command subsystems reference tables .......................................... 11-2
General notes ..................................................................................... 11-2
DISPlay command summary .............................................................. 11-3
FORMat command summary.............................................................. 11 -4
OUTPut command summary .............................................................. 11-5
SENSe command summary .............................................................. 11-6
SOURce command summary........................................................... 11 -13
STATus command summary............................................................. 11- 14
SYSTem command summary ........................................................... 11-15
12 Performance Verification.................................................................... 12-1
Introduction ............................................................................................... 12-2
Verification test requirements.................................................................... 12-2
Environmental conditions.................................................................... 12-2
Warm-up period .................................................................................. 12-2
Line power .......................................................................................... 12-3
Recommended test equipment ................................................................. 12-3
Resistor connections .......................................................................... 12-3
Resistor considerations ...................................................................... 12-4
Verification limits ....................................................................................... 12-4
Example limits calculation................................................................... 12-4
Performing the verification test procedures............................................... 12-4
Test summary ..................................................................................... 12-4
Test considerations ............................................................................. 12-5
Output voltage accuracy ........................................................................... 12-5
Voltage readback accuracy ....................................................................... 12-7
Compliance current accuracy.................................................................... 12-8
Current readback accuracy ....................................................................... 12-9
5 A range readback accuracy ............................................................. 12-9
500 mA range readback accuracy.................................................... 12-10
50 mA range readback accuracy...................................................... 12-12
5 mA range readback accuracy........................................................ 12-13
Digital voltmeter input accuracy .............................................................. 12-15
iv 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 11

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Table of Contents
Section Topic Page
13 Calibration.............................................................................................. 13-1
Introduction ............................................................................................... 13-2
Environmental conditions.......................................................................... 13-2
Temperature and relative humidity...................................................... 13-2
Warm-up period .................................................................................. 13-2
Line power .......................................................................................... 13-2
Calibration considerations......................................................................... 13-2
Calibration cycle ................................................................................. 13-3
Recommended calibration equipment....................................................... 13-3
Resistor connections .......................................................................... 13-3
Resistor considerations ...................................................................... 13-3
Front panel calibration............................................................................... 13-4
Step 1: Prepare the Model 2308 for calibration .................................. 13-4
Step 2: Perform battery channel calibration steps .............................. 13-5
Step 3: Perform charger channel calibration steps............................. 13-9
Step 4: Enter calibration dates, and save calibration........................ 13-10
Remote calibration .................................................................................. 13-11
Remote calibration display................................................................ 13-11
Remote calibration procedure........................................................... 13-11
Step 1: Prepare the Model 2308 for calibration ................................ 13-11
Step 2: Perform battery channel calibration steps ............................ 13-12
Step 3: Perform charger channel calibration steps........................... 13-13
Step 4: Program calibration date ...................................................... 13-14
Step 5: Save calibration constants and lock out calibration.............. 13-14
Changing the calibration code................................................................. 13-15
Changing the code from the front panel ........................................... 13-16
Changing the code by remote........................................................... 13-16
Resetting the calibration code .......................................................... 13-16
Viewing calibration date and count ......................................................... 13-17
Viewing date and count from the front panel .................................... 13-17
Acquiring date and count by remote................................................. 13-17
Appendix Topic Page
A Error and Status Messages ................................................................ A-1
Error and status message definitions......................................................... A-2
B Calibration Reference .......................................................................... B-1
Introduction ................................................................................................ B-2
Command summary ............................................................................ B-2
Miscellaneous commands.......................................................................... B-2
Detecting calibration errors ........................................................................ B-5
Reading the error queue...................................................................... B-5
Error summary..................................................................................... B-5
Status byte EAV (Error Available) bit ................................................... B-6
Generating an SRQ on error................................................................ B-6
Detecting calibration step completion ........................................................ B-6
Using the *OPC command................................................................... B-7
Using the *OPC? query ....................................................................... B-7
Generating an SRQ on calibration complete ....................................... B-7
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 v
Page 12

This page left blank intentionally .
Page 13

List of Figures
Section Figure Title Page
1 Figure 1-1 Model 2308 front panel ................................................................. 1-4
1 Figure 1-2 Model 2308 rear panel................................................................... 1-4
1 Figure 1-3 Simplified power supply diagram .................................................. 1-5
1 Figure 1-4 Model 2306-DISP Remote display option...................................... 1-6
1 Figure 1-5 Fuse drawer location .................................................................... 1-8
2 Figure 2-1 Battery channel preferred connection (maximum stability) ............ 2-3
2 Figure 2-2 Battery channel fastest transient response connection ................. 2-4
2 Figure 2-3 Charger channel 4-wire remote sense connection
from the DUT to the ouput ............................................................. 2-5
2 Figure 2-4 Local Sense Connections (battery channel and
charger channel)............................................................................ 2-6
2 Figure 2-5 Charger Control Circuit Testing.................................................... 2-19
2 Figure 2-6 Sink operation.............................................................................. 2-20
2 Figure 2-7 Preferred method ........................................................................ 2-20
2 Figure 2-8 Analog output Connections.......................................................... 2-22
3 Figure 3-1 Pulse current measurement........................................................... 3-2
3 Figure 3-2 Trigger delay for high pulse current measurement ........................ 3-3
3 Figure 3-3 Determining voltage and current characteristics for
battery channel .............................................................................. 3-9
3 Figure 3-4 Determining voltage and current characteristics for
charger channel .......................................................................... 3-10
3 Figure 3-5 PCURrent and SEARch time for pulse high measurement ......... 3-17
3 Figure 3-6 Sample pulse forms for step method........................................... 3-22
3 Figure 3-7 Sample one-shot only pulses for step method............................. 3-22
3 Figure 3-8 Sample :STEP Pulse measurement ............................................ 3-23
3 Figure 3-9 Pulse form with rise and fall steps ............................................... 3-23
3 Figure 3-10 Pulse form with down steps first (600msec step duration) .......... 3-24
4 Figure 4-1 Steady state for waveforms based on low pulse times .................. 4-3
4 Figure 4-2 Long integration, search, and reading time comparison ................ 4-5
4 Figure 4-3 TOUT and search time ................................................................ 4-13
5 Figure 5-1 External source relay control ......................................................... 5-3
5 Figure 5-2 Internal source relay control .......................................................... 5-3
5 Figure 5-3 Relay connector (9-pin D-sub)....................................................... 5-4
6 Figure 6-1 IEEE-488 connector....................................................................... 6-2
6 Figure 6-2 Daisy chaining ............................................................................... 6-3
7 Figure 7-1 Status model structure................................................................... 7-3
7 Figure 7-2 Status byte and service request..................................................... 7-6
7 Figure 7-3 Standard event status .................................................................... 7-9
7 Figure 7-4 Operation event status................................................................. 7-10
7 Figure 7-5 Measurement event status .......................................................... 7-11
7 Figure 7-6 Questionable event status ........................................................... 7-12
10 Figure 10-1 IEEE-754 single precision data format ........................................ 10-5
10 Figure 10-2 IEEE-754 double precision data format ....................................... 10-6
12 Figure 12-1 Connections for voltage verification tests .................................... 12-6
Page 14

List of Figures Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Section Figure Title Page
12 Figure 12-2 Connections for output current and 5 A range current
verification tests ........................................................................... 12-8
12 Figure 12-3 Battery channel connections for 500 mA current
verification tests ......................................................................... 12-11
12 Figure 12-4 Battery channel connections for 50 mA current
verification tests ......................................................................... 12-12
12 Figure 12-5 Connections for 5 mA current verification tests.......................... 12-14
12 Figure 12-6 Charger channel connections for DVM accuracy verification..... 12-15
13 Figure 13-1 Battery channel connections for voltage calibration ................... 13-6
13 Figure 13-2 Connections for 5 A, 500 mA, and 50 mA current calibration ...... 13-7
13 Figure 13-3 Connections for 5 mA range calibration....................................... 13-8
13 Figure 13-4 Charger channel connections for voltage calibration ................... 13-9
vii 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 15

List of Tables
Section Table Title Page
1 Table 1-1 Display Modes ............................................................................... 1-9
1 Table 1-2 Display mode examples............................................................... 1-10
1 Table 1-3 Factory defaults (RST)................................................................. 1-11
1 Table 1-4 Main MENU structure .................................................................. 1-13
2 Table 2-1 Current ranges............................................................................... 2-8
2 Table 2-2 Output bandwidth channel setting ............................................... 2-11
2 Table 2-3 SCPI command summary - outputting voltage and current......... 2-13
2 Table 2-4 SCPI commands: Measure V and I, and DVM input.................... 2-17
3 Table 3-1 Current range and trigger level settings......................................... 3-6
3 Table 3-2 TRIG NOT DETECTED message................................................ 3-11
3 Table 3-3 SCPI commands - pulse current measurements ......................... 3-12
3 Table 3-4 PCURrent FAST, SEARch, and DETect commands .................... 3-18
3 Table 3-5 Setting UP and DOWN commands.............................................. 3-21
3 Table 3-6 Trigger Level Setting.................................................................... 3-22
3 Table 3-7 Sample TLEV values ................................................................... 3-23
3 Table 3-8 Sample integration times ............................................................. 3-25
4 Table 4-1 TRIG NOT DETECTED message................................................ 4-10
4 Table 4-2 SCPI commands - long integration measurements ..................... 4-11
4 Table 4-3 FAST, SEARch, and DETect command reference ....................... 4-14
5 Table 5-1 Relay pinouts ................................................................................. 5-4
5 Table 5-2 SCPI command - output relay control............................................ 5-5
6 Table 6-1 General bus commands................................................................. 6-5
7 Table 7-1 Common and SCPI commands - reset registers and
clear queues .................................................................................. 7-4
7 Table 7-2 16-bit status register ...................................................................... 7-5
7 Table 7-3 Common and SCPI Commands - status byte and
service request enable registers.................................................... 7-8
7 Table 7-4 Common and SCPI commands - condition registers................... 7-12
7 Table 7-5 Common and SCPI commands - event registers ........................ 7-13
7 Table 7-6 Common and SCPI commands - event enable registers............. 7-13
7 Table 7-7 SCPI Commands - error queue ................................................... 7-16
8 Table 8-1 IEEE-488.2 common commands and queries ............................... 8-2
8 Table 8-2 *OPC and *OPC? commands........................................................ 8-3
9 Table 9-1 Signal-oriented measurement command summary ....................... 9-2
9 Table 9-2 Trigger on talk bus commands..................................................... 9-10
9 Table 9-3 Trigger continuous bus commands.............................................. 9-10
9 Table 9-4 Trigger continuous mode programming example ........................ 9-11
10 Table 10-1 SCPI commands - display ........................................................... 10-2
10 Table 10-2 SCPI commands - data format .................................................... 10-4
11 Table 11-1 DISPlay command summary ....................................................... 11-3
11 Table 11-2 FORMat command summary....................................................... 11-4
11 Table 11-3 OUTPut command summary ....................................................... 11-5
11 Table 11-4 SENSe command summary ........................................................ 11 -6
11 Table 11-5 SOURce command summary .................................................... 11-13
Page 16

List of Tables Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Section Table Title Page
11 Table 11-6 STATus command summary ...................................................... 11 -14
11 Table 11-7 SYSTem command summary..................................................... 11-15
12 Table 12-1 Recommended verification equipment ......................................... 12-3
12 Table 12-2 Output voltage accuracy limits ..................................................... 12-6
12 Table 12-3 Voltage readback accuracy limits................................................. 12-7
12 Table 12-4 Compliance current accuracy limits ............................................. 12-9
12 Table 12-5 5 A range current readback accuracy limits ............................... 12-10
12 Table 12-6 500 mA range current readback accuracy limits ........................ 12-11
12 Table 12-7 50 mA range current readback accuracy limits .......................... 12-13
12 Table 12-8 5 mA range current readback accuracy limits ............................ 12-14
12 Table 12-9 Digital voltmeter input accuracy limits ........................................ 12-16
13 Table 13-1 Recommended calibration equipment.......................................... 13-3
13 Table 13-2 Model 2308 front panel calibration summary ............................... 13-4
13 Table 13-3 Remote calibration summary ..................................................... 13-14
Appendix Table Title Page
A Table A-1 Error and status messages (all models)........................................ A-2
B Table B-1 Remote calibration command summary........................................ B-2
B Table B-2 Calibration errors........................................................................... B-6
ix 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 17

In this section:
Section 1
Getting Started
Topi c Page
Overview ..................................................................................................... 1-2
Applications................................................................................................. 1-2
Performance features ................................................................................. 1-2
Warranty information................................................................................... 1-2
Contact information..................................................................................... 1-2
Specifications.............................................................................................. 1-3
Inspection.................................................................................................... 1-3
Options and accessories............................................................................. 1-3
Power supply overview ............................................................................... 1-3
Remote display option ................................................................................ 1-5
Power-up..................................................................................................... 1-7
Line power connection ......................................................................... 1-7
Power-up sequence ............................................................................. 1-7
Fuse replacement................................................................................. 1-8
Display modes ............................................................................................ 1-8
Default settings ......................................................................................... 1-11
Setups - Save, Power-on, and Recall................................................. 1-12
Menu ......................................................................................................... 1-12
Getting around the MENU......................................................................... 1-14
SCPI programming ................................................................................... 1-15
Page 18

Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Overview
This manual describes Keithley Instruments Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger
Simulator, which is designed specifically for development and high-speed production testing of DC
battery-operated products.
Applications
Development and high speed testing of DC battery-operated products, such as:
• Cellular handsets
• Cellular components like RFIC power amplifiers
• Other high-volume precision electrical components.
Performance features
Key features and benefits include:
• The Model 2308 is a specialized power supply that has a very fast recovery to large, near
instantaneous load current transitions. Conventional power supplies do not have this
capability. The Model 2308 is designed specifically to respond to large load changes and
very short pulsed loads with small transient voltage drop and a very fast recovery time.
Typical devices that have these types of characteristic loads are mobile phones, wireless
communication modules, and other portable, battery operated devices. The Model 2308 can
maintain a near-constant output, even under quickly-changing load conditions.
• The power supply can measure a wide range of load currents. It can resolve down to 0.1 μA
and measure up to 5 A. It has fast measurement capability as well and can measure load
current pulses as narrow as 50
• The Model 2308 can simulate the output of a battery. Its programmable output resistance
can simulate a battery’s internal resistance so that the voltage output looks exactly like that
of a battery’s output.
• The two channels can also sink current so that one channel (the battery channel) simulates
a discharged battery, while the other channel (the charger channel) can be used to simulate
a charger.
μsec.
NOTE Information contained in this section applies to all power supply channels
(unless otherwise noted). In this manual, Channel 1 refers to the battery
channel, Channel 2 refers to the charger channel.
Warranty information
Warranty information is located at the front of this manual. Should your power supply require
warranty service, contact the Keithley Instruments representative or authorized repair facility in
your area for further information. When returning the instrument for repair, be sure to fill out and
include the service form at the back of this manual to provide the repair facility with the necessary
information.
Contact information
If you have any questions after reviewing this information, please contact your local Keithley
representative or call one of our Applications Engineers at 1-800-348-3735 (U.S. and Canada
1-2 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 19

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
only). A complete list of worldwide phone numbers are available on the Keithley Instruments
website at
www.keithley.com.
Specifications
Full Model 2308 specifications are included on the Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger
Simulator Product Information CD-ROM. Check the Keithley Instruments website at
www.keithley.com for the latest updates to the specifications.
Inspection
The power supply was carefully inspected electrically and mechanically before shipment. After
unpacking all items from the shipping carton, check for any obvious signs of physical damage that
may have occurred during transit
NOTE There may be a protective film over the display lens, which can be removed.
Report any damage to the shipping agent immediately. Save the original packing carton for
possible future shipment. The following items are included with every order:
.
• Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator with line cord
• Quick Disconnect Connector (2)
• Accessories as ordered
• Certificate of calibration
• Product Information CD-ROM that contains PDFs of Model 2308 User’s Manual and Model
2308 Quick Start Guide
Any improvements or changes concerning the instrument or manual will be explained in an
addendum included with the manual. Be sure to note these changes and incorporate them into the
manual.
Options and accessories
The following options and accessories are available for the power supply.
• 2306-DISP remote display unit
• Low inductance coaxial cable (SC-182)
• Single fixed rack mount kit (P/N 4288-1)
• Dual fixed rack mount kit (P/N 4288-2)
• IEEE-488 Interface for PCI bus (P/N KPCI-488LP)
• USB to GPIB adapter interface (P/N KUSB-488A)
• Double shielded premium GPIB cable, 0.5 m (1.6 ft) (P/N 7007-05)
• Double shielded premium GPIB cable, 1 m (3.2 ft) (P/N 7007-1)
• Double shielded premium GPIB cable, 2 m (6.5 ft) (P/N 7007-2)
• Double shielded premium GPIB cable, 3 m (10 ft) (P/N 7007-3)
• Double shielded premium GPIB cable, 4 m (13 ft) (P/N 7007-4)
Power supply overview
The Model 2308 power supply (see Figure 1-1) can simulate a battery channel (#1) or a charger
channel (#2). Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2 show the Model 2308 front and rear panels.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-3
Page 20

Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
POWER
DISPLAY
OPERATE
ENTER
SET
MENU
LOCAL
2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator
WARNING:
NO INTERNAL OPERATOR SERVICABLE PARTS,SERVICE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
CAUTION:
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD,REPLACE FUSE WITH SAME TYPE AND RATING.
MADE IN
U.S.A.
LINE RATING
100-120VAC, 200-240VAC
50, 60 HZ 165VA MAX
LINE FUSE
SLOWBLOW
2.0A, 250V
IEEE-488
(ENTER IEEE ADDRESS
FROM FRONT PANEL MENU)
REMOTE
DISPLAY
OPTION
+++
___
SOURCE SENSE
SOURCE
OUTPUT #1
ISOLATION FROM EARTH: 22 VOLTS MAX MAX.
RELAY
CONTROL
24VDC MAX
DVM IN
-30 VDC MAX
ANALOG
OUT
mA
(5/50)A(0.5/5)
+++
____
+
SOURCE SENSE
DVM IN
SOURCE
OUTPUT #2
Figure 1-1
Model 2308 front panel
Figure 1-2
Model 2308 rear panel
NOTE The output from each channel is isolated from the other channel.
CAUTION Allow for adequate ventilation around the front and rear-panel openings to
prevent the unit from overheating which may degrade performance.
Make sure that the maximum combined channel output is not exceeded (see complete
Specifications at
sink. For output voltages exceeding 5 V, the maximum sink current is less than 3 A (derate the
maximum sink current 0.2 A for each volt over 5 V).
NOTE When using the power supply as a sink (negative polarity), the power supply is
1-4 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
www.keithley.com). Also, do not exceed 3 A when using the power supply as a
dissipating rather than sourcing power (see
Sink operation).
Page 21
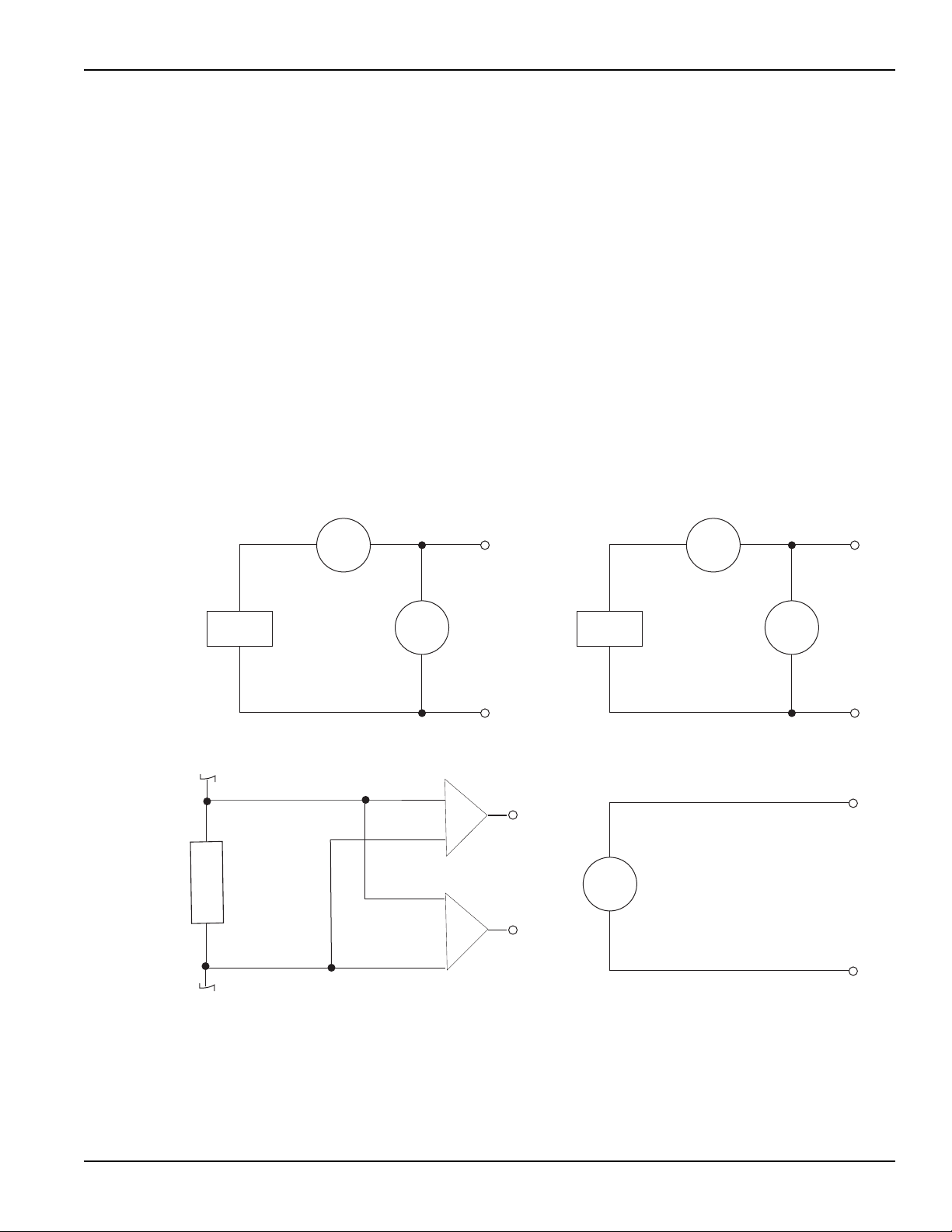
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
Battery Channel
(Channel #1)
Source
+
_
V-Source
with I-Limit
I meter
V meter
Charger Channel
(Channel #2)
Source
+
_
V-Source
with I-Limit
I meter
V meter
+
_
Digital
Voltmeter
DVM
Shunt
Current
Monitors
5/50mA
0.5/5A
A simplified diagram of the power supply is shown in Figure 1-3. Note that it can read back the
output voltage (V
) and current (I
meter
). Display resolution for voltage readback is 1mV.
meter
The battery channel (#1) has four current ranges: 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA and 5 mA. The charger has
5 A and 5 mA. The resolution on 5 A is 100 μA, and on 5 mA is 0.1 μA. The 500 mA is 10 μΑ and
50 mA is 1μΑ.
The power supply also has a digital voltmeter (DVM - on the charger channel only) that is
independent of the power supply circuit. The DVM can measure up to +30 V (1 mV resolution).
The power supply has analog output pins that allow acquisition of the load current waveform for indepth analysis on the battery channel only (see
Analog output for more information).
When used with a pulsed load, the power supply can read back peak current, idle current, and
average current (see
Section 3 for details). A long integration (up to 60 seconds) function is
provided to measure average current of a low frequency pulse (long period) or a series of pulses
(see
Section 4 for details).
Figure 1-3
Simplified power supply diagram
Remote display option
If you are mounting the power supply in a location where the display cannot be seen or the
controls are not easily accessible, use this option (see
Figure 1-4). This remote display module
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-5
Page 22

Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
ET
A
R
EP
O
R
E
TNE
T
E
S
Y
AL
P
SID
U
N
EM
LACOL
YALPS
I
D
E
TOMER
PSID-603
2
includes all front-panel instrument controls/features (with the exception of power). All features and
menus work as described for the Model 2308. A 9-foot cable attaches the remote display to the
rear-panel of the power supply, allowing the unit to be operated remotely.
Figure 1-4
Model 2306-DISP Remote display option
Plug the remote display module into the rear-panel connector labeled REMOTE DISPLAY
OPTION (see rear panel in
Figure 1-2). When plugged in, the main display module is disabled with
the following message displayed:
REMOTE PANEL
ENABLED
When the remote display module is unplugged, control returns to the main display module.
NOTE When using the remote display, VFD BRIGHTNESS may not appear in the main
menu (dependent on the firmware revision in the unit).
When connecting or disconnecting the remote display, allow a few seconds for
the power supply to recognize the action. Fast, repeated connects/disconnects
of the remote display may cause the power supply to hang or appear to hang.
Disconnecting the remote display and waiting a few seconds to reconnect it may
clear the problem. If not, cycling power on the power supply clears the condition.
1-6 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 23

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
Power-up
Line power connection
The power supply operates from a line voltage in the range of 100-120VAC/200-240VAC at a
frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, 165 V AC. Line voltage and frequency are automatically sensed,
therefore there are no switches to set. Check to see that the line power in your area is compatible.
Use the
NOTE See complete Specifications at www.keithley.com for the operating environment
Perform the following steps to connect the power supply to the line power and turn it on:
WARNING The power cord supplied with the Model 2308 contains a separate ground
:SYSTem::LFRequency? query (see Section 10) to read the line frequency.
requirements of the equipment before power-up.
for use with grounded outlets. When proper connections are made,
instrument chassis is connected to power line ground through the ground
wire in the power cord. Failure to use a grounded outlet may result in
personal injury or death due to electric shock.
1. Before plugging in the power cord, make sure the front-panel power switch is in the off (0)
position.
2. Connect the female end of the supplied power cord to the AC receptacle on the rear panel.
3. Turn on the power supply by pressing the front-panel power switch to the on (1) position.
Power-up sequence
On power-up, the power supply performs self-tests on its RAM and EPROM. After a blinking cursor
appears on line one, RAM tests are completed. After a blinking cursor appears on line two,
EPROM self tests are completed.
NOTE If a problem develops while the instrument is under warranty, return it to Keithley
Instruments for repair.
If the instrument passes the self tests, the following information is briefly
displayed:
• Top Line - The model number and the IEEE-488 address are displayed
(The factory default GPIB address is 16).
• Bottom Line - Firmware revision levels are displayed for the main board
and the display board. Also displayed is the detected line frequency.
After displaying the above information, any errors that occurred during the startup sequence will be
displayed. Then, the instrument goes to the default settings (*RST) or saved power-up settings
(SAV0-3) with the output off (see
over the bus using the :SYST:ERR? command (see Error queue).
Default settings). Any missed error messages may be viewed
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-7
Page 24

Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
LINE RATING
100-120VAC, 200-240VAC
50, 60 HZ 165VA MAX
LINE FUSE
SLOWBLOW
2.0A, 250V
REMOTE
DISPLAY
OPTION
DVM IN
-30 VDC MAX
+++
____
+
SOURCE SENSE
DVM IN
SOURCE
OUTPUT #2
Fuse drawer
Fuse replacement
A rear-panel fuse protects the power line input of the power supply.
To replace the line fuse:
1. Power off the unit and remove line cord.
2. The fuse drawer is located on the left side of the AC receptacle (see Figure 1-5). On the
right side of the fuse drawer is a small tab. At this location, use a screwdriver to pry the fuse
drawer open.
3. Slide the fuse drawer out to gain access to the fuse. Note that the fuse drawer does not pull
all the way out of the power module.
4. Snap the fuse out of the drawer and replace it with the same type (250 V, 2.0 A, 5 × 20 mm
time lag). The Keithley Instruments part number is FU-81.
CAUTION For continued protection against fire or instrument damage, only replace the
fuse with the type and rating listed. If the instrument repeatedly blows fuses,
locate and correct the cause of the problem before replacing the fuse.
5. Push the fuse drawer back into the power module.
Display modes
1-8 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Figure 1-5
Fuse drawer location
For voltage and current readings, there are five display modes described as follows:
• SINGLE V AND I DISPLAY - This display mode is used to read back the actual output
voltage and current on a single channel. The active channel dictates if the single channel
being displayed is for the battery or charger channel. This display mode is the RST default
(see
Section 2 for details).
• DUAL V AND I DISPLAY - This display mode is used to read back the actual output voltage
and current for both channels simultaneously. The top display line shows the voltage and
current readings for the battery channel while the bottom line shows the charger channel
Page 25

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
▲
▲
readings. The # symbol indicates the active channel (see Section 2 for details). For both
channels, the output state is indicated by:
• 0 (zero) if the output is OFF for that channel.
• l (lowercase L) if the output is ON for that channel..
NOTE With DUAL V AND I DISPLAY mode enabled, there is no indicator on the front
panel about voltage protection or current limit state. See
Section 2 for more
information on voltage protection and current limit.
• PULSE CURRENT - This mode is used to display high, low, or average pulse-current
measurements (see
Section 3 for details)
• LONG INTEGRATION - This mode is used to display average current measurements of a
pulse or pulses measuring periods between 850 msec to 60 sec (60 Hz line frequency) and
840 msec to 60 sec (50 Hz line frequency) (see
Section 4 for details).
• DVM INPUT (charger channel only) - This mode is used to display the DC voltage applied to
the DVM input of the power supply (see
Section 2 for details).
Use the SAVE SETUP item of the MENU to save the selected display mode in memory, and use
the POWER ON SETUP item to specify the power-on setup (
Setups - Save, Power-on, and Recall
for details). The Dual V and I display cannot be saved. A reset will not change this setting.
Recalling a setup may change the setting. If setup recalling has a channel function set to
something other than voltage or current then this setting is disabled otherwise the setting is left
unchanged.
Selecting (enabling) Dual V and I will switch the function to voltage for each channel unless the
function is already voltage or current. Dual V and I will be disabled if you change the display mode
on either channel to be Pulse Current, Long Integration, or DVM Input (Channel #2 only).
To select a display mode:
1. Press the DISPLAY key.
2. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired display mode.
Table 1-1
Display Modes
Battery channel (#1) Charger channel (#2)
• SINGLE V AND I
• DUAL V AND I
• LONG INTEGRATION
• PULSE CURRENT
3. Press the
NOTE Switching back to the original active channel will display the initial setting for that
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
channel.
• SINGLE V AND I
• DUAL V AND I
• LONG INTEGRATION
• PULSE CURRENT
• DVM INPUT
4. With the desired mode and active channel displayed, press ENTER.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-9
Page 26
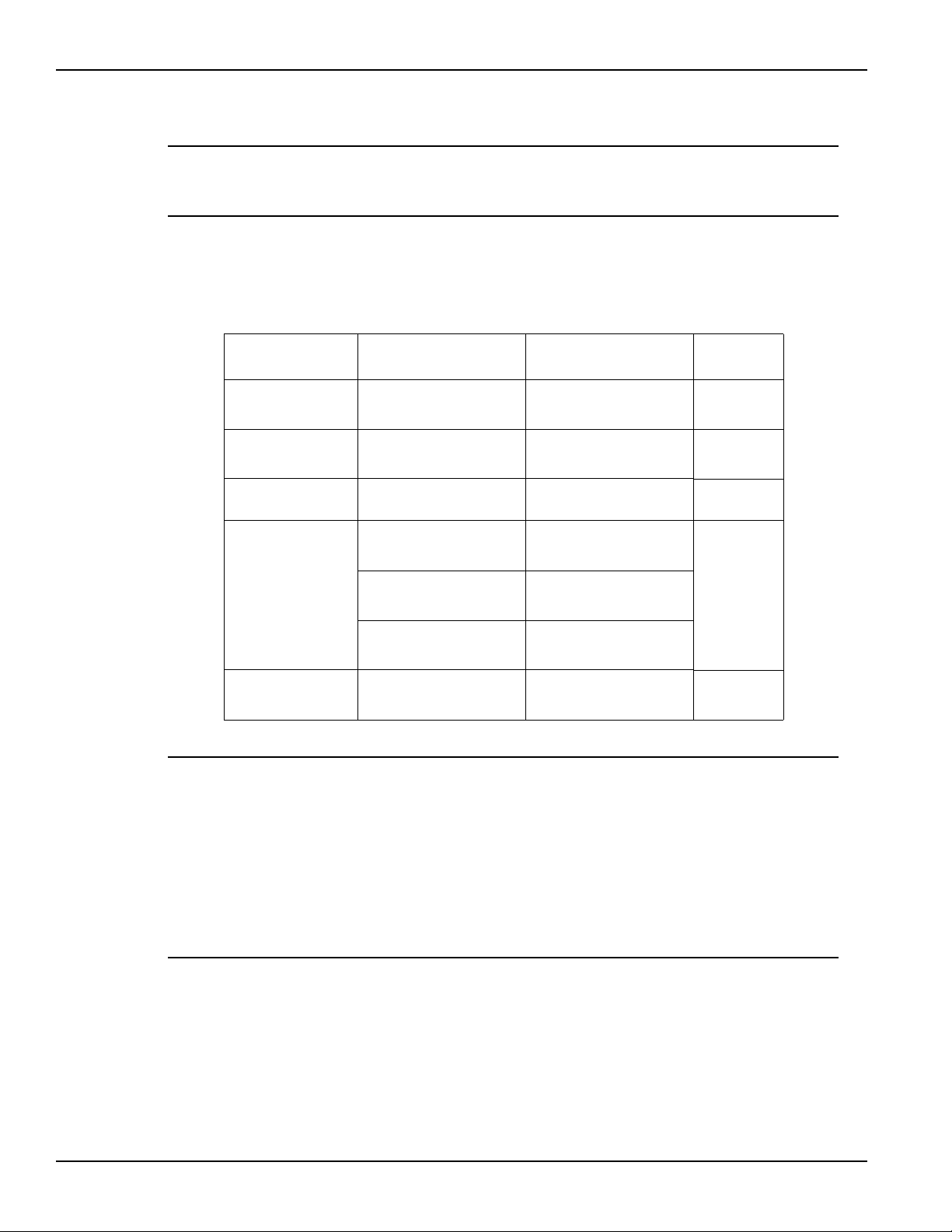
Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Examples of the display modes are shown in Table 1-2.
NOTE To select PULSE CURRENT high (HI), low (LO) or average (AVG) readings,
use the
▲ or ▼ keys to select the desired pulse measurement after selecting
pulse current as the display mode.
Table 1-2
Display mode examples
Samples for battery
Display mode
SINGLE V AND I: 6.116V #1 ON 6.116 V #2 ON Section 2
DUAL V AND I: 2.97V 25.7m 1# 2.97V 25.7m 1
DVM input: N/A
Pulse current: PULSE HI #1 ON PULSE HI #2 ON Section 3
Long integration: LONG INT #1 ON LONG INT #2 ON Section 4
channel (#1)
1.2058 A 1.2058 A
0.00V 0.00A 0 1.00V 0.17A 1#
(charger channel only)
2.1947 A 2.1947 A
PULSE LO #1 ON PULSE LO #2 ON
0.2147 A 0.2147 A
PULSE AVG #1 ON PULSE AVG #2 ON
1.1495 A 1.1495 A
1.0236 A 1.0236 A
Samples for charger
channel (#2) Reference
Section 2
DVM INPUT #2 OFF
5.321 V
Section 2
NOTE #1 or #2 indicates the active channel. ON indicates that the output is turned on.
With the output turned off, OFF is displayed (see
Section 2 for details on
outputting current and voltage).
NO PULSE is displayed if the output is OFF or pulses are not detected (output
ON) for pulse current and long integration display modes only.
When a change is made that affects the readings being taken, dashes are
displayed instead of readings. The dashes remain until a valid reading for the
new condition is taken.
1-10 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 27
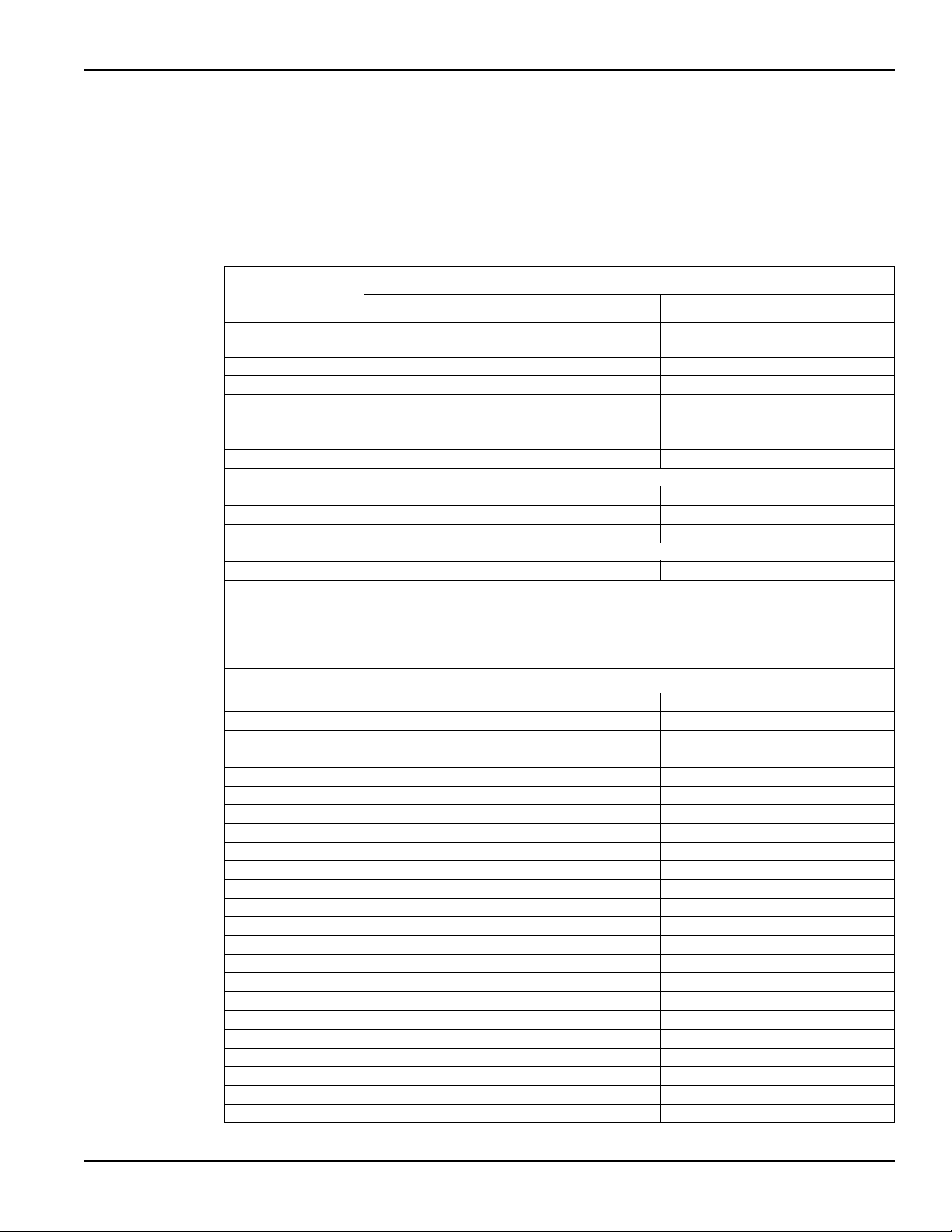
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
Default settings
The power supply can be set to power-on with the factory default conditions (RST defaults) or to
one of four user-saved setup conditions (SAV0 to SAV3). The factory default conditions are listed
in
Table 1-3.
Table 1-3
Factory defaults (RST)
Reset (RST) default
Setting Battery channel (#1) Charger channel (#2)
Output value
settings:
Voltage (V) 0.000V 0.000V
Current (A) 0.2500A 0.2500A
Output state
(operate)
Voltage protection 8 V, clamp off 8 V, clamp off
Display type Single V and I Single V and I
GPIB address* No effect (factory set to 16)
Current range 5 A (Auto Range OFF) 5 A (Auto Range OFF)
Integration rate 1.00 PLC 1.00 PLC
Average readings 1 1
Power on setup* No effect (factory set to RST)
Current limit mode LIM LIM
Auto Zero State ON (applies to both channels)
Output relay one*
Output relay two*
Output relay three*
Output relay four*
VFD brightness*
Output bandwidth LOW LOW
Output impedance 0.00 Ω Not Applicable
Pulse current:
High time 33 µsec 33 µsec
Low time 33 µsec 33 µsec
Average time 33 µsec 33 µsec
Digitize time 33 µsec 33 µsec
Timeout 1.000 sec 1.000 sec
Average readings 1 1
Trigger delay 0.00000 sec 0.00000 sec
Trigger level: 0 0
Step Off
Step Initial 2 sec
Step Sequence 0
Step Length 0
Step Skip 0
Step up 1
Step down 1
Step time 200µs
Step timeout 2ms
Step delay 0
Long integration:
Integration time 1 second 1 second
**Global settings (not channel-specific).
OFF OFF
No effect (after power
cycle, set to zero)
Over bus: 1 From display: FULL BRIGHTNESS
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-11
Page 28

Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Table 1-3
Factory defaults (RST)
Reset (RST) default
Setting Battery channel (#1) Charger channel (#2)
Pulse timeout 16 seconds 16 seconds
Trigger edge RISING RISING
Trigger level Same as “Trigger level” under Pulse Current
(above)
**Global settings (not channel-specific).
Same as “Trigger level” under
Pulse Current (above)
Setups - Save, Power-on, and Recall
Setups are configured by SAVE SETUP, POWER ON SETUP and RECALL SETUP items of the
MENU (which is accessed by pressing the MENU key). When a setup is saved, all settings that are
channel-specific settings will be saved to that setup. Saving/recalling a setup has no effect on
Global Settings (see Global settings in
channel-specific parameters from that setup.
NOTE Table 1-4 shows the menu structure. Rules to navigate the menu follow the
table.
Table 1-3). Similarly, recalling a setup loads only the
Menu
The setup MENU items are explained as follows:
• SAVE SETUP - Save the present power supply setup to a memory location;
SAV0-SAV3.
• RECALL SETUP - Return the power supply to the RST defaults (Table 1-3), or to one of
four user-saved setups; RST, SAV0-SAV3.
• POWER-ON SETUP - Select the setup to use at power-up; RST, SAV0-SAV3.
When powering up or recalling the SAV0, SAV1, SAV2, or SAV3 setup, the output will be OFF
regardless of the operate state when the setup was saved. For example, if the output is ON when
the setup is saved as SAV0, the power supply will power up with the output OFF for the SAV0
power-on setup.
NOTE For GPIB operation, the setups are saved and recalled using the *SAV, *RCL,
and
*RST commands (see Section 8 or details). The power-on setup is
selected using the SYSTem:POSetup command (see Section 10).
Many aspects of operation are configured from the menus summarized in Table 1-4. Use the rules
following the table to navigate through the menu structure.
NOTE The menu key is used to access the menu structure. However, if in remote for
IEEE-488 bus operation (“R” displayed below “ON/OFF”) the menu key returns
the instrument to LOCAL operation.
1-12 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 29
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
Table 1-4
Main MENU structure
Menu item Description Ref
GPIB ADDRESS
CURRENT RANGE #1/#2
NPLC RATE #1/#2
AVER READINGS #1/#2
SAVE SETUP
RECALL SETUP
POWER ON SETUP
CALIBRATE UNIT
VOLT PROTECT #1/#2
CURR LIM MODE #1/#2
AUTO ZERO STATE
OUTPUT RELAYS
REVISION NUMBER
SERIAL NUMBER
VFD BRIGHTNESS
OUT BANDWIDTH #1/#2
OUT IMPEDANCE #1
PULSE CURRENT #1/#2
HIGH TIME
LOW TIME
AVERAGE TIME
AUTO TIME
PULSE TIMEOUT
AVERAGE READINGS
TRIGGER DELAY
TRIGGER LEVEL
Set primary address (0 to 30)
Select current range:
Battery channel (#1) Charger channel (#2)
5 A 5 A
500 mA 5 mA
50 mA AUTO
5 mA
AUTO
Set integration rate in NPLC (0.002 to 10)
Set average reading count (1 to 10)
Save present setup in memory (SAV0–SAV3)
Recall setup from memory (RST, SAV0–SAV3).
Select power-on setup (RST, SAV0–SAV3)
Calibrate unit (see Calibration)
Set voltage protection range (0–8 V) and clamp (ON/OFF)
Select current limit mode (LIMit or TRIP)
Set auto zero state (ON/OFF)
Close (1) or open (0) relay control circuitry
Display firmware revision levels
Display serial number of the power supply
Set VFD display’s brightness level (OFF, FULL, 3/4, 1/2, 1/4)
Set bandwidth (HIGH, LOW)
Set battery channels impedance (0–1 Ω)
Pulse-current configuration.
Set high time integration rate (in µsec.).
Set low time integration rate (in µsec.).
Set average time integration rate (in µsec.).
Set pulse integration rates automatically.
Set pulse timeout (default is 1.000 second, incremented in
1ms steps)
Set average reading count (1 to 100).
Set trigger delay in seconds (0 to 100 msec).
Sets pulse current trigger level in Amps for the 5 A, 500 mA,
50 mA, or 5 mA current ranges:
Battery channel (#1) Charger channel (#2)
A(5.0) 0–5A in 5 mA steps A(5.0) 0–5 A in 5 mA steps
mA(500) 0–500 mA in 0.5 mA steps
mA (50) 0-50 mA in 0.05 mA steps
mA (5) 0-5 mA in 0.005 mA steps
Sect. 6
Sect. 2
Sect. 2
Sect. 2
Note 1
Note 1
Note 1
Sec. 13
Sect. 2
Note 2
Sect. 9
Sect. 5
Note 2
Note 3
Sect. 10
Sect. 2
Sect. 2
Sect. 3
The main menu structure is accessed by pressing the MENU key on the front panel.
Notes:
1. See Default settings in this section to save and recall setups.
2. Revision Number displays the firmware revision level for the microcontroller and the display.
3. Serial Number displays the serial number of the power supply.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-13
Page 30
Section 1: Getting Started Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲▲▲▲▲
▲
▲
▲
▲
▲
▲
▲
Table 1-4
Main MENU structure
Menu item Description Ref
LONG INTEGRAT #1/#2 Long integration configuration. Sect. 4
INTEGRATION TIME
AUTO TIME
PULSE TIMEOUT
TRIGGER EDGE
TRIGGER LEVEL
The main menu structure is accessed by pressing the MENU key on the front panel.
Notes:
1. See Default settings in this section to save and recall setups.
2. Revision Number displays the firmware revision level for the microcontroller and the display.
3. Serial Number displays the serial number of the power supply.
Manually set integration time (up to 60 sec).
Automatically set integration time.
Set the “NO PULSE” timeout period (1 to 63 sec).
Select trigger edge (rising, falling, or neither).
Sets long integration trigger level in Amps for the 5 A, 500 mA,
50 mA, or 5 mA current ranges:
Battery channel (#1) Charger channel (#2)
A (5.0) 0–5 A in 5 mA steps A (5.0) 0–5 A in 5 mA steps
mA (500) 0–500 mA in 0.5 mA steps
mA (50) 0-50 mA in 0.05 mA steps
mA (5) 0-5 mA in 0.005 mA steps
Getting around the MENU
• Press the MENU key to activate the menu.
• Press the ▲ or ▼ keys to scroll through the primary menu items.
• Press the or keys to toggle between Channel #1 and Channel #2.
NOTE If a channel number is not shown, the or keys presses will be ignored. Also
the or keys presses will be ignored if a submenu only exists on the battery
channel (not on the charger channel).
• The active channel may be changed in the main menu, and the top submenus for pulse
current and long integration. The active channel cannot be changed in all other submenus.
• Select the displayed primary menu item by pressing ENTER. With PULSE CURRENT or
LONG INTEGRATION selected, use the
pressing ENTER selects the displayed item).
NOTE Before pressing enter, make sure the desired channel is active. If ENTER is
pressed with the incorrect channel selected, press the MENU key (to cancel
changes), use the
ENTER to select the displayed primary menu item.
▲ or ▼ keys to display the secondary items (again,
or keys to scroll to the desired channel, and then press
• Display and change settings and selections (for a menu item) using the edit keys
( ▲, ▼, , or keys):
– For a setting, use or keys to place the cursor on the desired digit, then use the ▲ or
▼ keys to increase or decrease the value (unless noted otherwise).
– Rapid jump to minimum or maximum: To rapidly jump to the maximum value, increment
the most significant digit (the left further-most digit in the selection setting). If the most
1-14 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 31

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 1: Getting Started
▲
significant digit is not displayed, place the cursor on that digit’s menu location and
increment from there. To rapidly jump to the minimum value, decrement the most
significant digit menu location. To find the most significant digit for a setting, press the
key until the cursor stops moving.
– For a selection, use the
otherwise).
• With the desired setting or selection displayed, press ENTER for it to take effect. Pressing
MENU will cancel the edit operation.
•Use the MENU key to exit the MENU structure.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired option (unless noted
SCPI programming
SCPI programming information is integrated with front-panel operation throughout this manual.
SCPI commands are listed in tables, and additional information that pertains exclusively to remote
operation is provided after each table. Also, the SCPI tables may reference other sections of this
manual.
Except for Section 11, all SCPI tables in this manual are abridged. That is, they exclude most
optional command words and query commands. Optional command words and query commands
are summarized as follows.
Optional Command Words - In order to be in conformance with the IEEE-488.2 standard, the
power supply accepts optional command words. Any command word that is enclosed in brackets
( [ ] ) is optional and does not have to be included in the program message.
Query Commands - Most command words have a query form (exceptions are noted). A query
command is identified by the question mark (?) that follows the command word. A query command
requests (queries) the programmed status of that command. When a query is sent and the power
supply is addressed to talk, the response message is sent to the computer.
To send a SCPI command as a query, append a “?” to the fundamental form of the command
(make sure to add the “?” immediately following the command on the same line). For complete
details, see
Programming syntax.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 1-15
Page 32

This page left blank intentionally .
Page 33

In this section:
Section 2
Basic Power Supply Operation
Topi c Page
Test connections ........................................................................................ 2-2
Remote sense ...................................................................................... 2-5
Local sense .......................................................................................... 2-5
RFI considerations ............................................................................... 2-6
Outputting voltage and current.................................................................... 2-6
Setting voltage protection value ........................................................... 2-6
Selecting proper current range............................................................. 2-8
Selecting current limit mode ................................................................. 2-8
Editing output voltage and current limit values..................................... 2-9
Using the OPERATE key.................................................................... 2-11
Output bandwidth...................................................................................... 2-11
Output impedance..................................................................................... 2-12
Changing the battery channel’s output impedance ............................ 2-12
SCPI programming - outputting voltage and current................................. 2-13
Command notes (outputting voltage and current) .............................. 2-14
Reading back V and I................................................................................ 2-16
V and I display modes (Single or Dual) ............................................. 2-16
Measurement configuration................................................................ 2-16
SCPI programming — measure V and I, and DVM input.......................... 2-17
Command notes (measure V and I, and DVM input).......................... 2-18
Independent voltage measurements (DVM) ............................................. 2-18
DVM input display mode .................................................................... 2-18
Measurement configuration................................................................ 2-19
SCPI programming - DVM ........................................................................ 2-19
Sink operation ........................................................................................... 2-19
Programming examples............................................................................ 2-21
Outputting and reading back V and I.................................................. 2-21
DVM measurements........................................................................... 2-21
Analog output............................................................................................ 2-22
Page 34

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Test connections
WARNING When installing a unit into a test system, make sure the external power
sources do not apply voltage to the power supply in excess of its
maximum limits (see complete Specifications at
to do so could result in personal injury or death.
The source and measurement connections are provided with overvoltage
protection rated up to 500 V for 50 µs. Do not connect sources that
produce transient voltages greater than 500 V or the protection provided
by the equipment may be degraded.
Test connections to the power supply are made at the rear panel using a quick disconnect
connector (see rear panel in
screw terminals of the connector. Once the connector is wired up, plug it into the rear panel and
tighten the captive retaining screws.
Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 show optimum remote 4-wire connections for device-under-test (DUT)
preferred connection (Figure 2-1) and fastest transient response connection (Figure 2-2).
Figure 1-1 for connector location). Use up to #14 AWG wire for the
www.keithley.com). Failure
2-2 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 35

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
Quick Disconnect
Connector
DUT
Source -
Source -
Sense -
Sense +
Source +
Source +
Twisted Pair
(5mA/50mA)
(0.5A/5A)
Analog
Outputs
Internal
Oscilloscope
or
Digitizer
Load Test Leads
10mA/V
1A/V
Figure 2-1
Battery channel preferred connection (maximum stability)
NOTE Twist source leads together and twist sense leads together for optimum
performance.
The analog outputs provide a voltage output based on the measured current as
follows:
0.5/5 A Output referenced to Source - : 1 A/V (each volt out represents 1A)
5/50 mA Output referenced to Source - : 10 mA/V (each volt out represents
10
mA)
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-3
Page 36

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Quick Disconnect
Connector
DUT
Source -
Source -
Sense -
Sense +
Source +
Source +
Twisted Pair
(5mA/50mA)
(0.5A/5A)
Analog
Outputs
Internal
Oscilloscope
or
Digitizer
Load Test Leads
1A/V
10mA/V
Figure 2-2
Battery channel fastest transient response connection
NOTE Twist source leads together and twist sense leads together for optimum
performance.
The analog outputs provide a voltage output based on the measured current as
follows:
0.5/5 A Output referenced to Source - : 1 A/V (each volt out represents 1A)
5/50 mA Output referenced to Source - : 10 mA/V (each volt out represents
10
mA)
2-4 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 37

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
External Test Circuit
Quick Disconnect
Connector
Model 2308
Source Input/Output
DVM Input
DUT
+
-
DVM +
DVM -
Source -
Source -
Sense -
Sense +
Source +
Source +
Twisted Pair
Figure 2-3
Charger channel 4-wire remote sense connection from the DUT to the ouput
Remote sense
Local sense
NOTE Twist Source leads together and twist Sense leads together for
optimum performance.
As shown in Figure 2-1 the Model 2308 battery and charger channels are intended to be operated
with remote sense leads (4 wire connection). The Sense+ and Sense- pins provide output voltage
sensing. Without these terminals connected, the power supply operates without voltage feedback
and therefore supplies an unregulated voltage. This unregulated voltage value can be up to +18 V
or down to -5 V. Use voltage protection to turn off the output and protect against the extremes
(refer to
Setting voltage protection value).
Connect the sense inputs to the supply as close as possible to the load’s source inputs through
twisted pair leads (refer to
Figure 2-1). This is necessary to achieve the maximum transient
performance of the supply.
CAUTION Do NOT connect the sense inputs and supply outputs at the rear of the supply!
Connecting the sense leads in this fashion will severely compromise the
performance of Model 2308 with dynamic loads when using 4-wire sense.
The Model 2308 battery and charger channels can be connected to operate with local sense leads
(2-wire connection) as shown in
supply outputs are connected at the rear of the supply.
Figure 2-4. In this connection scheme, the sense inputs and
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-5
Page 38

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Quick Disconnect
Connector
Source -
Source -
Sense -
Sense +
Source +
Source +
Twisted Pair
DUT
Figure 2-4
Local Sense Connections (battery channel and charger channel)
RFI considerations
NOTE Twist Source leads together for optimum performance.
Operating the power supply in high Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) environments may result
in improper operation. For that reason, keep RFI to a minimum when operating the unit. Additional
shielding can be used to reduce RFI to an acceptable level.
Outputting voltage and current
Setting voltage protection value
NOTE The voltage protection value (VPT) is channel-specific. The number after the
Voltage protection value (VPT) is provided for the battery and charger channels. This function
monitors the SOURCE + pins (see
internal ground and will shut off the output voltage for either channel when the protection voltage
range (which equals the set voltage ± protection voltage) set by the user is exceeded. This voltage
2-6 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
is typically not the same voltage as at the device under test due to lead impedance and internal
sense resistor losses.
The VPT message will appear on the lower line of the display after the current reading indicator (A
or mA). The message will clear when the output it turned back ON, unless the condition causing a
the VPT message still exist. The VPT message takes precedence over the current limit messages.
See
Selecting current limit mode for more information on the current limit messages. The VPT
message will not appear if the display mode is set to DUAL V AND I.
number sign (#) indicates the channel affected by editing.
Figure 2-1 or Figure 2-4) with respect to the Model 2308’s
Page 39

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
▲▲▲
▲
VPT circuitry is useful in protecting the load from a high positive voltage if one of the remote
sensing leads is disconnected. When in VPT mode, the output is held in the Operate OFF position
until an Operate ON command is received (VPT will be displayed until the output is turned back
on). The voltage protection feature has a clamp setting, which can be turned ON or OFF. If ON,
protection voltage values below 0 volts (-0.6
volts) are not allowed. If OFF, protection voltage can
go negative to the extent of the set voltage - protection voltage.
For example: If PROT=4 V, and SET =6 V, VPT range is from +2 V to +10 V. If the SET voltage is
changed to 2 V and protection clamp set to OFF, the range would equal -2 V to +6 V. However, if
protection clamp is set to ON, the range would equal -0.6 V to +6 V.
NOTE Table 1-3 shows the menu structure. Rules to navigate the menu follow the
table.
CAUTION Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to the output connector pins may cause the VPT
circuitry to turn the output off. Use proper ESD handling precautions before
making any contact with the output connector pins or wires connected to the
pins.
To set the VPT value from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key to access the main menu.
2. Press the
3. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to VOLT PROTECT.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
4. Press ENTER to select.
5. Press the
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired VPT value and to select cOFF (voltage
protection clamp OFF) or cON (voltage protection clamp ON).
NOTE Setting changes can be canceled by pressing the MENU key.
6. Press ENTER to save your settings and return to the main menu.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-7
Page 40
Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
Selecting proper current range
NOTE The current range value is channel-specific. The number after the number sign
(#) indicates the channel affected by editing.
Power supply current ranges are listed in Table 2-1. When auto range is selected, the instrument
will automatically go to the most sensitive range to perform the measurement. The current range
setting may be the same or different for each channel
Table 2-1
Current ranges
Power supply Current ranges
battery channel (#1) 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, 5 mA or AUTO
charger channel (#2) 5 A, 5 mA, or Auto
NOTE Table 1-3 shows the menu structure. Rules to navigate the menu follow the
table.
.
To select the CURRENT RANGE from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key to access the main menu.
2. Press the
3. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to CURRENT RANGE.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
4. Press ENTER to select.
5. Press
NOTE Setting changes can be canceled by pressing the MENU key.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired current range value (see Table 2-1).
6. Press ENTER to save your settings and return to the main menu.
Selecting current limit mode
NOTE The current limit mode setting is channel-specific. The number after the number
sign (#) indicates the channel affected by editing.
If the current limit is reached, the output will either turn off (TRIP) or stay on (LIM). The two current
limit modes (LIM or TRIP) are explained as follows:
LIM mode - If LIM mode selected, the output will remain on when the current limit is reached. The
“LIM” message will appear on the lower line of the display after the current reading indicator (A or
mA). The message will clear when the limit condition is cleared.
The power supply may or may not be taken out of current limit by decreasing the output voltage or
increasing the current limit value, depending on how the circuit is connected. However, increasing
the current limit may compromise protection for the DUT.
2-8 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 41

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
▲
▲
While in the current limit, the power supply is operating as a constant-current source. As long as
the limit condition exists, the power supply output current will remain constant. The output voltage
is probably less than the programmed value when sourcing current, and probably greater than the
programmed value when sinking current. The LIM message will not appear if the display mode is
set to DUAL V AND I.
TRIP mode - If TRIP mode selected, the output will turn off when the current limit is reached. The
“TRIP” message will appear on the lower line of the display after the current reading indicator (A or
mA). The message will clear when the output is turned back on, unless it trips again because of a
current limit condition. The TRIP message will not appear if the display mode is set to DUAL V
AND I.
NOTE See Table 1-3 for an illustration of the menu structure. Rules to navigate the
menu follow the table.
To select the CUR LIM MODE from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key to access the main menu.
2. Press the
3. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to CUR LIM MODE.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
4. Press ENTER to select.
5. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired current limit mode (LIM or TRIP).
NOTE Setting changes can be canceled by pressing the MENU key.
6. Press ENTER to save your settings and return to the main menu.
Editing output voltage and current limit values
NOTE Output voltage and current limit values are channel-specific. The number after
the number sign (#) indicates the channel affected by editing.
Current limit is a feature that protects the load from damage under overload conditions. The
current limit setting indicates the maximum amount of current allowed to flow through the system.
The setting applies to any of the current range settings.
The current limit setting for the 5 A and AUTO range selections are “remembered.” For the
following examples, assume the current limit setting on the 5 A range is 3 A. Selecting the 5 mA,
50 mA or 500 mA range on the battery channel, or 5 mA on the charger channel defaults the
current limit setting to 1A since that is the maximum allowable setting on those ranges. Switching
back to the 5 A range or enabling auto ranging reinstates the 3 A limit. If the current limit value on
the 5 amps range is ≤1 A, the limit on the 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA ranges will be the same when
switching from the 5 A range to that range.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-9
Page 42

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
▲▲▲▲▲
▲
NOTE See Table 1-3 for an illustration of the menu structure. Rules to navigate the
menu follow the table.
To edit voltage and current values from the front panel:
NOTE The following steps assume that the appropriate current range is already
selected along with current limit mode and voltage protection.
1. Press the SET key to select the output settings mode. A blinking cursor appears in the
voltage field of the display.
2. Press the
• The cursor position (blinking digit) is controlled by the
• With the cursor positioned on a digit, increment or decrement the value using the
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired output voltage value.
or keys.
▲ or ▼
keys.
3. Press SET to move the blinking cursor to the current limit field.
4. Press the
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired current limit.
5. Press SET to exit from output settings mode.
Once in Set Mode (enter Set Mode by pressing the SET key), the active channel cannot be
changed. If Set Mode was inadvertently entered or entered in on the wrong channel, press the
SET key until the blinking cursor disappears to exit Set Mode (once out of Set Mode, active
channel switching is enabled).
Editing voltage and current values using the SET key cannot be canceled with the MENU key (the
values are immediately committed). Enter the old values by repeating the editing procedure and
manually using the
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired output voltage or current value(s).
SET key: This key is active in any front-panel menu or display mode - if not already in the output
settings mode, the SET key will select it.
Pressing the SET key to exit the output settings mode returns the instrument to the previous
display mode or front-panel menu.
V and I DACs are updated in real time - if the output is on, the output is updated immediately when
a value is altered.
If the display mode is set to DUAL V AND I, then entering SET mode will cause the display to exit
back into the SINGLE V AND I mode for the active channel. If dual is desired, select dual after
exiting set mode (see
V and I display modes (Single or Dual)).
Editing shortcuts
The following editing shortcuts can be used when the output is OFF:
• Output voltage can be quickly set to the maximum value by incrementing the tens digit
(MSD). Note that if the tens digit is zero, it is not displayed. Place the cursor to the left of the
units digit.
• Output voltage can be quickly set to zero (0.000 V) by decrementing the first leading zero of
the reading. If there is no leading zero, decrement the tens digit.
• Current limit can be quickly set to its maximum value by incrementing the units digit (MSD).
2-10 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 43
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
• Current limit on either range can be quickly set to the minimum value (0.006 A) by
decrementing the first leading zero of the reading. If there is no leading zero, decrement the
units digit.
Editing restrictions
The following editing restrictions are in effect when the output is ON:
• You cannot increment a digit that would display a value that jumps to the maximum. For
example, for the value 14.200 V, you cannot increment the “1” or the “4” since the resultant
value would exceed 15.000 V.
• When decrementing a digit, only that digit and digits to the left are affected. The digits to the
right of the cursor are not changed.
Using the OPERATE key
NOTE Pressing the OPERATE key is channel-specific. The number after the number
sign (#) indicates the channel affected by the OPERATE key.
Use the OPERATE key to control power supply output. This key toggles the output ON and OFF
for the active channel even if output status is not displayed. To display the output status for the
active channel, place the unit in readings or set mode (the output status is not shown in display
type menu, main menu, or submenus). When output status is displayed, ON or OFF will appear in
the upper right hand corner of the display.
NOTE DVM measurements can be performed with the output OFF on the charger
Output bandwidth
The battery and charger channel’s output bandwidth control has HIGH and LOW settings. The
HIGH setting will result in the fastest response with dynamic loads but, could be unstable with
certain loads. The LOW setting mode will have a slower response but will be stable for most loads.
Testing the performance of the battery charger circuitry in a handset does not require the high
bandwidth performance in Channel 1 or Channel 2 of the Model 2308. Since a charger circuit is a
voltage regulated circuit, it resembles a high capacitance load to the output of the Model 2308. For
this type of application, the LOW bandwidth output mode provides increased stability and
eliminates oscillations that may occur.
The bandwidth can be user-programmed at any time. However, if the output is OFF, the output
bandwidth is automatically set to LOW as summarized in
channel.
Table 2-2.
Table 2-2
Output bandwidth channel setting
Output Bandwidth
ON LOW or HIGH
(user selectable)
OFF LOW
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-11
Page 44
Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
V
drop
t() RIIt()
×
=
NOTE The following steps assume that the appropriate current range is already
selected along with current limit mode and voltage protection.
To set output bandwidth from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key to access the main menu.
2. Press
3. Press
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to OUT BANDWIDTH.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
4. Press ENTER to select.
5. Press the
NOTE Setting changes can be canceled by pressing the MENU key.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired bandwidth setting (HIGH or LOW).
6. Press ENTER to save your settings and return to the main menu.
Output impedance
Keithley Instruments Model 2308 has a variable output impedance feature on the battery channel
(#1). This output impedance setting allows the performance of the battery channel to closely
model a real battery's performance with a dynamic load. When setting the output impedance to a
certain value (R
), the output voltage drop will be proportional to the output current (see the voltage
I
drop equation below). The output voltage will be reduced by the voltage drop.
Voltage drop equation:
NOTE For a more detailed discussion of output impedance and the performance with
various types of loads, see Applications Note 2191 on the Product Information
CD-ROM.
Changing the battery channel’s output impedance
The Model 2308 output impedance can be checked or changed with the output on or off. The
output impedance is selectable from 0.00 Ω to 1.00 Ω in 10 mΩ steps (default is 0Ω).
NOTE The following steps assume that the appropriate current range is already
selected along with current limit mode and voltage protection.
To set output impedance from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key to access the main menu.
2. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to OUT IMPEDANCE #1 (Channel #1 only feature).
3. Press ENTER to select.
2-12 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 45

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
▲
▲
4. Press ▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired output impedance value.
NOTE Setting changes can be canceled by pressing the MENU key.
5. Press ENTER to save your settings and return to the main menu.
SCPI programming - outputting voltage and current
The commands to output voltage and current are summarized in Table 2-3 (a listing following the
table contains specific command notes). The programming example (“Outputting and reading back
V and I”) located at the end of this section demonstrates how to use these commands.
NOTE Brackets [ ] indicate optional (and default) command parameters.
Table 2-3
SCPI command summary - outputting voltage and current
Commands Description Default
SENSe[1]
:CURRent
:RANGe
[:UPPer] <n>
:AUTO <b>
SENSe2
:CURRent
:RANGe
[:UPPer] <n>
:AUTO <b>
[SOURce[1]]
:VOLTage <n>
:PROTection <NRf>
:STATe? <b>
:CLAMp <b>
:CURRent <n>
:TYPe <name>
:STATe?
SOURce2
:VOLTage <n>
:PROTection <NRf>
:STATe? <b>
:CLAMp <b>
:CURRent <n>
:TYPe <name>
:STATe?
OUTPut[1]
[:STATe] <b>
:BANDwidth <name>
:IMPedance <NRf>
OUTPut2
[:STATe] <b>
:BANDwidth <name>
SENSe[1] subsystem for battery channel (#1):
Current function:
Set current measurement range:
Specify expected current in amps: 0 to 5.
Enable or disable auto range.
SENSe2 subsystem for charger channel (#2):
Current function:
Set current measurement range:
Specify expected current in amps: 0 to 5.
Enable or disable auto range.
[SOURce1] subsystem for battery channel (#1):
Set voltage amplitude in volts: 0 to 15 (1mV resolution).
Sets VPT (voltage protection) range (0–8V).
Query state of VPT - no associated command.
Sets VPT clamp mode ON or OFF.
Set current limit value in amps: 0.006 to 5 (100µA res)
Select current limit type: LIMit or TRIP.
Query state of current limit - no associated command.
SOURce2 subsystem for charger channel (2):
Set voltage amplitude in volts: 0 to 15 (1 mV resolution).
Sets VPT range (0–8V).
Query state of VPT - no associated command.
Sets VPT clamp mode ON or OFF.
Set current limit value in amps: 0.006 to 5 (100 µA res).
Select current limit type: LIMit or TRIP.
Query state of current limit - no associated command.
OUTPut [1] subsystem for battery channel (#1):
Turn the power supply output ON or OFF.
Specifies output bandwidth (HIGH or LOW).
Specifies output impedance (0–1 Ω in 10 mΩ steps).
OUTPut2 subsystem for charger channel (#2):
Turn the power supply output ON or OFF.
Specifies output bandwidth (HIGH or LOW).
5.0
OFF
5.0
OFF
0.0
8V
OFF
0.25
LIM
0.0
8V
OFF
0.25
LIM
OFF
LOW
0
OFF
LOW
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-13
Page 46

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Table 2-3
SCPI command summary - outputting voltage and current (cont.)
Commands Description Default
:BOTHOUTON
:BOTHOUTOFF
Turns both power supply channels ON.
Turns both power supply channels OFF.
Command notes (outputting voltage and current)
SENSe[1]:CURRent:RANGe <n> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:CURRent:RANGe <n> Applies to charger channel (#2)
After specifying a current value, the instrument will go to the most sensitive range to accommodate
that reading. For example, if you are expecting a maximum current reading of 750mA, you can let
<n> = 0.75 (or 750e-3) to select the 5A range. Using the
current range disables auto range. Another way to select a range is to use the MINimum,
MAXimum, and DEFault parameters as follows:
SENS:CURR:RANG MIN Select the low current range (5mA) for battery
SENS2:CURR:RANG MAX Select the high current range (5A) for charger
SENS2:CURR:RANG DEF Select the default current range for charger
:RANGe command to manually select a
channel (#1) .
channel (#2 ).
channel (#2).
The response for :RANGe? query returns the selected range value, which can be 5.0000 A,
0.5000
0.0050
A, 0.0500 A, or 0.0050 A on the battery channel. Charger channel returns are 5.0000 A or
A.
SENSe[1]:CURRent:RANGe:AUTO <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:CURRent:RANGe:AUTO <b> Applies to charger channel (#2)
This command is coupled to the :RANGe <n> command. When auto range is enabled, the
response for
0.0500
If you then disable auto range, the instrument will remain at the last selected range.
NOTE If the limit setting is greater than 1A while on the 5A current range, the following
:RANGe? query returns the selected range value, which can be 5.0000 A, 0.5000 A,
A, or 0.0050 A on the battery channel. Charger channel returns are 5.0000 A or 0.0050 A.
message will be briefly displayed when ranging down:
CURRENT LIMIT ON
mA RANGE <= 1A
[SOURce1]:VOLTage <n> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SOURce2:VOLTage <n> Applies to charger channel (#2)
This command sets voltage amplitude in volts: 0 to 15 (1mV resolution).
2-14 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 47

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
[SOURce1]:CURRent <n> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SOURce2:CURRent <n> Applies to charger channel (#2)
With a milliamp measurement range selected, the maximum current limit is 1A. For the battery
channel, these ranges are 5 mA, 50 mA, or 500 mA. The charger channel range is 5 mA.
NOTE Sending a value that exceeds 1 A will generate a parameter out of range error
message (-222).
[SOURce[1]]:CURRent:STATe? Applies to battery channel (#1)
SOURce2:CURRent:STATe? Applies to charger channel (#2)
1. With the LIMit type selected, this command returns a “1” if the power supply is operating as
a constant-current source (current limit reached). With the TRIP type selected, a “1” is
returned if the output has turned off (tripped) due to current limit being reached. It will clear
to “0” when the output is turned back on.
2. The operation event register can be read to determine if the power supply is in current limit
and if the output has tripped (turned off) as a result of the current limit condition. See
Section 7 for details.
OUTput[1]:IMPedance <NRf> Applies to battery channel (#1)
This battery channel only command may be set from 0–1 Ω in 0.01 Ω steps. The command can be
used with the output ON or OFF.
OUTput[1]:BANDwidth <name> Applies to battery channel (#1)
OUTput2:BANDwidth <name> Applies to charger channel (#2)
This command specifies HIGH or LOW bandwidth. You can program the bandwidth at any time.
NOTE The bandwidth query will return user-specified settings, not necessarily the
present instrument value. Refer to
the actual bandwidth configuration.
Table 2-2 for how output state settings affect
BOTHOUTON Turns both channels ON
BOTHOUTOFF Turns both channels OFF
When sending either command, make note that the command is applied to battery channel (#1)
first and then to charger channel (#2). This allows both channels’ output state to be controlled with
a single bus command while preventing the outputs from being turned ON or OFF simultaneously.
No short form exists for this command.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-15
Page 48

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
▲
▲
Reading back V and I
V and I display modes (Single or Dual)
Measured output voltages and currents are displayed with either SINGLE or DUAL V AND I
display modes. Dual displays both channels simultaneously; single only shows the readings for
the active channel.
NOTE To display measured readings if the instrument is in the settings mode, press the
SET key until the blinking stops (the measured readings can then be displayed).
To determine if the instrument is in the settings mode, check for a blinking cursor
in a digit of the voltage or current field (if present, the instrument is in the setting
mode).
These display modes are selected as follows:
1. Press the DISPLAY key.
2. Press the
3. For SINGLE V AND I, press the
4. Press ENTER to select and return to display of readings.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to SINGLE V AND I or DUAL V AND I.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
NOTE Voltage readings are located on the top line of the display, and current readings
are located on the bottom line when in single display mode. For dual display
mode the top line has the voltage and current readings for battery channel, and
the bottom line has the readings for charger channel.
For details about display modes, see Display modes.
Measurement configuration
CURRENT RANGE #1/#2, INTEGRATION RATE #1/#2, and the AVER READINGS
#1/#2 can be checked or changed from the menu (which is accessed by pressing the MENU key).
The #1 (battery channel active) or #2 (charger channel active) will appear on the top line of the
display (use
NOTE See Table 1-3 for an illustration of the menu structure. Rules to navigate the
Current range
Current range is linked with current limit. Therefore, as a general rule, the user selects the current
range before setting the current limit. The current range can be changed at any time, but selecting
the lower range may change the current limit setting (see
on current range and current limit).
or keys to toggle the active channel).
menu follow the table.
Outputting voltage and current for details
NPLC rate
The integration (reading) rate of the instrument is specified as a parameter based on the number
of power-line cycles (NPLC), where 1 PLC for 60Hz line frequency is 16.67msec (1/60). In general,
the fastest integration time (0.002 PLC) results in increased reading noise. The slowest integration
2-16 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 49

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
time (10 PLC) provides the best common-mode and normal-mode rejection. In-between settings
are a compromise between speed and noise.
The NPLC RATE #2 menu item is also used to set the reading rate for DVM measurements. Note
that NPLC RATE #1/#2 is not used to set the integration rate for pulse current and long integration
measurements. These measurements are described in
Section 3 and Section 4, respectively.
Average readings
The average reading count (1 to 10) specifies the number of measurement conversions to average
for each reading. For example, with a reading count of 5, each displayed reading will be the
average of five measurement conversions.
The AVER READINGS #2 menu items are also used to set the average reading count for DVM
measurements. Note that AVER READINGS #1/#2 is not used to set the average reading count for
pulse current (see
Section 3) or long integration measurements (see Section 4).
SCPI programming — measure V and I, and DVM input
The commands to measure output voltage and current, and the DVM input are summarized in
Table 2-4 (a listing following the table contains specific command notes). The “Programming
examples” at the end of this section demonstrates how to use these commands.
Table 2-4
SCPI commands: Measure V and I, and DVM input
Commands Description Default
SENSe[1]
:FUNCtion <name>
:NPLCycles <n>
:AVERage <NRf>
SENSe2
:FUNCtion <name>
:NPLCycles <n>
:AVERage <NRf>
READ[1]? Trigger and return one reading for battery channel (#1)*.
READ[1]:ARRay? Trigger an array of readings and return them for battery channel
READ2? Trigger and return one reading for charger channel (#2)*.
READ2:ARRay? Trigger an array of readings and return them for charger channel
BOTHFUNC <name>
*
This command applies to the currently selected function.
SENSe[1] subsystem for battery channel (#1):
Select readback function: “VOLTage”,
“CURRent”.
Set integration rate (in line cycles) for voltage,
current, measurements: 0.002 to 10.
Specify the average count for voltage and current
measurements: 1 to 10.
SENSe2 subsystem for charger channel (#2):
Select readback function: “VOLTage”,
“CURRent”, or “DVMeter”.
Set integration rate (in line cycles) for voltage,
current, and DVM measurements: 0.002 to 10.
Specify the average count for voltage, current,
and DVM measurements: 1 to 10.
*
(#1)
.
*
.
(#2)
Sets the battery channel (#1), then the charger channel (#2) to
the function specified by <name>. Valid strings for <name> are
“VOLTage”, “CURRent”, “PCURrent”, or “LINTegration”. Since
"DVMeter" is a charger-only function, sending this command with
the name "DVMeter" will generate a string data error (-150)
message.
VOLT
1.0
1
VOLT
1.0
1
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-17
Page 50

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
Command notes (measure V and I, and DVM input)
SENSe[1]:FUNCtion <name> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:FUNCtion <name> Applies to charger channel (#2)
The parameter name can instead be enclosed in single quotes (for example: ‘CURRent’).
With “DVMeter” selected, the instrument measures the voltage applied to the input of the digital
voltmeter (DVM) on the charger channel (#2) only.
The “PCURrent” and “LINTegration” parameters for :FUNCtion (which are not listed in Table 2-
4) select the pulse current and long integration measurement modes. These measurement modes
are covered in Section 3 and Section 4, respectively.
SENSe[1]:AVERage <NRf> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:AVERage <NRf> Applies to charger channel (#2)
• When requesting a single reading (FETch?, READ?, or MEASure?), average count
specifies the number of measurement conversions to average for the reading. For example,
with the average count set to 10,
return (and display) the average of those 10 conversions for the battery channel. When
requesting an array of readings (
average count specifies the number of measurements to place in an array. For example,
with the average count set to 10,
readings (charger channel command similar).
• Signal-oriented measurement commands (for example: READ?) are covered in Section 9.
READ? will trigger 10 measurement conversions and
FETCh:ARRay?, READ:ARRay? or MEASure:ARRay?),
READ:ARRay? will trigger and return 10 battery channel
Independent voltage measurements (DVM)
The power supply has an independent digital voltmeter (DVM) on the charger channel (# 2) only
that can measure up to +30VDC and down to -5VDC. Connections for the DVM are shown in
Figure 2-1.
DVM input display mode
The DVM input display mode must be selected in order to measure voltage applied to DVM input
of the power supply.
NOTE To display measured readings if the instrument is in the settings mode, press the
SET key until the blinking stops (the measured readings can then be displayed).
To determine if the instrument is in the settings mode, check for a blinking cursor
in a digit of the voltage or current field (if present, the instrument is in the setting
mode).
This display mode is selected as follows:
1. Press the DISPLAY key to access the display menu.
2. Press the
3. Press the
4. Press ENTER to select.
or keys to scroll to DISPLAY TYPE #2 (DVM is a Channel 2 only feature).
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to DVM INPUT.
NOTE For details about display modes, see Display modes.
2-18 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 51

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
▲
▲
Channel 1
DUT
Channel 2
Program V
chan2
> V
Chan1
to force Channel 1 to sink current
Measurement configuration
The NPLC RATE #2 and AVER READINGS #2 for DVM measurements can be checked or
changed from the menu (which is accessed by pressing the MENU key). Select Channel #2 by
pressing the
NOTE Table 1-3 shows the menu structure. Rules to navigate the menu follow the
or keys.
tables.
These two measurement configuration menu items are the same ones used for SINGLE V AND I
measurements (see
Measurement configuration for details on NPLC rate and average readings).
SCPI programming - DVM
The commands to perform V AND I measurements on the charger channel (#2) are also used to
perform DVM measurements. These commands are documented in
The “DVM measurements” programming example at the end of this section demonstrates how to
use these commands to measure the DVM input.
Table 2-3.
Sink operation
Either channel can sink current if its load is at a higher voltage then the channel’s output. This
enables a channel to simulate a discharged battery, and the second channel to simulate a charger
so that a device’s charger-control circuitry can be tested.
Figure 2-5
Charger Control Circuit Testing
NOTE For Channel 1 to simulate a discharged battery (by sinking current), and for
Sink operation allows the power supply to be used as a constant current load. To function
as
a constant current load, the power supply must be in compliance (current limit). When operating
as a sink, the power supply is dissipating power rather than sourcing it.
example of how the power supply can be made to operate as a sink. An external source, such as a
battery charger circuit, whose voltage is higher than the programmed power supply voltage, is
connected as shown. If the supply is operated in remote sense and
Channel 2 to simulate a charger, program the Channel 2 voltage to be greater
than the Channel 1 voltage.
Figure 2-6 shows an
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-19
Page 52
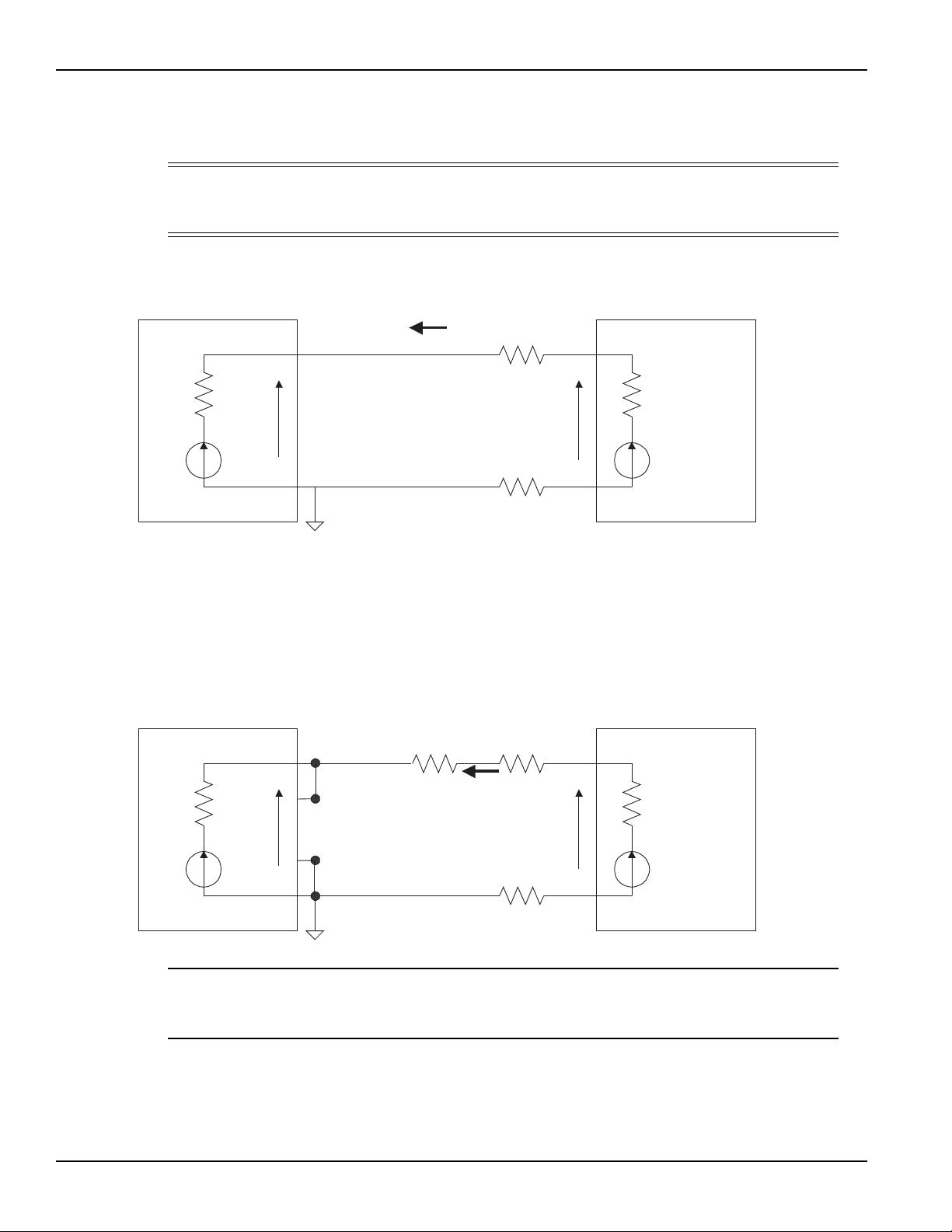
Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
+ sense
- sense
+ output
- output
Model
Charger
R
S
V
S
V
Charger
R
Cable
R
Cable
V
C
R
C
V
Supply
I
Sink
+ sense
- sense
+ output
- output
Model
Charger
R
S
V
S
V
Charger
R
Cable
R
Cable
V
Supply
= 0
R
Test
V
C
R
C
I
Sink
V
Charger
> V
Supply
+ I
sinkRcable
, is satisfied, current I
flows into the positive (+) terminal of the
sink
power supply. Current readback is negative.
CAUTION Exceeding current sink capacity (0–5 V: 3A max. 5 V–15 V: Derate 0.2 A per volt
above 5 V) could cause damage to the power supply that is not covered by the
warranty.
Figure 2-6
Sink operation
However, in this configuration current compliance may not be reached and current measurements
may be unstable if I
sinkRcable
is large. Figure 2-7 shows a preferred method for measuring the
current output of the charger circuit at a rated output voltage with the power supply operating in
local sense mode. Set the supply output voltage to 0.00 V and the enter the desired test
(compliance) current, I
I
test
and R
test
.
. Select R
test
so that V
test
, the desired test voltage, is the product of
charger
Figure 2-7
Preferred method
NOTE Figure 2-7 shows the preferred method for measuring current output of the
charger circuit at a rated output voltage with the power supply operating in local
sense mode.
2-20 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Unless high speed transient performance is absolutely required when operating as a sink, the
LOW bandwidth output mode provides superior results with a constant current or voltage load
such as a battery charger.
Page 53

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation
Programming examples
Outputting and reading back V and I
The following command sequences demonstrate how to output voltage and current, and read back
(measure) the actual voltage and current:
Battery channel (#1)
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Select battery channel as active one.
VOLT 5 ‘ Set output voltage to 5V.
SENS:CURR:RANG:AUTO ON ‘ Enable auto range for current.
CURR 750e-3 ‘ Set current limit to 750mA.
CURR:TYPE TRIP ‘ Select trip mode for current limit.
SENS:FUNC ‘VOLT’ ‘ Select the voltage measurement function.
SENS:NPLC 2 ‘ Set integration rate to 2 PLC.
SENS:AVER 5 ‘ Set average reading count to 5.
OUTP ON ‘ Turn on the power supply output.
READ? ‘ Trigger 5 voltage measurement conversions
SENS:FUNC ‘CURR’ ‘ Select current measurement function.
READ? ‘ Trigger 5 current measurement conversions and
and return the average of those
The average reading is displayed on the front panel.
return the average of those 5 conversions.
The average of the 5 readings is displayed on
the front panel.
5 conversions.
Charger channel (#2)
DISP:CHAN 2 ‘ Select charger channel as active one.
SOUR2:VOLT 5 ‘ Set output voltage to 5V.
SENS2:CURR:RANG:AUTO ON ‘ Enable auto range for current.
SOUR2:CURR 750e-3 ‘ Set current limit to 750mA.
SOUR2:CURR:TYPE LIM ‘ Select LIM mode for current limit.
SENS2:FUNC ‘VOLT’ ‘ Select the voltage measurement function.
SENS2:NPLC 4 ‘ Set integration rate to 4 PLC.
SENS2:AVER 4 ‘ Set average reading count to 4.
OUTP2 ON ‘ Turn on the power supply output.
READ2? ‘ Trigger 4 voltage measurement conversions
SENS2:FUNC ‘CURR’ ‘ Select current measurement function.
READ2:ARR? ‘ Trigger 4 current measurement conversions and
DVM measurements
The following command sequence demonstrates how to measure voltage applied to the DVM
input of the power supply:
Charger channel (#2)
DISP:CHAN 2 ‘ Set active channel - charger.
SENS2:FUNC ‘DVM’ ‘ Select the DVM Input function.
SENS2:NPLC 3 ‘ Set integration rate to 3 PLC.
SENS2:AVER 8 ‘ Set average reading count to 8.
READ2:ARR? ‘ Trigger and return 8 readings. The average
and return the average of those
‘ return all 4 conversions. The average of the
‘ 4 readings is displayed on the front panel.
‘ of the 8 readings is displayed on the front
‘ panel.
4 conversions.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 2-21
Page 54

Section 2: Basic Power Supply Operation Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Source -
5/50 m
A
0.5/5
A
Oscilloscope
or Digitizer
Analog output
There are two analog output terminals: a 0.5/5 A output terminal for use when the battery channel
is programmed for either the 5
the battery channel is programmed for either the 50
appropriate analog output terminal and the Source - terminal.
The analog outputs provide a voltage output based on the measured current as follows:
• 0.5/5 A Output referenced to Source - : 1 A/V (each volt out represents 1 A)
•5/50 mA Output referenced to Source - : 10 mA/V (each volt out represents 10 mA)
Each terminal's output impedance is nominally 1000 Ohms.
Figure 2-8
Analog output Connections
A or the 500 mA range and a 5/50 mA output terminal for use when
mA or the 5 mA range. Connect to the
2-22 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 55

In this section:
Section 3
Pulse Current Measurements
Topi c Page
Overview ..................................................................................................... 3-2
Trigger level.......................................................................................... 3-2
Trigger delay......................................................................................... 3-3
Integration times................................................................................... 3-3
Average readings count........................................................................ 3-4
Measurement configuration ........................................................................ 3-4
Current range ....................................................................................... 3-5
Integration times................................................................................... 3-5
Average readings count........................................................................ 3-5
Trigger delay and trigger level .............................................................. 3-6
Pulse current display mode .................................................................. 3-7
Pulse current measurement procedure....................................................... 3-7
No pulses detected............................................................................... 3-8
Determining correct trigger level (pulse current) .................................. 3-9
TRIG NOT DETECTED message ...................................................... 3-11
SCPI programming - pulse current measurements................................... 3-12
Command notes (pulse current measurements) ................................ 3-14
Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect .................................................... 3-16
Pulse current digitization........................................................................... 3-19
Pulse current step method........................................................................ 3-20
TLEV steps......................................................................................... 3-21
Timeout setting................................................................................... 3-25
Integration time................................................................................... 3-25
Range with pulse current step............................................................ 3-26
Programming examples............................................................................ 3-26
Pulse current measurements.............................................................. 3-26
Pulse current digitization .................................................................... 3-27
Pulse current STEP method (battery channel only) ........................... 3-27
Page 56

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Figure 3-1
Pulse current measurement
High Low
Average
High and average measurements triggered on leading edge of pulse
Low measurement triggered on falling edge of pulse
Overview
The power supply can perform current measurements for dynamic loads on either battery channel
(#1) or charger channel (#2). The built-in measurements include:
• Peak measured current - measures the peak (high) current of the pulse train.
• Idle measured current - measures the idle (low) current of the pulse train.
• Average transmit current - measures the average current of the pulse train.
The high, low, and average measurements of a pulse are illustrated in Figure 3-1. The high
measurement is triggered on the rising edge of the pulse, and an integration is performed for the
time specified for the high measurement. The falling edge of the pulse triggers the low
measurement, and an integration is performed for the time specified for the low measurement. An
average measurement is triggered on the rising edge, and the integration is specified by the
average measurement time setting. Each pulse current measurement reading will trigger on the
respective edge.
NOTE Two other measurements of pulse currents are available over the bus. Pulse
current digitization and Pulse current STEP method (battery channel only) for
details.
Available current measurement range(s) are 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, and 5 mA on
the battery channel and 5 A on the charger channel.
Trigger level
For the various current ranges on Model 2308, to avoid false pulse detection, you can use a trigger
level of up to 5A. All pulses, noise, or other transients that are less than the set trigger level will be
ignored. The charger channel has only one trigger level range setting from 0 to 5 A. The battery
channel (#1) has four trigger level settings that are applicable when the corresponding current
range is selected: 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, and 5 mA. For 5 A trigger level setting, the level may be
set from 0 to 5 A. Likewise, the level may be set from 0 to 500 mA for the 500 mA trigger level
3-2 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
setting, 0 to 50 mA for the 50 mA trigger level setting and 0 to 5 mA for the 5 mA trigger level
setting. These settings affect the trigger level setting when the corresponding current range is
Page 57

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
High Low
Average
High = integration time specified for high measurement time + Trigger Delay
Low = integration time specified for low measurement time + Trigger Delay
Average = integration time specified for average measurement time + Trigger Delay
Trigger Delay = Internal trigger delay (10ms) + User trigger delay
Internal Trigger
Delay (10ms)
User Trigger Delay
Trigger Delay
Integration Time
selected on the battery channel. For the charger channel, pulse current is only available on the
5
A current range.
Trigger delay
The high, low, or average integration times can either be manually or automatically set. When a
pulse is detected, there is a 10 μsec code execution delay (internal trigger delay - see
Figure 3-2) before the integration time begins. An additional user trigger delay can be set to allow
the leading edge pulse overshoot to settle. Regardless of the user trigger delay setting, the internal
trigger delay is always present.
Figure 3-2
Trigger delay for high pulse current measurement
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-3
The integration time will not start until the trigger delay period expires after detecting the pulse. For
accurate readings, make sure that the trigger delay (user and internal) plus the integration time
does not exceed the time for the overall pulse measurement. Refer to
containing the trigger delay relationships for a high pulse current measurement.
Integration times
The three integration time periods for pulse measurements can be set automatically or manually
by the user. When the pulse auto time operation is performed, the instrument measures the high
and low periods of the detected pulse and sets appropriate integration times. The pulse average
time is set to the sum of the measured high and low times. The three integration times apply for all
subsequent pulse measurements until another pulse auto time is performed or the times are
changed manually. The pulse auto time feature can detect pulses in the 80 μsec to 833 msec
range. Auto time (when used) accounts for the internal trigger delay (10 μsec).
You can manually set the pulse high time, pulse low time, and pulse average time. However, you
must make sure the integration time covers the portion of the pulse of interest. For example, if the
pulse is high for 600 μsec, the high integration time must be ≤600 μsec. If not, you will integrate a
low portion of the pulse, and the high pulse measurement will be compromised. Be sure to factor in
Figure 3-2 for an illustration
Page 58
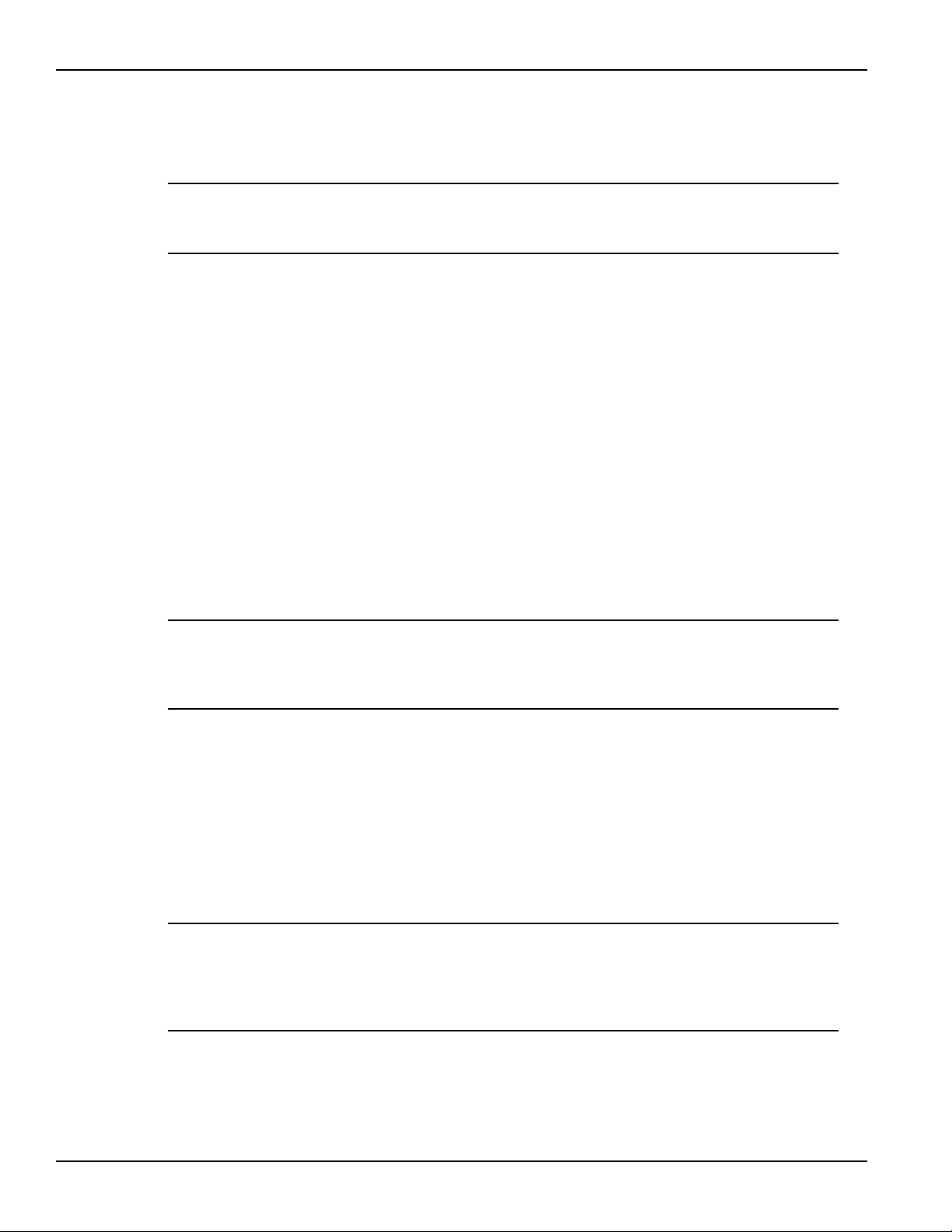
Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
the trigger delay (both internal plus user) when determining integration times (see Figure 3-2).
When manually set using the front-panel keys, the values are changed in increments of
33.3333
NOTE Auto time does not account for user trigger delay - if using auto time, make sure
After auto time acquires a time value (auto time), the auto time is adjusted for the internal trigger
delay of 10 μsec (auto internal time). The auto internal time is then adjusted to be an integral time
value of 33.3333
When a pulse time is set via the bus, the time is assumed to be an auto internal time (i.e., the
value is assumed to be adjusted for the internal delay value). This value is then adjusted to the
applicable integral value. For example:
μsec. This ensures that an integral value of 33.3333 μsec will be selected.
the user trigger delay is appropriately set for the desired overall measurement
time.
μsec (auto integral time). For example:
auto time value= 28.053 msec
auto internal time= 28.053 ms - 0.010 msec = 28.043 ms
auto integral time= 28.033 ms (response returned when time setting is queried)
manual time value= 5.040 msec
integral time= 5.033 ms (response returned when time setting is queried)
Average readings count
NOTE The menu item AVER READINGS #1/#2 applies to average readings for DVM, I
and V where AVERAGE READINGS under PULSE CURRENT #1/#2 menu item
applies to pulse current measurements. Note that DVM is supported by charger
channel (#2) only.
The average readings count specifies how many measurements (integrations) are performed and
averaged for each displayed reading. For example, assume that the pulse average readings count
is 10 and you are measuring PULSE HIGH. Each displayed reading will reflect the average of 10
peak pulse measurements.
Measurement configuration
NOTE Current range is selected from the CURRENT RANGE #1/#2 item of the menu.
Integration times, average readings count, trigger delay and trigger level are set
from the PULSE CURRENT item of the menu. Details on integration rate,
average readings count, trigger delay and trigger level are provided in the
Overview.
See Table 1-3 for an illustration of the menu structure. Rules to navigate the menu follow the table.
3-4 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 59

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
The menu item AVER READINGS #1/#2 applies to average readings for DVM, I, and V, where the
AVERAGE READINGS under PULSE CURRENT #1/#2 applies to pulse current measurement.
Current range
The instrument will not auto range with the pulse current measurement function selected. Changes
to the auto range setting are not used during pulse current measurements but are retained for
when pulse current measurements are no longer taken. Pulse current measurements may be
performed on any of the current ranges for the battery channel (#1). Pulse current measurements
are always performed on the 5 A range for charger channel (#2). Therefore, selecting pulse
current with the 5 mA range active on the charger channel (#2) will cause the supply to first switch
to the 5 A range regardless of the current range setting (5 mA or AUTO).
Current range is linked to current limit. Therefore, as a general rule, the user selects the current
range before setting the current limit (see
selected from CURRENT RANGE #1/#2 item of the menu (CURRENT RANGE #1 refers to the
battery channel while CURRENT RANGE #2 refers to the charger channel).
NOTE To get better trigger level resolution, make sure the current range (battery
channel only) is set appropriately for the expected measurement.
Outputting voltage and current). Current range is
Integration times
Use the following items of the PULSE CURRENT #1/#2 menu item to set integration times:
NOTE Set PULSE CURRENT integration times in the range of 33.3 μsec to 833 ms
• HIGH TIME - Use to set the integration period (in μsec) for high pulse-current
measurements. Make sure to account for the internal (10 μsec) and user trigger delay.
• LOW TIME - Use to set the integration period (in μsec) for low pulse-current
measurements. Make sure to account for the internal (10 μsec) and user trigger delay.
• AVERAGE TIME - Use to set the integration period (in μsec) for average
pulse-current measurements. Make sure to account for the internal (10 μsec) and user
trigger delay.
• AUTO TIME - Use to automatically set the integration times for high, low, and average pulsecurrent measurements. These times are based on detecting the pulse and remain until
another auto time is performed or the times are manually changed. Auto time accounts for
the internal (10
• PULSE TIMEOUT - Use to set the variable pulse current time-out feature for pulse current
measurements. The default value is 1.000 second (incremented in 1ms steps). See
FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information on properly setting this
TimeOUT variable.
(833333 μsec) in 33.3333 μsec steps.
μsec) delay but not the user trigger delay.
Using
Average readings count
Use the AVERAGE READINGS item of the PULSE CURRENT #1/#2 menu item to set the
average readings count. This count specifies the number of measurements (integrations) to
average for each reading. For example, with measurement count set to 10, each displayed
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-5
Page 60
Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
reading will reflect the average of 10 pulse current measurements. Each measurement needs to
start after detecting the respective edge for triggering.
NOTE Set AVERAGE READINGS count in the range of 1 to 100.
Trigger delay and trigger level
Use the following items of the PULSE CURRENT menu item to set trigger delay and trigger level:
• TRIGGER DELAY - Use to specify additional user trigger delay (0 to 100 msec in 10 µsec
steps). See
delay is in addition to the internal trigger delay of 10 μsec.
• TRIGGER LEVEL - Use to specify the trigger level for the 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA
current ranges (battery channel (#1) only). Note that pulse current only works on the 5 A
current range for the charger channel. Pulses less than the specified level are not detected.
Battery channel (#1): The following table shows the trigger levels for each current range
along with trigger hysteresis and trigger level step size:
Table 3-1
Current range and trigger level settings
Trigger delay previously discussed in this section for details. This user trigger
Current range Trigger level setting Trigger hysteresis Setting step size
5 A 0-5 A 10 mA 5 mA
500 mA 0-500 mA 1 mA 0.5 mA or 500 μA
50 mA 0-50 mA 0.1 mA 0.05 mA or 50 μA
5 mA 0-5 mA 0.01 mA 0.005 mA or 5μA
Trigger hysteresis is built into the hardware. If a pulse does not exceed the appropriate
hysteresis level, trigger detection will not occur. The trigger level ranges for the battery
channel (#1) are displayed as follows:
5 A range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
A(5.0) 0.000 A
500 mA range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
A(500) 0.0000 A
50 mA range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
mA (50) 0.00000A
5 mA range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
mA (5) 0.000000A
Charger channel (#2) - Set the trigger level from 0 to 5 A in 5 mA steps. However, there is
approximately 10 mA of trigger hysteresis built into the hardware. Therefore, if a pulse does
not exceed this level, trigger detection will not occur.
3-6 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 61

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
▲
▲▲▲
▲
▲
To change the trigger level setting for a current range (from within pulse current TLEV
menu screen):
NOTE For charger channel (#2), skip to step 3 (there is only one trigger level setting - 5
A).
Step 1: Place the blinking cursor on the “A” at the far right end of line two of the display.
Step 2: Press the
Step 3: Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to display the desired current range trigger level setting option.
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired trigger level setting (in amps).
Step 4: Press ENTER to update the trigger level setting for the displayed current range.
Pulse current display mode
Pulse current measurements are displayed with the pulse current display mode selected.
To display the pulse current:
NOTE If the instrument is in the settings mode, press the SET key until the blinking
stops (the measured readings can then be displayed). To determine if the
instrument is in the settings mode, check for a blinking cursor in a digit of the
voltage or current field (if present, the instrument is in the setting mode).
1. Press the DISPLAY key to access the display menu.
2. If the desired active channel is not selected, use the
#1 or DISPLAY TYPE #2.
3. Press the
4. Press ENTER to select.
5. Use the
PULSE AVG.
▲ or ▼ keys until PULSE CURRENT is displayed.
▲ or ▼ keys to display the desired pulse measurement; PULSE HI, PULSE LO, or
or keys to scroll to DISPLAY TYPE
NOTE For details on display modes, see Display modes.
Pulse current measurement procedure
The following steps summarize the procedure to perform pulse measurements:
1. Follow the instructions in Editing output voltage and current limit values to set the output
voltage and current limit.
2. Select the desired current range (see Selecting proper current range) for the battery
channel (5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA). Only the 5 A range is supported for the charger
channel. Changes to the auto range setting are not used during pulse current
measurements but are retained for when pulse current measurements are no longer take.
3. Press the MENU key to access the menu.
4. Press the
5. Press the
6. Press ENTER to select.
7. Press the
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-7
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to PULSE CURRENT.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to TRIGGER LEVEL.
Page 62

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
8. Press ENTER to select.
9. For the battery channel only, press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired current range
trigger level (5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA).
10. Use the
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired trigger level setting.
11. Press ENTER to select.
NOTE Pulse measurements for the battery channel are performed on the current range
selected (5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA); pulse measurements on the charger
channel are automatically performed on the 5 A current range. On the battery
channel, the trigger level setting will automatically update to the trigger level
associated with the selected current range.
12. From the PULSE CURRENT #1/#2 item of the menu, set the TRIGGER DELAY (optional),
INTEGRATION TIMES, and AVERAGE READINGS COUNT (optional).
13. Press MENU to exit the menu structure then press OPERATE.
14. Follow the instructions to select the pulse current display type in Pulse current display
mode.
NOTE Setting the trigger level with the output off will cause the pulse time-out message
to appear. However, the trigger level will be set.
No pulses detected
If no pulses are detected, current will not be measured (i.e. -----A) and the “NO PULSE” message
will be displayed. The “NO PULSE” message is displayed with dashes or the last valid pulse
reading. Dashes are shown if the pulse-current measurement settings are not appropriate for
detecting pulses. The last valid pulse is shown if the pulse disappears while taking readings and
no change in pulse settings was made.
Pulses are not detected with the output OFF. With the output ON, pulses will not be detected if the
trigger level is too low or too high. Perform the following procedure to find an appropriate trigger
level. Make sure the voltage and current settings are appropriate for detecting pulses.
3-8 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 63
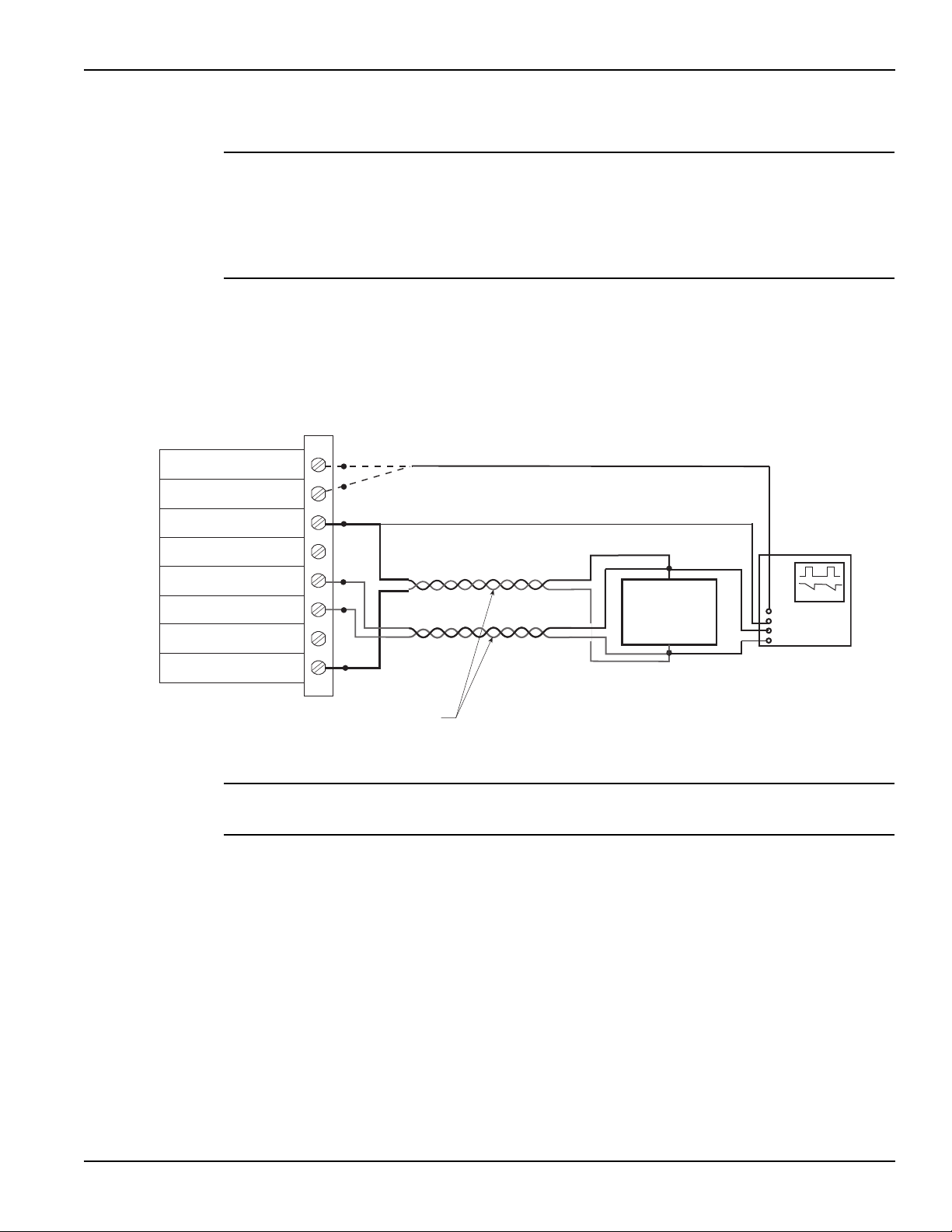
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
Quick Disconnect
Connector
DUT
Source -
Source -
Sense -
Sense +
Source +
Source +
Twisted Pair
(5mA/50mA)
(0.5A/5A)
Load Test Leads
Channel 1
Channel 2
Oscilloscope
Determining correct trigger level (pulse current)
NOTE If possible, always use an oscilloscope to determine the timing and transient
characteristics of a DUT. The waveform information is very useful in setting up
the Model 2308, reducing setup time and achieving maximum performance and
productivity. The voltage and current characteristics of the DUT can be
determined with a 2-channel Oscilloscope as shown in
oscilloscope inputs are required to prevent grounding the supply output leads.
Figure 3-3
Determining voltage and current characteristics for battery channel
Figure 3-3. Differential
NOTE Figure 3-3 contains a simple circuit for determining the dynamic voltage and
current characteristics of the DUT.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-9
Page 64

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
External Test Circuit
Quick Disconnect
Connector
DVM +
DVM Source Source -
Sense -
Sense +
Source +
Source +
Twisted Pair
Model 2308
Source Input/Output
DVM Input
Oscilloscope
0.1 W Current
Sense Resistor
CHANNEL 1
CHANNEL 2
DUT
+
-
▲
▲
▲
▲
Figure 3-4
Determining voltage and current characteristics for charger channel
1. Follow the instructions in Editing output voltage and current limit values to set the output
2. Select the desired current range (see Selecting proper current range) for the battery
3. Press OPERATE.
4. Follow the instructions to select the pulse current display type in Pulse current display
5. Press the MENU key.
6. Press the
7. Press the
8. Press ENTER to select.
9. Press the
10. Press ENTER to select.
11. For the battery channel only, press the
12. Press the
To find a suitable trigger level:
voltage and current limit.
channel (5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA). Only the 5 A range is supported for the charger
channel. Note changes to the auto range setting are not used during pulse current
measurements but are retained for when pulse current measurements are no longer take.
mode.
NOTE If the trigger level is too low or too high, the “NO PULSE” message will be
trigger level (5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA).
displayed.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to PULSE CURRENT.
or keys to select Channel #1 or #2.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to TRIGGER LEVEL.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to the desired current range
▲, ▼, , or keys to scroll to the desired trigger level.
3-10 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 65

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
13. Press ENTER to save your settings and return to the main menu.
NOTE If the trigger level is still too low or too high, the TRIG NOT DETECTED
message will be displayed briefly. Note that it may take a few seconds for the
message to appear (see TRIG NOT DETECTED message for more
information).
14. If the message appeared, repeat Step 9 until a valid trigger level is found.
15. Press MENU to exit the menu structure and display pulse current measurements.
TRIG NOT DETECTED message
The TRIG NOT DETECTED message is displayed when specific TLEV settings, coupled with
corresponding current range, have been set and a trigger has not been detected. Refer to
2 for the message preconditions.
Table 3-2
TRIG NOT DETECTED message
TLEV setting Current range TRIG NOT DETECTED Message displayed?
90 mA for 500 mA current
range
90 mA for 500 mA current
range
0.75 A for 5 A current range 5 A May appear*
0.1 A for 500 mA current
range
3.0 A for 5A current range 5 A May appear
0.03 A for 50 mA current
range
0.003 A for 5 mA current
range
1.1 A for 5 A current range 5 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
1.1 A for 5 A current range 500 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
*
Depends upon the OUTPUT:
If OFF, the message will appear.
If ON, display of the message will depend on the trigger level setting. If trigger level setting greater than the expected low
measurement and less than the expected high measurement, the message will not appear.
For example, if the expected pulse high value is 2.2 A and the expected pulse low value is 0.5 A, the output is on, and
the current range is 5 A, notice the following results:
Setting 0.3 A TRIG NOT DETECTED is displayed (setting too low).
Setting 3.0 A TRIG NOT DETECTED is displayed (setting too high).
Setting 1.1 A The message will not display (setting correct).
5 A No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
current range)
50 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
current range)
500 mA May appear
50 mA May appear
5 mA May appear
*
*
*
*
current range)
current range)
Table 3-
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-11
Page 66

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
See To change the trigger level setting for a current range for information on setting the trigger
level setting for a current range. For the charger channel (#2), the trigger level setting is only
available on the 5 A range.
NOTE Setting the trigger level and/or the current range may cause the PULSE CURR
TRIG NOT DETECTED message to appear.
SCPI programming - pulse current measurements
The commands for pulse current measurements are summarized in Table 3-3 (a listing following
the table contains specific command notes). Programming examples demonstrate how to use
these commands.
Table 3-3
SCPI commands - pulse current measurements
Command Description Default
SENSe[1]
:FUNCtion “PCURrent”
:PCURrent
:AVERage <NRf>
:MODE <name>
:TIME
:AUTO
:HIGH <NRf>
:LOW <NRf>
:AVERage <NRf>
:DIGitize <NRf>
:SYNChronize
[:STATe]
:TLEVel
[:AMP] <NRf>
:HUNDred <NRf>
:FIFTy <NRf>
:FIVE <NRf> Set the trigger level in amps for use when on the 5 mA
SENSe subsystem for battery channel (#1):
Select pulse current measurement function. VOLT
Pulse current configuration:
Specify average count:
1–100 (pulse current measurements) or
1–5000 (pulse current digitization).
Select measurement mode; HIGH, LOW or AVERage. HIGH
Set integration times:
Integration times set automatically.
Specify integration time (in sec) for high pulse
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
Specify integration time (in sec) for low pulse
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
Specify integration time (in sec) for average pulse
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
Specify integration time (in sec) for digitizing or burst
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
Pulse detection triggering:
Send ON to select pulse current measurements or
OFF to select pulse current digitization.
Trigger level:
Set the trigger level in amps for use when on the 5 A
current range: 0.0 A-5.0 A in 5 mA steps.
Set the trigger level in amps for use when on the
500mA current range: 0.0 mA-500 mA in 0.5 mA or 500 μA
steps.
Set the trigger level in amps for use when on the
50 mA current range: 0.0 mA-50 mA in 0.05
steps.
current range: 0.0-5 mA in 0.005 mA or 5 μA steps.
mA or 50 μA
1
3.333e-5
3.333e-5
3.333e-5
3.333e-5
ON
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
3-12 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 67
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
Table 3-3
SCPI commands - pulse current measurements (cont.)
Command Description Default
:DELay <NRf>
:STEP <b>
:UP <NRf>
:DOWN <NRf>
:TIME <NRf>
:TimeOUT <NRf>
:INITial <NRf>
:DELay <NRf>
:SEQuence
<NRf, NRf>
:LENgth <NRf>
:SKIP <b>
:TLEVx <NRf>
:FAST
:SEARch
:DETect
:TimeOUT
SENSe2
:FUNCtion “PCURrent”
:PCURrent
:AVERage <NRf>
:MODE <name>
:TIME
:AUTO
:HIGH <NRf>
Specify trigger delay in seconds:
0.0–0.1 (pulse current measurements) or
0.0–5.0 (pulse current digitization).
Performs a series of measurements (Pulse current
step method)
<0-20> (max is for both up and down combined) 1
<0-20> (max is for both up and down combined) 1
33.3μsec–100msec 200 μsec
TimeOUT (other than the first): 2msec–200msec 2 ms
First TimeOUT step: 10msec–60secs 2 sec
0msec–100msec (in 10msec steps) 0
Define up to 19 delay sequence values using the
index and the time value (e.g. "1,1e-3" sets the first delay to
1ms). Ranges: 1-19 (parameter 1) and 0 to 100e-3
(parameter 2).
Define the delay sequence length (0 to 19). Specify
zero to always use the
Specify whether (1) or not (0) to skip sequential
triggers.
1=Only requires 1 trigger
0 = Requires multiple triggers
Set trigger level for each TLEV step where x equals
1–20 (the maximum settings are based on the selected
current range. Therefore, the current range must be
selected before setting the step trigger level values)
Enable or disable pulse current fast readings. OFF
Enable or disable pulse current search. ON
Enable or disable pulse current detection mode. OFF
Specify length of timeout: 5ms - 32s incrementing in
1ms.
SENSe subsystem for charger channel (#2):
Select pulse current measurement function. VOLT
Pulse current configuration:
Specify average count:
1 to 100 (pulse current measurements), or
1 to 5000 (pulse current digitization).
Select measurement mode; HIGH, LOW or AVERage. HIGH
Set integration times:
Integration times set automatically.
Specify integration time (in sec) for high pulse
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
PCUR:STEP:DELay value.
0.0
OFF
0
0
0
0.0
1 (sec)
1
3.333e-5
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-13
Page 68

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Table 3-3
SCPI commands - pulse current measurements (cont.)
Command Description Default
:LOW <NRf> Specify integration time (in sec) for low pulse
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
:AVERage <NRf> Specify integration time (in sec) for average pulse
measurements; 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
:DIGitize <NRf> Specify integration time (in sec) for digitizing or burst
measurements 33.33e-6 to 0.8333.
:SYNChronize Pulse detection triggering:
[:STATe] Send ON to select pulse current measurements or
OFF to select pulse current digitization.
:TLEVel <NRf> Set trigger level in amps: 0.0–5.0 0.0
:DELay <NRf> Specify trigger delay in seconds:
0.0–0.1 (pulse current measurements) or
0.0–5.0 (pulse current digitization).
:FAST Enable or disable pulse current fast readings. OFF
:SEARch Enable or disable pulse current search. ON
:DETect Enable or disable pulse current detection mode. OFF
:TimeOUT Specify length of timeout: 5ms - 32s incrementing in
1ms.
READ[1]? Trigger and return one reading for battery channel (#1).
READ[1]:ARRay? Trigger an array of readings and return them for battery
channel (#1).
READ2? Trigger and return one reading for charger channel (#2).
READ2:ARRay? Trigger an array of readings and return them for charger
channel (#2).
3.333e-5
3.333e-5
3.333e-5
ON
0.0
1 (sec)
Command notes (pulse current measurements)
SENSe[1]:FUNCtion ‘PCURrent’ Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:FUNCtion ‘PCURrent’ Applies to charger channel (#2)
This parameter name can also be enclosed in single quotes (as shown above).
SENSe[1]:PCURrent:AVERage <NRf> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:PCURrent:AVERage <NRf> Applies to charger channel (#2)
1. When requesting a single reading (
specifies the number of pulse current measurement conversions to average for the reading.
For example, with the average count set to 10,
measurement conversions and return (and display) the average of those 10 battery channel
conversions (charger channel command similar).
2. When requesting an array of readings (
MEASure:ARRay?), average count specifies the number of pulse current measurements to
place in an array. For example, with the average count set to 10,
and return 10 battery channel readings (charger channel command similar).
3. For pulse current digitization, use an array reading command (such as
return the digitized readings.
4. Signal-oriented measurement commands (such as
3-14 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
FETch?, READ?, or MEASure?), average count
READ? will trigger 10 pulse current
FETCh:ARRay?, READ:ARRay? or
READ:ARRay? will trigger
READ:ARRay?) to
READ?) are covered in Section 9.
Page 69

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
SENSe[1]:PCURrent:TIME Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:PCURrent:TIME Applies to charger channel (#2)
When manually setting the pulse HIGH, LOW, AND AVERage time:
1. The integration time should only cover the portion of the pulse to be measured.
2. Factor in trigger delays (both internal and user) when determining integration times. Before
the integration process begins (after pulse detection) the internal trigger delay of 10 µs (for
code execution), in addition to any user-specified trigger delay, must elapse.
NOTE AUTO time will account for the internal trigger delay (10 μsec) but not for any
user trigger delay (user trigger delay is set using the DELay command).
SENSe[1]:PCURrent:TIME:DIGitize <NRf> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:PCURrent:TIME:DIGitize <NRf> Applies to charger channel (#2)
This command allows you to specify the integration time that occurs when Model 2308 is digitizing
or in burst mode (
you to sample a pulse load for a longer time by increasing the integration time from 33.3 μs.
NOTE Pulse current digitization is also known as pulse current burst mode.
SENS:PCUR:SYNC:STAT is OFF for the particular channel). This feature allows
SENSe[1]:PCURrent:SYNChronize <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:PCURrent:SYNChronize <b> Applies to charger channel (#2)
Boolean parameters:
• ON or 1 - Enables trigger synchronization for pulse current measurements. A pulse current
reading will not trigger until the specified trigger level is detected and the specified trigger
delay (both the internal plus the user delay) period expires.
• OFF or 0 - Disables trigger synchronization and selects pulse current digitization. See Pulse
current digitization for details on digitizing a current pulse or waveform.
:TLEVel Commands
A valid trigger level for detecting the pulse is needed whether trigger synchronization is ON or OFF
(see
:SYNChronize commands above).
SENSe[1]:PCURrent:SYNChronize:DELay <NRf>Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:PCURrent:SYNChronize:DELay <NRf> Applies to charger channel (#2)
1. The smallest step size for trigger delay is 10 µsec. If you specify a smaller step size, it is
adjusted up to the next 10 µsec step value (e.g., 43 µsec is adjusted up to 50 µsec).
2. After pulse detection but before the integration process begins, the internal trigger delay of
10 μsec (for code execution) in addition to any user specified trigger delay must elapse.
This command is used to set the user trigger delay.
3. Make sure this setting works with the
Although AUTO accounts for internal trigger delay, HIGH, LOW, and AVERage do not. Note
that none of the TIME commands account for the user trigger delay.
SENSe[1]: PulseCURrent:FAST <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2: PulseCURrent:FAST <b> Applies to charger channel (#2)
:TIME settings to produce an accurate reading.
See Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-15
Page 70

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
SENSe[1]:PulseCURrent:SEARch <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2: PulseCURrent:SEARch <b> Applies to charger channel (#2)
See Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information.
SENSe[1]: PulseCURrent:DETect <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2: PulseCURrent:DETect <b> Applies to charger channel (#2)
See Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information.
SENSe[1]:PulseCURrent:TimeOUT <NRf> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2: PulseCURrent: TimeOUT <NRf> Applies to charger channel (#2)
See Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information on properly setting the
TimeOUT variable.
Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect
Use the FAST command to have the quickest response for pulse current measurements triggered
by the measurement commands (for example,
use the
detecting pulses until a measurement command is sent. When the trigger level is set, use the
FAST command, there is no indication that the instrument is correctly configured for
SEARch command to retain quick responses to measurement commands and to ensure that the
instrument is configured correctly for detecting pulses. Use the
the unit is configured correctly and can read the pulse before sending a measurement command.
MEASure, READ or *TRG). Note that when you
DETect command to ensure that
Use FAST, SEARch, and DETect to control how background readings are taken. A background
reading is a measurement taken by the power supply between user triggered readings. The
selected function dictates how background readings are taken between user triggered readings.
For pulse current, a background reading involves looking for the pulse and optionally generating a
reading for the user. The various settings of
tune the function. This enables the function to perform the desired background readings (if any)
between user triggered readings. The default settings (
SEARch, FAST, and DETect allow the user to fine
FAST:OFF, SEARch:ON, and
DETect:OFF) allow the pulse current background readings to be taken. If no pulse is present, the
setting of TimeOUT affects how responsive the supply is to bus commands. If a pulse is present,
the search time affects how responsive the supply is to bus commands (refer to
3-4 contains the available settings for FAST, SEARch, and DETect commands and a description
of the resulting action.
In order to efficiently use FAST, SEARch, and DETect for pulse current measurements, the user
must know the approximate period of the expected pulse. TOUT (TimeOUT) specifies the timeout
length for searching for the pulse (default setting is 1 second). When the TOUT value is reached,
“NO PULSE” is displayed (top line of the front-panel display) if default settings for FAST, SEARch,
and DETect are used. See
settings are not used. Set the value for TOUT as follows:
TOUT = search Time + Period
Search Time = time allowed for detection of a pulse edge
Period = time between consecutive pulse edges
In other words, the timeout value should be set to allow sufficient time for detection of the pulse if
the edge is just missed. In
edge was just missed, (D) will be the first detectable rising edge. If the timeout is less than search
time, a pulse trigger time out (due to TOUT) may occur. Therefore, if the period
good TOUT value would be 0.5 seconds. A similar method for selecting a TOUT value would be to
use a value equal to 105% of the expected pulse period.
Table 3-4 for what is shown on the front-panel display if the default
Figure 3-5, (P) is the point to start looking for the pulse. Since the rising
Figure 3-5). Table
= 0.4 seconds, a
3-16 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 71

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
R
Search Time
D
P
TOUT setting must account for Search Time and Period.
P = Search for Pulse High edge started
R = Reading time taken
D = Detected pulse edge (Rising for pulse high
and average measurements)
Search Time:
Measured from when unit starts looking for the
pulse until the first detectable desired edge. This
is a rising edge for HIGH and AVG measurements,
and falling edge for LOW measurements.
Period: Time between consecutive pulse edges.
TOUT
Period
Figure 3-5
PCURrent and SEARch time for pulse high measurement
NOTE If a pulse is not present, timeout needs to elapse (TOUT). This (TOUT elapsing)
paces the unit for processing bus commands.
• If DETECT ON (only), search time needs to elapse before responding to a
bus command.
• If SEARCH OFF or FAST ON, search time and TOUT are not incurred
while processing non-user triggered commands (refer to
Section 9 of the
User’s Manual for examples of user triggered).
• Search time or TimeOUT needs to elapse when checking TLEV command
for valid setting, if enabled.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-17
Page 72
Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Table 3-4
PCURrent FAST, SEARch, and DETect commands
FAST SEARCH DETECT DESCRIPTION
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
The unit is most responsive to bus commands in this mode. The supply
does not wait for TOUT or search time for background pulse current
readings and TLEV command checks. front panel displays FAST HI / LO /
AVG (in remote mode) instead of PCUR HI / LO / AVG (if in local mode).
The bottom line may show a previous reading or dashes based on what
commands were sent previously when in remote mode.
With FAST set to ON, no pulse detection between user-triggered readings
occurs, no checking for the parameter of PCUR TLEV commands to detect
a pulse occurs, no setting of the pulse trigger timeout bits in the status
model between user-triggered readings occurs. front panel has no
indication that pulse is not detected. Over the bus, an overflow reading
indicates no pulse detected when asked for a user triggered reading.
For triggered readings, the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bit is latched until
read so the bit may still be set in the status model from a previous timeout
(see Section 7 on the status model for more information-Model 2308 User's
Manual). For triggered readings, the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bit will be
set if the reading times out and the pulse is not detected.
The unit is more responsive to bus commands in this mode since the supply
does not need to wait for TOUT or search time for pulse current background
readings. However, the supply does need to wait for TOUT or search time
when checking the parameter setting for TLEV commands. Refer to Figure
3-5. front panel displays NO SEARCH instead of PULSE HI / LO / AVG. The
bottom line may show a previous reading or dashes based on what
commands were sent previously when in remote mode.
The setting of the pulse trigger timeout bits in the status model will only
occur between user-triggered readings if TLEV commands are sent. For
triggered readings, the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bit will be set if the
reading times out and the pulse is not detected. Also, since the PTT bit is
latched until read, the bit may still be set in the status model from a previous
timeout (see Section 7 on the status model for more information-Model
2308 User's Manual).
Shaded cells designate command with precedence in each mode.
3-18 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 73

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
Table 3-4
PCURrent FAST, SEARch, and DETect commands (cont.)
FAST SEARCH DETECT DESCRIPTION
OFF ON ON This mode allows the user to know whether the pulse disappeared before a
user-triggered reading is requested. The responsiveness of bus commands
is governed by TOUT (if no pulses are detected), or by search time (if
pulses are detected). Therefore, the longest response time to bus
commands is approximately the greater of either TOUT or search time
values. Refer to Figure 3-5.
If the pulse is detected, the front panel will display DETECT HI / LO / AV on
the top line of the display. If no pulses are detected, the front panel will
display NO DETECT as well as the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bit being
set in the status model. Since the PTT bit is latched until read, a query for
the PTT bit may indicate that pulse trigger timeout occurred although the
display is showing DETECT (see Section 7 on the status model for more
information-Model 2308 User's Manual). The bottom line may show a
previous reading or dashes based on what commands were sent previously
when in remote mode.
Checking for the parameter of PCUR TLEV command may set the PTT bit
of the status model. For triggered readings, the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout)
bit will be set if the reading times out and the pulse is not detected.
OFF ON
OFF With DETect OFF, background pulse current measurements will occur
between user-triggered readings as well as pulse detection. If the pulse is
detected, the front panel will display PULSE HI / LO / AVG on the top line of
the display along with the reading on the bottom line. If no pulses are
detected, the front panel will display “NO PULSE” as well as the PTT (Pulse
Trigger Timeout) bit being set in the status model. Since the PTT bit is
latched, a query for the PTT bit may indicate that pulse trigger timeout
occurred although the display is displaying PULSE HI / LO / AVG and a
reading (see Section 7 on the status model for more information-Model
2308 User's Manual). Checking for the parameter of PCUR TLEV
commands to detect a pulse may set the PTT bit. If detecting pulses, the
supply's responsiveness to bus commands is affected by search time. If not
detecting pulses, the supply's responsiveness to bus commands is affected
by TOUT. Therefore, the longest response time to bus commands is
approximately the greater of either TOUT or search time (refer to Figure 3-
5).
In this mode, the front panel will show PULSE HI / LO / AVG on the top line
with a reading on the bottom. Checking the parameter of PCUR TLEV
commands to detect a pulse may set the PTT bit of the status model if TLEV
setting causes no pulse detection. For triggered readings, the PTT (Pulse
Trigger Timeout) bit will be set if the reading times out and the pulse is not
detected.
Shaded cells designate command with precedence in each mode.
Pulse current digitization
The following discussion explains how to digitize a current waveform. A programming example at
the end of this section demonstrates proper command sequence for pulse current digitization.
Overall steps for digitization:
1. Sync up to desired edge for measurement.
2. After detecting edge, wait for the internal and also any user trigger delay.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-19
Page 74

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
3. Take specified number of readings. The supply synchronizes to only the first reading. After
taking the first reading, the supply no longer synchronizes to the selected edge nor does it
wait for a trigger delay (internal or user trigger delay).
In the pulse current digitization mode with a integration time (SENS:TIME:DIG) of 33 μs, readings
are generated approximately every 244 μs for battery channel (313 μs for charger channel) and
placed in the instrument measurement output buffer. The 244 μs or 313 μs time interval is the sum
of the integration period, 33μsec, and the period required to convert this information into a
measurement, approximately 211 μsec for battery channel (280 μs for charger channel). These
conversions time will be needed as the integration time for digitization is increased. However, the
approximate time for a reading stored in the buffer will be the integration time + conversion time.
The instrument initiates the storage and conversion process for the desired number of iterations,
as specified with the AVERAGE command, when the :TLEVel threshold is exceeded. The
message DIGITIZE is displayed instead of readings. The NO PULSE message will be displayed if
the pulse is not detected. Pulse current digitization is selected by disabling trigger synchronization:
SENS[1]:PCUR:SYNC <b> battery channel (#1)
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC <b> charger channel (#2)
<b> = OFF Select pulse current digitization (trigger synchronization disabled).
= ON Select pulse current measurements (trigger synchronization enabled).
The commands to set the trigger level and trigger delay for pulse current measurements also apply
for pulse current digitization. However the trigger delay can be set up to five seconds.
SENS[1]:PCUR:SYNC:DEL <NRf> battery channel (#1)
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC:DEL <NRf> charger channel (#2)
<NRf> = 0 to 5 User trigger digitization delay in seconds
(10 μsec steps). For digitization, the internal
trigger delay is 10 μsec.
To detect the pulse, the digitization process synchronizes to the edge specified by the
following command:
SENS[1]:PCUR:MODE <name> battery channel (#1)
SENS2:PCUR:MODE <name> charger channel (#2)
<name> = HIGH or AVER Sync up to rising edge of pulse for 1st
reading of digitization.
= LOW Sync up to falling edge of pulse for 1st
reading of digitization.
After any specified delay period expires, the instrument takes the number of readings specified by
the average count command:
SENS[1]:PCUR:AVER <NRf> battery channel (#1)
SENS2:PCUR:AVER <NRf> charger channel (#2)
<NRf> = 1 to 5000 Digitize 1 to 5000 readings.
NOTE Pulse current digitization for a programming example.
Pulse current step method
Use the pulse current step method to perform a series of different trigger level measurements on
the same current range. This method is available on the battery channel through GPIB operation
only -
SENS:PCUR:STEP commands (see Table 3-3). Use this method to decrease the time
required to take a sequence of measurements. To use this method, properly set trigger level steps,
integration time, time-out setting, and current range for the entire sequence of measurements. Out
of these settings, only trigger level may be set to a unique value for each step
3-20 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
- settings for
Page 75

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
integration time and current range apply to all steps in the measurement sequence. Timeout has
two settings - one for the first step and one for the remaining steps in the sequence. Use an array
command to trigger this method since an array of values are returned (e.g.,
:READ[1]:ARRay?).
TLEV steps
TLEV (trigger level) steps are used to define the pulse sequence. A maximum of 20 steps may be
defined. These steps can be all UP steps, all DOWN steps, or a combination with the summation
of UP and DOWN steps to measure not exceeding 20 (see
measured before DOWN steps. To use the step method on pulse forms with DOWN steps first,
special programming considerations can be taken. Refer to
NOTE Do not change the current range after the trigger level ranges are selected.
Erroneous readings may result. Erroneous readings will occur if the existing
trigger level settings are out of range for the new current range, or if the trigger
level settings are unable to detect the pulse on the new current range.
When using the pulse current step method, select the current range first, then set the trigger level
step values. Select the most accurate current range suitable for the highest trigger level step
value. Current range needs to be specified before step values because the step values max
setting is based on selected current range. Also, only one current range is used during the step
operation. You may change current ranges; the step values will be verified against the new current
range (see
Changing ranges for more detail).
Table 3-5). UP steps are always
Pulse sequences - down steps first.
Table 3-5
Setting UP and DOWN commands
Command Description
:SENS:PCUR:STEP:UP 1
:SENS:PCUR:STEP:UP 20
:SENS:PCUR:STEP:DOWN 3
:SENS:PCUR:STEP:UP 12
:SENS:PCUR:STEP:DOWN 10
1 (UP) + 1 (DOWN default) ≤ 20 ∴ this command is ok.
20 (UP) + 1 (DOWN) > 20 ∴this command generates an
error message (-222, parameter out of range). Both the up
and down settings stay at 1.
3 (DOWN) + 1 (UP) ≤ 20 ∴ this command is ok.
12 (UP) + 3 (DOWN) ≤ 20 ∴this command is ok.
12 (UP) + 10 (DOWN) > 20 ∴ this command generates an
error message (-222, parameter out of range). The down
setting stays at 3.
Active steps refer to valid UP steps plus valid DOWN steps. If pulse current step method is
selected when a trigger command is received, the number of measurements taken equals the
number of active steps. Therefore, to receive all measurements at once, use array commands. If
array commands are not used, then a single reading is returned. This single reading represents
the average of the active step measurements.
NOTE If there are zero (0) active steps when a trigger command for step is received
(number of steps UP + the number of steps DOWN = 0), one reading will be
returned (an overflow).
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-21
Page 76

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
4 Up
3 Down
0 Up
4 Down
5 Up
0 Down
0 Up
5 Down
5 Up
0 Down
The step method can be used on a variety of pulse forms. See Figure 3-6 for pulse forms that can
be measured either as one-shot pulse or as a continuous pulse train. For other pulse forms that
can be measured as one-shot only pulses, see
Figure 3-7. For pulse trains that have steps that
rise and fall between steps, use the one-shot method to measure the step values (see Pulse
sequences - rising and falling). If the continuous method is used on these pulse trains, the first
step may trigger on any step that would be appropriate for that trigger level. For example, a first
step trigger level of 200 milliamps may trigger on any step with an expected value greater that 200
milliamps.
Figure 3-9 shows that with a first step TLEV of 200 milliamps that any one of the six
steps may actually trigger as a first step reading. Hence, the array of step readings may have
overflow readings and/or expected step values out of sequence. In addition, this would vary
between triggered step measurements.
Figure 3-6
Sample pulse forms for step method
Figure 3-7
Sample one-shot only pulses for step method
Trigger level settings
The trigger level may be set to a unique value for each active step. Use the TLEVx command to
set appropriate trigger levels for each active step in the waveform. Make sure that the maximum
setting for the selected current range is not exceeded (see
Figure 3-8 has 5 rising edge steps and 4 falling edge steps. Set the trigger levels for each step
measurement according to the expected pulses. Based on the wave form, the nine trigger levels
could be set as follows:
Table 3-6
Trigger Level Setting for Figure 3-8
Rising Falling
TLEV1
TLEV2
TLEV3
TLEV4
TLEV5
100 mA
300 mA
500 mA
700 mA
900 mA
TLEV6
TLEV7
TLEV8
TLEV9
Range with pulse current step).
900 mA
600 mA
400 mA
300 mA
For a programming example of this sample, see Sample step method.
3-22 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 77
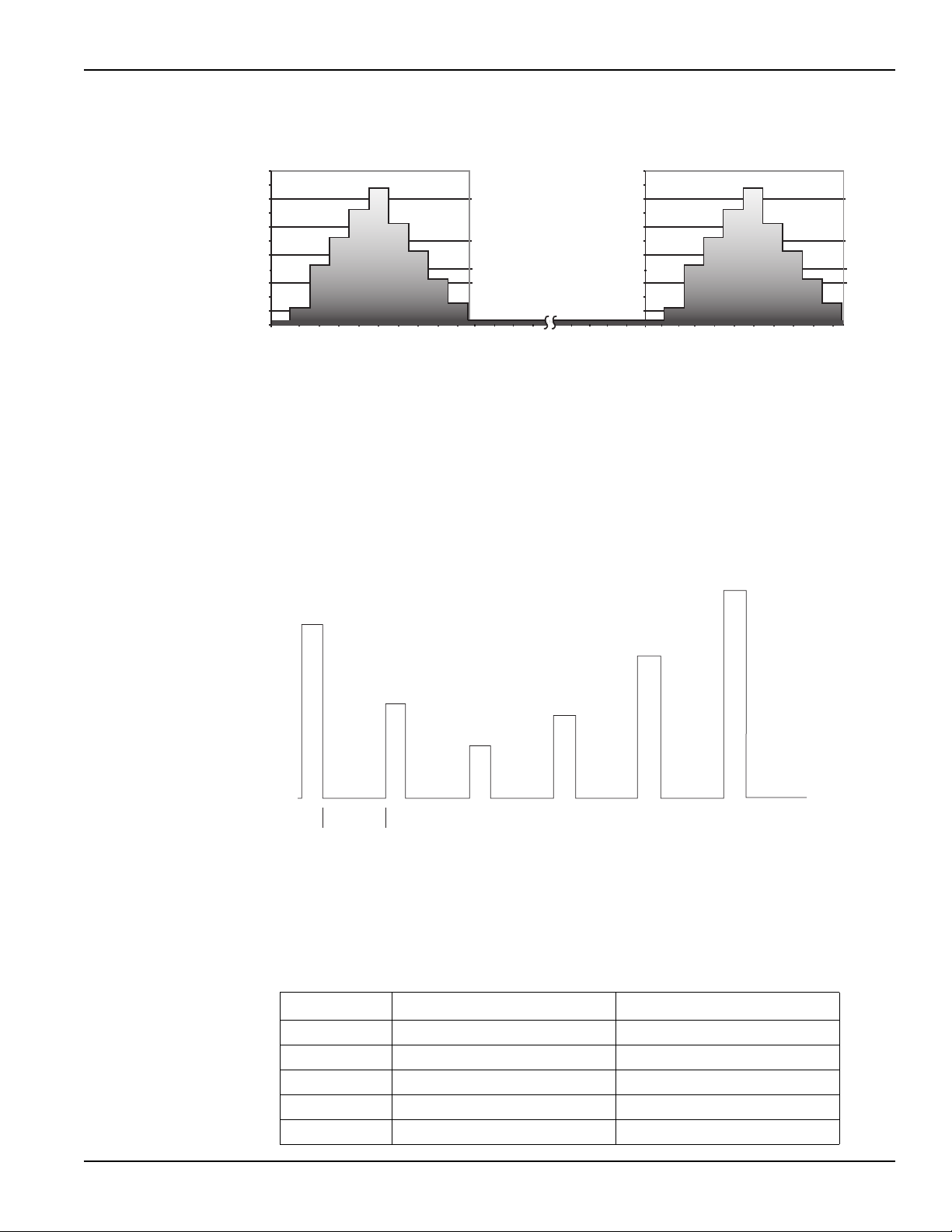
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
125
425
625
825
975
725
525
325
155
0
100
300
400
500
600
700
900
0.1
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
TIME (seconds)
300
TLEV1
TLEV2
TLEV3
TLEV4
TLEV5
TLEV9
TLEV8
TLEV7
TLEV6
900
TLEV mA
(rising edge)
mA TLEV
(falling edge)
125
425
625
825
975
725
525
325
155
100
300
400
500
600
700
900
300
TLEV1
TLEV2
TLEV3
TLEV4
TLEV5
TLEV9
TLEV8
TLEV7
TLEV6
900
TLEV mA
(rising edge)
mA TLEV
(falling edge)
0
2.1
2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5
0.6
0.7
1.8 1.9 2.0
3 Down
3 Up
350mA
600mA
875mA
725mA
425mA
600msec
275mA
4msec
Steady state current
Figure 3-8
Sample :STEP Pulse measurement
Pulse sequences - rising and falling
Consider the pulse form in Figure 3-9. This pulse form has three falling (DOWN) level steps
followed by three rising (UP) level steps. Since these steps rise and fall to the same steady state
current, active steps need to be designated as 6 UP and 0 DOWN to measure the step level
current. If DOWN steps are specified then, the step level current measured will be the steady state
current.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-23
Figure 3-9
Pulse form with rise and fall steps
For the active steps, the trigger level may be set to a value appropriate for each rising or falling
step, or set to the same value for all active steps. If using the same values for all TLEVx steps,
make sure the TLEV value set is appropriate for the smallest step (in
Figure 3-9, the TLEV value
could not be greater than 275mA). See Table 3-7 for sample trigger level values.
Table 3-7
Sample TLEV values for Figure 3-9
TLEVx Unique TLEVx value Same TLEVx value
TLEV1 550 mA 200 mA
TLEV2 325 mA 200 mA
TLEV3 200 mA 200 mA
TLEV4 300 mA 200 mA
TLEV5 500 mA 200 mA
Page 78

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
TLEV2
400mA
TLEV1
750mA
450mA
575mA
700mA
900mA
600mA
300mA
TLEV
3500mA
TLEV4
625mA
100mA
Table 3-7
Sample TLEV values for Figure 3-9
TLEVx Unique TLEVx value Same TLEVx value
TLEV6 800 mA 200 mA
Use the one-shot method for measuring the pulses since this pulse sequence rises and falls
between steps. To accomplish this, configure the Model 2308 for measuring the pulse sequence
then generate the pulse sequence (See the programming example
One-shot pulse).
Pulse sequences - down steps first
Consider the pulse form in Figure 3-10. This pulse form has three DOWN steps followed by three
UP steps but does not rise or fall between the steps.
Figure 3-10
Pulse form with down steps first (600μsec step duration)
To measure the up step values in this pulse sequence, set the value for UP steps to equal the sum
of actual UP steps plus one while setting the DOWN step value to zero. In
Figure 3-10, the UP
steps are set to 4 and DOWN steps to 0 (If UP steps are set to a non-zero value, the Model 2308
measures them first). Also set TLEV1 for the initial step. This value needs to be appropriate for
detecting the first DOWN step as an UP step measurement (in
Figure 3-10, this value is set at
750mA). For the UP steps, set the trigger level to a value appropriate for each rising step. The key
to detecting this pulse sequence is setting the step timeout to a value high enough to bypass the
remaining down steps after measuring the first step.
For Figure 3-10, the following expected measurement values and TLEV values were used:
Expected measurements:
UP 450 mA, 575 mA, and 700 mA (4th-6th pulses)
DOWN 900 mA, 600 mA, 300 mA (1st-3rd pulses)
3-24 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 79

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
TLEV values (all rising)
TLEV1 750 mA (1st pulse) TLEV3 500 mA (5th pulse)
TLEV2 400 mA (4th pulse) TLEV4 625 mA (6th pulse)
This pulse sequence can be measured using the continuous pulse method (see the programming
example
method. For the one-shot method, the first step trigger level value could be any value for detecting
the 900 milliamp step.
Continuous pulse train). Similarly, this pulse train could be measured using the one-shot
Timeout setting
TOUT (TimeOUT - timeout setting) specifies the timeout length for detecting a given pulse step.
When the TOUT value is reached, an overflow value for that step reading is returned. Although all
step measurements after the first TOUT step are returned as overflow readings, all step
measurements performed before TOUT was exceeded will have correct readings.
Two timeout settings are used: one for the initial step and another for the rest of the active steps.
The setting for the initial timeout should be set slightly longer than the period of the pulse for
continuous pulse trains. The other timeout setting should cover the longest step duration. Also,
make sure to account for trigger delays when determining timeout settings. There are two possible
trigger delays: the internal trigger delay (10 μsec necessary for code execution), and any user
specified trigger delay (optional). The trigger delays occur before the integration process begins
but after pulse detection.
To use the pulse current step method to measure a one-shot pulse train, set the initial timeout to
the maximum setting of 60 seconds. This allows the Model 2308 to be triggered for step
measurements, then a few seconds of delay before generating the one-shot pulse train. The few
seconds of delay are required to ensure the Model 2308 is setup and ready to detect the first step
when it happens along with the rest of the steps.
Integration time
For the pulse current step method, the integration time is required to be at least 400μsec less than
the step duration. This 400μsec allows for the Model 2308 to complete the previous measurement
conversion and become ready for the next pulse edge. With this in mind,
appropriate integration times. Integration time applies to all active steps when step measurements
are requested — each step has the same integration time.
Table 3-8 lists
Table 3-8
Sample integration times
Pulse step duration Step integration times
3.8 ms ≤ 3.4 ms
1.25 ms ≤ 0.85 ms
800 μsec ≤ 400 μsec
500 μsec ≤ 100 μsec
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-25
Page 80

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Range with pulse current step
Select an appropriate current range for the desired measurements. Four current ranges are
available: 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, and 5 mA. Make sure all TLEV values are valid in the selected
current range. There is only one current range for all active steps - each step does not have a
unique current range.
Changing ranges
When changing ranges, the currently active TLEV (trigger level) step values are checked. This
check verifies that the new range maximum setting does not exceed the range (i.e., 5 A for the 5 A
range, 500 mA for the 500 mA range, 50 mA for the 50 mA range, or 5 mA for the 5 mA range). If
just one of the active step TLEV values exceeds the maximum setting for the new current range,
then all step TLEV values are set to 0A.
For example: When changing from the 5 amp current range to the 500 mA range, a TLEV value
greater than 500 mA resets all active trigger level values. Alternatively, if you change from the 5
current range to the 500 mA range and no trigger level settings exceed 500 mA, the previous
settings will be used for the 500 mA range.
NOTE Change TLEV settings for each step using the :STEP:TLEVx command.
A
Programming examples
Pulse current measurements
The following command sequence will return the average of 10 peak pulse current measurements:
Battery channel (#1)
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Sets active channel - battery.
SENS:CURR:RANG 0.5 ‘ Select 500 mA range.
VOLT 15 ‘ Set output voltage to 15V.
CURR 0.75 ‘ Set current limit to 750mA.
OUTP ON ‘ Turn output on.
SENS:PCUR:SYNC ON ‘ Enable trigger synchronization.
SENS:PCUR:AVER 10 ‘ Set average count to 10.
SENS:PCUR:SYNC:TLEV:HUND 0.1 ‘ Set trigger level to 100mA for 500 mA trigger level setting.
SENS:PCUR:TIME:AUTO ‘ Set integration times automatically.
SENS:PCUR:MODE HIGH ‘ Configure to measure peak pulse.
SENS:FUNC “PCUR” ‘ Select pulse current function.
READ? ‘ Trigger 10 measurement conversions and
Charger channel (#2)
‘ return the average of those 10 conver‘ sions. The average of the 10 conversions
‘ is displayed on the front panel. Each of
‘ the ten conversion syncs to the rising
‘ edge.
DISP:CHAN 2 ‘ Sets active channel - charger.
SENS2:CURR:RANG 5 ‘ Select 5 A range.
SOUR2:VOLT 15 ‘ Set output voltage to 15V.
SOUR2:CURR 0.75 ‘ Set current limit to 750 mA.
OUTP2 ON ‘ Turn output on.
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC ON ‘ Enable trigger synchronization.
SENS2:PCUR:AVER 10 ‘ Set average count to 10.
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC:TLEV 0.1 ‘ Set trigger level to 100 mA.
SENS2:PCUR:TIME:HIGH 600e-3 ‘ Set integration high time to 600ms.
3-26 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 81

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC:DEL 50e-3 ‘ Set trigger delay to 50 msec.
SENS2:PCUR:MODE HIGH ‘ Configure to measure peak pulse (trigger
‘ on rising edge).
SENS2:FUNC “PCUR” ‘ Select pulse current function.
READ2? ‘ Trigger 10 measurement conversions and
‘ return the average of those 10 conver-
‘ sions. The average of the 10 conversions
‘ is displayed on the front panel. Each of
‘ the ten conversion syncs to the rising
‘ edge.
Pulse current digitization
The following command sequence returns 3600 digitized readings.
Battery channel (#1)
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Sets active channel - battery.
SENS:CURR:RANG 0.5 ‘ Select 500 mA range.
VOLT 15 ‘ Set output voltage to 15V.
CURR 0.75 ‘ Set current limit to 750 mA.
OUTP ON ‘ Turn output on.
SENS:PCUR:SYNC OFF ‘ Disable trigger synchronization.
SENS:PCUR:AVER 3600 ‘ Set average count to 3600.
SENS:PCUR:SYNC:TLEV:HUND 0.1 ‘ Set trigger level to 100 mA for 500 mA range.
SENS:PCUR:SYNC:DEL 500e-3 ‘ Set trigger delay to 500 msec.
SENS:PCUR:MODE LOW ‘ Configure to measure low pulse (trigger on
SENS:PCUR:TIME:DIG 1e-4 ‘ Set digitize integration time to 100us
SENS:FUNC “PCUR” ‘ Select pulse current function.
READ:ARR? ‘ Trigger and return 3600 readings after sync-
‘ falling edge).
‘ ing to the falling edge for the 1st reading only.
Charger channel (#2)
DISP:CHAN 2 ‘ Sets active channel - charger.
SENS2:CURR:RANG 5 ‘ Select 5 A range.
SOUR2:VOLT 15 ‘ Set output voltage to 15 V.
SOUR2:CURR 0.75 ‘ Set current limit to 750 mA.
OUTP2 ON ‘ Turn output on.
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC OFF ‘ Disable trigger synchronization.
SENS2:PCUR:AVER 3600 ‘ Set average count to 3600.
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC:TLEV 0.1 ‘ Set trigger level to 100 mA.
SENS2:PCUR:SYNC:DEL 50e-3 ‘ Set trigger delay to 50 msec.
SENS:PCUR:MODE LOW ‘ Configure to measure low pulse (trigger on falling edge).
SENS:PCUR:TIME:DIG 1e-4 ‘ Set digitize integration time to 100 us
SENS2:FUNC “PCUR” ‘ Select pulse current function.
READ2:ARR? ‘ Trigger and return 3600 readings after syncing to the
‘ falling edge for the 1st reading only.
Pulse current STEP method (battery channel only)
NOTE To function correctly, the current range must be selected before setting the
trigger level step settings.
Sample step method
The following command sequence measures pulses similar to the one shown in Figure 3-8. The
step duration is 50ms with a pulse period of 2 seconds.
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Set active channel - battery.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-27
Page 82

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
SENS:CURR:RANG 3 ‘ Select 5A current range.
SENS:PCUR:STEP ON ‘ Enable step.
SENS:FUNC ’PCUR’ ‘ Select PCUR function.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:UP 5 ‘ Specify 5 up steps.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:DOWN 4 ‘ Specify 4 down steps
‘ active steps = 9 (5 up + 4 down).
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TIME 20e-3 ‘ Specify 20 milliseconds integration time
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TOUT:INIT 3 ‘ Specify 3 seconds for first step timeout
SENS:PCUR:STEP:DEL 10e-3 ‘ Specify 10 milliseconds for user step delay.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV1 100e-3 ‘ Step 1 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV2 300e-3 ‘ Step 2 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV3 500e-3 ‘ Step 3 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV4 700e-3 ‘ Step 4 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV5 900e-3 ‘ Step 5 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV6 900e-3 ‘ Step 6 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV7 600e-3 ‘ Step 7 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV8 400e-3 ‘ Step 8 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV9 300e-3 ‘ Step 9 tlev value.
READ:ARR? ‘ Trigger and return the 9 step measurements.
‘ for all active steps must be within 400 μsec
‘ of step duration.
‘ (this has to be longer than pulse period).
‘ With 50 milliseconds of step duration, we
‘ use 50 milliseconds (step duration) ‘ 30 milliseconds
‘ Recall 400 microseconds needed for complet‘ ing previous step measurement and being
‘ ready for next.
= 20 milliseconds spare time.
NOTE Since this sample program is for a continuous pulse train, the pulse it measures
could also be measured using the single shot method (see One-shot pulse).
One-shot pulse
NOTE To function correctly, the current range must be selected before setting the
trigger level step settings.
The following command sequence measures pulses similar to the one shown in Figure 3-9 with a
one-shot pulse measurement. The step duration is 600 μsec with 4 msec between steps.
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Set active channel - battery.
SENS:PCUR:STEP ON ‘ Enable step.
SENS:FUNC ’PCUR’ ‘ Select PCUR function.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:UP 6 ‘ Specify 6 up steps.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:DOWN 0 ‘ Specify 0 down steps (remember the default
‘ is 1). Pulse sequences - rising and falling for more information.
SENS:CURR:RANG 3 ‘ Select 5 A current range.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TIME 100e-6 ‘ Specify 100 microseconds for step integra-
‘ tion time.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:DEL 50e-6 ‘ Specify 50 microseconds for step delay.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TOUT 8e-3 ‘ Specify 8 milliseconds for step timeout ex-
‘ Recall 400 microseconds needed for complet‘ ing previous step measurement and being
‘ ready for next. With 600 microseconds of
‘ step duration, we have 50 microseconds to
‘ spare:
‘ 600 (step duration) - 400 (step processing
‘ time) - 100 (step integration time) ‘ 50(step delay) = 50 (spare time).
3-28 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 83
Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TOUT:INIT 60 ‘ Specify 60 seconds for first step timeout.
‘ cept first one.
‘ Recall for one shot pulse measurement, need
‘ to have a long initial step timeout since
‘ want to trigger the 2308 for pulse step mea-
‘ surement and wait between 3 to 5 seconds be
‘ fore generating the one shot pulse to guar-
‘ antee the Model 2308 is waiting for
‘ detection of first step.
Using the same step trigger level for all steps is contained in the following sample. Table 3-7
contains a sample with the one trigger level (as shown) and also with unique trigger levels for each
step.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV1 200e-3 ‘ Step 1 TLEV value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV2 200e-3 ‘ Step 2 TLEV value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV3 200e-3 ‘ Step 3 TLEV value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV4 200e-3 ‘ Step 4 TLEV value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV5 200e-3 ‘ Step 5 TLEV value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV6 200e-3 ‘ Step 6 TLEV value.
READ:ARR? ‘ Trigger and return the 6 step measurements
After sending this command, wait a few seconds before generating a one shot pulse sequence.
Continuous pulse train
NOTE To function correctly, the current range must be selected before setting the
trigger level step setting.
The following command sequence measures pulses similar to the one shown in Figure 3-10 in a
continuous pulse train. The step duration is 600 μsec with a step period of 2 seconds.
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Set active channel - battery.
SENS:CURR:RANG 5 ‘ Select 5 A current range.
SENS:PCUR:STEP ON ‘ Enable step.
SENS:FUNC ’PCUR’ ‘ Select PCUR function.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:UP 4 ‘ Specify 4 up steps.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:DOWN 0 ‘ Specify 0 down steps.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TIME 100e-6 ‘ Specify 100 microseconds for step
SENS:PCUR:STEP:DEL 50e-6 ‘ Specific 50 microseconds for step delay.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TOUT 3e-3 ‘ Specify 3 milliseconds for step
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TOUT:INIT 3 ‘ Specify 3 seconds for first step timeout.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV1 750e-3 ‘ Step 1 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV2 400e-3 ‘ Step 2 tlev value.
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV3 500e-3 ‘ Step 3 tlev value.
‘ integration time.
‘ Recall 400 microseconds needed for complet-
‘ ing previous step measurement and being
‘ ready for next. With 600 microseconds of
‘ step duration, we have 50 microseconds to
‘ spare:
‘ 600 (step duration) - 400 (step processing
‘ time) - 100 (step integration time) -
‘ 50(step delay) = 50 (spare time).
‘ timeout except for first step. Recall
‘ timeout needs to be long enough to bypass
‘ the 600 mA, 300 mA, and 100 mA steps, but not
‘ so short it misses the 450 mA step (600μsec x
‘ 3 = 1.8 msec). Using 3 μsec accounts for the
‘ first step spare time as well.
‘ Recall for continuous pulse measurement,
‘ need to have an initial step timeout long
‘ enough to bypass the pulse period.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-29
Page 84

Section 3: Pulse Current Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
SENS:PCUR:STEP:TLEV4 625e-3 ‘ Step 4 tlev value.
READ:ARR? ‘ Trigger and return the 4 step measurements.
3-30 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 85

In this section:
Section 4
Long Integration Measurements
Topi c Page
Overview ..................................................................................................... 4-2
Integration time..................................................................................... 4-3
Trigger edge ......................................................................................... 4-3
Trigger level.......................................................................................... 4-3
Pulse timeout........................................................................................ 4-4
Measurement configuration ........................................................................ 4-6
Current range ....................................................................................... 4-6
Integration time..................................................................................... 4-6
Pulse timeout........................................................................................ 4-7
Trigger edge and trigger level............................................................... 4-7
Long integration display mode ............................................................. 4-8
Long integration measurement procedure.................................................. 4-8
General notes....................................................................................... 4-9
Determining correct trigger level (long integration)............................... 4-9
SCPI programming ................................................................................... 4-11
Command notes (long integration measurements) ............................ 4-12
Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect .................................................... 4-12
Programming examples............................................................................ 4-16
Page 86

Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
R
1
m
i
k 1=
n
∑
n
-----------------=
nint
I
t
1PLC
----------------
⎩⎭
⎨⎬
⎧⎫
=
Overview
Long integration is an average current measurement of one or more pulses that can be performed
on either the battery channel (#1) or the charger channel (#2). The integration time can be as long
as 60 seconds. Since long integration is an average measurement, the integration time should be
a complete pulse period or an integral number of pulse periods.
Long integration measurements are accomplished by taking an integral number of integration
cycles during the total measurement time. An integration cycle is the line cycle period (16.67 ms
for 60 Hz) plus a small processing time. The system calculates the number of integration cycles
required based on the total time and rounds down to the nearest integer. Therefore, the actual
measurement time can be slightly less than the requested measurement time by up to one line
cycle time (one cycle is 16.67 ms for 60 Hz and 20 ms for a 50 Hz line frequency. A long
integration reading, R
, is the average of a series of current measurements, mi, defined by:
1
where n is an integer given by:
where:
1PLC = one power line cycle
It = integration time
Here the integration time specified by the user and denominator represents the integration time of
1 PLC (16.67 msec for 60 Hz or 20 ms for 50 Hz) and processing overhead. The function int
rounds the argument down to next lowest integer.
Long integration is a technique to extend the capabilities of the power supply A/D circuit beyond its
maximum integration time period. The A/D can measure pulses up to 833 ms. To extend this time
period for longer pulses, the long integration technique uses a filtered and sampled measurement
of the waveform. This gives the power supply the ability to measure signals with periods up to 60
seconds.
The filtering of the waveform adds some restrictions to the types of pulses being measured. If a
pulse train has a high duty cycle, where the off time is less than 200 ms, the first period of the
measured waveform will not have settled to steady state, therefore it will be an inaccurate
measurement. In all cases where the off or low time is less than 200 ms, the filtered pulse will have
reached steady state in the second cycle of the waveform and, therefore, can be accurately
measured (
Figure 4-1). In other words, to measure a periodic waveform with low times less than
200 ms (high duty cycle), start measurements after the first period occurs. This is not a problem for
one-shot pulses or for pulses with off times greater than 200 ms.
4-2 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 87

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
t
low
> 200ms t
low
< 200ms
Steady
state
Steady
state
Figure 4-1
Steady state for waveforms based on low pulse times
Integration time
The integration time period can be set automatically or manually by the user. The integration time
can be as long as 60 seconds. For 60 Hz power line frequency, the minimum integration time
setting is 850 msec. For 50 Hz power line frequency, the minimum integration setting is 840 msec.
Trigger edge
Trigger level
Use AUTO TIME when you want to perform a long integration measurement of each pulse. When
the AUTO TIME operation is performed, the instrument measures the time between two rising
pulse edges and sets an appropriate integration time that will encompass the high and low periods
of the pulse. This integration time applies for all subsequent long integration measurements until
another AUTO TIME is performed or the time is changed manually.
If you want the integration period to encompass two or more pulses, you will have to set the
integration time manually. However, you must make sure that the integration time covers only the
portion of the pulse you want to measure. For example, if you want a long integration of two
pulses, you must make sure that the set integration time does not extend into the third pulse.
A pulse edge can be used to trigger the start of the measurement. Either a rising or a falling pulse
edge can start the measurement. A pulse has to be detected before a rising or falling pulse edge
can trigger a long integration measurement. All pulses that are less than the specified trigger level
are ignored (
Trigger level ). Pulse edges are ignored while a long integration is in process.
A third option is available if you do not want measurements controlled by pulse edges. With
NEITHER selected, measurements start as soon as the long integration function is selected. This
option does not need a valid trigger level to generate a reading. It will perform a measurement and
produce a reading of the current even if a pulse is not present. Therefore, with NEITHER selected,
the NO PULSE message will not appear on the display.
Before a rising or falling pulse edge can trigger the start of a long integration, the pulse must first
be detected. Trigger level specifies the minimum pulse level that will cause detection. For
example, if the trigger level is set for 2 A, pulses that are ≥2 A will be detected. Current pulses
<2 A are ignored.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-3
Page 88

Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
The charger channel has only one trigger level setting for the 5 A current range: 0 A to 5 A. The
battery channel (#1) has four trigger level settings (one for each one of the current ranges: 5 A,
500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA). For the 5 A current range, the trigger level may be set from 0 A to 5 A.
For the 500 mA current range, the trigger level may be set from 0 mA to 500 mA. Similarly, the
level setting may be set from 0
the 5 mA current range. These settings affect trigger level resolution and are only used when the
corresponding current range is selected. The trigger level setting option on the battery channel
allows you to set a trigger level with greater resolution.
mA to 50 mA for the 50 mA current range and from 0 to 5 mA for
Pulse timeout
TOUT (timeout) specifies the timeout length for the pulse. When the TOUT value is reached, “NO
PULSE” is displayed (top line of the front-panel display). Set the value for TOUT as follows:
TOUT = LINT TIME + x
where x makes TOUT > LINT TIME
TOUT = timeout (time allowed for detection of a pulse)
LINT TIME = long integration time (time allowed for reading after pulse occurs)
For example, if the trigger edge is set to rising, the timeout value should be set to allow sufficient
time for detection of the pulse if the rising edge is just missed. In
where we start looking for the pulse. Since the rising edge was just missed, point (B) will be the
first detectable rising edge. If the timeout is less than long integration time, a pulse trigger time out
(due to TOUT) may occur. Therefore, if long integration time = 1.8 seconds, a good TOUT value
would be 2 seconds. A similar method for selecting a TOUT value would be to use a value equal to
105% of the expected pulse period.
Figure 4-2, point (A) is the point
Summarizing Figure 4-2:
1. Reading begins searching for high pulse at point (A).
2. Earliest pulse detected at point (B).
3. Reading time equals Long integration time.
4-4 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 89

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
B
A
Long integration
time
Search time
TOUT
Reading
time
Figure 4-2
Long integration, search, and reading time comparison
NOTE If a pulse is not present, timeout needs to elapse (TOUT) before “NO PULSE”
appears on the display. Search Time needs to elapse when checking TLEV
command for valid setting.
PULSE TIMEOUT applies only to long integration measurements that are configured to be
triggered by rising or falling pulse edges. After the long integration function is selected, the
instrument searches for a pulse. If a pulse is not detected within the specified time (PULSE
TIMEOUT), the “NO PULSE” message will be displayed. While the “NO PULSE” message is
displayed, the instrument continues to search for a pulse. With a long timeout setting, the
instrument may appear locked up while it is searching for the pulse to start the long integration.
PULSE TIMEOUT can be set from 1.000 to 63.000 seconds.
With neither trigger edge selected, pulse timeout is not used and a pulse search is not conducted.
Therefore, the “NO PULSE” message is never displayed. Measurements start as soon as the long
integration function is selected, even if no pulse is present. It is the responsibility of the user to
determine if a pulse was present when the measurement was made.
NOTE For GPIB operation:
1. Use :SEARch to disable the search for pulses (see the :SEARch
command in Table 4-2).
2.
3.
:FAST (enables a fast readings mode) can be used with long integration
functionality (see the
:FAST command in Table 4-2).
:DETect may be enabled to only detect pulses between user triggered
readings (see the
:DETect command in Table 4-2).
4. See Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-5
Page 90
Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Measurement configuration
NOTE Current range is selected from the CURRENT RANGE #1/#2 item of the menu.
Integration time, trigger edge, trigger level, and pulse timeout are set from the
LONG INTEGRAT #1/#2 item of the menu. Details on integration time, trigger
edge, trigger level, and pulse timeout are provided in the Overview.
Table 1-3 shows the menu structure. Rules to navigate the menu follow the
table.
Current range
The instrument will not auto range with the long integration measurement function selected.
Changes to the auto range setting are not used during long integration measurements but are
retained for when long integration measurements are no longer taken. Long integration
measurements may be performed on any of the four ranges for battery channel (#1). Long
integration measurements are always performed on the 5 A range for the charger channel (#2).
Therefore, selecting long integration with the 5 mA range active will cause the supply to first switch
to the 5 A range on the charger channel.
NOTE To get better trigger level resolution, make sure the current range is set
Integration time
Use the following items of the LONG INTEGRAT #1/#2 menu item to set the integration time.
(LONG INTEGRAT #1 refers to the battery channel (#1) while LONG INTEGRAT #2 refers to the
charger channel).
INTEGRATION TIME
Manually set the long integration time. For 60Hz power line frequency, integration time can be set
from 850
set from 840
AUTO TIME
msec to 60 sec (1 ms step value). For 50Hz power line frequency, integration time can be
msec to 60 sec (1 ms step value).
appropriately for the expected measurement on the battery channel (#1).
Current range is linked to current limit. Therefore, as a general rule, the user
selects the current range before setting the current limit. See
and current for details on current range and current limit. Current range is
selected from CURRENT RANGE #1/#2 item of the menu (CURRENT RANGE
#1 refers to the battery channel (#1) while CURRENT RANGE #2 refers to the
charger channel).
Outputting voltage
Use to automatically set the integration time. When the AUTO TIME operation is performed, the
instrument measures the time between two rising pulse edges and sets an appropriate integration
time that will encompass the high and low periods of a single pulse.
AUTO TIME searches for two consecutive RISING edges (the setting of trigger edge does not
affect AUTO TIME). Therefore, with NEITHER edge set, the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bits in
the status model may get set (see
4-6 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Section 7 on the status model for more information). Although
Page 91

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
Auto Time does not use the user setting for trigger edge, the user setting for edge will be used for
trigger commands (For example,
READ? and MEASure?).
Pulse timeout
Use the PULSE TIMEOUT item of the LONG INTEGRAT #1/#2 menu item to set pulse timeout
(LONG INTEGRAT #1 refers to the battery channel (#1) while LONG INTEGRAT #2 refers to the
charger channel (#2)).
Set pulse timeout (from 1 to 63 seconds) for long integration measurements that are configured to
be triggered by RISING or FALLING pulse edges. If a pulse is not detected within the specified
time (PULSE TIMEOUT), the “NO PULSE” message will be displayed. While the “NO PULSE”
message is displayed, the instrument continues to search for a pulse. With NEITHER edge
selected, the PULSE TIMEOUT setting is inactive.
Trigger edge and trigger level
Use the following items of the LONG INTEGRAT#1/#2 menu item to set trigger edge, and trigger
level (LONG INTEGRAT #1 refers to the battery channel (#1) while LONG INTEGRAT #2 refers to
the charger channel (#2)).
Trigger edge
A pulse edge can be used to trigger the start of the measurement (TRIGGER EDGE). Select
RISING to use a rising pulse edge to start the measurement. Select FALLING to use a falling pulse
edge to start the measurement. A third option is available if you do not want measurements
controlled by pulse edges. With NEITHER selected, measurements will start as soon as the long
integration function is selected. A pulse has to be detected before a RISING or FALLING pulse
edge can trigger a long integration measurement (see
Trigger level ).
Trigger level
Before a RISING or FALLING pulse edge can trigger the start of a long integration, the pulse must
first be detected. TRIGGER LEVEL specifies the minimum pulse level that will cause detection on
the selected current range. For the battery channel (#1), any current range is acceptable and the
trigger level setting corresponding to the selected current range will be used to detect the pulse.
For the charger channel only, the 5
For battery channel (#1) - The trigger level can be set for either the 5 A, 500 mA, 50 mA, or 5 mA
current range. For the 5 A current range, the trigger level can be set from 0 to 5A in 5 mA steps.
For the current 500 mA range, the trigger level can be set from 0 to 500 mA in 0.5 mA steps. For
the current 50 mA range, the trigger level can be set from 0 to 50 mA in 0.05 mA steps. For the
5
mA current range, the trigger level can be set from 0 mA to 5 mA in 0.005 mA steps.
The four trigger level ranges are displayed as follows using the TRIGGER LEVEL menu option:
5 A range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
A range is used.
A(5.0) 0.000 A
500 mA range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
A(500) 0.0000 A
50 mA range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
mA (50) 0.00000A
5 mA range: PCUR TRIG LEV #1
mA (5) 0.000000A
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-7
Page 92

Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
▲
▲
To toggle the current range for the trigger level setting, place the blinking cursor on the “A” at the
far right end of line two of the display, and press the
▲ and ▼ keys. After keying in the trigger level
(in amps), press ENTER to update the displayed range for that trigger level setting only.
Charger channel (#2) - Set the trigger level from 0 to 5 A in 5 mA steps.
Long integration display mode
Long integration measurements are displayed with the long integration display mode selected.
To display Long Integration mode:
NOTE If the instrument is in the settings mode, press the SET key until the blinking
stops (the measured readings can then be displayed). To determine if the
instrument is in the settings mode, check for a blinking cursor in a digit of the
voltage or current field (if present, the instrument is in the setting mode).
1. Press the DISPLAY key to access the display menu.
2. Press the
3. Press the
or keys to select channel #1 or #2.
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to LONG INTEGRATION.
4. Press ENTER to select.=
NOTE For details on display modes, see Display modes .
Long integration measurement procedure
The following steps summarize the procedure to perform long integration current
measurements:
1. Follow the instructions in Editing output voltage and current limit values to set the output
voltage and current limit.
2. When using the battery channel (#1), select the desired current level range (5 A, 500 mA,
50 mA, or 5 mA) from the CURRENT RANGE #1 menu. For battery channel (#1), long
integration measurements may be performed on any of the four current ranges. As the
current range changes, the trigger level setting will update automatically with the
corresponding trigger level setting to detect pulses. For the charger channel, long
integration measurements are automatically performed on the 5 A current range.
3. Press OPERATE.
NOTE Setting the trigger level with the output off will also cause the pulse timeout
message to appear. However, the trigger level will be set.
4. From the LONG INTEGRAT #1/#2 item of the menu, set INTEGRATION TIME, PULSE
TIMEOUT, TRIGGER EDGE and TRIGGER LEVEL as appropriate (LONG INTEGRAT #1
refers to the battery channel (#1) while LONG INTEGRAT #2 refers to the charger channel
4-8 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 93

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
(#2)). If using the battery channel (#1), make sure to set the trigger level for the current
range selected in step 2.
NOTE If you select AUTO TIME to set the integration time, the pulse timeout message
LONG INT TRIG NOT DETECTED will occur if the output is OFF. This message
indicates that the integration time has not been updated. To update the
integration time, you will have to again select AUTO TIME after the output is
turned ON.
5. Press the DISPLAY key.
6. Press the
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll to LONG INTEGRATION.
7. Press ENTER to select.
8. Observe the long integration readings on the display.
General notes
Long integration readings will not be taken if the active channel is not the same as the selected
channel. For example, if the battery channel (#1) is set to LINT and the active channel is the
charger channel (#2) then, long integration readings will not be taken on the battery channel (#1).
Therefore, while the charger channel (#2) is active with the LINT function selected on the battery
channel (#1), you will not incur the LINT integration time or LINT timeout from the battery channel
(#1) while waiting for responses from the charger channel (#2). Since no long integration readings
are being taken, you will not get any information on whether the pulse is present or not on the
battery channel (#1).
• Make sure the voltage and current settings are appropriate for DUT.
• If a pulse timeout occurs (no pulses detected), current will not be measured (i.e. ----A) and
the NO PULSE message will be displayed. Pulses are not detected with the output OFF.
With the output ON, pulses will not be detected if the trigger level is too low or too high.
Perform the
Determining correct trigger level (long integration) procedure to find an
appropriate trigger level.
• While the NO PULSE message is displayed, the instrument continues to search for a pulse.
The search can be terminated by pressing any front-panel key. The NOT TRIG message
replaces the NO PULSE message. To restart the search, press
▲ or ▼ keys while displaying
long integration readings. The timeout or pulse detection will need to elapse before the
display changes.
• To stop taking long integration readings, press any front-panel key. As long as the
instrument remains in the long integration display state, the measurement process can be
resumed by pressing
▲ or ▼ keys. While readings are not being taken, the bottom line
displays the last valid long integration reading, or dashes if no pulse detected before being
stopped.
Determining correct trigger level (long integration)
1. After selecting the appropriate voltage and current values, turn on the output.
2. Follow instructions in Long integration display mode to select the long integration display
type.
NOTE If the trigger level is too low or too high, the “NO PULSE” message will be
displayed. If long integration measurements are instead being displayed, the
trigger level is valid. You can skip the rest of this procedure.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-9
Page 94

Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
3. Go into the main menu (press the MENU key twice - the first press will stop the readings
while the second press accesses the menu). Select LONG INTEGRAT #1/#2 (select LONG
INTEGRAT #1 for the battery channel (#1) and LONG INTEGRAT #2 for the charger
channel (#2)).
4. Select and adjust the TRIGGER LEVEL and press ENTER. The unit starts looking for the
rising edge of the pulse (this is regardless of the trigger edge setting). If the trigger level is
still too low or too high, the LONG INT TRIG NOT DETECTED message will be displayed
briefly. Note that it may take as long as the timeout value for the message to appear (see
LONG INT TRIG NOT DETECTED message for more information).
5. If the message appeared, repeat step 4 until a valid trigger level is found.
6. Press the MENU key to exit the menu structure and display long integration current
measurements.
NOTE For the battery channel (#1), make sure the current range setting agrees with
the trigger level setting set in Step 4.
LONG INT TRIG NOT DETECTED message
The TRIG NOT DETECTED message is possibly displayed when specific TLEV settings coupled
with specific current ranges have been set and a trigger has not been detected. Refer to
for message preconditions.
Table 4-1
See Long integration measurement procedure for information on setting the current range.
Table 4-1
TRIG NOT DETECTED message
TLEV setting Current range TRIG NOT DETECTED Message displayed?
90 mA for 500 mA current
range
90 mA for 500 mA current
range
0.75 A for 5 A current range 5 A May appear*
0.1 A for 500 mA current range 500 mA May appear
3.0 A for 5 A current range 5 A May appear
0.03 A for 50 mA current range 50 mA May appear
0.003 A for 5 mA current range 5 mA May appear
1.1 A for 5 A current range 5 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
1.1 A for 5 A current range 500 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
*
Depends upon the OUTPUT:
If OFF, the message will appear.
If ON, display of the message will depend on the trigger level setting. If trigger level setting greater than the expected low
measurement and less than the expected high measurement, the message will not appear.
For example, if the expected pulse high value is 2.2 A and the expected pulse low value is 0.5 A, the output is on, and the
current range is 5 A, notice the following results:
Setting 0.3 A TRIG NOT DETECTED is displayed (setting too low).
Setting 3.0 A TRIG NOT DETECTED is displayed (setting too high).
Setting 1.1 A The message will not display (setting correct).
5 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
current range)
50 mA No (not checked because TLEV setting does not match
current range)
*
*
*
*
current range)
current range)
4-10 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 95

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
NOTE Setting the trigger level and/or the current range may cause LONG INT TRIG
NOT DETECTED to appear.
SCPI programming
The commands for long integration measurements are summarized in Table 4-2 (a listing following
the table contains specific command notes). Programming examples demonstrate how to use
these commands.
Table 4-2
SCPI commands - long integration measurements
Command Description Default
:SENSe[1]
:FUNCtion “LINTegration”
:LINTegration
:TIME <NRf>
:AUTO
:TLEVel <NRf>
[:AMP] <NRf> Set the trigger level in amps for use when on
:HUNDred <NRf>
:FIFTy <NRf>
SENSe subsystem for battery channel (#1):
Select long integration measurement function. VOLT
Long integration configuration:
Set integration time (in sec): X to 60 (where X
is 0.850 for 60Hz, or 0.840 for 50Hz).
Integration time set automatically.
Path to set trigger level feature:
the 5A current range: 0.0 A-5.0 A in 5 mA steps
Set the trigger level in amps for use when
on the 500mA current range: 0.0 mA-500 mA in
mA or 500 μA steps.
0.5
Set the trigger level in amps for use when on
the 50mA current range: 0.0 mA-50 mA in 0.05 mA
or 50μA steps.
:FIVE <NRf> Set the trigger level in amps for use when
on the 5 mA current range: 0.0 mA-5 mA in
mA or 5 μA steps.
0.005
:TEDGe <name>
:TimeOUT <NRf>
:SEARch <b>
:FAST <b>
:DETect <b>
:SENSe2
:FUNCtion “LINTegration”
:LINTegration
:TIME <NRf>
:AUTO
:TLEVel <NRf>
Select trigger edge to initiate the
measurement:
RISING, FALLING, or NEITHER.
Specify length of timeout: 1–63 (sec). 16
Enable or disable pulse search. ON
Enable or disable long integrations fast
readings.
Enable or disable pulse detection mode. OFF
SENSe subsystem for the charger channel (#2):
Select long integration measurement function. VOLT
Long integration configuration:
Set integration time (in sec): X to 60 (where X
is 0.850 for 60Hz, or 0.840 for 50Hz).
Integration time set automatically.
Set trigger level in amps: 0–5 (5mA resolution). 0.0
1
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
RISING
OFF
1
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-11
Page 96

Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Table 4-2
SCPI commands - long integration measurements
Command Description Default
:TEDGe <name>
:TimeOUT <NRf>
:SEARch <b>
:FAST <b>
:DETect <b>
READ[1]?
READ2?
Select trigger edge to initiate the
measurement:
RISING, FALLING, or NEITHER.
Specify length of timeout: 1–63 (sec). 16
Enable or disable pulse search. ON
Enable or disable long integrations fast
readings.
Enable or disable pulse detection mode. OFF
Trigger and return one reading for battery channel
(#1).
Trigger and return one reading for charger channel
(#2).
RISING
OFF
Command notes (long integration measurements)
SENSe[1]:FUNCtion ‘LINTegration’ Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:FUNCtion ‘LINTegration’ Applies to charger channel (#2 )
The parameter name can be enclosed in single or double quotes (single - shown above, double shown in
Table 4-2).
SENSe[1]:LINTegration:SEARch <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:LINTegration:SEARch <b> Applies to charger channel (#2 )
Refer to Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information.
SENSe[1]:LINTegration:FAST <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:LINTegration:FAST <b> Applies to charger channel (#2 )
Refer to Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information.
SENSe[1]:LINTegration:DETect <b> Applies to battery channel (#1)
SENSe2:LINTegration:DETect <b> Applies to charger channel (#2 )
Refer to Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect for detailed usage information.
READ[1]? Applies to battery channel (#1)
READ2? Applies to charger channel (#2 )
After sending a trigger reading command to perform long integration measurements, do not
address the power supply to talk until all readings are completed. Details on
signal-oriented measurement commands are provided in
Using FAST, SEARch, and DETect
READ? and the other
Section 9.
Use the FAST command to have the quickest response for pulse current measurements triggered
by the measurement commands (for example,
use the
detecting pulses until a measurement command is sent. When the trigger level is set, use the
FAST command, there is no indication that the instrument is correctly configured for
MEASure, READ, or *TRG). Note that when you
SEARch command to retain quick responses to measurement commands and to ensure that the
instrument is configured correctly for detecting pulses. Use the
the unit is configured correctly and can read the pulse before sending a measurement command.
4-12 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
DETect command to ensure that
Page 97

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
B
A
Long Integration
Time
Search Time
TOUT
Reading
Time
Use FAST, SEARch, and DETect to control how background readings are taken. A background
reading is a measurement taken by the power supply between user triggered readings. The
selected function dictates how background readings are taken between user triggered readings.
For long integration, a background reading involves looking for the pulse and optionally generating
a reading for the user. The various settings of
tune the function. This enables the function to perform the desired background readings (if any)
between user triggered readings. The default settings (
SEARch, FAST, and DETect allow the user to fine
FAST:OFF, SEARch:ON, and
DETect:OFF) allow the long integration background readings to be taken. If no pulse is present,
the setting of TimeOUT affects how responsive the supply is to bus commands. If a pulse is
present, the search time plus reading time (TIME setting) affects how responsive the supply is to
bus commands (refer to
and DETect commands and a description of the resulting action. For more information on search
time, reading time, and
NOTE
Figure 4-3). Table 4-3 contains the available settings for FAST, SEARch,
TimeOUT, see Pulse timeout .
• If a pulse is not present, timeout needs to elapse (TOUT).
• If DETECT ON (only), search time needs to elapse before responding to a
bus command (reading time not incurred).
• If SEARCH OFF or FAST ON, search time and reading time not incurred.
Figure 4-3
TOUT and search time
NOTE Search time needs to elapse when checking TLEV command for valid setting.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-13
Page 98
Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Table 4-3
FAST, SEARch, and DETect command reference
FAST SEARch DETect Description
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF OFF ON The unit is more responsive to bus commands in this mode since the supply
OFF OFF OFF
ON ON The unit is most responsive to bus commands in this mode. The supply does
ON OFF
OFF ON
OFF OFF
not wait for TOUT or search time plus reading time for background readings
and TLEV command checks. Refer to
LINT” instead of “LONG INT”.
With FAST set to ON, no background long integration measurements occur, no
pulse detection between user-triggered readings occur, no checking for the
parameter of LINT TLEV commands to detect a pulse occur, no setting of the
pulse trigger timeout bits in the status model between user-triggered readings
occur.
For triggered readings to set the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bits in the status
model, set TEDGe to be RISING or FALLING. If TEDGe is set to NEITHER, the
PTT will not be set after the initial setting of FAST to ON and TEDGe to
NEITHER. The setting of NEITHER specifies no pulse edge for
synchronization or detection. The bit is latched until read so the bit may still be
set in the status model from a previous timeout (see
model for more information).
does not need to wait for TOUT or search time plus reading time for
background readings. However, the supply does need to wait for TOUT or
search time when checking the parameter setting for TLEV commands. Refer
Figure 4-3. front panel displays “NO SEARCH” instead of “LONG INT”.
to
Although no background long integration measurements or pulse detection
between user-triggered readings will occur, the checking for the parameter of
LINT TLEV commands to detect a pulse will occur. The setting of the pulse
trigger timeout bits in the status model will only occur between user-triggered
readings if TLEV commands sent. This is regardless of the TEDGe setting
since the RISING edge is used for this feature.
For triggered readings to set the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bits in the
status model, the TEDGe setting needs to be RISING or FALLING. If TEDGe is
set to NEITHER, the PTT will not be set after the initial setting of SEARch to
OFF and TEDGe to NEITHER. The setting of NEITHER specifies no pulse
edge for synchronization or detection. The bit is latched until read so the bit
may still be set in the status model from a previous timeout (see
the Status model for more information).
Figure 4-3. front panel displays “FAST
Section 7 on the status
Section 7 on
Shaded cells designate command with precedence in each mode.
4-14 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
Page 99

Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual Section 4: Long Integration Measurements
Table 4-3
FAST, SEARch, and DETect command reference
FAST SEARch DETect Description
OFF ON ON This mode allows the user to know whether the pulse disappeared before a
user-triggered reading is requested. The responsiveness of bus commands is
governed by LINT TOUT (if no pulses are detected), or by search time (if
pulses are detected). Reading time does not have to elapse after detecting the
pulse in this mode. Therefore, the longest response time to bus commands is
approximately the greater of either TOUT or search time values. Refer to
Figure 4-3.
With DETect ON, no background long integration measurements will occur
between user-triggered readings but pulse detection occurs. If the pulse is
detected, the front panel will display DETECT on top line of display instead of
LONG INT. If no pulses are detected, the front panel will display NO DETECT
as well as the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bit being set in the status model.
Since the PTT bit is latched (see
PTT bit may indicate that pulse trigger timeout occurred although the display is
showing DETECT. The checking for the parameter of LINT TLEV commands
will occur which may set the PTT bit since looking for a rising edge. This
functionality occurs if TEDGe is set to RISING or FALLING.
If TEDGe is set to NEITHER, pulse detection will fail since synchronization to
an edge for triggering does not occur (there is nothing for the unit to detect). In
this mode, the DETECT/NO DETECT on the front panel is not reliable and the
setting of the PTT bit of the status model will not happen. Since checking for
the parameter of LINT TLEV commands to detect a pulse looks for the RISING
edge, this will occur and may set the PTT bit of the status model.
OFF ON OFF With DETect OFF, background long integration measurements will occur
between user-triggered readings as well as pulse detection. If the pulse is
detected, the front panel will display LONG INT on top line of display along
with the reading on the bottom line. If no pulses are detected, the front panel
will display NO PULSE as well as the PTT (Pulse Trigger Timeout) bit being
set in the status model. Since the PTT bit is latched (see
Model), a query for the PTT bit may indicate that pulse trigger timeout occurred
although the display is displaying LONG INT and a reading. Checking for the
parameter of LINT TLEV commands to detect a pulse occurs by looking for a
rising edge. This may set the PTT bit. If detecting pulses, the supply’s
responsiveness to bus commands is affected by search time plus reading time.
If not detecting pulses, the supply’s responsiveness to bus commands is
affected by TOUT. Therefore the longest response time to bus commands is
approximately the greater of either TOUT or search time plus reading time
Figure 4-3). This functionality occurs if TEDGe is set to RISING or
(refer
FALLING.
If TEDGe is set to NEITHER, pulse detection will fail since synchronization to
an edge for triggering does not occur (there is nothing for the unit to detect). In
this mode, the front panel will show LONG INT on the top line with a reading on
the bottom. The user will have to determine if the pulse was present for the
reading or not. In this mode, the PTT bit of the status model will not be set as
well and therefore, not useful. Since checking the parameter of LINT TLEV
commands to detect a pulse looks for the RISING edge, this may set the PTT
bit of the status model if TLEV setting causes no rising edge pulse detection.
Section 7 on Status Model), a query for the
Section 7 on Status
Shaded cells designate command with precedence in each mode.
2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008 Return to Section Topics 4-15
Page 100

Section 4: Long Integration Measurements Model 2308 Portable Device Battery/Charger Simulator User’s Manual
Programming examples
Battery channel (#1)
DISP:CHAN 1 ‘ Sets display to battery channel.
SENS:CURR:RANG 300e-3 ‘ Select 500 mA range.
VOLT 15 ‘ Set output voltage to 15 V.
CURR 0.75 ‘ Set current limit to 750 mA.
OUTP ON ‘ Turn output on.
SENS:LINT:TLEV:HUND 0.1 ‘ Set trigger level to 100 mA for 500 mA trigger level range.
SENS:LINT:TEDG RISING ‘ Select rising trigger edge to initiate measurement.
SENS:LINT:TIME:AUTO ‘ Set integration time automatically for single pulse.
SENS:FUNC “LINT” ‘ Select long integration function.
READ? ‘ Trigger and return one reading and reading shown on display.
Charger channel (#2)
DISP:CHAN 2 ‘ Sets display to charger channel.
SENS2:CURR:RANG 5 ‘ Select 5 A range.
SOUR2:VOLT 15 ‘ Set output voltage to 15 V.
SOUR2:CURR 0.75 ‘ Set current limit to 750 mA.
OUTP2 ON ‘ Turn output on.
SENS2:LINT:TEDge RISING ‘ Select rising trigger edge to initiate
‘ measurement.
SENS2:LINT:TLEV 0.1 ‘ Set trigger level to 100 mA.
SENS2:LINT:TIME:AUTO ‘ Set integration time automatically for single pulse.
SENS2:FUNC “LINT” ‘ Select long integration function.
READ2? ‘ Trigger and return one reading and reading shown on display
4-16 Return to Section Topics 2308-900-01 Rev. A / July 2008
 Loading...
Loading...