Page 1

Thyristor Power Units
B 70.9040.0
Operating Instructions
02.06
/00089951
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction ......................................................................................... 7
1.1 Preface .................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Typographical conventions ................................................................................... 8
1.2.1 Warnings .................................................................................................................. 8
1.2.2 Note signs ............................................................................................................... 8
1.3 Description .............................................................................................................. 9
1.4 Type designation .................................................................................................... 9
1.4.1 Type extensions (extra codes) ................................................................................ 10
1.4.2 Standard accessories ............................................................................................ 10
1.4.3 Accessories ............................................................................................................ 11
1.5 Block diagram ...................................................................................................... 11
1.6 Front panel indicators and adjustments ............................................................ 12
2 Operating modes .............................................................................. 13
2.1 Phase-angle control with soft start and current limiting .................................. 13
2.2 Burst-firing operation, for resistive loads .......................................................... 14
2.3 Burst-firing operation for transformer loads and loads with a high positive tem-
perature coefficient TC (mixed operation) 15
3 Installation ......................................................................................... 17
3.1 Important installation notes ................................................................................ 17
3.2 Filtering and interference suppression .............................................................. 18
3.3 Installation site and climatic conditions ............................................................ 18
3.4 Wall mounting ....................................................................................................... 19
3.4.1 TYA-110/3, 025..100 .............................................................................................. 19
3.4.2 TYA-110/3,150 and TYA-110/3, 250 ...................................................................... 20
3.5 DIN rail mounting ................................................................................................. 21
3.5.1 TYA-110/3, 025 ..100 ............................................................................................. 21
4 Electrical connection ........................................................................ 23
4.1 Connection diagram ............................................................................................ 23
4.1.1 Type TYA-110/3, 025, - 050, - 075, - 100, ... .......................................................... 25
4.1.2 Type TYA-110/3, 150, ... ......................................................................................... 25
4.1.3 Type TYA-110/3, 250, ... ......................................................................................... 25
4.2 Single-phase operation: line/phase – N ............................................................. 26
4.3 Single-phase operation: phase – phase ............................................................. 27
4.4 Star configuration: with star point connected to N .......................................... 28
4.5 Open delta configuration (six-wire circuit) ........................................................ 29
Power units 02.06 3
Page 4

Contents
4.6 Free-running economy circuit, purely resistive loads ....................................... 30
4.7 Master-slave economy circuit, with resistive/inductive loads ......................... 31
5 Commissioning ................................................................................. 33
5.1 Adjust control input (full wave) ........................................................................... 33
5.1.1 Setting the maximum power output ....................................................................... 33
5.1.2 Input signal attenuator ........................................................................................... 33
5.2 Setting the base load ........................................................................................... 34
5.3 Setting the current limit ....................................................................................... 35
5.3.1 Alteration of the current limit Imax, as a function of the voltage on Terminal 9 ..... 36
5.4 Setting the phase angle for the first half-wave ................................................. 36
5.5 Load and part-load failure monitoring ............................................................... 37
5.5.1 Setting the threshold for load failure indication ................................................ 37
5.5.2 Setting for master-slave and free-running economy circuit ............................ 38
5.6 External changeover of operating modes ......................................................... 38
5.7 Blown fuse indication .......................................................................................... 38
6 Settings .............................................................................................. 39
6.1 Opening the housing ............................................................................................ 39
6.2 Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503 / X504 .......................... 40
6.3 Summary of possible settings ............................................................................ 42
6.4 Control inputs ....................................................................................................... 43
6.4.1 Combinations of external potentiometer and electronic controller ........................ 44
6.5 Subsidiary control loops ...................................................................................... 45
6.6 Actual (power) output .......................................................................................... 46
6.7 Load current adaptation (only with extra code TR/T0) ..................................... 47
6.8 Select operating modes and load types ............................................................ 47
6.9 Economy circuit .................................................................................................... 48
6.9.1 Free-running economy circuit (asynchronous switching) for resistive loads ......... 49
6.9.2 Master-slave economy circuit (synchronous switching) for resistive and transformer
loads 49
6.10 Firing-pulse inhibit ............................................................................................... 50
7 Technical data ................................................................................... 51
7.1 Load circuit ........................................................................................................... 51
7.2 Control ................................................................................................................... 51
7.3 General data ......................................................................................................... 51
4 Power units 02.06
Page 5

Contents
8 Faults .................................................................................................. 53
8.1 Fault-finding .......................................................................................................... 53
8.2 Replacing the semiconductor fuse .................................................................... 53
8.2.1 Type TYA-110/3, 025 to 100, ... .............................................................................. 53
8.2.2 Type TYA-110/3, 150, ... ......................................................................................... 54
8.2.3 Type TYA-110/3, 250, ... ......................................................................................... 54
Power units 02.06 5
Page 6

Contents
6 Power units 02.06
Page 7

1.1 Preface
B
1 Introduction
Please read these operating instructions before starting up the instrument.
Keep them in a place that is accessible to all users at all times.
Please help us to improve this manual.
Your suggestions will be welcome.
Fax: in Germany (0661) 6003-862
abroad +49 661 6003-607
H
H
If any difficulties arise during commissioning, you are asked not to
carry out any unauthorized manipulation. You could endanger your
rights under the instrument warranty!
Please contact the nearest subsidiary or the main factory in such a
case.
When returning chassis, modules or components, the regulations
of EN 100 015 “Protection of electrostatically sensitive components” must be observed. Use only the appropriate ESD packaging for transport.
Please note that we cannot accept any responsibility for damage
caused by ESD (electrostatic discharge).
Power units 02.06 7
Page 8

1 Introduction
1.2 Typographical conventions
1.2.1 Warnings
The signs for Danger and Caution are used in this manual under the following
conditions:
Danger
This symbol is used where there may be danger to personnel if the instruc-
V
A
E
tions are disregarded or not followed accurately!
Caution
This symbol is used where there may be damage to equipment or data if the
instructions are disregarded or not followed accurately!
Caution
This symbol is used if precautions must be taken when handling electrostati-
cally sensitive components.
1.2.2 Note signs
Note
H
v
1
abc
h Handling instructions
This symbol is used to draw your special attention to a remark.
Reference
This symbol refers to additional information in other manuals, chapters or
sections.
Footnote
Footnotes are comments that refer to specific parts of the text. Footnotes
consist of two parts:
1) The marking in the text, arranged as continuous superscript numbers.
2) The footnote text at the bottom of the page, in a smaller typeface than the
main text, and preceded by a number and a stop.
This symbol marks the description of a required action.
The individual steps are indicated by asterisks, for example:
h Disconnect the instrument completely from the supply
h Remove the instrument cover
8 Power units 02.06
Page 9

1 Introduction
1.3 Description
Application A thyristor power unit can be used wherevere sizeable resistive or inductive
loads are switched frequently – for instance, in industrial furnaces and plastics
processing.
Operating modes
Regulation Variations in the line supply voltage have no effect on the control-loop regula-
Versions The power stage is composed of 2 thyristors connected in anti-parallel, the in-
Standards The thyristor power units meet VDE 0160 5.5.1.3 (5/88) and VDE 0106 Part 100
The thyristor power units can operate under phase-angle control with adjustable current limiting or in burst-firing mode, depending on the setting of the internal switch. An external switch may also be used to change over the operating mode. In burst-firing mode, the phase angle can be cut back for the first
half-cycle, for driving transformer loads.
tion during operation. This is ensured by a subsidiary V
An input signal attentuator (trimmer) permits the restriction of the control
range, and a base load can be set by an external potentiometer. In burst-firing
mode an economy circuit can be used for multi-phase loads. With phase-angle control, the target phase angle that is set by the controller is gradually approached from the initial 180°, thus avoiding high surge currents (soft start).
sulated heatsink, and the control electronics. Thyristor units for up to 50A rated load can either be snapped onto a 35mm DIN rail, or mounted on a basplate fixed to a wall. Units for 75A or higher rated load can only be wallmounted.
(3/83). Earthing must be carried out in accordance with the regulations of the
local electrical supply utility.
2
, P or I2 control loop.
1.4 Type designation
The basic version, TYA-110/3, includes the following features:
- Voltage, current and potentiometer input
- Input signal is freely selectable
- Operating mode is freely selectable
- Phase-angle reduction of 1st half-wave for burst-firing operation
- Supply line voltage monitoring
- Input signal attentuation by trimmer
- Soft start in phase-angle operation
2
-V
-control with adjustable power level output signal
- Master-slave economy circcuit
- Firing-pulse inhibit
Power units 02.06 9
Page 10

1 Introduction
TYA-110/3 , . . . , . . . , . . Thyristor power unit for analog control
025 Load current 25A
050 Load current 50A
075 Load current 75A
100 Load current 100A
150 Load current 150A
250 Load current 250A
024 Rated load voltage 24V
042 Rated load voltage 42V
115 Rated load voltage 115V
230 Rated load voltage 230V
265 Rated load voltage 265V
400 Rated load voltage 400V
460 Rated load voltage 460V
500 Rated load voltage 500V
TR Indication of part-load failure or blown fuse through
built-in relay and LED.
TO Indication of part-load failure or blown fuse through
optocoupler
MS Master-slave circuit
2 pre-assembled power units on a mounting plate,
ready for connection
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1. Rated load voltage = supply voltage for the control electronics
1.4.1 Type extensions (extra codes)
TR Extended version, with indication of part-load failure (adjustable by trimmer) or
blown fuse through common relay contact and LED.
This version also includes:
- Current limiting (internal, external) and rated current adjustment at I ≤ I
2
- Free selection of the subsidiary control-loop type (V
, I2 or P).
/2
N
A free-running economy circuit can be implemented with P-control!
2
- Power level output signal can be switched to: V
, P, I
2
TO as for TR, but with signaling via optocoupler
MS Master-slave circuit: 2 pre-assembled power units on a mounting plate, ready
for connection.
1.4.2 Standard accessories
1 Mounting plate for wall-mounting
1 Operating Instructions
10 Power units 02.06
Page 11
1.4.3 Accessories
Super-fast semiconductor fuses to protect the thyristors from short-circuits
(no supply line fusing).
1 Introduction
32A for I
80A for I
125A for I
160A for I
350A for I
550 A for I
Assembly kit for DIN rail mounting, for 25A and 50A versions,
Sales No. 70/00067312
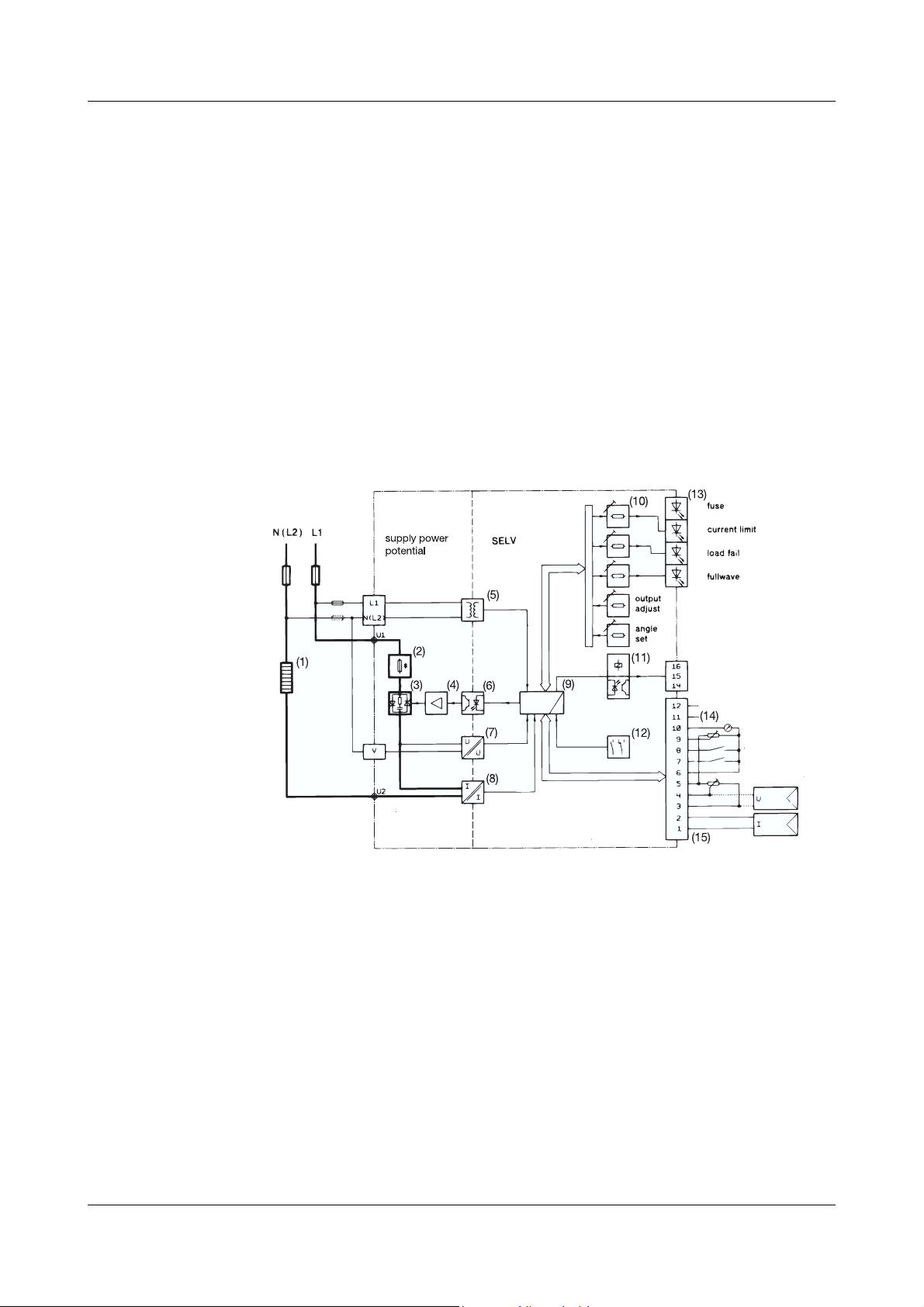
1.5 Block diagram
= 25A, Sales No. 70/00068009
N
= 50A, Sales No. 70/00068011
N
= 75A, Sales No. 70/00081800
N
= 100A, Sales No. 70/00081801
N
= 150A, Sales No. 70/00083318
N
= 250A, Sales No. 70/00371964
N
(
(1) Load (9) Control electronics
(2) Super-fast semiconductor fuse (10) Trimmer on front panel
(3) Thyristor module with RC
protection network
(4) Driver stage for thyristor module (12) Configuration switch
(5) Power supply for control electronics (13) Signal LEDs
(6) Optocoupler (14) Master-slave connections
(7) Voltage converter (15) Output level setting, operating inputs,
(8) Current transformer
(11) Error signal output
via relay or optocoupler
power level output signal
Power units 02.06 11
Page 12
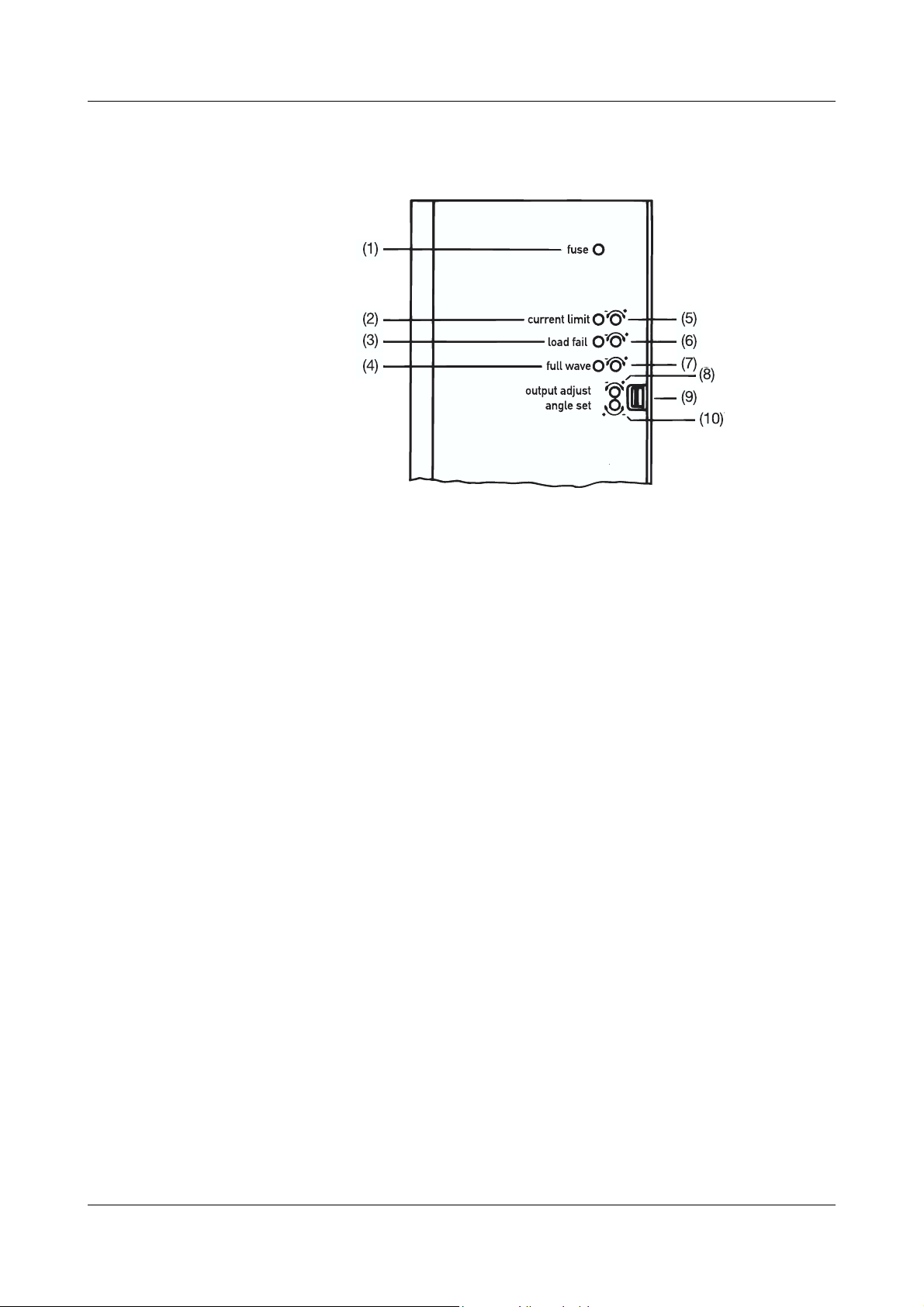
1 Introduction
1.6 Front panel indicators and adjustments
Indicator LED for blown semiconductor fuse
(1)
LED for current indication
(2)
LED for load-failure indication
(3)
LED for full-output indication
(4)
Adjustment of current limit in phase-angle
(5)
operation (with extra code TR or TO)
Adjustment of threshold for part-load failure
(6)
indication (with extra code TR or TO)
Adjustment of full output
(7)
Adjustment of power level signal
(8)
Spring clip to release cover
(9)
Adjustment of phase-angle reduction for 1st half-
(10)
wave in burst-firing operation
12 Power units 02.06
Page 13
2 Operating modes
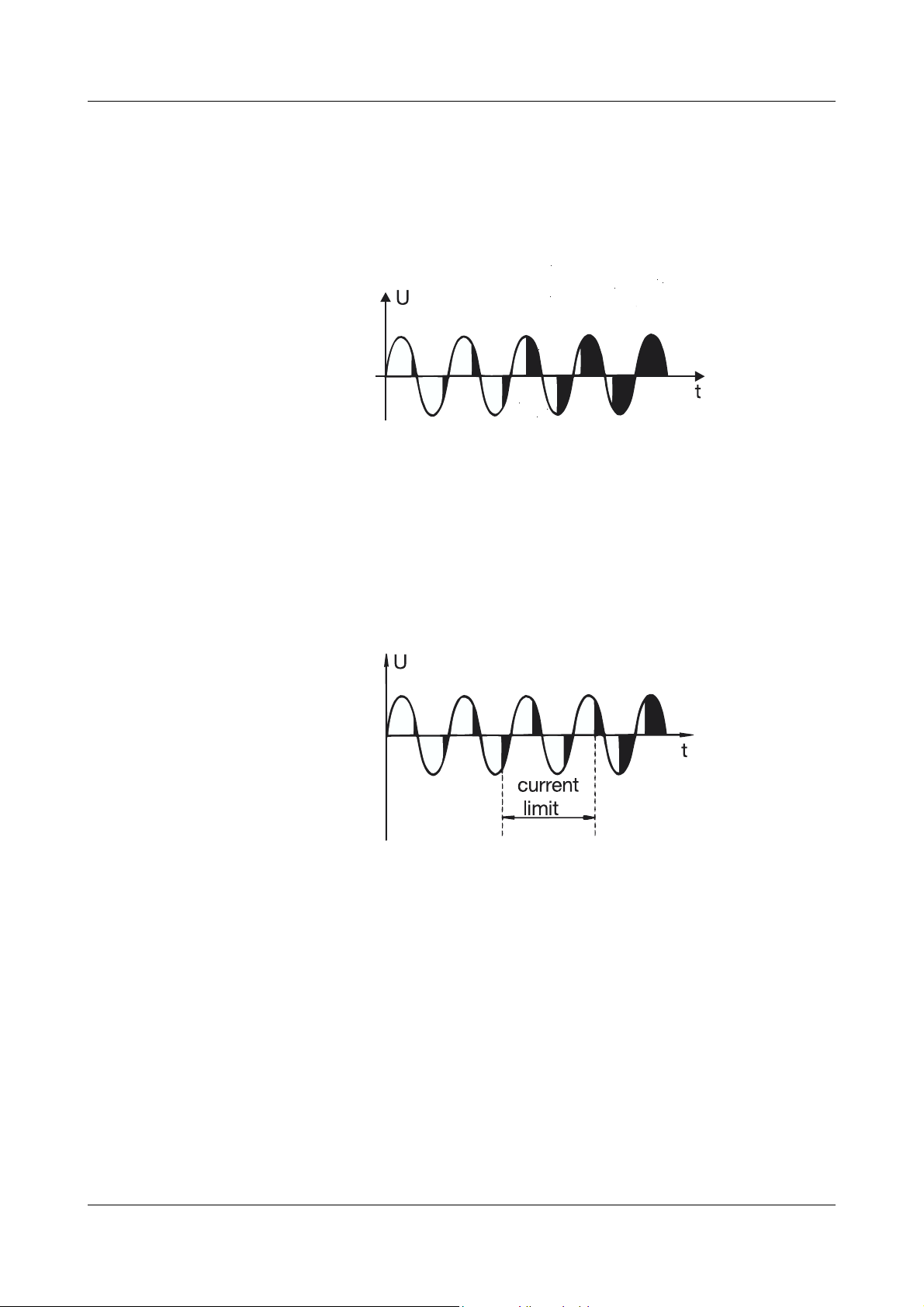
2.1 Phase-angle control with soft start and current limiting
In this mode of operation, the power is regulated by altering the phase angle.
This method is suitable for transformer and resistive loads. During the switchon period the phase-angle is gradually advanced by the controller to provide a
soft start. This prevents high surge currents at switch-on.
Current limiting For loads with an initial (cold) resistance that is significantly lower than the re-
sistance after warming up, such as Kanthal-Super heater elements, it is advisable to make use of current limiting (only with extra code TR or TO).
While current limiting is in operation, the phase angle during soft start remains
constant.
The maximum permissible effective (rms) current can be adjusted on the front
panel, by using the “current limit” trimmer.
v Section 5.3 “Setting the current limit”
Power units 02.06 13
Page 14
2 Operating modes
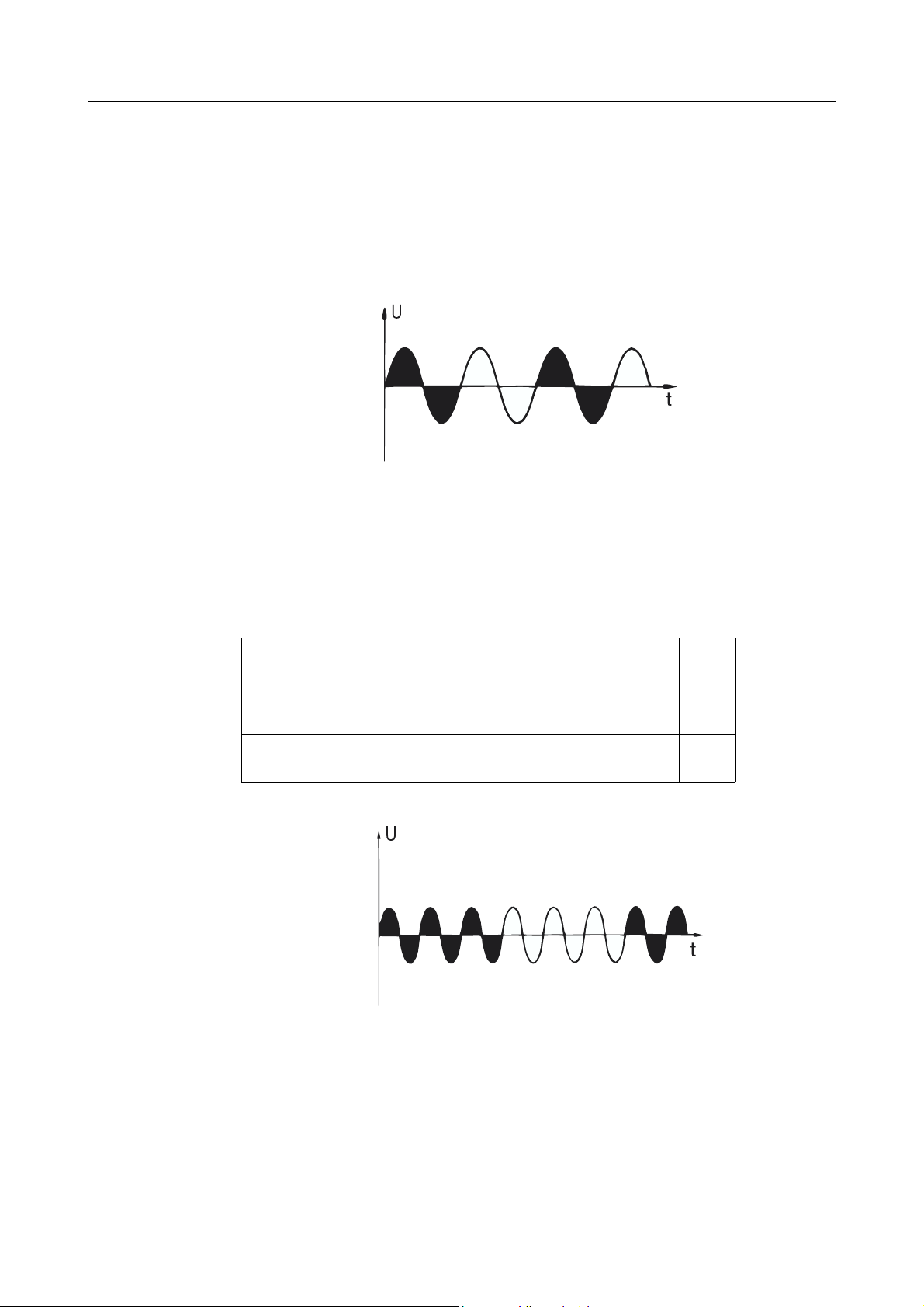
2.2 Burst-firing operation, for resistive loads
In this mode of operation, the power is regulated by changing the number of
full-wave cycles of the supply line voltage which are switched on during each
control period. This method is used for purely resistive loads which have a
cold resistance that is roughly the same as the hot resistance.
Since switching only takes place at the zero-crossing points, this mode of
operation produces very little RF-interference.
The internal switch S20 can be used to adjust the duty cycle to suit the system
being controlled.
v Section 6.2 “Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503 / X504”
Cycle time S 20
Variable cycle time
The control unit uses the shortest available cycle time
(for fast control loops)
Fixed cycle time (≈ 500ms)
Used for transformer loads, slow control loops
1
2
14 Power units 02.06
Page 15
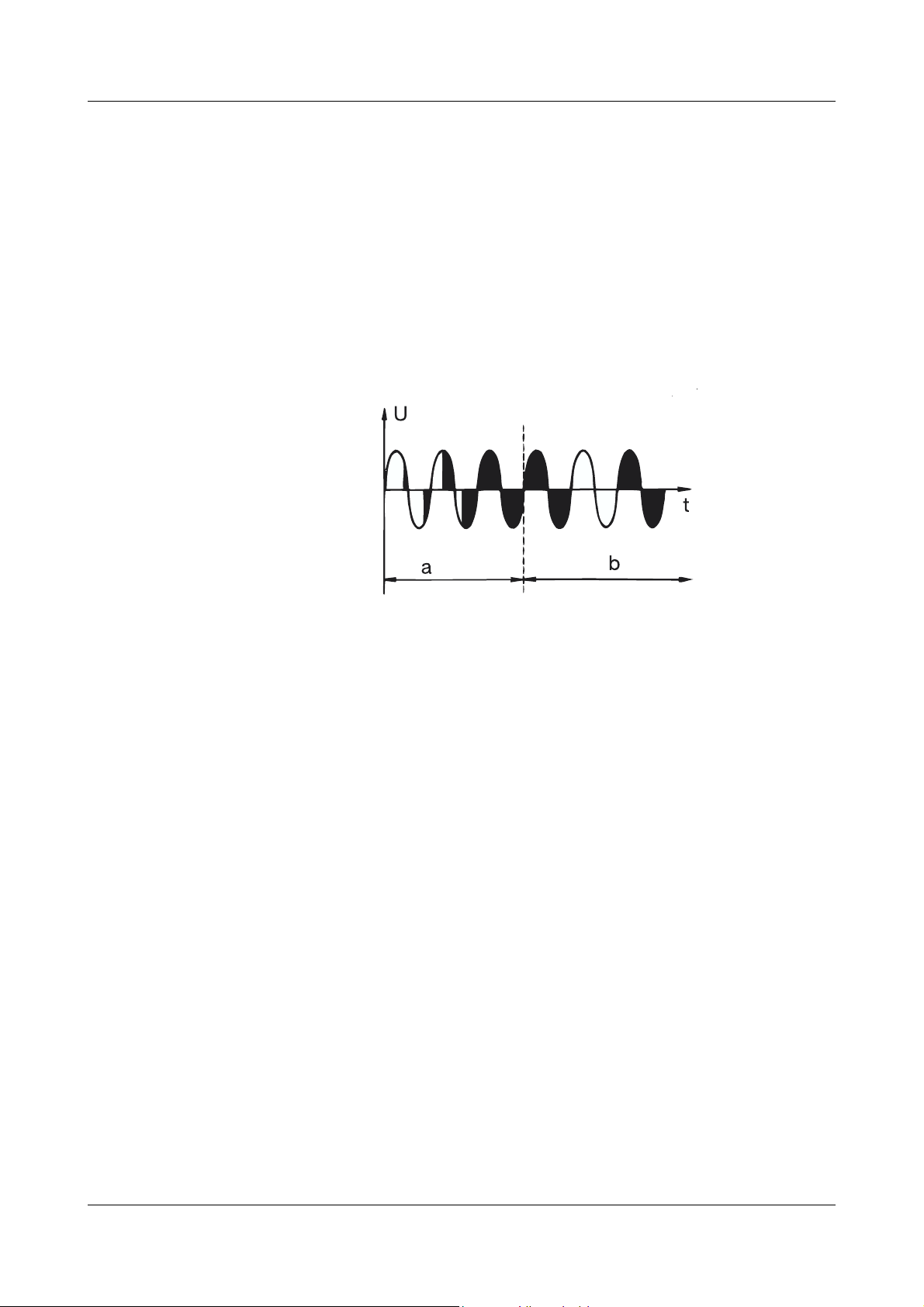
2 Operating modes
2.3 Burst-firing operation for transformer loads and loads with a high positive temperature coefficient TC (mixed operation)
It is not possible to change over to phase-angle control in this
H
Soft start For the first switch-on of the thyristor power unit, or after being switched off by
inhibiting the firing-pulses, after a supply line interruption, or if the setpoint
was switched off for more than 8seconds, there will always be a short phaseangle controlled start (area a in the diagram).
mode of operation.
After this soft start, the controller switches over automatically to burst-firing
operation if the given setpoint is larger than the minimum setpoint + 10% of
the setpoint range (area b in the diagram).
Example:
Setpoint range 2 — 10V
The changeover to burst-firing operation takes place at
2V + 10% of 8V = 2V + 0.8V = 2.8V
After this changeover, the power output is regulated to follow the setpoint input provided.
H
1. with extra codes TR/TO
If the power unit runs into current limiting1 during the phase-angle
controlled start, then the output is regulated according to the maximum current given by the curent limit setting, even for low levels of
the setpoint input.
Power units 02.06 15
Page 16
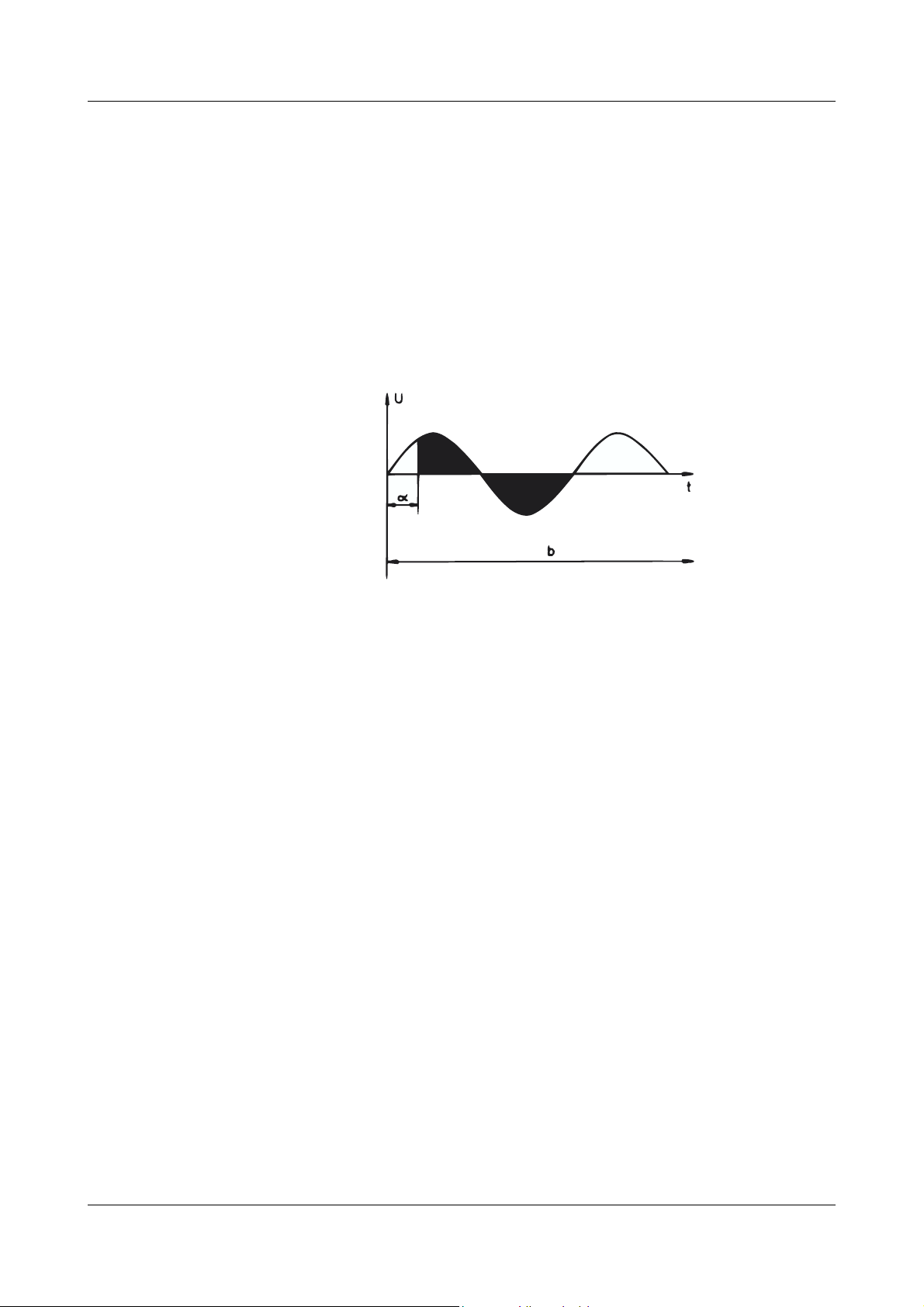
2 Operating modes
For transformer loads, the thyristor power unit operates in burst-firing mode
with a cut-back (retarded) phase-angle for the first half-wave. The factory setting is an angle α = 90°. This value can be altered on the front panel over a
range α = 0 — 90°.
v Section 5.4 “Setting the phase angle for the first half-wave”
H
We recommend that this setting is not changed!
16 Power units 02.06
Page 17

3.1 Important installation notes
3 Installation
Safety regulations
Fusing - In the event of a short-circuit in the load circuit, the power unit is protected
V
Interference suppression
Wiring Load and control cables should be laid separately, as far as feasible.
- The choice of cable, installation and electrical connection of the instrument
must meet the requirements of VDE 0100 “Regulations for the Installation of
Power Circuits with nominal voltages below 1000 V AC” or the
corresponding local regulations.
- Electrical installation must only be performed by properly qualified
personnel.
- The unit must be completely disconnected from the supply line (on all
poles) if there is a risk of contact with live parts during work on the unit.
by the built-in semiconductor fuse.
v Section 8.2 “Replacing the semiconductor fuse”
- Do not connect any additional loads to the output load terminals.
- The electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) meets the standards and
regulations cited in the technical data.
v Section 7 “Technical data”
The appropriate fuses for control circuitry (e.g. 2A, type Neozed) should be
used to protect the wiring.
Connections h Check the data given on the nameplate (rated load voltage, load current)
against the data for the system.
h Wire up the connections from supply line – thyristor power unit – load
according to the wiring diagram, and check them
h If the economy circuit configuration is used, check that the rotary electrical
field has clockwise phasing.
h Check the settings for the setpoint inputs
h Check the switch positions
Supply voltage h Connect the supply voltage for the control electronics as shown in the wi-
ring diagram.
h Link “N/L2” to “V”, unless the economy circuit is being used (slave unit).
Load connection
Phasing The supply voltage for the control electronics and the load voltage must
The electronic switching devices (2 antiparallel thyristors) are in circuit between the screw connections “U1” and “U 2”.
have the same phase.
h Terminal “L1” must be connected, via a control circuitry fuse, to the same
supply potential as terminal “U1”!
Power units 02.06 17
Page 18

3 Installation
Switch-on sequence
Control inputs The control connections (inputs and outputs) are designed for safety sepa-
The supply voltages for the load and control circuitry must be switched on
at the same time.
In no circumstances should the supply voltage for the control
A
ration from the supply line input (SELV). In order not to diminish this safety
separation, all connected circuits must also have safety separation. The
auxiliary voltages which are required must be safe extra-low voltages
(SELV).
electronics be switched on before the voltage for the load!
This is especially important for operating transformer loads and re-
sitive loads with a large variation between hot and cold resistance!
Connections must only be wired up by properly qualified
personnel!
V
3.2 Filtering and interference suppression
In order to prevent radio-frequency interference, such as would occur with
phase-angle control, electrical apparatus and systems must have interference
suppression implemented.
The control electronics of the thyristor power units conforms to the EMC Directive EN 61 326.
However, modules such as thyristor power units have no use by themselves,
but only as a component function within a system. For this reason, the load
circuit of the power unit must have suitable interference suppression filters fitted by the system provider.
Specialist companies have appropriate ranges of filters available to deal with
these problems. Such filters are normally supplied as complete modules that
are ready to be connected up.
3.3 Installation site and climatic conditions
The installation site should be, as far as possible, free from vibration. Electromagnetic fields, caused by equipment such as motors and transformers,
should be avoided. The ambient temperature at the installation site must be
within the range 0 to 45°C (measured about 100 mm below the unit) and the
relative humidity must be
in dry rooms. The inside of the unit must be kept free from conductive dirt and
corrosive gases.
≤ 75%. The thyristor power unit is intended for use
The thyristor power unit must be mounted vertically, to ensure good convection cooling. If it is mounted in a switchgear cabinet, adequate ventilation must
be provided. There must be at least 100 mm free space below, and 150 mm
18 Power units 02.06
Page 19

3 Installation
above the unit. The thyristor power unit has enclosure protection IP00, and so
it must be mounted in such a way that bodily contact is prevented (built-in
unit).
V
The heatsink can become very hot in operation!
Incorrect use - The unit is not suitable for installation in areas with an explosion hazard
(Ex areas).
- The installation site should be free from vibration, dust, and corrosive
media.
Ambient conditions
3.4 Wall mounting
- Side-by-side mounting of units is permitted
- Relative humidity ⱕ 75 %, no condensation
- Ambient temperature range: 0 to 45 °C
Storage temperature range: -10 to 70 °C
h Fix the aluminium mounting plate to the heatsink, using the cheese-head
screws provided.
h Fix the thyristor power unit with its mounting plate to the wall, using four
screws.
3.4.1 TYA-110/3, 025..100
Power units 02.06 19
Page 20

3 Installation
3.4.2 TYA-110/3,150 and TYA-110/3, 250
20 Power units 02.06
Page 21

3.5 DIN rail mounting
h Fix the DIN rail
h Snap the thyristor power unit and its mounting plate onto a standard rail (to
DIN EN 50 022) and lock it in place with the lever. This type of mounting is
only possible for thyristor power units up to 50A rated current.
3.5.1 TYA-110/3, 025 ..100
3 Installation
Power units 02.06 21
Page 22

3 Installation
22 Power units 02.06
Page 23

4.1 Connection diagram
V
The diagram shows the various connections that are available at the plug-in
screw terminals.
4 Electrical connection
Only properly qualified personnel are permitted to make electrical
connections!
h Disconnect the equipment completely (on all poles) from the supply line
h Connect the control cables (conductor cross-section 0.2 — 2.5 mm
screw terminals. Use cable lugs to DIN 46 212 for the load connections.
Tools required 1 screwdriver, 3 mm blade (max.)
1 socket wrench, 10 mm (for TYA-110/3, 100)
1 socket wrench, 13 mm ( for TYA-110/3,150 and TYA-110/3, 250)
Power units 02.06 23
2
) to the
Page 24

4 Electrical connection
Connection for Pin assignment Symbol
Supply voltage for control electronics;
link V to N/L2, unless economy circuit is being used
Load connection U1
L1 (line / phase 1)
N/L2 (neutral / phase 2)
V
U2
Current input
(differential input)
Voltage input
(referred to ground)
Logic input Current signal 0/20 mA 1-
Voltage signal 0/10 V 3⊥
Floating contact 4+
External manual adjustment with 5 kΩ potentiometer
(via voltage input)
Firing-pulse inhibit input I
(make or break contact)
Load-failure output with relay,
switching capacity 5A at 230 V AC, resistive load.
Relay drops out if fault occurs.
(extra code TR)
≈ 1mA
K
12+
3⊥
4+
2+
4+
5 (+10V, 2 mA)
3Start (⊥)
4Slider
5 End (+10V, 2mA)
6⊥
7+
16 P pole
15 O break contact
14 S make contact
or
Load failure output with optocoupler
I
= 2mA U
Cmax.
(extra code TO)
External changeover of operating mode
(phase-angle or burst-firing operation)
Actual (power) output 0 — 10V
I
≈ 2mA
max
Master-slave connection for
master-slave economy circuit
External current limiting
with 5 kΩ potentiometer
CEO max.
= 32V
15 Collector
16 Emitter
6⊥
8+
10+
6⊥
6⊥
11
12
5 Start (+10V, 2mA)
6 End (⊥)
9 Slider
24 Power units 02.06
Page 25

4.1.1 Type TYA-110/3, 025, - 050, - 075, - 100, ...
4.1.2 Type TYA-110/3, 150, ...
4 Electrical connection
4.1.3 Type TYA-110/3, 250, ...
Power units 02.06 25
Page 26

4 Electrical connection
4.2 Single-phase operation: line/phase – N
UL = phase-phase voltage P
= phase-neutral voltage IL = current in phase conductor
U
N
U
= voltage on thyristor power unit I
Thy
= total controlled power
tot
= current in thyristor power unit
Thy
26 Power units 02.06
Page 27

4 Electrical connection
4.3 Single-phase operation: phase – phase
UL = phase-phase voltage P
U
= phase-neutral voltage IL = current in phase conductor
N
= voltage on thyristor power unit I
U
Thy
= total controlled power
tot
= current in thyristor power unit
Thy
Power units 02.06 27
Page 28

4 Electrical connection
4.4 Star configuration: with star point connected to N
UL = phase-phase voltage P
U
= phase-neutral voltage IL = current in phase conductor
N
U
= voltage on thyristor power unit I
Thy
= total controlled power
tot
= current in thyristor power unit
Thy
28 Power units 02.06
Page 29

4 Electrical connection
4.5 Open delta configuration (six-wire circuit)
UL = phase-phase voltage P
= phase-neutral voltage IL = current in phase conductor
U
N
U
= voltage on thyristor power unit I
Thy
= total controlled power
tot
= current in thyristor power unit
Thy
Power units 02.06 29
Page 30

4 Electrical connection
4.6 Free-running economy circuit, purely resistive loads
Only possible in burst-firing mode with P-control
U
= phase-phase voltage P
L
U
= phase-neutral voltage IL = current in phase conductor
N
= voltage on thyristor power unit I
U
Thy
= total controlled power
tot
= current in thyristor power unit
Thy
30 Power units 02.06
Page 31

4 Electrical connection
4.7 Master-slave economy circuit, with resistive/inductive loads
Only possible in burst-firing mode
UL = phase-phase voltage P
= phase-neutral voltage IL = current in phase conductor
U
N
U
= voltage on thyristor power unit I
Thy
= total controlled power
tot
= current in thyristor power unit
Thy
Power units 02.06 31
Page 32

4 Electrical connection
32 Power units 02.06
Page 33

5.1 Adjust control input (full wave)
The trimmer (7) “full wave” on the front panel can be used to adjust the thyristor power unit so that the 100% (full wave) firing point is reached at the maximum output signal of the preceding controller.
5 Commissioning
5.1.1 Setting the maximum power output
h Apply the maximum controller output signal
h Turn the “full wave” trimmer clockwise or counter-clockwise until the green
LED for “full wave” just light up in phase-angle control, and does not light
up in burst-firing mode.
H
When using a logical control output (e.g. from a single-setpoint
controller) the “full wave” trimmer must be turned fully clockwise.
5.1.2 Input signal attenuator
h Turning the “full wave” trimmer counter-clockwise limits the maximum
power output of the thyristor power unit.
When using the free-running economy circuit, both thyristor power units
must be adjusted as described above.
When using the master-slave economy circuit, the adjustment is only made
on the master power unit.
v Section 4.6 “Free-running economy circuit, purely resistive loads” und
Section 4.7 “Master-slave economy circuit, with resistive/inductive loads”
Power units 02.06 33
Page 34

5 Commissioning
5.2 Setting the base load
A base load can be set, in addition to the analog current input and the potentiometer input. Since these input signals are added together, the input signal
gain must be corrected by adjusting the “full wave” trimmer (7).
For instance, if a heating system is to be operated with a 33% base load, with
the other 66% of the output being regulated by the controller, then the procedure is as follows:
Calculate the reduction factor of the controller signals.
In this example it would be 100% : 66% = 1.5.
Multiply this factor by the intended base load setting.
In this case: 1.5 x 33% = 50%.
The factor 0.5 means that the external potentiometer must be set to 50% of
the full-scale value.
Adjustment:
h Set the potentiometer to the calculated fraction of the full scale (e.g. 50%)
h Apply the maximum current (e.g. 20mA) to the current input
h Turn the “full wave” trimmer clockwise or counter-clockwise until the green
LED for “full wave” just light up in phase-angle control, and does not light
up in burst-firing mode.
34 Power units 02.06
Page 35

5.3 Setting the current limit
5 Commissioning
Internal current limiting
Current limiting is only possible in the phase-angle mode of control.
h The trimmer (5) “current limit” on the front panel can be used to limit the
effective (rms) value of the load current over a range from 10 — 100% of
the rated current for the thyristor control unit (I
1.5 turns clockwise correspond to increasing the threshold by about 10%
of the rated current.
The red LED lights up when the current limit is reached. Current limiting is
achieved by limiting the “ON” phase angle so that the set value for effective
current is not exceeded.
ThyN
).
External current limiting
An external voltage signal in the range 0 — 10 V can be applied to Terminal 9
to influence the internal current limit I
0V means no effect, 10 V means the maximum effect (the threshold is reduced
to the smallest value possible).
set by the “current limit” trimmer.
max
Power units 02.06 35
Page 36

5 Commissioning
5.3.1 Alteration of the current limit Imax, as a function of the voltage on Ter m i n al 9
With an internal limit of, for example, I
variation is only 0 to 8V.
= 0.8 x I
max
5.4 Setting the phase angle for the first half-wave
In the mode “burst-firing with phase-angle controlled start” the thyristor power
unit retards the firing point for the first half-wave after the start in burst-firing
mode.
The factory setting is an angle α = 90°(electrical). This value can be altered
over the range α = 0 — 90°by the trimmer (10) “angle set”.
The factory setting will be satisfactory in most cases.
, the external range of
Thy
If it is nevertheless necessary to make an adjustment, then the
H
Counter-clockwise (left) = advance the firing angle α
Clockwise (right) = retard the firing angle α
36 Power units 02.06
minimum switch-on current at the start of the burst is the criterion
for setting the angle α.
Page 37

5.5 Load and part-load failure monitoring
This function is only available with the extra code TR or TO. If there is a
change in the load resistance during operation, this is detected and indicated
by the part-load failure monitoring.
The signal output is available either as a floating contact (extra code TR) or an
optocoupler (extra code TO). If a part-load fault occurs, the relay drops out or
the collector-emitter of the optocoupler goes high-impedance. The signal output is also produced if there is a blown fuse.
The response threshold can be set by the front-panel trimmer (6) “load fail” to
a value between 20 and 100% of the rated current for the power unit. Partload failure monitoring functions in all operating modes.
5 Commissioning
H
v Section 6.2 “Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503 / X504”
The load/part-load failure monitoring (low current monitoring) can
also be used for overcurrent monitoring. To implement this, remove
the two jumpers on pin header X504, next to the “angle set” trimmer, turn them through 90° and replace.
5.5.1 Setting the threshold for load failure indication
(Factory setting is 50% of rated load)
h Connect up the load
h Apply full power
h Set the “load fail” trimmer so that the yellow “load fail” LED just goes out.
- turn clockwise (right) = LED lights up
- turn counter-clockwise (left) = LED goes out
h If necessary, the threshold can be reduced by further counter-clockwise ro-
tation, whereby 1.5 turns of the trimmer potentiometer correspond to a load
change of about 10% of the rated curent for the thyristor power unit.
If the load current is below the rated current of the power unit, then the number of turns required is reduced in the same proportion.
If load current I
v Section 6.3 “Summary of possible settings”
< 0.5 x I
L
then internal switch S15 must be in position 0.
ThyN
Power units 02.06 37
Page 38

5 Commissioning
Alternative setting:
Simulate a load failure, and then adjust the “load fail” trimmer so that the yellow “load fail” LED just lights up.
5.5.2 Setting for master-slave and free-running economy circuit
When using master-slave and free-running economy circuits, the
H
H
5.6 External changeover of operating modes
For this to be possible, an external switch must be wired between Terminal 8
and Terminal 6.
settings must be made in both thyristor power units.
The smallest change of resistance that can be detected is 5% of
the nominal load resistance (10% in an economy circuit).
Switch Operating mode
open burst-firing mode
closed phase-angle control
The external switch can only be used to change from burst-firing to
H
If the switches S12 and S13 are closed, an external changeover to phaseangle control is not possible.
v Section 6.3 “Summary of possible settings”
phase-angle control when the internal switch S3 is open, since this
switch is in parallel with the external switch S.
5.7 Blown fuse indication
If a short-circuit occurs, the built-in semiconductor fuse switches within half a
supply cycle, to protect the thyristors. When the fuse is blown, the “fuse” LED
lights up,
v Section 8.2 “Replacing the semiconductor fuse”
With extra code TR or TO, an output signal is also available.
v Section 4.1 “Connection diagram”
38 Power units 02.06
Page 39

6.1 Opening the housing
Adjustments must only be made while the unit is disconnected
from the supply power!
V
It is easier if these adjustments are carried out before the unit is installed.
h Use a screwdriver to lever the spring fixing lug outwards.
On the 150 A and 250 A versions: press both spring lugs inwards.
h Pull off the cover from the front.
6 Settings
Power units 02.06 39
Page 40

6 Settings
6.2 Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503 / X504
The switches S1 to 21 can be found on the back of the printed circuit board.
It is easier to access switches S15, S16 and S21 if the plug-in
H
40 Power units 02.06
screw terminals are first pulled off downwards.
Page 41

6 Settings
Power units 02.06 41
Page 42

6 Settings
6.3 Summary of possible settings
Switch position
Switch number
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
factory setting 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1
job-specific setting
Control input
0 — 20mA 1 0 0 1
4 — 20 mA 0 0 0 2
0 — 10V 1 0 0 1
2 — 10V 0 0 0 2
0 — 5V 1 0 1 1
1 — 5V 0 0 1 2
Logic signals 0/10V, 0/5V,
0 1 1 2 1
0/20mA or floating contact
Subsidiary control loop
2
V
1 0 0
P 0 1 0
2
I
0 0 1
Actual power output
2
V
1 0 0
P 0 1 0
2
I
Load current adaptation I
IL < 0.5 · I
IL ⱖ 0.5 · I
ThyN
ThyN
L
0 0 1
0
1
Firing-pulse inhibit
-external make contact 1
-external break contact
Operating mode:
Phase-angle control
for transformer/resistive load 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
Burst-firing mode:
■ for resistive load 0 1 0 1 1 1
■ for transformer load 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
- R ≈ constant 0 0
R
w
- > 1(soft start)
-----R
K
1 1
- fixed cycle (500ms) 2
- variable cycle 1
Economy circuit
(free-running)
■ for resistive load 0010 1 0001 11
(Master-slave)
-master, resistive load 0 1 0 1 1 1 1
2
-slave
, resistive load 0 1 0 0 22 1
-master, transformer load
2
-Slave
1. S5, S6, S8, S9, S15 only have an effect with extra code TR or TO.
2. The jumpers on pin header X503 must be turned through 90°. Section 6.2 “Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers
X503 / X504”. A changeover to phase-angle control is not possible for burst-firing mode with a transformer load and soft start.
, transformer load 0 0 1 1 1 0 2 2 2 1
0 0 1111 11 2 1
v Section 2.3
2
42 Power units 02.06
Page 43

6.4 Control inputs
The internal switches S1, S2, S 16, S19, S20 can be used to adapt the thyristor power unit to suit the available control signal (controller output signal).
There are separate voltage and current control inputs. The current inputs (+,-)
are designed for a differential current signal, i.e. they can have a common potential that is up to 10V above or below the ground reference potential (⊥).
If the current and voltage inputs are used simultaneously, they have an additive effect. Both analog and logical controller output signals may be used.
Control signal Internal switch
Signal start Signal end S1 S2 S16 S19 S20
0 mA 20 mA 1 0 0 1
4 mA 20 mA 0 0 0 2
0 V 10 V 1 0 0 1
2 V 10 V 0 0 0 2
0 V 5 V 1 011
1 V 5 V 0012
logic levels 0/10V 0/5V, 0/20mA or
floating contact
6 Settings
01121
Analog control inputs
The thyristor power unit can be operated by the following signals (for analog
power regulation):
- voltage signal (Terminals 3, 4)
- current signal (Terminals 1, 2)
-5 kΩ potentiometer (Terminals 3, 4, 5)
A 10 V source is provided at Terminal 5 for use with a potentiometer. The
switch settings are the same as for a 0 — 10 V signal.
Power units 02.06 43
Page 44

6 Settings
Logic control inputs
The thyristor power unit can also be operated by the following logical signals
(e.g. two-state/single-setpoint controller outputs):
(switching pulse bursts on or off):
- current signal 0/20mA (Terminals 1, 2)
- voltage signal 0/10V (Terminals 3, 4)
- floating contact (Terminals 4, 5)
6.4.1 Combinations of external potentiometer and electronic controller
Controller with current output
The voltage input (Terminals 3, 4) can be used together with the internal 10 V
source and a 5 kΩ potentiometer to provide manual setting.
Switch S
Automatic open open
Manual closed closed
a
S
b
To prevent unintended overdriving on the changeover to manual
H
operation, S
two signal sources will be added together for a moment.
should be mechanically coupled to Sb. Otherwise the
a
44 Power units 02.06
Page 45

6 Settings
Controller with voltage output
This only uses the voltage input of the thyristor power unit. A 5 kΩ potentionmeter is required on Terminals 3 and 5 for manual operation.
Switch S
Automatic operation position 1
Manual operation position 2
c
6.5 Subsidiary control loops
Subsidiary control loops are primarily used to eliminate or compensate external disturbances, such as supply-line fluctuations and changes in resistance
which would have a negative effect on the regulation. A subsidiary V
loop is set up ex-factory. With extra code TR or TO this can be changed to P
2
control. The free-running economy circuit must operate with a P control
or I
loop.
v Section 6.2 “Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503 / X504”
H
v Section 6.7 “Load current adaptation (only with extra code TR/T0)”
Control
type
2
V
With P or I2 control loops (extra code TR/TO) a load current adaptation must be made for operating currents that are less than half
the rated load current.
Internal switches Application
S4 S5 S6
100- positive TC,
2
control
- R ≈ constant
- brightness controls
Power units 02.06 45
Page 46

6 Settings
P 0 1 0 - temperature-dependent TC
- free-running economy circuit
2
I
0 0 1 - negative TC
6.6 Actual (power) output
The factory setting is that the actual (power) signal output corresponds to the
2
signal at the output of the power unit, and is therefore proportional to the
V
power in the load (R = constant). With the extra code TR/TO it can be switched
2
over to a P or I
v Section 6.3 “Summary of possible settings”
Actual (power) signal output Internal switches
2
V
P010
2
I
signal.
S7 S8 S9
100
001
Adjust output The signal at the actual (power) output is a voltage in the range 0 — 10V (cor-
responding to 0 — 100% of the particular measurement range). The trimmer
(8) “output adjust” can be used to adjust the range end value:
Action Response
Turn trimmer fully clockwise (right)
Turn trimmer fully counter-clockwise
(left)
H
v Section 6.7 “Load current adaptation (only with extra code TR/T0)”
With P or I2 control loops, a load current adaptation must be made
for operating currents that are less than half the rated load current!
Measurement range 0 — 100 %
corresponds to a signal 0 — 10V
Measurement range 0 — 100 %
corresponds to a signal 0 — 5V
46 Power units 02.06
Page 47

6 Settings
6.7 Load current adaptation (only with extra code TR/T0)
With P or I2 control, switch S15 must be in position 0 if the operating current is
less than half the rated current. This is to ensure proper measurement of the
load current for the subsidiary control loop, the current limiting, and the overcurrent / low current detection.
The factory setting must not be altered on the 150A and 250A
A
Load current adaptation Internal switch S 15
versions!
(Reserved for service purposes: 1A test mode)
< 0.5 x I
I
L
LL > 0.5 x I
ThyN
ThyN
k factory setting
6.8 Select operating modes and load types
The internal switches S3, S10 — S 13 and S20 are used to set the required
mode of operation.
In both phase-angle and burst-firing modes the thyristor power unit basically
operates with a subsidiary V
be changed over from V
v Section 6.5 “Subsidiary control loops”
Switch S3 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S17 S18 S19
Operating mode:
Phase-angle control
■ for resistive or
transformer load
2
control loop. With extra code T0 or TR this can
2
to P or I2 control.
1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
0
1
Burst-firing operation
■ resistive load
■ transformer load
- R ≈ constant
R
w
------
- > 1
R
K
- fixed cycle (500ms)
- variable cycle
0 1 0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
0 0
1 1
2
1
Power units 02.06 47
Page 48

6 Settings
It is not possible to change over to phase-angle control if S12 and S13 are
closed.
v Section 2.3 “Burst-firing operation for transformer loads and loads with a
high positive temperature coefficient TC (mixed operation)”
6.9 Economy circuit
Two single-phase units can be used at any time to implement an “economy
circuit” in a 3-phase system.
The switch settings that are required for this, depending on the type of load
and circuit, can be found in the table.
V
The thyristor power units must always be dimensioned for the
phase-phase voltage, regardless of whether the load is wired in a
star or delta configuration.
It is vital to ensure that the roating electrical field is right-handed,
i.e. clockwise rotation.
Terminal V must be linked to phase L2 on both power units.
v Section 4.6 “Free-running economy circuit, purely resistive loads” and
Section 4.7 “Master-slave economy circuit, with resistive/inductive loads”
48 Power units 02.06
Page 49

6 Settings
6.9.1 Free-running economy circuit (asynchronous switching) for resistive loads
A free-running economy circuit has the advantage that the average loading of
the supply network is reduced. Both power units operate independently and
regulate the required 3-phase power quite precisely. Even a possible part-load
failure will not necessarily have an effect on the temperature stability of the
control loop.
A subsidiary P control loop is required for both power units.
Switch S3 S4 S5 S6 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S17 S18 S20 S21
Economy circuit
(free-running)
■ resistive load 001010001112
(master-slave)
■ resistive load
- master function 0 1 0 1 1 1 1
- slave function 0 1 0 0 2 2 1
■ transformer load
- master function 0 011111121
- slave function 0 011102221
If S12 and S13 are closed, it is not possible to change over to phase-angle control.
v Section 2.3 “Burst-firing operation for transformer loads and loads with a
high positive temperature coefficient TC (mixed operation)”
6.9.2 Master-slave economy circuit (synchronous switching) for resistive and transformer loads
In the standard version, the master-slave economy circuit operates with a V
control. With extra code TO/TR it is also possible to use a P control and partload regulation. The control electronics of the master unit takes on the actual
power control function, and drives the slave unit in synchronization. This
makes it possible to drive transformer loads.
The combination of the fixed cycle time of the V
configuration makes it possible to achieve good voltage regulation for the individual load resistances, even in the event of a part-load failure.
v Section 4.7 “Master-slave economy circuit, with resistive/inductive loads”
The jumpers on pin header X503 of the slave unit must be turned
H
through 90° !
v Section 6.2 “Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503
/ X504”
2
control and the delta load
2
Power units 02.06 49
Page 50

6 Settings
6.10 Firing-pulse inhibit
Inhibiting the firing pulses is a simple way of switching high powers. In phaseangle control, the thyristor power unit commences with a soft start after firingpulse inhibit has been used. In burst-firing operation with a transformer load,
the power unit first starts up in phase-angle control and then switches over to
burst-firing.
In order to be able to disconnect a system, a contactor or main
switch must be fitted in the supply line circuit!
V
A contact can be wired between Terminals 6 and 7 to shut off the thyristors at
the next zero-crossing point. This external contact can be a make contact or a
break contact, depending on the position of S21.
v Section 6.2 “Adjustment switches S1 — 21 and pin headers X503 / X504”
Only a make contact can be used as the external contact for a
H
master-slave economy circuit.
External
contact
make (a) 1 Load is continuously shut off while the
break (b) 2 Load is continuously shut off while the
Internal switch
S21
Response
external contact is closed.
external contact is open.
50 Power units 02.06
Page 51

7.1 Load circuit
Nominal load voltage 24V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63Hz
Continuous load
current I
Load types resistive and resistive-inductive loads (B ≤ 1.2 Tesla)
Current limiting With phase-angle control, the load current can be adjusted over the range
Fusing super-fast semiconductor fuse
TSE circuit RC network as standard
Power loss ≈ 1.3V x I
Control accuracy Supply voltage fluctuations within the tolerance range (-20%/+15%)
7 Technical data
42V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63Hz
115V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63 Hz
230V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63 Hz
265V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63 Hz
400V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63 Hz
460V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63 Hz
500V-20%/+15% AC 45 — 63 Hz
(supply voltage for control electronics = nominal load voltage)
25A, 50A, 75A, 100 A, 150A, 250A
L
10 — 100% I
The limiting is based on the rms value of the load current.
by a trimmer on the front panel.
N
(A)
L
are accurately compensated.
Fluctuations ≤ 0.5%.
7.2 Control
Control signal 0 (4) — 20mA RI = 50 Ω
Input signal
attenuation
7.3 General data
Circuit variants - single-phase operation
Operating modes - phase-angle control for resistive and transformer loads, with soft start
Features Two single-phase units can be linked to form an economy circuit for burst-firing
Subsidiary control
types
0 (2) — 10V R
0 (1) — 5V R
0/10V (0/5V) R
0/20mA R
floating contact
or
manual control by an external 5 kΩ potentiometer
adjustment range 100 — 20%
- star circuit with accessible star point
- open delta circuit
- economy circuit using master-slave principle and subsidiary V
in burst-firing operation
- free-running economy circuit (star or delta) only with subsidiary P control
in burst-firing operation
(with current limiting for extra codes TR, TO)
- burst-firing operation for resistive or transformer load
operation.
- free-running economy circuit for resistive loads
- master-slave economy circuit for resistive and transformer loads
With extra code TR or TO: free choice of V
2
V
control as standard.
2
, P, I2 control via internal switches.
= 25kΩ
I
= 12kΩ
I
= 12kΩ
I
= 50Ω
I
2
control
Power units 02.06 51
Page 52

7 Technical data
Actual (power) output V2 signal as standard.
With extra code TR or TO: free choice between V
switches, adjustable from 0 — 5V to 0 — 10V. I
Electrical connection Control wiring by screw terminals for conductor cross-sections 0.2 — 2.5mm
Load connections by cable lugs to DIN 46 212.
Protection IP00 as per EN 60 529, heatsink is grounded
Permitted ambient
temperature range
Permitted storage
temperature range
Climatic conditions rel. humidity ≤ 75% annual mean, no condensation
Cooling natural convection
Operating position vertical
Operating conditions The thyristor power unit is designed as a built-in unit to:
Test voltage to VDE 0160 Table 4 (6/88)
Electromagnetic
compatibility
Creepage distance control electronics to load circuit ≥ 10mm
Housing TYA110/3, 25 (50) 110 x 195 x 152mm
Weight TYA110/3, 25 (50) 2.8 kg
Standard
accessories
Permitted current derated by 2% for each °C increase in ambient temperature;
the maximum permissible ambient temperature must not exceed 60°C.
pollution degree 2 to VDE 0110 Part 1 4.2 (1/89)
overvoltage category Ü III to VDE 0160 5.7 (5/88)
Control electronics to EN 61 326
control electronics to housing ≥ 10mm
Unit can be connected to SELV circuits.
SELV = Seperate Extra Low Voltage
TYA110/3, 75 (100) 125 x 195 x 170mm
TYA110/3, 150 (250) 150 x 220 x 280mm
TYA110/3, 75 (100) 3.7 kg
TYA110/3, 150 8.6 kg
TYA110/3 250 9.0 kg
1 mounting plate for wall-mounting
1 Operating Instructions B 70.9040
0 — 45°C
-10 to +70°C
VDE 0160 5.5.1.3 (5/88)
VDE 0106 Part 100 (3/83)
2
, P, or I2 signal via internal
≈ 2mA.
max
2
.
52 Power units 02.06
Page 53

The thyristor power unit does not require any maintenance.
In the event of a fault, the following points should be observed:
8.1 Fault-finding
If faults occur during commissioning, we recommend that you first check the
positions of the internal switches.
v Section 6.3 “Summary of possible settings”
If the fault persists, check the following items:
- Is the supply voltage present for the thyristor power unit?
Check the phase sequence as well.
- Are all other connections also correct?
- Is the controller operating properly?
Check the operation manually, by using an external potentiometer.
v Section 6.4 “Control inputs”
8.2 Replacing the semiconductor fuse
8 Faults
If the red LED “fuse” lights up, this means that a semiconductor fuse has
blown.
h Disconnect the system from the supply voltage.
v Section 6.1 “Opening the housing”
8.2.1 Type TYA-110/3, 025 to 100, ...
Wrench 10 mm a/f
Power units 02.06 53
Page 54

8 Faults
8.2.2 Type TYA-110/3, 150, ...
Wrench 13 mm a/f
8.2.3 Type TYA-110/3, 250, ...
Wrench 13 mm a/f
h Remove the two hexagonal head fixing screws (1) for the semiconductor
fuse, and take out the fuse.
h Insert a new semiconductor fuse!
54 Power units 02.06
Page 55

h Replace the fixing screws.
h Re-assemble the housing
Use only original replacement fuses. If other fuses are used, this
A
will invalidate the warranty!
8 Faults
Replacement fuses
v Section 1.4.3 “Accessories”
The pcbs carry supply line voltages. Work on the circuitry must
V
therefore only be carried out while the equipment is completely
disconnected from the supply!
To avoid dangerous situations, follow the regulations for “Working
on live equipment“ (VDE 0100 Part 410).
Power units 02.06 55
Page 56

JUMO GmbH & Co. KG
Street address:
Moltkestraße 13 - 31
36039 Fulda, Germany
Delivery address:
Mackenrodtstraße 14
36039 Fulda, Germany
Postal address:
36035 Fulda, Germany
Phone: +49 661 6003-0
Fax: +49 661 6003-607
E-mail: mail@jumo.net
Internet: www.jumo.net
JUMO Instrument Co. Ltd.
JUMO House
Temple Bank, Riverway
Harlow, Essex CM20 2TT, UK
Phone: +44 1279 635533
Fax: +44 1279 635262
E-mail: sales@jumo.co.uk
Internet: www.jumo.co.uk
JUMO Process Control, Inc.
8 Technology Boulevard
Canastota, NY 13032, USA
Phone: 315-697-JUMO
1-800-554-JUMO
Fax: 315-697-5867
E-mail:
Internet: www.jumo.us
info@jumo.us
 Loading...
Loading...