Page 1
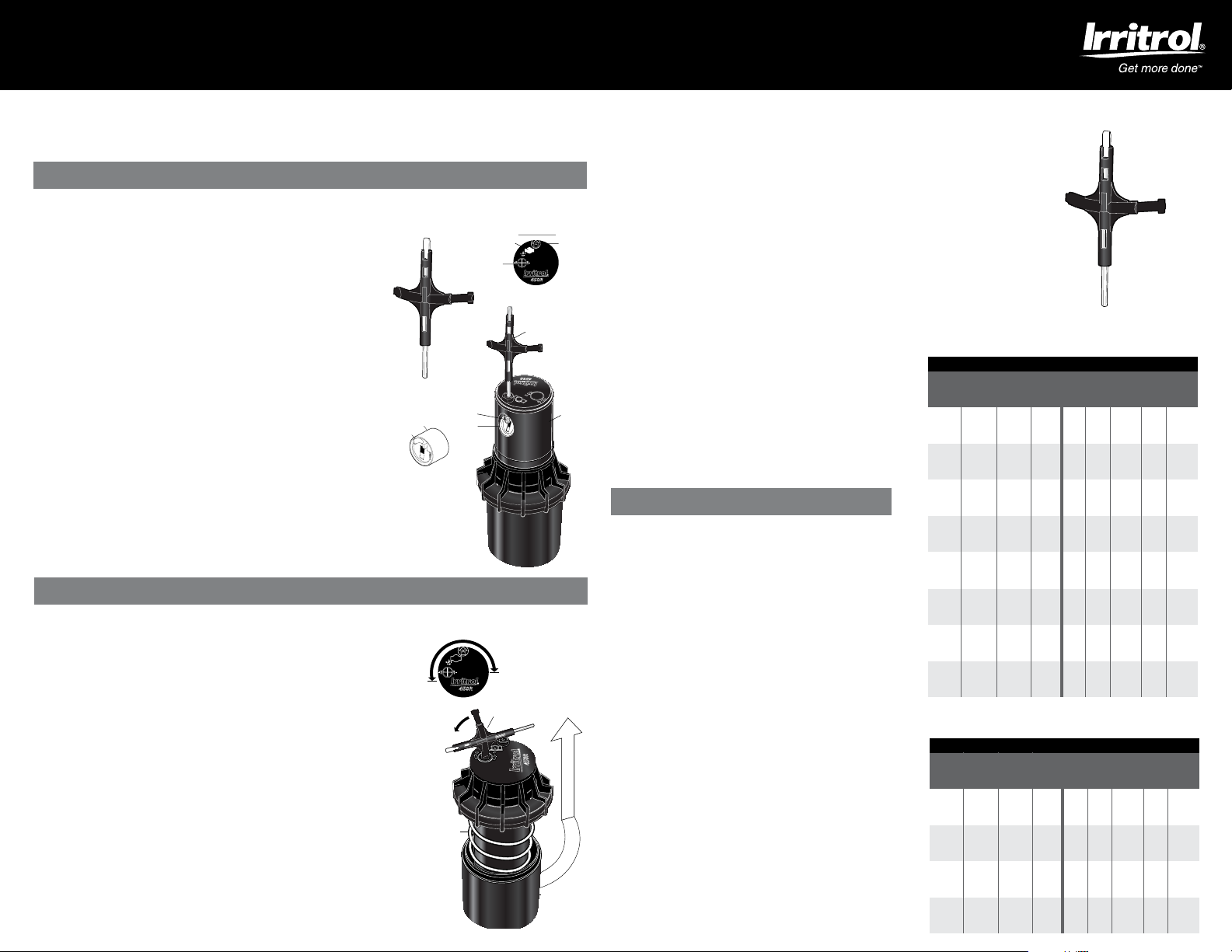
450R ROTOR SETTING INSTRUCTIONS
KEY IN KEYHOLE
NOZZLE
TURRET
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
NOZZLE
SOCKET
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
KEYHOLE
ARC SET
ADJUSTMENT
NOZZLE TURRET TOP
NOZZLE
NOZZLE
PRONGS
THGIRTFEL
UNIVERSAL TOOL
PULL UP KEY
FLAT BLADE
SCREWDRIVER
ARC
ADJUSTMENT
KEY
HEX FOR
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
A
C
B
D
KEY IN KEYHOLE
NOZZLE
TURRET
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
NOZZLE
SOCKET
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
KEYHOLE
ARC SET
ADJUSTMENT
NOZZLE TURRET TOP
NOZZLE
NOZZLE
PRONGS
LEFT
STOP
RIGHT
START
THGIRTFEL
UNIVERSAL TOOL
PULL UP KEY
FLAT BLADE
SCREWDRIVER
ARC
ADJUSTMENT
KEY
HEX FOR
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
A
C
B
D
SPRINKLER
ASSEMBLY
HOUSING
CAN
KEY IN KEYHOLE
LEFT
SPRINKLER
ASSEMBLY
HOUSING
CAN
KEY IN KEYHOLE
LEFT
UNIVERSAL TOOL
PULL UP KEY
FLAT BLADE
SCREWDRIVER
ARC
ADJUSTMENT
KEY
HEX FOR
NOZZLE
RETENTION
SCREW
A
C
B
D
STANDARD NOZZLE PERFORMANCE
TABLAS DE RENDIMIENTO - TOBERAS ESTÁNDAR
Pressure Radius Flow
Presion Radio Caudal
KPa Bars Meters L/M M3/H
Bares Metros
206 2.1 11.0 7.6 0.45
275 2.8 11.6 9.1 0.55
344 3.4 12.2 10.2 0.61
413 4.1 12.2 11.0 0.66
206 2.1 8.5 1.9 0.11
275 2.8 8.8 2.3 0.14
344 3.4 8.8 2.7 0.16
413 4.1 9.1 3.0 0.18
206 2.1 8.8 2.6 0.16
275 2.8 9.1 3.0 0.18
344 3.4 9.1 3.4 0.20
413 4.1 9.4 3.8 0.23
206 2.1 9.1 3.4 0.20
275 2.8 9.4 3.8 0.23
344 3.4 9.4 4.5 0.27
413 4.1 9.8 4.9 0.30
206 2.1 9.8 4.5 0.27
275 2.8 10.1 5.3 0.32
344 3.4 10.4 6.1 0.36
413 4.1 10.4 6.8 0.41
206 2.1 11.0 9.8 0.59
275 2.8 12.2 11.4 0.68
344 3.4 12.8 12.9 0.77
413 4.1 12.8 14.0 0.84
206 2.1 11.6 15.9 0.91
275 2.8 13.1 18.5 1.11
344 3.4 14.0 20.8 1.25
413 4.1 14.3 22.7 1.36
275 2.8 13.7 22.7 1.36
344 3.4 14.6 25.7 1.54
413 4.1 14.9 28.8 1.73
482 4.8 15.5 31.0 1.86
Nozzle Pressure Radius Flow
Tobera Presion Radio Caudal
PSI Ft. GPM
#3 30 36' 2.0
Factory
40 38' 2.4
Installed
50 40' 2.7
Nozzle
60 40' 2.9
#0.5 30 28' 0.5
40 29' 0.6
50 29' 0.7
60 30' 0.8
#0.75 30 29' 0.7
40 30' 0.8
50 30' 0.9
60 31' 1.0
#1 30 30' 0.9
40 31' 1.0
50 31' 1.2
60 32' 1.3
#2 30 32' 1.2
40 33' 1.4
50 34' 1.6
60 34' 1.8
#4 30 36' 2.6
40 40' 3.0
50 42' 3.4
60 42' 3.7
#6 30 38' 4.2
40 43' 4.9
50 46' 5.5
60 47' 6.0
#8 40 45' 6.0
50 48' 6.8
60 49' 7.6
70 51' 8.2
METRIC (METRICO)
U.S.
STANDARD NOZZLE PERFORMANCE
TABLAS DE RENDIMIENTO - TOBERAS ESTÁNDAR
Pressure Radius Flow
Presion Radio Caudal
KPa Bars Meters L/M M3/H
Bares Metros
206 2.1 11.0 7.6 0.45
275 2.8 11.6 9.1 0.55
344 3.4 12.2 10.2 0.61
413 4.1 12.2 11.0 0.66
206 2.1 8.5 1.9 0.11
275 2.8 8.8 2.3 0.14
344 3.4 8.8 2.7 0.16
413 4.1 9.1 3.0 0.18
206 2.1 8.8 2.6 0.16
275 2.8 9.1 3.0 0.18
344 3.4 9.1 3.4 0.20
413 4.1 9.4 3.8 0.23
206 2.1 9.1 3.4 0.20
275 2.8 9.4 3.8 0.23
344 3.4 9.4 4.5 0.27
413 4.1 9.8 4.9 0.30
206 2.1 9.8 4.5 0.27
275 2.8 10.1 5.3 0.32
344 3.4 10.4 6.1 0.36
413 4.1 10.4 6.8 0.41
206 2.1 11.0 9.8 0.59
275 2.8 12.2 11.4 0.68
344 3.4 12.8 12.9 0.77
413 4.1 12.8 14.0 0.84
206 2.1 11.6 15.9 0.91
275 2.8 13.1 18.5 1.11
344 3.4 14.0 20.8 1.25
413 4.1 14.3 22.7 1.36
275 2.8 13.7 22.7 1.36
344 3.4 14.6 25.7 1.54
413 4.1 14.9 28.8 1.73
482 4.8 15.5 31.0 1.86
Nozzle Pressure Radius Flow
Tobera Presion Radio Caudal
PSI Ft. GPM
#3 30 36' 2.0
Factory
40 38' 2.4
Installed
50 40' 2.7
Nozzle
60 40' 2.9
#0.5 30 28' 0.5
40 29' 0.6
50 29' 0.7
60 30' 0.8
#0.75 30 29' 0.7
40 30' 0.8
50 30' 0.9
60 31' 1.0
#1 30 30' 0.9
40 31' 1.0
50 31' 1.2
60 32' 1.3
#2 30 32' 1.2
40 33' 1.4
50 34' 1.6
60 34' 1.8
#4 30 36' 2.6
40 40' 3.0
50 42' 3.4
60 42' 3.7
#6 30 38' 4.2
40 43' 4.9
50 46' 5.5
60 47' 6.0
#8 40 45' 6.0
50 48' 6.8
60 49' 7.6
70 51' 8.2
METRIC (METRICO)
U.S.
Pressure Radius Flow
Presion Radio Caudal
KPa Bars Meters L/M M3/H
Bares Metros
Nozzle Pressure Radius Flow
Tobera Presion Radio Caudal
PSI Ft. GPM
METRIC (METRICO)
U.S.
LOWANGLE NOZZLE PERFORMANCE
TABLAS DE RENDIMIENTO - TOBERAS ÁNGULO BAJO
207 2.0 6.7 4.5 .34
275 3.0 7.3 6.4 .39
344 3.5 7.9 6.8 .41
413 4.0 8.5 7.6 .46
207 2.0 8.8 11.4 .68
275 3.0 9.8 11.7 .71
344 3.5 10.7 13.2 .80
413 4.0 11.3 14.4 .87
207 2.0 9.4 12.9 .78
275 3.0 10.4 14.8 .89
344 3.5 11.3 16.7 1.00
413 4.0 11.6 17.8 1.07
275 3.0 11.6 24.6 1.68
344 3.5 12.2 27.6 1.66
413 4.0 12.8 30.3 1.82
482 5.0 13.4 32.6 1.96
#1 30 22' 1.2
40 24' 1.7
50 26' 1.8
60 28' 2.0
#3 30 29' 3.0
40 32' 3.1
50 35' 3.5
60 37' 3.8
#4 30 31' 3.4
40 34' 3.9
50 37' 4.4
60 38' 4.7
#6 40 38' 6.5
50 40' 7.3
60 42' 8.0
70 44' 8.6
°
NOTE: THE 450R IS FACTORy PRESET WITH A 180
ARC SETTING, AND INCLUDES A PRE-INSTALLED #3 NOZZLE.
CHANGING A NOZZLE
1. R EMOVIN G THE N OZZLE RETEN TION SCRE W
Use the hex key end “A” of the universal tool to remove the nozzle
retention screw by turning counter-clockwise to remove and clockwise
to re-install.
2. P ULL UP THE RIS ER
Insert the “B” end of the universal tool in the keyhole on the top of the nozzle
turret and turn the key 1/4 turn to insure that the key does not slip out of the
keyhole when you pull it up. Firmly pull up the entire spring-loaded riser to access
the nozzle socket. Hold the riser assembly with one hand.
3. R EMOVIN G THE N OZZLE
With the nozzle retention screw removed, the nozzle may be removed by either
turning on the water (wear safety glasses when using this method), or by pulling
outward on the nozzle prongs with a pair of needle-nose pliers.
4. I NSTALL ING A NOZZ LE
Press the desired nozzle into the nozzle socket. Make sure the nozzle
number is visible and the nozzle “prongs” are up. Then, re-install the
nozzle retention screw.
Note: The nozzle retention screw is also a break-up screw and used to
adjust the distance of the spray.
SETTING THE ARC ADJUSTMENT
Note: The 450R gear driven sprinkler has a fixed right start and an adjustable left stop.
1. P OSITIO NING NO ZZLE TURRET TO ITS “RIGHT START ”
Place your finger on the top center of the nozzle turret. Rotate the turret
counter-clockwise to the left stop to complete any interrupted rotation cycle.
Rotate the nozzle turret clockwise to the “right start.” This is the fixed side
of the arc. The nozzle turret must be held in this position for arc adjustments.
The “right start” does not change.
2. A DJUST ING THE RIGHT (FIXE D) SIDE OF ARC
If the right side of the arc is not properly aligned, the sprinkler may spray in
areas not intended for watering such as driveways or adjacent properties. The
right side arc can easily be realigned.
OPTION 1: REPOSITION CAN ON THE FITTING: Turn the sprinkler can and
the fitting below it left or right to the desired position. This may require
temporary removal of the soil around the sprinkler to allow you to grip the
sprinkler can.
OPTION 2: REMOVE INTERNAL RISER ASSEMBLY AND REPOSITION: Unscrew the top
counter-clockwise and remove the internal riser assembly from the can. Once removed
with nozzle turret at its “right start,” reposition riser assembly so that nozzle arrow points
to the desired start position. Replace riser assembly back in the can and screw on the top.
At this point you have realigned the right arc stop, and you can adjust the left arc to an
appropriate setting.
3. ADJ USTING THE LE FT (VA RIABL E) SIDE OF THE ARC
INCREASING THE ARC: Insert the plastic key end “D” of the universal tool into
the arc set adjustment slot. While holding the nozzle turret at the “right start,” turn
the universal tool clockwise. Each full 360° turn of the universal tool will increase the
arc 90°. Adjust to any arc between 40° and 360°. The universal tool will stop turning,
or there will be ratcheting noise, when the maximum arc of 360°
has been reached.
DECREASING THE ARC: Insert the plastic key end “D” of the
universal tool into the arc set adjustment slot. While holding the
nozzle turret at the right start, turn the universal tool counterclockwise. Each full 360°
turn of the universal tool will decrease the arc 90°. Adjust to
any arc between 40° and 360°. The universal tool will stop turning, or
there will be a ratcheting noise, when the minimum arc of 40° has
been reached.
SPRINKLER INSTALLATION
1. INSTALL AN D BURy
Do not use pipe dope. Thread the sprinkler on the pipe. Bury the
sprinkler flush to grade. NOTE: Gear driven sprinklers and pop-up
sprays should not be installed on the same watering zone.
2. INSPEC TING T HE FILTE R
Unscrew the top and lift the complete sprinkler assembly out of the
housing can. The filter is located on the bottom of the sprinkler assembly and can be easily pulled out, cleaned and re-installed.
3. WIN TERIZ ATION TIPS
When using an air compressor to remove water from the system
please note the following:
a) Do not exceed 30 PSI.
b) Always introduce air into the system gradually to avoid air pressure surges. Sudden release of compressed air into the sprinkler
can cause damage.
c) Each zone should run no longer than 1 minute on air. Sprinklers
turn 10 to 12 times faster on air than on water. Over spinning rotors
on air can cause damage to the internal components.
© Irritrol 02/07 Form No 373-0427
Page 2
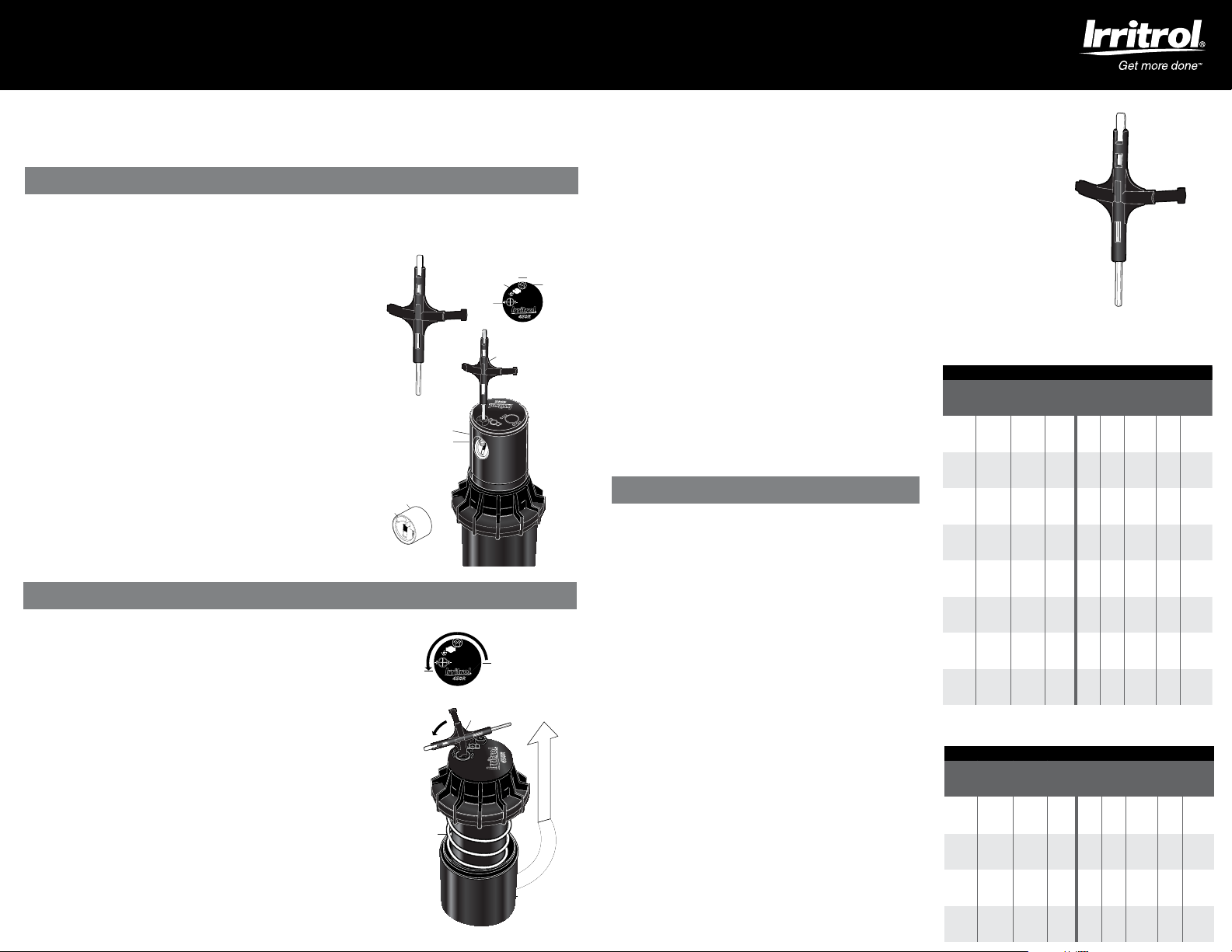
INSTRUCCIONES DE AJUSTE DEL ASPERSOR DE TURBINA 450R
LLAVE
TURBINA
EMERGENTE
TORNILLO DE
SUJECION
TOBERA
´
TOBERADIENTES
DE LA
TOBERA
TORNILLO
DE SUJECION
DE LA TOBERA
ORIFICIO
AJUSTE
DEL SECTOR
TAPA
´
HERRAMIENTA UNIVERSAL
LLAVE PARA
EXTENDER LA
TURBINA
LLAVE PARA
AJUSTE DEL
SECTOR
LLAVE
HEXAGONAL
A
B
D
ENSAMBUJE
INTERNO DE
LA TURBINA
LLAVE
IZQUIERDO
CARCASA
INICIO DE
ARROUQUE
AJUSTE
IZQUIERDO
IZQUIERDO DERECHO
LLAVE
TORNILLO
DE SUJECION
DE LA TOBERA
ORIFICIO
AJUSTE
DEL SECTOR
TAPA
´
HERRAMIENTA UNIVERSAL
LLAVE PARA
EXTENDER LA
TURBINA
LLAVE PARA
AJUSTE DEL
SECTOR
LLAVE
HEXAGONAL
A
B
D
STANDARD NOZZLE PERFORMANCE
TABLAS DE RENDIMIENTO - TOBERAS ESTÁNDAR
Pressure Radius Flow
Presion Radio Caudal
KPa Bars Meters L/M M3/H
Bares Metros
206 2.1 11.0 7.6 0.45
275 2.8 11.6 9.1 0.55
344 3.4 12.2 10.2 0.61
413 4.1 12.2 11.0 0.66
206 2.1 8.5 1.9 0.11
275 2.8 8.8 2.3 0.14
344 3.4 8.8 2.7 0.16
413 4.1 9.1 3.0 0.18
206 2.1 8.8 2.6 0.16
275 2.8 9.1 3.0 0.18
344 3.4 9.1 3.4 0.20
413 4.1 9.4 3.8 0.23
206 2.1 9.1 3.4 0.20
275 2.8 9.4 3.8 0.23
344 3.4 9.4 4.5 0.27
413 4.1 9.8 4.9 0.30
206 2.1 9.8 4.5 0.27
275 2.8 10.1 5.3 0.32
344 3.4 10.4 6.1 0.36
413 4.1 10.4 6.8 0.41
206 2.1 11.0 9.8 0.59
275 2.8 12.2 11.4 0.68
344 3.4 12.8 12.9 0.77
413 4.1 12.8 14.0 0.84
206 2.1 11.6 15.9 0.91
275 2.8 13.1 18.5 1.11
344 3.4 14.0 20.8 1.25
413 4.1 14.3 22.7 1.36
275 2.8 13.7 22.7 1.36
344 3.4 14.6 25.7 1.54
413 4.1 14.9 28.8 1.73
482 4.8 15.5 31.0 1.86
Nozzle Pressure Radius Flow
Tobera Presion Radio Caudal
PSI Ft. GPM
#3 30 36' 2.0
Factory
40 38' 2.4
Installed
50 40' 2.7
Nozzle
60 40' 2.9
#0.5 30 28' 0.5
40 29' 0.6
50 29' 0.7
60 30' 0.8
#0.75 30 29' 0.7
40 30' 0.8
50 30' 0.9
60 31' 1.0
#1 30 30' 0.9
40 31' 1.0
50 31' 1.2
60 32' 1.3
#2 30 32' 1.2
40 33' 1.4
50 34' 1.6
60 34' 1.8
#4 30 36' 2.6
40 40' 3.0
50 42' 3.4
60 42' 3.7
#6 30 38' 4.2
40 43' 4.9
50 46' 5.5
60 47' 6.0
#8 40 45' 6.0
50 48' 6.8
60 49' 7.6
70 51' 8.2
METRIC (METRICO)
U.S.
STANDARD NOZZLE PERFORMANCE
TABLAS DE RENDIMIENTO - TOBERAS ESTÁNDAR
Pressure Radius Flow
Presion Radio Caudal
KPa Bars Meters L/M M3/H
Bares Metros
206 2.1 11.0 7.6 0.45
275 2.8 11.6 9.1 0.55
344 3.4 12.2 10.2 0.61
413 4.1 12.2 11.0 0.66
206 2.1 8.5 1.9 0.11
275 2.8 8.8 2.3 0.14
344 3.4 8.8 2.7 0.16
413 4.1 9.1 3.0 0.18
206 2.1 8.8 2.6 0.16
275 2.8 9.1 3.0 0.18
344 3.4 9.1 3.4 0.20
413 4.1 9.4 3.8 0.23
206 2.1 9.1 3.4 0.20
275 2.8 9.4 3.8 0.23
344 3.4 9.4 4.5 0.27
413 4.1 9.8 4.9 0.30
206 2.1 9.8 4.5 0.27
275 2.8 10.1 5.3 0.32
344 3.4 10.4 6.1 0.36
413 4.1 10.4 6.8 0.41
206 2.1 11.0 9.8 0.59
275 2.8 12.2 11.4 0.68
344 3.4 12.8 12.9 0.77
413 4.1 12.8 14.0 0.84
206 2.1 11.6 15.9 0.91
275 2.8 13.1 18.5 1.11
344 3.4 14.0 20.8 1.25
413 4.1 14.3 22.7 1.36
275 2.8 13.7 22.7 1.36
344 3.4 14.6 25.7 1.54
413 4.1 14.9 28.8 1.73
482 4.8 15.5 31.0 1.86
Nozzle Pressure Radius Flow
Tobera Presion Radio Caudal
PSI Ft. GPM
#3 30 36' 2.0
Factory
40 38' 2.4
Installed
50 40' 2.7
Nozzle
60 40' 2.9
#0.5 30 28' 0.5
40 29' 0.6
50 29' 0.7
60 30' 0.8
#0.75 30 29' 0.7
40 30' 0.8
50 30' 0.9
60 31' 1.0
#1 30 30' 0.9
40 31' 1.0
50 31' 1.2
60 32' 1.3
#2 30 32' 1.2
40 33' 1.4
50 34' 1.6
60 34' 1.8
#4 30 36' 2.6
40 40' 3.0
50 42' 3.4
60 42' 3.7
#6 30 38' 4.2
40 43' 4.9
50 46' 5.5
60 47' 6.0
#8 40 45' 6.0
50 48' 6.8
60 49' 7.6
70 51' 8.2
METRIC (METRICO)
U.S.
Pressure Radius Flow
Presion Radio Caudal
KPa Bars Meters L/M M3/H
Bares Metros
Nozzle Pressure Radius Flow
Tobera Presion Radio Caudal
PSI Ft. GPM
METRIC (METRICO)
U.S.
LOWANGLE NOZZLE PERFORMANCE
TABLAS DE RENDIMIENTO - TOBERAS ÁNGULO BAJO
207 2.0 6.7 4.5 .34
275 3.0 7.3 6.4 .39
344 3.5 7.9 6.8 .41
413 4.0 8.5 7.6 .46
207 2.0 8.8 11.4 .68
275 3.0 9.8 11.7 .71
344 3.5 10.7 13.2 .80
413 4.0 11.3 14.4 .87
207 2.0 9.4 12.9 .78
275 3.0 10.4 14.8 .89
344 3.5 11.3 16.7 1.00
413 4.0 11.6 17.8 1.07
275 3.0 11.6 24.6 1.68
344 3.5 12.2 27.6 1.66
413 4.0 12.8 30.3 1.82
482 5.0 13.4 32.6 1.96
#1 30 22' 1.2
40 24' 1.7
50 26' 1.8
60 28' 2.0
#3 30 29' 3.0
40 32' 3.1
50 35' 3.5
60 37' 3.8
#4 30 31' 3.4
40 34' 3.9
50 37' 4.4
60 38' 4.7
#6 40 38' 6.5
50 40' 7.3
60 42' 8.0
70 44' 8.6
OBSERVACIÓNES: EL 450R VIENE CONFIGURADO PREVIAMENTE DE FáBRICA CON UN
AJUSTE DEL SECTOR A 180° E INCLUyE LA TOBERA N. 3 PREINSTALADA.
CAMBIO DE LA TOBERA
1. C ÓMO QUI TAR EL TOR NILLO D E SUJE CIÓN
Utilice el extremo “A” de la llave hexagonal de la herramienta universal,
para quitar el tornillo de sujeción de la tobera gire en el sentido contrario
al de las agujas del reloj, y en el sentido de las agujas del reloj para volverlo
a colocar.
2. E XTENS IÓN DE LA TUR BINA EMERGEN TE
Inserte el extremo “B” de la herramienta universal en el orificio situado en
la parte superior de la cabeza giratoria y gire la llave 1/4 de vuelta para
asegurarse de que la llave no se sale del agujero cuando levante el aspersor.
Tire con fuerza para acceder a la tobera y sujete el vástago con una mano
para poder acceder al cambio de tobera.
3. C ÓMO QUI TAR LA TOBERA
Una vez quitado el tornillo de sujeción de la tobera ésta se puede sacar
conectando el agua (póngase unas gafas de seguridad cuando emplee este
método), o tirando hacia fuera de los dientes de la tobera con unos alicates
(pinzas) de punta.
4. I NSTALA CIÓN DE UN A TOBE RA
Inserte presionando la tobera en su correspondiente hueco. Asegúrese de
que es visible el número de la tobera y que los “dientes” de ésta están hacia
arriba. A continuación, vuelva a colocar el tornillo de sujeción de la tobera.
OBSERVACIÓN: El tornillo de sujeción de latobera también es un tornillo que
se utiliza para ajustar el alcance del chorro.
DETERMINACIÓN DEL AJUSTE DEL SECTOR
OBS ERVAC IÓ N: El aspersor de turbina 450R dispone de un inicio de
arranque fijo a la derecha y ajustable hacia la izquierda.
1. CO LOCACIÓ N DE LA CABEZA GI RATORIA EN “I NICIO DE A RRANQUE A LA DER ECHA”
Ponga el dedo en la parte superior central de la cabeza giratoria. Gire la
cabeza en el sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj (hasta oír un “clic”
en el tope de la izquierda) y así completar el ciclo de rotación. Gire entonces
la cabeza en el sentido de las agujas del reloj hacia el “inicio de arranque a
la derecha”. Este es el lado fijo del arco. La cabeza giratoria habrá de man-
tenerse en esta posición para realizar el ajuste del arco. El “inicio de arranque
a laderecha” no cambia.
2.A JUSTE DEL LA DO DER ECHO (FIJ O) DEL ARC O
Si el lado derecho del arco no está correctamente alineado, el aspersor puede
rociar enzonas no deseadas de riego como caminos o edificios. El lado dere-
cho del arco se puede volver a alinear fácilmente.
OPCIÓN 1: COLOCACIÓN DEL ASPERSOR CON EL INICIO DEL SECTOR DE RIEGO.
Gire la carcasa del aspersor y su conexión situada debajo de ésta hacia la
izquierda o hacia la derecha hasta la posición deseada de inicio del sector
de riego. Para ello puede ser necesario retirar el césped o la tierra del suelo
alrededor del aspersor para permitirle sujetar la carcasa con la mano.
OPCIÓN 2: RETIRAR EL ENSAMBLAJE INTERNO DE LA TURBINA Y VOLVERLO A COLOCAR.
Desenrosque la tapa en el sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj y saque de la carcasa el
vástago con el muelle. Una vez quitado y con la cabeza giratoria en la posición de “inicio de
arranque a la derecha”, vuelva a colocar el vástago en la carcasa de modo que la flecha de la
tobera señale la posición de inicio de riego deseado y rosque la tapa en la carcasa. En este punto
se habrá realineado el punto de inicio del sector a la derecha y se podrá ajustar el sector izquierdo
hasta el arco de riego adecuado.
3. AJU STE IZ QUIERD O (VARI ABLE) DE L SECT OR
AUMENTO DEL SECTOR DE RIEGO: Inserte el extremo “D” de la llave de plástico de la
herramienta universal en la ranura de ajuste del sector. Mientras sujeta la cabeza giratoria en la
posición de “inicio de arranque a la derecha”, gire la herramienta universal en el sentido de las
agujas del reloj. Cada giro completo de 360° de la herramienta universal aumentará el arco 90°.
Ajuste el arco entre los 40° y 360°. La herramienta universal se detendrá o habrá un ruido de
trinquete (matraca) cuando se haya alcanzado el arco máximo de 360°.
DISMINUCIÓN DEL SECTOR DE RIEGO: Inserte el extremo “D”
de la llave de plástico de la herramienta universal en la ranura de
ajuste del sector. Mientras sujeta la cabeza giratoria en la posición de
“inicio de arranque a la derecha”, gire la herramienta universal en el
sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj. Cada giro completo de
360° de la herramienta universal disminuirá el arco 90°. Ajuste
el arco entre los 40° y 360°. La herramienta universal se detendrá o
habrá un ruido de trinquete (matraca) cuando se haya alcanzado el
arco mínimo de 40°
INSTALACIÓN DEL ASPERSOR
1. I NSTALA CIÓN y COLOCA CIÓN.
No utilice teflón o estopa en la rosca. Rosque el aspersor a la tubería.
Entierre el aspersor a nivel del suelo. OBSERVACIÓN: Los aspersores
de turbina y los difusores emergentes no deben ser instalados en la
misma zona de riego.
2. I NSPECC IÓN DE L FILTRO
Desatornille la tapa y saque de la carcasa el aspersor. El filtro está
situado en la parte inferior de la turbina y se puede sacar, limpiar y
volver a instalar fácilmente.
3. CONSEJ OS PARA EL INVIE RNO
Proceda a vaciar las tuberías a fin de evitar daños que ocasionan las
heladas. Cierre la llave general del agua que suministra la instalación
de riego. Accione después en el programador de riego todas las electroválvulas, hasta desaguar las tuberías. Anule los riegos programados y
ponga el Programador en OFF (apagado) o desconéctelo de la toma de
energía eléctrica. Al utilizar un compresor de aire para eliminar el agua
del sistema, tenga en cuenta lo siguiente:
a) No exceda los 2.00 bares.
b) Introduzca siempre aire en el sistema de forma gradual para evitar
aumentos repentinos de la presión. Una salida repentina de aire comprimido al aspersor puede causar daños.
c) Cada una de las zonas deberá funcionar con aire durante 1 minuto
como máximo. Los aspersores giran entre 10 y 12 veces más rápido
con aire que con agua. Un giro excesivo de los aspersores con aire
puede causar daños a los componentes internos.
 Loading...
Loading...