Page 1

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL
Technical Product Specification
Intel order number: D64569-007
Revision 2.3
May 2007
Enterprise Platforms and Services Division - Marketing
Page 2
Revision History Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Revision History
Date Revision
Number
September 2006 1.0 Initial release.
November 2006 2.0 Added technical updates and SAS board information.
January 2007 2.1 Removed processor that is not supported by board; added Post-Code Diagnostic
LED information.
September 2007 2.2 Updated product codes and processor information.
May 2010 2.3 Deleted CCC and CNCA.
Modifications
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied, by
estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel's
Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any
express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to
fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications. Intel may make
changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or
"undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or
incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The Intel® Server Board S5000VCL may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the
product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel Corporation server baseboards support peripheral components and contain a number of high-density VLSI and
power delivery components that need adequate airflow to cool. Intel’s own chassis are designed and tested to meet
the intended thermal requirements of these components when the fully integrated system is used together. It is the
responsibility of the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel developed server building blocks to consult vendor
datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of air flow required for their specific application and
environmental conditions. Intel Corporation can not be held responsible if components fail or the server board does
not operate correctly when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating limits.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2010.
Revision 2.3
ii
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 3

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................1
1.1 Server Board Use Disclaimer .................................................................................. 1
2. Product Overview.................................................................................................................2
2.1 Feature Set .............................................................................................................. 2
2.2 Server Board Layout................................................................................................ 3
2.2.1 Intel® Light-Guided Diagnostics LED Locations....................................................... 4
2.2.2 External I/O Connector Locations............................................................................ 5
3. Functional Architecture.......................................................................................................6
3.1 Intel® 5000V Memory Controller Hub (MCH) ........................................................... 8
3.1.1 System Bus Interface............................................................................................... 8
3.1.2 Processor Support ................................................................................................... 8
3.1.3 Memory Sub-system.............................................................................................. 10
3.2 Intel® 6321ESB I/O Controller Hub ........................................................................ 12
3.2.1 PCI Sub-system..................................................................................................... 13
3.2.2 Serial ATA Support ................................................................................................ 13
3.2.3 Parallel ATA (PATA) Support ................................................................................ 14
3.2.4 USB 2.0 Support.................................................................................................... 14
3.3 Video Support ........................................................................................................ 14
3.4 Network Interface Controller (NIC) ........................................................................ 15
3.4.1 Intel® I/O Acceleration Technolgy .......................................................................... 16
3.5 Super I/O ...............................................................................................................16
4. Platform Management........................................................................................................19
5. Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs .....................................................................20
5.1 Board Connectors.................................................................................................. 20
5.2 Power Connectors ................................................................................................. 21
5.3 Riser Card Slots..................................................................................................... 22
5.4 SSI Control Panel Connector................................................................................. 22
5.5 I/O Connector Pinout Definition ............................................................................. 23
5.5.1 VGA Connector...................................................................................................... 23
5.5.2 NIC Connectors ..................................................................................................... 23
5.5.3 IDE Connector ....................................................................................................... 24
5.5.4 SATA Connectors .................................................................................................. 25
5.5.5 Serial Port Connectors........................................................................................... 26
5.5.6 Keyboard and Mouse Connector ........................................................................... 26
5.5.7 USB Connector...................................................................................................... 27
5.6 Fan Headers .......................................................................................................... 28
6. Jumper Block Settings ......................................................................................................29
6.1 Recovery Jumper Blocks ....................................................................................... 29
6.1.1 CMOS Clear and Password Reset Usage Procedure ...........................................30
Revision 2.3
iii
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 4

Table of Contents Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
6.1.2 BMC Force Update Procedure .............................................................................. 30
6.2 BIOS Select Jumper .............................................................................................. 31
6.3 PCI Express* Select Jumper ................................................................................. 31
7. Intel® Light Guided Diagnostics........................................................................................32
7.1 5-Volt Standby System Status/Fault LED .............................................................. 32
7.2 DIMM LEDs ...........................................................................................................34
7.3 Post Code Diagnostic LEDs ..................................................................................35
8. Power and Environmental Specifications........................................................................36
8.1 Intel® Server Board S5000VCL Design Specifications ..........................................36
8.2 Baseboard Power Requirements........................................................................... 37
8.2.1 Processor Power Support...................................................................................... 37
8.2.2 Power Supply Output Requirements ..................................................................... 37
8.2.3 Turn On No Load Operation .................................................................................. 38
8.2.4 Grounding .............................................................................................................. 39
8.2.5 Standby Outputs .................................................................................................... 39
8.2.6 Remote Sense ....................................................................................................... 39
8.2.7 Voltage Regulation ................................................................................................39
8.2.8 Dynamic Loading ................................................................................................... 40
8.2.9 Capacitive Loading ................................................................................................ 40
8.2.10 Closed-Loop Stability............................................................................................. 40
8.2.11 Common Mode Noise ............................................................................................ 40
8.2.12 Ripple/Noise ..........................................................................................................41
8.2.13 Soft Starting ........................................................................................................... 41
8.2.14 Timing Requirements............................................................................................. 41
8.2.15 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby Mode ........................................................ 43
9. Regulatory and Certification Information.........................................................................44
9.1 Product Regulatory Compliance ............................................................................ 44
9.1.1 Product Safety Compliance ................................................................................... 44
9.1.2 Product EMC Compliance – Class A Compliance ................................................. 45
9.1.3 Certifications/Registrations/Declarations ............................................................... 45
9.2 Product Regulatory Compliance Markings ............................................................46
9.3 Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices .................................................................. 47
9.3.1 FCC Verification Statement (USA) ........................................................................ 47
9.3.2 ICES-003 (Canada) ............................................................................................... 48
9.3.3 Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity) .................................................................48
9.3.4 VCCI (Japan) ......................................................................................................... 48
9.3.5 BSMI (Taiwan) ....................................................................................................... 48
9.3.6 RRL (Korea)........................................................................................................... 49
9.4 Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Compliance................................... 49
Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips................................................................................50
Appendix B: Sensor Tables .....................................................................................................51
Revision 2.3
iv
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 5

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Table of Contents
Appendix C: POST Error Messages and Handling ................................................................53
Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder...............................................................56
Appendix E: Supported Intel® Server Chassis.......................................................................60
Glossary.....................................................................................................................................62
Reference Documents..............................................................................................................65
Revision 2.3
v
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 6

List of Figures Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
List of Figures
Figure 1. Components and Connector Location Diagram............................................................. 3
Figure 2. Intel
Figure 3. ATX I/O Layout .............................................................................................................. 5
Figure 4. Functional Block Diagram..............................................................................................7
Figure 5. CEK Processor Mounting ............................................................................................10
Figure 6. Memory Layout ............................................................................................................10
Figure 7. SMBUS Block Diagram................................................................................................ 19
Figure 8. Recovery Jumper Blocks (J3A1, J1C2, J1C4)............................................................. 29
Figure 9. System Status/Fault LED Location .............................................................................. 32
Figure 10. DIMM LED Locations................................................................................................. 34
Figure 11. POST Code Diagnostic LED Location ....................................................................... 35
Figure 12. Output Voltage Timing ...............................................................................................42
Figure 13. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals).............................................................. 43
Figure 14. Diagnostic LED Placement Diagram .........................................................................56
Figure 15. Intel
Figure 16. Intel
®
Light-Guided Diagnostics LED Locations............................................................. 4
®
Server System SR1530CL/SR1530CLR .......................................................... 60
®
Server System SR1530HCL/SR1530HCLR..................................................... 61
Revision 2.3
vi
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 7

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1. Processor Support Matrix ...............................................................................................9
Table 2. I
Table 3. Maximum Six-DIMM System Memory Configuration – x4 Single Rank ........................ 11
Table 4. Maximum Six-DIMM System Memory Configuration – x8 Dual Rank........................... 11
Table 5. PCI Bus Segment Characteristics................................................................................. 13
Table 6. Video Modes .................................................................................................................15
Table 7. NIC2 Status LED........................................................................................................... 16
Table 8. Serial A Port Header Pin-out (External DB9) ................................................................ 17
Table 9. Internal Serial B Port Header Pin-out............................................................................ 17
Table 10. Board Connector Matrix .............................................................................................. 20
Table 11. Power Connector Pin-out (J3K3) ................................................................................ 21
Table 12. 12V Power Connector Pin-out (J9E1)......................................................................... 21
Table 13. Power Supply Signal Connector Pin-out (J9C1) ......................................................... 22
Table 14. Front Panel SSI Standard 24-pin Connector Pin-out (J2K2) ......................................22
Table 15. VGA Connector Pin-out (J7A1)................................................................................... 23
Table 16. RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out (JA6A1, JA5A1)...................................... 23
Table 17. 44-pin IDE Connector Pin-out (J2K5) .........................................................................24
Table 18. SATA Connector Pin-out (J1J2, J1J1) ........................................................................ 25
Table 19. SATA/SAS Connector Pin-out (J1G2, J1G1, J1F1, J1E4).......................................... 25
Table 20. 9-pin Serial Header Pin-out (J8A1, J1A1)................................................................... 26
Table 21. Stacked PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Port Pin-out (J9A2) ........................................... 26
Table 22. External USB Connector Pin-out (J9A2)..................................................................... 27
Table 23. Internal USB Connector Pin-out (J3K1) ...................................................................... 27
Table 24. CPU Fan Connector Pin-out (J2K3, J2K4) .................................................................28
Table 25. PCI Fan Connector Pin-out (J1K1) ............................................................................. 28
Table 26. Recovery Jumpers (J3A1, J1C1, J1C2)...................................................................... 29
Table 27. BIOS Select Jumper (J3A2) ....................................................................................... 31
Table 28. PCI Express* x4/x8 Select Jumper (J1E1) ................................................................. 31
Table 29. 5V Standby System Status LED Indicators................................................................. 33
Table 30. Server Board Design Specifications ...........................................................................36
Table 31. Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5100 series and Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor
Table 32. 400W Load Ratings ....................................................................................................38
Table 33. No-load Operating Range ........................................................................................... 38
Table 34. Voltage Regulation Limits ........................................................................................... 39
Table 35. Transient Load Requirements..................................................................................... 40
Table 36. Capacitive Loading Conditions ...................................................................................40
Table 37. Ripple and Noise......................................................................................................... 41
Table 38. Output Voltage Timing ................................................................................................ 41
2
C Addresses for Memory Module SMB ......................................................................11
5300 series TDP Guidelines................................................................................................. 37
Revision 2.3
vii
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 8

List of Tables Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Table 39. Turn On/Off Timing ..................................................................................................... 42
Table 40. POST Error Messages and Handling.......................................................................... 53
Table 41. POST Error Beep Codes ............................................................................................55
Table 42. BMC Beep Codes ....................................................................................................... 55
Table 43. Example POST Progress Code LED .......................................................................... 56
Table 44. Diagnostic LED POST Code Decoder ........................................................................57
Revision 2.3
viii
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 9

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS List of Tables
< This page intentionally left blank. >
Revision 2.3
ix
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 10

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Introduction
1 Introduction
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) provides board-specific information about the
features, functionality, and high-level architecture of the Intel
®
Intel
5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet more information about board sub-
®
Server Board S5000VCL. See the
systems, including chipset, BIOS, system management, and system management software.
There are four product codes of the Intel Server Board S5000VCL:
SS5000VCL
S5000VCLSASBB
BBS5000VCLR
BBS5000VCLSASR
®
All references to the Intel
Server Board S5000VCL refer to all product codes listed above,
unless noted otherwise.
1.1 Server Board Use Disclaimer
Intel Corporation server boards support add-in peripherals and contain high-density VLSI and
power delivery components that need adequate airflow to cool. Intel ensures through its own
chassis development and testing that when Intel server building blocks are used together, the
fully integrated system will meet the intended thermal requirements of these components. It is
the responsibility of the system integrator who chooses not to use Intel developed server
building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount
of air flow required for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation
cannot be held responsible if components fail or the server board does not operate correctly
when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating limits.
Revision 2.3
1
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 11
Product Overview Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
2. Product Overview
The Intel® Server Board S5000VCL is a monolithic printed circuit boards that support the highdensity 1U server market.
2.1 Feature Set
Feature Description
Processors 771-pin LGA sockets supporting one or two Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processors 5100
series and low-voltage Quad-Core
speeds of 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz.
For a complete list of supported processors, see the following link:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000VCL
Memory Six keyed DIMM slots support fully buffered DIMM technology (FBDIMM) memory. 240-
pin DDR2-677 FBDIMMs must be used.
Chipset Intel® 5000V Chipset family, which includes the following components:
Intel® 5000V Memory Controller Hub
Intel
On-board
Connectors/Headers
Add-in PCI, PCI-X*, PCI
Express* Cards
On-board Video ATI* ES1000 video controller with 16 MB DDR SDRAM
On-board Hard Drive
Controller
LAN
System Fans Two CPU 4-pin fan headers supporting two system blowers and one 3-pin fan header
System Management
External connections:
Stacked PS/2* ports for keyboard and mouse
Two RJ45 NIC connectors for 10/100/1000 Mb connections
Two USB 2.0 ports
Video connector
Com 1 or Serial A (DB9)
Internal connectors/headers:
One USB port header, capable of providing two USB 2.0 ports
One DH10 Serial B header
Six SATA ports or four SAS ports via the Intel
One 40-pin (power + I/O) ATA/100 connector for optical drive support
SSI-compliant 24-pin control panel header
SSI-compliant 24-pin main power connector support the ATX-12 V standard on
8-pin +12 V processor power connector
One PCI super-slot that will support one 1U riser card with one PCI-X* and one PCI
Express* connectors
Six 3 Gb/s SATA ports, or four SAS ports
Intel® Embedded Server RAID Technology II with RAID levels 0, 1, 10
Two 10/100/1000 NICs supporting Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology
supporting a system fan
Support for Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub
These ports support 3Gb/s and integrated SW RAID 0 or 1
the first 20 pins
®
System Management Software
®
Xeon® processors 5300 series, with system bus
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub.
Revision 2.3
2
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 12
Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Product Overview
W
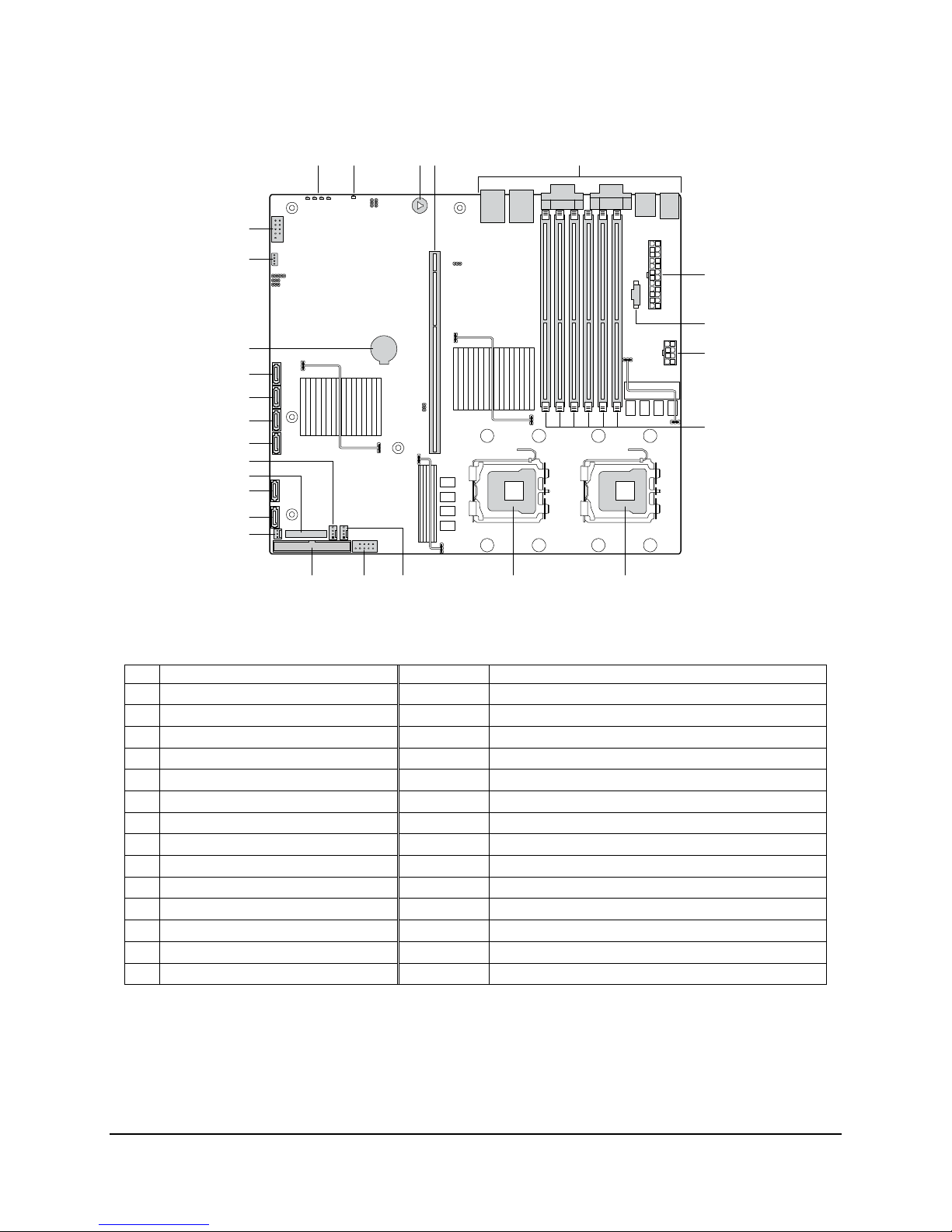
2.2 Server Board Layout
B
A
D E
C
Z
Y
X
V
U
T
S
R
Q
P
O
M
Figure 1. Components and Connector Location Diagram
F
G
H
I
JKLN
AF002052
Description Description
A Post code Diagnostic LEDs O System Fan Header
B System Fault/Status LED P SATA 0
C Speaker Q SATA 1
D Super Slot (Slot 6) R SSI 24-pin Control Panel Header
E External IO Connectors S CPU 1 Fan Header
F Main Power Connector T SATA 2/SAS 0
G Power Supply Auxiliary Connector U SATA 3/SAS 1
H CPU Power Connector V SATA 4/SAS 2
I FBDIMM Slots W SATA 5/SAS 3
J CPU Socket 1 X Battery
K CPU Socket 2 Y SATA SGPIO
L CPU 2 Fan Header Z Serial B Port Header
M Dual Port USB 2.0 Header Not shown SAS GPIO (SAS version of the server board only)
N Primary IDE Connector
Revision 2.3
3
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 13
Product Overview Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
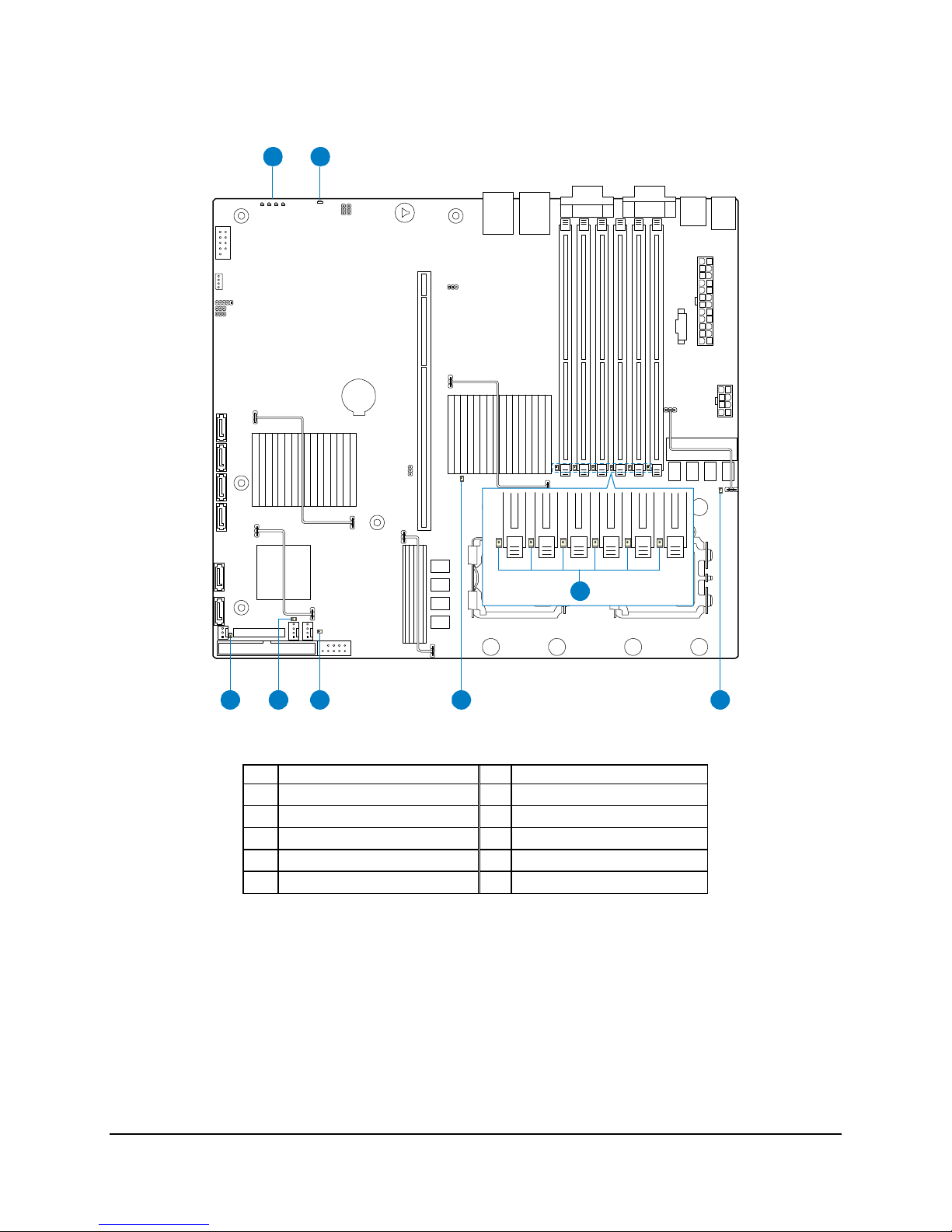
2.2.1 Intel
®
Light-Guided Diagnostics LED Locations
A
B
D
F E CH G
AF002053
Description Description
A Post-Code Diagonstic LEDs E CPU 2 Fan Fault LED
B System Fault/Status LED F CPU 1 Fan Fault LED
C CPU 1 Fault LED G System Fan Fault LED
D DIMM Fault LEDs H 5 VSB LED
E CPU 2 Fault LED
Figure 2. Intel® Light-Guided Diagnostics LED Locations
Revision 2.3
4
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 14
Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Product Overview
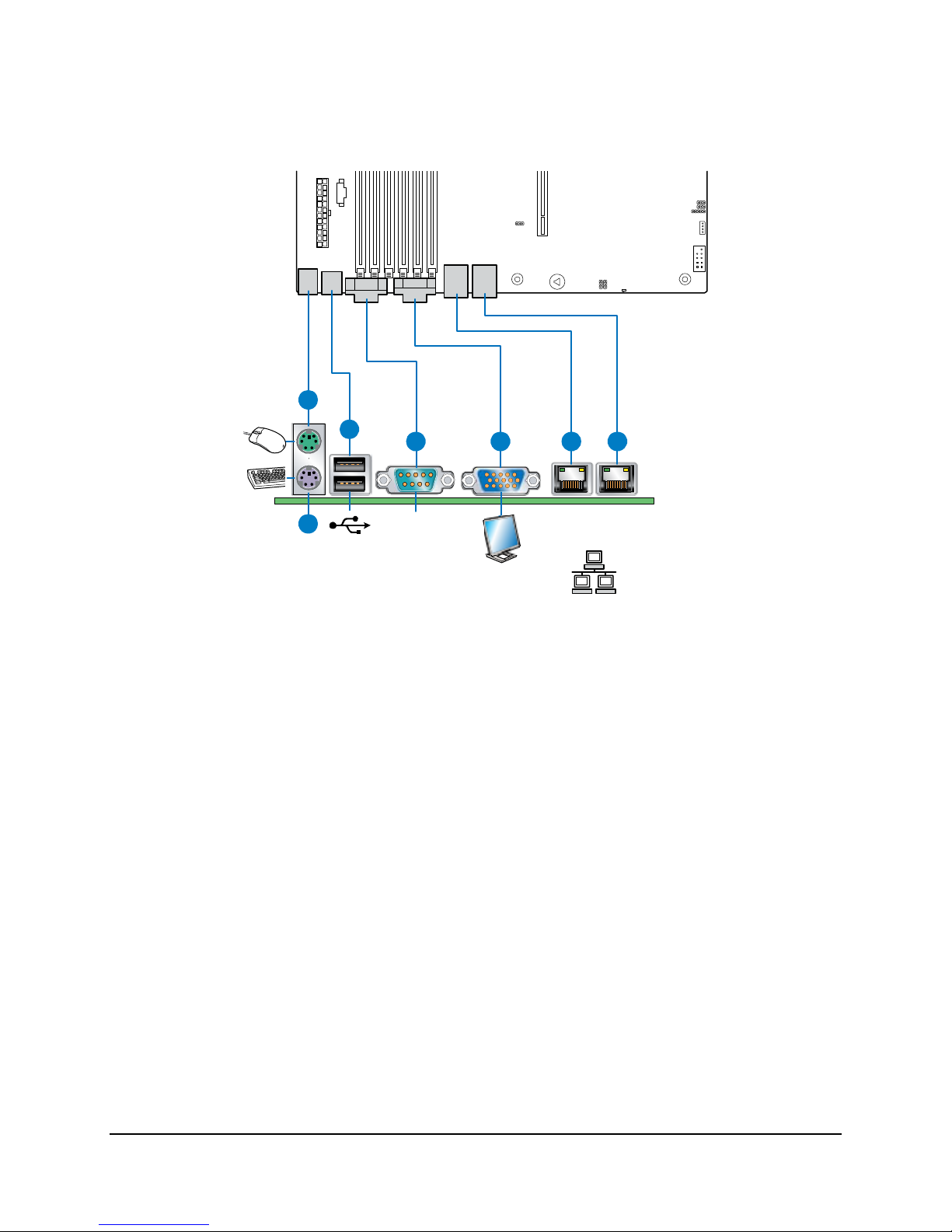
2.2.2 External I/O Connector Locations
A
B
C
USB
0-1
D
Serial A
E
F
NIC1
10/100/
1000 Mb
Network
G
NIC2
10/100/
1000 Mb
AF001640
Figure 3. ATX I/O Layout
Revision 2.3
5
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 15

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
3. Functional Architecture
The architecture and design of the Intel® Server Board S5000VCL is based on the Intel® 5000V
Chipset. The chipset is for systems based on the Dual-Core Intel
and low-voltage Quad-Core Intel
®
Xeon® processor 5300 series with system bus speeds of
®
Xeon® processor 5100 series
1067 MHz and 1333 MHz.
®
The chipset has two main components: the Intel
host bridge and the Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub for the I/O subsystem.
5000V Memory Controller Hub (MCH) for the
This chapter provides a high-level description of the functionality associated with each chipset
component and the architectural blocks that make up this server board. For in depth information
on each of the chipset components and each of the functional architecture blocks, see the Intel
5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
®
Revision 2.3
6
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 16
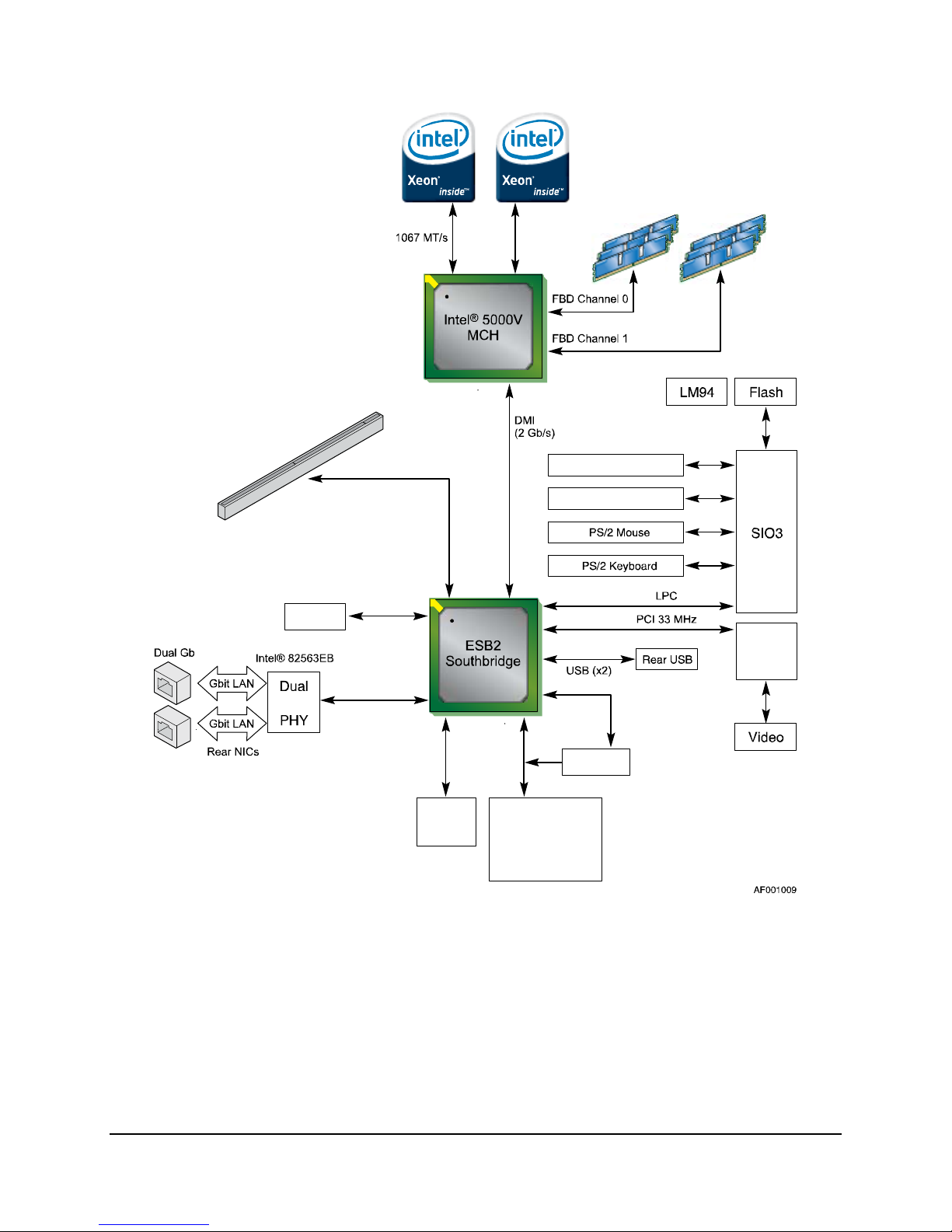
Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Functional Architecture
1333 MT/s
Super Slot
Serial Port B (Internal)
PCI-X* 64-bit/133 MHz
PCI-Express x4 (ESB2, Port 1)
PCI-Express x4 (ESB2, Port 2)
PATA
GBE
Figure 4. Functional Block Diagram
SATA0
SATA1
Serial Port A (Back Panel)
ATI*
ES1000
Video
PCI-X x4
LSI* 1064E
SATA2 / SAS0
SATA3 / SAS1
SATA4 / SAS2
SATA5 / SAS3
Revision 2.3
7
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 17

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
3.1 Intel
®
5000V Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
The memory controller hub (MCH) is a single 1432 pin FCBGA package that includes these
core platform functions:
System bus interface for the processor sub-system
Memory controller
PCI Express* ports including the enterprise south bridge interface (ESI)
FBD thermal management
SMBUS interface
3.1.1 System Bus Interface
The MCH is configured for symmetric multi-processing across two independent front side bus
interfaces that connect to the processors. Each front side bus on the MCH uses a 64-bit wide
1066- or 1333-MHz data bus. The 1333-MHz data bus can transfer data at up to 10.66 GB/s.
The MCH supports a 36-bit wide address bus, capable of addressing up to 64 GB of memory.
The MCH is the priority agent for both front side bus interfaces, and is optimized for one
processor on each bus.
3.1.2 Processor Support
The server board supports one or two Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processors 5100 series or low
voltage Quad-Core Intel
and 1333 MHz, and core frequencies starting at 1.6 GHz. Previous generations of the Intel
®
Xeon
processor are not supported.
®
Xeon® processor 5300 series, with system bus speeds of 1066 MHz,
®
For a complete list of supported processors, see the following link:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000VCL
®
Note: Only Dual-Core Intel
Xeon® processors 5100 series or low-voltage Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® processor 5300 series, that support system bus speeds of 1066 MHz, and 1333 MHz are
supported.
Revision 2.3
8
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 18
Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Functional Architecture
Table 1. Processor Support Matrix
Intel® Xeon
processor
Dual-Core Intel®
®
Xeon
5100 series
Low-Voltage Quad-
Core Intel
processor 5300
series
®
processor
®
Xeon®
System Bus Speed Core Frequency Support
533 MHz All No
800 Mhz All No
667 MHz All No
1066 MHz 1.60 GHz
1066 MHz 1.86 GHz
1333 MHz 2.00 GHz
1333 MHz 2.33 GHz
1333 MHz 2.66 GHz
1333 MHz 3.00 GHz
1066 MHz
1066 MHz
1333 MHz 2.00 GHz
1333 MHz 2.33 GHz
1.60 GHz
1.86 GHz
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
3.1.2.1 Processor Population Rules
When two processors are installed, both must be of identical revision, core voltage, and
bus/core speed. When only one processor is installed, it must be in the socket labeled CPU1.
The other socket must be empty.
The board provides up to 90A max, 70A TDC per processor. Processors with higher current
requirements are not supported.
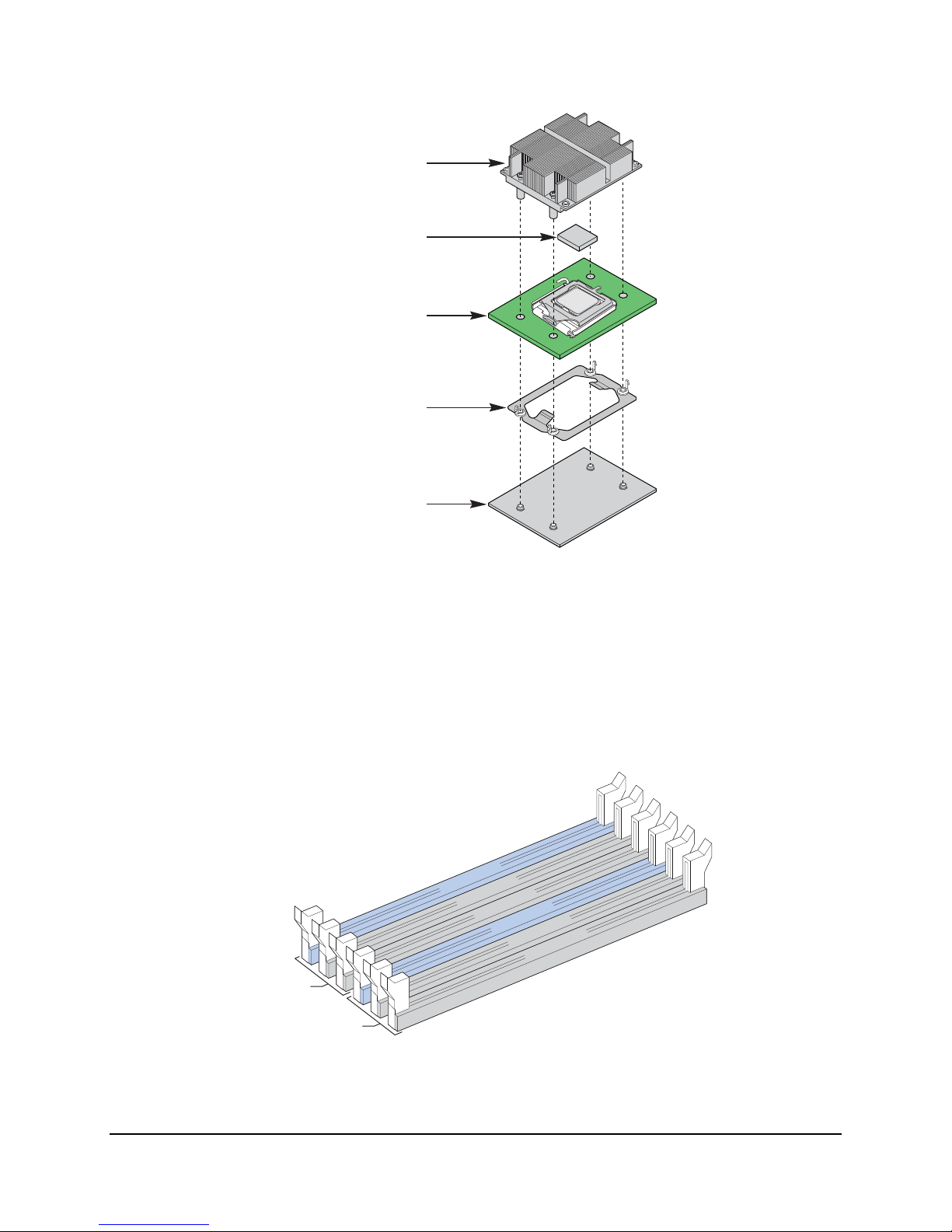
3.1.2.2 Common Enabling Kit (CEK) Design Support
The server board complies with Intel’s common enabling kit (CEK) processor mounting and heat
sink retention solution. The server board ships with a CEK spring snapped onto the underside of
the server board, beneath each processor socket. The heat sink attaches to the CEK, over the
top of the processor and the thermal interface material (TIM). See the figure below for the
stacking order of the chassis, CEK spring, server board, TIM, and heat sink.
The CEK spring is removable, allowing for the use of non-Intel heat sink retention solutions.
Revision 2.3
Intel order number: D64569-007
9
Page 19
Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Heatsink assembly
Thermal Interface
Material (TIM)
Server Board
TP02091
CEK Spring
Chassis
AF001010
Figure 5. CEK Processor Mounting
3.1.3 Memory Sub-system
The MCH masters two fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) memory channels. FBDIMM memory
utilizes a narrow high-speed frame-oriented interface referred to as a channel. The two
channels are routed to six DIMM slots and support registered DDR2-667 FBDIMM memory
(stacked or unstacked). Peak FBDIMM memory data bandwidth in dual channel mode is
8.0GB/s (2x4.0 GB/s) with DDR2-667/PC2-5300 (3.0 ns at CL5).
Channel A
Channel B
Revision 2.3
10
DIMM A1
DIMM A2
DIMM A3
DIMM B1
DIMM B2
DIMM B3
Figure 6. Memory Layout
Intel order number: D64569-007
AF001011
Page 20
Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Functional Architecture
To boot the system, the system BIOS uses a dedicated I2C bus to retrieve DIMM information
needed to program the MCH memory registers.
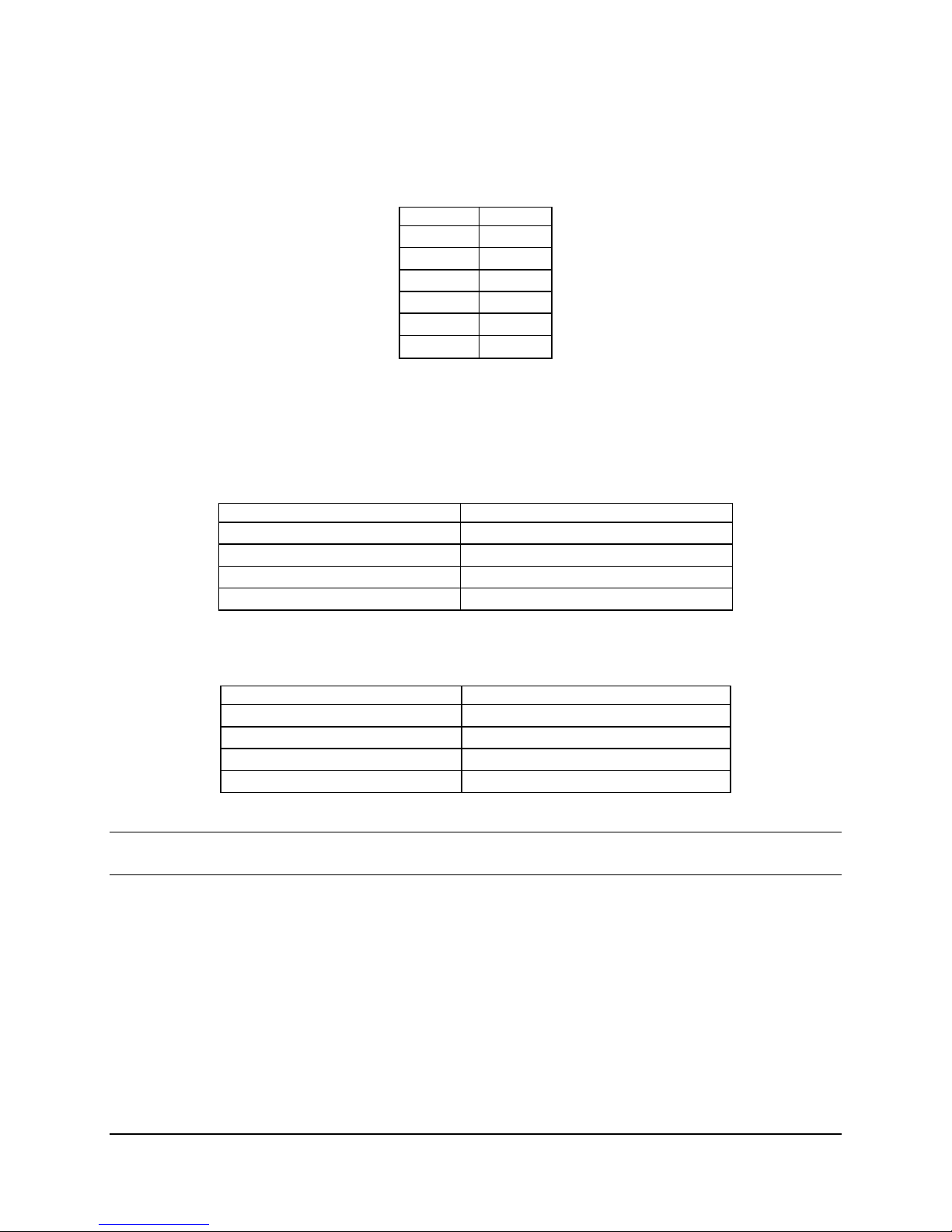
Table 2. I2C Addresses for Memory Module SMB
Device Address
DIMM A1 0xA0
DIMM A2 0xA2
DIMM A3 A4
DIMM B1 A0
DIMM B2 A2
DIMM B3 A4
3.1.3.1 Supported Memory
Up to six DDR2-667 fully-buffered DIMMs (FBD memory) can be installed.
Table 3. Maximum Six-DIMM System Memory Configuration – x4 Single Rank
DRAM Technology x4 Single Rank Maximum Capacity Non-Mirrored Mode
256 Mb 1.5 GB
512 Mb 3 GB
1024 Mb 6 GB
2048 Mb 12 GB
Table 4. Maximum Six-DIMM System Memory Configuration – x8 Dual Rank
DRAM Technology x8 Dual Rank Maximum Capacity Non-Mirrored Mode
256 Mb 1.5 GB
512 Mb 3 GB
1024 Mb 6 GB
2048 Mb 12 GB
Note: DDR2 DIMMs that are not fully buffered are NOT supported. See the Intel
S5000VCL Tested Memory List for a list of supported memory.
®
Server Board
Revision 2.3
11
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 21

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
3.1.3.2 DIMM Population Rules and Supported DIMM Configurations
DIMM population rules depend on the operating mode of the memory controller. The operating
mode is determined by the number of DIMMs installed. DIMMs must be populated in pairs in
DIMM slot order: A1 & B1, A2 & B2. DIMMs within a pair must be identical with respect to size,
speed, and organization, but DIMM capacities can be different across different DIMM pairs.
Note: The server board supports single DIMM mode operation. Intel will only validate and
support this configuration with a single 512 MB x8 FBDIMM installed in DIMM slot A1.
3.2 Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub
The Intel® 6321ESB I/O Controller Hub is a multi-function device that provides four distinct
functions: an IO Controller, a PCI-X* Bridge, a GB Ethernet Controller, and a baseboard
management controller (BMC). Each function within the controller hub has its own set of
configuration registers. Once configured, each appears to the system as a distinct hardware
controller.
The controller hub provides the gateway to all PC-compatible I/O devices and features. The
server board uses these Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub features:
1. PCI-X* bus interface
2. Six channel SATA interface w/SATA busy and fault LED control
3. Dual GbE MAC
4. Baseboard management controller (BMC)
5. Single ATA interface, with Ultra DMA 100 capability
6. Universal Serial Bus 2.0 (USB) interface
7. Removable media drives
8. LPC bus interface
9. PC-compatible timer/counter and DMA controllers
10. APIC and 8259 interrupt controller
11. Power management
12. System RTC
13. VT technology
14. General purpose I/O
For additional information, see the Intel
®
5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
Revision 2.3
12
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 22
Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Functional Architecture
3.2.1 PCI Sub-system
The primary I/O buses support one Super Slot connector, which supports one PCI riser
assembly that supports two PCI slots: one low-profile PCI Express* x8, and either a mid-height
PCI-X* 133, or one low-profile PCI Express*x4 and one mid-height PCI Express x4. The PCI
bus complies with the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.3. The PCI-X bus complies with
PCI-X Local BUS Specification, Revision 2.0, the PCI Express ports comply with the PCI
Express Base Specification, Revision 1.0a. PCI 32 supports the VGA ATI* ES1000 video
controller.
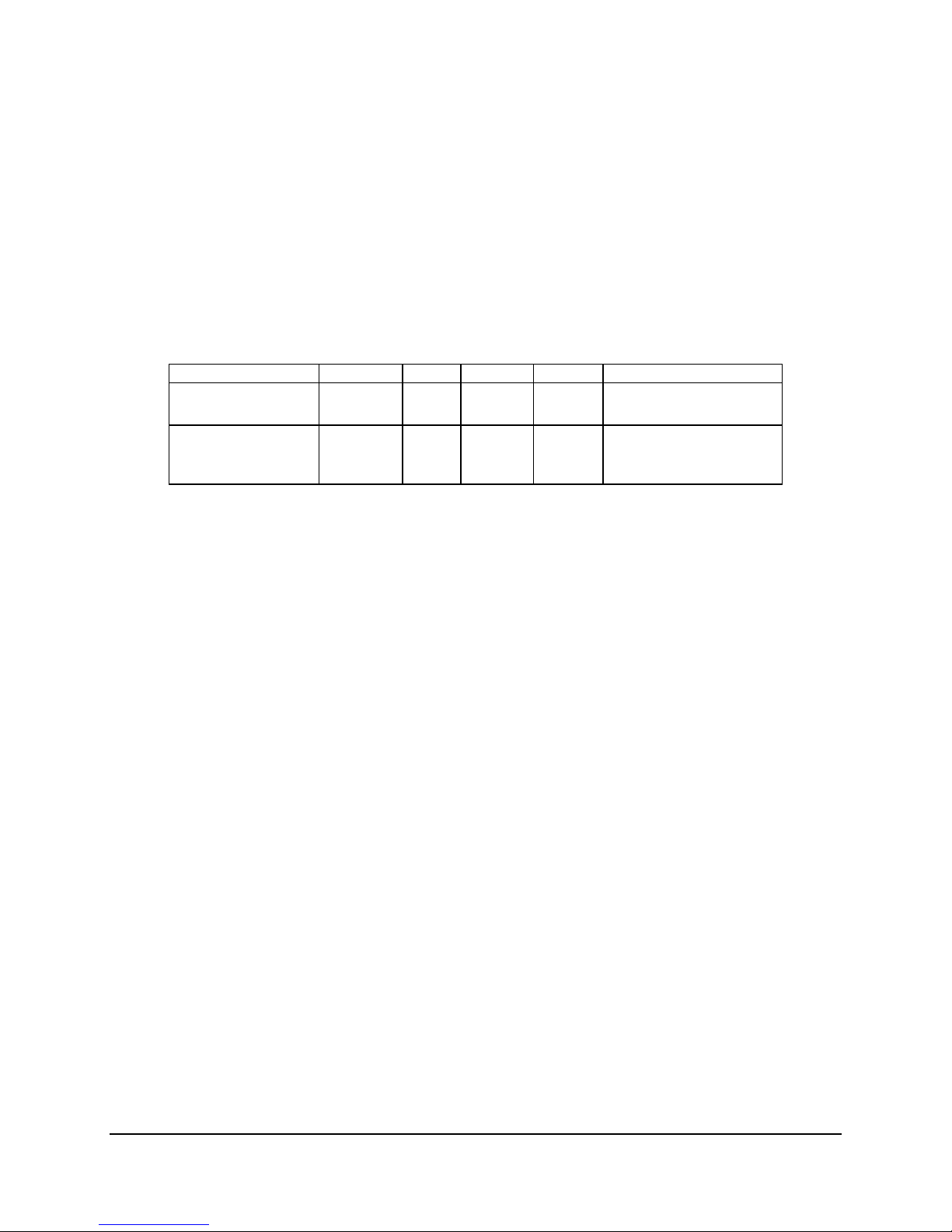
Table 5. PCI Bus Segment Characteristics
PCI Bus Segment Voltage Width Speed Type On-board Device Support
PXA
6321ESB
PE1, PE2
BNB PCI Express*
Ports 4, 5
3.3V/5.0V 64 bit 133 MHz PCI-X* Full-height riser slot
3.3V x8 20 Gb/S PCI
Express*
Low-profile riser slot
3.2.1.1 PXA: 64-bit, 133MHz PCI Subsystem
One 64-bit PCI-X* bus segment is directed through the 6321ESB ICH6. This PCI-X segment,
PXA, supports up to three PCI add-in cards on the full-height riser card.
3.2.1.2 PE2: One x4 PCI Express* Bus Segment
One x4 PCI Express* bus segment is directed through the 6321ESB. This PCI Express
segment, PE2, supports one x8 PCI Express segment to the proprietary I/O module mezzanine
connector.
3.2.1.3 PCI Riser Slot
The primary I/O buses for this server board supports one Super Slot connector which supports
one PCI riser assembly supporting two PCI slots:
One low-profile PCI Express* x8 and one mid-height PCI-X* 133.
Or one low-profile PCI Express*x4 and one mid-height PCI Express* x4.
3.2.2 Serial ATA Support
The Intel® 6321ESB I/O Controller Hub has an integrated Serial ATA (SATA) controller that
supports independent DMA operation on six ports and supports data transfer rates of up to
3.0 Gb/s. The six SATA ports on the server board are numbered SATA-0 thru SATA-5. The
SATA ports can be enabled/disabled and/or configured through the BIOS Setup Utility.
3.2.2.1 Intel
The embedded Intel
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology Support
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology solution offers data stripping (RAID
Level 0) and data mirroring (RAID Level 1). For higher performance, data stripping alleviates
disk bottlenecks by taking advantage of the dual independent DMA engines that each SATA
port offers.
Revision 2.3
13
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 23

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Data mirroring is for data security. If a disk fails, a mirrored copied of the failed disk is brought
on-line. There is no loss of either PCI resources (request/grant pair) or add-in card slots.
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology functionality requires these items:
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology Option ROM
®
Application Accelerator RAID edition drivers, most recent revision
At least two SATA hard disk drives
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology is not available in these configurations:
Intel
The SATA controller in compatible mode
Intel
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology has been disabled
3.2.3 Parallel ATA (PATA) Support
The integrated IDE controller of the 6321ESB ICH6 provides one IDE channel. It redefines
signals on the IDE cable to allow both host and target throttling of data and transfer rates of up
to 100 MB/s. The IDE channel provides optical drive support. The BIOS initializes and supports
ATAPI devices such as LS-120/240, CD-ROM, CD-RW and DVD-ROM. The IDE channel is
accessed through a high-density 40-pin connector ((J2K5) that provides I/O signals. The ATA
channel can be configured and enabled or disabled through the BIOS Setup Utility.
3.2.4 USB 2.0 Support
The USB controller functionality integrated into the 6321ESB provides the interface for up to
four USB 2.0 ports. Two external connectors are located on the back edge of the server board
and one internal 2x5 header supports two optional USB 2.0 ports.
3.3 Video Support
An ATI* ES1000 PCI graphics accelerator with 16 MB of video DDR SDRAM and support
circuitry for an embedded SVGA video sub-system is provided. The ATI ES1000 chip contains
an SVGA video controller, clock generator, 2D engine, and RAMDAC in a 359-pin BGA. One
4M x 16 x 4 bank DDR SDRAM chip provides 16 MB of video memory.
The SVGA sub-system supports modes up to 1024 x 768 resolution in 8/16/32 bpp modes
under 2D. It also supports both CRT and LCD monitors up to a 100 Hz vertical refresh rate.
Video is accessed using a standard 15-pin VGA connector found on the back edge of the server
board. Video signals are also made available through the 120-pin bridge-board connector that
provides signals for an optional video connector on the control panel. Video is routed to both the
rear video connector and a control panel video connector. Video is present at both connectors
simultaneously and cannot be disabled at either connector individually. Video monitors can be
hot-plugged.
Revision 2.3
14
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 24

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Functional Architecture
3.3.1.1 Video Modes
The ATI* ES1000 chip supports all standard IBM* VGA modes. The table shows the 2D modes
supported for both CRT and LCD.
Table 6. Video Modes
2D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz)
640x480 60, 72, 75, 85, 90, 100,
120, 160, 200
800x600 60, 70, 72, 75, 85, 90,
100, 120, 160
1024x768 60, 70, 72, 75, 85, 90,
100
1152x864 43, 47, 60, 70, 75, 80,
85
1280x1024 60, 70, 74, 75 Supported Supported Supported
1600x1200 52 Supported Supported Supported
8 bpp 16 bpp 32 bpp
Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported
2D Video Mode Support
3.3.1.2 Video Memory Interface
The memory controller sub-system of the ES1000 arbitrates requests from the direct memory
interface, the VGA graphics controller, the drawing co-processor, the display controller, the
video scalar, and the hardware cursor. Requests are serviced in a manner that ensures display
integrity and maximum CPU/co-processor drawing performance.
The server board supports a 16 MB (4 Meg x 16-bit x four banks) DDR SDRAM device for video
memory.
3.4 Network Interface Controller (NIC)
Network interface support is provided from the built in Dual GbE MAC features of the 6321ESB
in conjunction with the Intel
they provide support for dual LAN ports designed for 10/100/1000 Mbps operation.
The 82563EB device is based upon proven PHY technology integrated into Intel’s gigabit
Ethernet controllers. The physical layer circuitry provides a standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
interface for 1000BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 10BASE-T applications (802.3, 802.3u, and
802.3ab). The 82563EB device can transmit and receive data at rates of 1000 Mbps, 100 Mbps,
or 10 Mbps.
®
82563EB compact Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY). Together,
Revision 2.3
15
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 25

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Each network interface controller (NIC) drives two LEDs located on each network interface
connector. The link/activity LED at the right of the connector indicates network connection when
on, and Transmit/Receive activity when blinking. The speed LED at the left indicates 1000-Mbps
operation when amber, 100-Mbps operation when green, and 10-Mbps when off.
Table 7. NIC2 Status LED
LED Color LED State NIC State
Off 10 Mbps
Green/Amber (Left)
Green (Right)
Green 100 Mbps
Amber 1000 Mbps
On Active Connection
Blinking Transmit/Receive activity
3.4.1 Intel
Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology moves network data efficiently through Intel® Xeon
®
I/O Acceleration Technolgy
®
processor-based servers for improved application responsiveness across diverse operating
systems and virtualized environments.
®
Intel
I/OAT improves network application responsiveness by unleashing the power of Intel®
®
Xeon
processors through efficient network data movement and reduced system overhead. Intel
multi-port network adapters with Intel I/OAT provide high-performance I/O for server
consolidation and virtualization via stateless network acceleration that seamlessly scales across
multiple ports and virtual machines. Intel I/OAT provides safe and flexible network acceleration
through tight integration into popular operating systems and virtual machine monitors, avoiding
the support risks of third-party network stacks and preserving existing network requirements
such as teaming and failover.
3.5 Super I/O
Legacy I/O support is provided by a National Semiconductor* PC87427 Super I/O device. This
chip contains the necessary circuitry to support these functions:
GPIOs
Serial ports
Keyboard and mouse support
Wake up control
System health support
Revision 2.3
16
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 26

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Functional Architecture
3.5.1.1 Serial Ports
The server board provides an external DB9 serial port and an internal serial header.
Table 8. Serial A Port Header Pin-out (External DB9)
RJ45 Signal Abbreviation DB9
1 Request to Send RTS 7
2 Data Terminal Ready DTR 4
3 Transmitted Data TD 3
4 Signal Ground SGND 5
5 Ring Indicator RI 9
6 Received Data RD 2
7 DCD or DSR DCD/DSR 1 or 6 (see note)
8 Clear To Send CTS 8
Table 9. Internal Serial B Port Header Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Serial Port A Header Pin-out
1 DCD
2 DSR
3 RX
4 RTS
5 TX
6 CTS
7 DTR
8 RI
9 GND
Note: The RJ45-to-DB9 adapter should match the configuration of the serial device used. One
of two pin-out configurations is used, depending on whether the serial device requires a DSR or
DCD signal. The final adapter configuration should also match the desired pin-out of the RJ45
connector, as it can also be configured to support either DSR or DCD.
3.5.1.2 Floppy Disk Controller
The server board does not support a floppy disk controller (FDC) interface, but the system BIOS
recognizes USB floppy devices.
Revision 2.3
17
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 27

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
3.5.1.3 Keyboard and Mouse Support
Dual stacked PS/2 ports on the back edge of the server board support a keyboard and mouse.
Either port can support a mouse or keyboard. Neither port supports hot plugging.
3.5.1.4 Wake-up Control
The super I/O contains functionality allows events to power-on and power-off the system.
3.5.1.5 System Health Support
The super I/O provides an interface via GPIOs for BIOS and system management firmware to
activate the diagnostic LEDs, the FRU fault indicator LEDs for processors, FBDIMMS, fans, and
the system status LED. See section 7 to locate the LEDs.
Revision 2.3
18
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 28

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Platform Management
4. Platform Management
The platform management sub-system is based on the integrated baseboard management
controller (BMC) features of the Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub. The onboard platform
management subsystem consists of communication buses, sensors, system BIOS, and system
management firmware.
See Appendix B for onboard sensor data. For additional platform management information see
the Intel
®
5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
LM4
Revision 2.3
Figure 7. SMBUS Block Diagram
19
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 29

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
5. Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
5.1 Board Connectors
Table 10. Board Connector Matrix
Connector Quantity Server Board Reference Designators Connector Type Pin Count
Power supply 3 J9E1
J9B1
J9C1
CPU 2 J8H1, J5H1 CPU Sockets 771
Main Memory 8 J7A2, J7A3, J7A4, J7A5, J8A2, J8A3 DIMM Sockets 240
Super Slot 1 J4B2 Card Edge 98
IDE 1 J2K5 Shrouded Header 40
CPU Blowers #1
and #2
System Fan 2 J1K1 Header 3
Battery 1 XBT3E1 Battery Holder 3
Keyboard/Mouse 1 J9A2 PS2, stacked 12
Rear USB 2 J9A2 External 4
Serial Port A 1 J8A1 External 9
Serial Port B 1 J1A1 Header 9
Video connector 1 J7A1 External, D-Sub 15
LAN connector
10/100/1000
SSI Control Panel 1 J2K2 Header 24
Internal USB 1 J3K1 Header 10
Serial ATA (SATA) 2 J1J1, J1J2 Header 7
SATA/SAS 4 J1G2, J1G1, J1F1, J1E4 Header 7
System Recovery
Setting Jumpers
2 J2K3, J2K4 Header 4
2 JA6A1, JA5A1 External LAN connector
4 J1C2, J1C4 Jumper 3
CPU Power
Main Power
P/S Aux
with built-in magnetic
8
24
5
14
Revision 2.3
20
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 30

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
5.2 Power Connectors
The main power supply connection is obtained using an SSI compliant 2x12 pin connector
(J9B1). Two additional power related connectors; one SSI compliant 2x4 pin power connector
(J9E1) supports additional 12V. One SSI compliant 1x5 pin connector (J9C1) provides I
monitors the power supply.
Table 11. Power Connector Pin-out (J3K3)
Pin Signal Color Pin Signal Color
1 +3.3Vdc Orange 13 +3.3Vdc Orange
2 +3.3Vdc Orange 14 -12Vdc Blue
3 GND Black 15 GND Black
4 +5Vdc Red 16 PS_On# Green
5 GND Black 17 GND Black
6 +5Vdc Red 18 GND Black
7 GND Black 19 GND Black
8 PWR_OK Gray 20 RSVD_(-5V) White
9 5VSB Purple 21 +5Vdc Red
10 +12Vdc Yellow 22 +5Vdc Red
11 +12Vdc Yellow 23 +5Vdc Red
12 +3.3Vdc Orange 24 GND Black
2
C
Table 12. 12V Power Connector Pin-out (J9E1)
Pin Signal Color
1 GND Black
2 GND Black
3 GND Black
4 GND Black
5 +12Vdc Yellow/Black
6 +12Vdc Yellow/Black
7 +12Vdc Yellow/Black
8 +12Vdc Yellow/Black
Revision 2.3
21
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 31

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Table 13. Power Supply Signal Connector Pin-out (J9C1)
Pin Signal Color
1 SMB_CLK_ESB_FP_PWR_R Orange
2 SMB_DAT_ESB_FP_PWR_R Black
3 SMB_ALRT_3_ESB_R Red
4 3.3V SENSE- Yellow
5 3.3V SENSE+ Green
5.3 Riser Card Slots
The server board has one riser card slot. The riser card slot is capable of supporting one riser
card that supports one PCI-X* 133 full-height/mid-length add-in card and one low-profile PCI
Express* x8 add-in-card.
5.4 SSI Control Panel Connector
The server board provides a 24-pin SSI control panel connector (J2K2) for use with non-Intel
chassis. The following table provides the pin-out for this connector.
Table 14. Front Panel SSI Standard 24-pin Connector Pin-out (J2K2)
Pin Signal Name Control Panel Pin-out Pin Signal Name
1 P3V3_STBY 2 P3V3_STBY
3 Key 4 P5V_STBY
5 FP_PWR_LED_L 6 FP_ID_LED_L
7 P3V3 8 FP_STATUS_LED1_R
9 HDD_LED_ACT_R 10 FP_STATUS_LED2_R
11 FP_PWR_BTN_L 12 LAN_ACT_A_L
13 GND 14 LAN_LINKA_L
15 Reset Button 16 PS_I2C_3VSB_SDA
17 GND 18 PS_I2C_3VSB_SCL
19 FP_ID_BTN_L 20 FP_CHASSIS_INTRU
21 TEMP_SENSOR 22 LAN_ACT_B_L
23 FP_NMI_BTN_L
Power
LED
HDD
LED
Power
Button
Reset
Button
Sleep
Button
NMI
ID LED
ID Button
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O O
O
Cool Fault
System
Fault
LAN A
Link / Act
SMBus
Intruder
LAN B
Link / Act
24 LAN_LINKB_L
Revision 2.3
22
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 32

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
5.5 I/O Connector Pinout Definition
5.5.1 VGA Connector
The following table details the pin-out of the VGA connector (J7A1).
Table 15. VGA Connector Pin-out (J7A1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 V_IO_R_COnN Red (analog color signal R)
2 V_IO_G_COnN Green (analog color signal G)
3 V_IO_B_COnN Blue (analog color signal B)
4 TP_VID_COnN_B4 No connection
5 GND Ground
6 GND Ground
7 GND Ground
8 GND Ground
9 TP_VID_COnN_B9 No Connection
10 GND Ground
11 TP_VID_COnN_B11 No connection
12 V_IO_DDCDAT DDCDAT
13 V_IO_HSYNC_COnN HSYNC (horizontal sync)
14 V_IO_VSYNC_COnN VSYNC (vertical sync)
15 V_IO_DDCCLK DDCCLK
5.5.2 NIC Connectors
The server board provides two RJ45 NIC connectors oriented side-by-side on the back edge of
the board (JA6A1, JA5A1). The pin-out for each connector is identical.
Table 16. RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out (JA6A1, JA5A1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 GND 9 NIC_A_MDI0P
2 P1V8_NIC 10 NIC_A_MDI0N
3 NIC_A_MDI3P 11 (D1) NIC_LINKA_1000_N (LED
4 NIC_A_MDI3N 12 (D2) NIC_LINKA_100_N (LED)
5 NIC_A_MDI2P 13 (D3) NIC_ACT_LED_N
6 NIC_A_MDI2N 14 NIC_LINK_LED_N
7 NIC_A_MDI1P 15 GND
8 NIC_A_MDI1N 16 GND
Revision 2.3
23
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 33

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
5.5.3 IDE Connector
The server board includes an IDE connector that supports a single slimline optical drive such as
a CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive. The connector has 44 pins providing support for both power and
I/O singles.
Table 17. 44-pin IDE Connector Pin-out (J2K5)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 ESB_PLT_RST_IDE_N 2 GND
3 RIDE_DD_7 4 RIDE_DD_8
5 RIDE_DD_6 6 RIDE_DD_9
7 RIDE_DD_5 8 RIDE_DD_10
9 RIDE_DD_4 10 RIDE_DD_11
11 RIDE_DD_3 12 RIDE_DD_12
13 RIDE_DD_2 14 RIDE_DD_13
15 RIDE_DD_1 16 RIDE_DD_14
17 RIDE_DD_0 18 RIDE_DD_15
19 GND 20 KEY
21 RIDE_DDREQ 22 GND
23 RIDE_DIOW_N 24 GND
25 RIDE_DIOR_N 26 GND
27 RIDE_PIORDY 28 GND
29 RIDE_DDACK_N 30 GND
31 IRQ_IDE 32 TP_PIDE_32
33 RIDE_DA1 34 IDE_PRI_CBLSNS
35 RIDE_DA0 36 RIDE_DA2
37 RIDE_DCS1_N 38 RIDE_DCS3_N
39 LED_IDE_N 40 GND
Revision 2.3
24
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 34

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
5.5.4 SATA Connectors
The server board provides two SATA (Serial ATA) connectors: SATA-0 (J1J2), SATA-1 (J1J1),
and four SATA (Serial ATA)/SAS (serial-attached SCSI) connectors: SATA-2/SAS-0 (J1G2),
SATA-3/SAS-1 (J1G1), SATA-4/SAS-2 (J1F1), and SATA-5/SAS-3 (J1E4).
Table 18. SATA Connector Pin-out (J1J2, J1J1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 GND GND1
2 SATA#_TX_P_C Positive side of transmit differential pair
3 SATA#_TX_N_C Negative side of transmit differential pair
4 GND GND2
5 SATA#_RX_N_C Negative side of Receive differential pair
6 SATA#_RX_P_C Positive side of Receive differential pair
7 GND GND3
Table 19. SATA/SAS Connector Pin-out (J1G2, J1G1, J1F1, J1E4)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 GND GND1
2 SATA#_TX_P_C Positive side of transmit differential pair
3 SATA#_TX_N_C Negative side of transmit differential pair
4 GND GND2
5 SATA#_RX_N_C Negative side of Receive differential pair
6 SATA#_RX_P_C Positive side of Receive differential pair
7 GND GND3
Revision 2.3
25
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 35

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
5.5.5 Serial Port Connectors
The server board provides one external 9-pin Serial ‘A’ port (J8A1) and one internal 9-pin Serial
B port header (J1A1). The following tables define the pin-outs for each.
Table 20. 9-pin Serial Header Pin-out (J8A1, J1A1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 SPA_DCD DCD (carrier detect)
2 SPA_DSR DSR (data set ready)
3 SPA_SIN RXD (receive data)
4 SPA_CTS CTS (clear to send)
5 TP_SPA_RI RI (Ring Indicate)
6 SPA_RTS RTS (request to send)
7 SPA_SOUT SOUT (serial out)
8 SPA_DTR DTR (Data terminal ready)
9 GND Ground
5.5.6 Keyboard and Mouse Connector
Two stacked PS/2 ports (J9A2) are support both a keyboard and a mouse. Either PS/2 port can
support a mouse or a keyboard. The following table details the pin-out of the PS/2 connector.
Table 21. Stacked PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Port Pin-out (J9A2)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 KB_DATA_F Keyboard Data
2 NC No Connect
3 GND Ground
4 P5V_KB_F Keyboard/mouse power
5 KB_CLK_F Keyboard Clock
6 NC No Connect
7 MS_DATA_F Mouse Data
8 NC No Connect
9 GND Ground
10 P5V_KB_F Keyboard/mouse power
11 MS_CLK_F Mouse Clock
12 NC No Connect
13 GND Ground
14 GND Ground
15 GND Ground
16 GND Ground
17 GND Ground
Revision 2.3
26
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 36

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
5.5.7 USB Connector
The following table details the pin-out of the external USB connectors (J9A2) found on the back
edge of the server board.
Table 22. External USB Connector Pin-out (J9A2)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 USB_OC1_LAN USB_Power
2 USB_P1N_LAN DATAL1 (Differential data line paired with DATAH1)
3 USB_P1P_LAN DATAH1 (Differential data line paired with DATAL1)
4 GND Ground
5 USB_OC0_LAN USB_Power
6 USB_P0N_LAN DATAH0 (Differential data line paired with DATAL0)
7 USB_P0P_LAN DATAH0 (Differential data line paired with DATAL0)
8 GND Ground
One 2x5 connector on the server board (J3K1) provides an option to support an additional USB
2.0 port.
Table 23. Internal USB Connector Pin-out (J3K1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 P5V USB Power
2 P5V USB Power
3 USB_ESB_P5N USB Port 5 Negative Signal
4 USB_ESB_P4N USB Port 4 Negative Signal
5 USB_ESB_P5P USB Port 5 Positive Signal
6 USB_ESB_P4P USB Port 4 Positive Signal
7 Ground Ground
8 Ground Ground
9 -- No Pin
10 NC No Conncet
Revision 2.3
27
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 37

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
5.6 Fan Headers
The server board incorporates a system fan circuit that supports two SSI compliant 4-pin fan
connectors and one 3-pin connector. The 3-pin connector (J1K1) is for system cooling fans. The
two 4-pin fan connectors are for processor cooling fans: CPU1 fan (J2K3) and CPU2 fan (J2K4).
The 4-pin connectors can support CPU fans that draw a maximum of 1.2 amps each. The
system fan connectors can be found towards the front edge of the server board, CPU1 fan
(J2K3), CPU2 fan (J2K4) and system fan (J1K1). These connectors support a maximum fan
load of 3.5 Amps each. With the proper sensor data record (SDR) installed, Intel
Management Software can monitor all system fans in use.
The pin configuration for each fan connector is identical.
Table 24. CPU Fan Connector Pin-out (J2K3, J2K4)
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 Ground GND GROUND is the power supply ground
2 12V Power Power supply 12V
3 Fan Tach Out FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the fan speed
4 Fan PWM In FAN_PWM signal to control fan speed
®
System
Table 25. PCI Fan Connector Pin-out (J1K1)
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 Ground GND GROUND is the power supply ground
2 12V Power Power supply 12V
3 Fan Tach Out FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the fan speed
Note: Intel Corporation server baseboards support peripheral components and contain a
number of high-density VLSI and power delivery components that need adequate airflow to
cool. Intel’s own chassis are designed and tested to meet the intended thermal requirements of
these components when the fully integrated system is used together. It is the responsibility of
the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel developed server building blocks to consult
vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of air flow required for
their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation can not be held
responsible if components fail or the server board does not operate correctly when used outside
any of their published operating or non-operating limits.
Revision 2.3
28
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 38

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Jumper Block Settings
6. Jumper Block Settings
The server board has several 3-pin jumper blocks that can be used to configure, protect, or
recover specific features of the server board. Pin 1 on each jumper block is denoted by “▼”.
6.1 Recovery Jumper Blocks
Table 26. Recovery Jumpers (J3A1, J1C1, J1C2)
Jumper Name Pins What happens at system reset…
J3A1: BMC Force
Update
J1C4: Password
Clear
J1C2: CMOS
Clear
1-2
2-3 BMC Firmware Force Update Mode – Enabled
1-2
2-3 If these pins are jumpered, administrator and user passwords will be cleared on the next
1-2
2-3
BMC Firmware Force Update Mode – Disabled (Default)
These pins should have a jumper in place for normal system operation. (Default)
reset. These pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
These pins should have a jumper in place for normal system operation. (Default)
If these pins are jumpered, the CMOS settings will be cleared on the next reset. These
pins should not be jumpered for normal operation
Force Update
J3A1
33
1-2: Disabled
CMOS CLR
2-3: Enabled
J1C2
1-2: Normal
Operation (Default)
3
2-3: CLEAR CMOS
3
PASSWORD CLR
J1C4
1-2: Normal
Operation (Default)
3
2-3: CLEAR
PASSWORD
3
Figure 8. Recovery Jumper Blocks (J3A1, J1C2, J1C4)
Revision 2.3
Intel order number: D64569-007
AF001016
29
Page 39

Jumper Block Settings Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
6.1.1 CMOS Clear and Password Reset Usage Procedure
The CMOS Clear and Password Reset recovery features are designed for minimal system down
time. The usage procedure for these two features has changed from previous generation Intel
server boards. The following procedure outlines the new usage model:
1. Power down and remove AC power.
2. Open server.
3. Move jumper from the Default operating position (Pins1-2) to the Reset/Clear position
(Pins 2-3).
4. Wait 5 seconds.
5. Move jumper back to default position (Pins 1-2).
6. Close the server chassis.
7. Reconnect AC and power up the server.
The password and/or CMOS is cleared and can be reset in BIOS setup.
6.1.2 BMC Force Update Procedure
When performing a standard BMC firmware update procedure, the update utility places the
BMC into an update mode, allowing the firmware to load safely onto the flash device. In the
unlikely event that the BMC firmware update process fails due to the BMC not being in the
proper update state, the server board provides a BMC Force Update jumper which will force the
BMC into the proper update state. The following procedure should be following in the event the
standard BMC firmware update process fails:
1. Power down and remove AC power.
2. Open the server.
3. Move jumper from the Default operating position (pins1-2) to the Enabled position (pins
2-3).
4. Close the server chassis.
5. Reconnect AC and power up the server.
6. Perform the BMC firmware update procedure that is documented in README.TXT file
that is included in the given BMC Firmware Update package.
7. After successful completion of the firmware update process, the firmware update utility
may generate an error stating that the BMC is still in update mode.
8. Power down and remove the AC power.
9. Open the server.
10. Move the jumper from the Enabled position (pins 2-3) to the Disabled position (pins 1-2).
11. Close the server chassis.
12. Reconnect AC and power up the server.
Revision 2.3
30
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 40

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Jumper Block Settings
Note: Normal BMC functionality is disabled with the Force BMC Update jumper set to the
“Enabled” position. The server should never be run with the BMC Force Update jumper set in
this position and should only be used when the standard firmware update process fails. This
jumper should remain in the Default – Disabled position when the server is running normally.
6.2 BIOS Select Jumper
The jumper block located at J3A2, is used to select which BIOS image the system will boot to.
Pin 1 on the jumper is identified by ‘▼’. This jumper should only be moved to force the BIOS to
boot to the secondary bank, which may hold a different version of BIOS.
The rolling BIOS feature of the server board will automatically alternate the Boot BIOS to the
secondary bank if the BIOS image in the primary bank is corrupted and cannot boot.
Table 27. BIOS Select Jumper (J3A2)
Pins What happens at system reset…
1-2 Force BIOS to bank 2
2-3
System is configured for normal operation (bank 1) (Default)
6.3 PCI Express* Select Jumper
The jumper block located at J1E1 is used to select which PCI Express* speed to use. Pin 1 on
the jumper is identified by ‘▼’. This jumper will need to be moved to support the PCI Express*
speed.
Table 28. PCI Express* x4/x8 Select Jumper (J1E1)
Pins Description
1-2 PCI Express* two x4
2-3
PCI Express one x8 (Default)
Revision 2.3
31
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 41

Intel® Light Guided Diagnostics Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
/
7. Intel
®
Light Guided Diagnostics
The server board has several on-board diagnostic LEDs to assist in troubleshooting board-level
issues. This section shows the location of each LED and provides a high level-usage
description. For a more detailed description of what drives the diagnostic LED operation, see
the Intel
®
5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
7.1 5-Volt Standby System Status/Fault LED
Several system management features of this server board require that 5-volt standby voltage be
supplied from the power supply. The BMC within the 6321ESB, and onboard NICs require this
voltage be present when the system is off. The 5-volt Standby System Status LED is illuminated
when AC power is applied to the platform and 5-volt standby voltage is supplied to the server
board by the power supply. See the figure below to locate this LED.
System Status
Fault LED
Revision 2.3
32
Figure 9. System Status/Fault LED Location
Intel order number: D64569-007
AF001642
Page 42

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Intel® Light Guided Diagnostics
When the AC power is first applied to the system and 5-volt standby is present, the BMC on the
server board requires 15-20 seconds to initialize. During this time, the system status LED blinks
amber and green, and the power button functionality is disabled, preventing the server from
powering up. Once BMC initialization has completed, the status LED will stop blinking and the
power button functionality is restored and can be used to turn on the server.
The bi-color 5V Standby System Status LED operates as follows:
Table 29. 5V Standby System Status LED Indicators
Color State Criticality Description
Off N/A Not ready AC power off
Green/Amber Alternating
Blink
Green Solid on System OK System booted and ready.
Green Blink Degraded System degraded
Amber Blink Non-critical Non-fatal alarm – system is likely to fail
Amber Solid on Critical, non-
Not ready Pre-DC power on – 15-20 second BMC initialization when AC is
applied to the server. Control Panel buttons are disabled until the
BMC initialization is complete.
Unable to use all of the installed memory (more than one
DIMM installed).
Correctable errors over a threshold of 10 and migrating to a
spare DIMM (memory sparing). This indicates that the user
no longer has spared DIMMs indicating a redundancy lost
condition. Corresponding DIMM LED should light up.
In mirrored configuration, when memory mirroring takes
place and system loses memory redundancy. This is not
covered by the bullet above.
Redundancy loss such as power-supply or fan. This does
not apply to non-redundant sub-systems.
PCI-e link errors
CPU failure/disabled – if there are two processors and one
of them fails
Fan alarm – Fan failure. Number of operational fans should
be more than minimum number needed to cool the system
Non-critical threshold crossed – Temperature and voltage
Critical voltage threshold crossed
VRD hot asserted
Minimum number of fans to cool the system not present or
failed
In non-sparing and non-mirroring mode if the threshold of
ten correctable errors is crossed within the window
Fatal alarm – system has failed or shutdown
recoverable
DIMM failure when there is one DIMM present, no good
memory present
Run-time memory uncorrectable error in non-redundant
mode
IERR signal asserted
Processor 1 missing
Temperature (CPU ThermTrip, memory TempHi, critical
threshold crossed)
No power good – power fault
Processor configuration error (for instance, processor
stepping mismatch)
Revision 2.3
33
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 43

Intel® Light Guided Diagnostics Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
7.2 DIMM LEDs
The server board provides a memory fault LED for each DIMM slot. The DIMM fault LED is
illuminated when the system BIOS disables the specified DIMM after it reaches a specified
number of given failures or if specific critical DIMM failures are detected. See the Intel
Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
®
5000
A
Figure 10. DIMM LED Locations
AF001525
Revision 2.3
34
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 44

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Intel® Light Guided Diagnostics
7.3 Post Code Diagnostic LEDs
During the system boot process, BIOS executes a number of platform configuration processes,
each of which is assigned a specific hex POST code number. As each configuration routine is
started, BIOS will display the given POST code to the POST Code Diagnostic LEDs found on
the back edge of the server board. To assist in troubleshooting a system hang during the POST
process, the Diagnostic LEDs can be used to identify the last POST process to be executed.
See Appendix C for a complete description of how these LEDs are read, and for a list of all
supported POST codes.
TP02312
Figure 11. POST Code Diagnostic LED Location
Revision 2.3
35
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 45

Power and Environmental Specifications Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
8. Power and Environmental Specifications
8.1 Intel
®
Server Board S5000VCL Design Specifications
Operating the server board at conditions beyond those shown in the table may cause
permanent damage to the system. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect system reliability.
Table 30. Server Board Design Specifications
Operating Temperature 0º C to 55º C 1 (32º F to 131º F)
Non-Operating Temperature -40º C to 70º C (-40º F to 158º F)
DC Voltage ± 5% of all nominal voltages
Shock (Unpackaged) Trapezoidal, 50 g, 170 inches/sec
Shock (Packaged)
< 20 lbs
≥ 20 to < 40
≥ 40 to < 80
≥ 80 to < 100
≥100 to < 120
≥120
Vibration (Unpackaged) 5 Hz to 500 Hz 3.13 g RMS random
Operating Temperature 5º C to 50º C 1 (32º F to 131º F)
Non-Operating Temperature -40º C to 70º C (-40º F to 158º F)
DC Voltage ± 5% of all nominal voltages
Shock (Unpackaged) Trapezoidal, 50 g, 170 inches/sec
Shock (Packaged) (≥ 40 lbs to < 80 lbs) 24 inches
Vibration (Unpackaged) 5 Hz to 500 Hz 3.13 g RMS random
36 inches
30 inches
24 inches
18 inches
12 inches
9 inches
Note:
1
The chassis design must provide proper airflow to avoid exceeding the Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor
5100 series or Quad-Core Intel
®
Xeon® processor 5300 series maximum case temperature.
Disclaimer Note: Intel Corporation server boards support add-in peripherals and contain a
number of high-density VLSI and power delivery components that need adequate airflow to
cool. Intel ensures through its own chassis development and testing that when Intel server
building blocks are used together, the fully integrated system will meet the intended thermal
requirements of these components. It is the responsibility of the system integrator who chooses
not to use Intel developed server building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating
parameters to determine the amount of air flow required for their specific application and
environmental conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible, if components fail or the
server board does not operate correctly when used outside any of their published operating or
non-operating limits.
Revision 2.3
36
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 46

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Power and Environmental Specifications
8.2 Baseboard Power Requirements
This section provides power supply design guidelines for a system using the Intel® Server Board
S5000VCL, including voltage and current specifications and power supply on/off sequencing
characteristics.
8.2.1 Processor Power Support
The server board supports the Thermal Design Point (TDP) guideline for Dual-Core Intel® Xeon®
processors 5100 series and Quad-Core Intel
®
Xeon® processor 5300 series. The Flexible
Motherboard Guidelines (FMB) has also been followed to help determine the suggested thermal
and current design values for anticipating future processor needs. The following table provides
maximum values for Icc, TDP power and T
series family and Quad-Core Intel
Table 31. Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5100 series and Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor
TDP Power Max TCASE Icc MAX
108 W 70º C 90 A
®
Xeon® processor 5300 series family.
5300 series TDP Guidelines
for the Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5100
CASE
®
Note: These values are for reference only. The Dual-Core Intel
and Quad-Core Intel® Xeon
®
processor 5300 series Datasheet contains the actual specifications
for the processor. If the values found in the Dual-Core Intel
Datasheet are different than those published here, the Dual-Core Intel
Xeon® processor 5100 series
®
Xeon® processor 5100 series
®
Xeon® processor 5100
series Datasheet values will supersede these, and should be used.
8.2.2 Power Supply Output Requirements
This section is for reference purposes only. Its intent is to provide guidance to system designers
for determining a proper power supply for use with this server board. The contents of this
section specify the power supply requirements Intel used to develop a power supply for its 1U
server system.
The following table defines power and current ratings for this 400 W power supplies. The
combined output power of all outputs shall not exceed the rated output power. The power
supply must meet both static and dynamic voltage regulation requirements for the minimum
loading conditions.
Revision 2.3
37
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 47

Power and Environmental Specifications Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Table 32. 400W Load Ratings
Voltage Minimum Continuous Maximum Continuous Peak
+3.3 V 1 1.5 A 10 A
+5 V 1 1.0 A 20 A
+12 V 2 0.5 A 16 A 18 A
+12 V 3 0.5 A 16 A 18 A
+12 V 4 0.5 A 16 A
+12 V 5 0.5 A 16 A
-12 V 0 A 0.5 A
+5 VSB 0.1 A 3.0 A 3.5 A
Notes:
1. Combined 3.3 V and 5 V power shall not exceed 100 W.
2. Maximum continuous total DC output power should not exceed 400 W.
3. Peak load on the combined 12 V output shall not exceed 49 A.
4. Maximum continuous load on the combined 12 V output shall not exceed 44 A.
5. Peak total DC output power should not exceed 650 W.
6. Peak power and current loading shall be supported for a minimum of 12 seconds.
8.2.3 Turn On No Load Operation
At power on the system shall present a no load condition to the power supply. In this no load
state the voltage regulation limits for the 3.3V and 5V are relaxed to +/-10% and the +12V rails
relaxed to +10/-8%. When operating loads are applied the voltages must regulated to there
normal limits.
Table 33. No-load Operating Range
Voltage Minimum Continuous Maximum Continuous Peak
+3.3 V 0 A 7 A
+5 V 0 A 5 A
+12 V 1 0 A 5 A 7 A
+12 V 2 0 A 5 A 7 A
+12 V 3 0 A 6 A
+12 V 4 0 A 5 A
-12 V 0 A 0.5 A
+5 VSB 0.1 A 3.0 A 3.5 A
Notes:
1. Maximum continuous total DC output power should not exceed 400 W.
2. Peak load on the combined 12 V output shall not exceed 49 A.
3. Maximum continuous load on the combined 12 V output shall not exceed 44 A.
4. Peak total DC output power should not exceed 650 W.
Revision 2.3
38
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 48

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Power and Environmental Specifications
8.2.4 Grounding
The grounds of the pins of the power supply output connector provide the power return path.
The output connector ground pins shall be connected to safety ground (power supply
enclosure). This grounding should be well designed to ensure passing the maximum
allowed common mode noise levels.
The power supply shall be provided with a reliable protective earth ground. All secondary
circuits shall be connected to protective earth ground. Resistance of the ground returns to
chassis shall not exceed 1.0 m . This path may be used to carry DC current.
8.2.5 Standby Outputs
The 5 VSB output shall be present when an AC input greater than the power supply turn on
voltage is applied.
8.2.6 Remote Sense
The power supply has remote sense return (ReturnS) to regulate out ground drops for all output
voltages: +3.3 V, +5 V, +12 V1, +12 V2, +12 V3, -12 V, and 5 VSB. The power supply uses
remote sense (3.3 VS) to regulate out drops in the system for the +3.3 V output. The +5 V, +12
V1, +12 V2, +12 V3, –12 V and 5 VSB outputs only use remote sense referenced to the
ReturnS signal.
The remote sense input impedance to the power supply must be greater than 200 on 3.3 VS
and 5 VS; this is the value of the resistor connecting the remote sense to the output voltage
internal to the power supply. Remote sense must be able to regulate out a minimum of a
200 mV drop on the +3.3 V output.
The remote sense return (ReturnS) must be able to regulate out a minimum of a 200 mV drop in
the power ground return. The current in any remote sense line shall be less than 5 mA to
prevent voltage sensing errors. The power supply must operate within specification over the full
range of voltage drops from the power supply’s output connector to the remote sense points.
8.2.7 Voltage Regulation
The power supply output voltages must stay within the following voltage limits when operating at
steady state and dynamic loading conditions. These limits include the peak-peak ripple/noise.
Table 34. Voltage Regulation Limits
Parameter Tolerance Minimum Nominal Maximum Units
+ 3.3V - 5%/+5% +3.14 +3.30 +3.46 V
+ 5V - 5%/+5% +4.75 +5.00 +5.25 V
+ 12V - 5%/+5% +11.40 +12.00 +12.60 V
- 12V - 5%/+9% -11.40 -12.00 -13.08 V
+ 5VSB - 5%/+5% +4.75 +5.00 +5.25 V
rms
rms
rms
rms
rms
Revision 2.3
39
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 49

Power and Environmental Specifications Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
8.2.8 Dynamic Loading
The output voltages shall remain within limits for the step loading and capacitive loading
specified in the table below. The load transient repetition rate shall be tested between 50 Hz
and 5 kHz at duty cycles ranging from 10%-90%. The load transient repetition rate is only a test
specification. The step load may occur anywhere within the MIN load to the MAX load
conditions.
Table 35. Transient Load Requirements
Output Step Load Size (See note 2) Load Slew Rate Test Capacitive Load
+3.3 V 6.0 A
+5 V 4.0 A
12 V 18.0 A
+5 VSB 0.5 A
Notes:
1. Step loads on each 12 V output may happen simultaneously.
2. The +12 V should be tested with 2200 F evenly split between the four +12 V rails.
0.25 A/ sec 250 F
0.25 A/ sec 400 F
0.25 A/ sec 2200 F
0.25 A/ sec 20 F
1, 2
8.2.9 Capacitive Loading
The power supply shall be stable and meet all requirements with the following capacitive loading
ranges.
Table 36. Capacitive Loading Conditions
Output Minimum Maximum Units
+3.3 V 250 6,800
+5 V 400 4,700
+12 V 500 each 11,000
-12 V 1 350
+5 VSB 20 350
F
F
F
F
F
8.2.10 Closed-Loop Stability
The power supply shall be unconditionally stable under all line/load/transient load conditions
including capacitive load ranges. A minimum of: 45 degrees phase margin and -10 dB gain
margin is required. The power supply manufacturer shall provide proof of the unit’s closed-loop
stability with local sensing through the submission of bode plots. Closed-loop stability must be
ensured at the maximum and minimum loads as applicable.
8.2.11 Common Mode Noise
The common mode noise on any output shall not exceed 350 mV pk-pk over the frequency
band of 10 Hz to 30 MHz.
Revision 2.3
40
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 50

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Power and Environmental Specifications
The measurement shall be made across a 100 Ω resistor between each of the DC
outputs, including ground, at the DC power connector and chassis ground (power
subsystem enclosure).
The test set-up shall use an FET probe such as Tektronix* model P6046 or equivalent.
8.2.12 Ripple/Noise
The maximum allowed ripple/noise output of the power supply is defined in the following table.
This is measured over a bandwidth of 0 Hz to 20 MHz at the power supply output connectors. A
10 F tantalum capacitor in parallel with a 0.1 F ceramic capacitor are placed at the point of
measurement.
Table 37. Ripple and Noise
+3.3 V +5 V +12 V -12 V +5 VSB
50mVp-p 50mVp-p 120mVp-p 120mVp-p 50mVp-p
8.2.13 Soft Starting
The power supply shall contain a control circuit which provides a monotonic soft start for its
outputs without overstress of the AC line or any power supply components at any specified AC
line or load conditions. There is no requirement for rise time on the 5 V standby, but the turn
on/off shall be monotonic.
8.2.14 Timing Requirements
These are the timing requirements for the power supply operation. The output voltages must
rise from 10% to within regulation limits (T
allowed to rise from 1.0 to 25 ms. All outputs must rise monotonically. Each output voltage
shall reach regulation within 50 ms (T
vout_on
Each output voltage shall fall out of regulation within 400 msec (T
turn off. The following diagrams show the timing requirements for the power supply being turned
on and off via the AC input with PSOn held low, and the PSOn signal with the AC input applied.
Table 38. Output Voltage Timing
Item Description Minimum Maximum Units
T
T
T
Output voltage rise time from each main output. 5.0 * 70 * msec
vout_rise
All main outputs must be within regulation of each other
vout_on
vout_off
*The 5 VSB output voltage rise time shall be from 1.0 ms to 25.0 ms
within this time.
All main outputs must leave regulation within this time. 400 msec
) within 5 to 70 ms, except for 5VSB; it is
vout_rise
) of each other during turn on of the power supply.
) of each other during
vout_off
50 msec
Revision 2.3
41
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 51

Power and Environmental Specifications Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
V out
10% V out
V1
V2
V3
V4
T
T
vout_rise
T
vout_on
vout_off
AF001023
Figure 12. Output Voltage Timing
Table 39. Turn On/Off Timing
Item Description Minimum Maximum Units
T
sb_on_delay
T
ac_on_delay
T
vout_holdup
T
pwok_holdup
T
pson_on_delay
T
pson_pwok
T
pwok_on
T
pwok_off
T
pwok_low
T
sb_vout
T
5VSB_holdup
Delay from AC being applied to 5VSB being within regulation. 1500 msec
Delay from AC being applied to all output voltages being
within regulation.
Time all output voltages stay within regulation after loss of
AC. Measured at 75% of maximum load.
Delay from loss of AC to de-assertion of PWOK. Measured at
75% of maximum load.
Delay from PSOn# active to output voltages within regulation
limits.
2500
21
20
5 400
Delay from PSOn# deactive to PWOK being de-asserted. 50 msec
Delay from output voltages within regulation limits to PWOK
asserted at turn on.
Delay from PWOK de-asserted to output voltages (3.3V, 5V,
12V, -12V) dropping out of regulation limits.
Duration of PWOK being in the de-asserted state during an
off/on cycle using AC or the PSOn signal.
Delay from 5VSB being in regulation to O/Ps being in
regulation at AC turn on.
Time the 5VSB output voltage stays within regulation after
loss of AC.
100 500
1
100
50 1000
70
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
Revision 2.3
42
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 52

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Power and Environmental Specifications
AC Input
T
vout_holdup
V out
T
T
AC_on_delay
pwok_low
T
sb_on_delay
PWOK
5 VSB
PSON
T
pwok_on
T
pwok_holdup
T
sb_vout
AC turn on/off cycle PSON turn on/off cycle
T
T
pwok_off
5VSB_holdup
T
sb_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
pson_on_delay
T
pwok_off
T
pson_pwok
AF001024
Figure 13. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals)
8.2.15 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby Mode
The power supply shall be immune to any residual voltage placed on its outputs (typically a
leakage voltage through the system from standby output) up to 500 mV. There shall be no
additional heat generated, nor stress of any internal components with this voltage applied to any
individual output, and all outputs simultaneously. It also should not trip the power supply
protection circuits during turn on.
Residual voltage at the power supply outputs for a no load condition shall not exceed 100 mV
when AC voltage is applied and the PSOn# signal is de-asserted.
Revision 2.3
43
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 53

Regulatory and Certification Information Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
9. Regulatory and Certification Information
WARNING
To ensure regulatory compliance, you must adhere to the assembly instructions in this guide to
ensure and maintain compliance with existing product certifications and approvals. Use only the
described, regulated components specified in this guide. Use of other products/components will
void the UL listing and other regulatory approvals of the product and will most likely result in
noncompliance with product regulations in the region(s) in which the product is sold.
To help ensure EMC compliance with your local regional rules and regulations, before computer
integration, make sure that the chassis, power supply, and other modules have passed EMC
testing using a server board with a microprocessor from the same family (or higher) and
operating at the same (or higher) speed as the microprocessor used on this server board. The
final configuration of your end system product may require additional EMC compliance testing.
For more information please contact your local Intel Representative.
This is an FCC Class A device. Integration of it into a Class B chassis does not result in a Class
B device.
9.1 Product Regulatory Compliance
Intended Application – This product was evaluated as Information Technology Equipment
(ITE), which may be installed in offices, schools, computer rooms, and similar commercial type
locations. The suitability of this product for other product categories and environments (such as:
medical, industrial, telecommunications, NEBS, residential, alarm systems, test equipment,
etc.), other than an ITE application, may require further evaluation. This is an FCC Class A
device. Integration of it into a Class B chassis does not result in a Class B device.
9.1.1 Product Safety Compliance
UL60950 – CSA 60950 (USA/Canada)
EN60950 (Europe)
IEC60950 (International)
CB Certificate & Report, IEC60950 (report to include all country national deviations)
GOST R 50377-92 – Listed on one System License (Russia)
Belarus License – Listed on System License (Belarus)
CE - Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEE (Europe)
IRAM Certification (Argentina)
Revision 2.3
44
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 54

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Regulatory and Certification Information
9.1.2 Product EMC Compliance – Class A Compliance
FCC /ICES-003 - Emissions (USA/Canada) Verification
CISPR 22 – Emissions (International)
EN55022 - Emissions (Europe)
EN55024 - Immunity (Europe)
CE – EMC Directive 89/336/EEC (Europe)
VCCI Emissions (Japan)
AS/NZS 3548 Emissions (Australia/New Zealand)
BSMI CNS13438 Emissions (Taiwan)
GOST R 29216-91 Emissions - Listed on one System License (Russia)
GOST R 50628-95 Immunity –Listed on one System License (Russia)
Belarus License – Listed on one System License (Belarus)
RRL MIC Notice No. 1997-41 (EMC) & 1997-42 (EMI) (Korea)
9.1.3 Certifications/Registrations/Declarations
UL Certification or NRTL (US/Canada)
CE Declaration of Conformity (CENELEC Europe)
FCC/ICES-003 Class A Attestation (USA/Canada)
C-Tick Declaration of Conformity (Australia)
MED Declaration of Conformity (New Zealand)
BSMI Certification (Taiwan)
GOST – Listed on one System License (Russia)
Belarus – Listed on one System License (Belarus)
RRL Certification (Korea)
Ecology Declaration (International)
Revision 2.3
45
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 55

Regulatory and Certification Information Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
9.2 Product Regulatory Compliance Markings
The server board is provided with the following regulatory marks:
Regulatory Compliance Region Marking
UL Mark USA/Canada
CE Mark Europe
EMC Marking (Class A) Canada CANADA ICES-003 CLASS A
CANADA NMB-003 CLASSE A
BSMI Marking (Class A) Taiwan
C-tick Marking Australia/New Zealand
RRL MIC Mark Korea
Country of Origin Exporting Requirements MADE IN xxxxx (Provided by label, not silk
screen)
Model Designation Regulatory Identification Examples (Intel® Server Board S5000VCL) for
boxed type boards; or Board PB number for nonboxed boards (typically high-end boards)
Revision 2.3
46
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 56

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Regulatory and Certification Information
9.3 Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices
9.3.1 FCC Verification Statement (USA)
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Intel Corporation
5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway
Hillsboro, OR 97124-6497
Phone: 1-800-628-8686
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of these measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the grantee of this device could void
the user’s authority to operate the equipment. The customer is responsible for ensuring
compliance of the modified product.
All cables used to connect to peripherals must be shielded and grounded. Operation with
cables, connected to peripherals that are not shielded and grounded may result in interference
to radio and TV reception.
Revision 2.3
47
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 57

Regulatory and Certification Information Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
9.3.2 ICES-003 (Canada)
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites bruits radioélectriques applicables aux
appareils numériques de Classe B prescrites dans la norme sur le matériel brouilleur:
“Appareils Numériques”, NMB-003 édictée par le Ministre Canadian des Communications.
English translation of the notice above:
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled “Digital Apparatus,”
ICES-003 of the Canadian Department of Communications.
9.3.3 Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity)
This product has been tested in accordance too, and complies with the Low Voltage Directive
(73/23/EEC) and EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). The product has been marked with the CE Mark
to illustrate its compliance.
9.3.4 VCCI (Japan)
English translation of the notice above:
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for
Interference (VCCI) from Information Technology Equipment. If this is used near a radio or
television receiver in a domestic environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use
the equipment according to the instruction manual.
9.3.5 BSMI (Taiwan)
The BSMI Certification Marking and EMC warning is located on the outside rear area of the
product.
Revision 2.3
48
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 58

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Regulatory and Certification Information
9.3.6 RRL (Korea)
Following is the RRL certification information for Korea.
English translation of the notice above:
1. Type of Equipment (Model Name): On License and Product
2. Certification No.: On RRL certificate. Obtain certificate from local Intel representative
3. Name of Certification Recipient: Intel Corporation
4. Date of Manufacturer: Refer to date code on product
5. Manufacturer/Nation: Intel Corporation/Refer to country of origin marked on product
9.4 Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Compliance
Intel has a system in place to restrict the use of banned substances in accordance with the
European Directive 2002/95/EC. Compliance is based on declaration that materials banned in
the RoHS Directive are either (1) below all applicable substance threshold limits or (2) an
approved/pending RoHS exemption applies.
Note: RoHS implementing details are not fully defined and may change.
Threshold limits and banned substances are noted below.
Quantity limit of 0.1% by mass (1000 PPM) for:
- Lead
- Mercury
- Hexavalent Chromium
- Polybrominated Biphenyls Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE)
Quantity limit of 0.01% by mass (100 PPM) for:
- Cadmium
Revision 2.3
49
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 59

Reference Documents Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips
When adding or removing components or peripherals from the server board, AC power
must be removed. With AC power plugged into the server board, 5-volt standby is still
present even though the server board is powered off.
When two processors are installed, both must be of identical revision, core voltage, and
bus/core speed. Mixed processor steppings is supported. However, the stepping of one
processor can not be greater then one stepping back of the other.
Processors must be installed in order. CPU 1 is located near the edge of the server
board and must be populated to operate the board.
Only fully buffered DIMMs (FBD) are supported on this server board. For a list of
supported memory for this server board, see the Intel
Memory List.
For a list of Intel supported operating systems, add-in cards, and peripherals for this
server board, see the Intel
Only Dual-Core Intel
Xeon
®
processor 5300 series, with system bus speeds of 1066, or 1333 MHz are
®
Server Board S5000VCL Tested Hardware and OS List.
®
Xeon® processors 5100 series or low- voltage Quad-Core Intel®
supported on this server board. Previous generation Intel
supported.
For a complete list of supported processors, see the following link:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000VCL
Removing AC power before performing the CMOS clear operation will cause the system
to automatically power up and immediately power down after the procedure is followed
and AC power is re-applied. If this happens remove the AC power cord again, wait 30
seconds, and then reconnect the AC power cord. Power up the system and proceed to
the <F2> BIOS setup utility to reset desired settings.
Normal BMC functionality is disabled with the force BMC update jumper set to the
“enabled” position (pins 2-3). The server should never be run with the BMC force update
jumper set in this position and should only be used when the standard firmware update
process fails. This jumper should remain in the default (disabled) position (pins 1-2)
when the server is running normally.
When performing a BIOS update, the BIOS select jumper must be set to its default
position (pins 2-3).
®
Server Board S5000VCL Tested
®
Xeon® processors are not
Revision 2.3
50
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 60

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Appendix B: Sensor Tables
Appendix B: Sensor Tables
This appendix lists the sensor identification numbers and information regarding the sensor type,
name, supported thresholds, assertion and de-assertion information, and a brief description of
the sensor purpose. See the Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification, Version
1.5, for sensor and event/reading-type table information.
Sensor Type
The Sensor Type references the values enumerated in the Sensor Type Codes table in
the IPMI specification. It provides the context in which to interpret the sensor, e.g., the
physical entity or characteristic that is represented by this sensor.
Event/Reading Type
The Event/Reading Type references values from the Event/Reading Type Code Ranges
and Generic Event/Reading Type Codes tables in the IPMI specification. Note that digital
sensors are a specific type of discrete sensors, which have only two states.
Event Offset/Triggers
Event Thresholds are ‘supported event generating thresholds’ for threshold types of
sensors.
- [u,l][nr,c,nc] upper nonrecoverable, upper critical, upper noncritical, lower
nonrecoverable, lower critical, lower noncritical
- uc, lc upper critical, lower critical
Event Triggers are ‘supported event generating offsets’ for discrete type sensors.
The offsets can be found in the Generic Event/Reading Type Codes or Sensor Type
Codes tables in the IPMI specification, depending on whether the sensor
event/reading type is generic or a sensor specific response.
Assertion/De-assertion Enables
Assertion and de-assertion indicators reveal the type of events the sensor can generate:
- As: Assertions
- De: De-assertion
Readable Value/Offsets
- Readable Value indicates the type of value returned for threshold and other non-
discrete type sensors.
- Readable Offsets indicate the offsets for discrete sensors that are readable via the
Get Sensor Reading command. Unless otherwise indicated, all event triggers are
readable, i.e., Readable Offsets consists of the reading type offsets that do not
generate events.
Revision 2.3
51
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 61

Appendix B: Sensor Tables Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Event Data
This is the data that is included in an event message generated by the associated
sensor. For threshold-based sensors, these abbreviations are used:
- R: Reading value
- T: Threshold value
Rearm Sensors
- The rearm is a request for the event status for a sensor to be rechecked and updated
upon a transition between good and bad states. Rearming the sensors can be done
manually or automatically. This column indicates the type supported by the sensor.
The following abbreviations are used in the comment column to describe a sensor:
A: Auto-rearm
M: Manual rearm
Default Hysteresis
- Hysteresis setting applies to all thresholds of the sensor. This column provides the
count of hysterisis for the sensor, which can be 1 or 2 (positive or negative
hysteresis).
Criticality
- Criticality is a classification of the severity and nature of the condition. It also controls
the behavior of the Control Panel Status LED.
Standby
- Some sensors operate on standby power. These sensors may be accessed and/or
generate events when the main (system) power is off, but AC power is present.
Revision 2.3
52
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 62

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Appendix C: POST Error Messages and Handling
Appendix C: POST Error Messages and Handling
Whenever possible, the BIOS will output the current boot progress codes on the video screen.
Progress codes are 32-bit quantities plus optional data. The 32-bit numbers include class,
subclass, and operation information. The class and subclass fields point to the type of hardware
that is being initialized. The operation field represents the specific initialization activity. Based on
the data bit availability to display progress codes, a progress code can be customized to fit the
data width. The higher the data bit, the higher the granularity of information that can be sent on
the progress port. The progress codes may be reported by the system BIOS or option ROMs.
The Response section in the table is divided into two types:
Pause: The message is displayed in the Error Manager screen, an error is logged to the
SEL, and user input is required to continue. The user can take immediate corrective
action or choose to continue booting.
Halt: The message is displayed in the Error Manager screen, an error is logged to the
SEL, and the system cannot boot unless the error is resolved. The user needs to replace
the faulty part and restart the system.
Table 40. POST Error Messages and Handling
Error Code Error Message Response
004C Keyboard/interface error Pause
0012 CMOS date/time not set Pause
5220 Configuration cleared by jumper Pause
5221 Passwords cleared by jumper Pause
5223 Configuration default loaded Pause
0048 Password check failed Halt
0141 PCI resource conflict Pause
0146 Insufficient memory to shadow PCI ROM Pause
8110 Processor 01 internal error (IERR) on last boot Pause
8111 Processor 02 internal error (IERR) on last boot Pause
8120 Processor 01 thermal trip error on last boot Pause
8121 Processor 02 thermal trip error on last boot Pause
8130 Processor 01 disabled Pause
8131 Processor 02 disabled Pause
8160 Processor 01 unable to apply BIOS update Pause
8161 Processor 02 unable to apply BIOS update Pause
8190 Watchdog timer failed on last boot Pause
8198 Operating system boot watchdog timer expired on last boot Pause
0192 L3 cache size mismatch Halt
0194 CPUID, processor family are different Halt
0195 Front side bus mismatch Pause
0197 Processor speeds mismatched Pause
8300 Baseboard management controller failed self-test Pause
8306 Front panel controller locked Pause
Revision 2.3
53
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 63

Appendix C: POST Error Messages and Handling Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Error Code Error Message Response
8305 Hotswap controller failed Pause
84F2 Baseboard management controller failed to respond Pause
84F3 Baseboard management controller in update mode Pause
84F4 Sensor data record empty Pause
84FF System event log full Pause
8500 Memory Component could not be configured in the selected RAS mode. Pause
8520 DIMM_A1 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8521 DIMM_A2 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8522 DIMM_A3 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8523 DIMM_A4 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8524 DIMM_B1 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8525 DIMM_B2 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8526 DIMM_B3 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8527 DIMM_B4 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8528 DIMM_C1 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8529 DIMM_C2 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
852A DIMM_C3 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
852B DIMM_C4 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
852C DIMM_D1 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
852D DIMM_D2 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
852E DIMM_D3 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
852F DIMM_D4 failed Self Test (BIST). Pause
8540 Memory Component lost redundancy during the last boot. Pause
8580 DIMM_A1 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8581 DIMM_A2 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8582 DIMM_A3 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8583 DIMM_A4 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8584 DIMM_B1 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8585 DIMM_B2 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8586 DIMM_B3 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8587 DIMM_B4 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8588 DIMM_C1 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8589 DIMM_C2 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
858A DIMM_C3 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
858B DIMM_C4 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
858C DIMM_D1 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
858D DIMM_D2 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
858E DIMM_D3 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
858F DIMM_D4 Correctable ECC error encountered. Pause
8600 Primary and secondary BIOS IDs do not match. Pause
8601
8602 WatchDog timer expired (secondary BIOS may be bad!) Pause
8603 Secondary BIOS checksum fail Pause
Override jumper is set to force boot from lower alternate BIOS bank of flash
ROM
Pause
Revision 2.3
54
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 64

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Appendix C: POST Error Messages and Handling
POST Error Beep Codes
The following table lists POST error beep codes. Prior to system video initialization, the BIOS
uses these beep codes to inform users on error conditions. The beep code is followed by a user
visible code on POST Progress LEDs.
Table 41. POST Error Beep Codes
Beeps Error Message POST Progress Code Description
3 Memory error System halted because a fatal error related to the memory
was detected.
6 BIOS rolling back
error
The BMC may generate beep codes upon detection of failure conditions. Beep codes are
sounded each time the problem is discovered, such as on each power-up attempt, but are not
sounded continuously. Codes that are common across all Intel
use the Intel
®
5000 Series Chipsets are listed in Table 42. Each digit in the code is represented
by a sequence of beeps whose count is equal to the digit.
The system has detected a corrupted BIOS in the flash
part, and is rolling back to the last good BIOS.
®
server boards and systems that
Table 42. BMC Beep Codes
Code Reason for Beep Associated Sensors Supported?
1-5-2-1 CPU: Empty slot/population error – Processor
slot 1 is not populated.
1-5-2-2 CPU: No processors (terminators only) N/A No
1-5-2-3 CPU: Configuration error (e.g., VID mismatch) N/A No
1-5-2-4 CPU: Configuration error (e.g., BSEL mismatch) N/A No
1-5-4-2 Power fault: DC power unexpectedly lost (power
good dropout)
1-5-4-3 Chipset control failure N/A No
1-5-4-4 Power control fault Power Unit – soft power
CPU Population Error Yes
Power Unit – power unit
failure offset
control failure offset
Yes
Yes
Revision 2.3
55
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 65

Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
During the system boot, the BIOS executes platform configuration processes, each of which is
assigned a specific hex POST code number. As each configuration routine is started, the BIOS
displays the POST code on the POST Code Diagnostic LEDs on the back edge of the server
board. The Diagnostic LEDs identify the last POST process to be executed.
Each POST code is represented by a combination of colors from the four LEDs. The LEDs are
capable of displaying three colors: green, red, and amber. The POST codes are divided into an
upper nibble and a lower nibble. Each bit in the upper nibble is represented by a red LED and
each bit in the lower nibble is represented by a green LED. If both bits are set in the upper and
lower nibbles then both the red and green LEDs are lit, resulting in an amber color. If both bits
are clear, then the LED is off.
Example: The BIOS sends a value of ACh to the diagnostic LED decoder. The LEDs are
decoded as:
red bits = 1010b = Ah
green bits = 1100b = Ch
Since the red bits correspond to the upper nibble and the green bits correspond to the lower
nibble, the two are concatenated as ACh.
Table 43. Example POST Progress Code LED
8h 4h 2h 1h
LEDs Red Green Red Green Red Green Red Green
ACh 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0
Result Amber Green Red Off
MSB LSB
USB Port
USB Port
Diagnostic LEDs
Back edge of baseboard
LSBMSB
Figure 14. Diagnostic LED Placement Diagram
Revision 2.3
56
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 66

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
Table 44. Diagnostic LED POST Code Decoder
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Checkpoint
Host Processor
0x10h OFF OFF OFF R Power-on initialization of the host processor (bootstrap processor)
0x11h OFF OFF OFF A Host processor cache initialization (including AP)
0x12h OFF OFF G R Starting application processor initialization
0x13h OFF OFF G A SMM initialization
Chipset
0x21h Off Off R G Initializing a chipset component
Memory
0x22h Off Off A Off Reading configuration data from memory (SPD on DIMM)
0x23h Off Off A G Detecting presence of memory
0x24h Off G R Off Programming timing parameters in the memory controller
0x25h Off G R G Configuring memory parameters in the memory controller
0x26h Off G A Off Optimizing memory controller settings
0x27h Off G A G Initializing memory, such as ECC init
0x28h G Off R Off Testing memory
PCI Bus
0x50h Off R Off R Enumerating PCI busses
0x51h Off R Off A Allocating resources to PCI busses
0x52h Off R G R Hot Plug PCI controller initialization
0x53h Off R G A Reserved for PCI bus
0x54h Off A Off R Reserved for PCI bus
0x55h Off A Off A Reserved for PCI bus
0x56h Off A G R Reserved for PCI bus
0x57h Off A G A Reserved for PCI bus
USB
0x58h G R Off R Resetting USB bus
0x59h G R Off A Reserved for USB devices
ATA/ATAPI/SATA
0x5Ah G R G R Resetting PATA/SATA bus and all devices
0x5Bh G R G A Reserved for ATA
SMBUS
0x5Ch G A Off R Resetting SMBUS
0x5Dh G A Off A Reserved for SMBUS
Local Console
0x70h Off R R R Resetting the video controller (VGA)
0x71h Off R R A Disabling the video controller (VGA)
0x72h Off R A R Enabling the video controller (VGA)
Remote Console
0x78h G R R R Resetting the console controller
0x79h G R R A Disabling the console controller
0x7Ah G R A R Enabling the console controller
G=Green, R=Red, A=Amber
MSB LSB
Description
Revision 2.3
57
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 67

Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Checkpoint
Keyboard (PS2 or USB)
0x90h R Off Off R Resetting the keyboard
0x91h R Off Off A Disabling the keyboard
0x92h R Off G R Detecting the presence of the keyboard
0x93h R Off G A Enabling the keyboard
0x94h R G Off R Clearing keyboard input buffer
0x95h R G Off A Instructing keyboard controller to run Self Test (PS2 only)
Mouse (PS2 or USB)
0x98h A Off Off R Resetting the mouse
0x99h A Off Off A Detecting the mouse
0x9Ah A Off G R Detecting the presence of mouse
0x9Bh A Off G A Enabling the mouse
Fixed Media
0xB0h R Off R R Resetting fixed media device
0xB1h R Off R A Disabling fixed media device
0xB2h
0xB3h R Off A A Enabling/configuring a fixed media device
Removable Media
0xB8h A Off R R Resetting removable media device
0xB9h A Off R A Disabling removable media device
0xBAh
0xBCh A G R R Enabling/configuring a removable media device
Boot Device Selection
0xD0 R R Off R Trying boot device selection
0xD1 R R Off A Trying boot device selection
0xD2 R R G R Trying boot device selection
0xD3 R R G A Trying boot device selection
0xD4 R A Off R Trying boot device selection
0xD5 R A Off A Trying boot device selection
0xD6 R A G R Trying boot device selection
0xD7 R A G A Trying boot device selection
0xD8 A R Off R Trying boot device selection
0xD9 A R Off A Trying boot device selection
0XDA A R G R Trying boot device selection
0xDB A R G A Trying boot device selection
0xDC A A Off R Trying boot device selection
0xDE A A G R Trying boot device selection
0xDF A A G A Trying boot device selection
Pre-EFI Initialization (PEI) Core
0xE0h R R R Off Started dispatching early initialization modules (PEIM)
0xE2h R R A Off Initial memory found, configured, and installed correctly
G=Green, R=Red, A=Amber
MSB LSB
R Off A R
A Off A R
Detecting presence of a fixed media device (IDE hard drive detection,
etc.)
Detecting presence of a removable media device (IDE CDROM
detection, etc.)
Description
Revision 2.3
58
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 68

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Checkpoint
0xE1h R R R G Reserved for initialization module use (PEIM)
0xE3h R R A G Reserved for initialization module use (PEIM)
Driver Execution Environment (DXE) Core
0xE4h R A R Off Entered EFI driver execution phase (DXE)
0xE5h R A R G Started dispatching drivers
0xE6h R A A Off Started connecting drivers
DXE Drivers
0xE7h R A A G Waiting for user input
0xE8h A R R Off Checking password
0xE9h A R R G Entering BIOS setup
0xEAh A R A Off Flash Update
0xEEh A A A Off Calling Int 19. One beep unless silent boot is enabled.
0xEFh A A A G Unrecoverable boot failure/S3 resume failure
Runtime Phase/EFI Operating System Boot
0xF4h R A R R Entering Sleep state
0xF5h R A R A Exiting Sleep state
0xF8h
0xF9h
0xFAh
Pre-EFI Initialization Module (PEIM)/Recovery
0x30h Off Off R R Crisis recovery has been initiated because of a user request
0x31h Off Off R A Crisis recovery has been initiated by software (corrupt flash)
0x34h Off G R R Loading crisis recovery capsule
0x35h Off G R A Handing off control to the crisis recovery capsule
0x3Fh G G A A Unable to complete crisis recovery.
G=Green, R=Red, A=Amber
MSB LSB
A R R R
A R R A
A R A R
Operating system has requested EFI to close boot services
(ExitBootServices ( ) has been called)
Operating system has switched to virtual address mode
(SetVirtualAddressMap ( ) has been called)
Operating system has requested the system to reset (ResetSystem ()
has been called)
Description
Revision 2.3
59
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 69

Appendix E: Supported Intel® Server Chassis Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Appendix E: Supported Intel® Server Chassis
The Intel® Server Board S5000VCL/S5000VCLR (SATA) is supported in these Intel 1U high
density rack mount server systems: Intel
®
Server System SR1530CL/SR1530CLR and Intel®
Server System SR1530HCL/SR1530HCLR.
®
The Intel
Server Board S5000VCLSASBB/BBS5000VCLSASR (SAS) is supported in the Intel®
Server System SR1530HCLS/SR1530HCLSR.
See the Intel
®
Server Systems SR1535CL/SR1530HCL/SR1530HCLS and
SR1535CLR/SR1530HCLR/SR1530HCLSR Technical Product Specification for more
information.
E
D
C
B
A
G
H
I
A
AF001026
A Rack handles F 400 watt power supply
B Slimline drive bay (drive not included) G Processor air duct
C Power supply fans H Fan modules
D Intel® Server Board S5000VCL I Hard drive bays (drives not included)
E PCI add-in riser assembly
Figure 15. Intel® Server System SR1530CL/SR1530CLR
F
Revision 2.3
60
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 70

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Appendix E: Supported Intel® Server Chassis
F
E
D
C
B
A
G
M
H
L
K
J
A Rack handles H 400 W power supply
B Air baffle I Front panel board
C Power supply fans J Control panel
D Processor air duct K Hard drive bays (drives not included)
E Full-height PCI riser card L Optical drive bay (drive not included)
F Low-profile PCI riser card M Hard drive bay (drive not included)
G Intel® Server Board S5000VCL
Figure 16. Intel® Server System SR1530HCL/SR1530HCLR
I
A
AF001612
Revision 2.3
61
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 71

Glossary Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Glossary
Term Definition
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
AP Application Processor
APIC Advanced Programmable Interrupt Control
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
ASMI Advanced Server Management Interface
BIOS Basic Input/Output System
BIST Built-In Self Test
BMC Baseboard Management Controller
Bridge Circuitry connecting one computer bus to another, allowing an agent on one to access the other
BSP Bootstrap Processor
byte 8-bit quantity.
CBC Chassis Bridge Controller (A microcontroller connected to one or more other CBCs, together they
bridge the IPMB buses of multiple chassis.
CEK Common Enabling Kit
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CMOS In terms of this specification, this describes the PC-AT compatible region of battery-backed 128 bytes
of memory, which normally resides on the server board.
DPC Direct Platform Control
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
EHCI Enhanced Host Controller Interface
EMP Emergency Management Port
EPS External Product Specification
ESB2 Enterprise South Bridge 2
FBD Fully Buffered DIMM
FMB Flexible Mother Board
FRB Fault Resilient Booting
FRU Field Replaceable Unit
FSB Front Side Bus
GB 1024MB
GPIO General Purpose I/O
GTL Gunning Transceiver Logic
HSC Hot-Swap Controller
Hz Hertz (1 cycle/second)
I2C Inter-Integrated Circuit Bus
IA Intel® Architecture
IBF Input Buffer
ICH I/O Controller Hub
ICMB Intelligent Chassis Management Bus
IERR Internal Error
IFB I/O and Firmware Bridge
INTR Interrupt
IP Internet Protocol
IPMB Intelligent Platform Management Bus
Revision 2.3
62
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 72

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Glossary
Term Definition
IPMI Intelligent Platform Management Interface
IR Infrared
ITP In-Target Probe
KB 1024 bytes
KCS Keyboard Controller Style
LAN Local Area Network
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
LPC Low Pin Count
LUN Logical Unit Number
MAC Media Access Control
MB 1024KB
MCH Memory Controller Hub
MD2 Message Digest 2 – Hashing Algorithm
MD5 Message Digest 5 – Hashing Algorithm – Higher Security
ms milliseconds
MTTR Memory Type Range Register
Mux Multiplexor
NIC Network Interface Controller
NMI Nonmaskable Interrupt
OBF Output Buffer
OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer
Ohm Unit of electrical resistance
PEF Platform Event Filtering
PEP Platform Event Paging
PIA Platform Information Area (This feature configures the firmware for the platform hardware)
PLD Programmable Logic Device
PMI Platform Management Interrupt
POST Power-On Self Test
PSMI Power Supply Management Interface
PWM Pulse-Width Modulation
RAM Random Access Memory
RASUM Reliability, Availability, Serviceability, Usability, and Manageability
RISC Reduced Instruction Set Computing
ROM Read Only Memory
RTC Real-Time Clock (Component of ICH peripheral chip on the server board)
SDR Sensor Data Record
SECC Single Edge Connector Cartridge
SEEPROM Serial Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
SEL System Event Log
SIO Server Input/Output
SMI Server Management Interrupt (SMI is the highest priority nonmaskable interrupt)
SMM Server Management Mode
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
TBD To Be Determined
Revision 2.3
63
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 73

Glossary Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS
Term Definition
TIM Thermal Interface Material
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
UDP User Datagram Protocol
UHCI Universal Host Controller Interface
UTC Universal time coordinare
VID Voltage Identification
VRD Voltage Regulator Down
Word 16-bit quantity
ZIF Zero Insertion Force
Revision 2.3
64
Intel order number: D64569-007
Page 74

Intel® Server Board S5000VCL TPS Reference Documents
Reference Documents
Intel® 5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
Revision 2.3
65
Intel order number: D64569-007
 Loading...
Loading...