Page 1

Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
User Guide
A Guide for Technically Qualified Assemblers of Intel® Identified Subassemblies/
Products
Intel Order Number D36217-006
Page 2

Disclaimer
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied, by
estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel's
Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any
express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to
fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel products are not designed, intended or authorized for use in any medical, life saving, or life sustaining
applications or for any other application in which the failure of the Intel product could create a situation where
personal injury or death may occur. Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time,
without notice.
Intel server boards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery components that need adequate
airflow for cooling. Intel's own chassis are designed and tested to meet the intended thermal requirements of these
components when the fully integrated system is used together. It is the responsibility of the system integrator that
chooses not to use Intel developed server building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to
determine the amount of airflow required for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation
can not be held responsible if components fail or the server board does not operate correctly when used outside any
of their published operating or non-operating limits.
Intel, Intel Pentium, and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in
the United States and other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2006 - 2007, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved
ii Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 3

Safety Information
Important Safety Instructions
Read all caution and safety statements in this document before performing any of the
instructions. See also Intel Server Boards and Server Chassis Safety Information on the
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD and/or at http://support.intel.com/support/
Intel
motherboards/server/sb/cs-010770.htm.
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
Lesen Sie zunächst sämtliche Warnund Sicherheitshinweise in diesem Dokument, bevor
Sie eine der Anweisungen ausführen. Beachten Sie hierzu auch die Sicherheitshinweise zu
Intel-Serverplatinen und Servergehäusen auf der Intel
oder unter http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/sb/cs-010770.htm.
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD
Consignes de sécurité
Lisez attention toutes les consignes de sécurité et les mises en garde indiquées dans ce
document avant de suivre toute instruction. Consultez Intel Server Boards and Server
Chassis Safety Information sur le Intel
rendez-vous sur le site http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/sb/cs-
010770.htm.
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD ou bien
Instrucciones de seguridad importantes
Lea todas las declaraciones de seguridad y precaución de este documento antes de realizar
cualquiera de las instrucciones. Vea Intel Server Boards and Server Chassis Safety
Information en el Intel
support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/sb/cs-010770.htm.
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD y/o en http://
Page 4

重要安全指导
在执行任何指令之前,请阅读本文档中的所有注意事项及安全声明。 和/或
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/sb/CS-010770.htm
上的 Intel
Server Boards and Server Chassis Safety Information(《Intel
服务器主板与服务器机箱安全信息》)。
iv Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 5

Warnings
Heed safety instructions: Before working with your server product, whether you are
using this guide or any other resource as a reference, pay close attention to the safety
instructions. You must adhere to the assembly instructions in this guide to ensure and
maintain compliance with existing product certifications and approvals. Use only the
described, regulated components specified in this guide. Use of other products /
components will void the UL listing and other regulatory approvals of the product and
will most likely result in noncompliance with product regulations in the region(s) in which
the product is sold.
System power on/off: The power button DOES NOT turn off the system AC power. To
remove power from system, you must unplug the AC power cord from the wall outlet.
Make sure the AC power cord is unplugged before you open the chassis, add, or remove
any components.
Hazardous conditions, devices and cables: Hazardous electrical conditions may be
present on power, telephone, and communication cables. Turn off the server and
disconnect the power cord, telecommunications systems, networks, and modems attached
to the server before opening it. Otherwise, personal injury or equipment damage can
result.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) and ESD protection: ESD can damage disk drives,
boards, and other parts. We recommend that you perform all procedures in this chapter
only at an ESD workstation. If one is not available, provide some ESD protection by
wearing an antistatic wrist strap attached to chassis ground any unpainted metal surface on
your server when handling parts.
ESD and handling boards: Always handle boards carefully. They can be extremely
sensitive to ESD. Hold boards only by their edges. After removing a board from its
protective wrapper or from the server, place the board component side up on a grounded,
static free surface. Use a conductive foam pad if available but not the board wrapper. Do
not slide board over any surface.
Installing or removing jumpers: A jumper is a small plastic encased conductor that slips
over two jumper pins. Some jumpers have a small tab on top that you can grip with your
fingertips or with a pair of fine needle nosed pliers. If your jumpers do not have such a tab,
take care when using needle nosed pliers to remove or install a jumper; grip the narrow
sides of the jumper with the pliers, never the wide sides. Gripping the wide sides can
damage the contacts inside the jumper, causing intermittent problems with the function
controlled by that jumper. Take care to grip with, but not squeeze, the pliers or other tool
you use to remove a jumper, or you may bend or break the pins on the board.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL v
Page 6

vi Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 7

Preface
About this Manual
Thank you for purchasing and using the Intel® Server Board S5000PSL.
Multiple versions of the Intel
to server boards with the following product codes:
• S5000PSLSATA / S5000PSLSATAR
• S5000XSLSATA / S5000PXSLSATAR
• S5000PSLSAS / S5000PSLSASR
• S5000PSLROMB / S5000PSLROMBR
Where a feature varies from one product to the next, the difference will be noted in this
document. Unless specified, features apply to all versions of the server board.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, any references to the product code S5000PSLSATA or
S5000PSLSATAR also apply to product codes S5000XSLSATA or S5000XSLSATAR.
®
Server Board S5000PSL are available. This manual applies
This manual is written for system technicians who are responsible for troubleshooting,
upgrading, and repairing this server board. This document provides a brief overview of
the features of the board/chassis, a list of accessories or other components you may need,
troubleshooting information, and instructions on how to add and replace components on
the Intel
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL/.
®
Server Board S5000PSL. For the latest version of this manual, see
Manual Organization
Chapter 1 provides a brief overview of the Server Board S5000PSL. In this chapter, you
will find a list of the server board features, a photo of the product, and product diagrams to
help you identify components and their locations.
Chapter 2 provides instructions on using the utilities that are shipped with the board or
that may be required to update the system. This includes how to navigate through the
BIOS Setup screens, how to perform a BIOS update, and how to reset the password or
CMOS. Information about the specific BIOS settings and screens is available in the
Technical Product Specification. See “Additional Information and Software” on page viii
for a link to the Technical Product Specification.
Chapter 3 provides instructions on adding and replacing components. Use this chapter for
step-by-step instructions and diagrams for installing or replacing components such as the
memory, processor, and the CMOS battery.
Page 8
Chapter 4 provides troubleshooting information. In this chapter, you will find BIOS error
messages and POST code messages. You will also find suggestions for performing
troubleshooting activities to identify the source of a problem.
Product Accessories
This server board is compatible with the following Intel® Server Chassis:
• Intel
• Intel
You may need or want to purchase one or more of the following items for your server:
Processor, memory FBDIMMs, hard drive, USB floppy drive, CD-ROM or DVD-ROM
drive, RAID controller, operating system.
For information about which accessories, memory, processors, and third-party hardware
have been tested and can be used with your board, and for ordering information for Intel
products, see http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL/
compat.htm.
®
Server Chassis SC5400
®
Entry Server Chassis SC5299-E
Additional Information and Software
If you need more information about this product or information about the accessories that
can be used with this server board, use the following resources. These files are available at
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL/
Table 1. Additional Information and Software
For this Information or
Software
Technical information,
including BIOS settings
and chipset information
Hardware integration
instructions
Virtual system tours and
interactive repair
information
Accessories or other Intel
server products
®
Intel
Server Board S5000PSL Technical Product Specification and
the Intel
See the section on the web page titled Technical Specifications.
Intel
product box.
See the section on the web page titled Installation and Use.
A link to the SMaRT Tool is available under Other Resources at the
right side of the screen at
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL
Spares and Configuration Guide.
See the section on the web page titled Installation and Use.
®
®
Server Board S5000PSL Quick Start User's Guide in the
Use this Document or Software
S5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet.
viii Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 9

Table 1. Additional Information and Software
For this Information or
Software
Hardware and operating
systems that have been
tested with this product
Chassis that have been
tested with this product
Processors that have
been tested with this
product
FBDIMMs that have been
tested with this product
To make sure your system
falls within the allowed
power budget
Software to manage your
®
Intel
server
Drivers Driver (for an extensive list of available drivers),
Tested Hardware Operating Systems List.
See the section on the web page titled Compatibility.
Reference Chassis List.
See the section on the web page titled Compatibility.
Supported Processors.
See the section on the web page titled Compatibility.
Tested Memory List.
See the section on the web page titled Compatibility.
Power Budget Analysis Tool.
See the section on the web page titled Installation & Use
Intel System Management Software.
See the section on the web page titled Installation & Use
Operating System Driver (for operating system drivers).
See the section on the web page titled Software & Drivers.
Use this Document or Software
Firmware and BIOS
updates, or BIOS
recovery files
Diagnostics test software Diagnostics.
Firmware Updates.
See the section on the web page titled Software & Drivers.
See the section on the web page titled Software & Drivers.
See also the Intel® Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD that came with your server board.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL ix
Page 10

x Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 11

Contents
Safety Information ..................................................................................................... iii
Important Safety Instructions ................................................................................................ iii
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise ............................................................................................... iii
Consignes de sécurité .......................................................................................................... iii
Instrucciones de seguridad importantes ............................................................................... iii
Warnings ................................................................................................................................ v
Preface .......................................................................................................................vii
About this Manual ................................................................................................................ vii
Manual Organization ............................................................................................................vii
Product Accessories ............................................................................................................viii
Additional Information and Software ....................................................................................viii
Chapter 1: Server Board Features ............................................................................ 1
Connector and Header Locations ..........................................................................................5
Configuration Jumpers ........................................................................................................... 7
®
Intel
Light-Guided Diagnostics .............................................................................................9
Back Panel Features ...........................................................................................................12
RAID Support ....................................................................................................................... 13
SATA Server Board .....................................................................................................13
SAS Server Board .......................................................................................................14
ROMB Server Board ....................................................................................................15
Hardware Requirements ......................................................................................................16
Processor .................................................................................................................... 16
Memory ........................................................................................................................16
Power Supply ..............................................................................................................18
Optional Hardware ............................................................................................................... 19
®
Intel
RAID Activation Key ..........................................................................................19
®
Intel
RAID Smart Battery (Product Code S5000PSLROMB only) .............................19
Hard Disk Drives ..........................................................................................................19
®
Intel
Remote Management Module / Intel® Remote Management Module 2 and RMM
NIC / RMM2 NIC ..............................................................................................20
®
Intel
Local Control Panel ...........................................................................................20
Chapter 2: System Utilities ...................................................................................... 21
Using the BIOS Setup Utility ................................................................................................21
Starting Setup ..............................................................................................................21
If You Cannot Access Setup ........................................................................................21
Setup Menus ...............................................................................................................22
Upgrading the BIOS .............................................................................................................23
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL xi
Page 12

Preparing for the Upgrade ........................................................................................... 24
Upgrading the BIOS .................................................................................................... 24
Reverting to the Previous BIOS .......................................................................................... 25
Clearing the Password ........................................................................................................ 26
Clearing the CMOS ............................................................................................................. 27
Chapter 3: Hardware Installations and Upgrades ..................................................29
Before You Begin ................................................................................................................ 29
Tools and Supplies Needed ........................................................................................ 29
Installing and Removing Memory ........................................................................................ 29
Installing FBDIMMs ..................................................................................................... 29
Removing FBDIMMs ................................................................................................... 32
Installing or Replacing the Processor .................................................................................. 32
Installing the Processor ............................................................................................... 33
Installing the Heatsink(s) ............................................................................................. 37
Removing a Processor ................................................................................................ 40
Replacing the CMOS Battery .............................................................................................. 43
Appendix A: Troubleshooting .................................................................................45
System Boot Quiet Time ..................................................................................................... 45
Resetting the System .......................................................................................................... 45
Problems following Initial System Installation ...................................................................... 46
First Steps Checklist ................................................................................................... 46
Hardware Diagnostic Testing .............................................................................................. 47
Verifying Proper Operation of Key System Lights ....................................................... 47
Confirming Loading of the Operating System ............................................................. 47
Specific Problems and Corrective Actions .......................................................................... 48
Power Light Does Not Light ........................................................................................ 48
No Characters Appear on Screen ............................................................................... 49
Characters Are Distorted or Incorrect ......................................................................... 50
System Cooling Fans Do Not Rotate Properly ............................................................ 50
CD-ROM Drive or DVD-ROM Drive Activity Light Does Not Light .............................. 50
Cannot Connect to a Server ........................................................................................ 51
Problems with Network ............................................................................................... 51
System Boots when Installing PCI Card ..................................................................... 52
Problems with Newly Installed Application Software ................................................... 52
Problems with Application Software that Ran Correctly Earlier .................................. 53
Devices are not Recognized under Device Manager (Windows* Operating System) . 53
Hard Drive(s) are not Recognized ............................................................................... 53
Bootable CD-ROM Disk Is Not Detected .................................................................... 54
LED Information .......................................................................................................... 54
BIOS POST Beep Codes ............................................................................................ 54
Appendix B: Regulatory and Compliance Information .........................................57
Product Regulatory Compliance .......................................................................................... 57
xii Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 13

Product Safety Compliance .........................................................................................57
Certifications / Registrations / Declarations ................................................................. 58
Product Regulatory Compliance Markings ..................................................................58
Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices ................................................................................59
FCC (USA) ..................................................................................................................59
ICES-003 (Canada) .....................................................................................................60
Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity) .......................................................................60
VCCI (Japan) ...............................................................................................................60
BSMI (Taiwan) .............................................................................................................61
RRL (Korea) ................................................................................................................61
CNCA (CCC-China) .....................................................................................................61
Product Ecology Change (EU RoHS) .................................................................................. 62
Product Ecology Change (CRoHS) .....................................................................................62
China Packaging Recycle Marks (or GB18455-2001) ......................................................... 64
CA Perchlorate Warning ......................................................................................................64
End-of-Life / Product Recycling ...........................................................................................64
Appendix C: Getting Help ........................................................................................65
World Wide Web .................................................................................................................. 65
Telephone ............................................................................................................................65
Appendix D: System Issue Report Form ............................................................... 69
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL xiii
Page 14

xiv Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 15

List of Figures
Figure 1. Intel® Server Board S5000PSL.................................................................................. 1
Figure 2. Server Board Connector and Component Locations ................................................. 6
Figure 3. Configuration Jumpers............................................................................................... 8
Figure 4. Back Panel Connectors and LEDs........................................................................... 12
Figure 5. DIMM Sockets.......................................................................................................... 17
Figure 6. BIOS Bank Select Jumper in Force Lower Bank Position........................................ 25
Figure 7. Password Clear Jumper in Clear Password Position............................................... 26
Figure 8. CMOS Clr Jumper in the Clear CMOS Position....................................................... 27
Figure 9. Locating DIMM Sockets ........................................................................................... 30
Figure 10. Installing FBDIMMs................................................................................................ 31
Figure 11. Locating Processor Sockets................................................................................... 34
Figure 12. Opening Processor Socket Lever .......................................................................... 35
Figure 13. Opening Load Plate ............................................................................................... 35
Figure 14. Removing Protective Cover from Load Plate......................................................... 36
Figure 15. Setting Processor in Place..................................................................................... 36
Figure 16. Installing Heatsink (passive heatsink shown)......................................................... 38
Figure 17. Locating Active Heatsink Cable Connections ........................................................ 39
Figure 18. Opening Processor Socket Lever .......................................................................... 41
Figure 19. Opening Load Plate ............................................................................................... 41
Figure 20. Removing Processor from Socket.......................................................................... 42
Figure 21. Installing Protective Cover onto Load Plate ........................................................... 42
Figure 22. Locating and Removing the CMOS Battery ........................................................... 44
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL xv
Page 16

xvi Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 17

List of Tables
Table 1. Additional Information and Software .........................................................................viii
Table 2. Server Board Features ................................................................................................2
Table 3. NIC LEDs ..................................................................................................................12
Table 4. Setup Menu Key Use ................................................................................................22
Table 5. Heatsink Requirements for Compatible Intel
Table 6. Resetting the System ................................................................................................45
Table 7. POST Error Beep Codes ...........................................................................................54
Table 8. Error Beep Codes Generated by Intel
Table 9. Product Certification Markings ..................................................................................58
®
®
Server Chassis ................................. 37
Remote Management Module ....................55
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL xvii
Page 18

xviii Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 19

1 Server Board Features
This chapter briefly describes the main features of the Intel® Server Board S5000PSL.
This chapter provides a photograph of the product, a list of the server board features, and
diagrams showing the location of important components and connections on the server
board.
Figure 1. Intel
®
Server Board S5000PSL
Page 20
Table 2 summarizes the features of the server board.
Table 2. Server Board Features
Feature Description
Processor support
• Up to two Dual-Core Intel
sequence with a 677-, 1066-, or 1333-MHz front side bus
• Up to two Quad-Core Intel
with a 1066- or 1333-MHz front side bus
• Up to two 45nm 2P Dual-Core Intel
Product codes S5000PSLSATAR, S5000PSLSASR,
S5000PSLROMBR, and S5000XSLSATAR only
®
Xeon® processors 5000 or 5100
®
Xeon® processors 5300 sequence
®
Xeon® processors.
• Up to two 45nm next generation Quad-Core Intel
processors. Product codes S5000PSLSATAR,
S5000PSLSASR, S5000PSLROMBR, and S5000XSLSATAR
only
System memory support
• Eight FBDIMM sockets (DDR2-533 and DDR2-667) supporting
32 GB maximum memory
• Quad-channel memory architecture
®
Intel
5000P Chipset • Product codes S5000PSLSATA, S5000PSLSATAR,
S5000PSLSAS, S5000PSLSASR, S5000PSLROMB,
S5000PSLROMBR: Intel® 5000P Memory Controller Hub
• Product code S5000XSLSATA, S5000XSLSATAR: Intel
5000X Memory Controller Hub
®
• Intel
Cooling Support for
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub
• Two processor fans (4-pin headers)
• Four front fans (6-pin headers)
• Two rear fans (4-pin header)
3-pin fans are compatible with all fan headers. 4-pin fans should be
used only with the following fans:
• CPU1 Fan
• CPU2 Fan
• Sys Fan 1
• Sys Fan 2
• Sys Fan 5
• Sys Fan 6
Sys Fan 3 and Sys Fan 4 are connected to the CPU1 PWM, which
is programmed to work with the 4-pin active heatsink fans.
®
Xeon®
®
Add-in card slots Six expansion slots:
2 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
• One PCI-X* 64-bit / 100-MHz slot
• One PCI-X* 64-bit / 100- / 133-MHz slot
and one of from the following list
• Two PCI Express* x4 slots (product code S5000PSLSAS or
S5000PSLSASR)
• Two PCI Express x8 slots (product code S5000PSLSATA,
S5000PSLSATAR, S5000XSLSATA, or S5000XSLSATAR)
Page 21
Table 2. Server Board Features
Feature Description
Video support
• On-board ATI* ES1000 video controller with 16-MB DDR
SDRAM
• Dual-video is supported
Hard drive and optical
drive support
• Optical devices are supported
• Ultra ATA-100 support: One IDE channel that is capable of
supporting up to two drives
• One of the following:
– Product code S5000PSLSATA, S5000PSLSATAR,
S5000XSLSATA, or S5000XSLSATAR: Six SATA
connectors at 1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps
– Product code S5000PSLROMB or S5000PSLROMBR: Six
SATA connectors on the server board. Four internal and
four external SAS/SATA ports with expander support from
®
Intel
Integrated Server RAID
– Product code S5000PSLSAS or S5000PSLSASR: Four
SAS port connectors at 3 Gbps and two SATA port
connectors at 1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps
USB drive support One internal USB port
I/O control support External connections:
• PS/2* ports for keyboard and mouse
• DB9 serial port A connection
• One DH10 serial port B connector (optional)
• Two RJ45 NIC connectors for 10/100/1000 Mb connections:
Dual GbE with Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology
®
(Intel
I/O AT) through the Intel® 8256EB Network Connection
• Four USB 2.0 ports at the back of the board
Internal connections:
• One 9-pin USB header that supports two external USB 2.0
ports
• One internal USB port that supports a peripheral, such as a
floppy drive
• One DH10 serial port B header
• One of the following:
– Product code S5000PSLSATA, S5000PSLSATAR,
S5000XSLSATA, or S5000XSLSATAR: six SATA ports at
1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps
– Product code S5000PSLSAS or S5000PSLSASR: four
SATA / SAS ports and two SATA ports at 3 Gbps, two
SATA ports at 1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps
– Product code S5000PSLROMB or S5000PSLROMBR: six
onboard SATA ports, plus an Intel
module in slot 4 adds four internal and four external SAS
ports. The addition of the Intel
RAID DIMM adds intelligent RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, and 50.
• One ATA-100 40-pin connector
• One SSI-compliant 24-pin front control panel header
®
Integrated Server RAID
®
RAID Activation Key and a
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 3
Page 22

Table 2. Server Board Features
Feature Description
RAID support
Cooling fan support
Management support
• One of the following:
– Product code S5000PSLSATA an S5000PSLSATAR: Intel
Embedded Server RAID Technology II provides SATA
RAID 0, 1, and 10 with optional RAID 5 support provided by
the Intel
– Product code S5000PSLROMB and S5000PSLROMBR:
Intel
four external SAS ports. When the optional Intel
KEY AXXRAK18E and RAM are installed, hardware RAID
support is available for RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, and 50. Uses
specially keyed PCI Express slot, add-in card slot 4.
®
RAID Activation Key AXXRAKSW5
®
Integrated Server RAID provides four internal and
®
Activation
– Product code S5000PSLSAS and S5000PSLSASR: Intel
Embedded Server RAID Technology II provides SAS/SATA
RAID 0, 1, and 10 with optional RAID 5 support provided by
the Intel
®
RAID Activation Key AXXRAKSW5
• Two 4-pin processor fan connectors
• Four 6-pin front fan connectors
• Two 4-pin rear fan connectors
• Support for the Intel
sold separately)
• Support for Intel
NIC (optional component sold separately)
• Support for Intel
®
• Intel
Light-Guided Diagnostics on field replaceable units
®
Local Control Panel (optional component
®
Remote Management Module 2 and RMM2
®
System Management software
®
®
4 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 23
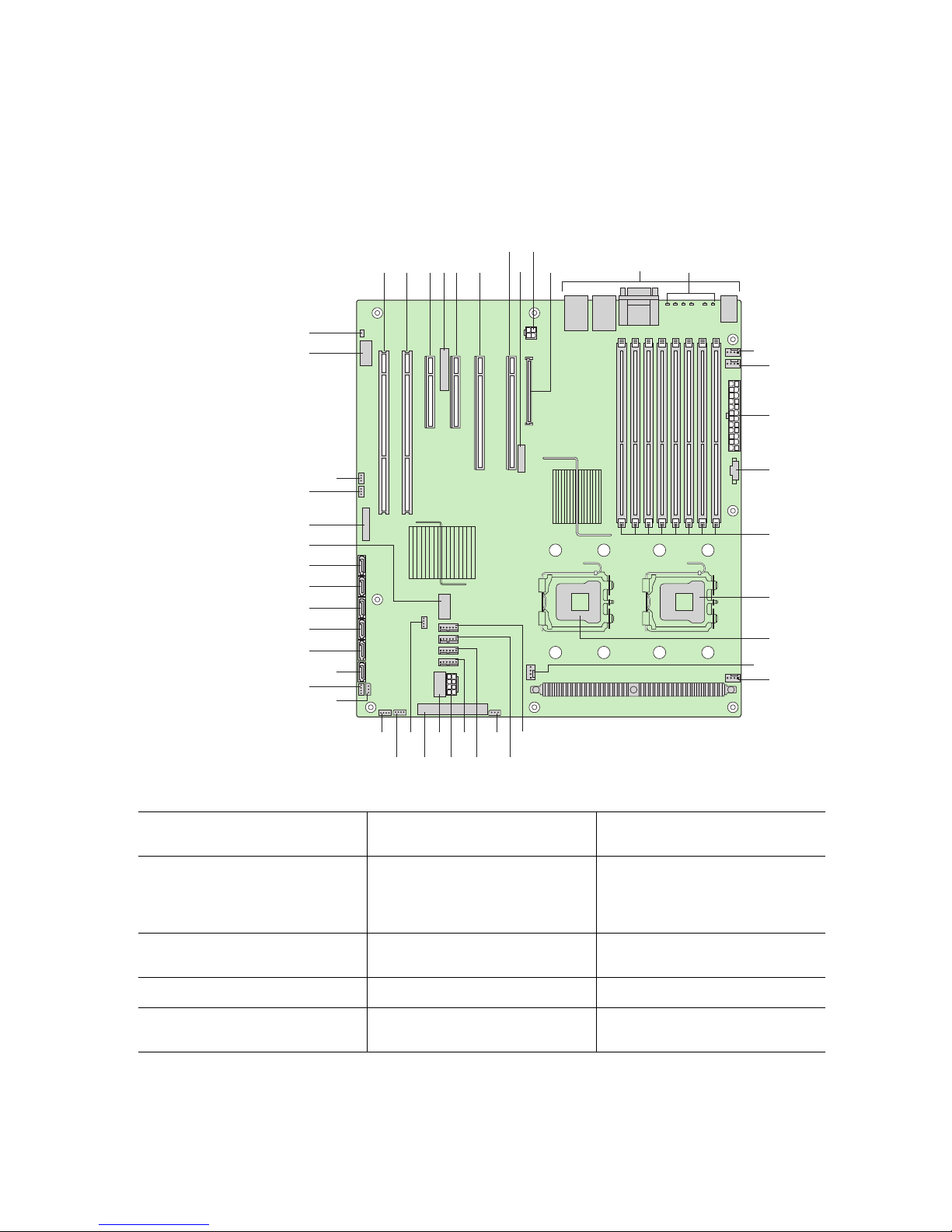
Connector and Header Locations
I
AB DGFEC
TT
SS
HJ
K
L
M
N
O
RR
QQ
PP
OO
NN
MM
LL
KK
JJ
II
HH
GG
A. PCI-X* 64-bit, 100-MHz
slot 1
B. PCI-X 64-bit, 100-/133-MHz
slot 2
T
V
FF BBDD
CCEE
AAZY
Q. DIMM sockets (see Figure 5
on page 17)
R. Processor 1 socket GG. Enclosure management
X
W
AF000247
FF. Hot-swap backplane B
header
SAS SES2 (product codes
S5000PSLSAS and
S5000PSLSASR only)
P
Q
R
S
U
C. PCI Express* x4 or x8 slot 3 S. Processor 2 socket HH. Hot-swap backplane A
D. RMM NIC connector T. Processor 2 fan header II. SATA 0
E. PCI Express x4 slot 4
(ROMB slot)
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 5
header
U. Processor 1 fan header JJ. SATA 1
Page 24
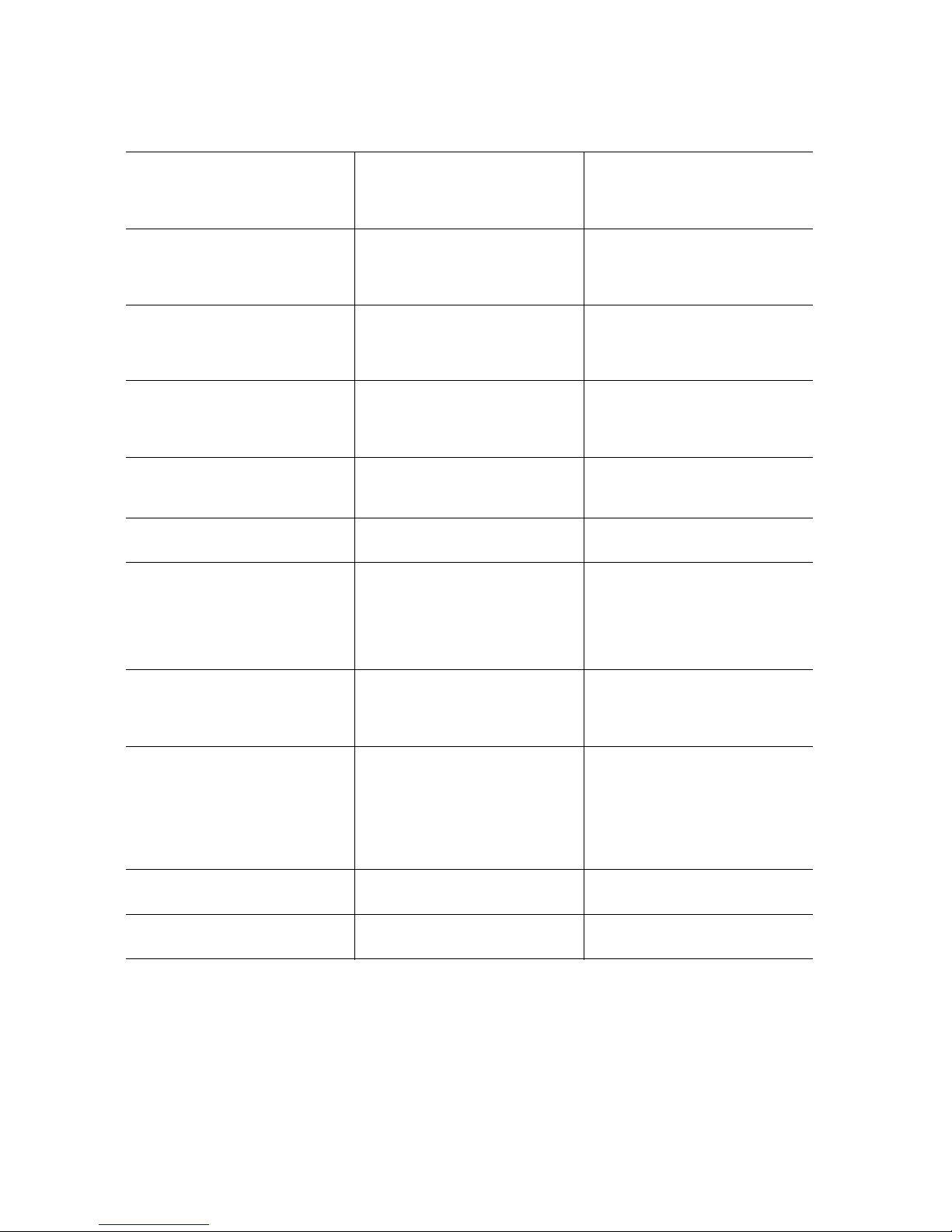
F. PCI Express x8 slot 5 V. System fan 4 header KK. SATA 2 or SAS 0 (SAS 0 is
available only on product
codes S5000PSLSAS and
S5000PSLSASR)
G. PCI Express x8 slot 6 W. System fan 3 header LL. SATA 3 or SAS 1 (SAS 1 is
available only on product
codes S5000PSLSAS and
S5000PSLSASR)
H. CMOS battery X. IPMB connector MM. SATA 4 or SAS 2 (SAS 2 is
available only on product
codes S5000PSLSAS, and
S5000PSLSASR)
I. P12V4 connector Y. System fan 2 header NN. SATA 5 or SAS 3 (SAS 3 is
available only on product
codes S5000PSLSAS and
S5000PSLSASR)
J. RMM connector (connector
for Intel
®
Remote
Z. System fan 1 header OO. USB port
Management Module)
K. Back panel I/O ports (see
AA. Processor power connector PP. Front control panel header
Figure 4 on page 12)
L. Diagnostic and Identify
LEDs (see Figure 4 on
page 12)
BB. USB header QQ. SATA_Key: SATA RAID 5
key connector (product
codes S5000PSLSATA,
S5000PSLSATAR,
S5000PSLROMB, and
S5000PSLROMBR only)
M. System fan 6 header CC. IDE connector RR. SAS_Key: SAS RAID 5 key
connector (product codes
S5000PSLSAS and
S5000PSLSASR only)
N. System fan 5 header DD. Enclosure management
SATA SGPIO header
SS. Serial B / emergency
management port header
(product codes
S5000SLSATA,
S5000SLSATAR,
S5000PSLROMB, and
S5000PSLROMBR)
O. Main power connector EE. Intel
®
Local Control Panel
TT. Chassis intrusion header
header
P. Auxiliary power signal
connector
Figure 2. Server Board Connector and Component Locations
6 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 25
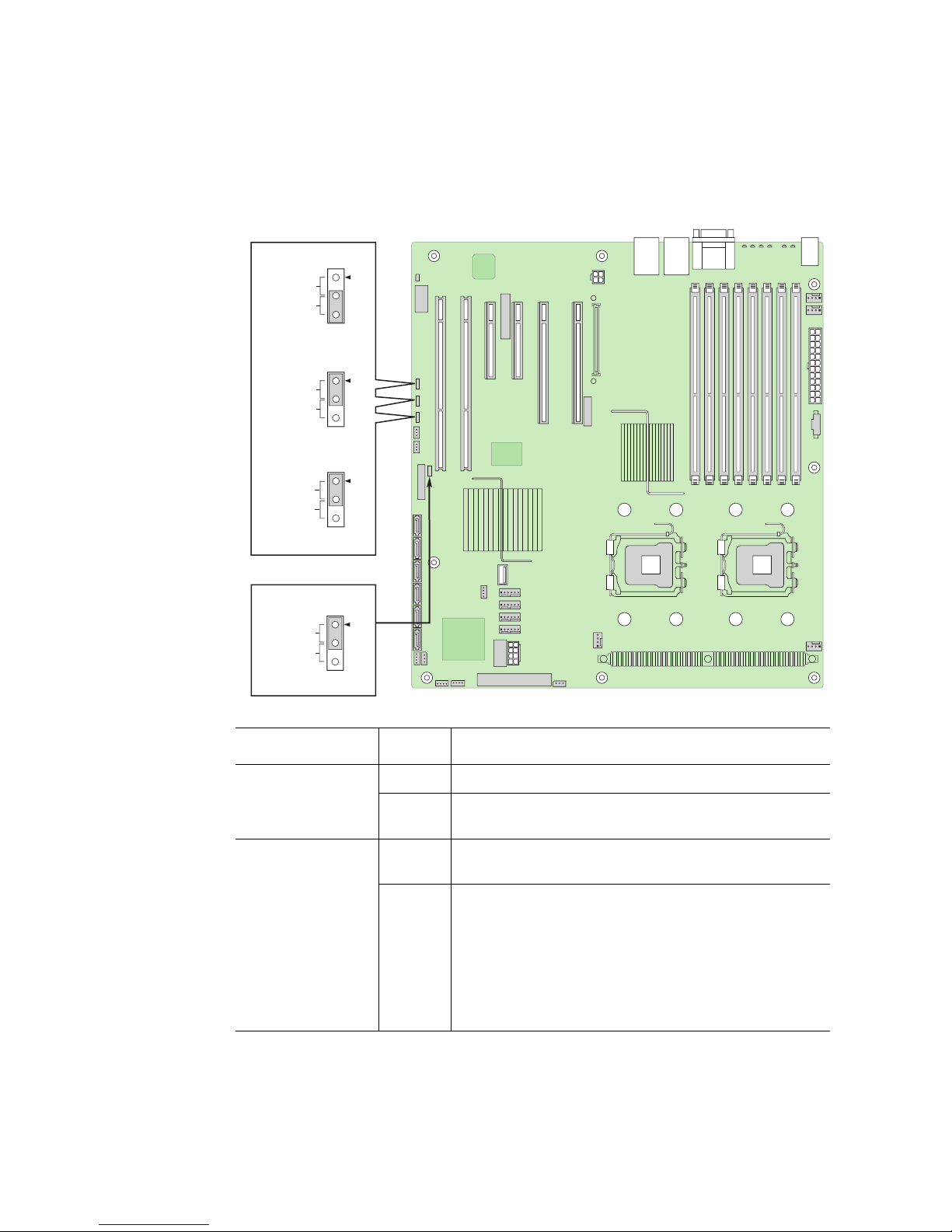
Configuration Jumpers
AF000422
3
2
CMOS Clear
3
2
Password Clear
J1E3
J1D1
Disable
Enable
3
2
BMC Force Update
J1D2
Disable
Enable
BIOS Bank Select
J1C3
3
2
Bank 0
Normal
Operation
Protect
Clear
Jumper Name Pins What Happens at System Reset
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 7
BIOS Bank Select
(J1C3)
CMOS Clear
(J1D1)
1 - 2 Bank 0: Boot to an alternate BIOS.
2 - 3 Boot from the standard BIOS. These pins should be
jumpered for normal operation.
1 - 2 Protect CMOS: these pins should be jumpered for normal
operation.
2 - 3 Erase CMOS: If these pins are jumpered for 5 to 10
seconds, the CMOS settings will be cleared on the next
server reset. These pins should not be jumpered for
normal operation.
To clear the CMOS: Power down the server, leaving AC
power connected. Place the jumper on pins 2 - 3 for 5 to
10 seconds. Move the jumper back to pins 1 - 2. Power on
the server.
Page 26

Jumper Name Pins What Happens at System Reset
Password Clear
(J1D2)
BMC Force Update
(J1E3)
1 - 2 Protect password: These pins should be jumpered for
normal operation.
2 - 3 Erase password: If these pins are jumpered, then the
password will be cleared on the next server boot. These
pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
To use this jumper to reset the password: Power down the
server. Place the jumper on pins 2 - 3. Power on the
server and wait 5 to 10 seconds. Power down the server.
Move the jumper back to pins 1 - 2. Power on the server.
1 - 2 Disable force update: These pins should be jumpered for
normal operation.
2 - 3 Enable force update: Jumpering these pins forces a BMC
update.
Figure 3. Configuration Jumpers
8 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 27
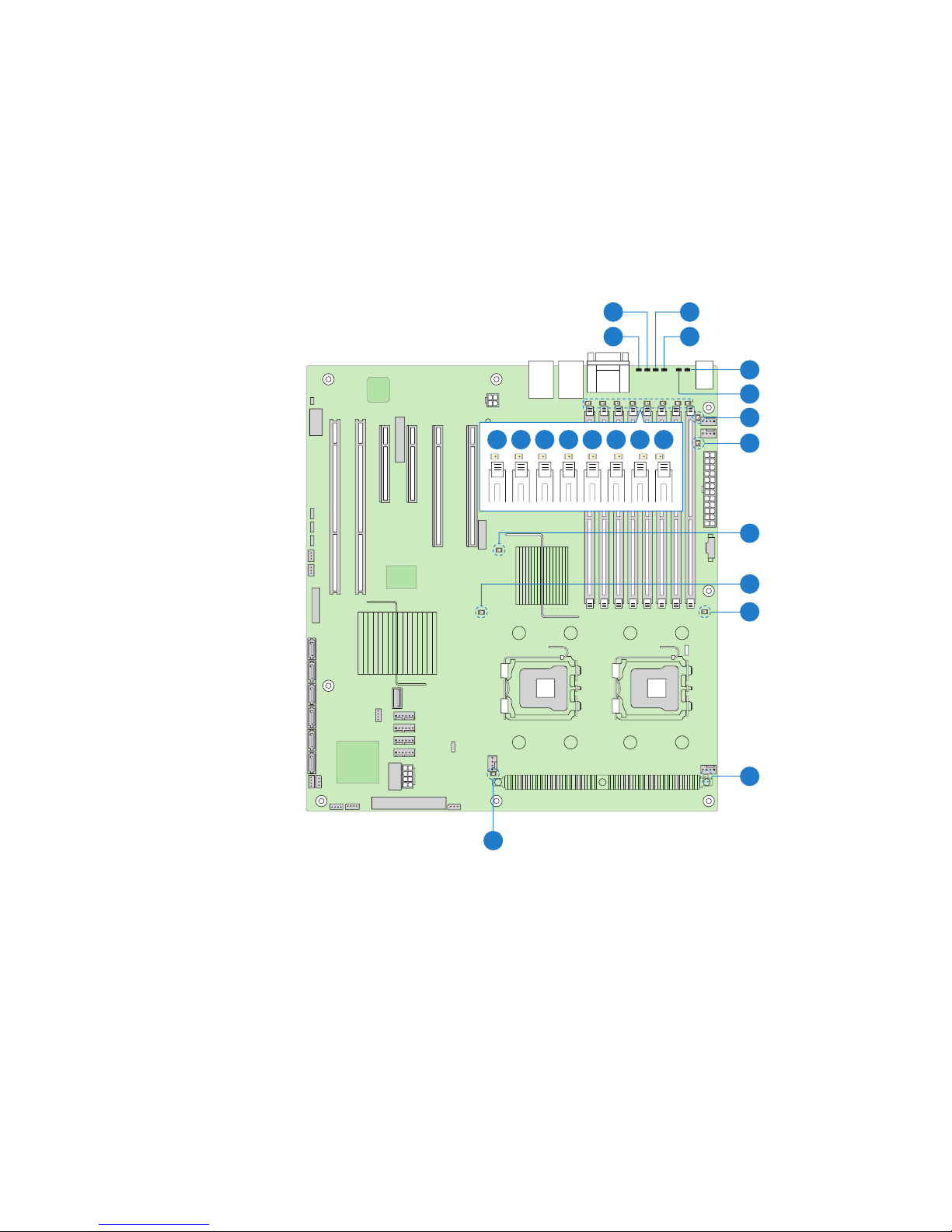
Intel® Light-Guided Diagnostics
The server board contains diagnostic LEDs to help you identify failed and failing
components and to help you identify the server from among several servers. Except for the
ID LED, the status LED, and the +5-volt standby LED, the LEDs turn on (amber) only if a
failure occurs.
A
B
I J K L M N O P
C
D
E
F
G
H
Q
R
S
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 9
T
U
AF000109
Page 28

Callout LED Function
A. Bit 3 LED POST LED. The sequence of lit POST LEDs is used
to identify specific errors that might occur during the
boot process. See the appendix of the Technical
Product Specification for a description of how to read
these LEDs.
B. LSB LED POST LED. The sequence of lit POST LEDs is used
to identify specific errors that might occur during the
boot process. See the appendix of the Technical
Product Specification for a description of how to read
these LEDs.
C. Bit 2 LED POST LED. The sequence of lit POST LEDs is used
to identify specific errors that might occur during the
boot process. See the appendix of the Technical
Product Specification for a description of how to read
these LEDs.
D. MSB LED POST LED. The sequence of lit POST LEDs is used
to identify specific errors that might occur during the
boot process. See the appendix of the Technical
Product Specification for a description of how to read
these LEDs.
E. Status LED The status LED indicates whether a system is
operating correctly, has experienced a minor fault, or
a major system error. For details about this LED, see
the Technical Product Specification.
F. ID LED This LED can be turned on and off either by pressing
a chassis button or by using system management
software. This LED is useful when the system is
grouped with several systems, such as in a rack, and
you need to easily find the system to perform
maintenance on it.
G. System fan 6 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with system
fan 6. See your server chassis documentation for
instructions to replace the fan.
H. System fan 5 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with system
fan 5. See your server chassis documentation for
instructions to replace the fan.
I. DIMM A1 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
J. DIMM A2 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
K. DIMM B1 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
10 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_A1. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_A2. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_B1. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
Page 29

Callout LED Function
L. DIMM B2 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_B2. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
M. DIMM C1 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_C1. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
N. DIMM C2 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_C2. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
O. DIMM D1 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_D1. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
P. DIMM D2 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
FBDIMM installed in socket DIMM_D2. Replace the
faulty FBDIMM.
Q. +5-volt standby LED This LED is green whenever AC power is applied to
the system. The system does not need to be
powered on in order for this LED to be on.
R. Processor 2 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
processor installed in socket CPU_2 socket. Replace
the faulty processor.
S. Processor 1 fault LED This LED indicates a fault has occurred with the
processor installed in socket CPU_1 socket. Replace
the faulty processor.
T. Processor 2 fan fault LED This LED applies only to server systems that use an
active heatsink. This LED indicates a fault has
occurred with fan that is installed on the heatsink for
processor 2. Replace the faulty unit.
U. Processor 1 fan fault LED This LED applies only to server systems that use an
active heatsink. This LED indicates a fault has
occurred with fan that is installed on the heatsink for
processor 1. Replace the faulty unit.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 11
Page 30

Back Panel Features
The diagram and table show the back panel connectors and LEDs. For information about
the LEDs, see “Intel
®
Light-Guided Diagnostics” on page 9.
C E G
A H I JB D F
AF000421
A. Mouse (top), Keyboard (bottom) F. Bit 1 LED (POST LED)
B. Status LED G. LSB LED (POST LED)
C. ID LED H. Serial A (top), Video (bottom)
D. MSB LED (POST LED) I. NIC1 (top), two USB (bottom)
E. Bit 2 LED (POST LED) J. NIC 2 (top), two USB (bottom)
Figure 4. Back Panel Connectors and LEDs
The NIC LEDs at the right and left of each NIC provide the following information.
Table 3. NIC LEDs
LED LED State Description
Left Off No network connection is in place
Solid green Active network connection is in place
Blinking green Transmit / receive activity is occurring
Right Off 10 Mbps connection (if left LED is on or blinking)
Solid green 100 Mbps connection
Solid amber 1000 Mbps connection
12 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 31

RAID Support
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL is available in a these models:
• The SATA model has product code S5000PSLSATA or S5000PSLSATAR. This
model provides only SATA support.
• The SAS model has product code S5000PSLSAS or S5000PSLSASR. It provides
both SAS and SATA support.
• The model that provides Intel
S5000PSLROMB or S5000PSLROMBR.
®
Integrated Server RAID has product code
For information about configuring RAID, see the RAID software user’s guide that is
included on the Intel
SATA Server Board
The SATA model of the Intel® Server Board S5000PSL (product code S5000PSLSATA
and S5000PSLSATAR) provides an embedded SATA controller that supports both 1.5 and
3.0 Gbps data transfer rates.
The BIOS Setup utility provides drive configuration options on the Advanced | ATA
Controller setup page, some of which affect the ability to configure RAID. The “Onboard
SATA Controller” option is enabled by default and when enabled, the “SATA Mode”
option can be set to either Legacy or Enhanced.
• Legacy supports four disk drives and does not provide RAID support.
• Enhanced supports six disk drives and is required for RAID configurations.
When enhanced mode is selected, you can enable or disable “AHCI Mode” or “Configure
SATA as RAID”. Intel
SATA as RAID.” The Intel
RAID modes 0, 1, and 10.
If RAID 5 is desired, the optional Intel
must be installed. This activation key is placed on the SATA_Key connector that is located
at the left side of the server board. For installation instructions, see the documentation that
is included with the activation key. See Figure 2 on page 6 for connection locations.
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD.
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology II is enabled by “Configure
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology II feature provides
®
RAID Activation Key AXXRAKSW5 accessory
®
When Intel
Embedded Server RAID Technology II is enabled, enclosure management is
provided through the SATA_SGPIO connector on the server board when a cable is
attached between this connector and the backplane or I
Notes:
• For help with navigating the BIOS Setup utility, see the Intel
S5000PSL Technical Product Specification.
• For help with enclosure management cabling, see the Enclosure Management
Cabling Guide for Pedestal Systems with Hot-swap Drive Backplanes. This guide is
on the Intel® Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 13
2
C interface.
®
Server Board
Page 32

SAS Server Board
In addition to the SATA features described above, SAS models of the server board
(product code S5000PSLSAS or S5000PSLSASR) also have a dual-mode 4-port Serial
Attached SCSI (SAS) controller that supports both SAS and SATA hard disk drives. This
controller is capable of data transfer rates of up to 3.0 Gbps per port.The SAS controller
supports up to 120 physical drives when expanders are used.
The BIOS Setup utility includes options on the Advanced | Mass Storage setup page to
enable or disable the SAS option ROM and the SAS controller. Both of these options must
be enabled to use RAID.
• When the SAS controller is enabled, the two black SATA ports on the server board
continue to function as SATA ports. The four blue ports can be used as either SAS or
SATA ports. When the SAS controller is disabled in the BIOS Setup utility, SATA
ports 0 and 1 (the two black ports) function as SATA ports and all other SAS / SATA
ports are disabled.
• When the SAS option ROM is enabled in the BIOS Setup utility, Intel
Server RAID Technology II is available. This enables SAS RAID modes 0, 1, or 10
for the four blue ports on the server board. With the SAS controller the user can mix
SAS and SATA drives. The RAID mode of the SAS controller supports up to eight
physical SAS/SATA drives and eight logical drives. The SAS mode of ESRT II
supports up to eight SATA / SAS hard drives and supports only one expander
backplane per chassis.
®
Embedded
Notes:
If the SAS option ROM is disabled in the BIOS Setup utility, but the SAS controller is
enabled, the four blue ports on the server board continue to function as either SAS or
SATA ports and the two black ports on the server board continue to function as SATAonly ports. However, RAID support is not available.
®
If RAID 5 is desired, the optional Intel
installed. To enable RAID 5, this activation key is placed on the SAS_Key connector that
is located at the left side of the server board. For information on how to install the Intel
RAID Activation Key AXXRAKSW5 can be
®
RAID Activation Key AXXRAKSW5 accessory to enable RAID 5, see the
documentation that is included with the accessory kit. See Figure 2 on page 6 for
connection locations.
Two SGPIO connectors are available on SAS models of the server board, one for the SAS
controller and one for the SATA controller.
SAS enclosure management is provided through the SES2 connector on the server board
when a cable is attached between the SES2 connector and the non-expander backplane.
When an expander backplane is installed, enclosure management support is inband and
this cable is not used.
• For help with navigating the BIOS Setup utility, see the Intel
®
Server Board
S5000PSL Technical Product Specification.
14 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 33

• For help with enclosure management cabling, see the Enclosure Management
Cabling Guide for Pedestal Systems with Hot-swap Drive Bacplanes. This guide is
on the Intel
®
ROMB Server Board
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD.
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL with product code S5000PSLROMB or
S5000PSLROMBR supports Intel
board includes the dual-mode six-port SATA Intel
®
Integrated Server RAID. This model of the server
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub, as
described in ”SATA Server Board”. In addition, it includes a controller that is installed
into a specially keyed PCI Express* x8 slot (slot 4). This SAS controller provides eight
additional SAS / SATA ports, four internal and four external, that are capable of three
modes.
In native SAS mode, the controller supports up to 120 physical drives when expanders are
used. If the optional Intel
and an expander are installed, the Intel
®
RAID Activation Key AXXRAK18E with a memory DIMM,
®
Integrated Server RAID module supports up to
16 physical drives and up to 64 logical drives. This provides intelligent RAID at RAID
levels 0, 1, 5, 10, and 50. See the Tested Hardware and Operating System List for
supported RAID DIMMs.
Enclosure management support is inband. No additional SGPIO or SES2 cable is required
for the expander.
Because the RAID features have firmware installed in them, each type of RAID has a
utility that can be run when the server is booted to configure the RAID options. If multiple
RAID methods are used, such as Intel
®
6321ESB I/O Controller Hub and SAS, multiple
configuration utilities are available. Each is available at a different time during the server
boot process.
®
The RAID drives can be managed and re-configured using the Intel
Console 2 utility that is on the Intel
provided in the Software User’s Guide: Intel
®
Integrated Server RAID, and Intel® RAID Controllers SRCSAS18E and
Intel
SRCSAS144E. This guide is on the Intel
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD. Instructions are
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology II,
®
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD.
RAID Web
®
The Intel
RAID Smart Battery can be installed to provide up to 65 hours of data cache
protection during a power outage. Intel
physical drives and up to 64 logical arrays when an expander is installed. Enclosure
management support is provided over SES2 (inband).
For help with enclosure management cabling, see the Enclosure Management Cabling
Guide for Pedestal Systems with Hot-swap Drive Bacplanes. This guide is on the Intel
Server Deployment Toolkit 2.0 CD.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 15
®
Integrated Server RAID supports up to 16
®
Page 34

Hardware Requirements
To avoid integration difficulties and possible board damage, your system must meet the
requirements outlined below. For a list of qualified components, see the links under
“Additional Information and Software” on page viii.
Processor
Memory
• One or two Dual-Core Intel
®
Xeon® processors 5300 sequence.
Intel
• One or two 45 nm next generation Quad-Core Intel
codes S5000PSLSATAR, S5000PSLSASR, S5000PSLROMBR, and
S5000XSLSATAR only)
• One or two 45 nm 2P Dual-Core Intel
S5000PSLSATAR, S5000PSLSASR, S5000PSLROMBR, and
S5000XSLSATAR only)
For a list of supported processors, see the links under “Additional Information and
Software”.
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL provides eight DIMM sockets in two branches. Each
branch contains two channels:
®
Xeon® processors 5000 / 5100 sequence or Quad-Core
®
Xeon® processors (Product
®
Xeon® processors (Product codes
• Branch 1 contains Channel A and Channel B
• Branch 2 contains Channel C and Channel D
Each channel contains two DIMM sockets:
• Channel A, nearest to the center of the server board, consists of DIMM sockets A1
and A2
• Channel B consists of DIMM sockets B1 and B2
• Channel C consists of DIMM sockets C1 and C2
• Channel D consists of DIMM sockets D1 and D2
16 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 35

See the following diagram to identify the DIMM sockets.
D E
C
B
A
F
G
H
Callout DIMM Socket Callout DIMM Socket
A. Branch 1, Channel A,
B. Branch 1, Channel A,
C. Branch 1, Channel B,
D. Branch 1, Channel B,
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 17
DIMM_A1
DIMM_A2
DIMM_B1
DIMM_B2
AF000093
E. Branch 2, Channel C,
DIMM_C1
F. Branch 2, Channel C,
DIMM_C2
G. Branch 2, Channel D,
DIMM_D1
H. Branch 2, Channel D,
DIMM_D2
Figure 5. DIMM Sockets
Page 36

A minimum of one 512 MB FBDIMM is required in DIMM socket DIMM_A1.
FBDIMMs must meet the following requirements:
• Use only FBDIMMs (DDR2-533 or DDR2-667).
• Use only 240-pin FBDIMMs.
• Use FBDIMMs with capacities of 512 MB, 1 GB, 2 GB, or 4 G.
• Use only FBDIMMs that comply with the JEDEC Rev 2.0 specifications.
• FBDIMMs in a given channel must be identical with respect to manufacturing,
speed, timing, and organization. For example, this means the FBDIMMs in sockets
A1 and B1 must be identical, and the FBDIMMs in sockets C1 and D1 must be
identical. FBDIMMs in adjacent sockets on the same channel do not need to be
identical.
The server will run in single-channel mode under the following conditions:
• Only a single FBDIMM is installed. This FBDIMM must be in socket DIMM_A1.
• The population of socket DIMM_A1 determines the mode that is selected. If
DIMM_A1 and DIMM_B1 are not identical, then the system reverts to singlechannel mode and DIMM_B1 is disabled.
• If the FBDIMMs in socket positions on adjacent channels of the branch are different
in terms of timing, technology, or size. If the FBDIMMs on adjacent channels of a
branch are not identical, the FBDIMM on the higher channel is disabled.
• If Branch 0 cannot support the dual-channel mode of operation for any reason, the
server will run in single-channel mode.
For dual-channel interleave, providing optimum performance, a minimum of two
FBDIMMs must be installed. Populate FBDIMMs of the same size in each channel.
Install these FBDIMMs in DIMM sockets DIMM_A1 and DIMM_B1. For dual-channel
interleave, FBDIMMs must be installed in pairs and populated as follows:
• DIMM_A1 and DIMM_B1: Populate these two sockets together first.
• Populate FBDIMMs in channel order, populating all FBDIMMs in each channel.
For example, if four FBDIMMs are to be installed, they need to be in sockets A1,
B1, C1, and D1.
• The minimum memory population for enabling Branch 1 is four FBDIMMs:
DIMM_A1, DIMM_B1, DIMM_C1 and DIMM_D1.
During the boot process, FBDIMMs that do not meet the population requirements are
disabled.
For a complete list of supported memory FBDIMMs, see the links under “Additional
Information and Software” on page viii
Power Supply
A minimum of 550 watts is required. Your power supply must provide a minimum of
3 amps of 5-volt standby current or the server will not boot.
18 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 37

Optional Hardware
Intel® RAID Activation Key
The Intel® RAID Activation Key AXXRAKSW5 can be purchased and installed to enable
RAID 5 support on your server board. For the SATA server board, product code
S5000PSLSATA or S5000PSLSATAR, an Intel
the SATA RAID 5 Key connector. For the SAS server board, product code S5000PSLSAS
or S5000PSLSASR, an Intel
RAID 5 Key connector, the SAS RAID 5 Key connector, or in each of these connectors.
®
®
RAID Activation Key can be installed in
RAID Activation Key can be installed in either the SATA
On the ROMB version of the server board, product code S5000PSLROMB or
S5000PSLROMBR, the Intel
and installed to enable intelligent RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, and 50.
For information about RAID support on this server board, see “RAID Support” on
page 13. See Figure 2 on page 6 to locate the connectors on the server board. Installation
instructions for the RAID Activation Key are included with the accessory.
®
RAID Activation Key AXXRAK18E can be purchased
Intel® RAID Smart Battery (Product Code S5000PSLROMB
only)
The Intel® RAID Smart Battery, product code AXXRSBBU3, is a small battery pack
accessory. The Smart Battery preserves the contents of the RAID Cache DIMM in the
event of a power failure. The Smart Battery circuit ensures that the backup battery is
maintained at a full charge for optimal performance when it is activated. When activated,
it provides backup power to the RAID DIMM for up to 64 hours.
Hard Disk Drives
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL supports different hard disk drive options, depending
on the version of the server board purchased.
• Optical hard disk drives
• Serial ATA (SATA) and (SAS):
— Product code S5000PSLSATA or S5000PSLSATAR: Six SATA ports at
1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps, no SAS ports
— Product code S5000PSLSAS or S5000PSLSASR: Four SAS ports at 3 Gbps and
two SATA ports at 1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps
— Product code S5000PSLROMB or S5000PSLROMBR: Six SATA ports on the
server board and four internal and four external SAS/SATA ports with expander
support from the Intel
• Parallel ATA (IDE): The server board includes one IDE connector.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 19
®
Integrated Server RAID controller.
Page 38

See the documentation included with your server chassis for additional drive information
and drive installation instructions.
Intel® Remote Management Module / Intel® Remote
Management Module 2 and RMM NIC / RMM2 NIC
The Intel® Remote Management Module / Intel® Remote Management Module 2 and the
RMM NIC / RMM2 NIC plug into connectors on the server board and act as components
of the server board, not as separate products. These two components must be installed
together.
These components provide a way to view and operate the server remotely, in real-time.
Keyboard, video, and mouse control (KVM) is redirected to a managing system. This
provides remote control. USB media redirection allows you to use a USB device
anywhere on the network as if it was installed on the managed server. For example, you
can insert a CD-ROM disk in a workstation CD-ROM drive and the managed server will
view it as its own CD-ROM drive.
Intel® Local Control Panel
The Intel® Local Control Panel provides enhanced system control by utilizing a LCD
display, which provides additional controls and indicators beyond the standard control
panel.
20 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 39

2 System Utilities
Using the BIOS Setup Utility
This section describes the BIOS Setup Utility options, which is used to change system
configuration defaults. You can run BIOS Setup with or without an operating system
being present. See “Additional Information and Software” for a link to the Technical
Product Specification where you will find details about specific BIOS setup screens.
Starting Setup
You can enter and start BIOS Setup under several conditions:
• When you turn on the server, after POST completes the memory test.
• When you have moved the CMOS jumper on the server board to the “Clear CMOS”
position (enabled).
In the two conditions listed above, during the Power On Self Test (POST), you will see
this prompt:
Press <F2> to enter SETUP
In a third condition, when CMOS/NVRAM has been corrupted, you will see warning
prompts but not the <F2> prompt:
Warning: CMOS checksum invalid
Warning: CMOS time and date not set
In this condition, the BIOS will load default values for CMOS and attempt to boot.
If You Cannot Access Setup
If you are not able to access BIOS Setup, you might need to clear the CMOS memory. For
instructions on clearing the CMOS, see “Clearing the CMOS” on page 27.
Page 40

Setup Menus
The BIOS Setup utility provides multiple pages to allow you to view and change system
settings. Some parameters are configured automatically and cannot be changed. If an
administrator password has been set, administrator privileges are required to change most
settings. If a value cannot be changed for any reason, the feature's value field is
inaccessible.
The following table describes the keyboard commands you can use in the BIOS Setup
menus.
Key to Press Description
<F1> Pressing <F1> on any menu invokes the general help window.
Table 4. Setup Menu Key Use
Left and right arrows The left and right arrow keys are used to move between the major menu
Up arrow Select Item up - The up arrow is used to select the previous value in a
Down arrow Select Item down - The down arrow is used to select the next value in a
<F5> or <-> Change Value - The minus key or the <F5> function key is used to
<F6> or <+> Change Value - The plus key or the <F6> function key is used to change
<Enter> Execute Command - The <Enter> key is used to activate submenus
<Esc> Exit - The <Esc> key provides a mechanism for backing out of any field.
pages. The keys have no affect if a submenu or pick list is displayed.
menu item's option list, or a value field pick list. Pressing the <Enter> key
activates the selected item.
menu item's option list, or a value field pick list. Pressing the <Enter> key
activates the selected item.
change the value of the current item to the previous value. This key
scrolls through the values in the associated pick list without displaying
the full list.
the value of the current menu item to the next value. This key scrolls
through the values in the associated pick list without displaying the full
list. On 106-key Japanese keyboards, the plus key has a different scan
code than the plus key on the other keyboard, but it has the same effect.
when the selected feature is a submenu, or to display a pick list if a
selected feature has a value field, or to select a sub-field for multi-valued
features like time and date. If a pick list is displayed, the <Enter> key will
undo the pick list, and allow another selection in the parent menu.
This key will undo the pressing of the <Enter> key. When the <Esc> key
is pressed while editing any field or selecting features of a menu, the
parent menu is re-entered. When the <Esc> key is pressed in any
submenu, the parent menu is re-entered. When the <Esc> key is
pressed in any major menu, the exit confirmation window is displayed
and the user is asked whether changes can be discarded.
22 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 41

Table 4. Setup Menu Key Use
Key to Press Description
<F9> Setup Defaults - Pressing <F9> causes the following to appear:
Setup Confirmation
Load default configuration now?
[Yes] [No]
If “Yes” is selected and the <Enter> key is pressed, all Setup fields are
set to their default values. If “No” is selected and the <Enter> key is
pressed, or if the <Esc> key is pressed, the user is returned to where
they were before <F9> was pressed without affecting any existing field
values.
<F10> Save and Exit - Pressing <F10> causes the following message to
appear:
If “Yes” is selected and the <Enter> key is pressed, all changes are
saved and Setup is exited. If “No” is selected and the <Enter> key is
pressed, or the <Esc> key is pressed, the user is returned to where they
were before <F10> was pressed without affecting any existing values.
Upgrading the BIOS
The upgrade utility allows you to upgrade the BIOS in flash memory. The code and data in
the upgrade file include the following:
• On-board system BIOS, including the recovery code, BIOS Setup utility, and
strings.
• On-board video BIOS and other option ROMs for devices embedded on the server
board.
• OEM binary area
• Microcode
Setup Confirmation
Save Configuration changes and exit now?
[Yes] [No]
• A way to change the BIOS language
When you perform an upgrade to your BIOS, the upgrade is performed into a secondary
BIOS partition on specialized server board hardware. When you boot your server, the
system checks for an upgraded BIOS in this secondary partition. If it finds a BIOS
upgrade has been installed, it attempts to boot with the new BIOS. If it encounters a
problem with the upgraded BIOS, the system reverts to the BIOS that was in place before
the upgrade was performed. This provides a safeguard against problems that might happen
during the upgrade, such as a power outage during the upgrade process. This is called the
rolling BIOS feature.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 23
Page 42

Preparing for the Upgrade
The steps below explain how to prepare to upgrade the BIOS, including how to record the
current BIOS settings and how to obtain the upgrade utility.
Note: In the unlikely event that a BIOS error occurs during the BIOS update process, a recovery
process may need to be followed to return the system to service. See “Additional
Information and Software” on page viii for a link to necessary software and instructions.
Recording the Current BIOS Settings
1. Boot the computer and press <F2> when you see the message:
Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
2. Write down the current settings in the BIOS Setup program.
Note: Do not skip step 2. You will need these settings to configure your computer at the end of
the procedure.
Obtaining the Upgrade
Download the BIOS image file to a temporary folder on your hard drive. See “Additional
Information and Software” for a link to the update software.
Note: Review the instructions and release notes that are provided in the readme file distributed
with the BIOS image file before attempting a BIOS upgrade. The release notes contain
critical information regarding jumper settings, specific fixes, or other information to
complete the upgrade.
Upgrading the BIOS
Follow the instructions in the readme file that came with the BIOS upgrade. When the
update completes, remove the bootable media from which you performed the upgrade.
Caution: Do not power down the system during the BIOS update process!
Note: You may encounter a CMOS Checksum error or other problem after reboot. If this
happens, shut down the system and boot it again. CMOS checksum errors require that you
enter Setup, check your settings, save your settings, and exit Setup.
24 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 43

Reverting to the Previous BIOS
AF000475
BIOS Bank Select
J1C3
3
2
Force Lower
Bank
Normal Operation
(default)
If you encounter a problem with your BIOS, you may want to revert to the previously
installed BIOS. Because of the rolling BIOS feature, your server contains two versions of
the BIOS: the current BIOS, and the BIOS that was previously installed.
Note: If you upgrade the BIOS more than once with the same BIOS version, the two versions of
the BIOS stored in your server will be identical.
To revert to the previous BIOS:
1. Power down the server and disconnect the AC power.
2. Open the chassis. See your chassis documentation for instructions on removing the
chassis cover.
3. Locate the BIOS Bank Select jumper at board position J1C3. See Figure 6.
4. Move the jumper from the normal operation position, covering pins 2 and 3, to the
Bank_0 position, covering pins 1 and 2, as shown by the diagram.
Figure 6. BIOS Bank Select Jumper in Force Lower Bank Position
5. Close the chassis.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 25
6. Reconnect the AC power and power up the server.
The BIOS will boot to the previous BIOS until you either move the jumper again or until
you perform another BIOS update.
Page 44

Clearing the Password
If the user or administrator password(s) is lost or forgotten, moving the password clear
jumper into the “clear” position clears both passwords. The password clear jumper must
be restored to its original position before a new password(s) can be set.
1. Power down the system. Leave the AC power cord connected.
2. Open the chassis. See your chassis documentation for instructions on removing the
chassis cover.
3. Locate the Password Clear jumper block at board position J1D2. See Figure 7.
4. Move the jumper from the normal operation position, covering pins 1 and 2, to the
Password Clear position, covering pins 2 and 3, as shown by the diagram.
PASSWRD CLR
Default
2
Clear
Password
3
J1D2
Figure 7. Password Clear Jumper in Clear Password Position
5. Power up the server and wait 10 seconds.
6. Power down the server.
7. Move the Password Clear jumper back to the original position, covering pins
1 and 2.
8. Close the chassis.
9. Power up the server.
26 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
AF000423
Page 45

Clearing the CMOS
If you are not able to access the BIOS setup screens, the CMOS Clear jumper will need to
be used to reset the configuration RAM.
1. Power down the system. Leave the AC power cord connected.
2. Open the chassis. See your chassis documentation for instructions on removing the
chassis cover.
3. Locate the CMOS Clr jumper block at board position J1D1. See Figure 8.
4. Move the jumper from the normal operation position, covering pins 1 and 2, to the
CMOS Clear position, covering pins 2 and 3, as shown by the diagram.
CMOS CLR
Default
2
Clear
CMOS
3
J1D1
Figure 8. CMOS Clr Jumper in the Clear CMOS Position
5. Wait 10 seconds.
6. Move the CMOS Clear jumper back to the original position, covering pins 1 and 2.
7. Close the chassis.
8. Power up the server.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 27
AF000424
Page 46

28 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 47

3 Hardware Installations and
Upgrades
Before You Begin
Before working with your server product, pay close attention to the “Safety Information”
on page iii.
Tools and Supplies Needed
• Phillips* (cross head) screwdriver (#1 bit and #2 bit)
• Needle nosed pliers
• Antistatic wrist strap and conductive foam pad (recommended)
Installing and Removing Memory
The silkscreen on the board for the FBDIMMs displays DIMM_A1, DIMM_A2,
DIMM_B1, DIMM_B2, DIMM_C1, DIMM_C2, DIMM_D1, and DIMM_D2, starting
from the inside of the board. DIMM_A1 is the socket closest to the MCH. See “Memory”
on page 16 for a discussion of the memory requirements and options. See “Additional
Information and Software” on page viii for a link to the list of tested FBDIMMs.
Installing FBDIMMs
To install FBDIMMs, follow these steps:
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions in “Safety Information” on page iii.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the server. Turn off the server.
3. Disconnect the AC power cord from the server.
4. Remove the chassis cover. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on removing the cover.
Page 48

5. Locate the DIMM sockets (see Figure 9).
6. Disconnect and remove any components necessary to access the DIMM sockets.
See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on removing
chassis components.
D E
C
B
A
F
G
H
Callout DIMM Socket Callout DIMM Socket
A. DIMM_A1 E. DIMM_C1
B. DIMM_A2 F. DIMM_C2
C. DIMM_B1 G. DIMM_D1
D. DIMM_B2 H. DIMM_D2
30 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
AF000093
Figure 9. Locating DIMM Sockets
Page 49

7. Make sure the clips at each end of the DIMM socket(s) are pushed outward to the
open position. See letter “A” in Figure 10.
8. Holding the FBDIMM by the edges, remove it from its anti-static package.
9. Position the FBDIMM above the socket. Align the notch on the bottom edge of the
FBDIMM with the key in the DIMM socket. The arrow for letter “B” in Figure 10
is pointing to the key in the socket.
10. Insert the bottom edge of the FBDIMM into the socket.
11. When the FBDIMM is inserted, push down on the top edge of the FBDIMM until
the retaining clips snap into place. See letter “C” in Figure 10.
12. Make sure the clips latch firmly in place. See letter “D” in Figure 10.
C
D
B
A
TP000425
Figure 10. Installing FBDIMMs
13. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the DIMM
sockets. See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on
removing chassis components.
14. Replace the chassis cover and reconnect the AC power cord. See the documentation
that came with your chassis for instructions on installing the chassis cover.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 31
Page 50

Removing FBDIMMs
To remove a FBDIMM, follow these steps:
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions in “Safety Information” on page iii.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the server. Turn off the server.
3. Remove the AC power cord from the server.
4. Remove the chassis cover. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on removing the cover.
5. Disconnect and remove any components necessary to access the DIMM sockets.
See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on removing
chassis components.
6. Push the clips at each end of the DIMM socket(s) outward to the open position. The
FBDIMM lifts from the socket.
7. Holding the FBDIMM by the edges, lift it from the socket. Store the FBDIMM in
an anti-static package.
8. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the DIMM
sockets. See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on
installing chassis components.
9. Replace the chassis cover and reconnect the AC power cord. See the documentation
that came with your chassis for instructions on installing the cover.
Installing or Replacing the Processor
Caution: Processor must be appropriate: You may damage the server board if you install a
processor that is inappropriate for your server. See “Additional Information and
Software” on page viii for a link to the list of compatible processor(s).
Caution: ESD and handling processors: Reduce the risk of electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage to
the processor by doing the following: (1) Touch the metal chassis before touching the
processor or server board. Keep part of your body in contact with the metal chassis to
dissipate the static charge while handling the processor. (2) Avoid moving around
unnecessarily.
32 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 51

Installing the Processor
Notes:
• Do not touch the contacts on either the processor or the processor socket.
• Do not force the processor socket into place. When correctly aligned, the socket will
easily drop into place.
To install a processor, follow these instructions:
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions in “Safety Information” on page iii.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the server. Turn off the server.
3. Disconnect the AC power cord from the server.
4. Remove the chassis cover. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on removing the cover.
5. Locate the processor sockets (see Figure 11).
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 33
Page 52

A B
AF000419
Callout Processor Socket Callout Processor Socket
A. CPU_2 B. CPU_1
Figure 11. Locating Processor Sockets
6. Disconnect and remove any components necessary to access the processor sockets.
See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on removing
chassis components.
7. Push down on the lever attached to the processor socket. While holding the lever
down, pull it towards the center of the board to disengage the lever from the hook.
Fully open the lever. See Figure 12.
34 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 53

Figure 12. Opening Processor Socket Lever
AF000095
AF000096
8. Push down on the rear tab of the load plate to swing the front of the load plate up
slightly. Fully open the load plate. See Figure 13.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 35
Figure 13. Opening Load Plate
Page 54

9. If the protective cover is attached from the load plate, remove it and store it for
AF000097
AF000101
future use.
Figure 14. Removing Protective Cover from Load Plate
10. Remove the processor from the box and remove the protective shipping cover.
11. Set the processor in the socket with the processor cutouts matching the processor
socket notches. See Figure 15.
12. Close the load plate.
13. Close the socket lever. Push downward on the socket lever while pushing it toward
the center of the processor socket to engage it under the hook on the processor
socket.
14. Install the heatsink(s). See “Installing the Heatsink(s)” on page 37 for instructions.
36 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Figure 15. Setting Processor in Place
Page 55

Installing the Heatsink(s)
Note: The heatsink has thermal interface material (TIM) located on the bottom of it. Use caution
when handling the heatsink so you do not damage the TIM.
Each processor requires a heatsink. Depending on your chassis, you may need to use
either a passive or an active heatsink. An active heatsink has a fan attached to the top of it
and a cable that needs to be connected to the server board. The following table shows the
®
server chassis compatible with this server board and whether each chassis requires
Intel
an active or a passive heatsink:
Table 5. Heatsink Requirements for Compatible Intel
Server Chassis Heatsink Requirement
®
Intel
Entry Server Chassis SC5299-E BRP Active heatsink
®
Intel
Entry Server Chassis SC5299-E DP
®
Entry Server Chassis SC5299-E WS
Intel
®
Server Chassis SC5400 BRP Passive heatsink
Intel
®
Intel
Server Chassis SC5400 LX Passive heatsink
®
Server Chassis SC5400 Base Passive heatsink
Intel
®
Server Chassis
Active heatsink
Active heatsink
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 37
Page 56

Use the following steps to install a heatsink.
AF000098
Chassis
Front
2
1
3
4
1. Install the processor. See “Installing the Processor” on page 33 for instructions.
2. Set the heatsink over the processor, lining up the four captive screws with the four
posts surrounding the processor.
3. Loosely screw in the captive screws on the heat sink corners in the order shown by
Figure 16. Do not fully tighten one screw before loosely attaching the others.
4. In the same order, gradually and equally tighten each captive screw until each is
firmly tightened. Do not fully tighten one screw at a time.
Figure 16. Installing Heatsink (passive heatsink shown)
38 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 57

5. Active heatsink only: Connect the heatsink cable to the server board.
AF000420
A
B
Callout
A. CPU_2 B. CPU_1
Processor Heatsink
Connector
Callout
Processor Heatsink
Connector
Figure 17. Locating Active Heatsink Cable Connections
6. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the
processor sockets. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on installing chassis components.
7. Replace the chassis cover and reconnect the AC power cord. See the documentation
that came with your chassis for instructions on installing the cover.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 39
Page 58

Removing a Processor
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions in “Safety Information” on page iii.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the server. Turn off the server.
3. Remove the AC power cord from the server.
4. Remove the chassis cover. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on removing the cover.
5. Disconnect and remove any components necessary to access the processor sockets.
See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on removing
chassis components.
6. Active heatsink only: Unplug the processor fan cable from the server board.
7. Loosen the four captive screws on the corners of the heat sink.
8. Twist the heat sink slightly to break the seal between the heat sink and the
processor.
9. Lift the heat sink from the processor. If it does not pull up easily, twist the heat sink
again. Do not force the heat sink from the processor. Doing so could damage the
processor.
Caution:
—Do not attempt to operate your server system without a heatsink installed over
each installed processor. Doing so will cause your server to overheat and may
cause permanent damage.
— The heatsink has Thermal Interface Material (TIM) located on the bottom of it.
Use caution when handling the heatsink so you do not damage the TIM.
40 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 59

10. Push down on the lever attached to the processor socket. While holding the lever
AF000095
AF000415
down, pull it towards the center of the board to disengage the lever from the hook.
Fully open the lever. See Figure 18.
Figure 18. Opening Processor Socket Lever
11. Push down on the rear tab of the load plate to swing the front of the load plate up
slightly. Fully open the load plate. See Figure 19.
Figure 19. Opening Load Plate
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 41
Page 60

12. Lift the processor from the socket. See Figure 15.
AF000416
AF000417
Caution: Do not touch the contacts on either the processor or the processor socket.
Figure 20. Removing Processor from Socket
13. Store the processor in the packaging materials in which it came.
14. Install the protective cover over the load plate if a replacement processor will not be
installed.
Figure 21. Installing Protective Cover onto Load Plate
42 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 61

15. Close the load plate.
16. Close the socket lever. Push downward on the socket lever while pushing it toward
the center of the processor socket to engage it under the hook on the processor
socket.
17. If installing a replacement processor, see “Installing the Processor” on page 33.
18. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the
processor sockets. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on installing chassis components.
19. Replace the chassis cover. See the documentation that came with your chassis for
instructions on installing the cover.
Replacing the CMOS Battery
The lithium CMOS battery on the server board powers the RTC in the absence of power.
When the battery starts to weaken, it loses voltage, and the system settings stored in
CMOS RAM in the RTC (for example, the date and time) may be wrong. Contact your
customer service representative or dealer for a list of approved devices.
Warni n g: Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Discard used batteries
according to manufacturer's instructions.
Advarsel: Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning må kun ske med
batteri af samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
Va r n i n g : Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ
som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens
instruktion.
Varoitus: Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo ainoastaan
laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden
mukaisesti.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 43
Page 62

1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions in “Safety Information” on page iii.
AF000099
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the server. Turn off the server.
3. Disconnect the AC power cord from the server.
4. Remove the chassis cover and locate the CMOS battery. See the documentation that
came with your chassis for instructions on removing the cover.
5. Use a finger to pull the lever away from the top of the battery until it clears the
battery. Use caution so you do not bend the lever.
6. Lift the battery from the socket.
Figure 22. Locating and Removing the CMOS Battery
7. Dispose of the battery according to local ordinance.
8. Remove the new battery from its package.
9. Being careful to observe the correct polarity, insert the battery into the battery
socket. The “+” side of the battery must face the lever side of the socketbattery
socket, toward the add-in card slots.
10. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the battery.
See the documentation that came with your chassis for instructions on installing
chassis components.
11. Replace the chassis cover and reconnect the AC power cord. See the documentation
that came with your chassis for instructions on installing the cover.
12. Run the BIOS Setup utility to restore the configuration settings to the real-time
clock.
44 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 63

Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This chapter helps you identify and solve problems that might occur while you are using
the system.
For any issue, first ensure you are using the latest software.These software updates
include updates for BIOS, the baseboard management controller (BMC), and the hot-swap
controller (HSC). See “Additional Information and Software” on page viii for a link to the
software updates. In addition to the system firmware and files, also update any drivers
used for components you have installed in your system, such as video drivers and network
drivers.
Intel provides a package called the “Platform Confidence Test” that may help with your
diagnostics. See “Additional Information and Software” for a link to this software.
If you are unable to resolve your server problems on your own, see “Getting Help” on
page 65 for assistance.
System Boot Quiet Time
The power-on self test (POST) process includes a quiet time, during which the system
may appear to be hung. This may last as long as 40 seconds. Do not power off or reboot
the system during this time. The POST LEDs will indicate activity. They may alternate
blinking between amber and green. When the quiet time completes, the status LED will
change to solid green.
Resetting the System
Before going through in-depth troubleshooting, attempt first to perform reset your system
using one of the methods below.
Table 6. Resetting the System
Soft boot reset to clear the system memory and reload the operating
system
Clear system memory, restart POST, and reload the operating system Reset button
Cold boot reset. Turn the system power off and then on. This halts power
to all peripherals, clears system memory, restarts POST, reloads the
operating system, and halts power to all peripherals
To do this Press
<Ctrl+Alt+Del>
Power off/on
button
Page 64

Problems following Initial System Installation
Problems that occur at initial system startup are usually caused by an incorrect installation
or configuration. Hardware failure is a less frequent cause. If the problem you are
experiencing is with a specific software application, see “Problems with Newly Installed
Application Software” on page 52.
First Steps Checklist
• Is AC power available at the wall outlet?
• Are the power supplies plugged in? Check the AC cable(s) on the back of the chassis
and at the AC source.
• Are all cables correctly connected and secured?
• Are the processors fully seated in their sockets on the server board?
• Are all standoffs in the proper location and not touching any components, causing a
potential short?
• Are all add-in PCI boards fully seated in their slots on the server board?
• Are all jumper settings on the server board correct?
• Are all jumper and switch settings on add-in boards and peripheral devices correct?
To check these settings, refer to the manufacturer's documentation that comes with
them. If applicable, ensure that there are no conflicts-for example, two add-in boards
sharing the same interrupt.
• Are all peripheral devices installed correctly?
• If the system has a hard disk drive, is it properly formatted or configured?
• Are all device drivers properly installed?
• Are the configuration settings made in Setup correct?
• Is the operating system properly loaded? See the operating system documentation.
• Did you press the system power on/off switch on the front panel to turn the server on
(power on light should be lit)?
• Is the system power cord properly connected to the system and plugged into a
NEMA 5 15R outlet for 100-120V or a NEMA 6-15R outlet for 200-240 V?
• Are all integrated components from the tested components lists? Check the tested
memory, and chassis lists, as well as the supported hardware and operating system
list. See “Additional Information and Software” on page viii for links to the tested
component lists.
46 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 65

Hardware Diagnostic Testing
This section provides a more detailed approach to identifying a hardware problem and
locating its source.
Caution: Turn off devices before disconnecting cables: Before disconnecting any peripheral cables
from the system, turn off the system and any external peripheral devices. Failure to do so
can cause permanent damage to the system and/or the peripheral devices.
1. Turn off the system and all external peripheral devices. Disconnect each device
from the system, except for the keyboard and the video monitor.
2. Make sure the system power cord is plugged into a properly grounded AC outlet.
3. Make sure your video display monitor and keyboard are correctly connected to the
system. Turn on the video monitor. Set its brightness and contrast controls to at
least two thirds of their maximum ranges (see the documentation supplied with
your video display monitor).
4. If the operating system normally loads from the hard disk drive, make sure there is
no diskette in drive A and no CD-ROM disk in the CD-ROM drive.
5. If the power LED does light, attempt to boot from a floppy diskette or from a CDROM disk.
6. Turn on the system. If the power LED does not light, see “Power Light Does Not
Light” on page 48.
Verifying Proper Operation of Key System Lights
As POST determines the system configuration, it tests for the presence of each mass
storage device installed in the system. As each device is checked, its activity light should
turn on briefly. Check for the following:
• Does the diskette drive activity light turn on briefly? If not, see “CD-ROM Drive or
DVD-ROM Drive Activity Light Does Not Light” on page 50.
• If system LEDs are illuminated, see “Intel
for a description of the lights.
®
Light-Guided Diagnostics” on page 9
Confirming Loading of the Operating System
Once the system boots up, the operating system prompt appears on the screen. The prompt
varies according to the operating system. If the operating system prompt does not appear,
see “No Characters Appear on Screen”.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 47
Page 66

Specific Problems and Corrective Actions
This section provides possible solutions for these specific problems:
• Power light does not light.
• No characters appear on screen.
• Characters on the screen appear distorted or incorrect.
• System cooling fans do not rotate.
• Hard disk drive activity light does not light.
• CD-ROM drive activity light does not light.
• There are problems with application software.
• The bootable CD-ROM is not detected.
Try the solutions below in the order given. If you cannot correct the problem, contact your
service representative or authorized dealer for help.
Power Light Does Not Light
Check the following:
• Did you press the power-on button?
• Is the system operating normally? If so, the power LED might be defective or the
cable from the control panel to the server board might be loose.
• Have you securely plugged the server AC power cord into the power supply?
• Some power supplies have a power switch on the back of the power supply, next to
the fan. If your system has one, is it turned on?
• Remove all add-in cards and see if the system boots. If successful, add the cards
back in one at a time with a reboot between each addition to determine which card
might be causing the problem.
• Make sure the memory FBDIMMs comply with the system requirements.
• Make sure the memory FBDIMMs have been populated according to the system
requirements.
• Remove the memory FBDIMMs and re-seat them.
• Make sure the processor(s) comply with the system requirements.
• Make sure the processor(s) have been populated according to the system
requirements.
• Remove the processor(s) and re-seat them.
• Make sure the chassis standoffs are installed only below mounting holes. Misplaced
standoffs can contact the pins on the bottom of the server board and cause a short.
• In a DC powered system, make sure all DC cables are connected.
48 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 67

No Characters Appear on Screen
Check the following:
• Is the keyboard functioning? Test it by turning the “Num Lock” function on and off
to make sure the Num Lock light is functioning.
• Is the video monitor plugged in and turned on? If you are using a switch box, is it
switched to the correct system?
• Are the brightness and contrast controls on the video monitor properly adjusted?
• Is the video monitor signal cable properly installed?
• Does this video monitor work correctly if plugged into a different system?
• Is the onboard video controller enabled in the BIOS?
• Remove all add-in cards and see if the video returns. If successful, add the cards
back in one at a time with a reboot between each addition to determine which card
might be causing the problem.
• Make sure the memory FBDIMMs comply with the system requirements.
• Make sure the memory FBDIMMs have been populated according to the system
requirements.
• Remove the memory FBDIMMs and re-seat them.
• Make sure the processor(s) comply with the system requirements.
• Make sure the processor(s) have been populated according to the system
requirements.
• Remove the processor(s) and re-seat them.
If you are using an add-in video controller board, do the following:
1. Verify that the video works using the onboard video controller.
2. Verify that the video controller board is fully seated in the server board connector.
3. Reboot the system for changes to take effect.
4. If there are still no characters on the screen after you reboot the system and POST
emits a beep code, write down the beep code you hear. This information is useful
for your service representative.
5. If you do not receive a beep code and characters do not appear, the video display
monitor or video controller may have failed. Contact your service representative or
authorized dealer for help.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 49
Page 68

Characters Are Distorted or Incorrect
Check the following:
• Are the brightness and contrast controls properly adjusted on the video monitor? See
the manufacturer's documentation.
• Are the video monitor's signal and power cables properly installed?
• Does this video monitor work correctly if plugged into a different system?
System Cooling Fans Do Not Rotate Properly
If the system cooling fans are not operating properly, it is an indication of possible system
component failure.
Check the following:
• Is the power-on light lit? If not, see “Power Light Does Not Light” on page 48.
• If your system has LED lights for the fans, is one or more of these LEDs lit?
• Are any other control panel LEDs lit?
• Have any of the fan motors stopped? Use the server management subsystem to
check the fan status.
• Have your fans speeded up in response to an overheating situation?
• Have your fans speeded up in response to a fan that has failed?
• Are the fan power connectors properly connected to the server board?
• Is the cable from the control panel board connected to the both the control panel
board and to the server board?
• Are the power supply cables properly connected to the server board?
• Are there any shorted wires caused by pinched-cables or have power connector
plugs been forced into power connector sockets the wrong way?
CD-ROM Drive or DVD-ROM Drive Activity Light Does Not
Light
Check the following:
• Are the CD-ROM/DVD-ROM drive's power and signal cables properly installed?
• Are all relevant switches and jumpers on the drive set correctly?
• Is the drive properly configured?
50 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 69

Cannot Connect to a Server
• Make sure the network cable is securely attached to the correct connector at the
system back panel.
• Try a different network cable.
• Make sure you are using the correct and the current drivers. See “Additional
Information and Software” on page viii for a link to the current drivers.
• Make sure the driver is loaded and the protocols are bound.
• Make sure the hub port is configured for the same duplex mode as the network
controller.
• Make sure the correct networking software is installed.
• If you are directly connecting two servers (without a hub), you will need a crossover
cable.
• Check the network controller LEDs next to the NIC connectors.
Problems with Network
The system hangs when the drivers are loaded
• Certain drivers may require interrupts that are not shared with other PCI drivers. For
these drivers, it may be necessary to alter settings so that interrupts are not shared.
See the documentation that came with your PCI card(s) for information on changing
interrupts.
Diagnostics pass but the connection fails
• Make sure the network cable is securely attached.
• Make sure you specify the correct frame type in your NET.CFG file.
• The controller stopped working when an add-in adapter was installed.
• Make sure the cable is connected to the port from the onboard network controller.
• Make sure your BIOS is current. See “Additional Information and Software” for a
link to the current version.
• Make sure the other adapter supports shared interrupts. Make sure your operating
system supports shared interrupts.
• Try reseating the add-in adapter.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 51
Page 70

The add-in adapter stopped working without apparent cause
• Reseat the adapter.
• Put the adapter in a different slot.
• The network driver files may be corrupt or deleted. Delete and then reinstall the
drivers.
• Run diagnostics.
System Boots when Installing PCI Card
System management features require full-time “standby” power. This means some parts of
the system have power going to them whenever the power cord is plugged in, even if you
have turned the system power off with the power button on the front panel. If you install a
PCI card with the AC power cord plugged in, a signal may be sent to command the system
to boot. Before installing a PCI card, you should always:
• Turn off the server power by using the power button on the front of the system.
• Unplug the AC power cord(s) from the server.
Problems with Newly Installed Application Software
Problems that occur when you run new application software are usually related to the
software, not the server hardware. Faulty equipment is unlikely, especially if other
software runs correctly.
Check the following:
• Make sure the system meets the minimum hardware requirements for the software.
See the software documentation.
• Make sure the software is properly installed and configured for the system. See the
software documentation.
• Use only an authorized copy. Unauthorized copies often do not work.
• If you are running the software from a USB floppy disk, CD-ROM or DVD-ROM,
try a different disk.
• Make sure the correct device drivers installed.
If the problems persist, contact the software vendor's customer service representative.
52 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 71

Problems with Application Software that Ran Correctly
Earlier
Problems that occur after the system hardware and software have been running correctly
sometimes indicate equipment failure. However, they can also be caused by file
corruption or changes to the software configuration.
Check the following:
• If you are running the software from a USB floppy disk, CD-ROM or DVD-ROM,
try a different disk.
• Check your system for a virus infection.
• Uninstall and reinstall the software. Make sure all necessary files are installed.
• If the problems are intermittent, there may be a loose cable, dirt in the keyboard (if
keyboard input is incorrect), a marginal power supply, or other random component
failures.
• If you suspect that a transient voltage spike, power outage, or brownout might have
occurred, reload the software and try running it again. Symptoms of voltage spikes
include a flickering video display, unexpected system reboots, and the system not
responding to user commands.
Note: Random errors in data files: If you are getting random errors in your data files, they may
be getting corrupted by voltage spikes on your power line. If you are experiencing any of
the above symptoms that might indicate voltage spikes on the power line, you may want to
install a surge suppressor between the power outlet and the system power cord.
Devices are not Recognized under Device Manager
(Windows* Operating System)
The Windows* operating systems do not include all of the drivers for the Intel® chipsets,
onboard NICs, and other components. See “Additional Information and Software” on
page viii for a link to the current drivers and chipset files.
Hard Drive(s) are not Recognized
Check the following:
• Make sure the drive is not disabled in BIOS Setup.
• Make sure the drive is connected correctly and that is plugged into the power supply.
• Make sure the drive is compatible. See “Additional Information and Software” for a
link to the tested drives.
• Make sure you have not exceeded the power budget for the server. See “Additional
Information and Software” for a link to software to check your power budget.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 53
Page 72

• Verify your SAS or SATA drives are connected to the correct ports on the server
board and the chassis backplane. See your chassis documentation for details about
backplane connections.
• If using ATA drives, verify that the master/slave settings are set correctly. See your
drive documentation for details on setting the master/slave settings.
• If using a RAID configuration with an add-in RAID adapter, make sure the RAID
adapter is installed correctly.
Bootable CD-ROM Disk Is Not Detected
Check the following:
• Make sure the BIOS is configured to allow the CD-ROM to be the first bootable
device.
LED Information
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL includes LEDs that can aid in troubleshooting your
system. For the location of the LEDs, see “Intel
BIOS POST Beep Codes
The table below lists the POST error beep codes. Prior to system video initialization, the
BIOS uses these beep codes to inform users of error conditions. Please note that not all
error conditions are supported by BIOS beep codes.
Number of
Beeps
1, 2, or 3 Memory error. Reseat the memory or replace the FBDIMMs with known
good modules.
4 - 7 or 9 - 11 Fatal error indicating a possible serious system problem. Remove all add-in
cards and re-start the system. If the error still occurs, contact your service
representative. If the beep codes are not generated after the add-in cards
are removed, insert the cards one at a time, booting the system between
each card addition, until the beeps again occur to reveal the malfunctioning
card.
8 Replace or reseat the system video add-in card. If on-board video is being
used, the server board may be faulty.
®
Light-Guided Diagnostics” on page 9.
Table 7. POST Error Beep Codes
Reason for Beeps and Action to Take
54 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 73

In addition to the beep codes above, additional beep codes are provided if an Intel®
Remote Management Module is installed. The Intel
®
Remote Management Module
provides the following additional beep codes.
®
Table 8. Error Beep Codes Generated by Intel
Remote Management
Module
Number of
Beeps
1 Front panel CMOS clear has been initiated.
1-5-1-1 Processor failure. Reseat or replace the failed processor.
1-5-2-1 No processor is installed or the CPU 1 socket is empty. Reseat or replace
the failed processor.
1-5-2-3 Processor configuration error or CPU 1 socket is empty. Reseat or replace
the failed processor. In a two-processor system, make sure the processors
are identical.
1-5-2-4 Front-side bus select configuration error.
1-5-4-2 DC power unexpectedly lost.
1-5-4-3 Chipset control failure.
1-5-4-4 Power control failure.
Reason for Beeps and Action to Take
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 55
Page 74

56 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 75

Appendix B: Regulatory and
Compliance Information
Product Regulatory Compliance
Product Safety Compliance
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL complies with the following safety requirements:
• UL60950 - CSA 60950 (USA / Canada)
• EN60950 (Europe)
• IEC60950 (International)
• CB Certificate & Report, IEC60950 (report to include all country national
deviations)
• CE - Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEE (Europe)
Product EMC Compliance - Class A Compliance
The Intel® Server Board S5000PSL has been has been tested and verified to comply with
the following electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations when installed a
compatible Intel
Server Builder Web site or contact your local Intel representative.
• FCC /ICES-003 - Emissions (USA/Canada) Verification
• CISPR 22 - Emissions (International)
• EN55022 - Emissions (Europe)
• EN55024 - Immunity (Europe)
• CE - EMC Directive 89/336/EEC (Europe)
• VCCI Emissions (Japan)
• AS/NZS 3548 Emissions (Australia / New Zealand)
• BSMI CNS13438 Emissions (Taiwan)
• RRL MIC Notice No. 1997-41 (EMC) & 1997-42 (EMI) (Korea)
®
host system. For information on compatible host system(s) see Intel's
Page 76

Certifications / Registrations / Declarations
• UL Certification (US/Canada)
• CE Declaration of Conformity (CENELEC Europe)
• FCC/ICES-003 Class A Attestation (USA/Canada)
• C-Tick Declaration of Conformity (Australia)
• MED Declaration of Conformity (New Zealand)
• BSMI Certification (Taiwan)
• RRL Certification (Korea)
• Ecology Declaration (International)
Product Regulatory Compliance Markings
This product is marked with the following Product Certification Markings:
Table 9. Product Certification Markings
Regulatory Compliance Region Marking
UL Mark USA/Canada
CE Mark Europe
EMC Marking (Class A) Canada CANADA ICES-003 CLASS A
CANADA NMB-003 CLASSE A
BSMI Marking (Class A) Taiwan
Ctick Marking Australia / New Zealand
RLL MIC Mark Korea See the regulatory information document
for additional information.
58 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 77

Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices
FCC (USA)
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
For questions related to the EMC performance of this product, contact:
Intel Corporation
5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway
Hillsboro, OR 97124-6497
1-800-628-8686
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit other than the one to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the grantee of this device could
void the user's authority to operate the equipment. The customer is responsible for
ensuring compliance of the modified product.
Only peripherals (computer input/output devices, terminals, printers, etc.) that comply
with FCC Class A or B limits may be attached to this computer product. Operation with
noncompliant peripherals is likely to result in interference to radio and TV reception.
All cables used to connect to peripherals must be shielded and grounded. Operation with
cables, connected to peripherals, that are not shielded and grounded may result in
interference to radio and TV reception.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 59
Page 78

ICES-003 (Canada)
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites bruits radioélectriques applicables aux
appareils numériques de Classe A prescrites dans la norme sur le matériel brouilleur:
“Apparelis Numériques”, NMB-003 édictee par le Ministre Canadian des
Communications.
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled: “Digital
Apparatus,” ICES-003 of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity)
This product has been tested in accordance too, and complies with the Low Voltage
Directive (73/23/EEC) and EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). The product has been marked
with the CE Mark to illustrate its compliance.
VCCI (Japan)
English translation of the notice above:
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for
Interference (VCCI) from Information Technology Equipment. If this is used near a radio
or television receiver in a domestic environment, it may cause radio interference. Install
and use the equipment according to the instruction manual.
60 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 79

BSMI (Taiwan)
声明
此为A级产品,在生活环境中,该产品可能会造成无线电干扰。在这种情况下,可能需要用户
对其干扰采取可行的措施。
The BSMI Certification Marking and EMC warning is located on the outside rear area of
the product.
RRL (Korea)
English translation of the notice above:
1. Type of Equipment (Model Name): On License and Product
2. Certification No.: On RRL certificate. Obtain certificate from local Intel
representative
3. Name of Certification Recipient: Intel Corporation
4. Date of Manufacturer: Refer to date code on product
5. Manufacturer/Nation: Intel Corporation/Refer to country of origin marked on
product
CNCA (CCC-China)
The CCC Certification Marking and EMC warning is located on the outside rear area of
the product.
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 61
Page 80

Product Ecology Change (EU RoHS)
Intel has a system in place to restrict the use of banned substances in accordance with the
European Directive 2002/95/EC. Compliance is based on declaration that materials
banned in the RoHS Directive are either (1) below all applicable threshold limits or (2) an
approved / pending RoHS exemption applies.
RoHS implementation details are not fully defined and may change.
Threshold limits and banned substances are noted below:
• Quantity limit of 0.1% by mass (1000 PPM) for:
—Lead
—Mercury
— Hexavalent Chromium
— Polybrominated Biphenyls Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE)
• Quantity limit of 0.01% by mass (100 PPM) for:
—Cadmium
Product Ecology Change (CRoHS)
CRoHS (China RoHS, or Ministry of Information Industry Order #39,
“Management Methods for Controlling Pollution by Electronic Information
Products.” ):
• China bans the same substances and limits as noted for EU RoHS; however require
product marking and controlled substance information Environmental Friendly
Usage Period (EFUP) Marking Is defined in number of years in which controlled
listed substances will not leak or chemically deteriorate while in the product. Intel
understands the end-seller (entity placing product into market place) is responsible
for providing EFUP marking.
• Intel “retail” products are provided with EFUP marking
• For “Business to Business” products, Intel intends to place EFUP marking on
product for customer convenience
• EFUP for Intel server products has been determined as 20 years.
Below is an example of EFUP mark applied to Intel server products.
62 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 81

CRoHS Substance Tables
␂ℝ䶵⚗₼⦌ᇵ䟄≰㋾ℶ❐㻰㩢㘶Ⓟ丰䚕┭㽤ᇶ䤓⭿㢝
0DQDJHPHQW0HWKRGVRQ&RQWURORI3ROOXWLRQIURP
(OHFWURQLF,QIRUPDWLRQ3UR
GXFWV
&KLQD5R+6GHFODUDWLRQ
ℶ❐₼㦘㹡㦘⹂䓸德䤓⚜䱿♙⚺摞
China CRoHS requires products to be provided with controlled substance information.
Intel understands the end-seller (entity placing product into market place) is responsible
for providing the controlled substance information. Controlled substance information is
required to be in Simplified Chinese. Substance table for this board product is as follows:
␂
㦘㹡㦘⹂䓸德㒥⏒侯捷ↅ⚜䱿
3DUWV
摠⻭捷ↅ
0HWDO3DUWV
◿Ⓠ㨎兓ↅ
3ULQWHG%RDUG$VVHPEOLHV
3%$
Ⴜ᧶嫷䯉年㦘㹡㦘⹂䓸德⦷年捷ↅ㓏㦘⧖德㧟㠨₼䤓⚺摞⧖⦷ 6-7 㪖屓⸩䤓
棟摞尐㻑ⅴₚᇭ
Ⴜ᧶,QGLFDWHVWKDWWKLVKD]DUGRXVVXEVWDQFHFRQWDLQHGLQDOOKRPRJHQHRXVPDWHULDOVRIWKLV
SDUWLVEHORZWKHOLPLWUHTXLUHPHQWLQ6-7
᧶嫷䯉年㦘㹡㦘⹂䓸德咂⺠⦷年捷ↅ䤓㩟⧖德㧟㠨₼䤓⚺摞怔⒉ 6-7 㪖
屓⸩䤓棟摞尐㻑ᇭ
᧶,QGLFDWHVWKDWWKLVKD]DUGRXVVXEVWDQFHFRQWDLQHGLQDWOHDVWRQHRIWKHKRPRJHQHRXV
PDWHULDOVRIWKLVSDUWLVDERYHWKHOLPLWUHTXLUHPHQWLQ6-7
⺈枏➽㡴䤓㓏➽ℶ❐㦻嫷㣍䯉㒠⏻⚇∪ㄣ枍䤓䟄≰㋾ℶ❐♾厌▔⚺扨K䓸德ᇭ㽷㎞᧶⦷
㓏➽ℶ❐₼♾厌↩♾厌ₜ↩⚺㦘㓏㦘㓏⒦䤓捷ↅ
7KLVWDEOHVKRZVZKHUHWKHVHVXEVWDQFHVPD\EHIRXQGLQWKHVXSSO\FKDLQRIRXU
HOHFWURQLFLQIRUPDWLRQSURGXFWVDVRIWKHGDWHRIVDOHRIWKHHQFORVHGSURGXFW1RWHWKDW
VRPHRIWKHFRPSRQHQWW\SHVOLVWHGDERYHPD\RUPD\QRWEHDSDUWRIWKHHQFORVHG
SURGXFW
杔
3E㻭+J柘&G
Ⴜ Ⴜ Ⴜ Ⴜ Ⴜ
Ⴜ Ⴜ Ⴜ Ⴜ Ⴜ
⏼ↆ杻
&U
⮩䅃勣啾
3%%
⮩䅃ℛ啾搩
3%'(
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 63
Page 82

China Packaging Recycle Marks (or GB18455-
2001)
Intel EPSD has the following ecological compliances:
Cardboard and fiberboard packaging will be marked as recyclable in China.
China Packaging Recycling Marks is required on retail packaging to be marked as
recyclable using China’s recycling logo. Due to regional variances in mark acceptances,
all three marks accepted worldwide will be implemented on Intel’s cardboard and
fiberboard. Examples of marks are shown below.
CA Perchlorate Warning
CA Lithium Perchlorate Warning (California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Division
4.5, Chapter 33: Best Management Practices for Perchlorate Materials):
The State of California requires a warning to be included for products containing a device
using Lithium Perchlorate.
Intel understands CA Lithium Perchlorate require a printed warning to be included with
all products containing a Lithium battery, either as an insert, in existing product literature,
or as part of the shipping memo wording.
Wording is as follows:
Perchlorate Material - special handling may apply. See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/
perchlorate
This notice is required by California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Division 4.5, Chapter
33: Best Management Practices for Perchlorate Materials. This product/part includes a
battery that contains Perchlorate material.
End-of-Life / Product Recycling
Product recycling and end-of-life take-back systems and requirements vary by country.
Contact the retailer or distributor of this product for information about product recycling
and / or take-back.
64 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 83

Appendix C: Getting Help
World Wide Web
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL.
Telephone
All calls are billed per incident, levied in local currency at the applicable credit card
exchange rate plus applicable taxes. (Intel reserves the right to change the pricing for
telephone support at any time without notice).
Before calling, fill out an “System Issue Report Form”. A sample form is provided on the
following pages. However, for the fastest service, please submit your form via the
Internet.
For an updated support contact list, see http://www.intel.com/support/9089.htm/
U.S. and Canada
For help, see http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL.
Europe
Belgium ..... 02 714 3182
Denmark ... 38 487077
Finland ...... 9 693 79297
France........ 01 41 918529
Germany ... 069 9509 6099
Holland...... 020 487 4562
Italy............ 02 696 33276
Norway ...... 23 1620 50
Spain .......... 91 377 8166
Sweden....... 08 445 1251
UK.............. 870 6072439
Page 84

In Asia-Pacific Region
Australia.... 1800 649931
Cambodia.. 63 2 636 9797 (via Philippines)
China ......... 800 820 1100 (toll-free)
.................... 8 621 33104691 (not toll-free)
Hong Kong 852 2 844 4456
India........... 0006517 2 68303634 (manual toll-free. You need an IDD-equipped
telephone)
Indonesia... 803 65 7249
Korea......... 822 767 2595
Malaysia .... 1 800 80 1390
Myanmar... 63 2 636 9796 (via Philippines)
New Zealand 0800 444 365
Pakistan..... 632 63684 15 (IDD via Philippines)
Philippines 1 800 1 651 0117
Singapore .. 65 6213-1311
Tai wa n ....... 2 2545-1640
Thailand .... 1 800 631 0003
Vietnam ..... 632 6368416 (IDD via Philippines)
Japan
Domestic.... 0120 868686
Outside country 81 298 47 0800
Latin America
Argentina .. Contact AT&T USA at 0-800 222 1288. Once connected, dial 800 843 4481
Brazil ......... 001-916 377 0180
Chile
Easter Island.. ............ Contact AT&T USA at 800 800 311. Once
connected, dial 800 843 4481
Mainland and Juan .. Contact AT&T USA at 800 225 288. Once
connected, dial 800 843 4481
66 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 85

Colombia ... Contact AT&T USA at 01 800 911 0010. Once connected, dial 800 843 4481
Costa Rica . Contact AT&T USA at 0 800 0 114 114. Once connected, dial 800 843 4481
Ecuador
(Andimate) .... Contact AT&T USA at 1 999 119. Once connected,
dial 800 843 4481
(Pacifictel) ..... Contact AT&T USA at 1 800 225 528. Once connected, dial
800 843 4481
Guatemala. Contact AT&T USA at 99 99 190. Once connected, dial 800 843 4481
Mexico ....... Contact AT&T USA at 001 800 462 628 4240. Once connected, dial 800 843
4481
Miami ........ 1 800 621 8423
Panama...... Contact AT&T USA at 00 800 001 0109. Once connected, dial 800 843 4481
Paraguay ... 001 916 377 0114
Peru ........... 001 916 377 0114
Uruguay..... 001 916 377 0114
Venezuela... Contact AT&T USA at 0 800 2255 288. Once connected, dial 800 843 4481
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 67
Page 86

68 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 87

Appendix D: System Issue Report
Form
Note: An on-line / automatic submission version of this form is available at http://
support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/S5000PSL/. For the fastest service,
please submit your form via the Internet.
Date Submitted: _______________________________________________________
Company Name: ______________________________________________________
Contact Name: ________________________________________________________
Email Address: _______________________________________________________
Intel Server Product: ___________________________________________________
Priority (Critical, Hot, High, Low): _______________________________________
Brief Problem Description. Provide a brief description below. See the last page for space
to include a detailed problem description.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
Board / Chassis Information
Baseboard Revision - PBA#: _____________________________________________
Baseboard Serial Number: _______________________________________________
Chassis Model:________________________________________________________
CPU1 Speed/Stepping/Spec: _____________________________________________
CPU2 Speed/Stepping/Spec: _____________________________________________
System BIOS Version: __________________________________________________
HSC Firmware Version: _________________________________________________
BMC Firmware Version: ________________________________________________
Page 88

FBDIMM Configuration
DIMM A1 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM A2 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM B1 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM B2 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM C1 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM C2 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM D1 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
DIMM D2 MB and vendor / part number: __________________________________
Operating System Information
Operating System:_____________________________________________________
Version: _____________________________________________________________
Service Pack / Update: _________________________________________________
Add-in Card, Peripheral, Video, NIC
Check each box below as applicable, and provide the requested information.
Peripheral Description
Add-in Card
Slot 1
Slot 2
Slot 3
Slot 4
Slot 5
Slot 6
Video
On-board video
Add-in video
NIC
Driver
Revision
IRQ
I/O Base
Address
FW
Revision
70 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
Page 89

Peripheral Description
On-board NIC1
On-board NIC2
Hard Drive Information
Driver
Revision
IRQ
I/O Base
Address
FW
Revision
Drive Type (SATA,
SAS, etc.)
Management Information
No management module installed _________________________________________
®
Remote Management Module _______________________________________
Intel
Make/Model
Hot-swap
or Fixed
IRQ
FW
Revision
Control Panel Information
Standard Control Panel _________________________________________________
®
Local Control Panel_______________________________________________
Intel
Intel® Server Board S5000PSL 71
Page 90

Complete Problem Description
In the space below, provide a complete description of the steps used to reproduce the
problem or a complete description of where the problem can be found. Please also include
any details on troubleshooting already done.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
72 Intel® Server Board S5000PSL
 Loading...
Loading...