Page 1

Intel® Server Board S3420GP
Technical Product Specification
Intel order number E65697-010
Revision 2.4
January, 2011
Enterprise Platforms and Services Division - Marketing
Page 2
Revision History Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Revision History
Date Revision
Number
Feb. 2009 0.3 Initial release.
May 2009 0.5 Update block diagram.
July. 2009 0.9 Updated POST error code and diagram.
Aug. 2009 1.0 Updated MTBF.
Nov. 2009 1.1 Additional details for memory configuration.
Dec. 2009 1.2 Added Intel® Server Board S3420GPV details.
Dec. 2009 2.0 Updated processor name.
Jan. 2010 2.1 Corrected the typo.
Apr. 2010 2.2 Corrected the typo, updated processor name and remove CCC certification
marking information.
July. 2010 2.3 Corrected the typo.
Jan.2011 2.4
Corrected the typo. Added RDIMM support on S3420GPV.
Updated Table 45.
Add USB device readiness beep code information.
Modifications
Revision 2.4
ii
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 3
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Disclaimers
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express
or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this
document. Except as provided in Intel's Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel
assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to
sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular
purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked
"reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The Intel
®
Server Board S3420GP may contain design defects or errors known as errata which
may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata
are available on request.
Intel Corporation server boards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery
components that need adequate airflow to cool. Intel’s own chassis are designed and tested to
meet the intended thermal requirements of these components when the fully integrated system
is used together. It is the responsibility of the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel
developed server building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to
determine the amount of airflow required for their specific application and environmental
conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible if components fail or the server board
does not operate correctly when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating
limits.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2011 Intel Corporation
.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
iii
Page 4
Table of Contents Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Chapter Outline ......................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Server Board Use Disclaimer .................................................................................... 1
2. Overview ................................................................................................................................. 2
2.1 Intel
2.2 Server Board Layout ................................................................................................. 5
2.2.1 Server Board Connector and Component Layout .................................................... 6
2.2.2 Intel
2.2.3 Server Board Rear I/O Layout ................................................................................ 14
3. Functional Architecture ....................................................................................................... 15
3.1 Processor Sub-System ........................................................................................... 17
3.1.1 Intel
3.1.2 Intel
3.1.3 Intel
3.1.4 Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) ....................................................................... 18
3.1.5 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
3.2 Memory Subsystem................................................................................................. 18
3.2.1 Memory Sizing and Configuration ........................................................................... 18
3.2.2 Post Error Codes ..................................................................................................... 19
3.2.3 Publishing System Memory .................................................................................... 20
3.2.4 Memory Map and Population Rules ........................................................................ 21
3.3 Intel
3.4 I/O Sub-system ........................................................................................................ 25
3.4.1 PCI Express Interface ............................................................................................. 25
3.4.2 Serial ATA Support .................................................................................................. 26
3.4.3 USB 2.0 Support ..................................................................................................... 26
3.5 Optional Intel
3.6 Integrated Baseboard Management Controller ...................................................... 27
3.6.1 Integrated BMC Embedded LAN Channel .............................................................. 29
3.6.2 Optional RMM3 Advanced Management Board ..................................................... 29
3.6.3 Serial Ports .............................................................................................................. 30
3.6.4 Floppy Disk Controller ............................................................................................. 30
3.6.5 Keyboard and Mouse Support ................................................................................ 30
3.6.6 Wake-up Control ..................................................................................................... 31
3.7 Video Support .......................................................................................................... 31
3.7.1 Intel
3.7.2 Video for Intel
3.8 Network Interface Controller (NIC) ......................................................................... 33
3.8.1 GigE Controller 82574L ........................................................................................... 33
®
Server Board S3420GP Feature Set ............................................................... 2
®
Server Board S3420GP Mechanical Drawings ............................................... 8
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series ....................................................................... 17
®
CoreTM Processor i3-500 Series and Intel® Pentium® Processor G6950 ...... 17
®
Turbo Boost Technology ............................................................................... 17
®
Technology ................................................................ 18
®
3420 Chipset PCH ......................................................................................... 24
®
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD ....................................... 27
®
Server Board S3420GPLX and Intel® Server Board S3420GPLC ............... 31
®
Server Board S3420GPV ............................................................... 32
Revision 2.4
iv
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 5

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Table of Contents
3.8.2 GigE PHY 82578DM ............................................................................................... 33
3.8.3 MAC Address Definition .......................................................................................... 33
3.9 Intel
®
I/O Acceleration Technology 2 (Intel® I/OAT2) ............................................. 34
3.9.1 Direct Cache Access (DCA) .................................................................................... 34
3.10 Intel
®
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d) ................................ 34
4. Platform Management ......................................................................................................... 35
4.1 Feature Support ...................................................................................................... 35
4.1.1 IPMI 2.0 Features .................................................................................................... 35
4.1.2 Non-IPMI Features .................................................................................................. 36
4.2 Optional Advanced Management Feature Support ................................................ 37
4.2.1 Enabling Advanced Management Features ........................................................... 37
4.2.2 Keyboard, Video, Mouse (KVM) Redirection .......................................................... 37
4.2.3 Media Redirection ................................................................................................... 38
4.2.4 Web Services for Management (WS-MAN) ............................................................ 38
4.2.5 Local Directory Authentication Protocol (LDAP) ..................................................... 39
4.2.6 Embedded Webserver ............................................................................................ 39
4.3 Management Engine (ME) ...................................................................................... 39
5. Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV .............................. 40
5.1 Super I/O ................................................................................................................. 40
5.1.1 Key Features of Super I/O ...................................................................................... 40
5.1.2 Sensor and Hardware Monitor ................................................................................ 40
5.1.3 Fan controller (Manual) ........................................................................................... 42
5.1.4 Voltage and Temperature Status Screen ............................................................... 44
5.2 SMBIOS ................................................................................................................... 45
5.2.1 Data Storage ........................................................................................................... 45
5.3 Event log and Viewer .............................................................................................. 45
5.3.1 Event Log Viewer in Setup ...................................................................................... 45
6. BIOS User Interface ............................................................................................................. 47
6.1 Logo/Diagnostic Screen .......................................................................................... 47
6.2 BIOS Boot Popup Menu .......................................................................................... 47
6.3 BIOS Setup utility .................................................................................................... 47
6.3.1 Operation ................................................................................................................. 48
6.3.2 Server Platform Setup Utility Screens .................................................................... 50
6.4 Loading BIOS Defaults ............................................................................................ 74
7. Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs ...................................................................... 76
7.1 Board Connector Information .................................................................................. 76
7.2 Power Connectors ................................................................................................... 76
7.3 System Management Headers ............................................................................... 77
7.3.1 Intel
®
Remote Management Module 3 (Intel® RMM3) Connector .......................... 77
7.3.2 LCP/IPMB Header ................................................................................................... 78
7.3.3 HSBP Header .......................................................................................................... 78
Revision 2.4
v
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 6

Table of Contents Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
7.3.4 SGPIO Header ........................................................................................................ 79
7.4 Front Control Panel Connector ............................................................................... 79
7.4.1 Power Button ........................................................................................................... 80
7.4.2 Reset Button ............................................................................................................ 80
7.4.3 NMI Button ............................................................................................................... 80
7.4.4 System Status Indicator LED .................................................................................. 80
7.5 I/O Connectors ........................................................................................................ 81
7.5.1 VGA Connector ....................................................................................................... 81
7.5.2 Rear NIC and USB connector ................................................................................. 82
7.5.3 SATA ....................................................................................................................... 83
7.5.4 50-pin PCI Express* Connector .............................................................................. 83
7.5.5 Serial Port Connectors ............................................................................................ 84
7.5.6 USB Connector ....................................................................................................... 84
7.6 PCI Express* Slot/PCI Slot/Riser Card Slot / ......................................................... 85
7.7 Fan Headers ............................................................................................................ 90
8. Jumper Blocks...................................................................................................................... 91
8.1 CMOS Clear and Password Reset Usage Procedure ............................................ 92
8.1.1 Clearing the CMOS ................................................................................................. 92
8.1.2 Clearing the Password ............................................................................................ 92
8.2 Integrated BMC Force Update Procedure (only for the Intel
®
Server Board
S3420GPLX and S3420GPLC) ................................................................................................. 93
8.3 ME Force Update Jumper ....................................................................................... 93
8.4 BIOS Recovery Jumper .......................................................................................... 94
9. Intel
9.1 System Status LED (For the Intel
®
Light Guided Diagnostics ......................................................................................... 95
®
Server Board S3420GPLX and S3420GPLC) 95
9.2 Post Code Diagnostic LEDs .................................................................................... 96
10. Design and Environmental Specifications ........................................................................ 97
10.1 Intel
®
Server Board S3420GP Design Specifications ............................................. 97
10.2 Board-level Calculated MTBF ................................................................................. 97
10.3 Server Board Power Requirements ........................................................................ 98
10.3.1 Processor Power Support ....................................................................................... 98
10.4 Power Supply Output Requirements ...................................................................... 99
10.4.1 Ground ing ................................................................................................................ 99
10.4.2 Standby Outputs ...................................................................................................... 99
10.4.3 Remote Sense ......................................................................................................... 99
10.4.4 Voltage Regulation ................................................................................................ 100
10.4.5 Dynamic Loading ................................................................................................... 100
10.4.6 Capacitive Loading ................................................................................................ 100
10.4.7 Closed-loop Stability ............................................................................................. 100
10.4.8 Common Mode Noise ........................................................................................... 101
10.4.9 Ripple/Noise .......................................................................................................... 101
Revision 2.4
vi
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 7

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Table of Contents
10.4.10 Timing Requirements ............................................................................................ 101
10.4.11 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby Mode ....................................................... 103
10.4.12 Protection Circuits ................................................................................................. 103
11. Regulatory and Certification Information ........................................................................ 105
11.1 Product Regulatory Compliance ........................................................................... 105
11.1.1 Product Safety Compliance .................................................................................. 105
11.1.2 Product EMC Compliance – Class A Compliance ................................................ 105
11.1.3 C ertifications/Registrations/Declarations .............................................................. 106
11.1.4 Product Ecology Requirements ............................................................................ 106
11.2 Product Regulatory Compliance Markings ........................................................... 107
11.3 Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices ................................................................. 109
11.3.1 FCC Verification Statement (USA) ....................................................................... 109
11.3.2 ICES-003 (Canada) ............................................................................................... 110
11.3.3 Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity) ................................................................ 110
11.3.4 VCCI (Japan) ......................................................................................................... 110
11.3.5 BSMI (Taiwan) ....................................................................................................... 111
11.3.6 RRL (Korea) .......................................................................................................... 111
Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips ............................................................................... 112
Appendix B: Integrated BMC Sensor Tables ......................................................................... 113
Appendix C: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder .............................................................. 119
Appendix D: POST Code Errors .............................................................................................. 123
Appendix E: Supported Intel
®
Server Chassis ...................................................................... 128
Glossary ..................................................................................................................................... 129
Reference Documents .............................................................................................................. 132
Revision 2.4
vii
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 8
List of Figures Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
List of Figures
Figure 1. Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX Picture ........................................................................ 5
Figure 2. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Layout ............................................................................. 6
Figure 3. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Key Connector and LED Indicator IDENTIFICATION 8
Figure 4. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Hole and Component Positions .................................. 9
Figure 5. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Major Connector Pin Location (1 of 2) ...................... 10
Figure 6. Intel® Server Board S3420GP –Major Connector Pin Location (2 of 2) ....................... 11
Figure 7. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Primary Side Keepout Zone ...................................... 12
Figure 8. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Secondary Side Keepout Zone ................................. 13
Figure 9. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Rear I/O Layout ............................................................ 14
Figure 10. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Functional Block Diagram For S3420GPLX .............. 15
Figure 11. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Functional Block Diagram From S3420GPLC ........... 16
Figure 12. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Functional Block Diagram From S3420GPV ............. 17
Figure 13. Integrated BMC Hardware .......................................................................................... 29
Figure 14. Server Management Bus (SMBUS) Block Diagram ................................................... 35
Figure 15. Setup Utility — Hardware Monitor Screen Display ..................................................... 41
Figure 16. Setup Utility — Fan controller (Manual) Display ......................................................... 43
Figure 17. Setup Utility — Voltage and Temperature Status Screen .......................................... 44
Figure 18. Event Log Viewer ........................................................................................................ 46
Figure 19. Setup Utility – Main Screen Display ............................................................................ 51
Figure 20. Setup Utility – Advanced Screen Display ................................................................... 53
Figure 21. Setup Utility – Processor Configuration Screen Display ............................................ 54
Figure 22. Setup Utility – Memory Configuration Screen Display ................................................ 56
Figure 23. Setup Utility – Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen Display ..................... 58
Figure 24. Setup Utility – Serial Port Configuration Screen Display ............................................ 59
Figure 25. Setup Utility – USB Controller Configuration Screen Display .................................... 60
Figure 26. Setup Utility – PCI Configuration Screen Display ....................................................... 62
Figure 27. Setup Utility – System Acoustic and Performance Configuration Screen Display ..... 63
Figure 28. Setup Utility – Security Configuration Screen Display ................................................ 64
Figure 29. Setup Utility – Server Management Configuraiton Screen Display ............................ 66
Figure 30. Setup Utility – Console Redirection Screen Display ................................................... 67
Figure 31. Setup Utility – Server Management System Information Screen Display .................. 69
Figure 32. Setup Utility – Boot Options Screen Display .............................................................. 70
Figure 33. Setup Utility – Delete Boot Option Screen Display ..................................................... 71
Figure 34. Setup Utility — Hard Disk Order Screen Display ........................................................ 72
Figure 35. Setup Utility – CDROM Order Screen Display ........................................................... 72
Figure 36. Setup Utility — Floppy Order Screen Display ............................................................. 73
Figure 37. Setup Utility – Network Device Order Screen Display ................................................ 73
Figure 38. Setup Utility – Boot Manager Screen Display ............................................................. 74
Figure 39. Jumper Blocks (J1A2, J1F1, J1F3, J1F2 and J1F5) .................................................. 91
Revision 2.4
viii
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 9

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS List of Figures
Figure 40. Power Distribution Block Diagram .............................................................................. 98
Figure 41. Output Voltage Timing............................................................................................... 102
Figure 42. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals) ............................................................ 103
Figure 43. Diagnostic LED Placement Diagram ........................................................................ 119
Revision 2.4
ix
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 10
List of Tables Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
List of Tables
Table 1. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Feature Set ...................................................................... 2
Table 2. Major Board Components ................................................................................................ 7
Table 3. Standard Platform DIMM Nomenclature ........................................................................ 21
Table 4. Memory Configuration Table .......................................................................................... 22
Table 5. UDIMM memory configuration rule ................................................................................ 23
Table 6. UDIMM Maximum configuration ..................................................................................... 23
Table 7. RDIMM memory configuration rule ................................................................................ 24
Table 8. RDIMM Maximum configuration ..................................................................................... 24
Table 9. Optional RMM3 Advanced Management Board Featu res ............................................. 30
Table 10. Serial B Header (J1B1) Pin-out .................................................................................... 30
Table 11. Video Modes ................................................................................................................. 31
Table 12. Dual Video Modes ........................................................................................................ 32
Table 13. Setup Utility — Hardware Monitor Screen Fields ........................................................ 41
Table 14. Setup Utility — Hardware Monitor Screen Fields ........................................................ 43
Table 15. Setup Utility — Voltage and Temperature Status Fields ............................................. 44
Table 16. BIOS Setup Page Layout ............................................................................................. 48
Table 17. BIOS Setup: Keyboard Command Bar ........................................................................ 49
Table 18. Setup Utility – Main Screen Fields ............................................................................... 51
Table 19. Setup Utility – Advanced Screen Display Fields .......................................................... 53
Table 20. Setup Utility – Processor Configuration Screen Fields ................................................ 54
Table 21. Setup Utility – Memory Configuration Screen Fields ................................................... 56
Table 22. Setup Utility – Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen Fields ......................... 58
Table 23. Setup Utility – Serial Ports Configuration Screen Fields ............................................. 59
Table 24. Setup Utility – USB Controller Configuration Screen Fields ........................................ 61
Table 25. Setup Utility – PCI Configuration Screen Fields .......................................................... 62
Table 26. Setup Utility – System Acoustic and Performance Configuration Screen Fields ........ 63
Table 27. Setup Utility – Security Configuration Screen Fields ................................................... 64
Table 28. Setup Utility – Server Management Configuration Screen Fields ............................... 66
Table 29. Setup Utility – Console Redirection Configuration Fields ............................................ 68
Table 30. Setup Utility – Server Management System Information Fields .................................. 69
Table 31. Setup Utility – Boot Options Screen Fields .................................................................. 70
Table 32. Setup Utility – Delete Boot Option Fields ..................................................................... 72
Table 33. Setup Utility — Hard Disk Order Fields ........................................................................ 72
Table 34. Setup Utility – CDROM Order Fields............................................................................ 73
Table 35. Setup Utility — Floppy Order Fields ............................................................................. 73
Table 36. Setup Utility – Network Device Order Fields ................................................................ 74
Table 37. Setup Utility – Boot Manager Screen Fields ................................................................ 74
Table 38. Board Connector Matrix ............................................................................................... 76
Table 39. Baseboard Power Connector Pin-out (J9A1) ............................................................... 77
Revision 2.4
x
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 11

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS List of Tables
Table 40. SSI Processor Power Connector Pin-out (J9C1) ......................................................... 77
®
Table 41. Intel
RMM3 Connector Pin-out (J2C1) ....................................................................... 78
Table 42. LPC/IPMB Header Pin-out (J1H2) ............................................................................... 78
Table 43. HSBP Header Pin-out (J1J1) ....................................................................................... 78
Table 44. SGPIO Header Pin-out (J1J3) ...................................................................................... 79
Table 45. Front Panel SSI Standard 24-pin Connector Pin-out (J1C1) ....................................... 79
Table 46. System Status LED Indicator States ............................................................................ 80
Table 47. VGA Connector Pin-out (J7A1) .................................................................................... 81
Table 48. RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out (J5A1) ..................................................... 82
Table 49. RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out (J6A1) ..................................................... 82
Table 50. SATA Connector Pin-out (J1H4, J1H1, J1G1, J1H3, J1G3, J1F4) ............................. 83
Table 51. 50-pin PCI Express* Connector Pin-out (J2H1) ........................................................... 83
Table 52. External Serial A Port Pin-out (J8A1) ........................................................................... 84
Table 53. Internal 9-pin Serial B Header Pin-out (J1B2) ............................................................. 84
Table 54. Internal USB Connector Pin-out ( J1E1, J1D1) ........................................................... 84
Table 55. Pin-out of Internal USB Connector for Floppy ( J1J2) ................................................. 85
Table 56. Pin-out of Internal USB Connector for low-profile Intel
®
Z-U130 Value Solid State
Drive (J3F2) ............................................................................................................................ 85
Table 57. Pin-out of adaptive riser slot/PCI Express slot 6 .......................................................... 85
Table 58. SSI 4-pin Fan Header Pin-out (J6D1, J1J4, J6J2, J7J1, J6B1) .................................. 90
Table 59. Server Board Jumpers (J1F1, J1F2, J1F3, J1F5, J1A2) ............................................. 91
Table 60. Front Panel Status LED Behavior Summary................................................................ 95
Table 61. POST Code Diagnostic LED Location ......................................................................... 96
Table 62. Server Board Design Specifications............................................................................. 97
Table 63. Intel
®
Xeon® Processor TDP Guidelines ...................................................................... 98
Table 64. 350-W Load Ratings ..................................................................................................... 99
Table 65. Voltage Regulation Limits ........................................................................................... 100
Table 66. Transient Load Requirements .................................................................................... 100
Table 67. Capacitve Loading Conditions ................................................................................... 100
Table 68. Ripple and Noise ........................................................................................................ 101
Table 69. Output Voltage Timing ................................................................................................ 101
Table 70. Turn On/Off Timing ..................................................................................................... 102
Table 71. Over-Current Protection (OCP) .................................................................................. 104
Table 72. Over-voltage Protection (OVP) Limits ........................................................................ 104
Table 73. Integrated BMC Core Sensors ................................................................................... 115
Table 74. POST Progress Code LED Example ......................................................................... 119
Table 75. Diagnostic LED POST Code Decoder ....................................................................... 120
Table 76. POST Error Messages and Handling ......................................................................... 123
Table 77. POST Error Beep Codes ............................................................................................ 127
Revision 2.4
xi
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 12

List of Tables Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
<This page is intentionally left blank.>
Revision 2.4
xii
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 13

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Introduction
1. Introduction
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) provides board specific information detailing the
features, functionality, and high-level architecture of the Intel
®
Server Board S3420GP.
In addition, you can obtain design-level information for specific subsystems by ordering the
External Product Specifications (EPS) or External Design Specifications (EDS) for a given
subsystem. EPS and EDS documents are not publicly available and must be ordered through
your local Intel representative.
1.1 Chapter Outline
This document is divided into the following chapters:
Chapter 1 – Introduction
Chapter 2 – Server Board Overview
Chapter 3 – Functional Architecture
Chapter 4 – Platform Management
Chapter 5 – BIOS User Interface
Chapter 6 – Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Chapter 7 – Jumpers Blocks
Chapter 8 – Intel
Chapter 9 – Design and Environmental Specifications
Chapter 10 – Regulatory and Certification Information
Chapter 11 – Regulatory and Certification Information
Appendix A – Integration and Usage Tips
Appendix B – Integrated BMC Sensor Tables
Appendix C – POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
Appendix D – POST Code Errors
Appendix E – Supported Intel
Glossary
Reference Documents
®
Light-Guided Diagnostics
®
Server Chassis
1.2 Server Board Use Disclaimer
Intel Corporation server boards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery
components that need adequate airflow to cool. Intel ensures through its own chassis
development and testing that when Intel server building blocks are used together, the fully
integrated system meets the intended thermal requirements of these components. It is the
responsibility of the system integrator who chooses not to use Intel developed server building
blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of
airflow required for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation
cannot be held responsible if components fail or the server board does not operate correctly
when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating limits.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
1
Page 14

Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
®
2. Overview
The Intel® Server Board S3420GP is a monolithic printed circuit board (PCB) with features
designed to support entry-level severs. It has three board SKUs: S3420GPLX, S3420GPLC,
and S3420GPV.
2.1 Intel® Server Board S3420GP Feature Set
Table 1. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Feature Set
Feature Description
Processor Support for one Xeon® Processor 3400 Series or Intel® CoreTM Processor i3-500
Series or Intel
2.5 GT/s point-to-point DMI interface to PCH
LGA 1156 pin socket
Memory Two memory channels with support for 1066/1333 MHz ECC Unbuffered (UDIMM) or
ECC Registered (RDIMM) (Intel
®
Server Board S3420GPLX and S3420GPLC
Intel
Up to 2 UDIMMs or 3 RDIMM (Intel
32 GB max with x8 ECC RDIMM (2 Gb DRAM) and 16 GB max with x8
®
Server Board S3420GPV
Intel
Up to 2 UDIMMs or 2 RDIMM (Intel
16 GB max with x8 ECC UDIMM (2 Gb DRAM) and 16 GB max with x8
Intel
Chipset
Server board S3420GPLX
Support for Intel
ServerEngines* LLC Pilot II BMC controller (Integrated BMC)
PCI Express* switch
®
Server board S3420GPLC
Intel
Support for Intel
ServerEngines* LLC Pilot II BMC controller (Integrated BMC)
®
Intel
Server board S3420GPV
Support for Intel
I/O
External connections:
DB-15 video connectors
DB-9 serial Port A connector
Four ports on two USB/LAN combo connectors at rear of board.
Internal connections:
Two USB 2x5 pin headers, each supporting two USB 2.0 ports (Only one
One 2x5 Serial Port B header (Intel
Six SATA II connectors
One connector supports for optional Intel
®
Pentium® Processor G6950 in FC-LGA 1156 socket package.
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series only) DDR3.
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series only)
per channel
ECC UDIMM (2 Gb DRAM)
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series only)
per channel
ECC RDIMM (2 Gb DRAM)
®
3420 Chipset Platform Controller Hub (PCH)
®
3420 Chipset Platform Controller Hub (PCH)
®
3420 Chipset Platform Controller Hub (PCH)
header for Intel
®
Server board S3420GPV)
®
Server board S3420GPLX and
S3420GPLC)
®
®
(Intel
Server board S3420GPLX)
Remote Management Module 3
Revision 2.4
2
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 15
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Overview
®
®
®
Feature Description
Intel
Add-in PCI Card, PCI
Express* Card
System Fan Support Five 4-pin fan headers supporting four system fans and one processor.
Video
Onboard Hard Drive Support for six Serial ATA II hard drives through six onboard SATA II connectors with
RAID Support
LAN
Server Board S3420GPLX
Slot1: One 3.3V/5V PCI 32 bit/33 MHz connector.
Slot2: One PCI Express* Gen1 x4 (x1 throughput) connector.
Slot3: One PCI Express* Gen1 x8 (x4 throughput) connector.
Slot4: One PCI Express* Gen2 x8 (x4 throughput) connector.
Slot5: One PCI Express* Gen2 x8 (x8 throughput) connector.
Slot6: One PCI Express* Gen2 x16 (x8 throughput) connector.
®
Server Board S3420GPLC/ S3420GPV
Intel
Slot1: One 3.3V/5V PCI 32 bit/33 MHz connector.
Slot3: One PCI Express* Gen1 x8 (x4 throughput) connector.
Slot5: One PCI Express* Gen2 x8 (x8 throughput) connector.
Slot6: One PCI Express* Gen2 x16 (x8 throughput) connector.
Server Board S3420GPLX/ S3420GPLC
Intel
Onboard ServerEngines* LLC Pilot II BMC Controller
Integrated 2D Video Controller with 8MB Video Memory
64-MB DDR2 667 MHz Memory
®
Server Board S3420GPV
Intel
Silicon Motion SM712GX04LF02-BA
SW RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10.
®
Server Board S3420GPLX:
Intel
Up to four SAS hard drives through option Intel
®
SAS Entry RAID Module
card
Intel
Server Board S3420GPLX /S3420GPLC/S3420GPV
Intel
®
Rapid Storage RAID through onboard SATA connectors provides
SATA RAID 0, 1, 5 and 10.
Intel
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology II through onboard SATA
connectors provides SATA RAID 0, 1, and 10.
®
Server Board S3420GPLX
Intel
Intel
®
Embedded Server RAID Technology II through optional Intel® SAS
Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD provides SAS RAID 0, 1, and 10 with
optional RAID 5 support provided by the Intel
®
RAID Activation Key
AXXRAKSW5
IT/IR RAID through optional Intel
®
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD
provides entry level hardware RAID 0, 1, 10, and native SAS pass through
mode
Four ports full featured SAS/SATA hardware RAID through optional Intel
Integrated RAID Module SROMBSASMR (AXXROMBSASMR) provides
RAID 0, 1, 5, 6 and striping capability for spans 10, 50, 60.
One Gigabit Ethernet device 82574L connect to PCI-E x1 interfaces on the
PCH.
One Gigabit Ethernet PHY 82578DM connected to PCH through PCI-E x1
interface.
®
Revision 2.4
3
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 16
Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
®
Feature Description
Server Board S3420GPLX/S3420GPLC:
Server Management
Intel
Onboard LLC Pilot II Controller (iBMC)
Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated BMC), IPMI 2.0
compliant
Integrated 2D video controller on PCI-E x1
®
Server Board S3420GPLX
Intel
Intel
®
Remote Management Module III (RMM3)
Revision 2.4
4
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 17

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Overview
2.2 Server Board Layout
Figure 1. Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX Picture
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
5
Page 18
Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
A
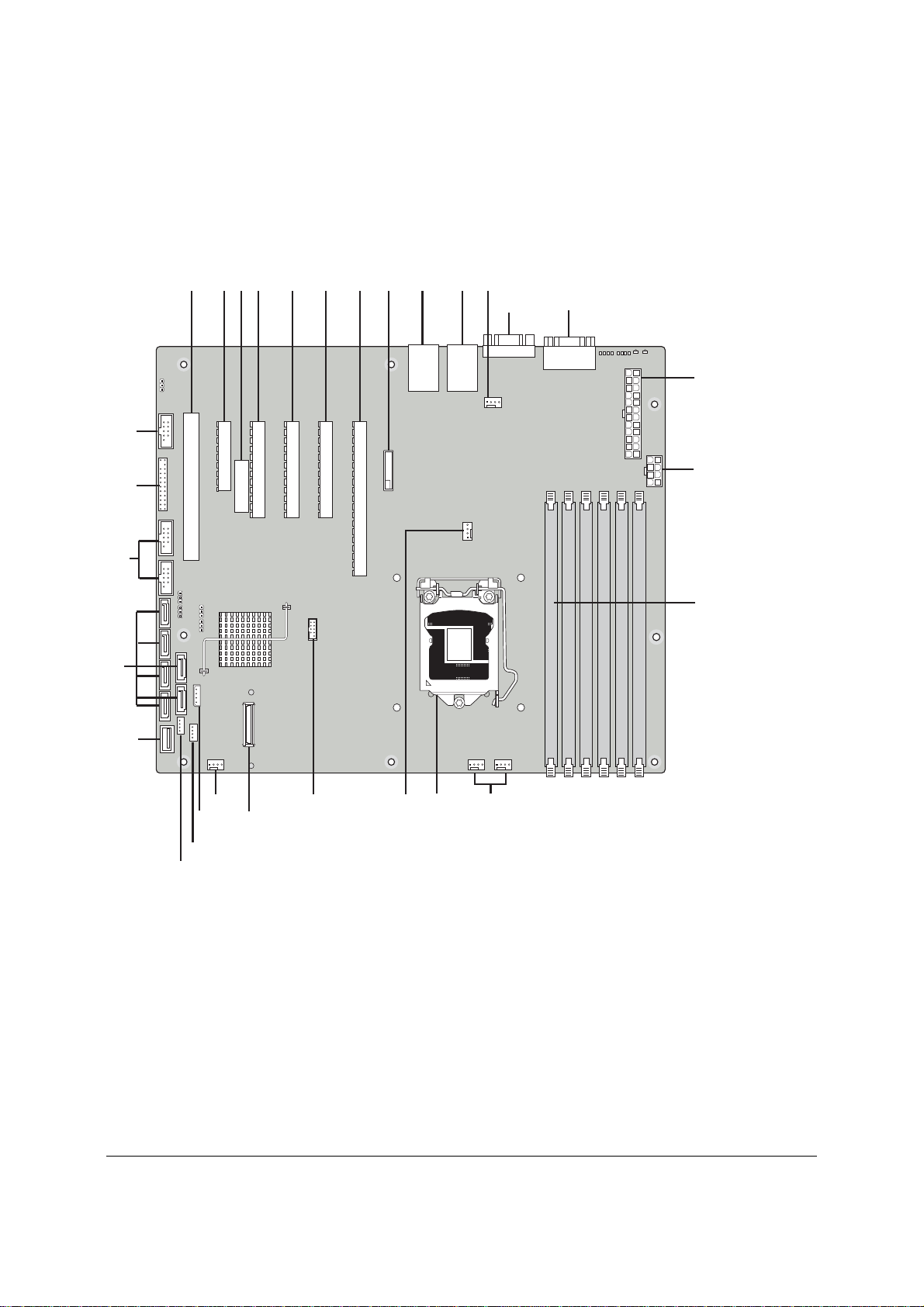
2.2.1 Server Board Connector and Component Layout
The following figure shows the board layout of the server board. Each connector and major
component is identified by a number or letter, and Table 2 provides the description.
ABCDEFGH
DD
CC
BB
J
I
K
LM
N
O
P
A
Z
V
W
X
Y
U
T
R
S
Q
AF003290
®
Figure 2. Intel
Server Board S3420GP Layout
Revision 2.4
6
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 19
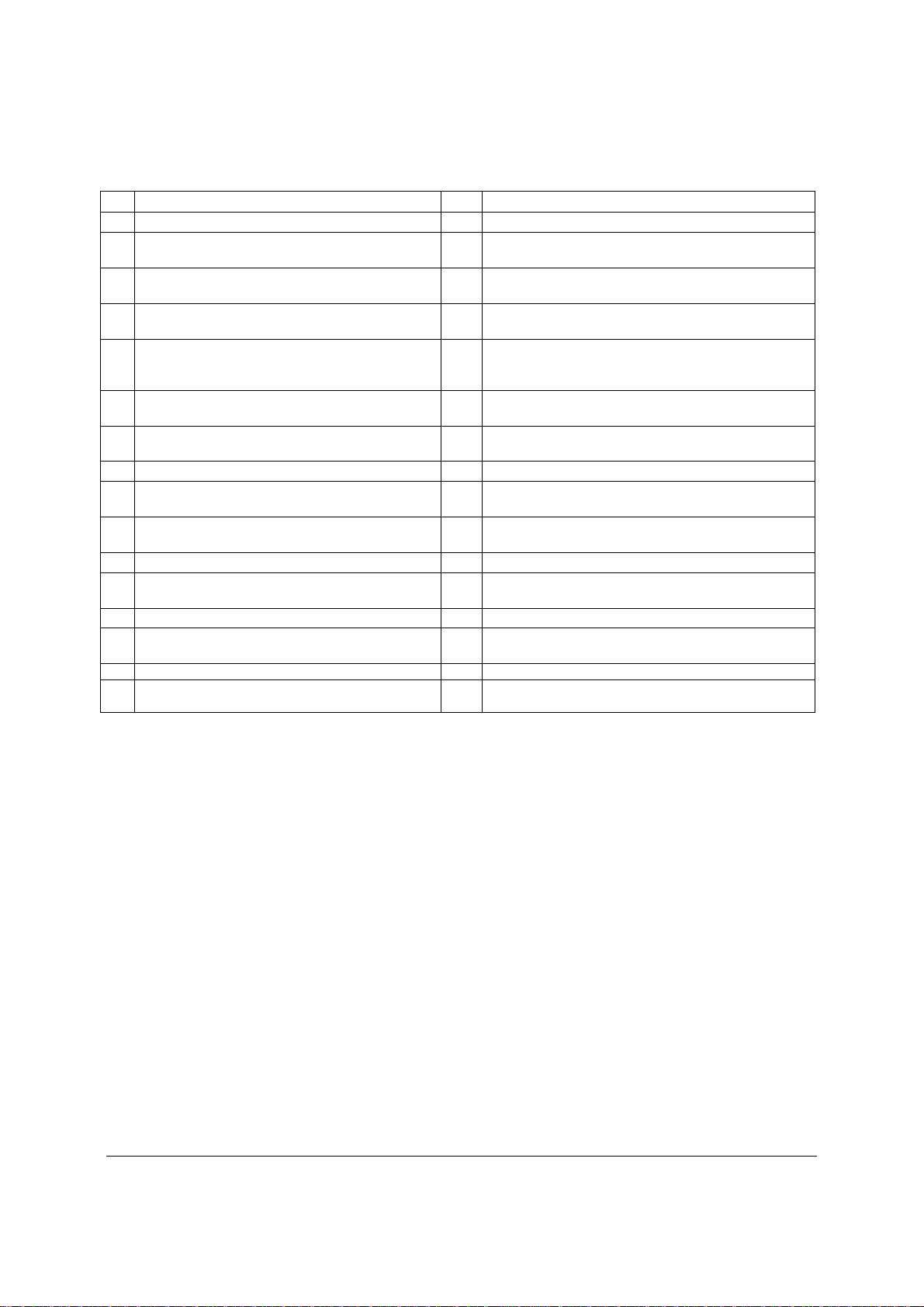
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Overview
®
Table 2. Major Board Components
Description Description
A Slot 1, 32 Mbit/33 MHz PCI Q System FAN2 and System FAN 3
B Slot 2, PCI Express* Gen1 x1 (x4 connector)
R CPU connector
(Intel Server Board S3420GPLX only)
C Intel RMM3 Connector(Intel Server Board
S CPU Fan connector
S3420GPLX only)
D Slot 3, PCI Express* Gen1 x4 (PCI Express*
Gen2 compliant)
E Slot 4, PCI Express* Gen2 x4 (x8 connector)
(x8 connector)( Intel
®
Server Board S3420GPLX
T USB SSD connector (Intel® Server Board
S3420GPLX and S3420GPLC)
U 50-pin PCI Express* connector (Intel
Server Board
S3420GPLX only)
only)
F Slot 5. PCI Express* Gen2 x8 (x8 connector) V System FAN 1 (Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX
and S3420GPLC)
G Slot 6, PCI Express* Gen2 x8 (x16 connector) W IPMB(Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and
S3420GPLC)
H CMOS battery X SATA_SGPIO
I Ethernet and Dual USB COMBO Y HSBP (Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and
S3420GPLC)
J Ethernet and Dual USB COMBO Z USB Floppy (Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and
S3420GPLC)
K System FAN 4 AA Six SATA ports
L Video port BB Internal USB Connector ( One for Internal USB
header on Intel
®
Server Board S3420GPV)
M External Serial port CC Front Panel Connector
N Main Power Connector DD Internal Serial Port (Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX
and S3420GPLC)
O CPU Power connector
P DIMM slots (4 slots on Intel® Server Board
S3420GPV)
Revision 2.4
7
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 20
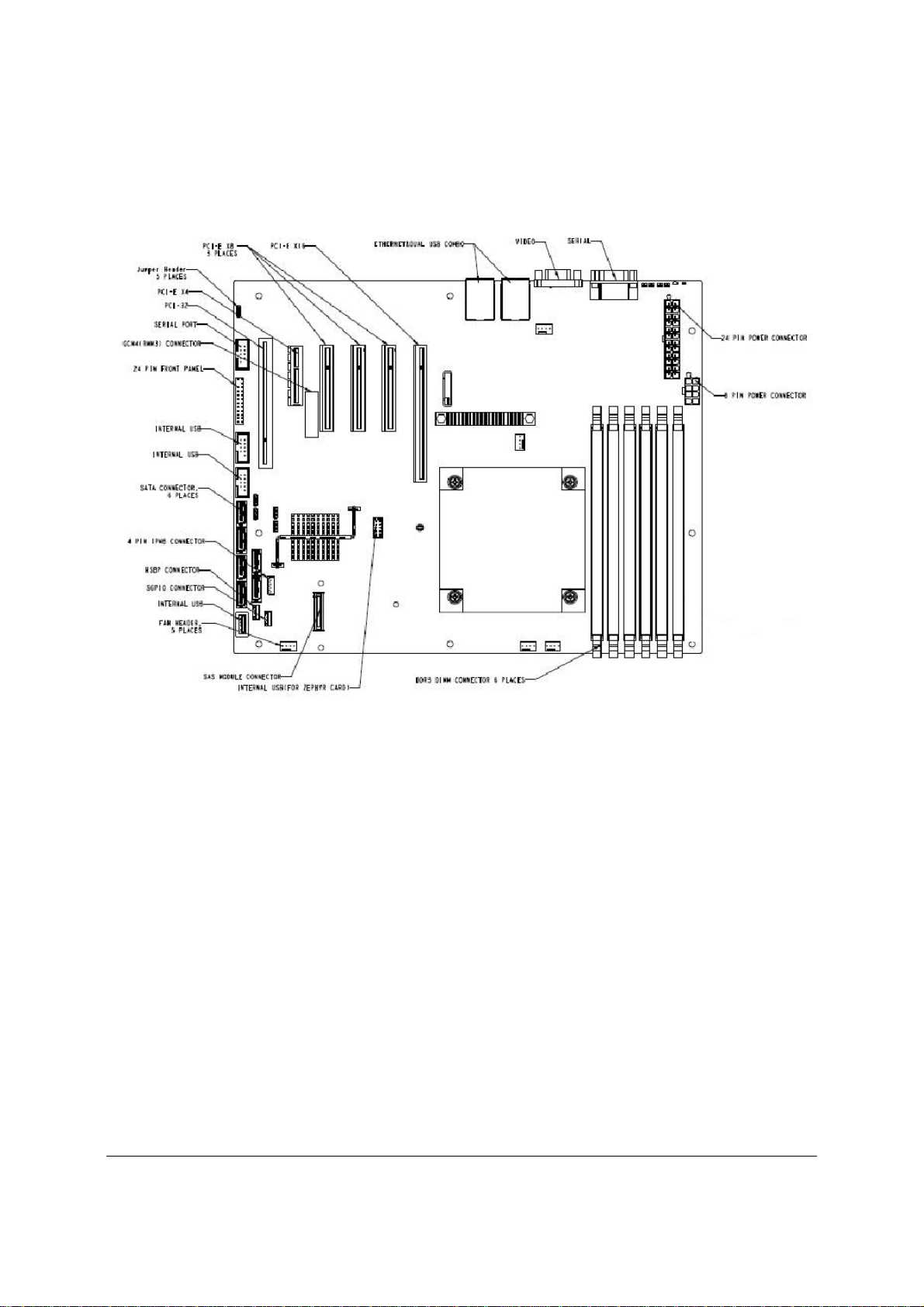
Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
2.2.2 Intel® Server Board S3420GP Mechanical Drawings
Figure 3. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Key Connector and LED Indicator IDENTIFICATION
Revision 2.4
8
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 21
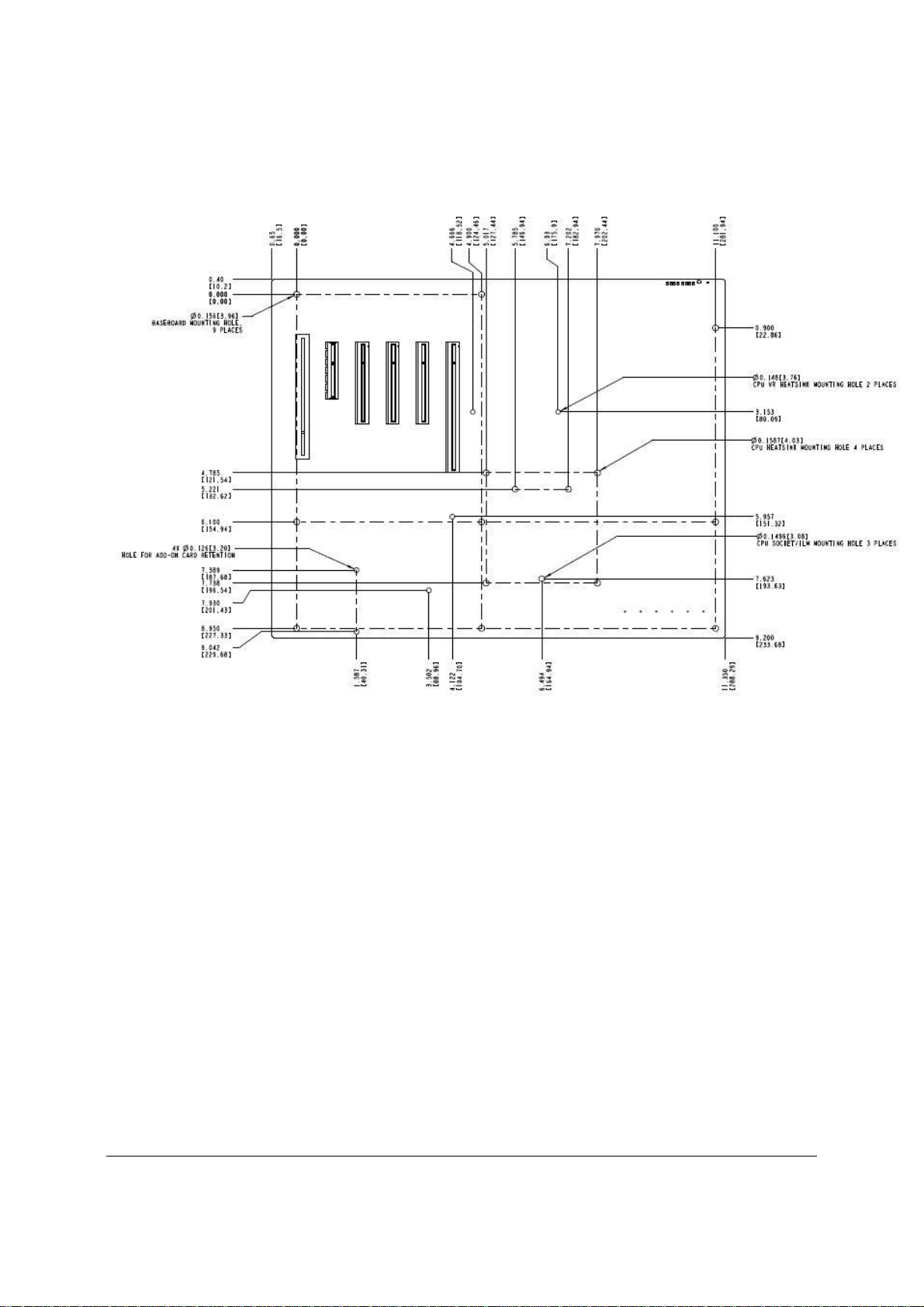
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Overview
Figure 4. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Hole and Component Positions
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
9
Page 22
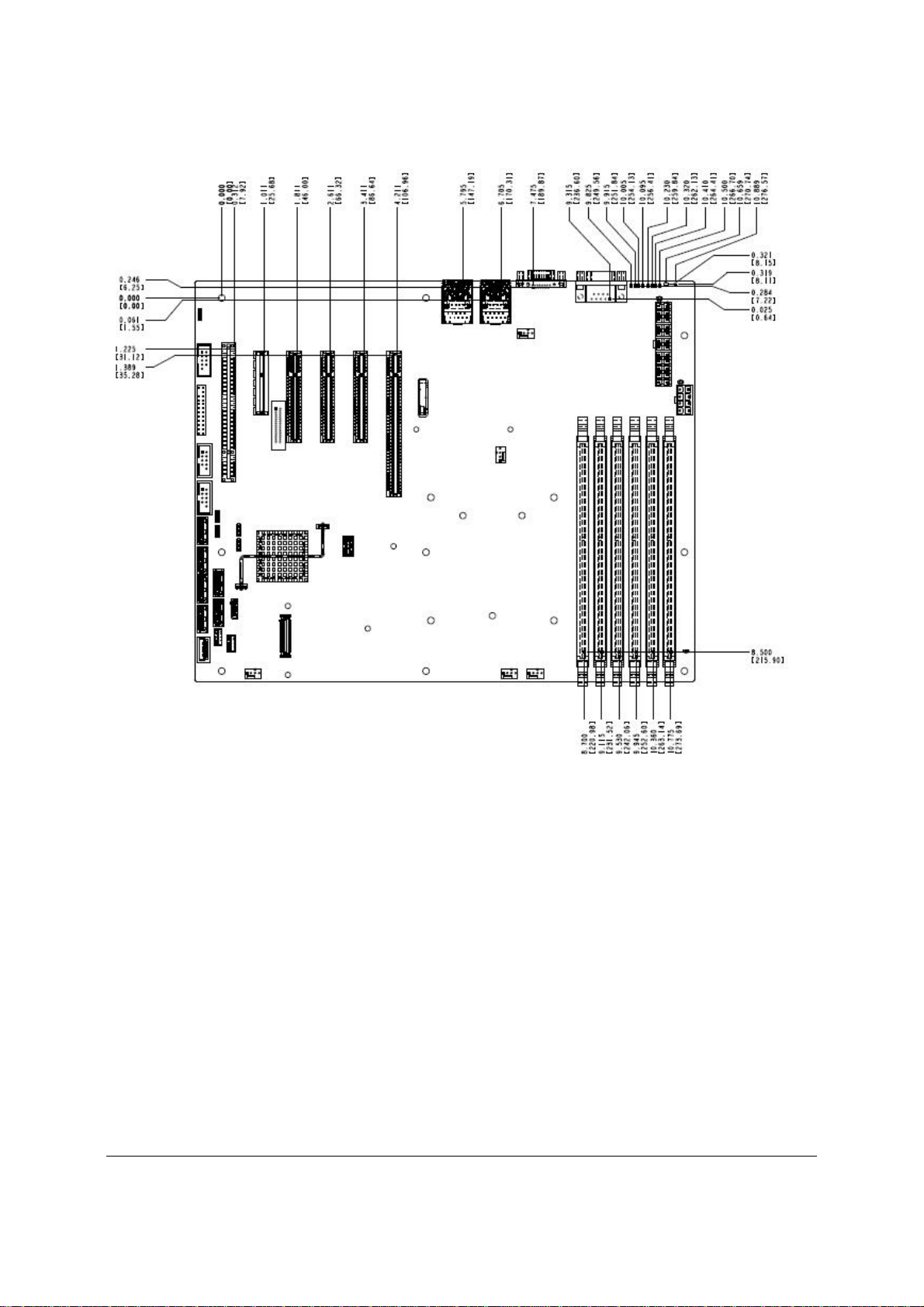
Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
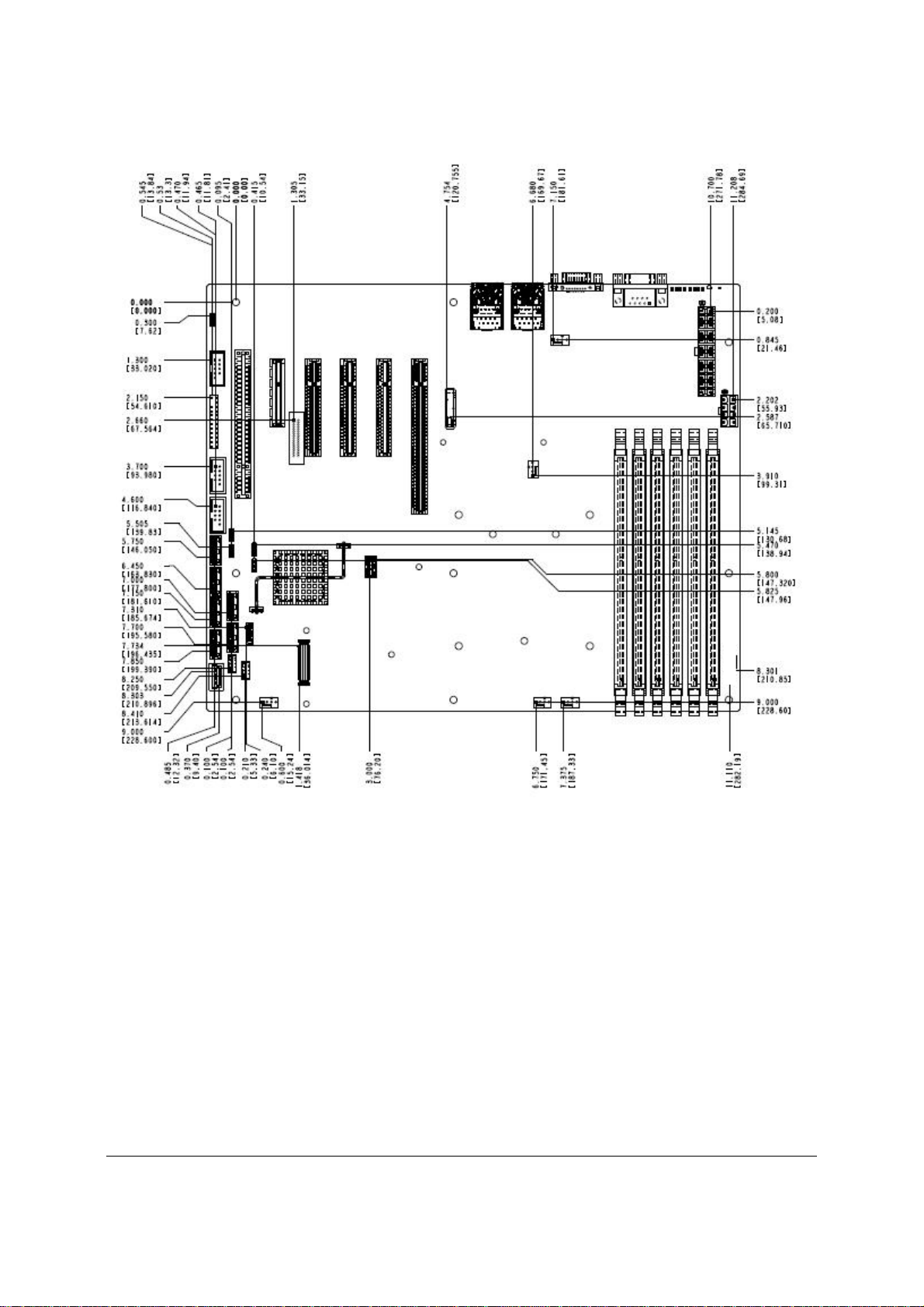
Figure 5. Intel
Revision 2.4
10
®
Server Board S3420GP – Major Connector Pin Location (1 of 2)
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 23
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Overview
Revision 2.4
Figure 6. Intel
®
Server Board S3420GP –Major Connector Pin Location (2 of 2)
Intel order number E65697-010
11
Page 24
Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
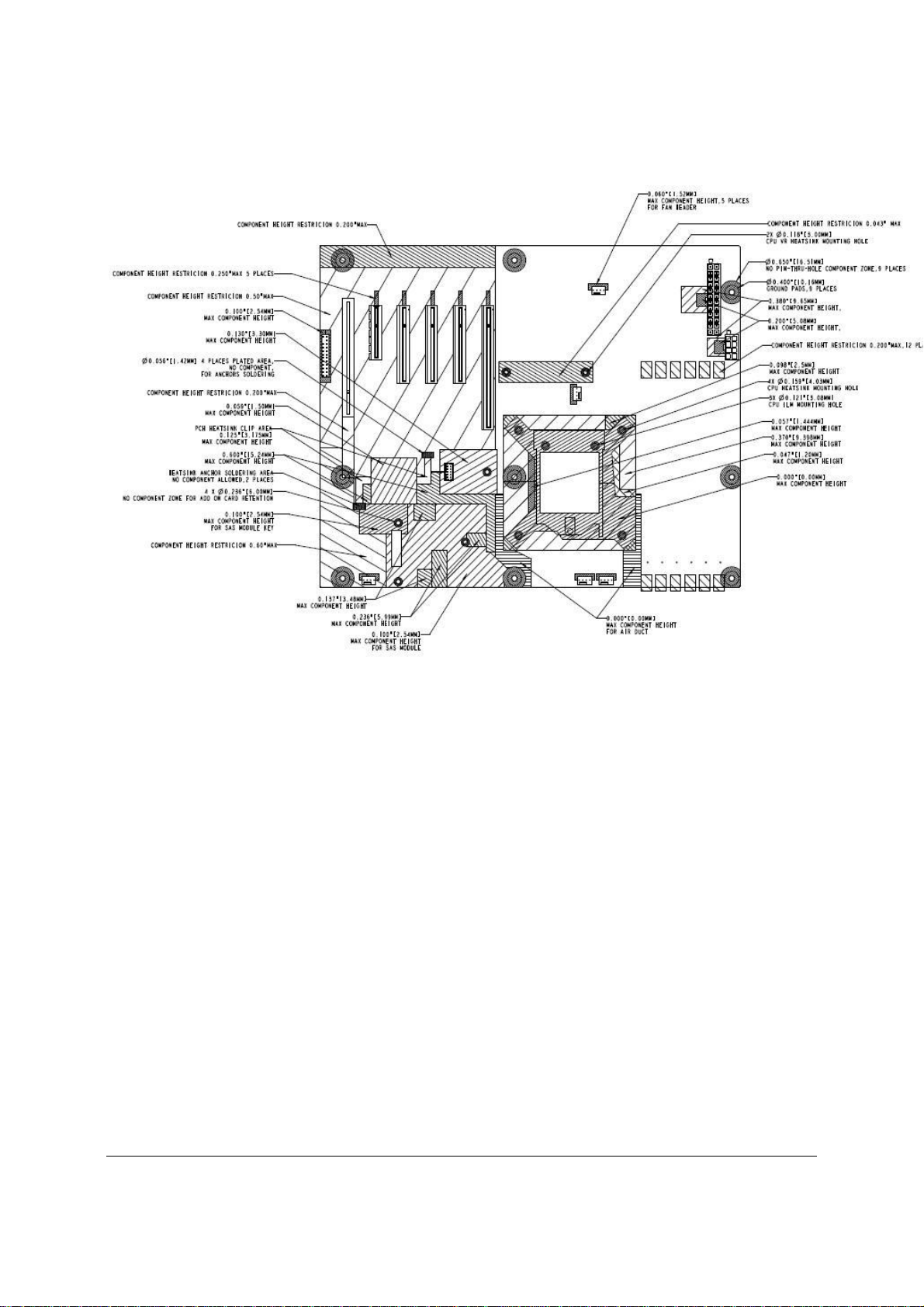
Figure 7. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Primary Side Keepout Zone
Revision 2.4
12
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 25
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Overview
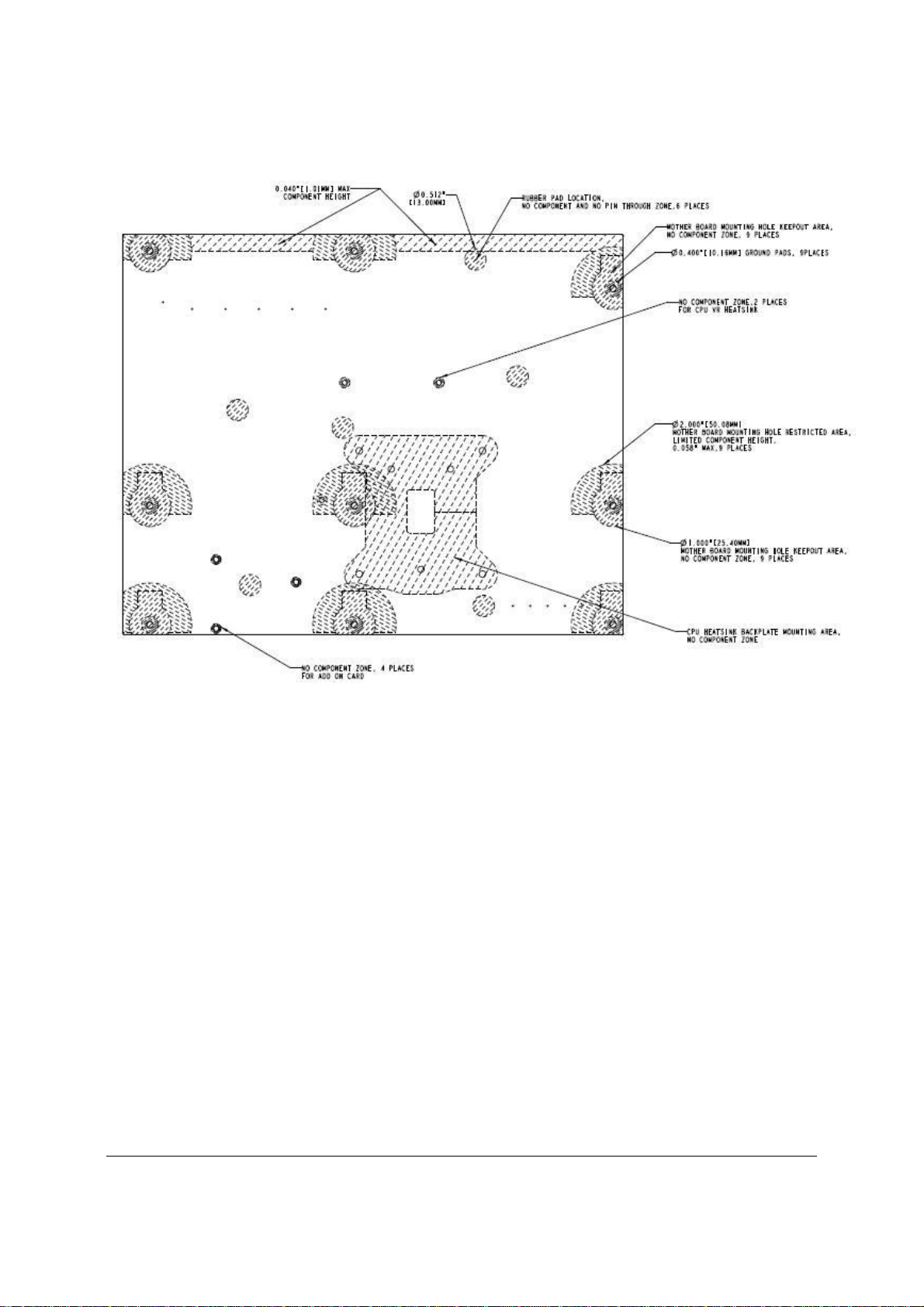
Figure 8. Intel® Server Board S3420GP – Secondary Side Keepout Zone
Revision 2.4
13
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 26
Overview Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
2.2.3 Server Board Rear I/O Layout
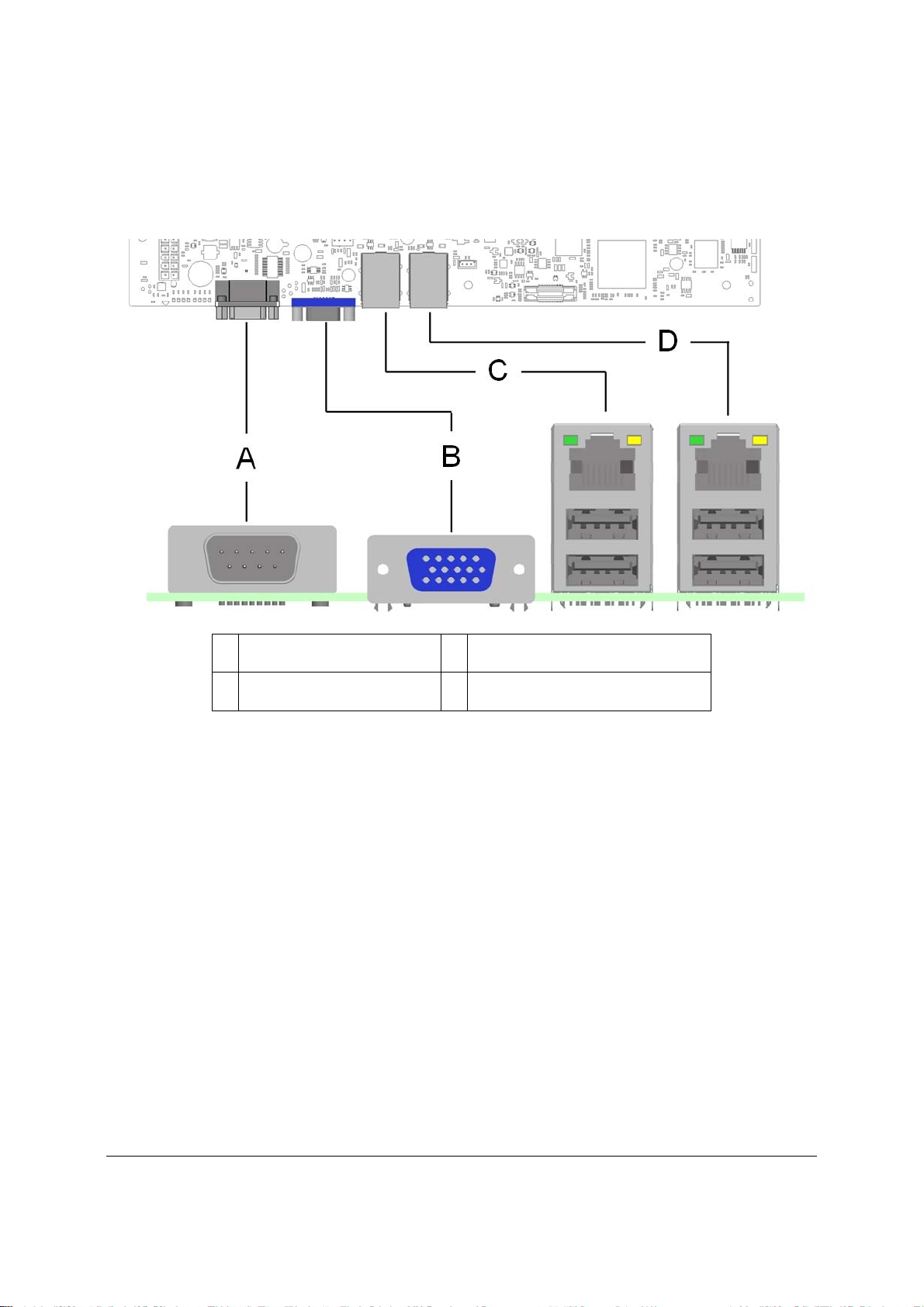
The following figure shows the layout of the rear I/O components for the server board.
A Serial Port A C NIC Port 1 (1 Gb) and Dual USB Port
Connector
B Video D NIC port 2 (1 Gb) and Dual USB Port
Connector
Figure 9. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Rear I/O Layout
Revision 2.4
14
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 27

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
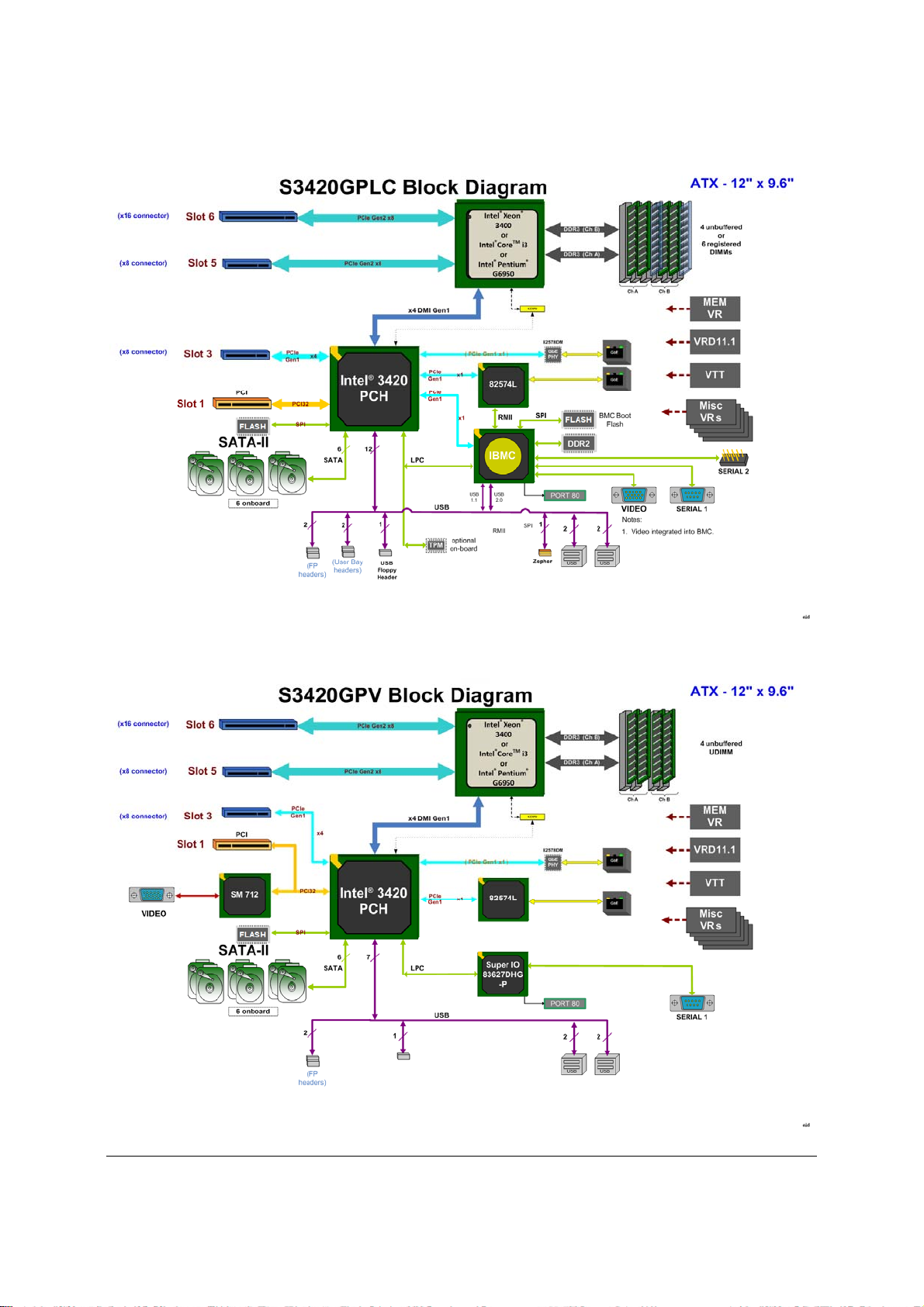
3. Functional Architecture
The architecture and design of the Intel® Server Board S3420GP is based on the Intel
Chipset. The chipset is designed for systems based on the Intel
or Intel
®
CoreTM i3-500 Desktop Processor Series or Intel® Pentium® Processor Processor
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series
®
3420
G6950in the FC-LGA 1156 socket package. The chipset contains two main components:
Intel
PCI Express* switch (Intel
®
3420 Chipset
®
Server Board S3420GPLX only).
This chapter provides a high-level description of the functionality associated with each chipset
component and the architectural blocks that make up the server board.
Figure 10. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Functional Block Diagram For S3420GPLX
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
15
Page 28
Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Figure 11. Intel
®
Server Board S3420GP Functional Block Diagram From S3420GPLC
Revision 2.4
16
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 29

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
Figure 12. Intel® Server Board S3420GP Functional Block Diagram From S3420GPV
3.1 Processor Sub-System
The Intel® Server Board S3420GP supports the following processor:
Intel
Intel
Intel
The Intel
nm processor technology. The Intel
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 series
®
CoreTM Processor i3-500 Desktop series
®
Pentium® Processor G6950
®
Xeon® 3400 Processor Series are made up of multi-core processors based on the 45
®
CoreTM Processor i3-500 Series and Intel® Pentium®
Processor G6950are made up of dual core processor based on the 32 nm processor technology.
3.1.1 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3400 Series
The Intel® Xeon® Processor 3400 Series highly integrated solution variant is composed of four
Nehalem-based processor cores.
FC-LGA 1156 socket package with 2.5 GT/s.
Up to 95 W Thermal Design Power (TDP); processors with higher TDP are not
supported.
The server board does not support previous generations of the Intel
®
Xeon® processors.
3.1.2 Intel® CoreTM Processor i3-500 Series and Intel® Pentium® Processor G6950
The Intel® Duo CoreTM Processor i3-500 Series and Intel® Pentium® Processor G6950 highly
integrated solution variant is composed of two processor cores.
FC-LGA 1156 socket package with 2.5 GT/s.
Up to 95 W Thermal Design Power (TDP); processors with higher TDP are not
supported.
Please get the detail supported processor list from Intel website.
3.1.3 Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology is featured on certain processors in the Intel® Xeon® Processor
3400 Series. Intel
processor to run faster than the marked frequency if the processor is operating below power,
temperature, and current limits. This results in increased performance for both multi-threaded
and single-threaded workloads.
®
Intel
Turbo Boost Technology operation:
Turbo Boost operates under Operating System control – It is only entered when the
operating system requests the highest (P0) performance state.
Turbo Boost operation can be enabled or disabled by BIOS.
Revision 2.4
®
Turbo Boost Technology opportunistically and automatically allows the
Intel order number E65697-010
17
Page 30

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Turbo Boost converts any available power and thermal headroom into higher frequency
on active cores. At nominal marked processor frequency, many applications consume
less than the rated processor power draw.
Turbo Boost availability is independent of the number of active cores.
Maximum Turbo Boost frequency depends on the number of active cores and varies by
processor configuration.
The amount of time the system spends in Turbo Boost operation depends on workload,
operating environment, and platform design.
If the processor supports the Intel
®
Turbo Boost Technology feature, the BIOS Setup provides
an option to enable or disable this feature. The default state is enabled.
3.1.4 Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT)
Most Intel® Xeon® processors support Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT). The BIOS detects
processors that support this feature and enables the feature during POST.
If the processor supports this feature, the BIOS Setup provides an option to enable or disable
this feature. The default is enabled.
3.1.5 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
Most processors support the Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® technology. This technology changes
the processor operating ratio and voltage similar to the Thermal Monitor 1 (TM1) feature. The
BIOS implements this technology in conjunction with the TM1 feature.
The BIOS enables a
combination of TM1 and TM2 according to the processor BIOS writer's guide.
3.2 Memory Subsystem
The Intel® Xeon® Processor 3400 Series has an Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) in its
package. Each Intel
memory. Each DDR3 channel in the IMC supports up to three DDR3 RDIMM slots or up to two
UDIMM slots. The DDR3 RDIMM frequency can be 800/1066/1333 MHz. DDR3 UDIMM
frequency can be 1066/1333 MHz. All RDIMMs and UDIMMs include ECC (Error Correction
Code) operation. Various speeds and memory technologies are supported.
Note: Intel
®
Xeon® Processor L3406 only supports DDR3 Unbuffered DIMM (UDIMM).
The Intel® CoreTM Processor i3-500 Series and Intel® Pentium® Processor G6950 have an
Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) supports DDR3 protocols with two independent, 64-bit wide
channels each accessing one or two DIMMs. Only DDR3 UDIMM can be supported with the
®
Intel
Core® i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium® Processor G6950.
RAS (Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability) is not supported on the Intel
S3420GP.
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series produces up to two DDR3 channels of
®
Server Board
3.2.1 Memory Sizing and Configuration
The Intel® Server Board S3420GP supports various memory module sizes and configurations.
These combinations of sizes and configurations are valid only for DDR3 DIMMs approved by
Intel Corporation.
Revision 2.4
18
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 31

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
S3420GP supports:
DIMM sizes of 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB, and 8 GB.
DIMMs composed of DRAM using 2 Gb technology.
DRAMs organized as single rank, dual rank, or quad rank DIMMS.
DIMM speeds of 800, 1066, or 1333 MT/s.
Registered or Unregistered (unbuffered) DIMMs (RDIMMs or UDIMMs).
Note: UDIMMs should be ECC, and may or may not have thermal sensors; RDIMMs must have
ECC and must have thermal sensors.
S3420GP has the following limitations:
256 Mb technology, x4 DRAM on UDIMM, and quad rank UDIMM are NOT supported
x16 DRAM on UDIMM is not supported on combo routing
Memory suppliers not productizing native 800 ECC UDIMMs
Intel
256 Mb/512 Mb technology, x4 and x16 DRAMs on RDIMM are NOT supported
All channels in a system will run at the fastest common frequency
No mixing of registered and unbuffered DIMMs
No mixing of different ranks or speeds on UDIMM or RDIMM.
®
Xeon® 3400 Series support all timings defined by JEDEC.
3.2.2 Post Error Codes
The range {0xE0 - 0xEF} of POST codes is used for memory errors in early POST. In late POST,
this range is used for reporting other system errors.
0xE8 - No Usable Memory Error: If no memory is available, the system emits POST
Diagnostic LED code 0xE8 and halts the system.
0xE8 - Configuration Error: If a DDR3 DIMM has no SPD information, the BIOS treats
the DIMM slot as if no DDR3 DIMM is present on it. Therefore, if this is the only DDR3
DIMM installed in the system, the BIOS halts with POST Diagnostic LED code 0xE8 (no
usable memory) and halts the system.
0xEB - Memory Test Error: If a DDR3 DIMM or a set of DDR3 DIMMs on the same
memory channel (row) fails HW Memory BIST but usable memory remains available, the
BIOS emits a beep code and displays POST Diagnostic LED code 0xEB momentarily
during the beeping and then continues POST. If all of the memory fails HW Memory
BIST, the system acts as if no memory is available, beeping and halting with the POST
Diagnostic LED code 0xE8 (No Usable Memory) displayed.
0xEA - Channel Training Error: If the memory initialization process is unable to
properly perform the DQ/DQS training on a memory channel, the BIOS emits a beep
code and displays POST Diagnostic LED code 0xEA momentarily during the beeping. If
there is usable memory in the system on other channels, POST memory initialization
continues. Otherwise, the system halts with POST Diagnostic LED code 0xEA staying
displayed.
0xED - Population Error: If the installed memory contains a mix of RDIMMs and
UDIMMs, the system halts with POST Diagnostic LED code 0xED.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
19
Page 32

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
0xEE - Mismatch Error: If more than two quad-ranked DIMMs are installed on any
channel in the system, the system halts with POST Diagnostic LED code 0xEE.
3.2.3 Publishing System Memory
The BIOS displays the Total Memory of the system during POST if Quiet Boot is
disabled in the BIOS setup. This is the total size of memory discovered by the BIOS
during POST, and is the sum of the individual sizes of installed DDR3 DIMMs in the
system.
The BIOS displays the Effective Memory of the system in the BIOS Setup. The term
Effective Memory refers to the total size of all active DDR3 DIMMs (not disabled) and not
used as redundant units.
The BIOS provides the total memory of the system in the main page of the BIOS setup.
This total is the same as the amount described by the first bullet in this section.
If Quiet Boot is disabled, the BIOS displays the total system memory on the diagnostic
screen at the end of POST. This total is the same as the amount described by the first
bullet in this section.
The BIOS provides the total amount of memory in the system.
3.2.3.1 Memory Reservation for Memory-mapped Functions
A region of size 40 MB of memory below 4 GB is always reserved for mapping chipset,
processor, and BIOS (flash) spaces as memory-mapped I/O regions. This region appears as a
loss of memory to the operating system. In addition to this loss, the BIOS creates another
reserved region for memory-mapped PCIe functions, including a standard 64 MB or 256 MB of
standard PCI Express* MMIO configuration space.
If PAE is turned on in the operating system, the operating system reclaims all these reserved
regions.
In addition to this memory reservation, the BIOS creates another reserved region for memorymapped PCI Express* functions, including a standard 64 MB or 256 MB of standard PCI
Express* Memory Mapped I/O (MMIO) configuration space. This is based on the selection of
Maximize Memory below 4 GB in the BIOS Setup.
If this is set to Enabled, the BIOS maximizes usage of memory below 4 GB for an operating
system without PAE capability by limiting PCI Express* Extended Configuration Space to 64
buses rather than the standard 256 buses. This is done using the MAX_BUS_NUMBER feature
offered by the Intel
®
S3420 I/O Hub and a variably-sized Memory Mapped I/O region for the PCI
Express* functions.
3.2.3.2 High-Memory Reclaim
When 4 GB or more of physical memory is installed (physical memory is the memory installed
as DDR3 DIMMs), the reserved memory is lost. However, the Intel
®
3420 chipset provides a
feature called high-memory reclaim, which allows the BIOS and operating system to remap the
lost physical memory into system memory above 4 GB (the system memory is the memory the
processor can see).
The BIOS always enables high-memory reclaim if it discovers installed physical memory equal
to or greater than 4 GB. For the operating system, the reclaimed memory is recoverable only if
the PAE feature in the processor is supported and enabled. Most operating systems support this
feature. For details, see the relevant operating system manuals.
Revision 2.4
20
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 33

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
3.2.3.3 ECC Support
Only ECC memory is supported on this platform.
3.2.4 Memory Map and Population Rules
The following nomenclature is followed for DIMM sockets:
Note: Intel
®
Server Board S3420GP may support up to three DIMM sockets per channel.
Table 3. Standard Platform DIMM Nomenclature
Channel A Channel B
A1 A2 A3 B1 B2 B3
3.2.4.1 TableMemory Subsystem Operating Frequency Determination
The rules for determining the operating frequency of the memory channels are simple, but not
necessarily straightforward. There are several limiting factors, including the number of DIMMs
on a channel and organization of the DIMM - that is, either single-rank (SR), dual-rank (DR), or
quad-rank (QR):
The speed of the processor’s IMC is the maximum speed possible.
The speed of the slowest component – the slowest DIMM or the IMC – determines the
maximum frequency, subject to further limitations.
A single 1333-MHz DIMM (SR or DR) on a channel may run at full 1333-MHz speed.
If two SR/DR DIMMs are installed on a channel, the speed is limited to 1066 MHZ.
A single QR RDIMM on a channel is limited to 1066 MHz.
Two QR RDIMMs or a mix of QR + SR/DR on a channel is limited to 800 MHz.
3.2.4.2 Memory Subsystem Nomenclature
1. DIMMs are organized into physical slots on DDR3 memory channels that belong to
processor sockets.
2. The memory channels are identified as channels A, B.
®
3. For Intel
Xeon® 3400 Series, each socket can support a maximum of six DIMM
sockets (three DIMM sockets per channel), which can support a maximum of six
DIMM sockets.
®
4. The Intel
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series on the Intel® Server Board S3420GP is
populated on the processor socket. It has an Integrated Memory Controller (IMC).
The IMC provides two DDR3 channels and groups DIMMs on the board into an
autonomous memory.
5. The DIMM identifiers on the silkscreen on the board provide information about the
channel and the processor socket to which they belong. For example, DIMM_A1 is
the first slot on channel A.
3.2.4.3 Memory Upgrade Rules
Upgrading the system memory requires careful positioning of the DDR3 DIMMs based on the
following factors:
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
21
Page 34

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Existing DDR3 DIMM population
DDR3 DIMM characteristics
Optimization techniques used by the supported processors to maximize memory
bandwidth
In the Independent Channel mode, all DDR3 channels operate independently. Slot-to-slot DIMM
matching is not required across channels (for example, A1 and B1 do not have to match each
other in terms of size, organization, and timing). DIMMs within a channel do not have to match
in terms of size and organization, but they operate in the minimal common frequency. Also,
Independent Channel mode can be used to support single DIMM configuration in channel A and
in the Single Channel mode.
You must observe the following general rules when selecting and configuring memory to obtain
the best performance from the system.
1. DDR3 RDIMMs must always be populated using a fill-farthest method.
2. DDR3 UDIMMs must always be populated on DIMM A1/A2/B1/B2.
3. Intel
4. Intel
®
Xeon® Processor 3400 Series support either RDIMMs or UDIMMs.
®
Xeon® Processor L3406, Intel® CoreTM Processor i3-500 series or Intel® Pentium®
Processor G6950 only support UDIMMs.
5. RDIMM and UDIMM CAN NOT be mixed.
6. The minimal memory set is {DIMMA1}.
7. DDR3 DIMMs on adjacent slots on the same channel do not need to be identical.
Each socket supports a maximum of six slots. Standard Intel
use the Intel
socket, and only one socket is supported on the Intel
®
3420 chipset support three slots per DDR3 channel, two DDR3 channels per
®
Server Board S3420GP.
®
server boards and systems that
3.2.4.4 Memory Configuration Table
Table 4. Memory Configuration Table
RDIMM
Revision 2.4
22
X
X X
X X X
X X
X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X X
Intel order number E65697-010
Channel A Channel B
A1 A2 A3 B1 B2 B3
Page 35

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
A2 A3 B1
UDIMM
X X X X X X
X
X X
X X
X X X
X X X X
Channel A Channel B
A1
B2 B3
This table defines half of the valid memory configurations. You can exchange Channel A DIMMs
with the DIMMs on Channel B to get another half.
3.2.4.5 UDIMM Configuration rules
DIMM slots per channel DIMMs populated per channel
2 1 1066, 1333 Single Rank, Dual Rank
2 2 1066, 1333 Single Rank, Dual Rank
Table 5. UDIMM memory configuration rule
Speed Ranks per channel
To get the maximum memory size on UDIMM, you get the detail information from below table.
Max Memory Possible 1Gb DRAM Technology 2Gb DRAM Technology
Single Rank UDIMM 4GB
(4x 1GB DIMMs)
Dual Rank UDIMMs 8GB
(4x 2GB DIMMs)
8GB
(4x 2GB DIMMs)
16GB
(4x 4GB DIMMs)
Table 6. UDIMM Maximum configuration
Intel® Server Board S3420GP has the following limitations on UDIMM.
Not support 800MHz ECC UDIMMs
No support for LV DIMMs
256Mb technology, x4 DRAM on UDIMM and quad rank UDIMM are NOT supported
x16 DRAM is not supported on combo routing
All channels in a system will run at the fastest common frequency
No mixing of registered and unbuffered DIMMs
Non-ECC UDIMMs not supported
Mixing ECC and non-ECC UDIMMs anywhere on the platform will prevent the system to
boot/function correctly
Revision 2.4
23
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 36
Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
3.2.4.6 RDIMM Configuration rules
DIMM slots per channel DIMMs populated per channel
3 1 1066, 1333 Single Rank, Dual Rank
3 1 1066 Quad Rank
3 2 1066, 1333 Single Rank, Dual Rank
3 2 800* Quad Rank
3 3** 800* Single Rank, Dual Rank
Speed Ranks per channel
Table 7. RDIMM memory configuration rule
To get the maximum memory size on RDIMM, refer to the following table:
Max Memory Possible 1Gb DRAM Technology
Single Rank RDIMM 6GB
(6x 1GB DIMMs)
Dual Rank RDIMMs 12GB
(6x 2GB DIMMs)
Quad Rank RDIMMs 16GB
(4x 4GB DIMMs)
2Gb DRAM Technology
12GB
(6x 2GB DIMMs)
24GB
(6x 4GB DIMMs)
32GB
(4x 8GB DIMMs)
Table 8. RDIMM Maximum configuration
Intel® Server Board S3420GP has the following limitations on RDIMM:
®
Note: Intel
Server Board S3420GPV has two DIMM slots per channel on board and totally four
DIMM slots which support maximum RDIMM size to 16GB (4x 4GB DIMMs) because of thermal
limitation without BMC control.
No support for LV DIMMs
256Mb/512Mb technology, x4 and x16 DRAMs on RDIMM are NOT supported
All channels in a system will run at the fastest common frequency
No mixing of registered and unbuffered DIMMs
Note : 1066MHz or 1333MHz RDIMMs run at 800MHz.
3.3 Intel® 3420 Chipset PCH
The Intel® 3420 Chipset component is the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). The PCH is designed
for use with Intel
S3420GP is to manage the flow of information between its eleven interfaces:
®
processor in a UP server platform. The role of the PCH in Intel® Server Board
DMI interface to Processor
Revision 2.4
24
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 37

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
PCI Express* Interface
PCI Interface
SATA Interface
USB Host Interface
SMBus Host Interface
SPI Interface
LPC interface to IBMC
JTAG interface
LAN interface
ACPI interface
3.4 I/O Sub-system
Intel® 3420 Chipset PCH provides extensive I/O support.
3.4.1 PCI Express Interface
Two different PCI-E configurations on single board are dependent on different board SKUs:
Intel
Intel
Intel
There is one 32-bit, 33-MHz, 3.3-V/5-V PCI slot.
Compatibility with the PCI addressing model is maintained to ensure all existing applications
and drivers operate unchanged.
The PCI Express* configuration uses standard mechanisms as defined in the PCI Plug-andPlay specification. The initial recovered clock speed of 1.25 GHz results in 2.5 Gb/s/direction,
which provides a 250-MB/s communications channel in each direction (500 MB/s total). This is
close to twice the data rate of classic PCI. The fact that 8b/10b encoding is used accounts for
the 250 MB/s where quick calculations would imply 300 MB/s. The external graphics ports
support 5.0 GT/s speed as well. Operating at 5.0 GT/s results in twice as much bandwidth per
lane as compared to 2.5 GT/s operation.
®
Server Board S3420GPLX
One PCI-E X16 slot connected to the PCI-E ports of CPU. Two PCI-E x8 slots and one SAS
module connected to PCI-E ports of PCIe switch. One PCI-E X8 slot and one PCI-E x4 slot
connected to the PCI-E ports of PCH.
®
Server Board S3420GPLC
One PCI-E X16 slot and one PCI-E X8 slot connected to the PCI-E ports of CPU. One PCIE x8 slot connected to the PCI-E ports of PCH.
®
Server Board S3420GPV
One PCI-E X16 slot and one PCI-E X8 slot connected to the PCI-E ports of CPU. One PCIE x8 slot connected to the PCI-E ports of PCH.
When operating with two PCI Express* controllers, each controller can operate at either 2.5
GT/s or 5.0 GT/s. The PCI Express* architecture is specified in three layers: Transaction Layer,
Data Link Layer, and Physical Layer. The partitioning in the component is not necessarily along
these same boundaries.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
25
Page 38

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
3.4.2 Serial ATA Support
The Intel® 3420 Chipset has two integrated SATA host controllers that support independent
DMA operation on up to six ports and supports data transfer rates of up to 3.0 GB/s (300 MB/s).
The SATA controller contains two modes of operation – a legacy mode using I/O space and an
AHCI mode using memory space.
Software that uses legacy mode does not have AHCI capabilities. The Intel
®
3420 Chipset
supports the Serial ATA Specification, Revision 1.0a. The Ibex Peak also supports several
optional sections of the Serial ATA II: Extensions to Serial ATA 1.0 Specification, Revision 1.0
(AHCI support is required for some elements).
3.4.2.1 Intel
The Intel
®
Matrix Storage Technology
®
3420 Chipset provides support for Intel® Matrix Storage Technology, providing both
AHCI (see above for details on AHCI) and integrated RAID functionality. The industry leading
RAID capability provides high-performance RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10 functionality on up to six SATA
ports of PCH. Matrix RAID support is provided to allow multiple RAID levels to be combined on
a single set of hard drives, such as RAID 0 and RAID 1 on two disks. Other RAID features
include hot spare support, SMART alerting, and RAID 0 autos replace. Software components
include an Option ROM for pre-boot configuration and boot functionality, a Microsoft Windows*
compatible driver, and a user interface to configure and manage the RAID capability of the
®
Intel
3420 Chipset.
3.4.3 USB 2.0 Support
On the Intel® 3420 Chipset, the USB controller functionality is provided by the dual EHCI
controllers with an interface for up to ten USB 2.0 ports. All ports are high-speed, full-speed, and
low-speed capable.
Four external connectors are located on the back edge of the server board.
Two internal 2x5 header (J1E2 and J1D1) are provided, each supporting two optional
USB 2.0 ports.
One port on internal vertical connector to support NIC.
One port on 1x4pin (J1J2) on-board header on Intel
S3420GPLC) to support floppy.
®
Server Board S3420GPLX and
3.4.3.1 Native USB Support
During the power-on self test (POST), the BIOS initializes and configures the USB subsystem.
The BIOS is capable of initializing and using the following types of USB devices.
USB Specification-compliant keyboards
USB Specification-compliant mouse
USB Specification-compliant storage devices that utilize bulk-only transport mechanism
USB devices are scanned to determine if they are required for booting.
The BIOS supports USB 2.0 mode of operation, and as such supports USB 1.1 and USB 2.0
compliant devices and host controllers.
Revision 2.4
26
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 39

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
During the pre-boot phase, the BIOS automatically supports the hot addition and hot removal of
USB devices and a short beep is emitted to indicate such an action. For example, if a USB
device is hot plugged, the BIOS detects the device insertion, initializes the device, and makes it
available to the user. During POST, when the USB controller is initialized, it emits a short beep
for each USB device plugged into the system as they were all just “hot added”.
Boards and systems based on the Intel
®
Server Board S3420GPLX or S3420GPLC are
designed to indicate USB readiness by a series of beep codes during POST, before video
becomes available. These beeps indicate that the USB is powered and initialized. Devices such
as a pen drive or USB CD/DVD ROM drive attached to external USB port will generate a beep
code once the device is recognized, powered and initialized. These beep codes do not signal
any error. They signal USB and external device readiness during POST.
Only on-board USB controllers are initialized by BIOS. This does not prevent the operating
system from supporting any available USB controllers including add-in cards.
3.4.3.2 Legacy USB Support
The BIOS supports PS/2 emulation of USB keyboards and mouse. During POST, the BIOS
initializes and configures the root hub ports and searches for a keyboard and/or a mouse on the
USB hub and then enables the devices that are recognized.
3.5 Optional Intel
The Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX provides one 50-pin PCI Express* connector (J2H1) for
the installation of an optional Intel
®
Intel
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD is detected, the x4 PCI Express* links from the
PCI switches to the 50-pin PCI Express* connector. The optional Intel
®
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD
®
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD. Once the optional
®
SAS Entry RAID Module
AXX4SASMOD includes a SAS1064e controller that supports x4 PCI Express* link widths and
is a single-function PCI Express* end-point device.
The SAS controller supports the SAS protocol as described in the Serial Attached SCSI
Standard, version 1.0, and also supports SAS 1.1 features. A 32-bit external memory bus off the
SAS1064e controller provides an interface for Flash ROM and NVSRAM (Non-volatile Static
Random Access Memory) devices.
The optional Intel
®
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD provides four SAS connectors that
support up to four hard drives with a non-expander backplane or up to eight hard drives with an
expander backplane.
4 ports full featured SAS/SATA hardware RAID through optional Intel
®
Integrated RAID Module
SROMBSASMR (AXXROMBSASMR), provides RAID 0, 1, 5, 6 and striping capability for spans
10, 50, 60.
3.6 Integrated Baseboard Management Controller
The Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and Intel® Server Board S3420GPLC have the integrated
baseboard management controller, but Intel
integrated baseboard management control.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
®
Server Board S3420GPV does not have the
27
Page 40

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
The ServerEngines* LLC Pilot II Integrated BMC is provided by an embedded ARM9 controller
and associated peripheral functionality that is required for IPMI-based server management.
Firmware usage of these hardware features is platform-dependant.
The following is a summary of the Integrated BMC management hardware features used by the
ServerEngines* LLC Pilot II Integrated BMC:
250 MHz 32-bit ARM9 Processor
Memory Management Unit (MMU)
Two 10/100 Ethernet Controllers with NC-SI support
16-bit DDR2 667 MHz interface
Dedicated RTC
12 10-bit ADCs
Eight Fan Tachometers
Four PWMs
Battery-backed Chassis Intrusion I/O Register
JTAG Master
Six I
General-purpose I/O Ports (16 direct, 64 serial)
2
C interfaces
Additionally, the ServerEngines* Pilot II part integrates a super I/O module with the following
features:
KCS/BT Interface
Two 16C550 Serial Ports
Serial IRQ Support
12 GPIO Ports (shared with BMC)
LPC to SPI Bridge
SMI and PME Support
The Pilot II contains an integrated KVMS subsystem and graphics controller with the following
features:
USB 2.0 for keyboard, mouse, and storage devices
USB 1.1 interface for legacy PS/2 to USB bridging
Hardware Video Compression for text and graphics
Hardware encryption
2D Graphics Acceleration
DDR2 graphics memory interface
Up to 1600x1200 pixel resolution
PCI Express* x1 support
Revision 2.4
28
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 41

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
Figure 13. Integrated BMC Hardware
3.6.1 Integrated BMC Embedded LAN Channel
The Integrated BMC hardware includes two dedicated 10/100 network interfaces.
Interface 1:
This interface is available from either of the available NIC ports in system that can
be shared with the host. Only one NIC may be enabled for management traffic at any time. To
change the NIC enabled for management traffic, please use the “Write LAN Channel Port” OEM
IPMI command. The default active interface is port 1 (NIC1).
Interface 2:
This interface is available from the optional RMM3 which is a dedicated
management NIC that is not shared with the host.
For these channels, support can be enabled for IPMI-over-LAN and DHCP.
For security reasons, embedded LAN channels have the following default settings:
IP Address: Static
All users disabled
3.6.2 Optional RMM3 Advanced Management Board
®
Intel
Server Board S3420GPLX provides one RMM3 module slot. RMM3 advanced
management board serves two purposes:
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
29
Page 42

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Give the customer the option to add a dedicated management 100 Mbit LAN interface to
the product.
Provide additional flash space, enabling the Advanced Management functions to support
WS-MAN and CIMON.
Table 9. Optional RMM3 Advanced Management Board Features
Feature Description
KVM Redirection Remote console access via keyboard, video, and mouse redirection over LAN.
USB Media Redirection Remote USB media access over LAN.
WS-MAN Full SMASH profiles for WS-MAN based consoles.
3.6.3 Serial Ports
The server board provides two serial ports: an external DB9 serial port connector and an
internal DH-10 serial header.
The rear DB9 serial A port is a fully-functional serial port that can support any standard serial
device.
The Serial B port is an optional port accessed through a 9-pin internal DH-10 header (J1B1).
You can use a standard DH-10 to DB9 cable to direct serial A port to the rear of a chassis. The
serial B interface follows the standard RS-232 pin-out as defined in the following table.
Table 10. Serial B Header (J1B1) Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Serial Port B Header Pin-out
1 DCD
2 DSR
3 RX
4 RTS
5 TX
6 CTS
7 DTR
8 RI
9 GND
3.6.4 Floppy Disk Controller
The server board does not support a floppy disk controller interface. However, the system BIOS
recognizes USB floppy devices.
3.6.5 Keyboard and Mouse Support
The server board does not support PS/2 interface keyboards and mouse. However, the system
BIOS recognizes USB specification-compliant keyboard and mouse.
Revision 2.4
30
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 43
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
3.6.6 Wake-up Control
The super I/O contains functionality that allows various events to power on and power off the
system.
3.7 Video Support
3.7.1 Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and Intel® Server Board S3420GPLC
The server board includes on-board Server Engine* LLC Pilot II* Controller with 64 MB DDR2
memory in which 8MB is usable/accessible memory for iBMC video/graphic display functions.
The graphic controller internally has access to larger memory for the internal operations. The
32MB memory reported by display driver is the attached memory. Attached memory can be
32MB or greater but only 8MB is accessible for display functions. The SVGA subsystem
supports a variety of modes, up to 1600 x 1200 resolution under 2D. It also supports both CRT
and LCD monitors up to a 100 Hz vertical refresh rate..
The video is accessed using a standard 15-pin VGA connector found on the back edge of the
server board. The on-board video controller can be disabled using the BIOS Setup utility or
when an add-in video card is detected. The system BIOS provides the option for dual-video
operation when an add-in video card is configured in the system.
3.7.1.1 Video Modes
The integrated video controller supports all standard VGA modes. The following table shows the
2D modes supported for both CRT and LCD.
Table 11. Video Modes
2D Mode
Resolution
640x480 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1152x864 Supported Supported Supported N/A
1280x1024 Supported Supported Supported N/A
8 bpp 16 bpp 24 bpp 32 bpp
60, 72, 75, 85 60, 72, 75, 85 60, 72, 75, 85 60, 72, 75, 85 Monitor
56, 60, 72, 75,
85
60, 70, 75, 85 60, 70, 75, 85 60, 70, 75, 85 60, 70, 75, 85 Monitor
75 75 75 N/A Monitor
60, 75, 85 60, 75, 85 60 N/A Monitor
2D Video Mode Support (Color Bit)
56, 60, 72, 75,
85
56, 60, 72, 75,
85
56, 60, 72, 75,
85
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
Monitor
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
Refresh Rate
Revision 2.4
31
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 44
Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
2D Mode
Resolution
1440x900 Supported Supported Supported N/A
1600x1200 Supported Supported N/A N/A
8 bpp 16 bpp 24 bpp 32 bpp
60 60 60 N/A Monitor
60, 65, 70, 75,
85
2D Video Mode Support (Color Bit)
(Hz)
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
60, 65, 70 N/A N/A Monitor
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
3.7.1.2 Dual Video
The BIOS supports both single-video and dual-video modes. The dual-video mode is disabled
by default.
In the single mode (dual monitor video = disabled), the on-board video controller is
disabled when an add-in video card is detected.
In single mode, the onboard video controller is disabled when an add-in video card is
detected.
In dual mode, the onboard video controller is enabled and is the primary video device.
The external video card is allocated resources and is considered the secondary video
device.
When KVM is enabled in iBMC FW, dual video is enabled.
Table 12. Dual Video Modes
Onboard Video
Dual Monitor Video
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Onboard video controller.
Warning: System video is completely disabled if
this option is disabled and an add-in video
adapter is not installed.
If enabled, both the onboard video controller and
an add-in video adapter are enabled for system
video. The onboard video controller becomes
the primary video device.
3.7.2 Video for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV
SM712 is a one video chip from Silicon Motion, Inc (SMI). It is one in SMI’s LynxEM family. It is
PCI 2.1 compliant with the standard PCI 33MHz & 66 MHz PCI Master/Slave interface.
33 MHz & 66 MHz PCI Master/Slave interface
PCI 2.1 compliant
Memory control is provided for the 4MB internal memory
Support 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768 resolution and up to 85Hz.
Dual Video mode is supported.
Revision 2.4
32
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 45

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Functional Architecture
3.8 Network Interface Controller (NIC)
The Intel
interfaces, One is provided from the onboard Intel
the other is the onboard Intel
3.8.1 GigE Controller 82574L
The 82574 family (82574L and 82574IT) are single, compact, low-power components that offer
a fully-integrated Gigabit Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) port.
The 82574 uses the PCI Express* architecture and provides a single-port implementation in a
relatively small area so it can be used for server and client configurations as a LAN on
Motherboard (LOM) design.
External interfaces provided on the 82574:
3.8.2 GigE PHY 82578DM
The 82578 is a single port Gigabit Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY). It connects to the
Media Access Controller (MAC) through a dedicated interconnect. The 82578DM supports
operation at 1000/100/10 Mb/s data rates. The PHY circuitry provides a standard IEEE 802.3
Ethernet interface for 1000BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 10BASE-T applications (802.3, 802.3u,
and 802.3ab).
The 82578 operates with the Platform Controller Hub (PCH) chipset that incorporates the MAC.
The 82578 interfaces with its MAC through two interfaces: PCIe-based and SMBus. The PCIe
(main) interface is used for all link speeds when the system is in an active state (S0) while the
SMBus is used only when the system is in a low power state (Sx). In SMBus mode, the link
speed is reduced to 10 Mb/s. The PCIe interface incorporates two aspects: a PCIe SerDes
(electrically) and a custom logic protocol.
®
Server Board S3420GPLX, S3420GPLC and S3420GPV support two network
®
82578 Gigabit Network controller.
®
82574L GbE PCI Express network controller;
PCIe Rev. 2.0 (2.5 GHz) x1
MDI (Copper) standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet interface for 1000BASE-T, 100BASETX,
and 10BASE-T applications (802.3, 802.3u, and 802.3ab)
NC-SI or SMBus connection to a Manageability Controller (MC)
EEE 1149.1 JTAG (note that BSDL testing is NOT supported)
3.8.3 MAC Address Definition
Each Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX has the following four MAC addresses assigned to it at
the Intel factory:
NIC 1 MAC address
NIC 2 MAC address – Assigned the NIC 1 MAC address +1
Integrated BMC LAN Channel MAC address – Assigned the NIC 1 MAC address +2
Intel
Each Intel
the Intel factory:
NIC 1 MAC address
NIC 2 MAC address – Assigned the NIC 1 MAC address +1
Revision 2.4
®
Remote Management Module 3 (Intel® RMM3) MAC address – Assigned the NIC 1
MAC address +3
®
Server Board S3420GPLC has the following three MAC addresses assigned to it at
Intel order number E65697-010
33
Page 46

Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Integrated BMC LAN Channel MAC address – Assigned the NIC 1 MAC address +2
®
Each Intel
®
Intel
NIC 1 MAC address
NIC 2 MAC address – Assigned the NIC 1 MAC address +1
Server Board S3420GPV has the following two MAC addresses assigned to it at the
factory:
3.9 Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology 2 (Intel® I/OAT2)
The Intel® 3420 chipset series platforms do not support Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology.
3.9.1 Direct Cache Access (DCA)
Direct Cache Access (DCA) is not supported on Intel® Xeon® Processor 3400 Series.
3.10 Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
The Intel® 3420 chipset provides hardware support for implementation of Intel® Virtualization
Technology with Directed I/O (Intel
components that support the virtualization of platforms based on Intel
®
VT-d). Intel VT-d Technology consists of technology
®
Architecture Processor.
Intel VT-d Technology enables multiple operating systems and applications to run in dependent
partitions. A partition behaves like a virtual machine (VM) and provides isolation and protection
across partitions. Each partition is allocated its own subset of host physical memory.
The Intel
sharing the same hardware resources. The Intel
®
Virtualization Technology is designed to support multiple software environments
®
Virtualization Technology can be enabled or
disabled in the BIOS setup. The default behavior is disabled.
Note: If the setup options are changed to enable or disable the Virtualization Technology setting
in the processor, the user must perform an AC power cycle for the changes
to take effect.
Revision 2.4
34
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 47

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Platform Management
4. Platform Management
This chapter is only for The Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and Intel® Server Board
S3420GPLC.
The platform management subsystem is based on the Integrated BMC features of the
ServerEngines* Pilot II. The onboard platform management subsystem consists of
communication buses, sensors, system BIOS, and server management firmware. The following
diagram provides an overview of the Server Management Bus (SMBUS) architecture used on
this server board.
Figure 14. Server Management Bus (SMBUS) Block Diagram
4.1 Feature Support
4.1.1 IPMI 2.0 Features
Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated BMC).
IPMI Watchdog timer.
Messaging support, including command bridging and user/session support.
Chassis device functionality, including power/reset control and BIOS boot flags support.
Event receiver device: The Integrated BMC receives and processes events from other
platform subsystems.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
35
Page 48

Platform Management Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Field replaceable unit (FRU) inventory device functionality: The Integrated BMC supports
access to system FRU devices using IPMI FRU commands.
System event log (SEL) device functionality: The Integrated BMC supports and provides
access to a SEL.
Sensor device record (SDR) repository device functionality: The Integrated BMC
supports storage and access of system SDRs.
Sensor device and sensor scanning/monitoring: The Integrated BMC provides IPMI
management of sensors. It polls sensors to monitor and report system health.
IPMI interfaces.
o Host interfaces include system management software (SMS) with receive
message queue support and server management mode (SMM).
o Terminal mode serial interface
o IPMB interface
o LAN interface that supports the IPMI-over-LAN protocol (RMCP, RMCP+)
Serial-over-LAN (SOL)
ACPI state synchronization: The Integrated BMC tracks ACPI state changes provided by
the BIOS.
Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated BMC) self test: The Integrated
BMC performs initialization and run-time self tests, and makes results available to
external entities.
For more information, refer to the IPMI 2.0 Specification.
4.1.2 Non-IPMI Features
The Integrated BMC supports the following non-IPMI features. This list does not preclude
support for future enhancements or additions.
In-circuit Integrated BMC firmware update.
Fault resilient booting (FRB): FRB2 is supported by the watchdog timer functionality
Chassis intrusion detection and chassis intrusion cable presence detection.
Basic fan control using TControl version 2 SDRs.
Acoustic management: Support for multiple fan profiles.
Signal testing support: The Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated
BMC) provides test commands for setting and getting platform signal states.
The Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated BMC) generates
diagnostic beep codes for fault conditions.
System GUID storage and retrieval.
Front panel management: The Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated
BMC) controls the system status LED and chassis ID LED. It supports secure lockout of
certain front panel functionality and monitors button presses. The chassis ID LED is
turned on using a front panel button or a command.
Power state retention
Power fault analysis
®
Intel
Light-Guided Diagnostics
Revision 2.4
36
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 49

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Platform Management
Power unit management: Support for power unit sensor. The Integrated Baseboard
Management Controller (Integrated BMC) handles power-good dropout conditions.
DIMM temperature monitoring: New sensors and improved acoustic management using
closed-loop fan control algorithm taking into account DIMM temperature readings.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): The Integrated BMC sends and responds to ARPs
(supported on embedded NICs)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP): The Integrated BMC performs DHCP
(supported on embedded NICs).
Platform environment control interface (PECI) thermal management support.
E-mail alerting
Embedded web server
Integrated KVM
Integrated Remote Media Redirection
Lightweight Directory Authentication Protocol (LDAP) support
4.2 Optional Advanced Management Feature Support
This section explains the advanced management features supported by the Integrated
Baseboard Management Controller (Integrated BMC) firmware.
4.2.1 Enabling Advanced Management Features
The Integrated BMC enables the advanced management features only when it detects the
presence of the Intel
RMM3, the advanced features are dormant. Only the Intel
RMM3 module interface.
4.2.1.1 Intel
The Intel
®
RMM3 provides the Integrated BMC with an additional dedicated network interface.
The dedicated interface consumes its own LAN channel. Additionally, the Intel
additional flash storage for advanced features like Web Services for Management (WS-MAN).
®
Remote Management Module 3 (Intel® RMM3) card. Without the Intel®
®
RMM3
®
Server Board S3420GPLX has a
®
RMM3 provides
4.2.2 Keyboard, Video, Mouse (KVM) Redirection
The Integrated BMC firmware supports keyboard, video, and mouse redirection over LAN. This
feature is available remotely from the embedded web server as a Java applet. This feature is
enabled only when the Intel
Environment (JRE) version 5.0 or later to run the KVM or media redirection applets.
4.2.2.1 Keyboard and Mouse
The keyboard and mouse are emulated by the Integrated BMC as USB human interface devices.
4.2.2.2 Video
Video output from the KVM subsystem is equivalent to the video output on the local console.
Video redirection is available after video is initialized by the system BIOS. The KVM video
resolution and refresh rates will always match the values set in the operating system.
®
RMM3 is present. The client system must have a Java Runtime
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
37
Page 50

Platform Management Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
4.2.2.3 Availability
Up to two remote KVM sessions are supported. The default inactivity timeout is 30 minutes;
however, this can be changed through the embedded web server. Remote KVM activation does
not disable the local system keyboard, video, or mouse. Unless the feature is disabled locally,
remote KVM is not deactivated by local system input.
KVM sessions persist across system reset but not across an AC power loss.
4.2.3 Media Redirection
The embedded web server provides a Java applet to enable remote media redirection. This may
be used in conjunction with the remote KVM feature or as a standalone applet.
The media redirection feature is intended to allow system administrators or users to mount a
remote IDE or USB CD-ROM, floppy drive, or a USB flash disk as a remote device to the server.
Once mounted, the remote device appears just like a local device to the server, allowing system
administrators or users to install software (including operating systems), copy files, update the
BIOS, and so forth, or boot the server from this device.
The following capabilities are supported:
The operation of remotely mounted devices is independent of the local devices on the
server. Both remote and local devices are usable in parallel
Either IDE (CD-ROM, floppy) or USB devices can be mounted as a remote device to the
server.
It is possible to boot all supported operating systems from the remotely mounted device
and to boot from disk IMAGE (*.IMG) and CD-ROM or DVD-ROM ISO files. Refer to the
Tested/supported Operating System List for more information.
It is possible to mount at least two devices concurrently.
The mounted device is visible to (and useable by) the managed system’s operating
system and BIOS in both pre-boot and post-boot states.
The mounted device shows up in the BIOS boot order and it is possible to change the
BIOS boot order to boot from this remote device.
It is possible to install an operating system on a bare metal server (no operating system
present) using the remotely mounted device. This may also require the use of KVM-r to
configure the operating system during install.
If either a virtual IDE or virtual floppy device is remotely attached during system boot, both
virtual IDE and virtual floppy are presented as bootable devices. It is not possible to present
only a single mounted device type to the system BIOS.
4.2.3.1 Availability
The default inactivity timeout is 30 minutes, but may be changed through the embedded web
server.
Media redirection sessions persist across system reset but not across an AC power loss.
4.2.4 Web Services for Management (WS-MAN)
The Integrated BMC firmware supports the Web Services for Management (WS-MAN)
specification, version 1.0.
Revision 2.4
38
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 51

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Platform Management
4.2.5 Local Directory Authentication Protocol (LDAP)
The Integrated BMC firmware supports the Local Directory Authentication Protocol (LDAP)
protocol for user authentication.
Note: IPMI users/passwords and sessions are not supported over LDAP.
4.2.6 Embedded Webserver
The Integrated BMC provides an embedded web server for out-of-band management. User
authentication is handled by IPMI user names and passwords. Base functionality for the
embedded web server includes:
Power Control – Limited control based on IPMI user privilege.
Sensor Reading – Limited access based on IPMI user privilege.
SEL Reading – Limited access based on IPMI user privilege.
KVM/Media Redirection – Limited access based on IPMI user privilege. Only available
when the Intel
IPMI User Management – Limited access based on IPMI user privilege.
The web server is available on all enabled LAN channels.
®
RMM3 is present.
See Appendix B for Integrated BMC core sensors.
4.3 Management Engine (ME)
Intel Management Engine is tied to essential platform functionality. This Management Engine
firmware includes the following applications:
Platform Clocks – Tune PCH clock silicon to the parameters of a specific board,
configure clocks at run time, power management clocks.
Thermal Report – ME FW reports thermal and power information available only on PECI
to host accessible registers/Embedded Controller via SMBus.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
39
Page 52

Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
5. Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board
S3420GPV
5.1 Super I/O
5.1.1 Key Features of Super I/O
The W83627DHG-P is from the Nuvoton's Super I/O product line. This family features the LPC
(Low Pin Count) interface. This interface is more economical than its ISA counterpart. It has
approximately forty pins less, yet it provides as great performance. In addition, the improvement
allows even more efficient operation of software, BIOS, and device drivers.
The W83627DHG-P provides below key features
Meet LPC Spec. 1.01
Integrated hardware monitor functions
Support ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
Support up to 2 16550-compatible UARTs ports
8042-based keyboard controller
Smart Fan control system
Five fan-speed monitoring inputs
Four fan-speed controls
GPIO
Support PECI 1.0 and 1.1a Specifications
5.1.2 Sensor and Hardware Monitor
Hardware Monitor Screen allows the user to configure Fan speed control and show the
monitored voltage to user. To access this screen from the BIOS Main screen, choose Server
Management > Hardware Monitor.
Fan Speed Control management has two options.
Auto – is for SC5299UP chassis support.
300m, 900m, 1500m, 3000m can be selected according to the local altitude where the
system is placed to assure the system is properly cooled. The default altitude setting
is 900m.
Revision 2.4
40
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 53

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV
Main
Advance
d
Security Server Management
Boot
Options
Boot
Manager
Hardware monitor
Real-time Temperature and Voltage Status
Fan Controller
CPU Fan Altitude
Board Fan Altitude
Auto/Manual
300m/900m/1500m/3000m
300m/900m/1500m/3000m
Figure 15. Setup Utility — Hardware Monitor Screen Display
Table 13. Setup Utility — Hardware Monitor Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Voltage and
Temperature Status
CPU Fan Controller Auto
CPU Fan Altitude 300m/900m/1500m/3000m Select CPU FAN default PWM
Board Fan Altitude 300m/900m/1500m/3000m Select Board Fan default PWM
Hysteresis 2 Degree Celsius
Default Fan PWM 40%
display monitored voltage, current
Fan speed PWM and temperature
CPU temperature control policy
Manual
3 Degree Celsius
4 Degree Celsius
60%
80%
100%
Auto -
Fan speed control setting by
default
Manual -
control setting value manually
according to altitude under Auto
mode
according to altitude under Auto
mode
Hysteresis – is used to smoothing
the FAN speed transition when
temperature approaching
temperature target upward or
downward. Select Hysteresis to keep
FAN at the same speed within the
range
Select Default FAN PWM to make
FAN speed keep the invariable
speed when temperature is below
FSC temperature target at low user
conditions. This delivers optimized
acoustic level
user adjust Fan speed
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
41
Page 54

Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Note: The two options of Hysteresis and Default Fan PWM apply to all the four fans
5.1.3 Fan controller (Manual)
Fan controller (Manual) allows the user to configure Fan speed control manually. To access this
screen from the Main screen, choose Server Management > Hardware Monitor > Fan
controller (Manual).
[Manual] is designed for the third party chassis which supports four fan headers. Each of them
has four minimum fan PWM output selections 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% and associated with
different cooling capabilities as well as different acoustic levels. The default PWM is 100% and
can be customized to 40%, 60%, 80% according to the third party chassis cooling capability and
acoustic requirement.
Hysteresis is used to prevent fan oscillation when temperature is crossing the target control
temperature back and forth.
Revision 2.4
42
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 55

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV
Advanc
Secu rit
Server
Main
ed
y
Management
Ha rd ware monitor
Real-ti me Temperature an d V olt age Status
Fan Controller Manual
CPU Fan
Hysteresis
Default Fan PW M
[2 Degree Celsius/3 Degree Cels ius/4 Degree Celsius
[40%/60 %/80%/ 100%]
System Fan
Hysteresis
Defa ult Fa n PWM
[2 Degree Celsius/3 Degree Celsius/4 Degree Celsius
[40%/60 %/80%/ 100%]
Auxiliary Fan 1
Boot
Optio n s
Boot Manager
Hysteresis
Defa ult Fa n PWM
[2 Degree Celsius/3 Degree Celsius/4 Degree Celsius
[40%/60 %/80%/ 100%]
Auxiliary Fan 2
Hysteresis
Defa ult Fa n PWM
[2 Degree Celsius/3 Degre e Cels ius/4 Degree Celsius
[40%/60 %/80%/ 100%]
Figure 16. Setup Utility — Fan controller (Manual) Display
Table 14. Setup Utility — Hardware Monitor Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Voltage and
Temperature Status
CPU Fan Controller Auto
display monitored voltage, current
Fan speed PWM and temperature
CPU temperature control policy
Manual
Auto - Fan speed control setting by
default
Manual - user adjust Fan speed
control setting value manually
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
43
Page 56

Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
CPU Fan Altitude
System Fan Altitude
Hysteresis 2 Degree Celsius
Default Fan PWM 40%
Note: the two options of Hysteresis and Default Fan PWM apply to all the four Fans
300m/900m/1500m/3000m
300m/900m/1500m/3000m
3 Degree Celsius
4 Degree Celsius
60%
80%
100%
Select CPU FAN default PWM
according to altitude under Auto
mode
Select Board Fan default PWM
according to altitude under Auto
mode
Hysteresis – is used to smoothing
the FAN speed transition when
temperature approaching
temperature target upward or
downward. Select Hysteresis to
keep FAN at the same speed
within the range
Select Default FAN PWM to make
FAN speed keep the invariable
speed when temperature is below
FSC temperature target at low
customized conditions. This
delivers optimized acoustic level
The change can
not take effect
immediately by
increasing the
PWM. It requires
a power cycle or
a thermal event
to take the
change in effect.
5.1.4 Voltage and Temperature Status Screen
Display monitored voltage, current Fan speed PWM and temperature
Server Management
Real time Temperature and PWM:
CPU Fan PWM
System Fan PWM
System temperature
Voltage status:
+Vccp
+12V
+3.3V
+5.0V
+1.5V
+1.05V
+3.3V(standby)
Figure 17. Setup Utility — Voltage and Temperature Status Screen
Table 15. Setup Utility — Voltage and Temperature Status Fields
Revision 2.4
44
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 57

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV
Setup Item Comments
CPU Fan PWM Get and display CPU fan PWM periodically
System Fan PWM Get and display system fan PWM periodically
System temperature Get and display current system temperature
monitored by system sensor
+Vccp Get and display +Vccp voltage periodically
+12V Get and display +12 voltage periodically
+3.3V Get and display +3.3 voltage periodically
+5.0V Get and display +5.0V voltage periodically
+1.5V Get and display +1.5V voltage periodically
+1.05V Get and display +1.05 voltage periodically
+3.3V(standby) Get and display +3.3V(standby)voltage periodically
5.2 SMBIOS
5.2.1 Data Storage
On Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and Intel® Server Board S3420GPLC with iBMC, the
SMBIOS type 1, 2, 3 are from FRUSDR by BMC. But on Intel
®
Server Board S3420GPV,
SMBIOS type 1, 2, 3 are stored in BIOS flash during manufactory build, so it’s also non-volatile
data storage.
BIOS retrieve the SMBIOS data from flash during POST, and it builds the SMBIOS type 1, 2, 3
into SMBIOS table and then transfers the control to operating system. Operating system and
system management software can use the SMBIOS table for system management purpose.
5.3 Event log and Viewer
5.3.1 Event Log Viewer in Setup
On Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX and Intel® Server Board S3420GPLC, there is a dedicated
utility to view the event log. There is no IPMI support - the way to view the event log in BIOS
Setup, on Intel
There is one page in BIOS setup for event log viewer. It is located in Error Manager Page.
®
Server Board S3420GPV.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
45
Page 58
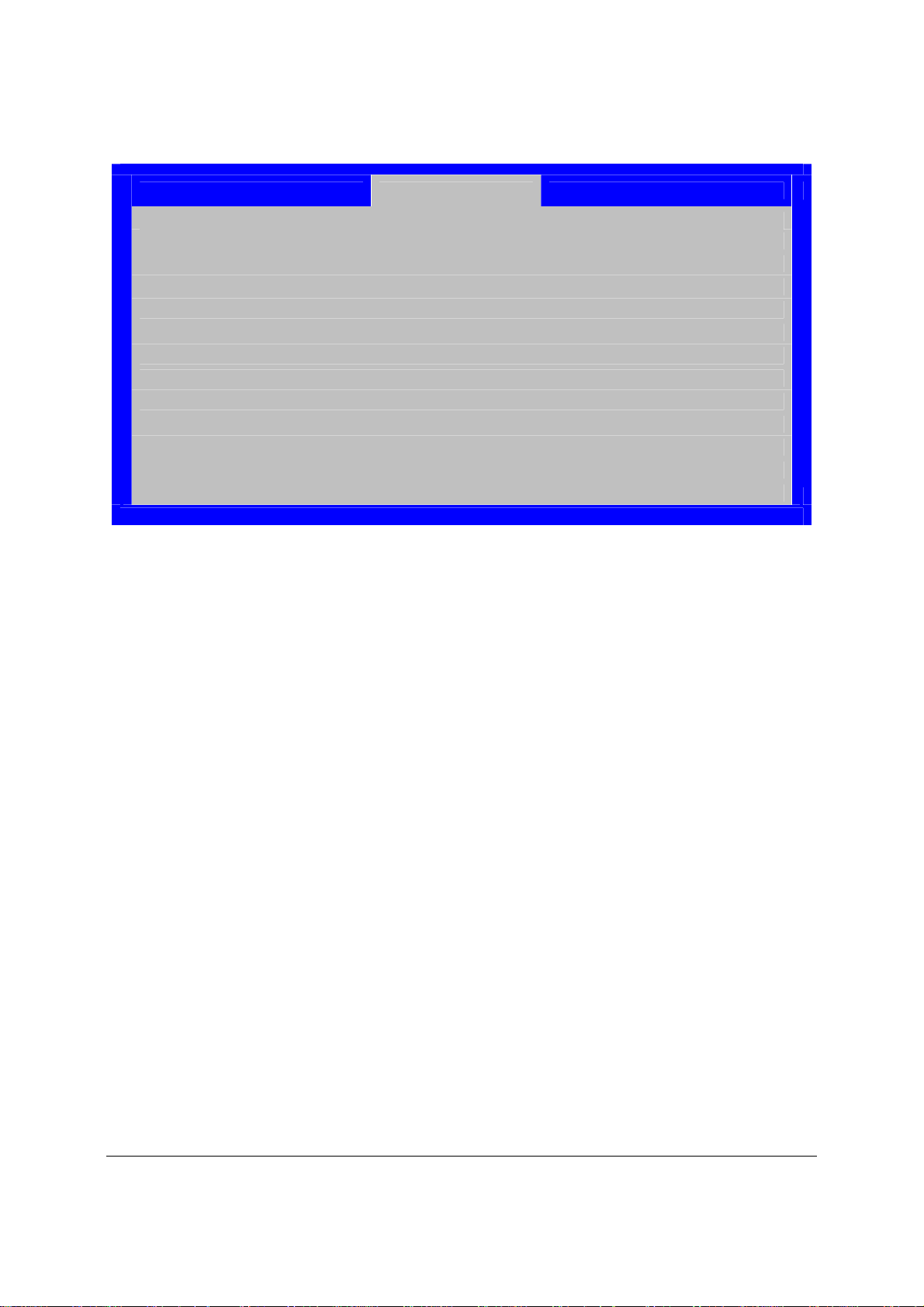
Server Management Capability for Intel® Server Board S3420GPV Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Error Manager
No. Event Info Time
005 M-BIT MEM ECC Error CPU0 Ch 0 Dimm0 10/15/09 15:12:23
004 S-BIT MEM ECC Error CPU0 Ch 0 Dimm0 10/15/09 15:11:25
003 PCIE UNCOR ERR Bus0 Dev 1C Fun0 10/15/09 15:08:36
002 MEM Parity Error CPU0 Ch 0 Dimm0 10/15/09 15:07:11
001 Thermal Trip Occurred. 10/15/09 15:05:05
Figure 18. Event Log Viewer
The Event log viewer is at another page than the BIOS error manager. The event log viewer can
display many log in one page. Each event log is displayed in one line. The latest one is on the
top. When there are more event logs on one page, Page Up and Page Down keys can be used.
There is a scroll bar to allow end-users to view the logs from top to bottom.
Revision 2.4
46
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 59

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
6. BIOS User Interface
6.1 Logo/Diagnostic Screen
The logo/Diagnostic Screen displays in one of two forms:
If Quiet Boot is enabled in the BIOS setup, a logo splash screen displays. By default,
Quiet Boot is enabled in the BIOS setup. If the logo displays during POST, press <Esc>
to hide the logo and display the diagnostic screen.
If a logo is not present in the flash ROM or if Quiet Boot is disabled in the system
configuration, the summary and diagnostic screen displays.
The diagnostic screen displays the following information:
BIOS ID
Platform name
Total memory detected (Total size of all installed DDR3 DIMMs)
Processor information (Intel branded string, speed, and number of physical processor
identified)
Keyboards detected (if plugged in)
Mouse devices detected (if plugged in)
6.2 BIOS Boot Popup Menu
The BIOS Boot Specification (BBS) provides for a Boot Popup Menu invoked by pressing the
<F6> key during POST. The BBS popup menu displays all available boot devices. The list order
in the popup menu is not the same as the boot order in the BIOS setup; it simply lists the
bootable devices from which the system can be booted.
When a User Password or Administrator Password is active in Setup, the password is to access
the Boot Popup Menu.
6.3 BIOS Setup utility
The BIOS setup utility is a text-based utility that allows the user to configure the system and
view current settings and environment information for the platform devices. The Setup utility
controls the platform’s built-in devices, boot manager, and error manager.
The BIOS setup interface consists of a number of pages or screens. Each page contains
information or links to other pages. The advanced tab in Setup displays a list of general
categories as links. These links lead to pages containing a specific category’s configuration.
The following sections describe the look and behavior for platform setup.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
47
Page 60

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
6.3.1 Operation
The BIOS Setup has the following features:
Localization - The BIOS Setup uses the Unicode standard and is capable of displaying
setup forms in all languages currently included in the Unicode standard. The Intel
®
server board BIOS is only available in English.
Console Redirection - The BIOS Setup is functional through console redirection over
various terminal emulation standards. This may limit some functionality for compatibility
(for example, color usage or some keys or key sequences or support of pointing
devices).
6.3.1.1 Setup Page Layout
The setup page layout is sectioned into functional areas. Each occupies a specific area of the
screen and has dedicated functionality. The following table lists and describes each functional
area.
Table 16. BIOS Setup Page Layout
Functional Area Description
Title Bar The title bar is located at the top of the screen and displays the title of the form
(page) the user is currently viewing. It may also display navigational information.
Setup Item List The Setup Item List is a set of controllable and informational items. Each item in the
list occupies the left column of the screen.
A Setup Item may also open a new window with more options for that functionality
on the board.
Item Specific Help Area The Item Specific Help area is located on the right side of the screen and contains
help text for the highlighted Setup Item. Help information may include the meaning
and usage of the item, allowable values, effects of the options, and so forth.
Keyboard Command Bar The Keyboard Command Bar is located at the bottom right of the screen and
continuously displays help for keyboard special keys and navigation keys.
6.3.1.2 Entering BIOS Setup
To enter the BIOS Setup, press the F2 function key during boot time when the OEM or Intel logo
displays. The following message displays on the diagnostics screen and under the Quiet Boot
logo screen:
Press <F2> to enter setup
When the Setup is entered, the Main screen displays. However, serious errors cause the
system to display the Error Manager screen instead of the Main screen.
6.3.1.3 Keyboard Commands
The bottom right portion of the Setup screen provides a list of commands used to navigate
through the Setup utility. These commands display at all times.
Each Setup menu page contains a number of features. Each feature is associated with a value
field except those used for informative purposes. Each value field contains configurable
parameters. Depending on the security option chosen and, in effect, by the password, a menu
Revision 2.4
48
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 61

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
feature’s value may or may not be changed. If a value cannot be changed, its field is made
inaccessible and appears grayed out.
Table 17. BIOS Setup: Keyboard Command Bar
Key Option Description
<Enter> Execute
Command
<Esc> Exit The <Esc> key provides a mechanism for backing out of any field. When the <Esc>
<Tab> Select Field The <Tab> key is used to move between fields. For example, <Tab> can be used
- Change Value The minus key on the keypad is used to change the value of the current item to the
+ Change Value The plus key on the keypad is used to change the value of the current menu item
<F9> Setup Defaults Pressing <F9> causes the following to display:
Select Item The up arrow is used to select the previous value in a pick list, or the previous
Select Item The down arrow is used to select the next value in a menu item’s option list, or a
Select Menu The left and right arrow keys are used to move between the major menu pages.
The <Enter> key is used to activate sub-menus when the selected feature is a submenu, or to display a pick list if a selected option has a value field, or to select a
sub-field for multi-valued features like time and date. If a pick list is displayed, the
<Enter> key selects the currently highlighted item, undoes the pick list, and returns
the focus to the parent menu.
key is pressed while editing any field or selecting features of a menu, the parent
menu is re-entered.
When the <Esc> key is pressed in any sub-menu, the parent menu is re-entered.
When the <Esc> key is pressed in any major menu, the exit confirmation window is
displayed and the user is asked whether changes can be discarded. If “No” is
selected and the <Enter> key is pressed, or if the <Esc> key is pressed, the user is
returned to where they were before <Esc> was pressed, without affecting any
existing settings. If “Yes” is selected and the <Enter> key is pressed, the setup is
exited and the BIOS returns to the main System Options Menu screen.
option in a menu item's option list. The selected item must then be activated by
pressing the <Enter> key.
value field’s pick list. The selected item must then be activated by pressing the
<Enter> key.
The keys have no affect if a sub-menu or pick list is displayed.
to move from hours to minutes in the time item in the main menu.
previous value. This key scrolls through the values in the associated pick list
without displaying the full list.
to the next value. This key scrolls through the values in the associated pick list
without displaying the full list. On 106-key Japanese keyboards, the plus key has a
different scan code than the plus key on the other keyboards, but will have the
same effect.
Load Optimized Defaults?
Yes No
If “Yes” is highlighted and <Enter> is pressed, all Setup fields are set to their
default values. If “No” is highlighted and <Enter> is pressed, or if the <Esc> key is
pressed, the user is returned to where they were before <F9> was pressed without
affecting any existing field values.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
49
Page 62
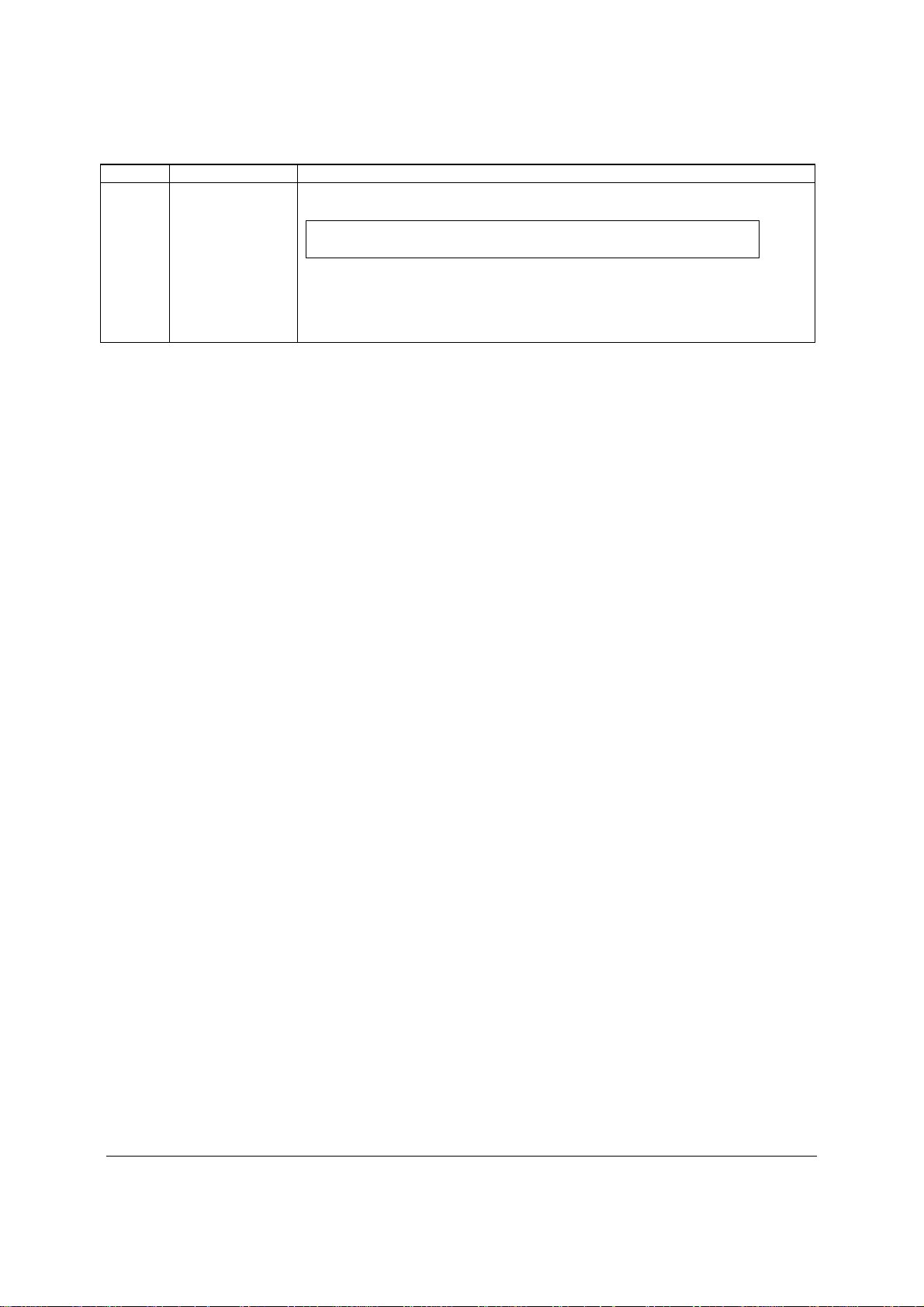
BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Key Option Description
<F10> Save and Exit Pressing <F10> causes the following message to display:
Save configuration and reset?
Yes No
If “Yes” is highlighted and <Enter> is pressed, all changes are saved and the Setup
is exited. If “No” is highlighted and <Enter> is pressed, or the <Esc> key is
pressed, the user is returned to where they were before <F10> was pressed
without affecting any existing values.
6.3.1.4 Menu Selection Bar
The Menu Selection Bar is located at the top of the BIOS Setup Utility screen. It displays the
major menu selections available to the user. By using the left and right arrow keys, the user can
select the menus listed here. Some menus are hidden and become available by scrolling off the
left or right of the current selections.
6.3.2 Server Platform Setup Utility Screens
The following sections describe the screens available for the configuration of a server platform.
In these sections, tables are used to describe the contents of each screen. These tables follow
the following guidelines:
The Setup Item, Options, and Help Text columns in the tables document the text and
values displayed on the BIOS Setup screens.
In the Options column, the default values display in bold. These values are not displayed
in bold on the BIOS Setup screen; the bold text in this document serves as a reference
point.
The Comments column provides additional information where it may be helpful. This
information does not display on the BIOS Setup screens.
Information enclosed in angular brackets (< >) in the screen shots identifies text that can
vary, depending on the option(s) installed. For example, <Current Date> is replaced by
the actual current date.
Information enclosed in square brackets ([ ]) in the tables identifies areas where the user
must type in text instead of selecting from a provided option.
Whenever information is changed (except Date and Time), the system requires a save
and reboot to take place. Pressing <ESC> discards the changes and boots the system
according to the boot order set from the last boot.
6.3.2.1 Main Screen
The Main screen is the first screen displayed when the BIOS Setup is entered, unless an error
occurred. If an error occurred, the Error Manager screen displays instead.
Revision 2.4
50
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 63
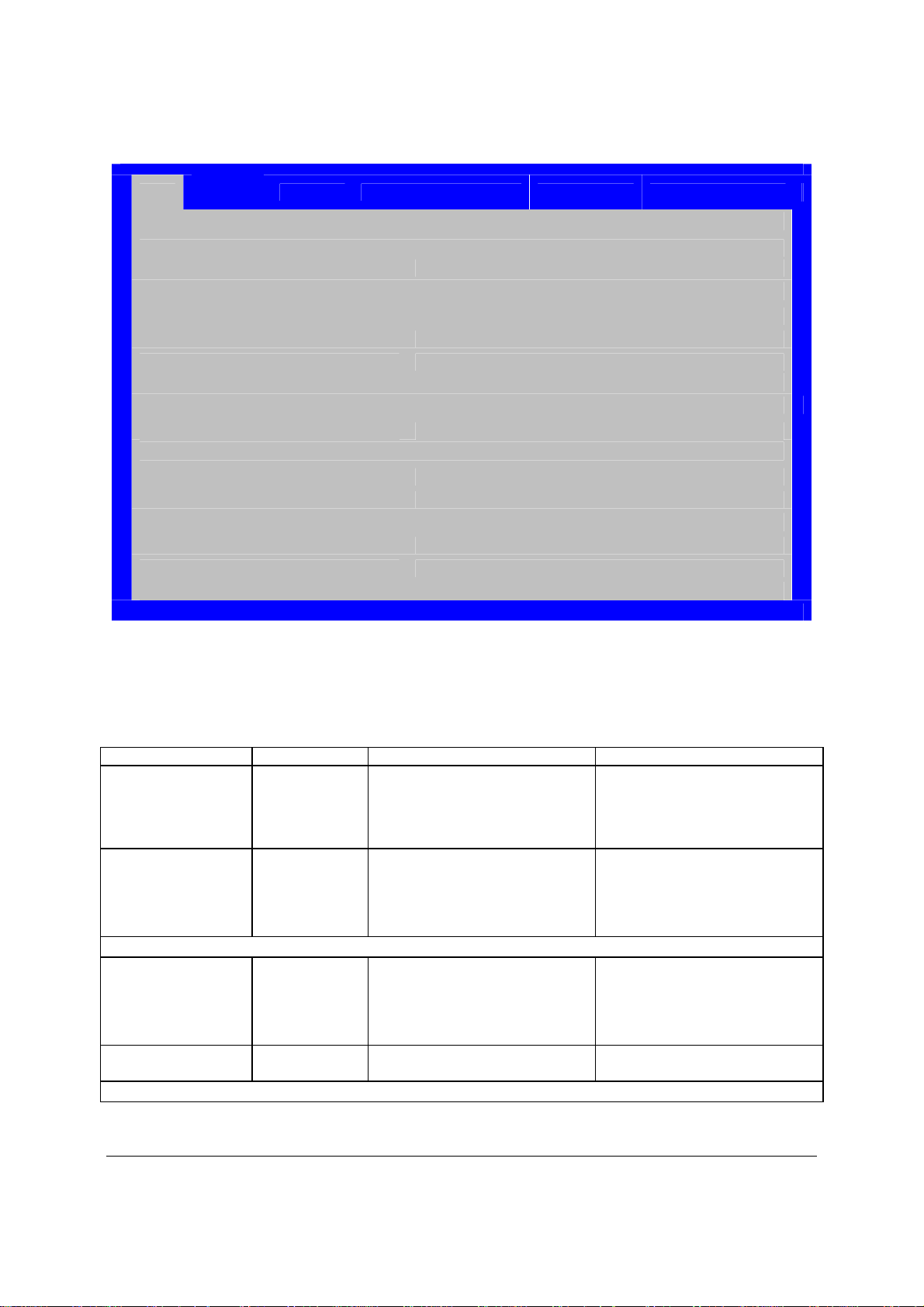
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Advance
d
Security Server Management Boot Options Boot Manager
Main
Logged in as <Administrator or User>
Platform ID
<Platform Identification String>
System BIOS
Version SXXXX.86B.xx.yy.zzzz
Build Date <MM/DD/YYYY>
Memory
Total Memory <How much memory is installed>
Quiet Boot Enabled/Disabled
POST Error Pause Enabled/Disabled
System Date <Current Date>
System Time <Current Time>
Figure 19. Setup Utility – Main Screen Display
Table 18. Setup Utility – Main Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Logged in as
Platform ID
System BIOS
Version
Build Date
Memory
Comments
Information only. Displays
password level that setup is
running in: Administrator or User.
With no passwords set,
Administrator is the default mode.
Information only. Displays the
Platform ID.
LX SKU: S3420GPX
LC SKU: S3420GPC
V SKU: S3420GPV
Information only. Displays the
current BIOS version.
xx = major version
yy = minor version
zzzz = build number
Information only. Displays the
current BIOS build date.
Revision 2.4
51
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 64

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Setup Item Options Help Text
Size
Quiet Boot Enabled
Disabled
POST Error Pause Enabled
Disabled
System Date [Day of week
MM/DD/YYYY]
System Time [HH:MM:SS] System Time has configurable
[Enabled] – Display the logo screen
during POST.
[Disabled] – Display the diagnostic
screen during POST.
[Enabled] – Go to the Error
Manager for critical POST errors.
[Disabled] – Attempt to boot and do
not go to the Error Manager for
critical POST errors.
System Date has configurable
fields for Month, Day, and Year.
Use [Enter] or [Tab] key to select
the next field.
Use [+] or [-] key to modify the
selected field.
fields for Hours, Minutes, and
Seconds.
Hours are in 24-hour format.
Use [Enter] or [Tab] key to select
the next field.
Use [+] or [-] key to modify the
selected field.
Comments
Information only. Displays the
total physical memory installed in
the system, in MB or GB. The term
physical memory indicates the total
memory discovered in the form of
installed DDR3 DIMMs.
If enabled, the POST Error Pause
option takes the system to the error
manager to review the errors when
major errors occur. Minor and fatal
error displays are not affected by
this setting.
6.3.2.2 Advanced Screen
The Advanced screen provides an access point to configure several options. On this screen,
the user selects the option they want to configure. Configurations are performed on the selected
screen, and not directly on the Advanced screen.
To access this screen from the Main screen, press the right arrow until the Advanced screen is
chosen.
Revision 2.4
52
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 65

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Advance
d
Security Server Management Boot Options Boot Manager
Main
► Processor Configuration
► Memory Configuration
► Mass Storage Controller Configuration
► Serial Port Configuration
► USB Configuration
► PCI Configuration
► System Acoustic and Performance Configuration
Figure 20. Setup Utility – Advanced Screen Display
Table 19. Setup Utility – Advanced Screen Display Fields
Setup Item Help Text
Processor Configuration View/Configure processor information and
Memory Configuration View/Configure memory information and
Mass Storage Controller Configuration View/Configure mass storage controller
Serial Port Configuration View/Configure serial port information and
USB Configuration
PCI Configuration
System Acoustic and Performance
Configuration
settings.
settings.
information and settings.
settings.
View/Configure USB information and
settings.
View/Configure PCI information and
settings.
View/Configure system acoustic and
performance information and settings.
6.3.2.2.1 Processor Screen
The Processor screen allows the user to view the processor core frequency, system bus
frequency, and to enable or disable several processor options. This screen also allows the user
to view information about a specific processor.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Advanced > Processor.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
53
Page 66

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Advanced
Processor Configuration
Processor Socket CPU 1
Processor ID <CPUID>
Processor Frequency <Proc Freq>
Microcode Revision <Rev data>
L1 Cache RAM Size of Cache
L2 Cache RAM
L3 Cache RAM
Size of Cache
Size of Cache
Processor 1 Version <ID string from Processor 1>
Current QPI Link Speed <Slow/Fast >
QPI Link Frequency <Unknown GT/s/4.8 GT/s/5.866 GT/s/6.4 GT/s>
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology Enabled/Disabled
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Tech Enabled/Disabled
Processor C3 Report Enabled/ Disabled
Processor C6 Report Enabled/ Disabled
Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology Enabled/Disabled
Core Multi-Processing All/1/2
Execute Disable Bit Enabled/Disabled
Intel® Virtualization Technology Enabled/ Disabled
Intel® VT for Directed I/O Enabled/ Disabled
Pass-through DMA Support Enabled/Disabled
Hardware Prefetcher Enabled/Disabled
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch Enabled/Disabled
Figure 21. Setup Utility – Processor Configuration Screen Display
Table 20. Setup Utility – Processor Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Processor ID
Processor Frequency
Core Frequency
Microcode Revision
L1 Cache RAM
Revision 2.4
54
Information only. Processor
CPUID.
Information only. Current
frequency of the processor.
Information only. Frequency
at which the processor are
currently running.
Information only. Revision of
the loaded microcode.
Information only. Size of the
Processor L1 Cache.
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 67

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
®
®
Setup Item Options Help Text
L2 Cache RAM
L3 Cache RAM
Processor Version
Current QPI Link Speed
QPI Link Frequency
Intel® Turbo Boost
Technology
Enabled
Disabled
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology allows the
processor to automatically increase its
frequency if it is running below power,
temperature, and current specifications.
Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
®
Technology
Enabled
Disabled
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
allows the system to dynamically adjust
processor voltage and core frequency, which
can result in decreased average power
consumption and decreased average heat
production.
Contact your OS vendor regarding OS
support of this feature.
Intel® Hyper-Threading
Technology
Enabled
Disabled
Intel® HT Technology allows multithreaded
software applications to execute threads in
parallel within the processor.
Contact your OS vendor regarding OS
support of this feature.
Core Multi-Processing All
1
Enable 1, 2 or All cores of installed
processor packages.
2
Execute Disable Bit Enabled
Disabled
Execute Disable Bit can help prevent certain
classes of malicious buffer overflow attacks.
Contact your OS vendor regarding OS
support of this feature.
Intel® Virtualization
Technology
Enabled
Disabled
Intel® Virtualization Technology allows a
platform to run multiple operating systems
and applications in independent partitions.
Note: A change to this option requires the
system to be powered off and then back on
before the setting takes effect.
Intel® Virtualization
Technology for Directed
Enabled
Disabled
I/O
Pass-through DMA
Support
Enabled
Disabled
Hardware Prefetcher Enabled
Disabled
Enable/Disable Intel
Technology for Directed I/O.
Report the I/O device assignment to VMM
through DMAR ACPI Tables
Enable/Disable Intel® VT-d Pass-through
DMA support.
Hardware Prefetcher is a speculative
prefetch unit within the processor(s).
Note: Modifying this setting may affect
system performance.
Technology
Virtualization
Comments
Information only. Size of the
Processor L2 Cache
Information only. Size of the
Processor L3 Cache.
Information only. ID string
from the Processor.
Information only. Current
speed that the QPI Link is
using.
Information only. Current
frequency that the QPI Link is
using.
This option is only visible if all
processor in the system
support Intel
®
Turbo Boost
Technology.
Only visible when Intel®
Virtualization Technology for
Directed I/O is enabled.
Revision 2.4
55
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 68

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Setup Item Options Help Text
Adjacent Cache Line
Prefetch
Enabled
Disabled
[Enabled] - Cache lines are fetched in pairs
(even line + odd line).
[Disabled] - Only the current cache line
required is fetched.
Note: Modifying this setting may affect
system performance.
Comments
6.3.2.2.2 Memory Screen
The Memory screen allows the user to view details about the system memory DDR3 DIMMs
installed. This screen also allows the user to open the Configure Memory RAS and Performance
screen.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Advanced > Memory.
Advanced
Memory Configuration
Total Memory <Total Physical Memory Installed in System>
Effective Memory <Total Effective Memory>
Current Configuration <Independent >
Current Memory Speed <Speed that installed memory is running at.>
►
DIMM Information
DIMM_A1 Installed/Not Installed/Failed/Disabled/Spare Unit
DIMM_A2 Installed/Not Installed/Failed/Disabled/Spare Unit
DIMM_A3 Installed/Not Installed/Failed/Disabled/Spare Unit
DIMM_B1 Installed/Not Installed/Failed/Disabled/Spare Unit
DIMM_B2 Installed/Not Installed/Failed/Disabled/Spare Unit
DIMM_B3 Installed/Not Installed/Failed/Disabled/Spare Unit
Figure 22. Setup Utility – Memory Configuration Screen Display
Table 21. Setup Utility – Memory Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Comments
Total Memory
Revision 2.4
56
Information only. The amount of memory available in the system
in the form of installed DDR3 DIMMs in units of MB or GB.
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 69

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Setup Item
Effective Memory
Current Configuration
Current Memory
Speed
DIMM_ XY Displays the state of each DIMM socket present on the board.
Information only. The amount of memory available to the
operating system in MB or GB.
The Effective Memory is the difference between the Total Physical
Memory and the sum of all memory reserved for internal usage,
RAS redundancy and SMRAM. This difference includes the sum of
all DDR3 DIMMs that failed Memory BIST during POST, or were
disabled by the BIOS during memory discovery phase to optimize
memory configuration.
Information only. Displays one of the following:
Independent Mode: System memory is configured for optimal
performance and efficiency and no RAS is enabled.
Sparing Mode: System memory is configured for RAS with
optimal effective memory.
Information only. Displays the speed the memory is running at.
Each DIMM socket field reflects one of the following possible
states:
Installed: There is a DDR3 DIMM installed in this slot.
Not Installed: There is no DDR3 DIMM installed in this slot.
Disabled: The DDR3 DIMM installed in this slot was disabled by
the BIOS to optimize memory configuration.
Failed: The DDR3 DIMM installed in this slot is
faulty/malfunctioning.
Spare Unit: The DDR3 DIMM is functioning as a spare unit for
memory RAS purposes.
Note: X denotes the Channel Identifier and Y denote the DIMM
Identifier within the Channel.
Comments
6.3.2.2.3 Mass Storage Controller Screen
The Mass Storage screen allows the user to configure the SATA/SAS controller when it is
present on the baseboard, midplane, or backplane of an Intel system.
To access this screen from the Main menu, select Advanced > Mass Storage.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
57
Page 70

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
®
Advanced
Mass Storage Controller Configuration
Intel® Entry SAS RAID Module Enabled/Disabled
Configure Intel® Entry SAS RAID Module LSI ® Integrated RAID/Intel® ESRTII
Onboard SATA Controller Enabled/Disabled
Configure SATA Mode ENHANCED/COMPATIBILITY/AHCI/SW RAID
► SATA Port 0 Not Installed/<Drive Info.>
► SATA Port 1 Not Installed/<Drive Info.>
► SATA Port 2 Not Installed/<Drive Info.>
► SATA Port 3 Not Installed/<Drive Info.>
► SATA Port 4 Not Installed/<Drive Info.>
► SATA Port 5 Not Installed/<Drive Info.>
Figure 23. Setup Utility – Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen Display
Table 22. Setup Utility – Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Unavailable if the SAS Module
Intel® Entry SAS RAID
Module
Configure Intel® Entry
SAS RAID Module
Onboard SATA
Controller
SATA Mode ENHANCED
Enabled
Disabled
LSI® Integrated
RAID
®
ESRTII
Intel
Enabled
Disabled
COMPATIBILITY
AHCI
Intel ESRT2
Matrix RAID
Enabled or Disable the Intel® SAS
Entry RAID Module
Integrated RAID - Supports
LSI
RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 1e, as
well as IT (JBOD) mode;
®
ESRTII - Intel® Embedded
Intel
Server RAID Technology II, which
supports RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID
10.
Onboard Serial ATA (SATA)
controller.
[ENHANCED] - Supports up to 6
SATA ports with IDE Native
Mode.
[COMPATIBILITY] - Supports up
to 4 SATA ports[0/1/2/3] with IDE
Legacy mode and 2 SATA
ports[4/5] with IDE Native Mode.
[AHCI] - Supports all SATA ports
using the Advanced Host
Controller Interface.
[Intel ESRT2] - Supports RAID
0/1/10 with Intel
Software RAIDII Technology.
[Matrix RAID] – Supports RAID
levels 0/1/10 and 5 with Intel
Matrix Storage RAID Technology.
®
Embedded
®
(AXX4SASMOD) is not present.
Note: This option is not
available on some models.
Unavailable if the SAS Module
(AXX4SASMOD) is disabled or
not present
Note: This option is not
available on some models.
Disappears when the Onboard
SATA Controller is disabled.
Revision 2.4
58
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 71

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Setup Item Options Help Text
SATA Port 0 < Not
Installed/Drive
information>
SATA Port 1 < Not
Installed/Drive
information>
SATA Port 2 < Not
Installed/Drive
information>
SATA Port 3 < Not
Installed/Drive
information>
SATA Port 4 < Not
Installed/Drive
information>
SATA Port 5 < Not
Installed/Drive
information>
Information only. This field is
unavailable when RAID Mode is
enabled.
Information only. This field is
unavailable when RAID Mode is
enabled.
Information only. This field is
unavailable when RAID Mode is
enabled.
Information only. This field is
unavailable when RAID Mode is
enabled.
Information only. This field is
unavailable when RAID Mode is
enabled.
Information only. This field is
unavailable when RAID Mode is
enabled.
Comments
6.3.2.2.4 Serial Ports Screen
The Serial Ports screen allows the user to configure the Serial A [COM 1] and Serial B [COM2]
ports.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Advanced > Serial Port.
Advanced
Serial Port Configuration
Serial A Enable Enabled/Disabled
Address 3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h
IRQ 3 or 4
Serial B Enable Enabled/Disabled
Address 3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h
IRQ 3 or 4
Figure 24. Setup Utility – Serial Port Configuration Screen Display
Table 23. Setup Utility – Serial Ports Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Serial A
Enable
Address 3F8h
Enabled
Disabled
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
Enable or Disable Serial port A.
Select Serial port A base I/O address.
Revision 2.4
59
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 72
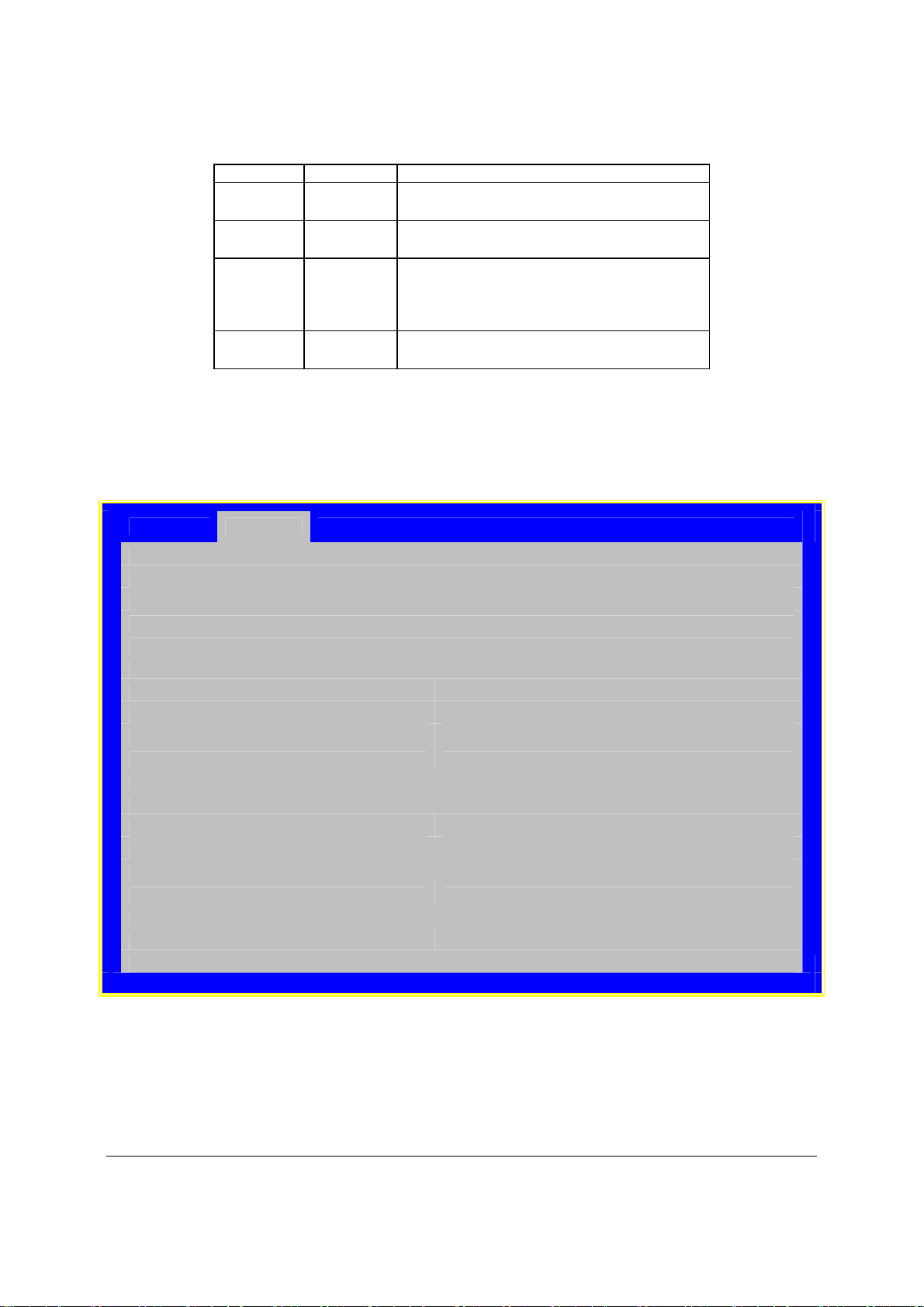
BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Setup Item Options Help Text
IRQ 3 4 Select Serial port A interrupt request (IRQ) line.
Serial B
Enable
Address 3F8h
IRQ 3 4 Select Serial port B interrupt request (IRQ).
Enabled
Disabled
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
Enable or Disable Serial port B.
Select Serial port B base I/O address.
6.3.2.2.5 USB Configuration Screen
The USB Configuration screen allows the user to configure the USB controller options.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Advanced > USB Configuration.
Advanced
USB Configuration
Detected USB Devices
<Total USB Devices in System>
USB Controller Enabled/Disabled
Legacy USB Support Enabled/Disabled/Auto
Port 60/64 Emulation Enabled/Disabled
Make USB Devices Non-Bootable Enabled/Disabled
USB Mass Storage Device Configuration
Device Reset timeout 10 seconds/20 seconds/30 seconds/40 seconds
Mass Storage Devices:
<Mass storage devices one line/device> Auto/Floppy/Forced FDD/Hard Disk/CD-ROM
USB 2.0 controller Enabled/Disabled
Figure 25. Setup Utility – USB Controller Configuration Screen Display
Revision 2.4
60
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 73
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Table 24. Setup Utility – USB Controller Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Detected USB
Devices
USB Controller Enabled
Legacy USB
Support
Port 60/64
Emulation
Make USB
Devices NonBootable
Device Reset
timeout
One line for each
mass storage
device in system
USB 2.0
controller
Information only. Shows the number
of USB devices in the system.
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Auto
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
10 sec
20 sec
30 sec
40 sec
Auto
Floppy
Forced FDD
Hard Disk
CD-ROM
Enabled
Disabled
[Enabled] - All onboard USB controllers are turned on and
accessible by the OS.
[Disabled] - All onboard USB controllers are turned off and
inaccessible by the OS.
USB device boot support and PS/2 emulation for USB
keyboard and USB mouse devices.
[Auto] - Legacy USB support is enabled if a USB device is
attached.
I/O port 60h/64h emulation support.
Note: This may be needed for legacy USB keyboard
support when using an OS that is USB unaware.
Exclude USB in Boot Table.
[Enabled] - This removes all USB Mass Storage devices
as Boot options.
[Disabled] - This allows all USB Mass Storage devices as
Boot options.
USB Mass Storage device Start Unit command timeout.
Setting to a larger value provides more time for a mass
storage device to be ready, if needed.
[Auto] - USB devices less than 530 MB are emulated as
floppies.
[Forced FDD] - HDD formatted drive are emulated as a
FDD (e.g., ZIP drive).
Onboard USB ports are enabled to support USB 2.0
mode.
Contact your OS vendor regarding OS support of this
feature.
Grayed out if the USB Controller is
disabled.
Grayed out if the USB Controller is
disabled.
Grayed out if the USB Controller is
disabled.
Grayed out if the USB Controller is
disabled.
Hidden if no USB Mass storage
devices are installed.
Grayed out if the USB Controller is
disabled.
This setup screen can show a
maximum of eight devices on this
screen. If more than eight devices
are installed in the system, the USB
Devices Enabled shows the correct
count, but only displays the first
eight devices here.
Grayed out if the USB Controller is
disabled.
6.3.2.2.6 PCI Screen
The PCI Screen allows the user to configure the PCI add-in cards, onboard NIC controllers, and
video options.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Advanced > PCI.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
61
Page 74

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Maximize Memory below 4GB Enabled/Disabled
Memory Mapped I/O above 4GB Enabled/Disabled
Onboard Video Enabled/Disabled
Dual Monitor Video Enabled/Disabled
Onboard NIC1 ROM Enabled/Disabled
Onboard NIC2 ROM Enabled/Disabled
Onboard NIC iSCSI ROM Enabled/Disabled
NIC 1 MAC Address <MAC #>
NIC 2 MAC Address <MAC #>
Figure 26. Setup Utility – PCI Configuration Screen Display
Table 25. Setup Utility – PCI Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Maximize Memory
below 4GB
Memory Mapped I/O
above 4GB
Onboard Video Enabled
Dual Monitor Video Enabled
Onboard NIC1 ROM Enabled
Onboard NIC2 ROM Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
If enabled. the BIOS maximizes usage of memory
below 4 GB for OS without PAE by limiting PCIE
Extended Configuration Space to 64 buses.
Enable or disable memory mapped I/O of 64-bit
PCI devices to 4 GB or greater address space.
Onboard video controller.
Warning: System video is completely disabled if
this option is disabled and an add-in video
adapter is not installed.
If enabled. both the onboard video controller and
an add-in video adapter are enabled for system
video. The onboard video controller becomes the
primary video device.
If enabled. loads the embedded option ROM for
the onboard network controllers.
Warning: If [Disabled] is selected, NIC1 cannot
be used to boot or wake the system.
If enabled. loads the embedded option ROM for
the onboard network controllers.
Warning: If [Disabled] is selected, NIC2 cannot
be used to boot or wake the system.
When disabled, the system
requires an add-in video
card for the video to be
seen.
Note: This option is not
available on some models.
Note: This option does not
appear on some models.
Revision 2.4
62
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 75

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Setup Item Options Help Text
Onboard NIC iSCSI
ROM
NIC 1 MAC Address No entry
NIC 2 MAC Address No entry
Enabled
Disabled
allowed
allowed
If enabled. loads the embedded option ROM for
the onboard network controllers.
Warning: If [Disabled] is selected, NIC1 and NIC2
cannot be used to boot or wake the system.
This option is grayed out
and not accessible if either
the NIC1 or NIC2 ROMs
are enabled.
Note: This option is not
available on some models.
Information only. 12 hex
digits of the MAC address.
Information only. 12 hex
digits of the MAC address.
Comments
6.3.2.2.7 System Acoustic and Performance Configuration
The System Acoustic and Performance Configuration screen allows the user to configure the
thermal characteristics of the system.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Advanced > System Acoustic and
Performance Configuration.
Advanced
System Acoustic and Performance Configuration
Set Throttling Mode Auto/CLTT/OLTT
Altitude 300m or less/301m-900m/901m – 1500m/Higher than 1500m
Set Fan Profile Performance, Acoustic
Figure 27. Setup Utility – System Acoustic and Performance Configuration Screen Display
Table 26. Setup Utility – System Acoustic and Performance Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Set Throttling
Mode
Auto
CLTT
OLTT
[Auto] – Auto Throttling mode.
[CLTT] – Closed Loop Thermal Throttling Mode.
[OLTT] – Open Loop Thermal Throttling Mode.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
Comments
Note: The OLTT
option is shown for
informational
purposes only. If
the user selects
OLTT, the BIOS
overrides that
selection if the
system can support
CLTT. OLTT is
configured only when
UDIMMs without
Thermal Sensors are
installed.
63
Page 76

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Setup Item Options Help Text
Altitude 300m or less
301m-900m
901m-1500m
Higher than 1500m
Set Fan Profile Performance
Acoustics
[300m or less] (980ft or less)
Optimal performance setting near sea level.
[301m - 900m] (980ft - 2950ft)
Optimal performance setting at moderate elevation.
[901m – 1500m] (2950ft – 4920ft)
Optimal performance setting at high elevation.
[Higher than 1500m] (4920ft or greater)
Optimal performance setting at the highest elevations.
[Performance] - Fan control provides primary system
cooling before attempting to throttle memory.
[Acoustic] - The system will favor using throttling of
memory over boosting fans to cool the system if
thermal thresholds are met.
Comments
Note: This option is
not available on
some models.
This option is grayed
out if CLTT is
enabled.
Note: This option is
not available on
some models.
6.3.2.3 Security Screen
The Security screen allows the user to enable and set the user and administrative password
and to lock out the front panel buttons so they cannot be used.
®
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) security is NOT supported on the Intel
Server S3420GP board.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Security.
Main Advanced Security Server Management Boot Options Boot Manager
Administrator Password Status
User Password Status
<Installed/Not Installed>
<Installed/Not Installed>
Set Administrator Password [1234aBcD]
Set User Password [1234aBcD]
Front Panel Lockout Enabled/Disabled
Figure 28. Setup Utility – Security Configuration Screen Display
Table 27. Setup Utility – Security Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Administrator Password
Status
<Installed
Not Installed>
Information only. Indicates
the status of the
administrator password.
Comments
Revision 2.4
64
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 77

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Setup Item Options Help Text
User Password Status <Installed
Not Installed>
Set Administrator
Password
Set User Password [123aBcD] User password is used to control entry
Front Panel Lockout Enabled
[123aBcD] Administrator password is used to
Disabled
control change access in BIOS Setup
Utility.
Only alphanumeric characters can be
used. Maximum length is 7 characters. It
is case sensitive.
Note: Administrator password must be
set in order to use the user account.
access to BIOS Setup Utility.
Only alphanumeric characters can be
used. Maximum length is 7 characters. It
is case sensitive.
Note: Removing the administrator
password also automatically removes
the user password.
If enabled, locks the power button and
reset button on the system's front panel.
If [Enabled] is selected, power and reset
must be controlled via a system
management interface.
Comments
Information only. Indicates
the status of the user
password.
This option is only to control
access to the setup.
Administrator has full
access to all the setup
items. Clearing the
Administrator password
also clears the user
password.
Available only if the
administrator password is
installed. This option only
protects the setup.
User password only has
limited access to the setup
items.
6.3.2.4 Server Management Screen
The Server Management screen allows the user to configure several server management
features. This screen also provides an access point to the screens for configuring console
redirection and displaying system information.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Server Management.
Revision 2.4
65
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 78

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Main
Advance
d
Security Server Management Boot Options Boot Manager
Assert NMI on SERR
Assert NMI on PERR
Resume on AC Power Loss
Clear System Event Log
Enabled/Disabled
Enabled/Disabled
Stay Off/Last state/Reset
Enabled/Disabled
FRB-2 Enable
Enabled/Disabled
O/S Boot Watchdog Timer
O/S Boot Watchdog Timer Policy
O/S Boot Watchdog Timer Timeout
Enabled/Disabled
Power off/Reset
5 minutes/10 minutes/15 minutes/20 minutes
ACPI 1.0 Support Enabled/Disabled
Plug & Play BMC Detection
Enabled/Disabled
► Console Redirection
► System Information
Figure 29. Setup Utility – Server Management Configuraiton Screen Display
Table 28. Setup Utility – Server Management Configuration Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Assert NMI on SERR Enabled
Disabled
Assert NMI on PERR Enabled
Disabled
Resume on AC
Power Loss
Clear System Event
Log
FRB-2 Enable Enabled
Stay Off
Last state
Reset
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
On SERR, generate an NMI and log an error.
Note: [Enabled] must be selected for the Assert NMI
on PERR setup option to be visible.
On PERR, generate an NMI and log an error.
Note: This option is only active if the Assert NMI on
SERR option is [Enabled] selected.
System action to take on AC power loss recovery.
[Stay Off] - System stays off.
[Last State] - System returns to the same state before
the AC power loss.
[Reset] - System powers on.
If enabled, clears the System Event Log. All current
entries will be lost.
Note: This option is reset to [Disabled] after a reboot.
Fault Resilient Boot (FRB).
If enabled, the BIOS programs the BMC watchdog
timer for approximately 6 minutes. If the BIOS does
not complete POST before the timer expires, the BMC
resets the system.
Revision 2.4
66
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 79

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Setup Item Options Help Text
O/S Boot Watchdog
Timer
O/S Boot Watchdog
Timer Policy
O/S Boot Watchdog
Timer Timeout
Plug & Play BMC
Detection
ACPI 1.0 Support Enabled
Console Redirection View/Configure console redirection information and
System Information View system information Takes the user to the
Enabled
Disabled
Power Off
Reset
5 minutes
10 minutes
15 minutes
20 minutes
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
If enabled, the BIOS programs the watchdog timer
with the timeout value selected. If the OS does not
complete booting before the timer expires, the BMC
resets the system and an error is logged.
Requires OS support or Intel Management Software.
If the OS boot watchdog timer is enabled, this is the
system action taken if the watchdog timer expires.
[Reset] - System performs a reset.
[Power Off] - System powers off.
If the OS watchdog timer is enabled, this is the
timeout value used by the BIOS to configure the
watchdog timer.
If enabled, the BMC is detectable by OSs that support
plug and play loading of an IPMI driver. Do not enable
if your OS does not support this driver.
[Enabled] - Publish ACPI 1.0 version of FADT in Root
System Description Table.
This may be required for compatibility with OS
versions that only support ACPI 1.0.
settings.
Grayed out when the O/S
Boot Watchdog Timer is
disabled.
Grayed out when the O/S
Boot Watchdog Timer is
disabled.
Needs to be [Enabled] for
Microsoft Windows 2000*
support.
Takes the user to the
Console Redirection
screen.
System Information
screen.
Comments
6.3.2.4.1 Console Redirection Screen
The Console Redirection screen allows the user to enable or disable console redirection and to
configure the connection options for this feature.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Server Management > Console
Redirection.
Server Management
Console Redirection
Console Redirection Disabled/Serial Port A/Serial Port B
Flow Control
Baud Rate
Terminal Type
Legacy OS Redirection
None/RTS/CTS
9.6k/19.2k/38.4k/57.6k/115.2k
PC-ANSI/VT100/VT100+/VT-UTF8
Disabled/Enabled
Figure 30. Setup Utility – Console Redirection Screen Display
Revision 2.4
67
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 80
BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Table 29. Setup Utility – Console Redirection Configuration Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Console Redirection Disabled
Serial Port A
Serial Port B
Flow Control None
RTS/CTS
Baud Rate 9600
19.2K
38.4K
57.6K
115.2K
Terminal Type PC-ANSI
VT100
VT100+
VT-UTF8
Legacy OS
Redirection
Disabled
Enabled
Console redirection allows a serial port to be used for server
management tasks.
[Disabled] - No console redirection.
[Serial Port A] - Configure serial port A for console redirection.
[Serial Port B] - Configure serial port B for console redirection.
Enabling this option disables the display of the Quiet Boot logo
screen during POST.
Flow control is the handshake protocol.
Setting must match the remote terminal application.
[None] - Configure for no flow control.
[RTS/CTS] - Configure for hardware flow control.
Serial port transmission speed. Setting must match the remote
terminal application.
Character formatting used for console redirection. Setting must
match the remote terminal application.
This option enables legacy OS redirection (i.e., DOS) on serial
port. If it is enabled, the associated serial port is hidden from the
legacy OS.
6.3.2.5 Server Management System Information Screen
The Server Management System Information screen allows the user to view part numbers,
serial numbers, and firmware revisions.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Server Management > System
Information.
Revision 2.4
68
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 81

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Server Management
System Information
Board Part Number
Board Serial Number
System Part Number
System Serial Number
Chassis Part Number
Chassis Serial Number
BMC Firmware Revision
HSC Firmware Revision
ME Firmware Revision
SDR Revision
UUID
Figure 31. Setup Utility – Server Management System Information Screen Display
Table 30. Setup Utility – Server Management System Information Fields
Setup Item Comments
Board Part Number Information only
Board Serial Number Information only
System Part Number Information only
System Serial Number Information only
Chassis Part Number Information only
Chassis Serial Number Information only
BMC Firmware Revision Information only
HSC Firmware Revision Information only
ME Firmware Revision Information only
SDR Revision Information only
UUID Information only
6.3.2.6 Boot Options Screen
The Boot Options screen displays any bootable media encountered during POST, and allows
the user to configure the preferred boot device.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Boot Options.
Revision 2.4
69
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 82

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Advance
d
Main
System Boot Timeout
Boot Option #1
Boot Option #2
Boot Option #x
Hard Disk Order
CDROM Order
Network Device Order
►Delete Boot Option
EFI Optimized Boot
Boot Option Retry
Security Server Management Boot Options Boot Manager
<0 - 65535>
<Available Boot devices>
<Available Boot devices>
<Available Boot devices>
Enabled/Disabled
Enabled/Disabled
Figure 32. Setup Utility – Boot Options Screen Display
Table 31. Setup Utility – Boot Options Screen Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text Comments
Boot Timeout 0 - 65535 The number of seconds the BIOS
should pause at the end of POST to
allow the user to press the [F2] key for
entering the BIOS Setup utility.
Valid values are 0-65535. Zero is the
default. A value of 65535 causes the
system to go to the Boot Manager
menu and wait for user input for every
system boot.
Boot Option #x Available boot
devices.
Hard Disk Order Set the order of the legacy devices in
CDROM Order Set the order of the legacy devices in
Floppy Order Set the order of the legacy devices in
Network Device Order Set the order of the legacy devices in Visible when one or more of
Set system boot order by selecting the
boot option for this position.
this group.
this group.
this group.
After entering the preferred
timeout, press the Enter key
to register that timeout value
to the system. These
settings are in seconds.
Visible when one or more
hard disk drives are in the
system.
Visible when one or more
CD-ROM drives are in the
system.
Visible when one or more
floppy drives are in the
system.
Revision 2.4
70
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 83

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Setup Item Options Help Text
this group. these devices are available
BEV Device Order Set the order of the legacy devices in
this group.
Add New Boot Option Add a new EFI boot option to the boot
order.
Delete Boot Option Remove an EFI boot option from the
boot order.
EFI Optimized Boot Enabled
Disabled
Boot Option Retry Enabled
Disabled
If enabled, the BIOS only loads
modules required for booting EFIaware Operating Systems.
If enabled, this continually retries nonEFI-based boot options without
waiting for user input.
in the system.
Visible when one or more of
these devices are available
in the system.
This option is only visible if
an EFI bootable device is
available to the system (for
example, a USB drive).
If the EFI shell is deleted,
you can restore it by setting
CMOS defaults (F9).
Comments
If all types of bootable devices are installed in the system, the default boot order is:
1. CD/DVD-ROM
2. Floppy Disk Drive
3. Hard Disk Drive
4. PXE Network Device
5. BEV (Boot Entry Vector) Device
6. EFI Shell and EFI Boot paths
6.3.2.6.1 Delete Boot Option Screen
The Delete Boot Option screen allows the user to remove an EFI boot option from the boot
order.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Boot Options > Delete Boot Options.
Boot Options
Delete Boot Option
Delete Boot Option Select one to Delete/Internal EFI Shell
Figure 33. Setup Utility – Delete Boot Option Screen Display
Revision 2.4
71
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 84

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Table 32. Setup Utility – Delete Boot Option Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Delete Boot Option Select one to Delete
Internal EFI Shell
Remove an EFI boot option from the
boot order.
6.3.2.6.2 Hard Disk Order Screen
The Hard Disk Order screen allows the user to control the hard disks.
To access this screen from the Main screen, choose Boot Options > Hard Disk Order.
Boot Options
Hard Disk #1 < Available Hard Disks >
Hard Disk #2 < Available Hard Disks >
Figure 34. Setup Utility — Hard Disk Order Screen Display
Table 33. Setup Utility — Hard Disk Order Fields
Setup Item Options
Hard Disk #1 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Hard Disk #2 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
Help Text
6.3.2.6.3 CDROM Order Screen
The CDROM Order screen allows the user to control the CDROM devices.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Boot Options > CDROM Order.
CDROM #1
CDROM #2
Boot Options
<Available CDROM devices>
<Available CDROM devices>
Figure 35. Setup Utility – CDROM Order Screen Display
Revision 2.4
72
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 85

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
Table 34. Setup Utility – CDROM Order Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
CDROM #1 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
CDROM #2 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
6.3.2.6.4 Floppy Order Screen
The Floppy Order screen allows the user to control the floppy drives.
To access this screen from the Main screen, choose Boot Options > Floppy Order.
Floppy Disk #1
Floppy Disk #2
Boot Options
<Available Floppy Disk >
<Available Floppy Disk >
Figure 36. Setup Utility — Floppy Order Screen Display
Table 35. Setup Utility — Floppy Order Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Floppy Disk #1 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Floppy Disk #2 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
6.3.2.6.5 Network Device Order Screen
The Network Device Order screen allows the user to control the network bootable devices.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Boot Options > Network Device Order.
Network Device #1
Network Device #2
Boot Options
<Available Network devices>
<Available Network devices>
Figure 37. Setup Utility – Network Device Order Screen Display
Revision 2.4
73
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 86

BIOS User Interface Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Table 36. Setup Utility – Network Device Order Fields
Setup Item Options Help Text
Network Device #1 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Network Device #2 Available
Legacy devices
for this Device
group.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
Set system boot order by selecting the boot
option for this position.
6.3.2.7 Boot Manager Screen
The Boot Manager screen allows the user to view a list of devices available for booting, and to
select a boot device for immediately booting the system.
To access this screen from the Main screen, select Boot Manager.
Main
Advance
[Internal EFI Shell]
<Boot device #1>
<Boot Option #x>
d
Security Server Management Boot Options Boot Manager
Figure 38. Setup Utility – Boot Manager Screen Display
Table 37. Setup Utility – Boot Manager Screen Fields
Setup Item Help Text
Internal EFI Shell Select this option to boot now.
Note: This list is not the system boot option order. Use the
Boot Options menu to view and configure the system boot
option order.
Boot Device #x Select this option to boot now.
Note: This list is not the system boot option order. Use the
Boot Options menu to view and configure the system boot
option order.
6.4 Loading BIOS Defaults
Different mechanisms exist for resetting the system configuration to the default values. When a
request to reset the system configuration is detected, the BIOS loads the default system
configuration values during the next POST. You can send the request to reset the system to the
defaults in the following ways:
Pressing <F9> from within the BIOS Setup utility.
Moving the clear system configuration jumper.
Revision 2.4
74
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 87

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS BIOS User Interface
IPMI command (set System Boot options command)
Int15 AX=DA209
Choosing Load User Defaults from the Exit page of the BIOS Setup loads user set
defaults instead of the BIOS factory defaults.
The recommended steps to load the BIOS defaults are:
1. Power down the system (Do not remove AC power).
2. Move the Clear CMOS jumper from pins 1-2 to pins 2-3.
3. Move the Clear CMOS jumper from pins 2-3 to pins 1-2.
4. Power up the system.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
75
Page 88
Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
7. Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
7.1 Board Connector Information
The following section provides detailed information regarding all connectors, headers, and
jumpers on the server board. It lists all connector types available on the board and the
corresponding reference designators printed on the silkscreen.
Table 38. Board Connector Matrix
Connector Quantity Reference Designators
Power supply 3 J9A1, J9C1 Main power
CPU 1 J6G1 CPU sockets 1156
Main memory 6 J8J3, J8J2, J8J1, J9J3, J9J2, J8J4 DIMM sockets 240
Intel® RMM3 1 J2C1 Header 34
50-pin PCI
Express*
Connector
CPU Fan 1 J6D1 Header 4
System Fans 4 J1J4, J6J2, J7J1, J6B1 Header 4
Battery 1 BT5C1 Battery holder 3
NIC/Stack 2x USB 2 J5A1, J6A1 Dual USB 8
Video 1 J7A1 External DSub 15
Serial port A 1 J8A1 Connector 9
Serial port B 1 J1B2 Header 9
Front panel 1 J4H3 Header 24
USB floppy 1 J1C1 Header 4
Dual- USB Internal
Header
PCI-E x16 1 J4B3 Card Edge 164
PCI-E x8 3 J2B2, J3B1, J4B2 Card Edge 98
PCI-E x4 1 J2B1 Card Edge 64
PCI 32 1 J1B1 Card Edge 120
XDP Connector 1 J5J1 Connector 60
Chassis Intrusion 1 J4B1 Header 2
Serial ATA 6 J1H4, J1H1, J1G1, J1H3, J1G3, J1F4 Header 7
IPMB 1 J1H2 Header 4
HSBP 1 J1J1 Header 4
Z-U130 USB 1 J3F2 Header 10
SATA_SGPIO 1 J1J3 Header 4
1 J2H1 Header 50
2 J1D1, J1E1 Header 10
Connector Type Pin Count
24
CPU power
8
7.2 Power Connectors
The main power supply connection uses an SSI-compliant 2x12 pin connector (J9A1). In
addition, there is one additional power related connector:
One SSI-compliant 2x4 pin power connector (J9C1), which provides 12-V power to the
CPU VRD.
Revision 2.4
76
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 89

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
The following tables define the connector pin-outs.
Table 39. Baseboard Power Connector Pin-out (J9A1)
Pin Signal Color Pin Signal Color
1 +3.3 Vdc Orange 13 +3.3 Vdc Orange
2 +3.3 Vdc Orange 14 -12 Vdc Blue
3 GND Black 15 GND Black
4 +5 Vdc Red 16 PS_ON# Green
5 GND Black 17 GND Black
6 +5 Vdc Red 18 GND Black
7 GND Black 19 GND Black
8 PWRGD_PS Gray 20 NC White
9 5 VSB Purple 21 +5 Vdc Red
10 +12 Vdc Yellow 22 +5 Vdc Red
11 +12 Vdc Yellow 23 +5 Vdc Red
12 +3.3 Vdc Orange 24 GND Black
Table 40. SSI Processor Power Connector Pin-out (J9C1)
Pin
1 GND Black
2 GND Black
3 GND Black
4 GND Black
5 +12 Vdc Yellow/black
6 +12 Vdc Yellow/black
7 +12 Vdc Yellow/black
8 +12 Vdc Yellow/black
Signal
Color
7.3 System Management Headers
7.3.1 Intel® Remote Management Module 3 (Intel® RMM3) Connector
A 34-pin Intel® RMM 3 connector (J2C1) is included on the server board to support the optional
®
Intel
Remote Management Module 3. This server board does not support third-party
management cards.
Note: This connector is not compatible with the Intel
RMM) or the Intel® Remote Management Module 2 (Intel® RMM2).
®
Remote Management Module (Intel®
Revision 2.4
77
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 90

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Table 41. Intel® RMM3 Connector Pin-out (J2C1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 P3V3_AUX 2 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_MDIO
3 P3V3_AUX 4 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_MDC
5 GND 6 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_RXD1
7 GND 8 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_RXD0
9 GND 10 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_CRS_DV
11 GND 12 CLK_50M_RMM3
13 GND 14 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_RX_ER
15 GND 16 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_TX_EN
17 GND 18 KEY
19 GND 20 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_TXD0
21 GND 22 RMII_IBMC_RMM3_TXD1
23 P3V3_AUX 24 SPI_IBMC_BK_CS_N
25 P3V3_AUX 26 TP_RMM3_SPI_WE
27 P3V3_AUX 28 SPI_IBMC_BK_DO
29 GND 30 SPI_IBMC_BK_CLK
31 GND 32 SPI_IBMC_BK_DI
33 GND 34 FM_RMM3_Present_N
7.3.2 LCP/IPMB Header
Table 42. LPC/IPMB Header Pin-out (J1H2)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 SMB_IPMB_5VSB_DAT Integrated BMC IMB 5V standby
2 GND Ground
3 SMB_IPMB_5VSB_CLK Integrated BMC IMB 5V standby
4 P5V_STBY +5 V standby power
7.3.3 HSBP Header
Table 43. HSBP Header Pin-out (J1J1)
data line
clock line
Pin Signal Name
1 SMB_HSBP_5V_DAT
2 GND
3 SMB_HSBP_5V_CLK
4 FM_HSBP_ADD_C2
Revision 2.4
78
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 91

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
7.3.4 SGPIO Header
Table 44. SGPIO Header Pin-out (J1J3)
Pin Signal Name
1 SGPIO_CLOCK SGPIO Clock Signal
2 SGPIO_LOAD SGPIO Load Signal
3 SGPIO_DATAOUT0 SGPIO Data Out
4 SGPIO_DATAOUT1 SGPIO Data In
Description
7.4 Front Control Panel Connector
The server board provides a 24-pin SSI front panel connector (J1C1) for use with Intel® and
third-party chassis. The following table provides the pin-out for this connector.
Table 45. Front Panel SSI Standard 24-pin Connector Pin-out (J1C1)
Pin Signal Name Description Pin Signal Name Description
1 P3V3_AUX
(Power_LED_Anode)
3 Key No Connection 4 P5V_STBY (ID LED
5 FP_PWR_LED_N Power LED - 6 FP_ID_LED_BUF_N ID LED -
7 P3V3
(HDD_ACTIVITY_Anode)
9 LED_HDD_ACTIVITY_N HDD Activity
11 FP_PWR_BTN_N Power Button 12 NIC1_ACT_LED_N NIC 1 Activity
13 GND (Power Button
GND)
15 RST_FP_BTN_N Reset Button 16 SMB_SENSOR_3V3ST
17 GND (Reset GND) Reset Button
19 FP_ID_BTN_N ID Button 20 FP_CHASS_INTRU Chassis Intrusion
21 PU_FM_SIO_TEMP_SE
NSOR
23 FP_NMI_BTN_N NMI Button 24 NIC2_LINK_LED_N NIC 2 Link LED -
Power LED + 2 P3V3_STBY Front Panel
Power
ID LED +
Anode)
HDD Activity
LED+
LED-
Power Button
Ground
Ground
Front Panel
Temperature
Sensor
8 FP_LED_STATUS_GR
EEN_N
10 FP_LED_STATUS_AM
BER_N
14 NIC1_LINK_LED_N NIC 1 Link LED -
B_DATA
18 SMB_SENSOR_3V3ST
B_CLK
22 NIC2_ACT_LED_N NIC 2 Activity
Status LED
Green -
Status LED
Amber
LED -
SMB Sensor
DATA
SMB Sensor
Clock
LED -
Combined system BIOS and the Integrated BMC support provide the functionality of the various
supported control panel buttons and LEDs. The following sections describe the supported
functionality of each control panel feature.
Note: Control panel features are also routed through the bridge board connector at location
J1C1 as is implemented in Intel® Server Systems configured using a bridge board and a hotswap backplane.
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
79
Page 92

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
7.4.1 Power Button
The BIOS supports a front control panel power button. Pressing the power button initiates a
request that the Integrated BMC forwards to the ACPI power state machines in the chipset. It is
monitored by the Integrated BMC and does not directly control power on the power supply.
Power Button — Off to On
The Integrated BMC monitors the power button and the wake-up event signals from the
chipset. A transition from either source results in the Integrated BMC starting the powerup sequence. Since the processor are not executing, the BIOS does not participate in
this sequence. The hardware receives the power good and reset signals from the
Integrated BMC and then transitions to an ON state.
Power Button — On to Off (Operating system absent)
The System Control Interrupt (SCI) is masked. The BIOS sets up the power button event
to generate an SMI and checks the power button status bit in the ACPI hardware
registers when an SMI occurs. If the status bit is set, the BIOS sets the ACPI power
state of the machine in the chipset to the OFF state. The Integrated BMC monitors
power state signals from the chipset and de-asserts PS_PWR_ON to the power supply.
As a safety mechanism, if the BIOS fails to service the request, the Integrated BMC
automatically powers off the system in 4 to 5 seconds.
Power Button — On to Off (Operating system present)
If an ACPI operating system is running, pressing the power button switch generates a
request using SCI to the operating system to shut down the system. The operating
system retains control of the system and the operating system policy determines the
sleep state into which the system transitions, if any. Otherwise, the BIOS turns off the
system.
7.4.2 Reset Button
The platform supports a front control panel reset button. Pressing the reset button initiates a
request forwarded by the Integrated BMC to the chipset. The BIOS does not affect the behavior
of the reset button.
7.4.3 NMI Button
The Intel® S3420GP Server Board family BIOS does not support the NMI button.
7.4.4 System Status Indicator LED
The Intel® Server Board S3420GP that uses the Intel® Xeon® Processor 3400 Series has a
system status indicator LED on the front panel. This indicator LED has specific states and
corresponding interpretation as shown in the following table.
Table 46. System Status LED Indicator States
Color State Criticality Description
Green Solid on Ok System booted and ready
Revision 2.4
80
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 93

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Color State Criticality Description
Green ~1 Hz blink Degraded System degraded:
Non-critical temperature threshold asserted.
Non-critical voltage threshold asserted.
Non-critical fan threshold asserted.
Fan redundancy lost, sufficient system cooling maintained.
This does not apply to non-redundant systems.
Power supply predictive failure.
Power supply redundancy lost. This does not apply to non-
redundant systems.
Correctable errors over a threshold of 10 and migrating to a
spare DIMM (memory sparing). This indicates the user no
longer has spared DIMMs indicating a redundancy lost
condition. Corresponding DIMM LED should light up.
Amber ~1 Hz blink Non-critical Non-fatal alarm – system is likely to fail:
CATERR asserted.
Critical temperature threshold asserted.
Critical voltage threshold asserted.
Critical fan threshold asserted.
VRD hot asserted.
SMI Timeout asserted.
Amber Solid on Critical, non-
recoverable
Off N/A Not ready AC power off, if no degraded, non-critical, critical, or non-recoverable
Notes:
1. The BIOS detects these conditions and sends a Set Fault Indication command to the Integrated BMC to provide
the contribution to the system status LED.
2. Support for upper non-critical limit is not provided in the default SDR configuration. However, if a user does
enable this threshold in the SDR, then the system status LED should behave as described.
Fatal alarm – system has failed or shutdown:
Thermtrip asserted.
Non-recoverable temperature threshold asserted.
Non-recoverable voltage threshold asserted.
Power fault/Power Control Failure.
Fan redundancy lost, insufficient system cooling. This does
not apply to non-redundant systems.
conditions exist.
1
There is no precedence or lock-out mechanism for the control sources. When a new request
arrives, all previous requests are terminated. For example, if the chassis ID LED is blinking and
the chassis ID button is pressed, then the chassis ID LED changes to solid on. If the button is
pressed again with no intervening commands, the chassis ID LED turns off.
7.5 I/O Connectors
7.5.1 VGA Connector
The following table details the pin-out definition of the VGA connector (J7A1).
Table 47. VGA Connector Pin-out (J7A1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 V_IO_R_CONN Red (analog color signal R)
2 V_IO_G_CONN Green (analog color signal G)
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
81
Page 94

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Pin Signal Name
3 V_IO_B_CONN Blue (analog color signal B)
4 TP_VID_CONN_B4 No connection
5 GND Ground
6 GND Ground
7 GND Ground
8 GND Ground
9 TP_VID_CONN_B9 No connection
10 GND Ground
11 TP_VID_CONN_B11 No connection
12 V_IO_DDCDAT DDCDAT
13 V_IO_HSYNC_CONN HSYNC (horizontal sync)
14 V_IO_VSYNC_CONN VSYNC (vertical sync)
15 V_IO_DDCCLK DDCCLK
Description
7.5.2 Rear NIC and USB connector
The server board provides two stacked RJ-45/2xUSB connectors side-by-side on the back edge
of the board (J6A1, J5A1). The pin-out for NIC connectors are identical and defined in the
following table.
Table 48. RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out (J5A1)
Pin Signal Name
1 P5V_USB_PWR75 2 USB_PCH_11_FB_DN
3 USB_PCH_11_FB_DP 4 GND
5 P5V_USB_PWR75 6 USB_PCH_10_FB_DN
7 USB_PCH_10_FB_DP 8 GND
9 P1V9_LAN2_R 10 NIC2_MDIP<0>
11 NIC2_MDIN<0> 12 NIC2_MDIP<1>
13 NIC2_MDIN<1> 14 NIC2_MDIP<2>
15 NIC2_MDIN<2> 16 NIC2_MDIP<3>
17 NIC2_MDIN<3> 18 GND
19 LED_NIC2_1 20 P3V3_AUX
21 LED_NIC2_LINK100_R_0 22 LED_NIC2_LINK1000_2
Pin Signal Name
Table 49. RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out (J6A1)
Pin Signal Name
1 P5V_USB_PWR75 2 USB_PCH_11_FB_DN
3 USB_PCH_11_FB_DP 4 GND
5 P5V_USB_PWR75 6 USB_PCH_10_FB_DN
7 USB_PCH_10_FB_DP 8 GND
9 P1V8_PHY_VCT_R 10 NIC1_MDIP<0>
11 NIC1_MDIN<0> 12 NIC1_MDIP<1>
13 NIC1_MDIN<1> 14 NIC2_MDIP<2>
15 NIC1_MDIN<2> 16 NIC2_MDIP<3>
17 NIC1_MDIN<3> 18 GND
19 LED_NIC1_LINK_ACT_0_R 20 P3V3_AUX
Revision 2.4
82
Pin Signal Name
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 95
Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Pin Signal Name
21 LED_NIC1_2 22 LED_NIC1_LINK1000_1
Pin Signal Name
7.5.3 SATA
The sever board provides up to six SATA connectors. The pin configuration for each connector
is identical and defined in the following table.
Table 50. SATA Connector Pin-out (J1H4, J1H1, J1G1, J1H3, J1G3, J1F4)
Pin Signal Name
1 GND Ground
2 SATA/SAS_TX_P_C Positive side of transmit differential pair
3 SATA/SAS_TX_N_C Negative side of transmit differential pair
4 GND Ground
5 SATA/SAS_RX_N_C Negative side of receive differential pair
6 SATA/SAS_RX_P_C Positive side of receive differential pair
7 GND Ground
Description
7.5.4 50-pin PCI Express* Connector
The Intel® Server Board S3420GPLX provides one 50-pin PCI Express* connector for Intel®
SAS Entry RAID Module AXX4SASMOD.
The pin configuration is identical and defined in the following table.
Table 51. 50-pin PCI Express* Connector Pin-out (J2H1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 P3V3_AUX 2 P3V3_AUX
3 PE_RST_IO_MODULE_N 4 GND
5 GND 6 PE2_ESB_RXP_C<0>
7 GND 8 PE2_ESB_RXN_C<0>
9 PE2_ESB_TXP_C<0> 10 GND
11 PE2_ESB_TXN_C<0> 12 GND
13 GND 14 PE2_ESB_RXP_C<1>
15 GND 16 PE2_ESB_RXN_C<1>
17 PE2_ESB_TXP_C<1> 18 GND
19 PE2_ESB_TXN_C<1> 20 GND
21 GND 22 PE2_ESB_RXP_C<2>
23 GND 24 PE2_ESB_RXN_C<2>
25 PE2_ESB_TXP_C<2> 26 GND
27 PE2_ESB_TXN_C<2> 28 GND
29 GND 30 PE2_ESB_RXP_C<3>
31 GND 32 PE2_ESB_RXN_C<3>
33 PE2_ESB_TXP_C<3> 34 GND
35 PE2_ESB_TXN_C<3> 36 GND
37 GND 38 CLK_100M_LP_PCIE_SLOT3_P
39 GND 40 CLK_100M_LP_PCIE_SLOT3_N
41 PE_WAKE_N 42 GND
43 P3V3 44 P3V3
Revision 2.4
83
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 96

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Pin Signal Name Pin
45 P3V3 46 P3V3
47 P3V3 48 P3V3
49 P3V3 50 P3V3
Signal Name
7.5.5 Serial Port Connectors
The server board provides one external DB9 Serial A port (J8A1) and one internal 9-pin serial B
header (J1B2). The following tables define the pin-outs.
Table 52. External Serial A Port Pin-out (J8A1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 SPA_DCD DCD (carrier detect)
2 SPA_SIN_L RXD (receive data)
3 SPA_SOUT_N TXD (Transmit data)
4 SPA_DTR DTR (Data terminal ready)
5 GND Ground
6 SPA_DSR DSR (data set ready)
7 SPA_RTS RTS (request to send)
8 SPA_CTS CTS (clear to send)
9 SPA_RI RI (Ring Indicate)
10 NC
Table 53. Internal 9-pin Serial B Header Pin-out (J1B2)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 SPB_DCD DCD (carrier detect)
2 SPB_DSR DSR (data set ready)
3 SPB_SIN_L RXD (receive data)
4 SPB_RTS RTS (request to send)
5 SPB_SOUT_N TXD (Transmit data)
6 SPB_CTS CTS (clear to send)
7 SPB_DTR DTR (Data terminal ready)
8 SPB_RI RI (Ring indicate)
9 SPB_EN_N Enable
10 NC
7.5.6 USB Connector
There are four external USB ports on two NIC/USB combinations. Section 5.5.2 details the pin-
out of the connector.
Two 2x5 connector on the server board (J1E1, J1D1) provides an option to support an
additional USB port, each connector supporting two USB ports. The following table defines the
pin-out of the connector.
Table 54. Internal USB Connector Pin-out ( J1E1, J1D1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 USB2_VBUS4 USB power (port 4)
2 USB2_VBUS5 USB power (port 5)
Revision 2.4
84
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 97

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Pin Signal Name
3 USB_ICH_P4N_CONN USB port 4 negative signal
4 USB_ICH_P5N_CONN USB port 5 negative signal
5 USB_ICH_P4P_CONN USB port 4 positive signal
6 USB_ICH_P5P_CONN USB port 5 positive signal
7 Ground
8 Ground
9 Key No pin
10 TP_USB_ICH_NC Test point
Description
One x connector (J1J2) on the server board provides an option to support a USB floppy
connector.
Table 55. Pin-out of Internal USB Connector for Floppy ( J1J2)
Pin Signal Name
1 +5V
2 USB_N
3 USB_P
4 GND
One 2x5 connectors (J3F2) on the server board provides an option to support an Intel® Z-U130
Value Solid State Drive. The following table defines the pin-out of the connector.
Table 56. Pin-out of Internal USB Connector for low-profile Intel® Z-U130 Value Solid State Drive
(J3F2)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 +5V USB power
2 NC N/A
3 USB Data - USB port ## negative signal
4 NC N/A
5 USB Data + USB port ## positive signal
6 NC N/A
7 Ground N/A
8 NC N/A
9 Key No pin
10 LED# Activity LED
7.6 PCI Express* Slot/PCI Slot/Riser Card Slot
A PCI-E Riser card will enable a PCI-E add-on card to be accommodated in the 1U chassis.
The following table shows the pin-out for this riser slot.
Table 57. Pin-out of adaptive riser slot/PCI Express slot 6
Pin Signal Description Pin
B1 +12V P12V A1 PRSNT1_N GND
B2 +12V P12V A2 +12V P12V
B3 RSVD P12V A3 +12V P12V
Signal Description
Revision 2.4
85
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 98

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Pin Signal Description Pin
B4 GND GND A4 GND GND
B5 SMCLK PU_S6_SMBCLK A5 JTAG2 P3V3_RISER_A5
B6 SMDATA PU_S6_SMBDAT A6 JTAG3 JTAG_S6_TDI
B7 GND GND A7 JTAG4 NC
B8 +3.3V P3V3 A8 JTAG5 P3V3_RISER_A8
B9 JTAG1 JTAG_S6_TRST_N A9 +3_3V P3V3
B10 +3.3VAUX P3V3_AUX A10 +3_3V P3V3
B11 WAKE_N FM_PE_WAKE_N A11
KEY KEY
KEY KEY
B12 RSVD NC A12 GND GND
B13 GND GND A13 REFCLKP CLK_100M_SLOT6A_DP
B14 PETP0 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<7> A14 REFCLKN CLK_100M_SLOT6A_DPN
B15 PETN0 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<7> A15 GND GND
B16 GND GND A16 PERP0 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<7>
B17 PRSNT2_N NC A17 PERN0 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<7>
B18 GND GND A18 GND GND
B19 PETP1 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<6> A19 RSVD NC
B20 PETN1 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<6> A20 GND GND
B21 GND GND A21 PERP1 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<6>
B22 GND GND A22 PERN1 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<6>
B23 PETP2 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<5> A23 GND GND
B24 PETN2 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<5> A24 GND GND
B25 GND GND A25 PERP2 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<5>
B26 GND GND A26 PERN2 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<5>
B27 PETP3 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<4> A27 GND GND
B28 PETN3 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<4> A28 GND GND
B29 GND GND A29 PERP3 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<4>
B30 RSVD NC A30 PERN3 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<4>
B31 PRSNT2_N NC A31 GND GND
B32 GND GND A32 RSVD NC
End of x4 End of x4
B33 PETP4 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<3> A33 RSVD NC
B34 PETN4 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<3> A34 GND GND
B35 GND GND A35 PERP4 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<3>
B36 GND GND A36 PERN4 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<3>
B37 PETP5 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<2> A37 GND GND
B38 PETN5 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<2> A38 GND GND
B39 GND GND A39 PERP5 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<2>
B40 GND GND A40 PERN5 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<2>
B41 PETP6 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<1> A41 GND GND
B42 PETN6 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<1> A42 GND GND
B43 GND GND A43 PERP6 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<1>
B44 GND GND A44 PERN6 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<1>
B45 PETP7 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXP<0> A45 GND GND
B46 PETN7 P2E_CPU_C_S6_TXN<0> A46 GND GND
B47 GND GND A47 PERP7 P2E_CPU_S6_RXN<0>
Signal Description
PERST_N RST_PE_S236_N_R1
Revision 2.4
86
Intel order number E65697-010
Page 99

Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Pin Signal Description Pin
B48 PRSNT2_N NC A48 PERN7 P2E_CPU_S6_RXP<0>
B49 GND GND A49 GND GND
End of x8 End of x8
B50 PETP8 NC A50 RSVD NC
B51 PETN8 NC A51 GND GND
B52 GND GND A52 PERP8 NC
B53 GND GND A53 PERN8 NC
B54 PETP9 NC A54 GND GND
B55 PETN9 NC A55 GND GND
B56 GND GND A56 PERP9 NC
B57 GND GND A57 PERN9 NC
B58 PETP10 NC A58 GND GND
B59 PETN10 NC A59 GND GND
B60 GND GND A60 PERP10 NC
B61 GND GND A61 PERN10 NC
B62 PExP11 NC A62 GND GND
B63 PETN11 NC A63 GND GND
B64 GND GND A64 PERP11 NC
B65 GND GND A65 PERN11 NC
B66 PETP12 NC A66 GND GND
B67 PETN12 NC A67 GND GND
B68 GND GND A68 PERP12 NC
B69 GND GND A69 PERN12 NC
B70 PETP13 NC A70 GND GND
B71 PETN13 NC A71 GND GND
B72 GND GND A72 PERP13 NC
B73 GND GND A73 PERN13 NC
B74 PETP14 NC A74 GND GND
B75 PETN14 NC A75 GND GND
B76 GND GND A76 PERP14 NC
B77 GND GND A77 PERN14 NC
B78 PETP15 NC A78 GND GND
B79 PETN15 NC A79 GND GND
B80 GND GND A80 PERP15 NC
B81 PRSNT2_N NC A81 PERN15 NC
B82
RSVD
NC
A82
Signal Description
GND GND
Three PCI Express* x8 connectors (J2B2, J3B1 and J4B2)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 PRSNT1# B1 +12V A26 HSIP[2] B26 GND
A2 +12V B2 +12V A27 GND B27 HSOP[3]
A3 +12V B3 RESERVED A28 GND B28 HSON[3]
A4 GND B4 GND A29
Revision 2.4
Intel order number E65697-010
HSIP[3]
B29 GND
87
Page 100
Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S3420GP TPS
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A5 JTAG2/TCk B5 SMCLK A30
A6 JTAG3/TDI B6 SMDAT A31 GND B31 PRSNT2#
A7 JTAG4/TDO B7 GND A32 RESERVED B32 GND
A8 JTAG5/TMS B8 +3.3V A33 RESERVED B33 HSOP[4]
A9 +3.3V B9 JTAG1/TRST# A34 GND B34 HSON[4]
A10 +3.3V B10 3.3VAUX A35
A11 PERST# B11 WAKE# A36
A12 GND B12 RESERVED A37 GND B37 HSOP[5]
A13 REFCLK+ B13 GND A38 GND B38 HSON[5]
A14 REFCLK- B14 HSOP[0] A39
A15 GND B15 HSON[0] A40
A16 HSIP[0] B16 GND A41 GND B41 HSOP[6]
A17 HSIN[0] B17 PRSNT2# A42 GND B42 HSON[6]
A18 GND B18 GND A43
A19 RESERVED B19 HSOP[1] A44
HSIN[3]
HSIP[4]
HSIN[4]
HSIP[5]
HSIN[5]
HSIP[6]
HSIN[6]
B30 RESERVED
B35 GND
B36 GND
B39 GND
B40 GND
B43 GND
B44 GND
A20 GND B20 HSON[1] A45 GND B45 HSOP[7]
A21 HSIP[1] B21 GND A46 GND B46 HSON[7]
A22 HSIN[1] B22 GND A47
A23 GND B23 HSOP[2] A48
A24 GND B24 HSON[2] A49 GND B49 GND
A25 HSIP[2] B25 GND
HSIP[7]
HSIN[7]
B47 GND
B48 PRSNT2#
One PCI Express* X4 connector (J2B1)
Pin# Signal Pin# Signal Pin# Signal Pin# Signal
A1 PRSNT1_N B1 +12V A17 PERN0 B17 PRSNT2_N
A2 +12V B2 +12V A18 GND B18 GND
A3 +12V B3 RSVD A19 RSVD B19 PETP1
A4 GND B4 GND A20 GND B20 PETN1
A5 JTAG2 B5 SMCLK A21 PERP1 B21 GND
A6 JTAG3 B6 SMDAT A22 PERN1 B22 GND
A7 JTAG4 B7 GND A23 GND B23 PETP2
A8 JTAG5 B8 +3.3V A24 GND B24 PETN2
Revision 2.4
88
Intel order number E65697-010
 Loading...
Loading...