Page 1

R
mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
March 2005
Document Number: 254239-002
Page 2

R
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The mPGA604 socket may contain design defects or errors known as errata, which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications.
Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents, which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling 1-800-5484725, or by visiting
Intel is a trademark or registered trademark of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Copyright © 2003-2005, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Intel's Web Site.
2 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 3

R
Contents
1 Introduction.......................................................................................................................7
1.1 Objective ................................................................................................................7
1.2 Purpose.................................................................................................................. 7
1.3 Scope ..................................................................................................................... 7
2 Assembled Component and Package Description........................................................ 9
3 Mechanical Requirements..............................................................................................11
3.1 Attachment ........................................................................................................... 11
3.2 Materials............................................................................................................... 11
3.2.1 Socket Housing....................................................................................... 11
3.2.2 Color........................................................................................................ 11
3.3 Cutouts for Package Removal .............................................................................11
3.4 Socket Standoffs Height ......................................................................................11
3.5 Markings............................................................................................................... 12
3.5.1 Name....................................................................................................... 12
3.5.2 Lock (Closed) and Unlock (Open) Markings........................................... 12
3.5.3 Lot Traceability........................................................................................ 12
3.6 Socket Size ..........................................................................................................12
3.7 Socket/Package Translation During Actuation ....................................................13
3.8 Orientation in Packaging, Shipping and Handling ...............................................13
3.9 Contact Characteristics........................................................................................ 13
3.9.1 Number of contacts................................................................................. 13
3.9.2 Base Material .......................................................................................... 13
3.9.3 Contact Area Plating ............................................................................... 13
3.9.4 Solder Ball Attachment Area Plating....................................................... 13
3.9.5 Solder Ball Characteristics...................................................................... 13
3.9.6 Lubricants................................................................................................ 13
3.10 Material and Recycling Requirements .................................................................13
3.11 Lever Actuation Requirements............................................................................. 14
3.12 Socket Engagement/Disengagement Force ........................................................ 14
3.13 Visual Aids ...........................................................................................................14
3.14 Socket BGA Co-Planarity..................................................................................... 14
3.15 Solder Ball True Position .....................................................................................14
3.16 Critical-to-Function Dimensions ........................................................................... 14
4 Electrical Requirements.................................................................................................17
4.1 Electrical Resistance............................................................................................ 18
4.2 Determination of Maximum Electrical Resistance ...............................................22
4.3 Inductance............................................................................................................ 23
4.3.1 Design Procedure for Inductance Measurements .................................. 24
4.3.2 Correlation of Measurement and Model Data Inductance ...................... 25
4.4 Pin-to-Pin Capacitance ........................................................................................ 25
4.5 Dielectric Withstand Voltage ................................................................................25
4.6 Insulation Resistance........................................................................................... 25
4.7 Contact Current Rating ........................................................................................ 25
5 Environmental Requirements........................................................................................27
5.1 Mixed Flowing Gas ..............................................................................................28
mPGA604 Socket 3
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 4

5.2
Solvent Resistance ..............................................................................................28
5.3 Durability ..............................................................................................................28
6 Validation Testing Requirements.................................................................................. 29
6.1 Applicable Documents .........................................................................................29
6.2 Testing Facility .....................................................................................................29
6.3 Funding ................................................................................................................29
6.4 Socket Design Verification ...................................................................................29
6.5 Reporting.............................................................................................................. 29
6.6 Process Changes................................................................................................. 29
6.7 Quality Assurance Requirements ........................................................................30
6.8 Socket Test Plan.................................................................................................. 30
6.8.1 Submission of an mPGA604 Socket for Validation Testing.................... 30
6.9 Mechanical Samples............................................................................................ 30
6.10 Socket Validation Notification ..............................................................................30
6.11 Production Lot Definition...................................................................................... 30
6.12 Socket Validation .................................................................................................30
7 Safety Requirements ......................................................................................................31
8 Documentation Requirements....................................................................................... 33
R
9 Mechanical Drawings .....................................................................................................35
Figures
4-1 Methodology for Measuring Total Electrical Resistance...................................... 18
4-2 Methodology for Measuring Electrical Resistance of the Jumper........................ 18
4-3 Electrical Resistance Fixtures Superimposed ..................................................... 19
4-4 Inductance Measurement Fixture Cross-Section................................................. 23
4-5 Inductance and Capacitance Fixture ................................................................... 23
5-1 Flow Chart of Knowledge-Based Reliability Evaluation Methodology ................. 27
9-1 mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4) ........................................................... 35
9-2 mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4) ........................................................... 36
9-3 mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4) ........................................................... 37
9-4 mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4) ........................................................... 38
9-5 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 1 of 6).......................................... 39
9-6 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 2 of 6).......................................... 40
9-7 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 3 of 6).......................................... 41
9-8 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing OLGA Keepout (Sheet 4 of 6)................ 42
9-9 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing FCBGA2 Keepout (Sheet 5 of 6)............ 43
9-10 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 6 of 6).......................................... 44
Tables
3-1 Package Critical-To-Function (CTF) Dimensions ................................................ 15
4-1 Electrical Requirements for Sockets.................................................................... 17
4-2 Definitions (Sheet 1 of 2) .....................................................................................17
4-3 Resistance Test Fixture Netlist (Sheet 1 of 2) ..................................................... 21
4-4 Net list for FSETV4 Rev 1 Edge Fingers ............................................................. 26
5-1 Use Conditions Environment ............................................................................... 27
4 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 5
R
Revision History
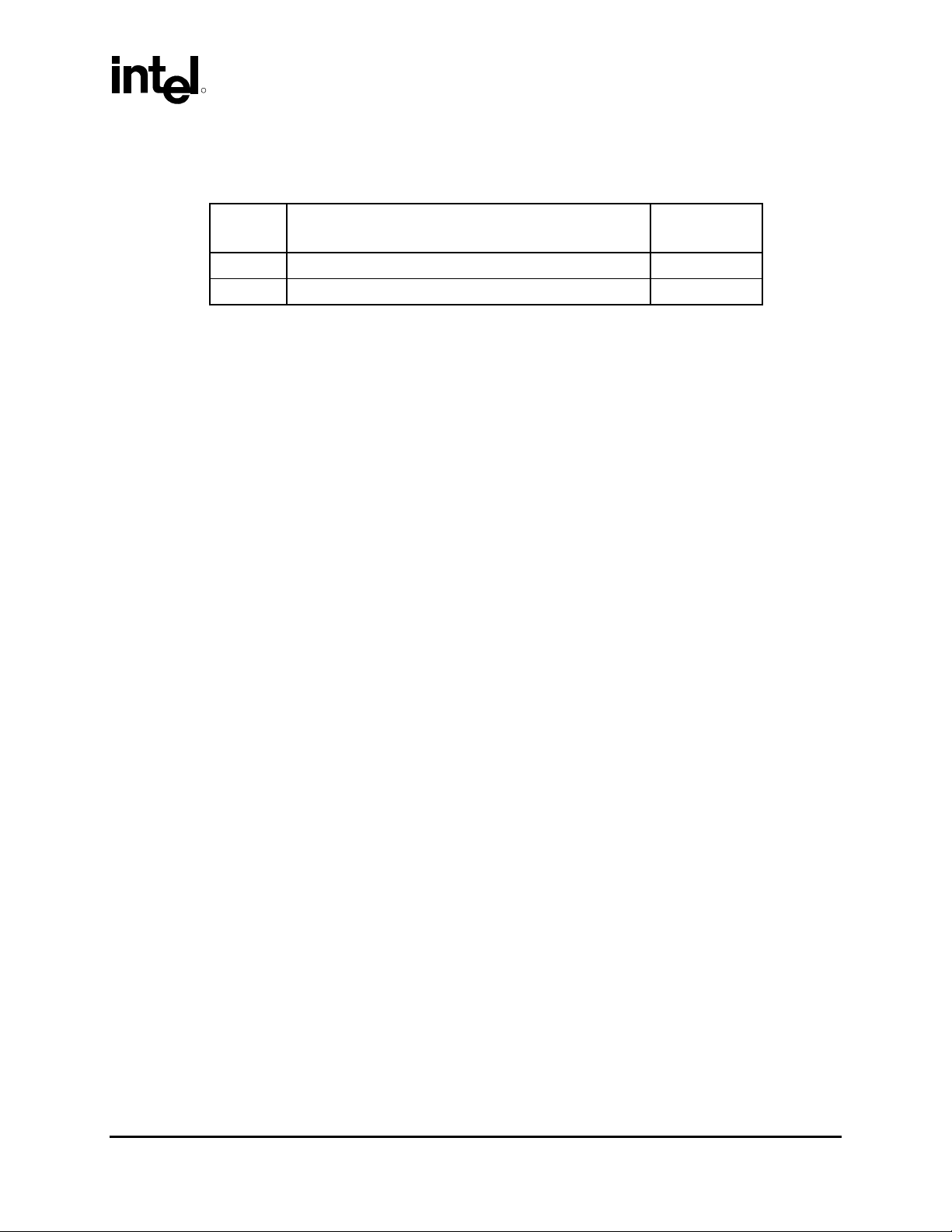
Revision
Number
001 • Initial release of the document. October 2003
002 • Updated for 2005 Intel® Xeon™ products. March 2005
Note: Not all revisions may be published.
Description Date
mPGA604 Socket 5
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 6

Re-Validation Notice to Socket Vendors
Any significant change to the socket will require submission of a detailed explanation of the change
at least 60 days prior to the planned implementation. Intel will review the modification and establish
the necessary re-validation procedure that the socket must pass. Any testing that is required MUST
be completed before the change is implemented.
Typical examples of significant changes include, but are not limited to, the following: plastic
material changes including base material or color; contact changes including base material, plating
material or thickness; and design modifications.
R
For details on validation testing requirements, see
Section 6.
6 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 7

R
1 Introduction
1.1 Objective
This document defines a surface mount, Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) socket intended for workstation
and server platforms based on Intel microprocessors. The socket provides I/O, power and ground
contacts. The socket contains 604 contacts arrayed about a cavity in the center of the socket with
solder balls/surface mount features for surface mounting with the motherboard. The mPGA604
Socket contacts have 1.27mm pitch with regular pin array, to mate with a 604-pin processor
package. A 604-pin package will be mated with a 603 solder ball socket. The dummy pin is a key
that allows either the 603-pin processor package or the 604-pin processor package to be used in the
same socket.
1.2 Purpose
To define functional, quality, reliability, and material (that is, visual, dimensional and physical)
requirements and design guidelines of the mPGA604 Socket in order to provide low cost, low risk,
robust, high volume manufacturable (HVM) socket solution available from multiple sources.
1.3 Scope
This design guideline applies to all 604-pin ZIF sockets purchased to the requirements of this design
guideline.
§
mPGA604 Socket 7
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 8

Introduction
R
8 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 9

R
2 Assembled Component and
Package Description
The mPGA604 socket dimensions and characteristics must be compatible with that of the processor
package and related assembly components. Processors using flip-chip pin grid array (FC- mPGA4)
package technology are targeted to be used with the mPGA604 socket.
The assembled component may consist of a cooling solution (heatsink, fan, and retention
mechanism), and processor package. The processor Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
document provides information for designing components compliant with the Intel reference design.
Relevant processor FC-mPGA4 package and pin-out information is given in the processor
Electrical, Mechanical and Thermal Specifications document.
§
mPGA604 Socket 9
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 10

Assembled Component and Package Description
R
10 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 11

R
3 Mechanical Requirements
3.1 Attachment
A retention system needs to isolate any load in excess of 222.41 N, compressive, from the socket
during the shock and vibration conditions outlined in
mechanical shock and vibration requirements listed in
retention mechanism attached. Socket can only be attached by the 603 contacts to the motherboard.
No external (i.e. screw, extra solder, adhesive....) methods to attach the socket are acceptable.
3.2 Materials
3.2.1 Socket Housing
Thermoplastic or equivalent, UL 94V-0 flame rating, temperature rating and design capable of
withstanding a temperature of 240°C for 40sec (minimum) typical of a reflow profile for solder
material used on the socket. The material must have a thermal coefficient of expansion in the XY
plane capable of passing reliability tests rated for an expected high operating temperature, mounted
on FR4type motherboard material.
Section 5. The socket must pass the
Section 5 with the associated heatsink and
3.2.2 Color
The color of the socket can be optimized to provide the contrast needed for OEM’s pick and place
vision systems. The base and cover of the socket may be different colors as long as they meet the
above requirement.
3.3 Cutouts for Package Removal
Recessed cutouts are required in the side of the socket to provide better access to the package
substrate, and facilitate the manual removal of inserted package (see
3.4 Socket Standoffs Height
Socket stand off height, cover lead in and cover lead in depth must not interfere with package pin
shoulder at worst-case conditions. The processor (not the pin shoulder) must sit flush on the socket
standoffs and the pin field cannot contact the standoffs (see
Section 9).
Section 9).
mPGA604 Socket 11
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 12

Mechanical Requirements
3.5 Markings
All markings required in this section must be able to withstand a temperature of 240 ºC for 40
seconds (minimum) typical of a reflow profile for solder material used on the socket, as well as any
environmental test procedure outlined in
Section 5.
3.5.1 Name
mPGA604 (Font type is Helvetica Bold – minimum 6 point).
This mark shall be molded or Laser Marked into the processor side of the socket housing.
Manufacturer’s insignia (font size at supplier’s discretion).
This mark will be molded or laser marked into the socket housing. Both marks must be visible when
first seated in the motherboard. Any request for variation from this marking requires a written
description (detailing size and location) to be provided to Intel for approval.
3.5.2 Lock (Closed) and Unlock (Open) Markings
R
The universal symbols for ‘Lock’ and ‘Unlock’ are to be marked on the socket in the appropriate
positions. Clear indicator marks must be located on the actuation mechanism that identifies the lock
(closed) and unlock (open) positions of the cover as well as the actuation direction. These marks
should still be visible after a package is inserted into the socket.
3.5.3 Lot Traceability
Each socket will be marked with a lot identification code that will allow traceability of all
components, date of manufacture (year and week), and assembly location. The mark must be placed
on a surface that is visible when mounted on a printed circuit board. In addition, this identification
code must be marked on the exterior of the box in which the units ship.
3.6 Socket Size
The socket size must meet the dimensions as shown in Section 9, allowing full insertion of the pins
in the socket, without interference between the socket and the pin field. The mPGA604 Socket and
actuation area must fit within the keep-in zone defined in
12 mPGA604 Socket
Section 9.
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 13

R
Mechanical Requirements
3.7 Socket/Package Translation During Actuation
The socket shall be built so that the post-actuated package pin field displacement will not exceed
1.27 mm. Movement will be along the Y direction. No Z-axis travel (lift out) of the package is
allowed during actuation.
3.8 Orientation in Packaging, Shipping and Handling
Packaging media needs to support high volume manufacturing.
3.9 Contact Characteristics
3.9.1 Number of contacts
Total number of contacts: 603.
Total number of contact holes: 604.
3.9.2 Base Material
High strength copper alloy.
3.9.3 Contact Area Plating
0.762 µm (min) gold plating over 1.27 µm (min) nickel underplate in critical contact areas (area on
socket contacts where processor pins will mate) is required. No contamination by solder in the
contact area is allowed during solder reflow.
3.9.4 Solder Ball Attachment Area Plating
3.81 µm (min) Tin/Lead (typically 85+-5Sn/Pb balance).
3.9.5 Solder Ball Characteristics
Tin/Lead (63/37 + 0.5% Sn).
3.9.6 Lubricants
For the final assembled product, no lubricant is permitted on the socket contacts. If lubricants are
used elsewhere within the socket assembly, these lubricants must not be able to migrate to the
socket contacts.
3.10 Material and Recycling Requirements
Cadmium shall not be used in the painting or plating of the socket.
mPGA604 Socket 13
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 14

Mechanical Requirements
CFCs and HFCs shall not be used in manufacturing the socket. It is recommended that any plastic
component exceeding 25g must be recyclable as per the European Blue Angel recycling design
guidelines.
3.11 Lever Actuation Requirements
• Lever closed direction—right.
R
• Actuation direction called out in
• 135º lever travel max.
• Pivot point in the center of the actuation area on the top of the socket.
Section 9.
Section 9.
3.12 Socket Engagement/Disengagement Force
The force on the actuation lever arm must not exceed 44N to engage or disengage the package into
the mPGA604 socket. Movement of the cover is limited to the plane parallel to the motherboard.
The processor package must not be utilized in the actuation of the socket. Any actuation must meet
or exceed SEMI S8-95 Safety Guidelines for Ergonomics/Human Factors Engineering of
Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment, example Table R2-7 (Maximum Grip Forces).
3.13 Visual Aids
The socket top will have markings identifying Pin 1. This marking will be represented by a clearly
visible triangular symbol (see
Section 9).
3.14 Socket BGA Co-Planarity
The co-planarity (profile) requirement for all solder balls on the underside of the socket is located in
Section 9.
3.15 Solder Ball True Position
The solder ball pattern has a true position requirement with respect to Datum A, B, and C (see
Section 9).
3.16 Critical-to-Function Dimensions
The mPGA604 socket shall accept a 604-pin processor pin field. All dimensions are metric.
Asymmetric features are designed to properly align the socket to the motherboard and prevent the
socket from being assembled incorrectly to the motherboard.
Critical-to-function (CTF) dimensions are identified in
the mPGA604 socket drawing in
document. Dimensional requirements identified in the drawing and in
dimensions will be verified as part of the validation process. Also, supplier will provide and
14 mPGA604 Socket
Section 9 and take precedence over all values presented in this
Table 3-1. The CTF values are detailed on
Table 3-1 must be met. These
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 15

R
Mechanical Requirements
maintain Critical Process Parameters controlling these CTFs or will provide direct measurements to
meet ongoing quality requirements.
Table 3-1. Package Critical-To-Function (CTF) Dimensions
Dimension
Socket Length
Socket Width
Socket Height (Interposer surface from MB)
Assembled Seating Plane Flatness
Ball Diameter
True Position of Balls (pattern relating)
Co-planarity (profile) of Balls
Actuation Distance (Cover Travel)
Through Cavity X
Through Cavity Y
Cover Hole Diameter (Must guarantee ZIF)
Cover Hole Countersink Depth (Must guarantee ZIF)
Cover Hole Countersink Diameter (Must guarantee ZIF)
Cover Hole Virtual Condition (Pattern Locating)
Cover Hole Virtual Condition (Feature Relating)
Cover Hole Field Depth wrt Seating Plane
Cover Thickness in Hole Area
Au Thickness
Ni Thickness
Alignment Post Virtual Condition
Contact Depth from Seating Plane
§
mPGA604 Socket 15
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 16

Mechanical Requirements
R
16 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 17

R
4 Electrical Requirements
Socket electrical requirements are measured from the socked-seating plane of the processor test
vehicle (PTV) to the component side of the socket PCB to which it is attached. All specification are
maximum values (unless otherwise stated) for a single socket pin, but includes effects of adjacent
pins where indicated. Pin and socket inductance includes exposed pin from mated contact to bottom
of the processor pin field.
Table 4-1. Electrical Requirements for Sockets
1 Mat lloop inductance, Loop <4.33 nH Refer to Table 4-2, Item 1
2 Mated partial mutual inductance, L NA Refer to Table 4-2,
3 Maximum mutual capacitance, C <1 pF Refer to Table 4-2
4 Maximum Ave Contact Resistance ≤ 17 mΩ Refer to Table 4-2, Item 4.
5 Measurement frequency(s) for
Pin-to-Pin/Connector-toConnector capacitance.
6 Measurement frequency(s) for
Pin-to-Pin/Connector-toConnector inductance.
7 Dielectric Withstand Voltage 360 Volts RMS
8 Insulation Resistance 800 MΩ
9 Contact Current Rating Read & record
400 MHz
1 GHz
Item 2a
Item 3
Refer to
more detail.
Refer to mPGA603 Socket
Design Guidelines for
electrical parameters with
INT3 packages.
Section 4.1 for
Table 4-2. Definitions (Sheet 1 of 2)
1 Mated loop inductance, Lloop
Refer to
2a Mated mutual inductance, L
Refer to
3 Maximum mutual capacitance, C
Refer to
Table 4-1, Item 1
Table 4-1, Item 2
Table 4-1, Item 3
The inductance calculated for two conductors,
considering one forward conductor and one
return conductor.
The inductance on a conductor due to any
single neighboring conductor.
The capacitance between two pins/connectors.
mPGA604 Socket 17
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 18

Electrical Requirements
Table 4-2. Definitions (Sheet 2 of 2)
4 Maximum Average Contact
Resistance. Refer to
Item 4
5 Measurement frequency(s) for
capacitance.
6 Measurement frequency(s) for
inductance.
4.1 Electrical Resistance
Table 4-1,
R
The max average resistance target is originally
derived from max resistance of each chain
minus resistance of shorting bars divided by
number of pins in the daisy chain. This value
has to be satisfied at all time. Thus, this is the
spec valid at End of Line, End of Life and etc.
Socket Contact Resistance: The resistance
of the socket contact, interface resistance to
the pin, and the entire pin to the point where
the pin enters the interposer; gaps included.
Capacitively dominate region. This is usually
the lowest measurable frequency. This should
be determined from the measurements done
for the feasibility.
Linear region. This is usually found at higher
frequency ranges. This should be determined
from the measurements done for the feasibility.
Figure 4-1and Figure 4-2 show the proposed methodology for measuring the final electrical
resistance. The methodology requires measuring interposer flush-mounted directly to the
motherboard fixtures, so that the pin shoulder is flush with the motherboard, to get the averaged
jumper resistance, Rjumper. The Rjumper should come from a good statistical average of 30
package fixtures flush mounted to a motherboard fixture. The same measurements are then made
with a package fixture mounted on a supplier’s socket, and both are mounted on a motherboard
fixture; this provides the R
Total. The resistance requirement, RReq, can be calculated for each chain as
will be explained later.
Figure 4-1. Methodology for Measuring Total Electrical Resistance.
Figure 4-2. Methodology for Measuring Electrical Resistance of the Jumper
18 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 19

R
Electrical Requirements
Figure 4-3 shows the resistance test fixtures separately and superimposed. The upper figure is the
package. The next figure is the baseboard. There are 48 daisy chain configurations on resistance test
board. The bottom figure is the two parts superimposed.
the number of pins per each chain and netlist.
Figure 4-3. Electrical Resistance Fixtures Superimposed
Table 4-3 shows these configurations with
mPGA604 Socket 19
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 20

Electrical Requirements
R
20 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 21

R
Electrical Requirements
Table 4-3. Resistance Test Fixture Netlist (Sheet 1 of 2)
DC Endpoints Edgefingers: Hi Edgefingers: Low
Daisy
Chain
1 14 AE2 AE16 A94 A93 A118 A117
2 14 AE29 AE16 A136 A135 A118 A117
3 16 AD1 AD16 A92 A91 A116 A117
4 14 AD30 AD16 A138 A137 A116 A117
5 14 AC30 AC16 A96 A95 A114 A117
6 14 AC30 AC16 A142 A141 A114 A113
7 12 AB4 AB16 A98 A97 A112 A111
8 14 AB29 AB16 A134 A133 A112 A111
9 12 AA5 AA16 A100 A99 A110 A109
10 12 AA28 AA16 A132 A131 A110 A109
11 10 Y6 Y16 A102 A101 A108 A107
12 10 Y25 Y16 A130 A129 A108 A107
13 10 AC1 N1 A90 A89 A46 A45
14 12 B1 N1 A64 A63 A46 A45
15 10 AC2 N2 A88 A87 A48 A47
16 12 B2 N2 A66 A65 A48 A47
17 10 AB3 N3 A86 A85 A50 A49
18 10 C3 N3 A68 A67 A50 A49
19 8 AA4 N4 A84 A83 A52 A51
20 10 D4 N4 A70 A69 A52 A51
21 16 E5 Y5 A72 A71 A120 A119
22 14 F6 W7 A74 A73 A104 A103
23 14 F7 W7 A76 A75 A104 A103
24 14 F8 W9 A78 A77 A106 A105
25 12 G9 W9 A82 A81 A106 A105
26 16 A1 A16 A62 A61 A42 A41
27 14 A30 A16 A18 A17 A42 A41
28 14 B3 B16 A60 A59 A40 A39
29 14 B30 B16 A14 A13 A40 A39
30 12 C4 C16 A58 A57 A38 A37
31 14 C29 C16 A20 A19 A38 A37
32 12 D5 D16 A56 A55 A36 A35
33 12 D28 D16 A22 A21 A36 A35
34 10 E6 E16 A54 A53 A44 A43
35 10 E25 E16 A24 A23 A44 A43
36 14 F9 F23 A80 A79 A28 A27
37 14 W23 F23 A128 A127 A28 A27
38 14 F24 W24 A26 A25 A126 A125
39 14 F25 W24 A2 A1 A126 A125
40 16 E26 Y26 A4 A3 A124 A123
41 16 E27 Y26 A6 A5 A124 A123
# of ©
per chain
Hi Low +I +V -V -I
mPGA604 Socket 21
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 22

Electrical Requirements
Table 4-3. Resistance Test Fixture Netlist (Sheet 2 of 2)
DC Endpoints Edgefingers: Hi Edgefingers: Low
R
Daisy
Chain
42 16 E28 Y28 A8 A7 A122 A121
43 10 D29 N29 A10 A9 A34 A33
44 8 AA29 N29 A146 A145 A34 A33
45 10 C30 N30 A12 A11 A32 A31
46 10 AB30 N30 A144 A143 A32 A31
47 12 A31 N31 A16 A15 A30 A29
48 12 AD31 N31 A140 A139 A30 A29
# of ©
per chain
Hi Low +I +V -V -I
4.2 Determination of Maximum Electrical Resistance
This section provides a guideline for the instruments used to take the measurements.
Note: The instrument selection should consider the guidelines in EIA 364-23A.
1. These measurements use a 4-wire technique, where the instruments provide two separate
circuits. One is a precision current source to deliver the test current. The other is a precision
voltmeter circuit to measure the voltage drop between the desired points.
2. These separate circuits can be contained within one instrument, such as a high quality micro-
ohmmeter, a stand-alone current source and voltmeter, or the circuits of a data acquisition
system.
3. Measurement accuracy in Ω is specified as ± 0.1% of reading, or ± 0.1 mΩ, whichever is
greater. The vendor is responsible for demonstrating that their instrument(s) can meet this
accuracy.
4. Automation of the measurements can be implemented by scanning the chains through the
edge or cable test connector using a switch matrix. The matrix can be operated by hand, or
through software.
5. Measure R
6. Measure R
for each daisy chain of “package + socket + motherboard” unit.
Total
for each daisy chain of 30 “package + motherboard” units. Calculate
jumper
for each daisy chain (There is 30 data for each daisy chain).
7. For each socket unit, calculate
is the average contact resistance for socket pin.
R
Req
22 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 23

R
Electrical Requirements
4.3 Inductance
The bottom fixture for the inductance measurement is a ground plane on the secondary side of the
motherboard with all pins grounded. The component side of the socket PCB does not contain a
plane. The top fixture is the package, which contains pins that will connect to the socket.
shows the inductance measurement fixture cross-section and the inductance measurement
methodology. The first figure shows the entire assembly. The second figure shows the assembly
without the socket; the socket-seating plane of the package is directly mounted to the component
side of the socket PCB. This is used to calibrate out the fixture contribution. The materials for the
fixture must match the materials used in the processor. Note the probe pad features exist on the
topside of the top fixture, and the shorting plane exists only on the bottom side of the bottom fixture.
Figure 4-5 presents the inductance and capacitance fixture design.
Figure 4-4. Inductance Measurement Fixture Cross-Section
Figure 4-4
Figure 4-5. Inductance and Capacitance Fixture
mPGA604 Socket 23
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 24

Electrical Requirements
4.3.1 Design Procedure for Inductance Measurements
The measurement equipment required to perform the validation is:
• Equipment - HP8753D Vector Network Analyzer or equivalent.
• Robust Probe Station (GTL4040) or equivalent.
• Probes - GS1250 & GSG1250 Air-Co-Planar or equivalent.
• Calibration – Cascade Calibration Substrates or equivalent.
• Measurement objects - Sockets, Motherboards.
Measurement Steps:
1. Equipment Setup:
a. Cables should be connected to the network analyzer and to the probes using the
appropriate torque wrench to ensure consistent data collection every time the
measurement is performed.
2. Set VNA:
a. Bandwidth = 300KHz – 3GHz with 801 points.
b. Averaging Factor = 16.
R
3. Perform Open/Short/Load Calibration:
a. Calibration should be performed at the start of any measurement session.
b. Create Calibration Kit if necessary for 1
st
time.
c. Do not perform port extension after calibration.
4. Check to ensure calibration successfully performed.
5. Measure the inductance of the socket mounted to the motherboard fixture by probing the
locations on the PGA Adapter and socket assembly:
a. Call this
L
.
assemblysocket
b. Export data into MDS/ADS or (capture data at frequency specified in item 6 of
Table 4-1).
6. Measure the inductance of the PGA Adapter by probing on the pads. Call this
L :
sandwich
a. Measure 30 units.
b. The test board for 30 units must be chosen from different lots. Use 5 different lots, 6
units from each lot.
c. Export data into MDS/ADS or (capture data at frequency specified in item 6
Table 4-1).
of
d. Calculate
L .
sandwich
e. For each socket unit, calculate
assemblysocketsocket
LLL −=
sandwich
It means
L will be subtracted from each
sandwich
L and the result will be
assemblysocket
compared with spec value for each individual socket unit.
24 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 25

R
Electrical Requirements
4.3.2 Correlation of Measurement and Model Data Inductance
To correlate the measurement and model data for loop inductance, one unit of measured socket
assembly (socket and shorted test fixture) and one unit of measured sandwich (shorted test fixture)
will be chosen for cross sectioning. Both units will be modeled based on data from cross sectioning
using Ansoft* 3D. The sandwich inductance will be subtracted from socket assembly inductance for
both measured and modeled data. This procedure results in loop inductance for socket contact. This
final result can be compared with the loop inductance from the supplier model for the socket. If
there is any difference between them, it will be called the de-embedded correction factor. Adding
the test board to the socket and then eliminating the contribution of the fixture creates this correction
factor because inductance is not linear.
4.4 Pin-to-Pin Capacitance
Pin-to-pin capacitance shall be measured using configuration 4, with the motherboard not connected
and only the measurements with the package mounted on the socket will be taken. Capture data at
frequency specified in item 5 of
Table 4-1.
4.5 Dielectric Withstand Voltage
No disruptive discharge or leakage greater than 0.5 mA is allowed when subjected to 360 V RMS.
The sockets shall be tested according to EIA-364, Test Procedure 20A, Method 1. The sockets shall
be tested unmounted and unmated. Barometric pressure shall be equivalent to Sea Level. The
sample size is 25 contact-to-contact pairs on each of 4 sockets. The contacts shall be randomly
chosen.
4.6 Insulation Resistance
The Insulation Resistance shall be greater than 800 M Ohm when subjected to 500 V DC. The
sockets shall be tested according to EIA-364, Test Procedure 21. The sockets shall be tested
unmated and unmounted. The sample size is 25 contact-to-contact pairs on each of 4 sockets. The
contacts shall be randomly chosen.
4.7 Contact Current Rating
Measure and record the temperature rise when the socket is subjected to rated current of 0.8A. The
sockets shall be tested according to EIA-364, Test Procedure 70A, Test Method 1. The sockets shall
be mounted on a test-board and mated with a package so those 370 pins are connected in series. The
recommended Test-board is the FSETV4 Rev 1 and the recommended package is FSETV5 Rev 1.
The wiring list is shown below. Mount the thermocouple as near to contact N3 or N 7 as possible.
Short the daisy chains by means of the edge fingers if possible. Sample size is one socket.
mPGA604 Socket 25
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 26

Electrical Requirements
Table 4-4. Net list for FSETV4 Rev 1 Edge Fingers
Edge Fingers
+I: A61 Jumpers:
-I: A145 A85-A89 A45-A17 A135-A141
A87-A95 A15-A13 A139-A143
A49-A47 A131-A137 A3-A1
A101-A99 A11-A9
A59-A57 A129-A133 A7-A5
R
26 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 27

R
5 Environmental Requirements
Design, including materials, shall be consistent with the manufacture of units that meet the
following environmental reference points.
The reliability targets in this section are based on the expected field use environment for a desktop
product. The test sequence for new sockets will be developed using the knowledge-based reliability
evaluation methodology, which is acceleration factor dependent. A simplified process flow of this
methodology can be seen in
Figure 5-1. Flow Chart of Knowledge-Based Reliability Evaluation Methodology
Figure 5-1.
A detailed description of this methodology can be found at:
http://developer.intel.com/design/packtech/245162.htm.
The use environment expectations assumed are for desktop processors, based on an expected life of
7 years, are listed in
Table 5-1. The target failure rates are <1% at 7 years (and <3% at 10 years).
Table 5-1. Use Conditions Environment
Speculative Stress Condition 7 Year Life Expectation
Temperature Cycle 1500 cycles with a mean ΔT = 40
THB / HAST 62,000 hrs at 30°C, 85%RH
BAKE 62,000 hrs at 100°C
Power Cycle 7,500 cycles
O
C
For additional information on mechanical shock and vibration testing conditions, refer to the
Thermal Mechanical Design Guidelines.
mPGA604 Socket 27
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 28

Environmental Requirements
5.1 Mixed Flowing Gas
Test will be defined in a future revision of this document.
5.2 Solvent Resistance
Requirement: No damage to ink markings if applicable. EIA 364-11A
5.3 Durability
Use per EIA-364, test procedure 09. Measure contact resistance when mated in 1st and 30th cycles.
The package should be removed at the end of each de-actuation cycle and reinserted into the socket.
The socket’s pick-and-place cover must be able to be inserted and removed from the socket at least
30 times.
R
28 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 29

R
6 Validation Testing Requirements
This section of the document outlines the tests that must be successfully completed in order for the
supplier’s socket to pass the design guidelines validations. It provides the test plan and procedure
required for validation.
6.1 Applicable Documents
• EIA-364-C
• Applicable processor Datasheet*
• Applicable processor Thermal Design Guidelines Documents*
Note: *For details on ordering this document, contact your Intel field sales representative.
6.2 Testing Facility
Testing will be performed by Intel’s designated test facility.
6.3 Funding
Socket supplier will fund socket validation testing .for their socket. Any additional testing that is
required due to design modifications will also be at the expense of the supplier.
6.4 Socket Design Verification
At the earliest possible date, a detailed drawing of the socket supplier's mPGA604 Socket must be
provided to Intel for review. This drawing should include all of the features called out in this design
guideline (marking, pinout, cam location, date code location and explanation, etc.) as well as
dimensional and board layout information. This drawing will be used to confirm compliance to this
design guideline.
6.5 Reporting
Test reports of the socket validation testing will be provided directly from the independent test
facility to Intel. Intel will also be given access to contact the test facility directly to obtain socket
validation status, explanation of test results and recommendations based on the test results.
6.6 Process Changes
Any significant change to the Socket will require submission of a detailed explanation of the change
at least 60 days prior to the planned implementation. Intel will review the modification and establish
the necessary re-validation procedure that the socket must pass. Any testing that is required MUST
be completed before the change is implemented.
mPGA604 Socket 29
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 30

Validation Testing Requirements
Typical examples of significant changes include, but are not limited to, the following: Plastic
material changes including base material or color; contact changes including base material, plating
material or thickness; and design modifications.
6.7 Quality Assurance Requirements
The OEM’s will work with the socket supplier(s) they choose to ensure socket quality.
6.8 Socket Test Plan
6.8.1 Submission of an mPGA604 Socket for Validation Testing
The socket supplier’s mPGA604 socket will be sent to Intel’s independent test facility for socket
validation testing. The sockets submitted must be per the drawing required in
Section 6.11 and 6.12 for production lot definition and number of samples required for validation
testing.
Section 6.4. Refer to
6.9 Mechanical Samples
R
A mechanical sample of mPGA604 Socket, package, and heat sink (or suitable mockups that
approximate size and mass of the planned heat sink) will be used during the mated socket validation
testing. The maximum mass for mPGA604 Socket package heat sink is recommended as (but not
limited to) 450g with the stipulation that the requirements of
related documentation for further information on heat sinks, thermal solutions and mechanical
support.
Section 3.1 be met. See data sheet and
6.10 Socket Validation Notification
Upon completion of the testing and receipt of test data, Intel and/or the Intel designated test facility
will prepare a summary report for the socket supplier and Intel that will provide notification as to
whether the socket has passed or failed socket validation testing
6.11 Production Lot Definition
A production lot is defined as a separate process run through the major operations including
modeling, contact stamping, contact plating and assembly. These lots should be produced on
separate shifts or days of the week. Lot identification marking needs to be provided to Intel as
verification of this process.
6.12 Socket Validation
Socket validation must meet or exceed all guidelines called out in this spec which include: Visual
Inspection, CTF Dimensional Verification, Electrical Resistance, Loop Inductance, Pin to Pin
Capacitance, Contact Current Rating, Dielectric Withstand Voltage, Insulation, Durability, Porosity,
Plating Thickness, Solvent Resistance (If Applicable), Solderability (Applicable for leaded sockets),
Post Reliability Visual and use conditions. The use conditions target failure rates are <1% at 7 years
and <3% at 10 years. Statistical sample sizes, taken randomly from multiple lots, for each test is
required.
30 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 31

R
7 Safety Requirements
Design, including materials, shall be consistent with the manufacture of units that meet the
following safety standards:
• UL 1950 most current editions.
• CSA 950 most current edition.
• EN60 950 most current edition and amendments.
• IEC60 950 most current edition and amendments.
§
mPGA604 Socket 31
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 32

Safety Requirements
R
32 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 33

R
8 Documentation Requirements
The socket supplier shall provide Intel with the following documentation:
• Multi-Line Coupled SPICE models for socket.
• Product design guidelines incorporating the requirements of these design guidelines.
• Recommended board layout guidelines for the socket consistent with low cost, high volume
printed circuit board technology.
The test facility shall provide Intel and the supplier with the following document:
• Validation Testing and Test Report supporting successful compliance with these design
guidelines.
§
mPGA604 Socket 33
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 34

Documentation Requirements
R
34 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 35

R
9 Mechanical Drawings
These drawings refer to the mPGA604 socket.
Note: Intel reserves the right to make changes and modifications to the design as necessary.
Note: Figures may not be to scale.
Figure 9-1. mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4)
mPGA604 Socket 35
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 36

Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-2. mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4)
R
36 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 37

R
Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-3. mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4)
mPGA604 Socket 37
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 38

Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-4. mPGA604 Socket Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4)
R
38 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 39

R
Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-5. 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 1 of 6)
mPGA604 Socket 39
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 40

Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-6. 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 2 of 6)
R
40 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 41

R
Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-7. 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 3 of 6)
mPGA604 Socket 41
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 42

Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-8. 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing OLGA Keepout (Sheet 4 of 6)
R
42 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 43

R
Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-9. 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing FCBGA2 Keepout (Sheet 5 of 6)
mPGA604 Socket 43
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 44

Mechanical Drawings
Figure 9-10. 603-Pin Interposer Assembly Drawing (Sheet 6 of 6)
R
§
44 mPGA604 Socket
Mechanical Design Guide
Page 45

R
Mechanical Drawings
mPGA604 Socket 45
Mechanical Design Guide
 Loading...
Loading...