Page 1

i
EtherExpress™ PRO/100 Mobile
Adapter 16-bit PC Card
-
With Integrated 100 Mbps Transceiver
User’s Guide
How to Use This Manual
This User’s Guide contains the latest and most complete information
available at press time on the installation and operation of the
PRO/100 PC Card. It is designed to help both new and experienced
network users install and configure the Intel product in the shortest
time possible.
Overview of the Installation Process
For an overview of the installation process, see the Quick Start Card
and Chapters 1 and 2 in this User’s Guide. For technical details on
configuration issues see Chapter 3, Configuration Reference.
How to Find More Infor mation
Use the Table of Contents, Index, and page and text headings in this
User’s Guide to find what you need. Check the README file on the
Intel Network Driver diskette. For updated drivers, access the Intel
support website at:
http://support.intel.com
See Appendix A for additional support information.
Page 2

ii
Copyright © 1997 Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel Corporation
5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway
Hillsboro, OR 97124-6497
Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this
guide. Nor does Intel make any commitment to update the information
contained herein.
*
Other product and corporate names may be trademarks of other companies
and are used only for explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to
infringe.
Second edition May 1997 668562-002
Page 3

iii
Contents
Hardware Installation.............................................. 7
Before Installing Hardware .................................................................. 7
What to Do Next ................................................................................. 11
Software Installation ............................................. 13
Microsoft Windows 95........................................................................ 14
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 ................................................................ 1 6
Microsoft Windows NT 3.51 .............................................................. 16
Microsoft MS-DOS............................................................................. 17
IBM OS/2 and OS/2 Warp .................................................................. 17
Microsoft Windows 3.x (including Windows f or Workgroups) ........ 17
Running the Intel Installation Program (Windows 3.x including
Windows for Wo rkgroups) ............................................................. 17
Completing the Installation ................................................................ 19
Alphabetical Reference ...................................................................... 20
Artisoft LANtastic version 6.0 ........................................................... 21
AT&T StarGROUP LAN Manager version 2.1a ............................... 21
Banyan VINES version 6.0................................................................. 22
DEC PATHWORKS versions 5.x or 6.x ............................................ 2 3
FTP Software LANWatch................................................................... 26
FTP Software PC/TCP........................................................................ 2 8
Generic Installation ............................................................................ 33
HP LAN Manager ............................................................................... 3 3
IBM Local Area Network Support Program ...................................... 3 3
IBM OS/2 and OS/2 Warp .................................................................. 36
IBM PC LAN and IBM DOS LAN Requester .................................. 36
Manual Installation ............................................................................. 37
Microsoft LAN Manager .................................................................... 37
Microsoft Windows for Workgroups.................................................. 4 0
Page 4

iv
CONTENTS
Novell NetWare ................................................................................... 46
NetWare Requester for OS/2 .............................................................. 47
SunSoft PC-NFS (version 3.5) ........................................................... 50
Ungermann-Bass Net/One for DOS and OS/2 .................................. 52
Wollongong PathWay Access for DOS .............................................. 5 4
Configuration Reference ...................................... 57
Who Should Consult This Chapter .................................................... 57
PRO/100 PC Card Features ................................................................ 5 8
Windows for Workgroups Using the ODI Driver with NetWar e
as Secondary Network.................................................................... 66
Windows 95 and Windows NT Driver Parameters Reference .......... 68
Windows 3.x Driver Parameters......................................................... 7 2
ODI Settings (for drivers M16AODI.COM and M16AODI.OS2) .... 73
NDIS 2.0.1 Settings (for drivers M16ANDIS.EXE and
M16ANDIS.OS2) ........................................................................... 75
Novell Server Driver Settings (for driver M16AODI.LAN) ............. 78
Packet Driver Settings (for driver M16APD.COM) .......................... 78
Diagnostic Test Utility Settings (M16ATEST.EXE) ......................... 79
Keyword Alphabetical Reference....................................................... 8 0
Troubleshooting .................................................... 85
LED Indicators .................................................................................... 86
Diagnostic Self Test ............................................................................ 8 7
Error Messages.................................................................................... 89
Windows 95 Troubleshooting ............................................................. 92
Microsoft Windows 3.x Troubleshooting .......................................... 9 6
Network Operating System Troubleshooting under Windows 3.x . 105
Artisoft LANtastic ............................................................................ 105
DEC Pathworks ................................................................................. 106
Windows for Workgroups ................................................................. 107
Novell NetWare ................................................................................. 111
Computer-Specific Troubleshooting ................................................ 112
General Troubleshooting Checklist ................................................. 11 9
Intel Automated Customer Support .................. 121
Page 5

v
CONTENTS
Specifications...................................................... 123
Media Interface Specifications ......................................................... 123
General Specifications ...................................................................... 124
Compatibility .................................................................................... 125
Technical Specifications ................................................................... 125
Limited Lifetime Warranty................................. 127
Network Software License Agreement.............. 131
Regulatory Agency Notices ............................... 135
Index..................................................................... 137
Page 6

vi
CONTENTS
Page 7

7
Follow the instructions in this chapter to install PRO/100 PC Card
hardware and network cabling.
See Chapter 2, Software Installation for instructions on how to
install network software using the Intel Installation Program.
Model Number
MBLA1600
This model provides access to both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX
networks with a single adapter cable, and detects 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps
network speed. Note that 100 Mbps operation requires Category 5
(data grade) unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling.
Before Installing Hardware
Check Package Contents
Use the following list to check the package contents:
• PRO/100 PC Card
• A network adapter cable with a 15-pin PC Card connector at one
end and a RJ-45 connector at the other (for 100Base-TX or
10Base-T Ethernet connectivity)
• Software on two 3.5-inch diskettes
• Quick Install Card
• User’s Guide
• Product registration card (in this guide)
• Protective adapter case
Chapter 1
Hardware Installation
Page 8

8
CHAPTER 1
Note
Please fill out the Product Registration Card and mail it
immediately to the Intel office indicated on the card.
Verify Other Required Equipment
To install the PRO/100 PC Card, you need the following:
1 An Ethernet local area network running at 10 or 100 Mbps and a
network operating system supported by the PRO/100 PC Card.
See Chapter 2, Software Installation for a list of the network
operating systems supported.
Note
Since the PRO/100 PC Card, automatically detects the
speed of the network to which it is connected, it may be
safely connected to either a 100Base-TX or 10Base-T
network, as specified in items 2 and 3 below.
2 For connection to a 100Base-TX Ethernet network, a Category 5
(data grade) unshielded twisted pair (UTP) network cable
terminating in a male RJ-45 connector.
Note
For 100 Mbps connectivity, network cable must be
Category 5 (data grade) unshielded twisted pair (UTP).
Category 3 (voice grade) wiring is reliable for 10 Mbps,
however Intel recommends using Category 5 wiring
whenever possible.
3 For connection to a 10Base-T twisted pair Ethernet network, a
network cable terminating in a male RJ-45 connector and
connected to a 10 Mbps hub or switch.
Determine System Requirements
During installation of the PRO/100 PC Card hardware, power to the
computer may be ON or OFF. For best results, the computer should be
ON and your standard operating software should be loaded. If
configured to do so, your system will detect the PRO/100 PC Card. For
details on how to install driver software for your particular
environment, see Chapter 2, Software Installation.
Page 9
9
Hardware Installation
Installing the Hardware
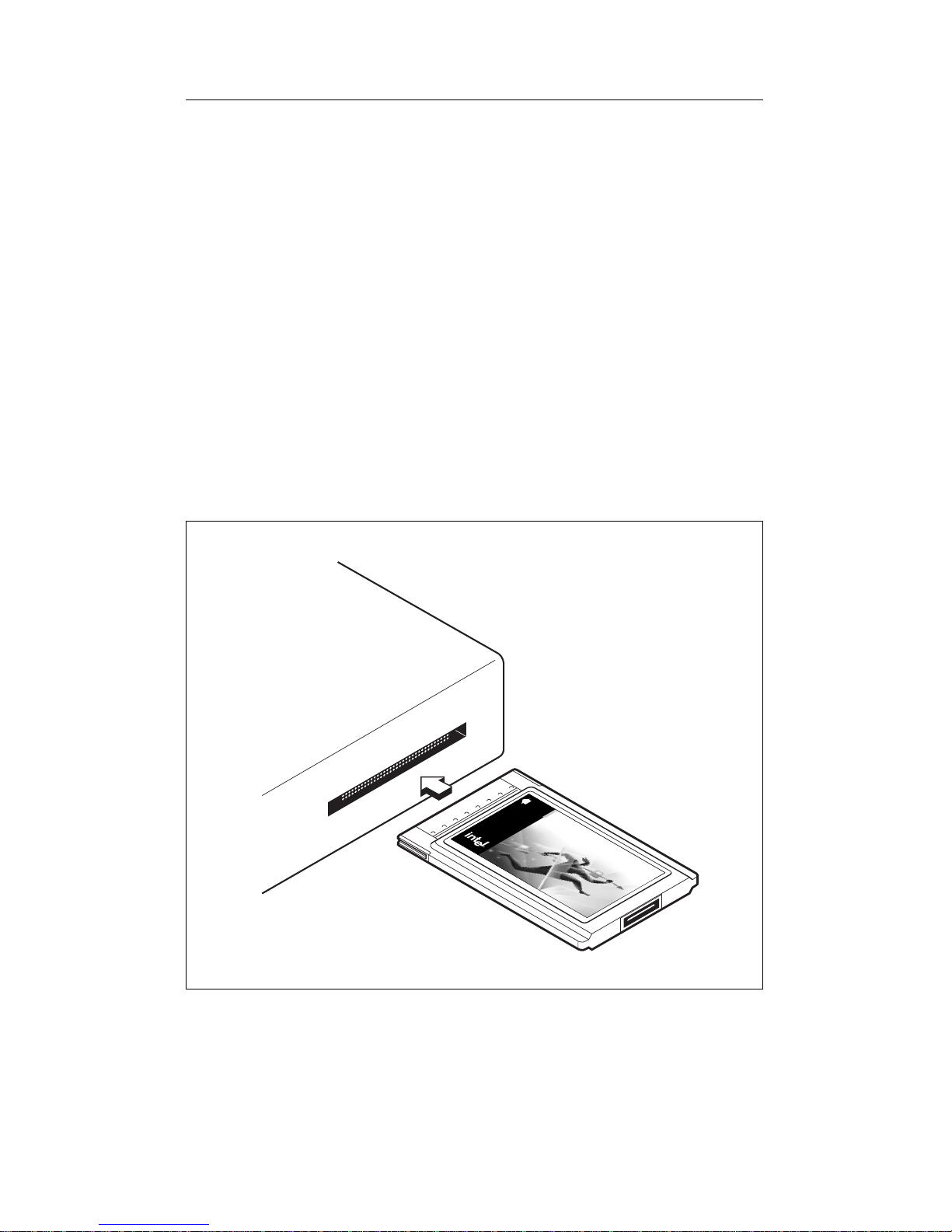
Insert the PRO/100 PC Card
1 Grasp the PRO/100 PC Card by the edges with the Intel label
facing upward and the wide PC Card connector next to the insert
slot.
2 Insert the PRO/100 PC Card into a PC Card slot and push it in until
it is firmly seated (the Intel Installation Program will determine
what slot the PRO/100 PC Card is in and configure accordingly).
Inserting the PRO/100 PC Card into the Computer
Removing the PRO/100 PC Card
Follow the PC card removal instructions specified in the documentation
for your computer.
The PRO/100 PC Card hardware is compatible with all type II and III
PC Card slots (16-bit or 32-bit). Installation and removal procedures
may vary on different computers. It can safely install in a CardBus, 32bit slot.
16 bit
PC Card
Intel EtherExpress
™
PRO/100 Mobile Adapter
Page 10
10
CHAPTER 1
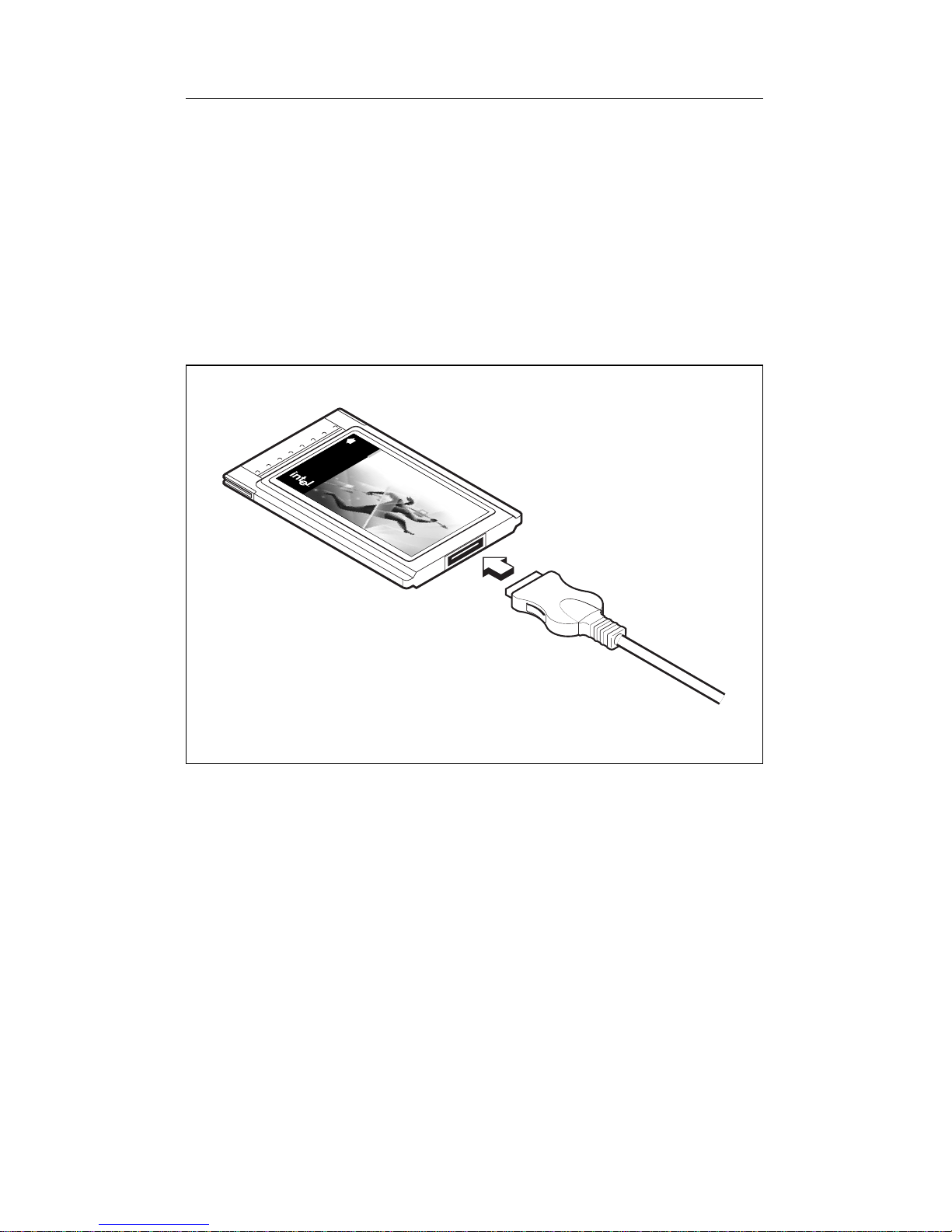
Connecting the 10Base-T/100Base-TX Adapter
Cable to the PRO/100 PC Card
• With the Intel logo facing up, attach the 15-pin connector at the
end of the adapter cable to the mating connector on the end of the
PRO/100 PC Card. Press the cable connector gently into the
connector on the PRO/100 PC Card until it clicks into place. Do
not force the connection.
Connecting the 10Base-T/100Base-TX Adapter Cable to the PRO/100
PC Card
16 bit
PC Card
Intel EtherExpress
™
PRO/100 Mobile Adapter
Page 11
11
Hardware Installation
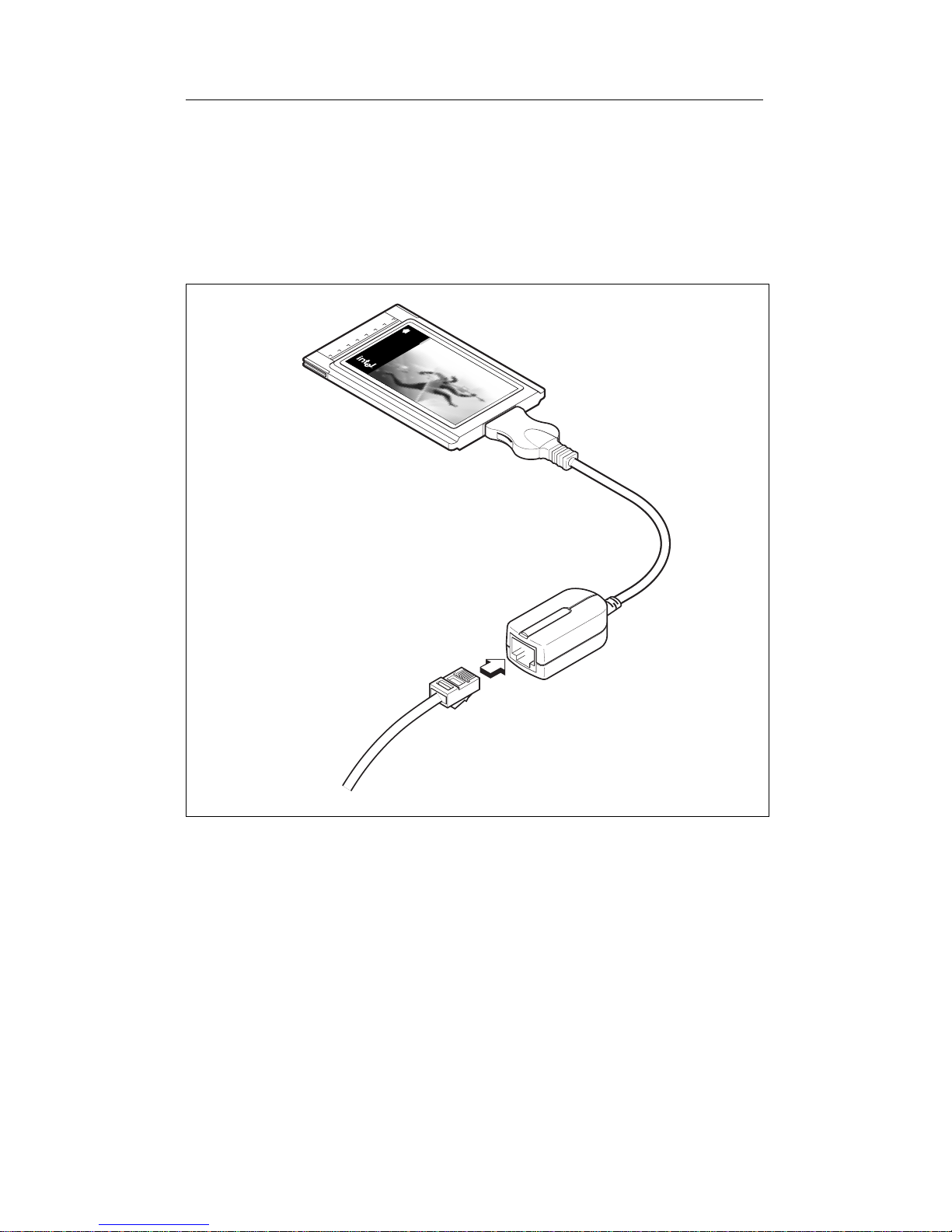
Connecting the Network Cable to the PRO/100 PC
Card
Model PRO/100 PC Card (100 or 10 Mbps Ethernet network)
• Plug the network cable into the female RJ-45 connector.
Connecting to the 10Base-T/100Base-TX Adapter Module
Note
The PRO/100 PC Card supports both 10 and 100 Mbps,
and auto-detects the network speed.
What to Do Next
After installing the hardware and connecting cables, proceed to
Chapter 2. Software Installation. You will need the Intel Installation
Disk (for Windows 3.1 only) and Network Drivers Disk.
16 bit
PC Card
Intel EtherExpress
™
PRO/100 Mobile Adapter
Page 12

12
CHAPTER 1
Page 13

13
This chapter provides driver installation instructions for the following
operating environments, in the order listed:
• Windows 95
• Windows NT
• MS-DOS
• IBM OS/2
• Windows 3.x (including Windows for Workgroups) using the
Intel Installation Program
These instructions assume a first-time installation of the PRO/100 PC
Card. For additional technical information, see Chapter 3,
Configuration Reference and Chapter 4, Troubleshooting.
Chapter 2
Software Installation
Page 14

14
CHAPTER 2
Microsoft Windows 95
Instructions are provided here for "Plug and Play" installation. For
detailed technical information see Windows 95 headings in Chapter 3,
Configuration Reference and Chapter 4, Troubleshooting.
NDIS 3 Driver
1 Insert the PRO/100 PC Card into a PC Card slot.
2 If Windows 95 detects the PRO/100 PC Card, proceed to step 3.
If it does not, click on the PC Card (PCMCIA) icon in the
Control Panel to enable PC Card services, then go to step 3.
3 If prompted for a manufacturer’s disk, insert Disk 2, Network
Drivers Disk. Windows will identify the product as a “PRO/100
Mobile Adapter 16.”
4 Complete the installation process as prompted by the Windows
95 software.
Technical Note
For best results with autodetection, do not load DOS real
mode PCMCIA Card and Socket Services and do not use
EMM386 (or if needed, do not use the HIGHSCAN keyword). If installing from a SCSI CD-ROM through a PC
Card, copy the \WIN95 directory from the CD-ROM to your
hard disk (35 MB required) and install from the hard disk.
For a more detailed discussion of these issues, see Chapter
4, Troubleshooting.
5 If the automated (autodetection) installation procedure is not
successful, proceed to the following section: “Verification and
Troubleshooting.”
Verification and Troubleshooting
1 To verify successful installation, double-click the System icon in
the Control Panel, choose the Device Manager tab in the System
Properties window, and look for Intel EtherExpress PRO/100
Mobile PC Card under Network adapters.
• If the PRO/100 Mobile 16 icon has no X or circled exclamation point on top of it, the installation has been successful.
Click OK to close the Network window, then restart the
computer when prompted. If you wish to verify configuration
Page 15

15
Software Installation
of a NetWare Client, proceed to the heading Verification of
NetWare Client Configuration.
• An X or a circled exclamation point on top of the PRO/100
Mobile Adapter 16 icon indicates a problem. Select PRO/100
Mobile Adapter 16 and click Properties to see an explanation.
Then continue with step 2 below.
2 To review the installed Adapter configuration, double-click the
Network icon in the Control Panel.
3 Select the PRO/100 Mobile Adapter 16 component and click
Properties.
4 From the Properties window, select the Advanced tab.
5 Confirm that the Properties and their associated Values are
correct and that there are no conflicts with other installed
devices. (For a technical discussion of these settings, see
Chapter 3, Configuration Reference in this User’s Guide. For
more detailed troubleshooting information, see Chapter 4,
Troubleshooting.)
Verification of NetWare Client Configuration
1 After installing the PRO/100 Mobile PC Card driver and
verifying the installation as described above, check for configuration of the NetWare Client by clicking on the Network icon.
You should see both “Client for Microsoft” and “Client for
Novell” listed. The installation process includes configuration
for a NetWare Client as a default. If “Client for Novell” does not
appear, you can configure the NetWare Client with the following steps:
2 In the Control Panel, double-click the Network icon.
3 From the Configuration tab in the Network window, click Add.
4 From the Select Network Component Type window, select
Client and click Add.
5 Under Manufacturers in the Select Network Client window,
select Microsoft.
6 In the Network Clients window, select Client for NetWare
Networks.
7 Click OK (you will be returned to the Network window).
Page 16

16
CHAPTER 2
8 From the Configuration tab in the Network window, click Add.
9 From the Select Network Component Type window, select
Protocol and click Add.
10 Select Microsoft as the manufacturer and IPX/SPX-compatible
Protocol under Network Protocols, then click OK to return to the
Network window.
11 Click OK to close the Network window, then restart the com-
puter when prompted.
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
NDIS 3 Driver
If your system is running Windows NT 4.0, proceed as follows:
1 Insert the PRO/100 PC Card into a PC Card slot.
2 Select Control Panel, double-click the Network icon. Click the
Adapters tab and then Add.
3 Insert Disk 2, Network Drivers Disk and click Have Disk.
Specify A:\ for diskette and click OK.
4 Select “EtherExpress PRO/100 PC Card Adapter 16.”
5 Click Close when the drivers have been copied.
6 Restart your computer when prompted by NT.
Microsoft Windows NT 3.51
NDIS 3 Driver
If your system is running Windows NT 3.51, proceed as follows:
1 Insert the PRO/100 PC Card into a PC Card slot.
2 Select Control Panel, Network, Add Adapter, and Other.
3 When prompted for a manufacturer’s disk, insert Disk 2,
Network Drivers Disk.
4 Select “EtherExpress PRO/100 PC Card Adapter 16.”
Page 17

17
Software Installation
5 Complete the installation process as prompted by the Windows
NT software.
Microsoft MS-DOS
For MS-DOS systems, see “Manual Installation” in the alphabetical
listing under the heading “Completing the Installation” later in this
chapter.
IBM OS/2 and OS/2 Warp
To install drivers on systems running IBM OS/2 and OS/2 Warp,
follow the instructions under Microsoft LAN Manager, Novell
NetWare Requester, or Ungermann-Bass Net/One in the alphabetical
listing under the heading “Completing the Installation” later in this
chapter.
Microsoft Windows 3.x (including Windows for
Workgroups)
Run the Intel Installation Program (as described under the next
heading) if you are using Microsoft Windows 3.1 or Windows for
Workgroups 3.11
Running the Intel Installation Program
(Windows 3.x including Windows for
Workgroups)
To install under Windows or Windows for Workgroups using the
Intel Installation Program, insert Disk 1, Installation Disk, into your
disk drive, and proceed as follows (substitute the correct drive letter for
your system):
1 From the Program Manager, choose File, then Run. In the
Command Line box, type the following:
A:SETUP
2 Press Enter or click OK.
Page 18

18
CHAPTER 2
3 Select your network operating system from the list displayed and
click OK.
4 Follow the on-screen instructions. Note the following variations
for NetWare and other network operating systems:
Novell NetWare Installation
With Novell NetWare highlighted, click the OK button. Intel
provides all software necessary to configure your NetWare
client workstation. Upon completion, the Installation Program
will reboot your system. When your system comes back up, log
in to the network.
Note
The NetWare VLM shell is used to connect to your NetWare
server. The Intel Installation Program will decompress and
configure the necessary files. If you do not plan to use the
Installation Program, see “Manual Installation” in the
alphabetical section of this chapter for instructions on how
to decompress and load the NetWare VLM files.
If you need NETX shell support, contact your System
Administrator.
Installation of Other Network Operating Systems
For listed network operating systems other than Novell NetWare, highlight your network operating system and click the
OK button. The Intel installation software will analyze your
system and create a custom Intel Network Drivers (device
drivers) Disk.
5 Once you have completed the steps prompted by the Intel
Installation Program, exit the program and find your network
operating system in this chapter of the User’s Guide, using the
alphabetical listing under the heading “Installing Network
Software.” Follow the procedures indicated there to complete
the installation.
The Installation Program will modify your AUTOEXEC.BAT,
CONFIG.SYS, and network configuration files to match the optimum
configuration for your system.
Page 19

19
Software Installation
For detailed technical information on configuration files and settings,
see Chapter 3, Configuration Reference and Chapter 4,
Troubleshooting.
Completing the Installation
The instructions in the rest of this chapter should be used only in the
following circumstances (they do not apply to Windows 95 or
Windows NT environments):
• To complete the installation of network software under Windows 3.x (including Windows for Workgroups) after you have
run the Intel Installation Program: Find your network operating
system in the alphabetical listing that follows.
• To install software for non-Windows operating systems not
supported by the Intel Installation Program (for example, OS/2
or MS-DOS without Windows): Find your network operating
system in the alphabetical listing that follows, or see the headings “Generic Installation” and “Manual Installation” in the
same listing.
• To install and configure Windows 3.x drivers manually, without
running the Intel Installation Program: See the heading “Manual
Installation” in the alphabetical listing that follows.
Use the Modified Intel Network Drivers Disk
When prompted for a device driver or manufacturer’s disk
by your network operating system install procedure, use
Intel Disk 2, Network Drivers Disk.
Page 20

20
CHAPTER 2
Alphabetical Reference
The following section is organized in alphabetical order by network
operating system vendor. Unless otherwise indicated, these instructions
are designed to be used under Windows 3.x (including Windows for
Workgroups) and with the Intel Installation Program. They assume a
first-time installation of client software on a workstation, using the
configuration values set by the Intel Installation Program or, when the
Installation Program is not used, using the default values listed in
Chapter 3, Configuration Reference.
The PRO/100 PC Card supports ODI, NDIS 2.01, and packet drivers
under Windows 3.x. To determine which of these drivers you need for
your networking environment, consult your network administrator or
network documentation.
Page 21

21
Software Installation
Artisoft LANtastic version 6.0
NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Artisoft LANtastic from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Run the Artisoft LANtastic 6.0 “install” program. Specify
C:\LANTASTI as the destination directory.
5 At the “Select network adapter” screen, choose “NDIS Support for
Network Adapters.”
6 When prompted for the “manufacturer’s driver disk” on the “Enter
NDIS driver directory” screen, insert the Intel Network Drivers
Disk (Disk 2).
7 Complete the Artisoft installation.
8 Reboot the computer and start LANtastic.
AT&T StarGROUP LAN Manager version 2.1a
NDIS 2.0 Driver
See Microsoft LAN Manager.
Page 22

22
CHAPTER 2
Banyan VINES version 6.0
NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Banyan VINES from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation. Note the IRQ value set by the Intel Installation
Program for use in step 10 below. The Installation Program also
creates a \VINES directory on your hard disk.
4 Copy the files from the VINES Master disk into the VINES
directory.
5 Copy the NDIS driver files from \NDIS directory on the VINES
LAN Drivers Disk into the VINES directory.
6 Change to the VINES directory.
7 Type PCCONFIG and select Network Card Settings, followed by
NDIS Ethernet.
8 At the PROTOCOL.INI bindings prompt, type INTELNET.
9 Enter the IRQ value set by the Intel Installation Program (see step
3 above).
10 Press F10 to save and Esc to return to the main menu.
11 Select Login Environment Settings, followed by Default
Communications Driver, followed by NDIS Ethernet.
12 Press Esc to return to the Main Menu and press F10 to save.
13 Reboot the PC.
Page 23

23
Software Installation
DEC PATHWORKS versions 5.x or 6.x
NDIS 2.0 Driver
These instructions are based on PATHWORKS documentation for
configuration of a PC as a client workstation, using a system service
already installed on a LAN Manager server and the LAN Manager
SETUP diskette.
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose DEC PATHWORKS from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation. Note the IRQ value set by the Intel Installation
Program for use in steps 5 and 23 below.
4 Check the README file on your PATHWORKS SETUP disk for
requirements such as lastdrive, setver, etc. You will need 500 K of
free conventional memory and about 1 MB of extended memory
to run PATHWORKS SETUP. Be sure you have a lastdrive
statement in your CONFIG.SYS file (lastdrive=g will work in
most cases).
5 Use a text editor to modify the file A:\NDIS\PI.TPL on the
PATHWORKS SETUP disk, as follows (A:\NDIS is a hidden
directory. You can access it by typing CD A:\NDIS):
Change the line (remove the semicolon)
;NI_IRQ = (irq value from step 3)
to read
NI_IRQ = (irq value from step 3)
The NI_IRQ value must be the same as the interrupt value you
will use for the Intel adapter.
Page 24

24
CHAPTER 2
6 Run the SETUP program from the PATHWORKS SETUP disk
for LAN Manager.
7 Choose Configure PC.
8 Choose Network.
9 Select DECnet as transport.
10 When prompted to choose a network adapter, choose “Other.”
11 Specify “Intel” as the Adapter Name.
12 When prompted for driver information, use the following:
a. for PATHWORKS 5.0:
NDIS Driver Path: a:\
NDIS Driver File: m16andis.exe
NDIS Driver Name: INTEL$
Other File: A:\M16ACFG.EXE
b. for PATHWORKS 5.1:
Driver file: a:\m16andis.exe
PROTOCOL.INI stub: a:\dec\protocol.ini
Additional Files: A:\M16ACFG.EXE
13 Insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk (Disk 2) when prompted.
14 Enter your node information when prompted.
At this point, the SETUP program will try to connect to the
DECnet server. Once connected, the SETUP program will map a
logical drive to your system service.
15 Highlight the logical drive mapped by the SETUP program, and
press Enter to run PWSETUP.
16 Press Enter to confirm the Software Destination C:\PW.
17 Choose Express (or Custom if you have a lot of prior installation
experience).
18 Select an appropriate Workstation Template, or create one.
19 Under Network Adapter Information, choose other network
adapter, with NDIS enabled, and verify the following information:
Non-Supported Network Adapter
Driver file: a:\m16andis.exe
PROTOCOL.INI stub: a:\dec\protocol.ini
Additional Files: A:\M16ACFG.EXE
Page 25

25
Software Installation
20 Insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk (Disk 2) when prompted.
21 Enter node information when prompted and proceed.
22 A PROTOCOL.INI file created by SETUP will display in edit
mode.
23 Remove the semicolon at the beginning of the ni_irq line, as
follows:
Change the line
;ni_irq = (irq value from step 3)
to read
ni_irq = (irq value from step 3)
The ni_irq value must be the same as the interrupt value used for
the Intel adapter.
24 Verify that the [m16andis] section has the following lines and
settings:
[m16andis]
drivername=intel$
25 Exit SETUP and reboot to start the network. (Some machines may
require a cold boot at this point—power the computer down and
back up again.)
Page 26

26
CHAPTER 2
FTP Software LANWatch
Packet and NDIS 2.0 Drivers
FTP Software’s LANWatch network monitor software can be installed
using Intel’s packet or NDIS 2.0 drivers. For information on which
driver is appropriate for your network environment, refer to the FTP
LANWatch documentation.
FTP Software LANWatch Packet Driver Installation
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose FTP LANWatch from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install LANWatch according to the instructions in your FTP
LANWatch manual.
5 Copy the files M16ACFG.EXE, M16APD.COM, and
INTELPD.BAT from the C:\INTEL\M16A directory to the
directory where your LANWatch files are stored. The file
INTELPD.BAT contains the correct command lines for the Packet
Driver.
6 (This step is not required for LANWatch versions 3.0 and later.)
Using a text editor, add the following line to your CONFIG.SYS
file:
DEVICE = [
path
]IFCUST.SYS
where [path] is the drive and directory where your LANWatch
files are stored.
7 Reboot the PC.
8 Change to the directory of where your LANWatch files are stored
and run INTELPD.BAT
9 Run LW.EXE.
Page 27

27
Software Installation
FTP Software LANWatch NDIS 2.0 Driver Installation
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose FTP LANWatch from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install LANWatch according to the instructions in your FTP
LANWatch manual.
5 Using a text editor, add the following lines to your CONFIG.SYS
file:
DEVICE = C:\NDIS\PROTMAN.SYS /I:C:\NDIS
DEVICE = C:\NDIS\M16ACFG.EXE
DEVICE = C:\NDIS\M16ANDIS.EXE
DEVICE = C:\NDIS\DIS_PKT.GUP
(Include the following line for LANWatch versions earlier than
3.0 only)
DEVICE = C:\LW\IFCUST.SYS
6 Create a directory called NDIS on your hard disk, by typing:
MD NDIS
7 At the DOS prompt, copy the files M16ACFG.EXE and
M16ANDIS.EXE from the C:\INTEL\M16A directory on your
hard disk and the file PROTOCOL.FTP from the \NDIS directory
on the Intel Network Drivers Disk to the \NDIS directory you
created in Step 6.
8 Use a text editor to modify the PROTOCOL.FTP file to match the
keywords and values in the sample PROTOCOL.INI file in the
\INTEL\M16A directory.
9 Copy all the files from the \NDIS directory on the FTP
Unsupported Software Disk A to the \NDIS directory created in
Step 6.
10 Reboot the PC.
11 Change to the \NDIS directory and run NETBIND.EXE.
12 Run LW.EXE.
Page 28

28
CHAPTER 2
FTP Software PC/TCP
Packet, NDIS 2.0, and ODI Drivers
FTP Software’s PC/TCP Generic Ethernet Kernel ETHDRV.EXE can
be installed using Intel’s Packet, ODI, or NDIS drivers. PC/TCP can
also be used concurrently with NetWare. For information on which
driver is appropriate for your network environment, see the FTP PC/
TCP documentation. For environments using values other than those
set by the Intel Installation Program, see Chapter 3, Configuration
Reference in this manual.
FTP PC/TCP 3.X with OnNet 1.1 and Windows for
Workgroups 3.11
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 From the Select Network Operating System screen, choose
Microsoft Windows for Workgroups then FTP PC/TCP 3.x.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Run the PC/TCP installation program OnNet 1.1.
5 Follow the prompts to the Network Card Screen, then select
“Other NDIS Driver or Updated Packet Driver.”
6 Insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk (Disk 2) when prompted.
7 Choose the appropriate driver then follow prompts to complete
the installation.
8a For NDIS installation, reboot the PC.
8b For ODI installation, do not reboot. Continue with step 9.
Additional Steps for ODI Installation
If you are using an ODI driver, continue with the following steps:
9 Change to the directory into which PC/TCP was installed.
10 Use a text editor to change the file PCTCP.INI as follows:
• In the section PCTCP ifcust 0 change the line
interface-type=NDIS
to read
interface-type=PKTDRV.
11 Save the file and exit the text editor.
Page 29

29
Software Installation
FTP PC/TCP 3.X with OnNet 1.1 with Windows 3.1
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 From the Select Network Operating System screen, choose FTP
PC/TCP.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel installation.
4 Run the PC/TCP installation program OnNet 1.1.
5 When prompted, insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk (Disk 2).
6 Follow prompts to complete the PC/TCP installation.
7a For an NDIS installation, reboot the PC.
7b For ODI installation, do not reboot. Continue with step 8.
Additional Steps for ODI Installation
If you are using an ODI driver, continue with the following steps:
8 Change to the directory into which PC/TCP was installed.
9 Use a text editor to change the file PCTCP.INI as follows:
• In the section PCTCP ifcust 0 change the line
interface-type=NDIS
12 Change to the C:\ (root) directory.
13 Use a text editor to modify the AUTOEXEC.BAT file as follows
(\PCTCP is the default installation directory):
• Move the line containing the STARTNET.BAT command or
the lines containing the network driver files to immediately
above the line
SET PCTCP=C:\PCTCP\PCTCP.INI
• Add the line
C:\PCTCP\ODIPKT
after the line
PCTCP=C:\PCTCP\PCTCP.INI
14 Save the file and exit the text editor.
15 Copy the file ODIPKT from disk 5 of the FTP PC/TCP
installation disks to the directory into which PC/TCP was
installed.
16 Reboot the PC.
Page 30

30
CHAPTER 2
to read
interface-type=PKTDRV
10 Save the file and exit the text editor.
11 Change to the C:\ (root) directory.
12 Use a text editor to modify the AUTOEXEC.BAT file as follows
(\PCTCP is the default installation directory):
• Move the line containing the STARTNET.BAT command or
the lines containing the network driver files to immediately
above the line
SET PCTCP=C:\PCTCP\PCTCP.INI
• Add the line
C:\PCTCP\ODIPKT
after the line
PCTCP=C:\PCTCP\PCTCP.INI
13 Save the file and exit the text editor.
14 Copy the file ODIPKT from disk 5 of the FTP PC/TCP
installation disks to the directory into which PC/TCP was
installed.
15 Reboot the PC.
FTP Software PC/TCP Packet Driver Installation
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose FTP PC/TCP from the Select Network Operating System
screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install PC/TCP software according to the directions given in the
PC/TCP documentation.
5 Copy the files M16ACFG.EXE, M16APD.COM, and
INTELPD.BAT from the C:\INTEL\M16A directory to the PC/
TCP directory specified in the PC/TCP install procedure. The file
INTELPD.BAT contains the correct command lines for the Packet
Driver.
Page 31

31
Software Installation
6 (This step is not required for PC/TCP versions 2.10 and later.)
Using a text editor, add the following lines to your CONFIG.SYS
file:
DEVICE=[
path
]IPCUST.SYS
DEVICE=[
path
]IFCUST.SYS
where [path] is the drive and directory specified at the PC/TCP
installation.
7 Reboot the PC.
8 Change to the directory where your PC/TCP files are stored and
run INTELPD.BAT by typing:
INTELPD
9 Run the ETHDRV.EXE kernel program supplied with PC/TCP.
This loads the PC/TCP kernel into memory. The packet driver
must always load before the kernel.
10 Continue your server or workstation startup as instructed in the
PC/TCP documentation.
ODI with FTP Software PC/TCP and NetWare
If you need to run Novell NetWare concurrently with FTP PC/TCP,
proceed as follows:
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose FTP PC/TCP from the Select Network Operating System
screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install PC/TCP according to the instructions in your FTP PC/TCP
manual.
5 (This step is not required for PC/TCP versions 2.10 and later.)
Using a text editor, add the following lines to your CONFIG.SYS
file:
DEVICE=[
path
]IPCUST.SYS
DEVICE=[
path
]IFCUST.SYS
where [path] is the drive and directory specified in the PC/TCP
installation.
Page 32

32
CHAPTER 2
6 Copy the files M16ACFG.EXE and NET.CFG from the
C:\INTEL\M16A directory and the files LSL.COM and
M16AODI.COM from the root directory of the Intel Network
Drivers Disk to the PC/TCP directory created in the PC/TCP
install procedure.
7 To start the workstation, load the software as follows:
M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=ODI
LSL
M16AODI
IPXODI
ODIPKT (Use the version supplied with PC/TCP)
ETHDRV
VLM
8 Change to the network drive (usually F:\LOGIN).
9 Log in to the network.
Page 33

33
Software Installation
Generic Installation
If your NOS is not listed in the Intel Installation Program, you can try
selecting “Generic NDIS Driver” or “Generic ODI Driver” in the Intel
Installation Program and clicking the Install button. A sample
configuration file containing parameters optimized for your system will
be created in the \INTEL\M16A directory on your hard disk. For NDIS,
this will be a custom PROTOCOL.INI file. For ODI, it will be a
custom NET.CFG file. Use this sample file to assist you in configuring
the actual configuration file for your system (or use the sample file
itself if appropriate).
HP LAN Manager
NDIS 2.0 Driver
See Microsoft LAN Manager.
IBM Local Area Network Support Program
IBM Local Area Network Support Program (version 1.36)
NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose IBM LAN Support Program from the Select Network
Operating System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install the IBM Local Area Network Support Program according
to the instructions in the IBM Local Area Network Support
Program User’s Guide.
5 Under Environment Information, respond “no” to the question
“Do you have adapter option disks?”
6 Choose an Intel Adapter from the list provided.
Page 34

34
CHAPTER 2
7 If prompted to do so, insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk (Disk
2) when prompted and type the path
A:\NDIS
8 Press Esc twice to bypass error messages.
9 Continue with the installation until finished.
10 Use a text editor to add the following two lines in your
CONFIG.SYS file at the location indicated by the “rem”
statement concerning insertion of the driver name:
device=\LSP\M16ACFG.EXE
device=\LSP\M16ANDIS.EXE
11 Copy the file M16ACFG.EXE and M16ANDIS.EXE from the
directory C:\INTEL\M16A to the C:\LSP directory on your hard
disk.
12 Use a text editor to edit the PROTOCOL.INI keyword settings in
the C:\LSP directory to match the keywords contained in the
sample PROTOCOL.INI file located at C:\INTEL\M16A as
required (unless you are using Intel PRO/100 PC Card default
settings).
13 Save the files and reboot the PC.
IBM Local Area Network Support Program (version 1.2)
NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose IBM LAN Support Program from the Select Network
Operating System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install the IBM Local Area Network Support Program according
to the instructions in the IBM Local Area Network Support
Program User’s Guide. The following instructions refer to the
prompts and messages displayed with the Configuration Aid
automated install software provided with the LAN Support
Program.
5 If a message appears during the LAN Support Program
installation indicating there are no IBM LAN adapters installed in
the workstation, bypass the message by pressing Enter.
6 Answer [N]o to program support for the PC Network Adapter.
Page 35

35
Software Installation
7 Answer [Y]es to use of programs needing the NETBIOS
interface.
8 When prompted, select the Etherand Network family of network
cards.
9 Continue with the installation until finished.
10 Use a text editor to replace the line in your CONFIG.SYS file that
reads:
device=\XX.DOS
with the two lines
device=\M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=NDIS
device=\M16ANDIS.EXE
11 Still in the CONFIG.SYS file, add the parameter O=N (where O
is a letter, not zero) to the line
device=\DXMT0MOD.SYS
as follows
device=\DXMT0MOD.SYS O=N
12 Copy the files M16ACFG.EXE and M16ANDIS.EXE from the
directory C:\INTEL\M16A to the root directory of your hard disk
or boot disk.
13 Change to the LANMAN directory on your hard disk or boot disk.
14 Use a text editor to modify the PROTOCOL.INI file in the
C:\LSP directory as follows:
• Under the ETHERAND section, change the line that reads
Bindings = TCMAC2
to:
Bindings = INTELNET
• Underneath that section insert a new section that reads as
follows:
[INTELNET]
DriverName = INTEL$
15 Use a text editor to edit the keyword settings in the
PROTOCOL.INI file in the C:\LSP directory to match the
keywords contained in the sample PROTOCOL.INI file located at
C:\INTEL\M16A as required (unless you are using Intel PRO/100
PC Card default settings).
16 Save the file and reboot the PC.
Page 36

36
CHAPTER 2
IBM OS/2 and OS/2 Warp
Use the instructions under Microsoft LAN Manager, Novell NetWare
Requester, or Ungermann-Bass Net/One to install drivers on systems
running OS/2 and OS/2 Warp.
IBM PC LAN and IBM DOS LAN Requester
1 Install the IBM LAN Support Program according to the
instructions under the heading “IBM Local Area Network Support
Program,” earlier in this section.
2 Reboot the PC.
3 Install IBM PC LAN or IBM DOS LAN Requester according to
the instructions in the IBM documentation.
4 Reboot the PC.
Page 37

37
Software Installation
Manual Installation
All network drivers provided on the Intel Network Drivers Disk can be
installed manually, without the Intel Installation Program. You must
copy the correct driver files to your hard disk and make appropriate
changes to CONFIG.SYS, AUTOEXEC.BAT, and configuration files
such as NET.CFG (for ODI) or PROTOCOL.INI (for NDIS). Manual
installation should only be performed by a system administrator or
someone with equivalent knowledge of the installation process for your
network operating system.
Note
For manual installation of Novell NetWare with VLM (available
only under MS-DOS or Windows 3.x) you must first decompress
the VLM files by running the MS-DOS batch file
DCOMPVLM.BAT from the Network Drivers Disk, as follows:
DCOMPVLM [
path
]
where [
path
] is the directory for NetWare files (usually
C:\NWCLIENT). DCOMPVLM will decompress and copy all
required files to the designated directory.
For an overview of the installation process, see the instructions
provided for your network operating system in the alphabetical section
of this chapter. Consult Chapter 3, Configuration Reference, for
detailed information on configuration files and settings. For additional
information, consult your network operating system documentation.
Microsoft LAN Manager
Microsoft LAN Manager (version 2.1)
NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Microsoft LAN Manager from the Select Network
Operating System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
Page 38

38
CHAPTER 2
4 Begin installation of LAN Manager using “setup.”
5 When prompted to select the available network adapter driver,
choose “Other Driver.”
6 When prompted, insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
7 Select “Intel EtherExpress PRO/100 Mobile Adapter 16-bit PC
Card” from the menu.
8 Continue with the installation until it is completed.
9 If installing Microsoft LAN Manager to run under Microsoft
Windows proceed to step 10. Otherwise, skip to step 15.
10 Run Windows.
11 Choose setup from “Main” group.
12 Select Startup, and under the “Options” screen select Change
System Settings.
13 Select Network then scroll to LAN Manager version 2.1.
14 Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
15 Reboot the PC.
Page 39

39
Software Installation
Microsoft LAN Manager (version 2.1) with Windows for
Workgroups 3.11
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Microsoft Windows for Workgroups from the Select
Network Operating System screen.
3 Select “Yes” on the Attached to Network File Server screen.
4 Select Microsoft LAN Manager.
5 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
6 Start Windows and, in the Network program group, double-click
on the Network Setup icon.
7 If you have not installed network support, choose Networks in the
Network Setup dialog box, select Install Microsoft Windows
Network, and click OK. Otherwise proceed with step 8.
8 In the Network Setup dialog box, choose Drivers.
9 In the Network Drivers dialog box, choose Add Adapter.
10 In the Add Network Adapter box, choose Unlisted or Updated
Network Adapter and click OK.
11 When prompted for an “unlisted, updated, or vendor-provided
network driver disk,” insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
12 Select “Intel M16A NDIS 2.01 Real Mode,” and click OK.
13 Close the Network Drivers dialog box and click OK in the
Network Setup box.
14 Complete the installation process, inserting the Intel Network
Drivers Disk if required.
15 Continue with the installation until it is completed.
16 Click on the Control Panel in the “Main” group.
17 Select Startup from the Control Panel.
18 In the Options for Enterprise Networking window click “Log on
to Windows NT or LAN Manager Domain.”
19 Save, exit, and reboot the PC.
Page 40

40
CHAPTER 2
Microsoft Windows for W orkgroups
NDIS 2.01 and ODI Drivers
Instructions are provided for installing Intel network drivers for the
first time on a system using Windows for Workgroups version 3.11
alone or with NetWare. These instructions assume that Windows for
Workgroups has already been installed. Remove any earlier version of
the Intel drivers before installing the new version. No NDIS 3 driver is
supplied for Windows for Workgroups.
The following topics are covered for Windows for Workgroups:
• How to install for Windows for Workgroups version 3.11 and
NetWare using the ODI driver
• How to install for Windows for Workgroups 3.11 using the NDIS
2.0 driver
• How to remove an existing Windows for Workgroups Installation
For troubleshooting tips for Windows for Workgroups, see Chapter 4,
Troubleshooting.
Windows for Workgroups Version 3.11 and NetWare (Using
the ODI driver)
1 To configure Windows for Workgroups with NetWare, run the
Intel Installation Program and choose Novell NetWare.
2 When the installation is complete, reboot the computer.
3 At the Intel menu, choose “Load Intel EtherExpress PRO/100
Mobile Adapter16 for Network Access.”
4 From the DOS prompt, run the NetWare Client install. Be sure to
install support for Microsoft Windows.
5 When the Novell Client install program asks for an ODI driver,
insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
6 Complete the installation process and reboot the computer.
7 Log in to NetWare.
8 Start Windows for Workgroups and, in the Network program
group, double-click on the Network Setup icon.
Page 41

41
Software Installation
Windows for Workgroups Network Setup will detect the NetWare
configuration and automatically select Novell NetWare as an
additional network. It will also prompt for Novell support files
(from Novell Client diskettes) if required during the installation.
(If necessary, use the Novell decompression utility to decompress
the required files.)
Windows for Workgroups Setup will also attempt to determine
what NetWare driver model you are using. If for some reason
Windows for Workgroups was unable to detect the driver model,
you should select IPXODI and LSL as the driver type.
Note (in steps 10a and 10b) that you can install NetWare as an
additional network under Windows for Workgroups, or by itself
but with Windows support.
9 In the Network Setup dialog box, choose Networks.
10a To install both Windows for Workgroups and NetWare,
choose Install Microsoft Windows Network and proceed to step
11.
10b To install for NetWare only with Windows support, choose
Install Windows Support for the Following Network Only, select
the NetWare configuration appropriate for your network, then
proceed to step 11.
11 Choose Other under Additional Network Support, then select the
NetWare configuration appropriate for your network.
12 In the Network Setup dialog box, choose Drivers.
13 In the Network Drivers dialog box, choose Add Adapter.
14 In the Add Network Adapter box, choose Unlisted or Updated
Network Adapter and click OK.
15 When prompted for an “unlisted, updated, or vendor-provided
network driver disk,” insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
16 Select “Intel M16A ODI for NetWare” and click OK.
17 Close the Network Drivers dialog box and click OK in the
Network Setup box.
18 Complete the installation process, inserting the Intel Network
Drivers Disk if required.
Page 42

42
CHAPTER 2
Note
Verify that the following lines have been added to your
AUTOEXEC.BAT and STARTNET.BAT files. If they are not there,
add them manually using a text editor.
Add the following command to the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, where
\WINDOWS is the directory into which Microsoft Windows was
installed:
C:\WINDOWS\NET START
Add the following command to the STARTNET.BAT file in your
NWCLIENT directory, where \WINDOWS is the directory into
which Microsoft Windows was installed:
C:\WINDOWS\ODIHLP.EXE
Page 43

43
Software Installation
Windows for Workgroups 3.11 Using the NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Microsoft Windows for Workgroups installation from the
Select Network Operating System screen.
3 Choose “No” on the Attached to Network File Server screen.
4 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
5 Start Windows for Workgroups and double-click on the Network
Setup icon in the Network Group.
6 If you have not installed network support, choose Networks in the
Network Setup dialog box, select Install Microsoft Windows
Network, and click OK. Otherwise proceed to Step 7.
7 In the Network Setup dialog box, choose Drivers.
8 In the Network Drivers dialog box, choose Add Adapter.
9 In the Add Network Adapter box, choose Unlisted or Updated
Network Adapter and click OK.
10 When prompted for an “unlisted, updated, or vendor-provided
network driver disk,” insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
11 Select “Intel M16A NDIS 2.01 Real Mode” and click OK.
12 Close the Network Drivers dialog box and click OK in the
Network Setup box.
13 Complete the installation process, inserting the Intel Network
Drivers Disk if required.
Page 44

44
CHAPTER 2
How to Remove an Existing Windows for Workgroups
Installation
1 Start Windows and select Network Setup in the Network program
group.
2 In the Network Setup dialog box, choose Drivers.
3 In the Network Drivers dialog box, choose Remove to discard any
existing network adapter drivers.
4 Choose Close and return to the Network Setup dialog box.
5 Exit the Network Setup program and exit Windows.
6 At the DOS prompt, change to the Windows system directory, as
follows
cd \windows\system
7 Make a directory called OEM, as follows
mkdir oem
8 Type
dir oem?.inf
to see a list of driver configuration files.
9 Use the DOS EDIT program to view each OEM file to determine
which ones reference Intel.
10 Copy the old Intel configuration files to the OEM directory.
11 Delete the old Intel configuration files from the Windows system
directory.
12 Restart Windows.
13 Follow the instructions for installing drivers for Windows for
Workgroups alone or Windows for Workgroups and NetWare.
Connecting to a Windows NT Server with Windows for Workgroups 3.11
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation
Disk.
2 Choose Microsoft Windows for Workgroups from the Select
Network Operating System screen.
3 Select “Yes” on the Attached to Network File Server screen.
4 Select Microsoft Windows NT or LAN Manager.
Page 45

45
Software Installation
5 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the installa-
tion.
6 Start Windows and, in the Network program group, double-click
on the Network Setup icon.
7 If you have not installed network support, choose Networks in
the Network Setup dialog box, select Install Microsoft Windows
Network, and click OK. Otherwise proceed with step 8.
8 In the Network Setup dialog box, choose Drivers.
9 In the Network Drivers dialog box, choose Add Adapter.
10 In the Add Network Adapter box, choose Unlisted or Updated
Network Adapter and click OK.
11 When prompted for an “unlisted, updated, or vendor-provided
network driver disk,” insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
12 Select “Intel M16A NDIS 2.01 Real Mode,” and click OK.
13 Close the Network Drivers dialog box and click OK in the
Network Setup box.
14 Complete the installation process, inserting the Intel Network
Drivers Disk if required.
15 Continue with the installation until it is completed.
16 Click on the Control Panel in the “Main” group.
17 Select Startup from the Control Panel.
18 In the Options for Enterprise Networking window click “Log on
to Windows NT or LAN Manager Domain.”
19 Save, exit, and reboot the PC.
Page 46

46
CHAPTER 2
Novell NetWare
ODI Driver
The Intel ODI driver allows for the concurrent use of Novell NetWare
and other protocols that support Novell’s Open Data-Link Interface
(ODI) specification.
NetWare
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Novell NetWare from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
4 The Intel Installation Program will reboot the computer and verify
the NetWare connection.
5 Reboot your computer again.
6 Log in to the network.
Note
The Intel Installation Program uses the NetWare VLM shell to
connect to your NetWare server. The Installation Program
decompresses and copies all the required files.
If you are installing manually, without the Intel Installation
Program (under MS-DOS or Windows 3.x) you must first
decompress the VLM files by running the MS-DOS batch file
DCOMPVLM.BAT from the Network Drivers Disk, as follows:
DCOMPVLM [
path
]
where [
path
] is the directory for NetWare files (usually
C:\NWCLIENT). DCOMPVLM will decompress and copy all
required files to the designated directory.
If you need NETX shell support, contact your System Administrator.
If using DOS 5.0, check your CONFIG.SYS file for the statement
LASTDRIVE=Z. If not present, add it.
Page 47

47
Software Installation
NetWare Requester for OS/2
NetWare Requester for OS/2 (versions 2.x)
These instructions explain how to load the Intel network driver as part
of the NetWare Requester installation process.
1 Run the NetWare Requester INSTALL program as instructed in
the NetWare Requester documentation and choose Requester on
workstation from the Installation menu.
2 After verifying your target directory and source drive for
NetWare Requester files, choose Edit CONFIG.SYS and Copy
Files at the Requester Installation dialog box.
3 When prompted for the Network Interface Card driver, type in the
name of the Intel driver: M16AODI.OS2. After completing the
other options in the dialog box, click on Save.
4 When asked if the driver you specified is the one you want to
install, choose Yes, then type in the path to the Intel driver:
A:\ODI\M16AODI.OS2
5 Remove the NetWare Requester install diskette and insert the
Intel Network Drivers Disk.
6 At the dialog box “Requester files will copy to:”, click on Copy.
7 Complete the installation and exit the NetWare Requester
installation utility.
8 Shut down OS/2 and reboot the computer.
Page 48

48
CHAPTER 2
Novell NetWare Requester version 2.11 for OS/2 Warp
This section describes the steps for manually installing Novell
NetWare Requester for OS/2 WARP without the Intel Installation
Program, using a two-slot generic machine without Card and Socket
Services. Some machines might require changes to the NET.CFG INT
and PORT settings.
1 Copy M16AODI.OS2 from the ODI directory of the Intel Driver
diskette to the OS2 subdirectory of the WorkStation Driver
(WSDRV) diskette from the NetWare Client package.
2 Run the INSTALL program from the NetWare Requester disk
(WSOS21). It will prompt you for the target directory and begin
installing. When it prompts you to choose a Network Interface
Card driver, enter M16AODI.OS2. The INSTALL program will
copy the drivers and modify the CONFIG.SYS for you.
3 After the files have been copied, you will be at the main screen of
the NetWare Workstation for the OS/2 Installation Utility. From
the menu bar, choose the “Configuration” menu, and the “This
workstation” command. Edit the NET.CFG following the sample
below, and including the correct frame types for your network.
Sample NET.CFG file
link driver M16AODI
frame ethernet_802.2
port 300
int 5
4 Save the NET.CFG. The main message area should report that
you have finished the installation. Close the installation utility.
You can verify that the CONFIG.SYS changes appear to be
correct.
5 Shut down the OS/2 desktop and reboot the machine. The drivers
should load without error. If an interrupt or IO port conflict is
detected, adjust the settings in your NET.CFG and repeat the
process from Step 3.
Page 49

49
Software Installation
Sample CONFIG.SYS
rem — NetWare Requester statements BEGIN —
SET NWLANGUAGE=ENGLISH
DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\LSL.SYS
RUN=D:\NETWARE\DDAEMON.EXE
rem — ODI-Driver Files BEGIN —
DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\M16AODI.OS2
rem — ODI-Driver Files END —
rem DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\ROUTE.SYS
DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\IPX.SYS
rem DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\SPX.SYS
rem RUN=D:\NETWARE\SPDAEMON.EXE
rem DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\NMPIPE.SYS
rem DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\NPSERVER.SYS
rem RUN=D:\NETWARE\NPDAEMON.EXE
DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\NWREQ.SYS
IFS=D:\NETWARE\NWIFS.IFS
RUN=D:\NETWARE\NWDAEMON.EXE
rem DEVICE=D:\NETWARE\NETBIOS.SYS
rem RUN=D:\NETWARE\NBDAEMON.EXE
DEVICE=D:\OS2\MDOS\LPTDD.SYS
rem — NetWare Requester statements END —
Page 50

50
CHAPTER 2
SunSoft PC-NFS (version 3.5)
NDIS 2.0 Driver
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose SunSoft PC-NFS from the Select Network Operating
System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install PC-NFS for Ethernet according to instructions in the PC-
NFS documentation. Choose NDIS setup, and follow the
instructions to complete the setup. Note the prompt that tells you
that further manual modifications will have to be made.
5 Reboot the computer. You will see some error messages.
Disregard them and continue with these instructions.
6 Rename the file PROTOCOL.NFS in the C:\LANMAN directory
to PROTOCOL.INI. Use an text editor to edit the
PROTOCOL.INI file as follows:
Replace the items
[your-mac-module]
drivername = YOURMAC$
option1 = value1 etc.
[NFS-NDIS]
drivername = NFSLINK1
bindings = your-mac-module
with
[INTELNET]
drivername = INTEL$
[NFS-NDIS]
drivername = NFSLINK$
bindings = INTELNET
7 Be sure the keyword settings in the PROTOCOL.INI file in the
C:\LANMAN directory match the settings in in the sample
PROTOCOL.INI file contained in the C:\INTEL\M16A directory.
8 Copy the files M16ACFG.EXE and M16ANDIS.EXE from the
C:\INTEL\M16A directory to the C:\LANMAN directory.
9 Use a text editor to insert the following lines in your
CONFIG.SYS file:
Page 51

51
Software Installation
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\M16ACFG.EXE
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\M16ANDIS.EXE
between the two lines
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\PROTMAN.SYS
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\NFS-NDIS.SYS
as follows:
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\PROTMAN.SYS
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\M16ACFG.EXE
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\M16ANDIS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN\NFS-NDIS.SYS
10 Verify that your AUTOEXEC.BAT file contains a line that reads
C:\LANMAN\NETBIND
before the line that reads
NET INIT
11 Configure PC-NFS options according to your PC-NFS
documentation, and reboot the computer.
Page 52

52
CHAPTER 2
Ungermann-Bass Net/One for DOS and OS/2
NDIS 2.0 Driver
The PRO/100 PC Card is supported on Ungermann-Bass Net/One LAN
Manager and MS-NET networks. There are two NDIS driver packages
available from UB: XNS BNS/NDIS and TCP BNS/NDIS. These
packages, used with a Intel NDIS driver, provide files that support
DOS and OS/2 workstations. They are available from UB and
authorized UB representatives.
Ungermann-Bass Net/One LAN Manager version 2.1
Installation
1 Begin installation of LAN Manager 2.1 using “setup.”
2 When prompted to select the available network adapter driver,
choose “Other Driver.”
3 When prompted, insert the Intel Network Drivers Disk.
4 Select “Intel EtherExpress PRO/100 Mobile Adapter 16-bit PC
Card” from the menu.
5 Continue with the installation until it is completed.
6 Copy the file M16ACFG.EXE from the root directory of your
Intel Network Drivers Disk to the drive and directory where you
installed your network operating system.
7 Following the UB instructions, modify your CONFIG.SYS file by
adding the following lines:
For DOS:
DEVICE = [
path
]M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=NDIS
DEVICE = [
path
]M16ANDIS.EXE
For OS/2:
DEVICE = [
path
]M16ANDIS.OS2
where [path] is the drive and directory in which you installed your
network operating system.
8 Use a text editor to modify your PROTOCOL.INI file as follows:
• For each protocol that you want to bind, set the protocol
definition area of the PROTOCOL.INI file to:
BINDINGS = UBLOOP
• At the end of the file, add the following fragments:
Page 53

53
Software Installation
[UBLOOP]
DRIVERNAME = UBLOOP$
BINDINGS = INTELNET
;INTEL ADAPTER
[INTELNET]
DRIVERNAME = INTEL$
9 Reboot the PC.
Page 54

54
CHAPTER 2
Wollongong PathWay Access for DOS
NDIS and ODI Drivers
Wollongong PathWay Access for DOS can be installed using Intel
NDIS or ODI drivers. Installation instructions for both types of driver
are provided below. For information on which driver is appropriate for
your network environment, refer to the Wollongong PathWay Access
for DOS documentation.
Wollongong PathWay NDIS Installation
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk
2 Choose Wollongong PathWay Access from the Select Network
Operating System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install PathWay Access for DOS Kernel and Drivers programs
according to the instructions in the PathWay Access for DOS
manual. Before rebooting the PC, continue with the following
steps.
5 Use a text editor to modify the CONFIG.SYS file. After the
statement that reads
DEVICE=C:\PATHWAY\PWTCP.SYS
add the lines
DEVICE=\PATHWAY\[PROTMAN FILE] /I:C:\PATHWAY
DEVICE=\PATHWAY\M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=NDIS
DEVICE=\PATHWAY\M16ANDIS.EXE
where [PROTMAN FILE] is equal to the PROTMAN2.EXE or
PROTMAN.EXE file that is located in your PATHWAY
directory. (Refer to the Wollongong PathWay Access for DOS
manual for information regarding the differences between these
two files.)
6 Copy the files M16ACFG.EXE, M16ANDIS.EXE, and
PROTOCOL.INI from C:\INTEL\M16A directory to the
PATHWAY directory on your hard disk or boot disk.
7 Continue with the “custom” instructions in the PathWay Access
for DOS manual.
8 Reboot the PC.
Page 55

55
Software Installation
6 Change to the PATHWAY directory and load the software in the
following order:
M16ACFG
LSL
M16AODI
IPXODI (only if using Novell NetWare)
VLM (only if using Novell NetWare)
7 Load the Wollongong file ODI.EXE.
8 Continue with the instructions in the PathWay Access for DOS
manual.
9 Reboot the PC.
Wollongong PathWay ODI Installation
1 Run the Intel Installation Program from Disk 1, Installation Disk.
2 Choose Wollongong PathWay Access from the Select Network
Operating System screen.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the Intel segment of the
installation.
4 Install PathWay Access for DOS Kernel and Drivers programs
according to the instructions in the PathWay Access for DOS
manual. Before rebooting the PC, perform the following steps.
5 Run the MS-DOS batch file DCOMPVLM.BAT from the
Network Drivers Disk, as follows:
DCOMPVLM PATHWAY
DCOMPVLM.BAT will decompress and copy all required files
from the Intel Network Drivers Disk to the PATHWAY directory
on your hard disk or boot disk. (The files are LSL.COM,
M16AODI.COM, IPXODI.COM, VLM.EXE, M16ACFG.EXE,
and NET.CFG.)
Page 56

56
CHAPTER 2
Page 57

57
Chapter 3
Configuration Reference
Who Should Consult This Chapter
This chapter contains additional information on PRO/100 PC Card
features and technical information on configuration requirements,
including sample configuration files for the Windows 3.x environment, and driver parameter settings, including registry values for
Windows 95 and NT. This information can be used to modify an
existing installation or perform a new installation manually without
the assistance of the Intel Installation Program.
Note
Intel recommends operations described in this chapter be
performed by a system or network administrator or a user
with equivalent technical experience.
Microsoft Windows 95 and Windows NT
Windows registry settings can be found on page 68, under the heading
“M16A.SYS Settings for Microsoft Windows 95 and Windows NT.”
Modifying Settings After Running the Intel Installation
Program (Windows 3.x)
The file modifications made by the Intel Installation Program should
allow most Windows 3.x users to log on to their network after
performing the steps outlined in Chapter 1, Hardware Installation
and Chapter 2, Software Installation.
Page 58

58
CHAPTER 3
If you followed those instructions and still have not been able to
successfully log on to your the network, you may need to modify the
configuration parameters set by the Intel Installation Program. You
can modify configuration settings by rerunning the Intel Installation
Program or by running IEDIT, the Intel System File Editor installed in
the Intel PRO/100 Windows program group.
Installation without the Intel Installation Program
The information in this chapter can be used to manually configure the
PRO/100 PC Card under Windows 3.x, MS-DOS, and IBM OS/2. For
manual installation, it is assumed that you have some experience with
manual setup of network adapters, and know how to access and
modify configuration files, using an ASCII text editor. Intel
recommends that manual installation be performed by a system
administrator or equivalent.
For Preliminary Troubleshooting
Review the configuration information in this chapter. For more
detailed information on specific installation problems, see Chapter 4.
Troubleshooting.
PRO/100 PC Card Features
Card and Socket Services
Note
Microsoft Windows 95 and Windows NT have this
functionality built-in and do not require separate Card and
Socket Services software.
The Personal Computer Memory Card International Association
(PCMCIA) has developed specifications governing the use of PC
Cards (formerly PCMCIA cards) in personal computer systems. The
software components that implement these specifications are called
Card and Socket Services. This software supports the ability of PC
Card-aware device drivers (known as clients) to share cards, sockets,
and system resources.
Unless you are using Windows 95 or Windows NT, Card and Socket
Services are required with the PRO/100 PC Card if you want to take
advantage of the full range of features and benefits of PC Card
capability. If your PC Card computer is not equipped with Card and
Socket Services, ask your computer manufacturer or dealer for details
on how to obtain them.
Page 59

59
Configuration Reference
HotSwap
The Intel PRO/100 PC Card supports HotSwap during connection to a
network or host computer from a PC Card computer using both Card
and Socket Services software (or the equivalent functionality of
Windows 95 or Windows NT). This feature allows the PRO/100 to be
removed from the computer, temporarily replaced with another type of
card such as a modem or memory card, then reinserted without loss of
network connection.
For example, a user could replace a PRO/100 PC Card connected to a
network with a PC Card flash or SRAM memory card. The network
drives become temporarily inaccessible. Any access from DOS or
Windows will return an “Invalid drive specification” message.
Meanwhile, the drive associated with the flash or SRAM card is
available for copying and data retrieval.
If the PRO/100 is returned to the PC Card slot within the timeout
period specified by the network operating system, then network
drives, path, and mappings will be reinstated exactly as they were
before the swap. The default timeout value varies for different
network operating systems.
Note
The HotSwap feature is not supported unless Card and
Socket Services software (or its equivalent under Windows
95 or Windows NT) is running on the PC Card computer.
Power Management Suspend/Resume
Power management features such as suspend/resume are supported by
the PRO/100 PC Card on PC Card systems running both Card and
Socket Services (or the equivalent functionality of Windows 95 or
Windows NT). This means that when the computer enters a reduced
power or power saving mode, an ongoing network connection will
remain active for the period of time allowed by the network operating
system. Even if the time period is exceeded, the network connection
can usually be restored by simply logging back in without rebooting.
Note
The suspend/resume feature is not supported unless Card
and Socket Services software (or its equivalent under
Windows 95 or Windows NT) is running on the PC Card
computer.
Page 60

60
CHAPTER 3
Power Management Guidelines
HotSwap and suspend/resume operations are subject to limitations
dictated by the network operating system. See the documentation for
your network operating system to determine how long the network
will wait for activity before dropping a connection, and whether this
time period is user configurable.
Full-Duplex Transmission (10Mbps Only)
The Intel PRO/100 PC Card hardware and network drivers are
designed to support full-duplex operation, or the ability to transmit
and receive on the network at the same time, on 10Mbps networks.
This feature is only available when the PRO/100 PC Card is connected
to a full-duplex 10Mbps switch. It is not available on 100Mbps
networks.
If your network supports full-duplex operation, activate the PRO/100
feature by including the keyword FULLDUPLEX in the configuration
file or on the command line for your network driver.
Note
To use full-duplex capabilities, your network must run at
10Mbps and have full-duplex hardware in place and
enabled. If you use the FULLDUPLEX keyword without fullduplex hardware, the network may become unusable due to
excessive collisions.
Advanced Look-Ahead Pipelining
The PRO/100 PC Card also uses pipelining technology to improve
performance. Advanced Look-Ahead Pipelining allows for processing
and transmission of packets before the entire packet has been loaded
into memory, resulting in significant gains in performance. This
feature is enabled automatically, without user intervention.
M16ACFG.EXE Configuration Utility (Windows 3.x)
A configuration utility (or “resource manager”) is required to support
the functions of Card and Socket Services on PC Card systems (except
under Microsoft Windows 95, Windows NT, and IBM OS/2). This
utility is called M16ACFG.EXE and is supplied on the Network
Drivers Disk. The utility can be run from the DOS command line or
included in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file or the CONFIG.SYS file.
M16ACFG.EXE allows the Intel PRO/100 PC Card to become a client
of Card Services. It must be run prior to loading a network driver on a
PC Card computer using Card and Socket Services.
Page 61

61
Configuration Reference
Note
M16ACFG.EXE is not used under Microsoft Windows 95,
Windows NT, or IBM OS/2.
Memory Exclusion (Windows 3.x)
When using a memory manager, you must exclude a 4K memory
range between C000 to EF00 for the use of the PRO/100 PC Card. For
example:
device=c:\dos\himem.sys
device=c:\dos\emm386.exe noems x=D200-D2FF
This example excludes 4K of the D200 segment for use by the PRO/
100 when using the default memory address D200. If the PRO/100 is
configured for a memory address other than the default, be sure to
exclude a corresponding 4K memory address range.
Sample Configuration Files for Selected Network
Operating Systems (Windows 3.x)
The following sample configuration files show default parameters for
some network operating systems run under Windows 3.x. This
information is designed to supplement the information provided in
Chapter 2. Software Installation.
Ar tisoft LANtastic/AI 6.0 (Windows 3.x)
Note
If you are using DOS multi-menu CONFIG.SYS, the three
LANtastic-related lines in the CONFIG.SYS will be located in
a COMMON section at the end of your CONFIG.SYS. You
will have to manually move those lines into the proper
menuitem section of your CONFIG.SYS. The same is true
for the line call c:\lantasti\startnet.bat in your
AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
Sample CONFIG.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D200-D2FF
REM DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS
REM INTEL PRO/100 — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
Page 62

62
CHAPTER 3
FILES=50
BUFFERS=30
REM INTEL PRO/100 — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
DEVICE=C:\LANTASTI\PROTMAN.DOS /I:C:\LANTASTI
DEVICE=C:\LANTASTI\M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=NDIS
DEVICE=C:\LANTASTI\M16ANDIS.EXE
REM INTEL PRO/100 — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
Sample AUTOEXEC.BAT
PATH=C:\UTIL;C:\DOS;
PROMPT $P$G
CALL C:\LANTASTI\STARTNET.BAT
Sample PROTOCOL.INI
;PROTOCOL.INI FOR LANTASTIC VERSION 6.00
;—————— USING INTEL PRO/100 PC CARD
;
[PROTMAN]
DRIVERNAME = PROTMAN$
DYNAMIC = YES
; PROTOCOL.INI SECTION FOR THE PRO/100 PC CARD.
[M16ANDIS_NIF]
DRIVERNAME = INTEL$
IOADDRESS=0X320
INT=5
MEM=0XD2000
NOEARLYRX
Sample STARTNET.BAT
@ECHO OFF
REM LANTASTIC VERSION 6.00 INSTALLED 95/01/26
11:31:28
REM (FOR DOS)
C:
CD C:\LANTASTI
Page 63

63
Configuration Reference
SET LAN_CFG=C:\LANTASTI
REM IF LANTASTIC IS DISABLED, SKIP EVERYTHING.
IF EXIST DISABLED GOTO :STARTNET_DONE
@ECHO ===== BEGIN LANTASTIC CONFIGURATION =====
PATH C:\LANTASTI;%PATH%
SET LAN_DIR=C:\LANTASTI.NET
LOADHIGH AI-NDIS BIND_TO=M16ANDIS_NIF
AILANBIO @STARTNET.CFG
REDIR T4700 @STARTNET.CFG
IF EXIST NOSHARE GOTO :NOSHARE
SERVER C:\LANTASTI.NET @STARTNET.CFG
NET LOGIN \\T4700
GOTO :CONTINUE
:NOSHARE
@ECHO LANTASTIC SERVER WAS INSTALLED BUT TURNED OFF.
:CONTINUE
REM IF CONNECT.BAT EXISTS, RUN IT TO SET UP CONNECTIONS
IF EXIST CONNECT.BAT GOTO :CONNECT
REM OTHERWISE SET UP CONNECTIONS SPECIFIED DURING
INSTALL.
NET USE LPT1: \\T4700\@PRINTER
NET LPT TIMEOUT 10
GOTO :CONNECT_DONE
:CONNECT
@ECHO SETTING UP LANTASTIC CONNECTIONS FROM CONNECT.BAT
REM BUILD CONNECT.BAT LIKE THIS: “NET SHOW/BATCH
>C:\LANTASTI\CONNECT.BAT”
REM (OR RUN THE BATCH FILE SETNET.BAT)
CALL CONNECT.BAT
:CONNECT_DONE
NET POSTBOX
@ECHO ===== END LANTASTIC CONFIGURATION =====
:STARTNET_DONE
CD \
Banyan VINES 5.5 (Windows 3.x)
Note
If you are using DOS Multi-menu CONFIG.SYS, the three
VINES related lines in the CONFIG.SYS will be located at the
end of your CONFIG.SYS. You will have to manually move
those lines into the proper menuitem section of your
CONFIG.SYS. If you get Banyan VINES Error codes 10xx,
check C:\VINES\NDISBAN.DOC for explanations of error
codes.
Sample CONFIG.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
(EMM)
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D200-D2FF
Page 64

64
CHAPTER 3
REM DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
FILES=40
BUFFERS=30
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
(NDIS)
DEVICE=C:\VINES\PROTMAN.DOS /I:C:\VINES
DEVICE=C:\VINES\M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=NDIS
DEVICE=C:\VINES\M16ANDIS.EXE
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
Sample AUTOEXEC.BAT
PATH=C:\UTIL;C:\DOS;
PROMPT $P$G
CD\VINES
LH BAN/NC
LH NDISBAN.COM
LH REDIRALL.EXE
NETBIND
ARSWAIT
Z:\LOGIN
Sample PROTOCOL.INI
; PROTOCOL.INI SECTION FOR THE INTEL PRO/100 PC CARD.
[INTELNET]
DRIVERNAME = INTEL$
IOADDRESS=0X320
INT=5
MEM=0XD2000
DEC PATHWORKS 5.0 or 5.1 (Windows 3.x)
Sample CONFIG.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D200-D2FF
FILES=40
BUFFERS=30
SHELL=C:\DOS\COMMAND.COM /P /E:1024
LASTDRIVE=G
Sample AUTOEXEC.BAT
CD\PW
STARTNET.BAT
Sample PROTOCOL.INI (after completion of install process)
[PROTOCOL MANAGER]
DRIVERNAME = PROTMAN$
[IPX4MAC]
DRIVER = IPX$MAC
BINDINGS = M16ANDIS
[IPX_XIF]
DRIVERNAME = IPX$
BINDINGS = M16ANDIS
Page 65

65
Configuration Reference
[NETBEUI]
DRIVERNAME = NETBEUI$
SESSIONS = 6
NCBS = 12
BINDINGS = M16ANDIS
LANABASE = 0
[DATALINK]
DRIVERNAME = DLL$MAC
LG_BUFFERS = 14
SM_BUFFERS = 6
OUTSTANDING = 32
BINDINGS = M16ANDIS
DECPARM = C:\PW\
NI_IRQ = 5
;; YOUR DECNET ADDRESS IS AA0004008407
;;
[M16ANDIS]
DRIVERNAME=INTEL$
INT=5
IOADDRESS=0X320
MEM=0XD2000
Windows for Workgroups 3.11
Sample CONFIG.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
(EMM)
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D200-D2FF
REM DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
FILES=40
BUFFERS=30
DEVICE=C:\WINDOWS\IFSHLP.SYS
LASTDRIVE=Z
Sample AUTOEXEC.BAT
C:\WINDOWS\NET START
Sample PROTOCOL.INI
[NETWORK.SETUP]
VERSION=0X3110
NETCARD=INTELMAC,1,INTELMAC,1
TRANSPORT=MS$NETBEUI,NETBEUI
TRANSPORT=MS$NDISHLP,MS$NDISHLP
LANA0=INTELMAC,1,MS$NETBEUI
LANA1=INTELMAC,1,MS$NDISHLP
[NETBEUI]
BINDINGS=INTELMAC,ASYMAC
LANABASE=0
DRIVERNAME=NETBEUI$
SESSIONS=10
NCBS=12
[PROTMAN]
DRIVERNAME=PROTMAN$
PRIORITY=MS$NDISHLP
[INTELMAC]
DRIVERNAME=INTEL$
Page 66

66
CHAPTER 3
INT=5
IOADDRESS=0X320
MEM=0XD2000
[MS$NDISHLP]
DRIVERNAME=NDISHLP$
BINDINGS=INTELMAC
Sample [NETWORK DRIVERS] SECTION IN SYSTEM.INI
[NETWORK DRIVERS]
DEVDIR=C:\WINDOWS
LOADRMDRIVERS=YES
NETCARD=M16ACFG.EXE,M16ANDIS.EXE
TRANSPORT=*NETBEUI,NDISHLP.SYS
Windows for Workgroups Using the ODI Driver with
NetWare as Secondary Network
Sample STARTNET.BAT
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
:M16A_MENU
@ECHO OFF
CLS
GOTO %CONFIG%
:M16A_INTEL
C:
CD C:\NWCLIENT
IF NOT EXIST M16AODI.COM GOTO INT_ERROR
M16ACFG.EXE DRIVER=ODI
LSL
M16AODI.COM
IPXODI
C:\WINDOWS\ODIHLP.EXE
VLM
IF NOT EXIST XCHECK.EXE GOTO S_M16A_INTEL
CLS
XCHECK.EXE -E -1 F:
:S_M16A_INTEL
F:
LOGIN
GOTO INT_END
:INT_ERROR
ECHO ERROR: UNABLE TO LOCATE DRIVER FILE.
:INT_END
C:
CD \
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
Sample CONFIG.SYS
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
(MENU)
[MENU]
MENUITEM=M16A_E_INTEL,LOAD INTEL PRO/100 PC CARD FOR
NETWORK ACCESS
MENUITEM=INT_END,DO NOT LOAD ANY INTEL DRIVERS
Page 67

67
Configuration Reference
MENUCOLOR=15,0
[M16A_E_INTEL]
[INT_END]
[COMMON]
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
DEVICE=C:\WINDOWS\HIMEM.SYS /TESTMEM:OFF
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE X=D000-DFFF
DOS=HIGH
DOS=UMB
BUFFERS=20
FILES=40
LASTDRIVE=Z
DEVICE=C:\WINDOWS\IFSHLP.SYS
STACKS=9,256
Sample AUTOEXEC.BAT
@ECHO OFF
PROMPT $P$G
PATH C:\WINDOWS;C:\DOS
SET TEMP=C:\DOS
C:\DOS\SMARTDRV.EXE /X C+
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
:M16A_MENU
@ECHO OFF
CLS
GOTO %CONFIG%
:M16A_INTEL
C:\WINDOWS\NET START
C:
CD C:\NWCLIENT
IF NOT EXIST C:\NWCLIENT\STARTNET.BAT GOTO INT_ERROR
CALL C:\NWCLIENT\STARTNET.BAT
GOTO INT_END
:INT_ERROR
ECHO ERROR: UNABLE TO LOCATE DRIVER FILE.
:INT_END
C:
CD \
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES BELOW
(PATH)
PATH=%PATH%;C:\NWCLIENT
REM INTEL PRO/100 ADAPTER — DO NOT CHANGE LINES ABOVE
Sample PROTOCOL.INI
[NETWORK.SETUP]
VERSION=0X3110
NETCARD=INTEL$ODI,1,INTEL$ODI,4
TRANSPORT=MS$NWLINKNB,NWLINK
TRANSPORT=MS$NETBEUI,NETBEUI
LANA0=INTEL$ODI,1,MS$NETBEUI
LANA1=INTEL$ODI,1,MS$NWLINKNB
[NET.CFG]
PATH=C:\NWCLIENT\NET.CFG
Page 68

68
CHAPTER 3
[INTEL$ODI]
[LINK DRIVER M16AODI]
DATA=FRAME ETHERNET_802.2
[NWLINK]
BINDINGS=M16AODI
[NETBEUI]
BINDINGS=M16AODI
LANABASE=0
SESSIONS=10
NCBS=12
Sample [network drivers] section in SYSTEM.INI
[NETWORK DRIVERS]
DEVDIR=C:\WINDOWS
LOADRMDRIVERS=NO
Sample NET.CFG file (located C:\NWCLIENT)
LINK DRIVER M16AODI
FRAME ETHERNET_802.3
FRAME ETHERNET_802.2
FRAME ETHERNET_II
FRAME ETHERNET_SNAP
INT 5
PORT 320
MEM D2000
Windows 95 and Windows NT Driver Parameters
Reference
Caution
Under most circumstances it will not be necessary to make
modifications directly to the registry. Incorrect settings can
result in undesirable changes to the configuration of
Windows 95 or NT. Consult Intel Customer Support for
assistance if you find it necessary to modify the registry.
M16A.SYS (NDIS 3) Settings for Microsoft Windows 95 and
Windows NT
M16A.SYS is an NDIS 3 driver. It conforms to the Microsoft Network
Driver Interface Specification (NDIS). It supports both Windows NT
and Windows 95.
Windows 95 Support
The files necessary for using M16A.SYS with Windows 95 include:
Page 69

69
Configuration Reference
NETM16A.INF Intel installation file for Windows 95
M16A.SYS Intel NDIS 3 driver for Windows 95
There are user-configurable parameters to the M16A.SYS driver
which can be modified using the Network Control Panel built into
Windows 95. This applet queries the user for parameter selections and
then sets the corresponding parameters in the registry. The userconfigurable parameters are as follows:
Parameter Default Valid Values Registry Value
CABLE TYPE AUTO AUTO 0
TWISTED PAIR 10BT 1
DIRECT ENABLE OFF OFF, ON 0
EARLY TRANSMIT ON OFF 0
ON 1
FULL DUPLEX OFF OFF 0
ON 1
LINE SPEED AUTO AUTO DETECT 0
10MBPS 1
100MBPS 2
LINK INTEGRITY ON OFF 0
ON 1
MODE I/O I/O 0
MEMORY MAPPED 1
NETWORKADDRESS
TRANSMITBUFFERSIZE 7168 1024-29696 1024-29696
The network node address can be modified by specifying a value for
‘NetworkAddress’ such as ‘00A0C9112233’. If the user does NOT
specify a ‘NetworkAddress’ then the M16A.SYS driver uses the
network node address contained in the PRO/100 PC Card Information
Structure.
There are parameters in the Windows 95 registry which specify the
configuration of the PRO/100 PC Card hardware to the M16A.SYS
driver. Many of these parameters correspond directly to the userconfigurable parameters. These parameters are found in the registry at
the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CURRENTCONTROLSET\SERVICES\CLASS\NET\000X
Page 70

70
CHAPTER 3
Caution
Under most circumstances it will not be necessary to make
modifications directly to the registry. Incorrect settings can
result in undesirable changes to the configuration of
Windows 95 or NT. Consult Intel Customer Support for
assistance if you find it necessary to modify the registry.
The registry parameters are as follows:
Keyword Default Valid Values
CABLETYPE “0” 0-1
DEVICEVXDS “M16A.SYS”
DEVLOADER “NDIS”
DIRECTENABLE “0” 0-1
DRIVERDESC “INTEL PRO/100 PC CARD”
EARLYTRANSMIT “1” 0-1
ENUMPROPPAGES “NETDI.DLL,ENUMPROPPAGES”
FULLDUPLEX “0” 0-1
INFPATH “NETM16A.INF”
INTERRUPTNUMBER 04 00 00 00
IOBASEADDRESS 02 00 00 00
LINESPEED “0” 0-2
LINKINTEGRITY “1” 0-1
MEMORYBASEADDRESS 01 00 00 00
MODE “0” 0-1
NETWORKADDRESS
PLATFORMTYPE “1” 1
TRANSMITBUFFERSIZE “7168” 1024-29696
‘InterruptNumber’, ‘IoBaseAddress’, and ‘MemoryBaseAddress’ are
NOT user-configurable and their values are assigned by the Windows
95 Configuration Manager.
Windows NT Support
Caution
Under most circumstances it will not be necessary to make
modifications directly to the registry. Incorrect settings can
result in undesirable changes to the configuration of
Windows 95 or NT. Consult Intel Customer Support for
assistance if you find it necessary to modify the
registry.The M16A.SYS driver supports the networking
environment in Windows NT versions 3.5 and greater.
The files necessary for using M16A.SYS with Windows NT include:
M16A.DLL Intel M16A installation DLL
OEMSETNT.INF Intel installation file for Windows NT
Page 71

71
Configuration Reference
M16A.SYS Intel NDIS 3 driver for Windows NT
There are user-configurable parameters to the M16A.SYS driver
which can be modified using the Network Control Panel built into
Windows NT. This applet uses the OEMSETNT.INF file to set the
corresponding parameters in the registry. The user-configurable
parameters are as follows:
Parameter Default Valid Values Registry
I/O PORT 0X320 0X200-0X3D0 SAME
MEMORY ADDRESS 0XD4000 0XA0000 - 0XFE000 SAME
INTERRUPT 5 3, 4, 5, 7, SAME
10, 11, 15
MODE I/O I/O 0
MEMORY MAPPED 1
CABLE TYPE AUTO AUTO DETECT 0
TWISTED PAIR... 1
LINE SPEED AUTO DETECT AUTO DETECT 0
10MBPS 1
100MBPS 2
EARLY TRANSMIT ENABLED DISABLED 0
ENABLED 1
LINK INTEGRITY ENABLED DISABLED 0
ENABLED 1
FULL DUPLEX DISABLED DISABLED 0
ENABLED 1
The network node address can be modified by manually editing the
registry and adding the parameter ‘NetworkAddress’ with a
hexadecimal string value, such as ‘00A0C9112233’. If the user does
NOT specify a ‘NetworkAddress’ then the M16A.SYS driver uses the
network node address contained in the PRO/100 PC Card Card
Information Structure.
Page 72

72
CHAPTER 3
There are parameters in the Windows NT registry which specify the
configuration of the PRO/100 PC Card hardware to the M16A.SYS
driver. Many of these parameters correspond directly to the userconfigurable parameters. These parameters are found in the registry at
the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CURRENTCONTROLSET\SERVICES\M16A1\PARAMETERS\
The registry parameters are as follows:
Keyword Default Valid Values
ADAPTERTYPE 0
BUSNUMBER 0
BUSTYPE 0X5
CABLETYPE 0 0-1
DIRECTENABLE 0 0-1
EARLYTRANSMIT 0X1 0-1
FULLDUPLEX 0 0-1
INTERRUPTNUMBER 0X5 3, 4, 5, 7, A, B, F
IOBASEADDRESS 0X320 0X200 - 0X3D0
IOLENGTH 0XF
LINESPEED 0 0-2
LINKINTEGRITY 0X1 0-1
MEMORYMAPPEDBASEADDRESS 0XD5000 A1000-FF000
MEMORYMAPPEDSIZE 0X1000
MODE 0 0-1
NETWORKADDRESS
PCCARDATTRIBUTE MEMORYADDRESS 0XD4000 A0000 - FE000
PCCARDATTRIBUTE MEMORYOFFSET 0
PCCARDATTRIBUTEMEMORYSIZE 0X1000
PCCARDMEMORYWINDOWOFFSET 0
PCMCIA 1 0-1
TRANSMITBUFFERSIZE 0X1C00 0X0400-0X1E800
‘Pcmcia’ defaults to ‘0’ for Windows NT 3.5.
Windows 3.x Driver Parameters
PRO/100 default settings may have to be changed in some PC Card
environments under Windows 3.x, when initialization is not successful
using the M16ACFG.EXE utility and the parameters selected by the
Intel Installation Program. The following paragraphs present
configuration guidelines for each of the driver types: NDIS, ODI, and
packet. These guidelines are followed by a comprehensive “keyword”
reference section and a list of error messages.
All of the drivers described here automatically detect the speed of the
network to which the adapter is attached (10Mbps or 100Mbps),
unless otherwise noted. Speed can also be specified with the
LINESPEED keyword.
Page 73

73
Configuration Reference
Full-duplex operation is only supported at 10Mbps and must be
explicitly configured with the FULLDUPLEX keyword. Full-duplex
operation is not supported at 100Mbps.
ODI Settings (for drivers M16AODI.COM and
M16AODI.OS2)
Custom parameters for networks using the ODI driver can be set up
with the Intel Installation Program or entered manually, using an
ASCII editor, in the NET.CFG file. If Card and Socket Services are
being used, the Intel M16ACFG.EXE configuration program
implements the appropriate parameters when the network driver is
loaded.
DOS ODI Driver Configuration Notes (M16AODI.COM)
The ODI driver M16AODI.COM conforms to the “Novell ODI
Specification: 16-bit DOS Client HSMs.” It is a DOS-based terminateand-stay-resident (TSR) program. The driver will configure itself
according to the options specified in the NET.CFG file. This file is
supplied on the Network Drivers Disk and must be present in the same
directory as the ODI driver. Files required for using M16AODI.COM
are
M16AODI.INS Intel installation information file
NET.CFG Network configuration file
M16AODI.COM Intel ODI driver
If Card and Socket Services are loaded, the Intel resource manager
M16ACFG.EXE must be run before M16AODI.COM to establish
connection between the PRO/100 PC Card and the computer.
Most installations will be able to use the settings implemented in the
NET.CFG file by the Intel Installation Program. If any parameters
need to be changed, use an ASCII text editor to open and modify the
NET.CFG file and insert the appropriate keywords and values after the
line
LINK DRIVER M16AODI
Parameters can also be implemented on the command line. Keyword
syntax can be found below. Keywords are not case sensitive. A
Keyword Alphabetical Reference follows the discussion of keyword
syntax.
Page 74

74
CHAPTER 3
NET.CFG Example
LINK DRIVER M16AODI
INT 5
PORT 280
MEM D2000
M16AODI.COM Keywords
Keyword Default Valid Values
FULLDUPLEX (NO KEYWORD = FULL-DUPLEX DISABLED)
INTERRUPT 5 (3 - 15)
IOADDRESS 320 (240 - 380)
IOWAITSTATES 0 (1 - 3)
LINESPEED AUTO (10 OR 100)
LINKDISABLE (NO KEYWORD = LINK INTEGRITY EN
ABLED)
LINK DRIVER M16AODI (REQUIRED FIRST ITEM IN NET.CFG)
MEMORY D2000 (C0000 - EE000)
MEMWAITSTATES 0 (1 - 3)
MODE MEM (MEM OR IO)
NOCHECK (NO KEYWORD = ADAPTER RESOURCE
VERIFICATION ENABLED)
NOEARLYRX (NO KEYWORD = EARLY RECEIVE EN
ABLED)
NOEARLYTX (NO KEYWORD = EARLY TRANSMIT EN
ABLED)
NOLED (NO KEYWORD = LEDS ENABLED)
S (COMMAND LINE ONLY: SHOW RESIDENT
LAN DRIVERS)
SOCKET AUTO (1 - 4)
U NOT USED (COMMAND LINE ONLY:
UNLOAD M16AODI)
WORDSIZE 16 (8 OR 16)
ODI Driver Example
A typical load sequence for the ODI driver M16AODI.COM with
M16ACFG.EXE in a NetWare environment would be
M16ACFG
LSL
M16AODI
IPXODI
VLM
OS/2 ODI Driver Configuration Notes (M16AODI.OS2)
The OS/2 ODI driver M16AODI.OS2 conforms to the Novell “ODI
Developer’s Guide for OS/2 Client Driver Hardware Specific Modules” version 2.1. It is an IBM OS/2-based device driver for use with
OS/2 versions 2.0 and later. The Novell OS/2 workstation ODI stack
including M16AODI.OS2 supports Novell’s NetWare Requestor for
OS/2 networking client environment.
Files required for using M16AODI.OS2 include Novell OS/2 Requestor files and the following files:
Page 75

75
Configuration Reference
NET.CFG Network configuration file
M16AODI.OS2 Intel ODI driver for OS/2
Most installations will be able to use the settings implemented in the
NET.CFG file by the Intel Installation Program. If any parameters
need to be changed, use an ASCII text editor to open and modify the
NET.CFG file and insert the appropriate keywords and values after the
line
LINK DRIVER M16AODI
Parameters can also be implemented on the command line. Keyword
syntax can be found below. Keywords are not case sensitive. A
Keyword Alphabetical Reference follows the discussion of keyword
syntax.
NET.CFG Example
LINK DRIVER M16AODI
INT 5
PORT 280
MEM D2000
M16AODI.OS2 Keywords
Keyword Default Valid Values
FULLDUPLEX (NO KEYWORD = FULL-DUPLEX DISABLED)
INTERRUPT 5 (3 - 15)
IOADDRESS 320 (240 - 380)
IOWAITSTATES 0 (1 - 3)
LINESPEED AUTO (10 OR 100)
LINKDISABLE (NO KEYWORD = LINK INTEGRITY EN
ABLED)
LINK DRIVER M16AODI (REQUIRED FIRST ITEM IN NET.CFG)
MEMORY D2000 (C0000 - EE000)
MEMWAITSTATES 0 (1 - 3)
MODE MEM (MEM OR IO)
NOCHECK (NO KEYWORD = ADAPTER RESOURCE
VERI- FICATION ENABLED)
NOEARLYRX (NO KEYWORD = EARLY RECEIVE EN
ABLED)
NOEARLYTX (NO KEYWORD = EARLY TRANSMIT EN
ABLED)
NOLED (NO KEYWORD = LEDS ENABLED)
SOCKET AUTO (1 - 4)
WORDSIZE 16 (8 OR 16)
NDIS 2.0.1 Settings (for drivers M16ANDIS.EXE and
M16ANDIS.OS2)
Custom parameters for the NDIS driver can be set up with the Intel
Installation Program or entered manually, using an ASCII editor, in
the PROTOCOL.INI file. If Card and Socket Services are being
used, the Intel M16ACFG.EXE resource manager program will
Page 76

76
CHAPTER 3
implement the appropriate parameters when the network driver is
loaded.
NDIS 2.0.1 DOS Driver Configuration Notes
The DOS NDIS driver M16ANDIS.EXE conforms to the 3Com/
Microsoft LAN Manager Network Driver Interface Specification
(NDIS) version 2.0.1. It is a DOS-based executable terminate-andstay-resident (TSR) program that will configure itself according to the
options specified in the PROTOCOL.INI file, which is supplied on the
Network Drivers Disk.
The files required for using M16ANDIS.EXE are:
PROTOCOL.INI Configuration and binding information
file
M16ADOS.NIF Intel installation file for Microsoft LAN
Manager
M16ANDIS.EXE Intel DOS NDIS 2.0.1 driver
If Card and Socket Services are loaded, the Intel resource manager
M16ACFG.EXE must be run before M16ANDIS.EXE to establish
connection between the PRO/100 PC Card and the computer.
Most installations will be able to use the settings implemented in the
PROTOCOL.INI file by the Intel Installation Program. If any parameters need to be changed, use an ASCII text editor to modify the
PROTOCOL.INI file with the appropriate keywords and values.
Keyword syntax for PROTOCOL.INI can be found below. Keywords
are not case sensitive, and can be abbreviated to a unique sequence of
initial characters (for example, IN for INTERRUPT, IO for
IOADDRESS). A Keyword Alphabetical Reference follows the
keyword listings.
NDIS 2.0.1 OS/2 Driver Configuration Notes
The OS/2 NDIS driver M16ANDIS.OS2 conforms to the 3Com/
Microsoft LAN Manager Network Driver Interface Specification
(NDIS) version 2.0.1. It is an IBM OS/2-based device driver for use
with OS/2 versions 2.0 and later.
The files required for using M16ANDIS.OS2 are:
PROTOCOL.INI Configuration and binding information
file
M16AOS2.NIF Intel installation file for Microsoft
LAN Manager
Page 77

77
Configuration Reference
M16ANDIS.OS2 Intel OS/2 NDIS 2.0.1 driver
Most installations will be able to use the settings implemented in the
PROTOCOL.INI file by the Intel Installation Program. If any parameters need to be changed, use an ASCII text editor to modify the
PROTOCOL.INI file with the appropriate keywords and values.
Keyword syntax for PROTOCOL.INI can be found below. Keywords
are not case sensitive, and can be abbreviated to a unique sequence of
initial characters (for example, IN for INTERRUPT, IO for
IOADDRESS). A Keyword Alphabetical Reference follows the
keyword listings.
PROTOCOL.INI Example
[INTELNET]
DRIVERNAME=INTEL$
MEM=0XD2000
MODE=IO
NDIS 2.0.1 Keywords (M16ANDIS.EXE and M16ANDIS.OS2)
Keyword Default Valid Values
DRIVERNAME=INTEL$ (REQUIRED FIRST ITEM IN PROTOCOL.INI)
FULLDUPLEX (NO KEYWORD = FULL-DUPLEX DISABLED)
INTERRUPT= 5 (3 - 15)
IOADDRESS= 320 (240 - 380)
IOWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
LINESPEED= AUTO (10 OR 100)
LINKDISABLE (NO KEYWORD = LINK INTEGRITY EN-
ABLED)
MEMORY= D2000 (C0000 TO EE000)
MEMWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
MODE= MEM (MEM OR IO)
NOCHECK (NO KEYWORD = ADAPTER RESOURCE VERI
FICATION ENABLED)
NOEARLYRX (NO KEYWORD = EARLY RECEIVE EN
ABLED)
NOEARLYTX (NO KEYWORD = EARLY TRANSMIT EN
ABLED)
NOLED (NO KEYWORD = LEDS ENABLED)
SOCKET= AUTO (1 - 4)
WORDSIZE= 16 (8 OR 16)
NDIS Driver Example - MS-DOS
The following example illustrates the use of M16ACFG.EXE with the
M16ANDIS.EXE driver in a CONFIG.SYS file supporting Microsoft
LAN Manager:
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN.DOS\DRIVERS\PROTMAN\PROTMAN.DOS /
I:C:\LANMAN.DOS
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN.DOS\DRIVERS\ETHERNET\INTEL\M16ACFG.EXE
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN.DOS\DRIVERS\ETHERNET\INTEL\M16ANDIS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\LANMAN.DOS\DRIVERS\PROTOCOL\TCPIP\TCPDRV.DOS
I:C:\LANMAN.DOS
Page 78

78
CHAPTER 3
M16ACFG.EXE must be loaded before the NDIS driver if Card and
Socket Services is being used.
Novell Server Driver Settings (for driver
M16AODI.LAN)
The driver M16AODI.LAN conforms to the Novell “ODI NetWare
Server Driver Development Tool Kit Driver Specification” version
3.3. It is a 32-bit driver. The NetWare Server ODI stack including
M16AODI.LAN supports NetWare versions 4.1 and 4.11.
Novell Server Driver Keywords
Parameters for configuring the Novell server driver must be specified
on the command line.
Keyword Default Valid Values
FULLDUPLEX (NO KEYWORD = FULL-DUPLEX DISABLED)
INT= 5 (3 - 15)
IOWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
LINESPEED= AUTO (10 OR 100)
LINKDISABLE (NO KEYWORD = LINK INTEGRITY EN-
ABLED)
MEM= D100 (C000 - EE00)
MEMWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
MODE= MEM (MEM OR IO)
NOCHECK (NO KEYWORD = ADAPTER RESOURCE
VERIFICATION ENABLED)
NOEARLYRX (NO KEYWORD = EARLYRX ENABLED)
NOEARLYTX (NO KEYWORD = EARLYTX ENABLED)
NOLED (NO KEYWORD = LEDS ENABLED)
PORT= 320 (240 - 380)
SOCKET= AUTO (1 - 4)
WORDSIZE= 16 (8 OR 16)
Packet Driver Settings (for driver M16APD.COM)
Packet driver parameters must be stated on the M16APD.COM
command line when running the packet driver.
Packet Driver Configuration Notes
The Intel packet driver M16APD.COM conforms to FTP Software’s
public domain packet-driver specification. It is a DOS-based terminate-and-stay-resident (TSR) program. The driver file M16APD.COM
is located in the \PKTDRV directory on the Network Drivers Disk.
Refer to your network documentation for instructions on how to install
the packet driver with your network. Most installations should be able
to use the default settings listed below. If Card and Socket Services
are loaded, run the utility M16ACFG.EXE before running
M16APD.COM.
Page 79

79
Configuration Reference
Keywords are not case sensitive, and can be abbreviated to a unique
sequence of initial characters (for example, IN for INTERRUPT).
Packet Driver Keywords
KEYWORD DEFAULT VALID VALUES
FULLDUPLEX (NO KEYWORD = FULL-DUPLEX DISABLED)
INTERRUPT= 5 (3 - 15)
IOADDRESS= 320 (240 - 380)
IOWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
LINESPEED= AUTO (10 OR 100)
LINKDISABLE (NO KEYWORD = LINK INTEGRITY EN
ABLED)
MEMORY= D2000 (C0000 - E8000)
MEMWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
MODE= MEM (MEM OR IO)
NOCHECK (NO KEYWORD = ADAPTER RESOURCE
VERIFICATION ENABLED)
NOEARLYRX (NO KEYWORD = EARLYRX ENABLED)
NOEARLYTX (NO KEYWORD = EARLYTX ENABLED)
NOLED (NO KEYWORD = LEDS ENABLED)
SINT 60 (60 - 80)
SOCKET= AUTO (1 - 4)
WORDSIZE= 16 (8 OR 16)
Packet Driver Example
A typical sequence for loading the packet driver M16APD.COM with
M16ACFG.EXE and default configuration settings is as follows:
M16ACFG
M16APD
ETHDRV
If nondefault configuration settings are used, these must be stated on
the M16APD.COM command line. For example,
M16ACFG
M16APD IOADDRESS=320 INT=7
ETHDRV
Diagnostic Test Utility Settings (M16ATEST.EXE)
The M16ATEST.EXE utility is a Intel utility for testing Intel adapter
hardware. It is an MS-DOS executable file.
M16ATEST.EXE tests the adapter hardware functionality, including
the PC Card interface, the serial EEPROM, the local SRAM, the
Ethernet controller, and the PHY interface (adapter modules). It
displays manufacturing information including serial number and date
and time of manufacture. It also displays configuration information
including interrupt, I/O address, and starting memory location used.
Page 80

80
CHAPTER 3
Parameters for the M16ATEST.EXE utility must be specified on the
DOS command line with the command M16ATEST. The parameters
are as follows:
M16ATEST.EXE Keywords
KEYWORD DEFAULT VALID VALUES
FULLDUPLEX (NO KEYWORD = FULL-DUPLEX DISABLED)
INTERRUPT= 5 (3 - 15)
IOADDRESS= 320 (240 - 380)
IOWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
LINESPEED= AUTO (10 OR 100)
LINKDISABLE (NO KEYWORD = LINK INTEGRITY ENABLED)
MEMORY= D2000 (C0000 - E8000)
MEMWAITSTATES= 0 (1 - 3)
MODE= MEM (MEM OR IO)
NOCHECK (NO KEYWORD = ADAPTER RESOURCE VERI
FICATION ENABLED)
NOEARLYRX (NO KEYWORD = EARLYRX ENABLED)
NOEARLYTX (NO KEYWORD = EARLYTX ENABLED)
NOLED (NO KEYWORD = LEDS ENABLED)
SILENT NOT USED (SUPPRESSES DISPLAY
DURING TEST AND RETURNS DOS ERROR CODES)
SOCKET= AUTO (1 - 4)
WORDSIZE= 16 (8 OR 16)
Keyword Alphabetical Reference
? (MS-DOS) displays command summary for
driver
CABLETYPE (NDIS 3) sets the driver to autodetect the
cable type or set unshielded twisted pair.
DRIVERNAME DRIVERNAME=INTEL$ required as first
item in the INTEL section of the
PROTOCOL.INI file for the M16ANDIS
driver.
EARLYTRANSMIT (NDIS 3) when set to OFF functions like
the keyword NOEARLYTX.
FULLDUPLEX (10 Mbps only) enables the PRO/100 PC
Card to send and receive data simultaneously when connected to a full-duplex
hub. Default is keyword not used, and
therefore full-duplex “disabled.” This
parameter is ignored in 100Mbps mode.
INT see INTERRUPT
Page 81

81
Configuration Reference
INTERRUPT specifies a PC Card port hardware
interrupt. Use 10 or 11 on most PCs.
Default (if parameter not specified) is 5.
Use 0 (zero) to force the adapter into a
polled mode.
IOADDRESS specifies the base I/O address of the Intel
adapter I/O ports, in hexadecimal notation.
Default address is 320.
I/O PORT see IOADDRESS.
IOWAITSTATES specifies the number of wait states to use
for accesses to the Intel adapter.
LINESPEED forces operation at 10 or 100Mbps. If the
keyword is not stated, the line speed will be
automatically detected.
LINKDISABLE disables link integrity for non-IEEE
10BASE-T networks such as StarLAN 10.
Without this keyword in the driver command line, the driver defaults to link
integrity ENABLED.
LINKINTEGRITY (NDIS 3) when set to OFF, operates like the
LINKDISABLE parameter.
LINK DRIVER LINK DRIVER M16AODI required as
first item in the NET.CFG file listing
configuration parameters for the M16AODI
driver. This must be the first keyword in the
section of the NET.CFG file for the Intel
adapter.
MEM see MEMORY.
MEMORY specifies the host PC memory location for
the Intel adapter in hexadecimal notation,
when. MODE MEMORY (memory-mapped
I/O) is being used (see MODE). The
memory block occupies 4Kbytes of host
memory.
MEMWAITSTATES specifies the number of waitstates to use for
memory accesses to the Intel adapter.
Values are decimal 1 to 3. The keyword is
provided as a troubleshooting aid.
Page 82

82
CHAPTER 3
MODE set this keyword to IO to disable requests
for memory-mapped mode on systems that
only support an I/O-driven card. The
MEMORY setting provides increased
performance on computers that allow
simultaneous availability of memory and
I/O resources.
NETWORKADDRESS allows user to override adapter’s unique
network node address by specifying a
different node address. Network node
address can be displayed with the
M16ATEST utility (MS-DOS).
NODEADDRESS see NETWORKADDRESS.
NOCHECK disables verification of adapter resources,
for troubleshooting purposes.
NOEARLYRX disables Advanced Look-ahead Pipelining
features of the Intel PRO/100 PC Card. This
parameter should be used in the NET.CFG
file when the ODI driver is used with
Microsoft Windows for Workgroups 3.11.
NOEARLYTX disables early transmit features of the Intel
PRO/100 PC Card. Try using this keyword
if you are experiencing a large number of
transmit underruns (in which hardware
reports not finding expected data in the
transmit buffer).
NOLED turns off LED indicators on LAN adapter
module to conserve power.
PORT (ODI) see IOADDRESS.
S (ODI)(MS-DOS command line only)
displays LAN drivers resident in memory.
SILENT (M16ATEST) disables display of informa-
tion on the screen and returns DOS error
code when tests are complete.
SINT (Packet Driver) is number from hexadeci-
mal 60 to 80 designating a software
interrupt. Default is 60.
Page 83

83
Configuration Reference
SOCKET the number of the host computer’s PC Card
slot or socket into which the Intel PRO/100
adapter is inserted. If a socket number is
specified, the only the specified socket is
checked for the Intel adapter. If no socket is
specified, the all sockets are searched until
the Intel adapter is found.
U (ODI)(MS-DOS command line only)
unloads driver from memory
WORDSIZE this parameter specifies the network data
path size. Values are 8 or 16 for 8- or 16-bit
transfers. Default is 16.
Page 84

84
CHAPTER 3
Page 85

85
This chapter contains troubleshooting information covering the most
common issues encountered when installing the PRO/100 PC Card,
based on information developed by Intel Customer Support.
This information is intended for users or network administrators who
are familiar with the PRO/100 PC Card and its user documentation,
and who have run into difficulties after having completed the installa-
tion procedures, as described in the preceding chapters of this User’s
Guide.
This chapter contains the following headings:
• LED Indicators
• Diagnostic Test
• Error Messages
• General Troubleshooting
• Network Operating System Troubleshooting (Artisoft LANtastic, DEC PATHWORKS, Windows 95, Windows for
Workgroups, Novell NetWare)
• Computer-Specific Troubleshooting
• Troubleshooting Checklist
Chapter 4
Troub leshooting
Page 86

CHAPTER 4
86
Additional Sources of Information
In addition to this User’s Guide, your computer and network documentation should also be consulted as needed. For the latest
information on the PRO/100 PC Card, see the README file on the
Intel Network Drivers Disk, or visit the Intel World Wide Web site at
http://support.intel.com. See Appendix A in this User’s Guide for
Intel support services access information.
LED Indicators
The LED indicators on the PRO/100 PC Card media module operate
under the following conditions: (1) the card is inserted into a PC Card
slot and (2) connected to the network, (3) computer is powered on, and
(4) network driver has been loaded.
LED Indicators (10Base-T/100Base-TX)
Transmission Activity
Yellow
Link Integrity
Orange = 100 Mbps
Green = 10 Mbps
Page 87

Troubleshooting
87
Diagnostic Self Test
Intel provides a DOS-based diagnostics program, located on the
Network Drivers Disk, that tests several PRO/100 PC Card functions.
It also reports test results, the serial number of the unit, and the
adapter node or network address. M16ATEST can only be run from
an MS-DOS command line (under Windows 95, use a DOS box, under
Windows NT boot to DOS).
Executing the Self Test
Use the following steps to execute the self test.
1 Install the PRO/100 PC Card according to the instructions
contained in Chapter 1, Hardware Installation in this User’s
Guide.
2 Start your computer from DOS (or use a DOS box). DO NOT
load a network driver.
Note
Do not run M16ATEST with a network driver loaded.
Loading a network driver before running M16ATEST
may cause unpredictable results when exiting the test
utility.
3 Run the diagnostic test by typing M16ATEST at the MS-DOS
prompt, followed by the appropriate keywords and parameters
(see Chapter 3), then press Enter. For example,
M16ATEST INT=10
The M16ATEST program executes all tests.
Note
If an error message displays when you execute the
self test, see “Error Messages” later in this chapter.
The M16ATEST program screen appears, displaying test parameters
and results. An explanation of the information displayed in the various
windows follows.
Self Test Window
Hardware, EEPROM, Init, and Memory Tests - The Hardware test
verifies that the PRO/100 PC Card is powered on and properly seated
in its slot. The EEPROM test reads the EEPROM and verifies that the
adapter data stored there is correct and readable. The Init test initial-
Page 88

CHAPTER 4
88
izes the PRO/100 PC Card memory and Ethernet controller. The
Memory test tests the SRAM on the PRO/100 PC Card.
A failure in any of these tests may indicate that service is required for
the PRO/100 PC Card. Contact Intel Customer Support.
Adapter Data Window
This section displays the model and serial numbers of the unit, its
manufacturing date and time, and its network node address. This
data has been preprogrammed at the factory and cannot be altered.
Important
Write down the PRO/100 PC Card model, serial
number, and network (node) address for reference.
Customer Support will ask you to supply the model and serial numbers
when requesting technical assistance or warranty service from Intel.
Configuration Window
This portion of the diagnostic screen lists current interrupt setting, port
or I/O address, and the starting memory location for the Intel PRO/100
PC Card.
Advanced Configuration Window
Line Speed - Indicates line speed: 10, 20 (full duplex), or 100Mbps.
Mode - Shows the memory mode of the adapter: either Memory
Mapped I/O mode or I/O-only mode.
Word Size - Indicates word size that the adapter is using: 16 (default)
or 8.
Early Receive - Indicates whether the adapter is operating in early
receive mode.
Early Transmit - Indicates whether the adapter is operating in early
transmit mode.
Page 89

Troubleshooting
89
Transmit Test Window
This test transmits a packet every 1/2 second. A failure indicates that
the PRO/100 PC Card is not accepting packets for transmission.
Network Traffic Graph Window
This graph provides a visual representation of the volume of traffic on
the local area network (LAN). If there is no traffic or if the PRO/100
PC Card is not connected to the LAN, a line of dots will display.
Instantaneous Packets - Displays the number of packets on the
network at half-second intervals.
Error Messages
Except as noted, these messages are specific to the Intel PRO/100 PC
Card. They are listed in strict numerical/alphabetical order, i.e.,
numbers appear before letters and messages starting with “The” are
under the letter T, initial “A” or “An” under the letter A.
For an explanation of other messages that may appear on the screen,
see the network-specific or computer-specific troubleshooting later in
this chapter, as well as your computer and network operating system
documentation.
An invalid I/O address was specified
The Intel PRO/100 PC Card requires 16 consecutive I/O locations.
This message indicates that the I/O address specified does not start on
a 32-byte boundary. The I/O address must begin on a 32-byte boundary. The PRO/100 PC Card supports all 32-byte boundary addresses
within the range defined by the platform. Some examples of valid I/O
addresses, in hexadecimal notation, are 300, 320, 240. Examples of
invalid I/O addresses are 301, 325, 247.
A PC Card was not detected
Page 90

CHAPTER 4
90
If the SOCKET keyword was stated, then no PC Card was detected in
the slot specified. If the SOCKET keyword was not used, then no PC
Card was detected in any slot.
Network Controller running in 8-bit mode
Either the driver has determined that the PC hardware does not
support 16-bit mode, or the Network Interface Controller (NIC) has
been forced to run in 8-bit mode with the keyword WORDSIZE set to
8 (default is 16-bit mode).
Network Controller running in I/O mode
Either the driver has determined that the PC hardware only supports I/
O-only mode, and not memory-mapped I/O mode, or the Network
Interface Controller (NIC) has been forced to run in I/O-only mode
with the keyword MODE IO (default is MEM).
Please specify 1, 2, or 3 for the IOWAITSTATES keyword
This message applies to both the ODI and NDIS 2.0 drivers. The value
specified under the IOWAITSTATES keyword in the NET.CFG or
PROTOCOL.INI file must be either 0, 1, 2, or 3.
Please specify 1, 2, or 3 for the MEMWAITSTATES keyword
This message applies to both the ODI and NDIS 2.0 drivers. The value
specified under the MEMWAITSTATES keyword in the NET.CFG or
PROTOCOL.INI file must be either 0, 1, 2, or 3.
Please specify a decimal number for the INTERRUPT keyword
This message applies only to the NDIS 2.0 Driver. The value specified
under the INTERRUPT keyword in the PROTOCOL.INI file must be
a decimal not a hexadecimal number.
Please specify a hexadecimal number for the IOADDRESS keyword
This message applies only to the NDIS 2.0 Driver. The value specified
under the IOADDRESS keyword in the PROTOCOL.INI file must be
a hexadecimal number.
Please specify a hexadecimal number for the MEMORY keyword
This message applies only to the NDIS 2.0 Driver. The value specified
under the MEMORY keyword in the PROTOCOL.INI file must be a
hexadecimal number.
Page 91

Troubleshooting
91
Please specify a non-zero decimal number for the SOCKET keyword
This message applies to both the ODI and NDIS 2.0 drivers. The value
specified under the SOCKET keyword in the NET.CFG or
PROTOCOL.INI file must be a decimal number other than zero.
Please specify either 8 or 16 for the WORDSIZE keyword
This message applies to both the ODI and NDIS 2.0 drivers. The value
specified under the WORDSIZE keyword in the NET.CFG or
PROTOCOL.INI file must be either 8 or 16.
Please specify either IO or MEM for the MODE keyword
This message applies to both the ODI and NDIS 2.0 drivers. The value
specified under the MODE keyword in the NET.CFG or
PROTOCOL.INI file must be either IO or MEM.
The card is unreadable, possible memory conflict
The Card Information Structure (CIS) of the PC Card was unreadable.
This could be a result of failure to exclude the selected memory range
from the memory managers loaded on the machine. Either exclude a
4K memory range, or select a memory range that has already been
excluded.
The I/O test failed - Please select a different I/O address
The driver failed the I/O test. Try a different I/O address.
The IRQ test failed - Please select a different IRQ
The driver failed the IRQ test. Try a different IRQ address.
The memory test failed - Please select a different memory address
The memory test will write data into the memory, read them back, and
verify if they are the same. In this case, the memory written and read
back were found to be different.
The Network Controller is not responding
A Intel PRO/100 PC Card adapter was detected, but subsequent
attempts to initialize the network controller failed. Try setting the
WORDSIZE parameter to 8.
The Intel PRO/100 PC Card has not been initialized
Page 92

CHAPTER 4
92
An error was detected during initialization. Usually another error
message will be displayed giving more detailed information about the
failure. For example, if the INTERRUPT keyword in the
PROTOCOL.INI has an invalid value of ‘0A’, the additional error
message Please specify a decimal number for the INTERRUPT
keyword is displayed after the Performance Series Adapter error
message.
M16AODI only supports the BUS ID PC Card, not the selected BUS
ID. Either delete the BUS ID keyword from the NET.CFG file or
change its value to 3.
This message applies only to the ODI driver. Do not use the keyword
BUS ID in the ODI NET.CFG file. If you do use it, you must set the
value to 3.
Windows 95 Troubleshooting
This troubleshooting information is intended primarily for users who
already had Microsoft Windows installed on their system and are
upgrading to Windows 95. It may also be helpful to new users of
Windows 95 who were unable to successfully install the Intel driver
using the instructions provided in Chapter 2, Software Installation.
Using Real Mode Card and Socket Services: When using Intel PC
Card adapters, should I still use DOS real mode Socket Services
Drivers?
No, it is recommended that you don’t load the real mode Card and
Socket Services drivers. It is also recommended that you boot the
machine without EMM386.exe in the CONFIG.SYS. In rare cases
where you still want to load EMM386.EXE, make sure you don’t use
the highscan keyword with EMM386.EXE. Windows 95 does not
detect devices correctly if there is a highscan keyword in the EMM386
line of the CONFIG.SYS file.
Installing from SCSI CDROM or EXTERNAL CDROM: I am installing Windows 95 from a SCSI CD-ROM attached to a SCSI PC Card
Adapter. How can I install Windows 95 if it is recommended that I
don’t load real mode card and socket services drivers since most SCSI
requires me to load a real mode SCSI driver?
Put a copy of the directory for CAB files of Windows 95 from the CDROM on to your local hard drive. This will take up approximately
Page 93

Troubleshooting
93
35MB of space. This will allow you to change settings on the system
without using your CD-ROM. This also allows you to install Windows
95 without depending on the real mode SCSI CDROM driver.
Installing Windows 95 PC Card support: How do I install PC Card
support for the PRO/100 PC Card?
To install PC Card Socket support, it is always advisable to let
Windows 95 do an autodetect to determine the type of PC Card
controller you have. Also make sure you have not loaded any real
mode Card and Socket Services drivers before proceeding.
1 Click the Start button in the lower left corner of the screen.
2 Choose the menu item: Settings.
3 Choose the menu item: Control Panel.
4 Double click on the “PC Card (PCMCIA)” icon.
5 One of two dialog boxes should appear:
a If a dialog box entitled “PC Card (PCMCIA) Properties”
appears, this means you have already installed the 32-bit PC
Card support and you are finished.
b If a dialog box entitled “Welcome to the PC Card (PCMCIA)
Wizard” appears, proceed to step 6.
c If neither of these dialog boxes appears, add PC Card support
by doing the following: double click on My Computer,
double click on Control Panel, double click on Add New
Hardware, and click Yes for Autodetect. After Windows 95
detects and installs PC Card support, restart Windows 95, and
go back to step 1.
6 The dialog box “Welcome to the PC Card (PCMCIA) Wizard”
will ask the following question: “Are you using a PC card
(networking card, CD-ROM connected to a SCSI card, etc.) to
install windows?” The default answer is No. If you did use a PC
Card SCSI adapter or a network card to install Windows 95, it is
recommended that you keep a copy of the Windows 95 directory
on your hard disk and not load any real mode PC Card or
network drivers. Press Enter to select No.
7 The dialog box “PC Card (PCMCIA) Wizard” should now
appear. It should read as follows: “Windows did not find any
Page 94

CHAPTER 4
94
existing real mode PC Card drivers. Either you did not have any,
or you have drivers that Windows couldn’t detect.” It will ask
you “Do you want to review your system files and select real
mode PC Card drivers so Windows can disable them?” The
default answer should be No. Now use the following decision
table:
a If you are not sure if you have real mode Card and Socket
Services or you do not know what they are, contact Microsoft
Customer Support or the manufacturer of your notebook
computer.
b If you know that you do not have real mode Card and Socket
Services installed, choose No and press Enter. Go on to step
8.
c If you know that you have real mode Card and Socket
Services and you wish to keep using them, this is not recommended. We recommend removing real mode drivers and
using the 32-bit driver.
d If you know that you have real mode Card and Socket
Services installed and Windows 95 either did or did not
detect them, you can now remove. Choose Yes and press
Enter.
e A new dialog box should appear and it should read: “Win-
dows has selected the known PC Card drivers in your
CONFIG.SYS file. Make sure that the correct drivers are
selected, or make any changes. When you click Next,
Windows will disable the selected PC card drivers in your
CONFIG.SYS file.” Choose option 1, 2, or 3 below:
Note
The dialog boxes displayed are the same except for
the name of the file to be modified. The first box
modifies the CONFIG.SYS, the next the
AUTOEXEC.BAT and the third the SYSTEM.INI file.
1 Let Windows 95 automatically find the drivers for you.
This is recommended. To do this click the Next button 3
times. This lets Windows 95 automatically modify the
following files: CONFIG.SYS, AUTOEXEC.BAT, and
SYSTEM.INI
Page 95

Troubleshooting
95
2 Choose the drivers yourself if none are selected. This is
recommended only for experienced users.
3 Override choices made by Windows 95. This is not
recommended. Only experienced users should attempt this.
f This is the next to last dialog box for the wizard. It should
read as follows: “You have finished the PC card wizard. To
enable 32-bit support, click Finish, and then restart your
computer for the changes to take effect.” Click on the Finish
button.
g A final box should appear entitled “System Settings Change”.
It should read as follows: “You must shut down Windows
and TURN YOUR COMPUTER OFF to continue setting up
this PC Card device. Would you like to shut down your
computer now?” Click Yes. Make sure that the computer is
completely turned off before turning it back on.
8 Insert your Intel PC Card adapter. Windows 95 should now
detect the Intel card, and put up a dialog box. It should automatically load the drivers from the Windows 95 directory. If it asks
you to supply a manufacturer’s disk, insert the Intel Network
Drivers Disk. Press Enter. It will ask you to restart now. Choose
yes. (We recommend copying the Windows 95 RETAIL or
WIN95 directory to your hard disk so that you won’t be dependent on the CD-ROM every time you need to reinstall.)
Hardware Specific Issues: Are there Laptops or Notebooks that don’t
work with Windows 95 and PC Card adapters?
Read the HARDWARE.TXT file in the Windows 95 directory. This
file is supplied by Microsoft and describes machine-specific problems.
NetWare Server is Not Found: Everything seems to load, I have
checked that I have installed the Microsoft Client for NetWare, but I
still can’t see my NetWare server when I click on Network Neighborhood.
Sometimes the Frametype autodetection fails. You can force the frame
type IPX uses by going to the My Computer, Control Panel, Network,
IPX/SPX compatible properties.
Page 96

CHAPTER 4
96
Microsoft Windows 3.x Troubleshooting
If any of the following situations occurs after you have completed the
installation procedure, review the accompanying information before
calling Customer Support.
The resource manager M16ACFG.EXE failed to load
If you are using Card and Socket Services, you must run the
M16ACFG.EXE resource manager before loading a PRO/100 PC Card
driver. If you are NOT using Card and Socket Services, or are running
Windows 95 or Windows NT, you do not need to run
M16ACFG.EXE.
Here are some of the symptoms that could appear if M16ACFG fails
to load:
A The message “No card services available” could indicate either
of two possibilities:
• Card and Socket Services are not being loaded and this is just
a notification message, not an error.
• The version of Card and Socket Services being loaded could
be obsolete or not supported. Contact your computer manufacturer to be sure you have the latest version.
B If the M16ACFG message “Exclusive use denied” displays, try
loading M16ACFG.EXE immediately before the Card and
Socket Services “generic card driver” in the CONFIG.SYS file.
“Generic card drivers” for the most popular Card and Socket
Services are as follows:
Manufacturer Filename
SystemSoft CARDID.EXE
Phoenix PCMSCD.EXE
IBM AUTODRV.SYS
C If you’re running Windows for Workgroups with the NDIS 2.0
driver and your machine hangs up at the NET START command, make the following change in the SYSTEM.INI:
Under the [NETWORK DRIVERS] section, remove
M16ACFG.EXE from the line that reads:
Page 97

Troubleshooting
97
NETCARD=M16ACFG.EXE, M16ANDIS.EXE
so that it reads:
NETCARD=M16ANDIS.EXE
If you are running Card and Socket Services with Windows for
Workgroups, be sure to load M16ACFG.EXE before the NET
START command, as follows:
C:\[PATH]M16ACFG
C:\[PATH]NET START
where [path] defines the locations of the referenced files for
your network.
A driver failed to load, and I’m using Card and Socket Services
Card and Socket Services are a set of drivers designed to support the
PC Card (PCMCIA) standard. These drivers are generally supplied by
the computer manufacturer. Among other functions they
• Hide the PC Card socket hardware implementation from the
PRO/100 PC Card driver.
• Control the allocation of resources (memory windows, I/O ports,
interrupts) to the PRO/100 PC Card.
Recommendations for Use of Card and Socket Services with
the PRO/100 PC Card.
A If the memory manager EMM386.EXE is being used, verify that
the memory required for the PRO/100 PC Card has been
excluded from use by the memory manager. Memory managers
are generally loaded in the CONFIG.SYS. The memory exclusion required when using Card and Socket Services is generally
larger than the exclusion needed by the PRO/100 PC Card alone.
The safest setting when troubleshooting is to “remark out” the
entire “C” and “D” memory ranges, as follows:
DEVICE=C:\[PATH]\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=C000-DFFF
After the driver has been successfully loaded, the memory
exclusion may be reduced through trial and error or in accordance with the Card and Socket Services documentation. The
system must be rebooted before the revised settings take effect.
Page 98

CHAPTER 4
98
B When the PRO/100 PC Card driver is loaded it either reads a
configuration file or uses command line parameters to determine
which resources it should use. The following is a list of driver
types, driver file names, and the configuration method used by
each:
Type File Name Configuration Method
ODI M16AODI.COM reads NET.CFG file
NDIS2 M16ANDIS.EXE reads PROTOCOL.INI file
Packet M16APD.EXE uses COMMAND LINE
parameters
Test M16ATEST.EXE uses COMMAND LINE
parameters
The default resources used by the PRO/100 PC Card in the
absence of a contrary setting in the configuration file or on the
command line are:
MEMORY D2000-D2FFF
IRQ 5
IOADDRESS (NDIS) 320
PORT (ODI) 320
C Card and Socket Services will generally try to assign a set of
resources (interrupt, memory window, I/O window) to the PRO/
100 PC Card. The resources configured for the PRO/100 PC
Card (in a configuration file or on a command line) must match
the resources assigned by Card and Socket Services. If they do
not, the driver will generally fail to load.
The way resources are assigned to the PC Card varies among
Card and Socket Services manufacturers. The following section
provides guidelines for the most popular Card and Socket
Services. Review your Card and Socket Services documentation.
To use Card and Socket Services with the PRO/100 PC Card,
you must know what resources will be assigned by Card and
Socket Services, then specify the same resources when configuring the PRO/100 PC Card.
Page 99

Troubleshooting
99
Note
You can display a list of resources available on your
computer by running the Intel resource manager
M16ACFG.EXE with the /DEBUG parameter, with no
network drivers loaded.
D If your computer requires Card and Socket Services, run the
resource manager M16ACFG.EXE before loading the PRO/100
PC Card driver to ensure that everything works together.
Suggestions arranged by Card and Socket Services manufacturers follow:
IBM
The following are the files generally loaded with IBM Card and
Socket Services.
DEVICE=C:\THINKPAD\IBMDSS01.SYS /S0=2
DEVICE=C:\THINKPAD\IBMDOSCS.SYS
DEVICE=C:\THINKPAD\DICRMU01.SYS /MA=C800-CFFF
(/MA
should match the EMM386 exclusion)
DEVICE=C:\THINKPAD\AUTODRV.SYS
C:\THINKPAD\AUTODRV.INI
(called a “generic” card driver)
The AUTODRV.INI file is used to assign resources to the PRO/
100 PC Card. M16ACFG.EXE should be loaded before the
AUTODRV.SYS line. The AUTODRV.INI file should be edited
to read as follows:
[ETHERNET]
CARDID=ETHER,CREDI
;OPTION=IGNORE
(The semicolon is required)
PORT1=320, IRQ=5, MEMORY1=C800, WAITSTATE=1
The same resources should be specified in the PRO/100 PC Card
driver initialization file.
E If M16ACFG.EXE returns the error message “Exclusive use
Page 100

CHAPTER 4
100
denied,” try loading M16ACFG.EXE immediately before the
Card and Socket Services “generic card driver” described above.
F If the Intel driver still fails to load, try using the PRO/100 PC
Card without Card and Socket Services, as described in the
following section.
Phoenix
The Phoenix Card and Socket Services super client driver
PCMSCD.EXE should NOT be configured with the PCM.EXE
program to support the PRO/100 PC Card. Use the default setup
and the following sequence of commands in your CONFIG.SYS
file.
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMSS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMCS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMRMAN.SYS
DEVICE=C:\INTEL\M16A\ODI\M16ACFG.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PMCPLUS3\PCMSCD.EXE
(called a “generic” card driver)
Be sure to verify that an EMM386 memory exclusion has been
stated to cover the region where the Intel card loads.
SystemSoft
The SystemSoft’s CardSoft Card and Socket Services are loaded
in the CONFIG.SYS file and generally include the following
lines:
DEVICE=C:\CARDSOFT\SOCKET_SERVICES_DRIVER
(This file varies by machine type)
DEVICE=C:\CARDSOFT\CS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\CARDSOFT\CSALLOC.EXE C:\CARDSOFT\CSALLOC.INI
DEVICE=C:\CARDSOFT\CARDID.EXE
(called a “generic” card driver)
Resources assigned by CardSoft Card and Socket Services are
controlled by the files CSALLOC.INI and CARDID.INI.
CSALLOC.INI contains a list of resources available to Card and
Socket Services. CARDID.INI controls how resources will be
assigned to specific types of cards. The setting in the PRO/100
 Loading...
Loading...