Page 1
ESM-2740/2743
Intel Pentium® M/Celeron® M /
Onboard Mobile Intel Celeron 600 MHz 512K L2 Cache
SOM-ETX CPU Module
User’s Manual
1st Ed – 13 February 2007
Part No. E2047274000R
Page 2
ESM-2740/2743
FCC Statement
THIS DEVICE COMPLIES WITH PART 15 FCC RULES. OPERATION IS
SUBJECT TO THE FOLLOWING TWO CONDITIONS:
(1) THIS DEVICE MAY NOT CAUSE HARMFUL INTERFERENCE.
(2) THIS DEVICE MUST ACCEPT ANY INTERFERENCE RECEIVED INCLUDING
INTERFERENCE THAT MAY CAUSE UNDESIRED OPERATION.
THIS EQUIPMENT HAS BEEN TESTED AND FOUND TO COMPLY WITH THE LIMITS
FOR A CLASS "A" DIGITAL DEVICE, PURSUANT TO PART 15 OF THE FCC RULES.
THESE LIMITS ARE DESIGNED TO PROVIDE REASONABLE PROTECTION AGAINTST
HARMFUL INTERFERENCE WHEN THE EQUIPMENT IS OPERATED IN A
COMMERCIAL ENVIRONMENT. THIS EQUIPMENT GENERATES, USES, AND CAN
RADIATE RADIO FREQUENCY ENERGY AND, IF NOT INSTATLLED AND USED IN
ACCORDANCE WITH THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL, MAY CAUSE HARMFUL
INTERFERENCE TO RADIO COMMUNICATIONS.
OPERATION OF THIS EQUIPMENT IN A RESIDENTIAL AREA IS LIKELY TO CAUSE
HARMFUL INTERFERENCE IN WHICH CASE THE USER WILL BE REQUIRED TO
CORRECT THE INTERFERENCE AT HIS OWN EXPENSE.
Notice
This guide is designed for experienced users to setup the system within the shortest time.
For detailed information, please always refer to the electronic user's manual.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2007 Avalue Technology Inc., ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, translated, or transmitted in any form
or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the prior written
permission of the original manufacturer.
Trademark Acknowledgement
Brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
owners.
2 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 3

User’s Manual
Disclaimer
Avalue Technology Inc. reserves the right to make changes, without notice, to any product,
including circuits and/or software described or contained in this manual in order to improve
design and/or performance. Avalue Technology assumes no responsibility or liability for the
use of the described product(s), conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright, or
masks work rights to these products, and makes no representations or warranties that
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work right infringement, unless
otherwise specified. Applications that are described in this manual are for illustration
purposes only. Avalue Technology Inc. makes no representation or warranty that such
application will be suitable for the specified use without further testing or modification.
Life Support Policy
Avalue Technology’s PRODUCTS ARE NOT FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN
LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE PRIOR WRITTEN APPROVAL
OF Avalue Technology Inc.
As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) are intended for
surgical implant into body, or (b) support or sustain life and whose failure to perform,
when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can
be reasonably expected to result in significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to
perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or
system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
A Message to the Customer
Avalue Customer Services
Each and every Avalue’s product is built to the most exacting specifications to ensure
reliable performance in the harsh and demanding conditions typical of industrial
environments. Whether your new Avalue device is destined for the laboratory or the factory
floor, you can be assured that your product will provide the reliability and ease of operation
for which the name Avalue has come to be known.
Your satisfaction is our primary concern. Here is a guide to Avalue’s customer services. To
ensure you get the full benefit of our services, please follow the instructions below carefully.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
3
Page 4
ESM-2740/2743
Technical Support
We want you to get the maximum performance from your products. So if you run into
technical difficulties, we are here to help. For the most frequently asked questions, you can
easily find answers in your product documentation. These answers are normally a lot more
detailed than the ones we can give over the phone. So please consult the user’s manual
first.
To receive the latest version of the user’s manual; please visit our Web site at:
http://www.avalue.com.tw/
If you still cannot find the answer, gather all the information or questions that apply to your
problem, and with the product close at hand, call your dealer. Our dealers are well trained
and ready to give you the support you need to get the most from your Avalue’s products. In
fact, most problems reported are minor and are able to be easily solved over the phone.
In addition, free technical support is available from Avalue’s engineers every business day.
We are always ready to give advice on application requirements or specific information on
the installation and operation of any of our products. Please do not hesitate to call or e-mail
us.
Headquarters
Avalue Technology Inc.
7F, 228, Lian-cheng Road,
Chung Ho City, Taipei,
Taiwan
Tel : +886-2-8226-2345
Fax : +886-2-8226-2777
http://www.avalue.com.tw
E-mail: service@avalue.com.tw
China Branch Office
Avalue Technology Shanghai Inc.
Room 909, 9F, Section B, No.900,
Yisan Road, Caohejing Hi-tech Park,
Shanghai 200233, China
Tel : +86-21-5423-4170
Fax : +86-21-5423-4171
http://www.avalue.com.tw
E-mail: service.china@avalue.com.tw
Europe Branch Office
Avalue Europe A/S
Nordre Strandvej 13,
3480 Fredensborg,
Denmark
Tel : +45-7025-0310
Fax : +45-4975-5026
http://www.avalue.com.tw
E-mail: service.europe@avalue.com.tw
US Branch Office
Avalue Technology Inc.
Suite 210, 200 Tornillo Way,
Tinton Falls, NJ 07712
USA
Tel: +1-732-578-0200
Fax: +1-732-578-0250
http://www.avalue.com.tw
E-mail: service.usa@avalue.com.tw
4 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 5

User’s Manual
Product Warranty
Avalue warrants to you, the original purchaser, that each of its products will be free from
defects in materials and workmanship for two years from the date of purchase.
This warranty does not apply to any products which have been repaired or altered by
persons other than repair personnel authorized by Avalue, or which have been subject to
misuse, abuse, accident or improper installation. Avalue assumes no liability under the
terms of this warranty as a consequence of such events. Because of Avalue’s high
quality-control standards and rigorous testing, most of our customers never need to use our
repair service. If any of Avalue’s products is defective, it will be repaired or replaced at no
charge during the warranty period. For out-of-warranty repairs, you will be billed according
to the cost of replacement materials, service time, and freight. Please consult your dealer
for more details. If you think you have a defective product, follow these steps:
1. Collect all the information about the problem encountered. (For example, CPU type and
speed, Avalue’s products model name, hardware & BIOS revision number, other
hardware and software used, etc.) Note anything abnormal and list any on-screen
messages you get when the problem occurs.
2. Call your dealer and describe the problem. Please have your manual, product, and any
helpful information available.
3. If your product is diagnosed as defective, obtain an RMA (return material authorization)
number from your dealer. This allows us to process your good return more quickly.
4. Carefully pack the defective product, a complete Repair and Replacement Order Card
and a photocopy proof of purchase date (such as your sales receipt) in a shippable
container. A product returned without proof of the purchase date is not eligible for
warranty service.
5. Write the RMA number visibly on the outside of the package and ship it prepaid to your
dealer.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
5
Page 6

ESM-2740/2743
Contents
1. Getting started............................................................................................................9
1.1 Safety Precautions....................................................................................................9
1.2 Packing List...............................................................................................................9
1.3 Document Amendment History...............................................................................10
1.4 Manual Objectives...................................................................................................11
1.5 System Specifications.............................................................................................12
1.6 Architecture Overview.............................................................................................14
1.6.1 Block Diagram................................................................................................................................ 14
1.6.2 Intel RG82855GME and FW82801DB (for ESM-2740) ................................................................. 15
1.6.3 Intel RG82852GM and FW82801DB (for ESM-2743).................................................................... 17
1.6.4 DRAM Interface (Intel RG855GME)............................................................................................... 18
1.6.5 DRAM Interface (Intel RG852GM)................................................................................................. 18
1.6.6 Chrontel CH7011 TV Transmitter................................................................................................... 19
1.6.7 PCI Interface .................................................................................................................................. 19
1.6.8 USB 2.0.......................................................................................................................................... 19
1.6.9 Ethernet..........................................................................................................................................20
1.6.10 Winbond W83627HF.................................................................................................................. 20
1.6.11 Winbond W83628F & W83629D PCI/ISA Bridge ...................................................................... 21
2. Hardware Configuration...........................................................................................22
2.1 Product Overview....................................................................................................23
2.2 Installation Procedure .............................................................................................24
2.1.1 Installing Processor........................................................................................................................ 24
2.1.2 Main Memory.................................................................................................................................. 26
2.3 Jumper and Connector List.....................................................................................28
2.4 Setting Jumpers & Connectors ...............................................................................29
2.4.1 FSB Select (SW2).......................................................................................................................... 29
2.4.2 ETX Connector X1 (ETXA) ............................................................................................................ 30
2.4.3 Signal Description – ETX Connector X1 (ETXA)........................................................................... 31
2.4.4 ETX Connector X2 (ETXB) ............................................................................................................ 33
2.4.5 Signal Description – ETX Connector X2 (ETXB)........................................................................... 34
2.4.6 ETX Connector X3 (ETXC)............................................................................................................ 36
2.4.7 Signal Description – ETX Connector X3 (ETXC)........................................................................... 37
2.4.8 ETX Connector X4 (ETXD)............................................................................................................ 39
2.4.9 Signal Description – ETX Connector X4 (ETXD)........................................................................... 40
3. BIOS Setup................................................................................................................43
3.1 Starting Setup .........................................................................................................44
6 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 7

User’s Manual
3.2 Using Setup ............................................................................................................45
3.3 Getting Help............................................................................................................ 46
3.4 In Case of Problems................................................................................................46
3.5 Main Menu..............................................................................................................47
3.5.1 Standard CMOS Features.............................................................................................................. 48
3.5.2 Advanced BIOS Features .............................................................................................................. 51
3.5.3 Advanced Chipset Features........................................................................................................... 55
3.5.4 Integrated Peripherals.................................................................................................................... 59
3.5.5 Power Management Setup............................................................................................................. 63
3.5.6 PnP / PCI Configuration................................................................................................................. 65
3.5.7 PC Health Status............................................................................................................................ 67
3.5.8 Frequency / Voltage Control .......................................................................................................... 67
3.5.9 Load Fail-Safe Defaults.................................................................................................................. 68
3.5.10 Load Optimized Defaults............................................................................................................ 68
3.5.11 Set Supervisor / User Password................................................................................................ 69
3.5.12 Save & Exit Setup...................................................................................................................... 70
3.5.13 Exit Without Save....................................................................................................................... 71
4. Drivers Installation ................................................................................................... 72
4.1 Install Chipset Driver (For Intel RG82855GME)......................................................73
4.2 Install Chipset Driver (For Intel RG82852GM) ........................................................74
4.3 Install Display Driver (For Intel RG82855GME) ......................................................75
4.4 Install Display Driver (For Intel RG82852GM).........................................................76
4.5 Install Audio Driver (For Intel 82801DB)..................................................................77
4.6 Install Ethernet Driver (For Realtek RTL810x, RTL813x Family) ............................78
5. Measurement Drawing .............................................................................................79
Appendix A: BIOS Revisions..........................................................................................81
Appendix B: AWARD BIOS POST Messages ................................................................82
Overview............................................................................................................................83
Post Beep..........................................................................................................................83
Error Messages .................................................................................................................83
1. CMOS BATTERY HAS FAILED.........................................................................................................83
2. CMOS CHECKSUM ERROR.............................................................................................................83
3. DISK BOOT FAILURE, INSERT SYSTEM DISK AND PRESS ENTER............................................ 83
4. DISKETTE DRIVES OR TYPES MISMATCH ERROR - RUN SETUP.............................................. 83
5. DISPLAY SWITCH IS SET INCORRECTLY...................................................................................... 84
6. DISPLAY TYPE HAS CHANGED SINCE LAST BOOT..................................................................... 84
7. EISA Configuration Checksum Error PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY................... 84
8. EISA Configuration Is Not Complete PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY................... 84
9. ERROR ENCOUNTERED INITIALIZING HARD DRIVE.................................................................... 84
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
7
Page 8

ESM-2740/2743
10. ERROR INITIALIZING HARD DISK CONTROLLER..................................................................... 84
11. FLOPPY DISK CNTRLR ERROR OR NO CNTRLR PRESENT ................................................... 84
12. Invalid EISA Configuration PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY.............................. 85
13. KEYBOARD ERROR OR NO KEYBOARD PRESENT................................................................. 85
14. Memory Address Error at .............................................................................................................. 85
15. Memory parity Error at ................................................................................................................... 85
16. MEMORY SIZE HAS CHANGED SINCE LAST BOOT................................................................. 85
17. Memory Verify Error at .................................................................................................................. 85
18. OFFENDING ADDRESS NOT FOUND......................................................................................... 85
19. OFFENDING SEGMENT: ..............................................................................................................85
20. PRESS A KEY TO REBOOT ......................................................................................................... 86
21. PRESS F1 TO DISABLE NMI, F2 TO REBOOT ........................................................................... 86
22. RAM PARITY ERROR - CHECKING FOR SEGMENT ... ............................................................. 86
23. Should Be Empty But EISA Board Found PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY....... 86
24. Should Have EISA Board But Not Found PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY ....... 86
25. Slot Not Empty ............................................................................................................................... 86
26. SYSTEM HALTED, (CTRL-ALT-DEL) TO REBOOT .................................................................... 86
27. Wrong Board In Slot PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY........................................ 87
28. FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (80) → Unable to reset floppy subsystem................................................... 87
29. FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (40) → Floppy Type dismatch..................................................................... 87
30. Hard Disk(s) fail (80) → HDD reset failed.................................................................................... 87
31. Hard Disk(s) fail (40) → HDD controller diagnostics failed.......................................................... 87
32. Hard Disk(s) fail (20) → HDD initialization error.......................................................................... 87
33. Hard Disk(s) fail (10) → Unable to recalibrate fixed disk............................................................. 87
34. Hard Disk(s) fail (08) → Sector Verify failed................................................................................ 87
35. Keyboard is locked out - Unlock the key........................................................................................ 87
36. Keyboard error or no keyboard present......................................................................................... 87
37. Manufacturing POST loop.............................................................................................................. 87
38. BIOS ROM checksum error - System halted. ................................................................................ 87
39. Memory test fail.............................................................................................................................. 87
40. POST Codes.................................................................................................................................. 88
8 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 9

User’s Manual
1. Getting started
1.1 Safety Precautions
Warning!
Always completely disconnect the power cord from your
chassis whenever you work with the hardware. Do not
make connections while the power is on. Sensitive
electronic components can be damaged by sudden power
surges. Only experienced electronics personnel should
open the PC chassis.
Caution!
Always ground yourself to remove any static charge before
touching the CPU card. Modern electronic devices are very
sensitive to static electric charges. As a safety precaution,
use a grounding wrist strap at all times. Place all electronic
components in a static-dissipative surface or static-shielded
bag when they are not in the chassis.
1.2 Packing List
Before you begin installing your single board, please make sure that the
following materials have been shipped:
z 1 x ESM-2740 Intel Pentium® M SOM-ETX CPU Module (Onboard
Mobile Intel Celeron 600 MHz 0K L2 Cache CPU for ESM-2743)
z 1 x Quick Installation Guide
z 1 x CD-ROM contains the followings:
— User’s Manual (this manual in PDF file)
— VGA drivers and utilities
— Audio drivers and utilities
— Ethernet driver and utilities
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
9
Page 10
ESM-2740/2743
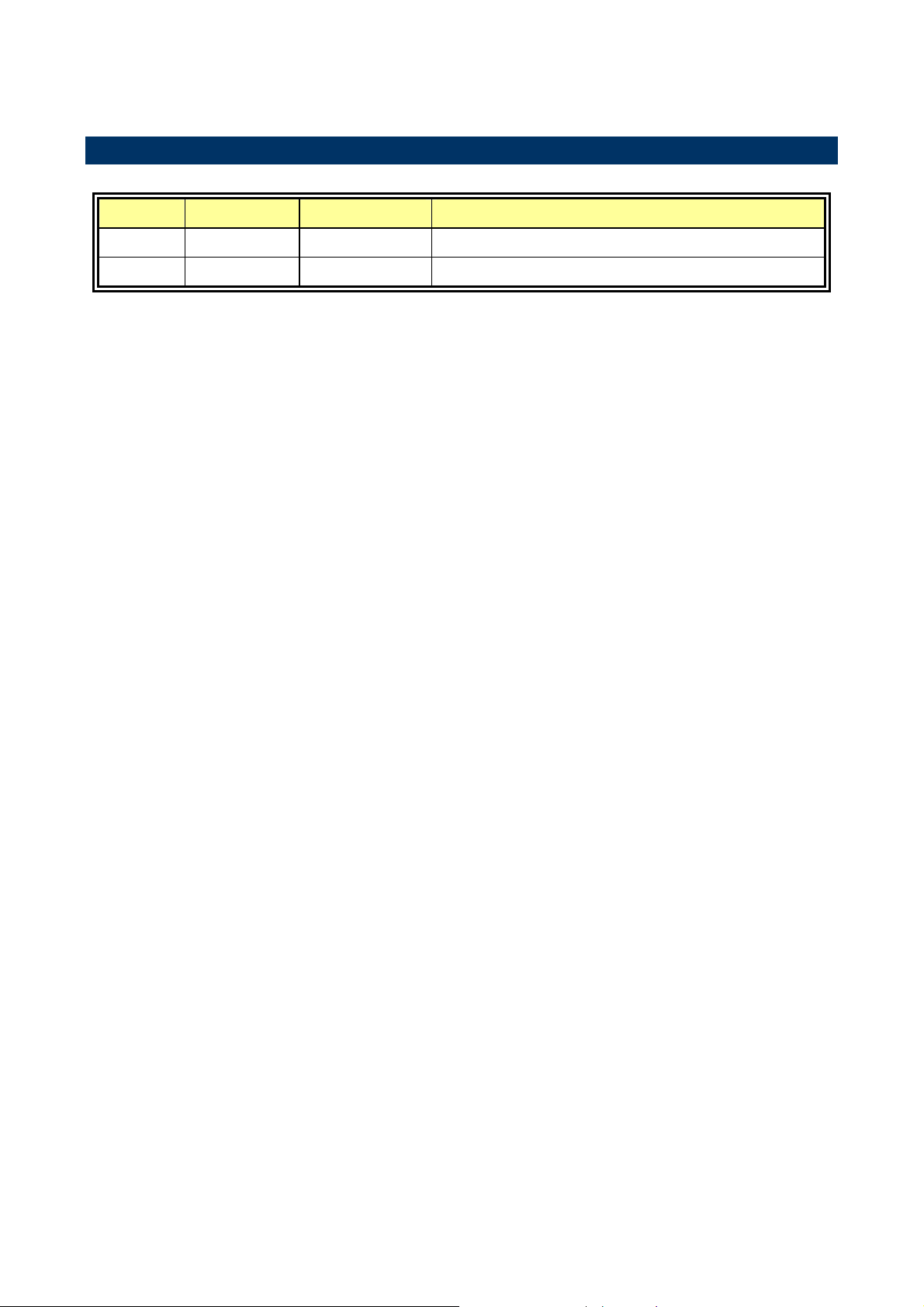
1.3 Document Amendment History
Revision Date By Comment
1st May 2005 Vicky Lin Initial Release
Feb. 2007 Lingo Tsai Logo Changed
10 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 11

User’s Manual
1.4 Manual Objectives
This manual describes in detail the Avalue Technology ESM-2740/2743 SOM-ETX CPU
Module.
We have tried to include as much information as possible but we have not duplicated
information that is provided in the standard IBM Technical References, unless it proved to
be necessary to aid in the understanding of this board.
We strongly recommend that you study this manual carefully before attempting to interface
with ESM-2740/2743 or change the standard configurations. Whilst all the necessary
information is available in this manual we would recommend that unless you are confident,
you contact your supplier for guidance.
Please be aware that it is possible to create configurations within the CMOS RAM that
make booting impossible. If this should happen, clear the CMOS settings, (see the
description of the Jumper Settings for details).
If you have any suggestions or find any errors concerning this manual and want to inform
us of these, please contact our Customer Service department with the relevant details.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
11
Page 12
ESM-2740/2743
1.5 System Specifications
System
CPU
BIOS
System Chipset
I/O Chip
System Memory
Watchdog Timer
Expansion
I/O
MIO
ESM-2740: Supports Intel® µFC-PGA 478 Pentium® M / Celeron® M
CPU with 0.13µ and 90nm process technology
ESM-2740-P11: Onboard Intel® µFC-BGA 479 Pentium® M 1.1 GHz
(Onboard Mobile Intel® Celeron® 600 MHz with 0K L2 Cache CPU for
ESM-2743 only)
Note: Available in different CPU speeds by request
Award 512 KB Flash BIOS
Intel® RG82855GME GMCH/FW82801DB ICH4
(Intel® RG82852GM GMCH/FW82801DB ICH4 for ESM-2743 only)
Winbond W83627HF-AW
One 200-pin SODIMM socket supports up to 1 GB DDR 200/266/333
SDRAM
Reset: 1 sec.~255 min. and 1 sec. or 1 min./step
Four PCI Master bus, ISA bus, SIRQ
4 x EIDE (Ultra DMA 100), 2 x FDD, 1 s LPT, 2 x TTL serial, 1x K/B, 1 x
IrDA
USB
Display
Chipset
Display Memory
Resolution
VGA/LCD Interface
LVDS
TV-Out
Mouse
115k bps, IrDA 1.0 compliant
4 x USB 2.0 ports
Intel® RG82855GME GMCH integrated Extreme Graphics 2 controller
(Intel® RG82852GM GMCH integrated Extreme Graphics controller for
ESM-2743 only)
Intel® DVMT 2.0 supports up to 64 MB video memory
CRT mode: 2048 x 1536 @ 16 bpp (75 Hz)
LCD/Simultaneous mode: 2048 x 1536 @ 16 bpp (75 Hz)
AGP 4x VGA/LCD interface
Intel® RG82855GME supports dual-channel 24-bit LVDS panels
(Intel® RG82852GM supports dual-channel 24-bit LVDS panels for
ESM-2743 only)
Chrontel CH7011 TV encoder supports both NTSC/PAL
Supports both S-video and composite video
12 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 13
Audio
User’s Manual
Chipset
AC97 Codec
Audio Interface
Ethernet
Chipset
Ethernet Interface
Remote Boot ROM
Mechanical & Environmental
Power Requirement
Power Type
Operation Temperature
Operating Humidity
Size ( L x W )
Weight
Intel® FW82801DB ICH4
VIA VT1616 supports 5.1 CH Audio
Mic in, Line in, CD Audio in, Line out, Rear out and Center/Subwoofer out
Realtek RTL8101L
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-Tx Fast Ethernet compatible
Optional built-in boot ROM in Flash BIOS
+ 5 V @ 3.60 A, + 3.3 V @ 0.01 A, +12 V @ 0.01 A, -5V @ 0.01A, -12 V @
0.01 A (with Intel® Pentium® M 1.8 GHz & 1 GB DDR SDRAM)
AT/ATX
0~60® C (32~140® F)
0%~90% relative humidity, non-condensing
4.5" x 3.7” (114 mm x 95 mm)
0.22 lbs (0.1 Kg)
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
13
Page 14
ESM-2740/2743
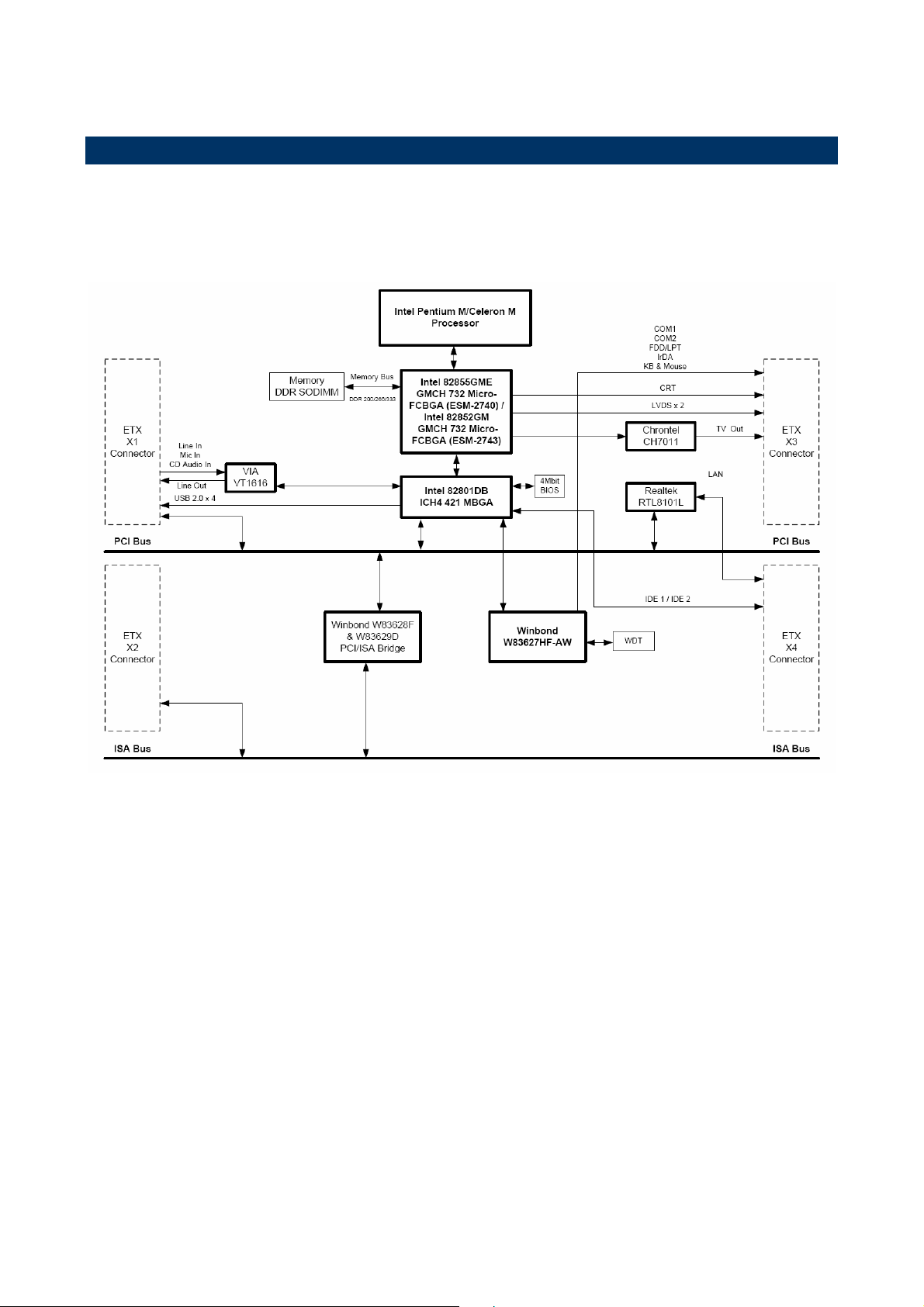
1.6 Architecture Overview
1.6.1 Block Diagram
The following block diagram shows the architecture and main components of
ESM-2740/2743.
The following sections provide detail information about the functions provided onboard.
14 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 15

User’s Manual
1.6.2 Intel RG82855GME and FW82801DB (for ESM-2740)
The Intel 855GM/855GME GMCH components provide the processor interface, DDR
SDRAM interface, display interface, and Hub interface. The Intel 855GME also has an
option for AGP external graphics port, in addition to integrated graphics support for added
board flexibility options.
The Intel 855GM GMCH is in a 732-pin Micro-FCBGA package and contains the following
functionality listed below:
• AGTL+ host bus supporting 32-bit host addressing with Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
technology support
• Supports a single channel of DDR SDRAM memory
• System memory supports DDR200/266 MHz (SSTL_2) DDR SDRAM
• Integrated graphics capabilities: Display Core frequency at 133 MHz or 200 MHz
• Render Core frequency at 100 MHz ,133 MHz, and 200 MHz
• Provides supports four display ports: one progressive scan analog monitor, dual
channel LVDS interface and two DVO port.
The Intel 855GME GMCH is in a 732-pin Micro-FCBGA package and contains all features
listed above and the additional functionality list below:
• Display Core frequency at 133 MHz, 200 MHz, or 250 MHz
• Render Core frequency at 100 MHz ,133 MHz, 166 MHz, 200 MHz, or 250 MHz
• System memory supports 200/266/333- MHz (SSTL_2) DDR SDRAM.
• Enhanced Power Management Graphics features
The GMCH IGD provides a highly integrated graphics accelerator delivering high
performance 2D, 3D, and video capabilities. With its interfaces to UMA using a DVMT
configuration, an analog display, a LVDS port, and two digital display ports (e.g. flat panel),
the GMCH can provide a complete graphics solution.
The GMCH also provides 2D hardware acceleration for block transfers of data (BLTs). The
BLT engine provides the ability to copy a source block of data to a destination and perform
raster operations (e.g., ROP1, ROP2, and ROP3) on the data using a pattern, and/or
another destination. Performing these common tasks in hardware reduces CPU load, and
thus improves performance. High bandwidth access to data is provided through the system
memory interface. The GMCH uses Tiling architecture to increase system memory
efficiency and thus maximize effective rendering bandwidth. The Intel 855GM/855GME
GMCH improves 3D performance and quality with 3D Zone rendering technology. The Intel
855GME GMCH also supports Video Mixer rendering, and Bi-Cubic filtering.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
15
Page 16

ESM-2740/2743
The Intel 855GM/855GME GMCH has four display ports, one analog and three digital. With
these interfaces, the GMCH can provide support for a progressive scan analog monitor, a
dedicated dual channel LVDS LCD panel, and two DVO devices. Each port can transmit
data according to one or more protocols. The data that is sent out the display port is
selected from one of the two possible sources, Pipe A or Pipe B.
The Intel 855GM/855GME GMCH have an integrated dual channel LFP Transmitter
interface to support LVDS LCD panel resolutions up to UXGA The display pipe provides
panel up-scaling to fit a smaller source image onto a specific native panel size, as well as
provides panning and centering support. The LVDS port is only supported on Pipe B. The
LVDS port can only be driven by Pipe B, either independently or simultaneously with the
Analog Display port. Spread Spectrum Clocking is supported: center and down spread
support of 0.5%, 1%, and 2.5% utilizing an external SSC clock.
The DVO B/C interface is compliant with the DVI Specification 1.0. When combined with a
DVI compliant external device (e.g. TMDS Flat Panel Transmitter, TV-out encoder, etc.),
the GMCH provides a high-speed interface to a digital or analog display (e.g. flat panel, TV
monitor, etc.). The DVO ports are connected to an external display device. Examples of this
are TV-out encoders, external DACs, LVDS transmitters, and TMDS transmitters. Each
display port has control signals that may be used to control, configure and/or determine the
capabilities of an external device. The GMCH provides two DVO ports that are each
capable of driving a 165-MHz pixel clock at the DVO B or DVO C interface. When DVO B
and DVO C are combined into a single DVO port, then an effective pixel rate of 330 MHz
can be achieved. The DVO B/C ports can be driven by Pipe A or Pipe
B. If driven on Pipe B, then the LVDS port must be disabled.
The ICH4 is a highly integrated multifunctional I/O Controller Hub that provides the
interface to the PCI Bus and integrates many of functions needed in today’s PC platform.
The GMCH and ICH4 communicate over a dedicated hub interface. The 82801DB ICH4
functions and capabilities include:
• PCI Rev. 2.2 compliant with support for 33MHz PCI operations
• Supports up to 6 Request/Grant pairs (PCI slots)
• Power management logic support
• Enhanced DMA controller, interrupt controller, and timer functions
• Integrated IDE controller; Ultra ATA/100/66/33
• USB host interface; 3 host controllers and supports 6 USB ports; includes a EHCI
high-speed 2.0 USB controller
16 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 17

User’s Manual
• Integrated LAN controller
• System Management Bus (SMBus) compatible with most IC devices; ICH4 has both
bus master and slave capability
• AC ’97 2.3 compliant link for audio and telephony codecs; up to 6 channels
• Low Pin Count (LPC) interface
• FWH Interface (FWH Flash BIOS support)
• Alert on LAN* (AOL and AOL2)
1.6.3 Intel RG82852GM and FW82801DB (for ESM-2743)
The Intel 852GM GMCH component provides the processor interface, DDR SDRAM
interface, display interface, and Hub Interface in an Intel 852GM chipset platform. The Intel
852GM GMCH is optimized for the Mobile Intel Pentium 4 Processor-M, Mobile Intel
Celeron processor and Intel Celeron M processor. It supports a single channel of DDR
SDRAM memory. Intel 852GM Chipset contains advanced power management logic. The
Intel 852GM Chipset platform supports the fourth generation mobile I/O Controller Hub to
provide the features required by a mobile platform.
The Intel 852GM GMCH is in a 732-pin Micro-FCBGA package and contains the following
functionality:
• Supports single Intel processor configurations at 400-MHz or 3 GB/s
• 1.2-1.30-V AGTL+ host bus supporting 32-bit host bus addressing with Enhanced
Intel SpeedStep® technology (Intel Celeron M processor and Intel Celeron
Processor do not support Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology).
• System Memory supports 200/266-MHz (SSTL_2) DDR DRAM Up to 1 GB (with
256-Mb technology and two SO-DIMMs) of PC1600/2100 DDR SDRAM without
ECC
• Integrated graphics capabilities, including 3D rendering acceleration and 2D
hardware acceleration
• Integrated 350-MHz, 24-bit RAMDAC with pixel resolution up to 1600x1200 at 85-Hz
and up to 1920x1440 @ 60 Hz
• One Dedicated Dual Channel LFP LVDS interface with frequency range of 25 MHz
to 112 MHz (single channel/dual channel) for support up to SXGA+ (1400x1050 @
60 Hz) panel resolutions with maximum pixel depth of 18-bpp
• Integrated PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) interface for LFP backlight inverter
control for panel brightness
• One 165-MHz, 12-bit, DVO interface for TV-out encoder and DVI (LVDS transmitter
and TMDS transmitter) support I2C and DDC channels supported
• Dual Pipe Independent Display with Tri-view support through LFP, DVO, and CRT
• Deeper Sleep state support
• Distributed arbitration for highly concurrent operation
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
17
Page 18

ESM-2740/2743
• Three USB host controllers provide high performance peripherals with 480 Mbps of
bandwidth, while enabling support for up to six USB 2.0 ports. This results in a
significant increase over previous integrated 1-4 port hubs at 12 Mbps
• The latest AC ’97 implementation delivers 20-bit audio for enhanced sound quality
and full surround sound capability. Integrated audio solutions continue to enjoy
success as a very cost-effective, yet high-performance solution
• LAN Connect Interface (LCI) provides flexible network solutions such as 10/100
Mbps Ethernet and 10/100 Mbps Ethernet with LAN manageability
• Dual Ultra ATA/100 controllers, coupled with the Intel® Application Accelerator – a
performance software package – support faster IDE transfers to storage devices
• Intel Application Accelerator software provides additional performance over native
ATA drivers by improving I/O transfer rates and enabling faster O/S load time,
resulting in accelerated boot times
• Communication and Network Riser (CNR) offers flexibility in system configuration
with a baseline feature set that can be upgraded with an audio card, modem card, or
network card
1.6.4 DRAM Interface (Intel RG855GME)
The 855GME GMCH system memory controller directly supports the following:
• One channel of PC1600/2100 DDR SDRAM memory
• One channel of PC1600/2100/2700 DDR SDRAM memory
• DDR SDRAM devices with densities of 128-Mb, 256-Mb, and 512-Mb technology
• Up to 1 GB (512-Mb technology) with two SDRAM
1.6.5 DRAM Interface (Intel RG852GM)
The 852GM GMCH system memory controller directly supports the following:
• One channel of PC1600/2100 DDR SDRAM memory
• DDR SDRAM devices with densities of 128-Mb, 256-Mb, and 512-Mb technology
• Variable page sizes of 2-kB, 4-kB, 8-kB, and 16-kB. Page size is individually selected
for every row and a maximum of 16 pages may be opened simultaneously
18 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 19

User’s Manual
1.6.6 Chrontel CH7011 TV Transmitter
The CH7011 is a Display controller device which accepts a digital graphics input signal, and
encodes and transmits data to a TV output (analog composite, s-video or RGB). The device
accepts data over one 12-bit wide variable voltage data port which supports five different
data formats including RGB and YCrCb.
The TV-Out processor will perform non-interlace to interlace conversion with scaling and
flicker filters, and encode the data into any of the NTSC or PAL video standards. The
scaling and flicker filter is adaptive and programmable to enable superior text display. Eight
graphics resolutions are supported up to 1024 by 768 with full vertical and horizontal
underscan capability in all modes. A high accuracy low jitter phase locked loop is integrated
to create outstanding video quality. Support is provided for Macrovision™ and RGB bypass
mode which enables driving a VGA CRT with the input data.
1.6.7 PCI Interface
The ICH4 PCI interface provides a 33 MHz, Rev. 2.2 compliant implementation. All PCI
signals are 5V tolerant, except PME#. The ICH2 integrates a PCI arbiter that supports up to
six external PCI bus masters in addition to the internal ICH4 requests.
1.6.8 USB 2.0
The ICH4 contains an Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) compliant host controller
that supports USB high-speed signaling. High-speed USB 2.0 allows data transfers up to
480Mb/s which is 40 times faster than full-speed USB. The ICH4 also contains three
Universal Host Controller Interface (UHCI) controllers that support USB full-speed and
low-speed signaling.
The ICH4 supports 6 USB 2.0 ports. All six USB ports are high-speed, full-speed, and
low-speed capable. ICH4’s port-routing logic determines whether a USB port is controlled
by one of the UHCI controllers or by the EHCI controller.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
19
Page 20

ESM-2740/2743
1.6.9 Ethernet
1.6.9.1 Realtek RTL8101L Ethernet Controller
The Realtek RTL8101L is a highly integrated and cost-effective single-chip Fast Ethernet
controller. Featuring an MC'97 interface, the device is able to provide a combo-solution for
LAN and software modem applications. It is equipped with a PCI and Boot ROM share
interface (Realtek patent pending) for both EPROM and Flash Memory to provide
maximum network security and ease of management.
The RTL8101L offers an ACPI (Advanced Configuration Power Interface) management
function to provide efficient power management for advanced operating systems with
OSPM (Operating System Directed Power Management). A remote wake-up function is
also provided by support to Magic Packet, Link Change, and Wake-up Frame to increase
cost-efficiency in network maintenance and management. In addition, it supports analog
Auto Power-down and provides an auxiliary power auto-detect function to further save
power.
1.6.10 Winbond W83627HF
The Winbond W83627F/HF is made to fully comply with Microsoft PC98 and PC99
Hardware Design Guide. Moreover, W83627F/HF is made to meet the specification of
PC98/PC99’s requirement in the power management: ACPI and DPM (Device Power
Management). Super I/O chip provides features as the following:
• Meet LPC Spec. 1.0
• Support LDRQ# (LPC DMA), SERIRQ (serial IRQ)
• Include all features of Winbond I/O W83977TF and W83977EF
• Integrate Hardware Monitor functions
• Compliant with Microsoft PC98/PC99 Hardware Design Guide.
• Support DPM (Device Power Management), ACPI
• Programmable configuration settings
• Single 24 or 48 MHz clock input
20 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 21

User’s Manual
1.6.11 Winbond W83628F & W83629D PCI/ISA Bridge
W83628F is a PCI-to-ISA bus conversion IC. W83629D (45-LQF) is a condensed
centralizer IC for IRQ and DMA control. W83628F (128-QFP) and W83629D together form
a complete set for the PCI-to-ISA bridge.
• Full ISA Bus Support including ISA Masters
• 5V ISA and 3.3V PCI interfaces
• PC/PCI DMA protocol for Software Transparent
• IRQ Serializer for ISA Parallel IRQ transfer to Serial IRQ
• Supports 3 fully ISA Compatible Slots without Buffering
• PCI Bus at 25MHz, 33MHz and up to 40MHz
• Supports Programmable ISA Bus Divide the PCI Bus Clock into 3 or 4
• All ISA Signals can be Isolate
• Supports Configuration registers for programming performance
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
21
Page 22
ESM-2740/2743
2. Hardware
Configuration
22 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 23
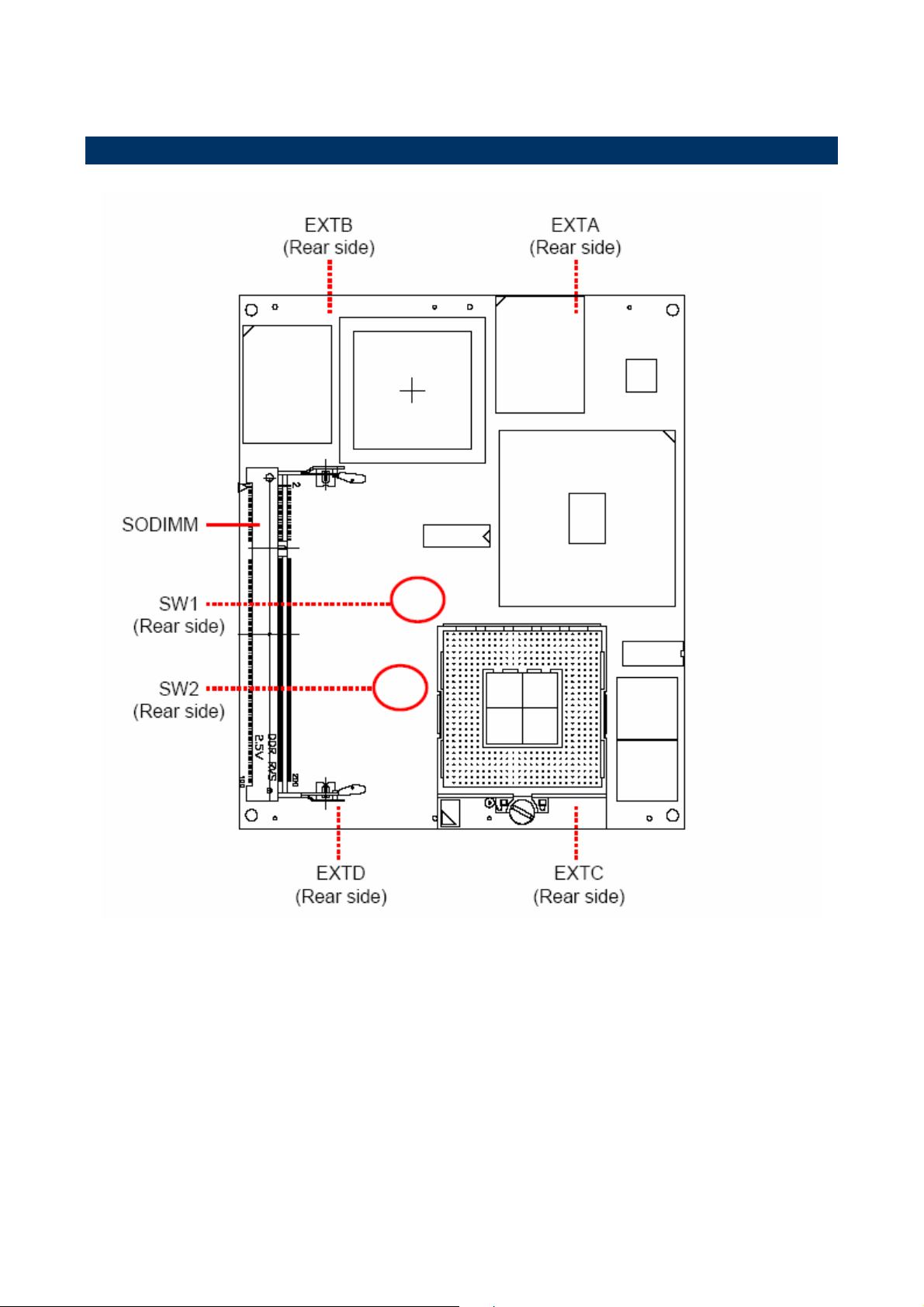
2.1 Product Overview
User’s Manual
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
23
Page 24
ESM-2740/2743
2.2 Installation Procedure
This chapter explains you the instructions of how to setup your system.
1. Turn off the power supply.
2. Insert the DIMM module (be careful with the orientation).
3. Insert all external cables for hard disk, floppy, keyboard, mouse, USB etc. except for flat
panel. A CRT monitor must be connected in order to change CMOS settings to support
flat panel.
4. Connect power supply to the board via the ATXPWR.
5. Turn on the power.
6. Enter the BIOS setup by pressing the delete key during boot up. Use the “LOAD BIOS
DEFAULTS” feature. The Integrated Peripheral Setup and the Standard CMOS Setup
Window must be entered and configured correctly to match the particular system
configuration.
7. If TFT panel display is to be utilized, make sure the panel voltage is correctly set before
connecting the display cable and turning on the power.
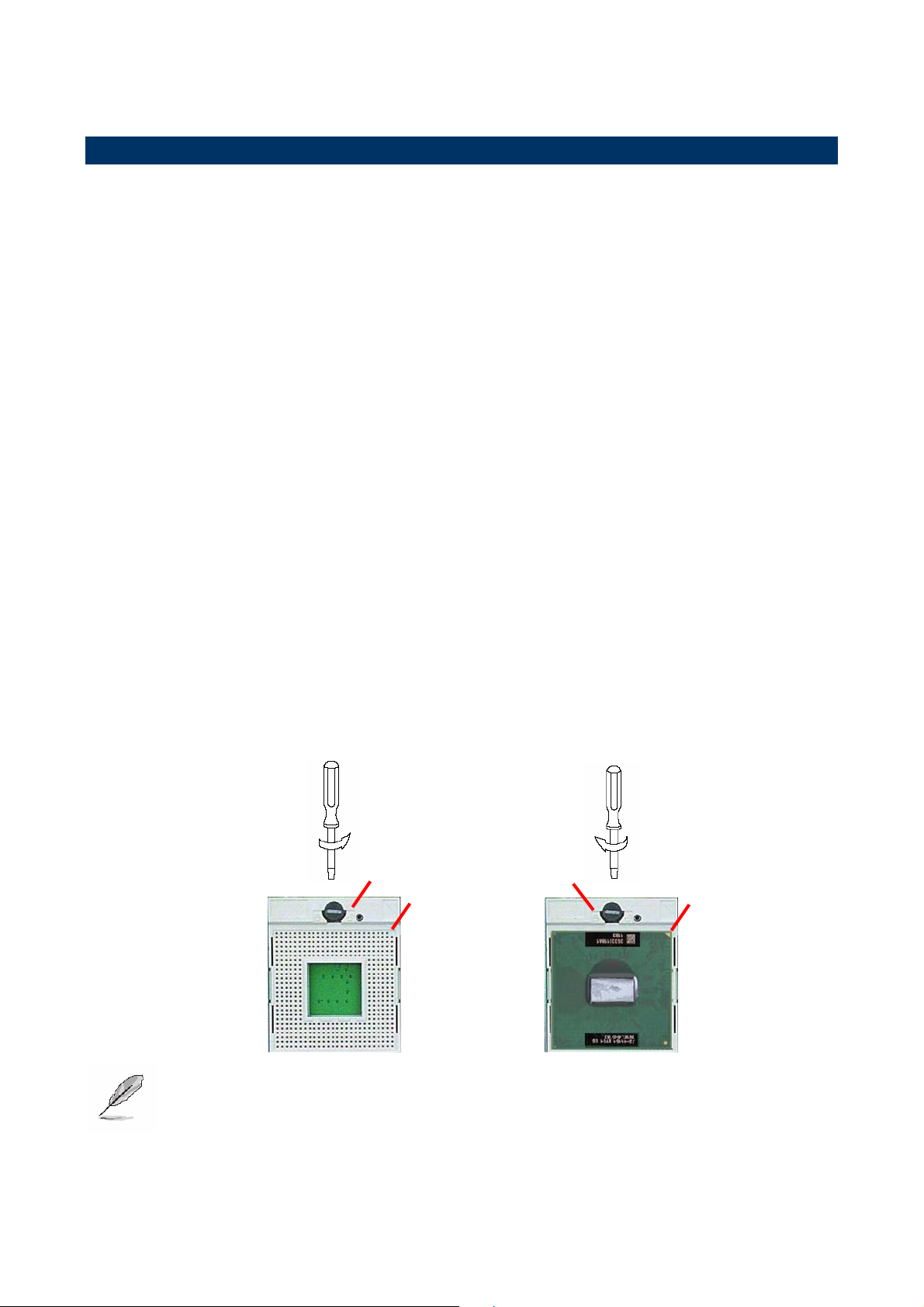
2.1.1 Installing Processor
2.1.1.1 Installing Pentium M CPU
• The processor socket comes with a screw to secure the processor, please unlock the
screw first.
• Position the CPU above the socket and the gold triangular mark on the CPU must
align with pin 1 of the CPU socket. Then Insert the CPU gently seated in place.
• Turn the screw to the lock position.
Unlock Lock
Pin 1 of the
socket
Gold
triangular
mark
Note: Do not force the CPU into the socket. It may bend the pins and damage the
CPU.
24 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 25
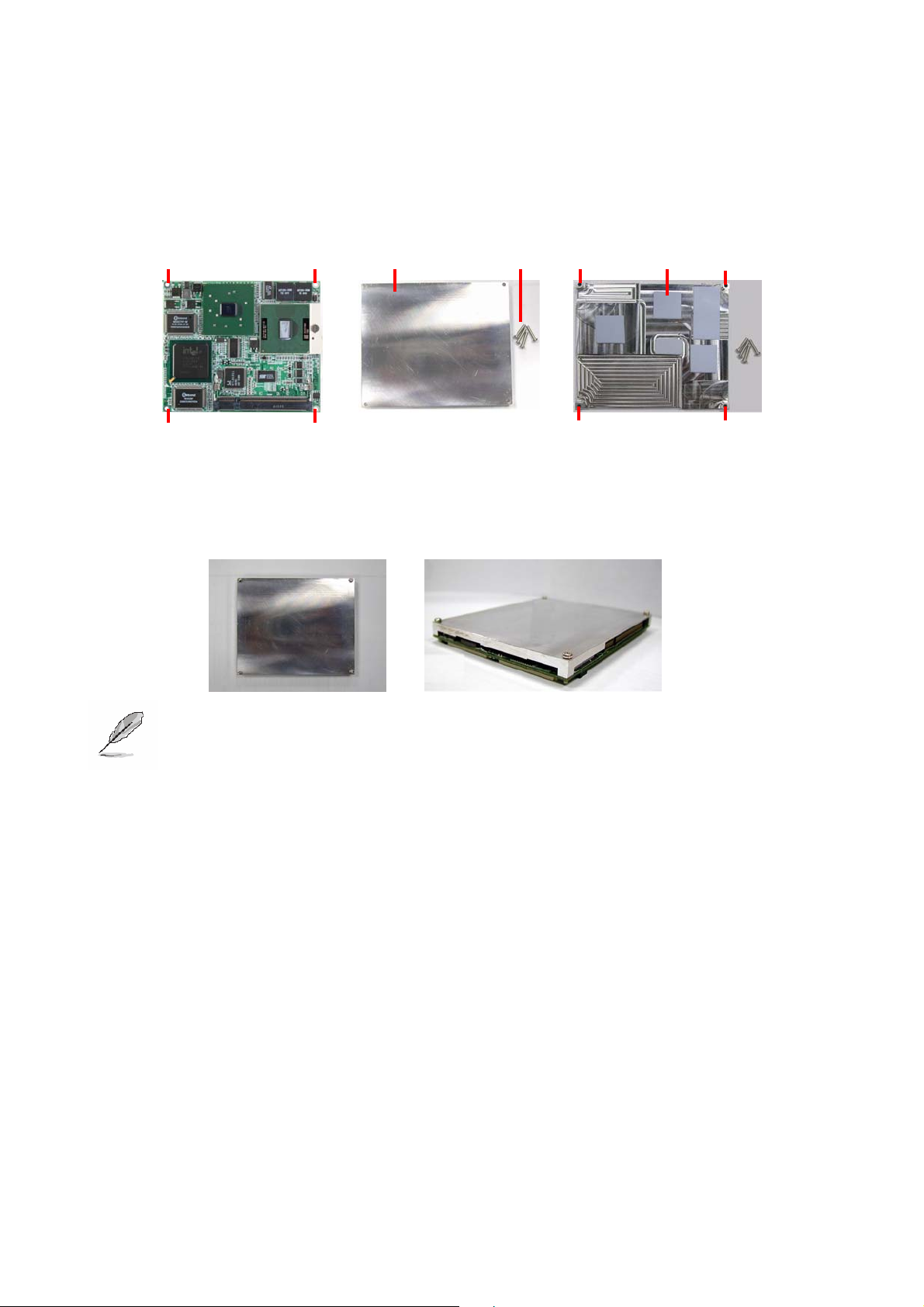
User’s Manual
2.1.1.2 Installing the Fan and Heat Sink
• Place the heat sink on the top of the board and match Hole 1-1 to 1-2, 2-1 to 2-2, 3-1
to 3-2, and 4-1 to 4-2.
Hole 1-1 Hole 2-1
Heat Sink Screws
Hole 2-2 Hole 1-2
1
Thermal
Pad x 5
2
3
4
5
Hole 3-1 Hole 4-1
(Front side)
Hole 4-2 Hole 3-2
(Rear side)
• Insert and fasten the screws to lock the board and heat sink through Hole 1-2 to Hole
1-1, Hole 2-2 to 2-1, Hole 3-2 to 3-1, and Hole 4-2 to 4-1.
• Assembling completed as below.
Note: Make sure the thermal pads stuck on the right position above the CPU and
chipsets to avoid overheating problem that would cause the system to hang
or unstable
2.1.1.1 Removing CPU
• Remove the screws and heat sink first.
• Unlock the Pentium M processor.
• Carefully lift up the existing CPU to remove it from the socket.
• Follow the steps of installing a CPU to change to another one.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
25
Page 26
ESM-2740/2743
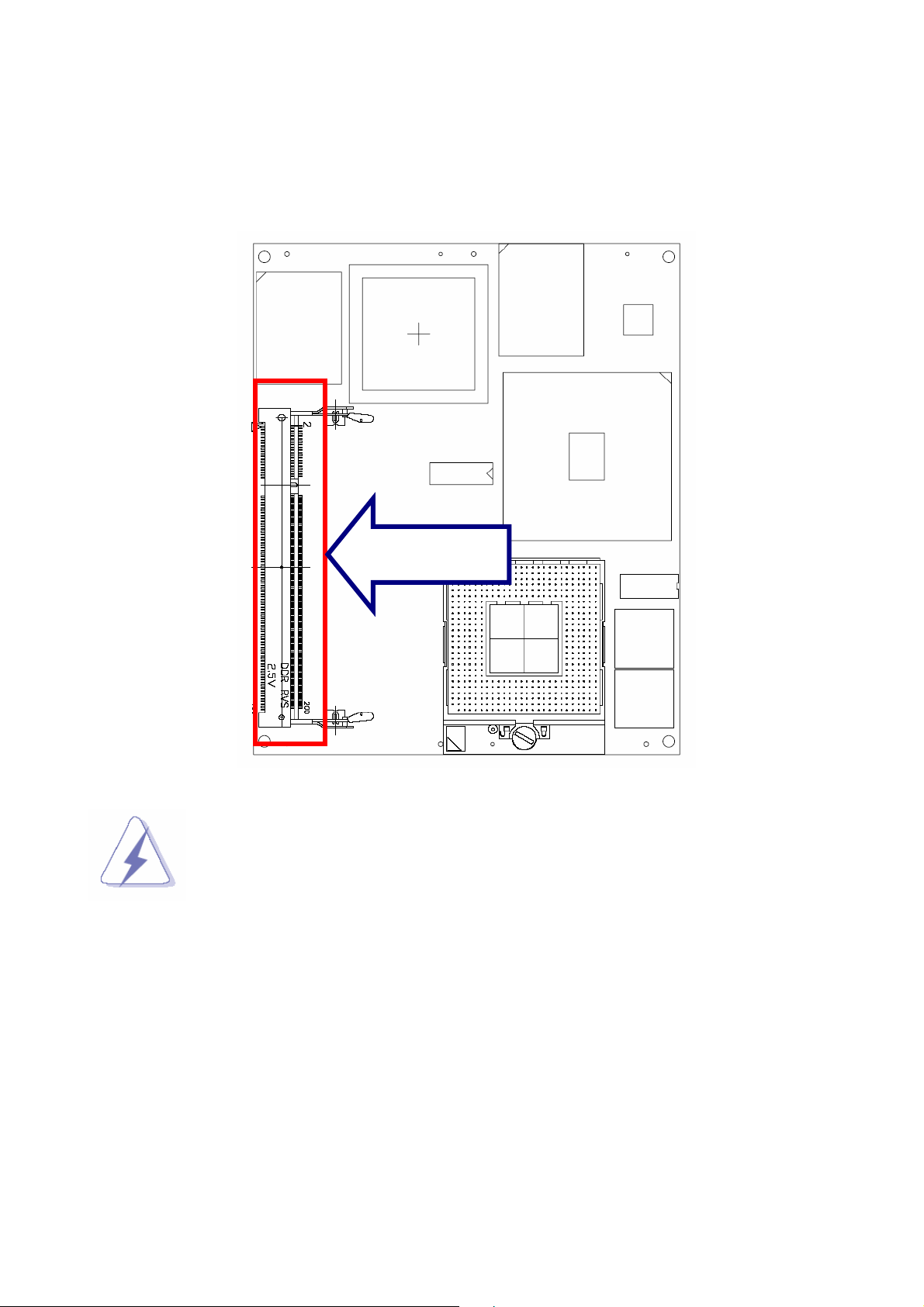
2.1.2 Main Memory
ESM-2740/2743 provides one 200-pin SODIMM sockets to support DDR SDRAM. The total
maximum memory size is 1GB.
SODIMM
Make sure to unplug the power supply before adding or removing SODIMMs
or other system components. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to
both the board and the components.
26 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 27
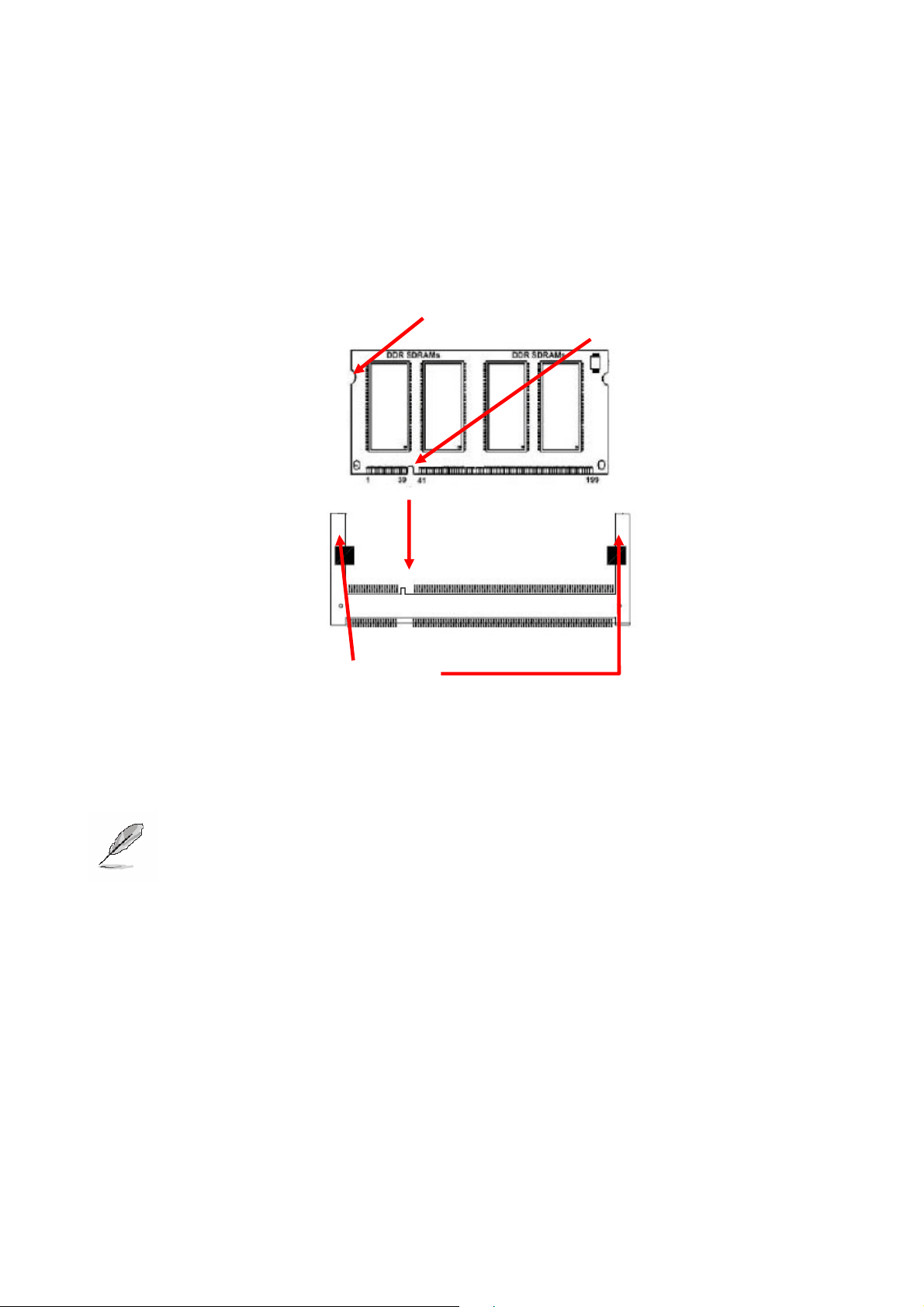
User’s Manual
• Locate the DIMM socket on the board.
• Hold two edges of the DIMM module carefully. Keep away of touching its connectors.
• Align the notch key on the module with the rib on the slot.
• Firmly press the modules into the socket automatically snaps into the mounting notch.
Do not force the DIMM module in with extra force as the DIMM module only fit in one
direction.
Mounting Notch
Notch Key
Ejector Tab
200-pin SODIMM
• To remove the DIMM modules, push the two ejector tabs on the slot outward
simultaneously, and then pull out the DIMM module.
Note: (1) Please do not change any DDR SDRAM parameter in BIOS setup to
increase your system’s performance without acquiring technical
information in advance.
(2) Static electricity can damage the electronic components of the computer
or optional boards. Before starting these procedures, ensure that you
are discharged of static electricity by touching a grounded metal object
briefly.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
27
Page 28

ESM-2740/2743
2.3 Jumper and Connector List
You can configure your board to match the needs of your application by setting jumpers. A
jumper is the simplest kind of electric switch.
It consists of two metal pins and a small metal clip (often protected by a plastic cover) that
slides over the pins to connect them. To “close” a jumper you connect the pins with the clip.
To “open” a jumper you remove the clip. Sometimes a jumper will have three pins, labeled 1,
2, and 3. In this case, you would connect either two pins.
The jumper settings are schematically depicted in this manual as follows:
A pair of needle-nose pliers may be helpful when working with jumpers.
Connectors on the board are linked to external devices such as hard disk drives, a
keyboard, or floppy drives. In addition, the board has a number of jumpers that allow you to
configure your system to suit your application.
If you have any doubts about the best hardware configuration for your application, contact
your local distributor or sales representative before you make any changes.
The following tables list the function of each of the board's jumpers and connectors.
Jumpers
Label Function Note
SW1
SW2
Connectors
Label
Reserved
FSB select SMD switch
Function Note
ETXA
ETXB
ETXC
ETXD
SODIMM
28 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
ETX connector X1 HIROSE FX8-100P-SV
ETX connector X2 HIROSE FX8-100P-SV
ETX connector X3 HIROSE FX8-100P-SV
ETX connector X4 HIROSE FX8-100P-SV
200-pin SODIMM socket
Page 29

User’s Manual
2.4 Setting Jumpers & Connectors
2.4.1 FSB Select (SW2)
Currently, SW2 is set with the below default for FSB selection. Please do not change the
default setting otherwise it might damage the CPU.
BIT1 BIT2
ON OFF DEFAULT
(Rear side)
* Default
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
29
Page 30

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.2 ETX Connector X1 (ETXA)
(Rear side)
Signal PIN PIN Signal
GND 1 2 GND
PCICLK3 3 4 PCICLK4
GND 5 6 GND
PCICLK1 7 8 PCICLK2
REQ3# 9 10 GNT3#
GNT2# 11 12 +3.3V
REQ2# 13 14 GTN1#
REQ1# 15 16 +3.3V
GNT0# 17 18 NC
+5V 19 20 +5V
SIRQ 21 22 REQ0#
AD0 23 24 +3.3V
AD1 25 26 AD2
AD4 27 28 AD3
AD6 29 30 AD5
CBE0# 31 32 AD7
AD8 33 34 AD9
GND 35 36 GND
AD10 37 38 AUXAL
AD11 39 40 MIC
AD12 41 42 AUXAR
AD13 43 44 ASVCC
AD14 45 46 SNDL
AD15 47 48 ASGND
CBE1# 49 50 SNDR
+5V 51 52 +5V
PAR 53 54 SERR#
GPERR# 55 56 NC
PME# 57 58 USB2#
LOCK# 59 60 DEVSEL#
TRDY# 61 62 USB3#
IRDY# 63 64 STOP#
FRAME# 65 66 USB2
GND 67 68 GND
AD16 69 70 CBE2#
AD17 71 72 USB3
AD19 73 74 AD18
AD20 75 76 USB0#
AD22 77 78 AD21
AD23 79 80 USB1#
AD24 81 82 CBE3#
+5V 83 84 +5V
AD25 85 86 AD26
AD28 87 88 USB0
AD27 89 90 AD29
AD30 91 92 USB1
PCIRST# 93 94 AD31
INTC# 95 96 INTD#
INTA# 97 98 INTB#
GND 99 100 GND
30 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 31

User’s Manual
2.4.3 Signal Description – ETX Connector X1 (ETXA)
2.4.3.1 PCI Signals
Signal Signal Description
PCI clock outputs for up to 4 external PCI slots or devices.
PCICLK [1:4]
REQ [0:3]#
GNT [0:3]#
AD [0:31]
CBE [0:3]#
PAR
SERR#
PERR# Parity Error. For PCI operation per exception granted by PCI 2.1 Specification.
LOCK#
DEVSEL#
TRDY#
IRDY#
STOP#
FRAME#
PCIRST#
INTRA#,
INTRB#,
INTRC#,
INTRD#
IDSEL
PME# Power management event..
The baseboard designer should route these clocks for 1300pS total delay from the
ETX connector pin to the clock pin of the PCI device. See the ETX Design Guide
for typical route length calculations.
Bus Request signals for up to 4 external bus mastering PCI devices. When
asserted, a PCI device is requesting PCI bus ownership from the arbiter.
Grant signals to PCI Masters. When asserted by the arbiter, the PCI master has
been granted ownership of the PCI bus.
PCI Address and Data Bus Lines. These lines carry the address and data
information for PCI transactions.
PCI Bus Command and Byte Enables. Bus command and byte enables are
multiplexed in these lines for address and data phases, respectively.
Parity bit for the PCI bus. Generated as even parity across AD [31:0] and CBE
[3:0]#.
System Error. Asserted for hardware error conditions such as parity errors
detected in DRAM.
Lock Resource Signal. This pin indicates that either the PCI master or the bridge
intends to run exclusive transfers.
Device Select. When the target device has decoded the address as its own cycle,
it will assert DEVSEL#.
Target Ready. This pin indicates that the target is ready to complete the current
data phase of a transaction.
Initiator Ready. This signal indicates that the initiator is ready to complete the
current data phase of a transaction.
Stop. This signal indicates that the target is requesting that the master stop the
current transaction.
Cycle Frame of PCI Buses. This indicates the beginning and duration of a PCI
access. The access will be either an output driven by the Northbridge on behalf of
the CPU, or an input during PCI master access.
PCI Bus Reset. This is an output signal to reset the entire PCI Bus. This signal is
asserted during system reset.
PCI interrupts.
These interrupts are sharable and are typically wired in rotation to PCI slots or
devices.
This pin is not present on the ESM-2740/2743 module connector, but it is present
on each PCI slot connector or device. IDSEL is an input to the device that is used
to set the device’s configuration address for PCI configuration cycles. The IDSEL
pin of each device is typically connected to one of the AD lines in order to set a
unique configuration address.
In ETX systems, the four external bus slots or devices are assumed to use
AD[19:22] for IDSEL connections.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
31
Page 32

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.3.2 Audio Signals
Signal Signal Description
Line-level stereo output left/ right. These outputs have a nominal level of 1 volt
SNDL/ SNDR
AUXAL/ AUXAR
MIC
ASGND
ASVCC
RMS into a 10K impedance load. These outputs cannot drive low-impedance
speakers directly.
Auxiliary A input left/ right. Normally intended for connection to an internal or
external CDROM analog output or a similar line-level audio source. Minimum input
impedance is 5KOhm.
Nominal input level is 1 volt RMS.
Microphone input. Minimum input impedance is 5KOhm, max. Input voltage is 0.15
Vp-p.
Analog ground for sound controller. Use this signal ground for an external amplifier
in order to achieve lowest audio noise levels.
Analog supply voltage for sound controller. This is an output which is used for
production test only. Do not make external connections to this pin.
2.4.3.3 USB Signals
Signal Signal Description
USB [0:3]
USB [0:3]-
Universal Serial Bus Port [0:3] positive signal.
These are the serial data pairs for USB Port N-and Port N#.
Universal Serial Bus Port [0:3] negative signal.
These are the serial data pairs for USB Port N-and Port N#.
32 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 33

2.4.4 ETX Connector X2 (ETXB)
(Rear side)
User’s Manual
Signal PIN PIN Signal
GND 1 2 GND
SD14 3 4 SD15
SD13 5 6 MASTER#
SD12 7 8 DREQ7
SD11 9 10 DACK7#
SD10 11 12 DREQ6
SD9 13 14 DACK6#
SD8 15 16 DREQ5
MEMW# 17 18 DACK5#
MEMR# 19 20 DREQ0
LA17 21 22 DACK0#
LA18 23 24 IRQ14
LA19 25 26 IRQ15
LA20 27 28 IRQ12
LA21 29 30 IRQ11
LA22 31 32 IRQ10
LA23 33 34 IO16#
GND 35 36 GND
SBHE# 37 38 M16#
SA0 39 40 OSC
SA1 41 42 BALE
SA2 43 44 TC
SA3 45 46 DACK2#
SA4 47 48 IRQ3
SA5 49 50 IRQ4
+5V 51 52 +5V
SA6 53 54 IRQ5
SA7 55 56 IRQ6
SA8 57 58 IRQ7
SA9 59 60 SYSCLK
SA10 61 62 REFSH#
SA11 63 64 DREQ1
SA12 65 66 DACK#
GND 67 68 GND
SA13 69 70 DREQ3
SA14 71 72 DACK3#
SA15 73 74 IOR#
SA16 75 76 IOW#
SA18 77 78 SA17
SA19 79 80 SMEMR#
IOCHRDY 81 82 AEN
+5V 83 84 +5V
SD0 85 86 SMEMW#
SD2 87 88 SD1
SD3 89 90 NOWS#
DREQ2 91 92 SD4
SD5 93 94 IRQ9
SD6 95 96 SD7
IOCHK# 97 98 RSTDRV
GND 99 100 GND
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
33
Page 34

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.5 Signal Description – ETX Connector X2 (ETXB)
2.4.5.1 ISA Signals
Signal Signal Description
These signals provide data bus bits 0 to 15 for any peripheral devices. All 8-bit
devices use SD[0:7] for data transfers. 16-bit devices use SD[0:15].
SD[0:15]
SA[0:19]
SBHE#
BALE
AEN
MEMR#
SMEMR#
MEMW#
SMEMW#
IOR#
IOW#
IOCHK#
IOCHRDY
M16#
IO16#
To support 8-bit devices, the data on SD[8:15] is gated to SD[0:7] during 8-bit
transfers to these devices. 16-bit CPU cycles will be automatically converted into
two 8-bit cycles for 8-bit peripherals.
Address bits 0 through 15 are used to address I/O devices. Address bits 0 through
19 are used to address memory within the system. These 20 address lines, in
addition to LA[17:23] allow access of up to 16MB of memory. SA[0:19] are gated
on the ISA-bus when BALE is high and latched on to the falling edge of BALE.
Bus High Enable indicates a data transfer on the upper byte of the data bus
SD[8:15]. 16-bit I/O devices use SBHE# to enable data bus buffers on SD[8:15].
BALE is an active-high pulse generated at the beginning of any bus cycle initiated
by a CPU module. It indicates when the SA[0:19], LA17.23, AEN, and SBHE#
signals are valid.
AEN is an active-high output that indicates a DMA transfer cycle. Only resources
with a active DACK# signal should respond to the command lines when AEN is
high.
MEMR# instructs memory devices to drive data onto the data bus. MEMR# is
active for all memory read cycles.
SMEMR# instructs memory devices to drive data onto the data bus. SMEMR# is
active for memory read cycles to addresses below 1MB.
MEMW# instructs memory devices to store the data present on the data bus.
MEMW# is active for all memory write cycles.
SMEMW# instructs memory devices to store the data present on the data bus.
SMEMW# is active for all memory write cycles to address below 1MB.
I/O read instructs an I/O device to drive its data onto the data bus. It may be driven
by the CPU or by the DMA controller. IOR# is inactive (high) during refresh cycles.
I/O write instructs an I/O device t o store the data present on the data bu s. It may be
driven by the CPU or by the DMA controller. IOW# is inactive (high) during refresh
cycles.
IOCHK# is an active-low input signal that indicates that an error has occurred on
the module bus. If I/O checking is enabled on the CPU module, an IOCHK#
assertion by a peripheral device sends a NMI to the processor.
The I/O Channel Ready is pulled low in order to extend the read or write cycles of
any bus access when required. The CPU, DMA controllers or refresh controll er can
initiate the cycle.
Any peripheral that cannot present read data or strobe in write data within this
amount of time use IOCHRDY to extend these cycles.
This signal should not be held low for more than 2.5 μs for normal operation. Any
extension to more than 2.5 μs does not guarantee proper DRAM memory content
due to the fact that memory refresh is disabled while IOCHRDY is low.
The M16# signal determines when a 16-bit to 8-bit conversion is needed for
memory bus cycles. A conversion is done any time the CPU module requests a
16-bit memory cycle while the M16# line is high. If M16# is high, 16-bit CPU cy cles
are automatically converted on the bus into two 8-bit cycles. If M16# is low, an
access to peripherals is done 16 bits wide.
The IO16# signal determines when a 16-bit to 8-bit conversion is needed for I/O
bus cycles. A conversion is done any time the CPU module requests a 16-bit I/O
cycle while the IO16# line is high. If IO16# is high, 16-bit CPU cycles are
automatically converted on the bus into two 8-bit cycles. If IO16# is low, an access
to peripherals is done at 16 bit width.
34 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 35

Signal Signal Description
REFSH#
NOWS#
MASTER#
SYSCLK
OSC
RESETDRV
DREQ
[0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7]
DACK
[0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7]#
TC
IRQ [3:7, 9,15]
REFSH# is pulled low whenever a refresh cycle is initiated. A refresh cycle is
activated every 15.6 us in order to prevent loss of DRAM data.
The Zero wait state signal tells the CPU to complete the current bus cycle without
inserting the default wait states. By default the CPU inserts 4 wait states for 8-bit
transfers and 1 wait state for 16-bit transfers.
This signal is used with a DRQ line to gain control of the system bus. A processor
or a DMA controller on the I/O channel may issue a DRQ to a DMA channel in
cascade mode and receive a DACK#. Upon receiving the DACK#, a bus master
may pull MASTER# low, which will allow it to control the system address, data and
control lines. After MASTER# is low, the bus master must wait one system clock
period before driving the address and data lines, and two clock periods before
issuing a read or write command. If this signal is held low for more than 15 us,
system memory may be lost as memory refresh is disabled during this process.
SYSCLK is supplied by the CPU module and has a nominal frequency of about 8
MHz with a duty cycle of 40-60 percent. The frequency supplied by different CPU
modules may vary. This signal is supplied at all times except when the CPU
module is in sleep mode.
OSC is supplied by the CPU module. It has a nominal frequency of 14.31818 MHz
and a duty cycle of 40-60 percent. This signal is supplied at all times except when
the CPU module is in sleep mode.
This active-high output is system reset generated from CPU modules. It is
responsible for resetting external devices.
The asynchronous DMA request inputs are used by external devices to indicate
when they need service from the CPU modules DAM controllers. DREQ0..3 are
used for transfers between 8-bit I/O adapters and system memory. DREQ5..7 are
used for transfers between 16-bit I/O adapters and system memory. DRQ4 is not
available externally. All DRQ pins have pull-up resistors on the CPU modules.
DMA acknowledge 0..3 and 5.7 are used to acknowledge DMA requests. They are
active-low.
The active-high output TC indicates that one of the DMA channels has transferred
all data.
These are the asynchronous interrupt request lines. IRQ0, 1, 2 and 8 are not
available as external interrupts because they are used internally on the CPU
module. All IRQ signals are active-high. The interrupt requests are prioritized.
IRQ9 through IRQ12 and IRQ14 through IRQ15 have the highest priority (IRQ9 is
the highest). IRQ3 through IRQ7 have the lowest priority (IRQ7 is the lowest). An
interrupt request is generated when an IRQ line is raised from low to high. The line
must be held high until the CPU acknowledges the interrupt request (interrupt
service routine).
User’s Manual
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
35
Page 36

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.6 ETX Connector X3 (ETXC)
(Rear side)
Signal PIN PIN Signal
GND 1 2 GND
R 3 4 B
HSY 5 6 G
VSY 7 8 DDCK
NC 9 10 DDDA
LCDDO16 11 12 LCDDO18
LCDDO17 13 14 LCDDO19
GND 15 16 GND
LCDDO13 17 18 LCDDO15
LCDDO12 19 20 LCDDO14
GND 21 22 GND
LCDDO8 23 24 LCDDO11
LCDDO9 25 26 LCDDO10
GND 27 28 GND
LCDDO4 29 30 LCDDO7
LCDDO5 31 32 LCDDO6
GND 33 34 GND
LCDDO1 35 36 LCDDO3
LCDDO0 37 38 LCDDO2
+5V 39 40 +5V
I2C_DAT
I2C_CLK
BIASON 45 46 DIGON
COMP 47 48 Y
NC 49 50 C
NC 51 52 NC
+5V 53 54 GND
STB# 55 56 AFD#
NC 57 58 PD7
IRRX 59 60 ERR#
IRTX 61 62 PD6
RXD2 63 64 INIT#
GND 65 66 GND
RTS2# 67 68 PD5
DTR2# 69 70 SLIN#
DCD2# 71 72 PD4
DSR2# 73 74 PD3
CTS2# 75 76 PD2
TXD2# 77 78 PD1
RI2# 79 80 PD0
+5V 81 82 +5V
RXD1 83 84 ACK#
RTS1# 85 86 BUSY#
DTR1# 87 88 PE
DCD1# 89 90 SLCT#
DSR1# 91 92 MSCLK
CTS1# 93 94 MSDAT
TXD1 95 96 KBCLK
RI1# 97 98 KBDAT
GND 99 100 GND
41 42 NC
43 44 ENBKL#
36 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 37

2.4.7 Signal Description – ETX Connector X3 (ETXC)
2.4.7.1 LVDS Flat Panel Interface Signals
Signal 1 Pixel / Clock LVDS Mode 2 Pixel / Clock LVDS Mode
LCDDO0 Txout0# Odd Txout0#
LCDDO1 Txout0 Odd Txout0
LCDDO2 Txout1# Odd Txout1#
LCDDO3 Txout1 Odd Txout1
LCDDO4 Txout2# Odd Txout2#
LCDDO5 Txout2 Odd Txout2
LCDDO6 Txclk# Odd Txclk#
LCDDO7 Txclk Odd Txclk
LCDDO8 Txout3# Odd Txout3#
LCDDO9 Txout3 Odd Txout3
LCDDO10 - Even Txout0#
LCDDO11 - Even Txout0
LCDDO12 - Even Txout1#
LCDDO13 - Even Txout1
LCDDO14 - Even Txout2#
LCDDO15 - Even Txout2
LCDDO16 - Even Txclk#
LCDDO17 - Even Txclk
LCDDO18 - Even Txout3#
LCDDO19 - Even Txout3
BIASON Controls panel contrast voltage.
DIGON Controls panel digital power.
ENBKL# Controls backlight power enable.
I2C_DAT, I2C_CLK
2
I
C interface for panel parameter EEPROM. This EERPOM is mounted on the
LVDS receiver. The data in the EEPROM allows the EXT module to automatically
set the proper timing parameters for a specific LCD panel.
2.4.7.2 IrDA (SIR) Signals
Signal Signal Description
IRTX, IRRX Infrared transmit and receive pins.
User’s Manual
2.4.7.3 Parallel Port Signals
Signal Signal Description
STB# This active-low signal is used to strobe the printer data into the printer.
AFD#
PD[0:7]
ERR# This active-low signal indicates an error situation has occurred at the printer.
INIT# This active-low signal is used to initiate the printer when low.
SLIN# This active-low signal selects the printer.
ACK#
This active-low output tells the printer to automatically feed the next single line
after each preceding line has been printed.
This bi-directional parallel data bus is used to transfer information between the
CPU and the peripherals.
This active-low output from the printer indicates that it has received the previous
data and that it is ready to receive new data.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
37
Page 38

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.7.4 PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Signals
Signal Signal Description
KBDAT Bi-directional keyboard data signal.
KBCLK Keyboard clock signal.
MSDAT Bi-directional mouse data signal.
MSCLK Mouse clock signal.
2.4.7.5 Serial Port Signals
Note that all serial port signals on ESM-2740/2743 connectors are logic level signals.
External transceiver devices are necessary for the conversion of the logic level signals to
the desired physical interface such as RS232, RS422, or RS485.
Signal Signal Description
DTR1#, DTR2#
RI1#, RI2#
TXD1, TXD2 Transmitter serial data output from serial port.
RXD1, RXD2 Receiver serial data input.
CTS1#, CTS2#
RTS1#, RTS2#
DCD1#, DCD2#
DSR1#, DSR2#
Active-low data terminal ready outputs for the serial port. Handshake output signal
notifies the modem that the UART is ready to establish a data communication link.
Active-low input is for the serial port. Handshake signals notify the UART when a
telephone ring signal is detected by the modem.
Active-low input for serial ports. Handshake signals notify the UART when the
modem is ready to receive data.
Active-low output for serial port. Handshake signals notify the modem when the
UART is ready to transmit data.
Active-low input for serial port. Handshake signals notify the UART when a carrier
signal is detected by the modem.
This active-low input is for serial port. Handshake signals are use to notify the
UART that the modem is ready to establish the communication link.
2.4.7.6 VGA Signals
Signal Signal Description
HSY
VSY
R, G, B
DDCK, DDDA
Horizontal Sync: This output supplies the horizontal synchronization pulse to the
CRT monitor.
Vertical Sync: This output supplies the vertical synchronization pulse to the CRT
monitor.
Red, green and blue analog video output signals for CRT monitors. These lines
should be terminated with 75 ohms to ground at the video connector.
These two pins can be used for a DDC interface between the graphics controller
chip and the CRT monitor.
38 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 39

2.4.8 ETX Connector X4 (ETXD)
(Rear side)
User’s Manual
Signal PIN PIN Signal
GND 1 2 GND
5V_SB 3 4 PWGIN
PS_ON 5 6 SPEAKER
PWRBTN# 7 8 BATT
KBINH 9 10 LILED
RSMRST# 11 12 ACTLED
NC 13 14 SPEEDLED
NC
+5V 17 18 +5V
OVCR# 19 20 NC
EXTSMI#
SMBCLK 23 24 SMBDATA
SIDE_CS3# 25 26 NC
SIDE_CS1# 27 28 DASP_S
SIDE_A2 29 30 PIDE_CS3#
SIDE_A0 31 32 PIDE_CS1#
GND 33 34 GND
PDIAG_S 35 36 PIDE_A2
SIDE_A1 37 38 PIDE_A0
SIDE_INTRQ 39 40 PIDE_A1
BATLOW 41 42 GPE1#
SIDE_AK# 43 44 PIDE_INTRQ
SIDE_RDY 45 46 PIDE_AK#
SIDE_IOR# 47 48 PIDE_RDY
+5V 49 50 +5V
SIDE_IOW# 51 52 PIDE_IOR#
SIDE_DRQ 53 54 PIDE_IOW#
SIDE_D15 55 56 PIDE_DRQ
SIDE_D0 57 58 PIDE_D15
SIDE_D14 59 60 P IDE_D0
SIDE_D1 61 62 PIDE_D14
SIDE_D13 63 64 PIDE_D1
GND 65 66 GND
SIDE_D2 67 68 PIDE_D13
SID E_D12 69 70 PIDE_D2
SIDE_D3 71 72 PIDE_D12
SIDE_D11 73 74 PIDE_D3
SIDE_D4 75 76 PIDE_D11
SIDE_D10 77 78 PIDE_D4
SIDE_D5 79 80 PIDE_D10
+5V 81 82 +5V
SIDE_D9 83 84 PIDE_D5
SIDE_D6 85 86 PIDE_D9
SIDE_D8 87 88 PIDE_D6
GPE2 89 90 CBLID_P#
RXD# 91 92 PIDE_D8
RXD 93 94 SIDE_D7
TXD# 95 96 PIDE_D7
TXD 97 98 HDRST#
GND 99 100 GND
15 16
21 22
2
CLK
I
I2DAT
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
39
Page 40

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.9 Signal Description – ETX Connector X4 (ETXD)
2.4.9.1 Ethernet Signals
Signal Signal Description
Ethernet Transmit Differential Pair. These pins transmit the serial bit stream on the
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cable. The current-driven differential driver can be
TXD#, TXD
RXD#, RXD
ACTLED
LILED
SPEEDLED
two-level (10BASE-T) or three-level (100BASE-TX) signals depending on the
mode of operation. These signals interface to the Ethernet cable through an
isolation transformer.
Ethernet Receive Differential Pair. These pins receive the serial bit stream from the
isolation transformer. The bit stream can be transmitted in either two-level
(10BASE-T) or three-level (100BASE-TX) signals depending on the mode of
operation. These signals interface to the Ethernet cable through an isolation
transformer.
The Activity LED pin indicates either transmitted or received data activity on the
Ethernet port.
This pin is asserted low when activity is detected. It can sink 5mA to ground
through an external LED and a limiting resistor to a 3.3V source.
The Link Integrity LED pin indicates link integrity. This pin is asserted low when the
link is valid. It can sink 5mA to ground through an external LED and a limiting
resistor to a 3.3V source.
The Speed LED pin indicates high speed operation. This LED is not supported by
ESM-2740/2743.
This pin is asserted low when a 100Mbps link is detected, and is not asserted for a
10Mbps link. It can sink 5mA to ground through an external LED and a limiting
resistor to a 3.3V source.
40 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 41

2.4.9.2 IDE Signals
Signal Signal Description
PIDE_D[0:15]/
SIDE_D[0:15]
PIDE_A[0:2]/
SIDE_A[0:2]
PIDE_CS1#/
SIDE_CS1#
PIDE_CS3#/
SIDE_CS3#
PIDE_DRQ/
SIDE_DRQ
PIDED_AK#/
SIDED_AK#
PIDE_RDY/
SIDE_RDY
PIDE_IOR#/
SIDE_IOR#
PIDE_IOW#/
SIDE_IOW#
PIDE_INTRQ/
SIDE_INTRQ
HDRST# Low-active hardware reset (RSTDRV inverted).
DASP_S
PDIAG_S
CBLID_P#
IDE Data Bus.
IDE Address Bus.
IDE Chip Select 1. This is the Chip Select 1 command output pin that enables the
IDE device to watch the Read/Write Command.
IDE Chip Select 3. This is the Chip Select 3 command output pin that enables the
IDE device to watch the Read/Write Command.
IDE DMA Request for IDE Master. This signal is asserted by an IDE device. It will
be active-high in DMA or Ultra-33 mode and always be inactive-low in PIO mode.
IDE DACK# for IDE Master. This signal grants the IDE DMA request to begin the
IDE Master Transfer in DMA or Ultra-33 mode.
IDE Ready. This is the input pin from the IDE Channel. It indicates that the IDE
device is ready to terminate the IDE command in PIO mode. The IDE device can
de-assert this input to expand the IDE command if the device is not ready. In
Ultra-33 mode, this pin has different functions.
IDE IOR# Command. This is the IOR# command output pin used to tell the IDE
device to assert the Read Data in PIO and DMA mode. In Ultra-33 mode, this pin
has different functions.
IDE IOW# Command. This is the IOW# command output pin used to notify the IDE
device that the available Write Data is already asserted by the IDE Busmaster in
PIO and DMA mode. In Ultra-33 mode, this pin has different functions.
Interrupt request signal from the IDE device.
Time-multiplexed, open collector output that indicates that a drive is active. Also
used for Master/Slave negotiation on the Secondary IDE channel.
The signal is used for Master/Slave negotiation on the Secondary IDE channel. It is
asserted by the Slave to indicate to a master that the slave has passed its internal
Diagnostic command. If an IDE device such as a Flash Disk exists onboard the
ETX module, this signal must be connected to the PDIAG_S pin of any other
device connected to the Secondary IDE channel. On ETX modules that support
DMA66 or DMA100, this pin may additionally be used to detect the presence of the
80 conductor IDE cable which is required to support these modes.
On ETX modules that support DMA66 or DMA100, this pin may be used to detect
the presence of an 80 conductor IDE cable on the primary IDE channel. This
allows BIOS or system software to determine whether to enable high-speed
transfer modes.
User’s Manual
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
41
Page 42

ESM-2740/2743
2.4.9.3 Miscellaneous Signals
Signal Signal Description
SPEAKER
BATT
I2CLK, I2DAT
SMBDATA, SMBCLK
KBINH Keyboard Inhibit. Asserting this pin disables data input from the keyboard.
OVCR#
PC speaker output signal. This logic-level signal can be connected to an external
transistor in order to drive a piezoelectric or dynamic speaker.
3V backup cell input. BATT is typically connected to a 3V lithium backup cell for
RTC operation and CMOS register non-volatility in the absence of system power.
These clock and data lines implement an I2C-bus which supports external slave
devices only. Data rate is approximate 1-10kHz. This interface is intended for
support of EEPROMs and other simple I/O-devices.
System Management Bus clock and data lines. May be used to support external
SMBUS devices such as temperature and battery monitoring chips. The addresses
of external SMBUS devices must be chosen so they do not conflict with addresses
used internally on the ETX module.
Over-current detect input. Used to monitor the USB power over-current. Pull with
open collector to GND if over-current is detected.
2.4.9.4 Power Control Signals
Signal Signal Description
Power input for the internal suspends and power control circuitry. Connect to a 5V,
5V_SB
PS_ON
PWRBTN#
100mA stand-by power source available. May be a no-connect if a standby supply
is not available.
Active-low output from ESM-2740/2743. Can be connected to the PS_ON input of
an ATX power supply in order to switch the main output. In order for this pin to
function, 5V_SB must be supplied to the ESM-2740/2743.
Power Button Input. Connect to GND with momentary-contact switch or open
collector driver to implement ATX power button control of PS_ON. In order for this
pin to function, 5V_SB must be supplied to the ESM-2740/2743.
2.4.9.5 Power Management Signals
Signal Signal Description
RSMRST#
EXTSMI
GPE2#
Resume Reset input. This input may be driven low by external circuitry in order to
reset the power management logic on the ETX module.
System management interrupt input. May be driven low by external circuitry to
initiate an SMI.
General purpose power management event input 2. May be driven low by external
circuitry to signal an external power management event. Within the ETX module,
this pin is commonly connected to the chipset’s RING# input.
42 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 43

User’s Manual
3. BIOS Setup
Note: Installation procedures and screen shots in this section are
for your reference and may not be exactly the same as
shown on your screen.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
43
Page 44

ESM-2740/2743
3.1 Starting Setup
The AwardBIOS™ is immediately activated when you first power on the computer. The
BIOS reads the system information contained in the CMOS and begins the process of
checking out the system and configuring it. When it finishes, the BIOS will seek an
operating system on one of the disks and then launch and turn control over to the operating
system.
While the BIOS is in control, the Setup program can be activated in one of two ways:
By pressing <Del> immediately after switching the system on, or
By pressing the <Del> key when the following message appears briefly at the bottom of the
screen during the POST (Power On Self Test).
Press DEL to enter SETUP
If the message disappears before you respond and you still wish to enter Setup, restart the
system to try again by turning it OFF then ON or pressing the "RESET" button on the
system case. You may also restart by simultaneously pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt>, and <Delete>
keys. If you do not press the keys at the correct time and the system does not boot, an error
message will be displayed and you will again be asked to.
Press F1 to Continue, DEL to enter SETUP
44 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 45

User’s Manual
3.2 Using Setup
In general, you use the arrow keys to highlight items, press <Enter> to select, use the
PageUp and PageDown keys to change entries, press <F1> for help and press <Esc> to
quit. The following table provides more detail about how to navigate in the Setup program
using the keyboard.
Button Description
↑
↓
←
→
Esc key
PgUp key Increase the numeric value or make changes
PgDn key Decrease the numeric value or make changes
+ key Increase the numeric value or make changes
- key Decrease the numeric value or ma ke changes
Move to previous item
Move to next item
Move to the item in the left hand
Move to the item in the right hand
Main Menu -- Quit and not save changes into CMOS
Status Page Setup Menu and Option Page Setup Menu -- Exit current page and
return to Main Menu
F1 key General help, only for Status Page Setup Menu and Option Page Setup Menu
(Shift) F2 key
F3 key Calendar, only for Status Page Setup Menu
F4 key Reserved
F5 key Restore the previous CMOS value from CMOS, only for Option Page Setup Menu
F6 key
F7 key Load the default
F8 key Reserved
F9 key Reserved
F10 key Save all the CMOS changes, only for Main Menu
Change color from total 16 colors. F2 to select color forward, (Shift) F2 to select
color backward
Load the default CMOS value from BIOS default table, only for Option Page Setup
Menu
• Navigating Through The Menu Bar
Use the left and right arrow keys to choose the menu you want to be in.
Note: Some of the navigation keys differ from one screen to another.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
45
Page 46

ESM-2740/2743
• To Display a Sub Menu
Use the arrow keys to move the cursor to the sub menu you want. Then press
<Enter>. A “¾” pointer marks all sub menus.
3.3 Getting Help
Press F1 to pop up a small help window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the
possible selections for the highlighted item. To exit the Help Window press <Esc> or the F1
key again.
3.4 In Case of Problems
If, after making and saving system changes with Setup, you discover that your computer no
longer is able to boot, the AwardBIOS™ supports an override to the CMOS settings which
resets your system to its defaults.
The best advice is to only alter settings which you thoroughly understand. To this end, we
strongly recommend that you avoid making any changes to the chipset defaults. These
defaults have been carefully chosen by both Award and your systems manufacturer to
provide the absolute maximum performance and reliability. Even a seemingly small change
to the chipset setup has the potential for causing you to use the override.
46 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 47

User’s Manual
3.5 Main Menu
Once you enter the AwardBIOS™ CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu will appear on the
screen. The Main Menu allows you to select from several setup functions and two exit
choices. Use the arrow keys to select among the items and press <Enter> to accept and
enter the sub-menu.
Note that a brief description of each highlighted selection appears at the bottom of the
screen.
Note: The BIOS setup screens shown in this chapter are for reference purposes
only, and may not exactly match what you see on your screen.
Visit the Avalue website (www.avalue.com.tw
product and BIOS information.
) to download the latest
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
47
Page 48

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.1 Standard CMOS Features
The items in Standard CMOS Setup Menu are divided into few categories. Each category
includes no, one or more than one setup items. Use the arrow keys to highlight the item and
then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to select the value you want in each item.
3.5.1.1 Main Menu Selection
This table shows the selections that you can make on the Main Menu.
Item Options Description
Date MM DD YYYY
Time HH : MM : SS Set the system time
IDE Channel 0 Master
IDE Channel 0 Slave
IDE Channel 1 Master
IDE Channel 1 Slave
Drive A
Drive B
Video
Halt On
Options are in its sub menu
None
360K, 5.25 in
1.2M, 5.25 in
720K, 3.5 in
1.44M, 3.5 in
2.88M, 3.5 in
EGA/VGA
CGA 40
CGA 80
MONO
All Errors
No Errors
All, but Keyboard
All, but Diskette
All, but Disk/Key
Set the system date. Note that the ‘Day’
automatically changes when you set the date
Press <Enter> to enter the sub menu of
detailed options
Select the type of floppy disk drive installed in
your system
Select the default video device
Select the situation in which you want the BIOS
to stop the POST process and notify you
48 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 49

Boot Display
Panel Type
TV Standard
Video Connector
Item Options Description
CRT
Select Display Device that the screen will be
shown
Select Panel Resolution that will be displayed
depending on the LCD Panel (LFP)
Select the output mode of TV Standard
Select the type of Video display connector
This item allows you to select different TV
signal format when the TV Standard item is not
off.
TV Format
LFP (LVDS)
CRT+LFP(LVDS)
TV
640x480 TFT
800x600 TFT
1024x768 TFT
1280x1024 TFT
Off
NTSC
PAL
SECAM
Automatic
Composite
Component
Both
Auto
NTSC_M
NTSC_M_J
NTSC_433
NTSC_N
PAL_B
PAL_G
PAL_D
PAL_H
PAL_I
PAL_M
PAL_N
PAL_60
SECAM_L
SECAM_L1
SECAM_B
SECAM_D
SECAM_G
SECAM_H
SECAM_K
SECAM_K1
User’s Manual
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
49
Page 50

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.1.2 IDE Adapter Setup
The IDE adapters control the hard disk drive. Use a separate sub menu to configure each
hard disk drive. The below Figure will shows the IDE primary master sub menu.
Use the following table to configure the hard disk.
Item Options Description
IDE HDD Auto-detection Press Enter
IDE Channel 0 Master
IDE Channel 0 Slave,
IDE Channel 1 Master,
IDE Channel 1 Slave
Access Mode
Capacity
The following options are selectable only if the ‘IDE Channel …’ item is set to ‘Manual’
Cylinder
Head
Precomp
Landing zone
Sector
Auto Display your disk drive
None
Auto
Manual
Normal
LBA
Large
Auto
size
Min = 0
Max = 65535
Min = 0
Max = 255
Min = 0
Max = 65535
Min = 0
Max = 65535
Min = 0
Max = 255
Press Enter to auto-detect the HDD on
this channel. If detection is
successful, it fills the remaining fields
on this menu.
Selecting ‘manual’ lets you set the
remaining fields on this screen.
Selects the type of fixed disk. "User
Type" will let you select the number of
cylinders, heads, etc. Note:
PRECOMP=65535 means NONE !
Choose the access mode for
this hard disk
Disk drive capacity (Approximated).
Note that this size is usually slightly
greater than the size of a formatted
disk given by a disk checking program.
Set the number of cylinders for this
hard disk.
Set the number of read/write heads
**** Warning: Setting a value of 65535
means no hard disk
****
Number of sectors per track
50 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 51

User’s Manual
3.5.2 Advanced BIOS Features
This section allows you to configure your system for basic operation. You have the
opportunity to select the system’s default speed, boot-up sequence, keyboard operation,
shadowing and security.
3.5.2.1 Virus Warning
Allows you to choose the VIRUS Warning feature for IDE Hard Disk boot sector protection.
If this function is enabled and someone attempt to write data into this area, BIOS will show
a warning message on screen and alarm beep.
Item Description
Enabled
Disabled
Activates automatically when the system boots up causing a warning message to
appear when anything attempts to access the boot sector or hard disk partition table.
No warning message will appear when anything attempts to access the boot sect or or
hard disk partition table.
3.5.2.2 CPU L1 & L2 Cache
This item allows you to speed up memory access. However, it depends on CPU design.
Item Description
Enabled Enable cache
Disabled Disable cache
3.5.2.3 CPU L3 Cache
This is the extra cache that sits on the motherboard between the processor and main
memory, since the processor already contains L1 and L2 cache and starting to ship with L3
cache built-in as well to speed up memory operations further. However, it depends on CPU
design.
Item Description
Enabled Enable cache
Disabled Disable cache
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
51
Page 52

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.2.4 Quick Power On Self Test
This category speeds up Power On Self Test (POST) after you power up the computer. If it
is set to Enable, BIOS will shorten or skip some check items during POST.
Item Description
Enabled Enable quick POST
Disabled Normal POST
3.5.2.5 First/Second/Third/Other Boot Device
The BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the sequence selected
in these items.
Item Description
Floppy Floppy Device
LS120 LS120 Device
HDD-0 First Hard Dis k Dev ice
SCSI SCSI Device
CDROM CDROM Device
HDD-1 Seconda ry Hard Disk Device
HDD-2 Third Hard Disk Devic e
HDD-3 Fourth Har d Disk Device
ZIP100 ZIP-100 Device
USB-FDD USB Floppy Device
USB-ZIP USB ZIP Device
USB-CDROM USB CD ROM Device
USB-HDD USB Hard Disk Device
LAN Network Device
Disabled Disabled any boot device
3.5.2.6 Swap Floppy Drive
This field is effective only in systems with two floppy drives. Selecting Enabled assigns
physical drive B to logical drive A, and physical drive A to logical drive B.
Item Description
Enabled Enable cache
Disabled Disable cache
3.5.2.7 Book Up Floppy Seek
Seeks disk drives during boot up. Disabling seeds boot up.
Item Description
Enabled Enable Floppy Seek
Disabled Disable Floppy Seek
3.5.2.8 Boot Up NumLock Status
Select power on state for NumLock.
Item Description
Enabled Enable NumLock
Disabled Disable NumLock
52 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 53

User’s Manual
3.5.2.9 Gate A20 Option
Select if chipset or keyboard controller should control Gate A20.
Item Description
Normal A pin in the keyboard controller controls GateA20
Fast Lets chipset control GateA20
3.5.2.10 Typematic Rate Setting
Key strokes repeat at a rate determined by the keyboard controller. When enabled, the
typematic rate and typematic delay can be selected.
The choice: Enabled/Disabled.
3.5.2.11 Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
When the typematic rate setting is enabled, you can select a typematic rate (the rate at
which character repeats when you hold down a key) of 6, 8, 10, 15, 20, 24 or 30 characters
per second.
The choice: Enabled/Disabled.
3.5.2.12 Typematic Delay
When the typematic rate setting is enabled, you ca select a typematic delay (the delay
before key strokes begin to repeat) of 250, 500, 750 or 1000 milliseconds.
The choice: Enabled/Disabled.
3.5.2.13 Security Option
Select whether the password is required every time the system boots or only when you
enter setup.
Item Description
System
Setup
The system will not boot and access to Setup will be denied if the correct password is
not entered at the prompt.
The system will boot, but access to Setup will be denied if the correct password is not
entered at the prompt.
Note: To disable security, select PASSWORD SETTING at Main Menu and then
you will be asked to enter password. Do not type anything and just press
<Enter>, it will disable security. Once the security is disabled, the system
will boot and you can enter Setup freely.
3.5.2.14 APIC Mode
The BIOS supports versions 1.4 of the Intel multiprocessor specification. When enabled,
the MPS Version 1.4 Control for OS can be activated.
The choice: Enabled/Disabled.
3.5.2.15 MPS Version Control For OS
This feature is to indicate the version of Multi-Processor Specification (MPS) that is using.
The choice: 1.1, 1.4
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
53
Page 54

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.2.16 OS Select for DRAM > 64MB
Select the operating system that is running with greater than 64MB of RAM on the system.
The choice: Non-OS2, OS2.
3.5.2.17 Report No FDD For WIN 95
The original Windows95 requires the presence of a floppy. Unless the BIOS tells it to
disregard the absence of the drive, it will generate an error message. For other operating
systems as Win98 etc this field is without relevance.
Item Description
No Don’t generate error message
Yes Generate error me ssage
3.5.2.18 Small Logo (EPA) Show
This item allows you enabled/disabled the small EPA logo show on screen at the POST
step.
Item Description
Enabled EPA Logo show is enabled
Disabled EPA Logo show is disabled
54 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 55

User’s Manual
3.5.3 Advanced Chipset Features
This section allows you to configure the system based on the specific features of the
installed chipset. This chipset manages bus speeds and access to system memory
resources, such as DRAM and the external cache. It also coordinates communications
between the conventional ISA bus and the PCI bus. It must be stated that these items
should never need to be altered. The default settings have been chosen because they
provide the best operating conditions for your system. The only time you might consider
making any changes would be if you discovered that data was being lost while using your
system.
The first chipset settings deal with CPU access to dynamic random access memory
(DRAM). The default timings have been carefully chosen and should only be altered if data
is being lost. Such a scenario might well occur if your system had mixed speed DRAM
chips installed so that greater delays may be required to preserve the integrity of the data
held in the slower memory chips.
3.5.3.1 DRAM Timing Selectable
This item allows you to select the DRAM timing value by SPD data or Manual by yourself.
The choice: Manual, By SPD.
3.5.3.2 CAS Latency Time
This item controls the time delay (in clock cycles - CLKs) that passes before the SDRAM
starts to carry out a read command after receiving it. This also determines the number of
CLKs for the completion of the first part of a burst transfer. In other words, the lower the
latency, the faster the transaction.
The Choices: 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
55
Page 56

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.3.3 Active to Precharge Delay
This item is the minimum delay time between Active and Precharge.
The Choices: 5, 6, 7.
3.5.3.4 DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
This option allows you to insert a delay between the RAS (Row Address Strobe) and CAS
(Column Address Strobe) signals. This delay occurs when the SDRAM is written to, read
from or refreshed. Naturally, reducing the delay improves the performance of the SDRAM
while increasing it reduces performance.
The Choices: 2, 3.
3.5.3.5 DRAM RAS# Precharge
This option sets the number of cycles required for the RAS to accumulate its charge before
the SDRAM refreshes. Reducing the precharge time to 2 improves SDRAM performance
but if the precharge time of 2 is insufficient for the installed SDRAM, the SDRAM may not
be refreshed properly and it may fail to retain data
So, for better SDRAM performance, set the SDRAM RAS Precharge Time to 2 but
increase it to 3 if you face system stability issues after reducing the precharge time.
The Choices: 2, 3.
3.5.3.6 DRAM Data Integrity Mode
Select ECC if your memory module supports it. The memory controller will detect and
correct single-bit soft memory errors. The memory controller will also be able to detect
double-bit errors though it will not be able to correct them. This provides increased data
integrity and system stability.
The choices: ECC, Non ECC.
3.5.3.7 MGM Core Frequency
This field sets the frequency of the DRAM memory installed.
The choices: Auto Max 266MHz, 400/266/133/200 MHz, 400/200/100/200 MHz,
400/200/100/133 MHz, 400/266/133/267 MHz, 533/266/133/200 MHz,
533/266/133/266 MHz, 533/333/166/266 MHz, 400/333/166/250 MHz,
Auto Max 400/333 MHz, Auto Max 533/333.
3.5.3.8 System BIOS Cacheable
This feature is only valid when the system BIOS is shadowed. It enables or disables the
caching of the system BIOS ROM at F0000h-FFFFFh via the L2 cache. This greatly
speeds up accesses to the system BIOS. However, this does not translate into better
system performance because the OS does not need to access the system BIOS much.
The Choice: Disabled, Enabled.
56 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 57

User’s Manual
3.5.3.9 Video BIOS Cacheable
This feature is only valid when the video BIOS is shadowed. It enables or disables the
caching of the video BIOS ROM at C0000h-C7FFFh via the L2 cache. This greatly speeds
up accesses to the video BIOS. However, this does not translate into better system
performance because the OS bypasses the BIOS using the graphics driver to access the
video card's hardware directly.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.3.10 Memory Hole At 15M-16M
Enabling this feature reserves 15MB to 16MB memory address space to ISA expansion
cards that specifically require this setting. This makes the memory from 15MB and up
unavailable to the system. Expansion cards can only access memory up to 16MB.
The choice: Enable, Disable.
3.5.3.11 Delayed Transaction
This feature is used to meet the latency of PCI cycles to and from the ISA bus. The ISA bus
is much, much slower than the PCI bus. Thus, PCI cycles to and from the ISA bus take a
longer time to complete and this slows the PCI bus down.
However, enabling Delayed Transaction enables the chipset's embedded 32-bit posted
write buffer to support delayed transaction cycles. This means that transactions to and from
the ISA bus are buffered and the PCI bus can be freed to perform other transactions while
the ISA transaction is underway.
This option should be enabled for better performance and to meet PCI 2.1 specifications.
Disable it only if your PCI cards cannot work properly or if you are using an ISA card that is
not PCI 2.1 compliant.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.3.12 Delay Prior to Thermal
When you system temperature higher, you can set the DRAM access time slowdown
between on 4 min – 32 min delay.
The choice: 4 Min, 8 Min, 16 Min, and 32 Min.
3.5.3.13 AGP Aperture Size
Select the size of Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) aperture. The aperture is a portion of
the PCI memory address range dedicated for graphics memory address space. Host cycles
that hit the aperture range are forwarded to the AGP without any translation.
The Choice: 4MB,8MB,16MB.32MB, 64MB,128MB,256MB.
3.5.3.14 On-Chip VGA
This item is enabled as the onboard VGA is used.
The Choices: Enabled, Disabled.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
57
Page 58

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.3.15 On-Chip Frame Buffer Size
This item is to select the amount of system memory that will be utilized as internal graphics
device memory.
The choices: 1MB, 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB.
58 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 59

3.5.4 Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to specify your settings for integrated peripherals.
User’s Manual
3.5.4.1 OnChip IDE Device
3.5.4.1.1 On-Chip Primary PCI IDE
The chipset contains a PCI IDE interface with support for two IDE channels. Select Enabled
to activate the primary IDE interface. Select Disabled to deactivate this interface.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.4.1.2 On-Chip Secondary PCI IDE
The chipset contains a PCI IDE interface with support for two IDE channels. Select Enabled
to activate the secondary IDE interface. Select Disabled to deactivate this interface.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
59
Page 60

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.4.1.3 Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO mode (0-4) for each
of the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. Modes 0 through 4 provide
successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the system automatically determines
the best mode for each device.
The choice: Auto, Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode 2, Mode 3, or Mode 4.
3.5.4.1.4 Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
Ultra DMA/33 implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive supports it and the
operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a third-party IDE bus
master driver). If your hard drive and your system software both support Ultra DMA/33,
select Auto to enable BIOS support.
The Choice: Auto, Disabled.
3.5.4.1.5 IDE HDD Block Mode
Block mode is also called block transfer, multiple commands, or multiple sector read/write.
If your IDE hard drive supports block mode (most new drives do), select Enabled for
automatic detection of the optimal number of block read/writes per sector the drive can
support.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.4.2 Onboard Device
3.5.4.2.1 USB / USB 2.0 Controller
This item allows you to set the USB / USB 2.0 Controller to Enabled/Disabled.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled
60 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 61

User’s Manual
3.5.4.2.2 USB Keyboard / Mouse Support
This item allows you to set the system’s USB keyboard/mouse to Enabled/Disabled.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled
3.5.4.2.3 AC97 Audio
This item allows you to decide to enable/disable the 815 chipset family to support AC97
Audio.
The choice: Auto, Disabled
3.5.4.2.4 Init Display First
This item allows you to decide to active whether PCI Slot or AGP first.
The choice: PCI Slot, AGP/Onboard.
3.5.4.3 Super IO Device
3.5.4.3.1 Onboard FDC Controller
Select Enabled if your system has a floppy disk controller (FDC) installed on the system
board and you wish to use it. If you install and-in FDC or the system has no floppy drive,
select Disabled in this field.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.4.3.2 Onboard Serial Port 1 / 2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first and second serial ports.
The Choice: Auto, 3F8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, Disable.
3.5.4.3.3 UART Mode Select
Select UART 2 mode as standard serial port or IR port.
The Choice: IrDA, ASKIR, Normal..
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
61
Page 62

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.4.3.4 RxD , TxD Active
This item allows you to determine the active of RxD, TxD level.
The Choice: Hi,Hi , Hi,Lo , Lo,Hi , Lo,Lo
3.5.4.3.5 IR Transmission Delay
This item allows you to enable/disable the IR Transmission Delay.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.4.3.6 UR2 Duplex Mode.
Select the value required by the IR device connected to the IR port. Full-duplex mode
permits simultaneous two-direction transmission. Half-duplex mode permits transmission in
one direction only at a time.
The choice: Half, Full.
3.5.4.3.7 Use IR Pins
This item allows you to determine the pin definition.
The Choice: RxD2,TxD2, IR-Rx2Tx2.
3.5.4.3.8 Onboard Parallel Port
Select a logical LPT port name and matching address for the physical parallel (printer) port.
The choice: Auto, 378/IRQ7, 278/IRQ5, 3BCH/IRQ7, Disabled.
3.5.4.3.9 Parallel Port Mode
Select an operating mode for the parallel port. Select Compatible or Extended unless you
are certain both your hardware and software support EPP or ECP mode.
The choice: SPP, EPP, ECP, ECP+EPP, Normal.
3.5.4.3.10 EPP Mode Select
Select EPP port type 1.7 or 1.9.
The choice: EPP1.7, EPP1.9.
3.5.4.3.11 ECP Mode Use DMA
Select a DMA channel for the port.
The choice: 3, 1.
3.5.4.3.12 PWRON After POW-Fail
When ATX power supply is used, this item is to set whether the system should reboot after
a power failure.
The choices: Off, On, Former-Sts.
3.5.4.4 Onboard Lan Boot
This item allows you to boot by the other system through LAN.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.4.5 Watch Dog Timer Select
This option will determine watch dog timer.
The choices: Disabled,10 ,20 ,30 ,40 Sec,1,2,4 Min.
62 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 63

User’s Manual
3.5.5 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to configure you system to most effectively save
energy while operating in a manner consistent with your own style of computer use.
3.5.5.1 ACPI Function
This item allows you to enable/disable the ACPI function.
The choice: Enable, Disable.
3.5.5.2 ACPI Suspend Type
This item will set which ACPI suspend type will be used.
The choice: S1(POS), S3(STR).S1&S3.
3.5.5.3 Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume
This item allows the system to initialize the VGA BIOS from S3 (Suspend to RAM) sleep
state.
The choice: Auto, Yes, No.
3.5.5.4 Power Management
There are three selections for Power Management, and each of them has fixed mode
settings.
Item Description
Min. Power Saving
Max. Power Saving
User Defined
Minimum power management,
HDD Power Down = 15 Min,
Maximum power management,
HDD Power Down =1 Min,
Allows you to set each mode individually. When not disabled, each of the
ranges are from 1 min. to 1 hr. except for HDD Power Down which ranges
from 1 min. to 15 min. and disable.
3.5.5.5 Video Off / In Method
This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked.
The choice: No, Yes.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
63
Page 64

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.5.6 Suspend Type
Select the suspend type.
The choice: Stop Grant, PwrOn Suspend.
3.5.5.7 MODEM Use IRQ
This determines the IRQ in which the MODEM can use.
The choice: 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, or NA.
3.5.5.8 Suspend Mode
Select the suspend type.
The choice: Disable, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 20, 30, 40 Min, 1 Hour.
3.5.5.9 HDD Power Down
After the selected period of drive inactivity, any system IDE devices compatible with the
ATA-2 specified timeout and then waking themselves up when accessed..
The choice: Disable, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 Min.
3.5.5.10 Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN
Pressing the power button for more than 4 seconds forces the system to enter the Soft-Off
state when the system has “hung”.(Only could working on ATX Power supply)
The choice: Delay 4 Sec, Instant-Off.
3.5.5.11 Wake-Up by LAN/PCI card
This will enable the system to wake up through LAN/PCI Card peripheral.
The choice: Enable, Disabled.
3.5.5.12 Power On by Ring
This determines whether the system boot up if there’s an incoming call from the Modem.
The choice: Enable, Disabled.
3.5.5.13 Resume by Alarm
This function is for setting date and time for your computer to boot up.
Reload Global Timer Events
3.5.5.14 Primary IDE 0/1,Secondary IDE 0/1,FDD,COM,LPT PORT,PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
Reload Global Timer events are I/O events whose occurrence can prevent the system from
entering a power saving mode or can awake the system from such a mode. In effect ,the
system remain alert for anything which occurs to a device which is configured as
Enabled ,even when the system is in a power down mode.
The choice: Enable, Disabled.
64 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 65

User’s Manual
3.5.6 PnP / PCI Configuration
This section describes configuring the PCI bus system. PCI, or Personal Computer
Interconnect, is a system which allows I/O devices to operate at speeds nearing the speed
the CPU itself uses when communicating with its own special components. This section
covers some very technical items and it is strongly recommended that only experienced
users should make any changes to the default settings.
3.5.6.1 Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset Extended System
Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have installed a new add-on and the
system reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict that the operating system cannot
boot.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
3.5.6.2 Resources Controlled By
The Award Plug and Play BIOS has the capacity to automatically configure all of the boot
and Plug and Play compatible devices. However, this capability means absolutely nothing
unless you are using a Plug and Play operating system such as Windows®95. If you set
this field to “manual” choose specific resources by going into each of the sub menu that
follows this field (a sub menu is preceded by a “¾”).
The choice: Auto, Manual.
3.5.6.3 IRQ / DMA Resources
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system interrupt a type, depending
on the type of device using the interrupt.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
65
Page 66

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.6.3.1 IRQ 3/4/5/7/9/10/11/12/14/15 Assigned to
This item allows you to determine the IRQ assigned to the ISA bus and is not available to
any PCI slot. Legacy ISA for devices compliant with the original PC AT bus specification
requiring a specific DMA channel, PCI/ISA PnP for devices compliant with the Plug and
Play standard whether designed for PCI or ISA bus architecture.
The choices: Legacy ISA, PCI/ISA PnP.
3.5.6.3.2 DMA 0/1/3/5/6/7 Assigned to
To assign to each system DMA channel as one of the flowing types, depending on the type
of device using the interrupt: Legacy ISA for devices compliant with the original PC AT bus
specification, PCI/ISA PnP for devices compliant with the Plug and Play standard whether
designed for PCI or ISA bus architecture.
The choices: Legacy ISA, PCI/ISA PnP.
3.5.6.4 PCI / VGA Palette Snoop
Leave this field at Disabled.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
66 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 67

3.5.7 PC Health Status
This section shows the status of your CPU, Fan & System.
User’s Manual
3.5.8 Frequency / Voltage Control
This menu specifies your setting for frequency/voltage control.
3.5.8.1 Auto Detect PCI Clk
This item allows you to enable/disable auto detect PCI Clock.
The choice: Enable, Disable.
3.5.8.2 Spread Spectrum
These options allow you to set Spread Spectrum and CPU Host/3V66/PCI clock into
various types of frequencies.
The choice: Enable, Disable.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
67
Page 68

ESM-2740/2743
3.5.9 Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Use this menu to load the BIOS default values for the minimal/stable performance for your
system to operate.
Press <Y> to load the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance
system operations.
3.5.10 Load Optimized Defaults
Use this menu to load the BIOS default values that are factory settings for optimal
performance system operations. While Award has designed the custom BIOS to maximize
performance, the factory has the right to change these defaults to meet their needs.
Press <Y> to load the default values setting for optimal performance system operations.
68 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 69

3.5.11 Set Supervisor / User Password
You can set either supervisor or user password, or both of them.
Supervisor Password: able to enter/change the options of setup menus.
User’s Manual
User Password: able to enter but no right to change the options of setup menus.
Type the password, up to eight characters in length, and press <Enter>. The password
typed now will clear any previously entered password from CMOS memory. You will be
asked to confirm the password. Type the password again and press <Enter>. You may also
press <Esc> to abort the selection and not enter a password. To disable a password, just
press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter the password. A message will confirm the
password will be disabled. Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you can
enter Setup freely.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
69
Page 70

ESM-2740/2743
PASSWORD DISABLED.
When a password has been enabled, you will be prompted to enter it every time you try to
enter Setup. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of your system
configuration. Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also require the BIOS to
request a password every time your system is rebooted. This would prevent unauthorized
use of your computer. You determine when the password is required within the BIOS
Features Setup Menu and its Security option (see Section 3). If the Security option is set to
“System”, the password will be required both at boot and at entry to Setup. If set to “Setup”,
prompting only occurs when trying to enter Setup
3.5.12 Save & Exit Setup
Save CMOS value changes to CMOS and exit setup.
Enter <Y> to store the selection made in the menus in CMOS, a special section in memory
that stays on after turning the system off. The BIOS configures the system according to the
Setup selection stored in CMOS when boot the computer next time.
The system is restarted after saving the values.
70 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 71

User’s Manual
3.5.13 Exit Without Save
Abandon all CMOS value changes and exit setup, and the system is restarted after exiting.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
71
Page 72

ESM-2740/2743
4. Drivers Installation
Note: Installation procedures and screen shots in this section are
for your reference and may not be exactly the same as
shown on your screen.
72 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 73

4.1 Install Chipset Driver (For Intel RG82855GME)
Insert the Supporting CD-ROM to
CD-ROM drive, and it should show the
index page of Avalue’s products
automatically. If not, locate Index.htm and
choose the product from the menu left, or
link to \Driver_Chipset\Intel\ 855GM.
Note: The installation procedures and
screen shots in this section are
based on Windows XP operation
system.
Step 3. Click Next.
User’s Manual
Step1. Locate \Driver_Chipset\Intel\
855GM\ infinst_enu.exe.
Step 2. Click Next.
Step 4. Click Finish to complete setup.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
73
Page 74

ESM-2740/2743
4.2 Install Chipset Driver (For Intel RG82852GM)
Insert the Supporting CD-ROM to
CD-ROM drive, and it should show the
index page of Avalue’s products
automatically. If not, locate Index.htm and
choose the product from the menu left, or
link to \Driver_Chipset\Intel\852GM.
Note: The installation procedures and
screen shots in this section are
based on Windows XP operation
system.
Step 3. Click Next.
Step1. Locate \Driver_Chipset\Intel\
Step 4. Click Finish to complete setup.
852GM\infinst_enu.exe.
Step 2. Click Next. Step 4. Click Finish to complete setup.
74 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 75

4.3 Install Display Driver (For Intel RG82855GME)
Insert the Supporting CD-ROM to
CD-ROM drive, and it should show the
index page of Avalue’s products
automatically. If not, locate Index.htm and
choose the product from the menu left, or
link to \Driver_Video\Intel\855GM.
Note: The installation procedures and
screen shots in this section are
based on Windows XP operation
system.
Step 3. Click Next.
User’s Manual
Step 1. Locate Driver_Video\Intel\
855GM\Win2K_XP\setup.exe.
Step 2. Click Next.
Step 4. Click Yes.
Step 5. Click Finish to complete setup.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
75
Page 76

ESM-2740/2743
4.4 Install Display Driver (For Intel RG82852GM)
Insert the Supporting CD-ROM to
CD-ROM drive, and it should show the
index page of Avalue’s products
automatically. If not, locate Index.htm and
choose the product from the menu left, or
link to Driver_Video\Intel\82852GM\
WinXP_2k.
Note: The installation procedures and
screen shots in this section are
based on Windows XP operation
system.
Step 3. Click Next.
Step 1. Locate Driver_Video\Intel\
Step 4. Click Yes.
82852GM\WinXP_2k\win2k_xp147.exe.
Step 2. Click Next. Step 5. Click Finish to complete setup.
76 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 77

4.5 Install Audio Driver (For Intel 82801DB)
Insert the Supporting CD-ROM to
CD-ROM drive, and it should show the
index page of Avalue’s products
automatically. If not, locate Index.htm and
choose the product from the menu left, or
link to \Driver_Audio\Intel\ 82801DB\
VT1616.
Note: The installation procedures and
screen shots in this section are
based on Windows XP operation
system.
Step 3. Select Install driver and click
Next.
User’s Manual
Step 1. Locate \Driver_Audio\Intel\
82801DB\VT1616\setup.exe.
Step 2. Click Next.
Step 4. Click Yes to complete the setup
and restart the computer.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
77
Page 78
ESM-2740/2743
4.6 Install Ethernet Driver (For Realtek RTL810x, RTL813x Family)
Insert the Supporting CD-ROM to
CD-ROM drive, and it should show the
index page of Avalue’s products
automatically. If not, locate Index.htm and
choose the product from the menu left, or
link to \Driver_Network\Realtek\
RTL810x_813X Family.
Note: The installation procedures and
screen shots in this section are
based on Windows XP operation
system.
Step 3. Click Yes to continue the
installation.
Step 1. Locate \Driver_Network\Realtek\
RTL810x_813X Family\Setup.exe.
Step 2. Setup executing.
78 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Step 4. Click Finish to complete the
setup.
Page 79

User’s Manual
5. Measurement
Drawing
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
79
Page 80

ESM-2740/2743
80 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 81

User’s Manual
Appendix A:
BIOS Revisions
BIOS Rev.
New Features
Bugs/Problems Solved
Known Problems
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
81
Page 82

ESM-2740/2743
Appendix B:
AWARD BIOS POST
Messages
82 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 83

User’s Manual
Overview
During the Power On Self-Test (POST), if the BIOS detects an error requiring you to do
something to fix, it will either sound a beep code or display a message.
If a message is displayed, it will be accompanied by:
PRESS F1 TO CONTINUE, CTRL-ALT-ESC OR DEL TO ENTER SETUP
Post Beep
Currently there are two kinds of beep codes in BIOS. This code indicates that a video
error has occurred and the BIOS cannot initialize the video screen to display any additional
information. This beep code consists of a single long beep followed by two short beeps.
The other code indicates that your DRAM error has occurred. This beep code consists of
a single long beep repeatedly.
Error Messages
One or more of the following messages may be displayed if the BIOS detects an error
during the POST. This list includes messages for both the ISA and the EISA BIOS.
1. CMOS BATTERY HAS FAILED
CMOS battery is no longer functional. It should be replaced.
2. CMOS CHECKSUM ERROR
Checksum of CMOS is incorrect. This can indicate that CMOS has become corrupt. This
error may have been caused by a weak battery. Check the battery and replace if
necessary.
3. DISK BOOT FAILURE, INSERT SYSTEM DISK AND PRESS ENTER
No boot device was found. This could mean that either a boot drive was not detected or the
drive does not contain proper system boot files. Insert a system disk into Drive A: and
press <Enter>. If you assumed the system would boot from the hard drive, make sure the
controller is inserted correctly and all cables are properly attached. Also be sure the disk
is formatted as a boot device. Then reboot the system.
4. DISKETTE DRIVES OR TYPES MISMATCH ERROR - RUN SETUP
Type of diskette drive installed in the system is different from the CMOS definition. Run
Setup to reconfigure the drive type correctly.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
83
Page 84

ESM-2740/2743
5. DISPLAY SWITCH IS SET INCORRECTLY
Display switch on the motherboard can be set to either monochrome or color. This indicates
the switch is set to a different setting than indicated in Setup. Determine which setting is
correct, and then either turn off the system and change the jumper, or enter Setup and
change the VIDEO selection.
6. DISPLAY TYPE HAS CHANGED SINCE LAST BOOT
Since last powering off the system, the display adapter has been changed. You must
configure the system for the new display type.
7. EISA Configuration Checksum Error
PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY
The EISA non-volatile RAM checksum is incorrect or cannot correctly read the EISA slot.
This can indicate either the EISA non-volatile memory has become corrupt or the slot has
been configured incorrectly. Also be sure the card is installed firmly in the slot.
8. EISA Configuration Is Not Complete
PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY
The slot configuration information stored in the EISA non-volatile memory is incomplete.
Note: When either of these errors appears, the system will boot in ISA mode,
which allows you to run the EISA Configuration Utility.
9. ERROR ENCOUNTERED INITIALIZING HARD DRIVE
Hard drive cannot be initialized. Be sure the adapter is installed correctly and all cables are
correctly and firmly attached. Also be sure the correct hard drive type is selected in Setup.
10. ERROR INITIALIZING HARD DISK CONTROLLER
Cannot initialize controller. Make sure the cord is correctly and firmly installed in the bus.
Be sure the correct hard drive type is selected in Setup. Also check to see if any jumper
needs to be set correctly on the hard drive.
11. FLOPPY DISK CNTRLR ERROR OR NO CNTRLR PRESENT
Cannot find or initialize the floppy drive controller. Make sure the controller is installed
correctly and firmly. If there are no floppy drives installed, be sure the Diskette Drive
selection in Setup is set to NONE.
84 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 85

User’s Manual
12. Invalid EISA Configuration
PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY
The non-volatile memory containing EISA configuration information was programmed
incorrectly or has become corrupt. Re-run EISA configuration utility to correctly program the
memory.
Note: When either of these errors appears, the system will boot in ISA mode,
which allows you to run the EISA Configuration Utility.
13. KEYBOARD ERROR OR NO KEYBOARD PRESENT
Cannot initialize the keyboard. Make sure the keyboard is attached correctly and no keys
are being pressed during the boot.
If you are purposely configuring the system without a keyboard, set the error halt condition
in Setup to HALT ON ALL, BUT KEYBOARD. This will cause the BIOS to ignore the
missing keyboard and continue the boot.
14. Memory Address Error at ...
Indicates a memory address error at a specific location. You can use this location along
with the memory map for your system to find and replace the bad memory chips.
15. Memory parity Error at ...
Indicates a memory parity error at a specific location. You can use this location along with
the memory map for your system to find and replace the bad memory chips.
16. MEMORY SIZE HAS CHANGED SINCE LAST BOOT
Memory has been added or removed since the last boot. In EISA mode use Configuration
Utility to reconfigure the memory configuration. In ISA mode enter Setup and enter the new
memory size in the memory fields.
17. Memory Verify Error at ...
Indicates an error verifying a value already written to memory. Use the location along with
your system's memory map to locate the bad chip.
18. OFFENDING ADDRESS NOT FOUND
This message is used in conjunction with the I/O CHANNEL CHECK and RAM PARITY
ERROR messages when the segment that has caused the problem cannot be isolated.
19. OFFENDING SEGMENT:
This message is used in conjunction with the I/O CHANNEL CHECK and RAM PARITY
ERROR messages when the segment that has caused the problem has been isolated.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
85
Page 86

ESM-2740/2743
20. PRESS A KEY TO REBOOT
This will be displayed at the bottom screen when an error occurs that requires you to reboot.
Press any key and the system will reboot.
21. PRESS F1 TO DISABLE NMI, F2 TO REBOOT
When BIOS detects a Non-maskable Interrupt condition during boot, this will allow you to
disable the NMI and continue to boot, or you can reboot the system with the NMI enabled.
22. RAM PARITY ERROR - CHECKING FOR SEGMENT ...
Indicates a parity error in Random Access Memory.
23. Should Be Empty But EISA Board Found
PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY
A valid board ID was found in a slot that was configured as having no board ID.
Note: When either of these errors appears, the system will boot in ISA mode,
which allows you to run the EISA Configuration Utility.
24. Should Have EISA Board But Not Found
PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY
The board installed is not responding to the ID request, or no board ID has been found in
the indicated slot.
Note: When either of these errors appears, the system will boot in ISA mode,
which allows you to run the EISA Configuration Utility.
25. Slot Not Empty
Indicates that a slot designated as empty by the EISA Configuration Utility actually contains
a board.
Note: When either of these errors appears, the system will boot in ISA mode,
which allows you to run the EISA Configuration Utility.
26. SYSTEM HALTED, (CTRL-ALT-DEL) TO REBOOT ...
Indicates the present boot attempt has been aborted and the system must be rebooted.
Press and hold down the CTRL and ALT keys and press DEL.
86 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 87

User’s Manual
27. Wrong Board In Slot
PLEASE RUN EISA CONFIGURATION UTILITY
The board ID does not match the ID stored in the EISA non-volatile memory.
Note: When either of these errors appears, the system will boot in ISA mode,
which allows you to run the EISA Configuration Utility.
28. FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (80) → Unable to reset floppy subsystem.
29. FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (40) → Floppy Type dismatch.
30. Hard Disk(s) fail (80) → HDD reset failed.
31. Hard Disk(s) fail (40) → HDD controller diagnostics failed.
32. Hard Disk(s) fail (20) → HDD initialization error.
33. Hard Disk(s) fail (10) → Unable to recalibrate fixed disk.
34. Hard Disk(s) fail (08) → Sector Verify failed.
35. Keyboard is locked out - Unlock the key.
BIOS detect the keyboard is locked. P17 of keyboard controller is pulled low.
36. Keyboard error or no keyboard present.
Cannot initialize the keyboard. Make sure the keyboard is attached correctly and no keys
are being pressed during the boot.
37. Manufacturing POST loop.
System will repeat POST procedure infinitely while the P15 of keyboard controller is pull
low. This is also used for M/B burn in test.
38. BIOS ROM checksum error - System halted.
The checksum of ROM address F0000H-FFFFFH is bad.
39. Memory test fail.
BIOS reports the memory test fail if the onboard memory is tested error.
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
87
Page 88

ESM-2740/2743
40. POST Codes
POST (hex) Description
CFh Test CMOS R/W functionality.
Early chipset initialization:
C0h
C1h
C3h Expand c ompressed BIOS code to DRAM
-Disable shadow RAM
-Disable L2 cache (socket 7 or below)
-Program basic chipset registers
Detect memory
-Auto-detection of DRAM size, type and ECC.
-Auto-detection of L2 cache (socket 7 or below)
C5h
0h1 Expand the Xgroup codes locating in physical address 1000:0
02h Reserved
03h Initial Superio_Early_Init switch.
04h Reserved
05h
06h Reserved
07h
08h
09h Reserved
0Ah
0Bh Reserved
0Ch Reserved
0Dh Reserved
0Eh
0Fh Reserved
Call chipset hook to copy BIOS back to E000 & F000 shadow
RAM.
1. Blank out screen
2. Clear CMOS error flag
1. Clear 8042 interface
2. Initialize 8042 self-test
1. Test special keyboard controller for Winbond 977 series Super I/O
chips.
2. Enable keyboard interface.
1. Disable PS/2 mouse interface (optional).
2. Auto detect ports for keyboard & mouse followed by a port & interface
swap (optional).
3. Reset keyboard for Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips.
Test F000h segment shadow to see whether it is R/W-able or not. If test
fails, keep beeping the speaker.
10h
11h Reserved
12h
13h Reserved
14h
88 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Auto detect flash type to load appropriate flash R/W codes into the run
time area in F000 for ESCD & DMI support.
Use walking 1’s algorithm to check out interface in CMOS
circuitry. Also set real-time clock power status, and then check for
override.
Program chipset default values into chipset. Chipset default
values are MODBINable by OEM customers.
Page 89

User’s Manual
POST (hex) Description
15h Reserved
16h Initial Early_Init_Onboard_Generator switch.
17h Reserved
18h Detect CPU information including brand, SMI type (Cyrix or
Intel) and CPU level (586 or 686).
19h Reserved
1Ah Reserved
1Bh Initial interrupts vector table. If no special specified, all H/W
interrupts are directed to SPURIOUS_INT_HDLR & S/W
interrupts to SPURIOUS_soft_HDLR.
1Ch Reserved
1Dh Initial EARLY_PM_INIT switch.
1Eh Reserved
1Fh Load keyboard matrix (notebook platform)
20h Reserved
21h HPM initialization (notebook platform)
22h Reserved
23h 1. Check validity of RTC value:
e.g. a value of 5Ah is an invalid value for RTC minute.
2. Load CMOS settings into BIOS stack. If CMOS checksum fails, use
default value instead.
3. Prepare BIOS resource map for PCI & PnP use. If ESCD is valid, take
into consideration of the ESCD’s legacy information.
4. Onboard clock generator initialization. Disable respective clock
resource to empty PCI & DIMM slots.
5. Early PCI initialization:
-Enumerate PCI bus number
-Assign memory & I/O resource
-Search for a valid VGA device & VGA BIOS, and put it
into C000:0.
24h Reserved
25h Reserved
26h Reserved
27h Initialize INT 09 buffer
28h Reserved
29h 1. Program CPU internal MTRR (P6 & PII) for 0-640K memory address.
2. Initialize the APIC for Pentium class CPU.
3. Program early chipset according to CMOS setup. Example: onboard
IDE controller.
4. Measure CPU speed.
5. Invoke video BIOS.
2Ah Reserved
2Bh Reserved
2Ch Reserved
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
89
Page 90

ESM-2740/2743
POST (hex) Description
1. Initialize multi-language
2Dh
2Eh Reserved
2Fh Reserved
30h Reserved
31h Reserved
32h Reserved
33h Reset keyboard except Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips.
34h Reserved
35h Reserved
36h Reserved
37h Reserved
38h Reserved
39h Reserved
3Ah Reserved
3Bh Reserved
3Ch Test 8254
3Dh Reserved
3Eh Test 8259 interrupt mask bits for channel 1.
3Fh Reserved
40h Test 8259 interrupt mask bits for channel 2.
41h Reserved
42h Reserved
43h Test 8259 functionality.
44h Reserved
45h Reserved
46h Reserved
47h Initialize EISA slot
48h Reserved
49h
4Ah Reserved
4Bh Reserved
4Ch Reserved
4Dh Reserved
4Eh
4Fh Reserved
50h Initialize USB
1. Put information on screen display, including Award title, CPU type,
CPU speed ….
1. Calculate total memory by testing the last double word of each 64K
page.
2. Program writes allocation for AMD K5 CPU.
1. Program MTRR of M1 CPU
2. Initialize L2 cache for P6 class CPU & program CPU with proper
cacheable range.
3. Initialize the APIC for P6 class CPU.
4. On MP platform, adjust the cacheable range to smaller one in case
the cacheable ranges between each CPU are not identical.
90 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 91

POST (hex) Description
51h Reserved
52h Test all memory (clear all extended memory to 0)
53h Reserved
54h Reserved
55h Display number of processors (multi-processor platform)
56h Reserved
1. Display PnP logo
57h
58h Reserved
59h Initialize the combined Trend Anti-Virus code.
5Ah Reserved
5Bh
5Ch Reserved
5Dh
5Eh Reserved
5Fh Reserved
60h
61h Reserved
62h Reserved
63h Reserved
64h Reserved
65h Initialize PS/2 Mouse
66h Reserved
67h
68h Reserved
69h Turn on L2 cache
6Ah Reserved
6Bh
6Ch Reserved
6Dh
6Eh Reserved
6Fh
70h Reserved
71h Reserved
72h Reserved
2. Early ISA PnP initialization
-Assign CSN to every ISA PnP device.
(Optional Feature)
Show message for entering AWDFLASH.EXE from FDD (optional)
1. Initialize Init_Onboard_Super_IO switch.
2. Initialize Init_Onbaord_AUDIO switch.
Okay to enter Setup utility; i.e. not until this POST stage can users enter
the CMOS setup utility.
Prepare memory size information for function call:
INT 15h ax=E820h
Program chipset registers according to items described in Setup &
Auto-configuration table.
1. Assign resources to all ISA PnP devices.
2. Auto assign ports to onboard COM ports if the corresponding item in
Setup is set to “AUTO”.
1. Initialize floppy controller
2. Set up floppy related fields in 40:hardware.
User’s Manual
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
91
Page 92

ESM-2740/2743
POST (hex) Description
(Optional Feature)
73h
74h Reserved
75h Detect & install all IDE devices: HDD, LS120, ZIP, CDROM…..
76h Reserved
77h Detect serial ports & parallel ports.
78h Reserved
79h Reserved
7Ah Detect & install co-processor
7Bh Reserved
7Ch Reserved
7Dh Reserved
7Eh Reserved
7Fh
Enter AWDFLASH.EXE if :
-AWDFLASH is found in floppy drive.
-ALT+F2 is pressed
1. Switch back to text mode if full screen logo is supported.
-If errors occur, report errors & wait for keys
-If no errors occur or F1 key is pressed to continue:
Clear EPA or customization logo.
80h Reserved
81h Reserved
1. Call chipset power management hook.
82h
83h Save all data in stack back to CMOS
84h Initialize ISA PnP boot devices
85h
86h Reserved
87h Reserved
88h Reserved
89h Reserved
90h Reserved
91h Reserved
92h Reserved
2. Recover the text fond used by EPA logo (not for full screen logo)
3. If password is set, ask for password.
1. USB final Initialization
2. NET PC: Build SYSID structure
3. Switch screen back to text mode
4. Set up ACPI table at top of memory.
5. Invoke ISA adapter ROMs
6. Assign IRQs to PCI devices
7. Initialize APM
8. Clear noise of IRQs.
93h Read HDD boot sector information for Trend Anti-Virus code
92 ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
Page 93

POST (hex) Description
1. Enable L2 cache
1. Program boot up speed
2. Chipset final initialization.
94h
95h
96h
FFh Boot attempt (INT 19h)
3. Power management final initialization
4. Clear screen & display summary table
5. Program K6 write allocation
6. Program P6 class write combining
1. Program daylight saving
1. Update keyboard LED & typematic rate
1. Build MP table
2. Build & update ESCD
3. Set CMOS century to 20h or 19h
4. Load CMOS time into DOS timer tick
5. Build MSIRQ routing table.
User’s Manual
ESM-2740/2743 User’s Manual
93
 Loading...
Loading...