Page 1

Intel® Desktop Board
DQ87PG
Technical Product Specification
May 2013
Part Number: G89983-001
The Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG may contain design defects or errors known as errata that may cause the product to deviate from published specifications.
Current characterized errata are documented in the Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Specification Update.
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
-001 First release of the Intel® Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product
Specification
This product spec ification applies to only the standar d Intel® Desktop Board with BIOS identifier
PGQ8710H.86A.
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNE CT I ON WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS
GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR
SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PROD UCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR
WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A P ARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, O R INFRINGEMENT
OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN
WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FO R ANY APPLICATION IN
WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH MAY OCCUR.
®
All Intel
computers (PC) for installation in home s , offices , schoo ls , com p uter room s , and sim ilar locati o ns . The
suitability of this product for other PC or embedded no n-PC app lic a tio ns or o ther e nviro nme nts , s uc h as
medical, industrial, alarm systems, te s t equipment, etc. may not be supported without further evaluation by
Intel.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending pa te nt app lic ations, trademarks, copyrights, or other
intellectual property rights that r e la te to the pres e nted subjec t matte r. The furnishing of documents and
other materials and inform ation doe s not provide any license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwis e ,
to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or othe r intelle c tua l p ro perty rights.
Intel may make changes to specifications and produc t descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristic s of any feature s or instructions marked “reserved”
or “undefined.” Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for
conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Intel desktop boards may contain design defe c ts or error s know n as err ata , which may c ause the prod uc t to
deviate from published specifications . C urrent characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales offic e or your distr ibutor to obtain the latest specifications before plac ing your
product order.
Intel and Intel Core are trademarks of Intel Corporatio n in the U.S. and/or other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the propert y of others.
Copyright 2013 Intel Corporation. All rig hts res erve d .
desktop boards are evaluated as Information Technology Equipment (I.T.E.) for use in personal
May 2013
Page 3
Board Identification Information
Basic Desktop Board DQ87PG Identification Information
AA Revision BIOS Revision Notes
G74154 PGQ8710H.86A 1,2
Notes:
1. The AA number is found on a small label on the component side of the board.
2. The Q87 chipset used on this AA revis io n co ns is ts of the follo w i ng co mponent:
Device Stepping S-Spec Numbers
Intel Q87 Express Chipset C1 SR137
Errata
Current characterized errata, if any, are documented in a separate Specification
Update. See
motherboards/motherboards.html?wapkw=desktop+boards for the latest
documentation.
http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/motherboards/desktop-
iii
Page 4

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
iv
Page 5

2
A map of the resou r ces of the Intel Desk top Board
3
The features supported by the BIOS Setup program
Preface
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) specifies the board layout, components,
connectors, power and environmental requirements, and the BIOS for Intel
Board DQ87PG.
Intended Audience
The TPS is intended to provide detailed, technical information about Intel Desktop
Board DQ87PG and its components to the vendors, system integrators, and other
engineers and technician s who need this level of information. It is specifical ly not
intended for general audiences.
What This Document Contains
Chapter Description
1 A description of the hardware used on Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG
4 A description of the BIOS error mes s a ges , beep codes, and POST codes
5 Regulatory comp lia nce and battery dis posal informati on
Typographical Conventions
®
Desktop
This section cont ains information abo u t t he conventions used in this sp ecification. No t
all of these symbols and abbreviations appear in all specifications of this type.
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE
Notes call attention to important information.
CAUTION
Cautions are included to help you avoid damaging hardware or losing data.
v
Page 6

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Other Common Notation
# Used after a signal name to identify an active-low sig nal (s uch as USB P0# )
GB Gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes)
GB/s Gigabytes per second
Gb/s Gigabits per second
KB Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
Kb Kilob it (1024 bits)
kb/s 1000 bits per second
MB Megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
MB/s Megabytes per sec ond
Mb Megabit (1,048,576 bits)
Mb/s Megabits per second
TDP Thermal Design Power
xxh An address or data value ending with a lowercase h indicates a hexadec ima l value.
x.x V Volts. Voltages are DC unless otherwise specified.
* This symbol is used to indicate third-party brand s and names tha t are the prop e rty of their
respective owners.
vi
Page 7

Contents
Revision History
Board Identification Information .................................................................. iii
Errata ...................................................................................................... iii
Preface
Intended Audience ..................................................................................... v
What This Document Contains ..................................................................... v
Typographical Conventions ......................................................................... v
1 Product Description
1.1 Overview ......................................................................................... 11
1.1.1 Feature Summary ................................................................. 11
1.1.2 Board Layout ........................................................................ 13
1.1.3 Block Diagram ...................................................................... 15
1.2 Online Support ................................................................................. 16
1.3 Processor ........................................................................................ 16
1.3.1 Processor Graphics Subsystem ................................................ 17
1.4 System Memory ............................................................................... 20
1.4.1 Memory Configurations .......................................................... 21
®
1.5 Intel
1.5.1 Direct Media Interface (DMI) .................................................. 23
1.5.2 USB ..................................................................................... 23
1.5.3 SATA Interfaces .................................................................... 24
1.6 Real-Time Clock Subsystem ............................................................... 25
1.7 Super I/O Controller ......................................................................... 25
1.8 Audio Subsystem .............................................................................. 26
1.8.1 Audio Subsystem Software ..................................................... 26
1.8.2 Audio Connectors and Headers ................................................ 27
1.9 LAN Subsystem ................................................................................ 28
1.9.1 Intel
1.9.2 LAN Subsystem Software ....................................................... 29
1.9.3 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs .............................. 29
1.10 Hardware Management Subsystem ..................................................... 30
1.10
1.10.2 Fan Monitoring ...................................................................... 30
1.10.3 Chassis Intrusion and Detection .............................................. 30
1.10.4 Thermal Monitoring ............................................................... 31
1.10.5 Intel
1.11 Intel
1.12 Power Management .......................................................................... 39
1.12.1 ACPI .................................................................................... 39
1.12.2 Hardware Support ................................................................. 41
Q87 Express Chipset ................................................................ 23
®
I217LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller ................................. 28
.1 Hardware Monitoring ............................................................. 30
®
®
Management Engine (Intel® ME) Software and Drivers ................. 37
vPro™ Technology ........................................................ 32
vii
Page 8

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2 Technical Reference
2.1 Memory Resources ........................................................................... 47
2.1.1 Addressable Memory.............................................................. 47
2.2 Connectors and Headers .................................................................... 48
2.2.1 Back Panel Connectors ........................................................... 49
2.2.2 Component-side Connectors and Headers ................................. 50
2.3 BIOS Security Jumper ....................................................................... 59
®
2.4 Intel
Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel® MEBX) Reset Header . 61
2.5 Mechanical Considerations ................................................................. 62
2.5.1 Form Factor .......................................................................... 62
2.6 Electrical Considerations .................................................................... 63
2.6.1 Power Supply Considerations .................................................. 63
2.6.2 Fan Header Current Capability ................................................ 64
2.6.3 Add-in Board Considerations ................................................... 64
2.7 Thermal Considerations ..................................................................... 65
2.8 Reliability ........................................................................................ 68
2.9 Environmental .................................................................................. 68
3 Overview of BIOS Features
3.1 Introduction ..................................................................................... 69
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization ........................................................ 70
3.3 Resource Configuration ..................................................................... 71
3.3.1 PCI Express Autoconfiguration ................................................ 71
3.4 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) ................................................. 71
3.5 Legacy USB Support ......................................................................... 71
3.6 BIOS Updates .................................................................................. 72
3.6.1 Language Support ................................................................. 72
3.6.2 Custom Splash Screen ........................................................... 73
3.7 BIOS Recovery ................................................................................. 73
3.8 Boot Options .................................................................................... 74
.1 Optical Drive Boot ................................................................. 74
3.8
3.8.2 Network Boot ........................................................................ 74
3.8.3 Booting Without Attached Devices ........................................... 74
3.8.4 Changing the Default Boot Device During POST ......................... 74
3.9 Adjusting Boot Speed ........................................................................ 75
3.9.1 Peripheral Selection and Configuration ..................................... 75
3.9.2 BIOS Boot Optimizations ........................................................ 75
3.9.3 Power Button Menu ............................................................... 76
3.10 Hard Disk Drive Password Security Feature .......................................... 76
3.11 BIOS Security Features ..................................................................... 77
3.12 BIOS Performance Features ............................................................... 79
viii
Page 9

Contents
4 Beep Codes, Error Messages, and POST Codes
4.1 BIOS Error Codes ............................................................................. 81
4.1.1 BIOS Beep Codes .................................................................. 81
4.1.2 Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes ......................................... 82
4.2 BIOS Error Messages ........................................................................ 82
4.3 Port 80h Power O n Self Test (POST) Codes .......................................... 83
5 Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
5.1 Regulatory Compliance ...................................................................... 89
5.1.1 Safety Standards................................................................... 89
5.1.2 European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement ................ 90
5.1.3 Product Ecology Statements ................................................... 91
5.1.4 China RoHS .......................................................................... 92
5.1.5 EMC Regulations ................................................................... 93
5.1.6 ENERGY STAR* 5.2, e-Standby, and ErP Compliance ................. 95
5.1.7 Regulatory Compliance Marks (Board Level) ............................. 96
5.2 Battery Disposal Information .............................................................. 97
Figures
1. Major Board Components .................................................................. 13
2. Block Diagram .................................................................................. 15
3. Memory Channel and DIMM Configuration ............................................ 22
4. Back Panel Audio Connectors ............................................................. 27
5. LAN Connector LED Locations ............................................................. 29
6. Thermal Sensors and Fan Headers ...................................................... 31
7. Location of the Intel ME “M” State LED ................................................ 38
8. Location of the Enhanced Standby Power LED ...................................... 45
9. Back Panel Connectors ...................................................................... 49
10. Component-side Connectors and Headers ............................................ 50
11. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Connector ..................................... 56
12. Connection Diagram for Front Panel USB 2.0 Connectors ....................... 58
13. Connection Diagram for the Front Panel USB 3.0 Connector ................... 58
. Location of the Jumper ...................................................................... 59
14
15. Intel MEBX Reset Header ................................................................... 61
16. Board Dimensions ............................................................................. 62
17. Localized High Temperature Zones ..................................................... 66
18. Intel Visual BIOS Screen ................................................................... 69
19. Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG China RoHS Material Self
Declaration Table .............................................................................. 92
Tables
1. Feature Summary ............................................................................. 11
2. Components Shown in Figure 1 .......................................................... 14
3. DisplayPort Status Conditions ............................................................. 17
4. Audio Formats Supported by the DisplayPort Interface .......................... 18
5. Supported Memory Configurations ...................................................... 20
6. Audio Jack Support ........................................................................... 26
ix
Page 10

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
7. LAN Connector LED States ................................................................. 29
8. Intel ME “M” State LED Behavior ........................................................ 37
9. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch ................................................... 39
10. Power States and Targeted System Power ........................................... 40
11. Wake-up Devices and Events ............................................................. 41
12. Component-side Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 10 ................ 51
13. Serial Port Connector ........................................................................ 52
14. Front Panel Audio Connector for Intel HD Audio .................................... 52
15. Front Panel Audio Connector for AC ’97 Audio ...................................... 52
16. Front Panel USB 2.0 Connectors ......................................................... 52
17. Front Panel USB 3.0 Connector ........................................................... 53
18. SATA Connectors .............................................................................. 53
19. S/PDIF Header ................................................................................. 53
20. Chassis Intrusion Header ................................................................... 54
21. Processor, Front, and Rear Chassis (4-Pin) Fan Headers ....................... 54
22. Internal Mono Speaker Header ........................................................... 54
23. Processor Core Power Connect or ........................................................ 55
24. Main Power Connector ....................................................................... 55
25. Front Panel Connector ....................................................................... 56
26. States for a One-Color Power LED ....................................................... 57
27. States for a Two-Color Power LED....................................................... 57
28. Alternate Front Panel Power/Sleep LED Header..................................... 57
29. BIOS Setup Security Jumper Settings ................................................. 60
30. Intel MEBX Reset Header Signals ........................................................ 61
31. Recommended Power Supply Current Values (High Power) .................... 63
32. Recommended Power Supply Current Values (Low Power) ..................... 64
33. Fan Header Current Capability ............................................................ 64
34. Thermal Considerations for Components ..............................................
35. Tcontrol Values for Components ......................................................... 67
36. Environmental Specifications .............................................................. 68
37. Intel Visual BIOS Setup Display Areas ................................................. 70
38. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys .................................................... 70
39. Acceptable Drives/Media Types for B IO S Recovery ................................ 73
40. Boot Device Menu Option s ................................................................. 74
41. Master Key and User Hard Drive Password Functions ............................ 76
42. Supervisor and User Password Functions ............................................. 78
43. BIOS Beep Codes ............................................................................. 81
44. Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes ..................................................... 82
45. BIOS Error Messages ........................................................................ 82
46. Port 80h POST Code Ranges .............................................................. 83
47. Port 80h POST Codes ........................................................................ 84
48. Typical Port 80h POST Sequence ........................................................ 88
49. Safety Standards .............................................................................. 89
50. EMC Regulations ............................................................................... 93
51. Regulatory Compliance Marks ............................................................ 96
67
x
Page 11
®
1 Product Description
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Feature Summary
Table 1 summarizes the major featur es of the board.
Table 1. Feature Summary
Form Factor
Processor
Memory
Chipset
Graphics
Audio 8-channel (6+2) Intel High Definition Audio via the Realtek* ALC662 audio codec
Micro-ATX (9.60 inches by 9.60 inches [243.84 millimeters by
243.84 millimeters])
• 4th generation Intel® Core™ processor with up to 95 W TDP in an LGA1150
socket
― One PCI Express* x16 grap hics inte rface
― Integrated memory controller with dual channe l DDR3 memory s uppor t
― Integrated graphics processing
― External graphics interface controller
• Four 24 0-pin DDR3 SDRAM Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) sockets
• Support for DDR3 1333 MHz to DDR3 1600 MHz DIMMs
• Support for 1 Gb, 2 Gb, and 4 Gb memory technology
• Support for up to 32 GB of system memory with four DIMMs using 4 Gb
memory technology
• Support for non-ECC memory
• Support for 1.5 V (standard voltage) and 1.35 V (low voltage) JEDEC memory
• Support for XMP memory
Intel
Q87 Express Chipset consisting o f the I nte l® Q87 Express Platform
Controller Hub (PCH)
• Integrated graphics support for processors with Intel® Graphics Technology:
― VGA
― DVI-D
― DisplayPort* v1.2
• Support for a PCI Express 3.0 x16 add-in graphics card
continued
11
Page 12
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 1. Feature Summary (continued)
Peripheral
Interfaces
Expansion
Capabilities
Intel® Visual BIOS
Instantly Available
PC Technology
LAN Support
Legacy I/O Control Nuvoton NCT6683 I/O controller for PS/2 port, serial port, parallel port, and
Hardware Monitor
Subsystem
Intel® vPro™
Technology
• USB 3.0 ports:
― Four USB 3.0 ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors
― Two front panel USB 3.0 ports are implemented throug h one inter nal
connector
• USB 2.0 ports:
― Two ports are implemented with stacked back p ane l connectors
― Six front panel ports are impleme nte d through three dual-port internal
headers
• Six Serial ATA (SATA) ports
• PS/2*-style keyboard/mouse port
• One serial port connector
• One parallel port connector on the back panel
• One PCI Express x16 3.0/ 2.x/1.x add-in card connector
• One PCI Express x1 2.x/ 1. x add-in card connector
• Two Conventional PCI bus add-in card connectors
®
• Intel
BIOS resident in the SPI Flash device
• Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), Plug and Play ,
and SMBIOS
• Support for PCI Express Revision 3.0
• Suspend to RAM support
• Wake on PCI, PCI Express, LAN, front panel, PS/2, serial, and USB ports
Gigabit (10/100/1000 Mb/s) LAN subsystem using the Inte l
Ethernet Controller
hardware management support
• Hardware monitoring through the Nuvoton I/O controller
• Voltage sense to detect out of range power supply voltages
• Thermal sense to detect out of range thermal values
• Three fan headers
• Two fan sense inputs used to monitor fan activity
• Fan speed control
®
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
Turbo Boost Technology for increased performanc e and power e ff ic ie ncy
®
Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT) for higher performance
®
Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT) 9.0
®
Virtualization (Intel® VT)
®
Virtualization for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
®
Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
®
Identity Protection Technology (Intel® IPT)
®
Anti-Theft Technology (Intel® AT)
• Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
®
I217LM Gigabit
12
Page 13
Product Description
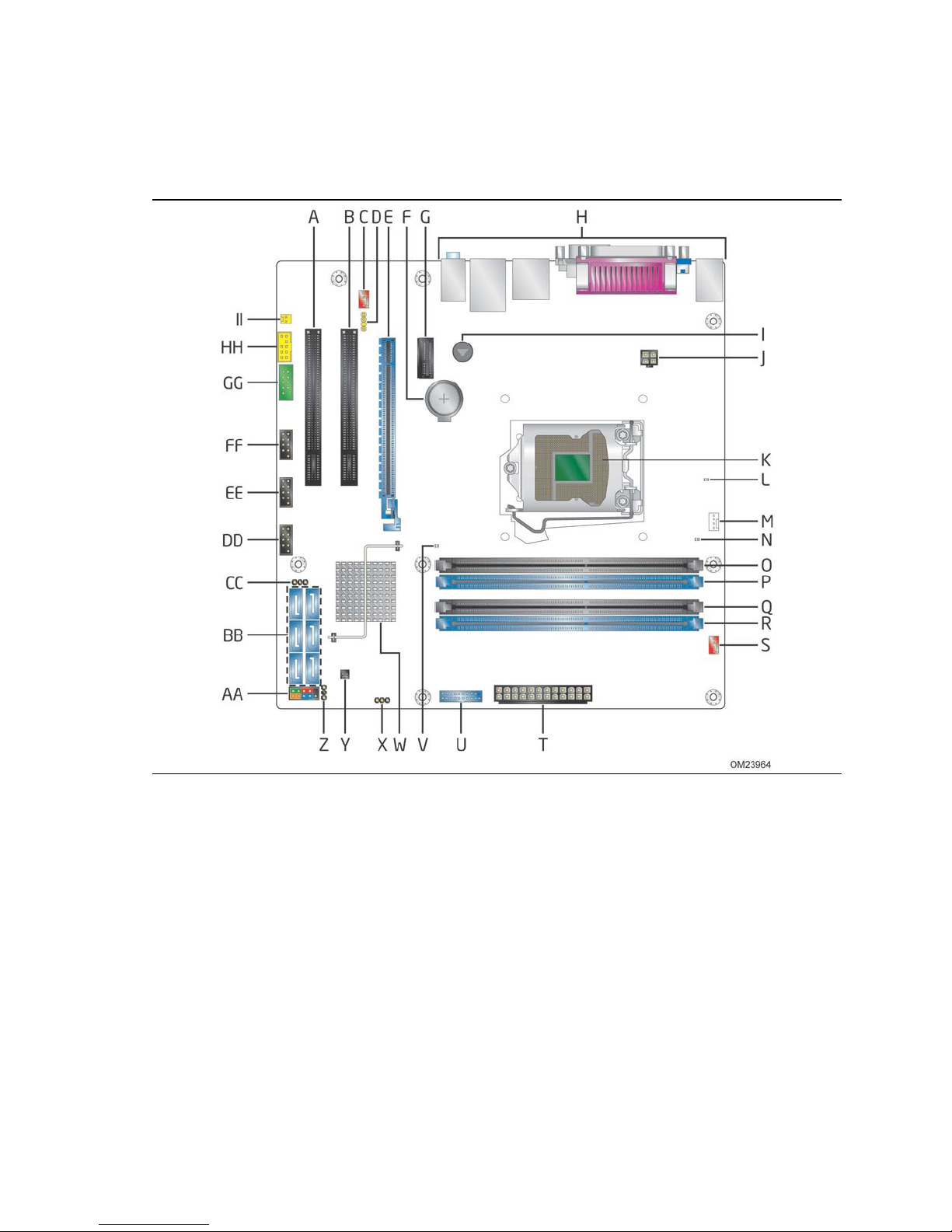
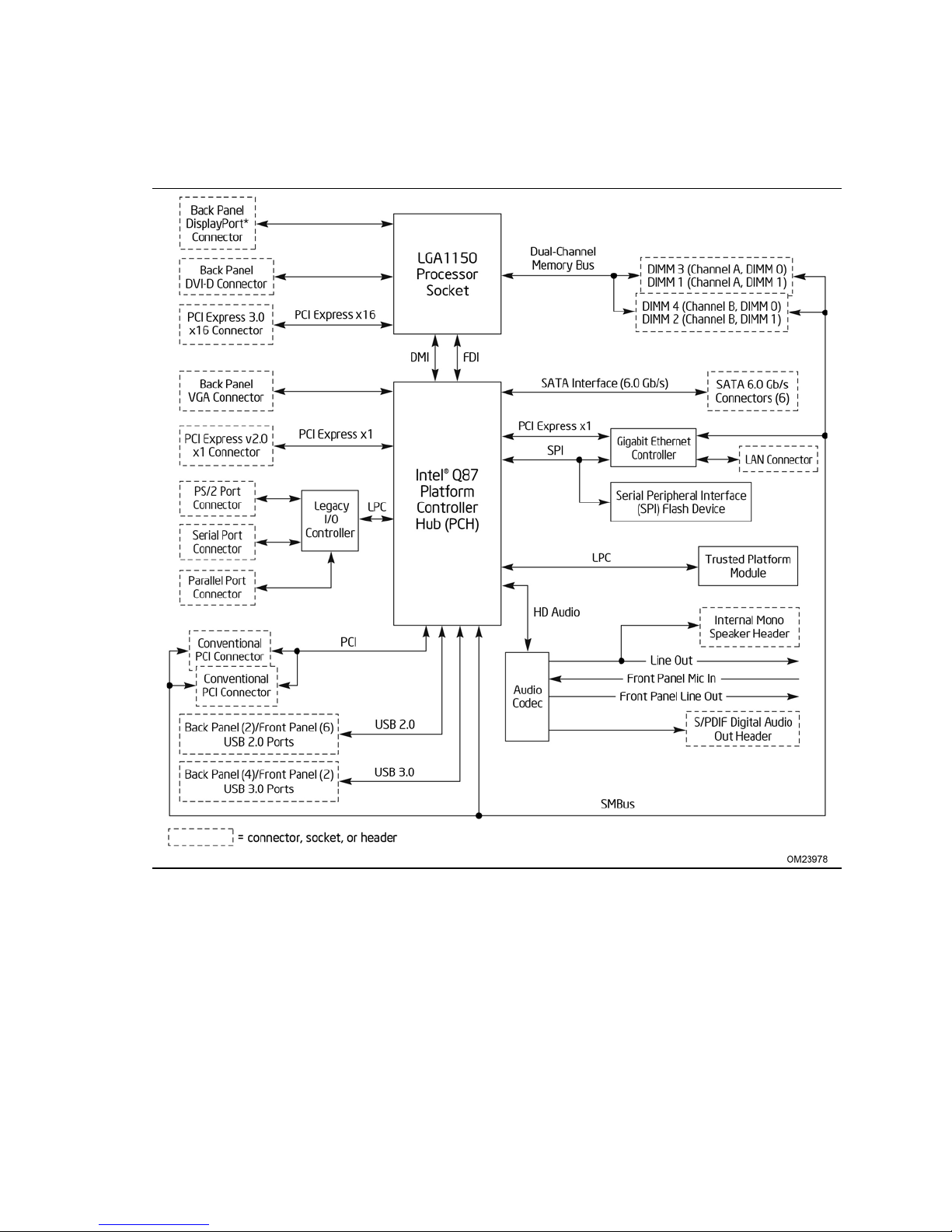
1.1.2 Board Layout
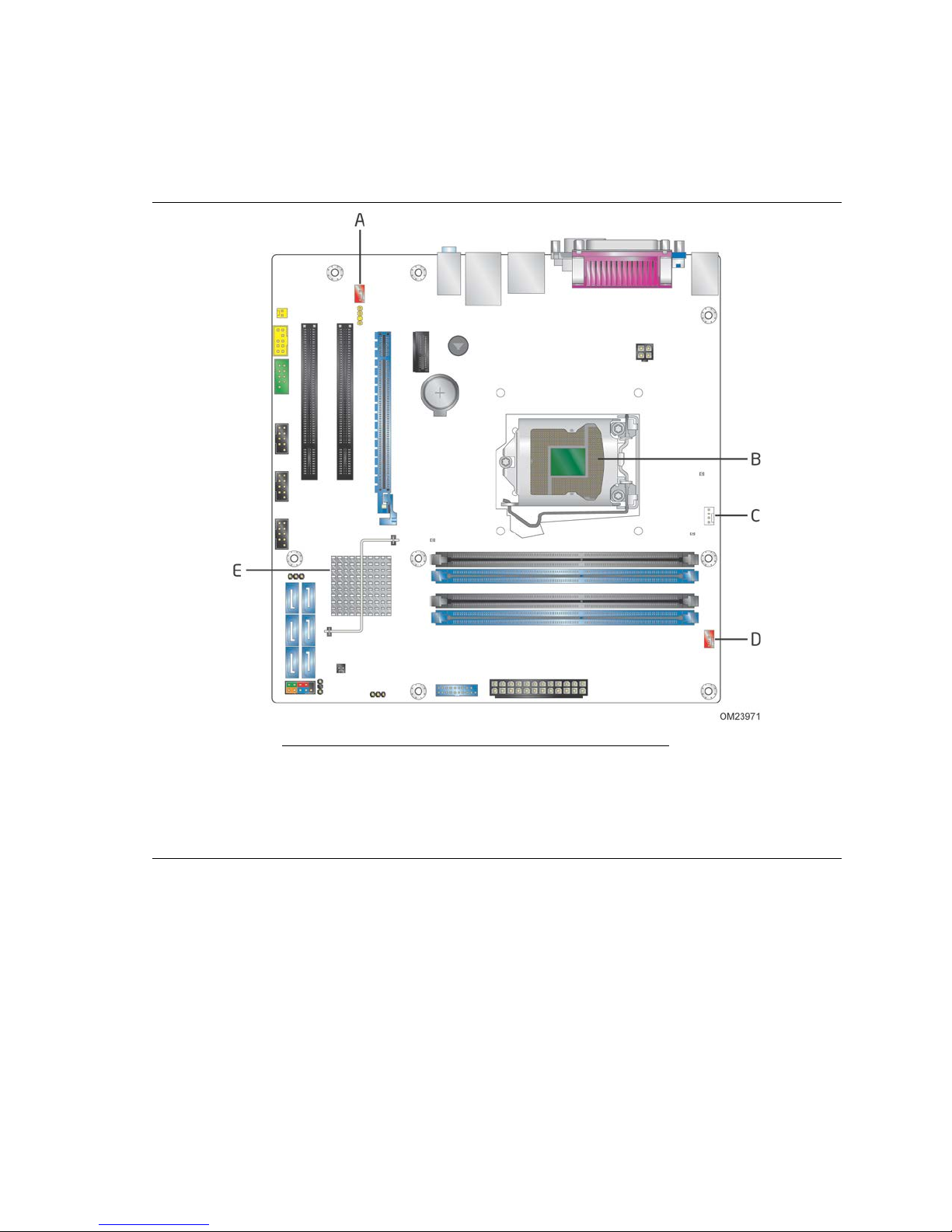
Figure 1 shows the location of the major components on Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG.
Figure 1. Major Board Components
13
Page 14
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 2 lists the components identified in Figure 1.
Table 2. Components Shown in Figure 1
Item/callout
from Figure 1 Description
A Conventional PCI add-in card connector
B Conventional PCI add-in card connector
C Rear fan header
D S/PDIF out header
E PCI Express x16 add-in card connector
F Battery
G PCI Express x1 add-in card connector
H Back panel connectors
I Piezoelectric speaker
J 12 V processor core voltage connector (2 x 2)
K LGA1150 processor socket
L Power supervisor LED
M Processor fan header
N Standby power LED
O DIMM 3 (Channel A DIMM 0)
P DIMM 1 (Channel A DIMM 1)
Q DIMM 4 (Channel B DIMM 0)
R DIMM 2 (Channel B DIMM 1)
S Front fan header
T Main po we r connector (2 x 12)
U Front panel USB 3.0 connector
V Intel® Management Engine “M” state LED
W Intel Q87 Express Chipset
X Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel® MEBX) Reset header
Y Chas s is intrusion header
Z Alternate front panel power/slee p LED head er
AA Front panel connector
BB SATA 6.0 Gb/s connectors
CC BIOS Setup configuration jumper block
DD Front panel USB 2.0 connector
EE Front panel USB 2.0 connector
FF Front panel USB 2.0 connector
GG Serial port connector
HH Fro nt p ane l audio connector
II Internal mono speaker header
14
Page 15
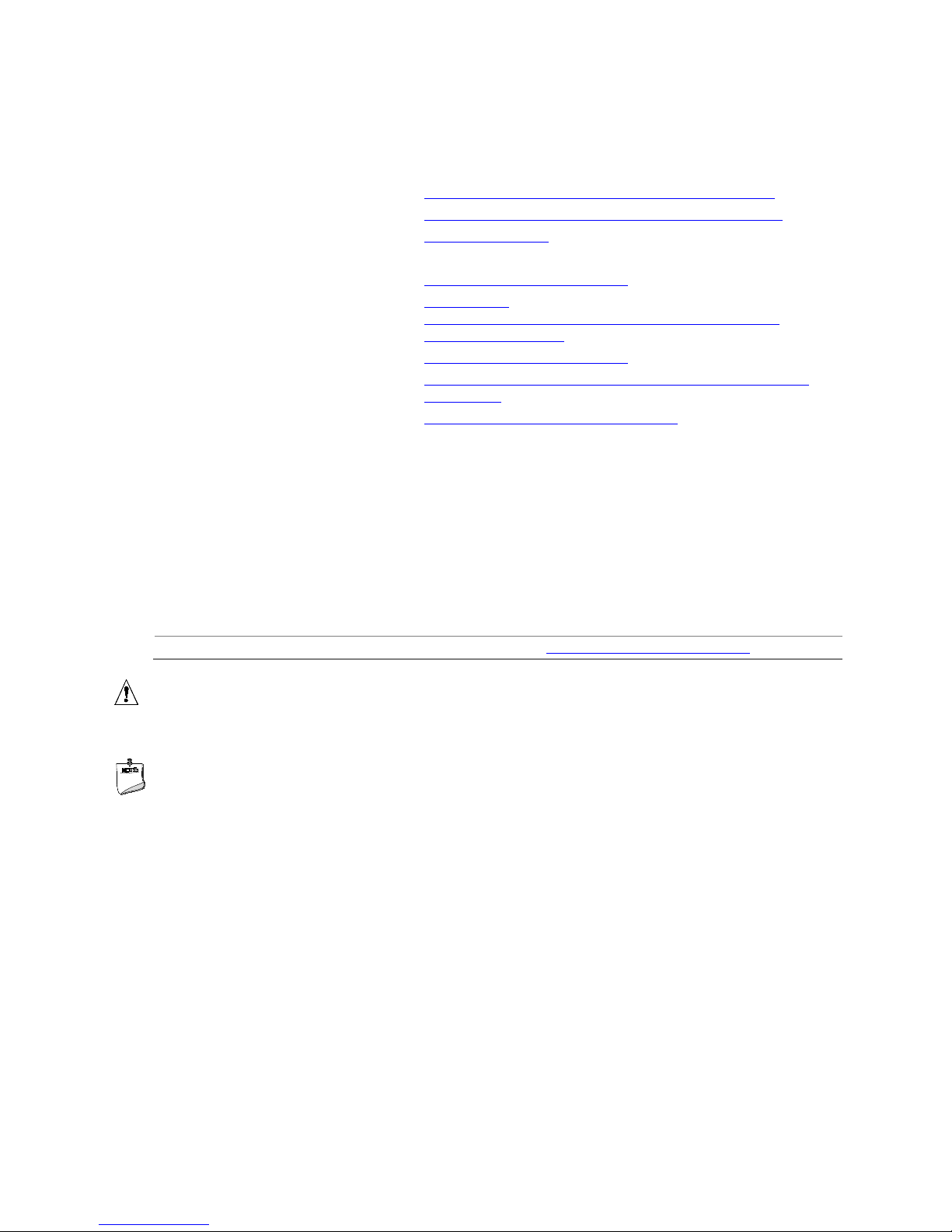
1.1.3 Block Diagram
Figure 2 is a block diagram of the major functional areas of the board.
Product Description
15
Figure 2. Block Diagram
Page 16
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.2 Online Support
To find information about… Visit this World Wide Web site:
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG http://www.intel.com/products/motherboard/index.htm
Desktop Board Support http://www.intel.com/p/en_US/support?iid=hdr+support
Available configurations for Intel
Desktop Board DQ87PG
Supported processors http://processormatch.intel.com
Chipset information https://www-
BIOS and driver updates http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Tested memory http://www.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/CS-
Integration informatio n http://www.intel.com/support/go/buildit
http://ark.intel.com
ssl.intel.com/content/www/us/en/chipsets/performancechipsets/chipsets.html
025414.htm
1.3 Processor
The board supports 4th generation Intel Core processors. Other processors may be
supported in the future. This board supports processors with a maximum wattage of
95 W Thermal Design Power (TDP). The processors listed above are only supported
when falling within the wattage requirements of Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG. See the
Intel web site listed below for the most up-to-date list of supported processors.
For information about… Refer to:
Supported processors http://processormatch.intel.com
CAUTION
Use only the processors listed on the web site above. Use of unsupported processors
can damage the board, the processor, and the power supply .
NOTE
This board has specific requirements for providing power to the processor. Refer to
Section 2.6.1 on page 63 for information on power supply requirements for this board.
16
Page 17

Product Description
(Note)
1.3.1 Processor Graphics Subsystem
The board supports graphics through either the processor Intel HD Graphics or a PCI
Express x16 add-in graphics card.
The board supports integrated graphics for processors with Intel HD Graphics.
1.3.1.1 Intel® High Definition (Intel® HD) Graphics
The Intel HD graphics controller features the following:
• 3D Features
DirectX* 11.1 support
OpenGL* 4.0 support
• Video
Next Generation Intel
video playback and enhancement fea tures tha t improve the end user’s viewing
experience
Encode/trans code HD content
Playback of high definition content incl uding Blu-ray* disc
Superior image quality with sharper, more colorful images
DirectX* Video Acceleration (DXVA) support for accelerating video processing
Full AVC/VC1/MPEG2 HW Decode
®
Intel
HD Graphics with Advanced Hardware Video Transcoding (Intel® Quick
Sync Video)
Note: Intel Quick Sync Video is enabled by an appropriate software application.
®
Clear Video Technology HD support is a collection of
1.3.1.2 DisplayPort*
DisplayPort is a digital c ommunication interface that utilizes differential signali ng to
achieve a high bandwidth bus interfac e designed to support connections between PCs
and monitors, projectors, and TV displays. DisplayPo rt is suitable for display
connections betw een co n sum er el ectr on ics devices such as high definition optical disc
players, set top boxes, and TV displays. DisplayPort output can also be converted to
HDMI using a DisplayPort-HDMI converter. The DisplayPort interface supports the
1.2 specification, including Multi-Stream Transport (MST) for monitor daisy-chaining.
DisplayPort’s maximum supported disp lay re solution is 3840 x 2160 @ 60Hz.
Table 3. DisplayPort Status Conditions
PCI Express x16 Connector Status DisplayPort Status
No add-in card installed Enabled
PCI Express x16 add-in card installed Enabled
Note: May require BIOS setup menu changes.
For information about Refer to
DisplayPort technology http://www.displayport.org
17
Page 18

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.3.1.3 Integrated Audio Provided by the DisplayPort Interface
The DisplayPort interface from the PCH supports audio. The processor supports two
High Definition audio streams on two digital ports simultaneously.
Table 4 shows the specific audio technologies supported by the PCH.
Table 4. Audio Formats Supported by the DisplayPort Interface
Audio Formats DisplayPort
AC-3 - Dolby* Digital Yes
Dolby Digital Plus Yes
DTS-HD* Yes
LPCM, 192 kHz/24 bit, 8 Channel Yes
Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master
Audio* (Lossless Blu-ray Disc Audio
Format)
Yes
1.3.1.4 High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP)
HDCP is the technology for protecting high definition content against unauthorized
copy or interception between a source (computer, digital set top boxes, etc.) and the
sink (panels, monitor, and TVs). The PCH supports HDCP 1.4 for content protection
over wired displays (DVI and DisplayPort).
1.3.1.5 Analog Display (VGA)
The VGA port supports analog displays. The maximum supported resolution is 2048 x
1536 (QXGA) at a 75 Hz refresh rate. The VGA port is enabled for POST whenever a
monitor is attached, regardless of the DVI-D connector status.
1.3.1.6 Digital Visual Interface (DVI-D)
The DVI-D port supports only digital DVI displays. The maximum supported resolution
is 1920 x 1200 at 60 Hz refresh (WUXGA). The DVI-D port is compliant with the
DVI 1.0 specification.
1.3.1.7 Multiple Display Configurations
The following multiple display config uratio n modes are s upport ed (with appropriate
driver software):
• Single Display is a mode with one display port activated to display the output to
one display device.
• Intel
• Extended Desktop is a mode with up to three display ports activate d to drive the
®
Display Clone is a mode with up to three display ports activated to drive the
display content of same color depth setting but potentially different ref r esh ra t e
and resolution settings to all the active display devices connected.
content with potentially different color depth, refresh rate, and resolution settings
on each of the active display devices connected.
18
Page 19

Product Description
1.3.1.8 PCI Express Graphics
4th generation Intel Core proces sors support PCI Express 3.0, 2.x, and 1.x:
• PCI Express 3.0 with a raw bit rate of 8.0 GT/s results in an effective bandwidth of
1 GB/s each direction per lane. The maximum theoretical bandwidth of the x16
interface is 16 GB/s in each direction, simultaneously, for a total bandwidth of
32 GB/s.
• PCI Express 2.x with a raw bit rate of 5.0 GT/s results in an effective bandwidth of
500 MB/s each direction per lane. The maximum theoretical bandwidth of the x16
interface is 8 GB/s in each direction, simultane ously, for a total bandwidth of
16 GB/s.
• PCI Express 1.x with a raw bit rate of 2.5 GT/s results in an effective bandwidth of
250 MB/s each direction per lane. The maximum theoretical bandwidth of the x16
interface is 4 GB/s in each direction, simultane ously, for a total bandwidth of
8 GB/s.
For information about Refer to
PCI Express technology http://www.pcisig.com
19
Page 20

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Capacity
Configuration
Density
Front-side/Back-side
Devices
1024 MB
SS
1 Gbit
128 M x8/empty
8
2048 MB
DS
1 Gbit
128 M x8/128 M x8
16
2048 MB
SS
2 Gbit
256 M x8/empty
8
4096 MB
DS
2 Gbit
256 M x8/256 M x8
16
8192 MB
DS
4 Gbit
512 M x8/512 M x8
16
1.4 System Memory
The board has four DIMM sockets and supports the following memory features:
• 1.5 V DDR3 SDRAM DIMMs with gold plated contacts, with the option to raise the
voltage to support higher performance DDR3 SDRAM DIMMs.
• 1.35 V Low Voltage DDR3 DIMMs (JEDEC specification)
• Two independent memory channels with interleaved mode support
• Unbuffered, sin gl e-sided or double-sided DIMMs with the following restriction:
DIMMs with x16 organization are not supported.
• 32 GB maximum total system memory (with 4 Gb memory technology). Refer to
Section 2.1.1 on page 47 for information on the total amount of addressable
memory.
• Minimum recommended total system memory: 1 GB
• Non-ECC DIMMs
• Serial Presence Detect
• DDR3 1600 MHz, DDR3 1333 MHz, and DDR3 1066 MHz SDRAM DIMMs
• XMP version 1.3 performance profile support for memory speeds of 1600 MHz or
lower
NOTE
To be fully compliant with all applicable DDR SDRAM memory specifications, the board
should be populated with DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data
structure. This allows the BIOS to read the SPD data and program the chipset to
accurately configure memory settings for optimum performance. If non-SPD memory
is installed, the BIOS will attempt to correctly configure the memory settings, but
performance and reliability may be impacted or the DIMMs may not function under the
determined fr eq u en cy.
Table 5 lists the supported DIMM configurations.
Table 5. Supported Memory Configurations
DIMM
4096 MB SS 4 Gbit 512 M x8/empty 8
Note: “DS” refers to double-sided memory modules (containing two rows of SDRAM) and “SS” refers to
single-sided memory modules (containing o ne row of SDRAM).
(Note)
SDRAM
SDRAM Organization
Number of SDRAM
20
Page 21
Product Description
For information about… Refer to:
Tested Memory http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb
/CS-025414.htm
1.4.1 Memory Configurations
4th generation Intel Core proces sors support the following types of memory
organization:
• Dual channel (Interleaved) mode. This mode offers the highest throughput for
real world applications. Dual channel mode is enabled when the installed memory
capacities of both DIMM channels are equal. Technology and device width can vary
from one channel to the other but the installed memory capacity for each channel
must be equal. If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest
memory timing will be used.
• Single channel (Asymmetric) mode. This mode is equivalent to single channel
bandwidth operation for real world applicat ions. This mode is used when only a
single DIMM is installed or the memory capacities are unequal. Technology and
device width can vary from one channel to the othe r. If different speed DIMMs are
used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used.
• Flex mode. This mode provides the most flexible performance characteristics.
The bottommost DRAM memory (the memory that is lowes t within the system
memory map) is mapped to dual channel operation; the to pm ost DRAM memory
(the memory that is nearest to the 8 GB address space limit), if any, is mapped to
single channel operation. Flex mode results in multiple zones of dual and single
channel operation across the whole of DRAM memory. To use flex mode, it is
necessary to populate b oth channels.
For information about… Refer to:
Memory Configuration Examples http://www.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/cs-
011965.htm
21
Page 22
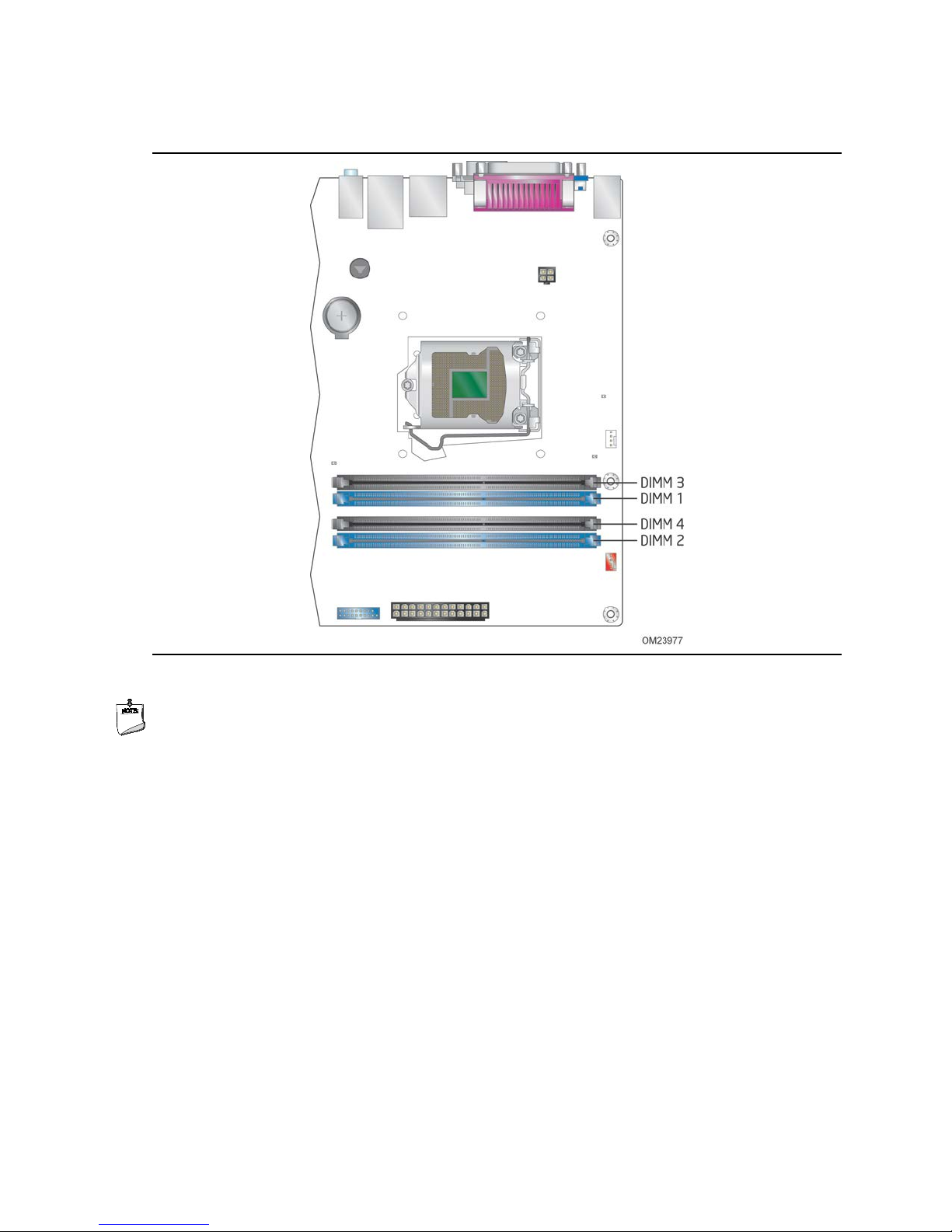
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Figure 3 illustrates the memory channel and D IMM configuration.
Figure 3. Memory Channel and DIMM Configuration
NOTE
For best memory performance always install memory in the blue DIMM sockets if
installing only two DIMMs on your board.
22
Page 23

Product Description
1.5 Intel® Q87 Express Chipset
Intel Q87 Express Chipset with Intel Flexible Display Inter connect (Intel FDI) and
Direct Media Interface (DMI) interconnect provides interfaces to the processor and the
display, USB, SATA, LPC, LAN, and PCI Express interfaces. The Intel Q87 Express
Chipset is a centralized controller for the board’s I/O paths.
For information about Refer to
The Intel Q87 chipset
Resources used by the chipset Chapte r 2
1.5.1 Direct Media Interface (DMI)
Direct Media Interface (DMI) is the chip-to-chip connection between the processor and
PCH. This high-speed interface integrates advanced priority-based servicing allowing
for concurrent traffic and true isochronous transfer capabilities.
1.5.2 USB
http://www.intel.com/products/desktop/chipsets/index.htm
The PCH contains up to two Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) host controllers
that support USB high-speed signaling. High-speed USB 2.0 allows data transfers up to
480 Mb/s. All ports are high-speed, fu l l-speed, and low-speed capable.
The PCH also contains an integrated eXtensible Host Controller Interface (xHCI) host
controller which supports USB 3.0 ports. This controller allows data transfers up to
5 Gb/s. The controller supports SuperSpeed (SS), high-speed (HS), full-speed (FS),
and low-speed (LS) traffic on the bus.
The Intel Q87 Express Chipset provides the USB controller for the USB 2.0/3.0 ports.
The port arrangement is as follows:
• USB 3.0 ports:
Four USB 3.0 ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors
Two front panel USB 3.0 ports are implemented through one internal connector
• USB 2.0 ports:
Two ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors
Six front panel ports are implemented through three dual-port internal headers
NOTE
Computer systems that have an unshielded ca b le a ttached to a USB port may not
meet FCC Class B requirements, even if no device is attached to the cable. Use a
shielded cable that meets the requirements for full-speed devices.
For information about Refer to
The location of the USB connectors on the back panel Figure 9, page 49
The location of the front panel USB headers Figure 10, page 50
23
Page 24
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.5.3 SATA Interfaces
The board provides six SATA connectors, through the PCH, which support one device
each.
The PCH provides independent SATA ports with a theoretical maximum transfer rate of
6.0 Gb/s. A point-to-point interface is used for host to device connections.
The PC H supports the Serial ATA Specification, Revision 3.0. The PCH also supports
several optional sections of th e Serial ATA II: Extensions to Serial ATA 1.0
Specification, Revision 1.0 (AHCI support is required for some elements).
For more information, see: http://www.serialata.org/
For information about Refer to
The location of the SATA connectors Figure 10, page 50
1.5.3.1 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology / SATA RAID
The PCH supports Intel® Rapid Storage Technology, providing both AHCI a nd
integrated RAID functionality. The RAID capability provides high-performance RAID 0,
1, 5, and 10 functionality on all SATA ports. Other RAID features include hot spare
support, SMART alerting, and RAID 0 auto replace. Software components include an
Option ROM for pre-boot configuration and boot functionality, a Microsoft* Windows*
compatible driver, and a user interface for configuration and management of the RAID
capability of the PCH.
.
1.5.3.2 Intel® Smart Response Technology
Intel® Smart Response Technology is a disk caching solution that can provide improved
computer system performance with improve d pow er savings. It allows configuration of
a computer system with the advantage of having HD Ds for maximum storage capacity
with system performance at or near SSD performance levels.
For more information on Intel Smart Response Technology, go to
http://www.intel.com/support/chipsets/sb/CS-032826.htm
NOTE
In order to use supported RAID and Intel Smart Response Technology features, you
must first enable RAID in the BIOS.
24
Page 25

Product Description
1.6 Real-Time Clock Subsystem
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When
the computer is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of
three years. When the computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power
supply extends the life of the battery. The c lock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at
25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied via the power supply 5V STBY rail.
NOTE
If the battery and AC power fail, date and time values will be reset and the user will be
notified during the POST.
When the voltage drops below a certain level, the BIOS Setup program settings stored
in CMOS RAM (for example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the
battery with an equivalent one. Figure 1 on page 13 shows the location of the battery.
1.7 Super I/O Controller
The I/O controller provides the following features:
• One serial port connector
• One back panel parallel port (with Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) and Enhanced
Parallel Port (EPP) support)
• PS/2-style keyboard/mouse interface on the back panel
• Serial IRQ interface compatible with serialized IRQ support for PCI systems
• Intelligent power management, including a program mable wake-up event interface
• Conventional PCI bus power m anagement support
The BIOS Setup program provides configuration options for the I/O controller.
25
Page 26
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.8 Audio Subsystem
The board supports Intel HD Audio via the Realtek ALC662 audio codec. The audio
subsystem supports the following features:
• Advanced jack sense for the back panel audio jacks that enables the audio codec to
recognize the device that is connected to an audio por t .
• Digital-to-Analog Converters (DAC) with 95 dB SNR (A-weighting) and Analog-toDigital Converters (ADC) with 90 dB SNR (A-weighting).
• Ten DAC channels support 16/ 2 0 /24-bit PCM format for 5.1 channel sound
playback, plus two channels of concurrent independent stereo sound output
(multiple streaming) through the front panel output.
• Two stereo ADCs support 16/20-bit PCM format, multiple stereo recording
• Microphone Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC), Noise S uppression (NS), and Beam
Forming (BF) technology for voice applications.
• Windows 7 Ultimate and Windows 8 Pro certification.
Table 6 lists the supported functions of the front panel and back panel audio jacks.
Table 6. Audio Jack Support
Audio Jack
Front panel - Green Default
Front panel - Pink Default
Back panel - Blue Default
Back panel - Green (ctrl panel) Default
Back panel - Pink Default
Microphone
Head-
phones
Line-Out
(Front
Speakers)
(ctrl panel)
Line-In
(Surround)
(ctrl panel)
1.8.1 Audio Subsystem Software
The latest audio software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining audio software and drivers Section 1.2, pa ge 16
Mic-In
(Center/Sub)
(ctrl panel)
26
Page 27
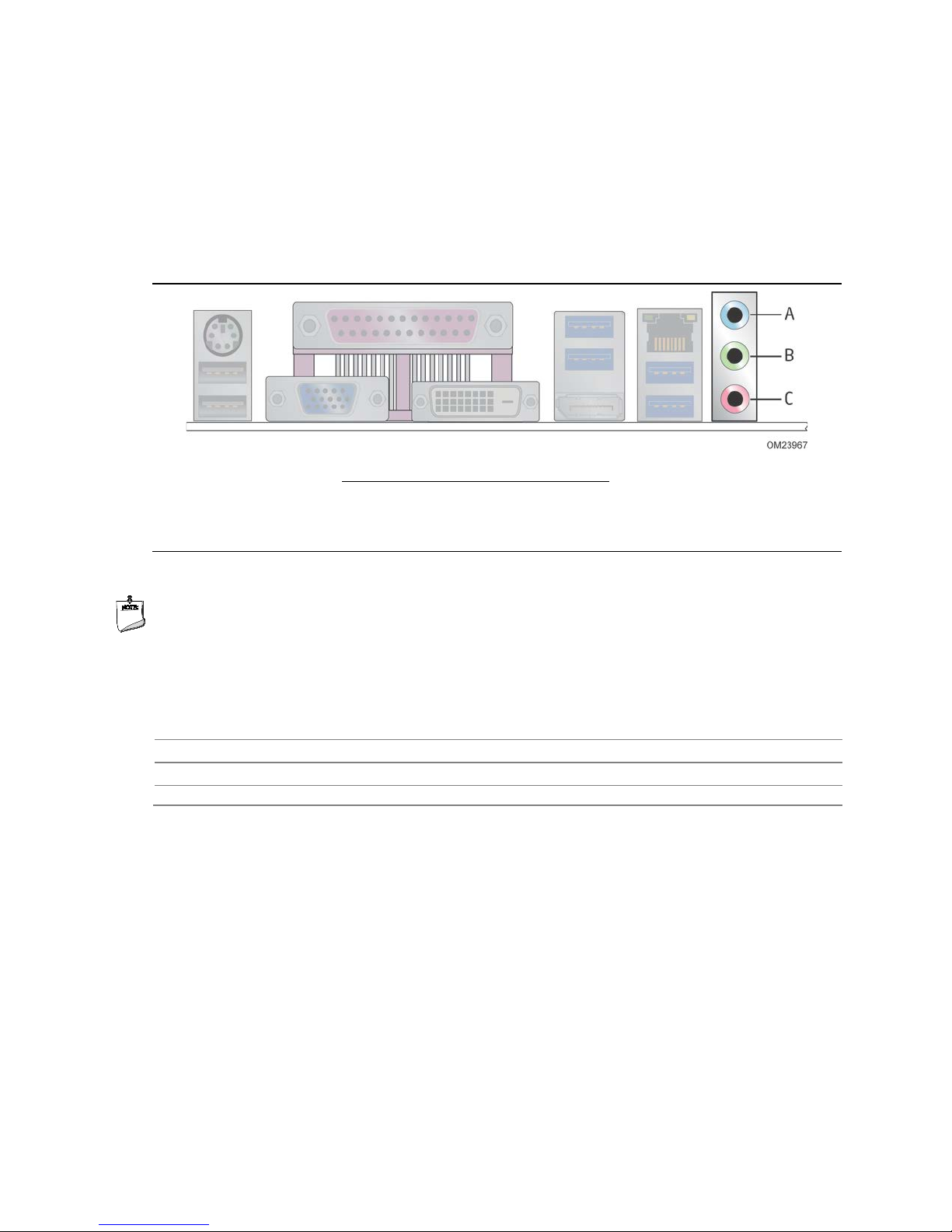
Product Description
1.8.2 Audio Connectors and Headers
The board contains audio connectors and headers on both the back panel and the
component side of the board. The component-side audio headers include front panel
audio (a 2 x 5-pin header that provides mic in and line out signals for front pa nel audio
connectors). The available configurable back panel audio connector s are shown in
Figure 4.
Item Description
A Line-in
B Line-out (front speakers)
C Mic-in (center/sub)
Figure 4. Back Panel Audio Connectors
NOTE
The back panel audio line out connector is designed to power headphones or amplified
speakers only. Poor audio quality occurs if passive (non-amplified) speakers are
connected to this output.
For information about Refer to
The locations of the front panel audio connector and S/PDIF audio header Figure 10, page 50
The signal names of the front panel audio connector a nd S/PDIF audio header Section 2.2.2.1, page 52
The back panel audio connectors Section 2.2.1, page 49
1.8.2.1 S/PDIF Header
The S/PDIF header allows connections to optical dong les for digital audio output.
1.8.2.2 Internal Mono Speaker Header
The internal mono speaker header allows co nnection to an internal, low-power speaker
for basic system sound capability. The subsystem is capable of driving a speaker load
of 8 Ohms at 1 W (rms) or 4 Ohms at 1.5 W (rms).
27
Page 28

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.9 LAN Subsystem
The LAN subsystem consists of the following:
• Intel I217LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller (10/100/1000 Mb/s)
• Intel Q87 Express Chipset
• RJ-45 LAN connector with integrated status LEDs
Additional features of the LAN subsystem include:
• CSMA/CD protocol engine
• LAN connect interface betw een the PCH and the LAN controller
• Conventional PCI bus power management
ACPI technology support
LAN wake capabilities
• ACPI technology support
• LAN wake capabilities
• LAN subsystem software
For information about
LAN software and drivers http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Refer to
1.9.1 Intel® I217LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller
The Intel I217LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller supports the following features:
Network Features:
• Compliant with the 1 Gb/s Ethernet 802.3, 802.3u, 802.3z, 802.3ab specifications
• Multi-speed operation: 10/100/1000 Mb/s
• Full-duplex operation at 10/100/1000 Mb/s; Half-duplex operation at 10/100 Mb/s
• Flow control support complia nt with the 802.3X specificatio n as well as the specific
operation of asymmetrical flow contro l defined by 802.3z
• VLAN support compliant with the 802.3q specification
• MAC address filters: perfect match unicast filters, multicast hash filtering,
broadcast filter, and promiscuous mode
Performance Features:
• Configurable receive and transmit data FIFO, programmable in 1 KB increments
• TCP segmentation capability compatible with Windows NT 5.x off-loading features
• Fragmented UDP checksum offload for packet reassem bly
• IPv4 and IPv6 checksum offload support (receive, transmit, and TCP segmentation
offload)
• Split header support to eliminate payload copy from user space to host space
• Receive Side Scaling (RSS) with two hardware receive queues
• Supports 9018 bytes of jumbo packets
• Packet buffer size
• LinkSec offload compliant with 802.3ae specification
• TimeSync offload compliant with 802.1as specification
28
Page 29
Product Description
LED
LED Color
LED State
Condition
Off
LAN link is not established.
Blinking
LAN activity is occurring.
Off
10 Mb/s data rate is selected.
Green
100 Mb/s data rate is selected.
Power Management Features:
• Magic Packet* wake-up enable with unique MAC address
• ACPI register set and power down functionality suppor ting D0 and D3 states
• Full wake up support (APM, ACPI)
• MAC power down at Sx, DMoff with and without WoL
• Auto connect battery saver at S0 no link and Sx no link
• Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) support
• Latency Tolerance Reporting (LTR)
• Optimized Buffer Flash/Fill (OBFF) support
• ARP and ND proxy support through LAN Connected Device proxy
• Wake on LAN (WoL) from Deep Sx
• Provides lower power usage to meet ENERGY STAR 5.2 and ErP specifications
1.9.2 LAN Subsystem Software
LAN software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining LAN software and drivers http://downloadcenter.intel.com
1.9.3 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs
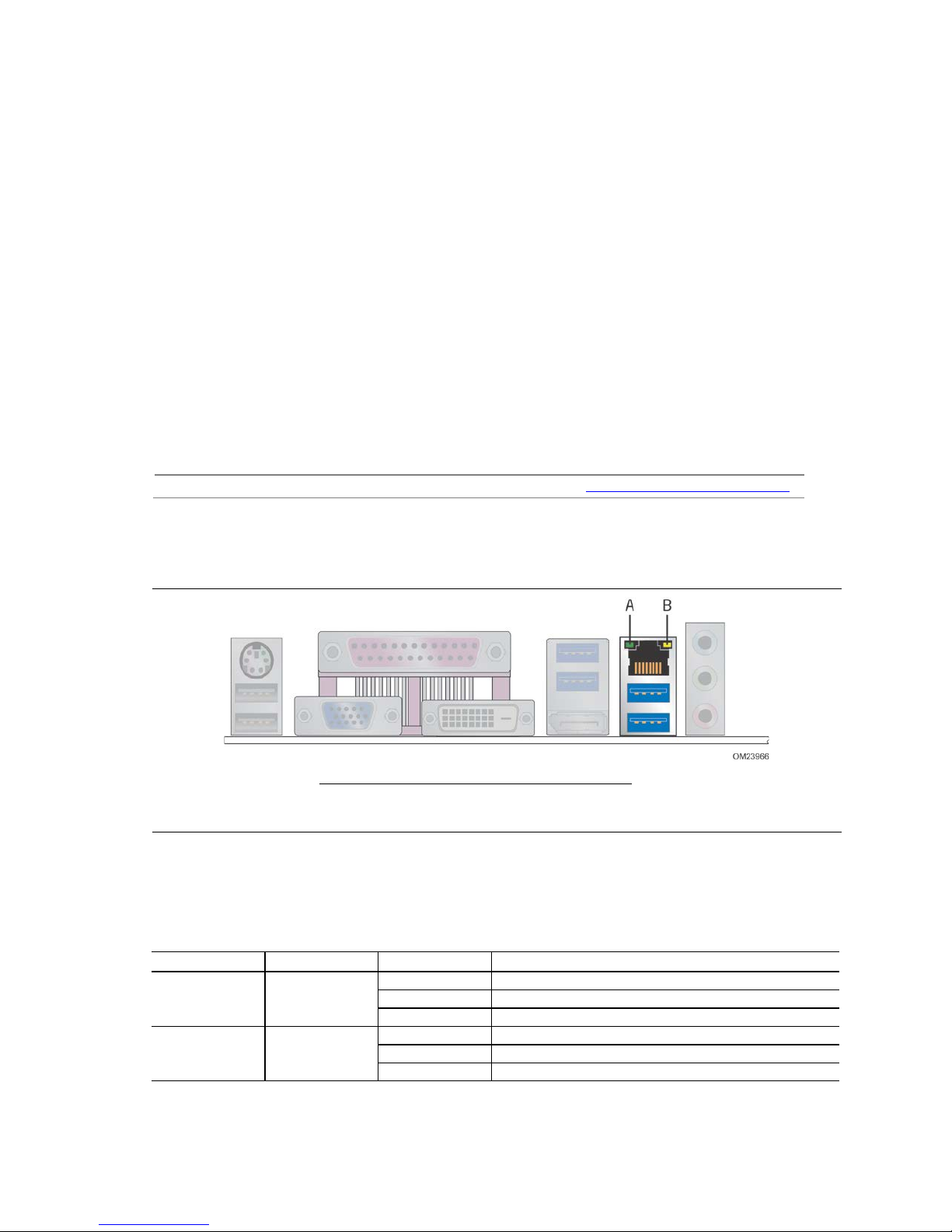
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connector (shown in Figure 5).
Item Description
A Link LED (Green)
B Data Rate LED (Green/Yellow)
Figure 5. LAN Connector LED Locations
Table 7 describes the LED states when the board is powered up and the LAN
subsystem is operating.
Table 7. LAN Connector LED States
Link Green
Data Rate Green/Yellow
29
On LAN link is established.
Yellow 1000 Mb/s data rate is selected.
Page 30

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.10 Hardware Management Subsystem
The hardware management features enable the board to be compatible with the Wired
for Management (WfM) specification. The board has several hardware management
features, including the following:
• Thermal and voltage monitoring
• Chassis intrusion detection
1.10.1 Hardware Monitoring
The hardware monitoring and fan control subsystem is based on the Nuvoton NCT6683
device, which supports the following:
• Processor and system ambient temperature monitoring
• Chassis fan speed monitoring
• Power monitoring of +12 V, +5 V, +3.3 V, V
• SMBus interface
SM
, +V
, and PCH VCC
CCP
1.10.2 Fan Monitoring
Fan monitoring can be implemented using Intel® Desktop Utilities or third-party
software.
For information about Refer to
The functions of the fan headers Section 1.12.2.2, page 42
1.10.3 Chassis Intrusion and Detection
The board supports a chassis security featur e that detects if the chassis cover is
removed. The security feature uses a mechan ical switch on the chass is that attaches
to the chassis intrusion header. When the chassis cover is removed, the mechanical
switch is in the closed position.
For information about Refer to
The location of the chassis intrusion header Figure 10, page 50
30
Page 31
1.10.4 Thermal Monitoring
Figure 6 shows the locations of the thermal sensors and fan headers.
Product Description
Item Description
A Rear chassis fan header
B Thermal diode, located on the processor die
C Processor fan header
D Front chassis fan header
E Thermal d iod e , loca ted on the Inte l Q87 PCH
Figure 6. Thermal Sensors and Fan Headers
31
Page 32

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.10.5 Intel® vPro™ Technology
Intel® vPro™ Technology is a set of processor and platform capabilities designed to
enable greater proactive security, enhanced maintenance, and improved remote
management both inside and outside the corporate firewall. These include:
• Intel Active Management Technology (Intel AMT)
• Intel Virtualization Technology (Intel VT)
• Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT)
• Intel Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel VT-d)
• Intel Fast Call for Help (Intel FCFH)
• Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
• KVM Remote Control
1.10.5.1 Intel® Active Management Technology
(Intel® AMT) 9.0
Intel Active Management Technology (Inte l AMT ) 9.0 offers IT organizations tamperresistant and persistent management capa bi lit ies. Specifically, Intel
hardware-based solution that uses out of band communication to manage access to
client systems in addition to offering encrypted and persistent asset management and
remote diagnostics and/or recovery ca pabilities for networked platforms. With Intel
AMT, IT organizations can easily get accurate platform information, and can perform
remote updating, diagnostics, debugging and repair of a system, regardless of the
state of the operating system or the power state of the system.
The Intel Active Management Technology subsystem consists of:
• Intel ME microcontroller embedded in the Intel Q67 PCH
• Intel I217LM Gigabit (10/100/1000 Mb/s) Ethernet LAN controller
• BIOS/SPI Flash (96 Mb/s)
AMT is a
NOTE
Software with AMT capability is required to take advantage of Intel AMT platform
management capabilities.
1.10.5.1.1 Intel AMT Features
The key features of Intel AMT include:
• Secure Out of Band (OOB) system management that allows remote management
of PCs regardless of system power or operating system state.
SSL 3.1/TLS encryption
HTTP authentication
TCP/IP
HTTP web GUI
XML/SOAP API
Web Services for Management (WS-MAN) protocol support
32
Page 33

Product Description
• Remote troubleshooting and recovery that can significantly reduce desk-side visits
and potentially increasing efficiency of IT technical staff.
System event log
IDE Redirection (IDE-R) or PXE boot: remote CD or network drive boot
Serial over LAN
OOB diagnostics
Remote control
Operating system repair
• Proactive alerting that decreases downtime and minimizes time to repair.
Programmable policies
Operating system lock-up alert
Boot failure alert
Hardware failure alerts
• Third party non-volatile storage that prevents users from removing critical
inventory, remote control, or virus protection agents.
Nonvolatile storage for agent s
Tamper-resistant
• Remote hardware and software asset tracking that eliminates time-consuming
manual inventory tracking, which also reduces asset accounting costs.
E-Asset Tag
HW/SW inventory
• System Defense 2. In addition to the in-bound and out-bound packet filtering of
the previous generation, System Defense 2 is an Intel AMT feature that uses
advanced heuristics to help protect against the propagation of worms through the
use of preset packet filters. The number of new connections made to a specific
port or IP address are counted over a specific time window. If a preset threshold is
exceeded, it will alert the Management Console and suspend the client’s network
activity until the system can be remediated.
• Remote Configuration (RCFG) minimizes the cost to deploy Intel AMT by
eliminating the need for IT personnel to touch each client system prior to
configuration. Remote Configuration consists of a single OEM BIOS/Firmware
image that provides the Intel AMT client with information to authenticate
connections and allows it to remotely perform a secure setup procedure. IT
departments must acquire an appropr iate Intel AMT-trusted certificate as well as
use a remote management application that supports Remote Co nfiguration.
Remote Configuration also requires the use of automatic IP addressing (DHCP).
33
Page 34

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
• KVM (Keyboard-Video-Mouse) Remote Control allows an IT administrator to
remotely control a user’s keyboard without having to rely on third-party software
applications. The user retains the ability to allow or discontinue the remote access
through on-screen pop-up windows. The maximum resolution supported by KVM
Remote Control is 2560 x 1600.
NOTE
KVM Remote Control requires the use of an Intel® processor with integrated
graphics. If using simultaneous integrated graphics and add-in PCI Express
Graphics, Integrated Graphics Device (IGD) must be set as the Primary
Video Device in the BIOS Setup in order for POST information to be seen
during a KVM Remote Control session. Likewise, IGD must be set as Primary
Video Device in the operating system for mouse functiona lity during a KVM
Remote Control session.
• PC Alarm Clock can wake the PC at scheduled times to run resource-intensive tasks
during off hours, improving security and performance of the platform.
For information about Refer to
Intel Active Management Technology (Inte l A MT )
http://www.intel.com/technology/platformtechnology/intel-amt/index.htm
1.10.5.1.2 Intel AMT Software and Drivers
Intel AMT software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site. The
package usually consists of the following components:
• Intel
®
Management Engine Interface (Intel® ME Interface)
• Serial Over LAN (SOL) driver
• Local Manageability Service (LMS)
• User Notification Se rvice (UNS)
®
ME WMI provider
®
Active Management Technology NAC Posture Plug-in
®
Control Center
®
Management and Security Status Application
page 16
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
For information about Refer to
Obtaining Intel AMT software and drivers Section Error! Reference source not found.,
34
Page 35

Product Description
1.10.5.2 Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
Intel Virtualization Technology (Intel VT) is a processor technology that enables a
platform to run multiple operating sys tems and applications as independent machines,
allowing one computer system to function as mult iple "virtual" systems. I t also
provides the “assisted hardware virtualization” required by some operating systems for
backward compatibility, such as Windows XP Mode for Windows 7.
NOTE
Requires an Intel processor that suppor ts Intel VT.
1.10.5.3 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT) helps protect the platform against
software-based attacks and preserves the confidentiality and integrity of the data
created and stored on the system. It accomplishes this by using a measured launch
and leveraging Intel VT to produce a protected environment for the execution of
sensitive applications.
NOTE
Requires an Intel processor that suppor ts Intel TXT.
1.10.5.4 Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O
(Intel® VT-d)
Intel Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel VT-d) compliments Intel VT by
providing the ability to isolate and re strict device accesses to the resources owned by
the virtual partition managing the device.
NOTE
Requires an Intel processor that suppor ts Intel VT.
35
Page 36

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.10.5.5 Intel® Fast Call for Help (Intel® FCFH)
Intel Fast Call for Help supplies remote maintenance connectivity for the Enterprise
user inside or outside the corporate firewall. Coupled with your enterprise’s
Management Presence Server, it provides both reactive and proactive maintenance.
Inside the firewall, this feature adapts Client Initiated Local Acce ss (CILA); outside the
firewall it uses Client Initiated Remo t e Access (CIRA).
Many of the features of Intel AMT are available with Intel Fast Call for Help. These
include Serial-over-LAN, IDE Redirection, KVM Remote Control, and PC Alarm Clock.
For information about Refer to
Intel FCFH Overview http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/fast-call-for-help-
overview/
1.10.5.6 Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
The ST Micro ST33TPM12LPC TPM version 1.2 revision 116 component is specifically
designed to enhance platform secur ity above-and-beyond the capabilities of today’s
software by providing a protected space for key operations and other security critical
tasks. Using both hardware and software, the TPM protects encryption and signature
keys at their most vulnerable stages—operations when the keys are being used
unencrypted in plain-text form. The TPM shields unencrypted keys and platform
authentication infor mati on fro m softwa re-based attacks.
For information about Refer to
ST Micro TPM Version 1.2 http://www.st.com/tpm
36
Page 37

Product Description
1.11 Intel® Management Engine (Intel® ME)
Software and Drivers
Intel ME software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining Intel ME software and drivers Section 1.2 on page 16
1.11.1.1 Intel Management Engine “M” State LED
The board has a blue-colored Intel ME “M” state LED (see Figure 7). The “M” state is
based on Intel ME status, as follows:
• M0 = Intel ME is in full control in S0
• M3 = Intel ME is in full control in S3-S5 for “out of bound” Intel manageability
• Moff = Intel ME is in sleep state after Intel ME timeout has occurred
Table 8 shows expected behavior of the “M” state LED.
Table 8. Intel ME “M” State LED Behavior
Sx/M3 Sx/Moff S0/M0
LED blinks Off On
37
Page 38

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Figure 7. Location of the Intel ME “M” State LED
38
Page 39

Product Description
state…
pressed for
…the system enters this state
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
1.12 Power Management
Power management is implemented at several levels, including:
• Software support through Advanced Configuration and Pow er Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support:
Power connector
Fan headers
LAN wake capabilities
Instantly Available PC technology
Wake from USB
Power Management Event signal (PME#) wake-up support
PCI Express WAKE# signal support
Wake from serial port
Wake from PS/2 devices
Wake from S5
+5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
1.12.1 ACPI
ACPI gives the operating system direct contro l over the power management and Plug
and Play functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with this board requires an
operating system that provides full ACPI support. ACPI features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration)
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in
boards may require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives
• Methods for achieving less than 15-watt system operation in the power-on/standby
sleeping state
• A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power-off the compute r
• Support for multiple wake-up events (see Table 11 on page 41)
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch
Table 9 lists the system states based on how long the power switch is pressed,
depending on how ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 9. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
If the system is in this
Off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
On
On
…and the power switch is
Less than four seconds Power-on
Less than four sec onds Soft-off/Standby
More than six seconds Fail safe power-off
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Sleep
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
39
Less than four seconds Wake-up
More than six seconds Power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Page 40

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.12.1.1 System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state
transitions. The operating system p uts devices in and out of low-power states based
on user preferences and knowledge of how devices are being used by applications.
Devices that are not being used can be turned off. The operating system uses
information from applications and user settings to put the system as a whole into a
low-power state.
Table 10 lists the power states supported by the board along with the associated
system power targets. See the ACPI specification for a complete description of the
various system and power states.
Table 10. Power States and Targeted System Power
Global States Sleeping States
G0 – working
state
G1 – sleeping
state
G1 – sleeping
state
G2/S5 S5 – Soft off.
G3 –
mechanical off
AC power is
disconnected
from the
computer.
Notes:
1. To tal system power is dependent on the system configuration, including add -in board s and per ipherals
powered by the system chassis’ power supply.
2. Dependent on the standby power consumption of wake-up devices used in the sys te m.
S0 – working C0 – working D0 – working
S3 – Suspend to
RAM. Context
saved to RAM.
S4 – Suspend to
disk. Context
saved to disk.
Context not saved.
Cold boot is
required.
No power to the
system.
Processor
States
No power D3 – no power
No power D3 – no power
No power D3 – no power
No power D3 – no power for
Device States
state.
except for
wake-up logic.
except for
wake-up logic.
except for
wake-up logic.
wake-up logic,
except when
provided by
battery or
external source.
Targeted System
Power
Full power > 30 W
Power < 5 W
Power < 5 W
Power < 5 W
No power to the system.
Service can be performed
safely.
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
(Note 2)
(Note 2)
40
Page 41

Product Description
Note 1)
(Note 1)
(Notes 1 and 3)
(Note 1)
(Notes 1 and 2)
1.12.1.2 Wake-up Devices and Events
Table 11 lists the devices or specific events that can wake the computer from specific
states.
Table 11. Wake-up Devices and Events
These devices/events can wake up the computer… …from this state
Power switch
RTC alarm
LAN
USB S3
PME# signal
WAKE#
Serial port S3
PS/2 devices
Notes:
1. S4 implies operating system support only.
2. PS/2 wake from S5 has a selection in the BIOS to enable wake from a combination key (Alt + Print
Screen) or the keyboard power button.
3. Wak e on LAN is only supported from sleep (S3) or hibernate (S4) in Windows 8.
NOTE
S3, S4, S5
S3, S4, S5
S3, S4, S5
S3, S4, S5
S3, S4, S5
S3, S4, S5
(
(Note 1)
The use of these wake-up events from an ACPI state requires an operating system
that provides full ACPI support. In addition, software, drivers, and peripherals mus t
fully support ACPI wake events.
1.12.2 Hardware Support
CAUTION
Ensure that the power supply provides adeq uate + 5 V standby current if LAN wake
capabilities and Instantly Available PC technology features are used. Failure to do so
can damage the power supply. The total amount of standby current required depends
on the wake devices supported and manufacturing o pti ons.
The board provides several power management hardware features, including:
• Power connector
• Fan headers
• LAN wake capabilities
• Instantly Available PC technology
• Wake from USB
• Power Management Event signal (PME#) wake-up support
• PCI Express WAKE# signal support
• Wake from serial port
• Wake from PS/2 devices
• Wake from S5
• +5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
41
Page 42

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
LAN wake capabilities and Instantly Available PC technology require power from the
+5 V standby line.
NOTE
The use of Wake from USB from an ACPI state requires an operating system that
provides full ACPI support.
1.12.2.1 Power Connector
ATX12V-compliant power supplies can turn off the system power through system
control. When an ACPI -enabled system receives the correct command, the power
supply removes all non-standby voltages.
When resuming from an AC power failure, the computer returns to the power state it
was in before power was interrupted (on or off). The computer’s response can be set
using the Last Power State feature in the BIOS Setup program’s Boot menu.
For information about Refer to
The location of the main power connector Figure 10, page 50
The signal names of the main power connector Table 24, page 55
1.12.2.2 Fan Headers
The function/operation of the fan headers is as follows:
• The fans are on when the board is in the S0 state
• The fans are off when the board is off or in the S3, S4, or S5 state
• Each fan header is wired to a fan tachometer input of t he hardware monitoring and
fan control ASIC
• All fan headers support closed-loop fan control that can adjust the fan speed or
switch the fan on or of f as needed
• All fan headers have a +12 V DC connection
• The fan headers are controlled by Pulse Width Modulation
For information about Refer to
The location of the fan headers Figure 10, page 50
The location of the fan headers and sensors for thermal monitoring Figure 6, page 31
42
Page 43

Product Description
1.12.2.3 LAN Wake Capabilities
CAUTION
For LAN wake capabilities, the +5 V standby line for the power supply must be capable
of providing adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide adequate standby
current when implementing LAN wake capabi li ti es can damage the power supply.
LAN wake capabilities enable remote wake-up of the computer through a network.
The LAN subsystem PCI bus network adapter monitors network traffic at the Media
Independent Interface. Upon detecting a Mag ic P a cket* frame, the LAN subsystem
asserts a wake-up signal that powers up the computer. Depending on the LAN
implementation, the board suppor ts L A N wake capabilities with ACPI in the following
ways:
• The PCI Express WAKE# signal
• By Ping
• Magic Packet
• The onboard LAN subsystem
1.12.2.4 Instantly Available PC Technology
CAUTION
For Instantly Available PC technology, the +5 V standby line for the power supply must
be capable of providing adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide adequate
standby current when implementing Instantly Availabl e PC technology can damage the
power supply.
Instantly Available PC technology enables the board to enter the ACPI S3 (Suspend-toRAM) sleep-state. While in the S3 sleep-state, the computer will appear to be off (the
power supply is off, and the front panel LED is amber if dual colored, or off if single
colored.) When signaled by a wake-up device or event, the system quickly returns to
its last known wake state. Table 11 on page 41 lists the devices and events that can
wake the computer from the S3 state.
The board supports the PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification. Add-in
boards that also support this specification can participate in power management and
can be used to wake the computer.
The use of Instantly Available PC technology requires operating system support and
PCI Express add-in cards and drivers.
43
Page 44

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
1.12.2.5 Wake from USB
USB bus activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S3 state.
NOTE
Wake from USB requires the use of a USB peripheral that supports Wake from USB.
1.12.2.6 PME# Signal Wake-up Support
When the PME# signal o n t h e Conventional PCI bus is asserted, the computer wakes
from an ACPI S3, S4, or S5 state (with Wake on PME enabled in the BIOS).
1.12.2.7 WAKE# Signal Wake-up Support
When the WAKE# signal on t he PCI Express bus is assert ed, the computer wakes from
an ACPI S3, S4, or S5 state.
1.12.2.8 Wake from Serial Port
Serial port activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S3 state.
1.12.2.9 Wake from PS/2 Devices
PS/2 keyboard activity wakes the computer from an AC PI S3, S4, or S5 state.
However, when the computer is in an ACPI S4 or S5 state, the only PS/2 activity that
will wake the computer is the Alt + Print Screen or the Power Key available only on
some keyboards.
1.12.2.10 Wake from S5
When the RTC Date and Time is set in the BIOS, the computer will automatically wake
from an ACPI S5 state.
1.12.2.11 Power Supervisor
The Power Supervisor actively monitors the input voltages from the power supply and
protects the board and any attached peripherals from electrical overstress and possible
physical damage. The Power Supervisor will activate if it detects the power supply
voltage rails have deviated outside the current ATX power supply specification and safe
operating levels.
If the Power Supervisor detects an out of spec voltage, the following will happen:
1. The board will be powered down immediately to protect circuits from electrical
overstress and possible physical damage.
2. A red warning LED (see Figure 1) on the board will activate as a visual cue.
44
Page 45

Product Description
3. During the next power on, a message will be displayed on the screen to notify the
user that the power supply voltage rails have deviated outside the current ATX
power supply specification and sa fe operating levels.
4. A message will be added to the BIOS Event Log for each event that takes place
until the BIOS Event Log is cleared.
1.12.2.12 Enhanced Standby Power LED
The enhanced standby power LED is lit when the b oard has +5 V standby voltage
applied to it. It also blinks as soon as the BIOS has started executing code, once the
power button has been pressed and before video has been initialized. Figure 8 shows
the location of the LED.
CAUTION
If AC power has been switched off and the sta ndby power indicator is still lit,
disconnect the power cord before installing or removing any devices connected to the
board. Failure to do so could damage the board and any a ttached devices.
Figure 8. Location of the Enhanced Standby Power LED
45
Page 46

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
46
Page 47

2 Technical Reference
2.1 Memory Resources
2.1.1 Addressable Memory
The board utilizes 32 GB of addressable system memory. Typically the address space
that is allocated for Conventional PCI bus add-in cards, PCI Express configuration
space, BIOS (SPI Flash device), and chipset overhead resides above the top of DRAM
(total system memory). On a system that has 32 GB of system memory installed, it is
not possible to use all of the installed memory due to system address space being
allocated for other system critical functions. These functions include t he following:
• BIOS/SPI Flash device (96 Mb)
• Local APIC (19 MB)
• Direct Media Interface (40 MB)
• PCI Express configuration space (256 MB)
• PCH base address registers PCI Express ports (up to 256 MB)
• Memory-mapped I/O that is dynamically allocated for Conventional PCI and PCI
Express add-in cards (256 MB)
The board provides the capability to reclaim the physical memory overlapped by the
memory mapped I/O logical address space. The board remaps physical memory from
the top of usable DRAM boundary to the 4 GB boundary to an equiva lent sized logical
address range located just above the 4 GB boundary. All installed system memory can
be used when there is no overlap of system addresses.
47
Page 48

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.2 Connectors and Headers
CAUTION
Only the following connectors and headers have overcurrent protection: back panel
and front panel USB, and PS/2.
The other internal connectors and headers are not overcurrent protected and should
connect only to dev i ces inside the computer’s chassis, such as fans and internal
peripherals. Do not use these connectors or headers to power devices external to the
computer’s chassis. A fault in the load presented by the external devices could cause
damage to the computer, the power cable, and the external devices themselves.
Furthermore, improper connection of USB header single wire connectors may
eventually overload the overcurrent protection and cause damage to the board.
This section describes the board’s connectors. The connectors can be divided into
these groups:
• Back panel I/O connectors
• Component-side connectors and headers (see page 50)
48
Page 49

2.2.1 Back Panel Connectors
Figure 9 shows the location of the back panel connectors for the board.
Item Description
A PS/2 port
B USB 2.0 ports
C VGA connector
D Parallel port
E DVI-D connector
F USB 3.0 connectors
G DisplayPort connector
H LAN port
I USB 3.0 connectors
J Line-in (surround)
K Line-out (front speakers)
L Mic-in (center/sub)
Technical Reference
Figure 9. Back Panel Connectors
NOTE
The back panel audio line out connector is des igned to power headphones or amplified
speakers only. Poor audio quality occurs if passive (non-amplified) speakers are
connected to this output.
49
Page 50

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.2.2 Component-side Connectors and Headers
Figure 10 shows the locations of the component-side connectors and headers.
Figure 10. Component-side Connectors and Headers
50
Page 51

Technical Reference
Table 12 lists the component-side connectors and headers identified in Figure 10.
Table 12. Component-side Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 10
Item/callout f
rom Figure 10 Description
A C onventional PCI add-in card connector
B C onventional PCI add-in card connector
C Rear fan header
D S/PDIF out header
E PCI Express x16 add-in card connector
F PCI Express x1 add-in card connector
G 12 V processor core voltage connector (2 X 2)
H Processor fan header
I Front chassis fan header
J Main power connector (2 x 12)
K Front panel USB 3.0 connector
L C has s is intrusion header
M Alternate front panel power/sleep LED header
N Front panel connector
O SATA 6.0 Gb/s connectors
P Front panel USB 2.0 connector
Q Front panel USB 2.0 connector
R Front panel USB 2.0 connector
S Serial port connector
T Front panel audio connector
U Internal mono speaker header
51
Page 52

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.2.2.1 Signal Tables for the Connectors and Headers
Table 13. Serial Port Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 DCD (Data Carrier Detect) 2 RXD# (Receive Data)
3 TXD# (Transmit Data) 4 DTR (Data Terminal Ready)
5 Ground 6 DSR (Data Set Ready)
7 RTS (Reques t To Send ) 8 CTS (Clear To Send)
9 RI (Ring Indicator) 10 Key (no pin)
Table 14. Front Panel Audio Connector for Intel HD Audio
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 [Port 1] Left channe l 2 Ground
3 [Port 1] Right c hanne l 4 PRESENC E# (Dongle present)
5 [Port 2] Right c hanne l 6 [Port 1] SENSE_RETURN
7 SENSE_SEN D (Jack d e tection) 8 Key (no pin)
9 [Port 2] Left channe l 10 [Port 2] SENSE_RETURN
Table 15. Front Panel Audio Connector for AC ’97 Audio
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 MIC 2 AUD_GND
3 MIC_BIAS 4 AUD_GND
5 FP_OUT_R 6 FP_RETURN_R
7 AUD_5V 8 KEY (no pin)
9 FP_OUT_L 10 FP_RETURN_L
Table 16. Front Panel USB 2.0 Connectors
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +5 V DC 2 +5 V DC
3 D- 4 D5 D+ 6 D+
7 Ground 8 Ground
9 KEY (no pin) 10 No Connect
52
Page 53
Table 17. Front Panel USB 3.0 Connector
Pin Signal Name Description
1 Vbus Power
2 IntA_P1_SSRX− USB3 ICC Port1 SuperSpeed Rx−
3 IntA_P1_SSRX+ USB3 ICC Port1 SuperSpe ed Rx+
4 GND Ground
5 IntA_P1_SSTX− USB3 ICC Port1 SuperSpeed Tx−
6 IntA_P1_SSTX+ USB3 ICC Port1 SuperS p eed Tx+
7 GND Ground
8 IntA_P1_D− USB3 ICC Port1 D− (USB2 Signal D−)
9 IntA_P1_D+ USB3 ICC Port1 D+ (USB2 Signal D+)
10 ID Over Current Protection
11 IntA_P2_D+ USB3 ICC Port2 D+ (USB2 Signal D+)
12 IntA_P2_D− USB3 ICC Port2 D− (USB2 Signal D−)
13 GND Ground
14 IntA_P2_SSTX+ USB3 ICC Port2 SuperS p eed Tx+
15 IntA_P2_SSTX− USB3 ICC Port2 SuperSpeed Tx−
16 GND Ground
17 IntA_P2_SSRX+ USB3 ICC Port2 SuperSpe ed Rx+
18 IntA_P2_SSRX− USB3 ICC Port2 SuperSpe ed Rx+
19 Vbus Power
20 Key No pin
Technical Reference
Table 18. SATA Connectors
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 TXP
3 TXN
4 Ground
5 RXN
6 RXP
7 Ground
Table 19. S/PDIF Header
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 S/PDIF out
3 Key (no pin)
4 +5 V DC
53
Page 54

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 20. Chassis Intrusion Header
Pin Signal Name
1 Intruder#
2 Ground
Table 21. Processor, Front, and Rear Chassis
(4-Pin) Fan Headers
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 +12 V
3 FAN_TACH
4 FAN_CONTROL
Note: These fan headers use Pulse Width Modulation control for fan speed.
(Note)
Table 22. Internal Mono Speaker Header
Pin Signal Name
1 −
2 +
2.2.2.2 Add-in Card Connectors
The board has the following add-in card connectors:
• One PCI Express x16 (3.0/ 2.x/ 1.x)
• One PCI Express x1 (2.x/1.x)
• Two Conventional PCI (rev 2.3)
Note the following considerations for th e Conventional PCI bus connectors:
• The Conventional PCI bus connectors are bus master capable.
• SMBus signals are routed to the Co n ventional PCI bus conne ctors. This enables
Conventional PCI bus add-in boards with SMBus support to access sensor data on
the desktop board. The specific SMBus signals are as follows:
The SMBus clock line is connected to pin A40.
The SMBus data line is connected to pin A41.
54
Page 55

Technical Reference
2.2.2.3
Power Supply Connectors
The board has the following power supply connectors:
• Main power – a 2 x 12 connector. This connector is compatible with 2 x 1 0
connectors previously used on Intel Desktop boards. The board supports the use
of ATX12V power supplies with either 2 x 10 or 2 x 12 main power cables. When
using a power supply with a 2 x 10 main power cable, attach that cable to the main
power connector, leaving pins 11, 12, 23, and 24 unconnected.
• Processor core power – a 2 x 2 connector. This connector provides power
directly to the processor voltage re gulator and must always be used. Failure to do
so will prevent the board from booting.
Table 23. Processor Core Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Ground 2 Ground
3 +12 V 4 +12 V
Table 24. Main Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +3.3 V 13 +3.3 V
2 +3.3 V 14 -12 V
3 Ground 15 Ground
4 +5 V 16 PS-ON# (power supply remote on/off)
5 Ground 17 Ground
6 +5 V 18 Ground
7 Ground 19 Ground
8 PWRGD (Power Good) 20 No connect
9 +5 V (Standby) 21 +5 V
10 +12 V 22 +5 V
11
12
Note: When using a 2 x 10 power supply cable, this pin will be unconnected.
+12 V
2 x 12 connector detect
(Note)
(Note)
23
24
(Note)
+5 V
Ground
(Note)
For information about Refer to
Power supply considerations Section 2.6.1 on page 63
55
Page 56

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.2.2.4 Front Panel Connector
This section describes the functions of t he front panel connector. Table 25 lists the
signal names of the front panel connector. Figure 11 is a connection diagram for the
front panel connector.
Table 25. Front Panel Connector
Pin Signal Name Description Pin Signal Name Description
1 HDD_POWER_LED Pull-up resistor
(750 Ω) to +5V
3 HDD_LED# [Out] Hard disk
activity LED
5 GROUND Ground 6 POWER_SWITCH# [In] Pow e r switch
7 RESET_SWITCH# [In] Reset switch 8 GROUND Ground
9 +5V_DC Power 10 Key No pin
2 POWER_LED_MAIN [Out] Front panel LED
(main color)
4 POWER_LED_ALT [Out] Front panel LED
(alt color)
Figure 11. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Connector
2.2.2.4.1 Hard Drive Activity LED Header
Pins 1 and 3 can be connected to an LED to provide a visual indicator that data is
being read from or written to a hard drive. Proper LED function requires a SATA hard
drive or optical drive connected to an onboard SATA connector.
2.2.2.4.2 Reset Switch Header
Pins 5 and 7 can be connected to a momentary single pole, single throw (SPST) type
switch that is normally open. When the switch is closed, the board resets and runs the
POST.
56
Page 57

Technical Reference
2.2.2.4.3 Power/Sleep LED Header
Pins 2 and 4 can be conne cted to a one- or two-color LED. Table 26 shows the
possible states for a one-color LED. Table 27 shows the possible states for a two-color
LED.
Table 26. States for a One-Color Power LED
LED State Description
Off Power off/sleeping
Steady Green Running
Table 27. States for a Two-Color Power LED
LED State Description
Off Power off
Steady Green Running
Steady Yellow Sleeping
NOTE
The colors listed in Table 26 and Table 27 are suggested colors only. Actual LED colors
are chassis-specific.
2.2.2.4.4 Power Switch Header
Pins 6 and 8 can be conne cted to a front panel momentary-contact power switch. The
switch must pull the SW_ON# pin to ground for at least 50 ms to signal the power
supply to switch on or off. (The time requirement is due to internal debounce circuitry
on the board.) At least two seconds must pass before the power supply will recognize
another on/off signal.
2.2.2.5 Alternate Front Panel Power/Sleep LED Header
Pins 1 and 3 of this header duplicate the signals on pins 2 and 4 of the front panel
header.
Table 28. Alternate Front Panel Power/Sleep LED Header
Pin Signal Name Description
1 POWER_LED_MAIN [Out] Front panel LED (main color)
2 Key (no pin)
3 POWER_LED_ALT [Out] Front panel LED (alt color)
57
Page 58
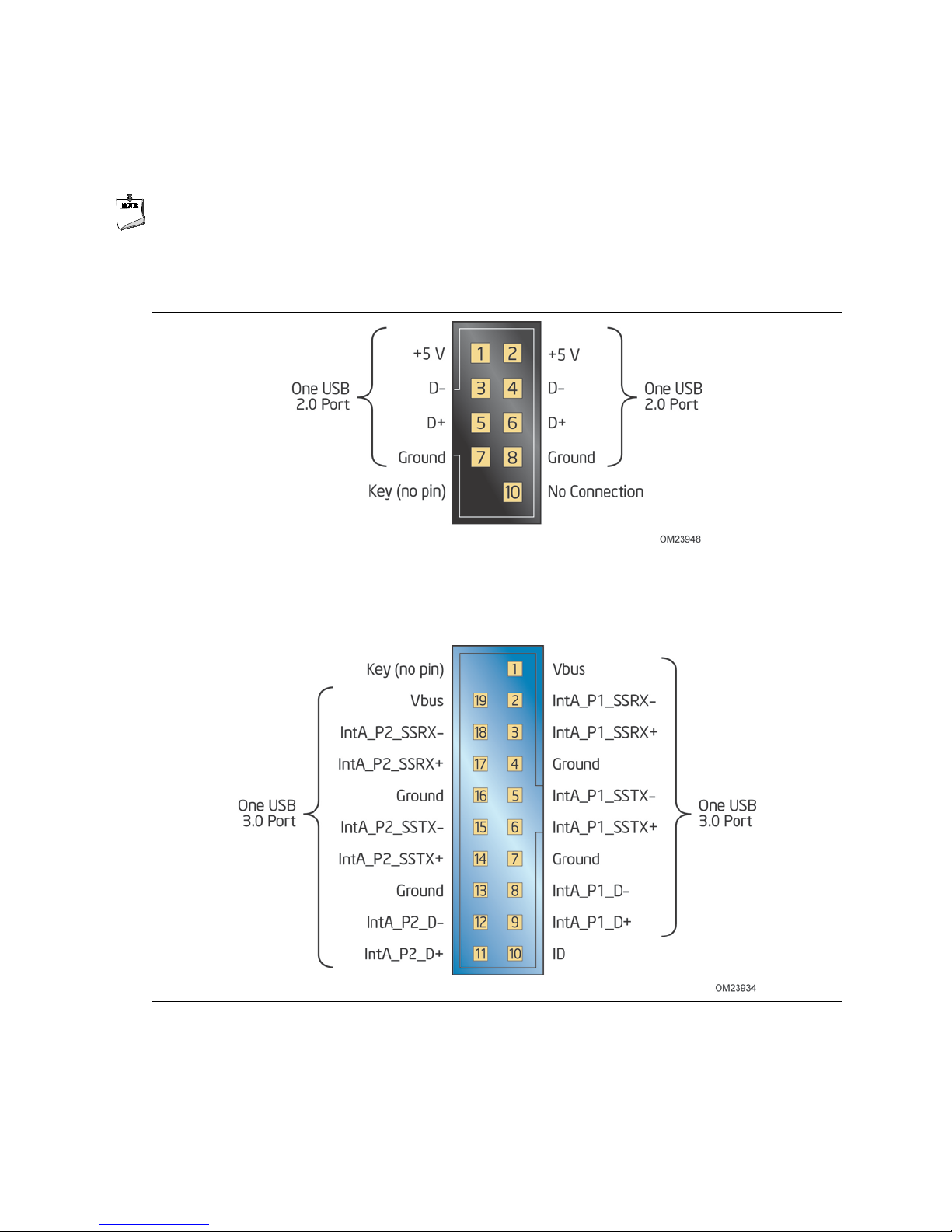
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.2.2.6 Front Panel USB Connectors
Figure 12 and Figure 13 are connection diagrams for the front panel USB connectors.
NOTE
• The +5 V DC power on the USB connectors is fused.
• Use only a front panel USB connector that conforms to the USB 2.0 specification fo r
high-speed USB devices.
Figure 12. Connection Diagram for Front Panel USB 2.0 Connectors
Figure 13. Connection Diagram for the Front Panel
58
USB 3.0 Connector
Page 59
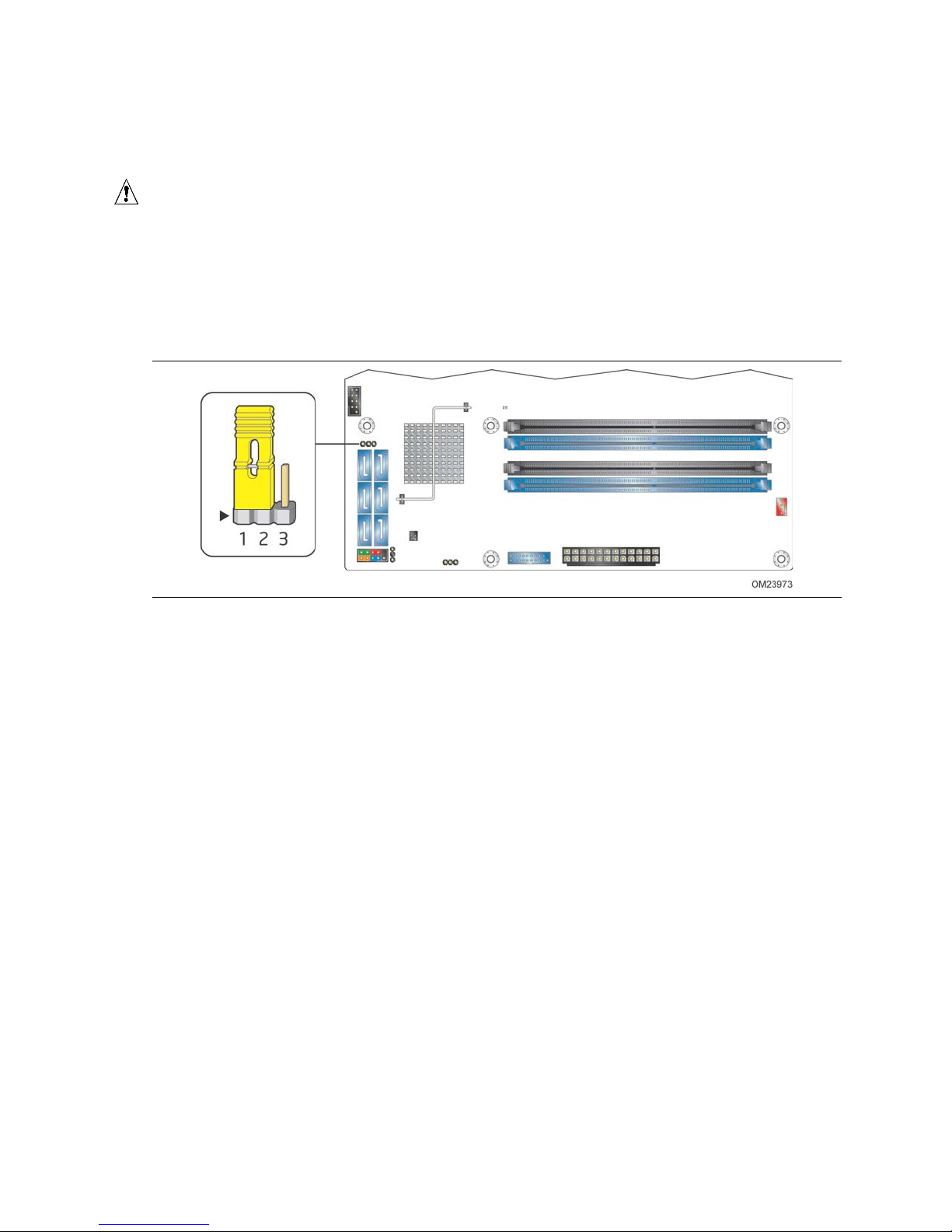
Technical Reference
2.3 BIOS Security Jumper
CAUTION
Do not move the jumper with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug the
power cord from the computer before changing a jumper setting. Otherwise, the
board could be damaged.
Figure 14 shows the location of the jumper. The 3-pin jumper determines the BIOS
Security pr og ram’s mode. Table 29 describes the jumper settings for the three
modes: normal, lockdown, and configuration.
Figure 14. Location of the Jumper
59
Page 60
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 29. BIOS Setup Security Jumper Settings
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
Normal 1-2 The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords
for booting.
Lockdown 2-3 The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords
for booting, except:
• All POST Hotkeys are suppre sse d (p ro mpts are not displayed
and keys are not accepted. For example, F2 for Setup, F10 for
the Boot Menu).
• Power Button Menu is not available (se e Sec tion 3.9.3 Power
Button Menu).
BIOS updates are not available except for auto m atic R ecover y
due to flash corruption.
Configuration
Mode
None BIOS Recov er y Upd ate pro cess if a matc hing * .bio file is found.
Recovery Update can be cancelled by pressing the Esc key.
If the Recovery Update was cancelled or a matching *.bio file
was not found, a Config Menu will be displayed. The Config Menu
consists of the following (followe d by the Power Button Menu
selections):
[1] Suppress this menu until the BIOS Security Jumper is
replaced.
[2] Clear BIOS User and Supervisor Passwords.
[3] Reset Intel AMT to default factory settings.
[4] Clear Trusted Platform Module.
See Section 3.9.3 Power Button Menu.
60
Page 61
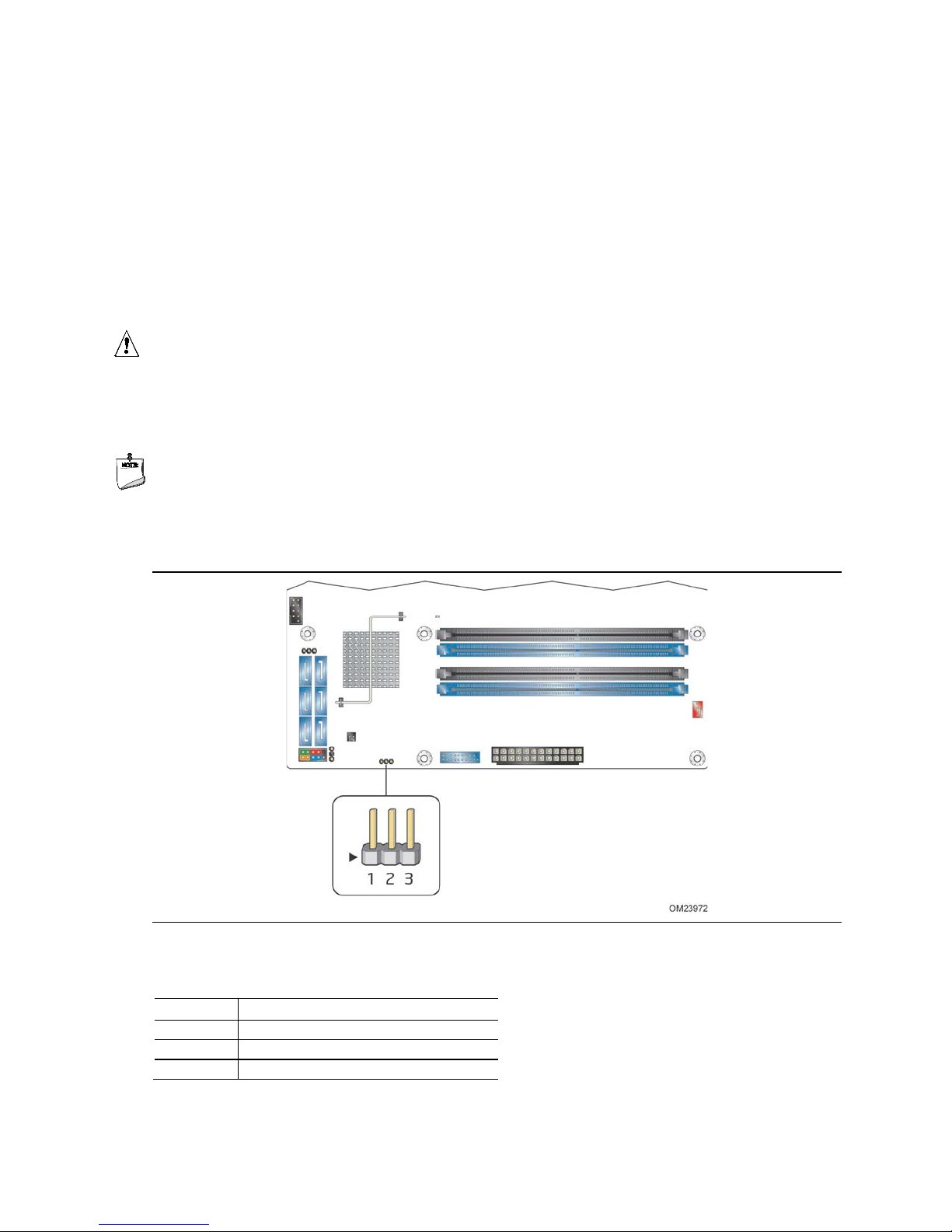
Technical Reference
2.4 Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension
®
(Intel
The Intel® MEBX reset header (see Figure 15) allows you to reset the Intel ME
configuration to the factory defaults. M omentarily shorting pins 1 and 2 with a jumper
(not supplied) will accomplish the following:
• Return all Intel ME parameters to their default values.
• Reset the Intel MEBX password to the default value (admin).
CAUTION
Always turn off the power and unplug the power cord from the computer before
installing an MEBX reset jumper. The jumper must be removed before reapplying
power. The system must be allowed to reach end of POST before reset is complete.
Otherwise, the board could be damaged.
NOTE
MEBX) Reset Header
After using the MEBX Reset, a “CMOS battery failure” warning will occur during the
next POST. This is expected and does not indicate a component failure.
Figure 15. Intel MEBX Reset Header
Table 30. Intel MEBX Reset Header Signals
Pin Function
1 PCH_RTCRST_PULLUP
2 Ground
3 No connection
61
Page 62
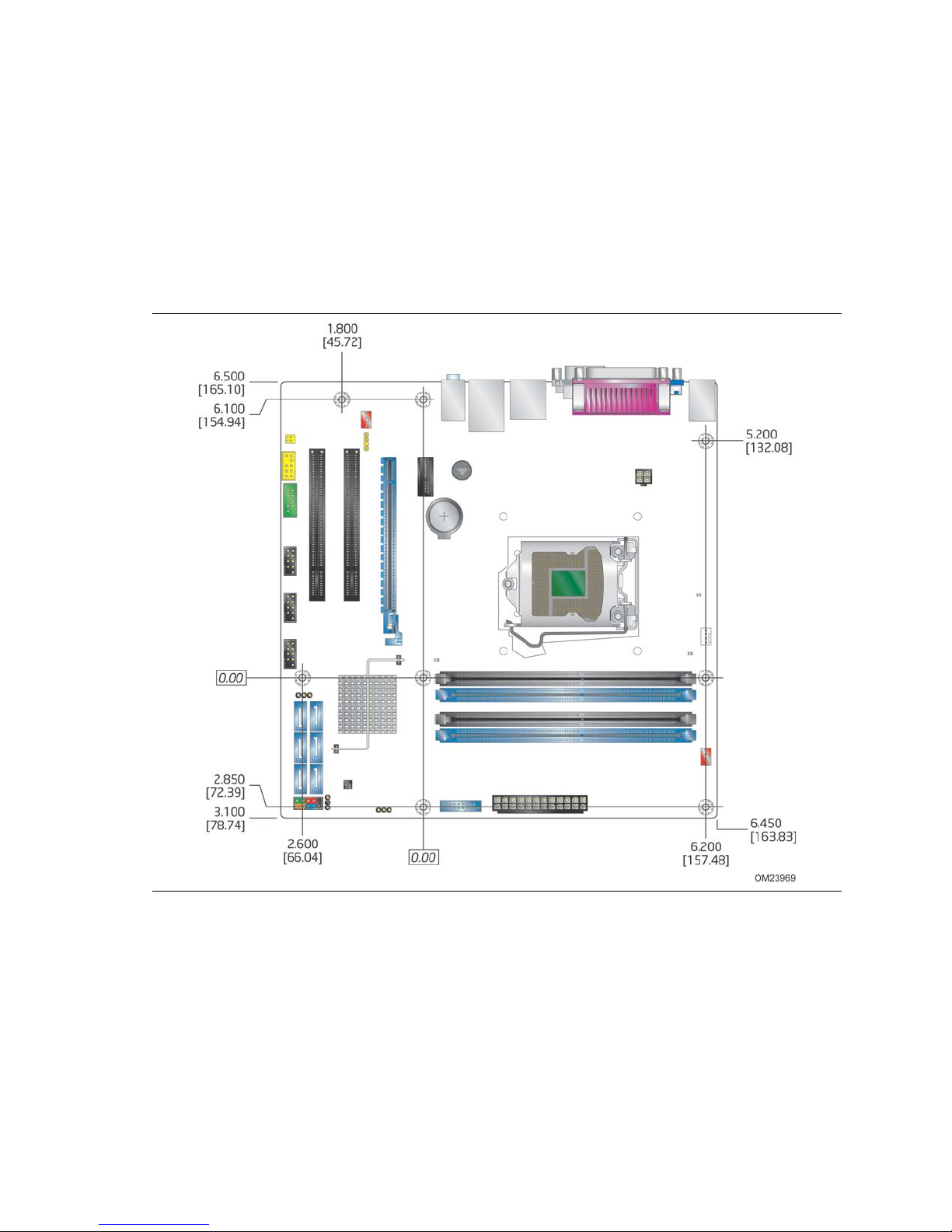
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.5 Mechanical Considerations
2.5.1 Form Factor
The board is designed to fit into an ATX-form-factor chassis. Figure 16 illustrates the
mechanical form factor for the board. Dimensions are given in inches [millimeters].
The outer dimensions are 9.60 inches by 9.60 inches [243.84 millimeters by
243.84 millimeters]. Loc ation of the I/O connecto rs and mounting holes are in
compliance w ith the ATX specification.
62
Figure 16. Board Dimensions
Page 63
Technical Reference
2.6 Electrical Considerations
2.6.1 Power Supply Considerations
CAUTION
The +5 V standby line from the power supply must be capabl e of providing adequate
+5 V standby current. Failure to do so can damage the power s upp ly. The total
amount of standby current require d depends on the wake devices supported and
manufacturing opt ions.
Additional power required will depend on configurations chosen by the integrator.
Due to improvements in 4
requirements for the processor’s power supply have changed. More specifically, the
latest Power Supply Design Guide rev 1.3 has indicated a minimum current of 0.05A
on +12 V2DC, and recommends 0A. This is to prevent P SU protec tion triggering during
minimu m loading.
th
generation Intel Core processor power efficiency, the
Intel recommends that system integrators and builders check the latest list of tested
PSUs for ones capable of supporting the 4
may be found at: http://www.intel.com/go/powersupplies/
th
generation Intel Core processor. This list
. From the filters at the top
right of the page, set 12V2 Min Load 0A to “Yes” to see which PSUs hav e been found
to support the processor’s new power requirements.
The power supply must comply with the indicated parameters of the ATX form factor
specification.
• The potential relation between 3.3 V DC and +5 V DC pow er rails
• The current capability of the +5 VSB line
• All timing parameters
• All voltage tolerances
For example, for a high power system consisting of a supported 95 W processor (see
Section 1.3 on page 16 for a list of supported processors), 4 GB DDR3 RAM, one high
end video card, one hard disk drive, one optical d rive, and all board peripherals
enabled, the minimum recommended power supply is 460 W. Table 31 lists possible
recommended power supply current rail values.
Table 31. Recommended Power Supply Current Values (High Power)
Output Voltage 3.3 V 5 V 12 V1 12 V2 -12 V 5 VSB
Current 22 A 20 A 20 A 20 A 0.3 A 2.5 A
63
Page 64

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
For example, for a l ow p owe r system consisting of a supported 45 W processor (see
Section 1.3 on page 16 for a list of supported proces sors), 2 GB DDR3 RAM, integrated
graphics, one SSD, one optical drive, and no extra onboard peripherals enabled, the
minimum recommended power supply is a 320 W. Table 32 lists possible
recommended power supply current rail values. Note: If the correct power supply and
system configuration is used, a smaller power supply will work.
Table 32. Recommended Power Supply Current Values (Low Power)
Output Voltage 3.3 V 5 V 12 V1 12 V2 -12 V 5 VSB
Current 20 A 20 A 15 A 15 A 0.3 A 1.5 A
For information about Refer to
Selecting an appropriate power s upply http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb
/CS-026472.htm
Selecting a power supply capable of
supporting the 4
processor
th
generation Intel Core
http://www.intel.com/go/powersupplies/
2.6.2 Fan Header Current Capability
CAUTION
The processor fan must be connected to the processor fan header, not to a chassis fan
header. Connecting the p rocessor fan to a chassis fan header may result in onboard
component damage that will halt fan operation.
Table 33 lists the current capability of the fan headers.
Table 33. Fan Header Current Capability
Fan Header Maximum Available Current
Processor fan 2.0 A
Front chassis fan 1.5 A
Rear chassis fan 1.5 A
2.6.3 Add-in Board Considerations
The board is designed to provide 2 A (average) of current for each add-in board from
the +5 V rail. The total +5 V current draw for add-in boards for a fully loaded board
(all three expansion slots filled) must not exceed the system’s power supply +5 V
maximum current or 14 A in total.
64
Page 65

Technical Reference
2.7 Thermal Considerations
CAUTION
A chassis with a maximum internal ambient temperature of 38 oC at the processor fan
inlet is a requirement. Use a processor heat sink that provides omni-directional airflow
to maintain required airflow across the processor voltage regulator area.
CAUTION
Failure to ensure appropriate airflow may result in reduced performance of both the
processor and/or voltage regulator or, in some instances, damage to the board. For a
list of chassis that have been tested with Intel desktop boards please refer to the
following website:
http://www3.intel.com/cd/channel/reseller/asmo-na/eng/tech_reference/53211.htm
All responsibility for determining the adequacy of any thermal or system design
remains solely with the reader. Intel makes no warranties or representations that
merely following the instructions presented in this document will result in a system
with adequate thermal performance.
CAUTION
Ensure that the ambient temperature does not exceed the board’s maximum operating
temperature. Failure to do so could cause components to exceed their maximum case
temperature and malfunction. For information about the maximum operating
temperature, see the environmental specifications in Section 2.9.
CAUTION
Ensure that proper airflow is maintained in the processor voltage regulator circuit.
Failure to do so may result in damage to the voltage regulator circuit. The processor
voltage regulator area (shown in Figure 17) can reach a temperature of up to 120
an open chassis.
o
C in
65
Page 66

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Figure 17 shows the locations of the localized high temperature zones.
Item Description
A Processor voltage regulator area
B Processor
C Intel Q87 Express Chipset
Figure 17. Localized High Temperature Zones
66
Page 67

Technical Reference
For information about
Refer to
Table 34 provides maximum case temperatures for the components that are sensitive
to thermal changes. The operating temperature, current load, or operating frequency
could affect case temperatures. Maximum case temperatures are important when
considering proper airflow to cool the board.
Table 34. Thermal Considerations for Components
Component Maximum Case Temperature
Processor For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and
processor specification updates
Intel Q87 Express Chipset 104 oC
To ensure functionality and reliability, the component is specified for proper operation
when Case Temperature is maintained at or below the maximum temperature listed in
Table 34. This is a requirement for sustained power dissipation equal to Thermal
Design Power (TDP is specified as the maximum sustainable power to be dissipated by
the components). When the component is dissipating less than TDP, the case
temperature should be below the Maximum Case Temperature. The surface
temperature at the geometric center of the compone nt corresponds to Case
Temperature.
It is important to note that the temperature measurement in the system BIOS is a
value reported by embedded thermal sensors in the components and does not directly
correspond to the Maximum Case Temperature. The upper operating limit when
monitoring this thermal sensor is Tcontrol.
Table 35. Tcontrol Values for Components
Component Tcontrol
Processor For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and
processor specification updates
Intel Q87 Express Chipset 104 oC
Processor datasheets and specificatio n upd ate s Section 1.2, page 16
Intel Q87 Express Chipset http://www.intel.com/products/desktop/
chipsets/
67
Page 68
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
2.8 Reliability
The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) prediction is calculated using a parts count
method. The calculation is based on the Telcordia SR-332, Issue 2; Method I Case 3
50% electrical stress, 55 ºC ambient. The MTBF prediction is used to estimate repair
rates and spare parts requirements. The MTBF data is calculated from predicted da t a
at 55 ºC. The MTBF for the Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG is 258,525 hours.
2.9 Environmental
Table 36 lists the environmental specifications for the board.
Table 36. Environmental Specifications
Parameter Specification
Temperature
Non-Operating
Operating
Shock
Unpackaged 50 g trapezoidal waveform
Velocity change of 170 inches/s²
Packaged Half sine 2 millisecond
Produc t Weig ht (po und s ) Free Fall (inches) V e locity Change (inches/s²)
<20 36 167
21-40 30 152
41-80 24 136
81-100 18 118
Vibration
Unpackaged 5 Hz to 20 Hz: 0.01 g² Hz sloping up to 0.02 g² Hz
20 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.02 g² Hz (flat)
Packaged 5 Hz to 40 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz (flat)
40 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz sloping down to 0.00015 g² Hz
Note: Before attempting to operate this board, the overall te m p eratur e of the board must be above the
minimum operating temperature spe c ifie d . It is recom me nded that the boa rd temper ature be at least
room temperature before attempting to power on the board.
-20 °C to +70 °C
0 °C to +55 °C
The operating temperature of the board may be determined by measur i ng the
air temperature from within 1 inch of the edge of the chipset/PCH heats i nk and
1 inch above the board, in a closed chassis, while the system is in operation.
(Note)
68
Page 69
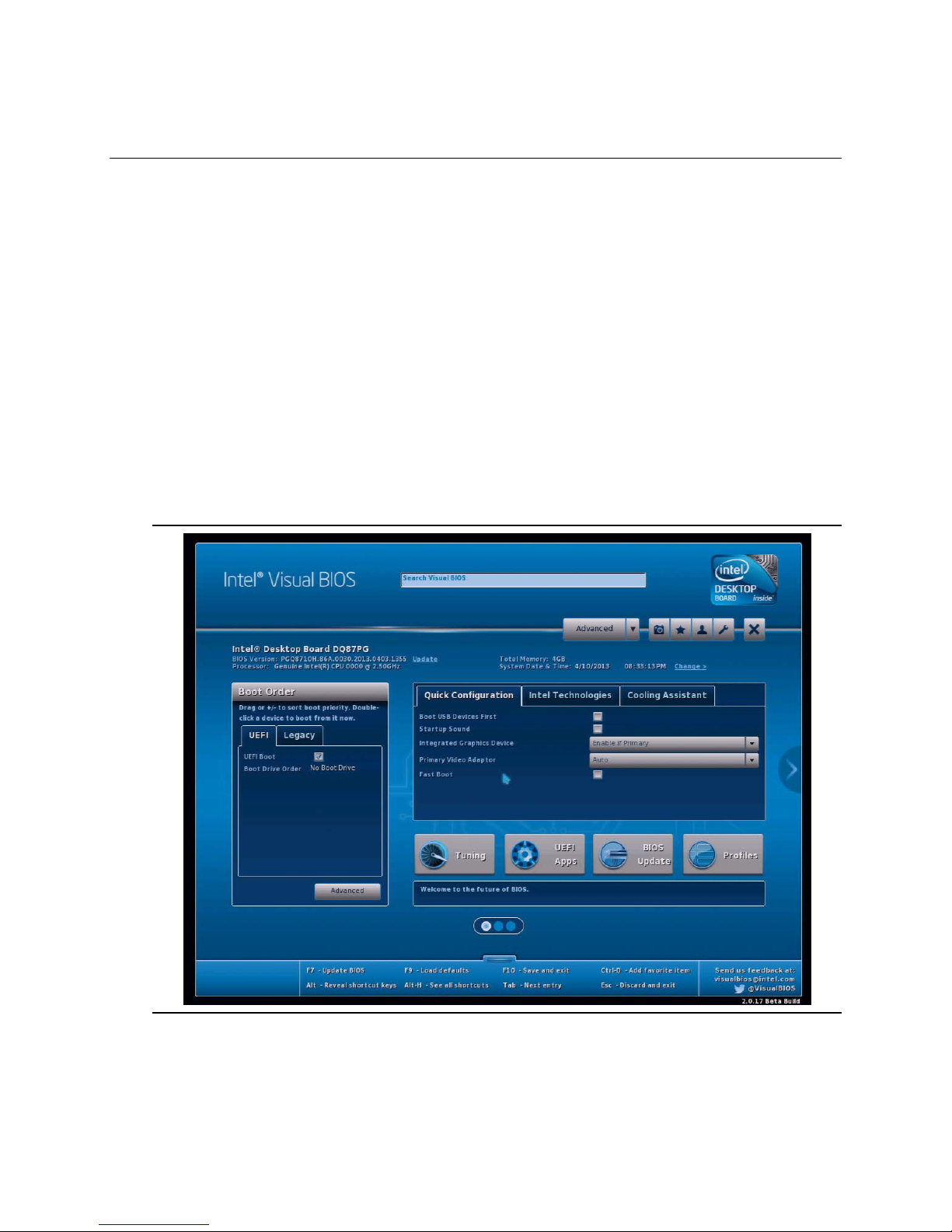
3 Overview of BIOS Features
3.1 Introduction
The board uses an Intel Visual BIOS that is stored in the Serial Peripheral Interface
Flash Memory (SPI Flash) and can be updated using a disk-based pro gram . The SPI
Flash contains the Visual BIOS Setup progra m, POST, the PCI auto-configuration
utility, LAN EEPROM information, and Plug and Play support.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and a revision
code. The initial production BIOSs are identified as
When the BIOS Setup configuration jumper is set to configure mode and the computer
is powered-up, the BIOS compares the CPU version and the microcode version in the
BIOS and reports if the two match.
The BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the
computer. The BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <F2> key after the
Power-On Self-Test (POST) memory test begins and before the operating sys tem boot
begins.
PGQ8710H.86A.
69
Figure 18. Intel Visual BIOS Screen
Page 70

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 37 lists the BIOS Setup program menu features.
Table 37. Intel Visual BIOS Setup Display Areas
Home 1
Displays
processor,
graphics,
memory, and
configuration with
quick launch to
tuning, UEFI
apps, BIOS
update, and
system profiles
Home 2
Environmental
monitoring
display and
attached SATA
devices
Home 3
System,
desktop
board,
chassis, and
processor
information
Main
Displays
processor,
memory,
configuration,
event log,
date, and
time
Devices &
Peripherals Cooling
Configures
advanced
features
available
through the
chipset and
other discrete
controllers
Table 37. Intel Visual BIOS Setup Display Areas (continued)
Performance Security Power Boot Exit
Displays and
Configures Memory,
Graphics, Bus, and
Processor overrides
Sets passwords
and security
features
Configures power
management features
and power supply
controls
Selects boot
options and
boot display
options
Table 38 lists the function keys available for menu screens.
Table 38. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
Real-time system
monitoring,
adjust fan
speeds, set
temperature set
points, and define
system voltage
settings
continued
Saves or discards
changes to Setup
program options
BIOS Setup Program
Function Key
<←> or <→>
<↑> or <↓>
<Tab> Se le c ts a field (Not im p le mente d )
Mouse Allows control of all options and slider controls in Intel Visual BIOS
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu
<F9> Load the default configuration value s for the cur rent m e nu
<F10> Save the current values and exits the BIOS Setup program
<Esc> Exits the menu
Description
Selects a different menu screen (Moves the cursor left or right)
Selects an item (Moves the cursor up or down)
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization
The Serial Peripheral Interface Flash Memory (SPI Flash) includes a 96 Mb (12288 KB)
flash memory device.
70
Page 71

Overview of BIOS Features
3.3 Resource Configuration
3.3.1 PCI Express Autoconfiguration
The BIOS can automatically configure PCI Express devices. PCI Express devices may
be onboard or add-in cards. Autoconfiguration lets a user insert or remove PCI
Express cards without having to configure t h e system. When a user turns on the
system after adding a PCI Express card, the BIOS a utomatically configures interrupts,
the I/O space, and other system resources . Any interrupts set to Available in Setup
are considered to be available for use by the add-in card.
3.4 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
SMBIOS is a Desktop Management Interface (DMI ) compliant method for managing
computers in a managed network.
The main component of SMBIOS is the Management Inf ormation Format (MIF)
database, which contains information about the computing system and its
components. Using SMBIOS, a system administra tor can obtain the system types,
capabilities, operational status, and installation dates for system components. The
MIF database defines the data and provides the method for accessing this information.
The BIOS enables applications such as third-party management software to use
SMBIOS. The BIOS stores and reports the following SMBIOS information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed
• Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging
Non-Plug and Play operating systems require an additional interface for obtaining the
SMBIOS information. The BIOS supports an SMBIOS table interface for such operating
systems. Using this support, an SMBIOS service-level application running on a
non-Plug and Play operating system can obtain the SMBIOS information. Additional
board information c an be found in the BIOS under the Additional Information header
under the Main BIOS page.
3.5 Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB support enables USB devices to be used even when the operating
system’s USB drivers are not yet available. Legacy USB support is used to access the
BIOS Setup program, and to install an operating system that supports USB. By
default, Legacy USB support is set to Enabled.
Legacy USB supp o rt op erates as follows:
1. When you apply power to the computer, legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. Legacy USB support is enabled by the BIOS allowing you to use a USB keyboard to
enter and configure the BIOS Setup program and th e maintenance menu.
4. PO ST co m p letes.
71
Page 72

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB
keyboards and mice are recognized and may be used to co nfigure the operating
system. (Keyboards and mice are not recognized during this period if Legacy USB
support was set to Disabled in the BIOS Setup program.)
6. After the operating system loads the USB drivers, all legacy and non-legacy USB
devices are recognized by the operating system, and Legacy USB support from the
BIOS is no longer used.
®
7. Additional USB legacy feature options can be access by using Intel
Integrator
Toolkit version 5.
To install an operating system that supports USB, verify that Legacy USB support in
the BIOS Setup program is set to Enabled and follow the opera ting system’s
installation instruct ions .
3.6 BIOS Updates
The BIOS can be updated us ing either of the following utilities, which are available on
the Intel World Wide Web site (see Section 1.2 on page 16):
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• Intel Visual BIOS Update Utility allows the user to select the BIOS .bio file from the
®
Express BIOS Update utility, which enables a utomated updating while in the
Windows environment . Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a
hard disk, a USB drive (a flash drive or a USB hard drive), or a CD-ROM, or from
the file lo cation on t he Web.
®
Flash Memory Update Utility, which requires booting from DOS. Using this
utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a har d disk , a USB drive (a flash
drive or a USB hard drive), or a CD-ROM.
®
F7 switch allows a user to select whe re the BIOS .bio file is located and
perform the update from that location/device . Similar to performing a BIOS
Recovery without removing the BIOS configuration jumper.
internet, USB device, hard disk drive, or other media.
All utilities verify that the updated BIO S m a tches the target system to prevent
accidentally installing an incompatible BIOS.
NOTE
Review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before attempting a BIOS
update.
For information about Refer to
BIOS update utilities http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb
/CS-022312.htm.
3.6.1 Language Support
The BIOS Setup program and help messages are supported in US English.
72
Page 73

Overview of BIOS Features
3.6.2 Custom Splash Screen
During POST, an Intel® splash screen is displayed by default. This splash screen can
be augmented with a custom splash screen. The Intel Integrator’s Toolkit version 5
that is available from Intel can be used to create a custom splash screen.
NOTE
If you add a custom splash screen, it will share space with the Intel branded logo.
For information about Refer to
Intel Integrator Toolkit http://www.intel.com/go/itk
3.7 BIOS Recovery
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt a BIOS update; however, if an interruption
occurs, the BIOS could be damaged. Table 39 lists the drives and media types that
can and cannot be used for BIOS recovery. The BIOS recovery media does not need
to be made bootable.
Table 39. Acceptable Drives/Media Types for BIOS Recovery
Media Type Can be used for BIOS recovery?
CD-ROM drive connected to the SATA interface Yes
USB removable drive (a USB Flash Drive, for example) Yes
USB diskette drive (with a 1.44 MB diskette) No
USB hard disk drive No
For information about Refer to
BIOS recovery http://www.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/
cs-023360.htm
73
Page 74
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
3.8 Boot Options
In the BIOS Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a hard drive, optical
drive, removable drive, or the network. The default setting is for the optical drive to
be the first boot device, the hard drive second, removable drive third, and the network
fourth.
3.8.1 Optical Drive Boot
Booting from the optical drive is supported in compliance to the El Torito bootable
CD-ROM format specification. Under the Boot menu in the BIO S Setup p rogram, the
optical drive is listed as a boot device. Boot devices are defined in priority order.
Accordingly, if there is not a bootable CD in the optical drive, the system will attempt
to boot from the next defined drive.
3.8.2 Network Boot
The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from the
onboard LAN or a network add-in card with a remote boot ROM installed.
Pressing the <F12> key during POST automatically forces booting from the LAN. To
use this key during POST, the User Access Level in the BIOS Setup program's Security
menu must be set to Full.
3.8.3 Booting Without Attached Devices
For use in embedded applications, the BIOS has been designed so that after passing
the POST, the operating system loader is invoked even if the following devices are not
present:
• Video adapter
• Keyboard
• Mouse
3.8.4 Changing the Default Boot Device During POST
Pressing the <F10> key during POST causes a boot dev ice menu to be displayed. This
menu display s the list of a vailable boot devices. Table 40 lists the boot device menu
options.
Table 40. Boot Device Menu Options
Boot Device Menu Function Keys Description
<↑> or <↓>
<Enter> Exits the menu and boots from the selected device
<Esc> Exits the menu and boots according to the boot priority
Selects a default boot device
defined through BIOS setup
74
Page 75

Overview of BIOS Features
3.9 Adjusting Boot Speed
These factors affect system boot speed:
• Selecting and configuring peripherals properly
• Optimizing BIOS boot parameters
• Enabling the Fast Boot feature
3.9.1 Peripheral Selection and Configuration
The following techniques help improve system boot speed:
• Choose a hard drive with parameters such as “power-up to data ready” in less than
eight seconds that minimizes hard drive startup delays.
• Select a CD-ROM drive with a fast initialization rat e. This rate can influence POST
execution time.
• Eliminate unnecessary add-in adapter features, such as logo displays, screen
repaints, or mode changes in POST. These features may add time to the boot
process.
• Try different monitors. Some monitors initialize and communicate with the BIOS
more quickly, which enables the system to boot more quickly.
3.9.2 BIOS Boot Optimizations
Use of the following BIOS Setup program settings reduces the POST execution time:
• In the Boot menu, enable the settings for Fast Boot. This option will allow the BIOS
to skip through various stages of POST and boot quickly to the last detected boot
device.
• In the Boot Menu, set the hard disk drive as the first boot device. As a result, the
POST does not first seek a diskette drive, which saves about one second from the
POST execution time.
• In the Peripheral Configuration submenu, disable the LAN device if it will not be
used. This can reduce option ROM boot time by up to four seconds.
NOTE
It is possible to optimize the boot process to the point where the system boots so
quickly that the Intel logo screen (or a custom logo splash screen) will not be seen.
Monitors and hard disk drives with minimum initialization times can also contribute to
a boot time that might be so fast that necessary logo screens and POST messages
cannot be seen.
This boot time may be so fast that some drives might be not be initialized at all. If
this condition should occur, it is possible to intro d uce a programmable delay ranging
from zero to 30 seconds by 5 second increments (usi n g t he Hard Disk Pre-Delay
feature of the Advanced Menu in the Drive Confi g uration Submenu of the BIOS Setup
program).
75
Page 76

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
3.9.3 Power Button Menu
The Power Button Menu can be accessed during po wer on if the user presses t he
power button and holds it down until three short beep sounds are emitted by the
board piezoelectric speaker. The BIOS will display t he following prompt and wait for a
keystroke:
[ESC] Normal Boot
[F2] Intel
[F3] Disable Fast Boot
[F4] BIOS Recovery
[F7] Update BIOS
[F10] Enter Boot Menu
[F12] Network Boot
NOTE
[F3] Disable Fast Boot is only displayed if at least one Fast Boot optimization is
enabled.
If an unrecognized key is pressed, the BIOS will beep and wait for another keystroke.
If one of the listed hotkeys is pressed, the BIOS will follow t he indicated boot path.
Password requirements must still be honored.
If Disable Fast Boot is selected, the BIOS w ill dis a b le a l l Fast B oot optimizations and
reset the system.
®
Visual BIOS
3.10 Hard Disk Drive Password Security Feature
The Hard Disk Drive Password Security feature blocks read and write accesses to the
hard disk drive until the correct password is given. Hard Disk Drive Passwords are set
in BIOS SETUP and are prompted for during BIOS POST. For convenient support of S3
resume, the system BIOS will automatically unlock drives on resume from S3.
The User hard disk drive password, when installed, will be required upon each powercycle until the Master Key or User hard disk drive password is submitted.
The Master Key hard disk drive password, when installed, will not lock the drive. The
Master Key hard disk drive password exists as an unlock override in the event that the
User hard disk drive password is forgotten. Only the installation of the User hard disk
drive password will cause a hard disk to be locked upon a system power-cycle.
Table 41 shows the effects of setting the Hard Disk Drive Passwords.
Table 41. Master Key and User Hard Drive Password Functions
Password Set Password During Boot
Neither None
Master only None
User only User onl y
Master and User Set Master or User
76
Page 77

Overview of BIOS Features
During every POST, if a User hard disk drive password is set, POST execution will
pause with the following prompt to force the user to enter the Master Key or User hard
disk drive password:
Enter Hard Disk Drive Password:
Upon successful entry of the Master Key or User hard disk drive password, the system
will continue with normal POST.
If the hard disk drive password is not correc tly entered, the system will go back to the
above prompt. The user will have three attempts to correctly enter the hard disk drive
password. After the third unsuccessful hard disk drive password attempt, the system
will halt with the message:
Hard Disk Drive Password Entry Error
A manual power cycle will be required to resume system operation.
NOTE
As implemented on DB85FL, Hard Disk Drive Password Security is only supported on
SATA port 0. The passwords are stored on the hard disk drive so if the drive is
relocated to another SATA port or computer that does not support Hard Disk Drive
Password Security feature, the drive will not be accessible.
NOTE
Hard Disk Drive Password Security is not supported in PCH RAID mode. Secured hard
disk drives attached to the system when the system is i n PCH RAID mode will not be
accessible due to the disabling of BIOS Hard Disk Drive Password support.
3.11 BIOS Security Features
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program
and who can boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be
set for the BIOS Setup program and for booting the computer, with the following
restrictions:
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the
Setup options in the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
• The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options i n the
BIOS Setup program. This is the user mode.
• If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password
prompt of the BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the
supervisor password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to
Setup respective to which password is entered.
• Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password
prompt will be displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor
77
Page 78
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
password is set, the computer boots without ask ing for a password. If both
passwords are set, the user can enter either password to boot the computer.
• For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user
passwords.
• Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9. Passwords may be up to
19 characters in length.
Table 42 shows the effects of setting the supervisor password and user password.
This table is for reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
Table 42. Supervisor and User Password Functions
Password
Set
Neither Can c hang e all
Supervisor
only
User only N/A Ca n cha ng e all
Supervisor
and user set
Note: If no password is set, any user can change all Setup options.
Supervisor
Mode
options
Can change all
options
Can change all
options
(Note)
User Mode
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited
number of
options
options
Can change a
limited
number of
options
(Note)
Setup Options
None None None
Supervisor Password Supervisor None
Enter Password
Clear User Password
Supervisor Password
Enter Password
Password
to Enter
Setup
User User
Supervisor or
user
Password
During
Boot
Supervisor or
user
NOTE
The BIOS complies with NIST Special Publication 800-147 BIOS Protection Guidelines /
Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Refer to
http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-147/NIST-SP800-147-April2011.pdf
more information.
for
78
Page 79

3.12 BIOS Performance Features
Overview of BIOS Features
The BIOS includes the following options to provide custom performance enhancements
when using 4
th
generation Intel Core processors in an LGA1150 socket.
• Processor maximum non-turbo ratio (processor multiplier can only be adjusted
down)
• Processor turbo ratio adjustment
• Host clock frequency
• Various other processor adjustments
• Memory multiplier adjustment
• Memory voltage adjustment
• Memory latency adjustments
• Graphics multiplier adjustment
• Graphics voltage adjustment
79
Page 80

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
80
Page 81

4 Beep Codes, Error Messages, and
POST Codes
4.1 BIOS Error Codes
The BIOS provides two types of Error Code indications during POST:
• Beep codes
• Blink codes
4.1.1 BIOS Beep Codes
Whenever a recoverable error occurs during POST, the BIOS causes the board’s
speaker (Figure 1, J) to beep an error code describing the problem (see Table 43).
Table 43. BIOS Beep Codes
Type Pattern Frequency
F2 Setup/F10 Boot Menu
Prompt
BIOS update in progress None
Video err or On-off (1.0 second each) two times, then
Memory error On-off (1.0 second each) three times, then
Thermal trip warning Alternate high and low beeps (1.0 second each)
One 0.5 second beep when BIOS is ready to
accept keyboard input.
2.5-second pause (off), entire pattern repeats
(beeps and pause) once and the BIOS will
continue to boot.
2.5-second pause (off), entire patter n repe ats
(beeps and pause) until the system is powered
off.
for eight beeps, followed by system shut down.
932 Hz
932 Hz
When no VGA option ROM is
found.
932 Hz
High beep 2000 Hz
Low beep 1500 Hz
81
Page 82

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
4.1.2 Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes
Whenever a recoverable error occurs during POST, the BIOS causes the board’s front
panel power LED to blink an error code describing the problem (see Table 44).
Table 44. Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes
Type Pattern Note
F2 Setup/F10 Boot Menu
Prompt
BIOS update in progress Off when the update begins, then on for
Video err or On-off (1.0 second each) two times, then
Memory error On-off (1.0 second each) three times, then
Thermal trip warning Each beep will be accompanied by the following
None
0.5 seconds, then off for 0.5 seconds. The
pattern repeats until the BIOS update is
complete.
2.5-second pause (off), entire patter n repe ats
(blink and pause) until the system is powered
off.
2.5-second pause (off), entire patter n repe ats
(blinks and pause) until the system is powered
off.
blink pattern: .25 seconds on, .25 seconds off,
.25 seconds on, .25 seconds off. This will result
in a total of 16 blinks.
When no VGA option ROM is
found.
4.2 BIOS Error Messages
The BIOS also displays error messages during POST. Table 45 lists the error
messages and provides a brief description of each.
Table 45. BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
CMOS Battery Low The battery may be losing power. Replace the battery soon.
CMOS Checksum Bad The CMOS checksum is incorrect. CMOS memory may have been
corrupted. Run Setup to reset values.
Memory Size Decreased Memory size has decreased since the last boot. If no memory
was removed, then memory may be bad.
No Boot Device Available System did not find a device to boot.
82
Page 83

Beep Codes, Error Messages, and POST Codes
Range
Subsystem
0x00 – 0x05
Entering SX states S0 to S5.
0x40, 0x50
0x08 – 0x0F
Security (SEC) phase
0x11 – 0x1F
PEI phase pre MRC execution
0x21 – 0x29
MRC Memory detection
0x2A – 0x2F
PEI phase post MRC execution
0x31 – 0x35
Recovery
0x36 – 0x3F
Platform DXE driver
0x41 – 0x4F
CPU Initialization (PEI, DXE, SMM)
0x50 – 0x5F
I/O Buses: PCI, USB, ISA, ATA etc. 0x5F is an unrecoverable error. Start with PCI .
0x60 – 0x6F
BDS
0x70 – 0x7F
Output Devices: All output consoles.
0x80 – 0x8F
For future use
0x90 – 0x9F
Input devices: Keyboard/Mouse.
0xA0 – 0xAF
For future use
consoles should be up at this point.
0xC0 – 0xCF
For future use
0xD0 – 0xDF
For future use
0xF0 – 0xFF
4.3 Port 80h Power On Self Test (POST) Codes
During the POST, the BIOS generates diagnostic progress codes (POST codes) to I/O
port 80h. If the POST fails, execution stops and the last POST code generated is left
at port 80h. This code is useful for determining the point where an error occurred.
Displaying the POST codes requires a PCI bus add-in card, often called a POST card.
The POST card can decode the port and display the contents on a medium such as a
seven-segment display.
NOTE
In order to view POST codes on a diagnostic card inserted into a PCI slot, the BIOS
must be enabled to route POST codes to the PCI slots. The default setting is to route
them to the LPC debug header, as this is required to pa ss Windows 8 certification.
The following tables provide information about the POST codes generated by the BIOS:
Table 46 lists the Port 80h POST code ranges
Table 47 lists the Port 80h POST codes themselves
Table 48 lists the Port 80h POST sequence
NOTE
In the tables listed above, all POST codes and range values are listed in hexadecimal.
Table 46. Port 80h POST Code Ranges
0x10, 0x20, 0 x30,
0xB0 – 0xBF Boot Devices: Inc lude s fixe d media and remov able media. Not that critical since
Resuming from SX states. 0x10 – S1, 0x20 – S2, 0x30 – S3, etc.
83
Page 84

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 47. Port 80h POST Codes
Port 80 Code Progress Code Enumeration
ACPI S States
0x00,0x01,0x02,0x03,0x04,0x05 Enter ing S0 , S2 , S3, S4, or S5 state
0x10,0x20,0x30,0x40,0x50 Resuming from S2, S3, S4, S5
Security Phase (SEC)
0x08 Starting BIOS executio n afte r CPU BIST
0x09 SPI prefetching and cac hing
0x0A Load BSP microcode
0x0B Load APs microcodes
0x0C Platfor m program baseaddresses
0x0D Wake Up All APs
0x0E Initialize NEM
0x0F Pass entry point of the PEI core
PEI before MRC
PEI Platform driver
0x11 Set bootmode, GPIO init
0x12 Early chipset registe r prog ramming including graphics init
0x13 Basic PCH init, discrete device init (1394, SATA)
0x14 LAN init
0x15 Exit early platform init dr iv er
PEI SMBUS
0x16 SMBUSriver init
0x17 Entry to SMBUS execute read/wr ite
0x18 Exit SMBUS execute read/write
PEI CK505 Clock Programming
0x19 Entry to CK505 programming
0x1A Ex it C K50 5 progr a mmi ng
PEI Over-Clock Programming
0x1B Entr y to e ntry to PEI over-clock programming
0x1C Exit PEI ove r-clock p r ogram ming
Memory
0x21 MRC entry point
0x23 Reading SPD from memory DIMMs
0x24 Detecting presence of memory DIMMs
0x27 Configuring memory
0x28 Testing memory
0x29 Exit MRC driver
continued
84
Page 85

Beep Codes, Error Messages, and POST Codes
Table 47. Port 80h POST Codes (continued)
Port 80 Code Progress Code Enumeration
PEI after MRC
0x2A S tart to Program MTRR Settings
0x2B D o ne Progr am ming MTRR Settings
PEIMs/Recovery
0x31 Crisis Recovery has initiate d
0x33 Loading recovery capsule
0x34 Start recovery capsule / valid cap s ule is found
CPU Initialization
CPU PEI Phase
0x41 Begin CPU PEI Init
0x42 XMM instruction enab l ing
0x43 End CPU PEI Init
CPU PEI SMM Phase
0x44 Begin CPU SMM Init smm relocate bases
0x45 Smm relocate bases for APs
0x46 End CPU SMM Init
CPU DXE Phase
0x47 CPU DXE Phase begin
0x48 Refresh memory space attribute s ac co rd ing to MTRR s
0x49 Load the microcode if needed
0x4A Initialize strings to HII database
0x4B Initialize MP Support
0x4C CPU DXE Phas e End
CPU DXE SMM Phase
0x4D CPU DXE SMM Phase begin
0x4E Relocate SM bases for all APs
0x4F CPU DXE SMM Phase end
IO BUSES
0x50 Enumerating PCI buses
0x51 Allocating resources to PCI bus
0x52 Hot Plug PCI controller initialization
USB
0x58 Resetting USB bus
0x59 Reserved for USB
ATA/ATAPI/SATA
0x5A R e s e tting PATA/SATA bus and all devices
0x5B Reserved for ATA
continued
85
Page 86

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 47. Port 80h POST Codes (continued)
Port 80 Code Progress Code Enumeration
BDS
0x60 BDS driver entr y po int initiali ze
0x61 BDS service ro utine entry po int (can be calle d multiple times)
0x62 BDS St ep2
0x63 BDS St ep3
0x64 BDS St ep4
0x65 BDS St ep5
0x66 BDS St ep6
0x67 BDS St ep7
0x68 BDS St ep8
0x69 BDS St ep9
0x6A B DS Step10
0x6B B DS Step11
0x6C BDS Step12
0x6D BDS Step13
0x6E BDS S t ep14
0x6F BDS return to DXE core (should not get here)
Keyboard (PS2 or USB)
0x90 Resetting keyboard
0x91 Disabling the keyboard
0x92 Detecting the presence of the keyboard
0x93 Enabling the keyboard
0x94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
0x95 Instructing keybo ard controller to run Self Test (PS2 only)
Mouse (PS2 or USB)
0x98 Resetting mouse
0x99 Detecting mouse
0x9A Detecting presence of mouse
0x9B Enabling mouse
Fixed Media
0xB0 Resetting fixed media
0xB1 Disabling fixed media
0xB2 Detecting presence of a fixed media (IDE hard drive detection etc.)
0xB3 Enabling/configuring a fixed media
continued
86
Page 87

Beep Codes, Error Messages, and POST Codes
Table 47. Port 80h POST Codes (continued)
Port 80 Code Progress Code Enumeration
Removable Media
0xB8 Resetting removable media
0xB9 Disabling removable media
0xBA Detecting presence of a removable media (IDE, CDROM detection
etc.)
0xBB Enabling/configur ing a removab le med ia
DXE Core
0xE4 Entered DX E phase
BDS
0xE7 Waiting for user inp ut
0xE8 Checking password
0xE9 Entering BIOS setup
0xEB Calling Legacy Optio n ROMs
Runtime Phase/EFI OS Boot
0xF8 EFI boot service ExitBootServices ( ) has been called
0xF9 EFI runtime s er v ice SetVirtualAddressMap ( ) has been called
87
Page 88

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
Table 48. Typical Port 80h POST Sequence
POST Code Description
21 I nitia lizing a chipset component
22 Reading SPD from memory DIMMs
23 Detecting presence of memory DIMMs
25 Configuring memory
28 Tes ting m e mory
34 Loading recovery capsule
E4 Entered DXE phase
12 Starting application processor initializa tio n
13 SMM initializ ation
50 Enumerating PCI buses
51 Allocating resourced to PCI bus
92 De te c ting the presence of the keyboard
90 Resetting keyboard
94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
95 Keyboard Self Test
EB Calling Video BIOS
58 Resetting USB bus
5A Resetting PATA/SATA bus and all devic e s
92 De te c ting the presence of the keyboard
90 Resetting keyboard
94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
5A Resetting PATA/SATA bus and all devic e s
28 Tes ting m e mory
90 Resetting keyboard
94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
E7 Waiting for user input
01 INT 19
00 Ready to boot
88
Page 89

5 Regulatory Compliance and Battery
Disposal Information
5.1 Regulatory Compliance
This section cont ains the following regulatory compliance information for Intel Desk t op
Board DQ87PG:
• Safety standards
• European Union Declaration of Conformity statement
• Product Ecology statements
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standar ds
• Product certification markings
5.1.1 Safety Standards
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG complies with the safety standards stated in Table 49
when correctly installed in a compatible host system.
Table 49. Safety Standards
Standard Title
CSA/UL 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment – Safety - Part 1: General
Requirements (USA and Canada)
EN 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment – Safety - Part 1: General
Requirements (European Union)
IEC 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment – Safety - Par t 1: General
Requirements (International)
89
Page 90

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
5.1.2 European Union Declaration of Conformity
Statement
We, Intel Corporation, declare under our sole responsibility that the product Intel®
Desktop Board DQ87PG is in conformity with all applicable essential requirements
necessary for CE marking, following the provisions of the European Council Directive
2004/108/EC (EMC Directive), 2006/95/EC (Low Voltage Directive), and 2002/95/EC
(ROHS Directive).
The product is properly CE marked demonstrating this conformity and is for
distribution within all member state s of the EU with no restrictions.
This product follows the provisions of the European Directives 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC, and 2002/95/EC.
Čeština Tento výrobek odpovídá požadavkům evropských směrnic 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC a 2002/95/EC.
Dansk Dette produkt er i overensstemmelse med det europæiske direktiv
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Dutch Dit product is in navolging van de bepalingen van Europees Directief
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Eesti Antud toode vastab Euroopa direktiivides 2004/108/EC, ja 2006/95/EC ja
2002/95/EC kehtestatud nõuetele.
Suomi Tämä tuote noudattaa EU-direktiivin 2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC
määräyksiä.
Français Ce produit est conforme aux exigences de la Directive Européenne
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Deutsch Dieses Produkt entspricht den Bestimmungen der E uropäischen Richtlinie
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Ελληνικά Το παρόν προϊόν ακολουθεί τις διατάξεις των Ευρωπαϊκών Οδηγιών
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC και 2002/95/EC.
Magyar E termék megfelel a 2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC és 2002/95/EC Európai
Irányelv előírásainak.
Icelandic Þessi vara stenst reglugerð Evrópska Efnahags Bandalagsins númer
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC, & 2002/95/EC.
Italiano Questo prodotto è conforme alla Direttiva Europea 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Latviešu Šis produkts atbilst Eiropas Direktīvu 2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC un
2002/95/EC noteikumiem.
Lietuvių Šis produktas atitinka Europos direktyvų 2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC, ir
2002/95/EC nuostatas.
Malti Dan il-prodott hu konformi mal-provvedimenti tad-Direttivi Ewropej
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC u 2002/95/EC.
Norsk Dette produktet er i henhold til bestemmelsene i det europeiske direktivet
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
90
Page 91

Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
Polski Niniejszy produkt jest zgodny z postanowieniami Dyrektyw Unii Europejskiej
2004/108/EC, 206/95/EC i 2002/95/EC.
Portuguese Este produto cumpre com as normas da Diretiva Européia 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Español Este producto cumple con las normas del Directivo Europeo 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Slovensky Tento produkt je v súlade s ustanoveniami európskych direktív
2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC a 2002/95/EC.
Slovenščina Izdelek je skladen z določbami evropskih direktiv 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC in 2002/95/EC.
Svenska Denna produkt har tillverkats i enlighet med EG-direktiv 2004/108/EC,
2006/95/EC & 2002/95/EC.
Türkçe Bu ürün, Avrupa Birliği’nin 2004/108/EC, 2006/95/EC ve 2002/95/EC
yönergelerine uyar.
5.1.3 Product Ecology Statements
The following information is provided to address worldwide product ecology concerns
and regulations.
5.1.3.1 Disposal Considerations
This product contains the following materials th at may be regulated upon disposal:
printed wiring board assembly and lithium battery.
91
Page 92
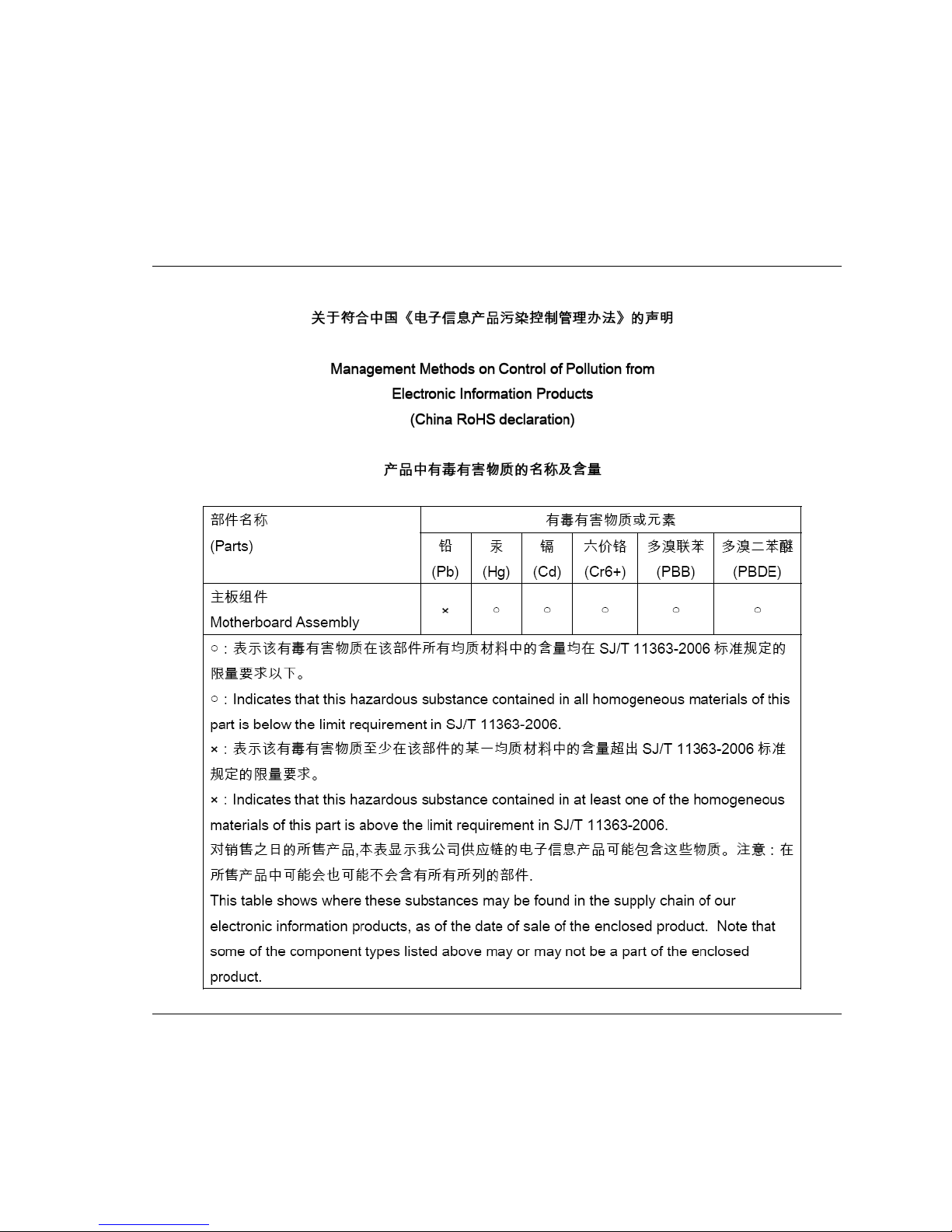
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
5.1.4 China RoHS
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG is a China RoHS-compliant product.
The China Ministry of Information Industry (MII) stipulates that a material Self
Declaration Table (SDT) must be included in a product’s user documentation. The SDT
for Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG is shown in Figure 19.
Figure 19. Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG China RoHS Material
92
Self Declaration Table
Page 93
Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
5.1.5 EMC Regulations
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG complies with the EMC regulations stated in Table 50
when correctly installed in a compatible host system.
Table 50. EMC Regulations
Regulation Title
FCC 47 CFR Part 15,
Subpart B
ICES-003 Interference-Causing Equipment Standard, Digital A pp aratus. (Canada)
EN55022
EN55024
EN55022
CISPR 22
CISPR 24
VCCI V-3, V-4
KN-22, KN-24
CNS 13438 Bureau of Standards, Metrology, and Inspection (Taiwan)
Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 15, Subpart B, Rad i o
Frequency Devices. (USA)
Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interf ere nce Characte ristics
of Information Technology Equipment. (European Union)
Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Char ac ter is tic s Lim its and
methods of measurement. (European Union)
Australian Communications Author i ty , S ta nd ard for Ele c tromag ne tic
Compatibility. (Australia and New Zealand)
Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Disturbance Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment. (International)
Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics – Limits and
Methods of Measurement. (International)
Voluntary Control for Interference by Information Technology Equipment.
(Japan)
Korean Communications Commission – Framework Act on
Telecommunications and Radio Waves Ac t (South Korea)
FCC Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules . Oper a t ion is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
For questions related to the EMC performance of this product, contact:
Intel Corporation, 5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway, Hillsboro, OR 97124
1-800-628-8686
This equipment has been tested and found to com ply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interfere nce
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following me asures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
93
Page 94

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
• Connect the equipment to an o ut let on a circuit other than the one to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Intel
Corporation could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Tested to comply with FCC standards for home or office use.
Canadian Department of Communications Compliance Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian
Department of Communications.
Le présent appareil numerique német pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les
limites applicables aux appareils numériques de la classe B prescrites dans le
Réglement sur le broullage radioélectrique édicté par le ministére des Communications
du Canada.
Japan VCCI Statement
Japan VCCI Statement translation: This is a Class B product based on the sta nda rd of
the Voluntary Control Council for Inter ference from Information Technology Equipment
(VCCI). If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic environment, it
may cause radio interference. Install and use the equipment according to the
instruction manua l.
Korea Class B Statement
Korea Class B Statement translation: This e quipment is for home use , and has
acquired electromagnetic conformity re gistration, so it can be used not only in
residential areas, but also other areas.
94
Page 95

Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
5.1.6 ENERGY STAR* 5.2, e-Standby, and ErP
Compliance
The US Department of Energy and the US Environmental Protection Agency have
continually revised the ENERGY STAR requirements. Intel has worked directly with
these two governmental agencies in the definition of new requirements.
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG allows for a compliant system built to meet the following
program requirements, in cl u ding appropriate selection of an efficient power supply:
• ENErGY STAR v5.2, category D
• EPEAT*
• Korea e-Standby
• European Union Energy-related Products Directive (ErP) Lot 6, Tier 2
• ENErGY STAR v6.0 draft 3
NOTE
ENERGY STAR denotes a system level energy specification, defined by the US
Environmental Protection Agency, that relies upon all of the system's components,
including processor, chipset, power supply, HDD, graphics controller, memory, etc. to
meet the specification. For more information on ENERGY STAR Computers Program
requirements version 5.2, go to:
http://www.energystar.gov/
For information about Refer to
ENERGY STAR requirements and recommended configurations http://www.intel.com/go/energystar
Electronic Product Environmental Assessment Tool (EPEAT) http://www.epeat.net/
Korea e-Standby Program http://www.kemco.or.kr/new_eng/pg02/
European Union Energy-related Products Directive 2009 (ErP) http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/policies/s
pg02100300.asp
ustainable-business/sustainableproduct-policy/ecodesign/index_en.htm
95
Page 96

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
5.1.7 Regulatory Compliance Marks (Board Level)
Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG has the regulatory compliance marks shown in Table 51.
Table 51. Regulatory Compliance Marks
Description Mark
UL joint US/Canada Recognized Compone nt mark. Inc ludes adjac e nt UL file
number for Intel Desktop Boards: E210882.
FCC Declaration of Conformity logo mark for Class B equipment.
CE mark. Declaring compliance to the European U nion (EU) EMC directive,
Low Voltage directive, and RoHS directive.
Australian Communications Author i ty (ACA) and New Zealand Radio
Spectrum Management (NZ RSM) C-tick mark. Includes adjacent Intel
supplier code number, N-232.
Japan VCCI (Voluntary Control Counci l for I nterference) mark.
Korea Certification mark. Includes an adja cent KC C (Kore an Communic ations
Commission) certificatio n number:
KCC-REM-CPU-DQ87PG.
Taiwan BSMI (Bureau of Standards, Metrology and Inspections) mark.
Includes adjacent Intel company number, D33025 .
Printed wiring board manufacturer ’s reco g nition mark. Consists of a unique
UL recognized manufacturer’s logo , along with a flamm ability rating (solder
side).
China RoHS/Environmentally Fr ie nd ly Use Per iod Logo: This is an example of
the symbol used on Intel Desktop Boards and associated collater a l. The color
of the mark may vary depending upon the application. The Environme ntal
Friendly Usage Period (EFUP) for Intel Desktop Boards has been determined
to be 10 years.
V-0
96
Page 97

Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
5.2 Battery Disposal Information
CAUTION
Risk of explosion if the battery is replaced with an incorrect type. Batteries should be
recycled where possible. Disposal of used batteries must be in accordance with local
environmental regulations.
PRÉCAUTION
Risque d'explosion si la pile usagée est remplacée par une pile de type incorrect. Les
piles usagées doivent être recyclées dans la mesure du possible. La mise au rebut des
piles usagées doit respecter les réglementations locales en vigueur en matière de
protection de l'environnement.
FORHOLDSREGEL
Eksplosionsfare, hvis batteriet erstattes med et batteri af en forkert type. Batterier
bør om muligt genbruges. Bortskaffelse af brugte batterier bør foregå i
overensstemmelse med gældende miljølovgivning.
OBS!
Det kan oppstå eksplosjonsfare hvis b a tteriet skiftes ut med feil type. Brukte batterier
bør kastes i henhold til gjeldende miljølovgivning.
VIKTIGT!
Risk för explosion om batteriet ersätts med felaktig batterityp. Batterier ska kasseras
enligt de lokala miljövårdsbestämmelserna.
VARO
Räjähdysvaara, jos pariston tyyppi on väärä. Paristot on kierrätettävä, jos se on
mahdollista. Käytetyt paristot on hävitettävä paikallisten ympäristömääräysten
mukaisesti.
VORSICHT
Bei falschem Einsetzen einer neuen Batterie besteht Explosionsgefahr. Die Batterie
darf nur durch denselben oder einen entspreche nden, vom Herstel l e r e m p foh l enen
Batterietyp ersetzt werden. Entsorgen Sie verbrauchte Batterien den Anweisungen
des Herstellers entsprechend.
AVVERTIMENTO
Esiste il pericolo di un esplosione se la pila non viene sostituita in modo corretto.
Utilizzare solo pile uguali o di tipo equivalente a quelle consigliate dal produttore. Per
disfarsi delle pile usate, seguire le istruzioni del produttore.
97
Page 98

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
PRECAUCIÓN
Existe peligro de explosión si la pila no se cambia de forma adecuada. Utilice
solamente pilas iguales o del mismo tipo que las recomendadas por el fabricante del
equipo. Para deshacerse de las pilas usadas, siga igualmente las instrucciones del
fabricante.
WAARSCHUWING
Er bestaat ontploffingsgevaar als de batterij wordt vervangen door een onjuist type
batterij. Batterijen moeten zoveel mogelijk worden gerecycled. Houd u bij het
weggooien van gebruikte batterijen aan de plaatselijke milieuwetgeving.
ATENÇÃO
Haverá risco de explosão se a bateria for substituída por um tipo de bateria incorreto.
As baterias devem ser recicladas nos locais apropriados. A eliminação de baterias
usadas deve ser feita de acordo com as regulamentações ambientais da região.
AŚCIAROŽZNAŚĆ
Існуе рызыка выбуху, калі заменены акумулятар неправільнага тыпу.
Акумулятары павінны, па магчымасці, перепрацоўвацца. Пазбаўляцца ад старых
акумулятараў патрэбна згодна з мясцовым заканадаўствам па экалогіі.
UPOZORNÌNÍ
V případě výměny baterie za nesprávný druh může dojít k výbuchu. Je-li to možné,
baterie by měly být recyklovány. Baterie je třeba zlikvidovat v souladu s místními
předpisy o životním prostředí.
Προσοχή
Υπάρχει κίνδυνος για έκρηξη σε περίπτωση που η μπαταρία αντικατασταθεί από μία
λανθασμένου τύπου. Οι μπαταρίες θα πρέπει να ανακυκλώνονται όταν κάτι τέτοιο είναι
δυνατό. Η απόρριψη των χρησιμοποιημένων μπαταριών πρέπει να γίνεται σύμφωνα με
τους κατά τόπο περιβαλλοντικούς κανονισμούς.
VIGYÁZAT
Ha a telepet nem a megfelelő típusú telepre cseréli, az felrobbanhat. A telepeket
lehetőség szerint újra kell hasznosítani. A használt telepeket a helyi környezetvédelmi
előírásoknak megfelelően kell kiselejtezni.
98
Page 99

Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
AWAS
Risiko letupan wujud jika bateri digantikan dengan jenis yang tidak betul. Bateri
sepatutnya dikitar semula jika boleh. Pelupusan bateri terpakai mestilah mematuhi
peraturan alam sekitar tempatan.
OSTRZEŻENIE
Istnieje niebezpieczeństwo wybuchu w przypadku zastosowania niewłaściwego typu
baterii. Zużyte baterie należy w miarę możliwości utylizować zgodnie z odpowiednimi
przepisami ochrony środowiska.
PRECAUŢIE
Risc de explozie, dacă bateria este înlocuită cu un tip de baterie necorespunzător.
Bateriile trebuie reciclate, dacă este posibil. Depozitarea bateriilor uzate trebuie să
respecte reglementările locale privind protecţia mediului.
ВНИМАНИЕ
При использовании батареи несоответствующего типа существует риск ее взрыва.
Батареи должны быть утилизированы по возможности. Утилизация батарей должна
проводится по правилам, соответствующим местным требованиям.
UPOZORNENIE
Ak batériu vymeníte za nesprávny typ, hrozí nebezpečenstvo jej výbuchu.
Batérie by sa mali podľa možnosti vždy recyklovať. Likvidácia použitých batérií sa musí
vykonávať v súlade s miestnymi predpismi na ochranu životného prostredia.
POZOR
Zamenjava baterije z baterijo drugačnega tipa lahko povzroči eksplozijo.
Če je mogoče, baterije reciklirajte. Rabljene baterije zavrzite v skladu z lokalnimi
okoljevarstvenimi predpisi.
UYARI
Yanlış türde pil takıldığında patlama riski vardır. Piller mümkün olduğunda geri
dönüştürülmelidir. Kullanılmış piller, yerel çevre yasalarına uygun olarak atılmalıdır.
OСТОРОГА
Використовуйте батареї правильного типу, інакше існуватиме ризик вибуху.
Якщо можливо, використані батареї слід утилізувати. Утилізація використаних
батарей має бути виконана згідно місцевих норм, що регулюють охорону довкілля.
99
Page 100

Intel Desktop Board DQ87PG Technical Product Specification
小心
주의
如果更換的電池類型不正確,可能會有爆炸的危險。請盡可能將電池送至回收處。請依照當地的環保
規範來處理使用過的電池。
배터리를 잘못된 종류로 교체할 경우 폭발 위험이 있습니다. 가능한 경우 배터리는 재활용해야
하며, 수명이 다한 배터리를 폐기할 때는 각 지역의 환경법을 따라야 합니다.
THẬN TRỌNG
Có nguy cơ xảy ra nổ nếu thay pin không đúng loại. Pin cần được tái chế nếu có thể
thực hiện được. Việc thải bỏ pin đã sử dụng phải tuân theo các quy định của địa
phương về môi trường.
100
 Loading...
Loading...