Intel CoreTM 2 Duo Processor, Intel CoreTM Duo Processor, 3100 Chipset, Core 2 Duo Processor, Core Duo Processor User Manual
Page 1

Intel® Core
Intel
Intel
User’s Manual
June 20 07
®
Core
®
3100 Chipset
TM
2 Duo P r oc e ssor and
TM
Duo Processor and
Order Number: 316639-002
Page 2

Lega l Li nes and Discla imers
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR
OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS
OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHAT SOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELA T ING
TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for
use in medical, life saving, life sustaining, critical control or safety system s, or in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights that relate to the
present e d subject matter. The furn i shi ng o f do c um en ts and other mate ria ls and information does not provide any license, express or implied, by es topp el
or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor family, not across different
processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details.
The Intel® Pentium® M Processor and Intel® 3100 Chipset Development Kit may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the
product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by calling
1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Intel and Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
BunnyPeople, Celeron, Celeron Inside, Centrino, Centrino logo, Core Inside, Dialogic, FlashFile, i960, InstantIP, Intel, Intel logo, Intel386, Intel486,
Intel740, IntelDX2, IntelDX4, IntelSX2, Intel Core, Intel Inside, Intel Inside logo, Intel. Leap ahead., Intel. Leap ahead. logo, Intel NetBurst, Intel
NetMerge, Intel NetStructure, Intel SingleDriver, Intel SpeedStep, Intel StrataFlash, Intel Viiv, Intel vPro, Intel XScale, IPLink, Itanium, Itanium Inside,
MCS, MMX, Oplus, OverDrive, PDCharm, Pentium, Pentium Inside, skoool, Sound Mark, The Journey Inside, VTune, Xeon, and Xeon Inside are
trademarks or register ed trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other na m es and bra nds may be claime d as the pro pe r ty of oth ers .
Copyright © 2007, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
User’s Manual June 2007
2 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 3

Contents
Contents
1.0 Product Description...................................................................................................7
1.1 Overview ..........................................................................................................7
1.1.1 Feature Summary ...................................................................................7
1.1.2 Board Layout ..........................................................................................9
1.2 Processors........................................................................................................11
1.3 System Memory................................................................................................11
1.3.1 DDR2-400 DIMM Slot Populations.............................................................11
1.3.2 DDR2 DIMM Ordering Overview................................................................12
1.4 Intel
1.5 Supported Operating Systems.............................................................................20
1.6 Supported BIOS Features...................................................................................21
1.7 Power Supply....................................................................................................22
1.8 Thermal and Mechanical Components...................................................................22
1.9 Physical and Mechanical Board Specifications........................................................ 25
1.10 Debug Ports .....................................................................................................25
1.11 Real Time Clock (RTC), CMOS SRAM, and Battery..................................................25
2.0 Platform Setu p ........................................................................................................26
2.1 Connecting the Wires.........................................................................................26
2.2 Connecting Other Peripherals.............................................................................. 30
2.3 Connect Power..................................................................................................33
2.4 Turning On and Resetting the Board ....................................................................36
3.0 Technical Reference ................................................................................................37
3.1 Memory Resources ............................................................................................37
3.2 DMA Channels ..................................................................................................37
3.3 Fixed I/O Map ...................................................................................................37
3.4 Interrupts ....................................................................................................... 37
3.5 PCI Conventional Interrupt Routing Map...............................................................38
3.6 Connectors.......................................................................................................39
3.7 Jumper Block....................................................................................................43
3.8 Mechanical Considerations..................................................................................46
®
3100 Chipset...........................................................................................14
1.4.1 On-Board Peripherals..............................................................................14
1.4.2 On-Board I/O.........................................................................................15
1.4.3 I/O Slots for Expansion Capabilities ..........................................................17
1.4.4 Rear Panel I/O Connectors.......................................................................18
1.4.5 Hardware Server Management Features ....................................................19
1.6.1 ACPI.....................................................................................................21
1.8.1 Heatsinks..............................................................................................23
1.9.1 Mounting Holes......................................................................................25
2.1.1 Connect SATA cables ..............................................................................27
2.1.2 Plugging In Memory................................................................................27
2.1.3 Connecting the Processor ........................................................................28
2.1.4 Connecting Heatsinks and Fans................................................................28
2.2.1 Add-in Connectors..................................................................................30
2.2.2 Rear Panel Connectors............................................................................ 31
2.2.3 Connecting a Floppy Drive.......................................................................32
2.2.4 Changing and/or Updating the BIOS Chip ..................................................32
2.2.5 Changing the CMOS Batte ry and Clearing CMOS......................................... 33
3.6.1 Back Panel Connectors............................................................................39
3.6.2 Component Side Connectors ...................................................................39
3.8.1 Form Factor...........................................................................................46
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 3
Page 4

Contents
3.9 Electrical Considerations.....................................................................................47
3.9.1 DC Loading............................................................................................47
3.9.2 Add-in Board Considerations ...................................................................48
3.9.3 Fan Connector Curr ent Capability..............................................................48
3.9.4 Power Supply Considerations ...................................................................48
3.10 Thermal Considerations .....................................................................................48
4.0 Overview of BIOS Features......................................................................................50
4.1 Introduction......................................................................................................50
4.2 Resource Configuration.......................................................................................51
4.2.1 PCI Auto Configuration............................................................................51
4.3 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) ..................................................................51
4.4 Legacy USB Support...........................................................................................51
4.5 BIOS Updates ...................................................................................................52
4.5.1 Language Support .................................................................................52
4.6 Boot Options ....................................................................................................52
4.6.1 CD-ROM Boot ........................................................................................52
4.6.2 Network Boot.........................................................................................52
4.6.3 USB Boot...............................................................................................53
4.6.4 Booting without Attached Devices ............................................................53
4.6.5 Changing the Boot Device........................................................................53
4.7 BIOS Security Features ......................................................................................53
5.0 Error Message s an d Bee p Co de s...............................................................................54
5.1 Speakers..........................................................................................................54
5.2 BIOS Beep Codes ..............................................................................................54
5.3 BIOS Error Messages .........................................................................................54
5.4 Port 80h POST Codes ........................................................................................54
Figures
1 Board Components.................................................................................................... 9
2 Two-DIMM Implementation........................................................................................12
3 Example of Single-Rank DIMM Population ....................................................................13
4 Example of Singl e-Rank and Dual-Rank DIMM Mixing Population.....................................13
5 Example of Dual-Rank DIMM Population ...................................................................... 13
6Intel
7 PCI On-Board Video Chip...........................................................................................15
8 Floppy Drive Connector .............................................................................................15
9 Front Panel Header...................................................................................................16
10 XDP Connector.........................................................................................................16
11 Rear Panel I/O Connectors.........................................................................................18
12 Intel
13 Processor Active Heatsink..........................................................................................24
14 Intel
15 SATA Ports ..............................................................................................................27
16 DIMM Sockets..........................................................................................................28
17 Processor Socket......................................................................................................28
18 Processor Fan Mounting Bracket .................................................................................29
19 Screwing the Processor Fan into the Mounting Bracket...................................................29
20 Fan Power Connectors............. ..................................................................................30
21 PCI Express* Connectors............................................................................. ..............31
22 Floppy Drive Connector .............................................................................................32
23 Firmware Hub ..........................................................................................................32
24 CMOS Battery..........................................................................................................33
®
3100 Chipset Block Diagram.............................................................................14
®
3100 Chipset Active Heatsink ...........................................................................23
®
3100 Chipset Passive Heatsink Design ...............................................................25
User’s Manual June 2007
4 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 5

Contents
25 CMOS Clear Jumper..................................................................................................33
26 Power Connector......................................................................................................34
27 ATX Power Connector...............................................................................................34
28 Power Connector Cables............................................................................................35
29 Power and Reset Buttons ..........................................................................................36
30 Back Panel Connectors..............................................................................................39
31 ATX Power Connector...............................................................................................40
32 SATA Power Connector .............................................................................................40
33 Front Panel Connector .............................................................................................41
34 Jumper Block Locations and Pin Connectors.................................................................43
35 Form Factor ............................................................................................................47
36 Menu Bar ................................................................................................................50
Tables
1 Feature Summary ......................................................................................................7
2 Development Kit Contents ...........................................................................................8
3 Component Layout Description ....................................................................................9
4 Supported Microprocessors........................................................................................11
5 Supported DDR2-400 DIMM Populations......................................................................11
6 Supported BIOS Features..........................................................................................21
7 Effects of Pressing the Power Switch...........................................................................21
8 Thermal and Mechanical Components .........................................................................22
9 DMA Channels.........................................................................................................37
10 I/O x APIC Interrupts ...............................................................................................38
11 PCI Interrupt Routing Map PCI Interrupt Source...........................................................39
12 Front Chassis Fan and Rear Chassis Fan Connectors .....................................................39
13 Main Power Connector Pin.........................................................................................40
14 SATA Power Connector .............................................................................................41
15 Auxiliary Front Panel Power and Reset Connector Pin .................................................... 41
16 Front Panel Connector ..............................................................................................41
17 Jumper Block Locations.............................................................................................44
18 DC Loading Characteristics Mode................................................................................48
19 Fan Connector Current Capability...............................................................................48
20 BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar ..................................................................................50
21 BIOS Setup Program Function Keys................................................................. ...........50
22 Beep Code Types.....................................................................................................54
23 BIOS Error Messages................................................................................................54
24 Port 80h POST Code Ranges...................................................................................... 55
25 Typical Port 80h POST Sequence................................................................................55
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 5
Page 6
Revision History
Date Revision Description
June 2007 002 Added support for Intel® Core
March 2007 001 I nitial public release.
Revision History
TM
2 Duo Processor L7400 to this Customer Reference Board design.
User’s Manual June 2007
6 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 7
Product Description
1.0 Product Description
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Feature Summary
Table 1 summarizes the major features of the Customer Reference Board (CRB).
Table 1. Feature Summar y
Feature Description
Form Factor ATX (12.00 inches by 10.75 inches)
Processors Refer to Table 4, “Supported Micropro ces sors” on page 11.
Support for 400 MHz DDR2 Registered ECC
Memory
Chipset Intel
Video On-board PCI ATI Rage* Mobility Video Chip
I/O Control Low Pin Count (LPC) B us I/O Controller
USB
Per ipheral Inte rfaces
BIOS
LAN Support Supports Dual Port PCI Express* Gigabit NIC
Expansion Capabilities
Hardware Mo ni t or Sub sys t em
2 Angled DIMM Sockets which support up to 4 GB RAM
Support for registered ECC only
®
3100 Chip se t
Support for USB 1.1 and 2.0 devices
T otal of four USB ports UHCI or EHCI configurations
Two serial ports
One parallel port
Total of six SATA Ports (two available modes):
• Enhanced IDE mode- Utilizes four SATA ports
• AHCI mode- Utilizes Six SATA ports
One floppy drive interface
PS/2* keyboard and mouse ports
Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), Plug and
Play, SMBIOS, and In tel® Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT)
Three PCI Express* x4 bus add-in card connectors
One PCI 32/33 bus add in card connector compliant with Specification 2.2
Hardware monitoring and fan control ASI
Voltage sense to detect out of range power supply voltages
Thermal sense to detect out of range thermal values
Four fan connectors
Four fan s ense inputs use to moni tor fan activity
Fan speed control
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 7
Page 8

Table 2 describes what is included in the Development Kit.
Table 2. Development Kit Contents
Feature Description
PCB
Processor
Memory Two 1 GB DDR2 DIMMs
Chipset Intel® 3100 Chipset
Processor Heatsink Coolermaster* Active Heatsink
Network Card Intel PC I Express* Gigabit NIC
Firmwa re Hub Socket ed Fir m ware Hub (BIOS)
Software Driver CD
Additional Peripherals
Product Description
®
CRB, Intel
Intel
Intel® CoreTM 2 Duo Pr ocessor L 7400, 1.50 GHz (installed)
Intel
Standoffs (with installation hardware) for Benchtop use
Warning:
Core™ 2 Duo Processor and Intel® Core™ Duo Processor an d
®
3100 Chipset
®
CoreTM Duo Proce s sor ULV U2500, 1.2 Ghz (s up pl i e d )
Placing the board on an unknown surface without standoffs may
short the CRB and result in damage. If CRB is not mounted in a
chassis, Intel recommends using provided Standoffs to prevent
risk of the bottom of the CRB shorting on a conductive surf ace.
User’s Manual June 2007
8 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 9
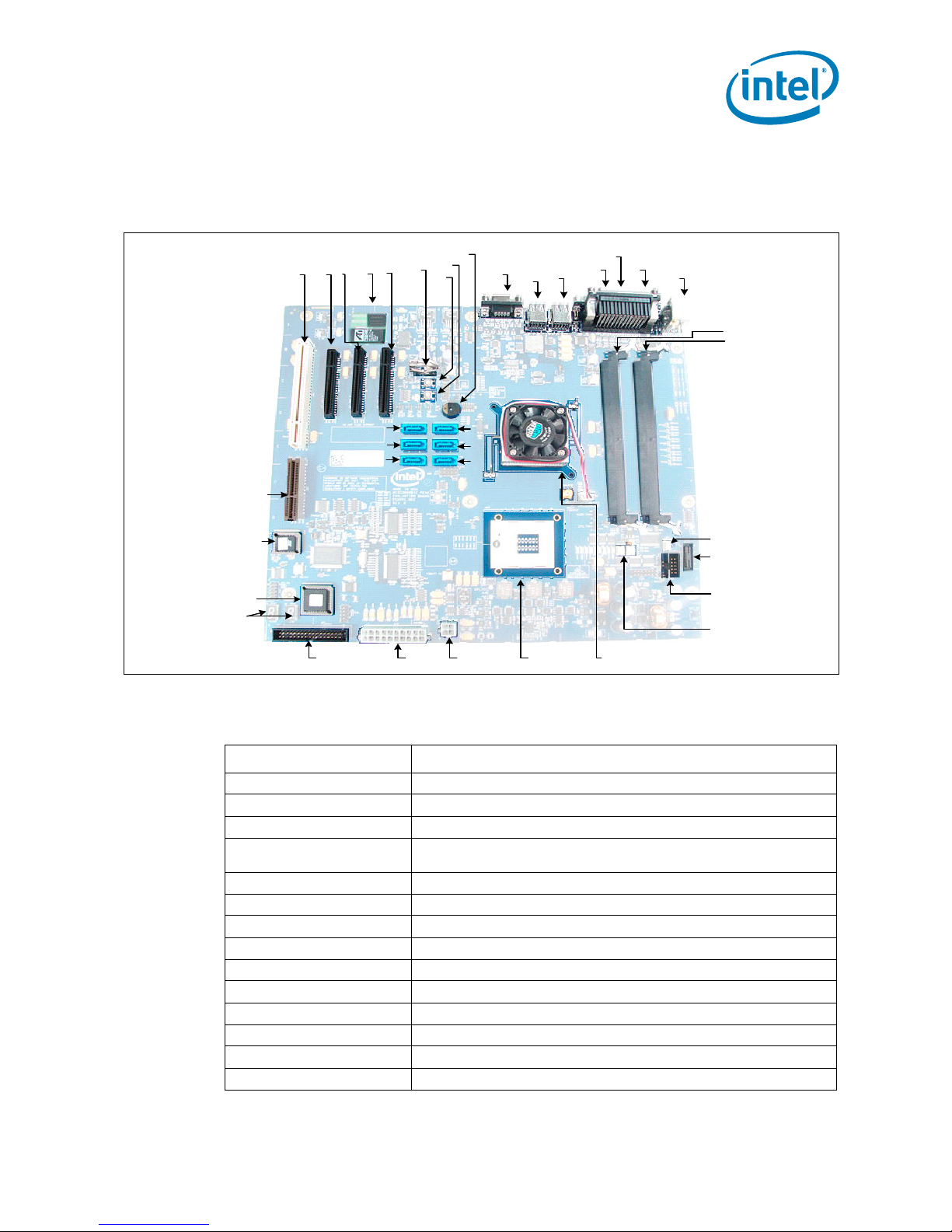
Product Description
1.1.2 Board Lay out
Figure 1 shows the location of the major components.
Figure 1. Board Components
21 3
9
8
6
5
4
7
10
11
131415
12
16
19
20
33
34
35
33
32
31
30
36
37
38
Table 3 lists the components shown in Figure 1.
Table 3. Component Layout Description (Sheet 1 of 2)
Callout Description
132-bit/33 MHz PCI connector
2 Port B x4 on l y PC I E xp r e ss* using x 8 c o nn e c to r
3 Port A x4 only PCI Express* using x8 connector (A1)
4
5 Port A x4 only PCI Express* using x8 connector (A0)
6CMOS battery
7 Power button
8Reset button
9 On-board speaker
10 Back panel 15 Pin VGA connector
11 USB ports (2) 3 top / 2 bottom
12 USB ports (2) 0 top / 1 bottom
13 Serial com port 2
14 Parallel port
On-board PCI ATI Rage* Mobility Video Chip if available (if not on-board a
PCI add-in Card is supplied)
21
22
23
24
2526272829
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 9
Page 10

Table 3. Component Layout Description (Sheet 2 of 2)
Callout Description
15 Serial com port 1
16 PS/2* top = mouse / bottom = keyboard
17 DIMM0 (Not used in This angled DIMM Design, two DIMMS only)
18 DIMM1 (Not used in This angled DIMM Design, two DIMMS only)
19 DIMM2
20 DIMM3 (closest to edge of board)
21 AUX FAN 1
22 XDP connector
23 JTAG connector
24 AUX FAN 0
®
25 Intel
26 Processor with active fan plugged into processor FAN
27 ATX 12 V for SATA power
28 ATX power connector
29 Floppy drive connector
30 Port 80 seven segme nt displays
31 Port 80 chip
32 Firmw ar e hub (BI OS )
33 Plug For validation only
34 SATA port 0
35 SATA port 1
36 SATA port 2
37 SATA port 3
38 SATA port 4
39 SATA port 5
3100 Chipset with active fan Connected to FAN1
Product Description
User’s Manual June 2007
10 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 11
Product Description
1.2 Processors
The CRB is designed to support the following processors with a 533 and 667 MHz FSB
speed.
Use only the processors listed below in Table 4. Use of unsupported processors can
damage the CRB, the process or, and the power supp ly.
Note: In this document Processor refers to all processor SKUs listed in Table 4.
Table 4. Supported Microprocessors
Microprocessor Cores
Intel® Core™ 2 Duo Processor L7400 Dual 1.50GHz 667MHz 4MB 17W
Intel® Core™ Duo proces sor ULV U2500 Dual 1.20GHz 533MHz 2MB 9W
Intel® Celeron® M Processor ULV 423 Single 1.06GHz 533MHz 1MB 5.5W
1.3 System Memory
The CRB has two DIMM sockets and supports the following memory features:
• DDR2-400 MHz registered ECC
•SEC/DED
• Up to four ranks of memory
• Minimum total system memory: 512 MB, maximum of 4 GB
• ECC DIMMs, 8 bits ECC
• Single ch ann el op erati on on ly
• Supports x4 and x8 DDR2- 512 Mb and DDR2 -1 Gb t echno l ogies a nd x4 DDR 2-2 Gb
technologies
1.3.1 DDR2-400 DIMM Slot Populations
Table 5 shows the supported DDR2-400 DIMM populations.
Table 5. Supported DDR2-400 DIMM Populations
CLK
Speed
FSB
Speed
L2
Cache
TDP
DIMM Configuration DIMM0 DIMM1 DIMM2 DIMM3
1 Single-rank N/A N/A Empty Single-rank
1 Dual-rank N/A N/A Empty Dual-rank
2 Single-rank N/A N/A Single-rank Single-rank
1 Dual-rank, 1 Single-rank N/A N/A Single-rank Dual-rank
2 Dual-rank N/A N/A Dual-rank Dual-rank
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 11
Page 12
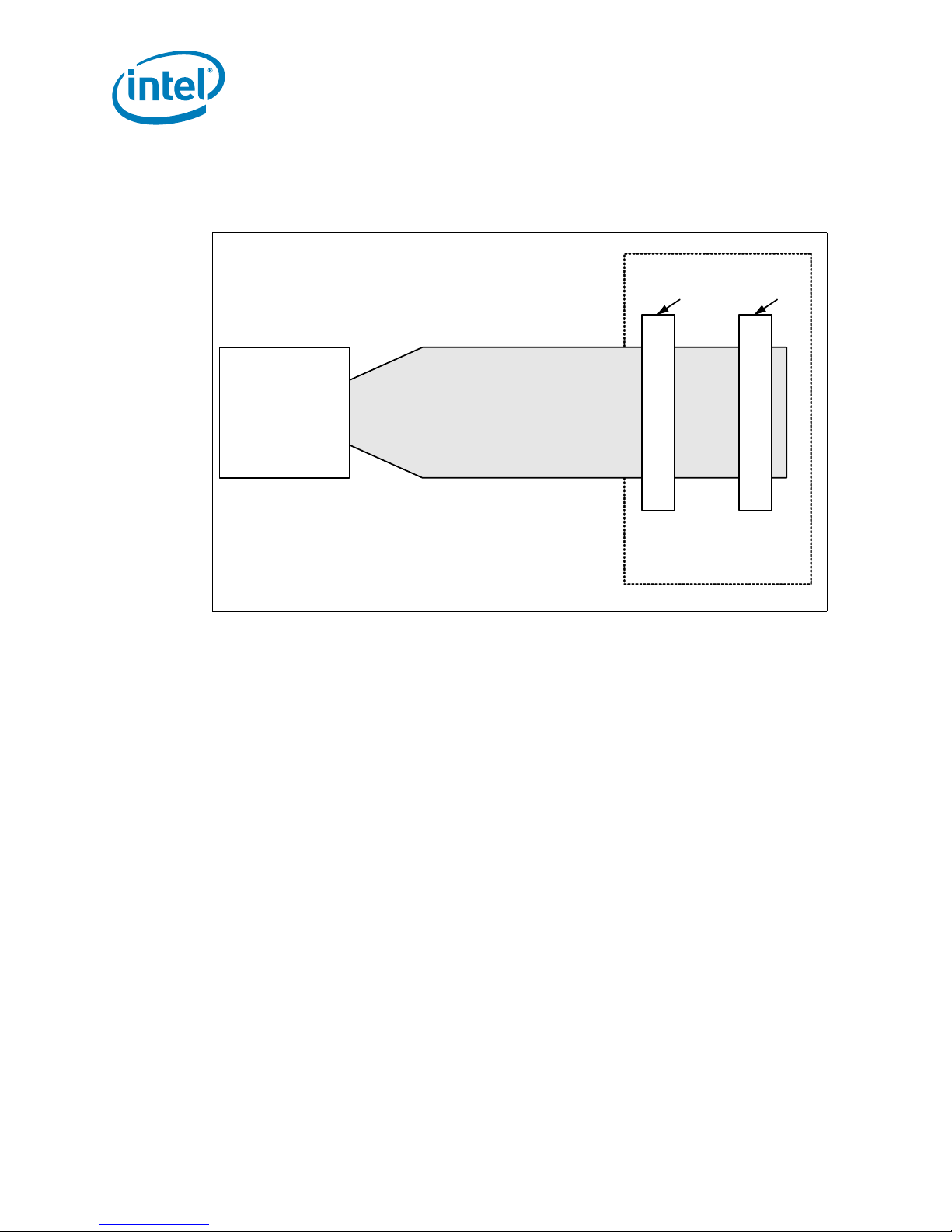
1.3.2 DDR2 DIMM Ordering Overview
Figure 2 shows the DIMM ordering and location.
Figure 2. Two-DIMM Implementation
Product Description
Fill Second Fill First
Can use two Dual-
Intel® 3100
Chipset
Rank DIMMs, One
Dual Rank and a
Single , or two single
rank DIMMS
The platform requires DDR2-400 DIMMs to be populated in order, starting with the
DIMM furthest from Intel
addition, dual-rank DIMMs must be populated farthest from Intel
a combination of single-rank and dual-rank DIMMs are used. This recommendation is
based on the chip select and on-die termination signals routing requirements of the
DDR2-400 interface. Intel recommends that you check for correct DIMM placement
during BIOS initialization and that all designs follow the DIMM ordering, clock enable
routing, command clock routing, and chip select routing shown in Figure 2. This
addressing must be maintained to be compliant with the BIOS code.
The two DIMMs that are provided with the development kit are 1 Gb singl e-rank
DIMMs. If other memory is used follow the illustrations in Figure 3, Figure 4, and
Figure 5. Figure 3 shows how to populate two single-rank DIMMs. Figure 4 shows how
to po pu la t e one du a l -r a nk and one single - r a nk DI MM s. Figure 5 shows how to populate
two dual-rank DIMMs.
®
3100 Chipset in a “fill-farthest” approach (see Figure 2). In
D
I
M
M
2
®
3100 Chipset when
D
I
M
M
3
User’s Manual June 2007
12 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 13
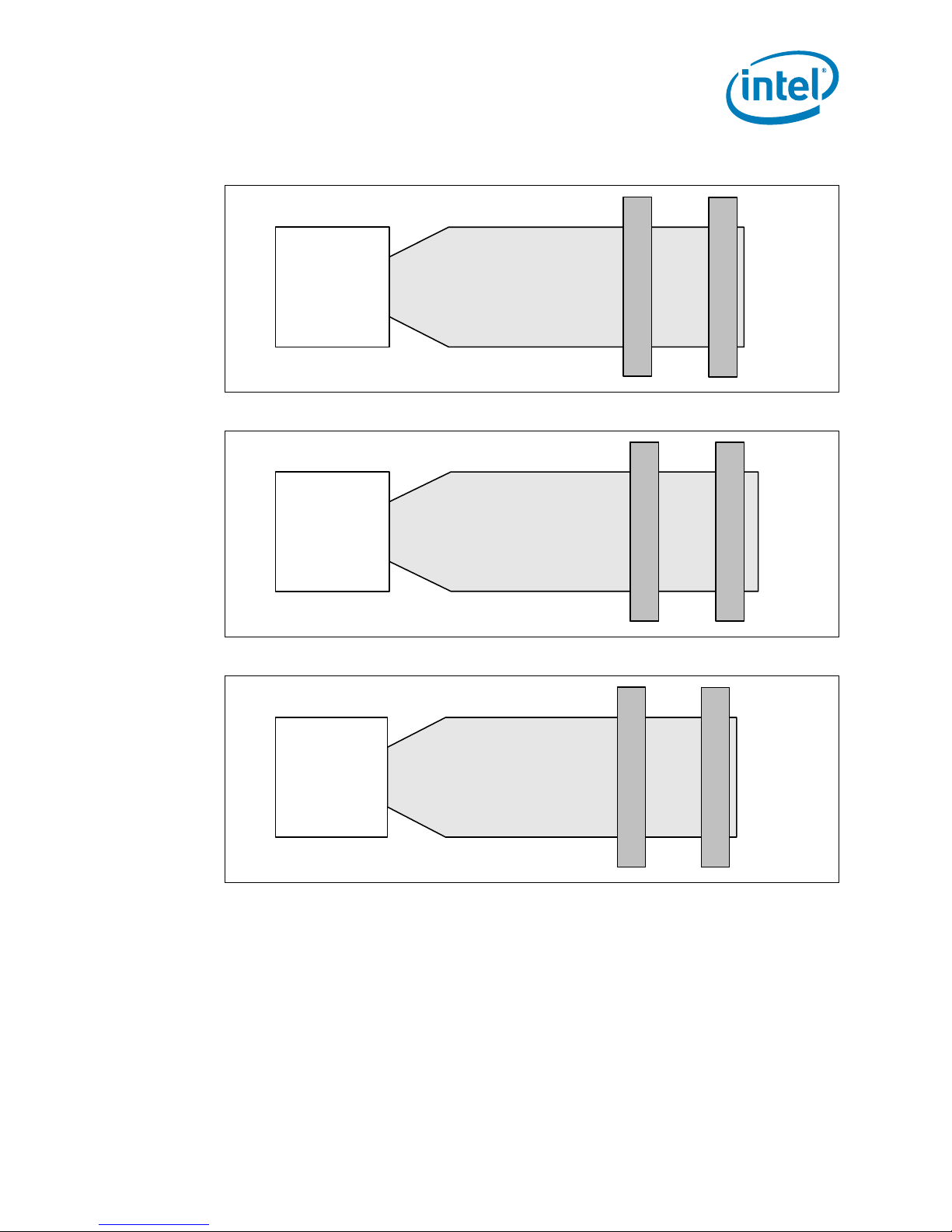
Product Description
Figure 3. Example of Single-Rank DIMM Population
Single Rank DIMM 2
Intel® 3100
Chipset
Figure 4. Example of Single-Rank and Dual-Rank DIMM Mixing Population
Single Rank DIMM 2
Intel® 3100
Chipset
Figure 5. Example of Dual-Rank DIMM Population
Single Rank DIMM 3
Dual Rank DIMM 3
Dual Rank DIMM 2
Intel® 3100
Chipset
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 13
Dual Rank DIMM 3
Page 14
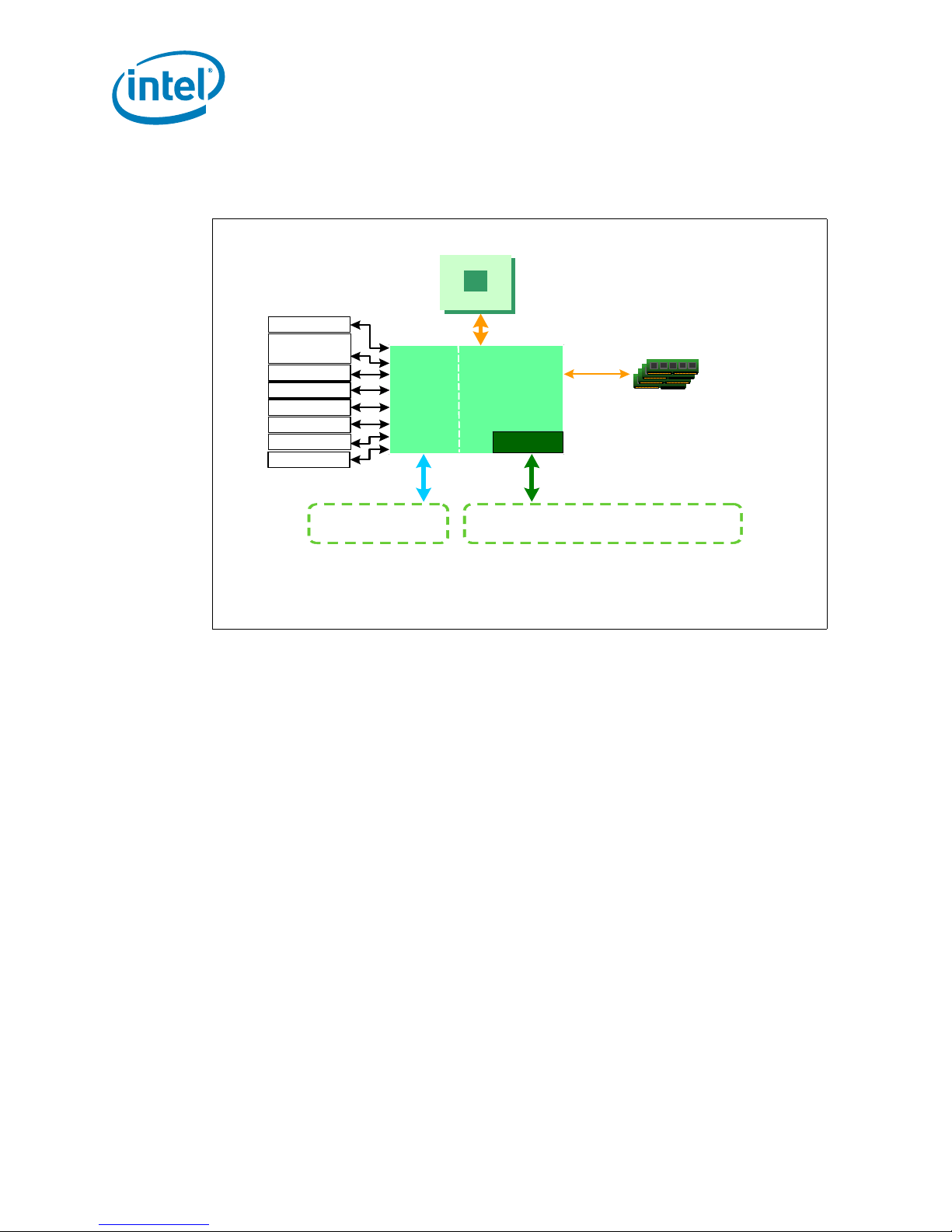
1.4 Intel® 3100 Chipset
Product Description
Figure 6. Inte l
®
3100 Chipset Block Diagram
Processor
WDT
Serial ATA
6 Drives
SM Bus x2
PCI 32/33
2 UART
4 USB-2 .0
38 GPIOs
LPC
Intel®3100 Chipset
IICH IMCH
Port B
PCI Express*
1x4 or 4x1
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
FSB
Single-Me m ory
Channel
EDMA
Port A
PCI Exp ress*
1x8 configurable as 2x4 or 2x1
Registered ECC
DDR2 400
B5990-01
1.4.1 On-Board Peripherals
Super I/O and PCI Video are included as on-board peripherals.
1.4.1.1 Super I/O
Super I/O includes a Low Pin Count (LPC) driven Super I/O device that can be disabled
by removing a resistor.
1.4.1.2 PCI Video
An ATI Rage* Mobility-M integrated video controller is located on the 32-bit, 33 MHz
PCI bus. Figure 7, “PCI On-Board Video Chip” on page 15 is a picture of the on board
chip.
User’s Manual June 2007
14 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 15
Product Description
Figure 7. PCI On-Board Video Chip
1.4.2 On-Board I/O
The following sections include all of the on-board I/O.
1.4.2.1 Serial ATA (SATA)
The CRB provides a total of six SATA interface connectors.
• Four usable SATA connectors in a SATA mode (BIOS setting) (SATA 0-3)
• Six SATA ports available in an AHCI mode (BIOS setting) (SATA 0-5)
• There are no RAID Capabilities on the chipset. Of course SW RAID is always and
option.
1.4.2.2 Serial Connector
The CRB has one 10-pin, dual-row header.
• Provides the COM3 port from the Super I/O
1.4.2.3 Floppy Drive
The CRB supplies a 34-pin, dual-row header.
• Floppy drive support comes from Super I/O
• The BIOS setup program configures the floppy drive interface
Figure 8. Floppy Drive Connector
1.4.2.4 LPC Debug Port
The CRB includes one 60-pin card edge connector for LPC.
• Aligned with PCI connector (used for Intel Validation Only)
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 15
Page 16

1.4.2.5 Front Panel Control Pins
1
The CRB includes a 10-pin, dual-row header.
• Provides Power Switch pins
• Provides Reset Switch pins
• Provides LED Power-On pins
• Provides LED HD Status pins
Figure 9. Front Panel Header
Product Description
Front Panel Heade r
1.4.2.6 XDP Connector
The CRB includes one 60-pin XDP connector. XDP stands for Extended Debug Port and
can be used for debugging and testing components of the board.
Figure 10. XDP Connector
B5786- 0
User’s Manual June 2007
16 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 17

Product Description
1.4.2.7 USB
The CRB has a 10-pin, dual-row header to route two USB Ports to an external USB
connector.
• Allows two USB 1.1 or 2.0 ports to be routed to the dual-stack rear I/O or
optionally to the 10-pin header from the internal I/O. These USB ports are Port 2
and Port 3. Rear panel ports 2 and 3 are not simultaneously functional.
• By default, routing for USB is to the dual-stack header on the rear panel I/O.
• In conjunction with the rear panel USB Ports there are only a total of four USB
ports.
More information is available in Section 1.4.4.3, “USB Ports” on page 18.
1.4.3 I/O Slots for Expansion Capabilities
1.4.3.1 PCI Express*
The CRB provides a total of 3 x4 PCI Express* ports.
• Port A provides two x4 connections through two x8 connectors
• Port B provides one x4 connection through one x8 connector
• 32-bit ECRC (Port A only) stays with packet ensuring correct data at destination
• 256 opportunistic combining for read completions to improve performance
• ONLY Port A provides posted writes between each x4 port
• ONLY Port A provides memory-to-I/O DMA
Note: The PCI Express* Ports are x8 connectors, but ONLY have the functionality of a x4
connector. This enables you to use a x8 card on the CRB but it has the bandwidth and
functionality of the x4.
Warning: Hot-Plug is NOT supported on this platform.
1.4.3.2 PCI
The CRB provides one PCI slot. It has the following characteristics:
• Specification 2.2 compliant
• 32-bit
• 33 MHz
• 12 0 MB / s th ro ughput
• 64-bit addressing through the DAC protocol
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 17
Page 18

1.4.4 Rear Pane l I/O Connect or s
Figure 11. Rear Pane l I/O Connectors
1.4.4.1 Serial COM ports
The CRB provides two Serial COM Ports.
• 9-pin male D-sub connectors
• COM1 port (closest to PS/2 ports on left, when looking at the back panel) and
COM2 port (closest to the USB ports)
1.4.4.2 PS2 Mouse and Key board Connectors
Product Description
The CRB has two stacked circular DIN PS2 connectors. Turn off power before a
keyboard or mouse is connected or disconnected.
• One for the keyboard (bottom)
• One for the mouse (top)
1.4.4.3 USB Ports
The rear panel provides two dual-stacked USB 2.0 ports. They cannot be run in both
modes simultaneously. Internal logic determines which interface is used.
• Total of four USB 2.0 ports
•Two USB modes
—UHCI
—EHCI
• Two Univers al Hos t Contr olle r Interf ac es (US B 1.1 )
— Two ports for each controller
— Accessible by I/O space
— Running voltage requirement: 3.3V
• One Enhanced Host Controller Interface (USB 2.0)
— Four ports
— Accessible by memory space
— Running voltage requirement: 400mV
User’s Manual June 2007
18 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 19

Product Description
1.4.4.4 Parallel Port
The CRB provides one parallel port on the rear panel. The Parallel Port can be viewed in
Figure 11, “Rear Panel I/O Connectors” on page 18
• 25-pin female D-sub connector (above COM ports)
1.4.4.5 VGA Port
The CRB provides one VGA connector for on-board video.
• 15-pin male D-sub connector
• On-board ATI RAGE Mobility PCI video
• If no “on-board Video”, a PCI video card is supplied with kit
1.4.5 Hardware Server Management Features
The CRB provides several server management features like a voltage monitor and
temperature monitor. It also provides control for overall protection of the platform.
1.4.5.1 Voltage Monitor
The CRB uses a Heceta* 7 (LM93) to monitor and communicate through the SMBus.
1.4.5.2 Watch Dog Timer (WDT)
The Watch Dog Timer (WDT) provides output from the Intel® 3100 Chipset t o generate
one of the following:
•PCI_RESET
• Illuminate an LED
1.4.5.3 Sleep States and Soft Off
• S0, S3 and S5 sleep states
• Soft off capability (S5)
— Operating system dependent
— Requires a complete OS boot when the system wakes
1.4.5.4 Wake Events
• Power switch
1.4.5.5 Hardware Clock Throttling
• Provides support for hardware clock throttling through STOPCLK#
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 19
Page 20

1.4.5.6 Fan Power Connection
• Direct +12 V DC power connectors
• One processor fan connector (CPUFAN)
®
• One fan for Intel
3100 Chipset (Fan1)
• Two auxiliary fan connectors (AUXFAN)
1.4.5.7 On Board Switches
The CRB has the following momentary push button switches to provide state control:
•Power
• Reset
• Wake (this button is not functional)
• Port 80/81
1.4.5.8 Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a component of the platform that is specifically
designed to enhance platform security above and beyond the capabilities of today’s
software. It provides protected space for key operations and other security critical
tasks. Using both hardware and software, the TPM protects encryption and signature
keys at their most vulnerable stages of operation, for instance, when the keys are
bein g use d in an unencrypt ed p la i n te x t fo rm . T he T PM i s s pe c if i ca l ly d e si g ned to shield
unencrypted keys and platform authentication information from software-based
attacks.
Product Description
1.5 Supported Operating Systems
The CRB is validated with the following operating systems:
•DOS
— BIOS supports the installation and booting of the DOS* 6.22 operating system
•Linux*
— BIOS supports the installation and booting of both Red Hat Enterprise Linux*
Version 3 and 4 and Linux Monta Vista Pro* and Monta Vista Carrier*.
•QNX*
• Microsoft Windows XP*
• Microsoft Embedded XP*
• Microsoft Windows Vista* (once available)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003*
•Free BSD
Note: Operating systems are to be purchased by the customer and are not distributed with
this development kit.
User’s Manual June 2007
20 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 21

Product Description
1.6 Supported BIOS Features
The BIOS has an AMI* core with the following components:
Table 6. Supported BIOS Features
Name of BIOS component Description
PCI 2.3 The BIOS is PCI 2.3 compliant.
SCSI boot The BIOS supports booting from a plug in SCSI device, if present.
LAN boot The BIOS supports booting from a plug in Ethernet device, if present.
Fiber-channel boot The BIOS supports booting from a plug in fiber-channel device, if present.
Serial ATA boot The BIOS supports booting from a Serial ATA hard drive.
CD-ROM boot The BIOS supports booting from a Serial ATA CD-ROM.
USB boot The BIOS supports booting from a USB boot device.
Floppy boot The BIOS supports booting from a floppy drive
PXH
PCI Express*
USB The BIOS supports the USB 1.1 and USB 2.0 interfaces.
CMOS Header The BIOS supports recognizing the clear CMOS header.
ECC support The BIOS detects and supports ECC memory.
Watchdog Timer (WDT) The BIOS provides watch dog timer support.
APIC and ACPI Control
Patch Update Mechanism
FSB Error Handling Control The BIOS has the capability to enable and/or disable FSB error handling.
The BIOS initializes and supports a PXH riser card if it is plugged into a PCI-E* slot
on the CRB.
The BIOS initializes and supports PCI Express* cards that are plugged into the
CRB.
The ability to enable and disable APIC and ACPI is present in the BIOS. Control is
also required for OS plug and play features. The BIOS supports the following ACPI
states:
•G0(S0) – Working
• G1(S3) – Sleeping [Suspend to RAM]
• G2(S5) – Soft Off
The BIOS supports C0, C1, C1E and C2 states.
The Patch Update Mechanism is used to upgrade and/or install micro-code
patches into BIOS is supported.
1.6.1 ACPI
ACPI gives the OS direct control over the power management and plug-and-play
functions of the platform. The use of ACPI with this CRB requires an OS that provides
full ACPI supp ort .
Table 7. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch (Sheet 1 of 2)
If the System is in this state...
Off
(ACPI G2/G5 - soft off)
On
(ACPI G0 - workin g state)
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 21
...and the power switch is
pressed for
Less than four second
Less than four seconds
...the system enters this
Power-on
(ACPI G0 - working state)
Soft-off/Standby
(ACPI G1 - sleeping stat e)
state
Page 22

Table 7. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch (Sheet 2 of 2)
Product Description
If the System is in this state...
On
(ACPI G0 - working state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 - sleeping state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 - sleeping state)
...and the power switch is
pressed for
More than four seconds
Less than four seconds
More than four seconds
1.6.1.1 System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the OS directs all system and device power state transitions by managing
devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and knowledge of
how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can be
turned off. The OS uses information from applications and user settings to put the
system as a whole into a low-power state.
1.7 Power Supply
The platform may not come with a power supply. If one is not provided please use a
standard off-the-shelf ATX12V power supply with a power rating of 450 W. (Customer
may use a smaller power supply as this is more power than necessary. This CRB total
system power is typically running at less then 100 W.)
1.8 Thermal and Mechanical Component s
...the system enters this
Fail Safe Power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 - soft off)
Wake-up
(ACPI G0 - working state)
Power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 - soft off)
state
Table 8. Thermal and Mechanical Components
Name Description
Standard Processor Th ermal Solutio n
Mounting
Processor Fan
®
Intel
3100 Ch ipset Heatsink
Active Intel
Power Measu rement
Fan Headers The CRB provides three fan headers.
Solder Down Anchors
Iso-chiller Attachment
®
3100 Chipset Heatsink
The CRB supports full power processor thermal solution mounting
provisions as deleanated in the processor thermal design guide.
The CRB provides a fan header for the processor that includes 12 V
with tachometer.
The CRB supports the Intel
requirements.
The CRB provides mounting provisions and a fan header for an active
®
Intel
3100 Chipset thermal solution.
The CRB provides a means for power measurement for the following
components:
• Processor
®
•Intel
•DDR2
The CRB provides solder down anchors for the Intel
The Intel
The iso-chiller attachment for the processor uses the iso-chiller kit
and should be mounted using the standard heatsink mounting holes.
The Intel
heatsink mounting holes for attachment.
®
®
®
3100 Chipset hea tsink mounting
3100 Chip se t
®
3100 Chipset includes active heatsink mounting holes.
3100 Chipset uses the iso-chiller kit and has active
3100 Chip set.
User’s Manual June 2007
22 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 23

Product Description
1.8.1 Heatsinks
There are both passive and active heatsink designs.
1.8.1.1 Active Heatsinks
Active heat si nk s (Figure 12 and Figure 13) u se po we r an d a r e po w e red b y th e p la tf o rm .
Figure 12. I nt el
®
3100 Chip set Active Heatsink
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 23
Page 24

Figure 13. Processor Active Heatsink
Product Description
User’s Manual June 2007
24 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 25

Product Description
1.8.1.2 Passive Heatsinks
Passive heatsinks (Figure 14) require no power and can replace active heatsinks in
appropriate environments. We are only exemplifying a passive Heatsink for the chipset,
as there are multiple passive heatsink designs for the Processor that can be used
(provided appropriate airflow) and are described in the Thermal Design Guide in which
your Intel representative can provide to you.
Figure 14. I nt el
®
3100 Chipset Passive Heatsink Design
1.9 Physical and Mechanical Board Specifications
1.9.1 Mounting Holes
The CRB provides non-p lated mounting holes with top and bottom ground rings in
locations that correlate with the ATX 2.3 specification. The size of the CRB is
approxima tely 10. 75 inch es long by 12 inch es wi de.
1.10 Debug Ports
The CRB provides an XDP header that can be used to debug the processor and the
®
Intel
3100 Chipset.
1.11 Real T ime Clock (RTC), CMOS SRAM, and Battery
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real time clock (RTC) and CMOS memory. The
battery has an estimated life of three years when it is not plugged in to a wall socket.
When the platform is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends
the life of the battery. The clock is accura te to ± 13 minutes/yea r at 25º C with 3.3 VSB
applied.
Note: If the battery and AC power fail, at boot-up the system will prompt you to either load
optimized defaults or enter BIOS and manually adjust your BIOS settings.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 25
Page 26

Platform Setup
2.0 Platform Setup
Note: Before connecting power make sure that the CRB (Customer Reference Board) is either
mounted in a chassis or is on a non-conductive surface to prevent grounding. Ensure a
safe work environment. Make sure you are in a static-free environment. Before
removing any components from their anti-static packaging. The evaluation board is
susceptible to electrostatic discharge, which may cause product failure or unpredictable
operation.
Caution: Connecting the wrong cable or reversing a cable may damage the evaluation board and
may damage the device being connected. Since the board is not in a protective chassis,
use caution when connecting cables to this product.
2.1 Connecting the Wires
Note: When you receive the CRB, all jumpers are correctly set and it is ready to boot.
User’s Manual June 2007
26 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 27

Platform Setup
2.1.1 Connect SATA cables
1. Ther e are six SATA (Serial ATA Figure 15) connectors on the CRB. Connect the
cables to the appropriate drive sequentially starting from connector Port SATA 0
P
Figure 15. SAT A Ports
through connector Port SATA 5. These connectors are located in coordinate E4.
Note: Intel recommends that your boot drive be connected to SATA Port 0.
2.1.2 Plugging In Memory
Note: Refer to section Section 1.3 for memory specific information refer to Figure 16 for
DIMM location while reading below steps.
1. Beginning with DIMM 3, (the DIMM connector closest to the edge of the CRB,
furthest from Intel
that the end clips are moved outward to the open position.
2. Gently push the DIMM into the socket until you hear or feel the side clips lock into
the side of the DIMMs.
Note: Continue adding memory to the system sequentially starting from DIMM 3 to DIMM 2.
®
3100 Chipset) line up the DIMM with the slot and make sure
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 27
Page 28

Figure 16. DIMM Sockets
2.1.3 Connecting the Processor
Figure 17 shows an empty processor socket.
Figure 17. Processor Socket
Platform Setup
1. For Pin Grid Array (PGA) sockets, look at the bottom of the processor to locate
which corner of the processor does not have a PIN in it.
2. Figure 17 shows the pin missing on the PGA479M socket.
3. In order to insert the processor i nto the socket, line up the corner that does not
have a pin and insert the processor into the socket.
Note: Do NOT force the pins of the processor into the socket, as it may cause damage to the
processor. Insertion of the processor should be smooth and gentle, when aligned
correctly.
4. Hold down the processor with your finger and use a small flat head screw driver to
turn the locking screw clockwise 180 degrees, to the locked position. Next to the
sides of the screw on the socket, there are diagrams of a closed lock and an open
lock indicating if the socket is locked or unlocked.
2.1.4 Connecting Heatsinks and Fans
1. The active heatsink for Intel® 3100 Chipset should already be connected to the
CRB. If this is not the case, plug the fan connector into the “FAN1” connector
located in the coordinate F7.
2. Connect the active CoolerMaster* heatsink to the processor and then plug the fan
into “CPUFan”.
User’s Manual June 2007
28 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 29

Platform Setup
a. Mount the self-adhes ive squ ar e metal bracket (Figure 18, found in the
CoolerMaster* box) on the bottom of the CRB underneath the processor. This
brack et lines up with the four holes mak in g a squa re arou nd the pro ce ssor and
provides the nut for the fan screws to plug into.
Note: If there is more than one bracket provided in the CoolerMaster* box, use the bracket
with the appropr iate length nut th reads. The se brac kets correl ate with the he ight of the
processor in the socket. Figure 19 shows how the bracket mounts to the bottom of the
CRB.
Figure 18. Processo r Fa n M oun ting B racket
b. Place the fan on top of the processor and screw it into the bracket as shown in
Figure 19.
Figure 19. Screwing the Processor Fan into the Mounting Bracket
c. Plug the fan connector into the motherboa rd. Thi s connect or is in coord inate H8
and label ed “CP UFAN” . A ny o the r f an s that y ou wi sh to u se c an be c onne ct ed t o
“AUX FAN 0” and/or “AUX FAN 1”. These are located next to “CPUFAN”. These
connect o rs ar e sh o wn in Figure 20.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 29
Page 30

Figure 20. Fan Power Connectors
2.2 Connecting Other Peripherals
2.2.1 Add-in Connect or s
1. Connect your PCI Express* add-in cards into the appropriate Port A or Port B x4
PCI Express* slot (Figure 21).
Platform Setup
Note: The PCI Express* connectors on this CRB are x8 connectors, but only utilize a x4
configuration.
2. Connect your PCI Cards into the PCI 32/33 slot. The connector is the white
connector on the CRB located in coordinates 1B through 1E.
User’s Manual June 2007
30 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 31
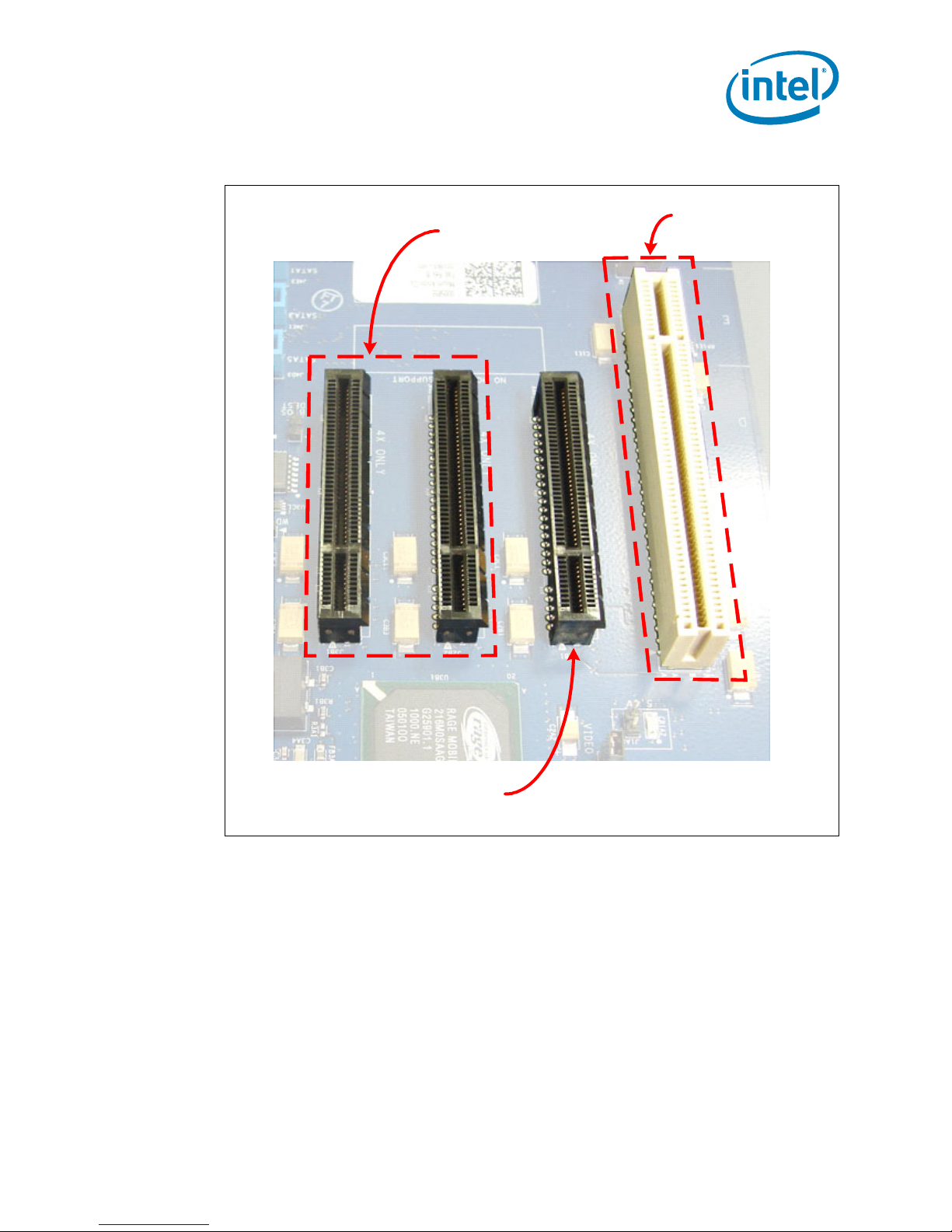
Platform Setup
1
Figure 21. PCI Express* Connectors
PCI 32/33
PCI-E Port A
2.2.2 Rear Panel Connectors
1. Connect a USB or PS/2* keyboard and/or mouse to the back panel connectors are
shown in Section 1.4.4, “Rear Panel I/O Connectors” on page 18.
2. If you are using the on-board video, connect your monitor to the 15-pin VGA
connector.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 31
PCI-E Port B
B5791-0
Page 32

2.2.3 Connecting a Floppy Drive
Figure 22. Floppy Drive Connector
In order to conn ect a f lop py dr iv e, pl ug the cable in to the so cke t sh own in Figure 22 by
guiding the ke yed plu g into the key ed socket. C onnect the othe r end of this ca ble to the
floppy drive and providing it power from the power supply.
2.2.4 Changing and/or Updating the BIOS Chip
In order to change the BIOS chip (see Figure 23, “Firmware Hub” on page 32, which is
located in Section 2.2.4, “Changing and/or Updating the BIOS Chip” on page 32 and is
component called out as number 32) without damaging the pins use an EEPROM chip
removal tool. Remove the BIOS chip by inserting the pinchers of the tool in each open
corner of the socket, close the pinchers around the chip and pull the chip out carefully.
Use a BIOS burn-in tool to update the firmware, then reinsert the chip by aligning the
dot on the BIOS chip with the triangle on the socket and gently pressing the chip into
place.
Platform Setup
Figure 23. Firmware Hub
User’s Manual June 2007
32 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 33

Platform Setup
2.2.5 Changing the CMOS Battery and Clearing CMOS
2.2.5.1 Changing the battery
a. With the board shut down (power supply still in on position), remove the battery
and replace with a new battery. picture in Figure 24, “CMOS Battery” on
page 33.
Note: CMOS batteries rarely go bad, but a good indication that one is bad is that after
unpluggin g the sy s te m and plu ggi ng it in a ga in, you have to rest ore your BIO S set ti ng s
and system time. This will occur every time power is removed from the powers supply.
2.2.5.2 Clearing the CMOS
a. With System shutdown unplug the power supply and/or switched the Power
supply switch to the off position (no power to board).
b. Remove jumper J4C3, shown in Figure 25, “CMOS Clear Jumper” on page 33.
from pins 1 and 2 and place it on pins 2 and 3.
c. Leave the Jumper in place for approx ima tely a min ute
d. Remove the jumper from pins 2 and 3 and place it back on pins 1 and 2.
Tip: If the CMOS did not clear at this point, make sure power is removed from platform and
Figure 24. CMO S Bat t ery
Figure 25. CMOS Clear Jumper
leave the jumper on pins 2 and 3 for a longer duration to assure CMOS is cleared. The
board should bring up a setup prompt before booting to either go with defaults or enter
BIOS.
2.3 Connect Power
Note: Not all Kits come with a power supply, therefore please use a standard ATX Power
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 33
supply and connect as described below
Page 34

1. Remove the extra four-pin connector (shown connected to 20 pin connector in
1
Figu re 27 on page 34), if attached, by sliding it out of the groove that attaches it to
the main connector. This connector is NOT to be used. Intel recommends adding a
label to prevent use.
Figure 26. Power Connector
2
1
2
1
Platform Setup
1
1
11
11
10
10
20
20
44
33
B5790-0
Warning: The four-pin connector tied to the main ATX connector is not to be used! The colors of
the wires in this connector are one yellow, one black, one red and one orange. These
are different voltages then used on the CRB and will DAMAGE the CRB if used.
Figure 2 7. ATX Power Co nn ector
User’s Manual June 2007
34 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 35

Platform Setup
1
Figure 28. Power Conn ect or Ca bl es
This connector is
NOT
USED
This connector is
USED
B5792-0
2. Plug the main connector into the motherboard located in coordinate K3-4 making
sure that the plug clip lines up with the clip lock and the connector pins fit easily
into their appropriate slots.
Warning: Do NOT force the ATX power plug into the connector, it should go in easily when
plugged in correctly. Plugging it in incorrectly will result in severe DAMAGE to the CRB.
3. Plug the four-pin connector that has two yellow wires and two black wires into the
four-pin connector that is approximately 1 inch to the right of the main ATX power
connector in coordinate K5.
4. Plug in the power connectors from each of the hard drives and disc drives.
5. Plug th e powe r cab le i nto t h e ba ck of t he po we r supp l y le av in g t he sw i t ch in t he off
position (switch pushed down to the side with the “0” on it) and PLUG THE CORD
INTO THE WALL ONCE THE BOARD IS SETUP. You can also turn the power supply
switch to the on “1” position once the CRB is setup.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 35
Page 36

2.4 Turning On an d Re se tt i n g the B oar d
There are two momentary switches on the CRB located in C4. One switch is the power
on switch (labeled PWR “SW4C1”) and the other switch is reset (labeled RESET
“SW4C2”). These buttons are shown in Figure 29, “Power and Reset Buttons” on
page 36.
Figure 29. Power and Reset Bu tto ns
Platform Setup
Note: The power switch is also used to wake a system that is in a sleep state.
Note: Refer to section Secti on 3.6.2.3, “Front Panel Connector ” on page 41 for information
on setup case switches and LEDs.
User’s Manual June 2007
36 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 37

Technical Reference
3.0 Technical Reference
3.1 Memory Resources
Deta il e d me m o ry i n f or m at i on for addr e ss ab l e me mory and me mo r y ma p s can be fou nd
in the Intel
®
3100 Chipset E xternal Design Specification.
3.2 DMA Channels
The DMA Channels below specify Partial DMA channels that are routed to specific
devices as well as other channels that are available.
Table 9. DMA Channels
Data Channel Data Width System Resource
08 Open
1 8 Paralle l Por t
2 8 Diskette Drive
3 8 Parallel Port (for ECP or EPP)
4 8 or 16 bits DMA Controller
516 bits Open
616 bits Open
716 bits Open
3.3 Fixed I/O Map
Refer to the Intel® 3100 Chipset External Design Specification for this information.
3.4 Interrupts
Interrupts can be routed through the I/O xAPIC and supports a total of 24 interrupts.
The I/O xAPIC is supported by Microsoft Windows XP*. Table 10 on page 38 provides
the interrupts and there correlating functions.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 37
Page 38

Table 10. I/O x APIC Interrupts
IRQ System Resource
NMI I/O channel check
0 Reserved, interval timer
1 Reserved, keyboard buffer full
2 Reserved, cascade input from slave PIC
3 User available
4COM1
5 User available
6Diskette drive
7LPT1
8Real-time clock
9 User available
10 User ava ilable
11 User ava ilable
12 On-board mouse port (if present, else available)
13 Reserved, math coprocessor
14 Primary Serial ATA
15 Secondary Serial ATA
16 User available (through PIRQA)
17 User available (through PIRQB)
18 User available (through PIRQC)
19 User available (through PIRQD)
20 User available (through PIRQE)
21 User available (through PIRQF)
22 User availab le (thr ough PIRQ G)
23 User available (through PIRQH)
Notes:
1. Default but can be changed to another IRQ.
2. Available in APIC mode only.
1
1
Technical Reference
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
3.5 PCI Conventional Interrupt Routing Map
This section describes interrupt sharing and how the interrupt signals are connected
between the PCI Conventional bus connectors and on-board PCI Conventional devices.
The PCI Conventional specification describes how interrupts can be shared between
devices attached to the PCI Conventional bus. In most cases, the small amount of
latency added by interrupt sharing does not affect the operation or throughput of the
devices. In some special cases where maximum performance is needed from a device,
a PCI Conventional device should not share an interrupt with other PCI Conventional
devices. Use the following information to avoid sharing an interrupt with a PCI
Conventional add -in card.
User’s Manual June 2007
38 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 39

Technical Reference
Table 11. PCI Interrupt Ro uting Map P C I Interrupt Source
Intel® 3100 Chipset PIRQ Signal Name
PIRQA# PIRQB# PIRQC# PIRQD#
PCI bus connector 1 INTA INTB INTC INTD
3.6 Connectors
Warning: Only the following connectors have over-current protection: back panel USB, front
panel USB, and PS/2* connector.
The other internal connectors are not over-current protected and should connect only
to devices inside the computer’s chassis, such as fans and internal peripherals. Do not
use these connec tors to powe r devices e xternal to th e computer’ s cha ssis. A fau lt in the
load presented by the external devices can damage the computer , the power cable, and
the external devices. This section describes the connectors. The connectors can be
divided into these groups:
•Back panel connectors
• Component side connectors
3.6.1 Back Panel Conn ec t o rs
Figure 30 shows the location of the back panel connectors for the CRB.
Figure 30. B a ck Pane l Conn ec tors
Parallel Port
Mouse
Keyboard
Serial com
Port 1
Table 12. Front Chassi s Fan and Rear Chassis Fan Connecto rs
Pin Connector
1 Control
2+12 V
3Tach
Serial com
Port 2
USB Ports (2)
3 = Top
2 = Bottom
USB Ports (2)
0 = Top
1 = Bottom
15-pin VGA on-
Board Video
B5787-01
3.6.2 Component Side Connectors
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 39
Page 40

3.6.2.1 Power Supply Connectors
1
1
1
3
The CRB has two power supply connectors. The main power connector and the SATA
power connector.
• Main power is supplied through a 2 x10 connector. The CRB requires a standard
ATX12V power supply.
Figure 3 1. ATX Power Co nn ector
Technical Reference
2
1
2
1
1
1
11
11
Table 13. Main Power Connector Pin
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +3.3 V 11 3.3 V
2 +3.3 V 12 -12 V
3 Ground 13 Ground
4 +5 V 14 PS-ON
5 Ground 15 Ground
6 +5 V 16 Ground
7 Ground 17 Ground
8 PWRGD (Power Good) 18 -5 V
9 +5 V (Standby) 19 +5 V
10 +12 V 20 +5 V
• The SATA power connector uses a 2 x2 connector.
Figure 32. SATA Power Connector
10
10
20
20
44
33
B5790-0
User’s Manual June 2007
40 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
2
4
B5988-0
Page 41

Technical Reference
1
1
3
5
7
9
Table 14. S ATA Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1GND312 V
2GND412 V
3.6.2.2 Add-in Card Connectors
The CRB has the following add-in card connectors:
• 2 x4 PCI Express* slots which are Port A
• 1 x4 PCI Express* slot which is Port B
• 1 32-bit PCI slot
Table 15. Auxiliary Front Panel Powe r and Rese t Co nne cto r Pin
Pin Signal Name In/Out Description
1 HDR_BLNK_GRN Out Front panel green LED
2 Not connected
3 HDR_BLNK_YEL Out F ro nt panel yellow LED
3.6.2.3 Front Panel Connector
This section describes the functions of the front panel connector. Table 16 lists the
signal names of the front panel connector. Figure 33 is a connection diagram for the
front panel connector.
Figure 33 . Front Panel Connect or
Tabl e 16. Front Pane l Connector
Pin Signal Name In/Output Description
1 HD_ACT_LED_P OUT Power side of hard drive activity LED
2 HD_ACT_LED_N OUT Ground side of hard drive activating LED
3 FRNTPNL_PWR_LED POWER OUT Power side of power o n L ED
4 FRNTPNL_P W R_LED Ground OUT Ground
5 Power Button pin (1) Power B utton Pin
6 FP_PWR_BTN_N (2) Power Button Pin 2
2
4
6
8
B5987-0
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 41
Page 42

Table 16. Front Panel Connector
7 FP_RST_BTN_N IN Pin (1) for Reset Button
8 Reset Grou nd pin out Pin(2) for reset Bu tton
9Ground Ground
Technical Reference
User’s Manual June 2007
42 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 43
Technical Reference
3.7 Jumper Block
Warning: Do not move jumpers when the power is on. Always turn off the power and unplug the
power cord from the computer before changing a jumper setting. Otherwise, the CRB
will be damaged.
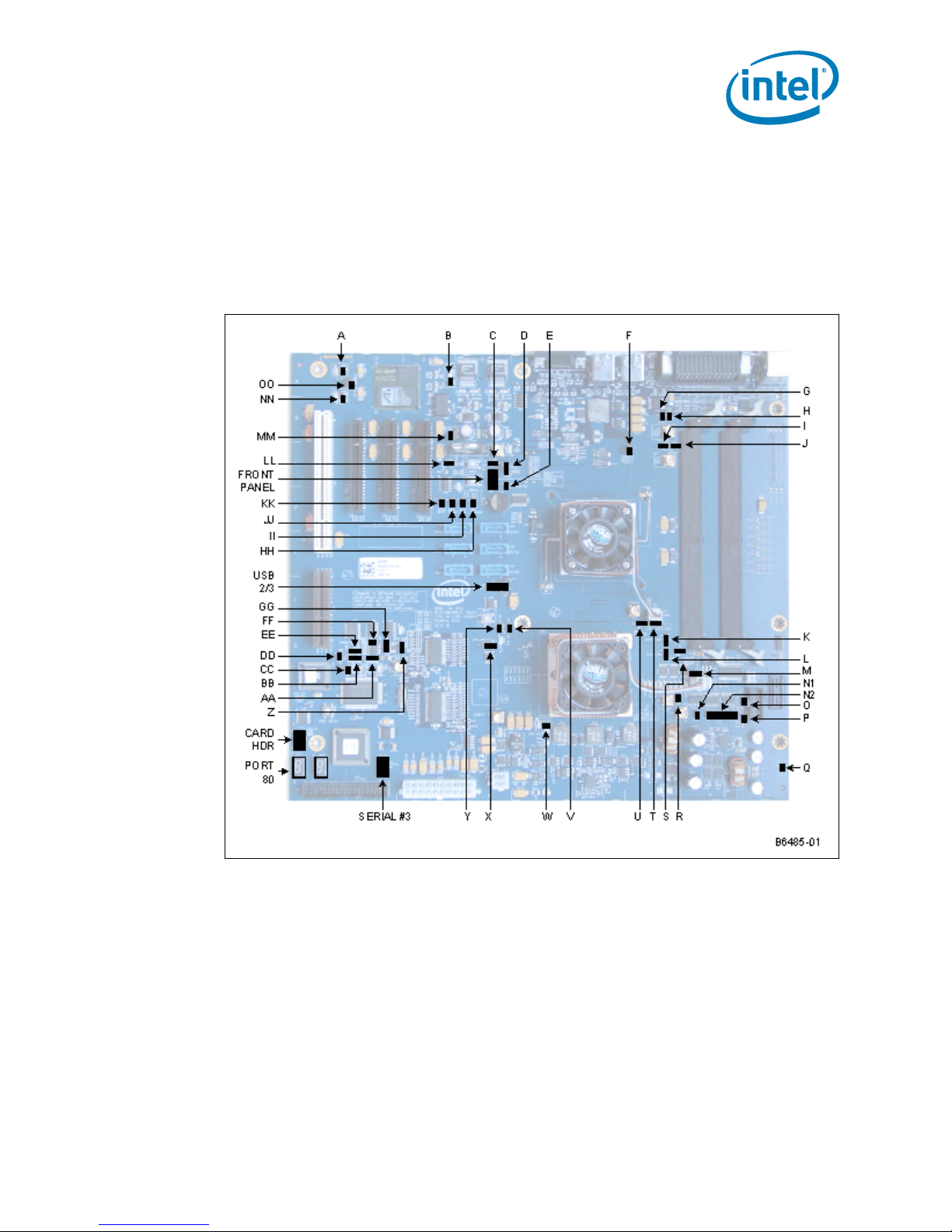
Figure 34 shows the l ocati on of t he jum per bl ock s. Figure 17, “Jumper Block Locations”
on page 44 describes the jumper settings for the platform.
Figure 34. Jumper Bloc k Loca ti on s and Pin Connec t or s
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 43
Page 44

Table 17. Jumper Block Locations (Sheet 1 of 3)
Technical Reference
Location Jumper/Header Name Ref Des Description
A 3.3 V Header J1A1
B 5.0 V Standby Header J3A1
C1.5 V HeaderJ4C2
1: Grou nd
2: 3.3 V
1: Grou nd
2: 5.0 V Stand by
1: 1.5 V
2: Grou nd
Clears CMOS
D CMOS Clear Jumper J4C3
1-2: Nor mal
2-3: Clear
®
3100 Chipset internal
E
F
Intel
1.5 VR enable
®
3100 Ch ipset BSEL
Intel
Jumper
J4C5
J7C4
G Test Mode Jumper J7B1
H
I
J
K
Software Co nfiguration Port
Address Jumper
®
3100 Chipset DDR V
Intel
Header (validation Only)
DDR DIM M Vref Header
(validation Only)
®
3100 Chipset Thermal
Intel
Diode Header
REF
J7B2
J7C1
J7C2
J7G3
1-2: Disable Intel
Open: Enable Intel
Access to DDR_DIMM_VREF
Access to Intel
®
3100 Chipset 1.5 V VR
®
3100 Chipset 1.5 V VR
1-2: 133 MH z
Open: 167 MHz
1-2: Test Mode
Open: Normal
1-2: 0x2E / 0x2F
Open: 0x4E / 0x4F
Access to DDR V
1: DDR_MICH_VREF
2: Grou nd
1: DDR_DIMM_VREF
2: Grou nd
®
3100 Chipset Thermal Diode
1: MICH_THRM_DC
2: MICH_T HR M _D A
3: Grou nd
Access to CPU Thermal Diode
L
Processor Thermal Diode
Header
J7G4
1: CPU_T HRM_DC
2: CPU_TH RM _DA
3: Grou nd
M Processor Fan Override Jumper J8H1
1-2: Full Speed
Open: Heceta* Controlled
Manual VID Select
N1 CPU0 VID Override Jumper J8J1
1-2: Manual Select
Open: CPU Select
REF
Default
Position
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
1-2
Open
1-2
Open
Open
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
1-2
Open
N2
CPU0 V ID Jumper
Short = 0; Open = 1
User’s Manual June 2007
44 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
J8J4
VID[0] = 1-2
VID[1] = 3-4
VID[2] = 5-6
VID[3] = 7-8
VID[4] = 9-1 0
VID[ 5] = 11-12
VID[ 6] = 13-14
Open
Page 45

Technical Reference
Table 17. Jumper Block Locations (Sheet 2 of 3)
Location Jumper/Header Name Ref Des Description
Inject CPU BPM3 Signal
O Processor BPM3 Inject Header J9H4
1: CPU_BPM0 input (apply 3.3 V here)
2: Ground
Inject CPU BPM0 Signal
P Processor BPM0 Inject Header J9J1
1: CPU_BPM0 input (apply 3.3 V here)
2: Ground
Q VCC1.8 J9K1
1.1.8 V
2.Ground
Access to CPU_GTLREF
R CPU_GTLREF Header J7H2
1: Ground
2: CPU_GT LR E F
S CPU Processor Hot Jumper J8G1
®
3100 Ch ipset Fan
T
U
Intel
Override Jumper
®
3100 Chipset FSB Vref
Intel
Header (validation Only)
J7G2
J7G1
1-2: Test Mode
Open: Normal
1-2: Full Speed
Open: Heceta* Controlled
Access to FSB_VREF
1: FSB_ VREF
2: Ground
Inject IMCH_STPCLK_N Signal
VStop Clock Inject HeaderJ4G3
1: IMCH_STPCLK_N input (apply 3.3 V here)
2: Ground
WCPU V
Header J5J1
CC
1: Ground
2: CPU_VCC
Default
Position
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
1-2
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
X
FSB Clock Frequency Override
(Host Clock Jumper)
J4G2
Y1.05 V HeaderJ4G1
Z IMCH SMBUS Segment Header J2G3
AA DIMM SMBUS Segment J2G7
BB VSBY SMBUS Segment Header J2G6
CC
FWH VPP Jumper (validation
Only)
J2H2
DD Top Block Lock Jumper J1G1
2-3: 133 MHz
Open: 167 MHz
1: Ground
2: 1.05 V
SMBUS Access Header
1: SMB_DATA
2: GND
3: SMB_CL K
SMBUS Access Header
1: SMB_DATA
2: GND
3: SMB_CL K
SMBUS Access Header
1: SMB_DATA
2: GND
3: SMB_CL K
1-2: Normal
Open: N/A
1-2: FW H Top Block Lock
Open: Normal
2-3
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
1-2
Open
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 45
Page 46

Table 17. Jumper Block Locations (Sheet 3 of 3)
Technical Reference
Location Jumper/Header Name Ref Des Description
SMBUS Access Header
EE PCI SMBUS Segment Header J2G5
FF Write Protect Jumpe r J2G1
GG
HH No Reboot Jumper J4D2
II Wake Event Header J4D1
JJ Top Swap Jumper J3D2
KK BIOS Destination Jumper J3D1
LL
MM Intruder Detect Header J3B2
NN 5.0 V Header J1A2
OO Enable Video Jumper J2A1
Board EEPROM SMBUS
Segment
Watch Dog Timer (WDT) Board
Reset
J2G4
J3C1
1-2: WDT Triggers Board Reset
Optional Intruder Switch Header
1: SMB_ DATA
2: GND
3: SMB_CLK
1-2: Not Write Protected
Open: Write Protected
SMBUS Access Header
1: SMB_ DATA
2: GND
3: SMB_CLK
1-2: No Reboo t
Open: Normal
Wake Event Header
1: FP_SLP_HDR_N
2: Grou nd
1-2: A16 Top Swap
Open: Normal
1-2: Offset
Open: Normal
Open: WDT Triggers LED Only
1: MICH_IN T RU DER HDR_N
2: GND
1: Grou nd
2: 5.0 V
Enable on Board Video
1-2: Enable
Open: Disable
Default
Position
Open
Do not short
Open
Open
Do not short
Open
Open
Do not short
Open
Open
Open
Open
Do not short
Open
Do not short
1-2
3.8 Mechanical Considerations
3.8.1 Form Fac t or
The CRB is designed to fit into an ATX-form-factor chassis. Figure 35 illustrates the
mechanical form factor for the CRB. Dimensions are given in inches. The outer
dimensions are 10.75 inches by 12 inches, which means that the CRB is actually about
an inch longer in depth measuring from the back panel across. Location of the I/O
connectors and mounting holes correlate with the ATX specification.
User’s Manual June 2007
46 Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2
Page 47

Technical Reference
Figure 35. Form Factor
10.75”
PCI
Port
FWH
PCI Express*
Ports
SATA
Connectors
Power co nn ec tor s
Processor
12”
Back P ane l C onnectors
Intel® 3100
Chipset
DDR2 Memory
Dimms
3.9 Electrical Considerations
3.9.1 DC Loading
Table 18 lists the DC loading characteristics of the CRB. This data is based on a DC
analysis of all act ive com po nen ts wit h in the CRB tha t imp ac t its pow er deli ve ry
subsy stems. The an al ysis does not in cl ud e PC I ad d- i n ca r ds . Mi n i mu m values ass ume a
light load placed on the CRB that is similar to an environment with no applications
running and no USB current draw. Maximum values assume a load placed on the CRB
that is similar to a heavy gaming environment with a 500 mA current draw per USB
port. These calculations are not based on specific processor values or memory
configurations but are based on the minimum and maximum current draw possible
from the CRB’s power delivery subsystems to the processor, memory, and USB ports.
Refer to the datasheets for overall system power requirements of the add-in cards
(e.g., PCI). The selection of a power supply at the system level is dependent on the
system’s usage model and not necessarily tied to a particular processor.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 316639 - 00 2 47
Page 48

Table 18. DC Loading Characteristics Mode
Technical Reference
DC Power
+3.3 V +5 V +12 V -12 V +5 VSB
Minimum Loading 300 W 5 A 11 A 19 A 0 A
Maximum Loading 500 W 25 A 27 A 36 A 0.40 A
DC Current at:
0.34 A ( S0)
1.25 A ( S3)
0.34 A ( S0)
1.25 A ( S3)
3.9.2 Add-in Board Considerations
The CRB is designed to provide 2 A (average) of +5 V current for each add-in board.
There is a total of three x4 PCI Express* slots and one PCI 32/33 add-in board.
3.9.3 Fan Connector Current Capability
Warning: The processor fan must be connected to the processor fan connector, not to a chassis
fan connector. Connecting the processor fan to a chassis fan connector may result in
on-board component damage that will halt fan operation.
Table 19. Fan Connector Current Capability
Fan Connector Maximum Available Current
CPU Fan 3.0 A
Fan 1 3.0 A
Aux Fan 0 3.0 A
Aux Fan 1 3.0 A
3.9.4 Power Supply Considerations
Warning: The +5 V standby line for the power supply must be capable of providing adequate
+5 V standby current. Failure to do so can damage the power supply. The total amount
of standby current required depends on the wake devices supported and manufacturing
options.
The power supply must comply with the following recommendations found in the
indicated sections of the ATX form factor specification.
• The voltage relationship between 3.3 VDC and +5 VDC power rails
• The current capability of the +5 VSB line
• All timing parameters
• All voltage tolerances
3.10 Thermal Considerations
This CRB features a thermal protection circuit in the processor voltage regulator area.
This circuit protects the processor voltage regulator from overheating and damaging
the CRB. Please consult the specific processor datasheet for details about the thermal
runoff features supported by the processors paired with the Intel
triggering temperature level causes the processor to enter a throttling mode (slowing
down the processor if it exceeds its maximum operating temperature) and allow the
processor voltage regulator to cool down.
®
3100 Chipset. The
User’s Manual June 2007
48 Order Nu mb er: 316639-002
Page 49

Technical Reference
Note: Use a processor heatsink that provides omni-directional airflow (similar to the type
shown in Section 1.8.1.2) to maintain required airflow across the processor voltage
regulator area.
Note: When using BIOS Setup program options to increase processor voltage and frequency
above the supported ranges, the temperature in the processor voltage regulator area
rises. This area of the CRB requires increased airflow. Direct airflow over the processor
voltage regulator is crucial to preventing throttling and keeping the processor voltage
regulator area cool. This is particularly important when using liquid cooling.
Note: All responsibility for determining the adequacy of any thermal or system design
remains solely with the reader. Intel makes no warranties or representations that
merely following the instructions presented in this document results in a system with
adequate thermal performance.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mb er: 316639-002 49
Page 50

4.0 Overview of BIOS Features
4.1 Introduction
The BIOS is stored in the Firmware Hub (FWH) and can be updated using a BIOS flash
programming tool. The FWH contains the BIOS Setup program, Power On Self Test
(POST), the PCI auto-configuration utility, and plug-and-play support.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and a revision
code.
The BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the
CRB. The BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <DELETE> key after the
POST test and memory test begins and before the operating system begins to boot.
The menu bar is shown below.
Overview of BIOS Features
Figure 36. Menu Bar
<MAIN> - <ADVA NCED> - <PCIPnP> - <BOOT> - <SECURITY> - <CHIPSET>-<EXIT>
Table 20 lists the BIOS setup program menu features.
Table 20. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar
Main ADVANCED PCIPnP BOOT SECURITY CHIPSET EXIT
Displays
processor and
memory
configurations
Configures
advanced
features and
settings
Setup for
PCI and PCI
Express*
Table 21. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
BIOS Setup Program Function Key Description
< or > Selects a different menu screen (moves the cursor left or right)
^ or ν Selects an item (moves the cursor up or down)
Enter Executes command or selects the submenu
F9
F7 Discard changes
F8 Load fail safe defaults
F10 Save the current values and exits the BIOS setup program
ESC Exits the m enu
Load the optimal d efault configuration value s for the cur rent
menu
Selects boot
options and
configuration s
Sets
passwords
and security
features
Configures
different
major
components
Saves or
discard
changes to
setup
program
options
User’s Manual June 2007
50 Order Nu mb er: 316639-002
Page 51

Overview of BIOS Features
4.2 Resource Configuration
4.2.1 PCI Auto Co nfiguration
The BIOS automatically configures PCI devices. Currently on the CRB there is a 32/33
PCI add-in card socket. Auto configuration lets a user insert or remove PCI cards
without having to manually configure the system. When a user turns on the system
after adding a PCI card, the BIOS automatically configures interrupts, the I/O space,
and other system r esources. Any interrupts set to AVAILABLE in Setup are considered
to be available for use by add-in card.
4.3 System Managem ent BIOS (SMBIOS)
SMBIOS is a Desktop Management Interface (DMI) compliant method for managi ng
computers in a managed network.
The main component of SMBIOS is the Management Information Format (MIF)
database, which contains information about the computing system and its components.
Using SMBIOS, a system administrator can obtain the system types, capabilities,
operational status, and installation dates for system components. The MIF database
defines the data and provides the method for accessing this information. The BIOS
enables applications such as third-party management software to use SMBIOS. The
BIOS stores and reports the following SMBIOS information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor clock frequency
• Dynamic data, such as event detectio n and error logging
Non-Plug and play operating syste ms, such as Microsoft Windows NT*, require an
additional interface for obtaining the SMBIOS information. The BIOS supports an
SMBIOS table interface for such operating systems. Using this support, an SMBIOS
service-level application running on a non-Plug and Play operating system can obtain
the SMBIOS information.
4.4 Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB support enables USB devices to be used even when the operating system’s
USB drivers are not yet av ailab le. Legacy USB support is us ed to access the BIO S Setup
program, and to install an operating system that supports USB.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mb er: 316639-002 51
Page 52

Legacy USB support operates as follows:
1. When you apply power to the computer, legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. Legacy USB support is enabled by the BIOS allowing you to use a USB keyboard to
enter and configure the BIOS Setup program and the maintenance menu.
4. POST completes.
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB keyboards
and mice are recognized and may be used to configure the operating system.
After the operating system loads the USB drivers, all legacy and non-legacy USB
devices are recognized by the operating system, and Legacy USB support from the
BIOS is no longer used.
To install an operating system that supports USB, follow the operating system’s
installation instructions.
4.5 BIOS Updates
The BIOS can be updated using the following tools:
• Using a BIOS burn-in tool (or flash programmer) is the best method to update the
BIOS for the CRB. These BIOS updates are available through your FAE. Floppy and
USB BIOS Upgrades can also be performed.
Overview of BIOS Features
Note: Review the instructions distribu ted with the upgrade utility before attempting a BIOS
update.
4.5.1 Language Support
The BIOS Setup program and help messages are supported in US English. Additional
languages are available in the Integrator’s Toolkit utility. Check the Intel website for
details.
4.6 Boot Options
In the BIOS Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a diskette drive, hard
drives, CD-ROM, USB or a network. The default setting is for the Floppy to be the first,
and the Hard Drive to be the second.
4.6.1 CD-ROM Boot
Booting from CD-ROM is supported in compliance to the El Torito bootable CD-ROM
format specification. Under the Boot menu in the BIOS Setup program, ATAPI CD-ROM
is listed as a boot device. Boot devices are defined in priority order. Accordingly, if there
is not a bootable CD in the CD-ROM drive, the system attempts to boot from the next
defined drive. Refer to Section 4.6.5, “Changing the Boot Device” on page 53 for how
to change this setting.
4.6.2 Netwo r k B oot
A network can be selected as a boot device provided you have plugged in the PCI
Express* Intel gigabit NIC. This selection allows booting from a network add-in card
with a remote boot ROM installed.
User’s Manual June 2007
52 Order Nu mb er: 316639-002
Page 53

Overview of BIOS Features
In order to boot from the LAN, enter the BIOS and select LAN boot as your first boot
device. Refer to Section 4.6.5, “Changing the Boot Device” on page 53 for how to
change this setting.
4.6.3 USB Boot
• In order to boot from a USB device, Enter BIOS and select USB boot as your first
boot device.
Note: Have USB device plugged in when changing this BIOS setting
4.6.4 Boo ting without Attached Devices
For use in embedded applications, the BIOS has been designed so that after passing
the POST, the operating system loader is invoked even if the following devices are not
present:
• Video adapter
• Keyboard
•Mouse
4.6.5 Changing the Boot Device
Pressing the <Delete> key during POST causes the BIOS menu to be displayed. Using
your arrow keys move ov er to <BOOT > and then arrow down to <Boot Device Pri ority>
and then select which device you would like to boot first and se cond.
Note: Ple a se fo llo w the inst r uc tio ns on the right side of the BIOS screen to navi ga te and
change BIOS settings.
4.7 BIOS Security Features
The BIO S in cl ud es se cu rit y f e atu res that restric t ac ce ss t o t he BIOS Setup pr og ra m a nd
who can boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be set for
the BIOS Setup program and for booting the computer, with the following restrictions:
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the
Setup options in the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
• The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options in the
BIOS Setup program. This is the user mode.
• If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password
prompt of the BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the
supervisor password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to
Setup respective to which password is entered.
• Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password
prom pt is d isplayed be f or e th e c om pu t er is b oot e d . I f o nl y t he su pe r v i sor pa ssword
is set, the computer boots without asking for a password. If both passwords are
set, the user can enter either password to boot the computer.
• For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user
passwords.
• Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9. Passwords may be up to 16
characters in length.
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mb er: 316639-002 53
Page 54
5.0 Error Messages and Beep Codes
5.1 Speakers
The CRB-mounted speaker provides audible error message (beep code) information
during POST. The location of the on-board speaker is coordinate D4.
5.2 BIOS Beep Codes
Whenever an error occurs during POST, the BIOS exerts and error tone which indicates
the pr o bl e m .
Table 22. Beep Code Types
Type Pattern Frequency
Memory Error Three long beeps 1280 Hz
Thermal Warning
Four alternating beeps: High tone, low tone, high
tone, low tone
Error Messages and Beep Codes
High tone: 2000 Hz
Low ton e: 1600 Hz
5.3 BIOS Error Messages
Table 23 lists the error messages and provides a brief description of each.
Table 23. BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
CMOS Battery Low The battery may be losing power. Replace the battery soon.
CMOS Checksum Bad
Memory Size Decreased
No Boot Device Available System did not find a device to boot.
The CMOS checksum is incorrect. CMOS memory may have been corrupted.
Run Setup to reset values.
Memory size has decreased since the last boot. If no memory was removed
then memory may be bad.
5.4 Port 80h POST Codes
During the POST, the BIOS generates diagnostic progress codes (POST-codes) to I/O
port 80h. If the POST fails or execution stops, the last POST code generated by the
BIOS is left at port 80h. This code is useful for determining the point where an error
occurred.
User’s Manual June 2007
54 Order Nu mb er: 316639-002
Page 55

Error Messages and Beep Codes
The f ol l o wi ng t a bl e s p r o vi d e informatio n a bo u t the POST co de s ge ne rated by t he BI O S:
• Table 24 lists the Port 80h POST code ranges
• Table 25 lists the Port 80h POST sequence
Table 24. Port 80h POST Code Ranges
Range (Hex) Category/Su bsystem
00 – 0F Debug codes: Can be used by any PEIM/driver for debug.
10 – 1F Host Processors: 1F is an unrecoverable processor error .
20 – 2F Memory/Chipset: 2F is no memory detected or no useful memory detected.
30 – 3F Recovery: 3F indicated recovery failure.
40 – 4F Reserved for future use.
50 – 5F
60 – 6F Reserved for future use (for new busses).
70 – 7F Output Devices: All output consoles. 7F is an unrecoverable error.
80 – 8F Reserved for future use (new output console codes).
90 – 9F Input devices: Keyboard/Mouse. 9F is an unrecoverable error.
A0 – AF Reserved for future use (new input console codes).
B0 – BF
C0 – CF Reserved for future use.
D0 – DF Boot device selection.
E0 – FF F0 – FF
I/O Busses: PCI, USB, ISA, ATA, etc. 5F is an unrecoverable error. Start
with P C I.
Boot Devices: Includes fixed media and removable media. BF is an
unrecoverable error.
FF processor exception. E0 – EE: Miscellaneous codes. EF boot/S3: resume
failure.
Table 25. Typical Port 80h POST Sequence (Sheet 1 of 2)
POST Code Description
21 Initializing a chipset component
22 Reading SPD from memory DIMMs
23 Detecting presence of memory DIMMs
25 Configuring memory
28 Testing memory
34 Loading recovery capsule
E4 Entered DXE phase
12 Starting Application processor initialization
13 SMM initialization
50 Enumerating PCI busses
51 Allocating resources to PCI bus
92 Detecting the presence of the keyboard
90 Resetting keyboard
94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
95 Keyboard Self Test EB Calling Video BIOS
58 Resetting USB bus
June 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mb er: 316639-002 55
Page 56

Table 25. Typical Port 80h POST Sequence (Sheet 2 of 2)
POST Code Description
5A Resetting PA TA/SAT A bus and all devices
92 Detect ing the presence of the keyboard
90 Resetting keyboard
94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
5A Resetting PA TA/SAT A bus and all devices
28 Testing memory
90 Resetting keyboard
94 Clearing keyboard input buffer
E7 Waiting for user input
01 INT 19
00 Ready to boot
Error Messages and Beep Codes
User’s Manual June 2007
56 Order Nu mb er: 316639-002
 Loading...
Loading...