Page 1

VHF MARINE TRANSCEIVER
iC- m88
Page 2

INTRODUCTION
This service manual describes the latest service information for
the IC-M88 VHF MARINE TRANSCEIVE R at the time of
publication.
To upgrade quality, all electrical or mechanical parts and internal circuits are subject to change without notice or obligation.
DANGER
NEVER connect the transceiver to an AC outlet or a
C
power supply that uses more than 8.3 V. This will ruin
e
transceiver.
DO NOT expose the transceiver to rain, snow or
liquids.
DO NOT reverse the polarities of the power supply
connecting the transceiver.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm
(
mW) to the antenna connector. This could damage th
e
transceiverís front end.
ORDERING PARTS
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component part number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
1110002750 S.IC TA7S01F IC-M88 MAIN UNIT 1 piece
8210019100 2600 Front panel IC-M88 CHASSIS 5 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
REPAIR NOTES
1. Make sure the problem is internal before disassembling the transceiver.
2. DO NOT open the transceiver until the transceiver is disconnected from its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An insulated tuning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the transceiver is defective.
6. DO NOT transmit power into a signal generator or a sweep generator.
7. ALWAYS connect a 40 dB or 50 dB attenuator between the transceiver and a deviation meter or spectrum analyzer when
using such test equipment.
8. READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly before connecting equipment to the transceiver.
Model
IC-M88
Version
U.S.A.
S.E. Asia
Symbol
FM I / S
Battery pack
USA NO
YES
NO BP-227
BP-227FM
BP-227
USA-1
SEA
D
th
any
when
100
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
SECTION 3 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4 - 1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS ................................................................................................... 4 - 1
4 - 2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS ............................................................................................ 4 - 2
4 - 3 PLL CIRCUITS................................................................................................................. 4 - 3
4 - 4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS ......................................................................................... 4 - 3
4 - 5 CPU PORT ALLOCATIONS ........................................................................................... 4 - 4
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
5 - 1 PREPARATION................................................................................................................ 5 - 1
5 - 2 SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT ........................................................................................... 5 - 4
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISASSEMBLY
SECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
9 - 1 CHARGER UNIT ............................................................................................................. 9 - 1
9 - 2 VR UNIT .......................................................................................................................... 9 - 1
9 - 3 CONNECTOR UNIT ........................................................................................................ 9 - 1
9 - 4 MAIN UNIT....................................................................................................................... 9 - 2
9 - 5 LOGIC UNIT .................................................................................................................... 9 - 4
SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAM
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
Page 4

SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
• Frequency coverage : TX: 156.025–157.425 MHz, RX: 156.050–163.275 MHz [MARINE]
TX/RX: 146.000–174.000 MHz [LMR]
• Number of free channels : 22 channels
• Type of emission : 16K0G3E (Wide; 25 kHz) [MARINE]
16K0F3E (Wide; 25 kHz), 8K50F3E (Narrow; 12.5 kHz) [LMR]
• Antenna connector : SMA (50 Ω)
• Power supply requirement : BP-227/FM (7.2 V DC, negative ground)
• Current drain (approx.) : Transmit at High (5.0 W) 1.6 A
at Middle (3.0 W) 1.2 A
at Low1 (1.0 W) 0.7 A
Receive at maximum audio 200 mA
at stand-by Less than 120 mA
• Usable temperature range : –20˚C to +60˚C; –4˚F to +140˚F [MARINE]
–30˚C to +60˚C; –22˚F to +140˚F [LMR]
7
• Dimensions (projections not included) : 62(W) × 97(H) × 39(D) mm; 2
• Weight (with antenna, BP-227/FM) : 280 g; 9
7
⁄8 oz (approx.)
TRANSMITTER
• RF output power (with BP-227/FM) : 5 W / 3 W / 1 W (High / Middle / Low)
• Modulation system : Variable reactance frequency modulation
• Maximum frequency deviation : ±5.0 kHz (Wide) [MARINE]
±5.0 kHz (Wide), ±2.5 kHz (Narrow) [LMR]
• Frequency error : ±5.0 ppm
• Spurious emissions : –70 dBc
• Adjacent channel power : 70 dB [MARINE]
70 dB (Wide), 60 dB (Narrow) [LMR]
• Audio harmonic distortion : 10% at 60% deviation
• FM Hum and noise : 40 dB [MARINE]
40 dB (Wide), 34 dB (Narrow) [LMR]
• Limiting charact modulation : 60–100% of maximum deviation
• Ext. microphone connector : 9-pin multi connector/2.2 kΩ
⁄16(W) × 313⁄16(H) × 117⁄32(D) in.
RECEIVER
• Receive system : Double conversion superheterodyne system
• Intermediate frequencies : 1st 31.05 MHz
2nd 450 kHz
• Sensitivity : 0.25 µV typical at 12 dB SINAD
• Squelch sensitivity : 0.35 µV typical at threshold
• Adjacent channel selectivity : 70 dB typical [MARINE]
70 dB typical (Wide), 60 dB typical (Narrow) [LMR]
• Spurious response rejection : 70 dB typical
• Intermodulation rejection ratio : 70 dB typical
• Hum and noise : 40 dB [MARINE]
40 dB (Wide), 34 dB (Narrow) [LMR]
• Audio output power (at 7.2 V DC) : 350 mW typical at 10% distortion with an 8 Ω load
• Ext. speaker connector : 9-pin multi connector/8 Ω
Specifications are measured in accordance with TIA/EIA-603.
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
1 - 1
Page 5
VHF MARINE CHANNEL LIST
Channel No. Frequency (MHz) Channel No.
CAN
USA
01A
03A
05A
06
07A
08
09
10
11
12
13*
14
15*
16
17*
18A
19A
20
20A
INT
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
2
13
14
2
1
15*
16
1
17
18
19
20
21
01
02
03
04A
05A
06
07A
08
09
10
11
12
13*
14
15*
16
17*
18A
19A
20*
21
1
1
1
1
Transmit
156.050
156.050
156.100
156.150
156.150
156.200
156.200
156.250
156.250
156.300
156.350
156.350
156.400
156.450
156.500
156.550
156.600
156.650
156.700
156.750
156.800
156.850
156.900
156.900
156.950
156.950
157.000
157.000
157.050
Receive
160.650
156.050
160.700
160.750
156.150
160.800
156.200
160.850
156.250
156.300
160.950
156.350
156.400
156.450
156.500
156.550
156.600
156.650
156.700
156.750
156.800
156.850
161.500
156.900
161.550
156.950
161.600
157.000
161.650
USA
21A
22A
23A
24
25
26
27
28
61A
63A
64A
65A
66A
67*
68
69
70*
71
72
INT
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
60
61
62
63
64
65
65A
66
66A
2
67
68
69
3
70*
71
72
CAN
21A
22A
23
24
25
26
27
28
60
61A
62A
64
64A
65A
3
Frequency (MHz) Channel No. Frequency (MHz)
Transmit
157.050
157.100
157.100
157.150
157.150
157.200
157.250
157.300
157.350
157.400
156.025
156.075
156.075
156.125
156.125
156.175
156.175
156.225
156.225
156.275
156.275
156.325
156.325
156.375
156.425
156.475
156.525
156.575
156.625
Receive
157.050
161.700
157.100
161.750
157.150
161.800
161.850
161.900
161.950
162.000
160.625
160.675
156.075
160.725
156.125
160.775
156.175
160.825
156.225
160.875
156.275
160.925
156.325
156.375
156.425
156.475
156.525
156.575
156.625
USA
73
74
77*
78A
79A
80A
81A
82A
83A
84
84A
85
85A
86
86A
87
87A
88
88A
INT
73
74
1
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
*1 Low power only, *2 Momentary high power, *3 Receive only
NOTE: Channels 3, 21, 23, 61, 64, 81, 82 and 83 CANNOT be used by the general public in USA waters.
Transmit
156.675
156.725
156.875
156.925
156.925
156.975
156.975
157.025
157.025
157.075
157.075
157.125
157.125
157.175
157.175
157.225
157.225
157.275
157.275
157.325
157.325
157.375
157.375
157.425
157.425
Receive
156.675
156.725
156.875
161.525
156.925
161.575
156.975
161.625
157.025
161.675
157.075
161.725
157.125
161.775
157.175
161.825
157.225
161.875
157.275
161.925
157.325
161.975
157.375
162.025
157.425
WX CHANNEL LIST
Weather
channel
WX01
WX02
WX03
WX04
WX05
Transmit
Receive only
Receive only
Receive only
Receive only
Receive only
Frequency (MHz) Frequency (MHz)
Receive
162.550
162.400
162.475
162.425
162.450
Weather
channel
1 - 2
WX06
WX07
WX08
WX09
WX10
Transmit
Receive only
Receive only
Receive only
Receive only
Receive only
Receive
162.500
162.525
161.650
161.775
163.275
Page 6
2 - 1
AF mute circuit
Q441* : 2SC4116
Q442* : CPH3403
Q443 : CPH3403
Q444 : DTC144EU
EEPROM
(IC591*: HN58X2416TI)
IN/EXT microphone switch
(Q461, Q462: UN911H)
Microphone amplifier
(IC471: NJM2904V)
AF mute
(IC481: TC4W66FU)
S5V regulator
(Q561: 2SA1588)
M5V regulator
Q551: 2SB1132
Q552: XP6501
Q553: DTC144EU
CPU
(IC661: µPD780316GC-511-9EB)
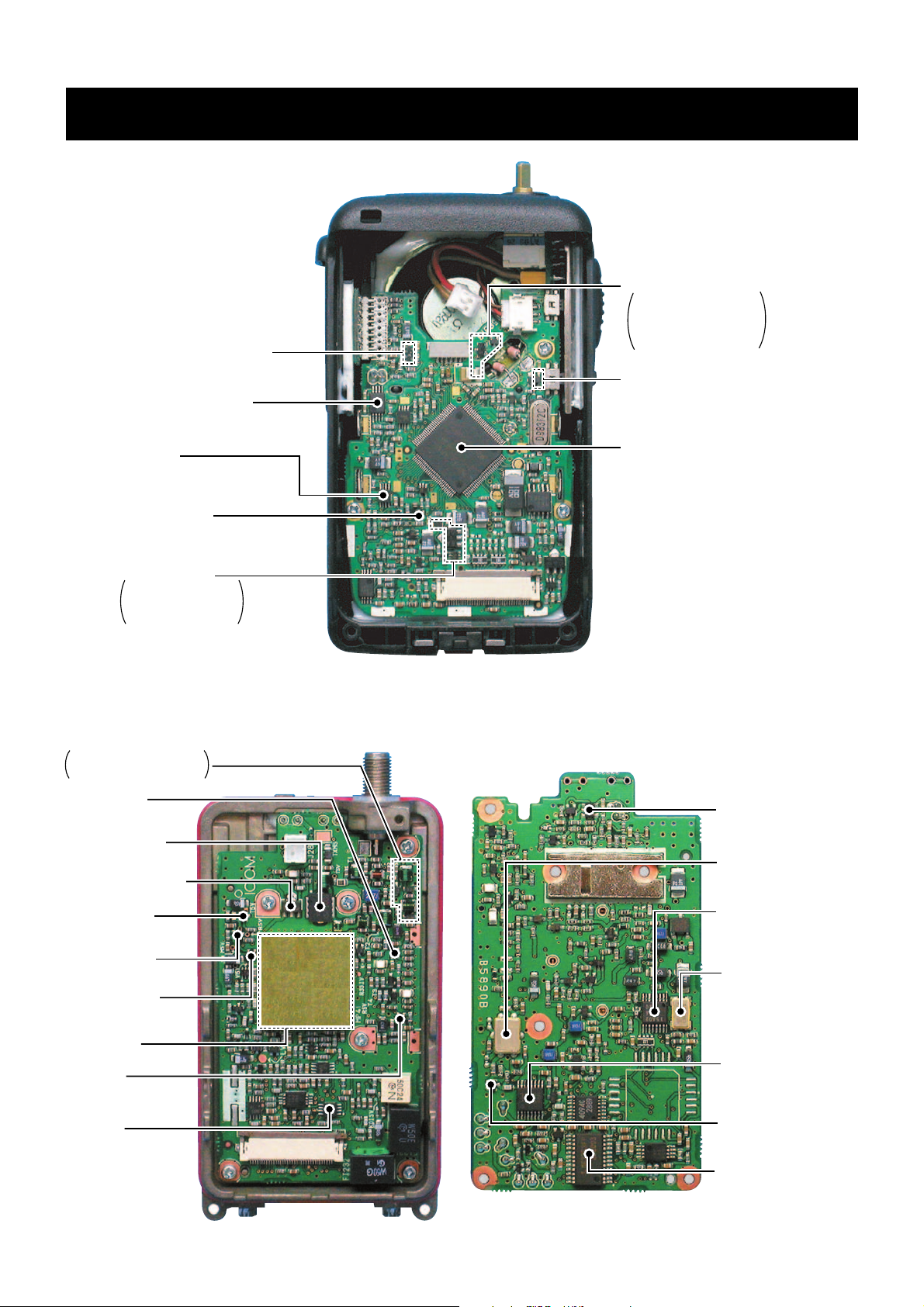
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
• LOGIC UNIT
Bottom view
*: Located in another side of
this point.
• MAIN UNIT
Top view
Bottom view
APC control
(IC141: TA75S01F)
Bandpass filter
(FI211: FL-355)
PLL IC
(IC1: MB15A02PFV)
Reference frequency
crystal
(X1: CR664A;
15.300 MHz)
FM IF IC
(IC231:
TA31136FN)
IF amplifier
(Q211: 2SC4215)
D/A converter
(IC251:
M62363FP-650C)
1st Mixer
(Q191: 3SK299)
VCO circuit
RF amplifier
(Q165: 3SK294)
Power amplifier
(Q111: RD07MVS1)
Antenna switching circuit
D131, D151: 1SV307
D152: MA77
AF mute
(IC281: TC4W66FU)
T5V regulator
(Q323: 2SA1588)
R5V regulator
(Q322: 2SA1588)
V5V regulator
(Q321: 2SA1588)
Pre-drive amplifier
(Q101: RD01MUS1)
Page 7
3 - 1
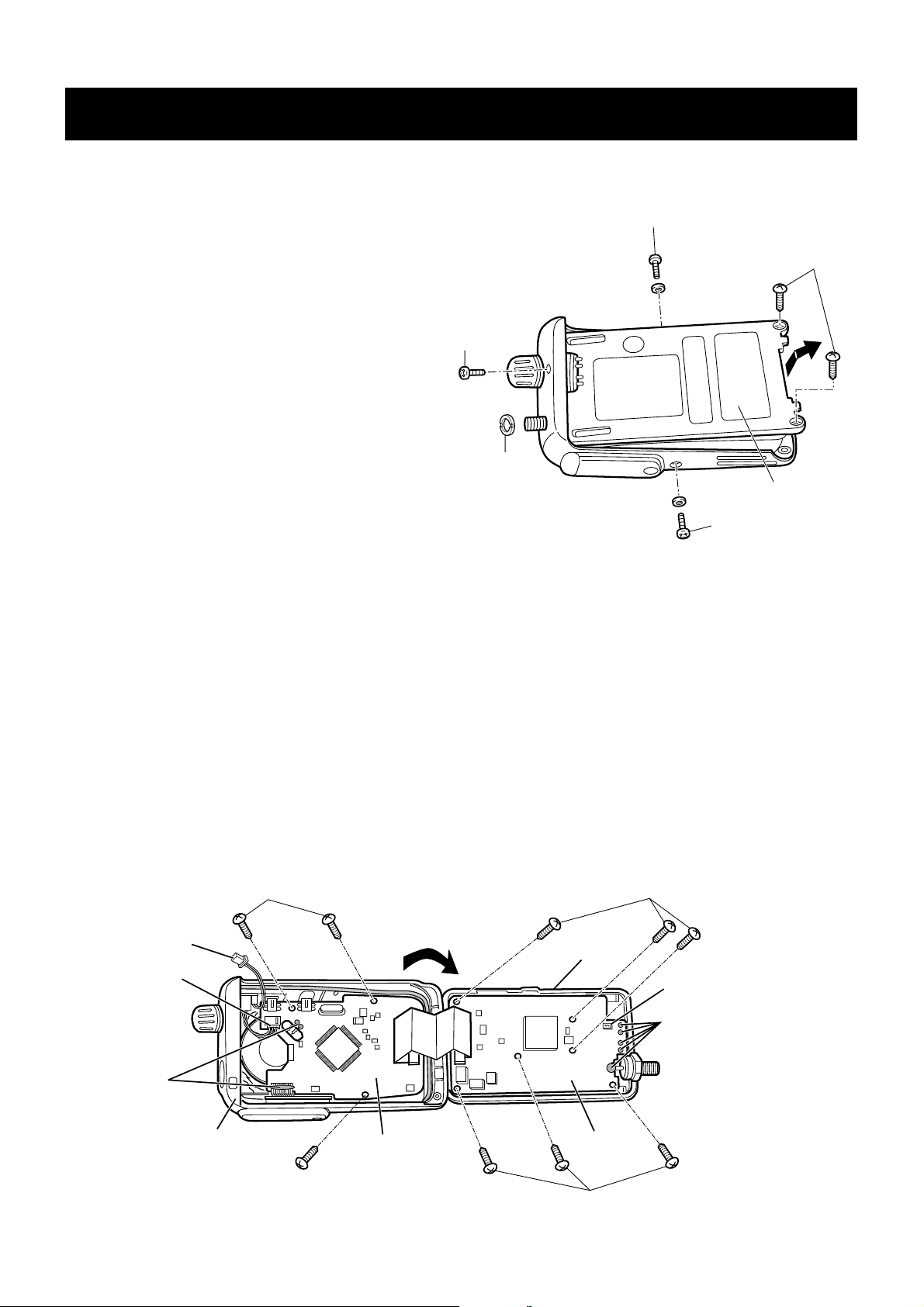
SECTION 3 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
1. Removing the chassis panel
2. Removing the LOGIC unit. 3. Removing the MAIN unit
q Remove nut
A.
w Unscrew 2 screws B (2 × 8 mm, black) and 3 screws C
(2 × 4 mm, black) from the chassis.
e Ta ke off the chassis in the direction of the arrow.
NOTE:* Tighten the screws in order of a number (q–y)
when assembling.
q Unplug the cable from J281 on the MAIN unit to separate
the LOGIC unit
w Separate the front panel from the chassis in the direction
of the arrow.
e Unsolder 2 leads of the speaker and connector unit (9
points).
r Unscrew 3 screws
D (2 × 4 mm, silver) to separate the
front panel.
NOTE:* Tighten the screws in order of a number (z–c)
when assembling.
q Unsolder 4 leads of contact spring and antenna connector
(1 point).
w Unscrew 6 screws
D (2 × 4 mm, silver) to separate the
chassis.
NOTE:* Tighten the screws in order of a number (q–y)
when assembling.
C
C
A
C
B
Chassis
q
w
e
r
t
y
q
r
tw
ey
z
x
c
MAIN UNIT
LOGIC UNIT
Front panel
VR unit
W801
D
D
E
E
Unsolder
(A contact spring
and antenna connector)
Chassis
J281
J281
Unsolder
(A SP and
connector unit)
Page 8
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
4-1-1 ANTENNA SWITCHING CIRCUIT
(MAIN UNIT)
The antenna switching circuit functions as a low-pass filter
while receiving and as resonator circuit while transmitting.
The circuit does not allow transmit signals to enter receiver
circuits.
Received signals from the antenna connector pass through
the low-pass filter (L131, L132, C131–C136) and antenna
switching circuit (D151, D152). The filtered signals are then
applied to the RF amplifier circuit (Q165).
4-1-2 RF AND 1ST MIXER CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signals to a
fixed frequency of the 1st IF signal with a PLL output
frequency. By changing the PLL frequency, only the desired
frequency will be passed through a pair of crystal filters at
the next stage of the 1st mixer.
The signals from the antenna switching circuit are passed
through the 2-stage bandpass filters (D154, D155, L154,
L155) and amplified at the RF amplifier (Q165). The
amplified signals are passed through another 2-stage
bandpass filters (D181, D182, L181, L182), and then
applied to the 1st mixer circuit (Q199).
The filtered signals are mixed at the 1st mixer (Q199) with
a 1st LO signal coming from the PLL circuit to produce
a 31.05 MHz 1st IF signal. The 1st IF signal is passed
through a pair of crystal filter (FI211) and is then amplified
at the IF amplifier (Q211).
The 1st IF signal is applied to a 2nd mixer section of the
FM IF IC (IC231, pin 16). The signal is then mixed with a
2nd LO signal for conversion into a 450 kHz 2nd IF signal.
IC231 contains the 2nd mixer, limiter amplifier, quadrature
detector and active filter circuits. A 30.6 MHz 2nd LO
signal is produced at the PLL circuit using the reference
frequency.
The 2nd IF signal from the 2nd mixer (IC231, pin 3)
passes through ceramic filters (FI231, FI232) to remove
unwanted heterodyned frequencies. It is then amplified at
the limiter amplifier section (IC231, pin 5) and applied to
the quadrature detector section (IC231, pins 10 and 11) to
demodulate the 2nd IF signal into AF signals.
4-1-4 AF CIRCUIT (MAIN AND LOGIC UNITS)
AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC231, pin 9) are fed to the
analog switch (IC282).
The AF signals (detected signals) passes through the AF
mute switch (IC281A, pins 2 and 1) via “DET” signal, and
are then applied to the analog switch (IC282, pin 1). The
signals are then applied to the low-pass filter (IC261B,
C266, C267, R270–R272).
The filtered AF signals are applied to and adjusted audio
level at the [VOL] control (VR unit; R801) via the “VOLIN”
signal. The level controlled signals are passed through the
AF mute switch (LOGIC unit; Q411) which is controlled by
“AFMS” signal from the CPU (IC661, pin 84). The passed
signals are applied to the AF power amplifier (IC421, pin
4), and then output to the internal speaker or [EXT SP] jack
after being passed through the de-emphasis circuit (R411,
C413) to obtain the –6 dB/octave frequency characteristics
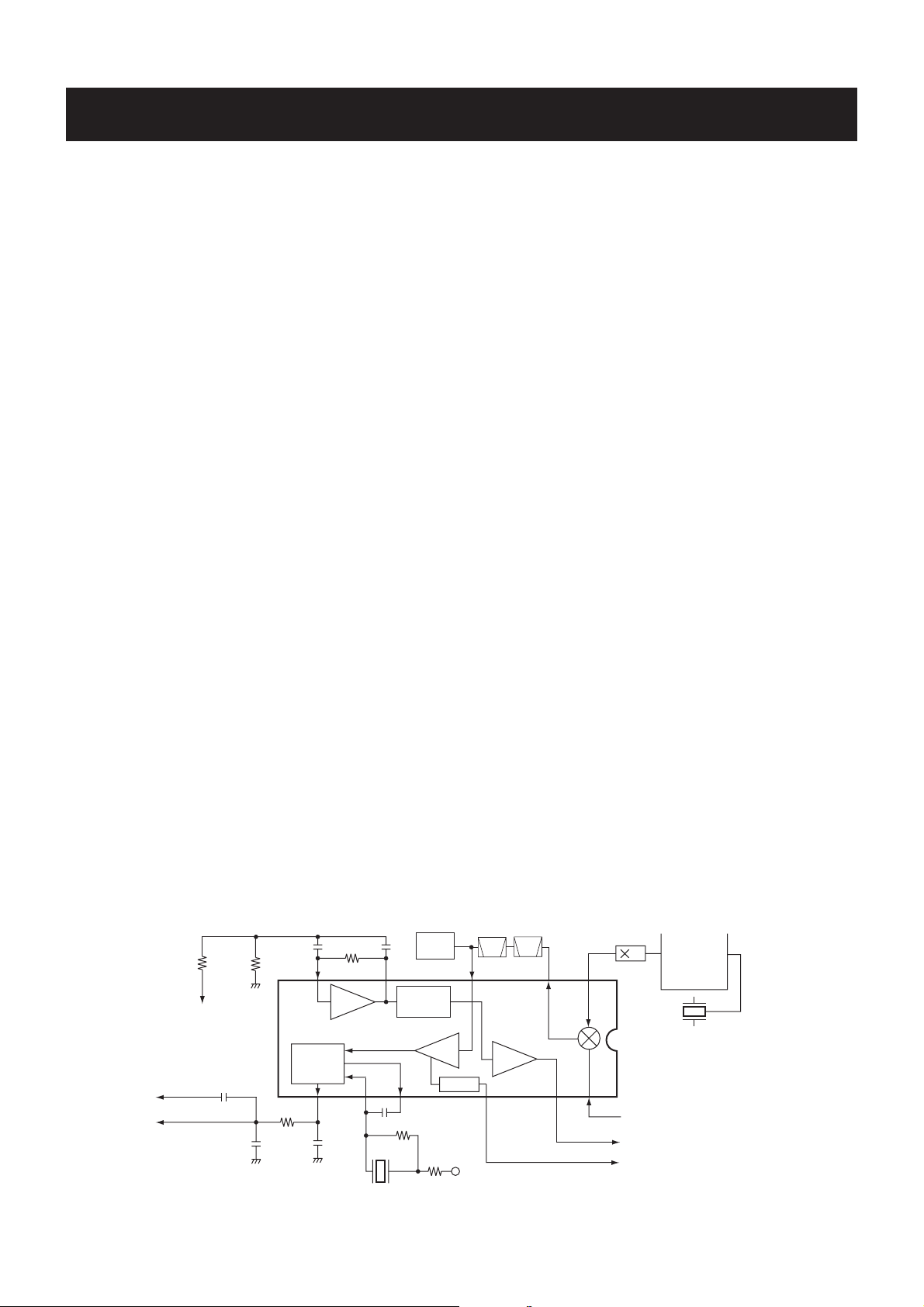
4-1-3 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The 2nd mixer circuit converts the 1st IF signal to a 2nd IF
signal. A double conversion superheterodyne system (which
converts receive signal twice) improves the image rejection
and obtain stable receiver gain.
• 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
Q231
Q232
W/N
SW
Noise
detector
IF amp.
11
R231
R232
R240
"SQCON" signal to the D/A
convertor IC (IC251, pin 2)
"SQLOUT" signal to the D/A
convertor IC (IC251, pin 1)
AF signal "DET"
R241
C242
C243
C238
R242
C239
R239
87 5
Active
filter
FM
detector
10
9
C232
C244
X231
450 kHz
RSSI
R5V
2nd IF filters
450 kHz
Fl232
Fl231
Noise
comp.
12
3
2nd
Mixer
14
30.6 MHz
2
Q221
2
16
17
IC231 TA31136FN(D)
"IF" (1st IF signal: 31.05 MHz)
from RF unit, Q211
"NOISV" signal to the CPU (pin 32)
"RSSIV" signal to the CPU (pin 33)
16
PLL IC
IC1
X1
15.3 MHz
4 - 1
Page 9
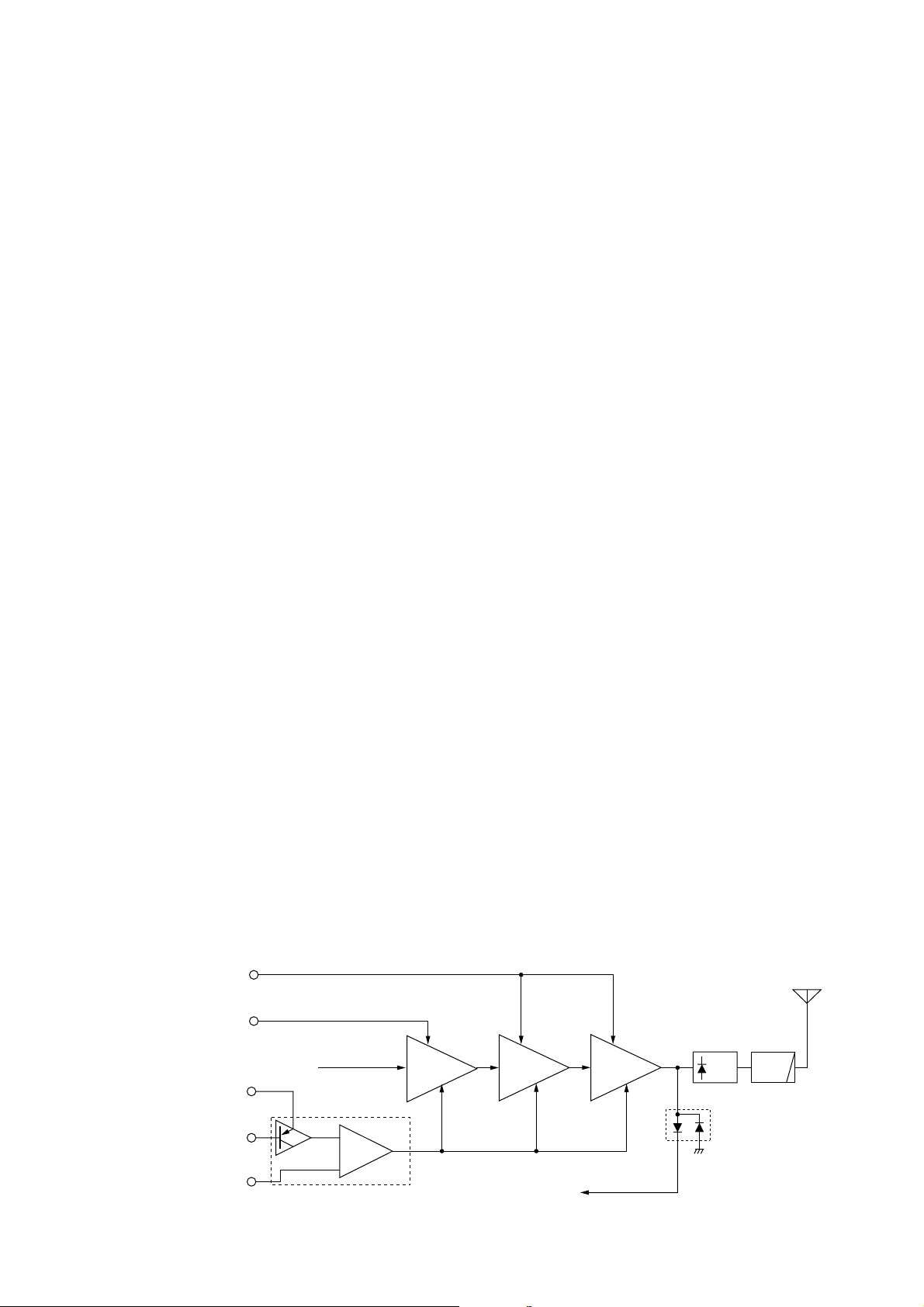
4-1-5 SQUELCH CIRCUIT
(MAIN AND LOGIC UNITS)
The noise squelch circuit cuts out AF signals when no RF
signals are received. By detecting noise components in the
AF signals, the squelch circuit switches the AF mute switch.
A portion of the AF signals divided by C242 from the
FM IF IC (IC231, pin 9) are applied to the D/A converter
(IC251, pin 2) to adjust amplitude. The signals from the
D/A converter (IC251, pin 1) are applied to the active filter
section (IC231, pin 8, R239–R241, C237, C238). The active
filter section amplifies and filters noise components. The
filtered signals are applied to the noise detector section
and output from IC231 (pin 14) as the “NOISV” signal.
The “NOISV” signal from IC231 (pin 14) is applied to the
CPU (LOGIC unit; IC611, pin 32). The CPU compares the
set squelch level voltage and “NOISV” signal voltage to
control the squelch output.
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
4-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
(LOGIC AND MAIN UNITS)
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies audio signals
with +6 dB/octave pre-emphasis characteristics from the
microphone to a level needed for the modulation circuit.
• In case of the internal microphone
The AF signals from the internal microphone (MC461) is
applied to the microphone amplifier (IC471a, pin 6) via the
“INMIC” signal.
• In case of external microphone
The AF signals from the external microphone (CP458) is
applied to the microphone amplifier (IC471a, pin 6) via the
“EXTMIC” signal.
4-2-2 MODULATION CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The modulation circuit modulates the VCO oscillating signal
(RF signal) using the microphone audio signals.
The audio signals “MOCON” change the reactance of D39
to modulate an oscillated signal at the TX VCO circuit (Q51,
D35–D38, L34, L51, C32, C33, C52–C54). The oscillated
signal is amplified at the buffer-amplifiers (Q61, Q62).
4-2-3 PRE-DRIVE/POWER AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The signal from the VCO circuit passes through the
transmit/receive switching circuit (D91, D92) and is applied
to the buffer-amplifier (Q91). The amplified signal is
amplified by the pre-driver (Q101) and the power amplifier
(Q101) to obtain 5 W of RF power (at 7.2 V). The amplified
signal passes through the antenna switching circuit (D131),
and low-pass filter (L131, L132, C131–C136) and is then
applied to the antenna connector.
The bias current of the buffer amplifier (Q91), pre-driver
(Q101) and power amplifier (Q111) is controlled by the
APC circuit to stabilize the output power.
4-2-4 APC CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The APC circuit provides stable output power from the
power amplifier even when the input voltage or temperature
changes, and, selects HIGH, MIDDLE, LOW or EXTRA
LOW output power. The APC circuit consists of a power
detector and APC control circuits.
• POWER DETECTOR CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The power detector circuit (D132) detects the transmit
output power level and converts it to DC voltage as the
“TDETV” signal. The detected signal is applied to the APC
control circuit.
The amplified signals are passed through the pre-emphasis
circuit (R463, C463) and are then applied to the AF mute
switch (IC481a, pin 1) via the “MICO” signal after being
passed through the another microphone amplifier (IC471b,
pins 2 and 1).
The AF signals are amplified again at the limiter-amplifier
(IC491a, pin 2) and then passed through the low-pass filter
(IC491b, pins 6 and 7). The filtered audio passes through
the analog swtich (MAIN unit; IC251, pins 4 and 3), and is
then applied to the MAIN unit as the “MOCON” signal.
• APC CIRCUIT
"TXMS" signal from the
expander IC (IC341, pin 12)
"T1CON" signal from the D/A
convertor IC (IC251, pin 14)
VCC
T5V
S5V
RF signal
from PLL
3
Q141
APC control circuit
1
IC141
Buffer
amp.
• APC CONTROL CIRCUIT (MAIN AND LOGIC UNITS)
The “TDETV” signal from the power detector circuit is
applied to the CPU (LOGIC unit; IC661, pin 31) to control
the input voltage of the buffer amplifier (Q91), pre-driver
(Q101) and power amplifier (Q111). When the output power
changes, the CPU (LOGIC unit; IC661) outputs APC control
signal to the D/A converter (IC190). And then “T1CON”
signal from the D/A converter controls the APC controller
(IC141) to provide stable output power.
antenna
Q101Q91
Pre-drive
amp.
"TDETV" to the CPU
(LOGIC unit; IC661, pin 31)
Power
amp.
Q111
D131
ANT
SW
Power detector
circuit (D132)
LPF
4 - 2
Page 10
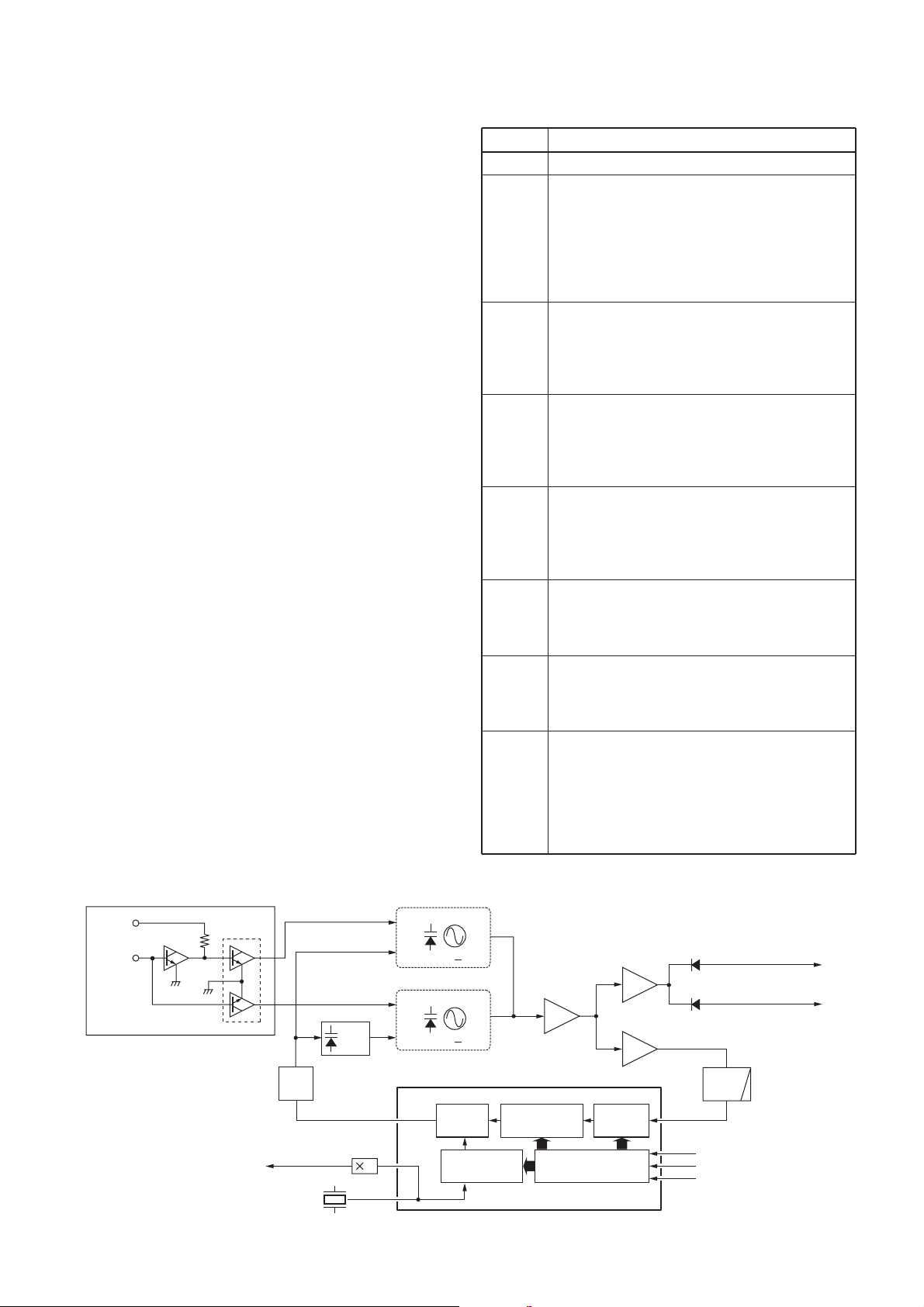
4-3 PLL CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
4-3-1 GENERAL
The PLL circuit provides stable oscillation of the transmit
frequency and receive 1st LO frequency. The PLL output
compares the phase of the divided VCO frequency to the
reference frequency. The PLL output frequency is controlled
by the divided ratio (N-data) of a programmable divider. IC1
is a PLL IC which controls both VCO circuit for TX and RX.
The PLL circuit, using a one chip PLL IC (IC1), directly
generates the transmit frequency and receive 1st IF
frequency with VCOs. The PLL sets the divided ratio
based on serial data from the CPU on the LOGIC unit and
compares the phases of VCO signals with the reference
oscillator frequency. The PLL IC detects the out-of-step
phase and output from the pin 6 for TX and RX. The
reference frequency (15.3 MHz) is oscillated at X1.
4-3-2 TX AND RX LOOP CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The generated signal at the TX-VCO circuit (Q51, D35
–D38, L34, L51, C32, C33, C52–C54) or RX-VCO (Q41,
D31–D34, L32, L41, C31, C41–C43) enters the PLL IC (IC1,
pin 8) and is divided at the programmable divider section
and is then applied to the phase detector section.
The phase detector compares the input signal with a
reference frequency, and then outputs the out-of-phase
signal (pulse-type signal) from pin 6.
The pulse-type signal is converted into DC voltage (lock
voltage) at the loop filter (R17–R19, C16–C19), and then
applied to varactor diodes (TX; D35–D38, RX; D31–D34)
of the TX-VCO and RX-VCO to stabilize the oscillated
frequency.
4-3-3 TX AND RX VCO CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The VCO circuit from Q41 (RX) and Q5 (TX) are buffer
amplified at the Q61 and Q62, and then sent to the TX/RX
swtich (D91, D92). The receive LO signal is applied to the
1st mixer circuit (Q191) through an attenuator (L203, R203
–R206, C202, C203), and the transmit signal is applied to
the buffer amplifier (Q91). A portion of the VCO output is
reapplied to the PLL IC (IC1, pin 8) via the Q71.
4-4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
VOLTAGE LINES
LINE
HV
VCC
CPU5V
M5V
R5V
T5V
V5V
S5V
The voltage from the attached battery pack.
The same voltage as the HV line (battery
voltage) which is controlled by the power switch
(VR unit; [OFF/VOL] control).
The output voltage is applied to the pre-drive
(MAIN unit; Q101), power amplifier (MAIN unit;
Q111), CPU5V and M5V regulator circuits
(LOGIC unit; IC551 and Q551–Q553).
Common 5 V converted from the VCC line by the
CPU5V regulator circuit (LOGIC unit; IC551).
The output voltage is applied to the CPU (LOGIC
unit; IC661), RESET circuit (LOGIC unit; IC581),
etc.
Common 5V converted from the VCC line by the
M5V regulator circuit (LOGIC unit; Q551–Q553).
The output voltage is applied to R5V, T5V, V5V and
S5V regulator circuits (LOGIC unit; Q322, Q323,
Q321 and Q561).
Receive 5V converted from the M5V line by the
R5V regulator circuit (MAIN unit; Q322).
The regulated voltage is applied to the 1st mixer
circuit (MAIN unit; Q191), RF and IF amplifiers
(MAIN unit; Q165, Q211).
Transmit 5V converted from the M5V line by the
T5V regulator circuit (MAIN unit; Q222).
The regulated voltage is applied to the buffer
amplifier (MAIN unit; Q91).
Common 5V converted from the M5V line by
the V5V regulator circuit (MAIN unit; Q321).
The regulated voltage is applied to the ripple
filter circuit (Q47).
Common 5V converted from the M5V line by the
S5V regulator circuit (LOGIC unit; Q561).
The regulated voltage is applied to the microphone
amplifier (LOGIC unit; IC471), limit amplifier
(LOGIC unit; IC491), LCD back light (LOGIC unit;
DS651–DS654), etc.
DESCRIPTION
• PLL CIRCUIT
S5V
Q82
VCOS
VCO SWITCH
Q81
Loop
filter
"2nd LO" signal (30.6 MHz)
to the FM IF IC (IC231, pin 2)
X1
15.3 MHz
D39
FM
MOD.
Q221
Q41, D31 D34
Q51, D35 D38
5
2
2
1
RX VCO
TX VCO
Phase
detector
Programmable
divider
4 - 3
Buffer
Q61
IC1 MB15A02PFV
Programmable
counter
Shift register
Buffer
Q62
Buffer
Q71
Prescaler
11
10
D91
to transmitter circuit
to the 1st mixer circuit
D92
LPF
8
PLSTBO
SDATAO
9
SCLKO
Page 11
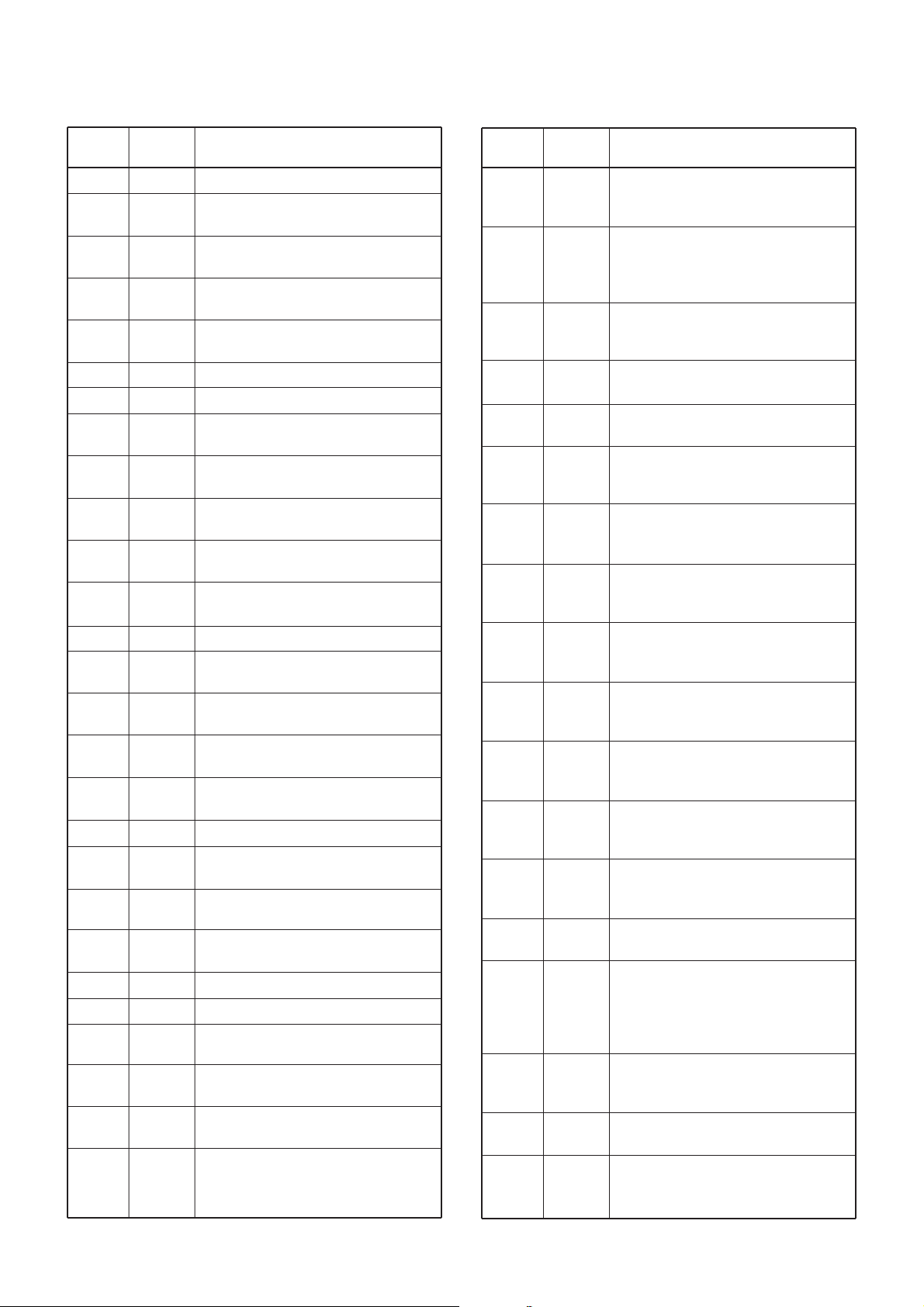
4-5 PORT ALLOCATIONS
4-5-1 CPU (LOGIC UNIT; IC661)
Pin
number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
11
12
13
17
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
38
46–48
51–70
75
76
Port
name
BEEP
VSSTB
EXSTB
DASTB
PLSTB
ERXDI
ETXDO
SDATA
SCLK
ESCK
ESDA
CSIFT
WDECV
WETIN
EXTSV
BATTV
TDETV
NOISV
RSSIV
LOINV
TEMPV
CDECV
ATIS
COM0–
COM2
SEG0–
SEG19
CONT1
CONT2
Description
Outputs beep audio signals.
Outputs strobe signals for the scrambler
IC (MAIN unit; IC381, pin 10).
Outputs strobe signals for the
expander IC (MAIN unit; IC341, pin 1).
Outputs strobe signals for the D/A
converter (MAIN unit; IC251, pin 6).
Outputs strobe signals for the PLL IC
(MAIN unit; IC1, pin 11).
Input port for cloning signals.
Outputs cloning signals.
Outputs serial data for PLL, scrambler
ICs, etc.
Outputs serial clock for PLL,
scrambler ICs, etc.
Outputs clock signal for the EEPROM
(IC591, pin 6).
I/O port for EEPROM data signal
(IC591, pin 5).
Outputs CPU clock shift signal.
High : While clock is shifted.
Input port for the WX tone detection.
Input port for the transceiver’s internal
inundation detection.
Input port for the external terminal
connecting detection.
Input port for the battery voltage
detection.
Input port for transmit RF level
detection.
Input port for noise level detection.
Input port for RSSI voltage level
detection.
Input port for VCO lock voltage level
detection.
Input port for the transceiver’s internal
temperature detection.
Input port for CTCSS/DTCS detection.
Outputs ATIS wave form.
Output LCD common signals
Output LCD segment signals.
Output LCD contrast control signals.
Pin
number
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
98
99
100
102
103
104
109
Port
name
STXMS
MICMS
ISPMS
LDTFS
W/NS
AFMS
AFVS
M5VS
S5VS
V5VS
R5VS
T5VS
CENC1
CENC2
CENC3
PTTIN
EPTTIN
BTYPE
SQL
Description
Outputs scrambler mute signal for the
AF mute circuit (IC481, pin 3).
Low : While scrambler is muting.
Outputs mic mute signal for the AF
mute circuit (IC481, pin 7).
Low : While the microphone is
muting.
Outputs the internal speaker control
signal.
High : While the speaker is muting.
Outputs DTCS’s low-pass filter cut-off
frequency control signal.
Outputs Wide/Narrow control signal.
high : While Narrow is selected.
Outputs the AF mute circuit control
signal.
High : The AF mute circuit is ON.
Outputs AF amplifier’s power supply
control signal.
High : The AF amplifier is ON.
Outputs M5V power supply control
signal.
Low : The common 5V is supplied.
Outputs S5V power supply control
signal.
Low : The common 5V is supplied.
Outputs V5V power supply control
signal.
Low : The common 5V is supplied.
Outputs R5V power supply control
signal.
Low : While receiving.
Outputs T5V power supply control
signal.
Low : While transmitting.
Output DTCS/CTCSS wave form.
Input port for [PTT] swtich detection.
High : While [PTT] switch is pushed.
Input port for HM-138 (optional
speaker-microphone)’s [PTT] swtich
detection.
Low : While HM-138’s [PTT] switch
is pushed.
Input port for the connecting battery
type detection.
Low : While using alkaline cells.
Input port for the [SQL] key.
Low : While [SQL] key is pushed.
77
78
LEDS1
LEDS2
Output LCD and key’s back light
dimmer control signal.
4 - 4
110
UP
Input port for the [UP] key.
Low : While [UP] key is pushed.
Page 12
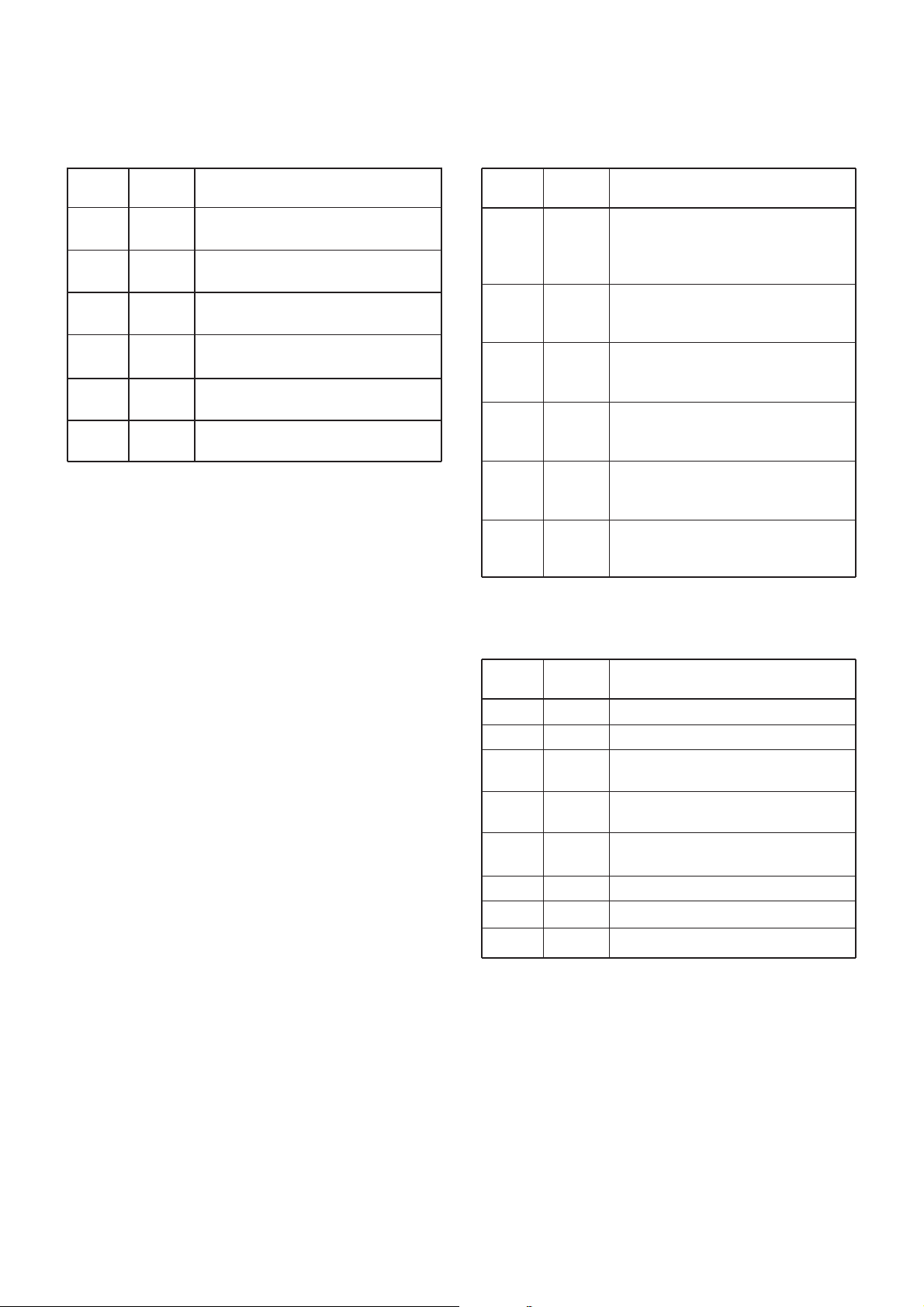
CPU–Continued
Pin
number
111
112
113
114
115
119
Port
name
DOWN
CH/WX
16/9
SCAN
H/L
UNLK
Description
Input port for the [DOWN] key.
Low : While [DOWN] key is pushed.
Input port for the [CH/WX] key.
Low : While [CH/WX] key is pushed.
Input port for the [16/9] key.
Low : While [16/9] key is pushed.
Input port for the [SCAN] key.
Low : While [SCAN] key is pushed.
Input port for the [H/L] key.
Low : While [H/L] key is pushed.
Input port for the PLL unlock signal.
High : PLL lock voltage is unlocked.
4-5-2 EXPANDER IC (MAIN UNIT; IC341)
Pin
number
5
6
7
11
12
13
Port
name
SRXMS
DETMS
CKSIS
ATTS
TXMS
VCOS
Description
Outputs the AF mute switch (IC281,
pin 3) control signal.
Low : While the scrambler decording
signal is muted.
Outputs the AF mute swtich (IC281,
pin 7) control signal.signal.
Low : While AF signal is muted.
Outputs the scrambler IC’s clock shift
control signal.
High : While the clock is shifted.
Outputs the RF attenuator control
signal.
High : While attenuator is ON.
Outputs the TX mute swtich (Q141)
control signal.
Low : While receiving.
Outputs the TX/RX VCO control
signal.
4-5-3 D/A CONVERTOR IC (MAIN UNIT; IC251)
Pin
number
2
3
10
11
14
15
22
23
Port
name
SQCON
MOCON
DTCON
FRCON
T1CON
T2CON
T3CON
T4CON
Description
Outputs squelch level control signal.
Outputs modulatin level control signal.
Outputs DTCS modulation balance
control signal.
Outputs reference frequency level
control signal.
Outputs bandpass filter1 tuned and
transmitting power control signals.
Outputs bandpass filter2 tuned signal.
Outputs bandpass filter3 tuned signal.
Outputs bandpass filter4 tuned signal.
4 - 5
Page 13

SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
5-1 PREPARATION
When adjusting IC-M88, optional OPC-966 CLONING CABLE, optional RS-232C CABLE and optional CS-M88 adj ADJUSTMENT
SOFTWARE
are required.
EQUIPMENT
DC power supply
RF power meter
(terminated type)
Frequency counter
Digital multimeter
Output voltage : 7.2 V DC
Current capacity : 3 A or more
Measuring range : 0.1–10 W
Frequency range : 100–300 MHz
Impedance : 50
SWR : Less than 1.2 : 1
Frequency range : 0.1–300 MHz
Frequency accuracy : ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Input impedance : 10 M
GRADE AND RANGE
Ω
Ω/DC or better
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
®
• Microsoft® Windows
95/98/ME
ADJUSTMENT SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
1. Boot up Windows®.
- Quit all applications when Windows
2. Insert the cloning software CD-ROM into the appropriate
CD-ROM drive.
3. Select ‘Run’ from the [Start] menu.
4. Type the setup program name using the full path name,
then push the [Enter] key. (For example; D:\ setup)
5. Follow the prompts.
6. Program group ‘CS-M88 ADJ’ appears in the ‘Programs’
folder of the [Start] menu.
®
is running.
EQUIPMENT
FM deviation meter
Audio generator
Standard signal
generator (SSG)
Attenuator
Frequency range : 30–300 MHz
Measuring range : 0 to ±10 kHz
Frequency range : 300–3000 Hz
Measuring range : 1–500 mV
Frequency range : 100–300 MHz
Output level : 0.1 µV–32 mV
Power attenuation : 40 dB or more
Capacity : 10 W or more
GRADE AND RANGE
(–127 to –17 dBm)
STARTING SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT
1. Connect IC-M88 and PC with the optional OPC-966 and
the RS-232C cable.
2. Boot up Windows®, and turn the transceiver power ON.
3. Click the program group ‘CS-M88 ADJ’ in the ‘Programs’
folder of the [Start] menu, then CS-M88 ADJ’s window is
appeared.
4. Click ‘Connect’ on the CS-M88 ADJ’s window, then
appears IC-M88’s up-to-date condition.
5. Set or modify adjustment data as desired.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the U.S.A. and other countries.
Screen shots produced with permission from Microsoft
Corporation. All other products or brands are registered
trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
5 - 1
Page 14

• CONNECTION
FM
deviation meter
to an RS-232C port
Attenuator
40 dB or 50 dB
RF power meter
0.1 10 W/50
Frequency
counter
Personal
computer
to the antenna connector
Standard signal generator
0.1 V to 32 mV
( 127 dBm to 17 dBm)
CAUTION:
DO NOT transmit while
SSG is connected to the
antenna connector.
Audio generator
DB9 female plug
RS-232C cable (straight)
OPC-966
(Cloning cable)
PTTE
PTT
MIC
MICE
*OPC-966
(JIG CABLE)
Add a jumper wire here
+
Audio generator
300 Hz to 3 kHz
SINAD meter
Speaker (8 )
AC
millivoltmeter
SP
SP+
+
5 - 2
Page 15

• SCREEN EXAMPLE
File
COM 1: OPEN
1
CS-M88 ADJ Rev.1.0
Option
Connect
2
Reload (F5) Disp para
10
12
14
16
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
13
15
17
[A / D]
BATT : 120 : 78h : 7.53 V
NOIS : 59 : 3Bh : 1.16 V
SD : 44 : 2Ch : 0.86 V
LVIN : 119 : 77h : 2.33 V
TEMPS : 178 : B2h : 26.86 ’C
TXDET : 0 : 00h : 0.00 V
WET : 255 : FFh : 5.00 V
[D / A]
FRQCON : 127 : 7Fh : 2.49 V
T1/POW : 92 : 5Ch : 1.80 V
T2 : 127 : 7Fh : 2.49 V
T3 : 86 : 56h : 1.69 V
T4 : 117 : 75h : 2.29 V
Dev : 0 : 00h : 0.00 V
CTCS BL : 0 : 00h : 0.00 V
SQL LEV : 76 : 4Ch : 1.49 V
3
NOTE:
The above values for settings are example only.
Each transceiver has its own specific values for each setting.
1
: Transceiver’s connection state
: Reload adjustment data
2
: Receive sensitivity measurement
3
: Connected battery voltage
4
: PLL lock voltage
5
: Dial mode select
6
: Operating channel select
7
: RF output power select
8
5 - 3
9
: Reference frequency
: RF output power
10
: FM deviation
11
: Modulation balance
12
: Receive sensitivity (automatically)
13
: Receive sensitivity (manually)
14
: Squelch level (automatically)
15
: Squelch level (manually)
16
: Adjustment items
17
Page 16

5-2 SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT
Select an operation using [↑] / [↓] keys, then set specified value using [←] / [→] keys on the connected computer keyboard.
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
UNIT
MEASUREMENT
LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT
PLL LOCK
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
FREQUENCY
OUTPUT
POWER
FM
DEVIATION
(Wide)
(Narrow)
MODULATION
BALANCE
(Wide)
• Operating channel : center frequency
1
• Receiving
• Operating channel : center frequency
2
• Connect the RF power meter or 50 Ω
dummy load to the antenna connector.
• Transmitting
• Operating channel : center frequency
1
• Connect the RF power meter or 50 Ω
dummy load to the antenna connector.
• Transmitting
• Operating channel : center frequency
1
• [H/L] switch : High
• Transmitting
• [H/L] switch : Mid
2
• Transmitting
• [H/L] switch : Low
3
• Transmitting
• [H/L] switch : Extra low
4
• Transmitting
• Operating channel : center frequency
1
• Channel spacing : Wide
• [H/L] switch : High
• Connect the audio generator to the
[MIC] jack and set as:
1.0 kHz/200 mV rms.
• Set the FM deviation meter as:
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis : OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• Transmitting
2
• Channel spacing : Narrow
• Transmitting
1
• Operating channel : center frequency
• Channel spacing : Wide
• [H/L] switch : High
• Set the DTCS as : Code 007
• Transmitting
MAIN
Top
panel
Top
panel
Top
panel
Top
panel
Connect the
the check point LV.
digital multimeter to
Loosely couple the frequency
counter to the antenna
connector.
Connect the RF power meter to
the antenna connector.
Connect the FM deviation
meter to the antenna connector
through the attenuator.
Connect the FM deviation meter
with an oscilloscope to the
antenna connector through the
attenuator.
1.5–3.0 V (Verify)
1.8–3.3 V (Verify)
160.000000 MHz
5.0 W
3.0 W
0.75 W
0.45
±4.15–4.25 kHz
±2.00–2.10 kHz
Set to flat wave
form
(Narrow)
2
• Channel spacing : Narrow
• Transmitting
Set to flat wave
form
5 - 4
Page 17

• MAIN UNIT TOP VIEW
LV
PLL lock voltage
check point
5 - 5
Page 18

SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT – continued
• Select an operation using [↑] / [↓] keys, then set specified value using [←] / [→] keys on the connected computer keyboard.
• “SQUELCH LEVEL ADJUSTMENT” must be performed after “RX SENSITIVITY ADJUSTMENT” is finished.
• “SQUELCH LEVEL ADJUSTMENT” must be performed when “RX SENSITIVITY ADJUSTMENT” is adjusted.
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT
RX
SENSITIVITY
[BPF T1]–[BPF T4]
1 • Operating frequency : center frequency
ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
• Channel spacing : Wide
• Connect a standard signal generator to
the antenna connector and set as:
Level :
Modulation : OFF
Deviation : ±3.0 kHz
• Receiving
10 µV* (–87 dBm)
CONVENIENT: The BPF T1–BPF T4 can be adjusted automatically.
1: Set the cursor to “BPF ALL” on the adjustment program and then push [ENTER] key.
2: The connected PC tunes BPF T1–BPF T4 to peak levels.
or
1: Set the cursol to one of BPF T1, T2, T3, or T4 as desired.
2: Push [ENTER] key to start tuning.
3: Repeat w-1 and w-2 to perform additional BPF tuning.
SQUELCH
LEVEL
[SQL]
• Operating frequency : center frequency
1
• Channel spacing : Wide
• Connect a standard signal generator to
the antenna connector and set as:
Level :
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation :
• Receiving
0.56 µV* (–112 dBm)
±3.0 kHz
UNIT
Top
panel
Top
panel
MEASUREMENT
Connect a SINAD meter with an
8 Ω load to the [SP] jack.
The “SQUELCH LEVEL” adjustment is adjusted by
“ADJUSTMENT SOFTWARE”, automatically.
LOCATION
VALUE
VALU E
Minimum distortion
level
*The output level of the standard signal generator (SSG) is indicated as the SSG’s open circuit.
5 - 6
Page 19

SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
[VR UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R801 7210003130 VAR TP76N97N-13F-10KA-2497
W801 8900011900 CBL OPC-1192
W802 8900011910 CBL OPC-1193 [US], [SEA]
8900012031 CBL OPC-1231A [US1]
EP801 0910055622 PCB B 5892B [US], [SEA]
0910055991 PCB B 5982A [US1]
DESCRIPTION
M.
LOCATION
H/V
[CONNECTOR UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
J851 6910014800 CNR IMSA-9230B-1-09Z133-T [US], [SEA]
6910015030 CNR IMSA-9230B-1-09Z135-T [US1]
EP851 0910055631 PCB B 5893A [US], [SEA]
0910055632 PCB B 5893B [US1]
DESCRIPTION
M.
LOCATION
H/V
[LOGIC UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
IC421 1110001810 S.IC TA7368F (ER) B 24.8/41.8
IC471 1110003800 S.IC NJM2904V-TE1 B 46.2/7.1
IC481 1130007300 S.IC TC4W66FU (TE12L) B 26.1/8.6
IC491 1110003800 S.IC NJM2904V-TE1 B 6.5/4.7
IC551 1110005350 S.IC NJM2870F05-TE1 B 12.6/39.7
IC581 1110005770 S.IC S-80942CNMC-G9C-T2 B 51.3/41
IC591 1130010390 S.IC HN58X2416TI T 51.2/40.6
IC661 1140011150 S.IC µPD780316GC-511-9EB 2600A B 36 /24.7
IC681 1130007300 S.IC TC4W66FU (TE12L) B 43.1/12.7
Q411 1530003090 S.TR 2SC4213-B (TE85R) T 62.2/40.6
Q431 1520000450 S.TR 2SB1132 T100 Q B 11.7/45.3
Q432 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB B 6.9/44.4
Q441 1530002850 S.TR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) T 51.8/28.5
Q442 1560001130 S.FET CPH3403-TL T 55/28
Q443 1560001130 S.FET CPH3403-TL B 57.8/29.4
Q444 1590000430 S.TR DTC144EUA T106 B 59.6/32.3
Q461 1590003430 S.TR UNR911HJ-(TX) B 56.1/13.8
Q462 1590003420 S.TR UNR911FJ-(TX) B 58.2/13.6
Q501 1590000430 S.TR DTC144EUA T106 B 11.9/15.9
Q531 1590001770 S.TR XP1213 (TX) B 17.9/14.6
Q532 1530002850 S.TR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) B 22/11.4
Q551 1520000450 S.TR 2SB1132 T100 Q B 17.1/22.9
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
M.
LOCATION
H/V
[LOGIC UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
Q552 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB B 13.3/23.7
Q553 1590000430 S.TR DTC144EUA T106 B 20.1/20.1
Q561 1510000670 S.TR 2SA1588-GR (TE85R) B 22/16
Q651 1590001770 S.TR XP1213 (TX) B 27.4/16.9
D451 1730002360 S.ZEN MA8062-M (TX) T 57/13.4
D452 1790000950 S.ZEN MA8056-M (TX) T 63.8/13.7
D453 1790000950 S.ZEN MA8056-M (TX) T 61.9/14
D454 1790000950 S.ZEN MA8056-M (TX) T 60/15.2
D581 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 48.8/40.1
D601 1790000620 S.DIO MA77 (TX) B 47.1/36.1
X601 6050011550 S.XTL CR-747 (9.8304 MHz) B 41.4/42.1
L421 6200010230 S.COL EXCCL3216U1 B 32.4/40.8
R411 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 62.9/42.5
R412 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 60/40.2
R413 7030003620 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) T 56.5/40.3
R414 7030003820 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 155 V (1.5 MΩ) T 54.3/43.1
R415 7030003820 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 155 V (1.5 MΩ) B 6.4/17.6
R421 7030003260 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω) B 19.7/44.7
R422 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) B 30.7/40.6
R431 7030003610 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ) B 16.5/42.1
R432 7030003800 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ) B 16.5/43.4
R433 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B 3.5/43.5
R434 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B 6.7/46.3
R435 7030003500 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) B 3.9/46.2
R441 7030003760 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) T 49.5/30.7
R442 7030003760 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) T 51.9/26.6
R443 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 57.4/28.7
R451 7030003280 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω) T 51.9/16.4
R452 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 55.4/14.2
R453 7410000950 S.ARY EXB-V8V 102JV T 61.9/10.4
R454 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 55.3/17.5
R461 7030003620 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B 54.5/9.8
R462 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 44.6/9.8
R463 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B 41/9.8
R464 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 60.9/11
R465 7030003690 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ) B 59/10.4
R466 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 57.7/10.4
R467 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 53.5/14.4
R468 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 55.7/15.7
R470 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 52/10.9
R471 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 41/7
R472 7030003590 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ) B 36.7/8.9
R473 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 39.7/7
R474 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 37.6/7.2
R475 7030010290 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 273 V (27 kΩ) B 36.4/10.2
R476 7030004740 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 392 V (3.9 kΩ) B 30.9/7.8
R477 7030004730 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 222 V (2.2 k
R478 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 52.2/14.2
R481 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 28.6/6.2
R482 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 24.7/5.3
R491 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 14.9/4.3
R492 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B 13.4/8.5
R493 7030003770 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 564 V (560 kΩ) B 11.1/5.9
R494 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 11.8/3.9
R495 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 13.1/5.6
R496 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B 9.8/10
R497 7030003710 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) B 16.8/11.6
R498 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 16.1/8.8
R501 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 10.6/7.8
R502 7030003620 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B 8.2/9.5
R503 7030003690 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ) B 6.9/9.5
R504 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 4.9/8.7
R511 7030003610 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ) B 12.9/10.4
R512 7030003700 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ) B 11.1/10
R513 7030003590 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ) B 14.2/14.4
R521 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B 4.9/10.2
R531 7030003600 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B 10/16
R532 7030003600 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B 9/12.5
R533 7030003650 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ) B 8.5/13.8
R534 7030003710 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) B 8.4/16.2
R535 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 17.1/5.8
R536 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 19.1/5.2
R537 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 19.1/6.5
R538 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 23.2/13.6
R539 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 19.9/8.5
R540 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 20.1/11.3
R551 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 18.1/26.3
R552 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B 14.4/20.2
DESCRIPTION
) B 35.6/6.7
Ω
US=USA, US1=USA−1 S.=Surface mount
M.
LOCATION
H/V
6 - 1
Page 20

[LOGIC UNIT] [LOGIC UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R553 7030003600 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B 12.4/19.4
R561 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 20.1/16.1
R562 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 22.3/20.1
R571 7030005930 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 334 V (330 kΩ) B 19.7/33.1
R572 7030008090 S.RES ERJ3EKF 1503 V (150 kΩ) B 22.3/33
R581 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 46.8/38.8
R582 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 54.5/20.2
R583 7410000750 S.ARY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ) T 53.3/22.3
R591 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 46.6/40.5
R592 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 46.6/43.2
R601 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) B 42.4/34
R602 7030003800 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ) B 43.7/34
R603 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B 44.8/38.1
R604 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B 45/34.1
R605 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B 48.9/33.7
R606 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 47.5/29.9
R611 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 4.4/17.3
R612 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 6.4/15.9
R621 7030003760 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) B 39.7/9.8
R631 7410000800 S.ARY EXB-V8V 103JV (10 kΩ) B 12.2/33.1
R632 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 12.2/26.6
R633 7410000800 S.ARY EXB-V8V 103JV (10 kΩ) B 12.2/29.1
R651 7030003380 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω) B 27.6/14.2
R652 7030003360 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω) B 26.3/14.2
R653 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 24.5/17.9
R654 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B 24.5/16.6
R681 7030003790 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 824 V (820 kΩ) B 43.3/16.4
R682 7030003730 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ) B 42.7/15.1
R683 7030003750 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 394 V (390 kΩ) B 45.9/15.1
R684 7030003830 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 185 V (1.8 MΩ) B 48.2/16
C411 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T T 65.7/42.5
C412 4550006140 S.TAN ECST1EY474R T 67.2/44.7
C413 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 61.7/43.9
C421 4550006210 S.TAN ECST1CX106R B 19.4/37.5
C422 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 18.5/42.6
C423 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 19.8/42.6
C424 4550006700 S.TAN ECST1AY106R B 17.7/46.5
C425 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B 30/43.4
C426 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 29.4/41.2
C427 4550007050 S.TAN ECST1AD157R B 26.8/36.4
C431 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 16.5/44.7
C432 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 3.9/44.8
C441 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 53.2/25.3
C451 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 50.6/16.4
C452 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 67.8/10.4
C453 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 55.6/10.3
C454 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 54.3/11.3
C455 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 57.5/15.8
C456 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 65.5/13.6
C457 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 59.4/12.9
C461 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 54.5/11.1
C462 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 46.6/10.4
C463 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 42.6/9.7
C464 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 62.9/10.4
C465 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 56.4/10.4
C466 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 56.8/17
C467 4550006700 S.TAN ECST1AY106R B 60.2/14.8
C471 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 47.8/4.4
C472 4550006950 S.TAN ECST0JX476R B 33.3/7.2
C473 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 45/4.4
C481 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 24.8/11
C491 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 2.9/7.4
C492 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 15.5/11.6
C502 4030007150 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 151J-T B 7.7/7.5
C503 4030006880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 472K-T B 13.4/7.2
C504 4030009980 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 152K-T B 11.9/13.8
C511 4030008650 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 332K-T B 14.2/11.6
C512 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 12.2/12.3
C521 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 4.9/7.4
C522 4030008880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 223K-T B 2.7/11.8
C531 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 18.1/11.6
C532 4030008910 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 393K-T B 21.9/5.2
C533 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 21.9/6.5
C534 4030009490 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 821K-T B 21.2/8.5
C535 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 24.6/12.3
C536 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 16/14.4
C551 4550006710 S.TAN ECST1AX226R B 21.3/24.7
C552 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 11.8/36.6
C553 4550006820 S.TAN ECST1DX106R B 16.1/38
C554 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 12.2/42.1
C555 4030011810 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 224K-T B 12.4/21.5
C556 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 13.2/36.6
C557 4550006710 S.TAN ECST1AX226R B 22/29.4
C561 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 20.6/18.2
C571 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 21/33
C581 4030008890 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 273K-T B 54.5/42
C582 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 52.9/18.9
C591 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 48.6/43.2
C601 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B 41.8/38.8
DESCRIPTION
M.
LOCATION
H/V
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C602 4030006980 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 070D-T B 42.8/37.5
C603 4030007070 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 330J-T B 44.1/36.1
C604 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 47/34.5
C605 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B 47/33.2
C606 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 47/31.9
C611 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 2.6/20.3
C612 4030008880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 223K-T B 2.6/17.6
C621 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 33.3/44
C622 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 1.6/32.1
C623 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 37.6/5.9
C641 4550006710 S.TAN ECST1AX226R B 16.1/17.8
C642 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 25.6/30
C643 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 28.1/32.6
C661 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 48.9/31.1
C662 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 50.2/31.1
C663 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 48.5/28.2
C664 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 49.2/26.2
C665 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 52.9/22.3
C666 4030008900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 333K-T B 51/22.2
C667 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 52.9/21
C668 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 49.5/20.1
C669 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 51.3/17.8
C670 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 50/17.8
C671 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 53.2/18.6
C681 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 38.4/11.2
C682 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T B 47.5/17.9
C683 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T B 44.6/17.7
C684 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T B 46.1/16.4
C685 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T B 45.7/19.2
J401 6510023520 S.CNR 54104-3692 B 5.8/30.8
J411 6510018350 S.CNR S3B-ZR-SM3A-TF B 65.5/37.9
DS651 5040002660 S.LED FY1101F-TR (LED) T 47.8/32.7
DS652 5040002660 S.LED FY1101F-TR (LED) T 47.8/16.7
DS653 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86 T 11.2/32.8
DS654 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86 T 11.2/16.6
DS681 5030002770 LCD L2-0390TAY-1
MC461 7700002630 MIC SKB-2246T-C33
S461 2230001060 S.SW EVQ-PUL 02K B 67.6/44.8
S641 2230001060 S.SW EVQ-PUL 02K B 51.4/44.8
W522 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 5.2/12.3
W523 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 2.7/14.6
W581 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 40.7/36.3
W641 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V [US1] only B 34.8/39.9
EP401 0910055613 PCB B 5891C
EP451 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 67.8/10.3
EP452 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 65.9/10.3
EP454 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 64.7/10.4
EP458 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 58.3/10.3
EP459 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 57/10.3
EP681 8930059150 LCT SRCN-2600-SP-N-W
[CHASIS UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
J41 6910014700 CNR 2600 ANT CONNECTOR
SP1 2510001092 SP 036D0801B <FG>
W1 7120000470 JMP ERDS2T0
W2 7120000470 JMP ERDS2T0
W41 8900011880 CBL OPC-1210 (P=0.5 N=36 L=70)
US=USA, US1=USA−1 S.=Surface mount
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
M.
LOCATION
M.
LOCATION
H/V
H/V
6 - 2
Page 21

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
IC1 1140005990 S.IC MB15A02PFV1-G-BND-ER B 34/35
IC141 1110002750 S.IC TA75S01F (TE85R) B 72.8/22.6
IC231 1110003200 S.IC TA31136FN (EL) B 17.6/11.3
IC251 1190000350 S.IC M62363FP-650C B 6.3/22.6
IC261 1110003800 S.IC NJM2904V-TE1 T 18.4/27.1
IC281 1130007300 S.IC TC4W66FU (TE12L) T 16.2/19.7
IC282 1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L) T 25.2/21.3
IC311 1120002830 S.IC NJM2125F-TE1 B 24.6/20.2
IC331 1190001860 S.IC EW-460-FT B 50.7/39.9
IC341 1130007570 S.IC BU4094BCFV-E2 B 15.8/22.1
IC381 1110004990 S.IC FX214LG/TR [US1] only B 18.3/34.6
IC382 1110003800 S.IC NJM2904V-TE1 B 7.7/35.2
IC383 1130007990 S.IC TC3W03FU (TE12L) T 17.1/35.9
Q1 1560000840 S.FET 2SK1829 (TE85R) T 29.6/35.5
Q2 1530002600 S.TR 2SC4215-O (TE85R) T 38.1/39.3
Q3 1560000540 S.FET 2SK880-Y (TE85R) T 29.2/31.7
Q41 1530002920 S.TR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T 49.2/32.5
Q47 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB T 45.8/37.8
Q51 1530002920 S.TR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T 49.1/26.6
Q61 1530002380 S.TR 2SC4215-Y (TE85R) T 50.3/22.3
Q62 1530002380 S.TR 2SC4215-Y (TE85R) T 47.5/17.3
Q71 1530002380 S.TR 2SC4215-Y (TE85R) T 36.2/17.5
Q81 1590001400 S.TR XP1214 (TX) B 43.5/24.3
Q82 1590000430 S.TR DTC144EUA T106 B 40.4/22.6
Q91 1530003420 S.TR 2SC5110-O (TE85R) B 49.2/26.7
Q101 1560001240 S.FET RD01MUS1] T 60.2/28
Q111 1560001230 S.FET RD07MVS1 T 59.8/21.9
Q141 1590000720 S.TR DTA144EUA T106 B 72.6/19
Q165 1580000750 S.FET 3SK294 (TE85L) T 50.1/5.9
Q171 1560000840 S.FET 2SK1829 (TE85R) T 50.7/13.5
Q191 1580000760 S.FET 3SK299-T1 U73 T 35.9/4.5
Q211 1530002600 S.TR 2SC4215-O (TE85R) B 20.4/4.2
Q221 1530002690 S.TR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R) B 34.4/21.7
Q231 1590000720 S.TR DTA144EUA T106 B 10.9/16.7
Q232 1530003310 S.TR 2SC5107-O (TE85R) B 18.1/15.8
Q291 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) T 29.5/23.7
Q321 1510000670 S.TR 2SA1588-GR (TE85R) T 49.7/36.5
Q322 1510000670 S.TR 2SA1588-GR (TE85R) T 54.1/39.4
Q323 1510000670 S.TR 2SA1588-GR (TE85R) T 58/38.1
Q381 1590000430 S.TR DTC144EUA T106 T 25.1/34.8
D1 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 34.2/31.5
D2 1750000830 S.VCP HVC362TRF T 32.6/37.5
D3 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 35.8/40.9
D31 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 39.9/32.7
D32 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 40/30.7
D33 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 37.9/33.4
D34 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 40/29.4
D35 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 39.1/27.4
D36 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 40.5/27.4
D37 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 39.8/25.4
D38 1750000710 S.VCP HVC350BTRF T 39.8/24.1
D39 1720000400 S.VCP 1SV245 (TPH3) B 40.1/18.6
D91 1790000620 S.DIO MA77 (TX) B 50.3/16.1
D92 1790000620 S.DIO MA77 (TX) B 52/12.6
D121 1790001670 S.DIO RB706F-40T106 B 67.1/15.5
D131 1750000580 S.DIO 1SV307 (TPH3) T 63.8/5.6
D132 1790001210 S.DIO 1SS375-TL B 68.7/3.9
D141 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) B 69.3/14.2
D151 1750000580 S.DIO 1SV307 (TPH3) T 63.9/2.8
D152 1790000620 S.DIO MA77 (TX) T 57.8/2.8
D153 1750000580 S.DIO 1SV307 (TPH3) B 62.9/8.8
D154 1720000780 S.VCP HVU350B TRF B 61.6/4.1
D155 1720000780 S.VCP HVU350B TRF B 54.6/6.3
D171 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 54.5/7.9
D181 1720000780 S.VCP HVU350B TRF T 44.2/6.8
D182 1720000780 S.VCP HVU350B TRF T 40.7/6.1
D231 1750000520 S.DIO DAN222TL B 4.6/9.1
D232 1750000520 S.DIO DAN222TL B 8.1/10.9
FI211 2030000210 S.MLH FL-353 (31.05 MHz) B 29.8/6.9
FI231 2020001270 CER CFWLB450KE2A-B0
FI232 2020001410 CER CFWLB450KGFA-B0
X1 6050011070 S.XTL CR-664A (15.300 MHz) B 34/40
X231 6070000190 S.DCR CDBCB450KCAY24-R0 T 21.1/5.6
X381 6050011560 S.XTL CR-746 (4.000 MHz) [US1] only T 19.4/40.3
L31 6200005540 S.COL ELJNC R47K-F B 42.2/31.6
L32 6200009460 S.COL 0.25-1.9-7TL 67N T 37.1/31.2
L33 6200005540 S.COL ELJNC R47K-F B 42.4/28
L34 6200008390 S.COL 0.25-1.9-9TL T 37/26.5
L35 6200008380 S.COL 0.28-1.0-11TR 42N B 38/28.9
L41 6200008190 S.COL 0.25-1.9-8TL 80N T 42.7/29.5
L47 6200002610 S.COL NL 252018T-R47J B 49.1/36
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
M.
LOCATION
H/V
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
L51 6200008390 S.COL 0.25-1.9-9TL T 44.1/24.7
L61 6200006980 S.COL ELJRE R10G-F T 48.1/20.6
L62 6200006980 S.COL ELJRE R10G-F T 46.1/19.4
L71 6200006980 S.COL ELJRE R10G-F T 38.1/17.7
L72 6200005720 S.COL ELJRE 33NG-F T 36.5/21
L81 6200007170 S.COL MLF1608A 3R3K-T B 47/26.9
L82 6200007170 S.COL MLF1608A 3R3K-T B 47.2/20.9
L92 6200005710 S.COL ELJRE 27NG-F B 50.5/29
L102 6200007690 S.COL LQW2BHN18NJ01L T 67.2/27.8
L112 6200008260 S.COL 0.30-1.7-8TL 60N T 65.7/21.1
L121 6200008510 S.COL 0.30-0.9-4TR 10.5N T 55.9/18.1
L122 6200008230 S.COL 0.30-1.3-5TL 22N T 56.9/12.7
L123 6200008280 S.COL 0.30-1.7-7TL 50N T 57.7/8
L124 6200003090 S.COL NL 322522T-2R7J-3 T 62.6/11
L131 6200009800 S.COL 0.26-1.1-7TR 30N T 66.9/9.7
L132 6200008580 S.COL 0.30-1.4-6TL 32N T 67.6/14.3
L151 6200008280 S.COL 0.30-1.7-7TL 50N T 67.2/3.6
L152 6200008280 S.COL 0.30-1.7-7TL 50N T 60.2/3
L153 6200003960 S.COL MLF1608A 1R0K-T B 62.8/11.2
L154 6200007750 S.COL LQW2BHN56NJ01L B 58.4/3.4
L155 6200007750 S.COL LQW2BHN56NJ01L B 52.2/4.1
L156 6200002150 S.COL ELJNC 56NK-F T 54.9/5.4
L165 6200003960 S.COL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T 46.5/11.5
L166 6200007750 S.COL LQW2BHN56NJ01L T 47.8/9
L181 6200007750 S.COL LQW2BHN56NJ01L T 41.4/3.4
L191 6200005540 S.COL ELJNC R47K-F T 34.7/8.5
L203 6200009180 S.COL ELJRE R10J-F3 B 41.2/4.5
L221 6200001980 S.COL NL 252018T-1R0J B 31.5/20
L222 6200001980 S.COL NL 252018T-1R0J B 26.1/14.9
R1 7030003700 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ) B 28.4/28.8
R2 7030003240 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω) B 31.5/30.4
R3 7410000950 S.ARY EXB-V8V 102JV B 28.6/33.3
R4 7510001660 S.TMR NTCG16 4LH 473KT B 29.9/39.3
R5 7030003940 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 104 V (100 kΩ) B 29.9/42
R6 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 29.9/37.6
R7 7030003610 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ) T 33.1/35.4
R8 7030003690 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ) T 31.8/35.4
R9 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 29.3/40.9
R10 7030003760 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) T 29.6/33.6
R11 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T 30.1/38.9
R12 7030003280 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω) T 40.3/39.2
R13 7030003670 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 823 V (82 kΩ) T 38/41.3
R14 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T 34.4/40.9
R15 7030003450 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ) T 39.7/37.3
R16 7030003290 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 560 V (56 Ω) B 35.8/28.9
R17 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B 39.2/34.6
R18 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 43.5/34.5
R19 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 44.9/34.5
R20 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 31.8/29.7
R21 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 31.3/31.7
R22 7030003550 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ) T 2.7/30.4
R31 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) B 44.6/31.8
R32 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 42.9/32.7
R33 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 36.9/29
R34 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) B 46/31.9
R35 7030003710 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) B 37.4/20.1
R36 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 37.7/17.5
R37 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 37.4/18.8
R38 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 36.3/14.7
R39 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 40.4/16.2
R41 7030003460 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) T 47.3/32.7
R42 7030006571 S.RES ERA3YED 392V T 45.4/33.2
R43 7030004040 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω) T 48.2/29.6
R47 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) T 45.8/35.9
R51 7030003490 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ) T 46.3/28
R52 7030005331 S.RES ERA3YED 562V T 46/29.3
R53 7030004040 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω) T 46.6/26.7
R61 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) T 49.7/19.1
R62 7030003660 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T 52.2/22
R63 7030004040 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω) T 45.5/21.4
R64 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T 45.3/17.4
R65 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) T 43.3/18.4
R71 7030003660 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T 40.5/19.8
R72 7030003360 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω) T 40.5/18.1
R81 7030003380 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω) B 45.7/25.7
R82 7030003390 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω) B 45.2/21.9
R83 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 38.2/22.1
R91 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 52.9/15
R92 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B 50.1/22.1
R93 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 50.1/19.3
R94 7030003460 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B 53.4/22.9
R95 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 52.5/27
R96 7030003500 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) B 51.9/29.3
R97 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) B 51.1/32.1
R98 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B 47.7/24.5
R101 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 67.3/31.6
R102 7030003620 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B 66.9/27.7
R103 7030003300 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 680 V (68 Ω) T 65.5/31.7
R111 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) T 65.5/24.7
DESCRIPTION
US=USA, US1=USA−1 S.=Surface mount
M.
LOCATION
H/V
6 - 3
Page 22

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R112 7030003200 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) T 66.9/24.7
R113 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 68.4/24.8
R114 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 66.9/23.5
R121 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 67/13.3
R122 7030000280 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 150 Ω (151) T 65.3/17.5
R131 7030003670 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 823 V (82 kΩ) T 70.1/12.9
R132 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 66.8/5
R133 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 67.8/7.4
R141 7030003700 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ) B 69.1/16.9
R142 7030003630 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ) B 72.4/17.1
R143 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B 70.4/19.7
R144 7030003490 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ) B 69.1/19.7
R145 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B 66.5/21.5
R146 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 67.8/21.1
R147 7030003700 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ) B 70.4/22.6
R148 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B 71.2/25.1
R149 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 69.6/29
R151 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B 60.8/9.9
R152 7030003600 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B 59.6/11.2
R153 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B 63.5/6
R154 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 65.8/7.8
R155 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B 54.2/9.4
R156 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 55.7/9.4
R165 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 51.8/7.9
R166 7030003730 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ) T 51.5/3.1
R167 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) T 47.6/3.1
R171 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 47.7/14.1
R172 7030003760 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) T 53/9.9
R173 7030003530 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ) T 52.9/13.4
R175 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 49.8/9.4
R181 7030003430 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω) T 46.5/5.1
R182 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) T 43.7/8.4
R183 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 43.7/9.7
R184 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 k
R185 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 40.7/9.1
R186 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) T 36.1/2.6
R191 7030003330 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 121 V (120 Ω) T 31.2/5.9
R192 7030003320 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) T 35.3/11.1
R193 7030003500 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) T 32.6/5.9
R201 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 49.5/11.8
R202 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 51.4/10.2
R203 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 49.2/6.9
R204 7030003210 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 120 V (12 Ω) B 48.6/8.9
R205 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 47.5/6.9
R206 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B 38.6/5.1
R211 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B 35.9/8.5
R213 7030003460 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B 23.3/4.3
R214 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 22.8/8.9
R215 7030003690 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ) B 22.9/5.6
R216 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B 21.8/6.9
R221 7030003780 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ) B 32.2/23.1
R222 7030003450 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ) T 32.9/19.6
R223 7030003340 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω) T 15.5/9.6
R231 7030003500 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) T 22.1/10.2
R232 7030003280 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω) T 25/9.2
R233 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 3.4/6.4
R234 7030003600 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B 7/9
R235 7030003600 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B 8.5/13.5
R236 7030004040 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω) B 4.9/11
R237 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B 4.7/15.7
R238 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B 11.1/13.4
R239 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) T 14.3/14
R240 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T 9.8/13.1
R241 7030003540 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ) T 10.7/11.1
R242 7030003390 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω) T 17.5/13.6
R243 7030004040 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω) B 9.8/10.9
R244 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B 20.7/14.9
R245 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 k
R246 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B 14.2/17.3
R251 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B 12.7/27.2
R261 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) [US1] only T 24.9/26
R262 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) T 22.6/25.3
R263 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T 25.8/29.9
R264 7030003550 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ) T 24.6/28.6
R265 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 22.6/28.1
R266 7030003530 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ) T 21.3/28.1
R267 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 24.6/27.3
R269 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 13.1/26.6
R270 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) T 22.2/30.4
R271 7030003650 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ) T 24.9/31.2
R272 7030003700 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ) T 22.2/31.7
R273 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 18.5/32.5
R274 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) [US1] only T 17.2/32.5
R275 7030003710 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) T 15.6/24.9
R276 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 13.1/21.4
R277 7030003750 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 394 V (390 kΩ) T 13.4/18.6
R278 7030010290 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 273 V (27 kΩ) T 42.4/38.5
R279 7030004910 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 332 V (3.3 kΩ) T 42.4/37.2
R280 7030004730 S.RES ERJ3GEYF 222 V (2.2 kΩ) T 42.4/39.8
R281 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 18.7/16.9
R283 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 22.1/22
R284 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 22/16.8
DESCRIPTION
) T 40.7/7.8
Ω
) B 14.1/15.8
Ω
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
M.
LOCATION
H/V
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R291 7030003660 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T 25.4/15
R292 7030003660 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T 28.2/17.6
R293 7030003660 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T 27.6/21
R294 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 30.9/18.8
R296 7030003580 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) T 31.5/20.8
R297 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 31.4/23.7
R298 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) T 28.6/27.2
R305 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T 30.2/20.8
R306 7030003660 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T 32.7/23.7
R307 7030003450 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ) T 28.6/25.9
R311 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 27.4/25.6
R312 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 28.9/23
R313 7030003630 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ) B 26.2/24
R314 7030003670 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 823 V (82 kΩ) B 23.5/23
R315 7030003750 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 394 V (390 kΩ) B 27/19.8
R316 7030003710 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) B 26.2/22.7
R317 7030003460 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B 21.5/22.6
R321 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 51.4/39.5
R322 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) T 42.4/35.9
R323 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 54/41.6
R324 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) T 52.9/37.1
R325 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 58/40.3
R326 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) T 55.1/36.6
R336 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 46.4/39.9
R381 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B 6.5/41.3
R382 7030003650 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ) B 7.1/39.8
R383 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 4.3/35.3
R384 7030003590 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ) B 8.4/28
R385 7030003500 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) B 8.4/29.3
R386 7030003680 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B 4.7/32
R387 7030003800 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ) T 20.4/35.1
R388 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T 23.2/35
R389 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T 25.8/37.7
C1 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 28.6/30.8
C2 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 30.4/26.7
C3 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 30.4/28
C4 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B 26.4/27.6
C5 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 28.6/42
C6 4550006560 S.TAN ECST1CY225R T 27.5/38.6
C7 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 30.6/40.9
C8 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T T 32.3/39.6
C9 4030007000 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 090D-T T 32.5/41.6
C10 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 40.8/41.3
C11 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T T 35.2/38.4
C12 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T T 37.8/36.7
C13 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 35.8/37.1
C14 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 35.2/26.9
C16 4550006300 S.TAN ECST1AY475R B 41.7/35.7
C17 4550006160 S.TAN ECST1CY155R B 46.7/35.9
C19 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 31.7/28.4
C20 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 32.6/32.6
C21 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 2.7/27.6
C31 4030009990 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 200J-T T 41.6/32.7
C32 4030007000 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 090D-T T 42.9/27
C33 4030007080 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 390J-T T 41.6/24.9
C34 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 37.7/16.2
C35 4030011340 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 471J-T B 39.1/14.7
C36 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 34.6/16
C37 4030009540 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 1R5B-T B 42.2/19.8
C41 4030009920 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 050B-T [US1] only T 45.4/31.9
C42 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 45.7/30.6
C43 4030007020 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T 49.7/29.6
C44 4030011340 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 471J-T T 51.8/31.6
C45 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 51.8/32.9
C46 4030009560 S.CER C1608 CH 1H R75B-T T 51.7/30.3
C47 4550006700 S.TAN ECST1AY106R T 45.1/41.5
C48 4550006700 S.TAN ECST1AY106R T 48.8/40.6
C49 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B 52.1/37.2
C51 4030009560 S.CER C1608 CH 1H R75B-T T 38.5/20.8
C52 4030011770 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 060B-T T 40.5/22.1
C53 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T 46.7/24.7
C54 4030007040 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 180J-T T 48.7/24.4
C55 4030011340 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 471J-T T 51.7/29
C56 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 51.7/27.6
C57 4030009500 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 0R5B-T T 51.4/25.5
C61 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 51.7/18.4
C62 4030006980 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 070D-T T 46.8/21.4
C63 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 43.3/17.1
C64 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 43.3/19.7
C65 4030007040 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 180J-T T 50.4/17.1
C71 4030009520 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 020B-T T 42.9/21
C72 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 40.5/16.8
C73 4030007020 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T 36.5/19.7
C74 4030007100 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 560J-T T 37.6/23.3
C75 4030007100 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 560J-T T 35.8/23.2
C81 4030007020 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 120J-T B 45/27.7
C82 4030007020 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 120J-T B 46.5/18.9
C83 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B 42.6/21.7
C91 4030007000 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 090D-T B 52.9/16.3
C92 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 53.4/20
C96 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 51.1/34.9
C97 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B 49.8/31.7
C98 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 48.5/31.7
C99 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 47.7/23.2
C103 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T B 53.4/34.1
C104 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 68.4/30.3
DESCRIPTION
US=USA, US1=USA−1 S.=Surface mount
M.
LOCATION
H/V
6 - 4
Page 23

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C105 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 66.9/29
C106 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 68.3/30.4
C107 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T 65.5/27.5
C111 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T T 64.1/26.2
C112 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 66.9/26.4
C113 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 69.7/26.4
C114 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 68.4/23.2
C115 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 68.4/20.3
C121 4030007100 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 560J-T T 56.9/15.7
C122 4030006990 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 080D-T T 55/12.7
C123 4030007030 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 150J-T T 59.6/12.4
C124 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 55.7/10.5
C125 4030007030 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 150J-T T 59.6/11.1
C126 4030007040 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 180J-T T 62.8/8
C127 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 60.8/7.7
C128 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 67.5/16.3
C129 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 65.4/12.2
C131 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 66.2/6.5
C132 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T 68.2/7.3
C133 4030011530 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 110J-T T 65/9.7
C134 4030009650 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 240J-T T 68.8/9.8
C135 4030006980 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 070D-T T 68.2/12.2
C136 4030007000 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 090D-T T 70.1/10
C137 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 66.1/3
C138 4030009510 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 010B-T B 68.7/6.1
C141 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 70.4/16.9
C142 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 66.9/17.7
C143 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 69.1/22.6
C144 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 74/25.1
C145 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 67.6/34
C151 4030007000 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 090D-T T 68.2/5.7
C152 4030007010 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 100D-T T 62.3/2.9
C153 4030009530 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 030B-T T 56.2/2.8
C154 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 61/7.9
C155 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 62.8/12.5
C156 4030011770 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 060B-T B 59.5/5.9
C157 4030007060 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 270J-T B 64/3.4
C158 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 65.5/5
C159 4030009550 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 2R5B-T B 61.3/2.4
C160 4030009510 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 010B-T B 56.7/3.2
C161 4030007100 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 560J-T B 52.8/6.5
C162 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 55.6/11.4
C163 4030009910 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 040B-T B 55.4/3.2
C164 4030006980 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 070D-T T 53.6/3.4
C165 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 50.2/3.1
C166 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 48.9/3.1
C167 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 46.1/9
C168 4030011770 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 060B-T T 58.9/5.6
C171 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T T 49.3/11.5
C172 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 52.2/5.9
C173 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 51.7/9.9
C181 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 47.3/6.5
C182 4030007120 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 820J-T T 43.7/3.1
C183 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 43.7/11
C184 4030009550 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 2R5B-T T 45.6/3.1
C185 4030009510 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 010B-T T 43.7/5.1
C186 4030007070 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 330J-T T 38.3/6.5
C187 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 37.9/8.4
C188 4030011770 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 060B-T T 39.7/3.1
C189 4030009920 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 050B-T T 38.4/3.1
C191 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 33.9/3.1
C192 4030007090 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T 31.9/3.8
C193 4030007100 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 560J-T T 34.6/6.5
C194 4030008880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 223K-T T 31.5/9.3
C195 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 31.5/8
C201 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 50.6/6.9
C202 4030007060 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 270J-T B 51.4/8.9
C203 4030006990 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 080D-T B 40.7/6.6
C210 4550006300 S.TAN ECST1AY475R B 39.4/12
C211 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 34.9/9.8
C213 4030011770 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 060B-T B 27.6/3.5
C215 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 26.6/10.3
C216 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 24.7/8.6
C217 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T B 19.8/7.1
C221 4030007010 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 100D-T B 32.4/28.1
C222 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 30.9/23.1
C223 4030007040 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 180J-T B 31.3/16.3
C224 4030009520 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 020B-T B 29.8/17.6
C225 4030007040 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 180J-T B 28.1/15.3
C226 4030007010 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 100D-T B 20.7/16.2
C231 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 15.5/8.2
C232 4030007130 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 101J-T T 20.1/10.9
C233 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 9.8/8.5
C234 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 9.8/13.7
C235 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 7.9/16
C236 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 11.1/10.5
C237 4030007140 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 121J-T T 13.5/12
C238 4030007140 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 121J-T T 11.5/13.1
C239 4550006300 S.TAN ECST1AY475R T 11.5/9.3
C240 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 12.4/9.3
C241 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 12.4/13.8
C242 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 17.4/14.9
C243 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 17.5/12.3
C244 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 20.7/13.6
C245 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 22.7/14.1
C246 4030011340 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 471J-T B 16.2/16.7
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
M.
LOCATION
H/V
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C247 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 17.4/11
C251 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 5.3/17
C252 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 12.3/19.3
C253 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 12.3/25.1
C261 4030008860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 153K-T [US1] only T 24.9/24.7
C262 4030008900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 333K-T T 22.1/23.3
C263 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T T 21.3/25.3
C265 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T 14.9/29.3
C266 4030007150 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 151J-T T 20.3/31.2
C267 4030006880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 472K-T T 24.9/32.5
C268 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T T 14.4/31.7
C269 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 13.6/24.7
C270 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 15.9/32.5
C271 4550006950 S.TAN ECST0JX476R B 40.7/40.4
C272 4030017480 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 474K-T T 20/16.1
C281 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 22.1/20.4
C282 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 70.5/31
C291 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 32.2/17
C292 4030009880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 682K-T T 26.9/16.3
C293 4030008900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 333K-T T 28.9/19.7
C294 4030009970 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 182K-T T 27.6/23.8
C301 4030008880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 223K-T T 31.6/26.2
C302 4030006870 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 222K-T T 28.6/28.5
C311 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 25.4/17.4
C312 4030008880 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 223K-T B 28.9/24.3
C313 4030009490 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 821K-T B 23.5/24.3
C314 4030009490 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 821K-T B 19.8/18.1
C315 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 28.4/21
C316 4030008920 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B 21.8/19.9
C322 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 51.3/41.6
C323 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 56/41
C324 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T 58/41.6
C325 4550006710 S.TAN ECST1AX226R B 58.9/39.4
C326 4550006300 S.TAN ECST1AY475R T 60.8/39.5
C327 4550006300 S.TAN ECST1AY475R B 25.3/41.1
C333 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 46.5/41.9
C341 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 12.3/22.3
C381 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 11.8/29.2
C382 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 10.1/39.7
C383 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 11.9/41
C384 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 5/37.3
C385 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 9.2/41.3
C386 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 10.4/29.4
C387 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 8.4/30.6
C388 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 4.3/34
C389 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 4.3/30
C391 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 26.3/39.3
C392 4030007060 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 270J-T T 21.7/35.1
C393 4030007060 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 270J-T T 21.1/37
C394 4030007140 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 121J-T T 13/38.2
C395 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T 13.6/33.8
C396 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 13.1/31.5
C397 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 15.1/27.5
C398 4030007020 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T 23.8/37
J281 6510023540 CNR B2B-PH-K-S
J351 6510023520 S.CNR 54104-3692 T 7.4/28.1
F281 5210000830 S.FUS ERBFE3R00U T 75.3/23.9
W40 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 37.6/31.8
W91 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 51.4/19.3
W92 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 51.4/22.1
W101 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 53.2/29.3
W102 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 52.7/32.1
W201 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 45.8/8.9
W202 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 42.9/8.9
EP1 0910055971 PCB B 5933A
EP2 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 28.6/39.3
EP3 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 28.8/37.3
EP101 6910013370 S.BEA BLM18BB221SN1D T 69.7/23.2
EP111 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 71.3/20.3
DESCRIPTION
US=USA, US1=USA−1 S.=Surface mount
M.
LOCATION
H/V
6 - 5
Page 24

MC461 7700002630 Microphone SKB-2246T-C33 1
MP441 6910014760 S. plate OG-503040 1
MP451 6910014760 S. plate OG-503040 1
MP462 8930059990 2600 Microphone sponge 1
MP461 8930059810 Microphone rubber 2246 1
MP681 8930058420 2600 LCD holder 1
MP682 8210019110 2600 Reflector 1
MP683 8930059700 Himelon sheet (CH) 1
DS681 5030002480 LCD L2-0390TAY 1
EP681 8930059150 LCD contact SRCN-2600-SP-N-W 1
7 - 1
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISASSEMBLY
Screw abbreviations
B0, BT: Self-tapping PH: Pan head
NI-ZU: Nickel-Zinc ZK: Black
R801 7210003130 TD76N-13F-10KA-2497 1
W801 8900011900 OPC-1192 1
W802 8900011910 OPC-1193 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
[VR UNIT]
EP1
EP2*
MP2
MP1
EP3
EP4
* Design is depended on versions.
J41 6910014700 2600 ANT connector 1
W1 7120000470 Jumper ERDS2T0 1
W2 7120000470 Jumper ERDS2T0 1
W41 8900011880 Cable OPC-1210 (P=0.5 N=36 L=70) 1
MP1 8210019140 2600 Front panel Ass'y 1
MP4 8930058380 2600 PTT button 1
MP5 8930058430 2600 PTT plate 1
MP6 8930058360 2600 PTT holder 1
MP7 8950005520 2403 9-PIN connector 1
MP8 8930055890 2403 Connector sheet 1
MP9 8930055730 2403 Connector seal 1
MP10 8930058720 2600 9-PIN sheet 1
MP11 8930058370 2600 6-Key 1
MP12 8310054270 2600 Window plate 1
MP13 8930058730 2600 Window sheet 1
MP15 8930060160 2600 PTT tape 1
MP16 8930060020 2600 Tape 1
MP21 8930059360 2600 Release button 1
MP22 8930055761 2403 Release plate-1 1
MP23 8930056540 Spring (AH) 2
MP31 8830001470 VR nut (N) 1
MP32 8930051500 O ring (AB) 1
MP33 8610011220 Knob N294 1
MP35 8810009510 Screw PH BT M2 × 4 NI-ZU 3
MP41 8010019080 2600 Chassis 1
MP42 8950005512 2403 Contact spring-2 1
MP43 8930055870 Seal O ring (AO) 1
MP44 8810007890 Screw PH B0 M2 × 4 SUS 1
MP45 8930058550 Seal O ring (AS) 1
MP46 8930058561 Seal 2403 A-main seal-1 1
MP47 8810009510 Screw PH BT M2 × 4 NI-ZU 6
MP51 8830001600 Nut (L) 1
MP52 8810010190 Bind M2 × 4 black SUS 2
MP53 8850001880 Sealing washer (W) 2
MP54 8810010190 Bind M2 × 4 black SUS 1
MP55 8810010120 Screw PH B0 M2 × 8 SUS ZK 2
MP65 8930059830 2600 Sheet 1
MP66 8930059800 2600 Pet sheet 1
MP71 8210017071 2337 C-panel-1 1
MP72 8810009270 Screw Truss M3 × 4 SUS ZK 1
SP1 2510001092 Speaker 036D0801B <KS> 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[CHASSIS PARTS]
QTY.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
[LOGIC UNIT]
MP41 8510013000 2336 VCO case Y534 1
MP42 8510015430 1922 VCO cover (A)-1 1
MP101 8510015250 2600 Shield case 1
MP111 8410002530 2681 PA heat sink 1
MP151 8510014860 2600 Shield plate 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
[MAIN UNIT]
EP1
Optional products
Antenna FA-S59V 1
EP2
Optional products
AC adaptor BC-147A [USA], [USA-1] 1
Optional products
AC adaptor BC-147E [SEA] 1
EP3
Optional products
Battery BP-227 [USA], [SEA] 1
Optional products
Battery BP-227FM [USA-1] 1
EP4
Optional products
Charger BC-152 1
MP1
Optional products
Hand strap HK-009 1
MP2
Optional products
Swivel belt clip MB-86 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
[ACCESSORIES]
Page 25

7 - 2
MP681 (L)
W801 (VR)
W802 (VR)
DS681 (L)
MP682 (L)
EP681 (L)
LOGIC UNIT
VR UNIT
MAIN UNIT
MP53 (C)
MP53 (C)
MP32 (C)
MP33 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP10 (C)
MP8 (C)
MP7 (C)
MP9 (C)
MP71 (C)
MP72 (C)
MP21 (C)
MP41 (M)
MP101 (M)
MP151 (M)
MP42 (C)
MP42 (C)
MP41 (C)
MP44 (C)
J41 (C)
MP45 (C)
MP46 (C)
MP41 (C)
MP43 (C)
MP65 (C)
MP66 (C)
MP55 (C)
(C) : CHASSIS PARTS
(L) : LOGIC UNIT
(M): MAIN UNIT
(VR): VR UNIT
MC461 (L)
MP22(C)
MP23 (C)
MP13 (C)
W41 (C)
1
2
3
12
MP11 (C)
MP1 (C)
Glued
Not putting glue to the depths
of a ditch of MP1.
Painting from
the lower part.
Painting with the
upper part from
a crack.
The glue must be applied to the areas when the front panel is replaced with new one, to ensure water tightness.NOTE 1 : Once the following parts are removed, an O ring or sealing washer
must be replaced with new one before reattachement.
REF. NO.
MP5 (C)
MP4 (C)
MP6 (C)
MP7 (C)
MP45 (C)
MP53 (C)
O ring
Sealing washer (W)
O ring (AB)
Antenna connector (J41)
MP52 (C) Screw
MP32 (C) R801
Mother parts
Daughter parts for
relayted replacement
Manufacture : Cemedine Co.
Type : Super-X
MP51 (C)
MP54 (C)
MP31 (C)
MP47 (C)
MP42 (M)
MP47 (C)
MP35 (C)
MP684 (L)
MP685 (L)
MP111 (M)
MP35 (C)
Apply a screw lock in the conclusion with J41 (C) and MP51 (C).
Reference No. : 89500001350
Reference Name : Screw lock 1401B
MP5 (C)
MP6 (C)
MP4 (C)
MP12 (C)
A basis to
install a
speaker
MP52 (C)
MP52 (C)
NOTE 1
NOTE 1
NOTE 3
NOTE 2
NOTE 3
NOTE3
NOTE3
NOTE 3
NOTE 2
NOTE 2
NOTE3
NOTE 1
NOTE 1
MP683 (L)
R801 (VR)
SP1 (C)
MP11 (C)
MP461 (L)
MP462 (L)
MP11 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP43 (M)
Page 26

7 - 3
13.7V
11.3V
7.1V 7.0V
7.7V
2.3V
0V
5.0V
0V
0V
2.6V
Power supply
CHARGER UNIT
R6
10k
R5
3.9k
R4
3.9k
DS1
TLG124A
J1
HEC2305-01-250
R3
10
C4
0.001
D3
DA204K
C5
0.001
C6
1
R8
47k
D4
MA8330
MP1
MP2
MP3
MP4
R9
2.2k
R20
220
D7
MA8051
R7
39k
R13
18k
OUT
VDD
VSSCDNC
R12
18k
C15
0.1
C13
1
D6
DAN202K
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
5
10
9
8
7
6
8
7
6
5
4
5
C3
0.1
Q1
2SD1664
Q2
2SA1162
Q3
2SJ417
IC2
MM1332BFBE
IC5
NJM2904M
IC1
AN78L05M
Q5
DTC144EKA
Q6
DTA144EKA
IC4
TB1009AF
Q4
2SB1132
B
T
IC3
S-80833CNMC
C1
0.01
C14
0.1
C2
47
W2
R10
100
C7
0.1
W1
R11
10k
R16
22k
R14
10k
R15
10k
W3
W4
D5
1SS355
C8
0.1
C91C10
0.1
C11
0.033
R17
294k
R28
10k
R19
18k
R29
330k
R23
27k
C12
0.1
R22
22k
R21
10k
R30
12k
R241R25
1
R27
47k
D2
MA8130
R1
1k
D1
SB07-03C
R2
10
SW1
SW2
LV
GND
VCC
EXT
CEL
CS
O
G
I
CHRGEOUT
SHORTDETECT
BTDETECT
LEDOUT
GND
VDD
TEST
PULSESELECT
COUNTERSELECT
OSC
• BC-152 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
• BC-152 CHARGER PARTS LIST
ELECTRICAL PARTS
MP7 (C)
MP1 (CH)
MP2 (CH)
MP3 (CH)
MP4 (CH)
MP5 (CH)
MP4 (C)
MP5 (C)
MP6 (C)
MP6 (C)
MP1 (C)
IC1 1180000970 S.IC AN78L05M-(E1) 1
IC2 1190001180 S.IC MM1332BFBE 1
IC3 1110005960 S.IC S-80833CNMC-B8S-T2 1
IC4 1190001470 S.IC TB1009AF(EL) 1
IC5 1110002700 S.IC NJM2904M-TE1 1
Q1 1540000550
S.TRANSISTOR
2SD1664 T100Q 1
Q2 1510000500
S.TRANSISTOR
2SA1162-GR (TE85R) 1
Q3 1590002880
S.FET
2SJ417-TL 1
Q4 1520000450
S.TRANSISTOR
2SB1132 T100 Q 1
Q5 1590000700
S.TRANSISTOR
DTC144EKA T146 1
Q6 1590000930
S.TRANSISTOR
DTA144EKA T146 1
D1 1790000670 S.DIODE SB07-03C-TB 1
D2 1730002540 S.ZENER MA8130-L(TX) 1
D3 1750000150 S.DIODE DA204K T146 1
D4 1730002460 S.ZENER MA8330-M(TX) 1
D5 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 1
D6 1160000070 S.DIODE DAN202K T146 1
D7 1730002320 S.ZENER MA8051-M(TX) 1
R1 7030000380 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1 kΩ(102) 1
R2 7030000140 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 Ω (100) 1
R3 7030000140 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 Ω (100) 1
R4 7030000450 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 3.9kΩ (392) 1
R5 7030000450 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 3.9kΩ (392) 1
R6 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ (103) 1
R7 7030002920 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHFX 39 kΩ (393) 1
R8 7030000580 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 47 kΩ (473) 1
R9 7030000420 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 2.2kΩ (222) 1
R10 7030000260 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 100 Ω (101) 1
R11 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ (103) 1
R12 7030000530 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 18 kΩ (183) 1
R13 7030001780 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHFX 18 kΩ (183) 1
R14 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ (103) 1
R15 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ (103) 1
R16 7030000540 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 22 kΩ (223) 1
R17 7030010150 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHF 2943 (294kΩ )1
R19 7030000530 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 18 kΩ (183) 1
R20 7030000300 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 220 Ω (221) 1
R21 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ (103) 1
R22 7030000540 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 22 kΩ (223) 1
R23 7030000550 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 27 kΩ (273) 1
R24 7030000020 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1 Ω (010) 1
R25 7030000020 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1 Ω (010) 1
R27 7030000580 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 47 kΩ (473) 1
R28 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ (103) 1
R29 7030000680 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 330 kΩ (334) 1
R30 7030000510 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 12 kΩ (123) 1
C1 4030004750 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 103K-T 1
C2 4510005340 ELECTROL 25 MV 47 HC 1
C3 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
C4 4030004720 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 102K-T 1
C5 4030004720 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 102K-T 1
C6 4510006160 ELECTROL 25 MV 10 HC 1
C7 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
C8 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
C9 4510006160 ELECTROL 25 MV 10 HC 1
C10 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
C11 4030008660 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 333K-T 1
C12 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
C13 4510006160 ELECTROL 25 MV 10 HC 1
C14 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
C15 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T 1
J1 6510023070 CONNECTOR HEC2305-01-250 1
DS1 5040001390 LED TLG124A 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
MP1 8010019100 Case 2612 1
MP4 8110007810 Cover 2612 1
MP5 8810008660 Screw BT M3 x 8 NI-ZU 3
MP6 8930039620 LEG cushion (A) 2
MP7 8930056330 Summary sheet (Z) TC-100TK (7 x 7) 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
MECHANICAL PARTS
CHASSIS PARTS (C)
MP1 8930051341 2338 TERMINAL-1 1
MP2 8930051341 2338 TERMINAL-1 1
MP3 8930051341 2338 TERMINAL-1 1
MP4 8930051341 2338 TERMINAL-1 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
CHARGER PARTS (CH)
MP1 8810001470 Screw.5 x 30 SUS 2
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
ACCESSORY PARTS
W1 7030000010 S.JUMPER MCR10EZHJ JPW (000) 1
W2 7030000010 S.JUMPER MCR10EZHJ JPW (000) 1
W3 7030000010 S.JUMPER MCR10EZHJ JPW (000) 1
W4 7030000010 S.JUMPER MCR10EZHJ JPW (000) 1
EP1 910055642 PCB B 5894B 1
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
QTY.
(C): CHASSIS PARTS
(CH): CHARGER PARTS
MP1
Page 27

8 - 1
SECTION PARTS LISTSECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
8 - 1 TRANSISTORS AND FETs
• MAIN unit and LOGIC unit
8 - 2 DIODES
• MAIN unit and LOGIC unit
• CHARGER unit
• CHARGER unit
A
C
DTC144EUA
1SV307 (TPH3)
(Symbol: TX)
DAN222TL
(Symbol: N-4)
HVC350BTRF
(Symbol: B0)
MA77(TX)
(Symbol: 4B)
MA8062-M(TX)
(Symbol: 6-2)
RB706F-40T106
(Symbol: 3J)
HVC362TRF
(Symbol: V2)
HVU350B TRF
(Symbol: 4)
MA2S728-(TX)
(Symbol: B)
2SB1132 T100 Q
2SA1588-GR
(Symbol: 5N)
(Symbol: QO/QY)
(Symbol: LL/LG)
2SC4215 O/Y
2SC4116 BL/GR
(Symbol: BAQ)
(Symbol: 26)
(Symbol: ZG)
2SC4213-B
(Symbol: AB)
2SC5107 O
(Symbol: MFO)
B
E
C
B
C
E
B
E
C
B
E
C
E1
E2
B2
C1
B1
C2
G
S
D
S
S
D
G
B
E
C
B
E
C
B
E
C
B
E
C
B
E
C
XP6501 AB
1SV245
(Symbol: T3)
1SS375-TL
(Symbol: FH)
(Symbol: A)
MA2S111
AC
AC
AC
AC
AC
AC
AC
ACAC
AC
AC
A
C
A
A
C
C
A
C
A
C
MA8056-M
(Symbol: 5-6)
DAN202K T146
(Symbol: N)
MA8051-M
(Symbol: 5-1)
MA8330-M
(Symbol: 33-)
SB07-03C-TB
(Symbol: 12)
DA204K T146
(Symbol: K)
1SS355 TE-17
(Symbol: A)
A1
A2
C
A
C
A
C
MA8130-L
(Symbol:13_ )
2SC4226-T1 R25
(Symbol: R25)
2SC5110-O (TE85R)
(Symbol: MGO)
2SK1829(TE85R)
(Symbol: KI)
2SK880Y
(Symbol: XY)
3SK294
(Symbol: UV)
3SK299-T1 U73
(Symbol: U73)
RD01MUS1
(Symbol: K2)
RD07MVS1
(Symbol: RD07MVS1)
UNR911FJ/HJ
(Symbol: 6O)
XP1213(TX)
(Symbol: 9L)
XP1214(TX)
(Symbol: 9H)
XP4601(TX)
(Symbol: 5C)
CPH3403-TL
(Symbol: KC)
DTA144EUA T106
(Symbol: 16)
B
E
C
B
E
C
B
E
C
B
E
C
E1
B1
B2
C1
C2
E1
B1
B2
C1
C2
E1
C2
B1
C1
E2
B2
D
S
G
D
S
G
2SD1664 T100Q
2SA1162-GR
(Symbol: 26)
(Symbol: J417)
DTC144EKA T146
2SJ417-TL
(Symbol: DAQ)(Symbol: SG )
DTA144EKA T146
(Symbol: 16)
B
E
C
B
C
E
S
D
G
G1
G2
S
D
G
S
D
D
G1
G2
S
D
Page 28

9 - 1
SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
51015 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 700
Horizontal
5
10
15
0
25
30
35
20
45
50
55
40
65
60
Vertical
510152025303540455055606570 0
Horizontal
5
10
15
0
25
30
35
20
45
50
55
40
65
60
Vertical
9 - 1 CHARGER UNIT (BC-152)
• TOP VIEW
• BOTTOM VIEW
1
VOLO
W801
W801
R801
W801
GND
VOLIN
to LOGIC UNIT J411
VCC
W802
W802
FHV
to MAIN UNIT
J281
510 0
5
10
0
Horizontal
Ver tical
J41
J41
J851
1357
2468
9
CP451
CP452
CP453
CP454
CP455
CP456
CP457
CP458
CP459
EXTVCC
EDETEDT
GND
ERESET
EXTRXD
EXTTXD
EXTMIC
EXTPTT
AFOUT
to LOGIC UNIT
• TOP VIEW • BOTTOM VIEW
9-2 VR UNIT
• TOP VIEW • BOTTOM VIEW
9-3 CONNECTOR UNIT
Page 29

9 - 2
to VR unit
W802
BATTERY
CP281
CP282
CP283
CP284
VCC
FHV
to
LOGIC
UNIT
J401
ANT
BEEPO
RSSIV
NOISV
EXSTBO
EXOEO
VCC
VCC
WDECV
VSSTBO
SMICO
MICO
SCLKO
LOINV
PLSTBO
DASTBO
UNLKI
MODIN
CDTENC
BTYPE
CDECV
SDATAO
VOLIN
TEMPV
W/NS
TDETV
M5V
T5VS
R5VS
V5VS
S5V
1
J351
51015 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 800
Horizontal
5
10
15
0
25
30
35
20
40
Vertical
• TOP VIEW
9-4 MAIN UNIT
The combination of this page and next page shows the
unit layout in the same configuration as the actual P.C.
Board.
Page 30

9 - 3
5101520253035404550556065707580 0
Horizontal
5
10
15
0
25
30
35
20
40
Vertical
MAIN UNIT
• BOTTOM VIEW
The combination of this page and previous page shows
the unit layout in the same configuration as the actual
P. C. Board.
Page 31

9 - 4
51015 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 700
Horizontal
5
10
15
0
25
30
35
20
45
50
40
Vertical
• TOP VIEW
9-5 LOGIC UNIT
The combination of this page and next page shows the
unit layout in the same configuration as the actual P.C.
Board.
Page 32

9 - 5
510152025303540455055606570 0
Horizontal
5
10
15
0
25
30
35
20
45
50
40
Vertical
to
MAIN
UNIT
J351
BEEPO
RSSIV
NOISV
EXSTBO
EXOEO
VCC
VCC
WDECV
VSSTBO
SMICO
MICO
SCLKO
LOINV
PLSTBO
DASTBO
UNLKI
MODIN
CDTENC
BTYPE
CDECV
SDATAO
VOLIN
TEMPV
W/NS
TDETV
M5V
T5VS
R5VS
V5VS
S5V
J401
1
GND
VOLO
VOLIN
to VR UNIT
J411
to CONNECT UNIT J851
CP441
CP442
AFOUT
SPE
SP1
CP451
CP452
CP453
CP454
CP455
CP456
CP457
CP458
CP459
EXTRXD
EXTTXD
EDETEDT
ERESET
EXTVCC
EXTPTT
EXTMIC
AFOUT
GND
MICROPHONE
MC461
+
–
PTT SQL
LOGIC UNIT
• BOTTOM VIEW
The combination of this page and previous page shows
the unit layout in the same configuration as the actual
P. C. Board.
Page 33

10 -1
SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAM
PLL
IC
FIL
LOOP
BUFF
BUFF
BUFF
BUFF
IF
AMP
RF
AMP
DRIVE
PRE
PWR
AMP
APC
CTRL
TX/RX
SW
ANT
SW
BPFBPFBPF
LPF
ANTENNA
CR-747
D/A
LCD
DRIVER
D/A
BATT
LIMIT
AMP
AF
MUTE
LPF
PWR
AMP
PWR
CTRL
POWER SW
R801
AF
MUTE
AF
MUTE
AF
MUTE
AF
MUTE
BPF
VCO
SW
FM
MOD
BUFFBUFF
LPF
LPF
LPF
LPF
✕ 2
BPF
CERAMIC
F281
FUSE
12
BPF
CERAMIC
AF
MUTE
AMP
AMP
FIL
RIPPLE
LPF
BPFBPF
V5VS
S5VS
M5VS
BTYPE
TDETV
WDECV
CDECV
RSSIV
NOISV
LVINV
TEMPV
BATTV
PTTIN
EPTTI
W/NS
LDTFS
BEEP
ISPMS
AFVS
AFMS
STXMS
MICMS
T5VS
R5VS
PWR
DET
30.6 MHz
15.3 MHz
REF
V5V
REG
S5V
REG
M5V
REG
R5V
V5V
T5V
M5V
CPU
5V
RESET
9.8304 MHz
EEPROM
BACK
LIGHT
KEY
CPU5V
CPU
VCO
RSSIV
PLL DATA BUS
Vcc
MIC
AMP
DEENPHA
Vcc
VR UNIT
VOLO
VOLIN
GND
Vcc
EDETEDT
AFOUT
CLONE
GND
PTT
EXP JACK
PTT
CONT
Vcc
DET
COMMON LINE
RX LINE
TX LINE
SQCON
31.05 MHz
PREENPHA
TDETV
TXMS
T1CON
MUTE
SW
T3CONT4CON T2CON
T1CON
DTCON
FRCON
SCRAMBLE
MOCON
D/A control BUS
MODIN
FIL
SW
CDTENC
CDECV
AFVS
SHIFT
SW
CSIFT
CENC 1, 2, 3
ATIS
ISPMS
EXTMIC
EXTPTT
EXTVCC
J851
J41
EPTTI
CONTROL LINE
Vcc
INTSP
MIC
LVINV
BEEPO
SCRAMBLE CODE DATA BUS
FM IF IC
W/N
SW
LOGIC UNIT
LOGIC UNIT
MAIN UNIT
MAIN UNIT
CHASSIS
S5V
REG
T5V
Q431: 2SB1132
Q432: XP6501
IC421
TA7368F
Q441: 2SC4116
Q442: CPH3403
Q443: CPH3403
Q444:DTC144EU
D451: MA8062
IN/EXT
MIC SW
MIC SW
IN/EXT
AMP
MIC
Q461:
UN911H
Q462:
UN911H
IC471A:
NJM2904V
NJM2904V
IC471B:
MICMS
IC481A:
TC4W66FU
STXMS
IC481B:
TC4W66FU
IC491A:
NJM2904V
IC491B:
NJM2904V
LDTFS
Q532:
Q531: XP1213
W/N
SW
ANALOG
SW
IC381:
FX214LG
IC282:
TC4W53FU
LPF
LPF
IC261A:
NJM2904V
NJM2904V
IC261B:
DETMS
SRXMS
IC281A:
TC4W66FU
TC4W66FU
IC281B:
Q411:
2SC4213
AFMS
BEEPO
WDETV
IC311:
NJM2125F
Q291:
XP4601
Q501:
DTC144EU
Q321: 2SA1588
Q323: 2SA1588
Q322: 2SA1588
IC382B:
NJM2904V
IC551:
NJM2870
REG
R5V
ATT
D154:
HVU350BHVU350B
D155:
HVU350B
D181:
HVU350B
D182: Q165:
3SK294
3SK299
Q191:
FI211: FL-353
W/N
SW
W/NS
W/N
SW
Q232: 2SC5107
Q231: DTA144EU
W/NS
FI231:
CFWM450E
FI232:
CFWM450G
D231:
DAN222
D232:
DAN222
Q221:
2SC4116
Q47: XP6501
Q3: 2SK880
Q1: 2SK1829
X1: CR-664A
IC1:
MB15A02PFV
D39:
1SV245
Q41: 2SC4226
V5V
VCOS
D31-34:
HVC350B
Q51:
2SC4226
D35-38:
HVC350B
Q61: 2SC4215 Q62: 2SC4215
Q71: 2SC4215
Q81: XP1214
Q82: DTC144EU
Q211:
2SC4215
D91: MA77
D92: MA77
Q91:
2SC5110
Q101: Q111:
IC141:
TA75S01F
Q141:
DTA144EU
D132:
1SS375
D131: 1SV307
D151: 1SV307
D152: MA77
146 –174 MHz
IC382A:
NJM2904V
X601: D601:
MA77
IC581: S-80942CNMC
Q561: 2SA1588
Q551: 2SB1132
Q552: XP6501
Q553: DTC144EU
IC591: HN58X2416TI
IC661:
µPD780316GC
DS651, DS652:
FY1101F
DS653, DS654:
SML-311YT
Q651: XP1213
RD01MUS1 RD07MVS1
X231:
CDBC450CX24
IC231:
TA31136FN
NOISV
2SC4116
CTIFS
CONNECTOR UNIT
BTYPE
IC331: EW-460
S5V
BTYPE
DET
IC251:
M62363FP-650C
Common
Transmit
Receive
Power supply
Page 34

11 - 1
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
to LOGIC
J411
to
LOGIC
UNIT
J401
1
2
3
38
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
37
J351
VCC
VCC
VOLIN
GND
BTYPE
S5V
M5V
V5VS
R5VS
T5VS
GND
MICO
SMICO
GND
W/NS
TEMPV
LVINV
CDECV
UNLKI
GND
MODIN
CDTENC
GND
VSSTB
EXSTB
DASTB
PLSTB
SDATA
SCLK
EXOE
GND
WDECV
RSSIV
NOISV
TDETV
BEEPO
GND
W801
W801
W801
VR UNIT
VOLIN
3
VOLO
2
GND
1
BATTERY
VOLIN
MICO
SMICO
CDECV
VSSTB
EXOE
WDECV
BEEPO
R801
10k-A
SCLK
VCC
VCC
S5V
J281
W802
1
FHV
C802
0.001
SDATA
W802
2
BTYPE
EXSTB
1
VCC
2
FHV
F281
ERBFE3R00U
CP281
CP282
CP283
CP284
V5VS
R5VS
T5VS
T5VS
BTYPE BTYPE
EXSTB
R5VS
HV
HV
M5V
V5VS
VCC
VCC
W/NS
TEMPV
LVINV
UNLKI
PLSTB
RSSIV
NOISV
TDETV
UNLKI
PLSTB
TEMPV
LVINV
S5V
S5V
S5V
S5V
MAIN UNIT
T5V
V5V
M5V
R1
SCLK
150k
EP2
SDATA
C1
0.1
R251
C251
470
0.01
C252
0.01
T5V
M5V
V5V
R2
22
UNLKI
SCLK
SDATA
PLSTB
S5V
R5
C5
100k
0.1
FRCON
DTCON
SDATA
SCLK
DA5V
MODIN
CDTENC
DASTB
4.92V
V5VS
R5VS
T5VS T5VS
Q1
2SK1829
R7
27k
R322
4.7k
C333
0.001
R6
10k
C6
2.2
R8
120k
R233
15k
RSSIV
NOISV
TDETV
T5V
R5V
M5V
Q321
2SA1588
C322
0.01
IC331 EW-460
R5V
W/NS
R321
10k
C221
10p
I
R3 1k
R4
NTCG16 4LH 473KT
R9
10k
C7
0.01
R10
470k
TX: 0.0V
RX: 3.54V
C222
R221
0.01
680k
D231
DAN222
W/NS
Q231
DTA144EU
WIDE: 0.0V
NARROW: 4.98V
R5V
O
G
LOCK: 4.85V
UNLK: 0.50V
EP3
D2
HVC362
R234
22k
TX: 0.0V
RX: 4.96V
Common Transmit
Power supply
Receive
R12
47
C10
0.1
R11
47k
R222
1.2k
L221
1.0µH
FI232
CFWM450G
12
C233
0.1
Q322
2SA1588
C323
0.01
R336
100k
PLL5V
D1
MA2S111
C8
100p
C9
9p
Q221
2SC4116
5
4
3
R236 4.7
R323
10k
C2
0.1
IC1 MB15A02PFV-1
9
CLOCK
10
DATA
11
LE
12
FC
13
NC
14
FOUT
15
P
16
B
X1
CR-664A 15.300MHz
D3
MA2S111
LVINV
2nd_Lo
R5V
C224
2p
C223
C225
18p
18p
R243
4.7
R237
12k
R235
22k
C234
0.1
TX: 4.87V
RX: 0.0V
T5V
C326
4.7
R326
4.7k
S5V S5V
CTFIS
DETMS
SRXMS
GND
VCC
OSCIN
345
R325
10k
EXSTB
SDATA
SCLK
CTFIS
SRXMS
DETMS
CKSIS
FIN
LD
DO
VP
C11
100p
C12
100p
4.78V
C4
47p
8
7
6
5
4
3
2nd_Lo
2
1
REFIN
R15
1.2k
C226
10p
12
C236
0.01
R238
15k
IC341
BU4094BCFV
1
STR
2
D
3
CLK
4
Q1
5
Q2
6
Q3
7
Q4
8
VSS9QS
15.3 MHz: 1.40 Vp-p
4.89V
Q2
2SC4215
C13
47p
R223
150
30.6 MHz: 0.2 Vp-p
C237
120p
R240
47k
C325
22
16
VDD
15
QE
14
Q5
13
Q6
12
Q7
11
Q8
10
QS
CKSIS
R239 220k
SQCON
M5V
EXOE
VCOS
TXMS
ATTS
C341
0.01
C238
120p
R241
6.8k
M5V
PLLIN
C239
4.7
C242
0.001
C327
4.7
ATTS
C3
0.001
OSCOUT
R13
82k
R14
47k
L222
1.0µH
FI231
CFWM450E
D232
DAN222
C235
0.1
Q323
2SA1588
C324
0.01
SCLK
SDATA SDATA
R17
100
R20
1k
R16
56
C14
0.001
C21
0.001
LVINV
IC231 TA31136FN
1
OSCIN
2
OSCOUT
3
MIXOUT
4
VCC
5
IFIN
6
DEC
7
FILOUT
8
FILIN
C240
0.001
DET
SQLOUT
TDETV
S5V
TXMS
VCOS
VCC
T5V
V5V
S5V
C241
0.1
DET
VCOS
R18
1k
C16
4.7
C19
0.001
Q3
2SK880
R22
8.2k
LVINV
PLLIN
R5V
IF5V
VSSTB
S5V
AFOUT
C243
0.001
C397
1
MIXIN
GND
N-REC
N-DET
RSSI
IFOUT
QUAD
R19
470
R21
10k
CP1
RXOUT
C396
1
C20
0.001
R242
390
C231
0.001
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C244
0.001
C17
1.5
RSSIV
RXIN
C245
0.001
R244
2.2k
MICO
S5V
R231
3.3k
C232
100p
SMICO
R245
47k
SCLK
Q47 XP6501
4
5
6
R47
2.2k
R232
47
R246
C246
47k
470p
SDATA
C387
R385
1
3.3k
C389
0.01
3
2
1
X231
CDBC450CX24
RSSIV
SCLK
VSSTB
R386
100k
R34
10
L34
92nH
TX: 0.0V
RX: 3.78V
Q232
2SC5107
10
SCIN
11
LD/LTH
12
AT
13
VSS
14
IC
15
RXOUT
C381
1
R384
18k
C47
10
R31
10
L33
0.47µH
D37
HVC350B
D38
HVC350B
R35
180k
C34
R36
0.001
47k
R214
470
R216
C217
680
100p
Q211
2SC4215
C247
0.001
7
8NC9
P/S
IC381
FX214LG
TXOUT16VBIAS17RXIN18HFO19HBMI20LBMI
TXOUT
RXIN
C384
0.1
C386
1
IC382
NJM2904V
1
2
3
45
L31
0.47µH
W40
D35
HVC350B
D36
HVC350B
R37
100k
21
C48
10
R215
120k
RSSIV
NC4NC5NC6NC
R381
10k
L32
67nH
D39
1SV245
C382
1
AG3V
R39
100k
SDIN
X/CLK
VDD
LFO/P
TXIN
8
7
6
R33
1k
C49
22p
VCO CASE
D33
HVC350B
D34
HVC350B
C32
9p
C37
1.5p
C35
470p
C215
0.001
C216
0.01
R213
1.5k
NOISV
NOISV
3
2
X
1
24
23
22
C383
1
R382
56k
R383
100k
L47
0.47µH
C385
0.1
C33
39p
R38
47k
D31
HVC350B
D32
HVC350B
SDATA
1 MHZ
S5V
TXIN
TXIN
VCC
T5V
V5FV
V5FV
C55
470p
DO1
DO1
R32
1k
L51
92nH
C51
0.75p
C36
1
S5V
S5V
C388
0.01
C53
22p
C52
6p
MOCON
VCOS
DO2
VCOS
PLLIN
R5V
31.05 MHz
RSSIV
A
B
S5V
1 MHZ
CKSIS
EXOE
VSSTB
DETOUT
DETIN
MICO
SMICO
AG3V
C
Page 35

11 - 2
DO2
DA5V
IC251 M62363FP-650C
VIN1
1
VOUT1
2
VOUT2
3
VIN2
4
VDD
5
LD
6
CLK
7
DI
8
VIN3
9
VOUT3
10
VOUT4
11
VIN4
12
VIN5
13
VOUT5
14
VOUT6
15
VIN6
16
DO
17
VDAREF
18
RESET
19
GND
20
VIN7
21
VOUT7
22
VOUT8
23
VIN8
24
R279
3.3k
R280
2.2k
C253
0.01
R278
27k
C271
47
R311
100k
R316
180k
R314
82k
R293
68k
R317
1.5k
R292
68k
C312
0.022
C315
0.1
C314
820p
C311
0.001
C313
820p
R312
100k
IC311
NJM2125F
1
2
3
4
5
C301
0.022
C293
0.033
R315
390k
R313
39k
C294
0.0018
C292
0.0068
C316
0.047
C262
0.033
R261
4.7k
R262
12k
R265
10k
R266
5.6k
R264
8.2k
R271
56k
R270
15k
C267
0.0047
C266
150p
IC261
NJM2904V
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
R269
100k
R276
10k
R277
390k
IC281
TC4W66FU
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
R273
1k
R274
2.2k
C268
0.047
R272
150k
C261
0.015
C263
0.047
R263
47k
R387
1M
X381
CR-746
4.000 MHz
C393
27p
IC383
TC3W03FU
CE
1
XT
2
XT
3
GND
4
Q
5
A
6
B
7
VCC
8
C391
0.1
C394
120p
R388
1k
C392
27p
C265
0.001
R275
180k
IC282
TC4W53FU
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
C272
0.47
R284
100k
C269
0.01
R267
10k
C281
0.01
R283
100k
Q291
XP4601
1
2
3
4
5
6
C302
0.0022
R306
68k
R305
100k
R291
68k
C291
0.01
R297
10k
R296
15k
R307
1.2k
R298
4.7k
R294
10k
R281
100k
R282
100k
C270
1
C395
0.1
R389
10k
C398
12p
Q381
DTC144EU
SQCON
SQLOUT
BEEPO
MOCON
T1CON
T2CON
DTCON
WDECV
WDECV
DETOUT
SCLK
DA5V
DA5V
DA5V
DA5V
T4CON
T3CON
DASTB
MODIN
CDTENC
CTFIS CTFIS
CTFIS
CTFIS
DETMS
DETMS
DETMS
RXDEC
RXDEC
CDECV
CDECV
R5V
SRXMS
SRXMS
SRXMS
DETIN
SDATA
DET
VOLIN
AG3V
AG3V
AG3V
AG3V
CKSIS
S5V
S5V
S5VS5V
S5V
R5V R5V
R5V
DET
DET
DET
S5V
S5VS5V S5V
S5V
S5V
S5V
VOLIN
BEEPO
FRCON
S5V
DETIN
S5V
1 MHZ
CKSIS
AG3V
DET
C195
0.001
C72
0.001
L62
0.1 H
R71
68k
L191
0.47 H
C135
7p
C63
0.001
C134
24p
R62
68k
C106
0.001
R113
4.7k
C129
0.001
R103
68
R94
1.5k
Q91
2SC5110
Q62
2SC4215
Q191
3SK299
L92
27 H
L112
60nH
R96
3.3k
C74
56p
C126
18p
C73
12p
MP41
R131
82k
C75
56p
L132
32nH
R101
4.7k
R91
1k
C121
56p
R192
100
C97
47p
R93
10k
Q61
2SC4215
D91
MA77
L123
50nH
Q71
2SC4215
L71
0.1 H
C105
0.001
C62
7p
D121
RB706F-40
C136
9p
R122
151
C114
47p
R112
10
R114
100k
L124
2.7 H
R98
100
C194
0.022
C99
0.001
C61
0.001
R72
220
C193
56p
CP131
ANT
J41
1
2
C133
11p
R64
47k
L61
0.1 H
L72 33nH
R132
10k
C132
22p
C127
0.001
R102
33k
C123
15p
C103
100p
R97
10
R92
100
R193
3.3k
C131
0.001
C112
0.001
C71
2p
D92
MA77
D131
1SV307
C92
0.001
C111
100p
C65
18p
C115
0.001
R121
15k
C104
0.1
L122
22nH
L102
18nH
EP101
C98
0.001
C145
0.001
R111
10
C91
9p
C64
0.1
C128
47p
C122
8p
C113
0.1
C107
22p
R95
470
IC141
TA75S01F
1
2
3
4
5
R1491kR148
100
R142
39k
R147
150k
R146
10k
R143
2.2k
C137
0.001
C143
0.1
C141
0.1
R144
2.7k
R145
12k
R141
150k
D141
MA2S728
Q141
DTA144EU
C144
0.01
L151
50nH
L152
50nH
L154
56nH
C151
9p
C152
10p
C153
3p
D151
1SV307
D152
MA77
C157
27p
C159
2.5p
D154
HVU350B
C156
6p
R153
220k
R154
10k
C160
1p
D155
HVU350B
C161
56p
R155
220k
R156
10k
C163
4p
L155
56nH
C164
7p
R165
100k
R166
270k
R167
470
C165
0.001
C166
47p
Q165
3SK294
C171
0.47
C181
0.001
C184
2.5p
C182
82p
C183
0.001
C185
1p
R181
820
R182
220k
D181
HVU350B
L166
56nH
D182
HVU350B
C186
33p
C187
0.001
C188
6p
L181
56nH
R183
10k
R184
220k
R185
10k
R186
4.7k
C189
5p
R191
120
R206
4.7k
R205
470
R204
12
R203
470
R202
10k
R201
1k
C202
27p
C201
0.001
L203
0.1 H
L165
1H
C167
0.01
FI211
FL-353
R211
1k
C211
0.001
C213
6p
Q171
2SK1829
Q111
RD07MVS1
Q101
RD01MUS1
D132
1SS375
R65
100
Q41
2SC4226
Q51
2SC4226
Q81 XP1214
1
2
34
5
Q82
DTC144EU
L41
80nH
L81
3.3 H
R42
3.9k
R41
1.5k
R43
4.7
R81
330
R52
5.6k
R51
2.7k
R53
4.7
R82
390
C42
47p
C41
5p
C43
12p
C82
12p
C56
0.01
C57
0.5p
L82
3.3 H
C54
18p
R83
10k
C81
12p
C46
0.75p
C83
47p
R63
4.7
C142
0.001
C191
0.001
C192
47p
C31
20p
C96
0.001
MP111
L121
10.5nH
C124
0.001
C125
15p
R152
22k
L153
1H
R151
100
C154
0.001
C155
0.001
C138
1p
C203
8p
C168
6p
L156
56nH
W91
W92
W101 W102
W201W202
C210
4.7
T5V
EP111
T5V T5V
T1CON
T1CON
T1CONT2CON
RSSIV
RSSIV
ATTS
T4CON T3CON
TXMS
VCOS
R5V
R5V
V5FV
PLLIN PLLIN
TDETV
S5V
RSSIV
S5V
S5V
RSSIV
S5V
S5V
T4CON
T3CON
T2CON
DET
VCOS
T5V
VCC
VCC VCC
31.05 MHz
RSSIV
DO2
PLLIN
R5V
C158
0.001
C162
0.001
D153
1SV307
S5V S5V
ATTS
TXMS
TDETV
T1CON
DO1
A
B
C
R61
100
C45
0.01
C44
470p
C172
0.001
R175
10k
R173
5.6k
R172
470k
R171
10k
D171
MA2S111
C173
47p
L131
30nH
R133
15k
MAIN UNIT
CKSIS
S5V
S5VS5V
S5V
VCO CASE
1
2
3
Common
Transmit
Receive
Power
supply
4.97V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 0.89V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 4.20V
TX: 3.52V
RX: 3.46V
TX: 3.51V
RX: 3.42V
TX: 1.87V
RX: 0.0V
TX: 1.10V
RX: 0.36V
TX: 4.86V
RX: 0.0V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 4.95V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 3.59V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 1.86V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 3.22V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 3.22V
TX: 0.93V
RX: 4.42V
2.11V
2.11V
2.11V
CTCS mode: 5.00V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 1.71V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 3.61V
Page 36

11 - 3
EXTSV
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
BEEPO
RSSIV
NOISV
EXSTBO
EXOEO
VCC
VCC
WDECV
VSSTBO
SMICO
MICO
SCLKO
LOINV
PLSTBO
UNLKI
MODIN
BTYPE
CDECV
VOLIN
TEMPV
W/NS
TDETV
M5V
T5VS
R5VS
V5VS
S5V
C522
0.022
R511
27k
R433
2.2k
C411
0.47
R432
1M
R494
100k
C683
0.47
C591
0.01
C682
0.47
Q432
XP6501
123
456
C503
0.0047
C422
0.1
C423
0.001
R461
33k
R521
680
R496
220k
IC581
S-80942CNMC-G9C
1
OUT
2
VDD
3
VSS NC
4
CD
5
Q431
2SB1132
R435
3.3k
R434
2.2k
C432
0.1
C431
1
R501
100k
C426
0.047
R495
4.7k
C521
0.1
R493
560k
C512
0.1
C684
0.47
C581
0.027
R491
15k
C413
0.1
R481
100k
C461
0.001
R422
10
C421
10
C502
150p
R512
150k
MC461
SKB-2746
R537
47k
Q532
2SC4116
R532
22k
R531
22k
R535
10k
C535
0.01
C536
0.047
C531
0.047
C534
820p
C532
0.039
C533
0.1
Q531
XP1213
2
34
5
R540
15k
R539
47k
R536
47k
R534
180k
R538
1k
R533
56k
C454
47p
C457
47p
C451
0.001
C453
0.1
R452
1k
R451
47
D451
MA8062
C452
0.001
D454
MA8056
D453
MA8056
D452
MA8056
C462
0.1
C492
1
L421
EXCCL3216U1
R415
1.5M
R414
4.5M
R482
100k
IC491
NJM2904V
1
2
3
45
6
8
R411
10k
R471
47k
R472
18k
R473
4.7k
R463
2.2k
R474
4.7k
C463
0.01
R462
4.7k
C464
0.1
C456
0.1
R454
10k
C471
0.01
C467
10
C466
0.1
R468
100k
Q461
UNR911HJ
Q462
UNR911FJ
R467
470
IC481
TC4W66FU
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
C47247R477
2.2k
R476
3.9k
R475
27k
C481
0.01
C491
0.01
C455
0.1
R604
12k
R605
12k
D601
MA77
C604
0.01
C511
0.0033
R611
10k
C611
0.001
R606
1k
C606
0.01
C605
47p
C553
10
Q552
XP6501
123
456
Q553
DTC144EU
R571
330k
R551
10k
IC551
NJM2870
CTRL
1
GND
2
NB3VOUT
4
VIN
5
C554
0.01
C552
0.001
C571
0.01
Q551
2SB1132
R572
150k
R552
2.2k
C551
22
R583
100k
R453
1k
Q501
DTC144EU
IC661
µPD780316GC
P30/TO0
P31/TI00
P32/TI01
P33/TO50/TI50
P34/TO51/TI51
P20/RXD0/SI3
P21/TXD0/SO3
P22/SCK3
P23/SI1
P24/SO1
P25/SCK1
P00/INTP0
P01/INTP1
P02/INTP2
P03/INTP3/ADTRG
P04/INTP4
P05/INTP5/BUZ/PCL
VPP
XT2
XT1
VSS1
VDD1X2X1
RESET
AVREF0
P10/ANI0
P11/ANI1
P12/ANI2
P13/ANI3
31
P14/ANI4
32
P15/ANI5
33
P16/ANI6
34
P17/ANI7
35
ANI8
36
ANI9
37
AVSS0
38
P120/AO0
39
AVREF1
40
CAPH
41
CAPL
42
VLCDC
43
VLC0
44
VLC1
45
VLC2
46
COM0
47
COM1
48
COM2
49
COM3
50
SCOM0
51
S0
52
S1
53
S2
54
S3
55
S4
56
S5
57
S6
58
S7
59
S8
60
S9
61
S1062S1163S1264S1365S1466S1567S1668S1769S1870S1971S2072S2173S2274S23
75
P90/S2476P91/S25
77
P92/S2678P93/S27
79
P94/S2880P95/S2981P96/S3082P97/S31
83
P80/S32
84
P81/S33
85
P82/S34
86
P83/S3587P84/S26
88
P85/S37
89
P86/S3890P87/S39
91
VSS0
92
VDD0
93
P60
94
P61
95
P62
96
P63
97
P64
98
P65
99
P66
100
P67
101
P40
102
P41
103
P42
104
P43
105
P44
106
P45
107
P46
108
P47
109
P50
110
P51
111
P52
112
P53
113
P54
114
P55
115
P56
116
P57
117
P70/TO4
118
P71/TI4
119
P72/TO52
120
P73/TI52
C671
0.1
R603
12k
C603
33p
R602
1M
R601
10
C602
7p
X601
CR-747
IC591
HN58X2416TI
A0
1
A1
2
A2
3
VSS
4
SDA
5
SCL
6
WP
7
VCC
8
C582
47p
C662
0.047
C663
0.047
C664
0.047
C666
0.033
C667
0.047
C665
0.047
C668
0.047
C669
0.047
C670
0.047
W581
R431
27k
Q411
2SC4213
C412
0.47
R413
33k
R412
10k
D581
MA2S111
J411
1
2
3
4
5
R562
4.7k
R561
10k
C561
0.01
Q561
2SA1588
R421
33
C424
10
IC421
TA7368F
NC
1
VCC
2
NC
3
VIN
4
RIPPLE
5
NF
6
PHASE
7
PREGND
8
PWGND
9
POUT
10
C425
47p
C427
150
R592
10k
R591
10k
R581
10k
C661
0.047
C643
0.01
C641
22
CP641
C642
0.01
R652
220
DS654
SML-311YT
Q651
XP1213
1
2
3
5
DS652
FY1101F-TR
R651
330
R654
680
R653
1k
DS651
FY1101F-TR
DS653
SML-311YT
DS681
L2-0390TAY
1
COM02COM13COM2
4
SEG05SEG16SEG27SEG38SEG49SEG510SEG611SEG712SEG813SEG9
14
SEG1015SEG1116SEG1217SEG1318SEG1419SEG1520SEG1621SEG1722SEG1823SEG19
R682
270k
R684
1.8M
R681
820k
R632
100k
C441
47p
Q441
2SC4116
R442
470k
Q442
CPH3403
R441
470k
Q444
DTC144EU
Q443
CPH3403
R443
100k
R553
22k
C555
0.22
C556
0.001
C557
22
C685
0.47
C601
22p
IC681
TC4W66FU
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
R683
390k
C681
0.1
R631
10k
R633
10k
S641
EVQ-PUL
S647
S646
S645
S644
S643
S642
C623
0.001
CP624
CP623
CP625
CP622
C621
0.001
C622
0.001
CP621
CP626
R621
470k
S461
EVQ-PUL
R465
120k
C465
0.01
R466
10k
R469
270k
R470
100k
IC471
NJM2904V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
C473
0.01
R464
15k
R503
120k
R502
33k
R497
180k
R498
100k
W522 W523
R478
4.7k
C612
0.022
R612
4.7k
C504
0.0015
R504
10k
R492
220k
W641
CP451
CP452
CP453
CP454
CP455
CP456
CP457
CP458
CP459
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
EP451
EP452
EP454
EP458
EP459
R513
18k
MP441
CENC3
CENC2
CENC1
EPTTI
LDTFS
LDTFSLDTFS
EXTRXD
EXTRXD
ERXDI
ETXDEXTTXD
EXTTXD
EDETEDT
EDETEDT
STXMS
ERESET
ERESET
OSC1
PTTIN
EPTTI
STXMS
MICMS
ISPMS
LDTFS
ETXD
ESDA
ESCK
ESCK
WDECV
EXTVCC
CENC1
CENC2
CENC3
TDEC
TDEC
CDECV
TEMPV
LOINV
RSSIV
NOISV
TDETV
S5VS
M5VS
M5V
SDATAO
PLSTBO
UNLKI
DASTBO
VSSTBO
SCLKO
EXSTBO
MOD
MOD
BATTV
H/L
CH/WX
DOWN
SQL
SQL
16/9
SCAN
UP
COM2
COM0
COM1
LEDS2
LEDS2
LEDS1
LEDS1
BTYPE
BTYPE
BTYPE
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
SEG0
AFMS
AFVS
M5VS
S5VS
V5VS
R5VS
T5VS
W/NS
W/NS
W/NS
W/NS
W/NS
AFVS
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG16
SEG17
SEG19
SEG18
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
COM0
COM1
COM2
EXOEO
MICMS
ETXDO
RES
SPE
ISPMS
ISPMS
AFMS
BEEPO
BEEPO
BEEPO
MICO
MICO
SMICO
SMICO
EXRES
EXRES
ERXDI
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
AF7V
AF7V
CONT1
CONT1
CONT2
CONT2
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
CPU5V
UNLK
UNLK
EXOE
EXOE
VSSTB
EXSTB
DASTB
PLSTB
SDATA
SCLK
EXTSV
PTTININMIC
INMIC
W461
W462
MOD3V
MOD3V
MOD3V
EXMIC
MODIN
CDTENC
SCRMS
S5V
S5V
S5V
S5V
S5V
S5V
S5V
VOLO
VOLIN
EXTPTT
EXTPTT
EXTMIC
EXTMIC
AFOUT
AFOUT
AFOUT
ATIS
J401
SDATAO
DASTBO
CDTENC
BEEPO
MODIN
CDTENC
LEDS2
LEDS1
W/NS
S5V
EPTTI
ERXDI
ETXD
STXMS
MICMS
PTTIN
EXTSV
VCC
W/NS
PTTIN
EPTTI
CENC1
CENC2
CENC3
R582
1k
MICO
SMICO
MICO
SMICO
4
CP642
to
MAIN
UNIT
J351
BEEPO
RSSIV
NOISV
WDECV
LOINV
CDECV
TEMPV
TDETV
T5VS
R5VS
V5VS
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
EXSTBO
EXOEO
VSSTBO
SCLKO
PLSTBO
SDATAO
DASTBO
OSC1
ESDA
ESCK
CSIFT
WDECV
OSC2
BATTV
BEEP
ETXDO
RES
ERXDI
VPP
WETIN
VSSTB
EXSTB
DASTB
PLSTB
SDATA
SCLK
EXTSV
SMICO
MICO
M5V
CDTENC
MODIN
VOLIN
VOLIN
CPU5V CPU5V
ATIS
ATIS
7
S5V
VCC
S5V
EXRES
ISPMS
W/NS
INMIC
INMIC
to
VR
UNIT
AFOUT
AFOUT
GND
EXTRXD
EXTTXD
EDETEDT
ERESET
EXTVCC
EXTPTT
EXTMIC
AFOUT
CONNECTOR
UNIT
LOGIC UNIT
CHASSIS
J41
J851
CP441
SP1
CP442
ESDA
ESCK
CPU5V
ERXDI
UNLK
EXOE
VSSTB
EXSTB
DASTB
PLSTB
SDATA
SCLK
CPU5V
BEEP
WETIN
EXRES
W/NS
MODIN
CDTENC
EXRES
ISPMS
MODIN
MODIN
ISPMS
S5V
VCC
AFMS
VCC
GND
INMIC
MODIN
CDTENC
M5V
VCC
S5V
M5V
S5V
AFVS
EXRES
ISPMS
S5V
S5V
W/NS
EXTSV
LEDS2
LEDS1
W/NS
W/NS
CONT1
CONT2
123456789
101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
1
+
–
PTT
SQL
Common
Transmit
Receive
Power
supply
4.90V
LED ON: 5.00V
LED ON: 5.00V
5.02V
9.8304 MHZ: 4.32 Vp-p
TRANSMIT DTCS: 4.99V
TRANSMIT CTCS: 0.08Vp-p
WIDE: 0.0V
NARROW:4.97V
TX: 1.93V
RX: 1.96V
TRANSMIT
CTCS CODE: 3.32Vp-p
TX: 2.03V
RX: 1.95V
4.95V
5.00V
TX: 0.0V
RX: 7.15V
TX: 0.40V
RX: 3.29V
1.97V
1.97V
PTT ON: 4.75
PTT OFF: 0.0V
EXT PTT ON: 0.0V
EXT PTT OFF: 4.45V
INT SP: 0.0V
EXT SP: 5.00V
Page 37

Asia Icom Inc.
6F No.68, Sec. 1 Cheng-Teh Road, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Phone : +886 (02) 2559 1899 Fax : +886 (02) 2559 1874
URL : http://www.asia-icom.com
E-mail : sales@asia-icom.com
Zac de la Plaine, 1, Rue Brindejonc des Moulinais
BP 5804, 31505 Toulouse Cedex, France
Phone : +33 (5) 61 36 03 03 Fax : +33 (5) 61 36 03 00
URL : http://www.icom-france.com
E-mail : icom@icom-france.com
Icom France S.a
Unit 9, Sea St., Herne Bay, Kent, CT6 8LD, U.K.
Phone : +44 (01227) 741741 Fax : +44 (01227) 741742
URL : http://www.icomuk.co.uk
E-mail : info@icomuk.co.uk
Icom (UK) Ltd.
Crta. de Gracia a Manresa Km. 14,750
08190 Sant Cugat del Valles Barcelona, SPAIN
Phone : +34 (93) 590 26 70 Fax : +34 (93) 589 04 46
URL : http://www.icomspain.com
E-mail : icom@icomspain.com
Icom Spain S.L
<Corporate Headquarters>
2380 116th Avenue N.E., Bellevue, WA 98004, U.S.A.
Phone : +1 (425) 454-8155 Fax : +1 (425) 454-1509
URL : http://www.icomamerica.com
E-mail : sales@icomamerica.com
<Customer Service>
Phone : +1 (425) 454-7619
Icom America Inc.
Glenwood Centre #150-6165
Highway 17 Delta, B.C., V4K 5B8, Canada
Phone : +1 (604) 952-4266 Fax : +1 (604) 952-0090
URL : http://www.icomcanada.com
E-mail : info@icomcanada.com
Icom Canada
A.B.N. 88 006 092 575
290-294 Albert Street, Brunswick, Victoria, 3056, Australia
Phone : +61 (03) 9387-0666 Fax : +61 (03) 9387-0022
URL : http://www.icom.net.au
E-mail : sales@icom.net.au
Icom (Australia) Pty. Ltd.
146A Harris Road, East Tamaki,
Auckland, New Zealand
Phone : +64 (09) 274 4062 Fax : +64 (09) 274 4708
URL : http://www.icom.co.nz
E-mail : inquiries@icom.co.nz
Icom New Zealand
1305, Wanshang Plaza, Shijingshan Road, Beijing China
Phone : +86 (010) 6866 6337 Fax : +86 (010) 6866 3553
URL : http://www.bjicom.com
E-mail : bjicom@bjicom.com
Beijing Icom Ltd.
Sopot, 3 Maja 54 Poland
Phone : +48 (58) 550 7135 Fax : +48 (58) 551 0484
E-mail : icompolska@icompolska.com.pl
Icom Polska
1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
Phone : +81 (06) 6793 5302
Fax: +81 (06) 6793 0013
URL : http://www.icom.co.jp/world/index.html
Communication Equipment
Himmelgeister Str. 100, D-40225 Dusseldorf, Germany
Phone : +49 (0211) 346047 Fax : +49 (0211) 333639
URL : http://www.icomeurope.com
E-mail : info@icomeurope.com
Icom (Europe) GmbH
Page 38

1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
S-13909MZ-C2-q
© 2002–2004 Icom Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...