Page 1

MF/HF MARINE TRANSCEIVER
iM802
SERVICE
MANUAL
Page 2

INTRODUCTION
This service manual describes the latest service information
for the IC-M802 MF/HF MARINE TRANSCEIVER at the time
of publication.
DANGER
NEVER connect the transceiver to an AC outlet or to a DC
power supply that uses more than 16 V. This will ruin the
transceiver.
DO NOT expose the transceiver to rain, snow or any liquids.
DO NOTre v erse the polarities of the power supply when con-
necting the transceiver.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm (100 mW)
to the antenna connector. This could damage the transceiver’s front end.
ORDERING PARTS
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component part number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
1110004080 S.IC µPC2709T IC-M802 MAIN UNIT 5 pieces
8810005770 Screw BiH M3×8 ZK IC-M802 Top cover 10 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
REPAIR NOTES
1. Make sure a problem is internal before disassembling the
transceiver.
2. DO NOT open the transceiver until the transceiver is
disconnected from its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn
them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An insu-
lated tuning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the trans-
ceiver is defective.
6. DO NOT transmit power into a signal generator or a
sweep generator.
7. ALWAYS connect a 50 dB to 60 dB attenuator between
the transceiver and a deviation meter or spectrum analyzer when using such test equipment.
8. READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly
before connecting equipment to the transceiver.
To upgrade quality, any electrical or mechanical par ts and
internal circuits are subject to change without notice or
obligation.
MODEL
IC-M802
VERSION
U.S.A.
Canada
Other
SYMBOL
USA
CAN
OTH
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
SECTION 3 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
SECTION 4 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
SECTION 5 PARTS LIST
SECTION 6 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISASSEMBLY
6 - 1 RC-25....................................................................................................................................................... 6 - 1
6 - 2 SP-24....................................................................................................................................................... 6 - 1
6 - 3 HM-135 .................................................................................................................................................... 6 - 1
6 - 4 IC-M802 ................................................................................................................................................... 6 - 1
SECTION 7 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS
8 - 1 HM-135
8 - 1 - 1 SW BOARD ............................................................................................................................ 8 - 1
8 - 1 - 2 MAIN BOARD......................................................................................................................... 8 - 1
8 - 2 RC-25
8 - 2 - 1 JACK BOARD......................................................................................................................... 8 - 1
8 - 2 - 2 CONNECT BOARD ................................................................................................................ 8 - 1
8 - 2 - 3 SENSOR BOARD................................................................................................................... 8 - 1
8 - 2 - 4 VR BOARD............................................................................................................................. 8 - 2
8 - 2 - 5 DISPLAY BOARD................................................................................................................... 8 - 3
8 - 3 IC-M802
8 - 3 - 1 DSP BOARD ............................................................................................................................8 - 5
8 - 3 - 2 MAIN UNIT.............................................................................................................................. 8 - 7
8 - 3 - 3 FILTER BOARD...................................................................................................................... 8 - 9
8 - 3 - 4 PLL UNIT.............................................................................................................................. 8 - 11
8 - 3 - 5 PA UNIT................................................................................................................................ 8 - 12
8 - 3 - 6 DRIVER BOARD................................................................................................................... 8 - 13
8 - 3 - 7 VARISTOR-1 BOARD ........................................................................................................... 8 - 13
8 - 3 - 8 VARISTOR-2 BOARD ........................................................................................................... 8 - 14
SECTION 9 BLOCK DIAGRAM
SECTION 10 WIRING DIAGRAM
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAMS
11 - 1 RC-25 and HM-135......................................................................................................... ........................11 - 1
11 - 2 IC-M802
11 - 2 - 1 MAIN UNIT (1)...................................................................................................................... 11 - 2
11 - 2 - 2 MAIN UNIT (2)...................................................................................................................... 11 - 3
11 - 2 - 3 MAIN UNIT (3)...................................................................................................................... 11 - 4
11 - 2 - 4 PA UNIT................................................................................................................................ 11 - 5
11 - 2 - 5 PLL UNIT (1)......................................................................................................................... 11 - 6
11 - 2 - 6 PLL UNIT (2)......................................................................................................................... 11 - 7
11 - 2 - 7 DSP BOARD......................................................................................................................... 11 - 8
11 - 2 - 8 FILTER BOARD.................................................................................................................... 11 - 9
Page 4
• IC-M802
‘‘
GENERAL
• Frequency coverage :
• Mode : TX/RX J3E (USB/LSB), J2B (AFSK), F1B (FSK), A1A (CW)
H3E [OTH]
RX H3E [USA], [CAN]
DSC J2B [USA], [CAN]
• Antenna impedance : 50 Ω
• Frequency stability : ±10 Hz [USA], [CAN],
±20 Hz [OTH]
• Power supply requirement : 13.6 V DC ±15% Negative ground
• Current drain (at 13.6 V DC) : RX; 3.0 A at Max. output power
TX; 30 A typical at Max. audio output
• Usable temperature range : –20˚C to +55˚C; –4˚F to +131˚F
• Dimensions (projections not included) :
240(W) × 94(H) × 238.4(D) mm; 2 7⁄16(W) × 3 11⁄16(H) × 9 3⁄8(D) in.
• Weight : 4.7 kg; 10.4 lb; 165.8 oz
‘‘
TRANSMITTER
• Output power : 150, 60, 20 W PEP
• Spurious emissions : –62 dB
• Carrier suppressions : 40 dB
• Unwanted sideband suppresion : 55 dB
• Microphone impedance : 600 Ω
‘‘
RECEIVER
• Sensitivity :
(Receiver)
(DSC) [USA], [CAN] : 0 dBµVe.m.f. (J2B; 2.1875, 4.2075, 6.3120, 8.4145, 12.5770, 16.8045 MHz)
• Squelch sensitivity :
• Spurious response rejection : More than 70 dB
• Clarity variable range : ±150 Hz
1 - 1
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
MODE
J3E, A1A
J2B, F1B
H3E
FREQUENCY
0.5–1.5999 MHz
1.6–1.7999 MHz
1.8–29.9999 MHz
1.6–1.7999 MHz
1.8–29.9999 MHz
1.5–1.5999 MHz
1.6–1.7999 MHz
1.8–3.9999 MHz
20 dB SINAD
30 dBµVe.m.f.
13 dBµVe.m.f.
8 dBµVe.m.f.
13 dBµVe.m.f.
8 dBµVe.m.f.
44 dBµVe.m.f.
30 dBµVe.m.f.
24 dBµVe.m.f.
10 dB S/N
16 dBµV
–1 dBµV
–6 dBµV
–1 dBµV
–6 dBµV
30 dBµV
16 dBµV
10 dBµV
MODE
J3E at 12.230 MHz
H3E at 1.000 MHz
Threshold
Less than +20 dBµV
Less than +30 dBµV
Tight
Less than +90 dBµV
Less than +110 dBµV
Receive
Transmit
DSC receive
[USA], [CAN]
500 kHz–29.9999 MHz
1.6000–2.9999 MHz 4.0000–4.9999 MHz
6.0000–6.9999 MHz 8.0000–8.9999 MHz
12.0000–13.9999 MHz 16.0000–17.9999 MHz
18.0000–19.9999 MHz 22.0000–22.9999 MHz
25.0000–27.5000 MHz
2.1875 MHz, 4.2075 MHz, 6.3120 MHz, 8.4145 MHz,
12.5770 MHz, 16.8045 MHz
Page 5

1 - 2
• RC-25 Remote controller
‘‘
GENERAL
• Microphone impedance : 600 Ω
• Audio output power : More than 5 mW at 16 Ω headphone with 10 % distortion
• Audio output impedance : 8–16 Ω
• Usable temperature range : –20˚C to +55˚C; –4˚F to +131˚F
• Dimension (projections not included) : 220(W)
× 110(H) × 84.4(D) mm; 8 21⁄32(W) × 4 11⁄32(H) × 3 5⁄16(D) in.
• Weight : 570 g; 1.3 lb; 20.1 oz
• SP-24 External speaker
‘‘
GENERAL
• Impedance : 4 Ω
• Input power : Rated input; 5 W
Maximum input; 7 W
• Usable temperature range : –20˚C to +60˚C; –4˚F to +140˚F
• Dimension (projections not included) : 110(W)
× 110(H) × 84.4(D) mm; 4 11 ⁄32(H) × 4 11 ⁄32(H) × 3 5⁄16(D) in.
• Weight : 370 g; 0.82 lb; 13.1 oz
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
Page 6
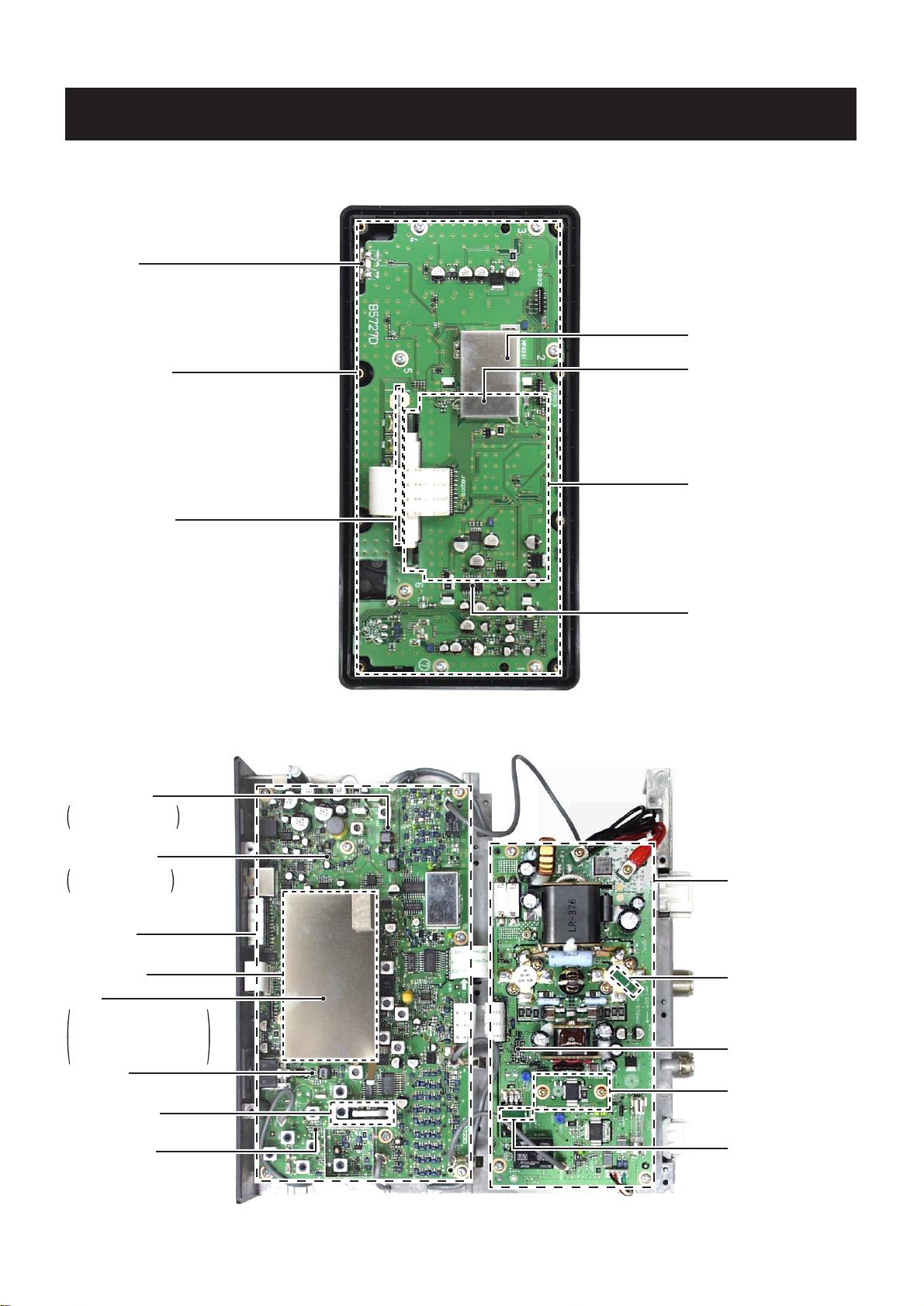
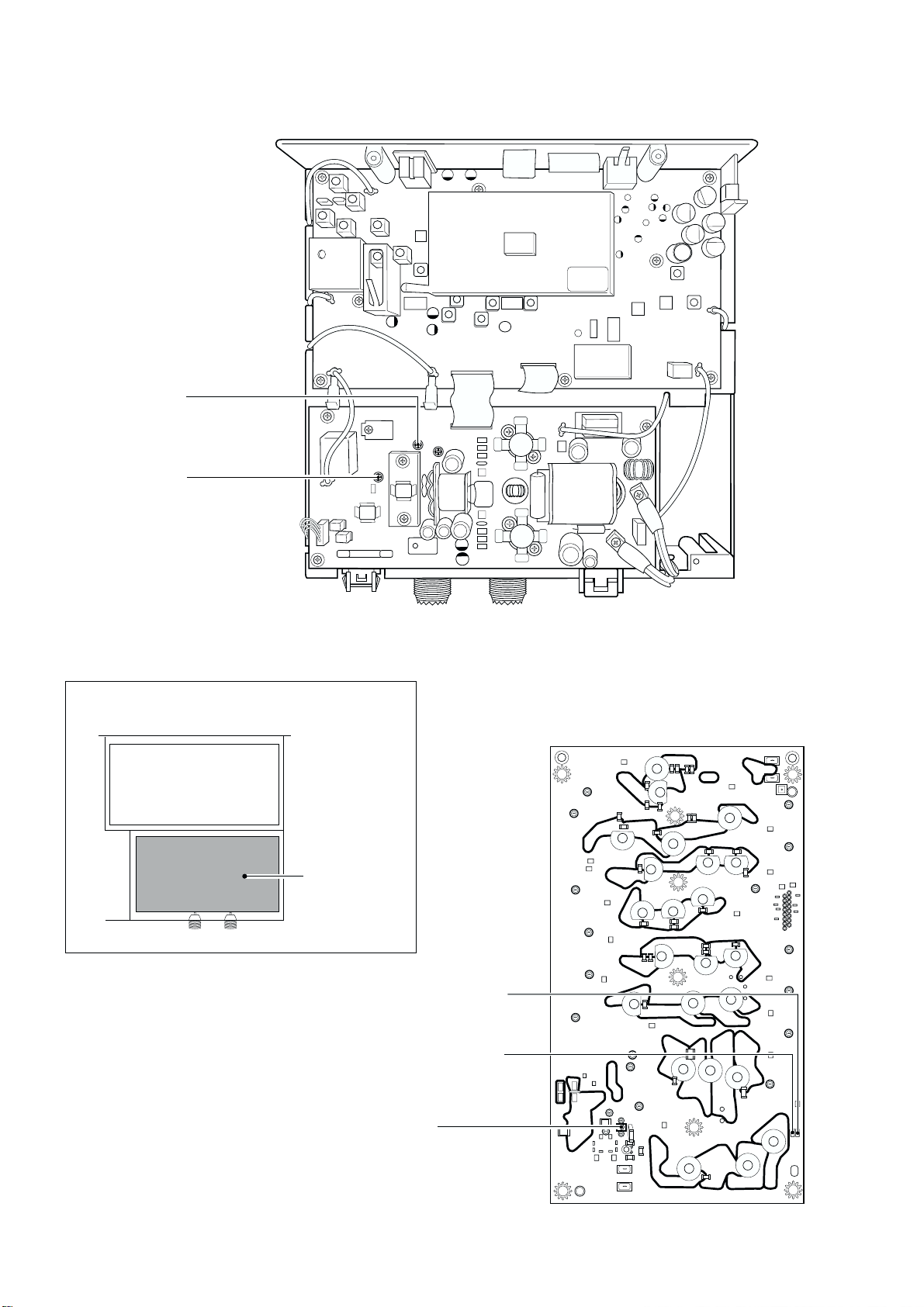
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
2 - 1
• RC-25
• IC-M802
VR BOARD
Reset IC
(IC8202: S-80942ANMP)
CPU
(IC8201: HD64F2134AFA20)
LCD unit
(DS8220: HLC770-018800)
Power amplifier
(IC8270: TA7368F)
DISPLAY BOARD
SENSOR BOARD
VR BOARD
Reset IC
(IC8202: S-80942CNMC)
CPU
(IC8201: HD64F2134AFA20)
LCD unit
(DS8220: HLC7700-018800)
Power amplifier
(IC8270: TA7368F)
DISPLAY BOARD
SENSOR BOARD
MAIN UNIT
DSP BOARD
CPU
(IC3303: M30624MGA)
2nd mixer
(D302: HSB88WS)
1st mixer circuit
1st IF amplifier
(Q203: 3SK131)
MAIN UNIT
DSC 1st mixer
D2301: HSB88WS
[USA],[CAN] only
DSC 2nd mixer
IC2701: TA4107F
[USA],[CAN] only
DSP BOARD
CPU
IC3303: M30624FGAFP
[USA],[CAN]
M30620FCAFP
[OTH]
2nd mixer
(D302: HSB88WS)
1st mixer circuit
1st IF amplifier
(Q203: 3SK131)
PA UNIT
VARISTOR-2 BOARD
VARISTOR-1 BOARD
FAN controller
(IC6501: TS522ID)
DRIVER BOARD
Page 7
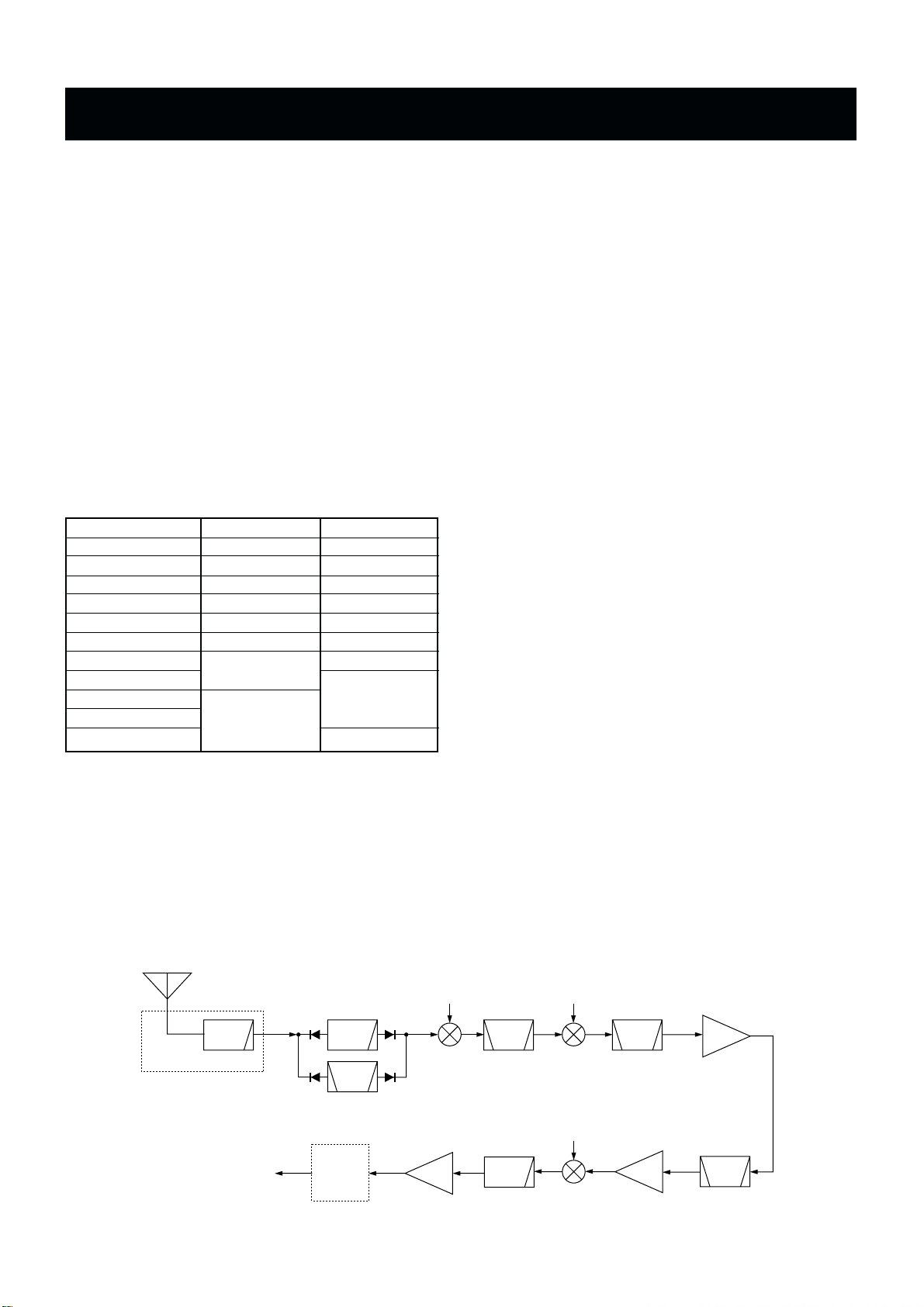
3 - 1
SECTION 3 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
3-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
3-1-1 RF FILTER CIRCUIT (FILTER AND MAIN
UNITS)
Received signals from the antenna connector are applied to
the transmit/receive switching and protection relay (FILTER
unit; RL7301) which is controlled by the CPU via the “TRXS”
line. The signals pass through the 30 MHz cut-off low-pass
filter (FILTER unit; L7321, C7321–C7323, C7325), and then
applied to the MAIN unit via the J7321.
The signals pass through the transmit/receive switch (D53)
and 1.6 MHz cut off high-pass filter (L51–L54, C54, C56,
C57, C59, C61–C64), and are then applied to one of the
bandpass filters (including one low-pass filter for below 2.0
MHz). These filters are selected by the filter control signals
(B0–B8) as described in the table below.
The filtered signals pass through the 33 MHz cut-off lowpass filter (L202, L203, C202–C206), and are then applied
to the 1st mixer circuit (Q201, Q202).
3-1-2 1ST MIXER AND IF CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signals into a
fixed frequency, 64.445 kHz 1st IF signal using PLL output
frequency. By changing the PLL frequency, only the desired
frequency is picked up at the pair of crystal filters (FI301a,
FI301b) via the 64.445 kHz bandpass filter (FI201) at the
next stage.
The IF amplifier (Q203) and resonator circuits are designed
between the filter pair. The PLL output signal (1LO) enters
the MAIN unit via the J601 and is amplified at the 1st LO
amplifier (Q601). The amplified signal is passed through the
100 MHz cut-off low-pass filter (L604, L605, C604,
C606–C610) to suppress harmonics components, and then
applied to the 1st mixer circuit (Q201, Q202).
3-1-3 2ND MIXER AND IF CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The 1st IF signal from the crystal filter (FI301b) is converted
again into a 455 kHz 2nd IF signal at the 2nd mixer circuit
(D302, L303, L304). The 2nd LO signal (2LO) from the PLL
unit enters the MAIN unit via the J301 to be applied to the
2nd mixer circuit.
3-1-4 3RD MIXER AND IF CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The 2nd IF signal passes through the low-pass filter (L305,
L306, C307–C311), and then applied to the IF amplifier
(Q401) via the ceramic bandpass filter (FI401). The amplified signal passes through the ceramic bandpass filter
(FI402), and then applied to the 3rd mixer circuit via the IF
amplifier (Q501). The 2nd IF signal is converted into a 12
kHz 3rd IF signal at the 3rd mixer circuit (IC501). The 3rd LO
signal (3LO) from the PLL unit enters the MAIN unit via the
J3601 to be applied to the 3rd mixer circuit.
3-1-5 DSP RECEIVER CIRCUIT (MAIN AND DSP
UNITS)
The DSP (Digital Signal Processor) circuit enables digital IF
filter, digital noise reduction, digital PSN (Pulse Shift
Network), phase demodulation, digital automatic notich, and
etc.
The 3rd IF signal is applied to the IF amplifier (MAIN unit;
IC1002, pin 5) after being passed through the low-pass filter
(MAIN unit; IC1002, pins 3, 1). The amplified 12 kHz 3rd IF
signal is amplified at the differential amplifiers (IC651a/b),
and is then applied to the A/D convertor section in the
CODEC IC (IC501) on the DSP board (EX-2432). At the
same time, the converted signal is level-shifted 5 V to 3.3 V
in the IC (IC501).
LPF
Antenna
FILTER unit
to transmit/receiver switch
LPF
FI301A
FI301B
FI401
FI402
Q401
Q5013rd mixer
IC501
IC1002
1st mixer
Q201
Q202
2nd mixer
Q201
Q202
1st LO
64—94 MHz
BPF
2—30 MHz
0.5—1.9999 MHz
BPF
Crystal
BPF
Crystal
IF
amp.
BPF
Crystal
LPF
IF
amp.
IF
amp.
DSP
UNIT
2nd LO
64 MHz
3rd LO
443 kHz
Frequency (MHz)
0.5–1.999
2–2.999
3–4.999
5–6.999
7–9.999
10–13.999
14–17.999
18–19.999
20–21.999
22–23.999
24–29.999
BPF ctrl signal
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
B8
LPF ctrl signal
L0
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
L6
L7
• RECEIVER CONSTRUCTION
Page 8
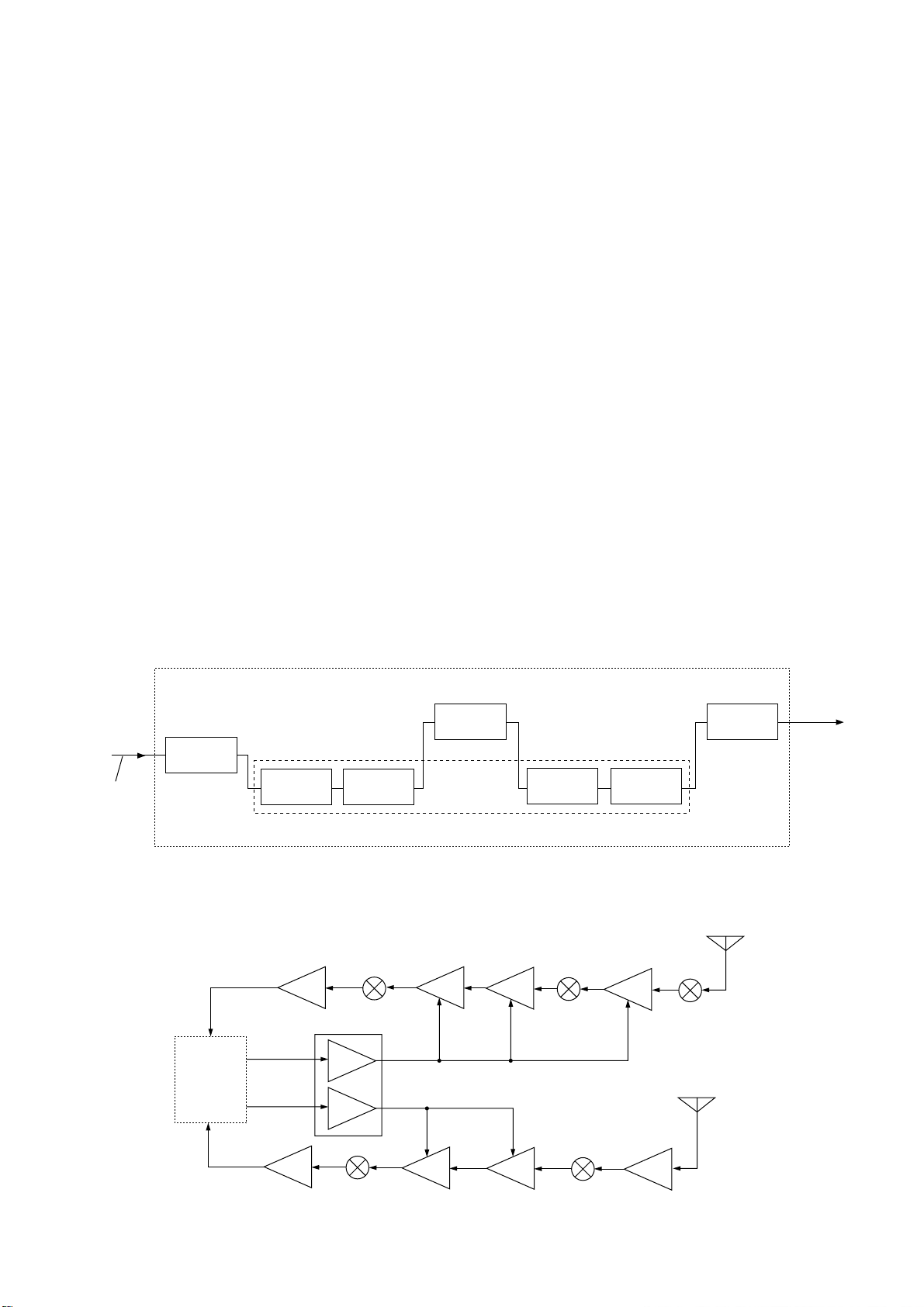
3 - 2
The level-shifted signal is applied to the DSP IC (IC301) for
the digital IF filter, demodulator, automatic notch and noise
reduction, etc.
The output signal from the DSP IC is applied to the D/A converter section in the CODEC IC (IC501) to convert into the
analog audio signals. Also the signals are level-shifted 3.3 V
to 5 V at the level converter section in the IC (IC501).
The level-shifted audio signals are passed through the
active filter (IC701a), and then applied to the MAIN unit via
J901 (pin 17) as the DRAF signal.
3-1-6 AGC CIRCUIT (DSP AND MAIN UNITS)
The AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit reduces IF amplifier gain and attenuates IF signal to keep the audio output at
a constant level.
The receiver gain is determined by the voltage on the AGC1
line from the DSP unit. The D/A converter for the AGC
(IC102) supplies control voltage to the AGC1 line and sets
the receiver gain with the [RF/SQL] control.
The 3rd IF signal from the CODEC IC (IC501) is detected at
the AGC detector section in the DSP IC (IC301). The output
signal from the DSP IC is level-shifted at the level converter
(IC101) and applied to the D/A converter (IC102). The AGC
voltage is amplified at the buffer amplifier section in the
IC102 and applied to the MAIN unit to control the AGC1 line.
When receiving strong signals, the detected voltage increases and the AGC1 voltage decreases. As the AGC1 voltage
is used for the bias voltage of the IF amplifiers (MAIN unit;
Q203, Q401, Q501), IF amplifier gain is decreased.
3-1-7 AF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (DSP AND MAIN
UNITS)
The AF amplifier amplifies the audio signals to the suitable
driving level for the speaker.
The AF signals from the DSP unit are passed through the
transmit/receive switch (MAIN unit; IC1703, pins 1, 6) via the
“DSPO1” signal, and then applied to the AF amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1702, pin 5) after being passed through the low-pass
filter (MAIN unit; IC1702, pins 3, 1). The amplified signal
passes through the the SQL gate (MAIN unit; IC1701, pins
7, 1) which is controlled by the CPU (IC3303, pin 49) via the
“SQLC” signal. The signal is applied to the electronic volume
IC (MAIN unit; IC1603, pin 2) which can control the volume
attenuation by AFG voltage from the CPU (MAIN unit;
IC3303). Beep, tone, side tone, monitor signals are applied
to the the elecronic volume IC too. The signal is applied to
the AF mute swtich, and then amplified at the AF power
amplifier (IC1601, pin 1). The amplified signal is applied to
the speaker (SP-24) after being passed through the speaker jack (J1451) via the “AFO” signal.
DSP
UNIT
IC1101
AGC1
2
6
1
7
AGC2
AGC
AGC
IC1002
DSPI1
IF
amp.
IC2702
DSPI2
AMP.
Q2502
IF
amp.
Q2401
IF
amp.
Q2301
Q2302
RF
amp.
Q501
IF
amp.
Q401
IF
amp.
Q203
From the
antenna
IF
amp.
From the
DSC antenna
Differential
converter
IC651b/a
DSP UNITMAIN UNIT
CODEC IC (IC501)
IC301 IC701a
DSPO1
AF
signals
DSPI1
(12 kHz)
3rd IF
signal
A/D
converter
D/A
converter
Level
converter
Active
filter
Level
converter
DSP IC
• DSP CIRCUIT
• AGC CIRCUIT
Page 9
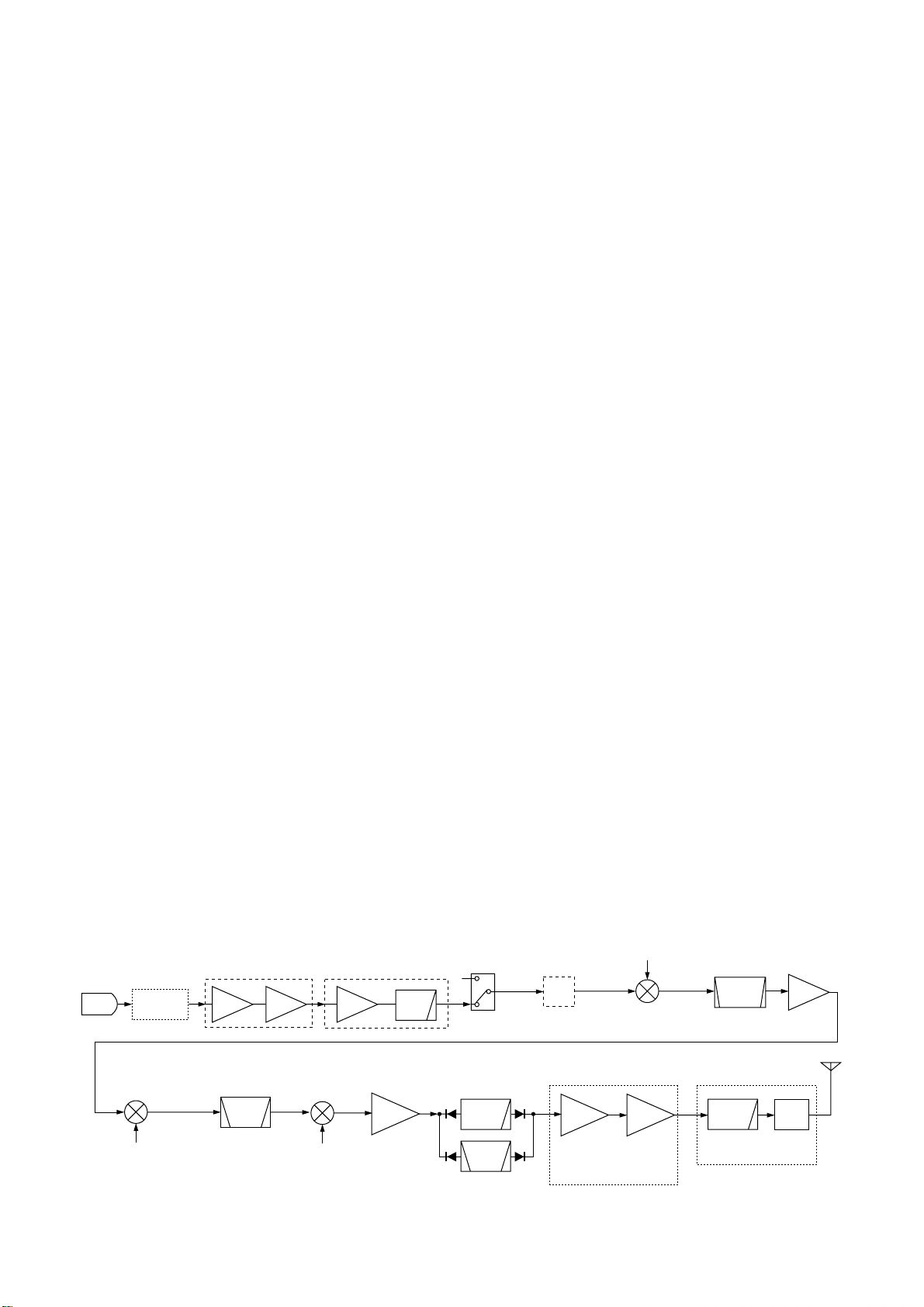
3 - 3
3-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
3-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
(RC-25, MAIN AND DSP UNITS)
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies microphone audio
signal to a level needed for the DSP circuit.
Audio signals from the [MIC] connector (J8701, pin 1) are
amplified at the AF amplifier (IC8280, pin 3), and then
applied to the gate modulator IC (MAIN unit; IC2001, pin 3)
via the J2051, pin 1 as “FMOD” signal. The signal is applied
to the DSP unit after being passed through the limitter amplifier and low-pass filter IC (MAIN unit; IC1051, pins 3, 7) as
“DSPI1” signal.
3-2-2 DSP TRANSMITTER CIRCUIT (DSP UNIT)
The DSP (Digital Signal Processor) circuit enables PSN
(Phase Shift Network)/Low Power/Phase modulator, transmitter monitor, side tone, and etc.
The microphone audio signals from the MAIN unit via the
“DISPI1” line are amplified at the differential amplifiers
(IC651a/b), and are then applied to the A/D converter section in the CODEC IC (IC501). at the same time, the converted signals are level-shifted 5 V to 3.3 V in the IC (IC501).
The level shifted signals are applied to the DSP IC (IC301)
and modulated at the DSP IC to p[roduce the 12 kHz transmitter IF signal.
The modulated IF signal from the DSP IC is applied to the
D/A convertor section in the CODEC IC (IC501) to convert
into the analog IF signal. Also the signal is level-shifted 3.3
V to 5 V at the level converter section in the IC (IC501).
The level-shifted IF signal is passed through the active filter
(IC701a), and then applied to the MAIN unit via J901 (pin
17) as the “DSPO1” signal.
3-2-3 SPEECH COMPRESSOR CIRCUIT
(DSP UNIT)
The DSP (Digital Signal Processor) circuit enables PSN
The speech compressor compresses the transmitter audio
input signals to increase the average output level (average
talk power).
When the speech compressor function is ON, the level-shifted signal from the CODEC IC (IC501) is applied to the DSP
IC (IC301) and compressed at the DSP IC to obtain an average audio level.
At the same time, the compressed signals are modulated at
the DSP IC and applied to the D/A converter section in the
CODEC IC (IC501).
3-2-4 IF AMPLIFIER AND MIXER CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The modulated 3rd IF signal from the DSP unit (“DSPO1”
signal: 12 kHz) passes through the transmit/receive swtich
(IC1703, pins 1, 5), and then applied to the 3rd mixer circuit
(IC901, pin 3). The applied 3rd IF signal is mixed with the
3rd LO signal from the DDS circuit (PLL unit; IC5701) to produce a 455 kHz 2nd IF signal.
The 2nd IF signal is output from IC901, pin 5 and passes
through the ceramic bandpass filter (FL402) to suppress the
unwanted signals via the D404. The filtered 2nd IF signal is
amplified at the 2nd IF amplifier (Q801), and then applied to
the 2nd mixer circuit after being passed through the D303
and low-pass filter (L304–L306, C304–C311, R306).
The 2nd IFsignal is mixed with 64 MHz 2nd LO signal, coming from the PLL circuit, at the 2nd mixer circuit (D302) to
obtain 64.455 MHz 1st IF signal. The 1st IF signal is passed
through the crystal bandpass filter (FI301A, FI301B) to cut
off the unwanted signals. The signal is applied to the transmitter mixer circuit (Q702, Q703) to obtain the desired signal via the transmit/receive switch (D301) and attenuator.
The operating (transmitting) frequency is produced at the 1st
IF mixer circuit (Q210, Q202) by mixing the 1st IF and 1st
LO signals. The mixed signal is then applied to the RF circuit.
FI402
Q801
MIC
BPF
Ceramic
LPF
6
IC1001
DSPI1 DSPO1
(12 kHz)
455 kHz
3rd LO
(443 kHz)
DSP
UNIT
IC1051IC2001
Controller
7
1
3
1
57
AMP. AMP.VCA
AMP.
2nd mixer
D302
2nd LO (64.00 MHz)
FI301b/a
64.455 kHz
Bandwidth:
15 kHz
Q401
BPF
Crystal
RF
amp.
1st mixer
Q702, Q703
1st LO
(64—94 MHz)
LPF
BPFs
2—30 MHz
0.5—1.9999 MHz
IC1
YGR
LPFs
PA UNIT FILTER UNIT
Antenna
D7271,
D7272
PWR
DET
Q6101, Q6801,
Q6851, Q6401,
Q6402
AMPs
• TRANSMIT CONSTRUCTION
Page 10
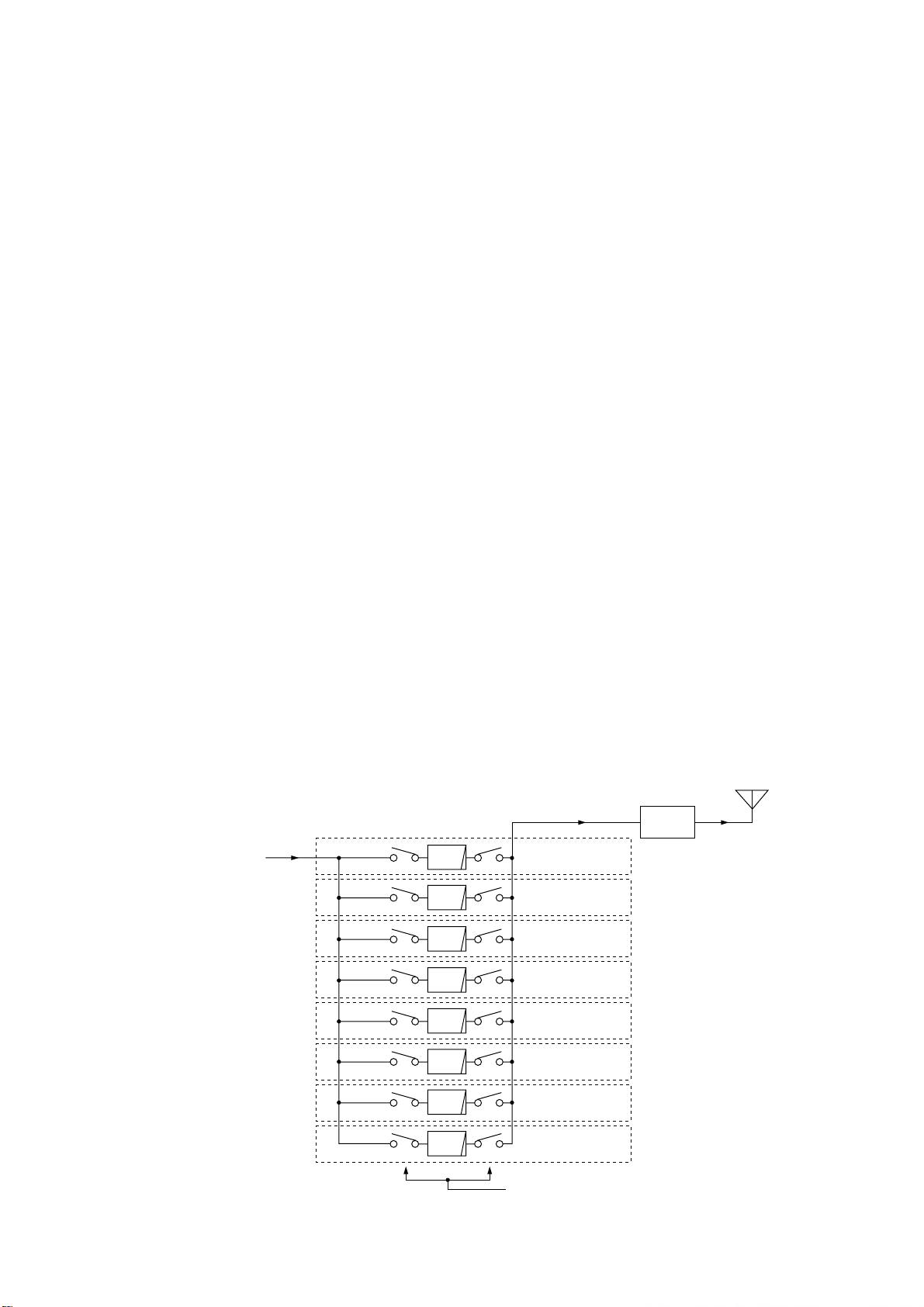
3 - 4
3-2-5 RF CIRCUIT (MAIN, PA UNITS AND DRIVER
BOARD)
The RF circuit amplifies operating (transmitting) frequency
to obtain 150 W of RF output.
The signal from the 1st IF mixer is passed through one of the
low-pass filter or bandpass filters (Refer to page 4-1 bandpass filters used), and then applied to the YGR amplifier
(IC1, pin 1) after being passed through the attenuator
(R5–R7). The amplified signal passes through the low-pass
filter (L1–L3, C1–C7) and attenuator (R1–R3), and then
applied to the PA unit via J1.
The signal applied from the MAIN unit is amplified at 2
amplifiers (PA unit; Q6101 and Q6801). A part of output signal from 2 amplifiers are applied to the amplifiers to improve
the frequency characteristic by feedback. The amplified signal is applied to the drive amplifier (DRIVER board; Q6851)
via the J6301 as “DRVI” signal. The signal from the DRIVER
board passes through the impedance converter (PA unit;
L6301), and then applied to push-pull amplifiers (PA unit;
Q6401, Q6402) to obtain a stable 150 W of RF output
power. A part of the RF output power returns to the amplifiers to obtain a stable gain between 1.6 MHz and 27.5 MHz
bands by using feedback transformer (L6404). The output
power is applied to the filter unit via the J6401 as “FLIN” signal.
The amplified signal is applied to the one of the 8 low-pass
filters which are composed chebychev type.
• 1.6–1.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7031)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L1M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 11). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7036–L7038, C7033–C7039,
C7041–C7045, C7049), and then applied to the RL7032.
• 2–2.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7061)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L2M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 12). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7066–L7068, C7063–C7084,
C7086, C7087), and then applied to the RL7062.
• 3–4.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7091)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L4M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 12). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7096–L7098, C7094–C7096,
C7098–C7101, C7105–C7107), and then applied to the
RL7092.
• 5–6.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7121)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L6M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 14). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7126–L7128, C7124–C7132,
C7136, C7137), and then applied to the RL7122.
• 7–9.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7151)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L8M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 15). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7066–L7068, C7063–C7084,
C7086, C7087), and then applied to the RL7152.
• 10–13.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7181)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L12M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 16). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7182–L7184, C7183–C7188,
C7193), and then applied to the RL7182.
Antenna
power
detector
LPF
LPF
Filter: L0
1.6—1.9999 MHz
Filter: L1
2—2.9999 MHz
Filter: L2
3—4.9999 MHz
Filter: L3
5—6.9999 MHz
Filter: L4
7—9.9999 MHz
Filter: L5
10—13.9999 MHz
Filter: L6
14—19.9999 MHz
Filter: L7
low-pass filter control signals
from the MAIN unit
20—29.9999 MHz
LPF
LPF
LPF
LPF
LPF
LPF
(L1M, L2M, L4M, L6M, L8M, L16M, L22M)
Transmitter signals
from the PA unit.
• RF FILTER CIRCUIT
Page 11
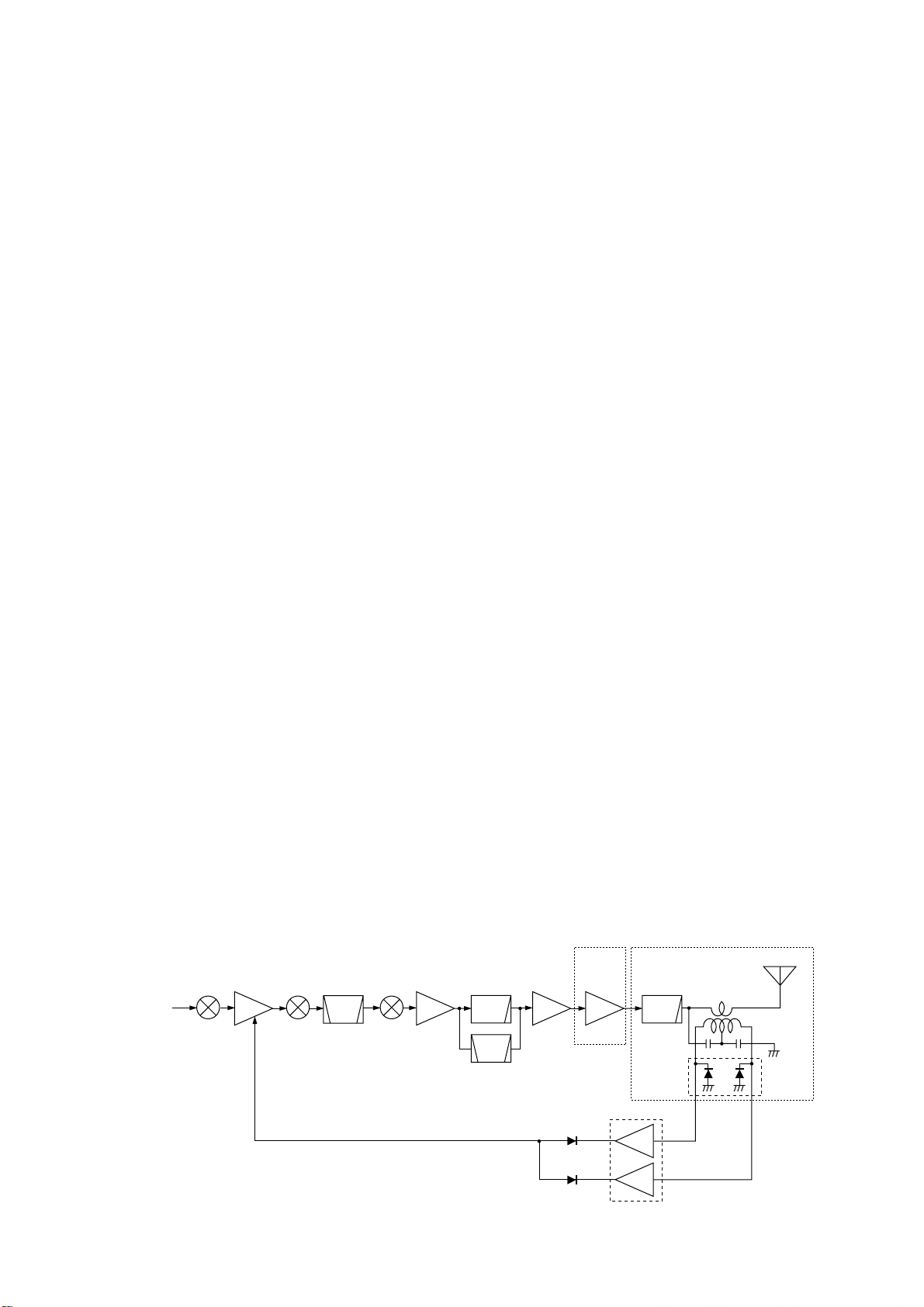
3 - 5
• 14–19.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7211)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L16M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 17). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7216–L7218, C7214, C7216,
C7217, C7221–C7225), and then applied to the RL7212.
• 20–29.9999 MHz signal
The signal is applied to the relay (FILTER unit; RL7241)
which is controlled by the band control IC (MAIN unit;
IC3602) as the “L22M” signal via the buffer amplifier (MAIN
unit; IC1301, pin 18). The signal passes through the lowpass filter (FILTER unit; L7245, L7246, L7248,
C7242–C7244, C7247–C7249, C7253, C7254), and then
applied to the RL7242.
The filtered signal is applied to the antenna connector after
being passed through the RL7301 and J7311.
3-2-6 ALC CIRCUIT (FILTER AND MAIN UNITS)
The ALC (Automatic Level Control) circuit controls the gain
of IF amplifiers in order for the transceiver to output a constant RF power set by the [RF PWR] control even when the
supplied voltage shifts, etc.
The RF power level is detected at the power detector circuit
(Filter unit; D7271) to be converted into DC voltage and
applied to the MAIN unit as the FOR signal.
The FOR signal is applied to the comparator (IC1201, pin 2).
The “POCV” signal, controlled by the [RF PWR] control via
the I/O expander (IC3606, pin 5), is also applied to the other
input (pin 3) for reference. The compared signal is output
from pin 1 and applied to the IF amplifier in the MAIN (Q801)
unit to control amplifying gain.
When the FOR signal exceeds the POCV voltage, ALC bias
voltage from the comparator controls the IF amplifiers. This
adjusts the output power to a specified level from the [RF
PWR] control until the FOR and POCV voltages are equalized.
3-2-7 APC CIRCUIT (FILTER AND MAIN UNITS)
The APC (Automatic Power Control) circuit protects the
power amplifiers on the PA unit from high SWR and excessive current.
• SWR APC CIRCUIT (FILTER AND MAIN UNITS)
The reflected wave signal appears and increases on the
antenna connector. When the antenna is mismatched,
D7272 of the power detector circuit (D7271, D7272, L7272)
in the FILTER unit detects the signal and applies it to the
ALC amplifier (IC1201, pin 9) in the MAIN unit as “REF” signal. The output signal decreases the bias voltage of the RF
APC amplifier to reduce the output power.
• CURRENT APC CIRCUIT (FILTER AND MAIN UNITS)
The power transistor current is detected from the different
voltage between both terminals of a 0.012 Ω resistor
(R6651) on the PA board. The detected voltage is applied to
the differential amplifier (IC6501). When the current of the
final transistors is more than 30 A, the detected voltage is
applied to the APC amplifier controller (IC1201) in the MAIN
unit to reduce the gate-2 voltage of the IF amplifier (Q801)
and thus reduce the output power.
3-2-8 RF METER CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The output of ALC amplifier (IC1201, pin 12) is applied to the
CPU (IC3303, pin 97) as “RFML” signal to indicate the transmit power level on the display.
For antenna current meter indication, the “ANTM” signal
from the optional AT-130E is applied to the meter amplifier
(IC1201, pin 12) via the J6701 in the PA unit.
3-2-9 MONITOR CIRCUIT (DSP AND MAIN UNITS)
The micorphone audio signals can be monitored to check
voice characteristics.
A portion of the transmit IF signal from the DSP IC (IC301)
is mixed with a 12 kHz LO signal to demodulate into the AF
signals. The demodulated signals are level-shifted 3.3 V to
5 V at the level converter (IC102) to convert into the analog
AF signals. The AF signals are then applied to the MAIN unit
as “MONI” signal.
The “MONI” signal from the DSP unit is amplified at the AF
amplifier (MAIN unit; IC1603, pin 2), and then applied to the
VCA amplifier to control the AF volume (pin 7). The amplified
signal passes through to the AF mute circuit (MAIN unit;
IC1602, pins 1, 7) which is controlled by the CPU via the
expander IC (MAIN unit; IC3603) as the “AFMS” signal. The
AF signal is applied to the AF power amplifier circuit (MAIN
unit; IC1601, pin 1) to drive a speaker.
2
D7271
D7272
IC1201
9
1
8
LPF LPFs
BPFs
ALC
ALC amplifier
Antenna
FILTER UNITPA
UNIT
Power
detector
IF
ALC
Q801
TX
signals
Crystal
BPF
3rd mixer 2nd mixer 1st mixer
RF YGR PA
ALC
• ALC CIRCUIT
Page 12
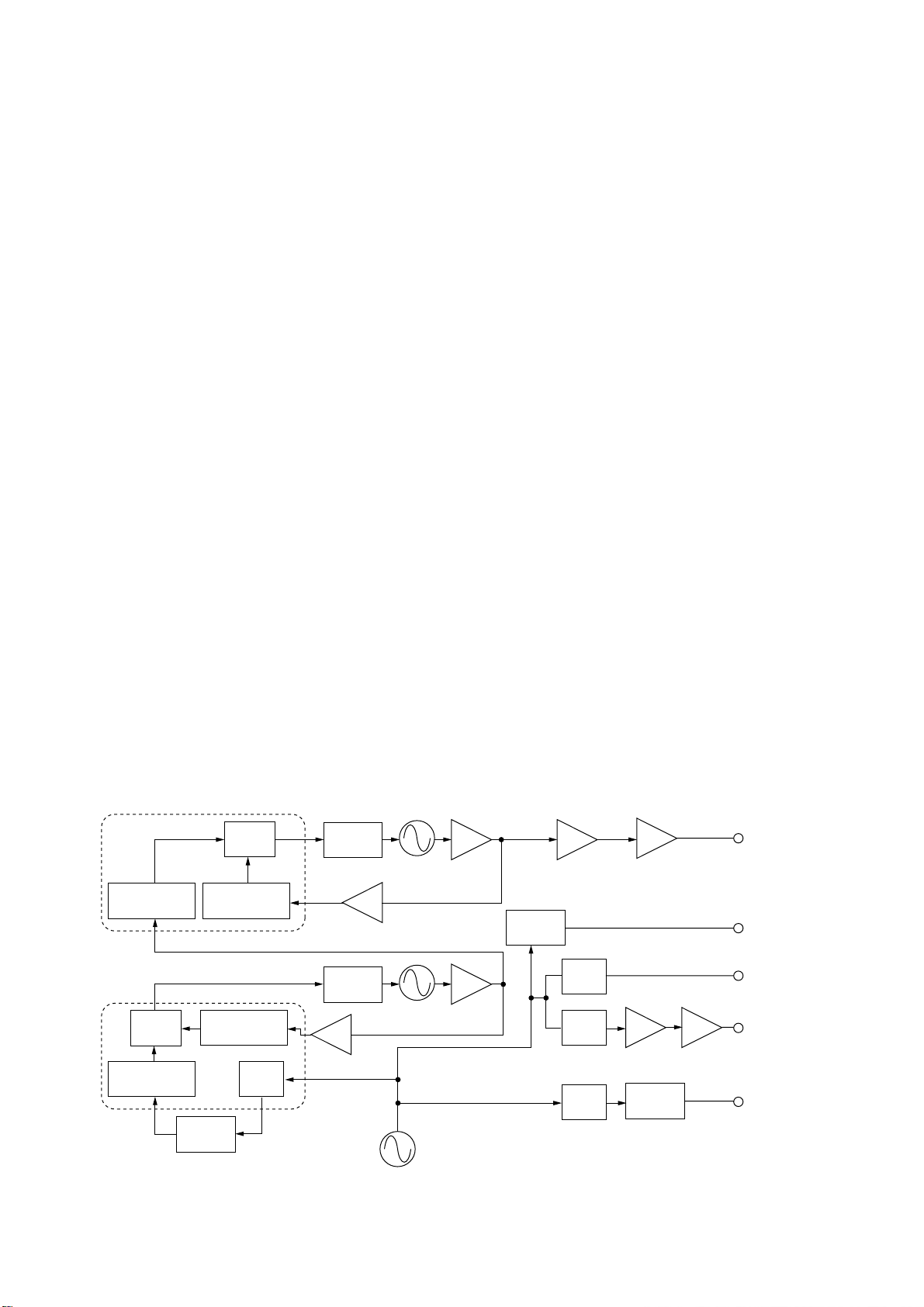
3 - 6
3-3 PLL CIRCUITS
3-3-1 GENERAL
The PLL circuits generate a reference frequency (32.000
MHz); 1st LO frequencies (64.485–94.455 MHz); 2nd LO
frequency (64 MHz), 3rd LO frequency (433.000 kHz).
The 1st LO PLL adopts a mixer-less dual loop PLL system.
The BFO uses a DDS and a 2nd LO as a fixed frequency
double that the crystal oscillator.
3-3-2 1ST LO PLL (PLL UNIT)
The 1st LO PLL contains a main and reference loop as a
dual loop system.
The reference loop generates an approximate 10.5 MHz frequency using a DDS circuit, and the main loop generates a
64.485 to 94.455 MHz frequency using the reference loop
frequency.
(1) REFERENCE LOOP PLL
The oscillated signal at the reference VCO (Q5301, D5301)
is amplified at the amplifiers (Q5302, Q5351) and is then
applied to the DDS IC (IC5101, pin 46). The signal is then
divided and detected on phase with the DDS generated frequency.
The detected signal output from the DDS IC (pin 56) is converted into DC voltage (lock voltage) at the loop filter
(R5136, R5146, C5112) and then fed back to the reference
VCO circuit (Q5301, D5301).
(2) MAIN LOOP PLL
The oscillated signal at one of the main loop VCOs (Q5521,
D5521, L5523) is amplified at the buffer amplifiers (Q5601,
Q5604) and is then applied to the PLL IC (IC5401, pin 6).
The signal is then divided and detected on phase with the
reference loop output frequency.
The detected signal output from the PLL IC (pin 2) is converted into a DC voltage (lock voltage) at the loop filter and
then fed back to one of the VCO circuits (Q5521, D5521,
L5523).
The oscillated signal from the buffer amplifier (Q5601) is
also applied to the MAIN unit as a 1st LO signal after being
amplified at LO (Q5602) and buffer (Q5603) amplifiers or
passed through the bandpass filter (L5602–L5604,
C5610–C5616).
3-3-3 2ND LO AND REFERENCE OSCILLATOR
CIRCUITS (PLL UNIT)
The reference oscillator (X5251; [USA], [CAN], X5281;
[OTH]) generates a 32.0 MHz frequency for the DDS circuits
as a system clock and for the LO output. The oscillated signal is doubled at the doubler circuit (Q5202) and the 64.0
MHz frequency is picked up at the double tuned filter
(L5203, L5204). The 64.0 MHz signal is applied to the RF
circuit as a 2nd LO signal.
3-3-3 3RD LO CIRCUIT (PLL UNIT)
The DDS IC (IC5701) generates a 10-bit digital signal using
the 32 MHz system clock. The digital signal is converted into
an analog wave signal at the D/A converter (R5701–R5720).
The converted analog wave is passed through the bandpass
filter (L5781–L5783, C5781–C5785) and then applied to the
MAIN unit as the 3rd LO signal (433.000 kHz) via the attenuator (R5781–R5783).
Phase
detector
Programmable
divider
Programmable
divider
Loop filter
Doubler
DDS
DDS
DDS
DDS
D/A
convertor
D/A
convertor
Buff LO
Buff
Loop filter
Buff
PLL IC (IC5401)
MAIN loop VCO
Q5601 Q5602
Q5202
Q5801
Q5901
Q5302
Q5301, D5301
Q5351
Reference OSC. (32 MHz)
X5251; [USA], [CAN]
X5281; [OTH]
Reference loop VCO
IC5701
Q5882 Q5881
Q5603
Q5521,
D5521,
L5523
DDS IC
(IC5101)
LO
LO
AMP.
Buff
1st LO
(64–94 MHz)
2nd LO
(64 MHz)
DSC 2nd LO
(10.7103 MHz)
[USA], [CAN] only
DSC 1st LO
(12.8875–
27.5045 MHz)
[USA], [CAN] only
3rd LO
(443 kHz)
Phase
detector
Programmable
divider
Programmable
divider
• PLL CIRCUIT
Page 13

3 - 7
3-4 DSC CIRCUITS ([USA], [CAN] ONLY)
3-4-1 DSC BANDPASS FILTER AND RF AMPLIFIER
CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The RF circuit filters out-of-band signals and amplifiers signals within the range of frequency coverage.
(1) 2–7 MHz signals
The signals from the antenna connector (J2101) pass
through the bandpass filter (L2201, L2202, L2207, L2210,
L2213, L2216, L2219, L2220, L2225, L2228, L2231, C2201,
C2204, C2207, C2210, C2213, C2216, C2219, C2222,
C2225, C2228, C2234, C2240) to obtain desired 2–6 MHz
signals and suppress any undesired signals.
(2) 8 MHz signals
The signals from the antenna connector (J2101) pass
through the bandpass filter (L2204, L2208, L2211, L2214,
L2217, L2221, L2222, L2229, L2232, C2202, C2205,
C2208, C2210, C2211, C2214, C2217, C2220, C2223,
C2226, C2236, C2241) to obtain desired 8 MHz signals and
suppress any undesired signals.
(3) 12 MHz signals
The signals from the antenna connector (J2101) pass
through the bandpass filter (L2235–L2242, L2244, L2245,
C2229, C2235, C2237, C2239, C2243–C2250,
C2252–C2254, C2263, C2264) to obtain desired 12 MHz
signals and suppress any undesired signals.
(4) 16 MHz signals
The signals from the antenna connector (J2101) pass
through the bandpass filter (L2205, L2206, L2209, L2212,
L2215, L2218, L2223, L2224, L2230, L2233, C2203, C2206,
C2209, C2212, C2215, C2218, C2221, C2224, C2226,
C2227, C2238, C2242) to obtain desired 16 MHz signals
and suppress any undesired signals.
The filtered signals are amplified at the RF amplifiers
(Q2301, Q2302), and then applied to the 1st mixer circuit
(D2301).
3-4-2 DSC 1ST MIXER AND 1ST IF CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signal into a fixed
frequency of the 1st IF signal with a PLL output frequency.
By changing the PLL frequency, only the desired frequency
will pass through a crystal filter at the next stage of the 1st
mixer.
The signals from the RF circuit are mixed at the 1st mixer
(D2301) with a 1st LO signal coming from the PLL circuit to
produce a 10.7 MHz 1st IF signal.
The 1st IF signal is applied to the crystal bandpass filters
(FI231) to suppress out-of-band signals. The filtered 1st IF
signal is amplified at the 1st IF amplifiers (Q2401, Q2501),
then applied to the 2nd mixer circuit (IC2701, pin 3).
3-4-3 DSC 2ND IF AND DSP CIRCUITS
(MAIN AND DSP UNITS)
The 2nd mixer circuit converts the 1st signal into a 2nd IF
signal. A double conversion superheterodyne system (which
converts receive signals twice) improves the image rejection
ratio and obtain stable receiver gain.
The 1st IF signal from the 1st IF amplifiers is applied to the
2nd mixer IC (IC2701, pin 3), and is mixed with the 2nd LO
signal to the converted into a 12 kHz 2nd IF signal.
The 12 kHz 2nd IF signal from the 2nd mixer (IC2701, pin 5)
is applied to the 2nd IF amplifier (IC2702, pin 3), and then
passes through the low-pass filter (IC2702, pins 5, 7). The
signal is applied to the DSP unit as the “DSPI2” signal.
The signal is amplified at the differential amplifier (DSP unit;
IC601), and is then applied to the A/D converter secition in
the CODEC IC (DSP unit; IC501). At the same time, the converted signal is level-shifted 5 V to 3.3 V in the IC (DSP unit;
IC501).
The level-shifted signal is applied to the DSP IC (DSP unit;
IC301) for the digital IF filter, demodulator and noise reduction, etc.
The output signal from the DSP IC is applied to the D/A converter section in the CODEC IC (DSP unit; IC501) to convert
into the analog audio signals. Also the signals are level-shifted 3.3 V to 5 V at the level converter section in the IC.
The level-shifted audio signals are passed through the
active filter (IC701b), and then applied to the MAIN unit via
the J1102 (pin 21) as the “DSPO2” signal.
3-4-4 DSC AGC CIRCUIT (DSP AND MAIN UNITS)
The receiver gain is determined by the voltage on the AGC2
line from the DSP unit. The D/A converter for the AGC
(IC102) supplies control voltage to the AGC2 line and sets
the DSC receiver gain.
The 3rd IF signal from the CODEC IC (IC501) is detected at
the AGC detector section in the DSP IC (IC301). The output
signal from the DSP IC is level-shifted at the level converter
(IC101) and applied to the D/A converter (IC102). The AGC
voltage is amplified at the buffer amplifier section in the
IC102 and applied to the MAIN unit to control the AGC2 line.
When receiving strong signals, the detected voltage increases and the AGC2 voltage decreases. As the AGC2 voltage
is used for the bias voltage of the IF amplifiers (MAIN unit;
Q2401, Q2501), IF amplifier gain is decreased.
3-5 FRONT UNIT (RC-25)
3-5-1 LCD CIRCUIT (DISPLAY AND CONNECT
BOARDS)
The LCD (CONNECT board; DS8220) is controlled by the
LCD driver (CONNECT board; IC8240) via the drive signals
(CL1, RES, CS, RS, WR, RD, DB0–DB7) from the display
board. The LCD’s back light employs 24 LED
(DS8300–DS8323). The LED are controlled by dimmer
(Q8300, Q8301) and dimmer controller (IC8280) circuits.
3-5-2 MICROPHONE CIRCUIT (DISPLAY BOARD)
The AF signals from the microphone are amplified at the AF
amplifier (IC8280) via the “MIC” signal. The signal is applied
to the IC-M802’s main unit through the J8903 via the “MI”
signal.
Page 14
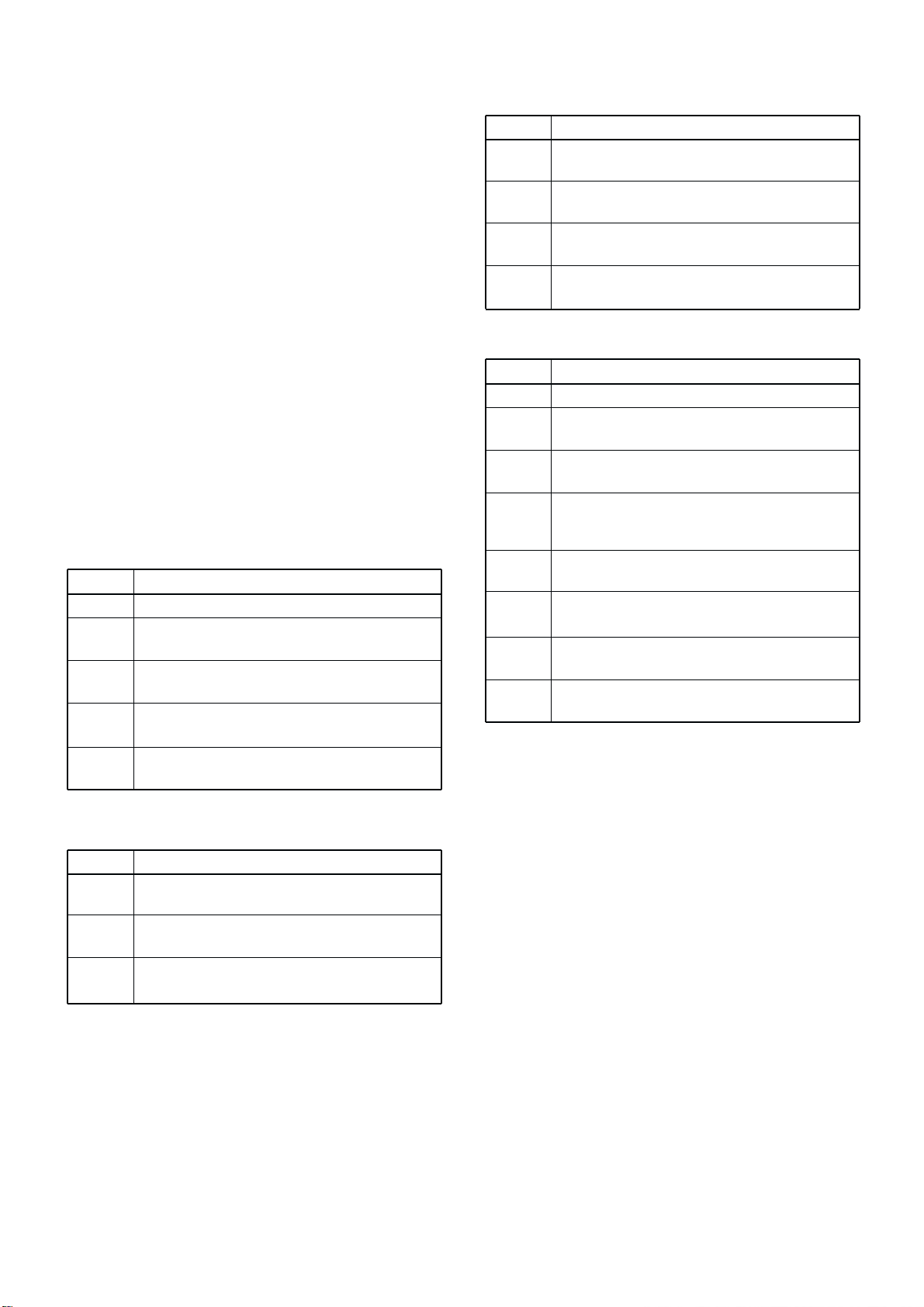
3 - 8
3-5-3 GROUP AND CHANNEL DIALS CIRCUIT
(DISPLAY AND SENSOR BOARDS)
• GROUP DIAL
The signals from the group dial (SENSOR board; S8801) is
applied to the FRONT CPU (IC8201, pins 76, 77) via the
“GPA” and “GPB” signals.
• CHANNEL DIAL
The signals from the channel dial (SENSOR board; S8802)
is applied to the FRONT CPU (IC8021, pins 74, 75) via the
“CHA” and “CHB” signals.
3-5-4 KEY’S BACK LIGHTS CIRCUIT (DISPLAY
BOARD)
The key”s back lights compose DS8340–DS8350, and are
controlled by the dimmer circuit (Q8340–Q8345). The dimmer circuit is controlled by the CPU via the “DIMMER” signal from the FRONT CPU.
3-5-5 RESET CIRCUIT (DISPLAY BOARD)
The reset IC (IC8202) resets the FRONT CPU (IC8201)
when IC-M802 is power ON or OFF.
3-6 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
3-6-1 PA UNIT VOLTAGE LINE
LINE
HV13
HV
S13V
PA8V
PAT8
DESCRIPTION
The voltage from an external power supply.
The same voltage as the HV13 line passed
through the fuse (F6701).
The same voltage as the HV13 line passes
through the switching relay (RL6701).
8 V for transmitter circuits regulated by the +8
regulator circuit (IC6601).
8 V for transmitter circuits regulated by the T8
regulator circuit (Q6601, Q6602).
3-6-2 DISPLAY BOARD (RC-25) VOLTAGE LINE
LINE
HV13
10V
5V
DESCRIPTION
The voltage from PA and MAIN units via the
J8602.
Common 10 V converted from the 13 V line and
regulated by the +10 regulator circuit (IC8301).
Common 5 V converted from the 5 V line and
regulated by the +5 regulator circuit (IC8290).
3-6-3 PLL UNIT VOLTAGE LINE
LINE
HV13
H5V
5V
8VL
DESCRIPTION
The voltage from PA and MAIN units via the
J5001.
Common 5 V line from the MAIN unit via the
J5071.
Common 5 V converted from the 13 V line and
regulated by the +5 regulator circuit (IC5001).
Common 8 V converted from the 13 V line and
regulated by the +8 regulator circuit (IC5031).
3-6-4 MAIN UNIT VOLTAGE LINE
LINE
S13V
R13V
8V
–5V
T8
R8
5V
H5V
DESCRIPTION
The voltage from the PA unit via the J1901.
Receive 13 V converted from the S13V line and
regulated by the R13 regulator circuit (IC1303).
Common 8 V converted from the 13 V line and
regulated by the +8 regulator circuit (IC1502).
Common –5 V converted from the 13 V line and
regulated by the –5 V DC-DC converter (IC1551,
D1551, D1552)
Transmit 8 V converted from the S13V line and
regulated by the T8 regulator circuit (Q1501).
Receive 8 V converted from the S13V line and
regulated by the R8 regulator circuit (Q1502).
Common 5 V converted from the 13 V line and
regulated by the +5 regulator circuit (IC1501).
Common 5 V converted from the 5 V line and
regulated by the +5 regulator circuit (IC3101).
Page 15
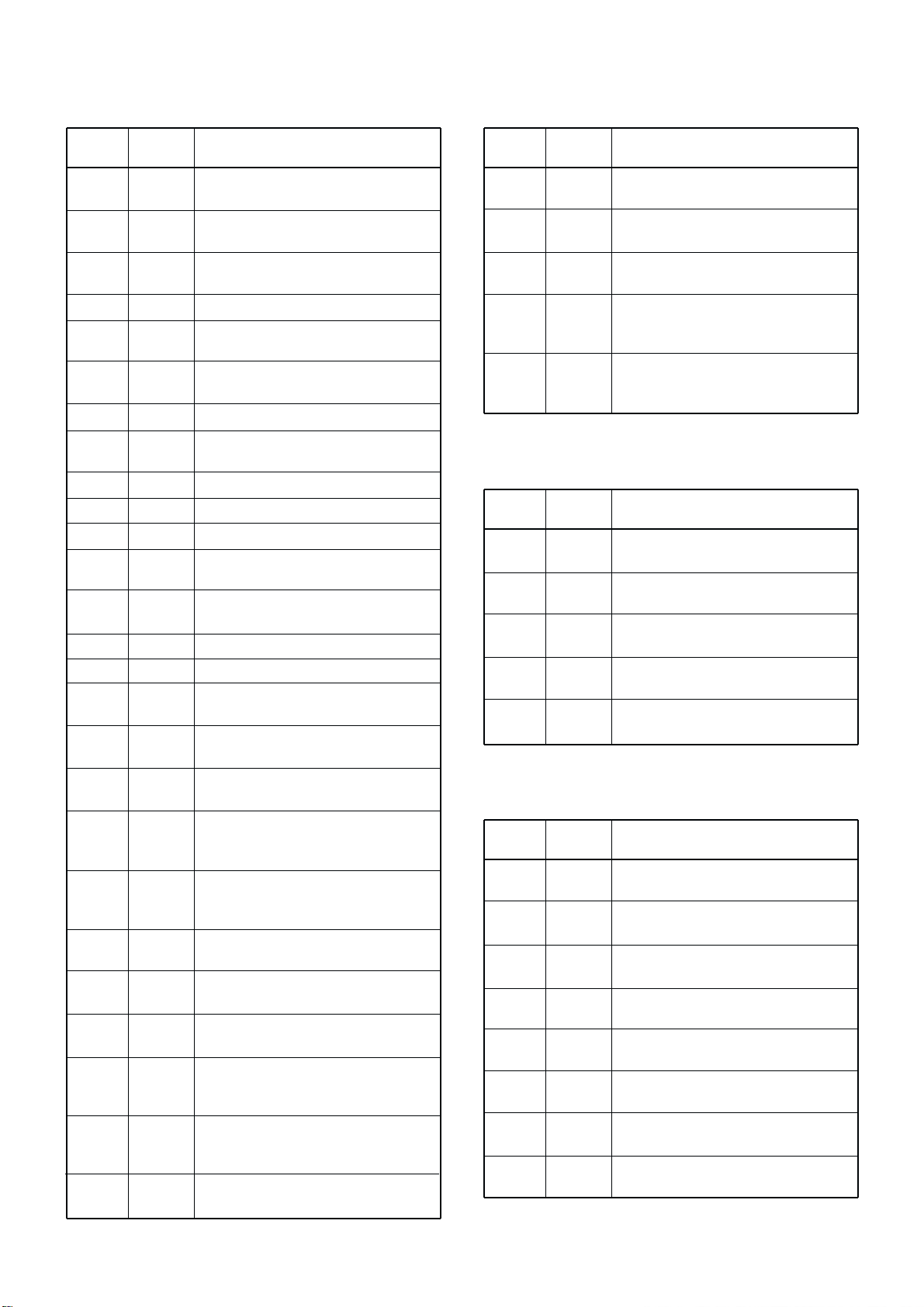
3 - 9
Pin
number
90
92
93
94
97
Port
name
ECK
ASEN
TEMP
NSEN
RFML
Description
Outputs serial clock signal for the
EEPROM (IC3301, pin 6).
Input port for the SEND signal from
the accessory connector (J1801).
Input port for the power amplifier temperature signal from the PA unit.
Input port for the SEND signal from
the AF/MOD connector (PLL unit;
J5051, pin 8) via the J3602.
Input port for the RF/ANTC meter’s
voltage from the meter amplifier
(IC1201, pin 14).
MAIN CPU (MAIN UNIT; IC3303)–continued
3-7-2 OUTPUT EXPANDER IC FOR THE PLL
STROBE (IC3601)
Pin
number
4
5
6
7
14
Port
name
PST1
PST2
PST3
PST4
PST5
Description
Outputs strobe signal for the DDS IC
(PLL unit; IC5101, pin 91).
Outputs strobe signal for the PLL IC
(PLL unit; IC5401, pins 13).
Outputs strobe signal for the DDS IC
(PLL unit; IC5701, pin 41).
Outputs strobe signal for the DDS IC
(PLL unit; IC5801, pin 41).
Outputs strobe signal for the DDS IC
(PLL unit; IC5901, pin 41).
3-7 PORT ALLOCATIONS
3-7-1 MAIN CPU (MAIN UNIT; IC3303)
Pin
number
1
2
3
4
6
7
11
19
23
24
26
27
28
29
30
32
33
34
37
38
47
48
49
79
80
89
Port
name
TXS
RXS
PSEL
BEEP
PDAT
PCK
UNLK
PWRS
DRES
STBO
RQO
RQI
DO
NMEI
NMEO
NMEI2
LSTB
DSTB
LCK
LDAT
MSTB
PSTB
SQLC
STAT
KEYS
EDT
Description
Outputs T8 regulator circuit (MAIN
unit; Q1501) control signal.
Outputs R8 regulator circuit (MAIN
unit; Q1502) control signal.
Outputs serial strobe signal to the
latch control IC (IC3601, pin 1).
Outputs beep audio signals.
Outputs serial data signal for the PLL
circuits.
Outputs serial clock signal for the PLL
circuit.
Input port for PLL unlock signal.
Outputs switching relay (PA unit;
RL6701) control signal.
Outputs the RESET signal.
Outputs strobe signal for the DSP unit.
Outputs data signal for the DSP unit.
Outputs serial data signal for the DSP
unit.
Input port for the serial data signal
from the DSP unit.
Input port for the NMEA signal.
Outputs NMEA signal for PLL unit.
Input port for the GPS signal from the
PLL unit.
Outputs serial strobe signal for the
IC3602, IC3603.
Outputs strobe signal for the D/A converter IC (IC3606).
Outputs serial clock signal for
IC3602–IC3605, D/A converter IC
(IC3606) and DSP unit.
Outputs serial data signal for the
IC3602, IC3603 and D/A converter IC
(IC3606).
Outputs serial strobe signal for the
IC3603, IC3605.
Outputs PLL strobe control signal for
the LATCH controller (IC3601).
Outputs squelch control signal for the
SQL switching IC (IC1701).
Outputs the optional antenna tuner
start control signal for the PA unit via
the J1901.
Input port for the optional antenna
tuner key control signal via the PA
unit.
I/O port for the serial data signals
from/to the EEPROM (IC3301, pin 5).
3-7-3 OUTPUT EXPANDER IC FOR THE FILTER
UNIT (IC3602)
Pin
number
4
5
6
7
11
12
13
14
Port
name
L0S
L1S
L2S
L3S
L7S
L6S
L5S
L4S
Description
Outputs 0.5–1.999999 MHz low-pass
filter control signal.
Outputs 2–2.999999 MHz low-pass filter control signal.
Outputs 3–4.999999 MHz low-pass filter control singnal.
Outputs 5–6.999999 MHz low-pass filter control signal.
Outputs 20–30 MHz low-pass filter
control signal.
Outputs 14–19.999999 MHz low-pass
filter control signal.
Outputs 10–13.999999 MHz low-pass
filter control signal.
Outputs 7–9.999999 MHz low-pass filter control signal.
Page 16
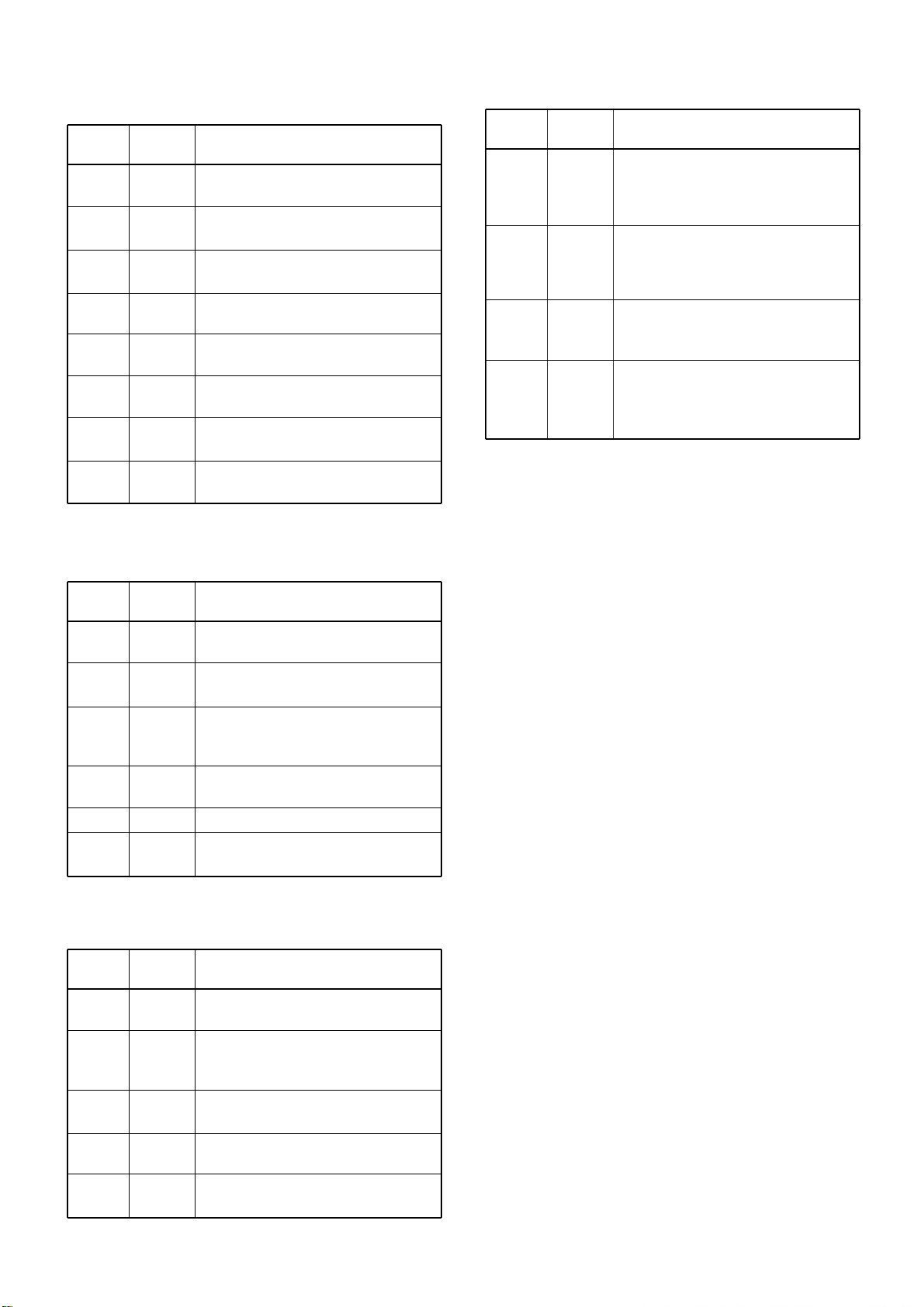
3 - 10
3-7-5 OUTPUT EXPANDER IC (IC3603)
Pin
number
4
5
6
11
13
14
Port
name
NMS
EMS
MMS
NMRS
AFMS
CSEN
Description
Outputs NBDP MOD control signal for
the gate mod IC (IC2001, pin 10).
Outputs external MOD control signal
for the gate mode IC (IC2001, pin 11).
Outputs microphone MOD control signal for the gate mode IC (IC2001, pin
9).
Outputs NMEA/RS-232C switching
singnal.
Outputs AF mute control signal.
Outputs SEND control signal for the
buffer amplifier (IC1303, pin 6).
3-7-6 OUTPUT EXPANDER IC (IC3605)
Pin
number
4
5
6
7
14
Port
name
B8S
DBP1
DBP2
DBP3
DBP4
Description
Outputs 24–30 MHz bandpass filter
control signal.
Outputs bandpass filter control signal
for DSC circuit (For 2.1875, 4.2075,
6.3120 MHz).
Outputs bandpass filter control signal
for the DSC circuit (8.4145 MHz).
Outputs bandpass filter control signal
for the DSC circuit (12.5770 MHz).
Outputs bandpass filter control signal
for the DSC circuit (16.8045 MHz).
3-7-4 OUTPUT EXPANDER IC FOR BANDPASS FIL-
TERS (IC3604)
Pin
number
4
5
6
7
11
12
13
14
Port
name
B0S
B1S
B2S
B3S
B7S
B6S
B5S
B4S
Description
Outputs 0.5–1.999999 MHz bandpass
filter control signal.
Outputs 2–2.999999 MHz bandpass
filter control signal.
Outputs 3–4.999999 MHz bandpass
filter control singnal.
Outputs 5–6.999999 MHz bandpass
filter control signal.
Outputs 18–23.999999 MHz bandpass filter control signal.
Outputs 14–17.999999 MHz bandpass filter control signal.
Outputs 10–13.999999 MHz bandpass filter control signal.
Outputs 7–9.999999 MHz bandpass
filter control signal.
3-7-7 D/A CONVERTER IC (IC3606)
Pin
number
5
6
11
13
Port
name
POCV
AFG
FANS
TRXS
Description
Outputs transmit power control signal.
The signal is applied to the ALC amplifier (IC1201, pin 3) and RF amplifier
(Q701).
Outputs the VCA control signal. The
signal is applied to the VCA amplifier
(IC1603, pin 8) and RC-25 controller
via the J2051, pin 5.
Outputs the cooling fan control signal.
The signal is applied to the fan controller (PA unit; IC6501, Q6501).
Outputs the transmitter/receiver
switching signal. The signal is applied
to the switching relay circuit (FILTER
unit; RL7301).
Page 17
3 - 11
3-7-8 FRONT CPU PORT ALLOCATIONS (RC-25,
DISPLAY BOARD; IC8201)
Pin
number
17
21
22
23
24
25
26
28
31
32
33
34
35
36
41–46
48–55
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
Port
name
DSEL
FUNK
TXK
RXK
FCHK
T0K
ENTK
PWRK
PMUT
FPTT
AFGL
M1AD
M2AD
M3AD
CL1
RS
RD
WR
RES
CS
DB7–DB0
T9K
T8K
T7K
T6K
T5K
T4K
T3K
T2K
T1K
EMLK
SETK
MODK
TUNK
DALK
CSCK
DSTK
Description
Outputs DISTRESS LED control signal.
Input port for the
O switch.
Input port for the [TX] switch.
Input port for the [RX] switch.
Input port for the [FREQ/CH] switch.
Input port for the [0] switch.
Input port for the [ENT] switch.
Input port for the [POWER] switch.
Input port for the phone plug insert
detection signal.
Input port for the [PTT] switch from the
microphone connector (J8701, pin 5).
Input port for the AF volume control.
Input port for the using microphone
detection signal.
Input port for the switch signal on the
microphone.
Input port for the microphone connecting detection.
Output LCD drive signals.
Output LCD drive signals.
Input port for the [9] switch.
Input port for the [8] swtich.
Input port for the [7] swtich.
Input port for the [6] switch.
Input port for the [5] switch.
Input port for the [4] switch.
Input port for the [3] switch.
Input port for the [2] switch.
Input port for the [1] switch.
Input port for [e-mail]/[DSC]/[TS]
switches.
Input port for the [SET] switch.
Input port for the [MODE] switch.
Input port for the [TUNE] switch.
Input port for [CANCEL]/[TELCALL]/
[TXF] switches.
Input port for [DSC]/[CALL]/[CH0]/
[SELCALL] switches.
Input port for the [DISTRESS]/[CALL]/
[ALM] switches.
Page 18
4 - 1
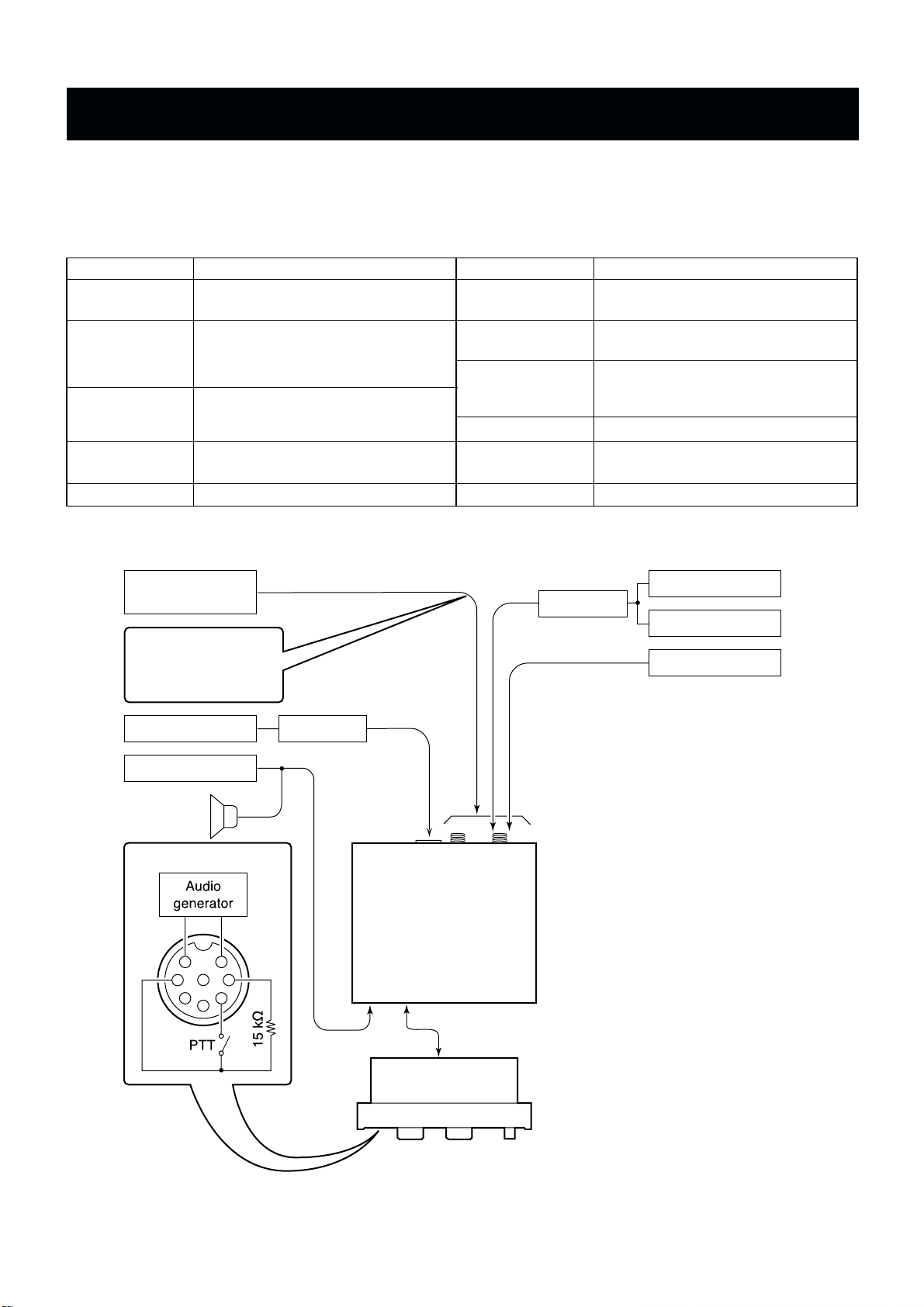
4-1 PREPARATION
When adjusting the contents on page 4-9, a JIG CABLE (see illustration as shown below) is required.
Some adjustments must be performed on the “ADJUSTMENT MODE”. Entering the “ADJUSTMENT MODE”, see the next page.
■ REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
SECTION 4 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
EQUIPMENT
DC power supply
RF power meter
(terminated type)
Frequency counter
FM deviation meter
Digital multimeter
GRADE AND RANGE
Output voltage : 13.6 V DC
Current capacity : 30 A or more
Measuring range : 1–100 W
Frequency range : 0.5–30 MHz
Impedance : 50 Ω
SWR : Less than 1.2 : 1
Frequency range : 0.1–600 MHz
Frequency accuracy : ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Frequency range : DC–600 MHz
Measuring range : 0 to ±5 kHz
Input impedance : 10 MΩ/V DC or better
EQUIPMENT
Audio generator
Attenuator
Standard signal
generator (SSG)
DC voltmeter
Oscilloscope
AC millivoltmeter
GRADE AND RANGE
Frequency range : 300–3000 Hz
Output level : 1–500 mV
Power attenuation : 40 or 50 dB
Capacity : 100 W or more
Frequency range : 0.5–30 MHz
Output level : 0.1 µV–32 mV
(–127 to –17 dBm)
Input impedance : 50 kΩ/V DC or better
Frequency range : DC–20 MHz
Measuring range : 0.01–20 V
Measuring range : 10 mV–10 V
to [SP]
to [CONTROLLER]
[MIC] connector
to antenna connector 1/2
to antenna connector 1
Speaker
6
5
4
2
3
8
7
1
Modulation analyzer
Distortion meter
Standard signal
generator
CAUTION!
DO NOT transmit while
an SSG is connected to
the antenna connector 1.
DC power supply Ammeter
Attenuator
Spectrum scope
+_
RF power meter
• CONNECTION
Page 19
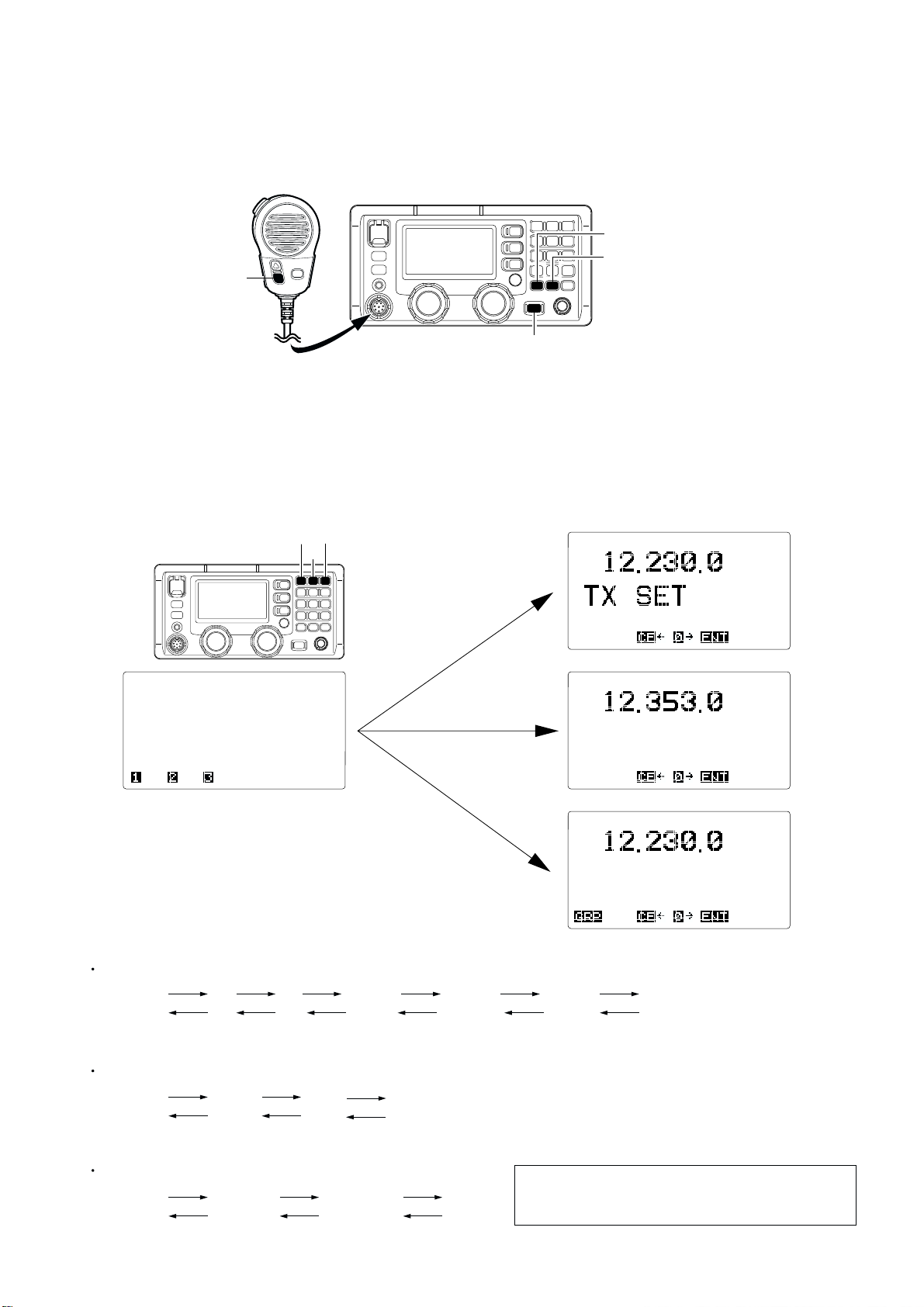
■ ENTERING THE ADJUSTMENT MODE
1 Turn the power OFF.
2 Push and hold the HM-135’s [DOWN] key, [TX] and [RX] buttons, then turn the power ON.
NOTE: Inserting the 15 kΩ resistor between 2 pin and 6 pin of HM-135 works same as pushing and holding HM-135’s [DOWN]
key (See the illustration on page 4-1).
■ OPERATING ON THE ADJUSTMENT MODE
• Enter the TX adjustment from the MAIN menu. : Push the [1] button
• Enter the RX adjustment from the MAIN menu. : Push the [2] button
• Enter the DSC adjustment from the MAIN menu. : Push the [3] button (except [OTH])
• Change the next adjustment item. : Push the [0] button
• Return to the pre-adjustment item. : Push the [CE] button
4 - 2
ADJUST
*** ***
MODE
RX
J3E
SET
DSC
ADJUSTMENT
8414.5
FRQ
ADJUST
*** ***
MODE
RX
J3E
SET
RX TOTAL GAIN
54(1.647)
ADJUST
*** ***
MODE
RX
J3E
SET
ADJUST
*** ***
MODE
[CANCEL]
BACK
TO HERE
[1] TX
[2]
RX
RX
[3] DSC
DSC
0.80-000
2.91-000
0.78
TX
[1]
[2]
[3]
Push [1]
Main menu
TX adjustment menu
RX adjustment menu
DSC adjustment menu
Push [2]
Push [3]
[RX]
[POWER]
[TX]
[DOWN] key
Connect to [MIC] connector.
MAIN
menu
TX ADJUSTMENT ITEM CHANGING
[1] [0] [0] [0] [0] [0]
[CE][CE][CE][CE][CE][CE]
TX
set
TX
gain
TX power
(High)
TX power
(Middle)
TX power
(Low)
TX tune
power
MAIN
menu
RX ADJUSTMENT ITEM CHANGING
DSC ADJUSTMENT ITEM CHANGING
[2] [0]
[0]
[CE]
[CE][CE]
RX total
gain
S level
zero
S level
8
MAIN
menu
[3] [0]
[CE][CE]
*DSC
demodulation
DSC
adjustment
DSC
self check
[0]
[CE]
*NOTE: DO NOT adjust the “DSC DEMODULATION”.
Thus, after adjusting the “DSC adjustment”,
push the [0] button twice to skip it.
Page 20
4 - 3
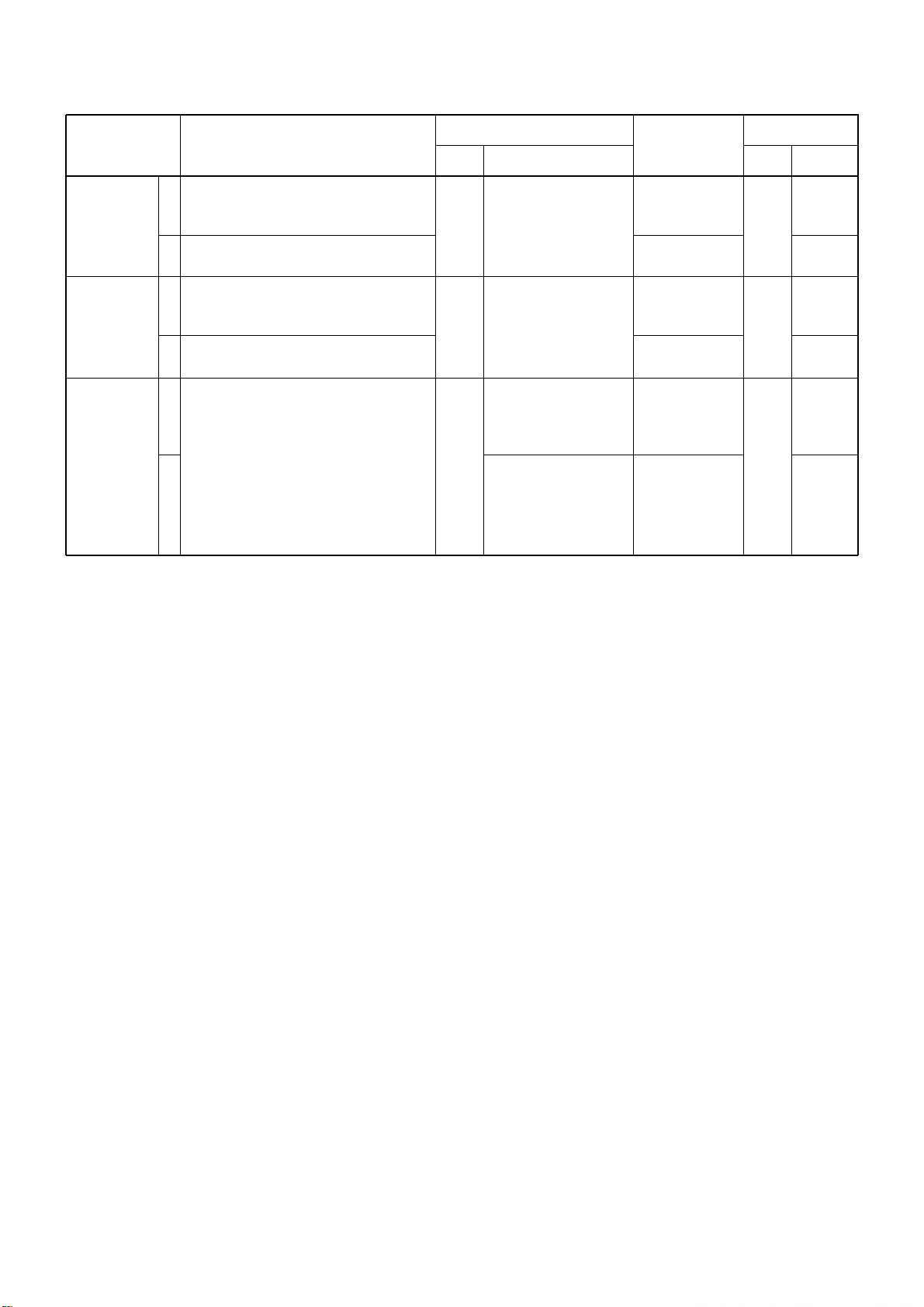
4-2 PLL UNIT ADJUSTMENT
LPL LOCK
VOLTAGE
HPL LOCK
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
FREQUENCY
1
2
1
2
1
2
• Operating frequency : 0.5000 MHz
• Mode : J3E
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 0.4999 MHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 29.9999 MHz
• Mode : J3E
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 0.0300 MHz
• Receiving
• Wait for 5 minutes after power ON.
• Terminate P5201 on the PLL unit to
ground with a 50 Ω resister.
• Receiving
PLL
PLL
PLL
Connect a digital multi
meter or oscilloscope
to check point
CP5301.
Connect a digital multi
meter or oscilloscope
to check point
CP5401.
Connect an RF voltmeter to check point
P5201.
Connect a frequency
counter to check point
P5201.
1.0 V
Less than 4.0 V
4.2 V
More than 0.8 V
Maximum level
63.999990 MHz
([USA], [CAN])
64.000000 MHz
([OTH])
PLL
PLL
PLL
C5305
Verify
C5521
Verify
L5203,
L5204
X5251
([USA],
[CAN])
C5294
([OTH])
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS
UNIT LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT ADJUST
MEASUREMENT ADJUSTMENT
Page 21
4 - 4
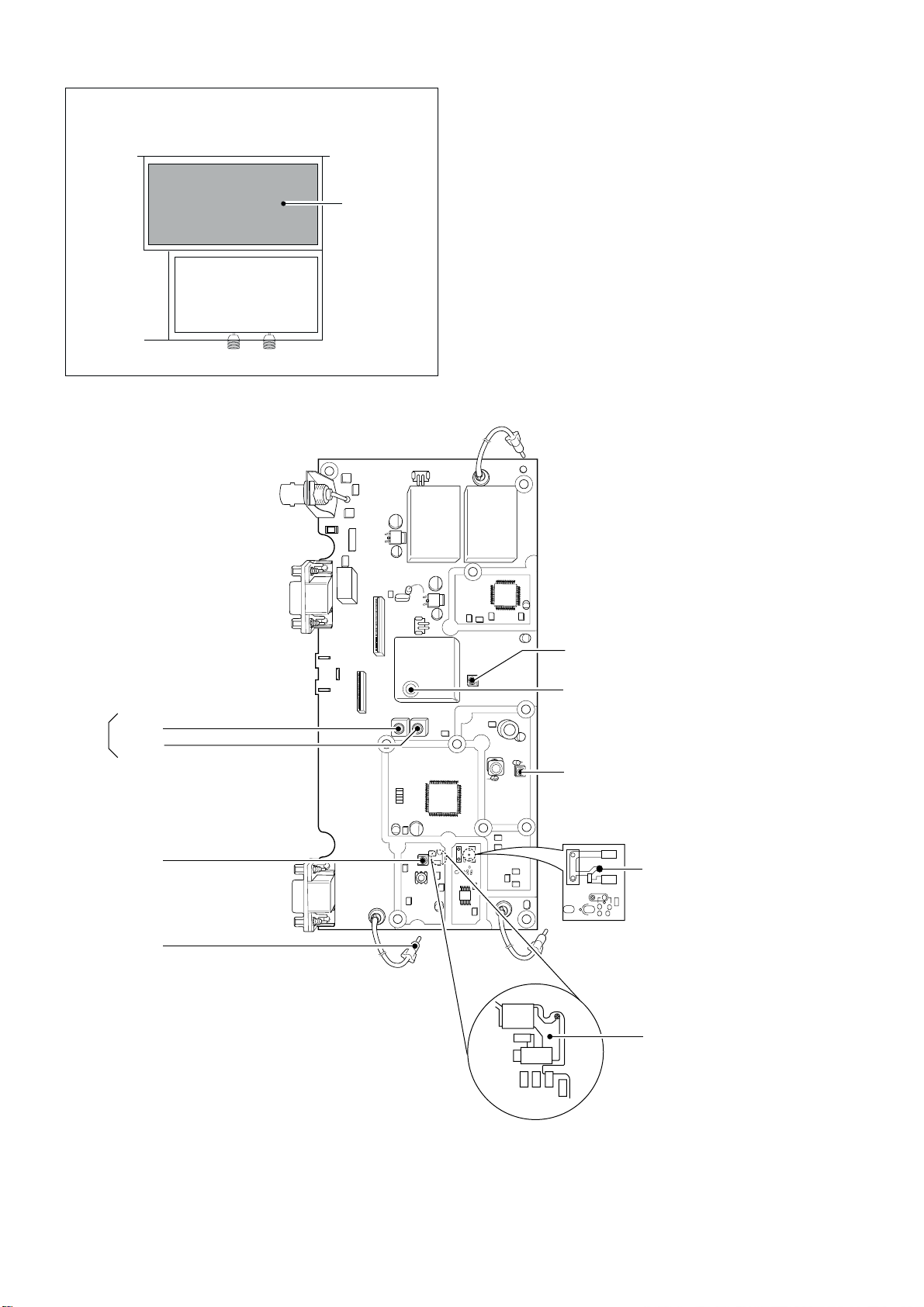
HPL lock voltage check point
CP5401
C5394
Reference frequency adjustment (USA, CAN)
X5251
LPL lock voltage check point
CP5301
Reference frequency check point
P5201
LPL lock voltage adjustment
C5305
LPL lock voltage adjustment
L5203
L5204
Reference frequency adjustment (OTH)
C5521
HPL lock voltage adjustment
• PLL UNIT TOP VIEW
PLL unit
• IC-M802 BOTTOM VIEW
Page 22
4 - 5
4-3 PA AND FILTER UNITS ADJUSTMENT
IDLING
CURRENT
(For drive
FETs)
(For final
transistors)
SWR
DETECTOR
12• Operating frequency : 12.2350 MHz
• Mode : J3E
• Apply no audio signal to the [MICRO-
PHONE] connector.
• Disconnect J6702.
• Preset R6304 and R6412 on the PA
unit to max. counter clockwise.
• Connect a dummy load or RF power
meter to the [ANT] connector.
• Transmitting
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 22.0000 MHz
• Mode : J3E
• Connect the CP7332 (FOR line) on
the FILTER unit to ground.
• Connect an audio generator to the
[MICROPHONE] connector and set
as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
• Transmitting
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
FIL-
TER
Connect an ammeter
(10 A) between an
external power supply
and the transceiver.
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Connect a DC voltmeter to check point,
CP7331.
2.0 A
0.7 A
140 W
Minimum level
PA
Audio
gen-
erator
FIL-
TER
R6304
R6412
Output
level
C7275
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS
UNIT LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT ADJUST
MEASUREMENT ADJUSTMENT
• After adjustment, connect J6701 to the PA unit.
1
2
• After adjustment, disconnect CP7332 (FOR line) on the FILTER unit from ground.
Page 23
SWR detector check point
CP7331 (REF line)
Connect to ground
CP7332 (FOR line)
SWR detector adjustment
C7275
4 - 6
R6304
Idling current adjustment
(For drive FETs)
R6412
Idling current adjustment
(For final transistors)
• IC-M802 TOP VIEW
• FILTER UNIT BOTTOM VIEW
FILTER unit
• IC-M802 BOTTOM VIEW
Page 24
4-4 RECEIVER ADJUSTMENTS
”TOTAL GAIN”, “S-METER” and “DSC PEAK” adjustments must be performed at “ADJUSTMENT MODE”.
NOISE NULL
POINT
RECEIVER
GAIN
TOTAL GAIN
S-METER
DSC PEAK
([USA],[CAN]
only)
DSC SELF
CHECK
([USA],[CAN]
only)
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
• Operating frequency : 0.5 MHz
• Mode : H3E
• Preset L402 and L405 to max. clock-
wise.
• Preset L401, L403, L404 and L801 to
max. counter clockwise.
• Set the standard signal generator to
OFF (no signal output).
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 12.2310 MHz
• Mode : J3E
• Connect a standard signal generator
to the [ANT] connector and set as:
Frequency : 12.2310 MHz
Level : 0.5 µV*
(–113 dBm)
Modulation : OFF
• Receiving
• While pushing HM-135’s “DOWN” key,
[TX] and [RX] switches, then turn
power ON.
• Push [2] swtich to enter the RX adjustment mode.
• Connect a standard signal generator
to the [ANT] connector and set as:
Frequency : 12.3540 MHz
Level : 320 µV*
(–57 dBm)
Modulation : OFF
• Receiving
• Set the standard signal generator to
OFF (no signal output).
• Set the standard signal generator as:
Frequency : 12.3540 MHz
Level : 10 mV*
(–27 dBm)
• Receiving
• Push [3] switch to enter the DSC
adjustment mode.
LCD displayed :“DSC ADJUSTMENT”.
• DSC frequency : 8.4145 MHz
• Connect a standard signal generator
to the [DSC ANT] connector and set
as:
Frequency : 8.4145 MHz
Level : 0.5 µV*
(–113 dBm)
Modulation : OFF
• Receiving
• LCD displayed :”DSC SELF CHECK”
• DSC frequency : 8.4145 MHz
• Connect an RF power meter to the
[DSC ANT] connector on the rear
panel.
• Receiving
Front
panel
Front
panel
Front
panel
Connect an AC millivoltmeter to the [SP]
jack with a 4 Ω dummy
load.
Connect an AC millivoltmeter to the [SP]
jack with a 4 Ω dummy
load.
Connect an AC millivoltmeter to the [SP]
jack with a 4 Ω dummy
load.
Minimum output
level
Maximum out-
put level
Maximum out-
put level
MAIN
MAIN
MAIN
L207
L208,
L209,
L210,
L301,
L302,
L307
L2306,
L2307
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS
UNIT LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT ADJUST
MEASUREMENT ADJUSTMENT
*The output level of the standard signal generator (SSG) is indicated as the SSG’s open circuit.
• Push the [ENT] switch to write the adjustment value in the mem-
ory.
• Push the [ENT] switch to write the adjustment value in the memory.
• Push the [ENT] switch to write the adjustment value in the memory.
4 - 7
• Push the [ENT] switch, and then verify to return to the “Main
menu” on the LCD display.
When this check is failure, displayed “NG” on LCD, and beep
sound.
Page 25

4 - 8
L307
Receiver gain adjustment
Noise null point adjustment
L302
L208
L209
L301
L210
L207
DSC peak adjustment
L2307
L2306
[ENT]
• IC-M802 TOP VIEW
• RC-25 FRONT PANEL
Page 26

4 - 9
4-5 TRANSMITTER ADJUSTMENTS
The following adjustments must be performed at “ADJUSTMENT MODE” after “SWR DETECTOR” and “RECEIVER” ADJUST-
MENTS in the SECTION 4-3 and 4-4.
TRANSMIT
PEAK AND
TOTAL GAIN
(TX PEAK)
(TOTAL GAIN)
TX POWER
(HIGH)
(MIDDLE)
(LOW)
TUNE
POWER
AM CARRIER POWER
([OTH] only)
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
• While pushing HM-135’s DOWN key,
[TX] and [RX] switches, turn power
ON.
• Connect an audio generator to the
[MICROPHONE] connector and set
as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : 10 mV
• Push [1] swtich to enter the TX adjustment mode
(LCD displayed: “TX SET”)
.
• Push [ENT] switch, then the transceiver is transmitting.
• After setting 75 W, push the [ENT] key
to write the adjustment value in the
memory.
• LCD displayed :“TX POWER HIGH”
• Set the audio generator as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : 100 mV
• After setting 140 W, push the [ENT]
key to write the adjustment value in
the memory.
• LCD displayed :“TX POWER MID”
• Set the audio generator as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : 100 mV
• After setting 70 W, push the [ENT] key
to write the adjustment value in the
memory.
• LCD displayed :“TX POWER LOW”
• Set the audio generator as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : 100 mV
• After setting 20 W, push the [ENT] key
to write the adjustment value in the
memory.
• LCD displayed :“TX POWER TUNE”
• Set the audio generator as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : 100 mV
• After setting 10 W, push the [ENT] key
to write the adjustment value in the
memory.
• LCD displayed :“TX POWER H3E”
• Set the audio generator as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : OFF
• After setting 45 W, push the [ENT] key
to write the adjustment value in the
memory.
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Connect an RF power
meter to the [ANT]
connector.
Maximum out-
put power
75 W
140 W
70 W
20 W
10 W
45 W
MAIN
RC-25
RC-25
RC-25
RC-25
RC-25
RC-25
L706
[CH]
DIAL
[CH]
DIAL
[CH]
DIAL
[CH]
DIAL
[CH]
DIAL
[CH]
DIAL
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS
UNIT LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT ADJUST
MEASUREMENT ADJUSTMENT
Page 27

[CH]
[ENT]
Transmit peak and total gain
adjustment
L706
R6516
Ic-APC adjustment
J3101 pin 15
Connect to ground
when adjusting IC-APC
4 - 10
• IC-M802 TOP VIEW
• RC-25 FRONT PANEL
TRANSMITTER ADJUSTMENTS(CONTINUE)
1 • Operating frequency : 12.2350 MHz
• Mode : J3E
• Set the audio generator as:
Frequency : 1.5 kHz
Level : 100 mV
• Preset R6516 on the PA unit to center
position.
• Connect the J3101 pin 15 (FOR line)
on the MAIN unit to ground.
• Transmitting
Rear
panel
Connect an ammeter
(50 A) between an
external power supply
and the transceiver.
34.5 A PA R6516
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS
UNIT LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT ADJUST
MEASUREMENT ADJUSTMENT
IC-APC
• After adjustment, disconnect J3101 pin 15 (FOR line) on the MAIN unit from ground.
2
Page 28

[MAIN UNIT]
5-1 IC-M802
[MAIN UNIT]
IC1 1110004080 S.IC µPC2709T-E3
IC501 1110005460 S.IC TA4107F (TE12L)
IC901 1110005460 S.IC TA4107F (TE12L)
IC1001
1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L)
IC1002
1110005450 S.IC TS522IDT
IC1051
1110005450 S.IC TS522IDT
IC1101
1110005450 S.IC TS522IDT
IC1201
1110005140 S.IC NJM3403AV-TE1
IC1301
1160000130 S.IC TD62783AF (TP1)
IC1302
1160000130 S.IC TD62783AF (TP1)
IC1303
1160000130 S.IC TD62783AF (TP1)
IC1501
1180000420 S.IC TA78L05F (TE12R)
IC1502
1180002180 S.IC TA78M08F (TE16L)
IC1551
1110001400 S.IC µPC1555G2-T1
IC1601
1110003090 IC LA4425A
IC1602
1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L)
IC1603
1110003300 S.IC M5282FP 70CD
IC1701
1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L)
IC1702
1110005450 S.IC TS522IDT
IC1703
1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L)
IC2001
1130008230 S.IC BU4053BCFV-E2
IC2701
1110005460 S.IC TA4107F (TE12L) [USA], [CAN]
IC2702
1110005450 S.IC TS522IDT [USA], [CAN]
IC3101
1180000420 S.IC TA78L05F (TE12R)
IC3201
1130005720 S.IC TC7W04F (TE12L)
IC3301
1130011210 S.IC CAT24WC64J-TE13 [OTH]
1140009240 S.IC HN58X24128FPI [USA], [CAN]
IC3302
1110005770 S.IC
S-80942CNMC-G9C-T2
[OTH], [CAN]
1130009110 S.IC
S-80942ANMP-DD6-T2
[USA]
IC3303
1140010050 S.IC M30620FCAFP [OTH]
1140010632 S.IC M30624FGAFP D5 [USA], [CAN]
IC3601
1130007700 S.IC BU4094BCF-E2
IC3602
1130007700 S.IC BU4094BCF-E2
IC3603
1130007700 S.IC BU4094BCF-E2
IC3604
1130007700 S.IC BU4094BCF-E2
IC3605
1130007700 S.IC BU4094BCF-E2
IC3606
1110003690 S.IC M62354GP 75EC
Q51 1530003090 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4213-B (TE85R)
Q201 1560000720 S.FET 2SK2171-4-TD
Q202 1560000720 S.FET 2SK2171-4-TD
Q203 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q401 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q501 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q601 1530003150 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4673D-TD
Q701 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q702 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q703 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q801 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS
Q1203 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R)
Q1204 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R)
Q1205 1530003090 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4213-B (TE85R)
Q1206 1530003090 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4213-B (TE85R) [OTH]
Q1207 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) [OTH]
Q1501 1540000440 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1619-T-TD
Q1502 1540000440 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1619-T-TD
Q1503 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q1504 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q1601 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q1801 1540000440 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1619-T-TD
Q2101 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106 [USA], [CAN]
Q2102 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
[USA], [CAN]
Q2301 1560000720 S.FET 2SK2171-4-TD [USA], [CAN]
Q2302 1560000720 S.FET 2SK2171-4-TD [USA], [CAN]
Q2401 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS [USA], [CAN]
Q2501 1580000620 S.FET 3SK131-T2 MAS [USA], [CAN]
Q3001 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q3004 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
D51 1750000810 S.DIODE UM9957F/TR
D52 1750000810 S.DIODE UM9957F/TR
S.=Surface mount
D53 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D101 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D102 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D103 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D104 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D105 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D106 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D107 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D108 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D109 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D110 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D201 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D301 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D302 1750000430 S.DIODE HSB88WSTR
D303 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D401 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D402 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D403 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D404 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D601 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX)
D602 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D901 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX)
D1102 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D1201 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D1202 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D1203 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D1204 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D1205 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D1206 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D1207 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D1501 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D1502 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D1551 1730002320 S.ZENER MA8051-M (TX)
D1552 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D1554 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX)
D1801 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D2101 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D2102 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D2103 1750000810 S.DIODE UM9957F/TR [USA], [CAN]
D2104 1750000810 S.DIODE UM9957F/TR [USA], [CAN]
D2201 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D2202 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D2203 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D2204 1790001770 S.DIODE MA80WK-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D2301 1750000430 S.DIODE HSB88WSTR [USA], [CAN]
D3001 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D3002 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D3003 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D3004 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D3006 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D3007 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D3301 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D3302 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D3336 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D3337 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
FI201 2010002600 XTAL FL-345 (64.455 MHz)
FI231 2010001880 MONOLITH FL-231 (10.700 MHz) [USA], [CAN]
FI301 2010002470 XTAL FL-315 (64.45500 MHz)
FI401 2020001960 CERAMIC CFWLB455KHFA-B0 (CFWM455H)
FI402 2020001330 CERAMIC
CFWLA455KHFA-B0 (CFWS455HT)
X3301 6050010501 S.XTAL CR-636A (14.7456 MHz)
L1 6200002650 S.COIL NL 252018T-R18J
L2 6200002910 S.COIL NL 252018T-R27J
L3 6200002860 S.COIL NL 252018T-4R7J
L51 6200002860 S.COIL NL 252018T-4R7J
L52 6200009880 S.COIL NL 252018T-820J
L53 6200004670 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R9J
L54 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
5 - 1
SECTION 5 PARTS LIST
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 29

[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
L55 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L56 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L101 6200003940 S.COIL NL 252018T-5R6J
L102 6200002860 S.COIL NL 252018T-4R7J
L103 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L104 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L105 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L106 6200009860 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R5J
L107 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L108 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J
L109 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L110 6200002850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R82J
L111 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L112 6200003660 S.COIL NL 252018T-R68J
L113 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L114 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J
L115 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L116 6200004960 S.COIL NL 252018T-R33J
L117 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L118 6200002860 S.COIL NL 252018T-4R7J
L119 6200002000 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R3J
L120 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L121 6200009860 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R5J
L122 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J
L123 6200003660 S.COIL NL 252018T-R68J
L124 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J
L125 6200009850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R39J
L126 6200002910 S.COIL NL 252018T-R27J
L127 6200002000 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R3J
L128 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L129 6200003660 S.COIL NL 252018T-R68J
L130 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J
L131 6200009850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R39J
L132 6200002910 S.COIL NL 252018T-R27J
L133 6200003940 S.COIL NL 252018T-5R6J
L134 6200004950 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R8J
L135 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J
L136 6200003660 S.COIL NL 252018T-R68J
L137 6200003270 S.COIL NL 252018T-R56J
L138 6200009850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R39J
L139 6200004960 S.COIL NL 252018T-R33J
L140 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L141 6200004950 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R8J
L142 6200004740 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R2J
L143 6200002850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R82J
L144 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L201 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L202 6200002910 S.COIL NL 252018T-R27J
L203 6200002910 S.COIL NL 252018T-R27J
L204 6140003620 COIL LR-403
L205 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L206 6200002630 S.COIL NL 252018T-R10J
L207 6150004270 COIL LS-483A (C-14924)
L208 6150005110 COIL LS-540
L209 6150005110 COIL LS-540
L210 6150004270 COIL LS-483A (C-14924)
L301 6150005110 COIL LS-540
L302 6150005110 COIL LS-540
L303 6140002810 S.COIL LR-317
L304 6140003530 COIL LR-395
L305 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L306 6200009870 S.COIL NL 252018T-120J
L307 6150005110 COIL LS-540
L401 6150005140 COIL LS-542
L402 6150005140 COIL LS-542
L403 6150002291 COIL LS-450
L404 6150005140 COIL LS-542
L405 6150005140 COIL LS-542
L406 6200003520 S.COIL ELJFB 102K-F
L502 6200003520 S.COIL ELJFB 102K-F
L504 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L505 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L506 6200003520 S.COIL ELJFB 102K-F
L601 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L602 6200002840 S.COIL NL 252018T-R22J
L603 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L604 6200004960 S.COIL NL 252018T-R33J
L605 6200002840 S.COIL NL 252018T-R22J
L701 6140002810 S.COIL LR-317
L702 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J
L703 6200003660 S.COIL NL 252018T-R68J
L704 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L705 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L706 6150004270 COIL LS-483A (C-14924)
L707 6140002810 S.COIL LR-317
L801 6150004440 COIL LS-495
L901 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L902 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L903 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L904 6150005170 COIL ELELN 102KA
L1301 6200005490 S.COIL NL 322522T-331J
L1302 6200005490 S.COIL NL 322522T-331J
L1551 6180001000 COIL LAL 04NA 102K
L1552 6180001000 COIL LAL 04NA 102K
L1601 6170000140 COIL LW-15
L1801 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L1802 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L1803 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L1804 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L1901 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L1902 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L1903 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L1904 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L1905 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L1906 6140002220 COIL LR-270 (TR6X3X2 3A9)
L1907 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L1908 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L2051 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L2052 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L2053 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L2054 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L2101 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2201 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J [USA], [CAN]
L2202 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2204 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2205 6180001730 COIL LAL 02NA 1R8K [USA], [CAN]
L2206 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2207 6200003710 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R7J [USA], [CAN]
L2208 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J [USA], [CAN]
L2209 6200007790 S.COIL LQW2BHNR15J01L [USA], [CAN]
L2210 6200004950 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R8J [USA], [CAN]
L2211 6180002380 COIL LAL 02NA 2R2K [USA], [CAN]
L2212 6180001730 COIL LAL 02NA 1R8K [USA], [CAN]
L2213 6200005030 S.COIL NL 252018T-180J [USA], [CAN]
L2214 6200002000 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R3J [USA], [CAN]
L2215 6200002850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R82J [USA], [CAN]
L2216 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J [USA], [CAN]
L2217 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J [USA], [CAN]
L2218 6180002300 COIL LAL 02NA 1R2K [USA], [CAN]
L2219 6200005040 S.COIL NL 252018T-220J [USA], [CAN]
L2220 6200003710 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R7J [USA], [CAN]
L2221 6180001210 COIL LAL 03NA 8R2K [USA], [CAN]
L2222 6200004960 S.COIL NL 252018T-R33J [USA], [CAN]
L2223 6200004740 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R2J [USA], [CAN]
L2224 6200007780 S.COIL LQW2BHNR12J01L [USA], [CAN]
L2225 6200004740 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R2J [USA], [CAN]
L2226 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J [USA], [CAN]
L2227 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J [USA], [CAN]
L2228 6200002000 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R3J [USA], [CAN]
L2229 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J [USA], [CAN]
L2230 6200007780 S.COIL LQW2BHNR12J01L [USA], [CAN]
L2231 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2232 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2233 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2235 6180000680 COIL LAL 02NA 4R7K [USA], [CAN]
L2236 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2237 6200007760 S.COIL LQW2BHN82NJ01L [USA], [CAN]
L2238 6180002920 COIL LAL 02NA 5R6K [USA], [CAN]
L2239 6200003660 S.COIL NL 252018T-R68J [USA], [CAN]
L2240 6200003940 S.COIL NL 252018T-5R6J [USA], [CAN]
L2241 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J [USA], [CAN]
L2242 6200007760 S.COIL LQW2BHN82NJ01L [USA], [CAN]
L2243 6200003270 S.COIL NL 252018T-R56J [USA], [CAN]
L2244 6200007760 S.COIL LQW2BHN82NJ01L [USA], [CAN]
L2245 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2301 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L2302 6140003660 COIL LR-409 [USA], [CAN]
L2304 6140003660 COIL LR-409 [USA], [CAN]
L2305 6200004940 S.COIL MLF1608D R27K-T [USA], [CAN]
L2306 6150005150 COIL LS-543 [USA], [CAN]
L2307 6150003640 COIL LS-409 [USA], [CAN]
L2401 6200010220 S.COIL NL 252018T-560J [USA], [CAN]
L2501 6200010220 S.COIL NL 252018T-560J [USA], [CAN]
L2701 6200003520 S.COIL ELJFB 102K-F [USA], [CAN]
5 - 2
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 30

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
L2702 6200003520 S.COIL ELJFB 102K-F [USA], [CAN]
L2703 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L3301 6200000970 S.COIL NL 322522T-100K
L3601 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L3602 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
R1 7030003270 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 390 V (39 Ω)
R2 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω)
R3 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω)
R4 7030003300 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 680 V (68 Ω)
R5 7030003230 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 180 V (18 Ω)
R6 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R7 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R8 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R54 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R56 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R57 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R58 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R59 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R60 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R61 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R101 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R102 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R103 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R104 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R105 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R106 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R107 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R108 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R109 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R110 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R201 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R202 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R203 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω)
R204 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R205 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R207 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R208 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R209 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω)
R210 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R211 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R212 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R213 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R214 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R215 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R301 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R306 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R307 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R309 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R401 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R404 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R405 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R406 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R407 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R408 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R409 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R410 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R413 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R414 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R415 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R502 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R503 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R504 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R505 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R506 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R507 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R508 7510001540 S.THERMISTOR NTCG16 4BH 332KT
R514 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R601 7030006220 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ470U (47 Ω)
R602 7030003290 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 560 V (56 Ω)
R603 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R604 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R605 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R606 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R607 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R701 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R702 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R703 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R704 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R705 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R706 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R707 7510001460 S.THERMISTOR NTCG16 3NH 471KT
R708 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R709 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R710 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R711 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R712 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R713 7030003230 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 180 V (18 Ω)
R714 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R715 7030003230 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 180 V (18 Ω)
R716 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R717 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R718 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R719 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R720 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
R722 7510001460 S.THERMISTOR NTCG16 3NH 471KT
R801 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R802 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω)
R804 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R813 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R901 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R902 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R903 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R904 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R910 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R911 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1002 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1003 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1004 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1005 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1006 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1007 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1008 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1009 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1010 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1011 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1014 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1015 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R1016 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1017 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1018 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1051 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1052 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1053 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1054 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1055 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1057 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1058 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1059 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1060 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R1101 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R1102 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R1103 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R1104 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R1105 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1106 7030003730 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ)
R1107 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R1108 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R1109 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1110 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1111 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1112 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1113 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1114 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1202 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R1203 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R1205 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R1206 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R1207 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1208 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1209 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R1210 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R1211 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R1212 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ)
R1213 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R1214 7030003770 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 564 V (560 kΩ)
R1215 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R1216 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R1217 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R1218 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R1219 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R1220 7030003840 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 225 V (2.2 MΩ)
R1221 7030003840 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 225 V (2.2 MΩ)
5 - 3
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 31

[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
R1222 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω)
R1223 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R1224 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1225 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1226 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R1228 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1230 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R1232 7030009930 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 825 V (8.2 MΩ)
R1233 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R1234 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1235 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1236 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) [OTH]
R1237 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) [OTH]
R1238 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) [OTH]
R1240 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1301 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1302 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1303 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1304 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1305 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1306 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1307 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1308 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R1309 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R1310 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1311 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1312 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1313 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1314 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1315 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1316 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1317 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1318 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R1319 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R1320 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1501 7030008190 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ330U (33 Ω)
R1502 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R1503 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R1504 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1505 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1551 7030006220 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ470U (47 Ω)
R1553 7030006220 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ470U (47 Ω)
R1555 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1556 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R1601 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1602 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1603 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R1606 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1607 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1609 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R1610 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R1611 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1612 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1613 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1614 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1615 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1701 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ)
R1702 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1703 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1704 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1705 7030005691 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 123V (12 kΩ)
R1706 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R1707 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R1709 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1710 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1711 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1712 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R1713 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1715 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
R1716 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R1717 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1718 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1719 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1720 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1721 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R1722 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1723 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1724 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R1801 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1802 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1803 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R1804 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R1901 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R1902 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R1903 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R2001 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R2002 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R2003 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R2101 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2102 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2103 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2104 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2105 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2106 7030003630 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2107 7030003630 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2201 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2202 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2203 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2204 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2205 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2206 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2207 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2208 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2301 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2302 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2303 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2306 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2401 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2402 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2403 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2404 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2405 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2406 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2501 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2502 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2503 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2504 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2505 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2506 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2701 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2702 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2703 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2704 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2705 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2706 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
5 - 4
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 32

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
R2708 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2709 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2710 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2711 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2712 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2713 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2714 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R2715 7030003230 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 180 V (18 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R2716 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R3001 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R3002 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R3003 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3004 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3006 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3007 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3008 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3009 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3010 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3011 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3012 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3013 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3014 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R3015 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3017 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3018 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3019 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3020 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3023 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3024 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3025 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3026 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3027 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R3028 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3029 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R3030 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R3035 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R3036 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3050 7030005691 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 123V
R3051 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R3052 7030005871 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 104V (100 kΩ)
R3101 7030008190 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ330U (33 Ω)
R3201 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3202 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R3203 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3204 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3301 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3302 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3303 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R3304 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R3305 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3306 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R3307 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3308 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3309 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3310 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3311 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3312 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3313 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R3314 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R3315 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3316 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3317 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3318 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3319 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3320 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3321 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3322 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3323 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3324 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3325 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3326 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3327 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3328 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3329 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3330 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3331 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3332 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3333 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3334 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3335 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3336 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3337 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3338 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3339 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3340 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3350 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R3402 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3403 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3404 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3405 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3406 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3408 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3409 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) [OTH]
R3412 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R3413 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) [OTH]
R3601 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3602 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3603 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3604 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3605 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3606 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3608 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3609 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3610 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3611 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3612 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3613 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3614 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3615 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3616 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3617 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3618 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3619 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3620 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3621 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3622 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3623 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3624 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3625 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3626 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3627 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3628 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3629 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3630 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3903 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3906 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3907 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3908 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3909 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3915 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3916 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3917 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3918 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3919 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3920 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R3921 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
C1 4030007110 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 680J-T
C2 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T
C3 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C4 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C5 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T
C6 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C7 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C9 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C10 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C11 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C54 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C56 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C57 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C59 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T
C61 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 153K-T
5 - 5
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 33

[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
C62 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C63 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 153K-T
C64 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C65 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C66 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C67 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C68 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C101 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C102 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C103 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C104 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C105 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C106 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C107 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C108 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C109 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C110 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C111 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T
C112 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T
C113 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T
C114 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T
C115 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T
C116 4030010750 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 201J-T
C117 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C118 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C119 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C120 4030010750 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 201J-T
C121 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C122 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T
C123 4030007080 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 390J-T
C124 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C125 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C126 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C127 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C128 4030009970 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 182K-T
C129 4030008470 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 272K-T
C130 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C131 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C132 4030007140 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 121J-T
C133 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T
C134 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T
C135 4030010760 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 331J-T
C136 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C137 4030011830 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 301J-T
C138 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C139 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T
C140 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T
C141 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T
C142 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C143 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C144 4030007140 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 121J-T
C145 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T
C146 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T
C147 4030008850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 123K-T
C148 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C149 4030009970 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 182K-T
C150 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C151 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C152 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C153 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C154 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C155 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C156 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C157 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C158 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C159 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C160 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T
C161 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C162 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T
C163 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C164 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C165 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C166 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C167 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C168 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C169 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C170 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C171 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T
C172 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C173 4030010760 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 331J-T
C174 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C175 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C202 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T
C203 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C204 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C205 4030006990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 080D-T
C206 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C207 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C208 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C209 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C210 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C211 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C212 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C213 4030007000 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 090D-T
C214 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C215 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C217 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T
C218 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C219 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C220 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C221 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C223 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C224 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C301 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C302 4030006970 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060D-T
C303 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T
C305 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T
C307 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C308 4030009580 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 681K-T
C309 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C310 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C311 4030010770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 392K-T
C312 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C314 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C401 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C402 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C403 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C404 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C405 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C406 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C407 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C408 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C409 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C410 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C411 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C412 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C413 4030007140 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 121J-T
C414 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T
C501 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C502 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C503 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C504 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C505 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C506 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C507 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C508 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C509 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C510 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C511 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C512 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C516 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C517 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C518 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C519 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C520 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C521 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C601 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C602 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C603 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C604 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C605 4030010760 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 331J-T
C606 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C607 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T
C608 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C609 4030006970 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060D-T
C610 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T
C611 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C612 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C701 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C702 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C703 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C705 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C706 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T
5 - 6
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 34

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
C707 4030006970 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060D-T
C709 4030007080 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 390J-T
C710 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C711 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C712 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C714 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C715 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T
C716 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C717 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C718 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C720 4030007080 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 390J-T
C801 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C802 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C804 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C805 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C806 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C901 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C902 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C903 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C904 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C905 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C906 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C907 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C908 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C909 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C910 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1001 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1002 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1003 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1004 4030009970 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 182K-T
C1005 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T
C1006 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1007 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1008 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1010 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1011 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1012 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1051 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1052 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1054 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C1055 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C1056 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C1057 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C1058 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C1059 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C1061 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C1062 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C1063 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C1064 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C1101 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1102 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1201 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1202 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1203 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1204 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1205 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1206 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C1208 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1209 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1210 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1211 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1212 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1213 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1214 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1223 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [OTH]
C1224 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [OTH]
C1301 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1302 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1303 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1304 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1305 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1306 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1307 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1308 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1309 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1310 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1311 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1312 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C1313 4510006850
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA4R7NR (16V 4.7)
C1314 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C1315 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1451 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1501 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C1502 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1503 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1504 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1505 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1506 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1507 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1508 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C1509 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1510 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1551 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1552 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C1555 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C1557 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1558 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1559 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1560 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1561 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T
C1562 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1563 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T
C1601 4510006670
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA471P
C1602 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1603 4510006670
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA471P
C1604 4510006670
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA471P
C1605 4510006670
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA471P
C1606 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C1607 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1608 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1609 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1610 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1611 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1612 4510006850
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA4R7NR (16V 4.7)
C1613 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1614 4510006670
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA471P
C1615 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1616 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1617 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1618 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C1619 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C1701 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1702 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1703 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1704 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1705 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T [USA], [CAN]
C1706 4510006850
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA4R7NR (16V 4.7)
C1707 4030008850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 123K-T
C1709 4030014300 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 563K-T
C1710 4030014300 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 563K-T
C1711 4030014300 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 563K-T
C1713 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1714 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C1715 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1716 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1717 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1801 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1802 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1803 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1804 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1805 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1806 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1807 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1901 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1902 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1903 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1904 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1905 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1906 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1907 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C1908 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C1910 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C2001 4510006850
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA4R7NR (16V 4.7)
[USA], [CAN]
C2002 4510006850
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA4R7NR (16V 4.7)
C2003 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C2004 4510006850
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA4R7NR (16V 4.7)
C2005 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C2006 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C2007 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C2008 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C2101 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T [USA], [CAN]
C2102 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2103 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
5 - 7
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 35

[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
C2104 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2105 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2106 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T [USA], [CAN]
C2107 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2202 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2203 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2204 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2205 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2206 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2207 4030009490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 821K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2208 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2209 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2210 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2211 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2212 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2213 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2214 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2215 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2216 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2217 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2218 4030009580 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 681K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2219 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2220 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2221 4030007110 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 680J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2222 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2223 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2224 4030007110 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 680J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2225 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2226 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2227 4030009580 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 681K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2228 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2229 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2232 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2234 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2235 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2236 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2237 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2238 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2239 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2240 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2241 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2242 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2243 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2244 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2245 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2246 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2247 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2248 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2249 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2250 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2251 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2252 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2253 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2254 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2263 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T [USA], [CAN]
C2264 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T [USA], [CAN]
C2266 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T [USA], [CAN]
C2267 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2268 4030007080 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 390J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2269 4030007080 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 390J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2270 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2271 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2301 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2302 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2303 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2304 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2307 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2308 4030006990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 080D-T [USA], [CAN]
C2309 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2310 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2311 4030007140 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 121J-T [USA], [CAN]
C2402 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2403 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2404 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2405 4030009910 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 040B-T [USA], [CAN]
C2406 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2409 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2501 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2502 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2503 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2504 4030009910 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 040B-T [USA], [CAN]
C2701 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2702 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2703 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2704 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2705 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR [USA], [CAN]
C2706 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2707 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2708 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2710 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR [USA], [CAN]
C2711 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR [USA], [CAN]
C2712 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2713 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2714 4030009970 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 182K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2715 4030010040 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 561K-T [USA], [CAN]
C2716 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C3001 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C3002 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C3003 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C3004 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C3005 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C3006 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3007 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C3008 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3009 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3101 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C3102 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3103 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3104 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C3201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3202 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C3302 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3303 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3304 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C3305 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C3306 4030008890 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 273K-T
C3307 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C3308 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3309 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C3310 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3311 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3312 4030006930 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 020C-T
C3601 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3602 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3603 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3604 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3605 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3606 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C3901 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
RL2101
6330001320 RELAY AHY103 [USA], [CAN]
J1 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J51 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J301 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J601 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J1101 6510021650 CONNECTOR IMSA-9180B-30B
J1102 6510022810 CONNECTOR IMSA-9180B-22B
J1301 6510022610 S.CONNECTOR 16FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J1451 6450000140 CONNECTOR HSJ0807-01-010
J1801 6510023670 CONNECTOR TCS4480-01-4151
J1901 6510022540 S.CONNECTOR 20FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J2051 6510023180 CONNECTOR TCS7282-01-211
J2101 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6 [USA], [CAN]
J2301 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6 [USA], [CAN]
J3001 6510022620 S.CONNECTOR 10FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J3601 6510022580 S.CONNECTOR 24FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J3602 6510021720 S.CONNECTOR 30FLT-SM1-TB
W501 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W803 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1011 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1101 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1102 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1227 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1231 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1601 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W1701 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W2001 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W2002 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
5 - 8
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 36

S.=Surface mount
[PLL UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
EP1 0910054676 PCB B 5722F
EP2 0880000900 UNIT BOARD EX-2432 #02 [USA], [CAN]
0880001190 UNIT BOARD EX-2432 #03 [OTH]
IC5001
1180001070 S.IC TA7805F (TE16L)
IC5031
1180001250 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L)
IC5081
1120002920 S.IC ADM202EARN
IC5082
1130006800 S.IC TC7W08F (TE12L)
IC5083
1130007040 S.IC TC7W32F (TE12L)
IC5084
1170000290 S.IC PS2701-1-F3
IC5085
1170000290 S.IC PS2701-1-F3 [USA], [CAN]
IC5101
1140007880 S.IC TC190G08AF-0046-Z/SC-1246A
IC5102
1130004830 S.IC TC7SU04F (TE85R)
IC5103
1130004830 S.IC TC7SU04F (TE85R)
IC5401
1130009230 S.IC LMX2306TMX
IC5701
1140004550 S.IC M65343FP/SC1287
IC5702
1130004830 S.IC TC7SU04F (TE85R)
IC5801
1140004550 S.IC M65343FP/SC1287 [USA], [CAN]
IC5802
1130004830 S.IC TC7SU04F (TE85R) [USA], [CAN]
IC5901
1140004550 S.IC M65343FP/SC1287 [USA], [CAN]
IC5902
1130004830 S.IC TC7SU04F (TE85R) [USA], [CAN]
Q5081 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
Q5082 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
Q5083 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q5084 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
Q5085 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q5101 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
Q5202 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5281 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5282 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R) [OTH]
Q5283 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R) [OTH]
Q5301 1560000330 S.FET 2SK210-GR (TE85R)
Q5302 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
Q5351 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5401 1590001330 S.TRANSISTOR DTA114EUA T106
Q5521 1560000490 S.FET 2SK508 K52 T2B
Q5553 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R)
Q5601 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5602 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5603 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5604 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5881 1530003150 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4673D-TD [USA], [CAN]
Q5882 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R) [USA], [CAN]
D5051 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D5081 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D5082 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D5083 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D5084 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D5085 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D5086 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) [USA], [CAN]
D5101 1750000270 S.DIODE 1SS301 (TE85R)
D5301 1790000540 S.VARICAP MA338 (TX)
D5302 1790001210 S.DIODE 1SS375-TL
D5303 1790001210 S.DIODE 1SS375-TL
D5402 1750000270 S.DIODE 1SS301 (TE85R)
D5521 1720000830 S.VARICAP KV1770STL
FI5101
2020001820 S.CERAMIC SFECV10M5FA00-R0
X5251 6050011520 XTAL
CR-604. (32.000 MHz)
[USA], [CAN]
X5281 6050011390 XTAL CR-338. (32.00056 MHz) [OTH]
L5005 6200009300 S.COIL ELJPA 100KF 10U
L5021 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L5101 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
L5201 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C [OTH]
L5202 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5203 6150004250 COIL LS-471A (C-14922)
L5204 6150004250 COIL LS-471A (C-14922)
L5281 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J [OTH]
L5283 6200003330 S.COIL NL 322522T-1R0J-3 [OTH]
L5284 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J [OTH]
L5285 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J [OTH]
L5301 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5302 6130001850 COIL LB-185
L5303 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
L5304 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5351 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5352 6200003100 S.COIL NL 322522T-3R9J-3
L5401 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
L5521 6170000400 COIL LW-38
L5522 6170000400 COIL LW-38
L5523 6190001280 COIL E544GN-110248
L5552 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5601 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5602 6200003420 S.COIL NL 322522T-R15J-3
L5603 6200003430 S.COIL NL 322522T-R10J
L5604 6200003430 S.COIL NL 322522T-R10J
L5605 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L5701 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
L5781 6200001710 S.COIL NL 322522T-220J
L5782 6200001710 S.COIL NL 322522T-220J
L5783 6200003150 S.COIL NL 322522T-180J
L5801 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J [USA], [CAN]
L5881 6200001850 S.COIL NL 322522T-5R6J [USA], [CAN]
L5882 6200001850 S.COIL NL 322522T-5R6J [USA], [CAN]
L5883 6200004900 S.COIL ELJFC 5R6K-F [USA], [CAN]
L5884 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J [USA], [CAN]
L5885 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J [USA], [CAN]
L5901 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J [USA], [CAN]
L5981 6200003150 S.COIL NL 322522T-180J [USA], [CAN]
L5982 6200001710 S.COIL NL 322522T-220J [USA], [CAN]
L5983 6200003140 S.COIL NL 322522T-150J [USA], [CAN]
R5002 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5003 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5004 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5005 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5006 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5008 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5009 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5010 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5011 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5021 7070000311 RESISTOR ERG1SJ 100 (10 Ω)
R5051 7030003430 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5081 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5082 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5083 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5084 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R5085 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R5086 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R5087 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R5088 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5089 7030009620 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ120U (12 Ω)
R5090 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5091 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5092 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5093 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5094 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5095 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5096 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5097 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5098 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5101 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5102 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5103 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5104 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5105 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5106 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5107 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5108 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5109 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5110 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5111 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5112 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
5 - 9
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[PLL UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 37

[PLL UNIT][PLL UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
R5113 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5114 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5115 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5116 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5117 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5118 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5119 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5120 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5121 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5122 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5123 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5124 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5125 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5126 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R5127 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R5128 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5129 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R5130 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R5131 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5132 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ)
R5133 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5134 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5135 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R5136 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R5137 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5138 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5139 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5140 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5141 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5142 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5143 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5144 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5145 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5146 7030003430 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω)
R5203 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5204 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R5205 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R5206 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R5207 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω) [OTH]
R5251 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5281 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5282 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5283 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R5284 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5285 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) [OTH]
R5287 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) [OTH]
R5288 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) [OTH]
R5289 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ) [OTH]
R5291 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ) [OTH]
R5292 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ) [OTH]
R5293 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω) [OTH]
R5302 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω)
R5303 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R5304 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R5305 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω)
R5306 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5307 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R5308 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5309 7030003430 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω)
R5310 7030003430 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω)
R5311 7030003430 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω)
R5312 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5351 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R5352 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5353 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5354 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R5403 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R5404 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5406 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R5407 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5408 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5410 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5522 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R5524 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5551 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5556 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R5557 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R5601 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5602 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5603 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5604 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R5605 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5606 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R5607 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5608 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R5609 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5610 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R5611 7030003250 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 270 V (27 Ω)
R5612 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R5613 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R5614 7030003350 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 181 V (180 Ω)
R5701 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5702 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5703 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5704 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5705 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5706 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5707 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5708 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5709 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5710 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V
R5711 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5712 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5713 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5714 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5715 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R5716 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5717 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R5718 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5719 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5720 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V
R5721 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R5722 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R5781 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R5782 7030007860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 8R2V (8.2 Ω)
R5783 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R5799 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R5801 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5802 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5803 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5804 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5805 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5806 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5807 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5808 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5809 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5810 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5811 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5812 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5813 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5814 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5815 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5816 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5817 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5818 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5819 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5820 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5821 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5822 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5881 7030000220 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 47 Ω (470)
[USA], [CAN]
R5882 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5883 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5885 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5886 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5887 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5888 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5889 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5890 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5891 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5892 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
5 - 10
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 38

S.=Surface mount
[PLL UNIT][PLL UNIT]
R5901 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5902 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5903 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5904 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5905 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5906 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5907 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5908 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5909 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5910 7030007210 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 102V [USA], [CAN]
R5911 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5912 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5913 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5914 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5915 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5916 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5917 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5918 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5919 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5920 7030007200 S.RESISTOR ERA3YEB 202V [USA], [CAN]
R5921 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
R5922 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
[USA], [CAN]
R5982 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
[USA], [CAN]
C5021 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C5022 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5023 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5024 4510007510 S.ELECTOR ECEV1AA470WR
C5031 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C5032 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5033 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5034 4510007510 S.ELECTOR ECEV1AA470WR
C5051 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5052 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5053 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5055 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5081 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5082 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5083 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5084 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5085 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C5086 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C5087 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C5088 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C5089 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5090 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T
C5091 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5092 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5101 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C5102 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C5103 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T
C5104 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5105 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5106 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5107 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5108 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5110 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C5111 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5112 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C5113 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5115 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5116 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C5117 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5118 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5120 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5121 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5122 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5123 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5124 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5125 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5126 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5201 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5202 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5203 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5204 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5205 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T
C5206 4030006910 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5C-T
C5207 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T
C5251 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T [USA], [CAN]
C5253 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5254 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C5281 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5282 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5283 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5284 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [OTH]
C5285 4510005600
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CS100SR [OTH]
C5287 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [OTH]
C5288 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T [OTH]
C5289 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T [OTH]
C5290 4030008230 S.CERAMIC C1608 UJ 1H 080D-T [OTH]
C5291 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [OTH]
C5292 4030000840 S.CERAMIC GRM2163C1H3R0CD01D [OTH]
C5293 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [OTH]
C5294 4610001850 S.TRIMMER TZB4R200AB10R00 [OTH]
C5295 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [OTH]
C5301 4550000730 S.TANTALUM TESVA 0J 225M1-8L
C5302 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5303 4030009650 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 240J-T
C5304 4030011570 S.CERAMIC CM105 CH 101G 50AT
C5305 4610001850 S.TRIMMER TZB4R200AB10R00
C5306 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C5307 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C5308 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T
C5309 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5310 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C5311 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5312 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C5313 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5314 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5315 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5351 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5352 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5353 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5354 4030010000 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 510J-T
C5355 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T
C5356 4030010000 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 510J-T
C5357 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5401 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5402 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5403 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5404 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5408 4550005980 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1A 475M-8L
C5521 4610001830 S.TRIMMER TZB4S100AB10R00
C5522 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C5523 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C5524 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5525 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C5526 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T
C5528 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5529 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C5551 4550005980 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1A 475M-8L
C5552 4550003250 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1V 474M-8L
C5556 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5557 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C5558 4510004590 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 470 HC
C5560 4510005430
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV0JA220SR
C5561 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C5601 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5602 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5603 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5604 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5605 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5606 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5607 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5608 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5609 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C5610 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C5611 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C5612 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C5613 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C5614 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C5615 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T
C5616 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C5617 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5618 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5619 4030006930 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 020C-T
C5701 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5702 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5703 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5704 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
5 - 11
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 39

[PLL UNIT][PLL UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
C5705 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5706 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5707 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5708 4510005600
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CS100SR
C5709 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C5710 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C5711 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C5781 4030008770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 562K-T
C5782 4030009490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 821K-T
C5783 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5784 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C5785 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C5794 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C5801 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5802 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5803 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5804 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5805 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5806 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5807 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5808 4510005600
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CS100SR [USA], [CAN]
C5809 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5810 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5811 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T [USA], [CAN]
C5881 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5882 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T [USA], [CAN]
C5883 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5884 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5885 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T [USA], [CAN]
C5886 4030009500 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5B-T [USA], [CAN
C5887 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T [USA], [CAN]
C5888 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T [USA], [CAN]
C5889 4030011770 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060B-T [USA], [CAN]
C5890 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5891 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5892 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5893 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T [USA], [CAN]
C5901 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5902 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5903 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5904 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5905 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5906 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5907 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5908 4510005600
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CS100SR [USA], [CAN]
C5909 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5910 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5911 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T [USA], [CAN]
C5981 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T [USA], [CAN]
C5982 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T [USA], [CAN]
C5983 4030009520 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 020B-T [USA], [CAN]
C5984 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T [USA], [CAN]
C5985 4030009530 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 030B-T [USA], [CAN]
C5986 4030009990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 200J-T [USA], [CAN]
RL5081
6330001640 RELAY ATX209
J5001 6510022580 S.CONNECTOR 24FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J5051 6510023120 CONNECTOR CD6109SA1J0 [USA], [CAN]
J5071 6510021720 S.CONNECTOR 30FLT-SM1-TB
J5081 6510023120 CONNECTOR CD6109SA1J0
J5091 6510023040 CONNECTOR 01K1621 [USA], [CAN]
W5051 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W5052 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W5053 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W5054 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W5081 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5082 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5203 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
W5251 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5401 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5402 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5409 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5502 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5981 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [USA], [CAN]
WS1 8970024010
SX2429 1.5D COAXIAL TUBE (3)/PL
[USA], [CAN]
8970024050
SX2429 1.5D COAXIAL TUBE (2)/PL
[OTH]
EP5001 0910054684 PCB B 5723D
IC6501 1110005450 S.IC TS522IDT
IC6601 1180001250 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L)
Q6101 1560001020 S.FET 2SK2973 (MTS101P)
Q6401 1590003040 TRANSISTOR SD1487
Q6402 1590003040 TRANSISTOR SD1487
Q6403 1540000500 TRANSISTOR 2SD1585K
Q6501 1540000550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1664 T100Q
Q6601 1510001040 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1037AKT146S
Q6602 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q6701 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q6801 1590003050 S.FET PD55003
D6601 1710001160 S.DIODE DF40SC4-4072
D6701 1160000140 S.DIODE DAP222 TL
D6702 1730000480 S.ZENER RD10M-T2B3
L6101 6200003840 S.COIL MLF2012D R22K-T
L6102 6180000990 COIL LAL 04NA 101K
L6202 6180001240 COIL LAL 04NA 820K
L6204 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L6301 6140003720 COIL LR-416
L6303 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L6401 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L6402 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L6403 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L6404 6140003590 COIL LR-400
L6405 6140003350 COIL LR-376
L6406 6140002030 COIL LR-230 (SK-10M-15Y 120)
L6407 2040000490 COIL EXC-ELDR25C
L6408 6110001730 COIL LA-262
L6501 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L6701 6200003590 S.COIL EXCCL3225U1
L6702 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L6703 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L6704 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L6705 6200008820 S.COIL HF70ACC 635050-T
L6706 6200008820 S.COIL HF70ACC 635050-T
R6101 7030003270 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 390 V (39 Ω)
R6102 7030003350 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 181 V (180 Ω)
R6103 7030003350 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 181 V (180 Ω)
R6104 7030003300 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 680 V (68 Ω)
R6105 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R6106 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R6107 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω)
R6109 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R6110 7030000210 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 39 Ω (390)
R6111 7030000210 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 39 Ω (390)
R6112 7030000210 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 39 Ω (390)
R6201 7030000250 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 82 Ω (820)
R6202 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R6203 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R6204 7030010800 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 2R7U (2.7 Ω)
R6206 7030000340 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 470 Ω (471)
R6301 7030000260 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 100 Ω (101)
R6302 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R6303 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R6304 7310004730 TRIMMER EVM-2AGA00 B33 (302)
R6401 7030010260 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 3R3 U
R6402 7030010260 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 3R3 U
5 - 12
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[PA UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 40

S.=Surface mount
[PA UNIT][PA UNIT]
R6403 7030010260 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 3R3 U
R6404 7030010260 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 3R3 U
R6405 7030010260 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 3R3 U
R6406 7030010260 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 3R3 U
R6407 7030001010 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 10 Ω (100)
R6408 7030001010 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 10 Ω (100)
R6409 7070000371 RESISTOR ERX2SJ 2R2 (2.2 Ω)
R6410 7070000371 RESISTOR ERX2SJ 2R2 (2.2 Ω)
R6411 7070000521 RESISTOR ERX3SJ 2R7 (2.7 Ω)
R6412 7310004710 TRIMMER EVM-2AGA00 B23 (202)
R6413 7030000300 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 220 Ω (221)
R6415 7070001030 RESISTOR ERG5SJ 470
R6502 7030005981 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 333V
R6503 7030005981 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 333V
R6504 7030005971 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 683V (68 kΩ)
R6505 7030005971 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 683V (68 kΩ)
R6507 7030003840 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 225 V (2.2 MΩ)
R6509 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R6510 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R6512 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R6513 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ)
R6514 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R6515 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R6516 7310004680 TRIMMER EVM-2AGA00 B14 (103)
R6517 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R6602 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R6603 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R6604 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R6651 7100000810 S.RESISTOR ERX5WQK 12MH
R6652 7100000810 S.RESISTOR ERX5WQK 12MH
R6702 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω)
R6704 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R6705 7510001550 S.THERMISTOR NTCG16 4LH 333KT
R6801 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R6802 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
C6101 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T
C6102 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T
C6103 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6104 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6105 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6106 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6108 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6109 4030005110 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1E 473K-T
C6201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6202 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6203 4030004750 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 103K-T
C6205 4030008700 S.CERAMIC GRM21BB11H473KA01L
C6206 4030008700 S.CERAMIC GRM21BB11H473KA01L
C6301 4030008960 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 104K-T
C6302 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6303 4510004590 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 470 HC
C6305 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6306 4510004600 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 1000 HC
C6307 4320000811 DIP MICA KD20C 681J5A
C6308 4030011790 S.CERAMIC GRM55RF52A684ZD01L
C6401 4030011760 S.CERAMIC GRM55R1X2D682JV01L
C6403 4030011760 S.CERAMIC GRM55R1X2D682JV01L
C6408 4030018370 S.CERAMIC ERF22X 6C1H 102J D01L
C6409 4030018370 S.CERAMIC ERF22X 6C1H 102J D01L
C6410 4030018230 S.CERAMIC ERF22X 6C2D 221JD
C6412 4510004600 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 1000 HC
C6413 4510004600 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 1000 HC
C6414 4030004740 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 472K-T
C6415 4030011790 S.CERAMIC GRM55RF52A684ZD01L
C6416 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C6417 4510004600 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 1000 HC
C6418 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6419 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6424 4030018370 S.CERAMIC ERF22X 6C1H 102J D01L
C6425 4320000681 DIP MICA KD19C 681J5A
C6427 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6428 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6432 4030011740 S.CERAMIC GRM32N2C2H201JV01L
C6433 4030011740 S.CERAMIC GRM32N2C2H201JV01L
C6501 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C6503 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6506 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6507 4510004590 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 470 HC
C6602 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6603 4510004590 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 470 HC
C6604 4510006230
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA470UP
C6605 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6606 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C6607 4510006230
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA470UP
C6608 4030008700 S.CERAMIC GRM21BB11H473KA01L
C6609 4510006020 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 2200 HC
C6610 4030017320 S.CERAMIC GRM21BB11H104KA11L
C6611 4030004740 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 472K-T
C6612 4030004720 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 102K-T
C6701 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C6702 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C6703 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C6704 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6705 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6706 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6707 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6708 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6801 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
RL6701
6330001470 RELAY AJS1311
J6301 6510021530 CONNECTOR IMSA-9230B-1-04Z024-T
J6302 6510021530 CONNECTOR IMSA-9230B-1-04Z024-T
J6401 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J6411 6510021390 CONNECTOR IMSA-9230B-1-03Z024-T
J6412 6510021390 CONNECTOR IMSA-9230B-1-03Z024-T
J6501 6510003390 CONNECTOR B03B-EH-S
J6701 6510022540 S.CONNECTOR 20FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J6702 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J6703 6510003400 CONNECTOR B04B-EH-S
F6701 5210000060 FUSE FGB 5A (FGB0 125V)
F6702 5220000230 HOLDER S-N5054 #01
F6703 5220000230 HOLDER S-N5054 #01
W6401 9054500690 WIRE 76/98/020/X98/X98
W6402 9054500690 WIRE 76/98/020/X98/X98
W6601 9045201001 WIRE 74/98/040/X98/X98
W6701 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
EP6001
0910054695 PCB B 5724E
EP6601
6910000630 BEAD FSRH070140RN000B
EP6602
6510018330 TERMINAL F4053A
EP6603
6510018330 TERMINAL F4053A
5 - 13
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 41

[FILTER UNIT][FILTER UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
Q7301 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
D7271 1750000190 S.DIODE 1SS322 (TE85R)
D7272 1750000190 S.DIODE 1SS322 (TE85R)
D7301 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
L7031 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7035 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7036 6140002830 COIL LR-236
L7037 6140002950 COIL LR-226
L7038 6140002960 COIL LR-227
L7061 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7065 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7066 6140002900 COIL LR-263
L7067 6140002820 COIL LR-235
L7068 6140002830 COIL LR-236
L7091 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7095 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7096 6140002850 COIL LR-238
L7097 6140002820 COIL LR-235
L7098 6140002820 COIL LR-235
L7121 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7125 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7126 6140002840 COIL LR-237
L7127 6140002900 COIL LR-263
L7128 6140002900 COIL LR-263
L7151 6200005050 S.COIL NL 252018T-330J
L7155 6200005050 S.COIL NL 252018T-330J
L7156 6140002860 COIL LR-241
L7157 6140002840 COIL LR-237
L7158 6140002840 COIL LR-237
L7181 6200005050 S.COIL NL 252018T-330J
L7182 6140002880 COIL LR-243
L7183 6140002870 COIL LR-242
L7184 6140002870 COIL LR-242
L7185 6200005050 S.COIL NL 252018T-330J
L7211 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L7215 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L7216 6140002870 COIL LR-242
L7217 6140002870 COIL LR-242
L7218 6140002870 COIL LR-242
L7241 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L7244 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L7245 6140002890 COIL LR-262
L7246 6140002890 COIL LR-262
L7248 6140002890 COIL LR-262
L7271 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7272 6140003490 COIL LR-391
L7273 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7321 6140001460 COIL LR-170
L7331 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L7332 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
R7271 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R7272 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ)
R7273 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R7274 7030008190 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ330U (33 Ω)
R7275 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R7276 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ)
R7277 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R7301 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R7314 7540000250 ABSORBER SA05C 401N
R7315 7030010650 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ823U (82 kΩ)
C7031 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7032 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C7033 4320000651 DIP MICA KD20C 102J5A
C7034 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7035 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7036 4320000981 DIP MICA KD20C 222J5A
C7037 4010005360 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 301J 500V
C7038 4010005880 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 271J 500V
C7039 4320000951 DIP MICA KD20C 272J5A
C7041 4030011120 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H100JV01L
C7042 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7043 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7044 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7045 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7046 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C7049 4010005850 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 181J 500V
C7061 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7062 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C7063 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7064 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7065 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7066 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7067 4010005880 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 271J 500V
C7068 4010005880 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 271J 500V
C7069 4010005880 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 271J 500V
C7070 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7071 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7072 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7073 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7074 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7075 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7076 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7077 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7078 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7079 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7080 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7081 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7082 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7083 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7084 4030011550 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H680JV01L
C7085 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C7086 4030011120 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H100JV01L
C7087 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7091 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7092 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7094 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7095 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7096 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7098 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7099 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7100 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7101 4010005360 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 301J 500V
C7102 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7105 4010006410 CERAMIC HM13SJ SL 471J 500V
C7106 4010005830 CERAMIC HM74SJ SL 151J 500V
C7108 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7121 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7122 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7124 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7125 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7126 4030011120 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H100JV01L
C7127 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7128 4010005880 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 271J 500V
C7129 4010005360 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 301J 500V
C7130 4030011510 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H560JV01L
C7131 4030011070 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H5R0CY21L
C7132 4010005360 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 301J 500V
C7133 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7136 4010005850 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 181J 500V
C7137 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7151 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7152 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7153 4030014460 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H820JV01L
C7154 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7155 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7156 4030011120 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H100JV01L
C7157 4010005930 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 391J 500V
C7158 4030014460 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H820JV01L
C7160 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7163 4010005850 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 181J 500V
C7164 4030014460 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H820JV01L
C7181 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7182 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7183 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7184 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
C7185 4010005880 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 271J 500V
C7186 4030011510 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H560JV01L
C7187 4010005370 CERAMIC HM11SJ SL 331J 500V
C7188 4030011180 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H220JV01L
C7190 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7193 4010005850 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 181J 500V
C7211 4510005480 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 1 HC
C7212 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7214 4030011240 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H470JV01L
C7216 4030011190 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H270JV01L
C7217 4030012480 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H121JV01L
5 - 14
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 42

S.=Surface mount
[DRIVER UNIT][FILTER UNIT]
C7218 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7221 4030014460 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H820JV01L
C7222 4010005860 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 201J 500V
C7223 4030014460 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H820JV01L
C7224 4030011210 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H330JV01L
C7225 4030011190 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H270JV01L
C7241 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7242 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7243 4030011510 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H560JV01L
C7244 4030011180 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H220JV01L
C7247 4030011190 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H270JV01L
C7248 4030011210 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H330JV01L
C7249 4030011230 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H390JV01L
C7250 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7253 4010005830 CERAMIC HM74SJ SL 151J 500V
C7254 4030011180 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H220JV01L
C7255 4030011080 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H6R0DV01L
C7272 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C7273 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C7274 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C7275 4610002230 TRIMMER TZB4Z100DB10B00
C7277 4010005850 CERAMIC HM95SJ SL 181J 500V
C7278 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C7301 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7302 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7303 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7304 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7321 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7322 4030011170 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H180JV01L
C7323 4030011730 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H101JV01L
C7325 4030011790 S.CERAMIC GRM55RF52A684ZD01L
C7332 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C7345 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
RL7031
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7032
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7061
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7062
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7091
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7092
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7121
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7122
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7151
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7152
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7181
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7182
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7211
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7212
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7241
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7242
6330001570 RELAY AJS1315
RL7301
6330000780 RELAY AGP 2013
CP7331
6910009670 S.CHECK P HK3-S-T [USA]
CP7332
6910009670 S.CHECK P HK3-S-T [USA]
J7311 6510007020 CONNECTOR TMP-J01X-V6
J7331 6510022560 CONNECTOR 16FMN-BTRK-A
W7333 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7334 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7335 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7336 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7337 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7338 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7339 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W7340 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
WS1 8970024020
SX2429 1.5D COAXIAL TUBE (2)/FI
EP7001
0910054706 PCB B 5725F
Q6851 1590003060 S.FET PD55015
R6851 7030010520 S.RESISTOR ERJ1TYJ 101U (100 Ω)
R6852 7030000020 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1 Ω (010)
C6851 4030004750 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 103K-T
EP6851 0910054751 PCB B 5744A
D6431 1790001760 S.VARISTOR MA30-(TX)
C6431 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
EP6431 0910054761 PCB B 5746A
D6432 1790001760 S.VARISTOR MA30-(TX)
C6432 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
EP6432 0910054771 PCB B 5747A
5 - 15
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[VARISTOR-1 BOARD]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[VARISTOR-2 BOARD]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 43

[DSP UNIT]
EX-2432
[DSP UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
IC1 1130010010 S.IC TC7WHU04FU
IC3 1130010540 S.IC SN74AHC74PWR
IC4 1130010540 S.IC SN74AHC74PWR
IC51 1130010010 S.IC TC7WHU04FU
IC101 1130010520 S.IC SN74HCT244APWR
IC102 1110004770 S.IC BU9480F-E2
IC152 1180002320 S.REG TK11218CMCL
IC161 1180002020 S.REG BA033FP-E2
IC171 1180002270 S.REG TK11250CMCL
IC201 1130010680 S.IC M29W102BB-70N1
IC202 1130008040 S.IC TC7SH04FU
IC203 1130008810 S.IC TC7SH32FU (TE85L)
IC301 1140010330 S.IC TMS320VC33PGEA120
IC401 1130010550 S.IC SN74AHC595PWR
IC403 1130010530 S.IC SN74AHCT374PWR
IC404 1130010530 S.IC SN74AHCT374PWR
IC405 1130004670 S.IC BU4021BF-T1
IC406 1130010540 S.IC SN74AHC74PWR
IC501 1190001610 S.IC AK4528-VF
IC601 1110005420 S.IC BA15532F-E2
IC651 1110005420 S.IC BA15532F-E2
IC701 1110001900 S.IC µPC4570G2-T1
IC801 1130010560 S.IC SN74AHC244PWR
Q201 1590001660 S.TRANSISTOR XP4312 (TX)
Q301 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q302 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
D301 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D302 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D303 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D304 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D901 1790000970 S.DIODE MA729 (TX)
X1 6050009860 S.XTAL CR-566 (12.288 MHz)
X51 6050011270 S.XTAL CR-709 (60.000 MHz)
L1 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L2 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L3 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L51 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L52 6200001980 S.COIL NL 252018T-1R0J
L101 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L102 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L301 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L302 6200009840 S.COIL LQH32CN2R2M21L
L401 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L403 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L404 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L405 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L406 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L501 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L502 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
L601 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L651 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L701 6200002040 S.COIL NL 252018T-101J
L801 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J
R1 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R2 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R51 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R52 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R151 7030007240 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ680U (68 Ω)
R161 7030008190 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ330U (33 Ω)
R162 7030007510 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ270U (27 Ω)
R171 7030007180 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ150U (15 Ω)
R201 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R303 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R304 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R305 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R306 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R307 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R308 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R309 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R310 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R311 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R312 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R313 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R317 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R318 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R320 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R321 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R322 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R323 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R324 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R325 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R326 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R327 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R328 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R329 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R330 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R331 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R332 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R501 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R601 7030006581 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 122V
R602 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R603 7030010450 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 391V
R604 7030010450 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 391V
R605 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R606 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R607 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R608 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R609 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R610 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R611 7030005331 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 562V
R651 7030010450 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 391V
R652 7030010450 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 391V
R653 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R654 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R655 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R656 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R657 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R658 7030009591 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 472V
R659 7030005331 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 562V
R701 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R702 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R703 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R704 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R705 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R706 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R707 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R708 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R751 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R752 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R753 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R754 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R755 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R756 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R757 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R758 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R801 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R802 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R803 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R804 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R805 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R901 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R902 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R903 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R904 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R905 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R906 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
C1 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C2 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C3 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T
C4 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C6 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C7 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C9 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T
C51 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C52 4030009920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050B-T
C53 4030009920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050B-T
5 - 16
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 44

S.=Surface mount
[DSP UNIT][DSP UNIT]
C54 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C101 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C102 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTI
C ECEV1CA100SR
C103 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C104 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C154 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C155 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C156 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C157 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C158 4550006080 S.TANTALUM TEMSVB2 1C 106M-8L
C161 4550006620 S.TANTALUM ECST0JY226R
C162 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C163 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C164 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C171 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C172 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C173 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C174 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C175 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C202 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C203 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C301 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C302 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C303 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C304 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C305 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C306 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C307 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C308 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C309 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C311 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C312 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C313 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C314 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C315 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C316 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C317 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C318 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C319 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C320 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C321 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C322 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C323 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C324 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C325 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C401 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C403 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C404 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C405 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C406 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C407 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C408 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C504 4510005860
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA2R2SR
C505 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C506 4550006620 S.TANTALUM ECST0JY226R
C507 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C508 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C509 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C510 4550006620 S.TANTALUM ECST0JY226R
C511 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C601 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C602 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C603 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C604 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C605 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C606 4510005830
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HAN010R
C651 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C652 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C653 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C654 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C655 4510005830
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HAN010R
C701 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C702 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C703 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C704 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C705 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C706 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C707 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP
C708 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C751 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C752 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C755 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C756 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C757 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP
C758 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C801 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C802 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C901 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
J901 6910013900 CONNECTOR IMSA-9180S-22A
J902 6910012460 CONNECTOR IMSA-9180S-30A
W1 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W2 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
W3 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W4 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
W5 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W151 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
W152 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W171 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
W201 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W202 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W203 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W302 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W303 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W308 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W309 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W310 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W311 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W312 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W501 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W502 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W503 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W504 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W505 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
W901 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W902 7030008240 S.JUMPER ERJ12YJ0R00U
W903 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W904 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W951 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [OTH]
W952 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
EP1 0910054518 PCB B 5666H
EP2 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
5 - 17
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 45
[DISPLAY UNIT]
RC-25
[FRONT UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
W8001 8900009531 CABLE OPC-942A (P=1 N=10 L=170)
W8005 8900008860 CABLE OPC-875 (N:20 L:70)
IC8201 1140010640 S.IC HD64F2134AFA20 (SX-2429B)
IC8202 1110005770 S.IC S-80942CNMC-G9C-T2
IC8250 1130005720 S.IC TC7W04F (TE12L)
IC8260 1130007350 S.IC TC74HC4066AF
IC8270 1110001810 S.IC TA7368F (TP1)
IC8280 1110002700 S.IC NJM2904M-TE1
IC8290 1180001070 S.IC TA7805F (TE16L)
IC8301 1110005580 S.IC AN8010M-(E1)
IC8310 1180001250 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L)
Q8251 1590001650 S.TRANSISTOR XP4601 (TX)
Q8260 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q8280 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8281 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8282 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106
Q8300 1540000440 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1619-T-TD
Q8301 1540000440 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1619-T-TD
Q8340 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8341 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8342 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8343 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8344 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q8345 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
D8201 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D8203 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D8204 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D8205 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D8250 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D8280 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D8701 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
X8211 6050010501 S.XTAL CR-636A (14.7456 MHz)
L8201 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
L8202 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L8203 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L8206 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L8270 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L8286 6200005010 S.COIL NL 252018T-100J
L8290 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L8701 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
R8201 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8202 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8203 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8204 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8205 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R8206 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8207 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8208 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R8209 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8210 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8211 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8212 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8213 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8214 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8215 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8216 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8218 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8219 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8221 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8222 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8223 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8224 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8225 7030003590 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ)
R8226 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R8227 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R8229 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R8230 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8231 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8232 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8233 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8234 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8235 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R8236 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R8237 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R8239 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8240 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8241 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8243 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8246 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8247 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω)
R8250 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8251 7030003590 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ)
R8252 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8253 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R8254 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R8255 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8260 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R8263 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8270 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω)
R8274 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R8275 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R8276 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8278 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R8279 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R8280 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R8281 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8282 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R8283 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8284 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R8285 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R8287 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R8288 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R8289 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R8290 7030006060 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ100U (10 Ω)
R8291 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8300 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R8301 7030006220 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ470U (47 Ω)
R8302 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R8303 7030006220 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ470U (47 Ω)
R8340 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R8341 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R8342 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R8343 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R8344 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R8345 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R8346 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R8347 7030003390 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω)
R8348 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R8349 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R8350 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R8351 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R8352 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8373 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω)
R8701 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
[USA], [OTH]
R8702 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
[USA], [OTH]
R8703 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R8704 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R8705 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R8706 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R8707 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R8708 7510001560 S.THERMISTOR NTCG16 4BH 102KT
C8201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8202 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP
C8203 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8204 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8205 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
5 - 18
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[DISPLAY UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 46

S.=Surface mount
[DISPLAY UNIT][DISPLAY UNIT]
C8206 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C8207 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C8208 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8209 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C8210 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8211 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8212 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8214 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8216 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8218 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8219 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8220 4030017480 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 474K-T
C8221 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8222 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8223 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8226 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8241 4510005310
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA220SR
C8242 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8243 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8244 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8250 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C8260 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8261 4510007110
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA220NP
C8270 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP
C8271 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8274 4510007120
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1AA101SP
C8277 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP
C8280 4510005310
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA220SR
C8281 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8282 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8283 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8284 4510005860
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA2R2SR
C8285 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C8286 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8287 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C8288 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8289 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8290 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8291 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8292 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8293 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8294 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C8295 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C8297 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8298 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8299 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C8300 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C8301 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8302 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8303 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8304 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8310 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8311 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8312 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C8313 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP
C8373 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
J8205 6510022540 S.CONNECTOR 20FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J8701 6510022440 CONNECTOR LTW-8MP-C
J8702 6450001630 CONNECTOR HSJ1406-01-050
J8902 6510022620 S.CONNECTOR 10FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J8903 6510022620 S.CONNECTOR 10FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
DS8300
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8301
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8302
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8303
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8304
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8305
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8306
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8307
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8308
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8309
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8310
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8311
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8312
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8313
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8314
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8315
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8316
5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8317 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8318 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8319 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8320 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8321 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8322 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8323 5040002600 LED TLYU1002
DS8340 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8341 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8342 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8343 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8344 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8345 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8346 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8347 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8348 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8349 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8350 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
W8201 7030000010 S.JUMPER MCR10EZHJ JPW (000)
W8202 7030000010 S.JUMPER MCR10EZHJ JPW (000)
W8238 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8242 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8270 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8271 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8280 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8281 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8296 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8340 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W8702 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V [CAN]
EP8201 0910054714 PCB B 5727D
EP8205 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
EP8292 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
EP8293 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
EP8294 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
EP8295 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
EP8296 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT
J8601 6510022620 S.CONNECTOR 10FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
J8602 6510023060 CONNECTOR TCS7186-01-201
EP8601 0910054961 PCB B 5812A
S8801 2250000220 ENCODER TP90N937E20-15F-1540
S8802 2250000220 ENCODER TP90N937E20-15F-1540
EP8801 0910054732 PCB B 5729B
5 - 19
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[JACK UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[SENSOR UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 47

HM-135
[MAIN UNIT][VR UNIT]
S.=Surface mount
R8901 7210002360 VARIABLE TP96N97-15F-10KB-1301
EP8901
0910054742 PCB B 5730B
L8220 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
L8221 6200001830 S.COIL NL 322522T-100J
R8241 7030003830 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 185 V (1.8 MΩ)
R8242 7030003840 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 225 V (2.2 MΩ)
R8243 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8244 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8245 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R8246 7030003830 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 185 V (1.8 MΩ)
C8230 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8231 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C8232 4550006450 S.TANTALUM ECST1EY105R
C8233 4550006450 S.TANTALUM ECST1EY105R
C8234 4550006450 S.TANTALUM ECST1EY105R
C8235 4550006450 S.TANTALUM ECST1EY105R
C8236 4550006450 S.TANTALUM ECST1EY105R
C8237 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
J8220 6510022540 S.CONNECTOR 20FMN-BMTTR-A-TBT
DS8220
5030002320 LCD M802 LCD ASSEMBLY C
EP8220
0910054783 PCB B 5751C
R1 7010006890 RESISTOR R20J 12 K Ω
R2 7010006910 RESISTOR R20J 33 K Ω
R3 7010006880 RESISTOR R20J 6.8K Ω
R4 7010006900 RESISTOR R20J 15 K Ω
C1 4010008030 CERAMIC DD104 B 471K 50V
MC1 7700002120 MICROPHONE KUC2123-030245
S1 2260002340 SWITCH SKHHAM024A
S2 2260002340 SWITCH SKHHAM024A
S3 2260002340 SWITCH SKHHAM024A
W1 9018490010 WIRE 71/98/010/X98/X98
W2 9018490010 WIRE 71/98/010/X98/X98
EP1 0910051480 PCB B 5324
EP2 9018230010 TUBE IRRAX D=0.7 L=4MM
S1 2260002330 SWITCH SKHHLP014A
EP1 0910051490 PCB B 5325
SP1 2510001170 SPEAKER 077P040P
W1 8900011090 CABLE OPC-1104
EP1 8930006760 M.OTHER SR-2P-4
5 - 20
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[SW BOARD]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[CONNECT UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
SP-24
[CHASSIS ]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 48

6-1 RC-25
6-2 SP-24
6-3 HM-135
[CHASSIS PARTS]
J4501 6510000370 Connector MR-DS 1
J4503 6510000370 Connector MR-DS [USA],[CAN] only 1
W4501 8900011050 Cable OPC-1109 1
W4502 8900011060 Cable OPC-1141 1
W4505 8900011220 Cable OPC-1143 1
W4506 8900008880 Cable OPC-877 1
W4507 8900011230 Cable OPC-1142 1
W4528 8900011030 Cable OPC-1130 1
MF4501 2710000520 Fan SB0812H-ICOM-00 1
MP4501 8010018820 2429 chassis 1
MP4502 8110007700 2429 T -co v er 1
MP4503 8110007711 2429 U-cover-1 1
MP4504 8110007691 2429 PA-cover-1 1
MP4505 8930057190 2429 earth plate [USA],[CAN] 2
8930057190 2429 earth plate [OTH] 1
MP4506 8930057980 Rubber foot (N) SJ-5023K 4
MP4508 8930035230 1546 TR-A clip 1
MP4509 8820000530 Flange bolt M4 × 8 NI 1
MP4511 8820000550 Cap bolt M4 × 8 ZK 2
MP4512 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3 × 8 NI-ZU 42
MP4513 8810005770 Screw BiH M3 × 8 ZK 14
MP4514 8810003170 Setscrew A M3 × 89
MP4515 8930057870 2429 earth spring 1
MP4516 8930058100 2429 DC plate 1
MP4517 8930050320 Thermally sheet (M) TC-500TK 1
MP4519 8930055990 Shield tape (H) 1
MP4521 8930058030 Insulate plate (GX) 1
MP4523 8930058030 Insulate plate (GX) [OTH] only 1
MP4524 8930058750 Insulate plate (HH) [OTH] only 1
MP4525 8930058740 2429 A-earth plate [OTH] only 1
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
6-4 IC-M802
SECTION 6 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISASSEMBLY
6 - 1
J8701 6510022440 Connector LTW-8MP-C 1
J8702 6450001630 Connector HSJ1406-01-050 1
MP8201 8510014560 2545 shield case 1
[FRONT PARTS]
W8001 8900009531 Cable OPC-942A 1
W8005 8900008860 Cable OPC-875 1
MP8001 8210018720 2545 front panel assembly [USA],[CAN] 1
8210019260 2545 front panel assembly (A) [OTH] 1
MP8002 8210018730 2545 rear panel assembly 1
MP8004 8210018620 2545 reflector 1
MP8005 8930057170 2545 20-key [USA],[CAN] 1
8930058690 2545 20-key (A) [OTH] 1
MP8006 8930057160 2545 3-key [USA],[CAN] 1
8930058680 2545 3-key (A) [OTH] 1
MP8007 8930057480 2545 LCD holder Y618 1
MP8008 8930057490 2545 LCD filter 1
MP8009 8830001630 VR nut (P) 1
MP8016 8610010851 Knob N279-1 1
MP8017 8610010861 Knob N280-1 2
MP8020 8810004430 Screw PH M3 × 6 ZK 8
MP8022 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3 × 8 NI-ZU 9
MP8023 8930057110 2545 phone cap 1
[CHASSIS PARTS]
W1 8900011080 Cable OPC-1108 1
MP1 8210015570 1823 front panel (B) 1
MP2 8210013620 1823 rear panel 1
MP4 8930039780 1823 seal 1
MP5 8930039750 1823 PTT holder 1
MP6 8930039760 1823 PTT rubber 1
MP7 8930039730 1823 key board 1
MP8 8930039720 1823 hanger knob 1
MP9 8930039740 1823 M-sheet 2
MP11 8810009250 Screw PH B0 2.6 × 16 SUS 5
MP12 8810009260 Screw PH BT 2 × 6 NI 5
MP13 8810009240 Screw BiH M4 × 10 ZK 1
MP14 8850001610 Spring washer M4 SUS 1
[CHASSIS PARTS]
W1 8900011090 Cable OPC-1104 1
EP1 8930006760 SR-2P-4 1
SP1 2510001170 Speaker 077P0401 1
MP1 8210018780 2431 front panel assembly 1
MP2 8210018790 2431 rear panel assembly 1
MP7 8810004430 Screw PH M3 × 6 ZK 4
MP8 8930057640 Insulate plate (GW) 1
[DISPLAY BOARD]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
J8602 6510023060 Connector TCS7186-01-201 1
[JACK BOARD]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
S8801 2250000220 TP90N937E20-15F-1540 1
S8802 2250000220 TP90N937E20-15F-1540 1
[SENSOR BOARD]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
R8901 7210002360 TP96N97-15F-10KB-1301 1
[VR BOARD]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
DS8220 5030002320 M802 LCD assembly C 1
[CONNECT BOARD]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
MC1 7700002120 Microphone KUC2123-030245 1
[MAIN BOARD]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
Page 49

[MAIN UNIT]
J1451 6450000140 Connector HSJ0807-01-010 1
J1801 6510023670 Connector TCS4480-01-4151 1
J2051 6510023180 Connector TCS7282-01-211 1
EP2 0880000900 DSP board [USA],[CAN] 1
0880001190 DSP board [OTH] 1
MP201 8510014610 2429 MIX case 1
MP202 8930005320 Filter spacer (for FI201) 1
MP231 8930005200
Sheet for crystal (for FI231)
[USA],[CAN] only 2
MP301 8510000180 117 shield plate 1
MP302 8930054530 2355 earth spring 1
MP303 8930005320 Filter spacer (for FI301) 2
MP701 8510011970 2177 OSC case 1
MP702 8510014600 2429 OSC cover 1
MP1501 8510013140 2241 DC-A case 1
MP2051 8930057990 2429 control plate Y630 1
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
[PLL UNIT]
J5051 6510023120 Connector CD6109SA1J0 1
J5081 6510023120 Connector CD6109SA1J0 1
J5091 6510023040 Connector 01K1621 1
MP5801 8510006941 DTMF shield case-1 [USA],[CAN] only 1
MP5901 8510006941 DTMF shield case-1 [USA],[CAN] only 1
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
Screw abbreviations PH:Pan head BiH: Binding head
BT, B0: Selt-tapping
SUS: Stainless NI: Nickel
NI-ZU: Nickel-Zinc ZK: Black
6 - 2
[ACCESSORIES]
• IC-M802
MC4001 0800006490 HM-135 1
J4002 6450001280 Connector TCP0587-71-5401 1
P4001 5610000290 Connector XMP-06V 1
P4002 5610000300 Terminal BXA-001T-P0.6 4
F4001 5210000090 Fuse FGB 30A 1
F4002 5210000060 Fuse FGB 5A 2
W4001 8900011041 Cable OPC-1107A 1
EP4002 0880000960 RC-25 [USA] 1
0880001230 RC-25 [CAN] 1
0880001200 RC-25 [OTH] 1
EP4003 0880001000 SP-24 1
MP4001 8010018980 2429 bracket 1
MP4002 8810001490 Screw A0 5 × 20 SUS 4
MP4003 8850000500 Spring washer SUS 4
MP4004 8850000180 Flat washer SUS 4
MP4005 8810009300 Setscrew (J) 4
MP4006 8950005720 Tie mount (CL8) 1
MP4007 8950005710 Release tie (RELK2R) 1
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
• RC-25
W8101 8900011070 Cable OPC-1106 1
MP8101 8010018860 2455 bracket 1
MP8102 8810001490 Screw A0 5 × 20 SUS 4
MP8103 8850000500 Spring washer SUS 4
MP8104 8850000180 Flat washer SUS 4
MP8105 8610010561 2040 knob bolt-1 2
MP8106 8950005110 2289 mic hanger 1
MP8107 8810004700 Screw A0 3 × 16 SUS 2
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
• SP-24
MP1 8010018870 2456 bracket 1
MP2 8810001490 Screw A0 5 × 20 SUS 2
MP3 8850000500 Spring washer SUS 2
MP4 8850000180 Flat washer SUS 2
MP5 8610010561 2040 knob bolt-1 2
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
MC4001 (M)
ACCESSORIES
MP8101 (R)
EP4003 (M)
MP1 (S)
MP4002 (M)
MP4005 (M)
W4001 (M)
F4001 (M)
F4002 (M)
P4001 (M)
P4002 (M)
J4002 (M)
(R): RC-25
(S): SP-24
(M): IC-M802
MP4004 (M)
MP4003 (M)
MP8105 (R)
MP8102 (R)
MP8104 (R)
MP8103 (R)
MP8106 (R)
MP8107 (R)
W8101 (R)
MP5 (S)
MP2 (S)
MP4 (S)
MP3 (S)
MP4006 (M)
MP4007 (M)
MP4001 (M) EP4002 (M)
Page 50

Unit abbreviations (F): FRONT PARTS
(D): DISPLAY BOARD
(J): JACK BOARD
(S): SENSOR BOARD
(V): VR BOARD
(C): CONNECT BOARD
RC-25
MP8020 (F)
J8602 (J)
J8061 (J)
MP8022 (F)
MP8022 (F)
W8005 (F)
W8001 (F)
MP8002 (F)
MP8201 (D)
JACK BOARD
J8702 (D)
J8701 (D)
S8801 (S)
MP8006 (F)
SENSOR
BOARD
VR
BOARD
DISPLAY
BOARD
S8802 (S)
R8901 (V)
MP8005 (F)
MP8001 (F)
W8005 (F)
W8001 (F)MP8004 (F)
MP8008 (F)
DS8220 (C)
MP8007 (F)
MP8023 (F)
MP8009 (F)
S8801 (S)
S8802 (S)
R8901 (V)
MP8016 (F)
MP8017 (F)
6 - 3
Page 51

6 - 4
MP6 (C)
MP5 (C)
MC1 (M)
MP14 (C)
MP8 (C)
MP9 (C)
MP11 (C)
MP4 (C)
W1 (C)
MP7 (C)
MP9 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP12 (C)
MP7 (C)
SP1 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP8 (C)
MP2 (C)
MF4501 (C)
MP4512 (C)
MP4504 (C)
MP4511 (C)
EP1 (C)
W1 (C)
MAIN BOARD
SW BOARD
MAIN UNIT
DRIVER BOARD
PA UNIT
FILTER BOARD
PLL UNIT
VARISTOR-1 BOARD
VARISTOR-2 BOARD
MP2 (C)
MP13 (C)
MP1 (A)
MP5 (A)
MP5 (A)
MP4502 (C)
MP4513 (C)
MP4516 (C)
MP4509 (C)
MP4512 (C)
J4503 (C)
W4502 (C)
J4501 (C)
W4507 (C)
to J4501 (C)
W4501 (C)
W4506 (C)
MP4505 (C)
MP4512 (C)
J5051 (P)
J5081 (P)
J5091 (P)
MP4513 (C)
MP4503 (C)
MP4501 (C)
MP4523 (C)
MP4521 (C)
MP4524 (C)
MP302 (M)
MP701 (M)
MP201 (M)
MP702 (M)
MP4515 (C)
MP301 (M)
J1801 (M)
J2051 (M)
W4528 (C)
MP4517 (C)
MP4512 (C)
MP4506 (C)
MP5901 (P)
MP4519 (C)
MP5801 (P)
W4505 (C)
W4528 (C)
J1451 (M)
MP4512 (C)
MP4508 (C)
MP2051 (M)
W4505 (C)
W4507 (C)
EP2 (M)
W4506 (C)
MP1501 (M)
SP-24
IC-M802
HM-135
Unit abbreviations (C): CHASSIS PARTS
(M): MAIN BOARD
Unit abbreviations (C): CHASSIS PARTS
(M): MAIN UNIT
(P): PLL UNIT
Unit abbreviations (C): CHASSIS PARTS
(A): ACCESSORY PARTS
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
PA unit
MP4512 (C)
MP4514 (C)
1
2
MP4525 (C)
Page 52

7 - 1
SECTION 7 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
• TRANSISTOR AND FET’S
2SA1037AK S 2SA1213 Y 2SA1586 GR 2SC2873 Y 2SC4116 BL
2SC4116 GR 2SC4213 B 2SC4215 O 2SC4673 D TD
2SD1585 K
2SD1619 T TD 2SD1664 T100Q 2SK210 GR 2SK508 K52 T2B
2SK2171 4 TD
2SK2973 3SK131 T2 MAS DTA114EUA T106 DTC114EUA T106
PD55003
PD55015S SD1487 XP4312
(Symbol: FS) (Symbol: NY) (Symbol: SG) (Symbol: M) (Symbol: LL)
(Symbol: LG) (Symbol: AB) (Symbol: QO) (Symbol: CO)
(Symbol: None)
(Symbol: DB) (Symbol: DAQ) (Symbol: YG) (Symbol: K52)
(Symbol: KM)
(Symbol: K1) (Symbol: V11) (Symbol: 14) (Symbol: 24) (Symbol: PD55003)
(Symbol: 7T)
XP4601
(Symbol: 5C)(Symbol: SD1487)(Symbol: PD55015)
• DIODES
1SS301 1SS322 1SS355 1SS375-TL DA221 TL
DAP222 TL DF40SC4 HSB88WSTR KV1770S
MA2S111
MA2S728 MA30-(TX) MA77 MA80WK
MA338
MA742 MA8043 H MA8051 M MA8091 M
RB706F-40 T106
RD10M B3 UM9957F/TR
(Symbol: B3) (Symbol: A9) (Symbol: A) (Symbol: FH) (Symbol: K)
(Symbol: P) (Symbol: Silver line) (Symbol: C7)
(Symbol: A)
(Symbol: B) (Symbol: 3B) (Symbol: 4B) (Symbol: M1Y)
(Symbol: 6H)
(Symbol: M1U)
MA729
(Symbol: 2B) (Symbol: 4^3) (Symbol: 5-1) (Symbol: 9-1)
(Symbol: 3J)
(Symbol: 103)
TLYU1002
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
D
S
G
B
C
E
B
C
E
S
D
G
B
E
S
G
D
A1
C
A2
C
B
E
E
C
B
G
C1
C2
AC
C
A
A
C
AC
A
A
C
A1
C
A2
C
A1
C
A2
AC
AC
G
S
D
S
G
S
D
D
G
S
S
G1
G2
E
B
C
B
E
S
D
C
E
B
C
E
E1
B1
C2
C1
B2
E2
B
E
E1
B1
C2
C
C1
B2
E2
G
S
D
D
G
S
S
AC
A
C
AC AC AC
yellow dot
AC
AC
Page 53

to IC-M802 MAIN
unit J2051
J8602
H13V
TXD
RXD
FAFG
FAF
GND
FMOD
FMODG
8 - 1
SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS
8-1 HM-135
8-1-1 SW BOARD
• TOP VIEW
8-1-2 MAIN BOARD
• TOP VIEW
PTT
GND PTT
UP
DN
P
SW MOD
8-2 RC-25
8-2-1 JACK BOARD
• TOP VIEW
8-2-2 CONNECT BOARD
• TOP VIEW
8-2-3 SENSOR BOARD
• TOP VIEW
to DISPLAY board
GRP CH
Page 54

H13V TXD RXD
FAFGFAFGND
FMOD FMODG
FMOD
91
to DISPLAY
board J8903
10 2
J8601
GND
FAFG
TXD
GND
FMODG
FAF
H13V
RXD
GND
VOL
to DISPLAY board
8 - 2
8-2-4 VR BOARD
• BOTTOM VIEW (JACK BOARD)
• BOTTOM VIEW (CONNECT BOARD)
9V
119
220
to DISPLAY board J8205
J8220
GND
CL1
CS
WR
GND
DB0
DB2
DB4
DB6
5V
GND
RES
RS
RD
GND
DB1
DB3
DB5
DB7
• BOTTOM VIEW (SENSOR BOARD)
Page 55

8-2-5 DISPLAY BOARD
• TOP VIEW
MICE
MIC
J8701
PTTE
MISW
AFE
PTT
AF1
AF2
DISTRESS
CLAR/RX
THRU/TUNE
CANSEL
/CALL
HEAD
PHONE
SET/MODE
TXF/TX FREQ/CH
0/DIMCE ENT
8/Mid7/Lo 9/Hi
5/AGC4/SP 6/RF-G
2/SQL1/NB
e-mail
F
DSC
MIC
3/SCAN
8 - 3
Page 56

• BOTTOM VIEW (DISPLAY BOARD)
W8702 [CAN]
[USA],[OTH]
GND
19
210
J8902
GND
FZMD
FZRS
FZRX
GND
NC
NC
FZTX
FZ5V
19
210
to JACK
board J8601
J8903
GND
RXD
H13V
FAF
FMODG
GND
TXD
FAFG
GND
FMOD
119
2
to CONNECT
board J8220
20
J8205
DB7
DB5
DB3
DB1
GND
RD
RS
RES
GND
5V
DB6
DB4
DB2
DB0
GND
WR
CS
CL1
GND
9V
1
1
14
85
4
8
5
7
14
8
1
20
60
41
21 40
80 61
1
5
10
6
MICE
PMUT
PHD
PHE
PMUT
PHD
MIC
PTTE MISW
AFE
PTT
AF1
AF2
to SENSOR board
to VR board
8 - 4
Page 57

8 - 5
8-3 IC-M802
8-3-1 DSP BOARD
• TOP VIEW
1
8
16
9
1
10
20
11
1
7
14
8
1
4
8
5
1
36
108
73
72 37
109 144
1
4
8
5
114
2815
13
64
13
64
Page 58

8 - 6
• BOTTOM VIEW (DSP BOARD)
1
21
to MAIN unit J1102
2
22
J901
DSPI1
GND
GND
GND
8V
GND
AGC2
GND
DSPO1
GND
GND
GND
GND
DSPI2
GND
8V
GND
AGC1
GND
GND
GND
DSPO2
29
1
MAIN unit J1101
30
2
DRES
KEYIN
GND1
OUT7
OUT5
OUT3
OUT1
GND1
OBSY
RQO
GND1
CK
RQI
GND1
GND1
GND1
UNLK
GND1
OUT8
OUT6
OUT4
OUT2
GND1
STBO
DO
GND1
DI
IBSY
GND1
192K
30
2
to MAIN unit J1101
29
1
J902
DRES
KEYIN
GND1
OUT7
OUT5
OUT3
OUT1
GND1
OBSY
RQO
GND1
CK
RQI
GND1
GND1
GND1
UNLK
GND1
OUT8
OUT6
OUT4
OUT2
GND1
STBO
DO
GND1
DI
IBSY
GND1
192K
110
20 11
110
20 11
18
169
110
2011
1
7
14
8
1
7
14
8
1
4
8
5
14
85
1
4
8
5
1
4
8
5
1
20
40
21
2
22
1
21
MAIN unit J1102
DSPI1
GND
GND
GND
8V
GND
AGC2
GND
DSPO1
GND
GND
GND
GND
DSPI2
GND
8V
GND
AGC1
GND
GND
GND
DSPO2
Page 59

[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN]
only
[OTH]
only
[USA],[CAN] only
[OTH] only
136
4
1
18
16 9
9
18 10
1
30
80
51
31 50
100 81
1
7
14
8
1
18
169
9
18 10
1
1
14
85
4
8
5
4
8
5
14
58
1
1
916
81
1
1
4
58
485
4
85
8
16
9
14
85
1
1
9
18
10
8
16
9
1816
9
1
4
58
1
1
14
85
4
85
1
1
8
16
9
4
85
4
8
5
1
4
58
1
5
10
6
1
4
8
5
GND30
to DSP board
2
29
1
J1102
GND
DSPO1
GND
AGC2
GND
8V
GND
GND
GND
DSPI1
DSPO2
GND
GND
GND
AGC1
GND
8V
GND
DSPI2
GND
GND
GND11
to DSP board
29
2
30
J1101
GND1
RQI
CK
GND1
RQO
OBSY
GND1
OUT1
OUT3
OUT5
OUT7
GND1
KEYIN
DRES
192K
GND1
IBSY
DI
GND1
DO
STBO
GND1
OUT2
OUT4
OUT6
OUT8
GND1
UNLK
GND1
to FLASH
writer
1
210
9
J3001
FZTXD
RESET
EPM
NMEI2
FZBUSY
CNVSS
GND
CE
FZCLK
VCC
to PLL unit J5071
1
230
29
J3602
NSEN
DSAFE
DSMDE
NC
D1D3D5
D7
NC
NC
RXPC
NMRS
RSSW
NMEI
GND
GND
DSAF
DSMD
GND
D0D2D4
D6
A16
NC
H5V
DTRM
NMEO
NMEI2
GND
to PLL unit J5001
1
224
23
J3601
H13P
S13P
S13P
PDAT
PST1
PST3
PST4
DRES
REFS
GND
M3LO
D2LO
S13P
S13P
UNLK
PCK
PST2
PCO2
PST5
NC
NC
GND
GND
GND
to FILTER
board J7331
115
216
J1301
TRXS
L22M
L12M
L6M
L2M
GND
REF
FOR
S13L
L16M
L8M
L4M
L1M
GND
GND
GND
to PA unit J6701
119
220
J1901
T8V
GND
GND
GND
ANTC
KEYS
S13
S13
FANC
HV
THRM
GND
GND
ICV
STAT
S13
S13
S13
HV
PON
to RC-25
JACK board
J8602
8746
5213
J2051
FAFG
FMODG
FMOD
GND
RXD
TXD
FAF
H13V
13.6V
AGND
FALC SCAN
AAF AMOD
SEND CWK
ACC
CONTROLLER
SP
to SP-24
SPE
SPO
from FILTER board J7321
MRX
P7321
from PLL unit J5601
M1LO
P5601
from PA
unit J6702
YGR
P6702
from PLL unit J5201
M2LO
P5201
from CHASSIS J4503
DSC ANT
P501
from PLL unit J5801
D1LO
P5801
[USA], [CAN] only
8-3-2 MAIN UNIT
• TOP VIEW
8 - 7
Page 60

• BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN UNIT)
8 - 8
Page 61

from CHASSIS J4501
ANT
to MAIN unit J51
MRX
P7321
to PA unit J6401
FLIN
P7001
TRXS
115
216
to MAIN
unit J1301
J7331
L22M
L12M
L6M
L2M
GND
REF
FOR
S13V
L16M
L8M
L4M
L1M
GND
GND
GND
8-3-3 FILTER BOARD
• TOP VIEW
8 - 9
Page 62

• BOTTOM VIEW (FILTER BOARD)
8 - 10
Page 63

[OTH]
[USA],[CAN]
R5207
[OTH]
L5201
[OTH] only
[OTH] only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN]
only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
34
34
12
11 1
23 33
22
34
34
12
11 1
23 33
22
18
16 9
14
65
14
85
44 34
33
23
1
11
12 22
1
100 76
26 50
25
75
51
1
8
16
9
51
69
J5081
NC
DTR
GND
DTR
PXRXD
PCTXD
51
69
J5051
GND
NSEND
NC
GND
AF
AF+
GND
MOD
MOD+
224
1
to MAIN unit J3601
23
J5001
H13V
S13V
S13V
PDAT
PST1
PST3
PST4
DRES
REFS
GND
M3LO
D2LO
S13V
S13V
UNLK
PCK
PST2
PCO2
PST5
REFV
PTMP
GND
GND
GND
129
2
to MAIN unit J3602
30
J5071
MSEN
DSAFE
DSMDE
ENAB
D1D3D5
D7
AACK
NC
RXPC
NMRS
RSSW
NMEI
GND
GND
DSAF
DSMD
GND
D0D2D4
D6
A16
NC
H5V
DTRM
NKME0
NMEI2
GND
REMOTE
GPS
AF/MOD
to MAIN unit J2301
D1LO
P5801
to MAIN unit J601
M1LO
P5601
to MAIN unit J301
M2LO
P5201
8-3-4 PLL UNIT
8 - 11
Page 64

1
4
8
5
1
4
J6703
to CHASSIS
W4502
KEY
START
13.6
ANTC/GND
4
1
J6301
to DRIVER
board
GND
GND
DRVI
DRVI
1
4
J6302
to DRIVER
board
DRVO
DRVO
GND
GND
13
J6411
to
VARISTOR-1
board
GND
VARO
VARI
13
to
VARISTOR-2
board
J6412
GND
GND
VARO
31
to FAN
J6501
GND
NC
FAN+
T8V
119
220
J6701
to MAIN unit J1901
GND
GND
GND
ANTC
KEYS
S13V
S13V
FANC
HV
THRM
GND
GND
ICV
STAT
S13V
S13V
S13V
HV
PON
to CHASSIS W4501
GND
HV13V
from FILTER board J7001
FLIN
P7001
from MAIN unit J1
YGR
8-3-5 PA UNIT
8 - 12
Page 65

8-3-6 DRIVER BOARD
• TOP VIEW
8 - 13
GND
VARO
VARI
to PA unit J6411
8-3-7 VARISTOR-1 BOARD
Page 66

DRVI
DRVI
GND
GND
to PA unit J6301
GND
GND
DRVO
DRVO
to PA unit J6302
• BOTTOM VIEW (DRIVER BOARD)
8 - 14
GND
GND
VARO
to PA unit J6412
8-3-8 VARISTOR-2 BOARD
Page 67

9 - 1
SECTION 9 BLOCK DIAGRAM
TX
RX
COMMON
Bus line
[USA],[CAN]
only
[USA],[CAN]
only
1.8V
REG
3.3V
REG
+5
REG
IC152
TK11218CM
IC-161
BA033FP
IC171
TK11250CM
8V
5V
3.3V1.8V
DIFF
CONV
DIFF
CONV
A/D A/D
DIFF
CONV
IC601
BA15532F
DIFF
CONV
LATCH
IC406
SN74AHC74PW
IC404
SN74AHCT374PW
LATCH
IC405
BU4021BF
PARA
-SERI
IC401
SN74AHC595PW
SERI
-PARA
ROM
IC201
M29W102BB-70N1
BUFF
OUT1-8
D/A D/A
TIMING
X1
CR-566
12.288 MHz
BUFF
IC102
BU9480F
D/A
BUFF
D/A
AGC1
AGC2
AGC
AMP
IC1101
TS522ID
AGC
AMP
IC1101
TS522ID
fc=98 kHz
LPF
BUFF
IC701A
µ
PC4570G2
fc=98 kHz
BUFF
LPF
IC701B
µ
PC4570G2
RX
DSPI2
DSPI1
60 MHz
TX
LPF
IF
AMP
RX
IC1002
TS522ID
LPF
IC501
TA4107F
IF
AMP
Q501
3SK131
LIMIT
AMP
IC1051
TS522ID
EXT MOD
GATE
IC2001
BU4053BCFV
EMOD
EMS
EXT
MOD
IC2001
BU4053BCFV
EXT MOD
GATE
MMOD
NBDP
MOD
NMS
AGC1
CERAMIC
BPF
BW=6 kHz
IF
AMP
CERAMIC
BPF
455 kHz
BW=6 kHz
FI401
CFWM455H
Q401
3SK131
IF
AMP
Q801
3SK131
LPF
D302
HSB88WS
XTAL
BPF
XTAL
BPF
64.455 MHz
BW=15 kHz
FI301B FI301A
FI-315
IF
AMP
BPF
64.455 MHz
BW=15 kHz
Q201,Q202
2SK2171
LPF
FI201
FL-345
33 MHz
RF
AMP
Q701
3SK131
LPF
LPF
BPF
0.5-2 MHz
BPF
2-3 MHz
BPF
3-5 MHz
BPF
5-7 MHz
BPF
7-10 MHz
BPF
10-14 MHz
BPF
14-18 MHz
BPF
18-24 MHz
ATT
Q702,Q703
3SK131
ATT
2LO
IC901
TA4107F
LPF
100MHz
Q601
2SC4673
LO
AMP
1LO
LPF
3LO
12 kHz
LPF
AF
AMP
IC1702
TS522ID
R13V
REG
IC1303
TD62783AF
IC1502
TA78M08F
+8
REG
IC1551 µPC1555G2
D1552 RB706F-40
D1551 MA8051
-
5
DC-DC
Q1501
2SD1619
T8
REG
Q1502
2SD1619
R8
REG
IC1501
TA78L05F
+5
REG
TXS
RXS
S13V
Q1204 2SA1586
Q1205 2SC4213
ADJ
SW
AJLC
Q1203
2SA1586
FALC
AM
EXT
ALC
I/F
AM
[OTH] only
ALC
CTRL
IC1201
NJM3403AV
ALC
AMP
IC1201
NJM3403AV
ALC
AMP
IC1201
NJM3403AV
ALC
AMP
ICA
REF
FOR
BUFF
IC1302
TD62783AF
24-30 MHz
IC3604
BU4094BCF
BCD
TO
DECI
HPF
1.6 MHz
LPF ATT
YGR
AMP
IC1
µPC2709T
ATT
AMP AMP AMP AMPATT LPF
BIASPPBIASPBIASPBIAS
F
LPF
0.5-2 MHz
LPF
2-3 MHz
LPF
3-5 MHz
LPF
5-7 MHz
LPF
7-10 MHz
LPF
10-14 MHz
LPF
14-20 MHz
LPF
20-30 MHz
LPF
30 MHz
PWR
DET
D7271
1SS322
D7272
1SS322
FOR
REF
L0
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
L6
L7
TEMP
DET
Q6501 2SD1664
IC6501 TS522ID
FUN
CTRL
Q6101
2SK2973
Q6801
PD55003
Q6851
PD55015
Q6401,
Q6402
SD1487 × 2
BIASPP
BIASP BIASD BIASE
PAT8
T8
REG
PA8V
APC
CTRLICDET
+8
REG
IC6601
TAZ808F
IC6501
TS522ID
ICA
13.6
D6601
DF40SC4
Q6601 2SA1037AK
Q6602 DTC114EU
SW
RL6701
AJS1311
HV13S13V
GND
HV
+
-
DSP01
DSP02
IC1201
NJM3403AV
METER
AMP
IC1601
LA4425A
PWR
AMP
AF
MUTE
IC1602
TC4W53FU
VCA
AF
AMP
IC1603
M5282FP
GATE
MOD
IC2001
BU4053BCFV
MMS
MMOD
AFO
AFG
ABWS
13V
SPEAKER
EX-2431
BUFF
NBDP
I/F
BUFF
EXT.AF
DSC AF
NBDP.AF
SQL
GATE
IC1701 TC4W53FU
IC5081
ADM202EARN
232C
RS-232C
DTRM RXPC
PHOTO
CPL
IC5082
TC7W08F
NMEA
I/F
I/F
IC5084 PS2701-1
NMEA
NMEA2
I/F
IC5082
TC7W08F
GPS
NMEA
BPF
FI231B
BW=15 kHz
FI231A
BW=15 kHz
BPF
D2301
HSB88WS
10.
RF
AMP
Q2301,Q2302
2SK2171
FL-231
Q2401
3SK131
IF
AMP
IF
AMP
Q2501
3SK131
BPF
2,4,6M
BPF
8M
BPF
12M
BPF
16M
DET
MUTE
Q2102
2SC4116
IC2701
TA4107F
AMP
IC2702
TS522ID
LPF
DAGC
IC3302
S-80942CNMC-G9C
IC3101
TA78L05F
RESET
CTRL
+5
REG
MATRIX
SLFP
UNLK
IC3601
BU4094BCF
RAM
BACK
UP
LATCH
CTRL
ACML S13V
LPF
BEEP
SQLC
BUFF
Q1801
2SD1619
SW
CSEND
IC1303
TD62783AF
IC3603
BU4094BCF
BCD
TO
DECI
ACC SEND
ASEN
NMRS
VSQL
X3301
CR-636A
14.7456 MHz
EEPROM
STRT
KEY
GND
13.6
ANT
TUNER
Q3004
2SC4116
CWKEY
I/F
CWKYIN
TX
BUFF
BCD TO
DECI
D/A
IC3606
M62354GP
BCD TO
DECI
BUFF
IC1303
TD62783AF
IC3605
BU4094BCF
LPF
BUFF
LO
AMP
D/A DDS DDS D/A LPF
IC5901
SC-1287
IC5801
SC-1287
Q5882
2SC4215
D2LO
D1LO
BPF
64.455-94.455 MHz
BUFF
Q5603
2SC4215
Q5881
[USA], [CAN] only
2SC4673
LO
AMP
Q5602
2SC4215
BUFF
Q5601
2SC4215
Q5521 2SK508
D5521 KV1770S
L5523 E544GN-110248
LO
AMP
Q5604
2SC4215
LOOP
FIL
PD
1/M
1/N
IC5401
PLL IC
LMX2306TM
BUFF
Q5302
DDS IC
2SC4116
Q5301 2SK210
D5301 MA338
LOOP
FIL
PD
LPF AMP
Q5351
2SC4215
DDS
IC5101
SC-1246A
BPFD/A
IC5102
TC7SU04F
AMP
SFECV10.5MA5S
10.5 MHz
BW=230 kHz
FI5101
UNLK
AMP
IC5103
TC7SU04F
BPF
X2
Q5202
2SC4215
64MHz
64MHz
M1LO
M2LO
BUFF
Q5281
2SC4215
HV13
ATT LPF D/A DDS AMP
IC5702
TC7SU04F
IC5701
SC-1287
X5251
[USA], [CAN]
only
[OTH] only
CR-604
32.000 MHz
X5281
CR-338
Q5282
2SC42150
32.00056 MHz
M3LO
+5
REG
+8
REG
IC5001
TA7805F
IC5031
TA7808F
5V
8VL
S13V
PWRS
TEMP
FANS
POCV
PLL UNIT
IC3303
M30624FGAFP [USA],[CAN]
M30620FCAFP [OTH]
CPU
PLL UNIT
FILTER BOARD
PA UNIT
MAIN UNIT
IC301
TMS320VC33PGEA120
DSP
DSP BOARD
PLUG
DET
GATE
CTRL
J8701
IC8260
TC74HC4066AF
PLUG
DET
J8702
CLONE
I/F
IC8250
TC7W04F
PHONE
/CLONE
AF 1
DIM
CTRL
IC8280
NJM2904M
IC8240
HD66421TBO
DRIVER
DS8220
HLC7700-018800
LCD
X8211
CR-636A
14.7456 MHz
FPTT
M1AD
M2AD
SMUT
IC8270
TA7368F
PWR
AMP
RESET
CTRL
TENKEYSWSELECT
SW
IC8202
S-80942CNMC-G9C
DIAL1
DIAL2
VOL
POWER SW
AF
AMP
IC8280
NJM2904M
MMOD
M1AD
MIC
MIC
DSEL
IC8201
HD64F2134AFA20
CPU
PHSM
M3AD
RC-25(Controller)
IC651
BA15532F
IC651
BA15532F
IC601
BA15532F
IC501
AK4528VF
TRX DSC
IC1
TC7WHU04FU
DSC TRX
Q203
3SK131
8V
R13V
-
5V
T8
R8
5V
RFML
12 kHz
HV13
H5V
NSEN
NBDP
SENB
AFMS
PWRK
PMUT
1
2
+10
REG
IC8301
AN8010M
+5
REG
IC8290
TA7805F
H13V
10V
5V
RX
TX
TRXS
IC1301
TD62783AF
IC3602
BU4094BCF
VC1S
MONI/SIDETONE
FAF
FI402
CFWS455HT
Q6403
2SD1585K
7 MHz
Page 68

10 - 1
SECTION 10 WIRING DIAGRAM
P5601
J5601
M1LO
P5201
J5201
M2LO
P5801
J5801
D1LO
AF/MOD
AF
-
GND
AF+
NSEND
GND
NC
MOD
-
MOD+
GND
GND
NC
DTR
PXRXD
PCTXD
J5051
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
REMOTE
J5081
2
1
7
6
3
8
4
9
5
J5091
GPS
GND
CHASSIS W4528
MSEN
DSAF
DSAFE
DSMD
DSMDE
GND
NC
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A16
NC
NC
NC
H5V
RXPC
DTRM
NMRS
NKME0
RSSW
NMEI2
NMEI
GND
GND
J5071
J5001
CHASSIS W4505
GND
D2LO
GND
M3LO
GND
GND
NC
REFS
NC
DRES
PST5
PST4
PCO2
PST3
PST2
PST1
PCK
PDAT
UNLK
S13V
S13V
S13V
S13V
HV13
DRVO
GND
J6302
GND
DRVO
DRVO
GND
GND
DRVO
GND
J6301
GND
DRVI
DRVI
GND
GND
DRVI
DRVI
J6702
YGR
KEY
13.6
PON
HV
HV
FANC
S13V
S13V
S13V
S13V
S13V
KEYS
STAT
ANTC
ICV
GND
GND
GND
J6701
GND
GND
THRM
T8V
FAN+
GND
FAN
CHASSIS MF4501
M
+
-
J6501
VARO
GND
J6411
VARI
GND
GND
J6412
VARO
VARO
GND
VARI
GND
GND
VARO
GND
GND
GND
GND
EP6602
CHASSIS W4501
HV13V
HV13V
HV13V
HV13V
EP6603
PA UNIT
J6401
FLIN
START
ANTC/GND
J6703
CHASSIS W4502
J7001
FLIN
GND
FOR
GND
REF
GND
GND
L1M
L2M
L4M
L6M
L8M
L12M
L16M
L22M
S13V
TRXS
CHASSIS W4507
J7331
FILTER BOARD
DSP BOARD
MAIN UNIT
JACK BOARD
CONNECT BOARD
DISPLAY BOARD
SENSOR BOARD
VR BOARD
PLL UNIT
J7311
ANT
CHASSIS
J4501
P7321
J7321
MRX
ANT
J301
M2LO
J601
M1LO
J51
MRX
YGR
J1
GND
FOR
GND
REF
GND
GND
L1M
L2M
L4M
L6M
L8M
L12M
L16M
L22M
S13L
TRXS
J1301
SPE
SPO
SP
J1451
T8V
THRM
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ICV
ANTC
STAT
KEYS
S13
S13
S13
S13
S13
FANC
HV
HV
PON
CHASSIS W4506
J1901
DSC ANT
DSC ANT
J4503
CHASSIS
J2101
FMODFMODG
FAF GNDFAFG
TXDRXD
13.6V
SCAN
AAF
AMOD
CWK
EALC
AGND
SEND
H13V
OPC-1106
4
76
3
12
5
8
GND
D2LO
GND
M3LO
GND
GND
REFS
NC
DRES
NC
PST5
PST4
PCO2
PST3
PST2
PST1
PCK
PDAT
UNLK
S13P
S13P
S13P
S13P
H13P
J3601
GND
NSEN
DSAF
DSAFE
DSMD
DSMDE
GND
NC
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A16
NC
NC
NC
H5V
RXPC
DTRM
NMRS
NMEO
RSSW
NMEI2
NMEI
GND
GND
J3602
to FLASH WRITER
FZTXD
CNVSS
RESET
GND
EPM
CE
NMEI2
FZCLK
FZBUSY
VCC
J3001
J2301
D1LO
ACC
CONTROLLER
6
1
45
3
7
2
J1801
8
DSPO2
GND
GND
GND
AGC1
GND
8V
GND
DSPI2
GND
GND
GND
DSPO1
GND
AGC2
GND
8V
GND
GND
GND
GND
DSPI1
J1102
DSPO2
GND
GND
GND
AGC1
GND
8V
GND
DSPI2
GND
GND
GND
DSPO1
GND
AGC2
GND
8V
GND
GND
GND
GND
DSPI1
J901
DI
DO
STBO
OUT2
OUT4
OUT6
OUT8
UNLK
RQI
CK
RQO
OUT1
OUT3
OUT5
OUT7
KEYIN
DRES GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
IBSY
GND1
192K
GND1
GND1
OBSY
GND1
GND1
GND1
J1101
PMUT
PMUT
PHE
PHO
PHO
J8702
HEADPHONE
/CLONE
GPB
GPA
GND
CHB
CHA
GND
GPB
GPA
GND
CHB
CHA
GND
GND
VOL
VR5V
VR5V
VOL
GND
MIC
1
2
3
4
5
678
J8701
AF1
AF2
PTT
MIC
MISWPTTE
MICE
AFE
FMOD
FMODG
GND
FAF
FAFG
H13V
TXD
RXD
GND
GND
FMOD
FMODG
GND
FAF
FAFG
H13V
TXD
RXD
GND
GND
J2051
FMODFMODG
FAF GNDFAFG
TXDRXD H13V
4
76
3
12
5
8
J8602
J8903J8601
CHASSIS W8001
CHASSIS W8005
FZ5V
FZRX
FZTX
FZRS
NC
FZMD
NC
GND
GND
GND
J8902
9V
5V
GND
GND
CL1
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
GND
GND
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
J8205
9V
5V
GND
GND
CL1
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
GND
GND
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
J8220
DI
DO
STBO
OUT2
OUT4
OUT6
OUT8
UNLK
RQI
CK
RQO
OUT1
OUT3
OUT5
OUT7
KEYIN
DRES GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
IBSY
GND1
192K
GND1
GND1
OBSY
GND1
GND1
GND1
J902
MICE(SHIELD)
(YELLOW)
(GREEN)
SW
MOD
MC1
PTT
PTTE
CHASSIS UNIT W1
MAIN UNIT
RC-25
HM-135
IC-M802
SP-24
1
2
3
4
5
678
SW BOARD
DRIVER BOARD
VARISTOR-1 BOARD
VARISTOR-2 BOARD
(BLACK)
(RED)
TUNER
POWER
[USA],[CAN] only
Page 69

11 - 1
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAMS
11-1 RC-25 and HM-135
C8218
10
1
2
345
678
J8701
MIC
C8222
0.0047
R8701 33 [USA],[OTH]
R8702 33
[USA],[OTH]
PMUT
PHE
PHO
L8701
10
µ
R8703
100k
C8219
10
R8704
100
DSTK
CSCK
DALK
TUNK
MODK
SETK
EMLK
T1K
T2K
T3K
T4K
T5K
T6K
T7K
T8K
T9K
ENTK
T0K
FCHK
RXK
TXK
FUNK
DISTRESS
/CALL/ALM
DSC/CALL
/CHO/SELCALL
CANCEL
/TELCAL/TXF
MODE(DIM)
SET
e-mail
/DSC/TS(ALE)
1(NB)
2(SQL)
3(SCAN)
4(SP)
5(AGC)
6(RF-G)
7(LO)
8(MID)
9(HI)
ENT
0
FREQ/CH
RX(CLAR)
TX(TXF)
FUNC
CP8201
GPB
W8702 [CAN]
CP8202
GPA
CP8203
GND
CP8204
CHB
CP8205
CHA
CP8206
GND
R8230
47k
R8231
47k
R8232
47k
R8233
47k
Q8340
2SC4116
R8341 470
R8340 22k
DS8340
DS8341
R8343 470
Q8341
2SC4116
R8342 22k
R8344 22k
Q8342
2SC4116
R8345 470
DS8342
R8346 56k
Q8343
2SC4116
R8347 390
DS8344
DS8343
R8348 68k
Q8344
2SC4116
R8349 330
DS8347
DS8346
DS8345
DS8348
DS8349
DS8350
R8351 330
Q8345
2SC4116
R8350 68k
DS8340-DS8350
SML-311YT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21222324252627282930313233343536373839
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61626364656667686970717273747576777879
80
DISTRESS
LED
POWER
LED
R8352 100k
W8340
C8223 0.0047
AF1
AF2
R8247
22
C8216 10
PTT
MIC
MISWPTTE
C8226
0.0047
L8202 10µ
L8203 10µ
W8201
W8202
D8204
1SS355
D8205
1SS355
R8224 47k
R8225 18k
R8226 1.8k
R8227
10k
C8244 10
C8241 22
R8235 3.3k
R8223 47k
R8237 68k
C8242 0.0047
C8243 47
R8222 1k
R8236 100
D8701
1SS355
R8260
10k
R8705
1M
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
I/O1
O/I1
O/I2
I/O2
CONT2
CONT3
VSS
VDD
CONT1
CONT4
I/O4
O/I4
O/I3
I/O3
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
IC8260
TC74HC4066AF
C8260 0.0047
R8263 47k
R8254
33k
R8253
6.8k
D8250
1SS355
IC8250
TC7W04F
C8250 0.01
R8252 100k
R8250 100k
R8255 47k
R8211 47k
R8212 47k
R8213 47k
NC
VCC
NC
VIN
RIPPLE
PREGND
PWGND
POUT
PHASE
NF
R8270 680
C8373 0.1
R8373 680
IC8270
TA7368F
C8274
100
C8277 100
R8284
56k
R8285
470
R8276
1k
IC8280
NJM2904M
2
3
1
+
R8282 120k
C8288
0.0047
C8282
10
Q8281
2SC4116
R8278
12k
R8279
22k
R8287
10k
R8289 1.5k
R8288
1.8k
Q8280
2SC4116
R8280
10k
R8281
100k
C8283
10
R8283
1k
C8284
2.2
W8281
W8280
R8274
68k
C8286
47
R8275
3.3k
D8280
DA221
C8285 10
Q8282
DTC114EU
C8280 22
C8281
0.0047
C8289
0.0047
L8286
10
µ
V+
GND
8
4
IC8280
NJM2904M
C8287
4.7
CP8201
CP8202
CP8203
CP8204
CP8205
CP8206
GPB
GPA
GND
CHB
CHA
GND
S8801
TP90N937E20-15F-1540
S8802
TP90N937E20-15F-1540
GROUP DIAL
CHANNEL DIAL
B
A
COM
A
COM
B
SENSOR BOARD
CP8209
CP8208
CP8207
VR5V
VOL
GND
R8901
TP96N97
VOLUME
CP8208
CP8209
CP8207
GND
VOL
VR5V
VR BOARD
FMOD
FMODG
GND
FAF
FAFG
H13V
TXD
RXD
GND
GND
FMOD
FMODG
GND
FAF
FAFG
H13V
TXD
RXD
GND
GND
FMOD
FMODG
GND
FAF
FAFG
H13V
TXD
RXD
GND
GND
J8602J8903 J8601
JACK BOARD
R8291
1k
EP8295
EP8294
EP8296
EP8292
EP8293
W8296
C8271 0.0047
C8270 100
L8270
100
µ
FE1
W8270
W8271
Q8260
DTC114EU
R8229
10k
R8203
47k
R8202
47k
C8202
100
C8201
0.1
R8204
47k
L8201
10
µ
R8216
47k
R8206
47k
R8207
47k
D8201
DA221
D8203
DA221
R8239
1k
R8240
1k
OUT
VDD
VSSCDNC
C8208 0.1
R8209 100k
C8209 0.01
IC8202
S-80942CNMC-G9C
C8220
0.47
R8210
47k
C8205
0.01
X8211
CR-636A
C8207 12p
C8206 12p
R8201 47k
R8215
47k
OI
G
C8292 0.1
C8293 47
IC8290
TA7805F
C8291 0.1
C8290 47
OI
C8304 47
G
C8303 0.1
C8302 0.1
IC8301
AN8010M
C8301 47
R8290 10
OI
C8313 47
G
C8312 0.0047
C8311 0.0047
IC8310
TA7808F
C8310 47
C8203 0.1
R8301 47
R8300
3.9k
DS8302
DS8305
DS8308
DS8311
DS8301
DS8310
DS8307
DS8304
DS8300
DS8309
DS8306
DS8303
R8303 47
R8302
3.9k
DS8314
DS8323
DS8320
DS8317
DS8313
DS8322
DS8319
DS8316
DS8312
DS8321
DS8318
DS8315
Q8300
2SD1619
Q8301
2SD1619
R8214 47k
R8241
100k
W8242
W8238
+
7
6
5
IC8280
NJM2904M
R8243 100k
R8707
1k
R8708
NTCG16
R8706
100
CP8240
CP8239
CP8236
CP8235
CP8234
CP8233
CP8232
CP8231
CP8221
CP8222
CP8223
CP8224
CP8225
CP8226
CP8227
CP8228
CP8229
CP8241
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
R8242
2.2M
R8245
47k
R8243
47k
R8244
47k
C8230 0.1
C8231 0.1
C8232 1
C8233 1
C8234 1
C8235 1
C8236 1
R8241
1.8M
R8246
1.8M
C8237
0.1
LCL1
LRES
LCS
LRS
LWR
LRD
LDB0
LDB1
LDB2
LDB3
LDB4
LDB5
LDB6
LDB7
L8221 10µ
L8220 10µ
GND1
VLCD1
VCC1
V5O
V4O
V3O
V2O
V1O
GREF
IREFM
IREFP
VLCD2
VLCD3
VCC2
GND2
GND3
VCC3
OSC1
OSC2
OSC
CO
DCON
CL1
FLM
M
M/S
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
VCC4
GND4
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
VCC5
GND5
VCC6
VLCD4
GND6
COM100
COM99
COM98
COM51
SEG160
SEG159
SEG158
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
COM50
COM49
COM3
COM2
COM1
IC8240
HD66421TBO
DS8220
HLC7700-018800
LCD
CONNECT BOARD
LCL1
LRES
LCS
LRS
LWR
LRD
LDB0
LDB1
LDB2
LDB3
LDB4
LDB5
LDB6
LDB7
9V
5V
GND
GND
CL1
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
GND
GND
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
9V
5V
GND
GND
CL1
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
GND
GND
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
RES
XTAL
EXTAL
MD1
MD0
NMI
STBY
VCC2(VCL)
SCK0/P52
RXD0/P51
TXD0/P50
VSS
WAIT/P97
EXCL/P96
IOS/AS/P95
HWR/P94
RD/P93
IRQ0/P92
IRQ1/P91
ADTRG/IRQ2/P90
P60/FTCI/CIN0/KIN0
P61/FTOA/CIN1/KIN1
P62/FTIA/CIN2/KIN2/TMIY
P63/FTIB/CIN3/KIN3
P64/FTIC/CIN4/KIN4
P65/FTID/CIN5/KIN5
P66/FTOB/CIN6/KIN6/IRQ6
P67/CIN7/KIN7/IRQ7
AVCC
P70/AN0
P71/AN1
P72/AN2
P73/AN3
P74/AN4
P75/AN5
P76/AN6/DA0
P77/AN7/DA1
AVSS
P40/TMCI0/TXD2/IRTXD
P41/TMO0/RXD2/IRRXD
SCK1/IRQ5/P86
RXD1/IRQ4/P85
TXD1/IRQ3/P84
P83
P82
P81
P80
VSS
D7/P37
D6/P36
D5/P35
D4/P34
D3/P33
D2/P32
D1/P31
D0/P30
A0/P10
A1/P11
A2/P12
A3/P13
P14/A4
P15/A5
P16/A6
P17/A17
VSS
P20/A8
P21/A9
P22/A10
P23/A11
P24/A12
P25/A13
P26/A14
P27/A15
VCC1
P47/PWX1
P46/PWX0
P45/TMRI1
P44/TMO1
P43/TMCI1
P42/TMRI0/SCK2
IC8201
HD64F2134AFA20
DISPLAY BOARD
MI
FE1
AFIN
LRXD
LTXD
FP
MCE
MC
M2
GPB
GPA
CHB
CHA
R8234
1k
EP8205
FUNK
TXK
RXK
FCHK
TOK
ENTK
FP
M1
M2
M1
CLONE
R8221 1k
R8218 1k
R8219 1k
C8214
0.0047
C8211
0.0047
C8212
0.0047
C8210
0.0047
R8246 47k
C8204
0.1
MCE
MC
FE1
AFIN
MI
PHE
AF
FZ5V
FZRX
FZTX
FZRS
FZMD
FZ5V
FZRX
FZTX
FZRS
NC
FZMD
NC
GND
GND
GND
J8902
J8205 J8220
FZTX
FZRX
FZMD
FZRS
GPB
GPA
CHB
CHA
DSTK
CSCK
DALK
TUNK
MODK
SETK
EMLK
T1K
T2K
T3K
T4K
T5K
T6K
T7K
T8K
T9K
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
CS
RES
WR
RD
RS
CL1
to IC-M802
MAIN unit
J2051
J8702
HEADPHONE
/CLONE
3
2
1
3
2
1
POWER
TUNE
(THRU/METER)
C8261
22
MICE
AFE
C8221
0.0047
AF
1
2
3
5
4
DS3800-DS8311
TLYU1002
1
2
3
4
5
10
9
8
7
6
R8208
56k
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
654
123
Q8251
XP4601
R8251 18k
5V5V
5V
5V
R8205 10k
FZ5V
L8206
HF50ACC322513-B
DS8312-DS8323
TLYU1002
306
305
304
257
256
255
254
99
98
97
96
95
49
48
47
CL1
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
5V
DIMMER
C8295
100p
C8294
1000p
C8297
0.0047
LRXD
LTXD
C8300
47p
C8299
47p
L8290
HF50ACC322513-B
C8298
0.0047
87612
35
4
MICE(SHIELD)
(BLACK)
PTT(RED)
SW(GREEN)
MOD(YELLOW)
S1
SKHHAMG24A
R2
33k
S1
SKHHAMG24A
P
SW UNIT
CHASSIS UNIT W1
MAIN UNIT
R3
6.8k
UP
S2
SKHHAMG24A
R4
15k
DN
S3
SKHHAMG24A
R1
12k
C1
470p
W1
W2
MC1
HM-135
4.95V
6.42V
1.97V
1.91V
1.98V
1.92V
12.9V
10.11V
7.83V
4.73V
4.73V
MESUREMENT CONDITIONS
frequency: 12.29 MHz
mode: J3E(USB)
*ANT(RX): no input
(TX): no modulation
Digital tester
unit: V
range: 20V
input impedance: 10M
Ω
no specification
: voltage at RX
Page 70

11 - 2
11-2 IC-M802
11-2-1 MAIN UNIT (1)
e
8V
g
f
d
c
b
a
T8
HV13
RXS
T8T8
R8
R13V
8V
5V
5V
-
5V
S13V
R8R8
0.1
C1315
T8 T8
HV13 HV13
0.1
C2003
1k
R2003
4.7
C2004
S13V
POCV
R13V
R8
DSC ANT DSC ANT
FMODG
FAFG
S13V
S13V
R8
SPE
SPO
0.1
C1905
C2007 0.1
(2)
UNIT
MAIN
470
R1606
LA4425A
IC1601
3
2
1
5
4
33
R1501
220
R705
220
R202
47p
C124
330p
C173
220
R101
270p
C119
AMOD
47k
R3608
330
µ
L1302
HF50ACC322513-B
L1908
HF50ACC322513-B
L1904
0.1
C1903
unit J6701
to PA
4.7
R1318
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
220
R56
10k
R61
POCV
R3611 47k
R3609 47k
R3610 47k
HV13
RXS
TXS
1k
R718
2SC4116
Q2102
1
C2106
470
R2105
100
µ
L2101
0.1
C2104
0.1
C2107
UM9957
D2104
UM9957
D2103
39k
R2107
39k
R2106
33k
R2104
10k
R2102
0.047
C2105
22k
R2101
MA2S728
D2101
15p
C2102
10p
C2101
DTC114EU
Q2101
100
R2103
MA2S111
D2102
0.0047
C2103
AHY103
RL2101
FAF
S13V
AFO
W1601
1
C1611
0.1
C1902
0.1
C1559
MA8091
D1554
10
C1558
47
R1553
0.1
C1557
1m
L1552
220p
C1561
220p
C1563
S13V
10k
R1555
220k
R1556
VCC
DISCHARGE
VTH
VCONTRESET
OUT
TRG
GND
µ
PC1555G2
IC1551
5
6
7
8
0.1
C1560
4
3
2
1
0.1
C1562
47
C1555
RB706F-40
D1552
47
C1552
47
R1551
MA8051
D1551
1m
L1551
1
C1551
S13V
T8
470
R1607
0.1T8C1610
-
5V
5V
-
5V
5V
1
C1609
TC4W53FU
IC1602
AFMS
0.1
C1608
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
DTC114EU
Q1601
ABWS
0.047
C1619
1k
R1602
10
C1607
4.7k
R1603
0.01
C1606
470
C1605
470
C1604
LW-15
L1601
470
C1603
0.1
C1602
470
C1601
470
R1601
TA78L05F
IC1501
0.1
C1502
OGI
47
C1501
0.1
C150310C1504
TA78M08F
IC1502
10
S13V
C1505
0.1
C1506
OGI
0.1
C1507
47
C1508
8V
8V
DTC114EU
Q1504
1
C1510
RB706F-40
D1502
2SD1619
Q1502
1k
R1505
4.7
R1503
TXS
DTC114EU
Q1503
1
C1509
RB706F-40
D1501
2SD1619
Q1501
1k
R1504
4.7
R1502
8.2k
R720
0.001
C718
18
R713
270
R717
270
R714
LR-317
L707
0.001
C716
0.1
C714
1k
R709
3SK131
Q703
0.1
C3121kR309
39p
C720
0.001
C717
270
R716
18
R715
270
R712
LS-483A
L706
5p
C715
470
R711
100
µ
L705
1k
R703
0.1
C702
0.1
C712
220
R710
100
µ
L704
3SK131
Q702
1k
R708
0.1
C705
22p
C711
39p
C709
33p
C706
18p
C710
6p
C707
0.68µ
L703
1.0
µ
L702
100
R706
NTCG16
R707
47k
R704
0.1
C703
560
R702
NTCG16
R722
3SK131
Q701
220
R701
0.1
C701
100
R719
LR-317
L701
0.1
C611
1k
R607
0.001
C214
470
R207
0.1
µ
L206
MA80WK
D602
1k
R606
1p
C610
10p
C608
10p
C606
6p
C609
1p
C607
0.22µ
L605
0.33µ
L604
0.001
C604
27p
C612
M1LO
56
R602
0.22µ
L602
0.0047
C602
1.5k
R604
10
R605
330p
C605
2SC4673
Q601
2.2
µ
L603
0.0047
C603
5.6k
R603
MA8091
D601
47
R601
R8
0.0047
C601
10
µ
L601
R8
R13V
0.0047
C208
100
µ
L20522R203
0.0047
C211
0.1
C212
0.1
C207
2SK2171
Q202
2SK2171
Q201
R205 470
C210 0.1
C209 0.1
R204 470
W2002
LR-403
L204
100p
C206
150p
C204
82p
C202
8p
C205
22p
C203
0.27µ
L203
0.27µ
L202
MA80WK
D201
0.1
C201
470
R201
100
µ
L201
100µL144
470
R110
MMS
NMS
EMS
A
C2008 0.0047
C2006 0.0047
C2005 0.0047
DSMDE
DSMD
-
5V
W2001
[USA],[CAN]
C2002 4.7
C2001 4.7
[USA],[CAN]
R2001 10k
R2002 10k
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
98
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C
B
A
X0
X1
X
Y
VDD
VSS
VEE
INH
Z0
Z
Z1
Y0
Y1
BU4053BCFV
IC2001
DBP1
DBP2
DBP3
DBP4
CSEN
B8S
47
C1314
0.1
C1311
4.7
R1319
CSEND
330
µ
L1301
4.7
C1313
3.3k
R1320
DBPL
DBPH
DBPM
DBPN
B8
R8
S13V
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
VS
IN8
IN7
IN6
IN5
IN4
IN3
IN1
IN2
GND
08
07
06
05
04
03
01
02
TD62783AF
IC1303
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
DSC ANT
CONTROLLER
CHASSIS
J4503
[USA],[CAN] only
J2101
100
µ
L2052
100
µ
L2053
L2051 100
µ
FMOD
FAF
RXD
TXD
100
µ
L2054
J2051
4
76
3
12
5
8
AFO
HF50ACC322513-B
L1907
0.1
C1451
SP
J1451
TEMP
ICA
STAS
KEYC
FANS
PWRS
L1903 100
µ
L1905 100
µ
0.1
C1906
0.1
C1903
0.1
C1901
L1906 LR-270
0.0047
C1907
0.1
C1904
0.0047
C1910
R1902 1k
R1901 4.7
R1903 1k
L1901 100
µ
L1902 100
µ
T8V
THRM
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ICV
ANTC
STAT
KEYS
S13
S13
S13
S13
S13
FANC
HV
HV
PON
J1901
J301
unit J5201
from PLL
M2LO
J601
unit J5601
from PLL
M1LO
B0S
B1S
B2S
B3S
B4S
B5S
B6S
B7S
47
C1312
0.1
C1310
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
R1317 3.3k
R1316 3.3k
R1315 3.3k
R1314 3.3k
R1313 3.3k
R1312 3.3k
R1311 3.3k
R1310 3.3k
VS
IN8
IN7
IN6
IN5
IN4
IN3
IN1
IN2
GND
08
07
06
05
04
03
01
02
TD62783AF
IC1302
L0S
L1S
L2S
L3S
L4S
L5S
L6S
L7S
0.1
C1309
4.7
R1309
VS
IN8
IN7
IN6
IN5
IN4
IN3
IN2
IN1
GND
08
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
TD62783AF
IC1301
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
R1301 10
R1302 10
R1303 10
R1304 10
R1305 10
R1306 10
R1307 10
R1308 10
C1308 0.1
C1307 0.1
C1306 0.1
C1305 0.1
C1304 0.1
C1303 0.1
C1302 0.1
C1301 0.1
FOR
REF
TRXS
GND
FOR
GND
REF
GND
GND
L1M
L2M
L4M
L6M
L8M
L12M
L16M
L22M
S13L
TRXS
board J7331
to FILTER
J1301
220
R108
B8
MA77
D110
MA80WK
D109
0.33µ
R8
S13V
R13V
0.1
C167
100p
C166
0.001
C154
0.27µ
L132
150p
C142
100p
C143
150p
C117
18p
C126
0.27µ
L126
0.33µ
L116
0.1
C108
100
µ
L117
MA77
D105
B7
B6
220
R107
0.39µ
L138
0.1
C165
150p
C164
0.39µ
L131
0.0015
C153
180p
C140
180p
C141
200p
C116
22p
C125
0.39µ
L125
0.47µ
L114
0.1
C107
100
µ
L115
MA80WK
D108
MA80WK
D107
220
R106
0.1
C163
0.56µ
L137
180p
C162
0.0015
C152
0.47µ
L130
270p
C138
220p
C139
220p
C115
18p
C175
0.47µ
L124
0.68µ
L112
0.1
C106
100
µ
L113
MA80WK
D104
B5
220
R105
0.68µ
L136
0.1
C161
220p
C160
0.0022
C151
0.68µ
L129
270p
C136
300p
C137
390p
C114
39p
C123
0.68µ
L123
0.82µ
L110
0.1
C105
100
µ
L111
B4
220
R104
0.82µ
L143
0.1
C174
0.0047
C159
0.0022
C150
1.0
µ
L135
470p
C146
330p
C135
470p
C113
56p
C122
1.0
µ
L122
1.0
µ
L108
0.1
C104
100
µ
L109
MA80WK
D103
B3
220
8VR8R13V
S13V
R103
0.1
C172
1.2
µ
L142
470p
C171
0.0015
C158
0.0018
C149
1.8
µ
L134
120p
C144
560p
C145
100p
C121
470p
C134
560p
C112
1.5
µ
L121
1.5
µ
L106
0.1
C103
100
µ
L107
220
R102
B2
1.8µL141
0.1
C170
0.001
C169
0.0022
C157
0.0047
C148
2.2
µ
L128
0.0015
C131
560p
C133
270p
C118
560p
C111
120p
C132
2.2
µ
L120
2.2
µ
L104
0.1
C102
100
µ
L105
MA80WK
D102
MA80WK
D106
MA80WK
D101
220
R109
0.047
C127
0.0018
C128
0.0022
C109
4.7
µ
L118
5.6
µ
L101
B1
5.6µL133
0.1
C156
0.0015
C155
0.012
C147
3.3
µ
L127
0.0027
C129
0.0015
C130
0.0015
C110
200p
C120
3.3
µ
L119
0.1
C101
100
µ
L103
4.7
µ
L102
0.1
C168
100
µ
L140
B0
0.1
C65
100µL56
470
R58
100µL55
470
R57
0.1
C11
BUS LINE2
BUS LINE1
MA80WK
D53
0.1
C64
100µL54
560
R54
82
µ
L52
0.0022
C62
3.9µL53
0.015
C63
0.015
C61
0.0012
C59
4.7µL51
0.01
C57
0.0022
C56
0.1
C54
1k
R59
1k
R60
0.1
C68
2SC4213
Q51
UM9957
D52
UM9957
D51
0.1
C67
0.1
C66
J51
board J7321
from FILTER
MRX
470
R8
8V
0.1
C8
68
R4
0.1
C10
270
R7
18
R5
270
R6
0.1
C9
1
µ
PC2709T
IC1
235
6
4
4.7µL3
0.1
C6
0.1
C7
0.27µ
L2
22p
C4
82p
C5
150p
C3
68p
C1
82p
C2
0.18µ
L1
150
R3
39
R1
150
R2
YGR
J1
unit J6702
from PA
MAIN UNIT(1)
[USA],[CAN] only
5.69V
TX: 4.96V
band 10.7V
unselected
band 11.76V
unselected
13.36V
13.41V
4.92V
unselected band
TX: 6.66V
no specification: voltage at RX
input impedance: 10MΩ
range: 20V
unit: V
Digital tester
(TX): no modulation
* ANT(RX): no input
mode: J3E(USB)
frequency: 12.29 MHz
MESUREMENT CONDITIONS
5.63V
2.77V
11.88V
TX: 7.44V
TX: 0.44V
RX: 13.29V
TX: 12.88V
TX: 7.89V
7.88V
RX: 13.00V
TX: 13.13V
RX: 13.35V
TX: 13.20V
RX: 0.05V
TX: 4.86V
11.22V
selected 4.96V
e-mail H3E
RX: 4.86V
TX: 0.05V
Page 71

11 - 3
11-2-2 MAIN UNIT (2)
h
4
8
RXS
e
DAGC
ICA
1k
R1057
4
8
RXS
DSPO2
T8
MAGC
T8
R8
4
8
27k
R503
0.1
C403
2SA1586
Q1203
MAGC
g
f
d
c
b
a
8.2M
R1232
0.0047
C805
FOR
(3)
UNIT
MAIN
0.1
C2254
18p
C2251
4.7
R2303
100
R2710
100
R2709
10
C2710
GND
V+
TS522ID
IC2702
10
C2711
100
R1109
100
R1110
10
C1101
0.1
C1102
TS522ID
IC1101
V+
GND
4
8
4
8
470
R1703
100
R1611
2.2k
R1609
AFG
0.0047
C903
0.1
C1012
100
R1009
100
R1008
10
C1010
10
C1011
TS522ID
IC1002
V+
GND
1k
R504
0.0047
C504
LS-495
R8
FOR
POCV
REF
L801
MA77
D1206
11
4
100
R1225
100
R1224
0.1
C1202
0.1
C1203
NJM3403AV
IC1201
V+
GND
0.001
C314
0.0047
C224
LS-540
L208
(1)
UNIT
MAIN
MAIN UNIT(2)
REF
POCV
HV13HV13
RXS
DSPI1
MAGC
-
5V
S13V
5V
8V
BUS LINE2
BUS LINE1
A
S13V
-
5V
8V
R1060
0.022
C1064
1k
R1058
0.022
C1063
0.022
C1062
1k
R1059
0.001
C1061
TSS522ID
IC1051
0.01
C1059
+
3
2
1
R1011 1k
1k
R1055
0.022
C1058
1k
R1054
0.022
C1056
1k
R1053
0.022
C1057
0.01
C1054
0.001
C1055
7
6
5
+
-
TS522ID
IC1051
4.7
C1612
22k
R1610
10k
R1016
56k
R1015
1k
R1014
1
2
3
+
-
TS522ID
IC1002
W1011
1k
R1010
0.0047
C1008
1k
R1007
0.0047
C1007
0.0047
C1006
1k
R1006
560p
C1005
0.0018
C1004
+
-
TS522ID
IC1002
5
6
7
0.1
C1003
DSPO1
56
µ
L2501
4p
C2504
470
R2506
0.1
C2503
100
R2505
100
R2504
0.0047
C2502
0.0047
C2501
470k
R2503
3SK131
Q2501
1.5k
R2502
6.8k
R2501
0.0047
HV13
DAGC
8V
S13V
C2409
0.1
C2406
56
µ
L2401
4p
C2405
2.2k
R2406
100
R2405
3SK131
Q2401
0.0047
C2404
100
R2404
0.0047
C2403
15k
R2402
1M
R2403
68k
R2401
0.0047
C2402
D1LO
LS-409
L2307
S13V
8V
8V
FL-231
FI231b
18p
C2307
8p
C2308
FL-231
FI231a
18p
C2309
LS-543
L2306
HSB88WS
D2301
LR-409
L2304
0.1
C2303
2SK2171
Q2302
2SK2171
Q2301
LR-409
L2302
22
R2302
0.1
C2302
0.1
C2301
1k
R2301
100
µ
L2301
100
R2203
DBPH
100
µ
L2233
0.1
C2242
0.1
C2270
0.12µ
L2230
680p
C2227
0.12µ
L2224
680p
C2218
560p
C2209
0.15µ
L2209
0.1
C2238
0.1
C2203
3.3k
R2208
100
µ
L2206
C2221 68p
C2212 150p
68p
C2224
1.2
µ
L2218
10p
C2266
1.2
µ
L2223
0.82µ
L2215
47p
C2215
1.8
µ
L2212
0.1
C2235
47p
C2206
1.8
µ
L2205
100
µ
L2236
3.3k
R2207
1p
C2264
1p
C2263
DBPN
100
R2204
MA80WK
D2204
100
µ
L2245
82n
L2244
0.001
C2249
0.0012
C2253
82n
L2242
0.001
C2250
0.001
C2246
0.0012
C2237
0.001
C2243
82n
L2237
270p
C2252
C2247 150pC2244 220p
1.0
µ
L2241
27p
C2248
5.6
µ
L2240
0.56
µ
L2243
0.47
µ
L2227
0.68µ
L2239
15p
C2229
27p
C2245
5.6
µ
L2238
27p
C2239
4.7
µ
L2235
MA80WK
D2202
390p
C2236
47p
C2271
39p
C2268
C2269
39p
DBPM
100
R2202
0.1
C2241
56p
C2232
100
µ
L2232
0.0015
C2226
0.47µ
L2229
C2220 180p
L2221 8.2
µ
180p
C2223
2.2
µ
L2217
1.0
µ
L2226
0.0022
C2217
0.1
C2202
0.1
C2267
3.3k
R2206
100
µ
L2204
0.33µ
L2222
0.0015
C2208
0.47µ
L2208
C2211 220p
L2214 3.3
µ
220p
C2214
2.2
µ
L2211
0.1
C2205
DBPL
MA80WK
D2203
100
R2201
3.3k
R2205
0.1
C2240
100
µ
L2231
0.0012
C2225
3.3
µ
L2228
0.001
C2216
2.7
µ
L2220
820p
C2207
2.7
µ
L2207
0.1
C2201
100
µ
L2202
47p
C2228
0.1
C2234
1.2
µ
L2225
C2219 100p
L2219 22
µ
0.0012
C2222
2.2
µ
L2216
C2210 220p
L2213 18
µ
1.8
µ
L2210
0.0012
C2213
0.001
C2204
2.2
µ
L2201
MA80WK
D2201
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
1k
R1017
100
R1018
1k
R1005
0.1
C1002
470
R1003
1k
R1004
470
R1002
0.1
C1001
S13V
T8
5V
8V
-
5V
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
TC4W53FU
IC1001
1k
R1723
1k
R1722
0.1
C1717
470
R1721
RXS
470
R1720
RXS
TC4W53FU
IC1703
10k
R1719
0.1
C1716
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
10
C1051
10
C1052
TS522ID
IC1051
V+
GND
100
R1052
100
R1051
0.1
C904
0.1
C1715
1k
R1717
10k
R1718
2.2k
R1716
R1715 8.2k
TS522ID
IC1702
2
3
1
+
-
1k
R1713
TS522ID
IC1702
10
C1714
10
C1713
GND
V+
100
R1711
100
R1712
0.056
C1711
1k
R1710
0.056
C1710
0.056
C1709
1k
R1709
0.012
C1707
TS522ID
IC1702
5
6
7
+
-
4.7
C1706
DSAFE
W1701
[USA],
[CAN]
[USA],
[CAN]
[USA],
[CAN]
1
C1705
560
R1707
DSAF
5V
4.7k
R1724
0.1
C1704
15k
R1706
S13V
AAF
12k
R1705
0.1
C1703
470
R1704
SQLC
TC4W53FU
IC1701
8
7
6
54
3
2
1
0.1
C1702
1k
R1612
1
C1618
1k
R1614
10
C1615
10k
R1702
2.7k
R1701
0.0047
C1701
10
C1617
10k
R1615
10
C1616
DSPO2
1k
R1613
VCC2
IN+
IN
-
OUT
GND
VCC
VCAOUT
CTL
VCAIN
NC
M5282FP
IC1603
5
4
3
2
1
10
9
8
7
6
BEEP
-
5V
470
C1614
0.1
C1613
10
C908
0.1
C907
0.1
C910
1k
R910
100µL902
47
R904
100µL903
0.1
C909
100µL901
0.1
C905
0.1
C906
8
7
5
6
4
2
3
1
IF1
IF2
GND
L01
VCC
L02
RF2
TA4107F
IC901
RF1
1k
R901
1m
L904
POCV
OUT8
MA80WK
D901
1k
R911
0.1
C901
1k
R902
0.1
C902
1k
R903
M3LO
0.1
C511
0.1
C509
0.1
C521
M3LOK T8
0.1
C518
0.1
C517
10
C520
0.1
C519
100µL504
1000µ
L506
1k
R514
100
µ
L505
8
7
6
54
3
2
1
0.15VC516
IF1
IF2
GND
L02
RF1
RF2
VCC
L01
TA4107F
IC501
0.1
C508
47
C51047C512
0.1
C507
100
R507
1000µ
L502
470
R506
560
R505
0.1
C506
NTCG16
R508
3SK131
Q501
0.0047
C505
0.1
C503
120k
R502
0.0047
C502
0.1
C501
W5012.2k
R415
MA77
D402
MA77
D404
LS-542
L405
1k
R413
0.1
C410
180p
C414
0.0047
C412
CFWS455HT
FI402
IO
0.0047
C407
120p
C413
0.1
C411
1k
R414
1000µ
L406
LS-542
L404
MA77
D403
1k
R410
0.1
C409
MA77
D401
LS-450
L403
100
R409
0.1
C408
470
R408
0.1
C404
0.1
C406
100
R407
0.0047
C405
3SK131
Q401
470k
R406
10k
R405
47k
R404
0.0047
C402
LS-542
L402
T8
5V
8V
-
5V
W1227
AJLC
S13V
T8
5V
8V
-
5V
EALC
10
C1205
2.2k
R1223
0.001
C1206
220
R1226
0.1
C1209
10k
R1235
10k
R1234
2SA1586
Q1204
2SA1586
Q1207
2SC4213
Q1205
2SC4213
Q1206
1k
R1228
1
C1208
1
C1211
1
C1210
RFML
8V
ICA
470k
R1202
470k
R1203
0.1
C1223
0.1
[OTH] only
C1224
470k
R1233
100k
R1205
100k
R813
MA2S728
D1201
NJM3403AV
IC1201
470k
R1206
1k
R1236
14
+
13
12
-
47k
R1210
100k
R1213
560k
R1214
W1231
47k
R1218
MA2S111
D1203
NJM3403AV
IC1201
2.2M
R1221
8
+
9
10
-
MA2S111
D1202
47k
R1209
47k
R1216
REF
ICA
8V
8V
BUS LINE2
47k
R1215
10k
R1208
NJM3403AV
IC1201
2.2M
R1220
NJM3403AV
IC1201
7
+
6
5
-
1
C1213
1
C1212
470k
R1230
MA2S111
D1204
1
C1204
22
R1222
220k
R1219
1
+
-
3
2
220k
R1217
0.1
C1214
100k
R1211
330k
1k
R1212
R1240
10k
R1207
MA2S111
D1207
MA2S111
D1205
0.0047
C1201
470
R804
10k
R1238
22k
C804
W803
3SK131
Q801
22
R802
0.1
C802
2.2k
R801
10k
R1237
47
C806
0.1
C801
OI
CFWM455H
FI401
1k
R401
0.1
C401
LS-542
L401
MA80WK
D303
0.0039
C311
0.0047
C310
12
µ
L306
10
µ
L305
0.1
C309
1k
R307
680p
C308
47
R306
270p
C307
LR-395
L304
M2LO
470p
C305
LR-317
L303
HSB88WS
D302
LS-540
L302
R8
MAGC
5p
C303
FL-315
FI301b
LS-540
L307
FL-315
FI301a
6p
C302
LS-540
L301
1k
R301
0.0047
C301
MA80WK
D301
0.0047
C223
100
R215
LS-483A
L210
2.2k
R214
3SK131
Q203
1M
R212
0.0047
C219
0.0047
C221
100
R213
0.0047
C220
2.2k
R211
R8
0.0047
C218
10k
R210
5p
C217
22
R209
LS-540
L209
FL-345
FI201
12p
C215
100
R208
LS-483A
L207
C213 9p
BUS LINE1
TX: 7.2V
1.39V
6.14V
7.46V
1.46V
6.13V
1.42V
4.76V
7.2V
0.24V
7.2V
0.46V
0.23V
0V
0V
1.48V
6.72V
1.14V
13.09V
1.50V
6.70V
no specification: voltage at RX
input impedance: 10MΩ
range: 20V
unit: V
Digital tester
(TX): no modulation
*ANT(RX): no input
mode: J3E(USB)
frequency: 12.29 MHz
MESUREMENT CONDITIONS
Page 72

11 - 4
11-2-3 MAIN UNIT (3)
h
H5V
10k
R3315
NMR
UNLK
DRES
LSTB
MSTB
LDAT
LCK
FNCO
PODN
TRVS
TXVS
USAS
STMD
GENE
8V
S13V
H5V
5V
R3340
220
DRES
PTMP1
ECK
ESIO
H5V
W1102
W1101
H5V
8V
5V
S13V
DAGC
ASEN
NSEN
47k
R3903
INITIAL
M30624FGAFP
[USA],[CAN]
M30620FCAFP [OTH]
IC3303
P97
AVCC
VREF
P100/AN0
AVSS
P101/AN1
P102/AN2
P103/AN3
P104/AN4/KI0
P105/AN5/KI1
P106/AN6/KI2
P107/AN7/KI3
P00/D0
P01/D1
P02/D2
P03/D3
P04/D4
P05/D5
P06/D6
P07/D7
P10
P11
P12
P13/D11
P14/D12
P15/D13/INT3
P16/D14/INT4
P17/D15/INT5
P20/A0
P21/A1
P22/A2
P23/A3
P24/A4
P25/A5
P26/A6
P27/A7
VSS
P30/A8
VCC
P31/A9
P32/A10
P33/A11
P34/A12
P35/A13
P36/A14
P37/A15
P40/A16
P41/A17
P42/A18
P43/A19
P44
P45
P46/CS2
P47/CS3
P50/WRL/WR
P51/WRH/BHE
P52/RD
P53/BCLK
P54/HLDA
P55/HOLD
P56/ALE
P57/RDY
P60
P61/CLK0
P62/RXDO
P63/TXDO
P64
P65
P66
P67
P70
P71
P72
P73
P74/TA2OUT
P75/TA2IN
P76/TA3OUT
P77/TA3IN
P80/T4OUT/U
P81/TA4IN/U
P82/INT0
P83/INT1
P84/INT2
P85/NMI
VCC
XIN
VSS
XOUT
RESET
P86/XCOUT
P87/XCIN
CNVSS
BYTE
P90
P91
P92/DA1
P93/DA0
P94
P95
P96
to FLASH WRITER
0.1
C1807
FZBUSY
FZCLK
0.1
C3901
MA2S111
D3004
4
5
3
2
1
0.1
C3310
0.1
C3311
47k
R3201
10
µ
L3301
C3009 0.1
(2)
UNIT
MAIN
MAIN UNIT(3)
M3LO
D2LO
47k
R3613
EALC
NMEI1
NMEI3
NMEO1
DTR
RPC
NSEN
DSAF
DSAFE
DSMD
DSMDE
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A16
RSS
R3915 220
R3916 220
R3917 220
R3918 220
R3919 220
R3920 220
R3921 220
GND
NSEN
DSAF
DSAFE
DSMD
DSMDE
GND
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A16
H5V
RXPC
DTRM
NMRS
NMEO
RSSW
NMEI2
NMEI
GND
GND
J3602
unit J5071
to PLL
L2305
0.27µ
J2301
470p
C2304
C2310
100p
C2311
120p
D1LO
D1LO
unit J5801
from PLL
FANS
TRXS
POCV
ABWS
AFG
DSTB
0.1
C3606
DBP3
DBP2
DBP1
B8S
AJLC
DBP4
0.1
C3605
B7S
B6S
B5S
B4S
B3S
B2S
B1S
B0S
0.1
C3604
0.1
C3603
0.1
C3602
16
15
14
13
12
10
9
11
8
7
6
5
4
3
1
M62354GP
IC3606
2
VSS
NC
A03
A04
A05
A06
VCC
VDD
GND
NC
A02
A01
DI
CLK
DO
LD
47k
R3612
47k
R3204
AFMS
REFS
CSEN
MMS
EMS
NMS
L3S
L2S
L1S
L0S
L7S
L6S
L5S
L4S
1k
R3203
0.0047
C3202
100k
R3202
0.1
C3601
PCK
PDAT
PSEL
PST4
PST3
PST2
PST1
PSTB
DRES
PST5
PST4
PCO2
PST3
PST2
PST1
PCK
PDAT
UNLK
R3601 47k
R3602 47k
R3603 47k
R3604 47k
R3605 47k
R3606 47k
L3601 HF50ACC322513-B
L3602 HF50ACC322513-B
GND
D2LO
GND
M3LO
GND
GND
REFS
DRES
PST5
PST4
PCO2
PST3
PST2
PST1
PCK
PDAT
UNLK
S13P
S13P
S13P
S13P
H13P
unit J5001
to PLL
J3601
16
15
14
13
12
10
9
11
8
7
6
5
4
3
1
BU4094BCF
IC3605
2
QS
QS
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
VDD
QE
VSS
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
CLK
STR
D
16
15
14
13
12
10
9
11
8
7
6
5
4
3
1
BU4094BCF
IC3604
2
QS
QS
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
VDD
QE
VSS
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
CLK
STR
D
16
15
14
13
12
10
9
11
8
7
6
5
4
3
1
BU4094BCF
IC3603
2
QS
QS
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
VDD
QE
VSS
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
CLK
STR
D
16
15
14
13
12
10
9
11
8
7
6
5
4
3
1
BU4094BCF
IC3602
2
QS
QS
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
VDD
QE
VSS
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
CLK
STR
D
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
98
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
BU4094BCF
IC3601
QS
QS
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
QE
VDD
VSS
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
CLK
D
STR
R3906 47k
R3331 220k
R3330 220k
R3329 220k
R3328 220k
R3326 220k
R3325 220k
R3324 220k
R3322 220k
A11
A7A5A4A3A2
A1
R3314 100k
R3313 100k
R3316 220k
R3327 220k
R3323 220k
R3321 220k R3320 220k
R3319 220k
R3318 220k
R3317 220k
R3412 10k [USA],[CAN]
VERO
A8
R3409 10k [OTH]
FNC1
A12
R3413 10k [OTH]
R3408 10k
R3406 10k
R3405 10k
R3404 10k
R3403 10k
R3402 10k
0.1
C3201
RSS
TC7W04F
IC3201
8
7
6
54
2
1
3
0.0047
C3309
0.1
C3308
ASEN
RFML1
ACML1
NSEN1
TEMP1
ASEN1
27k
R3306
0.047
R3350
220k
C3307
REF
10k
R3302
10k
R3301
0.1
C3302
SDA
SCL
WP
VCC
H5
VSS
A2
A1
A0
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
HN58X24128FPI
[USA],[CAN]
CAT24WC64J [OTH]
IC3301
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
R3307
220
PSTB
OUT1R
OUT7R
OUT4R
OUT3R
OUT2R
OUT5R
A7
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A11
A16
R3909 47k
R3908 47k
R3907 47k
SQLC1
MSTB
EPM
LDAT
R3339 220
220
R3338
220
R3337
220
R3336
MA2S111
D3336
MA2S111
D3337
LCK
47k
R3332
47k
R3334
NMEI3
FZTXD
R3335 220
R3333 220
D3302 MA2S111
D3301 MA2S111
DSTB
LSTB
FZTXD
CNVSS
RESET
EPM
FZCLK
FZBUSY
100p
C3007
FZTXD
CNVSS
RESET
GND
EPM
CE
NMEI2
FZCLK
FZBUSY
VCC
J3001
0.1
C1804
0.1
C1803
MA2S111
D1801
CWK
CSEND
0.1
C1801
0.0047
C1802
R1803 3.3k
R1802 3.3k
R1801 3.3k
2SD1619
Q1801
C1805 0.1
100
µ
L1804
AAF
0.1
C1806
100
µ
L1803
AMOD
HF50ACC322513-B
L1801
HF50ACC322513-B
L1802
ACC
6
1
45
3
7
2
J1801
8
DSPO2
GND
GND
GND
AGC1
GND
8V
GND
DSPI2
GND
GND
GND
DSPO1
GND
AGC2
GND
8V
GND
GND
GND
GND
DSPI1
J1102
STBOR
KEYINR
RQOR
RQIR
DOR
DI
DO
STBO
OUT2
OUT4
OUT4R
OUT2R
STBOR
DOR
OUT4
OUT2
STBO
DO
R3622 220
R3620 220
R3615 220
R3614 220
R3625 47k
R3627 47k
R3629 47k
OUT6
OUT8
UNLK
KEYINR
OUT7R
OUT5R
OUT3R
OUT1R
RQOR
RQIR
R3616 220
RQI
CK
R3617 220
R3619 220
RQO
R3621 220
R3623 220
R3624 220
R3626 47k
OUT1
R3628 47k
OUT3
OUT5
R3618 220
R3630 47k
OUT7
KEYIN
DRES GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
IBSY
GND1
192K
GND1
GND1
OBSY
GND1
GND1
GND1
J1101
to DSP
board J902
to DSP
board J901
NMEO1
NMEI1
DTR
RPC
PWRSR
27p
C3305
C3304 27p
CR-636A
X3301 X3301
10k
R3305
56k
R3303
56k
R3304
0.1
C3303
HV13
0.027
C3306
CP3301
C3312
2p
S-80942CNMC-G9C
IC3302
NC
CD
VSS
VDD
OUT
RESET
UNLK
R3312 1k
CNVSS
R3052 100k
R3051 4.7k
PCK
R3311 220
PDAT
R3310 220
PC02
R3309 220
BEEP1
TXS1
RXS1
PSEL
R3308 220
DTC114EU
Q3001
STAS
47k
R3026
47k
R3025
R3024 1k
R3023 1k
TXD
RXD
RB706F-40
D3003
RB706F-40
D3002
22k
R3030
2SC4116
Q3004
15k
R3029
47k
R3028
4.7k
R3027
CWK
RB706F-40
D3001
R3020 47k
KEYC
R3019 1k
5V
47
C3104
0.1
C3103
TA78L05F
IC3101
OGI
0.1
C3102
47
C3101
33
R3101
HV13
5V
S13V
BEEP1
ASEN1
TEMP1
NSEN1
ACML1
RFML1
SQLC1
TXS1
RXS1
PWRSR
R3018 47k
R3015 10k
R3013 10k
R3017 220
R3014 1M
C3008.0.1
C3006.0.1
C3005 0.047
C3004 0.047
C3003 0.047
C3002 0.047
C3001 0.047
R3036 47k
BEEP
R3012 1k
R3011 1k
ASEN
TEMP
R3010 1k
NSEN
R3009 1k
R3008 1k
R3007 1k
RFML
R3006 1k
SQLC
R3004 220
R3003 220
TXS
RXS
RB706F-40
D3007
RB706F-40
D3006
R3002 1.5k
R3001 1.5k
R3050 12k
PWRS
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50494847464544434241403938373635343332
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
MAGC
AGC2
TS522ID
IC1101
100k
R1103
1M
R1104
10k
R1112
270k
R1106
100
R1114
1M
R1108
+
-
6
5
7
TS522ID
IC1101
AGC1
100
R1113
10k
R1111
4.7k
R1102
D1102
MA2S728
100k
R1101
3.3k
R1105
1M
R1107
+
-
2
3
1
D2LO
1k
R2713
DSPI2
1k
R2714
0.1
C2716
TS522ID
IC2702
TS522ID
IC2702
7
5
6
+
560p
C2715
0.0018
C2714
1k
R2712
0.0047
C2713
0.0047
C2712
1k
R2711
0.0047
C2708
1k
R2708
56k
R2705
1
3
2
+
-
56k
R2704
56k
R2702
10k
R2703
0.1
C2707
0.1
C2706
1000µ
L2702
1000µ
L2701
1k
R2701
L2703 100
µ
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
IF1
IF2
GND
L02
10
C2705
0.1
C2704
0.1
C2702
270
R2716
270
R2706
18
5V
R2715
C2701 0.1
C2703 0.1
RF1
RF2
VCC
L01
TA4107F
IC2701
BUS LINE2
BUS LINE1
S13V
5V
8V
OUT8
22k
R3035
R2306
47
R1804
10k
CP1101
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
4.13V
1.69V
2.80V
1.69V
1.61V
1.49V
0.05V 0.05V
4.17V
RX: 0V
TX: 11.7V
: voltage at RX
no specification
input impedance: 10MΩ
range: 20V
unit: V
Digital tester
(TX): no modulation
*ANT(RX): no input
mode: J3E(USB)
frequency: 12.29 MHz
MESUREMENT CONDITIONS
DSP BOARD
DSPO2
GND
GND
GND
AGC1
GND
8V
GND
DSPI2
GND
GND
GND
DSPO1
GND
AGC2
GND
8V
GND
GND
GND
GND
DSPI1
J901
DI
DO
STBO
OUT2
OUT4
OUT6
OUT8
UNLK
RQI
CK
RQO
OUT1
OUT3
OUT5
OUT7
KEYIN
DRES GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
IBSY
GND1
192K
GND1
GND1
OBSY
GND1
GND1
GND1
J902
Page 73

11 - 5
11-2-4 PA UNIT
from MAIN
unit J1
J6702
YGR
to MAIN
unit J1901
PON
HV
HV
FANC
S13V
S13V
S13V
S13V
S13V
KEYS
STAT
ANTC
ICV
GND
GND
GND
J6701
KEY
START
13.6
ANTC/GND
J6703
FAN+
GND
J6501
GND
GND
GND
GND
EP6602
HV13V
HV13V
HV13V
HV13V
EP6603
to CHASSIS W4501
from FILTER
board J7001
J6401
FLIN
R6110 39
C6202
0.1
Q6851
PD55015
DRVO
GND
J6302
GND
DRVO
Q6401
SD1487
VARO
GND
J6411
VARI
VARISTOR-1 BOARD
GND
GND
J6412
VARO
VARISTOR-2 BOARD
D6431 MA30PXB
C6431 0.047
D6601
DF40SC4-4072
EP6601
4
8
V+
GND
IC6501
TS522ID
+
G
OI
IC6601
TA7808F
R6111 39
R6112 39
GND
GND
THRM
T8V
L6706
HF70ACC635050-T
PA UNIT
L6705
HF70ACC635050-T
+
R6102 180
R6103 180
C6101 82p
C6102 82p
R6101
39
L6101
0.22
µ
C6103
0.1
C6105
0.1
R6107
680
R6104
68
C6104
0.1
R6105
2.2k
R6106
4.7k
Q6101
2SK2973
C6201
0.1
L6102
100µ
R6109
470
C6109
0.047
C6801
0.1
R6801
560
R6802
1
Q6801
PD55003
R6204
2.7
C6203
0.01
R6202
3.9k
R6203
4.7k
R6201
82
C6106 0.1
C6108 0.1
F6702
F6703
F6701
L6202 82
µ
R6206 470
C6301
0.1
R6301 100C6302 0.1
R6302 2.2k
R6303 1.2k
R6304
3k
C6205
0.047
C6206
0.047
L6204
EXC-ELDR25C
C6303 470
C6308 0.68
C6305 0.1
C6306 1000
L6303
EXC-ELDR25C
Q6601
2AS1037AK
R6603
4.7k
C6602 0.0047
R6602
4.7k
Q6602
DTC114EU
R6604 15k
C660447C6603
470
C6605
0.1
C6606
0.1
C6607
47
L6703 100
µ
L6704 100
µ
C6707 0.0047
C6708 0.0047
C6706 0.0047
W6701
L6501
100µ
C6704
0.0047
R6515
4.7k
L6702
100µ
C6703
0.047
C6702
0.047
R6702
680
R6705
NTCG16
R6704
1.8k
D6702
RD10M
Q6701
DTC114EU
D6701 DAP222
C6705 0.0047
L6701
EXCCL3225U
C6701
0.047
RL6701
AJS1311
C6506 0.1
C6507 470
Q6501
2SD1664
R6510
1k
R6513
330k
R6517
1k
R6512
100k
IC6501
TS522ID
7
6
5
R6514
100k
C6503 0.1
C6608 0.047
C6609 2200
C6610 0.1
C6611 0.0047
C6612 0.001
R6509
100
R6507 2.2M
R6505
68k
R6516
10k
R6504
68k
C6501
100p
R6652
0.012
R6651
0.012
R6503
33k
R6502
33k
R6413
220
C6419
0.0047
R6412
2k
C6418 0.0047
C6416 0.047
C6417 1000
L6403
EXC-ELDR25C
L6407
EXC-ELDR25C
C6403 0.0068
R6406 3.3
R6405 3.3
R6404 3.3
L6402
EXC-ELDR25C
C6401 0.0068
R6403 3.3
L6401
EXC-ELDR25C
R6402 3.3
R6401 3.3
C6424 0.001
C6425 680p
L6301
LR-416
C6307 680p
C6408 0.001
C6409 0.001
C6410 220p
R6415 47
C6432
200p
C6433
200p
L6404
LR-400
Q6402
SD1487
R6408 10 R6407 10
R6409 2.2
R6410 2.2
L6405
LR-376
L6408
LA-262
R6411 2.7
L6406 LR-230
C6415 0.68
C6414 0.0047
C6413 1000
C6412 1000
D6432 MA30PXB
C6432 0.047
R6852
1
R6851
100
C6851 0.01
Q6403
2SD1585K
to TUNER
to FAN
C6427 0.1C6428 0.1
DRIVER BOARD
1
2
IC6501
TS522ID
1
2
3
GND
J6301
GND
DRVI
DRVI
TX: 2.54V
TX: 6.30V
RX: 8.03V
TX: 3.59V
TX: 0.47V
TX: 4.03V
TX: 0.69V
RX: 0.15V
RX: 10.43V
TX: 2.02V
RX: 4.86V
TX: 7.48V
RX: 2.29V
TX: 7.30V
RX: 8.03V
TX: 7.97V
TX: 1.36V
MESUREMENT CONDLTIONS
frequency: 12.29 MHz
mode: J3E(USB)
*ANT(RX): no input
(TX): no modulation
Digital tester
unit: V
range: 20V
input impedance: 10MΩ
Page 74

11 - 6
11-2-5 PLL UNIT (1)
AF/MOD
to MAIN
unit
J3602
AF
GND
AF+
NSEND
GND
MOD
GND
MOD+
R5901
2k
R5902
1k
R5903
1k
R5904
1k
R5905
1k
R5906
1k
R5907
1k
R5908
1k
R5909
1k
R5910
1k
R5911
2k
R5912
2k
R5913
2k
R5914
2k
R5915
2k
R5916
2k
R5917
2k
R5918
2k
R5919
2k
R5920
2k
C5902
0.0047
R5922
100
R5921
1M
IC5902
TC7SU04F
C5906
0.0047
C5903
0.0047
C5901
0.0047
C5905
0.0047
C5907
0.0047
C5908
10
C5904
0.0047
PCK
PDAT
PST5
DRES
L5981
18µ
L5982
22µ
L5983
15µ
C5983
2p
C5985
3p
C5986
20p
C5984
22p
C5982
12p
R5982 1k
C5981
0.1
W5981
C5910
0.001
C5911
10p
L5901
10µ
3
2
1
4
5
C5702
0.0047
R5720
2k
R5719
2k
R5718
2k
8VL
5V
R5717
2k
R5716
2k
R5715
1k
R5714
2k
R5713
2k
R5712
2k
R5710
1k
R5709
1k
R5708
1k
R5707
1k
R5706
1k
R5705
1k
R5704
1k
R5703
1k
R5702
1k
R5711
2k
R5701
2k
R5722
100
R5721
1M
IC5702
TC7SU04F
C5706
0.0047
C5703
0.0047
C5701
0.0047
C5705
0.0047
C5707
0.0047
C5708
10
C5704
0.0047
PDAT
PCK
PST3
DRES
L5782
22µ
L5781
22µ
L5783
18µ
C5782
820p
C5784
0.0015
C5783
0.01
C5785
0.01
C5781
0.0056
C5794
0.047
R5799 1k
C5710
0.001
C5711
10p
L5701
10µ
3
2
1
4
5
R5002 470
R5008 470
R5003 470
R5009 470
R5004 470
R5010 470
R5005 470
R5011 470
R5006 470
IO
G
OI
G
J5001
GND
D2LO
GND
M3LO
GND
GND
PTMP
REFS
REFV
DRES
PST5
PST4
PCO2
PST3
PST2
PST1
PCK
PDAT
UNLK
S13V
S13V
S13V
S13V
HV13
CP5001
CP5006
CP5007
CP5008
CP5009
CP5010
CP5011
CP5012
CP5013
CP5014
CP5015
CP5023
CP5902
CP5904
CP5021
CP5701
CP5703
CP5018
CP5017
CP5016
L5005
10µ
C5031
47
L5021
EXC-ELDR25C
R5021
10
C5032
0.1
C5021
47
C5022
0.1
IC5031
TA7808F
IC5001
TA7805F
R5783 560
R5781 560
R5782
8.2
CP5003
CP5004
CP5002
C5033
0.1
C5034
47
C5023
0.1
C5024
47
PCTXD
PXRXD
GND
DTR
REMOTE
Q5081
2SC4116
C5092
0.0047
R5081
47k
R5086
10k
C5084
0.01
Q5082
2SC4116
R5088
47k
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VCC
GND
T1O
R1I
R1O
T1I
T2I
R2O
C1+
V+
C1
C2+
C2
V
T2O
R2I
IC5081
ADM202EARN
C5086 1
C5087
1
R5093
47k
R5094
47k
C5090
1
C5088 1
C5085 1
Q5085
DTC114EU
R5092
4.7k
R5089
12
R5087
100k
D5084
MA2S111
D5085
MA2S111
Q5084
2SC4116
C5083
0.01
D5083
MA2S111
R5084
220
R5085
220
Q5083
DTC114EU
R5082
470
C5081
0.0047
D5081
MA2S111
IC5083
TC7W32F
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
R5096
47k
C5091
0.01
D5082
MA2S111
C5082
0.0047
R5083
470
IC5084
PS2701-1
IC5085
PS2701-1
4
3
2
1
IC5082
TC7W08F
8
7
6
5
R5090
4.7k
D5086
MA2S111
C5089
0.01
R5091
4.7k
R5097
47k
R5095
47k
R5098
47k
RL5081
ATX209
W5082
W5081
J5081
J5051
C5051
0.1
C5052
0.1
C5053
0.1
C5055
0.1
W5051
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN] only
[USA],[CAN]
[USA],[CAN]
[USA],[CAN]
[USA],[CAN] only
W5052
W5053
W5054
D5051
MA2S111
R5051
820
GND
MSEN
DSAF
DSAFE
DSMD
DSMDE
GND
ENAB
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A16
AACK
H5V
RXPC
DTRM
NMRS
NKME0
RSSW
NMEI2
NMEI
GND
GND
J5071
H5V
5V
8VL
J5091
CP5092
CP5091
GPS
5V
VSS
DA0
DA1
DA2
DA3
DA4
VSS
DA5
DA6
DA7
DA8
VDD
CON CLK
DATA
STRB
VSS
VDD
P2
TREE
P1
UL
VSS
VDD
NUM2
NUM1
NUM0
SYS CLK
VDD
ETC1
ETC0
FSK0
FSK1
VSS
DA9
VDD
ROMCE
RESET
VSS
VDD
PDM0
PDM1
PDM2QI
VSS
DA0
DA2
DA3
DA4
DA5
DA1
DA6
VSS
DA7
DA8
VDD
CON CLK
DATA
STRB
VSS
VDD
P2
TREE
P1
UL
VSS
VDD
NUM2
NUM1
NUM0
SYS CLK
VDD
ETC1
ETC0
FSK0
FSK1
VSS
DA9
VDD
ROMCE
RESET
VSS
VDD
PDM0
PDM1
PDM2QI
IC5901
SC-1287
IC5701
SC-1287
CP5024
DRES
PST5
PST4
PCO2
PST3
PST2
PST1
PCK
PDAT
UNLK
(PCO0)
(PCO1)
C5709
0.0047
C5909
0.0047
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2324252627282930313233
11
10
987654321
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
13
12
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2324252627282930313233
11
10
987654321
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
PLL UNIT(1)
to MAIN
unit J3601
8VL
5V
HV13V
BUS LINE
8VL
5V
HV13V
a
M2LO
PLL UNIT(2)
M2LO
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
M3LO
CP5019
CP5020
2
1
7
6
3
8
4
9
5
MESUREMENT CONDITIONS
frequency: 12.29 MHz
mode: J3E(USB)
*ANT(RX): no input
(TX): no modulation
Digital tester
range: 20V
input impedance: 10MΩ
no specification
: voltage at RX
unit: V
11.22V
Page 75

11 - 7
11-2-6 PLL UNIT (2)
C5802
0.0047
R5820
2k
R5819
2k
R5818
2k
R5817
2k
R5816
2k
R5815
2k
R5814
2k
R5813
2k
R5812
2k
R5810
1k
R5809
1k
R5808
1k
R5807
1k
R5806
1k
R5805
1k
R5804
1k
R5803
1k
R5802
1k
R5811
2k
R5801
2k
R5822
100
R5821
1M
IC5802
TC7SU04F
C5806
0.0047
C5803
0.0047
C5801
0.0047
C5805
0.0047
C5807
0.0047
C5808
10
C5804
0.0047
PDAT
PCK
PST4
DRES
L5882
5.6µ
L5881
5.6µ
L5883
5.6µ
C5886
0.5p
C5888
1p
C58877pC5889
6p
C5885
7p
C5884
0.0047
R5889 1.2k
C5810
0.001
C5811
10p
R5891
470
C5883
0.1
R5886
1k
R5887 1.2k
R5885
270
C5891
0.1
Q5882
2SC4215
C5882
12p
R5890
560
R5883
1.2k
C5881 0.047
R5881 47
R5882
1k
Q5881
2SC4673
R5888 47
C5892
0.1
L5884 10
µ
R5892 33
C5893 150p
L5885 100
µ
C5890
0.0047
3
2
1
4
5
P5201
J5201
M2LO
CP5202
to MAIN
unit J301
P5801
J5801
D1LO
CP5802
to MAIN
unit J2301
L5202
100µ
R5203
100
C5201
0.001
R5204
22k
W5203
[USA],[CAN]
C5202
0.001
R5205
10k
R5206
220
C5204
0.0047
Q5202
2SC4215
L5203
LS-471A
C5206
0.5p
C5205 15p
L5204
LS-471A
C5207 15p
CP5041
CP5251
W5251
CP5223
CP5222
CP5221
C5282
0.001
R5283
2.2k
R5284
4.7k
R5281
470
C5281
0.0047
Q5281
2SC4215
R5282
100
C5283
0.0047
GND
OUT
5V
TEMP
VCC
76
123
5
4
X5251
CR-604
[USA],[CAN]
C5251
100p
[USA],[CAN]
R5251
470
[USA],[CAN]
C5253
0.0047
C5254
10
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
50494847464544434241403938373635343332313029282726
7677787980818283848586878889909192939495969798
99
100
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
C5124
0.0047
C5125
0.1
R5143 47k
R5140 47k
R5144 47k
R5141 47k
R5145 47k
R5142 47k
C5116
47
C5117
0.0047
C5118
0.0047
C5115
0.0047
C5126
0.1
C5120
0.0047
C5123
0.0047
R5112
2k
R5111
2k
R5110
2k
R5109
2k
R5108
2k
R5107
2k
R5106
2k
R5105
2k
R5104
2k
R5103
2k
R5102
2k
R5101
2k
R5113
1k
R5114
1k
R5115
1k
R5116
1k
R5117
1k
R5118
1k
R5119
1k
R5120
1k
R5121
1k
R5122
1k
R5123
1k
R5124
2k
C5103
5p
C5102
10p
C5101
27p
R5129
330
C5107
0.0047
R5131
470
R5132
2.7k
Q5101
2SC4116
R5130
1.5k
C5108
0.0047
C5106
0.0047
R5128
100
FI5101
SFECV10.5MA5S
C5105
0.001
R5127
330
IC5102
TC7SU04F
3
2
1
4
5
R5126
1M
R5125
100
C5104
0.0047
IC5103
TC7SU04F
1
2
3
5
4
R5135
1M
C5111
0.0047
R5133
47k
R5134
47k
C5110
10
L5601
100µ
C5602
0.001
C5604
0.0047
R5602
100
R5601
4.7k
C5607
0.0047
L5605
100µ
C5618
0.0047
R5612
330
R5613
56k
C5619
2p
Q5604
2SC4215
Q5601
2SC4215
C5601
0.0047
C5605
0.0047
R5606
330
R5607
4.7k
R5604
56k
R5614
180
C5603
0.0047
Q5602
2SC4215
R5603
1k
R5608
4.7k
R5610
220
Q5603
2SC4215
R5611
27
C5609
47p
R5605
100
R5609
100
C5608
0.0047
C5611
47p
L5603
0.1µ
L5604
0.1µ
C5613
12p
C5615
7p
C5610
270p
L5602
0.15
µ
C5612
27p
C5614
27p
C5616
18p
Q5553
2SC4116
R5556
10k
C5556
0.001
C5557
0.1
C5558
470
C5560
22
R5557
10k
L5552
100µ
C5561
470p
R5524
100
C5529
470p
L5522
LW-38
C5528
0.001
C5522
100p
L5521
LW-38
C5521
10p
C5523
10p
Q5521
2SK508
C5524
0.0047
L5523
E544GN-110248
C5526
1p
C5525
0.0022
W5502
R5522
270
D5521
KV1770S
R5551
100
C5551
4.7
C5552
0.47
CP5601
CP5603
C5122
0.0047
C5617
0.001
FLO
CPO
GND
GND
FIN
FIN
VCC1
OSCIN
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VP
VCC2
PO/LD
LE
DATA
CLOCK
CE
GND
IC5401
LMX2306TM
R5407
1k
C5408
4.7
R5406
100k
Q5401
DTA114EU
D5402
1SS301
W5401
L5401
10
µ
W5402
C5404
0.0047
R5403
1.2k
W5409
CP5401
CP5402CP5403
C5401
0.1
C5402
0.001
C5403
0.01
R5404 1k
R5408 1k
R5410 1k
PDAT
L5801
10
µ
L5101
10
µ
R5138 1k
R5139 1k
R5304
100k
R5306
100
Q5301
2SK210
C5307
150p
C5308
150p
C5309
0.0047
C5311
0.0047
C5312
10
L5303
10
µ
R5306
150
L5304
100µ
R5308
100
R5307
120k
C5313
0.0047
Q5302
2SC4116
C5314
0.0047
R5310
820
R5309
820
R5311
820
C5315
0.0047
L5351
100µ
C5351
0.0047
R5351
12k
R5352
470
C5353
0.0047
C5352
0.0047
L5352
3.9µ
C5355
5p
C5354
51p
C5356
51p
Q5351
Q5283
2SC4215
Q5282
2SC4215
2SC4215
R5353
1k
R5354
470
D5302
1SS375
D5303
1SS375
R5312
470
C5357 0.0047
D5101
1SS301
R5137
1k
C5113
0.0047
L5302
LB-185
R5303
100k
C5306
150p
C5305
20p
C5304
100p
C5302
0.0047
D5301
MA338
C5303
24p
L5301
100µ
C5301
2.2
R5302
150
CP5301 CP5302
C5112
47p
R5136
100k
CP5303
P5601
J5601
M1LO
CP5602
to MAIN
unit J601
VSS
DA0
DA2
DA3
DA4
DA5
DA1
DA6
VSS
DA7
DA8
VDD
CON CLK
DATA
STRB
VSS
VDD
P2
TREE
P1
UL
VSS
VDD
NUM2
NUM1
NUM0
SYS CLK
VDD
ETC1
ETC0
FSK0
FSK1
VSS
DA9
VDD
ROMCE
RESET
VSS
VDD
PDM0
PDM1
PDM2QI
PD2
PD1
VDD
PD0
VSS
PDTRI
VDD
REFOSC
RC
FCK
VSS
Q16MA
Q4MA
VDD
VSS
ETCO7
ETCO6
ETCO5
VSS
ETCO4
ETCO3
VSS
ETCO2
ETCO1
ETCO0
VDD
TE3
TE2
TE1
VDD
DA11
DA10
DA9
DA8
VSS
VSS
DA7
DA6
DA5
DA4
VSS
DA3
DA2
DA1
DA0
VDD
VDD
SYSCLK0
VDD
DIVOUT
VSS
REFIN
PDIN
VSS
OSCO
VSS
VDD
OSCF
VSS
OSCI
VDD
VSS
SYSRESET
VDD
VDD
TEOUTH4
TEOUTH3
TEOUTH2
TEOUTH1
TEOUTH0
VDD
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VDD
BUM2I
BUN2I
BUN2I
VDD
BUM2O
BUN2O
BUN2O
VSS
VDD
SYS-CLK
VSS
VSS
STRB
CON2
CON1
CON0
VSS
BUSY
VSS
CONTCLK
DATA
VDD
IC5101
SC-1246A
IC5801
SC-1287
CP5203
CP5201
CP5801
CP5803
13
12
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2324252627282930313233
11
10
987654321
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
C5809
0.0047
5V
8VL
PCK
PST2
UNLK
8VL
PST1
PCO2
PDAT
PCK
DRES
C5121
0.0047
BUS LINE
8VL
5V
HV13V
a
M2LO
PLL UNIT(1)
5V
M2LO
8VL
5V
PLL UNIT(2)
5V
M2LO
D1LO
M2LO
5V
D1LO
C5310
10p
DULS
VSS
VSS
8VL
R5146
820
C5203
0.0047
C5606
0.001
8VL 8VL8VL
L5281
C5284
0.0047
C5287
0.0047
C5292
3p
C5295
0.001
C5293
0.0047
C5291
0.0047
X5281
CR-338
C5288
100p
C52908pC5294
20p
C5285
10
R5285
12k
R5293
220
R5292
6.8k
R5289
3.9k
R5291
1.8k
R5287
100
R5288
1.5k
C5289
100p
L5284
10
µ
L5285
10
µ
L5283
1
µ
L5201
EXC-ELDR25C
10µ
[USA],[CAN] only
R5207
47
[OTH]
[USA],[CAN] only
[OTH] only
7.65V
7.20V
7.76V
6.91V
7.0V
3.82V
3.6V
0.0V
7.71V
7.20V
4.85V
4.21V
2.77V
MESUREMENT CONDITIONS
frequency: 12.29 MHz
mode: J3E(USB)
*ANT(RX): no input
(TX): no modulation
Digital tester
unit: V
range: 20V
input impedance: 10M
Ω
no specification
: voltage at RX
Page 76
11 - 8
11-2-7 DSP BOARD
TMS320VC33PGEA120
IC301
1
A20
2
VSS
3
A19
4
A18
5
A17
6
DVDD
7
A16
8
A15
9
VSS
10
A14
11
A13
12
CVDD
13
A12
14
A11
15
DVDD
16
A10
17
A9
18
VSS
19
A8
20
A7
21
A6
22
A5
23
DVDD
24
A4
25
VSS
26
A3
27
A2
28
CVDD
29
A1
30
A0
31
DVDD
32
PAGE3
33
PAGE2
34
VSS
35
PAGE1
36
PAGE0
37
DVDD38H139H340VSS
41
STRB42R/W43DVDD44IACK45RDY46CVDD47HOLD48HOLDA49VSS50D3151D3052D2953DVDD54D28
55
D2756VSS57D2658D2559D2460DVDD61D2362D2263VSS64D2165D2066CVDD67D1968D1869DVDD70D1771D1672VSS
73
D15
74
D14
75
D13
76
D12
77
DVDD
78
D11
79
D10
80
VSS
81
D9
82
D8
83
CVDD
84
D7
85
D6
86
DVDD
87
D5
88
D4
89
VSS
90
D3
91
D2
92
D1
93
D0
94
DVDD
95
EMU1
96
EMU0
97
VSS
98
TCK
99
TDO
100
TDI
101
CVDD
102
TMS
103
TRST
104
DR0
105
VSS
106
FER0
107
CLKR0
DVDD
109
CLKX0
110
FSX0
111
DX0
112
VSS
113
TCLK1
114
TCLK0
115
DVDD
116
XF1
117
XF0
118
VSS
119
INT3
120
INT2
121
INT1
122
INT0
123
124
EDGEMODE
125
MCBL/MP
126
VSS
127
RESET
128
SHZ
129
130
EXTCLK
131
PLLVDD
132
XOUT
133
XIN
134
PLLVSS
135
CLKMD1
136
CLKMD0
137
CVDD
138
RSV1
139
RSV0
140
VSS
141
A23
142
A22
143
DVDD
144
A21
R321
4.7k
R320
4.7k
C325 0.0047
C324 0.0047
C323 0.1
C322
0.0047
C321
0.1
C320
0.1
R317 10k
R318 10k
C313 0.1
C314 0.0047
C315 0.1
C316 0.0047
C317 0.1
C318 0.0047
C319 0.0047
CP306
CP307
CP308
C301
0.0047
C302
0.0047
C304
0.0047
0.1
C306
C303
0.1
C305
0.1
R303
2.2k
R304
2.2k
R305
10k
R306
10k
R307
10k
R308 10k
R309 10k
R310 10k
R311
10k
R312
10k
R313
10k
C307 0.1
C308 0.1
C309 0.0047
C311 0.0047
C312 0.1
W308
W309
W1
W501
W502
W503
W504
W505
W903
W904
W310
CP300
IC403
SN74AHCT374PW
1
O-CTRL
2
1Q
3
1D
4
2D
5
2Q
6
3Q
7
3D
8
4D
9
4Q
10
GND
11
CLK
12
5Q
13
5D
14
6D
15
6Q
16
7Q
17
7D
18
8D
19
8Q
20
VCC
IC404
SN74AHCT374PW
1
O-CTRL
2
1Q
3
1D
4
2D
5
2Q
6
3Q
7
3D
8
4D
9
4Q
10
GND
11
CLK
12
5Q
13
5D
14
6D
15
6Q
16
7Q
17
7D
18
8D
19
8Q
20
VCC
L404 2.2µ
L403
2.2µ
C404
0.0047
C403
0.0047
SN74AHC595PW
IC401
1
QB
2
QC
3
QD
4
QE
5
QF
6
QG
7
QH
8
GND9QH’
10
SCLR
11
SCK
12
RCK
13
G
14
SI
15
QA
16
VCC
C401
0.0047
L401 2.2µ
SN74AHC74PW
IC406
V+
14
GND
7
SN74AHC74PW
IC406
1
CLK
2
D
3
CK
4
PR
5
Q
6
Q
SN74AHC74PW
IC406
13
CLK
12
D
11
CK
10
PR
9
Q
8
Q
CP302
CP305
CP304
CP303
R322
47
L405
2.2µ
C406
0.0047
L406
2.2µ
µPC4570G2
IC701b
6
5
7
C752
100p
C751
270p
R753
3.3k
R754
6.8k
R756
6.8k
R755
3.3k
R752
4.7k
R751
4.7k
C755
100p
C758
10
µPC4570G2
IC701a
2
3
1
3.3k
R705
270p
C701
6.8k
R706
100p
C702
6.8k
R704
4.7k
R701
4.7k
R702
3.3k
R703
100p
C705
10
C708
µPC4570G2
IC701
V+
8
GND
4
C703 0.1
C901
0.001
C704 10
L701
100µ
BA15532F
IC651a
2
3
1
BA15532F
IC651b
6
5
7
R656
4.7k
R657
4.7k
R655
4.7k
R651
390
R652
390
R658
4.7k
R6531kR654
1k
C654
0.1
C651
0.0015
BA15532F
IC651
V+
8
GND
4
C652 0.1
C653 10
L651
100µ
C655
1
4.7k
R610
4.7k
R609
4.7k
R608
390
R603
1
C606
10C604
100µ
L601
BA15532F
IC601
V+
8
GND
4
0.1
C605
0.1C603
1k
R606
390
R604
0.0015
C602
BA15532F
IC601b
6
5
7
1k
R605
BA15532F
IC601a
2
3
1
4.7k
R607
R601
1.2k
R602
4.7k
C601
10
AK4528VF
IC501
1
VCOM
2
AINR+
3
AINR-
4
AINL+
5
AINL-
6
VREF
7
AGND
8
VA
9
P/S
10
MCLK
11
LRCK
12
BICK
13
SDTO
14
SDTI
15
CDTI
16
CCLK
17
CSN
18
DFS
19
PDN
20
DEM0
21
DEM1
22
VT
23
VD
24
DGND
25
AOUTL-
26
AOUTL+
27
AOUTR-
28
AOUTR+
IC801
SN74AHC244PW
1
ENA
2
A1
3
YB4
4
A2
5
YB3
6
A3
7
YB2
8
A4
9
YB1
10
GND
11
B1
12
YA4
13
B2
14
YA3
15
B3
16
YA2
17
B4
18
YA1
19
ENB
20
VCC
X51
CR-709
R51
1M
C52
5p
C53
5p
L52
1.0µ
C54
0.01
TC7WHU04FU
IC51
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
CP301
TC7WHU04FU
IC1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
27p
C2
47p
C6
10p
C8
0.001
C802
5p
C9
CR-566
(12.288 MHz)
X1
27p
C3
1M
R1
L51
2.2µ
L1
2.2µEP2
C1
0.0047
C51
0.0047
IC101
SN74HCT244APW
1
ENA
2
A1
3
YB4
4
A2
5
YB3
6
A3
7
YB2
8
A4
9
YB1
10
GND11B1
12
YA4
13
B2
14
YA3
15
B3
16
YA2
17
B4
18
YA1
19
ENB
20
VCC
SN74AHC74PW
IC3
1
CLK
2
D
3
CK
4
PR
5
Q
6
Q
SN74AHC74PW
IC3
13
CLK
12
D
11
CK
10
PR
9
Q
8
Q
SN74AHC74PW
IC4
1
CLK
2
D
3
CK
4
PR
5
Q
6
Q
SN74AHC74PW
IC4
13
CLK
12
D
11
CK
10
PR
9
Q
8
Q
SN74AHC74PW
IC3
V+
14
GND
7
SN74AHC74PW
IC4
V+
14
GND
7
L2
2.2µ
C4
0.0047
L3
2.2µ
C7
0.1
C201
0.1
TC7SH04FU
IC202
1
2
3
4
5
TC7SH32FU
IC203
1
2
3
4
5
C202
C203
0.1
0.1
W202
W203
W302
W303
C101
0.1
C407
0.001
L101
2.2µ
L102
2.2µ
C103
0.1
C102
10
C104
10
L801
2.2µ
R801 100k
R329 1k
R330 1k
R331 1k
R332 1k
R201
47k
R802 100k
C801 0.0047
R803 100k
R804 100k
R805 100k
R323
10k
R324
10k
W311
W312
C508 0.1
C507 0.1
C511 22p
C506 22
C504 2.2
C505 0.1
R501
4.7
C509 0.1
C510 22
L502
2.2µ
L501
2.2µ
C154 0.1
C155 0.1
C156 0.1
C157 10
R151
68
TK11250CM
IC171
CONT
1
GND
2
N.BYPASS
3
VOUT
4
GND
5
VIN
6
0.1C173
15R171
10C174
0.1C171
0.1C172
C162 0.1
C163 0.1
C161 22
C164 10
TK11218CM
IC152
CONT
1
GND
2
N.BYPASS
3
VOUT
4
GND
5
VIN
6
R161 33
R162 27
L301
2.2µ
L302
2.2µ
W201
J901
W901
D901
MA729
R904
10k
2
30 29
1
1
21 22
2
R903 10k
R902 10k
R901 10k
R905
10k
R906
10k
M29W102BB
IC201
A9
1
A10
2
A11
3
A12
4
A13
5
A14
6
A15
7
NC
8
W
9
VCC
10
RP
11
E
12
DQ15
13
DQ14
14
DQ13
15
DQ12
16
DQ11
17
DQ10
18
DQ9
19
DQ820VSS
21
DQ7
22
DQ6
23
DQ5
24
DQ4
25
DQ3
26
DQ2
27
DQ1
28
DQ0
29
G
30
A0
31
A1
32
A2
33
A3
34
A4
35
A5
36
A6
37
A7
38
A8
39
VSS
40
BA033FP
IC161
I
O
G
R52
100
R2
1k
W151
W902
IC405
BU4021BF
1
H
2
QF
3
QH
4
D
5
C
6
B
7
A
8
VSS9P/S
10
CLK
11
SER
12
QG
13
E
14
F
15
G
16
VDD
C405
0.0047
C408
0.001
CP1
C.P8S
BU9480F
IC102
OUTR
1
REF
2
GND
3
OUTL
4
LRCLK
5
SDATA
6
BCLK
7
VCC
8
R328
10k
R327
10k
R326 10k
R325
10k
R611
5.6k
R659
5.6k
R707
1k
R708
1k
C706
0.1
C707
100
C756
0.1
C757
100
R758
1k
R3
47k
R757
1k
C175 10
C158 10
J902
W171 W152
W4
W5
W3
W2
CP351
CP352
CP353
CP354
CP355
CP356
CP357
CP358
CP359
CP360
CP801
CP802
CP803
CP804
CP805
CP806
CP807
CP808
CP809
CP810
W951 [OTH] only
W952
CP811
CP812
Q302
DTC144EU
Q301
D302
D301
DA221
DA221
D303
DA221
D304
DA221
DTC144EU
D15
D00
D01
D02
D03
D04
D05
D06
D07
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
A00
A01
A02
A03
A05
A06
A07
A08
A09
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A04
D07
D06
D05
D04
D03
D02
D01
D00
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
D12
D13
D14
D15
D11
D10
D09
D08
OUT5
OUT6
OUT7
OUT8
D07
D01
D02
D05
D00
D04
D03
D06
DI
ROO
RQI
IBS
OBS
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D09
D08
D01
D02
D03
D04
D05
D06
D07
A00
A01
A02
A03
A04
A05
A06
A07
A08
A09
A10
A11
A12
A14
A15
A13
OBSY
IBSY
OBS
IBS
FDIS
FINT
GND
GND
to MAIN
unit J1102
to MAIN
unit J1101
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
AGC2
AGC1
GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
KEYIN
OUT7
OUT5
OUT3
OUT1
OBSY
GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
GND1
DRES
192K
IBSY
DO
OUT2
OUT4
OUT6
OUT8
UNLK
DIDI
STBOSTBO
CK
RQI
RQO
D09
D08
D00
D0G
D0F
D0E
D0G
D0F
D0E
DO
STBO
CK
D0H D0A
D0B
D0C
D0D
D0H
D0D
D0C
D0B
D0A
FSTB
FDAT
8V
8V
8V
DSPO2
DSPO1
DSPI1
DSPI2
TRST
TCK
EMU0
TMS
TDO
TDI
EMU1
PD
FCK
DRES
DRES
GND1
GND1
FOK
FBSY
KEYIN
UNLK
FENA
108
J1101
J1102
2
1
22 21
12
29 30
DSP BOARD
CVDD
DVDD
GND1
KEYIN
OUT7
OUT5
OUT3
OUT1
GND1
OBSY
RQO
GND1
CK
RQI
GND1
GND1
DRES
GND1
UNLK
OUT8
OUT6
OUT4
OUT2
GND1
STBO
DO
GND1
DI
IBSY
GND1
192K
GND1
GND
GND
DSPO1
GND
AGC2
GND
8V
GND
GND
GND
DSPI1
DSPO2
GND
GND
GND
AGC1
GND
8V
GND
DSPI2
GND
GND
MAIN UNIT (3)
XP4312
Q201
3
2
6
5
1
4
MEASUREMENT CONDITIONS
frequency : 14.1MHz USB
SG input : off
Voltage at rx
Digital tester
Oxilloscope(20MHz)
2.3V
80ns
0.9V
0V
2.6V
160ns
0.4V
3.3V
0V
0V
10.4µs
AGC1DSP02
3.3V
0V
20.8µs
1.7V
1.5V
0V
AGC1DSP02 AGC1DSP02
DSP02 DSP02 DSP02
1.82V
3.36V
7.61V
4.07V
A
B
C
CBA
2.83V
3.93V
5.01V
6.84V
2.83V
2.83V
2.83V
2.5V
3.84V
3.84V
2.5V
2.49V
2.49V
Page 77

11 - 9
11-2-8 FILTER BOARD
C7035 470p C7038 270p C7049 180p
C7042 390p
RL7032
AJS1315
C7067 270p C7075 330p C7081 120p
RL7062
AJS1315
C7094 330p C7106 150p C7100 100p
RL7092
AJS1315
C7127 120p
C7131 5p
RL7122
AJS1315
C7156 10p
RL7152
AJS1315
C7184 120p
C7186 56p C7188 22p
RL7182
AJS1315
C7224 33p
RL7212
AJS1315
C7254 22p
C7242 100p
RL7242
AJS1315
GND
FOR
GND
REF
GND
GND
L1M
L2M
L4M
L6M
L8M
L12M
L16M
L22M
S13V
TRXS
J7331
to MAIN
unit J1301
C7069 270p
P7001
to PA
unit
J6401
J7001
FLIN
L1M
L2M
L4M
L6M
L8M
L12M
L16M
L22M
R7314 SA05C
J7311
ANT
J4501
P7321
to
MAIN
unit
J51
J7321
MRX
C7275
10p
W7339
W7338
W7337
W7336
W7335
W7334
W7333
W7340
FILTER BOARD
1.6-1.9999 MHz
2-2.9999 MHz
3-4.9999 MHz
5-6.9999 MHz
7-9.9999 MHz
10-13.9999 MHz
14-19.9999 MHz
20-29.9999 MHz
L7031 100µ
L7035
100
µ
L7065
100
µ
RL7031
AJS1315
C7032
0.1
C7062
0.1
RL7061
AJS1315
L7095
100
µ
RL7091
AJS1315
C7092
0.0047
L7125
100
µ
RL7121
AJS1315
C7122
0.0047
L7155
33
µ
RL7151
AJS1315
C7152
0.0047
L7185
33
µ
RL7181
AJS1315
C7182
0.0047
L7215
10
µ
RL7211
AJS1315
C7212
0.0047
L7244
10
µ
RL7241
AJS1315
C7241
0.0047
L7036 LR-236 L7037 LR-226 L7038 LR-227
C7037 300pC7034 470p
C7041 10p
C7033 0.001
C7036 0.0022
C7039 0.0027
C7043 390p
C7044 390p
C7045 330p
C7063 100p
C7064 470p
C7065 470p
C7086 10p
C7087 120p
C7070 100p
C7071 470p
C7072 470p
C7076 330p
C7073 470p
C7077 330p
C7078 390p
C7079 470p
C7082 390p
C7083 390p
C7084 68p
L7068 LR-236L7067 LR-235L7066 LR-263
L7096 LR-238 L7098 LR-235L7097 LR-235
L7127 LR-263 L7128 LR-263L7126 LR-237
L7156 LR-241 L7158 LR-237L7157 LR-237
L7183 LR-242 L7184 LR-242L7182 LR-243
L7216 LR-242 L7218 LR-242L7217 LR-242
L7248 LR-262 L7246 LR-262L7245 LR-262
C7066 330p C7074 470p C7080 120p
C7068 270p
C7126 10p
C7124 120p
C7130 56p
C7153 82p
C7155 120p
C7158 82p
C7214 47p C7216 27p
C7244 22p
C7247 27p
C7105 470p
C7108 330p
C7095 390p
C7096 390p
C7098 330p
C7099 470p
C7101 300pC7132 300p
C7129 300p
C7128 270p
C7125 390p
C7137 100p
C7136 180p
C7154 390p
C7164 82p
C7157 390p
C7163 180p
C7183 120p
C7185 270p
C7187 330p
C7193 180p
C7221 82p
C7223 82p
C7225 27p
C7222 200p
C7217 120p
C7248 33p
C7249 39p
C7253 150p
C7243 56p
C7255 6p
C7046
0.1
C7031 1
L7061 100µ
C7061 1
C7085
0.1
C7102
0.0047
C7091 1
L7091 100µ
L7121 100µ
C7121 1
C7133
0.0047
C7160
0.0047
C7151 1
L7151 33
µ
L7181 33
µ
C7181 1
C7190
0.0047
C7218
0.0047
C7211 1
L7211 10
µ
C7250
0.0047
L7241 10
µ
CP7332
CP7331
L7271
100
µ
R7272
2.7k
R7273
4.7k
D7271
1SS322
C7272
0.01
R7274 33
C7277
180p
C7278
47p
C7345
0.0047
R7271
10k
R7277
4.7k
R7276
2.7k
C7273
47p
L7273
100
µ
C7274
0.0022
D7272
1SS322
R7275
10k
R7315 82k
L7272
LR-391
C7302 0.0047
C7303 0.0047
D7301 1SS355
C7301 0.0047
Q7301
DTC114EU
RL7301
AGP2013
R7301 10
C7332
0.0047
C7304
0.0047
C7325
0.68
L7321
LR-170
C7322
18p
C7323
100p
C7321
100p
L7332 100µ
L7331 100µ
ANT
2
1
4
3
6
5
Page 78

Asia Icom Inc.
6F No.68, Sec. 1 Cheng-Teh Road, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Phone : +886 (02) 2559 1899 Fax : +886 (02) 2559 1874
URL : http://www.asia-icom.com
E-mail : sales@asia-icom.com
Zac de la Plaine, 1, Rue Brindejonc des Moulinais
BP 5804, 31505 Toulouse Cedex, France
Phone : +33 (5) 61 36 03 03 Fax: +33 (5) 61 36 03 00
URL : http://www.icom-france.com
E-mail : icom@icom-france.com
Icom France S.a
Unit 9, Sea St., Herne Bay, Kent, CT6 8LD, U.K.
Phone : +44 (01227) 741741 Fax : +44 (01227) 741742
URL : http://www.icomuk.co.uk
E-mail : info@icomuk.co.uk
Icom (UK) Ltd.
Crta. de Gracia a Manresa Km. 14,750
08190 Sant Cugat del Valles Barcelona, SPAIN
Phone : +34 (93) 590 26 70 Fax : +34 (93) 589 04 46
URL : http://www.icomspain.com
E-mail : icom@icomspain.com
Icom Spain S.L
<Corporate Headquarters>
2380 116th Avenue N.E., Bellevue, WA 98004, U.S.A.
Phone : +1 (425) 454-8155 Fax : +1 (425) 454-1509
URL : http://www.icomamerica.com
E-mail : sales@icomamerica.com
<Customer Service>
Phone : +1 (425) 454-7619
Icom America Inc.
Glenwood Centre #150-6165
Highway 17 Delta, B.C., V4K 5B8, Canada
Phone : +1 (604) 952-4266 Fax : +1 (604) 952-0090
URL : http://www.icomcanada.com
E-mail : info@icomcanada.com
Icom Canada
A.B.N. 88 006 092 575
290-294 Albert Street, Brunswick, Victoria, 3056, Australia
Phone : +61 (03) 9387-0666 Fax : +61 (03) 9387-0022
URL : http://www.icom.net.au
E-mail : sales@icom.net.au
Icom (Australia) Pty. Ltd.
146A Harris Road, East Tamaki,
Auckland, New Zealand
Phone : +64 (09) 274 4062 Fax : +64 (09) 274 4708
URL : http://www.icom.co.nz
E-mail : inquiries@icom.co.nz
Icom New Zealand
1305, Wanshang Plaza, Shijingshan Road, Beijing China
Phone : +86 (010) 6866 6337 Fax : +86 (010) 6866 3553
URL : http://www.bjicom.com
E-mail : bjicom@bjicom.com
Beijing Icom Ltd.
Sopot, 3 Maja 54 Poland
Phone : +48 (58) 550 7135 Fax : +48 (58) 551 0484
E-mail : icompolska@icompolska.com.pl
Icom Polska
1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
Phone : +81 (06) 6793 5302
Fax : +81 (06) 6793 0013
URL : http://www.icom.co.jp/world/index.html
Communication Equipment
Himmelgeister Str. 100, D-40225 Dusseldorf, Germany
Phone : +49 (0211) 346047 Fax : +49 (0211) 333639
URL : http://www.icomeurope.com
E-mail : info@icomeurope.com
Icom (Europe) GmbH
Page 79

1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
S-13901HZ-C1-2
C 2002, 2003 Icom Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...