Page 1

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description Contents
Contents
1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Product Orientation ..........................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.1 Introduction to Huawei Mobile Softswitch Solution .............................................................................1-2
1.1.2 Features of Huawei Mobile Softswitch Solution ...................................................................................1-3
1.1.3 Introduction to the MSOFTX3000 .........................................................................................................1-6
1.2 Product Features ...............................................................................................................................................1-8
1.2.1 Dynamic Service Provision Capabilities................................................................................................1-8
1.2.2 Powerful and Flexible Networking Capabilities ....................................................................................1-9
1.2.3 Large Capacity and High Integration ...................................................................................................1-10
1.2.4 Powerful Processing Capabilities .........................................................................................................1-10
1.2.5 Highly Reliable .....................................................................................................................................1-11
1.2.6 Capabilities for Smooth Expansion ......................................................................................................1-11
1.2.7 Advanced Charging Capabilities ..........................................................................................................1-12
1.2.8 Excellent Performance Measurement Function ...................................................................................1-12
1.2.9 Convenient and Useful O&M Function ...............................................................................................1-13
1.2.10 Support for 2G/3G Integration............................................................................................................1-13
2 System Structure ........................................................................................................................2-1
2.1 Hardware Structure...........................................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.1 Appearance..............................................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.2 Physical Structure ...................................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.3 Logical Structure.....................................................................................................................................2-5
2.2 Software Structure ............................................................................................................................................2-8
2.2.1 Overview .................................................................................................................................................2-8
2.2.2 Host Software..........................................................................................................................................2-9
2.2.3 BAM Software ......................................................................................................................................2-10
2.3 Capacity Expansion........................................................................................................................................2-12
2.3.1 Cabinet Configuration...........................................................................................................................2-12
2.3.2 Expansion Configuration ......................................................................................................................2-14
3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols .......................................................................................3-1
3.1 Physical Interfaces............................................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.1 Classification...........................................................................................................................................3-2
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary i
Page 2

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Contents
3.1.2 Interface Specifications...........................................................................................................................3-3
3.2 Protocol Interface .............................................................................................................................................3-4
3.2.1 Standard Interface ...................................................................................................................................3-4
3.2.2 CDR Interface .........................................................................................................................................3-6
3.2.3 Interception Interface ..............................................................................................................................3-6
3.3 Signaling and Protocols....................................................................................................................................3-7
Product Description
4 O&M System...............................................................................................................................4-1
4.1 Overview of O&M ...........................................................................................................................................4-2
4.1.1 Basic Concept..........................................................................................................................................4-2
4.1.2 Terminal System......................................................................................................................................4-2
4.1.3 Network Management Networking ........................................................................................................4-4
4.1.4 Introduction to MML Command Line....................................................................................................4-4
4.2 O&M Function .................................................................................................................................................4-4
4.2.1 Configuration Management ....................................................................................................................4-4
4.2.2 Fault Management...................................................................................................................................4-5
4.2.3 Performance Measurement .....................................................................................................................4-7
4.2.4 Security Management .............................................................................................................................4-7
4.2.5 CDR Management...................................................................................................................................4-7
4.2.6 Environment Monitoring ........................................................................................................................4-8
5 Services and Functions..............................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Basic Services...................................................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.1 Teleservices.............................................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.2 Supplementary Services..........................................................................................................................5-3
5.1.3 ODB Services..........................................................................................................................................5-6
5.1.4 IN Services ..............................................................................................................................................5-7
5.1.5 Value Added Services .............................................................................................................................5-8
5.2 Basic Functions ..............................................................................................................................................5-10
5.2.1 Mobility Management...........................................................................................................................5-10
5.2.2 Security Management ...........................................................................................................................5-11
5.2.3 Handover ...............................................................................................................................................5-13
5.2.4 Call Processing......................................................................................................................................5-14
5.2.5 Charging................................................................................................................................................5-15
5.2.6 SSP ........................................................................................................................................................5-21
5.3 Description of Features ..................................................................................................................................5-22
5.3.1 List of Features......................................................................................................................................5-22
5.3.2 V100R005 Version................................................................................................................................5-24
5.3.3 V100R003 Version................................................................................................................................5-31
6 Networking and Application...................................................................................................6-1
6.1 Typical Networking..........................................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.1 MSC Networking ....................................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.2 GMSC Networking .................................................................................................................................6-4
ii Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 3

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description Contents
6.1.3 TMSC Networking..................................................................................................................................6-6
6.1.4 Dual-Homing Networking ......................................................................................................................6-7
6.1.5 Multi-Area Networking ........................................................................................................................6-10
6.1.6 Solution for Huawei NGN Interworking with CS Domain..................................................................6-11
6.1.7 Evolution Strategy of Huawei Mobile Core Network..........................................................................6-12
6.2 Network Application Cases............................................................................................................................6-13
6.2.1 Multi-area Commercial Network of Company A.................................................................................6-13
6.2.2 Dual-Homing Commercial Network of Company B ...........................................................................6-15
7 Reliability and Security Design..............................................................................................7-1
7.1 Reliability Design.............................................................................................................................................7-2
7.1.1 Hardware Reliability...............................................................................................................................7-2
7.1.2 Software Reliability ................................................................................................................................7-3
7.1.3 Reliability of Charging System ..............................................................................................................7-5
7.2 Security Design ................................................................................................................................................7-6
7.2.1 Networking Application Security ...........................................................................................................7-6
7.2.2 Data Security...........................................................................................................................................7-6
7.2.3 O&M Security.........................................................................................................................................7-7
7.2.4 Security Authentication Information ......................................................................................................7-7
8 Technical Specifications and Environmental Requirements ............................................8-1
8.1 Technical Specifications...................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.1 System Capacity......................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.2 System Processing Capability.................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.3 Protocol Processing Capability...............................................................................................................8-3
8.1.4 CDR Processing Capability ....................................................................................................................8-3
8.1.5 Number Analysis Capability...................................................................................................................8-4
8.1.6 Reliability Specifications........................................................................................................................8-4
8.1.7 Environmental Specifications.................................................................................................................8-4
8.1.8 Mechanical Data of Cabinet ...................................................................................................................8-5
8.1.9 Power Supply ..........................................................................................................................................8-6
8.1.10 Power Consumption..............................................................................................................................8-6
8.2 Introduction to Clock Synchronization System...............................................................................................8-8
8.2.1 Technical Features...................................................................................................................................8-8
8.2.2 Technical Specifications .........................................................................................................................8-8
8.3 EMC Specifications........................................................................................................................................8-10
8.4 Environmental Requirements.........................................................................................................................8-10
8.4.1 Storage Environment.............................................................................................................................8-10
8.4.2 Transportation Environment .................................................................................................................8-12
8.4.3 Running Environment...........................................................................................................................8-15
9 Compliant Specifications .........................................................................................................9-1
9.1 3GPP Specifications .........................................................................................................................................9-2
9.2 ITU-T Specifications........................................................................................................................................9-6
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary iii
Page 4

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Contents
9.3 Other Technical Specifications.........................................................................................................................9-9
Product Description
10 Installation...............................................................................................................................10-1
iv Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 5

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description Figures
Figures
Figure 1-1 Huawei mobile softswitch solution .....................................................................................................1-2
Figure 1-2 MSOFTX3000 in 2G/3G integration networking.............................................................................1-13
Figure 2-1 Appearance of an MSOFTX3000 cabinet ...........................................................................................2-2
Figure 2-2 Overall structure of the OSTA subrack ...............................................................................................2-3
Figure 2-3 Hardware structure of the MSOFTX3000...........................................................................................2-4
Figure 2-4 Logical structure of the MSOFTX3000 hardware..............................................................................2-6
Figure 2-5 Software structure of the MSOFTX3000............................................................................................2-8
Figure 2-6 Relationship between BAM server software, operating system, and database................................ 2-11
Figure 2-7 Configuration of MSOFTX3000 cabinets (when the NET Switch is configured in the integrated
configuration cabinet)...........................................................................................................................................2-12
Figure 2-8 Configuration of MSOFTX3000 cabinets (when the NET Switch is configured outside the cabinet)
...............................................................................................................................................................................2-13
Figure 2-9 Expansion configuration of the MSOFTX3000................................................................................2-14
Figure 3-1 Protocol interfaces provided by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile network .........................................3-5
Figure 4-1 Network structure of the terminal system ...........................................................................................4-3
Figure 5-1 Networking model of Overlay network mode ..................................................................................5-21
Figure 5-2 Networking model of target network mode ......................................................................................5-22
Figure 5-3 Mini-A-Flex networking ...................................................................................................................5-32
Figure 5-4 Iu-Flex network architecture .............................................................................................................5-33
Figure 5-5 Ordinary encoding and decoding speech operation..........................................................................5-36
Figure 5-6 Encoding and decoding speech operation after activating TFO.......................................................5-36
Figure 5-7 Encoding and decoding speech operation after activating TrFO......................................................5-37
Figure 6-1 MSC networking..................................................................................................................................6-2
Figure 6-2 GMSC networking...............................................................................................................................6-5
Figure 6-3 TMSC networking ...............................................................................................................................6-6
Figure 6-4 1+1 backup networking.......................................................................................................................6-8
Figure 6-5 1+1 mutual assistance networking ......................................................................................................6-8
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary v
Page 6

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Figures
Figure 6-6 N+1 backup networking (N = 2) .........................................................................................................6-9
Figure 6-7 N+1 mutual assistance networking (N = 2) ......................................................................................6-10
Figure 6-8 MA networking ..................................................................................................................................6-11
Figure 6-9 Networking structure for Huawei NGN interworking with the CS domain ....................................6-12
Figure 6-10 Evolution strategy of Huawei mobile core network .......................................................................6-12
Figure 6-11 Solution of Huawei R5 ....................................................................................................................6-13
Figure 6-12 Multi-area commercial network of company A ..............................................................................6-14
Figure 6-13 Dual-homing commercial network of company B .........................................................................6-15
Figure 8-1 Maximum allowed input jitter and lower limit of wander..................................................................8-9
Product Description
vi Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 7

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description Tab les
Tables
Table 1-1 Functions of the MSC server and the MGW ........................................................................................1-3
Table 1-2 Benefits offered by mobile softswitch networks ..................................................................................1-5
Table 1-3 Protocols ................................................................................................................................................1-7
Table 1-4 Related abbreviations ............................................................................................................................1-8
Table 1-5 Protocols, links, and signaling modes supported and interfaces provided by the MSOFTX3000......1-9
Table 1-6 Measures taken in designing the MSOFTX3000................................................................................1-11
Table 3-1 Numbers and functions of physical interfaces ......................................................................................3-2
Table 3-2 Specifications of FE electrical interfaces.............................................................................................. 3-3
Table 3-3 Specifications of E1 interfaces..............................................................................................................3-3
Table 3-4 Specifications of clock interfaces..........................................................................................................3-4
Table 3-5 Interfaces and protocols supported by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile network .................................3-5
Table 3-6 Signaling and protocols supported by the MSOFTX3000. ..................................................................3-7
Table 5-1 Original CDR generation scenario......................................................................................................5-16
Table 5-2 List of the features supported by the MSOFTX3000 .........................................................................5-22
Table 7-1 Security authentications ........................................................................................................................7-7
Table 8-1 System capacity .....................................................................................................................................8-2
Table 8-2 Reference traffic model .........................................................................................................................8-2
Table 8-3 System processing capability ................................................................................................................8-2
Table 8-4 Protocol processing capability ..............................................................................................................8-3
Table 8-5 CDR processing capability....................................................................................................................8-3
Table 8-6 Number analysis capability ...................................................................................................................8-4
Table 8-7 Reliability specifications .......................................................................................................................8-4
Table 8-8 Environmental adaptation (long term operation)..................................................................................8-4
Table 8-9 Noise specifications...............................................................................................................................8-5
Table 8-10 Mechanical data of cabinet..................................................................................................................8-5
Table 8-11 Power supply........................................................................................................................................8-6
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary vii
Page 8

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Tabl es
Table 8-12 Overall power consumption ................................................................................................................8-6
Table 8-13 Power consumption (functional units) ................................................................................................8-7
Table 8-14 Technical specifications of the clock synchronization system...........................................................8-8
Table 8-15 Climate environment requirements (for storage)..............................................................................8-10
Table 8-16 Density requirements for mechanically active materials (for storage) ............................................8-11
Table 8-17 Density requirements for chemically active materials (for storage) ................................................8-11
Table 8-18 Mechanical stress requirements (for storage)...................................................................................8-11
Table 8-19 Waterproof requirements ...................................................................................................................8-12
Table 8-20 Climate environment requirements (for transportation)...................................................................8-12
Table 8-21 Density requirements for mechanically active materials (for transportation)..................................8-13
Table 8-22 Density requirements for chemically active materials (for transportation) .....................................8-13
Table 8-23 Mechanical stress requirements (for transportation) ........................................................................8-14
Table 8-24 Temperature and humidity requirements ..........................................................................................8-15
Table 8-25 Other climate environment requirements..........................................................................................8-15
Product Description
Table 8-26 Density requirements for mechanically active materials (for equipment running) .........................8-16
Table 8-27 Density requirements for chemically active materials (for equipment running) .............................8-16
Table 8-28 Mechanical stress requirements (for equipment running) ................................................................8-16
Table 9-1 The compliant 3GPP R4 specifications (2004.12) of the MSOFTX3000............................................9-2
Table 9-2 The compliant ITU-T specifications of the MSOFTX3000.................................................................9-6
Table 9-3 Technical specifications.........................................................................................................................9-9
viii Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 9
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
1 Introduction
About This Chapter
The following table lists the contents of this chapter.
Section Describes
1.1 Product Orientation Huawei mobile softswitch solution and the
MSOFTX3000.
1.2 Product Features Features of the MSOFTX3000.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-1
Page 10
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
parts, namely, the MSC server and the MGW, in the 3GPP R4 and later versions.
Table 1-1
describes the function of the MSC server and the MGW.
Table 1-1 Functions of the MSC server and the MGW
Network
Function Product
Element
MSC
server
It connects with the BSS or the UTRAN,
and performs the following control
functions of the CS domain:
z
Mobility management
z
Security management
z
Handover processing
z
Signaling processing
z
Call processing
z
Subscriber data management (function
of the VLR)
MGW It is the endpoint of the MSOFTX3000's
connection with the PSTN or the PLMN,
and performs the following functions:
z
Media transformation
z
Bearer management
z
Coding/Decoding of digital signals
z
Echo cancellation
z
Conference bridging
The MSOFTX3000 provided by
Huawei serves as an MSC
server, as shown in
Figure 1-1.
The UMG8900 provided by
Huawei serves as an MGW, as
shown in
Figure 1-1.
PLMN = Public Land Mobile Network
1.1.2 Features of Huawei Mobile Softswitch Solution
Support for 2G/3G Integration
The carriers who are operating or will operate on both 2G and 3G networks must consider
how toprotect the investment in the 2G network when expanding it.
Huawei offers a combined GSM/UMTS solution to help carriers solve the problem. This
solution supports that the BSS and the UTRAN can connect to the network simultaneously, so
as to provide services for 2G and 3G subscribers at the same time. The 2G and 3G networks
can share equipment resources. Therefore, the solution has the following benefits:
z
Reducing the capital expenditure (CAPEX) of carriers
z
Improving subscriber satisfaction
z
Unifying network operation
z
Simplifying network topology
z
Saving network resources
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-3
Page 11

1 Introduction
This solution can be upgraded online and configured dynamically during the evolution from
the GSM to the UMTS.
High Efficiency
In Huawei mobile softswitch solution, MGWs can be located in many cities, and IP bearers
can be used between MGWs. This simplifies the network interconnection topology and
network management, and saves transmission resources for carriers.
The Huawei mobile softswitch equipment enjoys:
z
z
z
It saves equipment room space, and reduces the power consumption. Carriers can focus their
O&M on a small number of softswitch offices, thereby reducing the operation expenditure
(OPEX).
On the basis of an open architecture and distributed software technology, the Huawei mobile
softswitch solution helps carriers quickly develop services. Statistics shows that the
development cycle of services based on mobile softswitch networks is 50% shorter than that
based on conventional switching equipment.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
High integration
Large capacity
Powerful processing capability
Highly Reliable
The innovative dual homing solution provided by Huawei ensures the high reliability (1+1
mutual aid and N + 1 backup) for MSC Servers. It supports the Iu-Flex scheme, as well as
multiple backup modes of HLR. Based on specific conditions, Huawei is able to use these
modes flexibly.
With the network-level flow control mechanism, Huawei ensures that the voice quality is not
affected when the IP bearer network is congested. The advanced flow control mechanism
ensures that the network remains highly reliable even when traffic is heavy.
Smooth Evolution
The fixed mobile convergence (FMC) is the trend of network development. During this
process, it is important to integrate the equipment of fixed and mobile networks. At present,
Huawei provides a number of devices that can be used in both fixed and mobile networks, and
also provides integrated services.
In the future, the fixed and mobile networks can be integrated through the IMS subsystem at
the network level. The Huawei mobile softswitch equipment MSC Server and MGW can also
be evolved to the equipment in IMS smoothly. This saves the capital expenditure (CAPEX)
for carriers.
More Benefits
Compared with the conventional switched circuit network (SCNs), mobile softswitch
networks offer carriers the benefits, as listed in
Table 1-2:
1-4 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 12
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
1 Introduction
Product Description
1.1 Product Orientation
1.1.1 Introduction to Huawei Mobile Softswitch Solution
By separating the bearer from the control, a networking model with the softswitch technology
as the core can use bearer networks such as the IP and TDM. This is a key feature of the
softswitch technology. At present, the softswitch technology is chosen by most carriers to
build mobile core networks (CNs). By using distributed networking mode and IP bearers,
mobile softswitches offer carriers the following benefits:
z
Reducing operation costs by improving the efficiency of network transmission
z
Protecting the carrier investment by providing smooth evolution from one model to
another as the subscriber base and traffic increases
The mobile softswitch solution of Huawei is based on the networking requirements and
network features of carriers. It provides a 2G or 3G integration networking scheme that is
easy to operate and maintain. The solution supports networking schemes of the GSM, 3GPP,
R99, 3GPP R4, and 3GPP R5.
softswitch solution of Huawei for 3GPP R4.
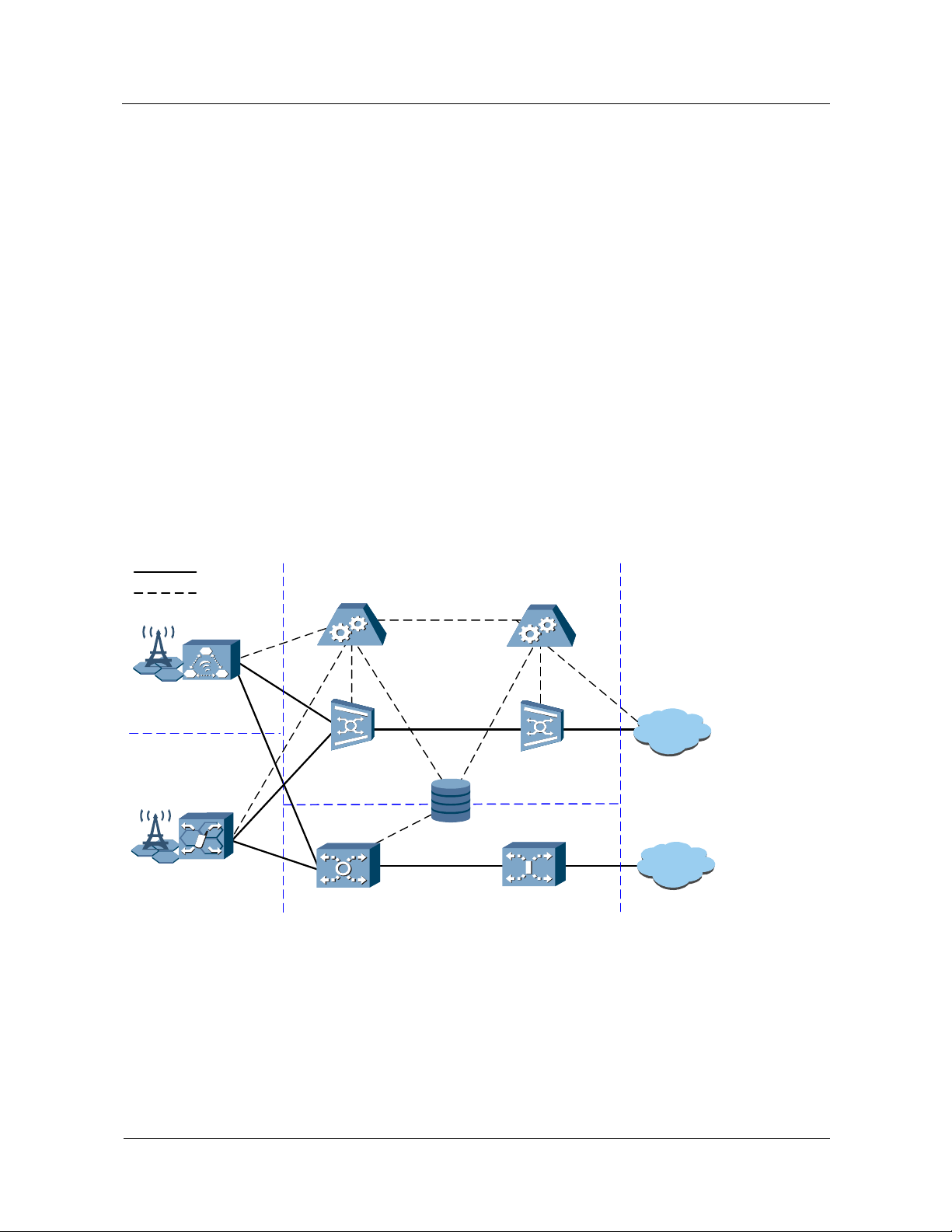
Figure 1-1 shows a typical networking model of the mobile
Figure 1-1 Huawei mobile softswitch solution
Bearer
Signaling
BSS
2G Access
3G Access
UTRAN
GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node HLR: Home Location Register MGW: Media Gateway
MSC Server: Mobile Switching Center Server CN: Core Network CS: Circuit Switched domain
SGSN: Serving GPRS Support Node PS: Packet Switched domain PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network
UTRAN: UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network BSS: Base Station Subsystem
MSC Server
(MSOFTX3000)
MGW
(UMG8900)
SGSN
CN
HLR
GMSC Server
(MSOFTX3000)
MGW
(UMG8900)
GGSN
CS
PS
Other
Networks
PSTN
Internet
Based on the evolution strategy of the CS domain of the mobile CN and the requirement for
constructing an all IP networking, the MSC in the GSM and 3GPP R99 is divided into two
1-2 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 13
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
Table 1-2 Benefits offered by mobile softswitch networks
Benefit Description
The CAPEX is
lowered.
The OPEX is
lowered.
In contrast to the closed structure of the conventional SCN, a
mobile softswitch network uses the following to provide services:
A control core
Open interfaces
Universal protocols
It helps carriers to build an open and low-cost network and
improve the speed of service deployment. The mobile softswitch
technology also enables smooth migration from 2G to 3G and IMS
networks. This decrease the CAPEX for network migration.
The centralized mobile softswitch equipment with large capacity
has higher equipment resource utilization in the following aspects:
z
The distributed media gateway reduces alternative routes in local
transmission.
z
The flat networking mode does not require the construction of
tandem layer.
z
IP bearer cuts down the transmission costs for the whole
network.
Statistics shows that the CAPEX of a mobile softswitch network is
20% to 30% lower than that of a conventional SCN.
Compared with the conventional switching equipment, the mobile
softswitch equipment enjoys:
z
Better processing capability
z
A higher level of integration
z
Lower power consumption
This helps save 60% to 70% of the equipment room area and 30%
power consumption. With the bearer separated from the control,
the core of the mobile softswitch network can be located and
managed in a centralized manner. This reduces the network O&M
costs.
Network security is
enhanced.
The mobile softswitch network uses network-level reliability
mechanisms, such as the following:
z
Dual homing
z
Iu-Flex
The dual homing mode realizes the backup of mobile softswitch
equipment. When a mobile softswitch is faulty, the system can
smoothly switch the service to the standby softswitch. This ensures
that the service is not affected.
The Iu-Flex technology enables networks to share multiple CN
equipment nodes. Hence, services are not affected when a single
MGW is faulty and the network is more secure .
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-5
Page 14
1 Introduction
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Benefit Description
New services can be
offered quickly and
easily
New services can be provided on the mobile softswitch layer
without affecting the MGW in the bearer layer. Therefore, the
mobile softswitch network allows users to develop and offer new
services more flexibly and quickly in the following ways:
z
The open network structure shortens the cycle of developing
services.
z
Centralized service management makes service deployment
easy.
z
The network supports SIP. This enhances the capability of
providing multimedia services.
Note:
CAPEX = Capital Expenditure; OPEX = Operational Expenditure; SIP = Session Initiation Protocol
1.1.3 Introduction to the MSOFTX3000
Overview
The HUAWEI MSOFTX3000 Mobile SoftSwitch Center (called MSOFTX3000 in this
manual) is a large capacity mobile softswitch developed by Huawei. It provides:
z
Advanced software and hardware technologies
z
Dynamic service provision capabilities
z
Powerful networking functions
The MSOFTX3000 serves as the MSC server at the control layer of the CS domain in the
WCDMA core network. It implements functions, such as call control and connection
management for voice and data services based on IP or TDM.
By supporting protocols and functions of both the GSM and the WCDMA, the MSOFTX3000
allows for smooth evolution from the GSM to the WCDMA. With the bearer separated from
the control, the MSOFTX3000 can function as the core of a network with different bearer
networks such as IP and TDM. During the upgrade of the CN of the mobile network (GSM ->
3GPP R99 -> 3GPP R4 -> 3GPP R5), the MSOFTX3000 can serve as many network elements
(NEs), including the following:
z
VMSC Server/VLR
z
GMSC Server
z
TMSC Server
z
MSC/SSP
VMSC Server/VLR
The MSOFTX3000 supports many protocols, including H.248, BICC, SIP, CAP, BSSAP,
RANAP, MAP, ISUP, TUP, and BSSAP+. It can provide the functions of a VMSC server and
a VLR. When connected with the UMG8900 and the shared interworking function (SIWF) of
Huawei, the MSOFTX3000 supports the BSS/UTRAN access and can serve as a 2G VMSC, a
3G VMSC, or a 2G/3G integrated VMSC.
1-6 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 15
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
Tab le 1-3 lists the protocols.
Table 1-3 Protocols
Abbreviation Full Name
BICC Bearer Independent Call Control Protocol
CAP CAMEL Application Part
BSSAP Base Station Subsystem Application Part
RANAP Radio Access Network Application Part
MAP Mobile Application Part
ISUP Integrated Services Digital Network User Part
TUP Telephone User Part
BSSAP+ Base Station Subsystem Application Part+
When the MSOFTX3000, UMG8900, and SIWF of Huawei are used together in the GSM or 3GPP R99,
they are called the MSC9880.
GMSC Server
The GMSC server is a node between the CS domain of the CN and external networks. With
the GMSC server, a mobile network can exchange signaling with the following:
z
PSTN
z
NGN
z
Integrated services digital network (ISDN)
z
Other PLMNs
The GMSC server performs the following functions:
z
Serving as a mobile gateway office between networks
z
Analyzing routing
z
Implementing call connection and settlement between networks
The MSOFTX3000 supports H.248, MAP, and ISUP. It provides the following functions:
z
Black and white lists
z
Call authentication
z
Call interception
z
Storage of a large number of CDRs
When connected with the UMG8900 of Huawei, the MSOFTX3000 can serve as a GMSC
server.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-7
Page 16
1 Introduction
TMSC Server
MSC/SSP
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
As a toll tandem office, the TMSC server performs the following functions:
z
Routing analysis
z
Intra-network toll call convergence
In applications, a layered structure is used in a large network. The MSOFTX3000 supports
H.248, ISUP, and BICC. When connected with the UMG8900 of Huawei, the MSOFTX3000
can serve as a TMSC server. It provides a large number of TDM trunks or IP bearer channels.
The MSOFTX3000 can provide the functions of a gsmSSF. It supports CAP, CAMEL 1,
CAMEL 2, CAMEL 3, and CAMEL 4. In the target network mode, the MSOFTX3000 can
serve as an SSP.
The MSOFTX3000 can also support the Overlay network mode and trigger mobile IN
services based on number segments.
Tab le 1-4 lists related abbreviations.
Table 1-4 Related abbreviations
Abbreviation Full Name
SSF Service Switching Function
CAP CAMEL Application Part
INAP Base Station Subsystem Application Part
CAMEL Customized Applications for Mobile Network Enhanced Logic
SSP Service Switching Point
IP Intelligent Peripheral
IN Intelligent Network
1.2 Product Features
1.2.1 Dynamic Service Provision Capabilities
The MSOFTX3000 supports protocols and functions of both the GSM and the WCDMA. It
can also serve as different types of NEs, and provides the following services:
z
Basic services: voice, SMS, GSM fax, GSM bearer, and UMTS bearer
z
Supplementary services: call forwarding, call restriction, number identification, call
completion, multiparty, unstructured data transfer, closed user group, explicit call
transfer, and enhanced multi-level precedence and preemption
z
Operator determined barring services: barring of all outgoing calls, barring of outgoing
international calls, barring of outgoing international calls except those to the home
1-8 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 17
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
PLMN country, barring of all incoming calls, barring of supplementary management, and
barring of incoming calls when roaming outside home PLMN country
z
IN services: prepaid and mobile virtual private network
z
Value-added service: multimedia, mobile location, ring back tone, equal access, charging
based on time and area, enhanced roaming restriction, alternate line service, and voice
and video double number
1.2.2 Powerful and Flexible Networking Capabilities
The MSOFTX3000 provides open and standard interfaces. It supports GSM, 3GPP R99, and
3GPP R4 networking and allows smooth upgrades and expansion.
links, and signaling modes supported, and interfaces provided by the MSOFTX3000 to
interwork with other NEs.
Table 1-5 Protocols, links, and signaling modes supported and interfaces provided by the
MSOFTX3000
Table 1-5 lists the protocols,
Protocol,
Interface Interworking and Benefits
Link and
Signaling
Mode
H.248 Mc For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the MGW
BSSAP A For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the BSC when
the MSOFTX3000 is connected with the MGW
RANAP Iu For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the RNC in a
WCDMA network when the MSOFTX3000 is connected
with the MGW
MTP, TUP,
and ISUP
MAP C, D, E,
- For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the STP and
PSTN switches
For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the HLR, VLR,
G, and Lg
MSC, SMC, and GMLC in a GSM or WCDMA network
CAP - For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the SCP in an
IN
SIP - For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the IMS or
NGN
BICC - Provides the Nc interface for the MSOFTX3000 to
interconnect with the MSC server
BSSAP+ Gs For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the SGSN in
the PS domain
SIGTRAN
(M2UA,
- For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the SG and the
MGW with built-in SG function
M3UA, and
IUA)
R2 - For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with PSTN switches
that support only R2
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-9
Page 18
1 Introduction
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Protocol,
Interface Interworking and Benefits
Link and
Signaling
Mode
PRA - For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the PBX
Supporting
virtual multiple
signaling point
codes
- Meets the requirements of a large number of trunks in the
case of GMSC networking.
Improves reliability of networking by using load sharing
networking mode between virtual multiple signaling points
and remote signaling points.
TDM 2-Mbit/s
links
- Improves the traffic capacity between two signaling points,
simplifies signaling networking, and lowers network
construction costs.
ATM 2-Mbit/s
links
- Supports ATM bearer through E1 demultiplexing, provides
flexible networking schemes, reuses existing equipment
and transmission resources, and reduces network
construction costs. At present, the ATM 2-Mbit/s links
support the MAP signaling only.
Satellite
transmission
Mc and Iu Makes networking more flexible and networks more
adaptive to ground conditions.
links
FTP and
FTAM
- For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the billing
center
MML - For the MSOFTX3000 to interconnect with the NMC
Note:
NMC: Network management center
1.2.3 Large Capacity and High Integration
The MSOFTX3000 provides the advanced hardware technology, featuring modular hardware
structure, large capacity, and high integration:
z
All boards use advanced integrated circuits such as the ASIC, PLD, and FPGA. This
simplifies the MSOFTX3000 and improves the integration of the system.
z
In full configuration, the MSOFTX3000 can support up to 1.8 million subscribers
(serving as a VMSC) or 450 thousand TDM circuits (serving as a TMSC).
z
The MSOFTX3000 in full configuration requires only three cabinets, thus occupying less
space. In addition, the power consumption of the MSOFTX3000 is low (less than six
kW).
1.2.4 Powerful Processing Capabilities
With a distributed hardware structure, high performance chips, high speed buses, and high
speed PowerPC processors, the MSOFTX3000 provides powerful processing capabilities (the
following data is based on the full configuration):
1-10 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 19
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
z
When serving as a VMSC server, the MSOFTX3000 supports up to 2700k BHCA.
z
When serving as a GMSC server, the MSOFTX3000 supports up to 7200k BHCA.
z
When serving as a TMSC server, the MSOFTX3000 supports up to 9000k BHCA.
1.2.5 Highly Reliable
The MSOFTX3000 is highly reliable, because the following are carefully designed
z
Hardware
z
Software
z
Billing system
For details, see
Table 1-6.
Table 1-6 Measures taken in designing the MSOFTX3000
Item Measure
Hardware design
z
Active/standby backup, load sharing, and redundancy techniques
for boards.
z
Optimized fault detection and isolation techniques. This improves
the system maintenance.
z
Dual connections for important components and dual plane and
mesh connection design. This ensures that the system is not
affected when a single node is faulty.
Software design Layered modular structures which enable the protection, fault
tolerance, and fault monitoring functions of the software
Billing The billing gateway of the MSOFTX3000 is the iGWB of Huawei.
The iGWB uses dual system hot backup and Hot RAID5 hard disk
array. This enables dual backup of billing data and mass storage.
The reliability assessment method adopted shows the following:
z
The MTBF of the MSOFTX3000 reaches 24 years (in full configuration)
z
The MTBF of the MSOFTX3000 reaches 42 years (when configured with only one
subrack).
z
The MTTR of the MSOFTX3000 is lesser than one hour (not considering the preparation
time).
MTBF is short for Mean Time Between Failure. MTTR is short for Mean Time To Repair.
1.2.6 Capabilities for Smooth Expansion
The designs of the hardware and the system processing function of the MSOFTX3000 take
future network expansion into account. The MSOFTX3000 supports smooth expansion of
networks:
z
Hardware design: The MSOFTX3000 uses the open standards telecom architecture
(OSTA) platform as the hardware platform. The OSTA provides a modular overlay
structure. The number of subracks ranges from 1 to 10. The subracks are connected
through LAN Switches to help in smooth expansion.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-11
Page 20

1 Introduction
z
System processing function design: The MSOFTX3000 provides excellent processing
performance and reserves space for future service expansion.
1.2.7 Advanced Charging Capabilities
The MSOFTX3000 supports the charging of many services, including the following:
z
Vo i c e ,
z
Data service
z
Vide o servic e
z
SMS
z
Supplementary services
With over 40 types of original CDRs, the MSOFTX3000 offers different types of charging.
The features of charging are as follows:
z
Supporting CDR types, such as mobile-originated call ticket, mobile-terminated call
ticket, call forwarding ticket, transit ticket, mobile-originated SMS ticket,
mobile-terminated SMS ticket, outgoing gateway exchange ticket, incoming gateway
exchange ticket, roaming ticket, supplementary service ticket, IN mobile-originated call
ticket, IN mobile-terminated call ticket, IN call forwarding ticket, and IN pickup ticket
z
Supporting the storage of CDRs based on modules, services, or time
z
Supporting standard FTP and FTAM charging interfaces
z
Supporting a charging accuracy of 10 milliseconds
z
Supporting the generation of intermediate CDRs
z
Supporting the call restriction function in the case of CDR pool threshold crossing
z
Supporting hot billing
z
Supporting Advice of Charge
z
Supporting IN announcement charging
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
1.2.8 Excellent Performance Measurement Function
The MSOFTX3000 provides excellent performance measurement (PM) functions. And
supports many PM entities and tasks. It uses tables and figures to display data in real time and
report service loading and system running status. The performance measurement features of
the MSOFTX3000 are as follows:
z
Supporting the measurement and record of traffic (up to 200 tasks and 3,000 short or
1,000 long subtasks can be run at the same time; up to 4,000 measurement objects are
supported)
z
Predefining measurement items and time, automatically starting and stopping
measurement at specified time on specified dates, canceling predefined items, and
measuring one or many items based on the actual requirements
z
Supporting at least four measurement periods every day for predefined measurement
items and automatically exporting measurement results to terminals and network
management centers
z
Supporting the measurement of the number of times that a supplementary service is
activated or cancelled
z
Supporting the performance measurement of the IP port traffic of the softswitch system
1-12 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 21
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 1 Introduction
1.2.9 Convenient and Useful O&M Function
The MSOFTX3000 provides convenient and useful O&M functions:
z
The MSOFTX3000 provides many O&M modes. The terminal system of the
MSOFTX3000 is based on the Client/Server distributed structure. It provides several
maintenance modes, such as the graphic user interface (GUI) and man machine language
(MML) commands. Local and remote clients can access the MSOFTX3000 at the same
time. Carriers can set up management network based on network components,
management requirements, and investment scale.
z
The MSOFTX3000 provides the GUI with a special navigation tree. The GUI is visual,
which minimizes the need for memory. The GUI features graphic topology views of
network components and device panel views.
z
The MSOFTX3000 provides the call tracing, signaling tracing, and interface tracing
functions, as well as message the explanation function. The trace viewer tool allows
operators to analyze and locate faults easily.
z
The MSOFTX3000 supports the real time fault management function based on H.248.
The system receives and displays fault reports of network equipment in real time. This
helps operators to find the source of a fault quickly and take measures to restore the
services.
z
The MSOFTX3000 supports hot software patches, dynamic data setting, and quick
version upgrade/rollback.
z
The MSOFTX3000 supports the associated subscriber tracing functions to provide the
entire network tracing feature. This helps carriers troubleshoot faults by locating the
faults. Therefore, carriers can effectively process subscribers' complains.
1.2.10 Support for 2G/3G Integration
The MSOFTX3000 supports mixed networking and interworking of GSM, 3GPP R99, 3GPP
R4, and 3GPP R5 networks. That is, the MSOFTX3000 supports the 2G/3G integrated
networking. It can connect with the BSS and UTRAN and provide services for 2G and 3G
subscribers at the same time.
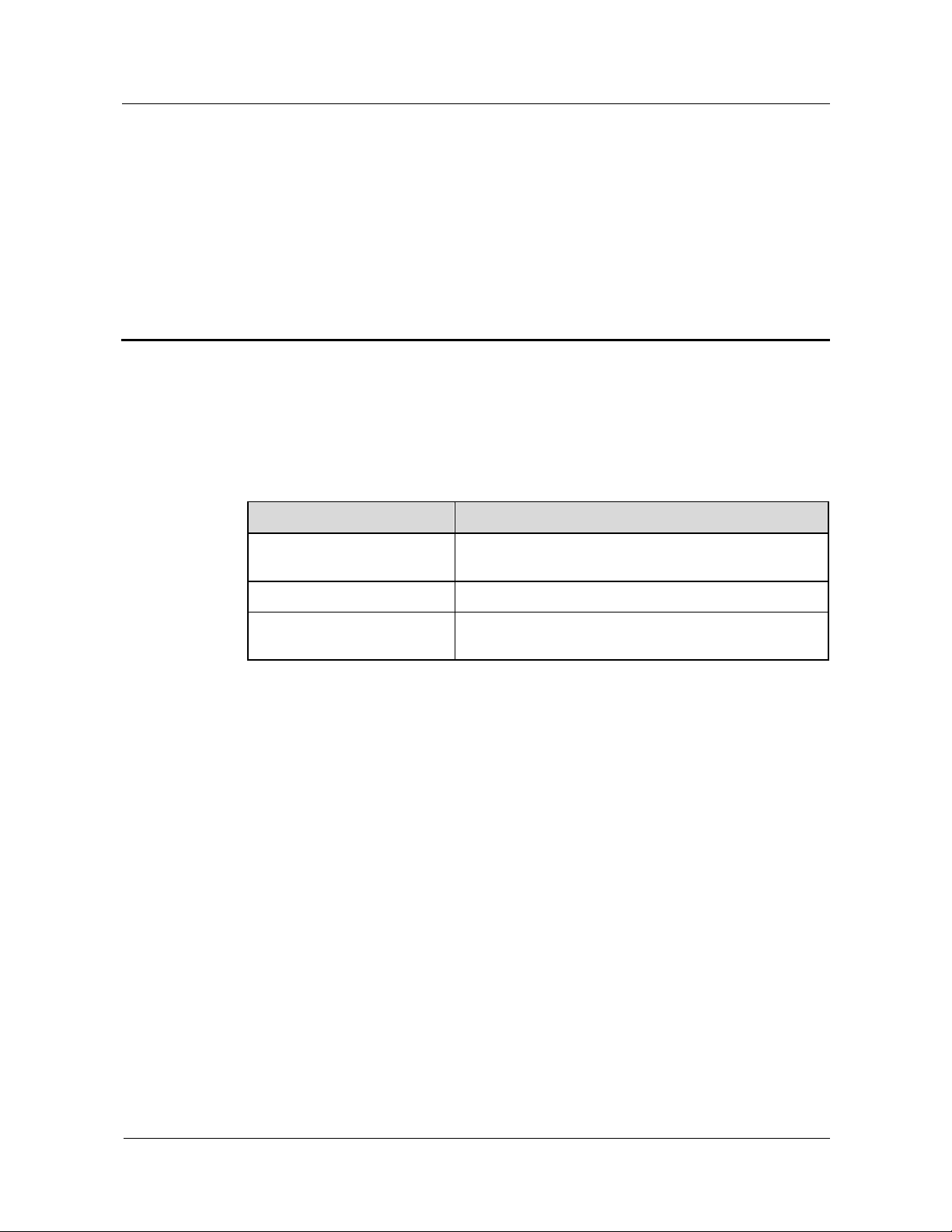
Figure 1-2 MSOFTX3000 in 2G/3G integration networking
MSC
MSOFTX3000
A
BSS
Iu-CS
UMG8900
UTRAN
Figure 1-2 shows a typical networking model.
TUP/ISUP
BICC
GM SC
MSOFTX3000
UMG8900
TUP/ISUP
PSTN/
PLMN
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 1-13
Page 22

1 Introduction
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
In the 2G/3G integration networking structure, the MSOFTX3000 and the UMG8900 can be
used as an MSC (GMSC or TMSC) function entity:
z
The MSC provides A and Iu-CS interfaces to support the access of GSM and UMTS
subscribers. One MSOFTX3000 can be connected with many UMG8900s. The
UMG8900 can be located remotely.
z
The MSOFTX3000 allows subscribers' handover between GSM and UMTS systems.
The MSOFTX3000 enables the network to control the subscriber access.
z
GSM and UMTS subscribers can access the MSOFTX3000 at the same time. This makes
network upgrades smooth, and services of original subscribers of the network are not
affected during the upgrades.
1-14 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 23
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
2 System Structure
About This Chapter
The following table lists the contents of this chapter.
Section Describes
2.1 Hardware Structure The physical and logical structures of the MSOFTX3000
hardware.
2.2 Software Structure The logical structure of the MSOFTX3000 software.
2.3 Capacity Expansion The normal and expanded configuration of the
MSOFTX3000 cabinets.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-1
Page 24

2 System Structure
2.1 Hardware Structure
2.1.1 Appearance
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
The MSOFTX3000 is composed of the N68-22 cabinets of Huawei.
appearance of an N68-22 cabinet:
Figure 2-1 Appearance of an MSOFTX3000 cabinet
Figure 2-1 shows the
The N68-22 cabinet is a 19-inch standard cabinet that complies with the following
international standards:
z
IEC60297-1, Dimensions of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series Part
1:Panels and racks
z
IEC60297-2, Dimensions of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series Part
2:Cabinets and pitches of rack structures
z
IEC60297-3, Dimensions of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series Part
3:Subracks and associated plug-in units
2.1.2 Physical Structure
Introduction to OSTA Platform
The OSTA platform is used in the MSOFTX3000 as the hardware platform. The platform uses
the Ethernet bus as the bus of the backplane. This ensures high reliability of the
2-2 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 25
2 System Structure
z
Alarm boards
z
Power boards (each occupies two standard slots)
The remaining 12 slots are used for service boards and interface boards.
Hardware Structure of the MSOFTX3000
The MSOFTX3000 hardware mainly consists of three parts:
z
OSTA subrack
z
BAM
z
iGWB (it is the billing gateway.)
BAM is short for Back Administration Module.
The OSTA subracks form the host of the MSOFTX3000. The host provides the functions of
signaling and service processing and resource management.
The BAM, the local maintenance terminals (LMTs) and the iGWB form the background of
the MSOFTX3000. The background offers the OAM functions and CDR management.
Figure 2-3 shows the hardware structure of the MSOFTX3000.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Figure 2-3 Hardware structure of the MSOFTX3000
FE
2×FE
2×FE
NET Switch 0
NET Switch 0
NET Switch 0
FE
NET Switch 1
NET Switch 1
NET Switch 1
FE
FE
FE
LAN Switch 0
LAN Switch 0
LAN Switch 0
LAN Switch 1
LAN Switch 1
LAN Switch 1
机框
机框
机框
Host
主机部分
0#
0# Subrack
1#
1# Subrack
2# Subrack
2#
9# Subrack
9#
FE: Fast Ethernet LMT: Local Maintenance Terminal
2×FE
FE
FE
FE
2×FE
2×FE
2×FE
To IP MAN
FE
FE
To IP MAN
FE
FE
iGWB
主用
Active iGWB
Standby iGWB
备用
Background
后台部分
EWS
iGWB
BAM
BAM
BAM
To Billing Center
FE
To Billing Center
LAN Switch
LAN Switch
LAN Switch
WS WS WS
WS WS WS
WS WS WS
To network
management
center
2-4 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 26

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
Inter-Device Communication
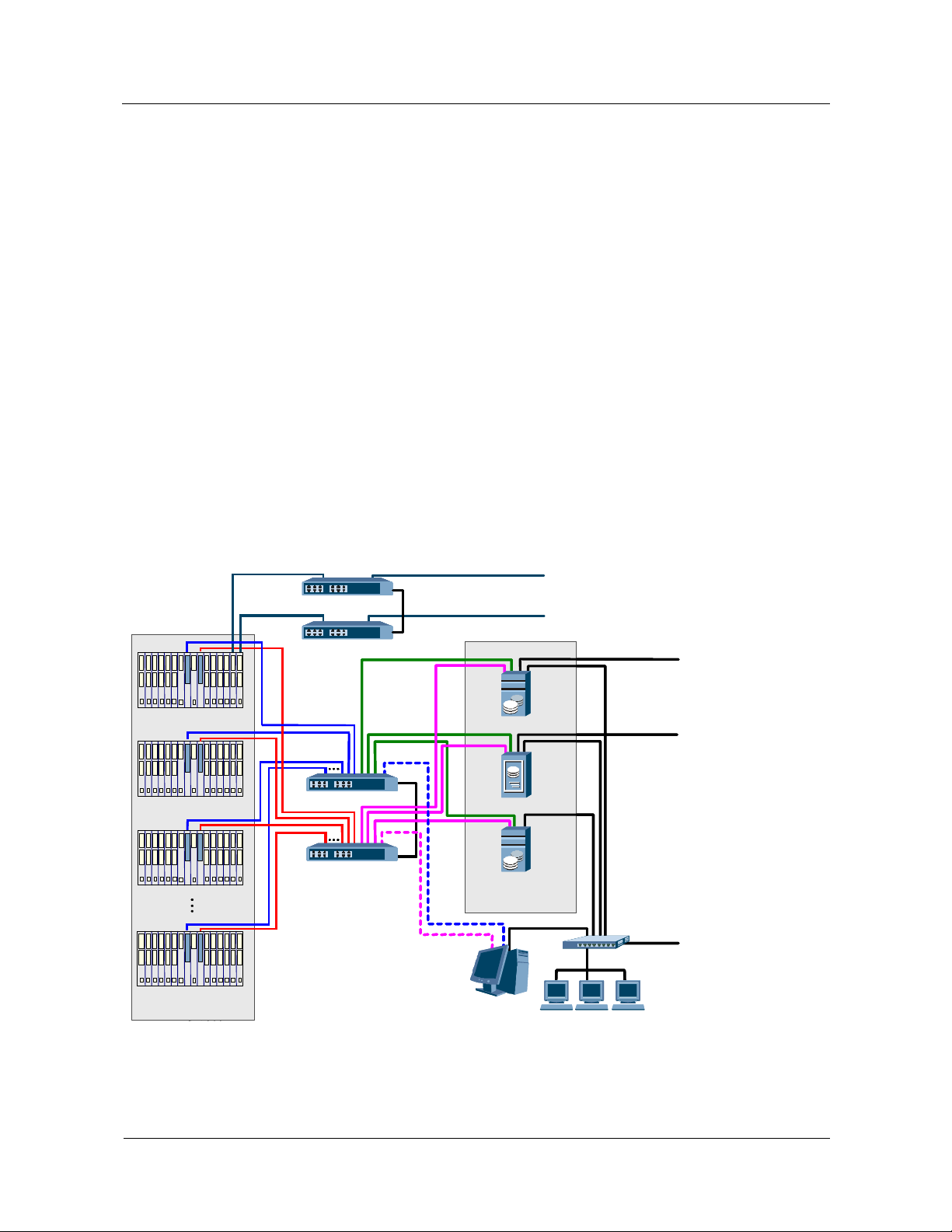
The inter-device communication of the MSOFTX3000 system is as follows:
z
The subracks communicate with each other through the internal Ethernet. Each subrack
is connected to LAN Switches 0 and 1 through two network cables.
z
The subracks communicate with the BAM and iGWB through the internal Ethernet. The
BAM and the iGWB are connected to the LAN Switches 0 and 1 through two network
cables.
z
The BAM and the iGWB are each connected to a LAN Switch through a network cable.
The LMTs interact with the BAM and the iGWB through the TCP/IP protocols in
client/server mode.
System Capacity
The system capacity is determined by the number of service processing subracks which
ranges from 1 to 10 in the MSOFTX3000. Hence, the MSOFTX3000 can expand its capacity
smoothly.
Complying With International Standards
The OSTA subracks and boards comply with the following international standards:
z
IEEE1101.1-1991, IEEE stand for Mechanical Core Specification for Microcomputers
Using IEC 60603-2 connectors
z
IEEE1101.10-1996, IEEE stand for Additional Mechanical Core Specification for
Microcomputers Using IEEE Std 1101.1-1991 Equipment Practice
z
IEEE1101.11-1998, IEEE stand for Mechanical Rear Plug-in Units Specification for
Microcomputers Using IEEE 1101.10 Equipment Practice
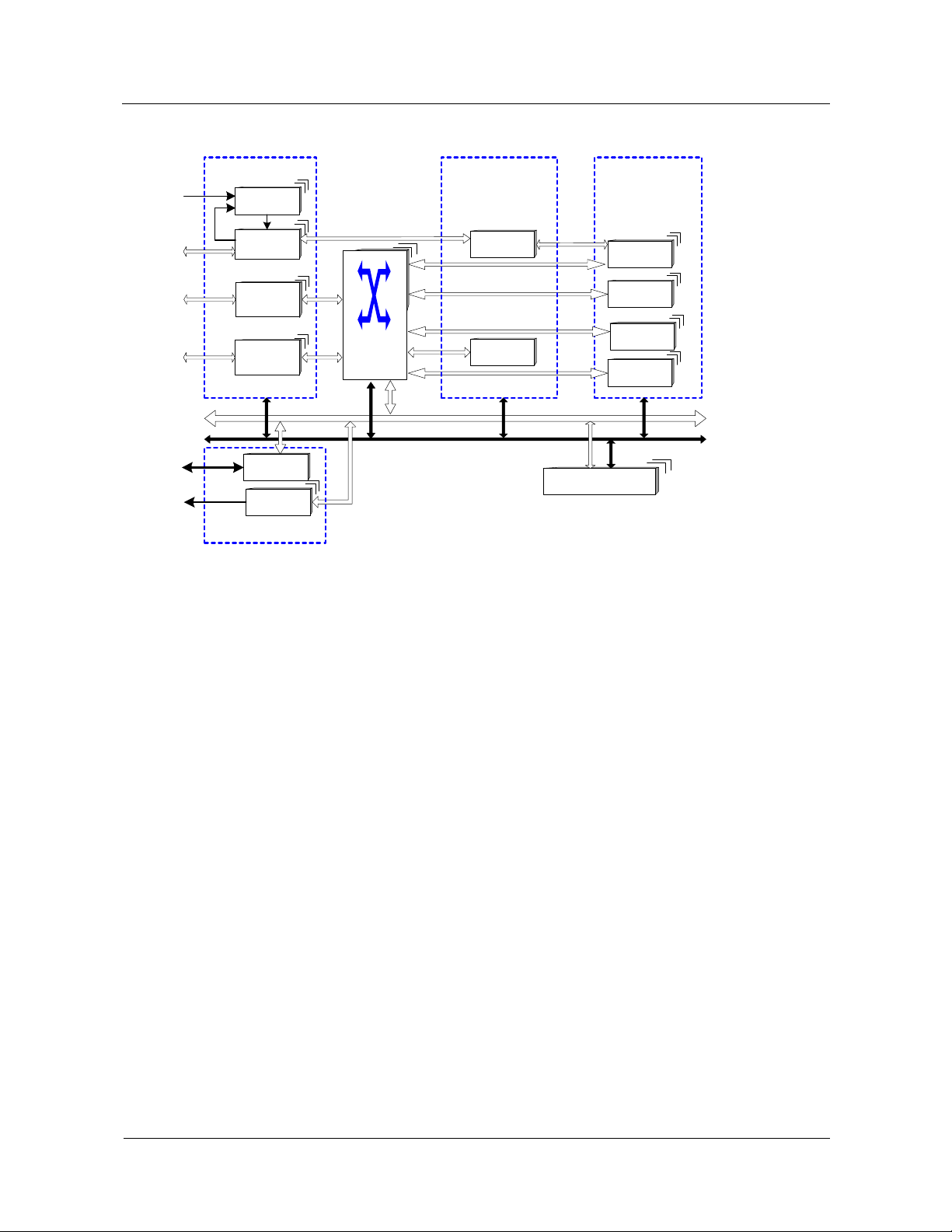
2.1.3 Logical Structure
The logical structure of the MSOFTX3000 hardware system includes five modules:
z
System support module (SSM)
z
Interface module (IM)
z
Signaling lower-layer processing module (SLLPM)
z
Service processing module (SPM)
z
Operation & maintenance module (OMM)
Figure 2-4 shows the logical structure of the MSOFTX3000 hardware.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-5
Page 27
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
MSOFTX3000. As a result, the MSOFTX3000 can exchange and transfer data packets of
variable lengths.
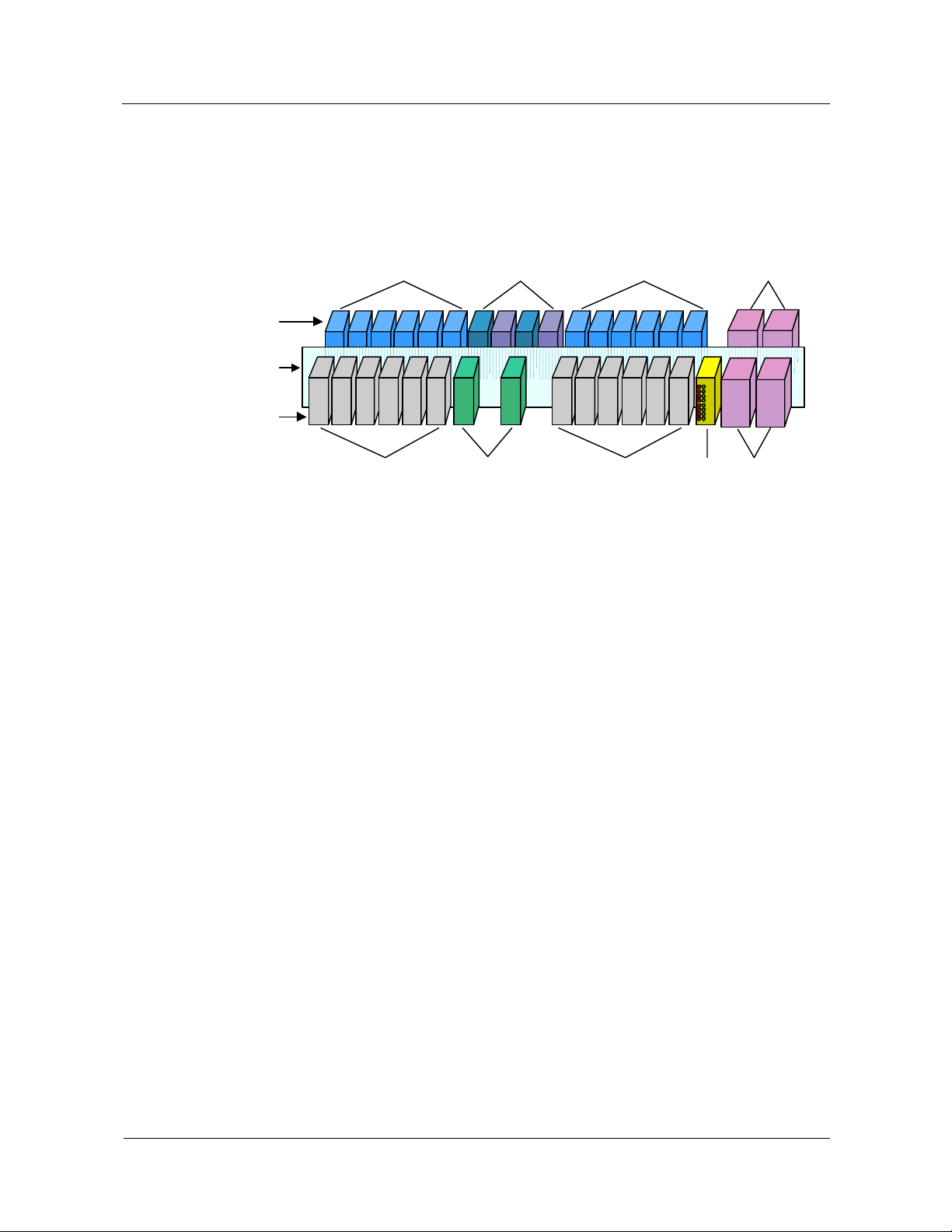
The OSTA platform is structured in a standard subrack, which is 19 inches wide and 9U high.
Front boards and back boards are installed, as shown in
Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 Overall structure of the OSTA subrack
(3) (1)(2) (2)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7) (8) (7) (9) (1)
(1) Power boards (2) Interface boards (3) Ethernet communication boards
(4) Back boards (5) Backplane (6) Front boards
(7) Service boards (8) System management boards (9) Alarm board
In the OSTA subrack, the front boards are:
z
Service boards
z
System management boards
z
Alarm boards
In the OSTA subrack, the back boards are:
z
Interface boards
z
Ethernet communication boards
Power boards can be installed either at the front or at the back. The front and back installation
mode separates the functions of the front boards from those of the back boards, and has the
following advantages:
z
Simplifying the board design
z
Unifying the board functions
z
Simplifying the hardware structure
z
Improving reliability of the system
z
Improving versatility of the boards
z
Enhancing flexibility of system configuration
In the MSOFTX3000, all subracks have the same hardware structure. The width of the
subrack is 21 times the width of a standard board slot. The following boards must be
configured in the fixed slots of the subrack, occupying the width of nine standard board slots:
z
System management boards
z
Ethernet communication boards
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-3
Page 28
2 System Structure
Figure 2-4 Logical structure of the MSOFTX3000 hardware
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Interface
Module
BITS
E1/T1
Interface
ATM-2M
Interface
FE
Interface
NMS
WS
BC
WCKI
WEPI
WEPI/
WEAM
WBFI/
WIFM
BAM
iGWB
Operation &
Maintenance Module
System Support Module
WHSC
Signaling
Lower-Layer
Processing
Module
CPC
WBSG
Service
Processing
Module
WCCU
WVDB
WCDB
WMGC
WSIU/WSMU
System Support Module
LAN
bus
OSTA bus
The SSM implements the following functions:
z
Software and data loading
z
Device management and maintenance
z
Inter-board communications
It comprises the following units:
z
System management unit (WSMU)
z
System interface unit (WSIU)
z
Hot-swap and control unit (WHSC)
z
Core LAN Switch
The WSMU is the main control board of a subrack. Through the system buses and the serial
port, the WSMU can achieve the following functions of all the devices in the system:
z
Loading control
z
Data configuration
Working status controlThe WHSC implements the following functions:
z
Bridge connection between the left and right shared resource buses
z
Hot swappability control of board
z
Intra-subrack LAN bus switching
2-6 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 29

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
The signaling traffic streams are formed through the LAN bus provided by the WHSC. The
WHSC is not configured with a CPU. Therefore, the WHSC is directly configured and
maintained by the WSMU through the Ethernet bus.
The core LAN Switch implements the following functions:
z
Interconnection of multiple subracks
z
Connection between these subracks and management devices
Interface Module
The IM provides various physical interfaces to meet the system networking demands,
including:
z
Narrowband interface: The E1_pool interface unit (WEPI) provides eight E1 interfaces
to realize the framing and line interfacing function (MTP1 function). The WEPI
interworks with the MTP2 processing unit WCPC (subboard of the WCSU) of the
signaling lower layer processing module through the internal HW.
z
ATM-2M interface: The WEPI provides eight E1 interfaces and two 8-Mbit/s HW signal
cables to connect with the WEAM. The WEAM segments and re-assembles the ATM
cells in the data streams, and transfers signaling to the WBSG through internal LAN bus.
z
FE interface: The WIFM provides the 100-Mbit/s Ethernet electrical interface by
configuring the FEP subboard and the WBFI. It distributes and brings together
broadband signaling information streams, and distributes them to the specified
processing unit based on the IP address and the port number.
z
The narrowband signaling requires clock synchronization. The MSOFTX3000 provides
two kinds of clock sources, BITS and E1, and the WCKI provides external interfaces.
Signaling Lower-Layer Processing Module
The SLLPM offers the lower layer protocol processing function. It includes SS7 MTP2
processing unit (WCPC) and SCTP processing unit (WBSG):
z
The WCPC processes SS7 MTP2 over narrowband E1 and communicates with the
service processing unit (WCSU) through the internal bus. The WCPC is a subboard of
the WCSU.
z
The WBSG handles the lower layer signaling over IP and ATM (by using the ATM
2-Mbit interface), and distributes it to the upper layer service processing board.
Service Processing Module
The SPM is composed of the service processing unit (WCCU/WCSU), central database unit
(WCDB), VLR database unit (WVDB) and media gateway control unit (WMGC):
z
The WCCU processes the signaling protocols on Layer 3 or a higher layer (MTP3,
M3UA, ISUP, SCCP, TCAP, MAP and CAP) necessary for service features. It also
implements call control on the application layer and processes intelligent CAMEL
services. In this system, two WCPCs pinched on the WCCU make a WCSU.
z
As the central database unit, the WCDB stores centralized resources, such as inter-office
trunk resources, local office subscriber data, and gateway capability status. It also
provides the call resource query service for the service processing unit.
z
The WVDB is a dynamic database, which provides the functions of the VLR.
z
The WMGC controls the H.248 media gateways.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-7
Page 30
2 System Structure
The WCCU/WCSU, WCDB, WBSG, WMGC, WIFM and WAFM are universal processing boards in the
system. They are pinched with different subboards and loaded with different software. They
communicate with each other through Ethernet.
Operation & Maintenance Module
The OMM has the following functions:
z
Implementing operation, maintenance and management of the equipment
z
Providing man-machine interfaces to users to implement local O&M
z
Providing interfaces for the Network Management System (NMS)
To provide CDRs, the iGWB must be configured in the MSOFTX3000 to manage CDRs and
provide billing interfaces for the billing center.
2.2 Software Structure
2.2.1 Overview
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
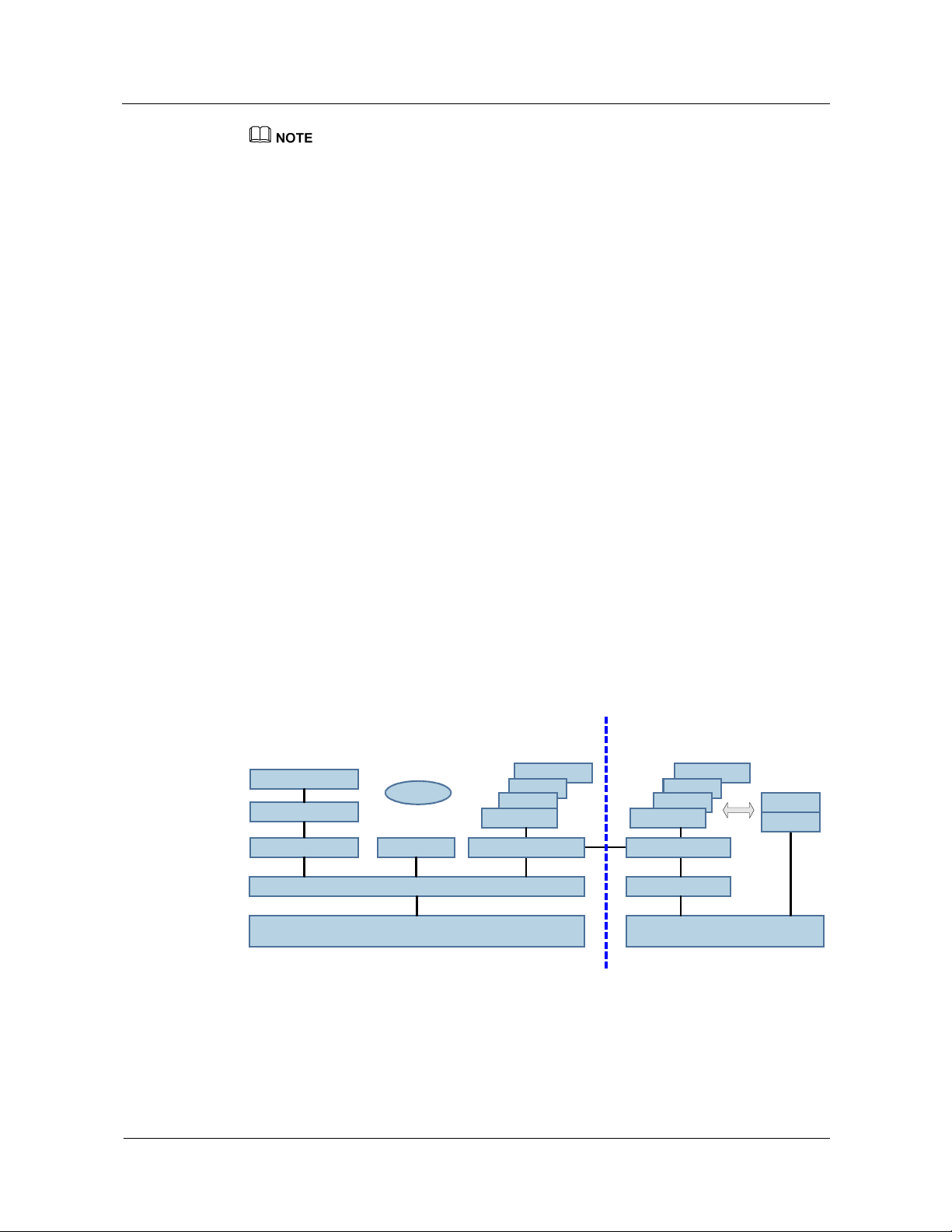
The MSOFTX3000 adopts a distributed software structure. The system distributes its software
functions and features to boards and servers. You can configure them flexibly to meet the
actual requirement. Based on its location, the MSOFTX3000 software consists of two parts:
z
Host software
z
BAM software
Figure 2-5 shows the software structure of the MSOFTX3000.
Figure 2-5 Software structure of the MSOFTX3000
Host software BAM software
Service processing
Protocol processing
Database
Device mgmtSignaling bearer
Middleware
Operating system
Performance
Bill
Alarm
Maintenance
Communication Exchange
Database software
Performance
Bill
Alarm
Maintenance
Operating system
GUI
MML
2-8 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 31

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
2.2.2 Host Software
The host software runs on boards in the OSTA subracks of the MSOFTX3000. It performs the
following functions:
z
Signaling access and processing
z
Call processing
z
Service control
z
Resource management
z
Charging information generation
Along with the BAM software, the host software can also perform the following operations on
the host in response to commands:
z
Data management
z
Equipment management
z
Alarm management
z
Performance measurement
z
Signaling trace
z
CDR management
The host software adopts a layered modular design and consists of the following parts:
z
Operating system
z
Middleware
z
Various application software
Operating system
The operating system of the host software is VxWorks, real-time software.
Middleware
The MSOFTX3000 adopts the middleware technology (DOPRA_C), so the high level service
software becomes irrelevant to the operating system.
The use of middleware facilitates the migration of software functions between different
platforms. This ensures that new and stable product versions can be released quickly.
Application Software
The application software is the functional part of the MSOFTX3000 software. Loaded with
different software, boards can provide different functions. The MSOFTX3000 application
software can be divided into five types:
z
The signaling bearer software: It is configured on WEPI, WIFM, WAFM, and WBSG. It
accesses broadband and narrowband signaling, and processes bottom layer protocols.
z
The service processing software: It is configured on WCCU/WCSU and WMGC. It
carries out signaling and call processing, mobility management, and resource
management.
z
The database software: It is configured on the WCDB and WVDB. It manages the data
of MSOFTX3000 and dynamic subscriber data.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-9
Page 32

2 System Structure
z
The system support software: It is configured on the WSMU and WHSC. It carries out
system management and device interworking.
z
The O&M software: It is configured in the WSMU and other boards. It receives
instructions from the BAM and returns results.
2.2.3 BAM Software
The BAM software runs on the BAM, the iGWB and the LMTs. Along with the host software,
it enables the maintenance staff to implement the following functions:
z
Data management
z
Equipment management
z
Alarm management
z
Performance measurement
z
Signaling tracing
z
CDR management
The BAM software adopts the client/server mode, and consists of four parts:
z
BAM server software: It is installed on the BAM, the server side.
z
Emergency workstation software: It is installed on the emergency workstation, the server
side.
z
Billing gateway software: It is installed on the iGWB, the server side.
z
LMT software: It is installed on LMTs, the client side.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
BAM Server Software
The BAM server software is the core of the terminal OAM software. As an integrated
communication server and the database server, the BAM server software can perform the
following functions:
z
Forward the OAM commands from all workstations (WS) to the host.
z
Direct the response or operation results from the host to the workstations.
The BAM server software is based on the Windows 2000 Server, and uses the SQL Server
2000 as the database platform. It provides functions of the terminal OAM software through
multiple parallel service processes, such as:
z
Maintenance process
z
Data management process
z
Alarm process
z
Performance measurement process
Figure 2-6 shows the relationship between the BAM server software, the operating system,
and the database.
2-10 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 33

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
Figure 2-6 Relationship between BAM server software, operating system, and database
BAM server software
Applicaiton
program layer
Operating system layer
SQL Server 2000
Windows 2000 Server
Emergency Workstation Software
The EWS software is the same as the BAM server software. The EWS is a backup of the
BAM and is not connected with the host when the BAM is functioning normally. When the
BAM is faulty, you can replace the BAM with the EWS. After the EWS is restored, switch
back to the BAM.
Billing Gateway Software
The billing gateway software is the core component of the CDR management system. It runs
on the iGWB and performs the following functions:
z
It stores and backs up CDRs generated by the service processing modules (that is, the
WCCUs/WCSUs) of the MSOFTX3000 to the hard disks.
z
It provides billing interfaces to the billing center through FTP or FTAM.
LMT Software
The LMT software runs on the WSs and connects with the BAM and iGWB servers as a client
in client/server mode. It provides subscribers with graphical terminals based on the MML.
WSs can be located locally or remotely. For example, a WS is connected with the BAM server
by using the dialup access through a wide area network (WAN).
You can use the following maintenance functions on the WSs:
z
Data maintenance
z
Equipment management
z
Alarm management
z
Performance measurement
z
Call and signaling tracing
z
CDR management
z
Report functions
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-11
Page 34

2 System Structure
2.3 Capacity Expansion
2.3.1 Cabinet Configuration
Based on the configurations, the MSOFTX3000 cabinets fall into two categories:
z
Integrated configuration cabinets
z
Service processing cabinets
In full configuration, the MSOFTX3000 has one integrated configuration cabinet and two
service processing cabinets. See
Figure 2-7 Configuration of MSOFTX3000 cabinets (when the NET Switch is configured in the
integrated configuration cabinet)
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Figure 2-7.
Integrated configuration
cabinet
Power distribution subrack (2U)
Expansion subrack (01) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Basic subrack (00) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
KVMS (1U)
LAN Switch 1 (1U)
Cabling trough (1U)
LAN Switch 0 (1U)
Cabling trough (1U)
Blank filler panel (3U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
BAM (2U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
iGWB 1 (2U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
iGWB 0 (2U)
NET Switch 1 (1U)
Cabling trough (1U)
(2U)
NET Switch 0 (1U)
Cabling trough (1U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
Service processing
cabinet 1
Power distribution subrack (2U) Power distribution subrack (2U)
Expansion subrack (05) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack (04) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack (03) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack (02) (9U)
Blank filter panel (2U)
Service processing
cabinet 2
Expansion subrack (09) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack (08) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack (07) (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack (06) (9U)
Blank filter panel (2U)
2-12 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 35

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 2 System Structure
Figure 2-8 Configuration of MSOFTX3000 cabinets (when the NET Switch is configured outside
the cabinet)
Integrated
configuration cabinet
Power distribution
subrack (2U)
Basic subrack (9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Blank filler panel ( 1U)
KVMS (1U)
LANSwitch (1U)
Cabling trough (1U)
LANSwitch (1U)
Cabling trough (
Disk Array(3U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
BAM (2U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
iGWB (2U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
iGWB (2U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
Blank filler panel (2U)
Blank filler panel (1U)
1U)
Service processing
cabinet
Power distribution
subrack (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Blank filler panel ( 2U)
Service processing
cabinet
Power distribution
subrack (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Air deflector (2U)
Expansion subrack
(9U)
Blank filler panel (2U)
An integrated configuration cabinet is mandatory for the MSOFTX3000 and includes the
following components:
z
Power distribution subrack
z
Up to two service processing subracks
z
Air deflector
z
KVMS (Keyboard, Video, Mouse, and Switcher)
z
Core LAN Switch (up to two)
z
iGWB (configured for charging, usually two)
z
BAM
A service processing cabinet is configured based on the capacity requirements of carriers. It
includes the following components:
z
Power distribution subrack
z
Up to four service processing subracks
z
Air deflector
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 2-13
Page 36

2 System Structure
2.3.2 Expansion Configuration
You can add subracks to increase the capacity of the MSOFTX3000. The MSOFTX3000
supports up to 1.8 million subscribers. Figure 2-9 shows a typical configuration of the
MSOFTX3000:
Figure 2-9 Expansion configuration of the MSOFTX3000
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
0 - 200 k
200 k - 1 M
1 M - 1.8 M
The configuration principles are as follows:
z
If only the basic subrack is configured, the basic subrack supports 50 thousand
subscribers.
z
If both the basic subrack and expansion subracks are configured, the service processing
board cannot be configured in the basic subrack. Each expansion subrack supports 200
thousand subscribers. With all nine expansion subracks, the MSOFTX3000 supports up
to 1.8 million subscribers.
2-14 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 37
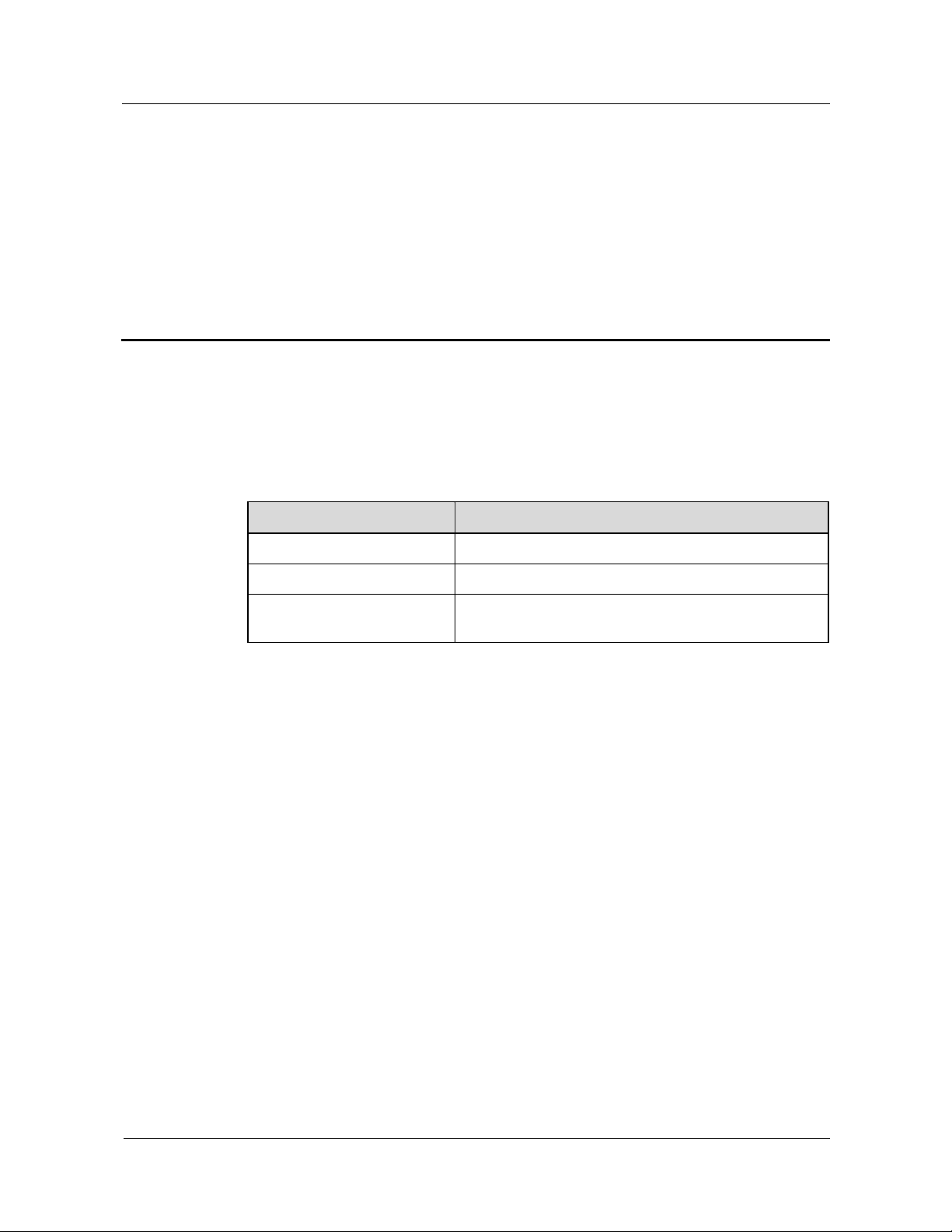
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
About This Chapter
The following table lists the contents of this chapter.
Section Describes
3.1 Physical Interfaces The physical interfaces supported by the MSOFTX3000.
3.2 Protocol Interface The protocol interfaces supported by the MSOFTX3000.
3.3 Signaling and Protocols The signaling and protocols supported by the
MSOFTX3000.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 3-1
Page 38
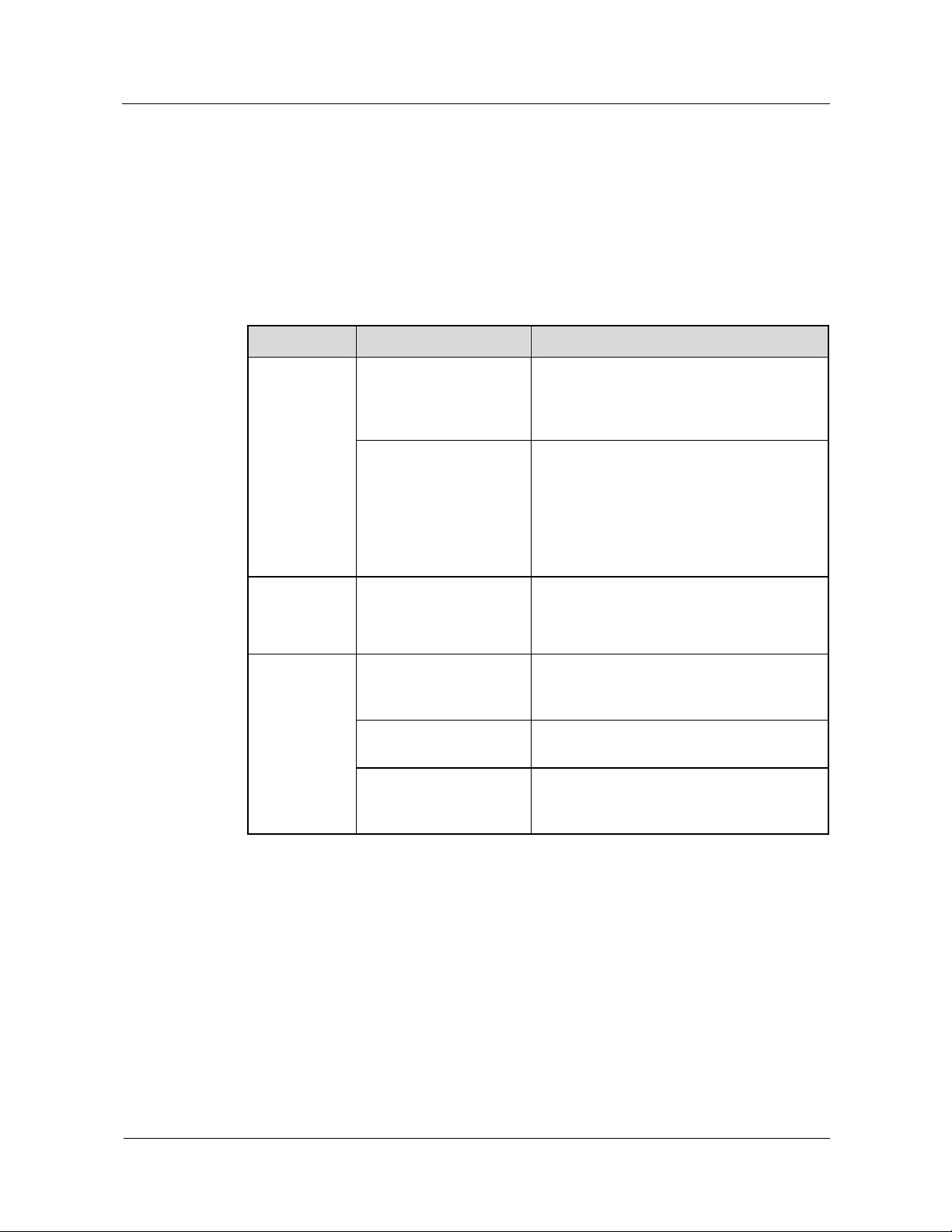
3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
3.1 Physical Interfaces
3.1.1 Classification
The MSOFTX3000 supports physical interfaces, such as FE, E1, and clock interfaces.
Tab le 3-1 lists the numbers of interfaces and their functions.
Table 3-1 Numbers and functions of physical interfaces
Interface Maximum Number Function
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
FE electrical
interface
E1 interface
Clock
interface
Host: 8 (4 pairs, each
including an active
interface and a standby
one)
BAM: 3 To provide bearer channels for TCP/IP-based
End office: 288
Gateway office : 360
Tandem office: 360
2.048 Mbit/s interface: 2
2.048 MHz interface 2
RS422 interface: 16
To provide bearer channels for IP-based
service signaling or protocols, such as H.248,
BICC, M2UA, M3UA, IUA, SIP, and SIP-T
network management or file transfer
protocols, such as SNMP, MML, FTP, and
FTAM (The FE electrical interfaces are
provided by the BAM and the iGWB for the
networking of network management and
billing)
To provide 64-kbit/s and 2-Mbit/s MTP links
for SS7
To receive 2.048-Mbit/s input clock signals
(line clock) from the BITS equipment or E1
interface boards
To receive 2.048-MHz input clock signals
from the BITS equipment
To provide 8 kHz output clock signals
(internal interface) for E1 interface boards of
the service subracks
3-2 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 39

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
3.1.2 Interface Specifications
Specifications of FE Electrical Interfaces
Tab le 3-2 lists the specifications of FE electrical interfaces:
Table 3-2 Specifications of FE electrical interfaces
Item Value
Compliant recommendation or standard IEEE 802.3u
Transfer rate 10/100Mbit/s self-adaptation
Transferable distance 100 m
Frame format 10BASE-T / 100BASE-TX
Interface type RJ-45
Nominal impedance 100 ohm
Specifications of E1 Interfaces
Tab le 3-3 lists the specifications of E1 interfaces:
Table 3-3 Specifications of E1 interfaces
Item Value
Compliant
recommendation or
standard
Transfer rate 2.048Mbit/s
Line code type HDB3
Transferable distance ≥300m
Transmission channel 32 (31 transmission channels and one synchronization channel)
Nominal impedance 75 ohm coaxial cable or 120 ohm twisted pair cable
Interface type SMB (when coaxial cables are used)
ITU-T I.431, G.703, G.736, G.823, G.704, G.706, Q.703, G.732
ANSI T1.403
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 3-3
Page 40

3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
Specifications of Clock Interfaces
Tab le 3-4 lists the specifications of clock interfaces:
Table 3-4 Specifications of clock interfaces
Item 2.048 MHz Clock Interface 2.048 Mbit/s Clock Interface
Compliant
recommendation
or standard
Interface type SMB SMB
Signal type G.703.10 G.703.6
ITU-T G.703 ITU-T G.703
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Detection
threshold
Impedance
matching
Balance mode Unbalanced Unbalanced
Electrical isolation 300 V / 50 Hz, > 1 minute 300 V / 50 Hz, > 1 minute
≤-24dB ≤-24dB
75 ohm 75 ohm
3.2 Protocol Interface
3.2.1 Standard Interface
Protocol interfaces in Mobile Network
The MSOFTX3000 provides open and standard protocol interfaces to support signaling and
protocols. It can interwork with many types of equipment. Figure 3-1 shows the protocol
interfaces provided by the MSOFTX3000 when it serves as a VMSC Sever, GMSC Sever,
TMSC Sever, or an SSP in a mobile network:
3-4 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 41

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
Figure 3-1 Protocol interfaces provided by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile network
BC
FTAM
MML
M2000
SG
TUP/ISUP
SIGTRAN
Gs
SGSN
PSTN
PLMN
BSC: Base Station Controller GMLC: Gateway Mobile Location Center HLR: Home Location Register
BC: Billing Center SCP: Service Control Point SMC: Short Message Center
SG: Signaling Gateway SGSN: Serving GPRS Support Node RNC: Radio Network Controller
MGW: Media Gateway PLMN: Public Land Mobile Network
HLR
FTP/
MSOFTX 3000
MGW
Mc
SCP
CAP/ LC/D
Lg
GMLC
lu-CS
E
Nc / E
SMC
MSC Server
A
RNC
Service
Layer
Control
Layer
BSC
Access
Layer
Tab le 3-5 lists the interfaces and protocols supported by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile
network:
Table 3-5 Interfaces and protocols supported by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile network
Connected Entities Interface Protocol
MSC Server—MGW Mc H.248
MSC Server—RNC Iu-CS RANAP
MSC Server—BSC (GSM) A BSSAP
MSC Server—VLR B Internal protocol
MSC Server—HLR C MAP
VLR—HLR D MAP
MSC Server—MSC Server Nc MAP, TUP/ISUP/BICC
MSC—MSC (GSM) E MAP, TUP/ISUP/BICC
MSC Server—SMC E MAP
MSC Server—VLR G MAP
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 3-5
Page 42
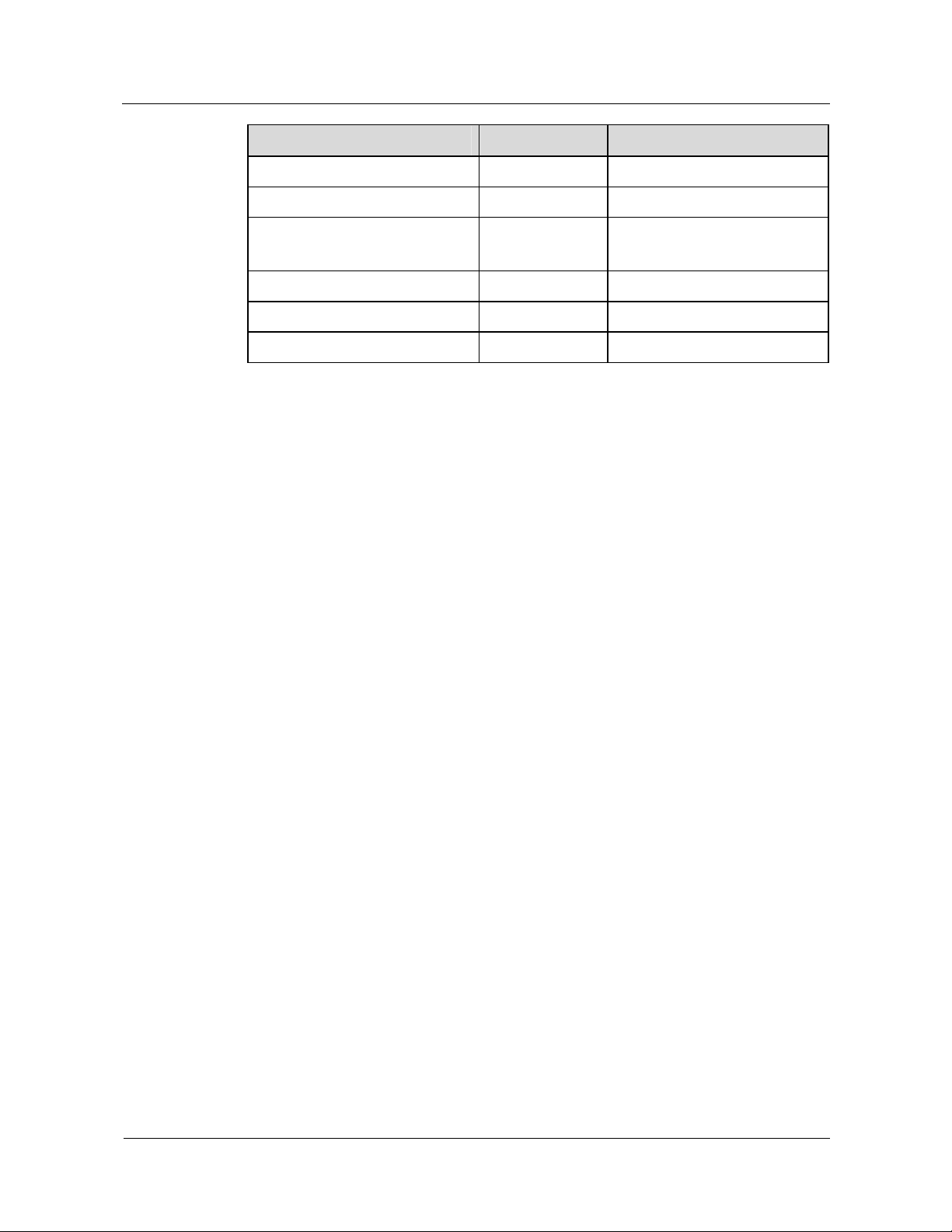
3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
Connected Entities Interface Protocol
MSC Server—GMLC Lg MAP
SSP—SCP - CAP
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
GMSC Server—PSTN
GMSC Server—PLMN
MSC Server—SGSN Gs BSSAP+
MSC Server—NMS - MML
MSC Server—BC - FTP/FTAM
3.2.2 CDR Interface
CDR Transfer Protocol
The MSOFTX3000 supports the standard FTP/FTAM. By interworking with the billing center,
the MSOFTX3000 allows its iGWB to send CDR data to the billing center through the FTP or
FTAM interface.
CDR File Format
The MSOFTX3000 supports CDR files in ASN.1 and binary formats:
z
ASN.1 format: ASN.1 is short for Abstract Syntax Notation One. ASN.1 is widely used
as the standard for the protocol syntax at the application layer, because it can be used to
clearly describe complex data structures. The CDR interface in ASN.1 format is
recommended by both Huawei and 3GPP.
z
Binary format: The MSOFTX3000 provides the CDR interface in binary format for 2G
equipment in the current network. The format is used by 2G offices and certain special
offices. The format is not recommended in normal cases.
- TUP/ISUP
CDR Content Format
The iGWB of the MSOFTX3000 supports CDR content formats defined by 3GPP, by
configuring database files of CDR content formats.
3.2.3 Interception Interface
The MSOFTX3000 supports four standard interception interface protocols:
z
LICI (Lawful Interception Center Interface)
z
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute)
z
SOSM (System of Operative-Search Measures)
z
SPBX (Special Private Branch Exchange)
By interworking with the lawful interception center, the MSOFTX3000 allows national
security bodies to intercept certain mobile subscribers in real time.
3-6 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 43

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
SPBX is developed by Huawei based on mobile communication protocols and requirements
of security bodies. It is applicable to the lawful interception systems in most countries. To use
SPBX interception interfaces, carriers must sign a contract with Huawei because SPBX is a
private protocol of Huawei.
3.3 Signaling and Protocols
The MSOFTX3000 provides open and standard protocol interfaces to support signaling and
protocols. It can interwork with many NEs. Table 3-6 describes the signaling and protocols
supported by the MSOFTX3000:
Table 3-6 Signaling and protocols supported by the MSOFTX3000.
Signaling
or
Protocol
H.248 Media gateway control protocol, used by
SCTP Stream control transmission protocol, used
M2UA MTP2 user adaptation layer, used by the
M3UA MTP3 user adaptation layer, used by the
IUA ISDN Q.921 user adaptation protocol, used
MTP Message transfer part, used for the
Function Compliant
the MSOFTX3000 to control the MGW
to provide reliable data packet transfer
services for the adaptation protocols of
IP-based switched circuit network (SCN)
signaling
MSOFTX3000 to interwork with MGWs
with built-in M2UA SG functions
MSOFTX3000 to interwork with M3UA
SGs
by the MSOFTX3000 to interwork with
MGWs with built-in IUA SG functions
interworking between the MSOFTX3000
and the SS7 signaling network. This is to
enable the MSOFTX3000 to interwork with
SPs or STPs in the SS7 signaling network.
Recommendation or
Standard
3GPP TS 29.232 V4.7.0
IETF, RFC2960, Stream
Control Transmission
Protocol (SCTP)
IETF, RFC3331, SS7 MTP2
User Adaptation Layer
(M2UA)
IETF, RFC3332, SS7
MTP3-User Adaptation Layer
(M3UA)
IETF, RFC3057, ISDN
Q.921-User Adaptation Layer
(IUA)
ITU-T Q.701~Q.707
TUP Telephone user part, used for the
interworking between the MSOFTX3000
and the PSTN or other MSCs. This is to
enable the MSOFTX3000 to provide TUP
trunks through MGWs.
ISUP Integrated services digital network user
part, used for the interworking between the
MSOFTX3000 and the PSTN or other
MSCs. This is to enable the MSOFTX3000
to provide ISUP trunks through MGWs.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 3-7
ITU-T Q.721~Q.725
ITU-T Q.761~Q.764, Q.730
Page 44

3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Signaling
Function Compliant
or
Protocol
SCCP Signaling connection control part, used to
bear the MAP and CAP protocols so that
circuit-independent signaling connections
can be established between the
MSOFTX3000 and entities, such as the
VLR, HLR, EIR, MSC, SMC, GMLC, and
SCP through the SS7 signaling network
TCAP Transaction capability application part,
used to provide functions and routines not
related to specific applications. This is to
enable the MSOFTX3000 to establish MAP
or CAP dialogs with entities, such as the
VLR, HLR, EIR, MSC, SMC, GMLC, and
SCP.
MAP Mobile application part, used to define the
information exchanging mode between
network entities to implement roaming of
MSs. This is to enable the MSOFTX3000
to interwork with network entities, such as
the VLR, HLR EIR, MSC, SMC, and
GMLC through the C, D, E, G, and Lg
interfaces.
Recommendation or
Standard
ITU-T Q.711~Q.716
ITU-T Q.771~Q.775
3GPP TS 29.002 V4.11.0
CAP CAMEL application part, used to define
standard communication routines between
network entities. This is to enable the
MSOFTX3000 to perform the SSF, CCF,
SRF, and CCAF functions and serve as the
SSP in an IN.
BSSAP Base station subsystem application part
used to define the A interface between the
MSC and the BSC. This is to enable the
MSOFTX3000 to interwork with the BSC
through the MGW.
RANAP Radio access network application part, used
to define the Iu interface between the MSC
server and the RNC. This is to enable the
MSOFTX3000 to interwork with the RNC
through the MGW.
BSSAP+ Base station subsystem application part+,
used to define the Gs interface between the
SGSN in the PS domain and the MSC in
the CS domain. This is to enable the
MSOFTX3000 to interwork with the
SGSN.
3GPP TS 29.078 V4.7.0
3GPP TS 48.008 V4.8.0
3GPP TS 24.008 V4.9.0
3GPP TS 25.413 V4.7.0
3GPP TS 24.008 V4.9.0
3GPP TS 29.018 V4.4.0
3-8 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 45
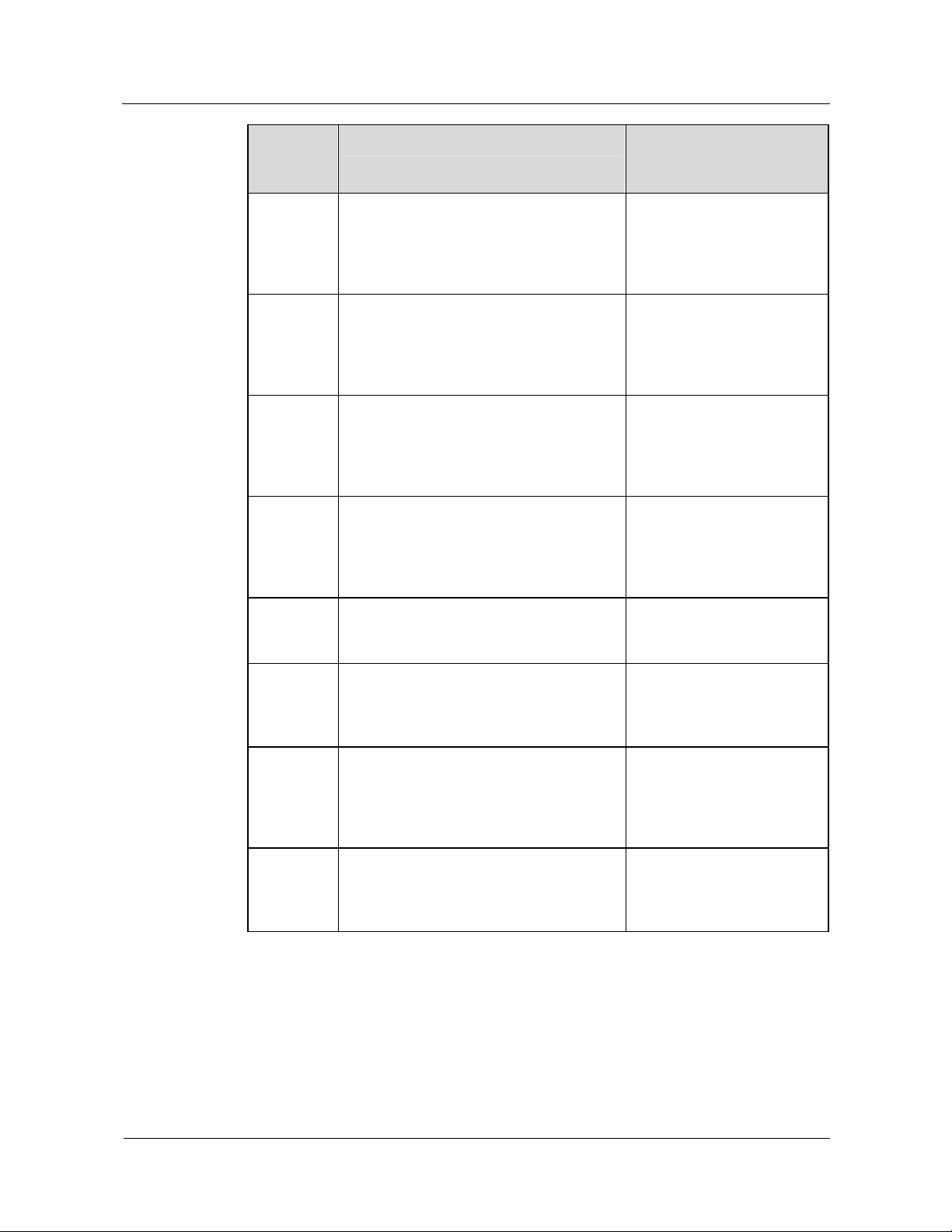
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 3 Interfaces, Signaling, and Protocols
Signaling
or
Protocol
R2 Standard channel associated signaling, used
Function Compliant
Recommendation or
Standard
ITU-T, Q.400~Q.499
for the interworking between the
MSOFTX3000 and exchanges of old mode.
This is to enable the MSOFTX3000 to
provide CAS trunks through the MGW.
PRA ISDN subscriber network signaling, used
for the interworking between the
ITU-T I.430, I.431, Q.921,
Q.931
MSOFTX3000 and PBXs. This is to enable
the MSOFTX3000 to provide primary rate
interfaces (PRIs) through the MGW.
BICC Bearer independent call control protocol,
used to establish, modify, and end calls.
This is to enable the MSOFTX3000 to send
3GPP TS 23.205 V4.6.0
ITU-T, Q.1902
call control signaling to other MSC servers
through the E interface.
SIP Session initiation protocol, used for the
interconnection between the MSOFTX3000
IETF, RFC3261, Session
Initiation Protocol (SIP)
and other softswitches or SIP application
servers, and to access SIP multimedia
packet terminals
SIP-T Extension protocol of SIP, used for the
transparent transmission of ISUP signaling
FTP File transfer protocol, used to support the
interconnection between the MSOFTX3000
and billing centers. This is to enable the
MSOFTX3000 to provide FTP interfaces.
FTAM File transfer access and management
protocol, used to support the
interconnection between the MSOFTX3000
and billing centers. This is to enable the
MSOFTX3000 to provide FTAM interfaces
NTP Used to support the clock synchronization
between the MSOFTX3000 BAM and the
NTP Server. This is to ensure the time of all
devices in the network is synchronized.
IETF, RFC3372, Session
Initiation Protocol for
Telephones (SIP-T)
IETF, RFC0959, File
Transfer Protocol (FTP)
ISO, ISO8571, File Transfer
Access and Management
Protocol (FTAM)
IETF,RFC1305,Network
Time Protocol (NTP)
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 3-9
Page 46
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 4 O&M System
4 O&M System
About This Chapter
The following table lists the contents of this chapter.
Section Describes
4.1 Overview of O&M The structure of the MSOFTX3000 terminal system.
4.2 O&M Function The O&M functions supported by the MSOFTX3000.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 4-1
Page 47

4 O&M System
4.1 Overview of O&M
4.1.1 Basic Concept
O&M refers to the tasks performed by carriers on running softswitch systems. O&M ensures
normal operation of the system and quality of the teleservices.
The MSOFTX3000 provides a graphical Man Machine Language (MML) environment
through which it provides the following O&M functions:
z
Configuration management
z
Fault management
z
Performance measurement
z
Security management
z
CDR management
z
Environment monitoring
4.1.2 Terminal System
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
The O&M functions of the MSOFTX3000 can be performed on the local maintenance
terminal (LMT) or the local maintenance center of Huawei iManager M2000. The terminal
system is the key hardware platform to carry out O&M functions. The terminal system
consists of the following parts. See
z
BAM
z
iGWB
z
Emergency workstation
z
LMTs
Figure 4-1.
4-2 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 48

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 4 O&M System
Figure 4-1 Network structure of the terminal system
MSOFTX3000 host
LAN Switch
To BC
WAN
Acti ve
iGWB
HUB
LMT
BAM: Back administration module iGWB: Charging gateway of Huawei
BC: Billing center NMC: Network management center
LMT LMT LMT
BAM
Standby
iGWB
To NMC
Emergency workstation
WAN
The terminal system works in client/server mode.
The BAM and the iGWB function as the servers. They are connected with the host of the
MSOFTX3000 and the external computer network through the Ethernet.
The LMTs function as the clients. Based on the requirements, they can be configured as the
following:
z
Maintenance console
z
Data management console
z
Alarm console
z
Performance measurement console
z
CDR console
iManager
M2000
In the terminal system, the BAM is the core hardware to achieve the O&M functions. It
forwards the O&M commands from the LMTs to the host, and directs the response from the
host to the mapping LMT.
To ensure reliability of the terminal system, the MSOFTX3000 has the following features:
z
Two Ethernet connections working in active/standby mode, which connect the
BAM/iGWB and the host.
z
Two iGWBs working in active/standby mode, which ensures the security of CDRs.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 4-3
Page 49

4 O&M System
z
An emergency workstation (EW) is designed as the online backup of the BAM. When
the BAM is faulty, the EW can replace the BAM; at the same time, it can restore the
BAM with the backup data stored in its hard disk.
4.1.3 Network Management Networking
The MSOFTX3000 provides the external MML network management (NM) interface through
the BAM, which can be connected to the NMC. If the NMC adopts the Huawei iManager
M2000 as the NM part of the network, the carrier can connect the NMC to the BAM through
the MML interface, as shown in
Figure 4-1. In this case, the iManager M2000 works as a
remote workstation of the MSOFTX3000 terminal system.
4.1.4 Introduction to MML Command Line
The MML command line is also known as MML. It is a set of human-machine interfaces
based on the ITU-T Z.301 to Z.341. MML provides a command set to operate and query the
MSOFTX3000. Through this, you can monitor and manage the data on the MSOFTX3000. In
normal cases, the BAM can process ten MML commands in one second.
The features of MML are as follows:
z
The MML command set encapsulates the services of the MSOFTX3000. A command
maps a function, but not an operation.
z
The MML command set is equal to a group of application programming interfaces (APIs)
in terms of the MSOFTX3000. All other application programs are based on the MML
command set. For a GUI terminal, the interface operations are translated into commands,
and then transferred to the MML system. The MML system runs the commands and
returns the results in text format. The results are exported by the GUI terminal to the
operation terminal of subscribers. Thus, the running of the entire network is not affected
by a single application program issue, thereby ensuring stability of the system.
z
The MML system performs strict data consistency check. When a function is executed,
the MML system checks the mapping between the tables. This is an effective way to
avoid producing junk data.
z
The input and output of the MML system are based on pure character streams. Programs
such as TELNET are supported to interact with the MSOFTX3000. Therefore, the client
can override all types of platforms, for example, supporting a dumb terminal without
processing capabilities. This is beneficial to a centralized network management, and
follows the development trends of telecommunication products.
z
The MML system supports the search function and the standard Windows search
functions such as keyword search and fuzzy search. It also provides complete online help
documents for subscribers to study and use MML commands.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
4.2 O&M Function
4.2.1 Configuration Management
The MSOFTX3000 provides the following database operation methods:
z
Addition
z
Deletion
z
Modification
4-4 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 50

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 4 O&M System
z
Query
z
Storage
z
Backup
z
Restoration
With these methods, you can effectively manage and maintain the following data of the
MSOFTX3000:
z
Hardware data
z
Office information data
z
Gateway data
z
Signaling data
z
Routing data
z
Number analysis data
z
Mobile service data
z
IN service data
The MSOFTX3000 configuration management also provides the following functions:
z
Offline or online data configuration
z
Local and remote configuration
z
Online upgrade of data
z
Data verification (ensuring consistency of host data and BAM data)
4.2.2 Fault Management
Overview
Fault management function helps you check, locate and fix system faults of the
MSOFTX3000 during operation. This function provides tools for routine maintenance of the
system. The tools can also prevent the occurrence of faults.
Fault management includes the following items:
z
System self-test
z
Alarm management
z
Maintenance management
z
Trace management
System Self-Test
The MSOFTX3000 tests its resource occupation regularly. The MSOFTX3000 also performs
the following functions:
z
Checking the occurrence and severity of overload, and processing the overload
z
Coordinating the usage of the system software
z
Minimizing the impact of faults on the system
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 4-5
Page 51

4 O&M System
Alarm Management
The alarm management system of the MSOFTX3000 performs the following alarm
management operations:
z
Detects and reports in real time any fault or abnormity of the equipment
z
Generates audio and visual alarm signals through the alarm terminal devices, such as
alarm box and alarm console, based on the type and level of the alarm
z
Sends the alarm information after resolution to the NMC through the NM interface.
z
Stores the alarm information, query the alarm record, configures the troubleshooing
method, and provides CPU threshold data in the reported alarm information when the
CPU usage rate is too high
z
Presents the alarm information as well as handling suggestions at the local maintenance
terminal to help users troubleshoot the faults efficiently
Maintenance Management
The maintenance management function provides the following maintenance control methods
through the MML commands:
z
Query
z
Display
z
Switchover
z
Reset
z
Isolation
z
Block
z
Activation
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Using these methods, you can effectively and efficiently manage and maintain the following:
z
Hardware components of the MSOFTX3000
z
System resources
z
Signaling links
z
Physical ports
z
Gateways controlled by the MSOFTX3000 and the related bearer resources
Tracing management
The tracing management of the MSOFTX3000 offers the graphic interface, and provides the
following functions:
z
Connection tracing
z
Signaling tracing
z
Interface tracing
z
Message interpretation
With these functions, you can conduct real time and dynamic tracing on the following items
related to the terminal subscribers, trunk circuits, signaling links, and interface protocols:
z
Connection process
z
State transition
4-6 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 52

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 4 O&M System
z
Resource occupancy
z
Telephone number information transfer
z
Control information streams
The tracing information can be stored for future reference, enabling the two functions of:
z
Fault analysis
z
Location capabilities
4.2.3 Performance Measurement
The performance measurement (PM) system provides original data by measuring the
following items:
z
Traffic
z
Connection process
z
QoS
z
Cause of failure
This helps subscribers know the equipment operation status, equipment management situation
and network optimization.
The PM tasks can be created, modified, carried out, suspended, deleted and queried.
The system can display the measurement results in the bar chart or the fold-line graph, and
conduct data analysis based on the result.
4.2.4 Security Management
Authority Management
The O&M system of the MSOFTX3000 can be used by many operators. Operator authorities
are divided by levels, to ensure system security. Operators can run MML commands
depending on their authorities.
Log Management
It helps in querying MML operation records. By querying the log, you can check whether any
operation that may affect the operation of the system has been performed.
4.2.5 CDR Management
The iGWB Server provides CDR management features in the MSOFTX3000. The main
functions of the iGWB Server are as follows.
Real time Receipt of CDR Data Generated by MSOFTX3000
The generated CDRs are stored in the host CDR pool, and then sent to the iGWB Server
through the LAN immediately to avoid overflow of the CDR pool.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 4-7
Page 53

4 O&M System
Reliable Storage and Backup of Original CDR Data
The hard disk of iGWB Server can be expanded conveniently. It can store a large amount of
CDR data for a long time. The CDR data stored in the iGWB Server can be backed up in the
network.
Preprocessing of Original CDR Data
The iGWB Server performs pre-processing such as format conversion, CDR sorting and CDR
filtering on original CDRs to generate the final ones and store them in the local hard disk. You
can operate and query the CDRs locally through the iGWB Server.
Providing FTP/FTAM Interface for Billing Center
The billing center fetches CDRs through the FTP or the FTAM interface. The iGWB Server
supports automatic fetching of CDRs.
Providing CDR Operation Log
The iGWB Server logs user operations for future reference during troubleshooting, including:
z
Operator account
z
Operation time
z
Operation data
z
Detailed operation
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
4.2.6 Environment Monitoring
The MSOFTX3000 presets the following external environment alarm types during
initialization:
z
High temperature
z
Low temperature
z
High humidity
z
Low humidity
z
Access control
z
Smoke detection
z
Fire
z
Wate r
z
Commercial power supply fault
z
Low voltage
The alarm types can meet the requirements of most carriers.
4-8 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 54
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
5 Services and Functions
About This Chapter
The following table lists the contents of this chapter.
Section Describes
5.1 Basic Services The service functions consisting of circuit switched domain
services, such as, teleservices, supplementary services, IN
services, and value added services.
5.2 Basic Functions The mobile network functions consisting of the mobility
management, security management, call control, location
services, and service switching function.
5.3 Description of Features Features and functions except the basic services and the
functions.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-1
Page 55

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
Originating SMS: This service transmits a short message from user equipment (UE) to a
message handling system (service center). After the service center receives the message,
it sends an acknowledgement message.
z
Terminating SMS: This service transmits a short message from a service center to UE.
After the UE receives the message, it sends an acknowledgement message.
GSM Fax Services
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the GSM G3 transparent fax that complies with 3GPP
TS 03.45 and ITU-T T.30. The rate of the transparent fax can be 9.6 kbit/s, 4.8 kbit/s or 2.4
kbit/s during the fax service. Service types consist of TS61 and TS62.
z
TS61: The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the alternate of G3 transparent digital fax
and speech. The rate can be 2.4 kbit/s, 4.8 kbit/s or 9.6 kbit/s during the fax service.
z
TS62: The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports image fax but not file fax and ECM error
correction mode. The rate can be 2.4 kbit/s, 4.8 kbit/s or 9.6 kbit/s during the fax service.
GSM Bearer Services
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the following BS20 bearer services of which the fixed
network user rate can be 2.4 kbit/s, 4.8 kbit/s or 9.6 kbit/s:
z
Transparent asynchronous bearer services-3.1kHz audio.
z
Transparent asynchronous bearer services-UDI of which rate adaptation is V.110.
z
Non-transparent asynchronous bearer services-3.1kHz audio.
z
Non-transparent asynchronous bearer services-UDI of which the rate adaptation is V.110.
UMTS Bearer Services
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the following BS20 and BS30 bearer services:
z
Non-transparent asynchronous bearer services-3.1kHz audio, and under the UMTS, fixed
network user rate is 9.6/14.4/19.2/28.8 kbit/s.
z
Non-transparent asynchronous bearer services-UDI, and under the UMTS, the fixed
network user rate is 9.6/14.4/19.2/28.8 kbit/s, and the rate adaptation is V.110/V.120.
z
Transparent synchronous bearer services-UDI multimedia, fixed network user rate is 56
kbit/s or 64 kbit/s.
5.1.2 Supplementary Services
Overview
The supplementary services (SSs) are the supplement or convert the basic teleservices. The
SSs provided for the subscribers are based on the basic teleservices, and they must be
provided for the subscribers together with basic services.
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the following multiple SSs defined in the 3GPP
specifications.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-3
Page 56

5 Services and Functions
Call Forwarding Services
Call forwarding (CF) services: The system forwards calls to third parties based on the
requirements of carriers, networks, and subscribers.
Call forwarding services consist of the following services:
z
Call Forwarding Unconditional (CFU): When a mobile subscriber is a called party, all
the calls are forwarded to the third party. The third party can either be a subscriber in the
PLMN, PSTN and ISDN or the service console (such as Voice Mailbox).
z
Call Forwarding Busy (CFB): When a called mobile subscriber is busy, the call is
forwarded to the third party. The CFB can be divided into Network Determined User
Busy (NDUB) and User Determined User Busy (UDUB) based on the forwarding cause.
z
Call Forwarding on No Reply (CFNRy): When the mobile subscriber does not answer
the call for a long time after receiving the network ALERTING message, and the No
reply duration timer expires, the calls are forwarded to the third party.
z
Call Forwarding on Mobile Subscriber Not Reachable (CFNRc): If the network is
disconnected from the radio channel of the mobile subscriber and the mobile subscriber
is the called party, all the calls are forwarded to the third party. The Not Reachable
conditions include paging no reply, radio channel allocation failure, and subscriber
power-off. The CFNRc is classified into the home CF and destination CF based on the
forwarding locations.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Call Barring Services
Calls barring services consist of two types:
z
Barring of outgoing calls (BO)
z
Barring of incoming calls (BI)
The BO service includes:
z
Barring of All Outgoing Calls (BAOC)
z
Barring of All Outgoing International Calls (BOIC)
z
Barring of Outgoing International Calls except those directed to the Home PLMN
Country (BOIC-exHC)
The BI service includes:
z
Barring of All Incoming Calls (BAIC)
z
Barring of Incoming Calls When Roaming Outside Home PLMN Country (BIC-ROAM)
The following describes the BO and BI services.
z
BAOC: When the service is activated, the subscribers can originate only emergency
calls.
z
BOIC: If the mobile subscribers are roaming in the home PLMN, they are not allowed to
originate calls to the overseas subscriber. If the mobile subscribers are roaming outside
the home PLMN, they can originate calls to the local subscribers only.
z
BOIC-exHC: When the service is activated, the subscribers are unable to originate the
international toll calls except calls in home country.
z
BAIC: When the service is activated, the subscribers are unable to answer all incoming
calls.
5-4 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 57

5 Services and Functions
5.1 Basic Services
5.1.1 Teleservices
Overview
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the following basic teleservices:
z
Speech services
z
Short Message Service (SMS)
z
GSM fax services
z
GSM bearer services
z
UMTS bearer services
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 provides bidirectional communication capability for the
following:
z
Mobile subscribers of local office
z
Other connected subscribers, such as mobile subscribers of other offices and fixed
network subscribes
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Speech Services
The speech service is the basic function of the telecom network, including telephony (TS 11),
emergency call (TS 12) and emergency call for special service:
z
z
z
SMS
Short message (SM) means that the length of cell content transferred each time is short in the
SMS. Based on the definition of relevant technical specifications (ETSI GSM 03.40 and ETSI
GSM 03.41) in the current ETSI GSM, each Point-to-Point (PTP) SM includes a maximum of
140 bytes, that is, 160 ASCII characters or 70 Chinese characters. Each broadcast SM
includes a maximum of 82 bytes/page. That is, 92 ASCII characters or 41 Chinese characters,
and a maximum of 15 pages macro broadcast messages can be sent continuously. The PTP
SMS allows subscribers to send or receive the SM at any time. The broadcast SMS allows
subscribers to receive public messages regularly and selectively.
Telephony: The carriers provide the telephony service for PSTN, ISDN, and PLMN
subscribers through the function.
Emergency call: When a mobile subscriber presses an emergency key or dials 112, the
call is connected to the answer phone notice equipment. The answer phone tells
subscribers how to call the emergency center. The subscribers can make emergency calls
even without a SIM or USIM.
Emergency call for special service: When dialing 119 (fire alarm center), 110 (mobster
alarm center), 120 (first-aid center) and 122 (traffic accident center), the mobile
subscribers access the nearest special service centers based on the BTS that the
subscribers are located in. These calls can generate the alarms. The carriers can decide
whether to charge the subscribers, and then performs related settings.
The SMS includes PTP SMS and point-to-multipoint SMS. The PTP SMS includes the
following:
5-2 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 58

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
BAIC-ROAM: When the service is activated and the mobile subscribers are roaming
outside the home PLMN country, they cannot receive incoming calls from other
subscribers.
Line Identification Services
The system provides the following functions:
z
Calling number display or restriction for called party
z
Called number display or restriction for calling party
Line identification services include:
z
Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP)
z
Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR)
z
Connected Line Identification Presentation (COLP)
z
Connected Line Identification Restriction (COLR)
The following describes the line identification services:
z
CLIP: CLIP is a service provided for a called mobile subscriber. When a mobile
subscriber receives a call, the system shows the calling number to the subscriber. The
subscriber can then determine whether to connect, reject or forward the call.
z
CLIR: CLIR is a service provided for a calling mobile subscriber. When a mobile
subscriber is a calling party, the system does not show the calling number to the called
party.
z
COLP: When a mobile subscriber calls, the system shows the called number to the caller.
When the callee activates the CF service, the caller communicates with the forwarded
subscriber instead of the original callee. The system shows the forwarded number to the
caller.
z
COLR: When a mobile subscriber is the callee, the system is not allowed to show the
called number to the caller. When the calleer is a forwarded one, the system does not
show the forwarded number to the caller
Call Completion Services
Call completion services consist of Call Waiting (CW) and Call Hold (HOLD):
z
CW: When mobile subscribers are in a conversation, they can connect another call. At
that time, the system prompts that another call is waiting, and the called subscriber can
determine whether to connect this call.
z
HOLD: A subscriber terminates the current call temporarily and connects a new
incoming call. After the new call is connected, the subscriber can shift between the old
and the new one, and another call is in HOLD state.
Multiparty Service
A mobile subscriber who registers this service can organize a multiparty telephone conference
(MPTY) (this mobile subscriber included). Up to 6 subscribers can have a conversation at the
same time through the MPTY. During the MPTY, the main control subscriber can add,
disconnect, or isolate the remote subscriber. Here ‘isolate’ means the chairman of the MPTY
isolates one subscriber from the meeting temporarily.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-5
Page 59

5 Services and Functions
Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) contains the following cases:
z
The subscriber enters the operation command of the un-standardized supplementary
service consistent with the USSD format and originates a special service request to the
network
z
The network side sends a USSD command to the network to carry out a special service.
Compared with the SMS, the USSD service can exchange messages in real time. It is
convenient for services such as stock query.
The USSD center provides the following services:
z
Airline information
z
Finance and stock information
z
Foreign exchange information
z
Gymnasium match result
z
Cinema ticket information
z
Bank account information
In addition, the USSDhelps mobile subscribers to query and manage their service data, for
example:
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
z
After the MSC is connected to IN network, subscribers can manage IN service data by
using the USSD.
z
Subscribes can query data (such as MSISDN number) in the VLR and HLR.
Closed User Group Service
Closed User Group (CUG): One or several users with the same attributes form a group. The
members have the same call attribute. The CUG service is applicable to a small group with
several members or a large enterprise with thousands of subscribers.
5.1.3 ODB Services
Overview
Operator Determined Barring (ODB) is controlled by network carriers. It is carried out
through HLR data management. Carriers restrict the call capabilities of subscribers based on
different characteristics, especially economic capability. This ensures that carriers do not pay
heavy conversation fees.
The ODB can be used in all the user terminal services and bearer services except emergency
calls. Compared with the SSs mentioned earlier, the ODB enjoys higher priority. When two
services conflict, the preceding SS is prohibited.
Relationship Between ODB and Call Barring Services
Both ODB and call barring services implement the barring service. There are however, a few
differences.
z
The ODB subscriber state is controlled by carriers, but that of the call barring services is
controlled by the subscriber himself or the carrier.
5-6 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 60

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
The ODB can be activated automatically, while call barring service is activated by
carriers or subscribers.
Supported ODB Services
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 supports the following ODB services:
z
Barring outgoing calls
z
Barring outgoing international calls
z
Barring outgoing international calls except those directed to the home PLMN country
z
Barring of outgoing calls when roaming outside the home PLMN country
z
Barring incoming calls
z
Barring incoming calls when roaming outside the home PLMN country
z
Barring of Roaming outside the home PLMN country
z
Barring of outgoing Premium Rate Calls (information)
z
Barring of outgoing Premium Rate Calls (Entertainment)
z
Barring of Supplementary Services Management
5.1.4 IN Services
Overview
PPS
MVPN
The Huawei MSOFTX3000 provides the gsmSSF function. The MSOFTX3000 supports
CAMEL 3, Prepaid Service (PPS) and Mobile Virtual Private Network (MVPN), and it is
compatible with CAMEL 2 and CAMEL 1.
The PPS is a card number service. To set up an account, the PPS subscriber must pay some
money in advance or purchase the capital card with a fixed face value (rechargeable card,
storable card and renewable card) for the conversation fees.
The carriers do not identify the ID of the subscriber. The carriers and the subscribers share
only a prepaid agreement relation. The PPS is convenient for both carriers and subscribers.
The system determines whether to connect or disconnect the call based on the account balance.
Once the call is connected, the system performs real-time charge and deducts the PP money
from the subscriber account. If the account balance is used up, the call is disconnected. Thus,
the PPS helps carriers avoid loss of conversation fees.
The carriers establish the private network of logic voice channel on the PLMN and PSTN.
This enables the convenient communication among an enterprise and group subscribers
through the following ways:
z
Private numbering plan
z
Abbreviated dialing
If the MVPN service is activated in the PLMN, it provides a private network service similar to
the PSTN Private Branch Exchange (PBX) for the mobile subscriber of the group registering
this service.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-7
Page 61

5 Services and Functions
The MVPN service provides the following functions for MVPN subscribers:
z
In-net calling
z
Off-net calling
z
Private label
z
Abbreviated label
z
Group access number
z
Override
The MVPN service provides a preferential charging rate for groups and enterprises. This helps
mobile carriers not lose VIP customers. Based on specifications, the MVPN service requires
the following:
z
All MSCs/GMSCs/HLRs support the MAP2+.
z
All MSCs/GMSCs have the SSP function and they can trigger IN services through
O-CSI/T-CSI.
5.1.5 Value Added Services
Multimedia Services
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Supported by the UDI bearer service, multimedia services realize video communication in the
Circuit Switched (CS) domain. The multimedia services support the following services:
z
Videotelephony
z
Video conference
z
Video On Demand (VOD)
z
Mobile television
Mobile Location Services
With the gateway mobile location center (GMLC) , the MSOFTX3000 performs the following
functions:
z
Supports the Lg interface.
z
Stores the mobile subscriber location information.
z
Provides the information at any time
The services include:
z
Mobile called subscriber location service: The external device can locate a mobile
terminal.
z
Mobile calling subscriber location service: The mobile terminal sends a location request.
z
Emergency call location service: The network locates the subscriber in case of
emergency.
z
Subscriber privacy protection: The location requester will be restricted based on the
subscriber request to protect privacy.
Ring Back Tone Service
The MSOFTX3000 supports the Ring Back Tone (RBT) service. The RBT service replaces
the traditional ring-back tone with customized music and other special tones.
5-8 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 62

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
Equal Access Service
The mobile subscriber can select the network of each toll carrier. This realizes the equal
competition of toll carriers.
For the performance of the equal access service, each toll carrier is allocated with a carrier
identification code (CIC). After signing an agreement with a toll carrier, the mobile subscriber
can select the toll network of this toll carrier to originate a call by adding the CIC of this toll
carrier. Two two modes to use the service are: Preset CIC and Dial up freely CIC.
A mobile subscriber can add the function of presetting network selection. The mobile
subscriber can select a toll carrier through the preset function. The mobile subscriber can then
select a preset toll network channel of one carrier to originate a toll call without dialing the
CIC.
Enhanced Roaming Restriction Service
The differences between the enhanced roaming restriction (ERR) and the common roaming
restriction (CRR) are as follows:
In the CRR, the VLRs which a subscriber can roam to are configured directly on an HLR. The
minimum restriction area is on a VLR area basis. This kind of restriction is not flexible,
because the subscribers must be configured one by one, and the restricted areas may be too
wide.
The ERR does not require HLR subscription and the roaming restriction data is configured
directly on the MSC or VLR. You can restrict the roaming of a specific subscriber or even
subscribers within a number segment in the MSC/VLR area. The minimum restriction area is
on a cell basis.
Alternate Line Service
For Alternate Line Service (ALS), a mobile subscriber can use one mobile terminal and one
SIM card, and the two MSISDNs can be charged separately. The service requires to be
supported by MSC/VLR as well as mobile terminals that can set Line1 and Line2. The
features of the service are as follows:
z
Two MSISDNs are for Line1 and Line2. If a mobile terminal originates a call with a line,
its MSISDN is displayed as the caller ID.
z
A mobile terminal can only originate or answer a call through either Line1 or Line2 at a
given time. Therefore, a caller can only dial one MSISDN that corresponds to Line1 or
Line2. Otherwise, the call connection fails. For example, if a mobile terminal uses Line1,
but a caller dials the MSISDN that corresponds to Line2, the call connection fails.
z
For the two MSISDNs, you can subscribe to different supplementary services such as
call forwarding, call barring and call waiting.
z
When a mobile subscriber uses the MSISDN that matches Line1, speech services and
related supplementary services are allowed. ODB is used to bar services.
z
When a mobile subscriber uses the MSISDN that matches Line2, short messages can
only be received but not sent. USSD operation cannot be performed.
Voice and Video Double Number
Voice and Video Double Number (VVDN): The service enables the setting of different
MSISDNs for both voice and videophone services. The MSISDN is displayed as the caller ID.
For example, if a mobile subscriber originates a voice call, the MSISDN related to voice
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-9
Page 63

5 Services and Functions
service is displayed as the caller ID on the terminal of the called party. The same applies to
videophone calls. When a caller calls a mobile subscriber, either the MSISDN for voice
service or videophone service can be used.
5.2 Basic Functions
5.2.1 Mobility Management
Overview
Through the mobility management function, namely location management (LM) function, the
network can trace current location of MS and store location information in the following:
z
HLR
z
MSC
z
VLR
z
MS (SIM/USIM card)
LM flow ensures that the location information stored in the three entities is the same. The LM
function of network devices realizes the roaming function for mobile subscribers.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Common Location Update
During powering on or movement, if the location area identifier received by the MS is
inconsistent with that in the MS, the MS originates location update request to the network to
update the location area identifier. The MSOFTX3000 supports the following location update
flows:
z
Location update in the same MSC Server/VLR area
z
Location update cross different MSC Server/VLR areas and originated by the IMSI
z
Location update cross different MSC Server/VLR areas and originated by the TMSI
Periodic Location Update
The MS originates location update periodically, whether it moves to new location area or not.
If the MS does not originate periodic location update flow after a specified period expires, the
VLR sets the status of the IMSI to detach. Thus, the waste of circuit resource and wireless
resource can be reduced.
IMSI Attach/Detach
If the network allows the MS to access the network, the VLR automatically sets the status of
subscriber IMSI to attach. It indicates that the subscriber is activated and valid.
When the MS is switched off for a long time, the VLR automatically sets the status of
subscriber to detach. When a subscriber who is in detach status is called, the system does not
originate call attempt to the subscriber. Thus, wireless channel resources are saved. The
MSOFTX3000 supports the following IMSI detach types:
z
Implicit IMSI detach: After the implicit IMSI detach timer times out, the VLR
automatically sets the status of subscriber to detach.
5-10 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 64

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
Explicit IMSI DETACH: The MS originates the IMSI detach flow and the VLR sets
status of subscriber to detach.
Combined Location Update
When the network is configured with Gs interface and the MS supports both CS services and
PS services, the combined location update flow is originated in the following cases:
z
The MS moves to a new route area
z
A mobile phone that has attached GPRS attach originates IMSI attach
z
Both GPRS attach and IMSI attach are originated at the same time.
Association is established between the SGSN and the VLR. Either of them saves the ISDN
number of the other.
5.2.2 Security Management
Overview
The MSOFTX3000 supports the security management (SM) function defined by the 3GPP
specifications, such as the following:
z
Authentication
z
Encryption
z
Integrity protection
z
TMSI reallocation
z
IMSI identification
z
IMEI identification
The SM function can perform the following:
z
Preventing prohibited subscribers from connecting the network
z
Preventing fraud network from spoofing subscribers
z
Ensuring the reliable transmission of the subscriber signaling data
GSM Authentication and Encryption
The MSOFTX3000 supports the authentication encryption algorithm and flow defined by the
GSM.
z
Supporting general authentication
z
Supporting 1/N authentication
Through data configuration, only one authentication flow is performed for multiple
location updates and services accesses.
z
Supporting authentication parameter multiplex
An authentication flow requires a group of authentication parameters (APs). If the APs
used for each authentication flow are different, the signaling load from the MSC to the
HLR increases and the processing capacity of the HLR decreases.
You can configure the AP multiplex function and count. Therefore, the same APis used
for multiple authentication flows, which decreases the network load and increases the
processing capacity of the HLR.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-11
Page 65

5 Services and Functions
z
Supporting all the encryption defined by the GSM
UMTS Authentication and Encryption
The MSOFTX3000 supports authentication encryption algorithm and authentication flow
defined by the UMTS. The authentication triplet for the GSM evolves into authentication
quintuple for the UMTS.
Second Authentication
If the first authentication of the mobile subscriber fails (for example, the SRES sent to the
MS/UE side is different from that on the switch side), the network side must originate the
second authentication request in the same event and use RAND2 that is different from
RAND1 in the first authentication request. If the second authentication fails, the network side
sends an Authentication_Reject message to the terminal.
Conversion Between Authentication Triplet and Quintuple
The MSOFTX3000 supports the conversion between the triplet encryption for the GSM and
quintuple encryption for the UMTS. This facilitates the roaming and handover between the
GSM and the UMTS.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
TMSI Reallocation
The temporary mobile subscriber identity (TMSI) indicates a string of numbers allocated to
subscribers temporarily and identifies an MS in a location area. TMSI managed by the
MSC/VLR is allocated to the MS when the MS registers for the first time in a location area,
and deregistered when the MS is out of the location area. The TMSI rather than the IMSI is
transmitted in the radio channel, which can prevent the third party from identifying and
tracing the mobile subscriber by eavesdropping the signal in the radio channel.
The MSOFTX3000 supports the TMSI reallocation during:
z
Location update
z
Call setup
z
SS operations
IMSI Identification
The IMSI identification indicates that the network originates an IMSI identification flow if it
cannot identify the TMSI used for the network access of the mobile subscriber. After
receiving the identification response, the network can allocate a new TMSI.
IMEI Identification
The MSOFTX3000 can coordinate with the EIR to perform the IMEI check to the MS. By
querying the IMEI record (white list, grey list, and black list) in the database, the
MSOFTX3000 determines whether to provide service for the MS.
Embedded EIR
The embedded EIR indicates that a virtual EIR is configured with illegal IMEI information in
the MSC to enable the Check IMEI function for the carrier. The Check IMEI function enables
5-12 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 66

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
the MSOFTX3000 to obtain the IMEI from the mobile devices and sends the IMEI to the EIR
for the device status check.
The embedded EIR of the MSOFTX3000 can save up to 20.000 records.
5.2.3 Handover
Overview
Handover indicates the MSC hands over from one radio channel to another because of the
network signal problem or subscriber's removal during the call.
In respect of the GSM network and the UMTS network, the handovers provided by
MSOFTX3000 for network side consist of the following:
z
Intra-GSM handover
z
Intra-UMTS handover
z
Handover between the UMTS and the GSM
In respect of the MSC, the handovers performed by the MSC consists of the following:
z
Intra-MSC handover
z
Inter-MSC basic handover
z
Subsequent handover
Intra-MSC Handover
Intra-MSC handover indicates that the radio channel of a mobile subscriber hands over from
the current BSS/RNS to another BSS/RNS of the same MSC. The whole handover is
controlled by one MSC. The intra-MSC handover can be divided into intra-MSCa handover
and intra-MSCb handover. The MSC in which a call is established firstly is called a
controlling MSC (Anchor MSC). The handover that occurs in the controlling MSC is called
intra-MSCa handover. The handover that occurs in the non-controlling MSC is called
intra-MSCb handover.
Inter-MSC Basic Handover
Inter-MSC handover indicates that the handover occurs when a mobile subscriber moves from
the BSS/RNS coverage area of one MSC to the BSS/RNS coverage area of another MSC
during communication. In the inter-MSC basic handover, the controlling MSC (MSCa)
controls the whole handover procedure, and it must perform the following:
z
Sending handover request from the RNC
z
Selecting the destination MSC
z
Originating a handover resources request to the non-controlling MSC (MSCb) through
the MAP signaling
z
Establishing the inter-MSC bearer
z
Call control after the handover
The MSCb must establish the wireless side resources required for the handover, and
coordinate with the controlling MSC to perform the call control after the handover.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-13
Page 67

5 Services and Functions
Subsequent Handover
The subsequent handover indicates the inter-MSC handover originated by the non-controlling
MSC after the inter-MSC basic handover. The subsequent handover consists of:
z
Subsequent handover back to controlling MSCa
z
Subsequent handover to the third party (non-controlling MSCb')
The procedures of the subsequent handover back to MSCa are as follows:
Step 1 MSCb responds to the handover request of the BSS or the RNS.
Step 2 MSCb originates the "subsequent handover back to MSCa" to MSCa through the MAP
signaling.
Step 3 MSCa instructs the local BSS and the RNS to allocate the resources,
Step 4 MSCa notifies MSCb to send a handover command.
Step 5 MSCb releases the bearer between MSCa and MSCb.
----End
The procedures of the subsequent handover to the third party (MSCb') are as follows:
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Step 1 MSCb responds to the handover request of the BSS or the RNS.
Step 2 MSCb originates the "subsequent handover to the third party (MSCb')" to MSCa through the
MAP signaling.
Step 3 MSCa informs MSCb' of preparing for the handover.
Step 4 MSCb' instructs the local BSS and the RNS to allocate the resources.
Step 5 MSCb' notifies MSCb to send a handover command.
Step 6 MSCb releases the bearer between MSCa and MSCb.
----End
5.2.4 Call Processing
Call Connection
The MSOFTX3000 supports incoming and outgoing call connection functions of both
common services and IN services. The MSOFTX3000 provides the following call connection
functions of local call, outgoing call, incoming call and incoming tandem office call:
z
Querying MSRN number of mobile subscriber based on an MSISDN number and then
connects the call to the VMSC according to the MSRN number
z
Originating call attempt based on IMSI/TMSI number of mobile subscriber and location
area/service area where the subscriber is roaming
z
Pre-paging function
z
Emergency calls and special service calls defined by carriers
z
Alarm function for emergency calls or malicious calls
z
DN tone sending and failure tone sending
5-14 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 68

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
Delay ringing function
Number Analysis
The MSOFTX3000 provides a powerful number analysis function that has various
applications:
z
Supports receiving and storing numbers with up to 32 digits
z
Supports number analysis of up to 32 digits
z
Supports 30000 called number prefixes
z
Supports 4096 GT codes
z
Supports service check function
z
Supports call authority check function
z
Supports pre-processing function for incoming number and outgoing number
z
Supports caller number discrimination function
z
Supports black and white list call barring function
z
Supports the restriction of minimum number length and maximum number length
z
Supports changing numbers (caller numbers, callee numbers and roaming numbers)
based on number location or specified characters
z
Supports changing caller number or callee number based on association relationship
between them in number analysis range
z
Supports changing caller type, caller address property indicator and callee address
property indicator in the sent inter-office originated address message IAM/IAI.
Route Selection
The MSOFTX3000 can select the route to connect calls based on the number analysis result
and caller information. The route selection function supports the following:
z
z
z
z
z
z
5.2.5 Charging
Types of CDRs
The MSOFTX3000 supports more than 40 types of original CDRs, and meets various
requirements of carriers.
CDRs.
Intra-office route selection function (to the BSC/RNC that the MSC belongs to) and
inter-office route selection function (to other office)
Route selection function according to sequence or percentage
Dynamic route selection based on time
Avoidance peer route alternative function
Multi-gateway static route function, and inter-gateway route selection based on random,
percentage and alternate selection policy
Optimal route function
Table 5-1 describes the generation scenarios of various original
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-15
Page 69
5 Services and Functions
Table 5-1 Original CDR generation scenario
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Type Of Original
CDR
Mobile originated call
(MOC) record
Mobile terminated call
(MTC) record
Mobile originated call
forwarding attempt
Generation Scenario
If a non-IN mobile subscriber originates a call, and the call is
answered, the MSC generates a CDR called mobile-originated
call record or MOC CDR for the caller when the call ends or the
timer of long time call CDRs expires.
If a non-IN mobile subscriber receives a call, the MSC generates
a CDR called mobile-terminated call record or MTC CDR for the
callee when the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs
expires.
During a call connection, assume that:
z
B is a non-IN mobile subscriber.
z
B registers the call forwarding service.
z
C is the forwarded-to destination code.
A calls B, and the call is forwarded to C by the MSC serving B.
C answers the call. When the call ends or the timer of long time
call CDRs expires, the MSC generates a CDR called call
forwarding record or CFW CDR for B.
If A, B, and C are mobile subscribers served by the same
MSC/VLR, the MSC generates an MOC CDR for A, a CFW
CDR for B, and an MTC CDR for C when the call ends or the
timer of long time call CDRs expires.
SMS MOC record If a mobile subscriber sends an SM to the SMC successfully, the
MSC generates a CDR called SMS MOC record or MO_SMS
CDR.
Short message communication uses the signaling channel to
transfer characters. Compared with the common call CDR, the
short message CDR consists of SM content, SM operation result,
number of SM bytes, and SMSC address.
SMS MTC record If a mobile subscriber receives an SM from the SMC
successfully, the MSC generates a CDR called SMS MTC record
or MT_SMS CDR.
Transit call attempt When an incoming trunk originates a call, the MSC (TMSC)
connects the call to certain an outgoing trunk after analyzing the
call. That is, the call is neither originated nor terminated in the
local MSC. If the type of incoming and outgoing office directions
is "Local network", the MSC generates a CDR called transit
record or TRANSIT CDR when the call ends or the timer of long
time call CDRs expires.
5-16 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 70

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
Type Of Original
Generation Scenario
CDR
Inter-network transit
call attempt
When an incoming trunk originates a call, the MSC (TMSC)
connects the call to an outgoing trunk after analyzing the call.
That is, the call is neither originated nor terminated in the local
MSC. If the types of incoming and outgoing office directions are
"Other network" (Other PLMN or PSTN), the MSC generates a
CDR called inter-network transit call record or OT_TRANSIT
CDR, when the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs
expires.
OutGtewayRecord When an incoming trunk originates a call, the MSC (GMSC)
connects the call to an outgoing trunk after analyzing the call.
That is, the call is neither originated nor terminated in the local
MSC. If the type of incoming office direction is "Local network",
and the type of outgoing office direction is "Other network"
(Other PLMN or PSTN), the MSC generates a CDR called
outgoing gateway record or GWO CDR when the call ends or the
timer of long time call CDRs expires.
IncGatewayRecord When an incoming trunk originates a call, the MSC (GMSC)
connects the call to an outgoing trunk after analyzing the call.
That is, the call is neither originated nor terminated in the local
MSC. If the type of incoming office direction is "Other network"
(Other PLMN or PSTN), and the type of outgoing office
direction is "Local network", the MSC generates a CDR called
incoming gateway record or GWI CDR when the call ends or the
timer of long time call CDRs expires.
Roaming record
Note:
The MSOFTX3000 provides the roaming record only for the 3G network
subscribers.
Assume that a non-IN roaming mobile subscriber is called The
call must be routed and connected to the GMSC of the home
PLMN. When the call ends, or the timer of long time call CDRs
expires, the GMSC generates a CDR called roaming record or
ROAM CDR for the callee.
Call attempt record Determining that a call type is a transfer call, an inter-network
transit call, an outgoing gateway exchange call, or incoming
gateway exchange call, the MSC generates a CDR called call
attempt record or ATTEMP CDR if the call fails to be set up.
The ATTEMP CDR is used to record the network resources
occupation for an unsuccessful call. That is, the ATTEMP CDR
is a TRANSIT CDR, an OT_TRANSIT CDR, a GWO CDR or a
GWI CDR. The only difference is that the release cause value in
the ATTEMP CDR is unsuccessfulCallAttempt. Based on the
value, the billing center can pick up the ATTEMP CDR.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-17
Page 71

5 Services and Functions
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Type Of Original
Generation Scenario
CDR
IN pickup record Assume that:
z
The MSC in office A cannot function as the SSP.
z
The MSC in office B can function as the SSP.
z
Office A routes the IN calls in office A to office B through the
Overlay mode.
z
The MSC in office B triggers the IN service.
When a non-IN subscriber in office A or incoming trunk calls IN
subscriber X (non-forwarding call), office A routes the call to
office B. Therefore, office A cannot get the precise location of IN
mobile subscriber X.
After triggering the IN service, office B can get the precise
location of IN mobile subscriber X. If subscriber X answers the
call, when the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs
expires, the MSC in office B generates a CDR called IN pickup
record or AI_MOI CDR. The CDR is provided for the billing
center to charge the caller accurately.
The AI_MOI CDR is generated only after the incoming trunk in
Overlay mode triggers the called IN service. When the mobile IN
network adopts networking of the destination network, the MSC
does not generate the AI_MOI CDR.
IN mobile-originated
call record
IN mobile-terminated
call record
If an IN subscriber originates a call, and the call is answered, the
MSC (SSP) triggering the IN service generates a CDR called IN
mobile-originated call record or AI_MOC CDR for the caller
when the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs expires. .
That is, the AI_MOC CDR is an MOC CDR. The only difference
is that the subscriber type in the AI_MOC CDR is CAMEL user.
Based on the value, the billing center can pick up the AI_MOC
CDR.
If an IN subscriber receives a call, and the call is answered, the
MSC (SSP) triggering the IN service generates a CDR called IN
mobile-terminated call record or AI_MTC CDR for the callee
when the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs expires.
That is, the AI_MTC CDR is an MTC CDR. The only difference
is that the subscriber type in the AI_MTC CDR is CAMEL user.
Based on the value, the billing center can pick up the AI_MTC
CDR.
5-18 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 72

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
Type Of Original
Generation Scenario
CDR
IN call forwarding
record
Assume that:
z
B is an IN mobile subscriber.
z
B registers the CFW service.
z
C is the forwarded-to destination code.
A calls B and the call is forwarded to C. C answers the call.
When the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs expires,
the MSC triggering the IN service generates a CDR called call
forwarding record or CFW CDR for B.
That is, the AI_CFW CDR is a CFW CDR. The only difference
is that the subscriber type in the AI_CFW CDR is CAMEL user.
Based on the value, the billing center can pick up the AI_CFW
CDR.
Location request If the MSC receives a location request of any type from the BSC
or the RNC, the MSC generates a CDR called location request
record or LCS CDR for the location operation.
The LCS CDR records the location method, location time, and
location results.
Supplementary service
actions
When a non-IN mobile subscriber executes non-call related
operations, such as registering, canceling, activating and
deactivating the SS, the MSC generates a CDR called
supplementary service actions or SS_ACT CDR for the
operation.
Hot billing record When confirming that a mobile subscriber has registered the hot
billing service, the MSC generates a CDR called hot billing
record or HOTBILL CDR if the subscriber succeeds in
originating any call, such as MOC, MTC, SMS-MO, and
SMS-MT. For a subscriber who has registered the hot billing
service, the MSC sends the CDRs related to the call to the billing
center immediately.
That is, the HOTBILL CDR is an MOC CDR, MTC CDR,
MO_SMS CDR, or MT_SMS CDR. The only difference is that
the hot billing flag in the HOTBILL CDR is true. Based on the
information, the billing center can pick up the HOTBILL CDR.
Check IMEI record If the MSC executes the Check IMEI flow in the process of the
location update and the service access, the MSC generates a CDR
called check IMEI record or CHECK_IMEI CDR.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-19
Page 73

5 Services and Functions
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Type Of Original
Generation Scenario
CDR
HLR interrogation During a call connection, assume that:
z
The callee is a non-IN mobile subscriber.
z
The MSC requests route information from the HLR through
The MAP signaling.
z
The HLR returns the MSRN to the MSC through the MAP
signaling.
The MSC generates a CDR called HLR interrogation record or
QUERY_HLR CDR.
If the callee is an IN mobile subscriber, the MSC must query the
HLR twice. By default, the MSC generates a QUERY_HLR
CDR when querying the HLR for the second time. If you set
Ticket control flag to Generate HLR interrogation record after
getting T-CSI with MOD GBILLCTRL, the MSC generates a
QUERY_HLR CDR when querying the HLR for the first time.
That is, the MSC generates two QUERY_HLR CDRs.
TCAMEL callee
record
During a call connection, if a mobile subscriber that has
registered the CAMEL service (with the T-CSI), receives a call,
and answers the call, the GMSC (SSP) triggering the IN service
generates a CDR called TCAMEL callee record or TCAMEL
CDR when the call ends or the timer of long time call CDRs
expires.
Common equipment
usage record
Handover event record If the MSC achieves call related handover, call hold, call waiting,
Failure record When a mobile subscriber fails to activate the location service,
Charge Advice Services
Charge advice services consist of Advice of Charge Information supplementary service (AoCI)
and Advice of Charge Charging supplementary service (AoCC):
During a call connection or a call, if the MSC in office A uses the
public device resources (such as conference resources) in office
A or in the MSC of office B, the MSC in office A generates a
CDR called common equipment usage record or
COMMONEQUIP CDR.
multiparty call establishment, and multiparty call split, the MSC
generates a CDR called handover event record or HO_EVENT
CDR.
The HO_EVENT CDR exists in the format of an original CDR.
Although the iGWB merges the HO_EVENT CDR into the MOC
CDR and MTC CDR, there is no HO_EVENT CDR in the final
CDR.
SS, or USSD service, the MSC generates a CDR called failure
record.
z
AoCI: This service provides real-time display of charging. After subscribers register
AoCI services, the network side delivers the rate information, and the MS automatically
5-20 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 74
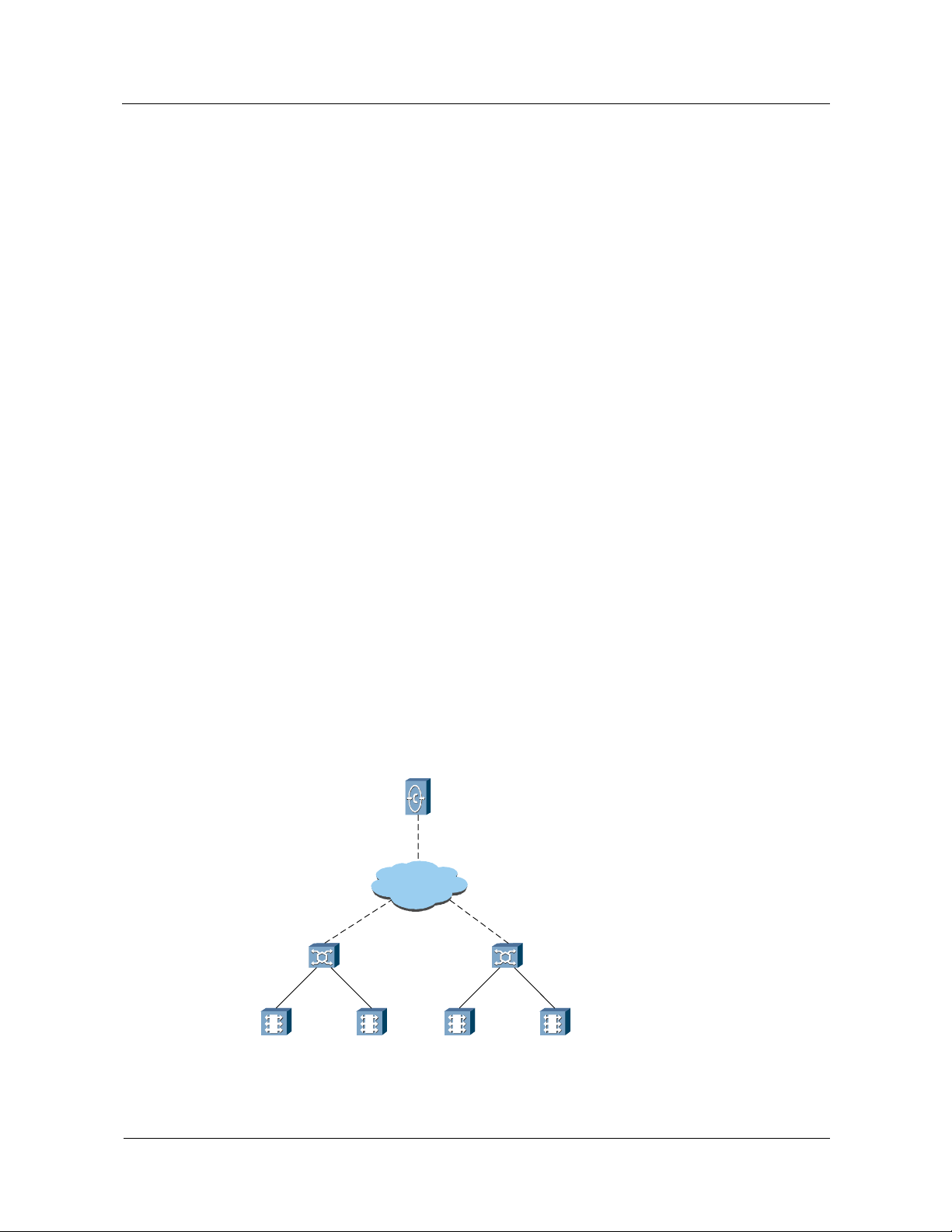
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
calculates the charge. Subscribers can obtain the present call charge and the accumulated
call charge through the menu. CDR charges of AoCI services are settled at the network
side. Mobile subscribers only obtain charging information of this call.
z
AoCC: CDR charges of AoCC services are settled at the terminal MS. The MSC is
responsible for delivering the rate information. Coordination of the terminal MS that
supports Phase2 standard and a special SIM card is required. AoCC is a simple mode that
helps realize leased phone or prepaid services.Hot Billing
After the MSOFTX3000 sends the original CDR generated during a call to the iGWB, the
iGWB allocates one single channel to store the final CDR and sends them to the billing center
in real time to realize the billing for the subscriber.
5.2.6 SSP
Overview
The MSOFTX3000 supports the mobile SSP functions, including the following
z
Call control function (CCF)
z
Service switching function (SSF)
z
Specialized resource function (SRF)
The MSOFTX3000 supports CAMEL 4 and is compatible with CAMEL 3, CAMEL 2, and
CAMEL 1.
Overlay Networking Mode
The Overlay network mode is suitable for the transitional stage, that is, when the
VMSC/GMSC cannot act as an SSP. In this mode, the VMSC/GMSC routes IN calls to the
SSP (the process is called Overlay) and then the SSP triggers IN services. In Overlay network
mode, the MSOFTX3000 acts as a VMSC/GMSC and does not need to provide the SSP
function in Overlay network mode.
Figure 5-1 Networking model of Overlay network mode
SSP
Figure 5-1 shows the networking model.
SCP
SS7 signaling
network
SSP
VMSC VMSC
GMSC GMSC
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-21
Page 75

5 Services and Functions
Target Networking Mode
The target networking mode is used when all local MSCs can act as SSPs. In this mode, the
MSC triggers IN services based on the CAMEL subscription information (CSI) in the HLR.
Figure 5-2 shows the networking model.
Figure 5-2 Networking model of target network mode
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
SCP
SS7 signaling
network
GMSC/
SSP
VMSC/
SSP
VMSC/
SSP
VMSC/
SSP
In this mode, the VMSC acts as the SSP to trigger MO, MF, and MVT calls. The GMSC acts
as the SSP to trigger MT and MF calls. MO, MT, MF, MVT are short for Mobile Originating,
Mobile Terminating, Mobile Forwarding, and Mobile VMSC Terminating.
5.3 Description of Features
5.3.1 List of Features
Tab le 5-2 lists the features supported by the MSOFTX3000.
Table 5-2 List of the features supported by the MSOFTX3000
Name of Feature Earliest Supporting Version
User Differentiated Service V100R005
Enhanced Flow Control V100R005
GMSC/
SSP
VMSC/
SSP
Inter-System Handover Based on Services V100R005
Mobile Virtual Network Operator V100R005
Call Failure Short Message Indication V100R005
MNP Service V100R005
5-22 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 76
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
Name of Feature Earliest Supporting Version
IP Facsimile V100R005
Multiple Time Zones V100R005
Paging Classification V100R005
Dual Transfer Mode V100R005
LCS Services V100R005
INClassMark Trigger IN Service V100R005
Configuration Rollback V100R005
Alarm Association Service V100R005
Management of Area-based Authority V100R005
Device Archive Management V100R005
Client Software Automatic Adaptation Management V100R005
M2000 Online Monitor and Management for Logging
V100R005
Subscriber
Mini-A-Flex Networking V100R003
Iu-Flex Networking V100R003
Network Sharing In Connected Mode V100R003
SCCP Policing V100R003
MAP Policing V100R003
ECT Service V100R003
SOR Function V100R003
TFO Function V100R003
TrFO Function V100R003
IN Announcement Charging V100R003
IN DCH Setting V100R003
2G/3G Network Access Control Based on Different
V100R003
Subscribers
Half-Rate-Based Subscriber Access Classification V100R003
Specified Circuit Dialing Test V100R003
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-23
Page 77

5 Services and Functions
5.3.2 V100R005 Version
User Differentiated Service
Development of the market and change of the competition environment, carriers must provide
services of different levels to subscribers with different requirements. The user differentiated
service is designed to meet carriers' requirement. The service provides a specific service
strategy for subscribers in a specific group. For example, services of high quality are offered
to subscribers of high priority; services of low quality are offered to subscribers of low
priority.
The MSOFTX3000 determines the priority of a call based on the following information:
z
Subscription information (Category, eMLPP, CARP and E-category)
z
Call type (such as MO, MT and SMS)
z
Access network type (2G and 3G)
Carriers can provide the following service strategies that correspond to the priority level:
z
The call can be set up rapidly in the radio channel. To shorten the time for setting up the
call, the system skips some processes including the authentication, encryption and TMSI
reassignment.
z
The ability of contention of a channel is offered. During congestion, the system allows
the call to pre-empt the call resource that can be occupied. The system prefers the
resource of calls of the lowest priority for contention.
z
The queuing ability is offered when the system fails to select a route. When the system
fails to select a route, the call is retained. The system arranges the call to wait for an idle
circuit in the queue. As soon as an idle circuit is available, the call is connected; or the
call is released because of timeout. When the system handles the calls in the queue, calls
of high priority level are set up faster than those of low priority level.
z
It is assured that a subscriber of high priority can obtain better network services, because
the differentiated access function based on half rate is provided for the 2G networking.
z
Access priority is offered when the system performance is unsatisfying. This can ensure
that subscribers with high-end services can obtain better network services.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Enhanced Flow Control
The MSOFTX3000 may be overloaded for some reasons (such as traffic becomes heavy, the
bandwidth for transferring signaling becomes less because of link faults, and many services
become invalid due to overload at peer network element.) The enhanced flow control function
helps the MSOFTX3000 to detect the overloads, and carry out effective traffic balance and
flow control. This can ensure the MSOFTX3000 to run at a high service processing rate in a
secure way. In addition, the enhanced flow control supports differentiated processing for
subscribers of different priority levels in the case of overload and allows the subscribers of
high priority level to connect to the network by preference.
There are examples as follows:
z
The traffic load causes that the CPU occupation rate of the service processing boards
(such as the WCCU, WCSU and WCDB) of the MSOFTX3000 exceeds the overload
threshold. The enhanced flow control function helps the MSOFTX3000 detect the
overload and activate flow control at the preliminary stage of overload. As a result, the
CPU occupation rate of the board does not increase, and a high service success rate and a
stable CPU occupation rate can be retained.
5-24 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 78

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
When the MSOFTX3000 is upgraded or cut over, there may be a large number of
location update requests. The links of the HLR are congested because the location update
flow occupies a large scale of bandwidth of the links from the MSOFTX3000 to the
HLR. This leads to many location update failures and slows down the service recovery.
The enhanced flow control function helps the MSOFXT3000 to detect the Hard To
Reach (HTR) occurring to location update flows at some HLRs and activate flow control.
This can retain a relatively high success rate of location updates when the load of the
links is reduced.
z
When processing service requests from the BSC/RNC, the MSOFTX3000 can distribute
resources in a balanced way based on the current load of the WCCU and WCSU. This
can ensure secure operation and make full use of the processing capability of the boards.
Inter-System Handover Based on Services
The inter-system handover indicates that the handover occurs when mobile subscribers in the
network move from the 3G coverage area to the 2G coverage area or from the 2G coverage
area to the 3G coverage area. The inter-system handover provides carriers with a solution to
balance the service load between the GSM network and the UMTS network.
For the MSOFTX3000, the IMSI segment, subscriber category and service type determine
whether the inter-system handover is allowed, and the preferred network type (GSM or
UMTS). If the current network is not the preferred network in configuration (for example, a
subscriber registers to the GSM network at present, but the UMTS network is selected as the
preferred network for data service when the carrier configures data), when the mobile
subscriber uses the data service, the MSOFTX3000 sends the assignment request message to
require the BSC or RNC to start the handover, that is, to hand the call over to the UMTS
network.
The service-based inter-system handover supported by the MSOFTX3000 provides the
following services:
z
Service handover from 2G speech service to the UMTS network
z
Service handover from 3G speech service to the GSM network
z
Service handover from 2G nontransparent transmission data service to the UMTS
network
z
Service handover from 3G nontransparent transmission data service to the GSM network
z
Service handover from 2G transparent transmission data service to the UMTS network
z
Service handover from 3G transparent transmission data service to the GSM network
z
Service handover from 2G VP service support fallback to the UMTS network
z
Service handover from 3G VP service support fallback to the GSM network
Mobile Virtual Network Operator
The mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) is a networking mode in which multiple
carriers provide their services by sharing all or part of their network resources. For subscribers,
the MVNO service is transparent and realizes seamless service provision. For carriers, the
MVNO service reduces the cost on network construction and helps build a network quickly in
a densely populated area.
The MVNO feature supported by the MSOFTX3000 provides the following functions:
z
The network name can be set on the MSC side and is sent to mobile stations by using the
MM_information message.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-25
Page 79

5 Services and Functions
z
The MVNO CDR can be sorted. That is, when the iGWB generates CDRs, the
NetworkOperatorId is filled in the CDR to identify CDRs of local subscribers or MVNO
subscribers. In this case, when sorting the CDRs, the iGWB saves the CDRs to different
directories based on the NetworkOperatorId information. The charging centers of
different carriers obtain the required CDRs from the directories assigned to them.
Call Failure Short Message Indication
The call failure short message (SM) indication is to prompt the callee that there is a missed
call through the SM. That is, when a caller originates a call, the call may fail because of the
following causes:
z
The callee's phone is powered off.
z
The callee is unreachable.
z
The callee does not answer the call.
z
The network is busy.
When the call fails, the network side sends a specified SM to the callee to prompt the date, the
time and the calling number of the missed call.
The call failure SM indication service is excluded from the call forwarding service and the
voice mailbox (VM) service. That is, the system can trigger the call failure SM indication
service only when the call forwarding service and the VM service are not employed.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
MNP Service
When the MSOFTX3000 serves as the GMSC or terminating VMSC, the system triggers the
SM indication service in the following abnormal cases:
z
GMSC: After obtaining the route information, it is found that the callee is absent (for
example, the phone is powered off).
z
Terminating VMSC: During an incoming call to the office, it is found that the callee's
phone is powered off or does not have the roaming authority.
z
Terminating VMSC: During an incoming call to the office, it is found that the callee does
not respond the paging, or the response times out.
z
Terminating VMSC: During an incoming call to the office, it is found that the callee is in
conversation.
z
Terminating VMSC: During an incoming call to the office, it is found that the network is
congested.
z
Terminating VMSC: After an incoming call to the office, it is found that the callee does
not answer the call.
The mobile number portability (MNP) allows a mobile subscriber to change the subscription
network in a country or an area. In addition, the subscriber can retain the original MSISDN.
When the subscriber uses the MNP service, all services provided by the original subscription
network are cut over to the new subscription network. At the same time, the current
subscription network assigns a new IMSI number to the MNP subscriber.
In the same subscription network, MNP subscribers are not different from non-MNP
subscribers in service application. There are, however, some differences in quality service,
such as additional call setup delay for MNP subscribers. The MNP service supported by the
MSOFTX3000 provides the following functions:
5-26 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 80

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
No need to change MSISDN: The MSISDN does not vary with carriers or subscription
networks.
z
Independent subscription service: The original network does not have any impact upon
services of the subscriber. If the services supported by the original network are not
supported by the new network, the subscribers in the new network can choose the
services.
z
Ported many times: A network allows its numbers to be ported out and numbers of
another network to be ported in. One MSISDN can be ported many times. It can also be
ported back and forth among multiple networks.
z
Independent service: It does not conflict with any other mobile service.
IP Facsimile
IP facsimile is the facsimile service over IP. It is important to ensure the quality of data
transmission, because the quality of data transmission determines the facsimile quality. The
data stream redundancy is a solution to the data packet loss during transmission. The
MSOFTX3000 supports the transmission of data redundancy. This can effectively enhance the
transmission quality, and reduce or avoid service interruptions due to low quality of data
transmission.
During a call process, the MSOFTX3000 determines whether to send redundancy parameter
2198 of data service to the MGW based on the data configuration, and also determines
whether to notify the MGW to perform facsimile event detection after the call is started. After
the MGW reports the facsimile tone detection event or facsimile status detection event, the
MSOFTX3000, based on the report, can send the CODEC attribute modification request to
the MGW to support the data service redundancy.
Multiple Time Zones
The MSOFTX3000 can work for multiple time zones or areas deploying different daylight
saving time (DST) schedules in one time zone. The multiple time zones provide the following
functions:
z
The time stamp in CDRs is consistent with the actual time in the place where the
subscriber is located, because automatic time adjustment is performed in CDRs based on
information like, the subscriber location and whether the DST is adopted.
z
The time stamp reported to the SCP is allowed to contain the DST information to ensure
that the SCP can charge calls accurately.
z
The accuracy of time report is ensured.
z
The terminal time can be changed based on the subscriber location.
Paging Classification
In 3GPP 48.008 specifications, the optional IE “Channel Needed” is defined in the Paging
message. This IE indicates the radio channel type that may be used in the subsequent service
flows. When the BSC supports the Channel Needed IE in the Paging message, if the traffic is
heavy, the MSOFTX3000 performs flow control for the services of low priority, such as short
message service. This can reduce the load of the BSC and ensure access of services of high
priority. Based on the Channel Needed IE, the BSC can also reduce unnecessary occupation
of the TCH bearer channel.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-27
Page 81

5 Services and Functions
There are examples as follows:
z
During a mobile termination call, the MSOFTX3000 can identify whether the full rate
channel or dual rate channel is used in subsequent services by using the “Channel
Needed” IE in the Paging message.
z
For the SMS reception service, USSD service or the LCS, the MSC identifies that the
SDCCH bearer channel is used in subsequent services by using the Channel Needed IE
in the Paging message.
z
If the BSC does not support the Channel Needed IE, the Paging message is not required
to carry the IE.
Dual Transfer Mode
The MSOFTX3000 supports the dual transfer mode (DTM) function defined in the 3GPP TS
03.55 specifications. The DTM indicates that in the 2G network, a terminal supports both CS
and PS domains to trigger services at the same time. That is, the terminal can retain the calls
of the CS domain as well as the data transmission of the PS domain.
LCS Services
By working with other devices, such as the BSC, RNC and GMLC, the MSOFTX3000 can
support not only the LCS services based on the Iu interface, but also LCS services based on
the A interface. This can allow the MSOFTX3000 to provide the function to store location
information of subscribers.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
z
Mobile callee location service: The external device can locate a mobile terminal.
z
Mobile caller location service: The mobile terminal originates the locating request.
z
Emergency call location service: The network side can locate the subscriber in an
emergency call.
z
Subscriber privacy protection: The party who requests locating can be restricted based on
the requirement on the subscriber privacy.
INClassMark Trigger IN Service
The INClassMark trigger IN service function uses the SS-CODE IE in the forwarding
information of a subscriber to identify whether the subscriber is an IN one. If SS-CODE is
plmn-specificSS-4 (0xF4) in a subscriber's subscription information, the subscriber is an IN
subscriber; otherwise, the subscriber is a common subscriber. During location update, the
HLR sends the data to the VLR for record.
During connection of a call, if the subscriber data contains the SS-CODE with the extended
option, the MSOFTX3000 adds a service attribute SERVICE13 for the subscriber. By using
the caller character handle data and caller character analysis data configured on the
MSOFTX3000 side, the MSOFTX3000 can trigger IN services for the subscriber.
If a subscriber uses INClassMark to trigger IN services and subscribes forwarding services,
the application scenario is as follows:
z
In the early forwarding process, when the MSOFTX3000 requests the HLR to provide
the roaming number, the HLR returns the subscription data to the MSOFTX3000 through
an SRI. After call forwarding occurs, the MSOFTX3000 judges whether the IN flow
needs to be triggered for the subscriber based on the SS-CODE with the extended option.
If it is required to trigger the IN flow, the MSOFTX3000 triggers the MF IN flow based
on the caller attribute. If it is not required to trigger the IN flow, the MSOFTX3000
forwards the call based on common flow.
5-28 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 82

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
In the late forwarding, the subscriber data is sent to the VLR through location update.
After call forwarding occurs, the MSOFTX3000 judges whether the IN flow needs to be
triggered for the subscriber based on the SS-CODE IE. If it is required to trigger the IN
flow, the MSOFTX3000 triggers the MF IN flow based on the caller attribute. If it is not
required to trigger the IN flow, the MSOFTX3000 forwards the call based on common
flow.
Configuration Rollback
During deployment or maintenance, some errors of data configuration may occur. In this case,
a function is required to return the configuration to the state before the errors. The function is
called configuration rollback. The MSOFTX3000 supports configuration rollback to avoid
traffic loss due to mistakes and improve the network security.
There are examples as follows:
z
Configuration in advance: Data can be configured before preset cutover, and the
configurations are not effective at once. You can determine the time for validating the
configurations.
z
Swiftly to be effective: After your confirmation, the configured data can be effective
within the designated time, and enter the state of trial-run and observation.
z
Swift rollback: When errors of configured data occur and cause abnormal operations
during trial-run, the system can be swiftly rolled back to the state of original data, so as
to avoid large-scale impacts on the system service.
z
Comparison of configured data: You can compare the data before modification with the
data after modification to make sure what has changed. This can help you locate the
errors easily.
z
Activation/rollback table: When data configuration is performed by several teams, the
MSOFTX3000 supports that each team has the specific data table for configuration, so
each team can work independently, and activate or roll back its own configured table.
Alarm Association Service
The alarm association service helps operation and maintenance (O&M) personnel to quickly
locate and analyze a problem. The MSOFTX3000 provides the following functions:
z
Filtering and shielding the child alarm. After receiving the parent alarm, the
MSOFTX3000 can shield the received child alarm within the specified period.
z
Reactivating the child alarm: If the recovery information of the child alarm is not
received within the specified period, the MSOFTX3000 reactivates the child alarm that
has been processed in related recovery.
z
Querying alarm-related information: If you query the information relevant to an alarm,
the MSOFTX3000 lists all alarms relevant to the alarm. This helps you locate and
analyze problems easily.
z
Hardware alarm correlation:
− Alarms for faults of upper level boards and alarms for faults of lower level boards can
be correlated.
− Alarms for board faults, alarms for network port faults, and alarms for faults of
internal communication links can be correlated.
− Alarms for CPC faults and alarms for faults of links provided by the CPC can be
correlated.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-29
Page 83

5 Services and Functions
z
Gateway alarm correlation: Alarms for gateway faults and alarms for faults of links and
circuits of the gateway are correlated.
z
The alarm correlation function can be enabled or disabled by using configuration
commands.
Management of Area-based Authority
The MSOFTX3000 terminal system supports management of area-based authority. That is,
the system resource of the MSOFTX3000 is divided into sections based on geographical areas.
Operators in each area can use the system resource independently. The system resource
operations in one area do not affect those in another area. In this case, operators in one area
can only perform configurations and alarms for the area only, and cannot affect the
information in another area. This can ensure the security of the system resource operation.
Device Archive Management
Through the NMS, the MSOFTX3000 can obtain the detailed information, such as:
z
Basic information of device
z
Connection information
z
Module information
z
Configuration information
z
Peer devicet information
z
Host version information
z
Cabinet information
z
Frame information
z
Information of boards and the Flash electronic label of boards
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
After receiving the command from the NMS (M2000), the BAM creates XML files of device
archives. Then, the NMS can send a command to the BAM, instructing it to upload the files to
a specified folder of the NMS.
Client Software Automatic Adaptation Management
For maintenance, the client software is distributed to different types of workstations at
different places. The MSOFTX3000 supports the function of the client software automatic
adaptation, which enables carriers to control the distributed client software versions in a
centralized way and improve the maintenance efficiency.
The MSOFTX3000 establishes a version control mechanism on the BAM to achieve the
function of the client software automatic adaptation. When operation and maintenance
personnel logs on to the BAM from a client and detects that the version of the client software
differs from that of the BAM, the client prompts users to download the version that matches
that of the BAM. Then there are two cases:
z
The subscriber confirms loading.
The system upgrades the client software automatically, and then uses the upgraded
version to log on to the BAM.
z
The subscriber refuses loading.
The system can use the mismatched version to log on to the BAM forcibly.
5-30 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 84

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
M2000 Online Monitor and Management for Logging Subscriber
The MSOFTX3000 can cooperate with the Huawei iManager M2000 (M2000 for short) to
provide the function of the online monitor and management for logging subscriber. The
function has the following features:
z
The M2000 manages the IP port, port status, version of network elements (NEs), number
of NEs of the same version, number of boards, faulty boards, cell status, distribution
condition, and resources capacity of each port (such as the number of 2-Mbit/s ports,
signaling ports, GE interfaces, FE interfaces, and CPUs).
z
The M2000 manages the input information of users, for example, the information of
leased circuits.
z
You can refresh managed resources data at the MSOFTX3000 side manually or at a set
time.
z
After refreshing the managed resources data, the M2000 can show the changed
information in audio and visual way. For example, it can show added, deleted and
modified information with different colors.
z
The M2000 can export information.
5.3.3 V100R003 Version
Mini-A-Flex Networking
Mini-A-Flex is also called intra-MSC A-FLEX. It is a GSM networking mode that can
enhance the reliability of A interface. Normally, the MSOFTX3000 is connected with the BSC
through the MGW and one BSC can only be connected with one MGW. If the MGW
connected with the BSC is faulty, all the services handled by the BSC are completely
interrupted.
To avoid the BSC service failure caused by the MGW upgrade and MGW failure, the
MSOFTX3000 supports the Mini-A-FLEX networking, which allows one BSC to connect
with multiple MGWs controlled by a same MSC. These MGWs adopt the load sharing mode
for service management. When one MGW is faulty, other MGWs can take up the service.
Figure 5-3 shows the Mini-A-Flex networking.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-31
Page 85
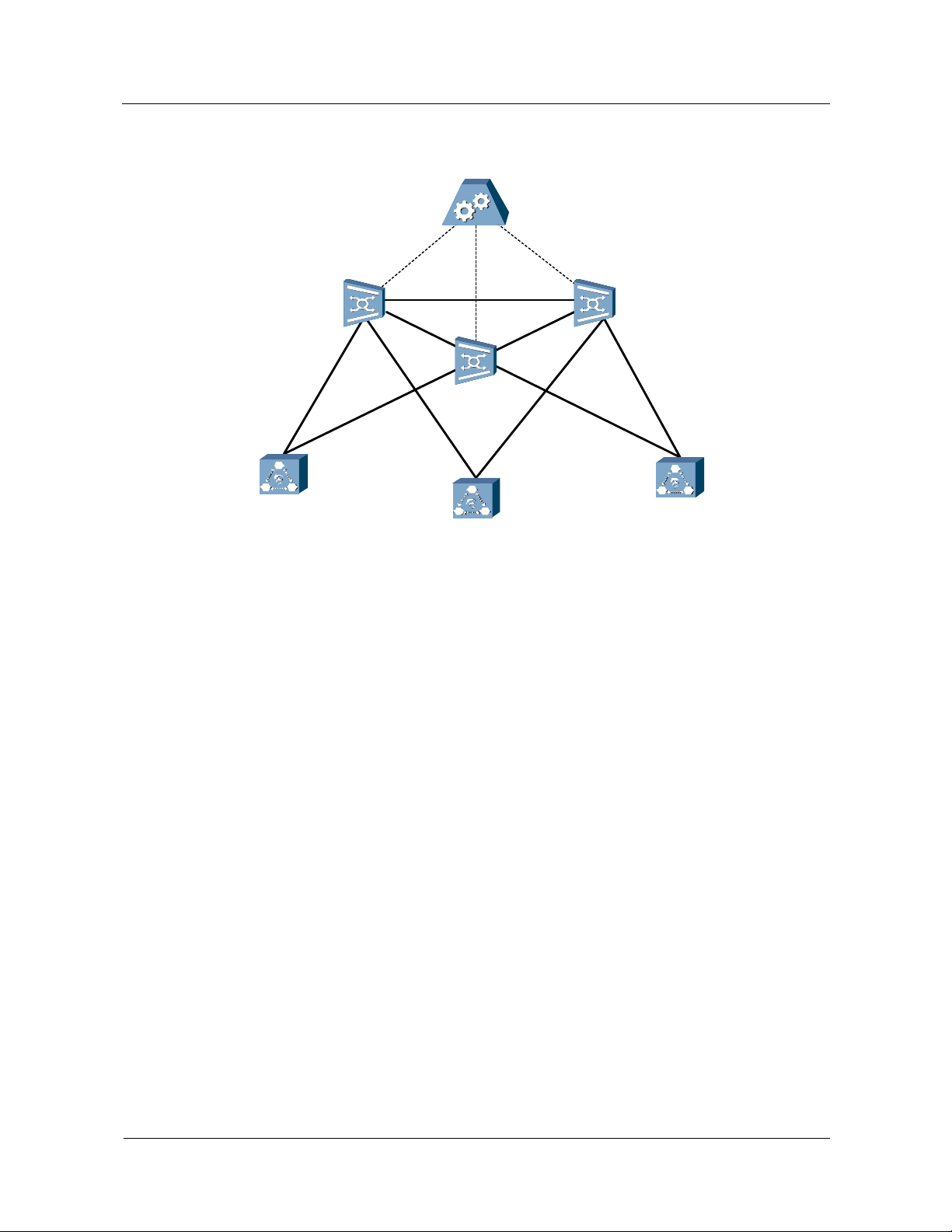
5 Services and Functions
Figure 5-3 Mini-A-Flex networking
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
MSOFTX3000
MGW 1
MGW 2
BSC 1
BSC 2
MGW 3
BSC 3
The Mini-A-Flex networking performs the following functions:
z
One BSC can be connected with multiple MGWs. The MSOFTX3000 can select the
circuit resources of the corresponding MGW as needed. Thus the system disaster
recovery function is provided based on the bearer network layer.
z
When the BSCs where a caller and a callee are located are connected with a same MGW,
the MSOFTX3000 selects corresponding A interface circuits on the same MGW first.
This can avoid wasting the circuit resources between MGWs.
z
During the incoming and the outgoing trunk call, handover and call reconnection, if the
MGW of one call party is settled, the MSOFTX3000 can optimize the selection of the
MGW for selecting A interface circuits. That is, the MSOFTX3000 selects the common
MGW first. This can avoid wasting the speech channel resources between MGWs.
Iu-Flex Networking
The intra-domain connection of RAN nodes to multiple CN nodes (Iu-Flex) is a networking
mode where one RAN node can be connected with multiple CN nodes in a same domain. In
the CS domain, Iu-Flex is also called MSC Pool.
architecture.
5-32 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Figure 5-4 shows the Iu-Flex network
Page 86
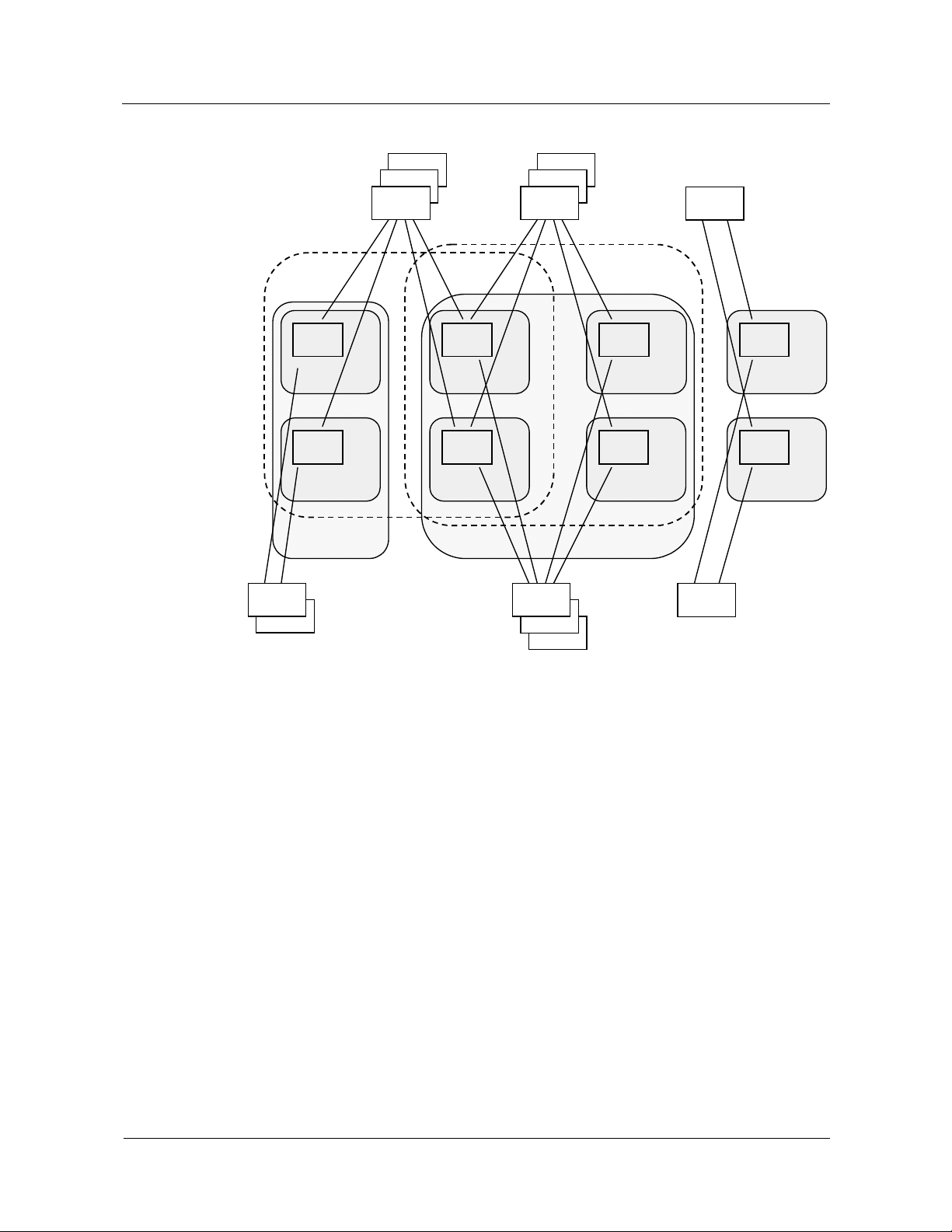
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
Figure 5-4 Iu-Flex network architecture
SGSN 1
SGSN 2
CS pool-
area 1
RAN
node
Area 1
RAN
node
Area 5
MSC 3
MSC 2
MSC 1
RAN
node
Area 2
RAN
node
Area 6
MSC 6
MSC 5
MSC 4
SGSN 3
SGSN 4
SGSN 5
PS pool-area 2PS pool-area 1
CS pool-
area 2
RAN
node
Area 3
RAN
node
Area 7
MSC 7
RAN
node
Area 4
RAN
node
Area 8
SGSN 6
As shown in
Figure 5-4, MSC 1, MSC 2 and MSC 3 make up of one MSC pool, while MSC 4,
MSC 5 and MSC 6 make up of another MSC pool. Each RAN node in an MSC pool is
connected with all MSCs in the pool and the service load is shared among these MSCs. The
Iu-Flex network allows multiple carriers to share the RAN resources. This networking mode
has the following advantages:
z
Multiple CN nodes can share the load of an RAN. This can improve the usage ratio of
CN nodes and reduce the loss resulted from the fault of a single CN node.
z
The service area of a single CN node is expanded. The number of CN node updates
during roaming and the number of cross-CN node handovers are reduced. This
subsequently cuts down the signaling flow of the core network.
Network Sharing In Connected Mode
The network sharing in connected mode provides the handover restriction function that
restricts the subscriber access to the network in connected mode. At present, the roaming
restriction of the mobile network means the roaming restriction controlled by the CN side in
idle mode, such as ZC roaming restriction and enhanced roaming restriction.
However, in the case that a subscriber is moving during a call, CN cannot restrict the roaming
area. Thus during a call, the subscriber can enter the area where the subscriber cannot enter
when idle. The networking sharing in connected mode can solve the problem. For example,
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-33
Page 87

5 Services and Functions
when two 2G carriers share one 3G network, the carriers can control their subscribers to use
their own 2G networks respectively by using the function.
The function needs the cooperation of the MSOFTX3000 and the RNC. On the
MSOFTX3000 side, the operator configures the information of roaming restriction that is in
connected mode and the information of the share network. The MSOFTX3000 sends the
roaming restriction information to the RNC. Based on the information, the RNC then
completes the roaming restriction in connected mode. The share network information is used
to set share network areas, which is the minimal roaming unit. The subscriber roaming
restriction information is configured based on the IMSI number segment of a subscriber. The
operator can achieve the roaming restriction function in connected mode by configuring the
allowed share network area group.
SCCP Policing
When interconnecting with the HLR, VLR, MSC, SMC and SCP in the mobile network, the
MSOFTX3000 can achieve the following by using the SCCP Policing function:
z
z
z
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Control the traffic of incoming signaling messages such as the MAP and the CAP
messages generated by the HLR, VLR, MSC, SMC and SCP within a specified range.
Avoid the congestion and overload of signaling links between the MSOFTX3000 and the
HLR, VLR, MSC, SMC and SCP.
Ensure the signaling network security.
MAP Policing
ECT Service
The local MSC can start the SCCP shielding control in the SCCP layer when the following
requirements are met:
z
The MSOFTX3000 enables the SCCP Policing function.
z
The local MSC receives incoming signaling messages such as the MAP and CAP
messages generated by other devices.
The SCCP shielding control is enabled based on the SPC, SSN and GT information in the
SCCP calling and called addresses contained in the message.
If the number of SCCP signaling packets received by the local MSC within a unit time
exceeds a specified threshold, the MSOFTX3000 will discard the extra SCCP signaling
messages and reject the subsequent message processing operations.
The MSOFTX3000 supports the MAP Policing function. With this function, a local MSC can
shield a given MAP operation request (such as getting MSRN or inserting subscriber data)
from a given network element (NE) in the receiving direction. That is, when a given NE sends
a given MAP operation request to a local MSC, the MSOFTX3000 can return a MAP
dialogue reject response to the peer end.
The function aims to shield unexpected incoming MAP messages sent to a local MSC,
achieve self-protection and prevent resources exhaustion.
The explicit call transfer (ECT) is a supplementary service. It is applicable to the UMTS and
the GSM network.
Suppose that A calls B and C respectively. In any of the following two cases, A can make B
and C connected and then quit the conversation by using the ECT function:
5-34 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 88

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
z
Both B and C are in conversation with A.
z
Either B or C in conversation with A and the other is hearing the ringing of the call made
by A.
The following are requirements of the ECT service:
z
B and C can be local mobile subscribers, non-local mobile subscribers or PSTN
subscribers.
z
A must have the authority of call hold supplementary service.
z
A is not an IN service subscriber.
SOR Function
The support optimal route (SOR) is a routing selection function applicable to inter-network
calls. The function has the following advantages:
z
Decrease the call alternative route between two networks and increase the network usage
ratio.
z
Cut down call costs for callers.
The SOR function has the following three flows:
z
Basic SOR flow: When a mobile subscriber calls a mobile subscriber, the GMSC of the
PLMN where the caller is located fetches the called MSRN from the HLR to which the
callee belongs. The GMSC then routes the call to the VMSC of the PLMN where the
callee is located.
z
Early forwarding SOR flow: If early forwarding occurs to the call between two mobile
subscribers and the SOR charging rule is applicable to the call, the GMSC of the PLMN
where the caller is located fetches the forwarded-to number of the callee from the HLR
to which the callee belongs. The GMSC then routes the call to the MSC to which the
forwarded-to number belongs.
z
Late forwarding SOR flow: If late forwarding occurs to the call between two mobile
subscribers and the SOR charging rule is applicable to the call, the GMSC of the PLMN
where the caller is located fetches the forwarded-to number of the callee from the VLR
to which the callee belongs. The GMSC then routes the call to the MSC to which the
forwarded-to number belongs.
TFO Function
The tandem free operation (TFO) is an operation without the second encoding and decoding
operations. It is a process of inband negotiation of the adopted Codec mode between two
Transcoders (TC) after the call is set up. For calls between two mobile subscribers,
unnecessary speech encoding and decoding conversion can be avoided in the sending end and
the receiving end. Thus the speech quality is promoted.
However, without the TFO function, four encoding and decoding operations are needed for
one call channel, as shown in
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-35
Figure 5-5.
Page 89

5 Services and Functions
Figure 5-5 Ordinary encoding and decoding speech operation
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Transcoding Functions
PLMN A
MS/UE MS/UE
ENCODING DECODING DECODINGENCODING
Compressed
Speech
Transcoding
Function
ITU-T G.711 A-Law/u-Law
Transcoding
Function
PLMN B
Compressed
Speech
The speech encoding performed by TC is lossy compression. Each encoding and decoding
operation will decrease the speech quality and increase the transit delay. Though the TFO
function does not require TC to perform encoding and decoding conversion, the TC is still
required to work, such as monitoring signaling in the TFO message, and transparently
transmitting speech stream. Therefore, the TFO function does not save the TC resources. On
each call channel, there is only one encoding and decoding operation, as shown in
Figure 5-6.
Figure 5-6 Encoding and decoding speech operation after activating TFO
Transcoding Functions
PLMN A
MS/UE MS/UE
Transcoding
Function
Transcoding
Function
PLMN B
TrFO Function
ENCODING
Compressed
Speech
Transparent
transmission
Compressed
Speech
Transparent
transmission
Compressed
Speech
DECODING
The TFO function is applicable to the GSM and the UMTS networks. Because the TFO
adopts the inband signaling TC control function, the TFO is suitable for the speech call
between two mobile subscribers only.
The transcoder free operation (TrFO) is an operation without any encoding and decoding
operation. During the speech transmission, TC is not required for speech processing. For calls
between two mobile subscribers, the end to end speech transmission function of high fidelity
and low delay can be provided.
Compared with the TFO function, TrFO does not need TC for speech transmission. No related
conversion or encoding and decoding operation is needed and thus the speech quality is
promoted. On each call channel, there is only one encoding and decoding operation, as shown
in Figure 5-7.
5-36 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 90

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
Figure 5-7 Encoding and decoding speech operation after activating TrFO
Transcoding Functions
Bypassed
PLMN A
MS/UE
ENCODING DECODING
The TrFO function is applicable to the UMTS network only. Because the TrFO function
adopts the outband signaling TC control function, the TrFO function is suitable for the speech
call between mobile subscribers and between the mobile subscriber and the subscriber of
external networks.
IN Announcement Charging
During the IN announcement process, carriers can determine whether to generate the call
detail record (CDR) in the end office based on announcement devices (end office or
independent IP) and announcement flows. The following are announcement flows:
z
Play announcement.
z
Receive number and play announcement.
z
Play announcement and receive number.
z
Play announcement and connect call.
z
Play announcement, receive number and connect call.
Transcoding
Function
Compressed
Speech
Transcoding
Function
PLMN B
MS/UE
After determining the charging rule of IN resources, carriers can use the IN announcement
charging function to make the MSOFTX3000 perform the following:
z
z
IN DCH Setting
The subscription information of IN subscriber in the HLR contains Default Call Handling
(DCH) that indicates which handling mode is adopted by the MSC when abnormal IN call
occurs. The MSOFTX3000 support the DCH setting function to define different handling
modes at the MSC side for different service keys and abnormal situations. The handling
modes include:
z
z
z
The IN DCH setting function has the following functions:
z
Provide the charging service of IN resources usage for subscribers
Flexibly specify the IN resources service to be charged.
Release the call by force.
Continue the call by force.
Use the default call handling method subscribed by the IN subscriber.
Carriers can set the data so as to continue the call by force for high-end IN subscribers or
to release the call by force for low-end IN subscribers.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-37
Page 91

5 Services and Functions
z
When the traffic is in the peak hours and the SCP response speed is reduced, such setting
can realize differential service, increase the call completion rate of high-end subscribers,
and improve the service quality.
2G/3G Network Access Control Based on Different Subscribers
For GSM/UMTS dual-mode subscribers, this function allows the MSOFTX3000 to control
the access of subscriber to the BSS or UTRAN network.
Provision of this function requires the collaboration of the MSOFTX3000 and HLR and the
HLR must support the Access Restriction Data (ARD) subscription function. The
MSOFTX3000 controls the authority needed by subscribers for accessing the GERAN or
UTRAN network. For example, the GERAN Allowed/UTRAN NOTAllowed service is
configured upon the subscription of ARD in the HLR, if the local MSOFTX3000 supports the
ARD 3G function:
z
If a subscriber originates location update to the local MSOFTX3000 from the 2G BSS,
and the local office does not restrict ARD 2G roaming, the MSOFTX3000 allows the
subscriber to access the 2G network.
z
If a subscriber originates location update to the local MSOFTX3000 from the 3G
UTRAN, and the local office restricts ARD 2G roaming, the MSOFTX3000 rejects the
subscriber to access the 2G network.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Half-Rate-Based Subscriber Access Classification
The half-rate-based subscriber access classification service ensures the QoS of high-priority
GSM subscribers in heavy-traffic hours.
Leveled subscriber indicates the MSOFTX3000 grants different priorities for each type of
subscriber of the HLR. Half rate indicates the MSOFTX3000 controls the BSC to distribute
speech channels for mobile subscribers according to the following policies in the condition
that the service is available when the reported handset capability is either full rate or half rate.
z
The MSOFTX3000 sets the channel type to full rate channel for the high-priority
subscribers. The BSC will always assign full-rate channels for these subscribers.
z
The MSOFTX3000 sets the channel type to both (full rate and half rate) for low-priority
subscribers. The BSC will assign full-rate channels to these subscribers when there are
sufficient resources, and will assign half-rate channels when otherwise.
Specified Circuit Dialing Test
This function allows maintenance personnel to test the availability of the circuits through the
A interface. The maintenance personnel can find such problems as self-loop and one-way
audio by unblocking trunk circuits. In this way, the means to locate faults is improved.
The MSOFTX3000 supports the dialing test on circuits both on the caller side and the callee
side.
z
Dialing test on circuits on the caller side: The caller who initiates the test call must be a
mobile subscriber. The callee can be a mobile subscriber, PSTN subscriber or virtual
subscriber. If the callee is a virtual subscriber, the MSC can play announcements to
continue the test.
z
Dialing test on circuits on the callee side: The callee who receives the test call must be a
mobile subscriber. The caller can be a mobile subscriber or a PSTN subscriber.
5-38 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 92

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 5 Services and Functions
In practice, in the dialing test on circuits on the caller side, the callee can be a virtual
subscriber. This makes the means flexible, the location process simple, and the maintenance
convenient.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 5-39
Page 93
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 6 Networking and Application
6 Networking and Application
About This Chapter
The following table lists the contents of this chapter.
Section Describes
6.1 Typical Networking The typical networking solutions of the MSOFTX3000.
6.2 Network Application Cases The typical network application cases of the
MSOFTX3000.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 6-1
Page 94

6 Networking and Application
6.1 Typical Networking
6.1.1 MSC Networking
The MSOFTX3000 supports various protocols, such as the H.248, BSSAP, RANAP, MAP,
CAP, ISUP, TUP, and BSSAP+. It can work as the mobile switching center (MSC) server and
the VLR in the network. When deployed with Huawei UMG8900 and the Shared
InterWorking Function (SIWF), the MSOFTX3000 supports the BSS/UTRAN accessing
mode and can function as the 2G VMSC, 3G VMSC, or 2G/3G integrated VMSC in the
network. The typical networking is as shown in
Figure 6-1 MSC networking
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Figure 6-1.
UMG8900
H.248
BSSAP
BSS
RANAP
UTRAN
Access network Core network
BSS: GSM Base station subsystem UTRAN: UMTS terrestrial radio access
BC: Billing center HLR: Home location register SMC: Short message center
GMLC: Gateway mobile location center SCP: Service control point SGSN: Serving GPRS support node
PSTN: Public switched telephone network PLMN: Public land mobile network
BSSAP+
CAP
network
ISUP/BICC
MSOFTX3000
(MSC)
IP backbone network/
No.7 signaling network
MAP
GMLC
UMG8900
H.248
FTAM
MAPMAP
GMSC
FTP/
MML
HLRSMCSCPSGSN
TUP/ISUP
BC
M2000
GMSC: Gateway mobile switching
center
PSTN/
PLMN
Bearer
channel
Signaling
channel
In the networking as shown in
Figure 6-1, the MSOFTX3000 terminates the mobile
subscriber/network signaling defined by the R99 24.008 and R98 04.08 specifications, and
converts the signaling to the inter-office signaling transferred on the Nc interface. In addition,
the MSOFTX3000 has an embedded VLR to store the subscription data of mobile subscribers
and the related CAMEL data. The interworking between the MSOFTX3000 and the
6-2 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 95

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 6 Networking and Application
PSTN/PLMN is realized by the GMSC. Through the Mc interface, the MSOFTX3000
controls the bearer terminal and media stream at the access network and backbone network
side in the UMG8900. The interface, protocol and physical interface mode between the
MSOFTX3000 and other network elements are as follows:
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> UMG8900: Mc interface. It is the standard interface of the control
layer and bearer layer in the core network. It adopts the extended H.248 protocol defined
by the ITU-T. Through the Mc interface, the MSOFTX3000 controls the bearer resources
at the radio access side and trunk side. The interface is an IP-based interface added in the
R4 stage.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> BSC: A interface. It is the standard interface in the control layer
between the core network and the BSS radio access network based on the GSM. It adopts
the BSSAP protocol and realizes the termination of the controlling signaling messages
for the service access in the circuit switched (CS) domain for the 2G mobile subscribers.
The A interface provides the following functions:
− Mobility management
− Call control
− Circuit allocation
− Circuit reset
− Handover
− Short message processing
It is a TDM-based interface adopting the BSSAP protocol for the GSM MSC. It can also
be connected through the UMG8900 with the SIGTRAN function. In this case, it adopts
the M2UA protocol.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> RNC: Iu interface. It is the standard interface in the control layer
between the core network and the UTRAN based on the WCDMA. It adopts the RANAP
protocol and realizes termination of the controlling signaling messages for the service
access in the CS domain for the 3G mobile subscribers. The Iu interface provides the
following functions:
− Mobility management
− Call control
− RAB allocation
− Reset and overload control
− RNC re-allocation
− Short message processing
This interface inherits the functions in the R99 stage. It can be an IP-based (M3UA)
interface. When there is no direct interface between the MSOFTX3000 and the RNC, the
Iu interface can be connected through the UMG8900.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> GMSC/GMSC Server: The MSOFTX3000 adopts the ISUP/TUP
protocol for interworking with the GMSC. When the MSOFTX3000 interworks with the
GMSC Server, the interface is called the Nc interface. The Nc interface is the inter-office
signaling interface in the control layer of the CS domain. It is an IP-based or TDM-based
interface adopting the ISUP/TUP or BICC protocol. It is added in the R4 stage.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> MSC: E/G interface. It is only adopted between the neighboring
MSCs (not shown in the figure). It is a TDM-based or IP-based interface adopting the
MAP protocol, used for inter-office handover and location update.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> HLR: C/D interface. Adopting the MAP protocol, it is used for the
location update of network level in the CS domain, and the management of routing data
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 6-3
Page 96

6 Networking and Application
and subscription data. It is a TDM-based or IP-based interface directly inherited from the
R99 stage. It adopts the SIGTRAN protocols.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> SCP: The interface adopts the CAP protocol. It provides the
following functions:
− Realizing the standard connection between the SSP and SCP in the CS domain
integrated in the MSOFTX3000
− Reporting the O/T-BCSM call state event and executing the commands from the SCP
Therefore, in the R4 stage, the intelligent services in the R99 and GSM stage can be
realized in the transparent subscriber mode. The interface is a TDM-based or IP-based
interface directly inherited from the R99 stage.
z
MSOFTX3000<->SMC: E interface. Adopting the MAP protocol, it transfers the mobile
originated and mobile terminated short messages between the SMC and the
MSOFTX3000.
z
MSOFTX3000<->GMLC: Lg interface. Adopting the MAP protocol, the Lg interface
between the MSOFTX3000 and the GMLC supports the location application out of the
PLMN to exchange the subscriber authentication data required by the location service
and the data (such as the IMSI) required by the network resource allocation with the
MSC through the GMLC and locate the QoS.
z
MSOFTX3000<->SGSN: Gs interface. Adopting the BSSAP+ protocol, the Gs interface
between the MSOFTX3000 and the SGSN integrates some functions of the packet
switched (PS) domain and the CS domain (such as the united location update) to
effectively save the wireless resources.
z
MSOFTX3000<->BC: The interface adopts the FTP/FTAM protocol and enables the BC
to automatically fetch CDRs from the iGWB of the MSOFTX3000.
z
MSOFTX3000<->M2000: The interface adopts the MML protocol and supports the
MSOFTX3000 to access Huawei iManager M2000 network management system.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
6.1.2 GMSC Networking
The MSOFTX3000 supports various protocols, such as the H.248, MAP, CAP, ISUP, and TUP.
It provides abundant functions, such as:
z
Black and white list
z
Call authentication
z
Call intercept
z
Mass storage of CDRs
When deployed with Huawei UMG8900, the MSOFTX3000 can function as the GMSC in the
network.
Figure 6-2 shows the typical networking.
6-4 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 97
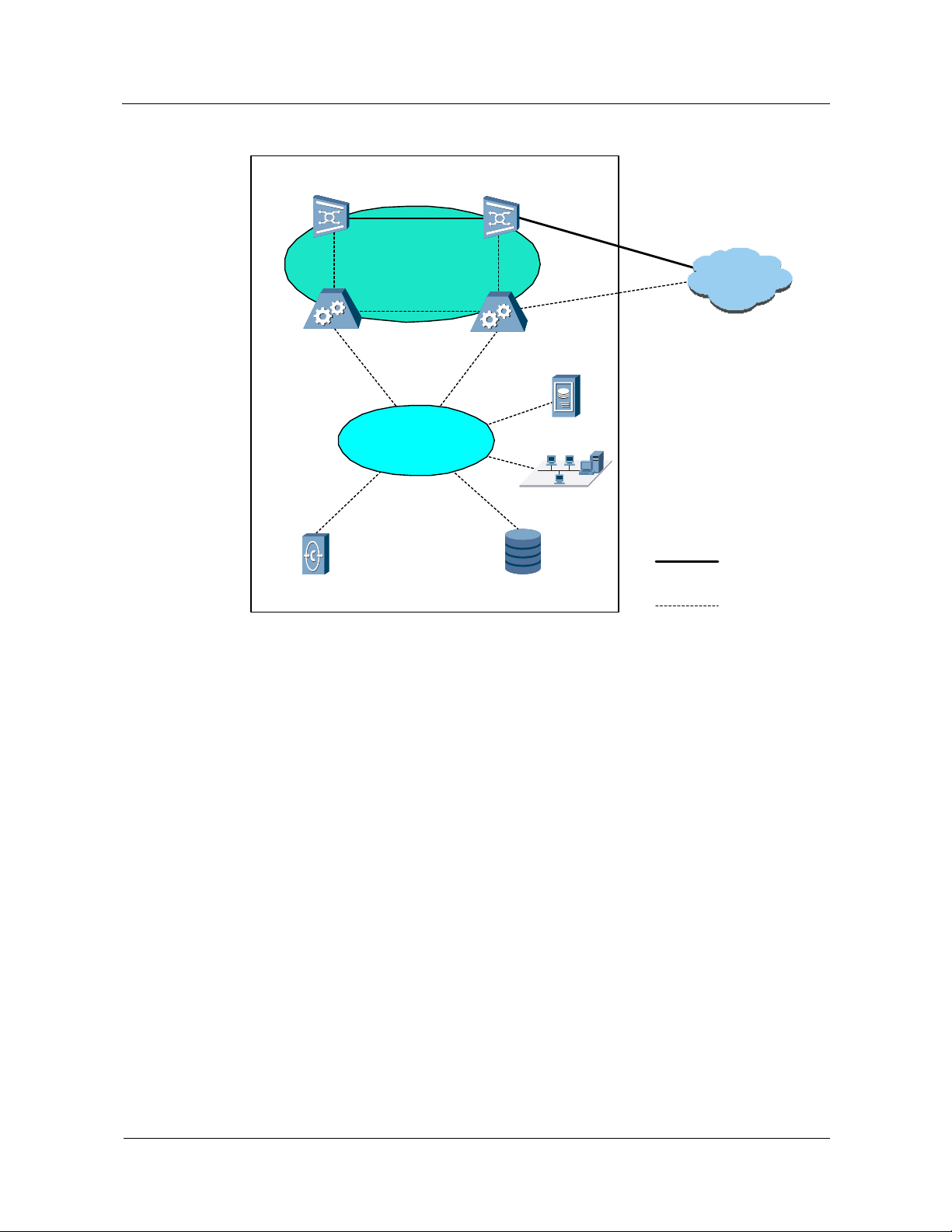
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 6 Networking and Application
Figure 6-2 GMSC networking
UMG8900
H.248
ISUP/BICC
MSC/VL R
IP backbone network/
No.7 signaling network
CAP
SCP
MSC: Mobile switching center VLR: Visitor location register BC: Billing center
HLR: Home location register SCP: Service control point PSTN: Public switched
PLMN: Public land mobile network
UMG8900
H.248
MAP
MSOFTX3000
(GMSC)
FTP/
FTAM
BC
MML
M2000
HLR
TUP/ISUP
telephone network
PSTN/
PLMN
Bearer
channel
Signaling
channel
In the networking as shown in
Figure 6-2, the MSOFTX3000 terminates the signaling (such
as the BICC) on the Nc interface with other MSCs and the call control ISUP/TUP signaling
with the traditional external network (PSTN/PLMN). It realizes the route search for the called
mobile subscriber and the number change between the mobile network and fixed network.
Through the Mc interface, the MSOFTX3000 controls the bearer terminal (IP) at the core
network side in the UMG8900 and the bearer terminal (TDM trunk) at the traditional fixed
network side. In the GMSC networking, the MSOFTX3000 provides the following interfaces
as follows:
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> UMG8900: Mc interface. It is the standard interface of the control
layer and bearer layer in the core network. It adopts the extended H.248 protocol defined
by the ITU-T. Through the Mc interface, the MSOFTX3000 controls the bearer resources
at the radio access side and trunk side. The interface is an IP-based interface added in the
R4 stage.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> MSC/MSC Server: The MSOFTX3000 adopts the ISUP/TUP
protocol for interworking with the MSC. When the MSOFTX3000 interworks with the
MSC Server, the interface is called the Nc interface. The Nc interface is the inter-office
signaling interface in the control layer of the CS domain. It is an IP-based or TDM-based
interface adopting the ISUP/TUP or BICC protocol. It is added in the R4 stage.
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 6-5
Page 98
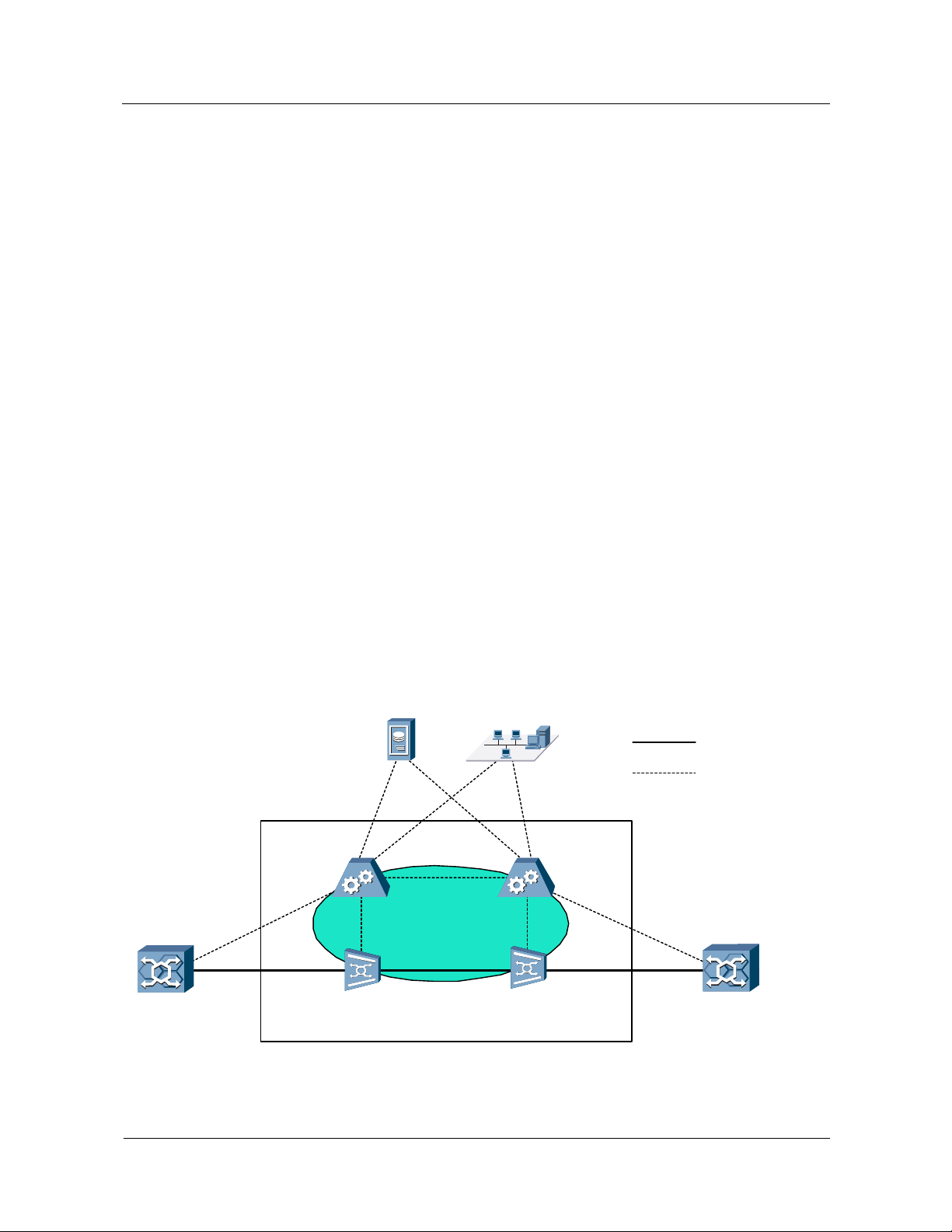
6 Networking and Application
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> PSTN/PLMN: Adopting the TUP or ISUP protocol, the interface
sends and receives the call control messages between the mobile network of the local CS
domain and the PSTN/PLMN. It is a TDM-based (MTP3) interface directly inherited
from the R99 stage.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> HLR: C/D interface. Adopting the MAP protocol, the interface is
used to obtain the routing information for the called mobile subscriber from the
PSTN/PLMN. It is a TDM-based or IP-based interface directly inherited from the R99
stage. It adopts the SIGTRAN protocols.
z
MSOFTX3000 <-> SCP: The interface adopts the CAP protocol. It provides the
following functions:
− Realizing the standard connection between the SSP and SCP in the CS domain
integrated in the MSOFTX3000
− Reporting the O/T-BCSM call state event and executing commands of the SCP
Thus, in the R4 stage, the intelligent services in the R99 and GSM stage can be realized
in the transparent subscriber mode. The interface is a TDM-based or IP-based interface
directly inherited from the R99 stage.
z
MSOFTX3000<->BC: The interface adopts the FTP/FTAM protocol and enables the BC
to automatically fetch CDRs from the iGWB of the MSOFTX3000.
z
MSOFTX3000<->M2000: The interface adopts the MML protocol and supports the
MSOFTX3000 to access the Huawei iManager M2000 network management system.
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
6.1.3 TMSC Networking
The MSOFTX3000 supports various protocols, such as the H.248, ISUP, and BICC. When
deployed with Huawei UMG8900, it provides TDM trunks or IP bearer channels of large
capacity. It can function as the tandem mobile switching center (TMSC) in the hierarchical
network.
Figure 6-3 TMSC networking
TUP/ISUP
Figure 6-3 shows the typical networking.
MSOFTX3000
(TMSC)
H.248
BC
FTP/
FTAM
ISUP/BICC
M2000
MML
H.248
Bearer
channel
Signaling
channel
MSOFTX3000
(TMSC)
TUP/ISUP
Other MSC
UMG8900
UMG8900
Other MSC
6-6 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
Page 99

HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description 6 Networking and Application
The networking as shown in
Figure 6-3 is suitable for the GSM and 3GPP R99 hierarchical
network structures, in which, the call signaling and bearer connection are connected through
the TMSC hierarchically. The MSOFTX3000 realizes the call connection and route selection
functions in the PLMN and controls the bearer terminal (IP) at the core network side in the
UMG8900 and the bearer terminal (TDM trunk) at the traditional fixed network side.
In the 3GPP R4 all-IP network, the MSOFTX3000 realized the end-to-end bearer connection
between the originating end and the terminating end through the BICC signaling. That is, the
call signaling messages are transferred hierarchically through the TMSC, but the bearer does
not require hierarchical processing. In this case, the media gateway (MGW, such as
UMG8900) is not required in the networking, as shown in
Figure 6-3.
6.1.4 Dual-Homing Networking
Overview
Dual-homing is a mechanism where in the networking of 3GPP R4 or later, one MGW
belongs to two MSC Servers. Normally, one MGW registers only with the active MSC Server.
When the active MSC Server breaks down or an emergency occurs, this MGW can register
with the standby MSC Server so that the network can continue providing services.
z
In the networking structure of 3GPP R4 or later, the MSC Server: Controls multiple
MGWs.
z
Covers a large area.
If the MSC Server breaks down or an emergency occurs, the following cases occur:
z
All MGWs are out of control.
z
Services are interrupted widely.
z
Huge loss of data occurs.
To ensure secure and reliable operation of the mobile network, the MSOFTX3000 provides
the dual-homing mechanism to support the remote disaster tolerance feature of the MSC
Server. The MSOFTX3000 supports the following kinds of dual-homing networking
solutions:
z
1+1 backup networking
z
1+1 mutual assistance networking
z
N+1 backup networking
z
N+1 mutual assistance networking
1+1 Backup Networking
In 1+1 backup networking, two MSOFTX3000s work in active/standby mode as MSC
Servers. That is, one MSOFTX3000 works as the active MSC Server, the other as the standby
MSC Server.
Figure 6-4 shows the networking:
Issue 05 (2007-05-20) Huawei Technologies Proprietary 6-7
Page 100

6 Networking and Application
Figure 6-4 1+1 backup networking
MSOFTX3000 A
HUAWEI MSOFTX3000
Product Description
Heartbeat link
MSOFTX3000 B
Acti ve
control channel
Standby
control channel
MGW 1 MGW 2
MSC area A
In
Figure 6-4, MSOFTX3000 A works as the active MSC Server. Normally, it controls the
services in MSC areas A and B. MGWs 1 to 4 register only with MSOFTX3000 A while
MSOFTX3000 B does not process any service.
When MSOFTX3000 A breaks down or an emergency occurs, MSOFTX3000 B takes over
the service control of the MSC areas A and B. In this case MGWs 1 to 4 register with
MSOFTX3000 B.
1+1 Mutual Assistance Networking
In 1+1 mutual assistance networking, two MSOFTX3000s work as MSC Servers in mutual
assistance mode. Each MSOFTX3000 works as the active MSC Server and as the standby
MSC Server for the other at the same time.
Figure 6-5 1+1 mutual assistance networking
MSOFTX3000 A
Figure 6-5 shows the networking.
Heartbeat link
MGW3 MGW4
MSC ar ea B
MSOFTX3000 B
control channel
Standby
control channel
Acti ve
MGW 1 MGW 2
MSC area A
MGW3 MGW4
MSC ar ea B
6-8 Huawei Technologies Proprietary Issue 05 (2007-05-20)
 Loading...
Loading...