Page 1

HP StorageWorks
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide
Part number: AA–RVHWB–TE
Second edition: September 2005
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
© Copyright 2005 Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated.
Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
This document contains proprietary information, which is protected by copyright. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or
translated into another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard. The information is provided “as is” without warranty of any
kind and is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Java is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide
Page 3

Contents
About this guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Intended audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Related documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x master glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Document conventions and symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
HP technical support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
HP-authorized reseller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Helpful web sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1 Introducing Fabric OS CLI procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
About procedural differences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Scope and references . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
About the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Help information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Displaying command help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Additional help topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2 Performing basic configuration tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Connecting to the Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Connecting with telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Connecting through the serial port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Setting the IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Setting the default account passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Changing the default passwords at login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Setting the date and time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Setting the date and time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Synchronizing local time with an external source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Setting the time zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Maintaining licensed features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Unlocking a licensed feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Removing a licensed feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Customizing the switch name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Customizing the switch name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Customizing the chassis name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Changing the chassis name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Disabling and enabling a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Disabling a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Enabling a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Disabling and enabling a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Disabling a port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Enabling a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Activating Ports on Demand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Activating Ports on Demand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Making basic connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Connecting to devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Connecting to other switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Working with domain IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Displaying domain IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Setting the domain ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Linking through a gateway. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Configuring a link through a gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Checking status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Checking switch operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Verifying HA features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 3
Page 4

Verifying fabric connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Verifying device connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Tracking and controlling switch changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Enabling the TC feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Displaying the status of the TC feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Viewing the switch status policy threshold values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Setting the switch status policy threshold values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3 Configuring standard security features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Secure protocols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Ensuring network security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Configuring the telnet interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Disabling telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Enabling telnet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Blocking listeners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Accessing switches and fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Creating and maintaining user-defined accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Displaying account information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Creating a user-defined account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Deleting a user-defined account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Changing account parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Recovering user-defined accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Changing an account password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Changing the password for the current login account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Changing the password for a different account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Setting up RADIUS AAA service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Configuring the RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Adding the attribute to the server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Creating the user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Enabling clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Enabling CHAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Configuring users. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring the RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Displaying the current RADIUS configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Adding a RADIUS server to the switch configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Enabling or disabling RADIUS service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Deleting a RADIUS server from the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Changing a RADIUS server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Changing the order in which RADIUS servers are contacted for service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Enabling and disabling local authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Configuring for the SSL protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Browser and Java support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Summary of SSL procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Choosing a CA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Generating a public/private key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Generating and storing a CSR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Obtaining certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Installing a switch certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Activating a switch certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Configuring the browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Checking and installing root certificates on Internet Explorer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Checking and installing root certificates on Mozilla . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Installing a root certificate to the Java Plug-in. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Displaying and deleting certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Troubleshooting certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Configuring SNMP agent and traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4
Page 5

Setting the security level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Using the snmpConfig command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Using legacy commands for SNMPv1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Configuring secure file copy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Setting the boot PROM password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade
4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Without a recovery string . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade
4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Recovering forgotten passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4 Maintaining configurations and firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Maintaining configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Displaying configuration settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Backing up a configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Restoring a configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Restoring configurations in a FICON environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Downloading configurations across a fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Printing hard copies of switch information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Maintaining firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Obtaining and unzipping firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Checking connected switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
About the download process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Effects of firmware changes on accounts and passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Considerations for downgrading firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Considerations for FICON CUP environments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Upgrading HP StorageWorks switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Summary of the upgrade process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Upgrading 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32 . . . . . . . . . . 80
Upgrading HP StorageWorks directors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Summary of the upgrade process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Upgrading the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Troubleshooting firmware downloads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
5 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director . . . . . . 87
Identifying ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
By slot and port number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
By port area ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Basic blade management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Powering port blades off and on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Powering off a port blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Providing power to a port blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Disabling and enabling port blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Disabling a port blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Enabling a port blade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Conserving power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Blade terminology and compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
CP blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Port blade compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Setting chassis configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Obtaining slot information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Displaying the status of all slots in the chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Configuring a new SAN Director 2/128 with two domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Converting an installed SAN Director 2/128 to support two domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Setting the blade beacon mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 5
Page 6

6 Routing traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
About data routing and routing policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Specifying the routing policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Assigning a static route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Specifying frame order delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Forcing in-order frame delivery across topology changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Restoring out-of-order frame delivery across topology changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Using DLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Checking and setting DLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Viewing routing path information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Viewing routing information along a path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
7 Administering FICON fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
FICON overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Configuring switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Preparing a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configuring a single switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configuring a high-integrity fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Setting a unique domain ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Displaying information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Link incidents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Registered listeners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Node identification data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
FRU failures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Swapping ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Clearing the FICON management database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Using FICON CUP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Setup summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Enabling and disabling FMS mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Setting up CUP when FMS mode is enabled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Displaying the fmsmode setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Displaying mode register bit settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Setting mode register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Persistently enabling and disabling ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Port and switch naming standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Adding and removing FICON CUP licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Zoning and PDCM considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Backing up and restoring configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Identifying ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Backing up FICON files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Uploading the configuration files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Downloading configuration files with Active=Saved mode enabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Downloading configuration files with Active=Saved mode disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Recording configuration information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Sample IOCP configuration file for the SAN Switch 2/32, Core Switch 2/64, and SAN Director 2/128
120
Sample Resource Management Facility configuration file for mainframe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
8 Configuring the Distributed Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Enabling and disabling the platform services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Enabling platform services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Disabling platform services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Controlling access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Displaying the management server ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Adding a member to the ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Deleting a member from the ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Configuring the server database. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Viewing the contents of the management server database. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
6
Page 7

Clearing the management server database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Controlling topology discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Displaying topology discovery status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Enabling topology discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Disabling topology discovery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
9 Working with diagnostic features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Viewing POST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Viewing switch status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Viewing the overall status of the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Displaying switch information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Displaying the uptime for a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Viewing port information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Viewing the status of a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Displaying the port statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Displaying a summary of port errors for a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Viewing equipment status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Displaying the status of the fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Displaying the status of a power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Displaying temperature status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Viewing the system message log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Displaying the system message log, with no page breaks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Displaying the system message log, one page at a time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Clearing the system message log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Viewing the port log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Configuring for syslogd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Configuring the host. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Configuring the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Specifying syslogd hosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Setting the facility level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Removing a syslogd host from the list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Viewing and saving diagnostic information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Setting up automatic trace dump transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Specifying a remote server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Enabling the automatic transfer of trace dumps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Setting up periodic checking of the remote server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Saving a comprehensive set of diagnostic files to the server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
10Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Most common problem areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Gathering information for technical support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Troubleshooting questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Analyzing connection problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Checking the logical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Checking for Fibre Channel connectivity problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Checking the Simple Name Server (SNS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Checking for zoning problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Restoring a segmented fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Reconciling fabric parameters individually . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Downloading a correct configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Reconciling a domain ID conflict . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Correcting zoning setup issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Correcting a fabric merge problem quickly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Verifying a fabric merge problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Editing zone configuration members. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Reordering the zone member list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Recognizing MQ errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Correcting I2C bus errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Checking fan components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 7
Page 8

Checking the switch temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Checking the power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Checking the temperature, fan, and power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Correcting device login issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Identifying media-related issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Testing a port’s external transmit and receive path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Testing a switch’s internal components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Testing components to and from the HBA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Correcting link failures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Determining whether the negotiation was successfully completed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Checking for a loop initialization failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Checking for a point-to-point initialization failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Correcting a port that came up in the wrong mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Correcting marginal links. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Inaccurate information in the system message log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Port initialization and FCP auto-discovery process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
11Administering extended fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
About extended link buffer allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, and SAN Switch 2/32, Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128,
and 4/256 SAN Director (FC2-16 port blades). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, SAN Switch 4/32, and 4/256 SAN Director (FC4-16
and FC4-32 port blades) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Fabric considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Choosing an extended ISL mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Configuring an extended ISL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Trunking over distance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
12Administering ISL trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
About ISL trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Standard trunking criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Fabric considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Initializing trunking on ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Disabling and reenabling the switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Disabling and reenabling ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Monitoring traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Using the portperfshow command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Enabling and disabling ISL trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Enabling or disabling ISL trunking on one port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Enabling or disabling ISL trunking for all of the ports on a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Setting port speeds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Setting the speed for one port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Setting the speed for all of the ports on the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Displaying trunking information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Trunking over extended fabrics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Troubleshooting trunking problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Listing link characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Recognizing buffer underallocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Getting out of buffer-limited mode on E_Ports or LD_Ports: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
13Administering advanced zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Zoning terminology. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Zoning concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Zone types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Zone objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Zone aliases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Zone configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Zoning enforcement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Software-enforced zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Hardware-enforced zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
8
Page 9

Rules for configuring zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Creating and managing zone aliases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Creating an alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Adding members to an alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Removing members from an alias. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Deleting an alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Viewing an alias in the defined configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Creating and maintaining zones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Creating a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Adding devices (members) to a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Removing devices (members) from a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Deleting a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Viewing a zone in the defined configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Merging zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Creating and modifying zoning configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Creating a zoning configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Adding zones (members) to a zoning configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Removing zones (members) from a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Deleting a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Clearing changes to a configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Viewing all zone configuration information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Viewing selected zone configuration information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Viewing a configuration in the effective zone database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Maintaining zone objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Copying a zone object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Deleting a zone object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Renaming a zone object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Managing zoning configurations in a fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Adding a new switch or fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Splitting a fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Using zoning to administer security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Resolving zone conflicts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
14Administering advanced performance monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Displaying and clearing the CRC error count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Monitoring EE performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Adding EE monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Monitoring the traffic from Host A to Dev B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Monitoring the traffic from Dev B to Host A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Setting a mask for EE monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Displaying the current EE mask of a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Displaying a monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Deleting EE monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Monitoring filter-based performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Adding standard filter-based monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Adding custom filter-based monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Adding filter-based monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Deleting filter-based monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Monitoring ISL performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Monitoring trunks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Displaying monitor counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Clearing monitor counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Saving and restoring monitor configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Collecting performance data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
A Configuring the PID format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
About PIDs and PID binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Summary of PID formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Impact of changing the fabric PID format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 9
Page 10

Host reboots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Static PID mapping errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Changes to configuration data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Selecting a PID format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Evaluating the fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Planning the update procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Online update. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Offline update. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Hybrid update. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Changing to Core PID format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Changing to Extended Edge PID format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Converting port number to area ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
PID format changes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Executing the basic procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Executing the HP–UX procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Executing the AIX procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Swapping port area IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
B Configuring interoperability mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
C Using the HP Remote Switch feature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
D Understanding legacy password behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Password management information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Password prompting behaviors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Password migration during firmware changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Password recovery options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
E Zone merging scenarios. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
F Upgrading firmware in single-CP mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Upgrading HP StorageWorks SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, and SAN
Switch 4/32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Upgrading a single Core Switch 2/64 or SAN Director 2/128 blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Figures
1 Cascaded configuration with two switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
2 Cascaded configuration with three switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
3 FICON switch configuration worksheet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
4 Distribution of traffic over ISL trunking groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
5 Zoning example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
6 Hardware-enforced non-overlap ping zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
7 Hardware-enforced overlapping zones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
8 Zoning with hardware assist (mixed-port and WWN zones) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
9 Session-based hard zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
10 Setting EE monitors on a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
11 Proper placement of EE performance monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
12 Mask positions for EE monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
13 4/256 SAN Director with Extended Edge PID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Tables
1 Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2 Maximum number of simultaneous sessions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3 Conversion from UTC to local time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4 Secure protocol support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5 Items needed to deploy secure protocols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6 Main security scenarios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
7 Blocked listener applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8 Access defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
10
Page 11

9 SSL certificate files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
10 Commands to display and delete SSL certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
11 SSL messages and actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
12 Backup and restore in a FICON CUP environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
13 Recommended firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
14 Effects of firmware changes on accounts and passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
15 HP StorageWorks director terminology and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
16 Blades supported by each HP StorageWorks director. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
17 Supported configuration options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
18 Fabric OS commands related to FICON and FICON CUP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
19 FICON CUP mode register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
20 Port error summary description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
21 Commands for port log management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
22 Fabric OS and UNIX message severities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
23 Common troubleshooting problems and tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
24 Types of zone discrepancies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
25 Commands for debugging zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
26 Component test descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
27 Switch component tests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
28 Switchshow output and suggested action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
29 Loopback modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
30 Extended ISL modes: switches with Bloom ASIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
31 Extended ISL modes: switches with Goldeneye ASIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
32 Extended ISL modes: switches with Condor ASIC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
33 Types of zoning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
34 Approaches to fabric-based zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .179
35 Enforcing hardware zoning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
36 Resulting database size: 0 to 96K . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
37 Resulting database size: 96K to 128K . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .189
38 Resulting database size: 128K to 256K . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
39 Resulting database size: 256K to 1M. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
40 Zoning database limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
41 Considerations for zoning architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
42 Advanced performance monitoring commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
43 Commands to add filter-based monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .205
44 Predefined values at offset 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
45 Effects of PID format changes on configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
46 PID format recommendations for adding new switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
47 Earliest Fabric OS versions for Extended Edge PID format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
48 Account and password characteristics matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
49 Password prompting matrix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
50 Password migration behavior during firmware upgrade and downgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
51 Password recovery options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
52 Zone merging scenarios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 11
Page 12

12
Page 13

About this guide
This guide provides information about:
• Fabric OS procedures
• Basic configuration tasks
• Security features
• Diagnostics
• Extended fabrics
• ISL trunking
• Zoning
• Performance monitoring
NOTE: FICON is not supported on HP B-Series Fibre Channel switches. The FICON information in this
document is included for reference only.
Intended audience
This guide is intended for:
• System administrators responsible for setting up HP StorageWorks Fibre Channel Storage Area
Network (SAN) switches
• Technicians responsible for maintaining the Fabric Operating System (OS)
Related documentation
Documentation, including white papers and best practices documents, is available on the HP web site:
http://www.hp.com/country/us/eng/prodserv/storage.html
IMPORTANT: For late breaking, supplemental information, access the latest version of the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x release notes using the following steps.
To access current Fabric OS related documents:
1. Locate the IT storage products section of the web page.
2. Under Networked storage, click SAN infrastructure.
3. From the SAN Infrastructure web page, locate the SAN Infrastructure products section.
4. Click Fibre Channel Switches.
5. Locate the B-Series Fabric-Enterprise Class section. Click 4/256 SAN Director and 4/256 SAN Director
power pack, to access Fabric OS 5.x documents (such as this document).
The switch overview page displays.
6. Go to the Product Information section, located on the right side of the web page.
7. Click Technical documents.
8. Follow the onscreen instructions to download the applicable documents.
.
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x master glossary
This guide uses industry standard SAN terminology. However, some terms are intrinsic to Fabric OS 5.x.
See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x master glossary for a complete list of terms and definitions.
Access the master glossary from the HP StorageWorks SAN Switch Documentation CD that shipped with
your switch. Also, access from the HP web site using the procedure outlined in ”Related documentation”.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 13
Page 14

Document conventions and symbols
Table 1 Document conventions
Convention Element
Medium blue text: Figure 1 Cross-reference links and e-mail addresses
Medium blue, underlined text
(http://www.hp.com)
Bold font • Key names
Italics font Text emphasis
Monospace font • File and directory names
Monospace, italic font • Code variables
Monospace, bold font Emphasis of file and directory names, system output, code, and text
Web site addresses
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as into a box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu and list
items, buttons, and check boxes
• System output
• Code
• Text typed at the command-line
• Command line variables
typed at the command line
WARNING! Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
CAUTION: Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT: Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE: Provides additional information.
TIP: Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
HP technical support
Telephone numbers for worldwide technical support are listed on the HP support web site:
http://www.hp.com/support/
Collect the following information before calling:
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Product model names and numbers
• Applicable error messages
.
14
Page 15

• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed, specific questions
For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
HP strongly recommends that customers sign up online using the Subscriber's choice web site:
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
• Subscribing to this service provides you with e-mail updates on the latest product enhancements,
newest versions of drivers, and firmware documentation updates as well as instant access to numerous
other product resources.
• After signing up, you can quickly locate your products by selecting Business support and then Storage
under Product Category.
HP-authorized reseller
For the name of your nearest HP-authorized reseller:
• In the United States, call 1-800-282-6672.
• Elsewhere, visit the HP web site: http://www.hp.com
telephone numbers.
Helpful web sites
For other product information, see the following HP web sites:
.
. Click Contact HP to find locations and
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/support/
• http://www.docs.hp.com
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 15
Page 16

16
Page 17
1 Introducing Fabric OS CLI procedures
This chapter contains procedures for configuring and managing an HP StorageWorks Storage Area
Network (SAN) using the Fabric OS Command Line Interface (CLI).
The guide applies to the following HP StorageWorks product models:
• HP StorageWorks switches: 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch
2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch
4/32
These HP StorageWorks models contain a fixed number of ports (they are fixed-port switches). The
SAN Switch 4/32, 4/8 SAN Switch, and 4/16 SAN Switch allow you to license and activate extra
fixed ports with the Ports on Demand feature.
• HP StorageWorks directors: Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
These HP StorageWorks models can contain a variable number of ports, which you install by plugging
port blades into the director chassis. The 4/256 SAN Director can have up to 256 ports; the Core
Switch 2/64 and SAN Director 2/128 can have up to 128 ports.
About procedural differences
As a result of the differences between fixed-port and variable-port devices, procedures sometimes differ
among HP StorageWorks models. Also, because the domain architecture of the Core Switch 2/64 differs
from that of the SAN Director 2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director, there are sometimes procedural
differences among these models. As new HP StorageWorks models are introduced, new features
sometimes apply only to those models.
When procedures or parts of procedures apply to some models but not others, this guide identifies the
specifics for each model. For example, a number of procedures that apply only to variable-port devices
are found in ”Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director” on
page 87. Procedures that apply only to the SAN Switch 4/32 are labeled as such.
NOTE: When command examples in this guide show user input enclosed in quotation marks, the
quotation marks are required for versions of Fabric OS earlier than 4.0.0. They are optional in later
versions, unless specifically called for in the procedures.
Scope and references
Although many different software and hardware configurations are tested and supported by HP,
documenting all possible configurations and scenarios is beyond the scope of this guide. In some cases,
earlier releases of Fabric OS are documented to present considerations for interoperating with them.
The installation guides for HP StorageWorks products describe how to power up devices and set their IP
addresses. After the IP address is set, you can use the CLI procedures contained in this guide.
This guide provides only the level of detail required to perform the procedures. If you need more
information about the commands used in the procedures, see online help or the HP StorageWorks Fabric
OS 5.x command reference guide.
You can use several access methods to configure a switch:
• CLI
• A telnet session into logical switches
• A telnet session into active and standby CPs for director class switches
• A serial console, including active and standby CPs for director class switches
• An optional modem, which behaves like a serial console port
For CLI details, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 17
Page 18

• Advanced Web Tools: For Advanced Web Tools procedures, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS
5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide.
• Fabric Manager: For Fabric Manager procedures, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric Manager 5.x
administrator guide.
• A third-party application using the API: For third-party application procedures, see the third-party API
documentation.
About the CLI
The Fabric OS CLI is the complete fabric management tool for HP StorageWorks SANs that enables you
to:
• Access the full range of Fabric OS features, based on license keys
• Configure, monitor, dynamically provision, and manage every aspect of the SAN
• Configure and manage the HP StorageWorks fabric on multiple, efficient levels
• Identify, isolate, and manage SAN events across every switch in the fabric
• Manage switch licenses
• Perform fabric stamping
To manage a switch using telnet, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), and Advanced Web
Tools, the switch must be connected to a network through the switch Ethernet port (out of band) or from the
Fibre Channel (in band). The switch must be configured with an IP address to allow for the network
connection. See the installation guide for your switch model for information on physically connecting to
the switch.
You can access switches from different connections, such as Advanced Web Tools, CLI, and API. When
these connections are simultaneous, changes from one connection might not be updated to the other, and
some modifications might be lost. When simultaneous connections are used, make sure that you do not
overwrite the work of another connection.
In a mixed fabric containing switches running various Fabric OS versions, you should use the latest-model
switches running the most recent release for the primary management tasks. The principal management
access should be set to the core switches in the fabric. For example, to run Secure Fabric OS, use the
latest-model switch as the primary Fabric Configuration Server (FCS), the location to perform zoning tasks,
and the time server.
A number of management tasks are designed to make fabric-level changes; for example, zoning
commands make changes that affect the entire fabric. When executing fabric-level configuration tasks,
allow time for the changes to propagate across the fabric before executing any subsequent tasks. For a
large fabric, it might be take a few minutes.
Help information
Each Fabric OS command provides Help information that explains the command function, its possible
operands, its level in the command hierarchy, and additional pertinent information.
Displaying command help
To display help information:
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. To display a list of all command help topics for a given login level, issue the help command with no
arguments.
For example, if you are logged in as user and issue the help command, a list of all user-level
commands that can be executed is displayed. The same rule applies to the admin role. In addition,
any user-configured command that uses a switchAdmin role also displays commands available to
users with the switchAdmin role.
3. To display help for a specific command for a given login level, issue help command, where
command is the name of the command for which you need information.
18 Introducing Fabric OS CLI procedures
Page 19

For example:
switch:admin> help configure
Administrative Commands configure(1m)
NAME
configure - change system configuration settings
SYNOPSIS
configure
AVAILABILITY
admin
DESCRIPTION
This command changes some system configuration settings,
including:
o Arbitrated loop settings
o Switch fabric settings
o System services settings
o Virtual channel settings
(output truncated)
Additional help topics
The following commands provide help files for specific topics:
• diagHelp provides diagnostic information
• ficonHelp provides Fibre Connection (FICON) information
• fwHelp provides Fabric Watch information
• licenseHelp provides license information
• perfHelp provides Performance Monitoring information
• routeHelp provides routing information
• trackChangesHelp provides Track Changes (TC) information
• zoneHelp provides zoning information
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 19
Page 20

20 Introducing Fabric OS CLI procedures
Page 21
2 Performing basic configuration tasks
This chapter contains procedures for performing basic switch configuration tasks using the Fabric OS CLI.
Connecting to the Command Line Interface
You can connect to the CLI either through a telnet connection or through the serial port.
Connecting with telnet
1. Verify that the switch is connected to the IP network through the RJ-45 Ethernet port.
Switches in the fabric that are not connected through Ethernet can be managed through switches that
use IP over Fibre Channel. The embedded port must have an assigned IP address.
2. Open a telnet connection using the IP address of the logical switch to which you want to connect.
If you telnet to the active Control Processor (CP) or log in to the active CP console, you are prompted
for the switch number when the platform is set up in dual (or multiple) switch mode. For example, the
SAN Director 2/128 does not prompt you if you are using configuration option 1, but does prompt
you if you have used configuration options 2–4. See ”Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director
2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director” on page 87 for details about director configuration options.
The Core Switch 2/64 and SAN Director 2/128 (configured with two domains) have two logical
switches (sw0 and sw1).
The login prompt is displayed when the telnet connection finds the switch in the network.
3. Enter the account ID (defaults are user or admin) at the login prompt.
4. Enter the password.
The default password is password.
If you have not changed the system passwords from the default, you are prompted to change them.
Enter the new system passwords, or press Ctrl-c to skip the password prompts.
5. Verify that the login was successful.
The prompt displays the switch name and user ID to which you are connected.
login: admin
password: xxxxxxx
switch:admin>
6. Observe the following considerations for telnet connections:
• Never change the IP address of the switch while two telnet sessions are active; if you do, your next
attempt to log in fails. To recover, gain access to the switch by one of these methods:
• Perform a fast boot using Advanced Web Tools. When the switch comes up, the telnet quota is
cleared. (For instructions on performing a fast boot with Advanced Web Tools, see the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide.)
• If you have the required privileges, connect through the serial port, log in as root, and use
operating system commands to identify and kill the telnet processes without disrupting
the fabric.
• For admin level accounts, Fabric OS limits the number of simultaneous telnet sessions per switch to
two. For details on session limits, see ”Configuring the telnet interface” on page 41 and ”Creating
and maintaining user-defined accounts” on page 43.
Connecting through the serial port
1. Connect the serial cable to the serial port on the switch and to an RS-232 serial port on
the workstation.
If the serial port on the workstation is RJ-45 instead of RS-232, remove the adapter on the end of the
serial cable and insert the exposed RJ-45 connector into the RJ-45 serial port on the workstation.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 21
Page 22
2. Open a terminal emulator application (such as HyperTerminal on a PC, or TERM, TIP, or Kermit in a
UNIX® environment), and configure the application as follows:
• In a Windows® environment:
Parameter
Bits per second 9600
Databits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
• In a UNIX environment, enter the following string at the prompt:
tip /dev/ttyb -9600
If ttyb is already in use, you can use ttya (enter tip /dev/ttya -9600).
3. Observe the following considerations for serial connections:
• Some procedures require that you connect through the serial port, for example, setting the IP
address or setting the boot PROM password.
• If secure mode is enabled, connect through the serial port of the primary FCS switch.
• For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, you can connect to
CP0 or CP1 using either of the two serial ports.
Setting the IP address
Value
You must connect through the serial port to set the IP address (see ”Connecting through the serial port” on
page 21). After connecting, issue the ipAddrSet command to set the IP address.
CAUTION: The use of IP address 0.0.0.0 is not supported. Do not use this address.
Fabric OS versions beginning with 2.6.0, 3.1.0, and 4.0.0 support Classless Inter-Domain
Routing (CIDR).
Setting the default account passwords
For each logical switch (domain), there are admin and user default access accounts. These accounts
designate the following levels of authorization—called roles—for using the system:
• Admin level for administrative use
• User level for non-administrative use, such as monitoring system activity
• SwitchAdmin level for administrative use, except for security, user management, and zoning
Two accounts—factory and root—are reserved for development and manufacturing. You can change their
passwords, which is optional, but do not use these accounts under normal circumstances.
Table 2 shows the number of simultaneous login sessions allowed for each role.
Table 2 Maximum number of simultaneous sessions
User name Maximum sessions
admin 2
user 4
For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32,
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, SAN Switch 4/32, SAN Director 2/128, and the
4/256 SAN Director (default configuration with one domain), there is one set of default access accounts.
22 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 23

For the Core Switch 2/64 and SAN Director 2/128 (configured with two domains), each logical switch
has its own set of default access accounts. The default account names and passwords are the same for
both of the logical switches.
You can also create up to 15 additional accounts per logical switch and designate their roles as either
admin, switchAdmin, or user. See the procedures for doing so in ”Creating and maintaining user-defined
accounts” on page 43.
For large enterprises, Fabric OS supports RADIUS services, as described in ”Setting up RADIUS AAA
service” on page 45.
In addition to the account access passwords, each switch can set a boot PROM password. For greater
security, HP recommends that you set this password to protect system boot parameters from unauthorized
access. See ”Setting the boot PROM password” on page 67.
Each of the default access accounts has an associated password. The first time you connect to a
Fabric OS switch, you are prompted to change these default account passwords.
If you do not change the default passwords, you are prompted to do so at each subsequent login until all
system passwords have been changed from their default values. Thereafter, use the passwd command to
change passwords.
For more background information on passwords, see ”Changing an account password” on page 45.
Changing the default passwords at login
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
The default password for all default accounts is password.
2. At each of the Enter new password prompts, either enter a new password or skip the prompt.
You can skip a prompt by pressing Enter. You can bypass all further prompts by pressing Ctrl-c.
Although the root and factory accounts are not meant for general use, change their passwords if
prompted to do so, and save the passwords in case they are needed for recovery purposes.
You cannot reuse the default passwords.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 23
Page 24

NOTE: Record the passwords exactly as entered and store them in a secure place; recovering
passwords requires significant effort and fabric downtime. The initial login prompt accepts a maximum
password length of eight characters. Characters beyond the eighth are ignored. Only the default
password is subject to the eight-character limit. Any password set by the user can have a length of 8 to 40
characters.
login: admin
Password:
Please change your passwords now.
Use Control-C to exit or press 'Enter' key to proceed.
for user - root
Changing password for root
Enter new password: *****
Password changed.
Saving password to stable storage.
Password saved to stable storage successfully.
Please change your passwords now.
for user - factory
Changing password for factory
Enter new password: *****
Password changed.
Saving password to stable storage.
Password saved to stable storage successfully.
Please change your passwords now.
for user - admin
Changing password for admin
Enter new password: *****
Password changed.
Saving password to stable storage.
Password saved to stable storage successfully.
Please change your passwords now.
for user - user
Changing password for user
Enter new password: *****
Password changed.
Saving password to stable storage.
Password saved to stable storage successfully.
switch:admin>
Setting the date and time
Switches maintain the current date and time in flash memory. Date and time are used for logging events.
Switch operation does not depend on the date and time; a switch with an incorrect date and time value
still functions properly. Because the date and time are used for logging, set them correctly.
NOTE: If secure mode is not enabled, a change in date or time to one switch is forwarded to the
principal switch and distributed to the fabric. If secure mode is enabled, you can make date or time
changes only on the primary FCS switch and then distribute the changes to the fabric.
24 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 25
Setting the date and time
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the date command using the following syntax:
date “mmddHHMMyy”
where:
• mm is the month; valid values are 01 through 12.
• dd is the date; valid values are 01 through 31.
• HH is the hour; valid values are 00 through 23.
• MM is minutes; valid values are 00 through 59.
• yy is the year; valid values are 00 through 99 (values greater than 69 are interpreted as
1970–1999, and values less than 70 are interpreted as 2000–2069). For example:
switch:admin> date
Fri Jan 29 17:01:48 UTC 2000
switch:admin> date "0227123003"
Thu Feb 27 12:30:00 UTC 2003
switch:admin>
For details about changing time zones, see the tsTimeZone command in the HP StorageWorks Fabric
OS 5.x command reference guide.
Synchronizing local time with an external source
To synchronize the local time of the principal or primary FCS switch to an external NTP server:
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
tsclockserver “ipadd”
where ipaddr is the IP address of the NTP server, which the switch must be able to access. This
operand is optional; by default its value is LOCL, which uses the local clock of the principal or primary
switch as the clock server. For example:
switch:admin> tsclockserver
LOCL
switch:admin> tsclockserver “132.163.135.131”
switch:admin> tsclockserver
132.163.135.131
switch:admin>
HP recommends that you synchronize time with an external NTP server, as described on ”Synchronizing
local time with an external source”. If you cannot do so, use the next procedure.
Setting the time zone
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the tsTimeZone command as follows:
tsTimeZone [houroffset [, minuteoffset]]
•For Pacific Standard Time enter tsTimeZone -8,0.
• For Central Standard Time enter tsTimeZone -6,0.
• For Eastern Standard Time enter tsTimeZone -5,0.
The default time zone for switches is Universal Time Conversion (UTC), which is 8 hours ahead of
Pacific Standard Time. Table 3 shows additional time zone conversion values.
The parameters do not apply if the time zone of the switch has already been changed from the default
(8 hours ahead of Pacific Standard Time).
See the tsTimeZone command in the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide for
detailed information about the command parameters.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 25
Page 26

Repeat the procedure on all switches for which the Time Zone needs to be set. This needs to be done only
once; the value is written to nonvolatile memory. For U.S. time zones, use Table 3 to determine the correct
parameter for the tsTimeZone command.
Table 3 Conversion from UTC to local time
Local time Difference from UTC for
tstimezone
Atlantic Standard –4, 0
Atlantic Daylight –3, 0
Eastern Standard –5, 0
Eastern Daylight –4, 0
Central Standard –6, 0
Central Daylight –5, 0
Mountain Standard –7, 0
Mountain Daylight –6, 0
Pacific Standard –8, 0
Pacific Daylight –7, 0
Alaskan Standard –9, 0
Alaskan Daylight –8, 0
Hawaiian Standard –10, 0
Maintaining licensed features
Feature licenses might be part of the licensed Power Pack supplied with switch software, or you can
purchase licenses separately from your switch vendor, who will provide you with keys to unlock the
features. License keys are provided on a per-chassis basis, so for products that support multiple logical
switches (domains), a license key applies to all domains within the chassis.
To unlock a licensed feature, you can either use the license key provided in the Power Pack or execute the
following procedure to generate a license key at the HP web site:
http://webkey.external.hp.com/welcome.asp
NOTE: For each chassis to be licensed, you need a transaction key and a license ID. The transaction key
is in the Power Pack supplied with the switch software; or, when you purchase a license, your switch
vendor gives you a transaction key to be used to obtain a license key. To see a switch license ID, issue the
licenseIdShow command.
Unlocking a licensed feature
1. If you already have a license key, go to step 10.
If you do not have a key, launch an Internet browser and visit the HP web site:
http://webkey.external.hp.com/welcome.asp
2. Click products.
3. Click Software Products.
4. In the Related Links panel on the right side of the page, select Software License Keys.
The Software License Keys instruction page appears.
.
.
26 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 27

5. If you want to generate a single license key, select Generate 1 license key.
If you want to generate multiple license keys, select Batch Generation of Licenses.
The Software License Key instruction page opens.
6. Enter the requested information in the required fields.
When generating multiple license keys, enter the worldwide names and transaction keys in the table
at the bottom of the screen. If you need additional rows in the table, select Add More Rows.
7. Click Next.
A verification screen appears.
8. Verify that the information is correct.
Click Submit if the information displayed is correct. If the information is incorrect, click Previous and
change the information.
9. After the information is corrected, click Submit.
An information screen displays the license keys. You also receive an e-mail from the HP licensing
company.
10.Activate and verify the license as follows:
a. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
b. Activate the license using the licenseAdd command:
switch:admin> licenseadd “key”
The license key is case-sensitive and must be entered exactly as given. The quotation marks
are optional.
For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, licenses are effective
on both CP blades and on all logical switches, but are valid only when the CP blade is inserted
into a chassis that has an appropriate license ID stored in the World Wide Name (WWN) card. If
a CP is moved from one chassis to another, the license works in the new chassis only if the WWN
card is the same in the new chassis. Otherwise, a new license key is generated.
For example, if you swap one CP blade at a time, or replace a single CP blade, the existing CP
blade (the active CP blade) propagates the licenses to the new CP blade.
If you move a standby CP from one chassis to another, the active CP propagates its configuration
(including license keys).
c. Verify that the license was added by issuing the licenseShow command.
The licensed features currently installed on the switch are listed. If the feature is not listed, reissue
the licenseAdd command.
d. Some features may require additional configuration, or you might need to disable and reenable
the switch to make them operational; see the feature documentation for details. For example:
switch:admin> licenseshow
SbeSdQdQySyriTeJ:
Web license
Zoning license
Fabric license
Remote Switch license
Extended Fabric license
Fabric Watch license
Performance Monitor license
Trunking license
Security license
SbbebdQS9QTscfcB:
Ports on Demand license - additional 8 port upgrade
SbbebdQS9QTcgfcz:
Ports on Demand license - additional 8 port upgrade
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 27
Page 28

Removing a licensed feature
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the licenseShow command to display the active licenses.
3. Remove the license key using the licenseRemove command:
switch:admin> licenseremove “key”
The license key is case-sensitive and must be entered exactly as given. The quotation marks
are optional. After removing a license key, the optionally licensed feature is disabled when the switch
is rebooted or when a switch disable or enable is performed.
4. Issue the licenseShow command to verify that the license is disabled. For example:
switch:admin> licenseshow
bQebzbRdScRfc0iK:
Web license
Zoning license
SybbzQQ9edTzcc0X:
Fabric license
switch:admin> licenseremove “bQebzbRdScRfc0iK”
removing license key “bQebzbRdScRfc0iK”
switch:admin>
After a reboot (or switchDisable and switchEnable):
switch:admin> licenseshow
SybbzQQ9edTzcc0X:
Fabric license
switch:admin>
If there are no license keys, licenseShow displays the message No licenses.
Customizing the switch name
Switches can be identified by IP address, Domain ID, WWN, or by customized switch names that are
unique and meaningful.
Version 4.0.0 (and later) switch names can be from 1 to 15 characters long, must begin with a letter, and
can contain letters, numbers, or the underscore character. It is not necessary to use quotation marks.
The default names are the following:
• For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32: the name is
swd77.
• For the Core Switch 2/64: the name varies depending on the number of logical switches. The two
logical switches have different default names. The name swd77 is used for the logical switch
containing the port blades in slots 1 through 4; swd76 is used for the logical switch containing the
port blades in slots 7 through 10.
• For the SAN Director 2/128 and the 4/256 SAN Director: the name is swd77.
NOTE: Changing the switch name causes a domain address format Registered State Change
Notification (RSCN) to be issued.
Customizing the switch name
1. For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32: Proceed to the
next step.
For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director: Open a telnet window
for each logical switch and issue the switchName command.
28 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 29
2. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
3. For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, and SAN Switch 4/32: Proceed to the next step.
For the SAN Director 2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director: If configured for one domain (the default)
proceed to the next step. If configured with two domains, proceed as for the Core Switch 2/64.
For the Core Switch 2/64: Choose the logical switch that you want to change. Enter the value that
corresponds to that logical region:
• Enter 0 to configure logical switch 0 (slot 1 through 4).
• Enter 1 to configure logical switch 1 (slot 7 through 10).
4. Issue the switchName command with the following syntax:
switchname “newname”
where newname is the new name for the switch.
5. Record the new switch name for future reference.
6. For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director configured with two
domains: Disconnect from the session and repeat the procedure for the second logical switch. For
example:
switch:admin> switchname “switch62”
Committing configuration...
Done.
switch62:admin>
Customizing the chassis name
Beginning with Fabric OS 4.4.0, HP recommends that you customize the chassis name for each switch.
Some system logs identify switches by chassis names, so if you assign meaningful chassis names in
addition to meaningful switch names, logs are more useful.
Changing the chassis name
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the chassisName command, with the following syntax:
chassisname “newname”
where newname is the new name for the chassis.
Chassis names can contain 1 to 15 characters, must begin with a letter, and can consist of letters,
numerals, and the underscore character. The quotation marks are optional.
3. Record the new chassis name for future reference.
Disabling and enabling a switch
By default, the switch is enabled after power is applied and diagnostics and switch initialization routines
have finished. You can disable and reenable it as necessary.
Disabling a switch
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the switchDisable command.
All Fibre Channel ports on the switch are taken offline. If the switch was part of a fabric, the fabric
reconfigures.
Enabling a switch
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the switchEnable command.
All Fibre Channel ports that pass the Power-on Self Test (POST) are enabled. If the switch has
interswitch links (ISLs) to a fabric, it joins the fabric.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 29
Page 30

Disabling and enabling a port
All licensed ports are enabled by default. You can disable and reenable them as necessary. Ports that you
activate with Ports on Demand must be enabled explicitly, as described in ”Activating Ports on Demand”
on page 30.
Disabling a port
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32: Issue the
following command:
portdisable portnumber
where portnumber is the port number of the port you want to disable.
For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director: Issue the following
command:
portdisable slotnumber/portnumber
where slotnumber and portnumber are the slot and port numbers of the port you want to disable.
NOTE: If the port is connected to another switch, the fabric might reconfigure.
Enabling a port
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32: Issue the
following command:
portenable portnumber
where portnumber is the port number of the port you want to enable.
For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director: Issue the following
command:
portenable slotnumber/portnumber
where slotnumber and portnumber are the slot and port numbers of the port you want to enable.
(Slots are numbered 1 through 4 and 7 through 10, counting from left to right.)
NOTE: If the port is connected to another switch, the fabric might reconfigure. If the port is connected to
one or more devices, these devices become available to the fabric.
If you change port configurations during a switch failover, the ports might become disabled. To bring the
ports online, reissue the portEnable command after the failover is complete.
Activating Ports on Demand
The SAN Switch 4/32 can be purchased with 16, 24, or 32 licensed ports. As your needs increase, you
can activate unlicensed ports (up to the maximum of 32 ports) by purchasing and installing the HP Ports
on Demand optional, licensed product.
The 4/8 SAN Switch and 4/16 SAN Switch can be purchased with 8 ports and no E_Port, 8 ports with
full-fabric access (4/8 SAN Switch), and 16 ports with full-fabric access (4/16 SAN Switch). If you
purchase the 4/8 SAN Switch with 8 ports enabled, you can activate unlicensed ports in 4-port
increments up to 16 ports by purchasing and installing the HP StorageWorks 4/8 SAN 4-Port Upgrade
License. You can also purchase a full-fabric upgrade license if your switch does not support full-fabric
access.
Ports on Demand is ready to be unlocked in the switch firmware. Its license key might be part of the
licensed software supplied with your switch, or you can purchase the license key separately from your
30 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 31

switch vendor. You might need to generate a license key from a transaction key supplied with your
purchase. If so, launch an Internet browser and visit the HP web site:
http://webkey.external.hp.com/welcome.asp
to generate the key.
By default, ports 0 through 15 are activated on the SAN Switch 4/32. Each Port upgrade license
activates the next group of eight ports in numerical order. Before installing a license key, you must insert
transceivers in the ports to be activated. Remember to insert the transceivers in the lowest group of
inactive port numbers first. For example, if only 16 ports are currently active and you are installing one
8-Port Upgrade License key, make sure to insert the transceivers in ports 16 through 23. If you later install
a second license key, insert the transceivers in ports 24 through 31. For details on inserting transceivers,
see the HP StorageWorks SAN Switch 4/32 installation guide.
After you install a license key, you must enable the ports to complete their activation. You can do so
without disrupting switch operation by issuing the portEnable command on each port. You can also
disable and reenable the switch to activate ports.
. Select Generate a license key and follow the instructions
Activating Ports on Demand
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Optional: To verify the current states of the ports, issue the portShow command.
In the portShow output, the Licensed field indicates whether or not the port is licensed.
3. Install the HP Port Upgrade License.
For instructions, see ”Maintaining licensed features” on page 26.
4. Issue the portEnable command to enable the ports.
5. Optional: issue the portShow command to check the newly activated ports.
If you remove a Port Upgrade License, the licensed ports become disabled after the next platform reboot
or the next port deactivation.
Making basic connections
You can make basic connections to devices and to other switches.
Before connecting a version 4.0.0 (or later) switch to a fabric that contains switches running earlier
firmware versions, you must first set the same port identifier (PID) format on all the switches. The presence
of different PID formats in a fabric causes fabric segmentation.
For information on PID formats and related procedures, see ”Selecting a PID format” on page 215.
For information on configuring the routing of connections, see ”Routing traffic” on page 97.
For information on configuring extended interswitch connections, see ”Administering extended fabrics” on
page 163.
Connecting to devices
To minimize port logins, power off all devices before connecting them to the switch. For devices that
cannot be powered off, first use the portDisable command to disable the port on the switch, and then
connect the device. When powering the devices back on, wait for each device to complete the fabric
login before powering on the next one.
Connecting to other switches
See the SAN Switch installation guide for your switch model for ISL connection and cable management
information. The standard (default) ISL mode is L0, which you can configure with the portCfgLongDistance
command. ISL Mode L0 is a static mode, with the following maximum ISL distances:
• 10 km at 1 Gbit/second
• 5 km at 2 Gbit/second
• 2.5 km at 4 Gbit/second
ISL mode L0 is available on all Fabric OS releases. When you upgrade from Fabric OS 4.0.0 to Fabric
4.1.0 or later, all extended ISL ports are set to L0 mode.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 31
Page 32

For information on extended ISL modes, which enable longer-distance ISLs, see ”Administering extended
fabrics” on page 163.
Working with domain IDs
Although domain IDs are assigned dynamically when a switch is enabled, you can reset them manually to
control the ID number or to resolve a domain ID conflict when you merge fabrics.
If a switch already has a domain ID when it is enabled, and that domain ID conflicts with a switch already
in the fabric, the conflict is resolved. The process can take several seconds, during which traffic is
delayed.
The default domain ID for HP StorageWorks switches is 1. The default domain ID applies to the logical
switches in the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director that are configured
for two domains. To prevent domain conflict, you can either disable one of the switches until the other is
connected to the fabric, and then reenable the switches so that unique domain IDs are assigned, or you
can use the procedure ”Setting the domain ID” on page 33 to make the domain IDs unique before
connecting the logical switches to the fabric.
CAUTION: On switches running Fabric OS 4.0.0 and later, do not use domain ID 0, which is reserved
for another purpose. The use of this domain ID can cause the switch to reboot continuously.
Avoid changing the domain ID on the FCS in secure mode. To minimize down time, change the domain
IDs on the other switches in the secure fabric.
Displaying domain IDs
1. Connect to a switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the fabricShow command.
Fabric information is displayed, including the domain ID (D_ID), for example:
ras045:admin> fabricshow
Switch ID Worldwide Name Enet IP Addr FC IP Addr Name
------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1: fffc01 10:00:00:60:69:e4:00:3c 10.32.220.80 0.0.0.0 "ras080"
2: fffc02 10:00:00:60:69:e0:01:46 10.32.220.1 0.0.0.0 "ras001"
3: fffc03 10:00:00:60:69:e0:01:47 10.32.220.2 0.0.0.0 "ras002"
5: fffc05 10:00:00:05:1e:34:01:bd 10.32.220.5 0.0.0.0 "ras005"
6: fffc06 10:00:00:05:1e:34:02:3e 10.32.220.6 0.0.0.0 "ras006"
7: fffc07 10:00:00:60:69:34:02:0c 10.32.220.7 0.0.0.0 "ras007"
10: fffc0a 10:00:00:60:69:80:04:46 10.32.220.10 10.32.219.0 "ras010"
11: fffc0b 10:00:00:60:69:80:04:47 10.32.220.11 10.32.219.1 "ras011"
15: fffc0f 10:00:00:60:69:80:47:74 10.32.220.15 0.0.0.0 "ras015"
16: fffc10 10:00:00:60:69:80:47:75 10.32.220.16 0.0.0.0 "ras016"
19: fffc13 10:00:00:05:1e:34:00:ad 10.32.220.19 0.0.0.0 "ras019"
20: fffc14 10:00:00:05:1e:34:00:63 10.32.220.20 0.0.0.0 >"ras020"
30: fffc1e 10:00:00:60:69:90:02:21 10.32.220.30 0.0.0.0 "ras030"
31: fffc1f 10:00:00:60:69:90:02:60 10.32.220.31 0.0.0.0 "ras031"
32: fffc20 10:00:00:60:69:90:02:68 10.32.220.32 0.0.0.0 "ras032"
33: fffc21 10:00:00:60:69:90:03:20 10.32.220.33 0.0.0.0 "ras033"
34: fffc22 10:00:00:60:69:90:03:01 10.32.220.34 0.0.0.0 "ras034"
40: fffc28 10:00:00:60:69:50:06:7f 10.32.220.40 0.0.0.0 "ras040"
45: fffc2d 10:00:00:05:1e:34:c5:17 10.32.220.45 0.0.0.0 "ras045"
50: fffc32 10:00:00:60:69:c0:06:64 10.32.220.50 0.0.0.0 "ras050"
51: fffc33 10:00:00:60:69:c0:1e:43 10.32.220.51 0.0.0.0 "ras051"
60: fffc3c 10:00:00:60:69:12:34:44 10.32.220.60 0.0.0.0 "ras060"
62: fffc3e 10:00:00:60:69:12:32:76 10.32.220.62 0.0.0.0 "ras062"
63: fffc3f 10:00:00:60:69:12:45:6e 10.32.220.63 0.0.0.0 "ras063"
64: fffc40 10:00:00:60:69:12:1d:51 10.32.220.64 0.0.0.0 "ras064"
The Fabric has 25 switches
ras045:admin>
32 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 33

The fields in the fabricShow display are:
• Switch ID: The switch Domain_ID and embedded port D_Id.
• Worldwide Name: The switch WWN.
• Enet IP Addr: The switch Ethernet IP address.
• FC IP Addr: The switch FC IP address.
• Name: The switch symbolic name. An arrow (>) indicates the principal switch.
Setting the domain ID
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the switchDisable command to disable the switch.
3. Issue the configure command.
4. Enter y after the Fabric Parameters prompt:
Fabric parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
5. Enter a unique domain ID at the Domain prompt. Use a domain ID value from 1 through 239 for
normal operating mode (FCSW compatible):
Domain: (1..239) [1] 3
6. Respond to the remaining prompts (or press Ctrl-d to accept the other settings and exit).
7. Issue the switchEnable command to reenable the switch.
Linking through a gateway
A gateway merges SANs into a single fabric by establishing point-to-point E_Port connectivity between
two Fibre Channel switches that are separated by a network with a protocol such as IP or SONET.
Except for link initialization, gateways are transparent to switches; the gateway simply provides E_Port
connectivity from one switch to another.
By default, switch ports initialize links using the Exchange Link Parameters (ELP) mode 1. However,
gateways expect initialization with ELP mode 2 (also called ISL R_RDY mode). Therefore, to enable two
switches to link through a gateway, the ports on both switches must be set for ELP mode 2.
Any number of E_Ports in a fabric can be configured for gateway links, provided the following rules
are followed:
• All switches in the fabric must be upgraded to Fabric OS 3.1.0 or later, or to 4.1.0 or later.
• To prevent fabric segmentation, make sure that all switches in the fabric are using the core PID format,
as described in section ”Configuring a link through a gateway” next.
• When determining switch count maxima, include the switches connected to both sides of the gateway.
• Extended links (those created using the Extended Fabrics licensed feature) and the security features in
Secure Fabric OS are not supported through gateway links.
Configuring a link through a gateway
1. If you are not sure that the PID format is consistent across the entire fabric, issue the configShow
command on all switches to check the PID settings. If necessary, change the PID format on any
non-conforming switches, as described in ”Configuring the PID format” on page 213.
2. Connect to the switch on one end of the gateway and log in as admin.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 33
Page 34

3. Issue the portCfgIslMode command:
For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch,
SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16, SAN
Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP
p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32:
For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director
2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director:
In the following example, slot 2, port 3 is enabled for a gateway link:
switch:admin> portcfgislmode 2/3, 1
Committing configuration...done.
ISL R_RDY Mode is enabled for port 3. Please make sure the PID
formats are consistent across the entire fabric.
switch:admin>
4. Repeat the steps for any additional ports to be connected to the gateway.
5. Repeat the procedure on the switch at the other end of the gateway.
portCfgIslMode port mode
Specify a port number. Valid values for port number
depend on the switch type. The mode operand is
required: Specify 1 to enable ISL R_RDY mode
(gateway link) or specify 0 to disable it.
portCfgIslMode slot/port, mode
Specify a slot/port number pair. Valid values for
slot and port number depend on the switch type.
The mode operand is required: Specify 1 to enable
ISL R_RDY mode (gateway link) or specify 0 to
disable it.
See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide for more information about the
portCfgIslMode command.
Checking status
You can check the status of switch operation, high availability (HA) features, and fabric connectivity.
Checking switch operation
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the switchShow command.
A switch summary and a port summary are displayed.
3. Verify that the switch and ports are online.
4. Issue the switchStatusShow command to further check the status of the switch.
Verifying HA features
HA features provide maximum reliability and non-disruptive replacement of key hardware and software
modules. To verify these features, connect to the switch as admin and use any of the following commands:
• The chassisshow verifies the field replaceable units (FRUs).
• For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director:
•The haShow command verifies that HA is enabled, that the heartbeat is up, and that the HA state
is synchronized between the active and standby CP blades.
•The slotShow command inventories and displays the current status of each slot in the system.
Verifying fabric connectivity
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the fabricShow command.
A summary of all the switches in the fabric is displayed. For example:
34 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 35
switch:admin> fabricshow
Switch ID Worldwide Name Enet IP Addr FC IP Addr Name
------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1: fffc01 10:00:00:60:69:80:04:5a 192.168.186.61 192.168.68.193 “switch61”
3: fffc03 10:00:00:60:69:10:9c:29 192.168.186.175 0.0.0.0 “switch175”
4: fffc04 10:00:00:60:69:12:14:b7 192.168.174.70 0.0.0.0 “switch70”
5: fffc05 10:00:00:60:69:45:68:04 192.168.144.121 0.0.0.0 “switch121”
6: fffc06 10:00:00:60:69:00:54:ea 192.168.174.79 192.168.68.197 “switch79”
7: fffc07 10:00:00:60:69:80:04:5b 192.168.186.62 192.168.68.194 “switch62”
8: fffc08 10:00:00:60:69:04:11:22 192.168.186.195 0.0.0.0 ”switch195”
9: fffc09 10:00:00:60:69:10:92:04 192.168.189.197 192.168.68.198 “switch197”
10: fffc0a 10:00:00:60:69:50:05:47 192.168.189.181 192.168.68.181 “switch181”
11: fffc0b 10:00:00:60:69:00:54:e9 192.168.174.78 192.168.68.196 “switch78”
15: fffc0f 10:00:00:60:69:30:1e:16 192.168.174.73 0.0.0.0 “switch73”
33: fffc21 10:00:00:60:69:90:02:5e 192.168.144.120 0.0.0.0 “switch120”
44: fffc2c 10:00:00:60:69:c0:06:8d 192.168.144.121 0.0.0.0 “switch121”
97: fffc61 10:00:00:60:69:90:02:ed 192.168.144.123 0.0.0.0 “switch123”
98: fffc62 10:00:00:60:69:90:03:32 192.168.144.122 0.0.0.0 “switch122”
The Fabric has 15 switches
switch:admin>
Verifying device connectivity
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Optional: Issue the switchShow command to verify that devices, hosts, and storage are connected.
3. Optional: Issue the nsShow command to verify that devices, hosts, and storage have successfully
registered with the Name Server.
4. Issue the nsAllShow command.
The 24-bit Fibre Channel addresses of all devices in the fabric are displayed. For example:
switch:admin> nsallshow
{
010e00 012fe8 012fef 030500 030b04 030b08 030b17 030b18
030b1e 030b1f 040000 050000 050200 050700 050800 050de8
050def 051700 061c00 071a00 073c00 090d00 0a0200 0a07ca
0a07cb 0a07cc 0a07cd 0a07ce 0a07d1 0a07d2 0a07d3 0a07d4
0a07d5 0a07d6 0a07d9 0a07da 0a07dc 0a07e0 0a07e1 0a0f01
0a0f02 0a0f0f 0a0f10 0a0f1b 0a0f1d 0b2700 0b2e00 0b2fe8
0b2fef 0f0000 0f0226 0f0233 0f02e4 0f02e8 0f02ef 210e00
211700 211fe8 211fef 2c0000 2c0300 611000 6114e8 6114ef
611600 620800 621026 621036 6210e4 6210e8 6210ef 621400
621500 621700 621a00
75 Nx_Ports in the Fabric }
switch:admin>
The number of devices listed should agree with the number of devices that are connected.
Tracking and controlling switch changes
The TC feature allows you to keep a record of specific changes that might not be considered switch
events, but might provide useful information. The output from the TC feature is dumped to the system
messages log for the switch. Use the errDump or errShow command to view the log.
Items in the log created from the TC feature are labeled TRCK.
Trackable changes are:
• Successful login
• Unsuccessful login
• Logout
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 35
Page 36

• Configuration file change from task
• TC feature on
• TC feature off
An SNMP-TRAP mode can also be enabled; see the trackChangesHelp command in the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide.
For troubleshooting information on the TC feature, see ”Inaccurate information in the system message log”
on page 161.
Enabling the TC feature
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the trackChangesSet 1 command to enable the TC feature:
A message is displayed, verifying that the TC feature is on:
switch:admin> trackchangesset 1
Committing configuration...done.
switch:admin>
The output from the TC feature is dumped to the system message log for the switch. Use the errDump or
errShow command to view the log.
Items in the system message log created from the TC feature are labeled TRCK:
2004/08/24-08:45:43, [TRCK-1001], 212,, INFO, ras007, Successful login by user
admin.
Displaying the status of the TC feature
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the trackChangesShow command.
The status of the TC feature is displayed as either on or off. The display tells whether the TC feature is
configured to send SNMP traps:
switch:admin> trackchangesshow
Track changes status: ON
Track changes generate SNMP-TRAP: NO
switch:admin>
Viewing the switch status policy threshold values
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the switchStatusPolicyShow command.
Whenever there is a switch change, an error message is logged and an SNMP connUnitStatusChange
trap is sent.
For the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32,
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32: The output is similar to
the following:
switch:admin> switchstatuspolicyshow
The current overall switch status policy parameters:
Down Marginal
--------------------------------- PowerSupplies 2 1
Temperatures 2 1
Fans 2 1
Flash 0 1
MarginalPorts 5 2
FaultyPorts 2 1
MissingSFPs 2 1
switch:admin>
36 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 37

For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director: The output is similar to the
following:
switch:admin> switchstatuspolicyshow
The current overall switch status policy parameters:
Down Marginal
--------------------------------- PowerSupplies 3 0
Temperatures 2 1
Fans 2 1
WWN 0 1
CP 0 1
Blade 0 1
Flash 0 1
MarginalPorts 2 1
FaultyPorts 2 1
MissingSFPs 0 0
switch:admin>
The policy parameter determines the number of failed or inoperable units for each contributor that triggers
a status change in the switch.
Each parameter can be adjusted so that a specific threshold must be reached before that parameter
changes the overall status of a switch to MARGINAL or DOWN. For example, if the FaultyPorts
DOWN parameter is set to 3, the status of the switch changes if 3 ports fail. Only one policy parameter
needs to pass the MARGINAL or DOWN threshold to change the overall status of the switch.
For more information about setting policy parameters, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x
administrator guide.
Setting the switch status policy threshold values
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the switchStatusPolicySet command.
The current switch status policy parameter values are displayed first. You are then prompted to enter
values for each DOWN and MARGINAL threshold parameter:
3. Verify the threshold settings you have configured for each parameter by issuing the
switchStatusPolicyShow command to view your current switch status policy configuration.
NOTE: By setting the DOWN and MARGINAL values for a parameter to 0,0 that parameter is no
longer used in setting the overall status for the switch.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 37
Page 38

For the SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP
p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32: The following example shows the command as executed on
a SAN Switch 2/32. The output is similar on SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, Brocade 4Gb SAN
Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32:
:
switch:admin> switchstatuspolicyset
To change the overall switch status policy parameters
The current overall switch status policy parameters:
Down Marginal
--------------------------------- FaultyPorts 2 1
MissingSFPs 0 0
PowerSupplies 2 1
Temperatures 2 1
Fans 2 1
PortStatus 0 0
ISLStatus 0 0
Note that the value, 0, for a parameter, means that it is
NOT used in the calculation.
** In addition, if the range of settable values in the prompt is (0..0),
** the policy parameter is NOT applicable to the switch.
** Simply hit the Return key.
The minimum number of
FaultyPorts contributing to
DOWN status: (0..32) [2] 3
FaultyPorts contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..32) [1] 2
MissingSFPs contributing to
DOWN status: (0..32) [0]
MissingSFPs contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..32) [0]
Bad PowerSupplies contributing to
DOWN status: (0..2) [2]
Bad PowerSupplies contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..2) [1]
Bad Temperatures contributing to
DOWN status: (0..5) [2]
Bad Temperatures contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..5) [1]
Bad Fans contributing to
DOWN status: (0..6) [2]
Bad Fans contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..6) [1]
Down PortStatus contributing to
DOWN status: (0..32) [0]
Down PortStatus contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..32) [0]
down ISLStatus contributing to
DOWN status: (0..32) [0]
down ISLStatus contributing to
MARGINAL status: (0..32) [0]
Policy parameter set has been changed
For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director: Command output includes
parameters related to CP blades.
38 Performing basic configuration tasks
Page 39

3 Configuring standard security features
This chapter provides information and procedures for configuring standard Fabric OS security features
such as account and password management.
Additional security features are available when secure mode is enabled. For information about licensed
security features available in Secure Fabric OS, see the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator
guide.
Secure protocols
Fabric OS supports the secure protocols shown in Table 4.
,
Table 4 Secure protocol support
Protocol Description
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Supports SSLv3, 128-bit encryption by default. Fabric OS uses SSL to support
HTTPS. A certificate must be generated and installed on each switch to enable
SSL.
HTTPS Advanced Web Tools supports the use of HTTPS.
Secure File Copy (scp) Configuration upload and download support the use of scp.
SNMPv3 SNMPv1 is also supported.
SNMP is a standard method for monitoring and managing network devices. Using SNMP components,
you can program tools to view, browse, and manipulate HP StorageWorks switch variables and set up
enterprise-level management processes.
Every HP StorageWorks switch carries an SNMP agent and Management Information Base (MIB). The
agent accesses MIB information about a device and makes it available to a network manager station. You
can manipulate information of your choice by trapping MIB elements using the Fabric OS CLI, Advanced
Web Tools, or Fabric Manager.
The SNMP Access Control List (ACL) provides a way for you to restrict SNMP get and set operations to
certain hosts and IP addresses. This is used for enhanced management security in the SAN.
For details on HP StorageWorks MIB files, naming conventions, loading instructions, and information
about using the HP SNMP agent, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x MIB reference guide.
Table 5 describes additional software or certificates that you must obtain to deploy secure protocols.
Table 5 Items needed to deploy secure protocols
Protocol Host side Switch side
Secure telnet (sectelnet) Sectelnet client License not required, but a switch certificate
issued by HP is required
Secure Shell (SSH) SSH client None
HTTPS No requirement on host
side except a browser that
supports HTTPS
Secure File Copy (scp) SSH daemon, scp server None
Switch IP certificate for SSL
SNMPv3, SNMPv1 None None
The security protocols are designed with the four main usage cases described in Table 6.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 39
Page 40
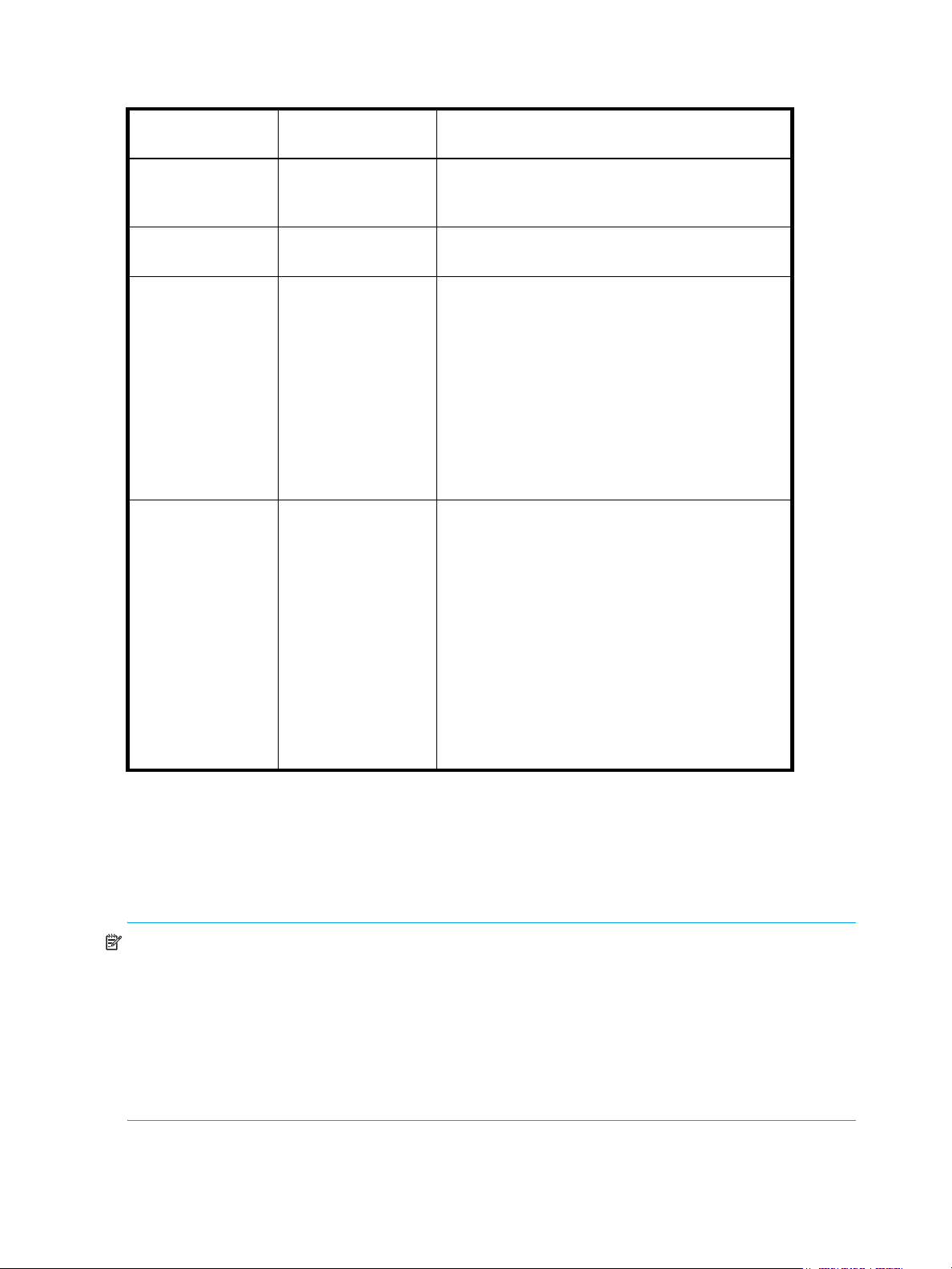
Table 6 Main security scenarios
Fabric Management
interfaces
Nonsecure Nonsecure No special setup is need to use telnet or HTTP. An
Nonsecure Secure Secure protocols may be used. An SSL switch
Secure Secure Secure protocols are supported on Fabric OS
Secure Nonsecure You must use sectelnet because telnet is not
Comments
HP switch certificate must be installed if sectelnet
is used.
certificate must be installed if SSH/HTTPS is used.
4.4.0 (and later) switches. Switches running
earlier Fabric OS versions can be part of the
secure fabric, but they do not support secure
management.
Secure management protocols must be
configured for each participating switch.
Nonsecure protocols may be disabled on
nonparticipating switches.
If SSL is used, certificates must be installed.
allowed in secure mode.
Nonsecure management protocols are necessary
under these circumstances:
Ensuring network security
To ensure security, Fabric OS supports SSH encrypted sessions. SSH encrypts all messages, including the
client’s transmission of password during login. The SSH package contains a daemon (sshd), which runs
on the switch. The daemon supports a wide variety of encryption algorithms, such as Blowfish-CBC
and AES.
NOTE: To maintain a secure network, avoid using telnet or any other unprotected application when you
are working on the switch. For example, if you use telnet to connect to a machine, and then start an SSH
or secure telnet session from that machine to the switch, the communication to the switch is in clear text
and, therefore, is not secure.
Nor is the FTP protocol secure. When you use FTP to copy files to or from the switch, the contents are in
clear text. When you use FTP to copy files to or from
login and password, are in clear text
configUpload, configDownload, and firmwareDownload.
• The fabric contains switches running
Fabric OS 3.2.0.
• The presence of software tools that do not
support Secure protocols: for example, Fabric
Manager 4.0.0.
• The fabric contains switches running Fabric
OS versions earlier than 4.4.0. Nonsecure
management is enabled by default.
the switch, the contents, including the remote FTP server’s
. This limitation affects the following commands: saveCore,
40 Configuring standard security features
Page 41

Commands that require a secure login channel must be issued from an original SSH session. If you start
an SSH session, and then use the login command to start a nested SSH session, commands that require
a secure channel are rejected.
Fabric OS 4.4.0 and later supports SSH protocol 2.0 (ssh2). For more information on SSH, see the SSH
IETF web site: http://www.ietf.org/ids.by.wg/secsh.html
Shell: The Definitive Guide by Daniel J. Barrett, Richard Silverman.
Fabric OS 4.4.0 comes with the SSH server preinstalled; however, you must select and install the SSH
client. For information on installing and configuring the F-Secure SSH client, visit the following web site:
http://www.f-secure.com
.
Configuring the telnet interface
Telnet is enabled by default. To prevent users from passing clear text passwords over the network when
they connect to the switch, you can disable the telnet interface.
NOTE: Before disabling the telnet interface, make sure you have an alternate method of establishing a
connection with the switch.
Disabling telnet
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
Connect through some other means than telnet, for example, through SSH.
2. Issue the following command:
configure telnetd
3. In response to the System Services prompt, enter y.
4. In response to the telnetd prompt, enter off .
The telnet interface is disabled. If you entered the command during a standard telnet session, the
session terminates. For example:
. Another informative source is SSH, The Secure
switch:admin> configure telnetd
Not all options will be available on an enabled switch.
To disable the switch, use the “switchDisable” command.
Configure...
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
http attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
snmp attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
rpcd attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
cfgload attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
[31454]: Read 1 license entries for generation 1.
[31454]: Read 1 license records.
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
rstatd (on, off): [off]
rusersd (on, off): [off]
telnetd (on, off): [on] off
Enabling telnet
1. Connect to the switch through a means other than telnet (for example, SSH) and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
configure telnetd
3. In response to the System Services prompt, enter y.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 41
Page 42

4. In response to the telnetd prompt, enter on.
The telnet interface is enabled.
Blocking listeners
HP StorageWorks switches block Linux® subsystem listener applications that are not used to implement
supported features and capabilities. Table 7 lists the listener applications that HP StorageWorks switches
either block or do not start.
Table 7 Blocked listener applications
Listener application Core Switch 2/64, SAN
Director 2/128, and 4/256
SAN Director
chargen Do not start Do not start
echo Do not start Do not start
daytime Do not start Do not start
discard Do not start Do not start
ftp Do not start Do not start
rexec Block with packet filter Do not start
rsh Block with packet filter Do not start
rlogin Block with packet filter Do not start
time Block with packet filter Do not start
rstats Do not start Do not start
rusers Do not start Do not start
Accessing switches and fabrics
4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN
Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/8-EL, SAN
Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch
for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN
Switch 4/32
Table 8 lists the defaults for accessing hosts, devices, switches, and zones.
Table 8 Access defaults
Category Default
Hosts Any host can access the fabric by SNMP.
Any host can telnet to any switch in the fabric.
Any host can establish an HTTP connection to any switch in the fabric.
Any host can establish an API connection to any switch in the fabric.
Devices All device ports can access SES.
All devices can access the management server.
Any device can connect to any FC port in the fabric.
Switch access Any switch can join the fabric.
All switches in the fabric can be accessed through serial port.
Zoning Node WWNs can be used for WWN-based zoning.
42 Configuring standard security features
Page 43

Creating and maintaining user-defined accounts
In addition to the default administrative and user accounts, Fabric OS supports up to 15 user-defined
accounts in each logical switch (domain). These accounts expand your ability to track account access and
audit administrative activities.
User-defined accounts can be assigned either admin-, switchAdmin-, or user-level roles. Admin-level
accounts allow up to two simultaneous login sessions. User-level accounts allow up to four simultaneous
login sessions. The total number of simultaneous login sessions allowed per logical switch is 15.
You can change passwords on user-defined accounts as described in ”Changing an account password” on
page 45.
If the TC feature is enabled, the system keeps track of account names and login attempts. (See ”Tracking
and controlling switch changes” on page 35 for details on enabling the TC feature.)
For large enterprises, Fabric OS also supports RADIUS services, as described in ”Setting up RADIUS AAA
service” on page 45.
The following procedures are for operations you can perform on user-defined accounts.
NOTE: If you are operating in secure mode, you can perform these operations only on the primary FCS
switch.
Displaying account information
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue one of the following commands:
• userConfig --show -a to show all account information for a logical switch
• userConfig --show -b to show all backup account information for a logical switch
• userConfig --show username to show account information for the specified account name
Accounts with the admin role can display information about all accounts on the logical switch. Accounts
with the switchAdmin role can display information about all accounts on the logical switch; however, they
cannot display information about security, user management, or zoning. Accounts with the user role can
display information only about themselves.
Creating a user-defined account
Accounts with the admin role can create accounts. Accounts with the user role cannot.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
userConfig --add username -r rolename [-d description]
where:
username Specifies the account name, which must begin with an alphabetic
character. The name can consist of 8 to 40 characters. It is case-sensitive
and can contain alphabetic and numeric characters, the dot, and the
underscore. It must be different from all other account names on the
logical switch.
-r rolename Specifies the role: either admin, switchAdmin, or user in nonsecure
mode; admin, user, or nonfcsadmin in secure mode.
-d description Is an optional argument that adds a description to the account. The
description field can be up to 40 printable ASCII characters. The
following characters are not allowed: asterisk (*), quotation mark (“),
exclamation point (!), semicolon (;), and colon (:).
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 43
Page 44

3. In response to the prompt, enter a password for the account.
The password is not displayed when you enter it on the command line.
Deleting a user-defined account
Only accounts with the admin role can delete user-defined accounts on the logical switch.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
userConfig --delete username
where username specifies the account name. You cannot delete the default accounts. An account
cannot delete itself. All active CLI sessions for the deleted account are logged out.
3. Enter y at the prompt for confirmation.
Changing account parameters
Accounts with the admin role can change information for accounts that have lesser permissions. Accounts
with the user role cannot.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
userconfig --change username [-r rolename] [-d description] [-e yes | no]
where:
username Changes the account attribute for username. The account must already
exist.
-r rolename Is an optional argument that changes the role: either admin,
switchAdmin, or user in nonsecure mode; admin, user, or
nonfcsadmin in secure mode.
An account cannot change its own role.
You can change the role name of a user-defined account only with a
lower level of authorization.
-d description Is an optional argument; the account description. The description field
can be up to 40 printable ASCII characters. The following characters are
not allowed: asterisk (*), quotation mark (“), exclamation point (!),
semicolon (;), and colon (:).
You can change the description of a user-defined account only with a
lower level of authorization.
-e Is an optional argument; enter yes to enable the account or enter no to
disable it. If you disable an account, all active CLI sessions for that
account are logged out. You can enable or disable user-defined or
default accounts.
Recovering user-defined accounts
If a backup account exists (in secure mode), you can recover it with the following command:
userConfig --recover
The following conditions apply to recovering user accounts:
• Only accounts with admin or higher roles can recover accounts.
• The attributes in the backup database replace the attributes in the current account database.
• An event is stored in the system message log, indicating that accounts have been recovered.
44 Configuring standard security features
Page 45

Changing an account password
At each level of account access, you can change passwords for that account and accounts that have
lesser privileges.
If you log in to a user account, you can change only that account’s password.
If you log in to an admin account, you can change admin and user passwords. You must provide the old
password when the account being changed has the same or higher privileges than the current login
account. For example, if you are logged in as admin, you need admin passwords to change passwords
for admin accounts (except when you change the default user account password at login), but you do not
need user passwords to change passwords for user accounts.
A new password must have at least one character different from the old password. The following rules
also apply to passwords:
• You cannot change passwords using SNMP.
• Password prompting is disabled when security mode is enabled.
• With Fabric OS 4.4.0 and later, you can use Advanced Web Tools to change admin-level account
passwords.
• With Fabric OS 3.2.0 and later, you cannot change default account names.
For information on password behavior when you upgrade (or downgrade) firmware, see ”Effects of
firmware changes on accounts and passwords” on page 79.
Changing the password for the current login account
1. Connect to the switch and log in as either admin or user.
2. Issue the password command:
passwd
3. Enter the requested information at the prompts.
Changing the password for a different account
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following password command:
passwd name
where name is the name of the account.
3. Enter the requested information at the prompts.
If the named account has lesser privileges than the current login account, the old password of the named
account is not required. If the named account has equal or higher privileges than the current login
account, you are prompted to enter the old password of the named account.
Setting up RADIUS AAA service
Fabric OS 3.2, 4.4.0 and later support RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting service
(AAA). When configured for RADIUS, a switch becomes a RADIUS client. In this configuration,
authentication records are stored in the RADIUS host server database. Login and logout account name,
assigned role, and time-accounting records are also stored on the RADIUS server for each user.
By default, RADIUS service is disabled, so AAA services default to the switch local database.
To enable RADIUS service, HP recommends that you access the CLI through an SSH connection so that the
shared secret is protected. Multiple login sessions can configure simultaneously; the last session to apply a
change leaves its configuration in effect. After a configuration is applied, it persists after a reboot or an
HA failover.
The configuration is chassis-based, so it applies to all logical switches (domains) on the switch and
replicates itself on a standby CP blade, if one is present. It is saved in a configuration upload and applied
in a configuration download.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 45
Page 46

Configure at least two RADIUS servers so that if one fails, the other assumes service. You can set the
configuration with both RADIUS service and local authentication enabled so that if all RADIUS servers do
not respond (because of power failure or network problems), the switch uses local authentication.
Consider the following effects of the use of RADIUS service on other Fabric OS features:
• When RADIUS service is enabled, all account passwords must be managed on the RADIUS server. The
Fabric OS mechanisms for changing switch passwords remain functional; however, such changes
affect only the involved switches locally. They do not propagate to the RADIUS server, nor do they
affect any account on the RADIUS server.
When RADIUS is set up for a fabric that contains a mix of switches with and without RADIUS support,
the way a switch authenticates users depends on whether a RADIUS server is set up for that switch. For
a switch with RADIUS support and configuration, authentication bypasses the local password
database. For a switch without RADIUS support or configuration, authentication uses the switch’s local
account names and passwords.
• When Secure Fabric OS secure mode is enabled, the following behaviors apply:
• Account passwords stored in the switch-local password database are distributed among all
switches in the same fabric. RADIUS configuration is not affected.
• There are separate admin and nonfcsadmin roles in secure mode. A nonfcsadmin account on a
RADIUS server cannot access FCS switches, even if the account is properly authenticated.
• If a nonfcsadmin account on a RADIUS server logs in to a switch in nonsecure mode, the switch
grants the user admin role privileges.
• The following behaviors apply to Advanced Web Tools:
• Advanced Web Tools client and server keep a session open after a user is authenticated. A
password change on a switch invalidates an open session and requires the user to log in again.
When integrated with RADIUS, a switch password change on the RADIUS server does not
invalidate an existing open session, although a password change on the local switch does.
• If you cannot log in because of a RADIUS server connection problem, Advanced Web Tools
displays a message indicating server outage.
Configuring the RADIUS server
You must know the switch IP address or name to connect to switches. Use the ipAddrShow command to
display a switch IP address.
For HP StorageWorks SAN Directors (chassis-based systems), the switch IP addresses are aliases of the
physical Ethernet interfaces on the CP blades. When specifying client IP addresses for the logical switches
in such systems, use the CP blade IP addresses. For accessing both the active and standby CP blade, and
for the purpose of HA failover, both of the CP blade IP addresses should be included in the RADIUS server
configuration.
User accounts should be set up by their true network-wide identity, rather than by the account names
created on a Fabric OS switch. Along with each account name, assign appropriate switch access roles.
To manage a nonsecure fabric, these roles can be user or admin. To manage a secure fabric, these roles
can be user, admin, or nonfcsadmin.
When they log in to a switch configured with RADIUS, users enter their assigned RADIUS account names
and passwords at the prompt. After RADIUS server authenticates a user, it responds with the assigned
switch role in an HP Vendor-Specific Attribute (VSA), as defined in the RFC. An Authentication-Accept
response without such VSA role assignment, assigns the user role.
The following sections describe how to configure a RADIUS server to support HP clients under different
operating systems.
46 Configuring standard security features
Page 47

Linux
The following procedures work for FreeRADIUS on Solaris and Red Hat Linux. FreeRADIUS is a freeware
RADIUS server that you can find at the following web site: www.freeradius.org
.
Follow the installation instructions at the web site. FreeRADIUS runs on Linux (all versions), FreeBSD,
NetBSD, and Solaris. If you make a change to any of the files used in this configuration, you must stop the
server and restart it for the changes to take effect.
FreeRADIUS installation places the configuration files in $PREFIX/etc/raddb. By default, the PREFIX
is /usr/local.
Configuring RADIUS service on Linux consists of the following tasks:
• Adding the HP attribute to the server
• Creating the user
• Enabling clients
Adding the attribute to the server
1. Create and save the file $PREFIX/etc/raddb/dictionary.brocade with the following
information:
#
# Brocade FabricOS v5.0.1 dictionary
#
VENDOR Brocade 1588
#
# attribute 1 defined to be Brocade-Auth-Role
# string defined in user configuration
#
ATTRIBUTE Brocade-Auth-Role 1 string Brocade
This defines the vendor ID as 1588, the vendor attribute 1 as Brocade-Auth-Role, and it is a string
value.
2. Open the file $PREFIX/etc/raddb/dictionary in a text editor and add the following line:
$INCLUDE dictionary.brocade
As a result, the file dictionary.brocade is located in the RADIUS configuration directory and
loaded for use by the RADIUS server.
Creating the user
Open the $PREFIX/etc/raddb/user file in a text editor and add user names and roles for users who
will be accessing the switch and authenticating RADIUS. The user logs in using the role specified with
Brocade-Auth-Role. The valid roles include root, factory, admin, switchAdmin, and user. You must
use quotation marks around “password” and “role”.
For example, to set up an account called JohnDoe with the admin role:
JohnDoe Auth-Type := Local, User-Password == “johnPassword” Brocade-Auth-Role =
“admin”
The next example uses the local system password file to authenticate users. (This does not work when
using NIS for authentication. The only way to enable authentication with the password file is to force the
HP StorageWorks switch to authenticate using PAP; this requires the -a pap option with the aaaConfig
command.) For example:
JohnDoe Auth-Type := System, Brocade-Auth-Role = “admin”
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 47
Page 48

Enabling clients
Clients are the switches that use the RADIUS server; each client must be defined. By default, all IP
addresses are blocked.
On dual-CP switches (Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director), the switch
sends its RADIUS request using the IP address of the active CP. When adding clients, add both the active
and standby CP IP addresses so that users can still log in, in case of a failover.
1. Open the $PREFIX/etc/raddb/client.config file in a text editor and add the switches that are
to be configured as RADIUS clients.
For example, to configure the switch at IP address 10.32.170.59 as a client:
client 10.32.170.59
In this example, shortname is an alias used to easily identify the client and Secret is the shared
secret between the client and server. Make sure that the shared secret matches that configured on the
switch (see ”Adding a RADIUS server to the switch configuration” on page 51).
2. Save the file $PREFIX/etc/raddb/client.config and then start the RADIUS server as follows:
$PREFIX/sbin/radiusd
Windows 2000
secret = Secret
shortname = Testing Switch
nastype = other
Configuring RADIUS service on Windows 2000 consists of the following tasks:
• Installing Internet Authentication Service (IAS). For more information and instructions on installing IAS,
see the Microsoft® web site.
• Enabling the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). If CHAP authentication is
required, Windows must be configured to store passwords with reversible encryption. Reverse
password encryption is not the default behavior; it must be enabled.
NOTE: If a user is configured prior to enabling reverse password encryption, the user’s password is
stored and cannot use CHAP. To use CHAP, the password must be reentered after encryption is enabled.
If the password is not reentered, CHAP authentication does not work and the user is then unable to
authenticate from the switch.
• Configuring a user: IAS is the Microsoft implementation of a RADIUS server and proxy. IAS uses the
Windows native user database to verify user login credentials; it does not list specific users, but
instead lists user groups. Each user group should be associated with a specific switch login role. For
example, configure a user group for root, admin, factory, switchAdmin, and user, and then add any
users whose logins you want to associate to the appropriate group.
Enabling CHAP
1. From the Windows Start menu, select Programs > Administrative Tools > Local Security Policy to open
the Local Security Settings window.
2. In the Local Security Settings window, expand the Account Policies folder and select the Password
Policy folder.
3. From the list of policies in the Password Policy folder, right-click Store password using reversible
encryption for all users in the domain, and select Security from the pop-up menu.
An additional Local Security Settings window opens.
4. Select the Enabled radio button and then click OK.
48 Configuring standard security features
Page 49
Configuring users
1. From the Windows Start menu, select Programs > Administrative Tools > Computer Management to
open the Computer Management window.
2. In the Computer Management window, expand the Local Users and Groups folder and select the
Groups folder.
3. Right-click the Groups folder and select New Group from the pop-up menu.
4. In the New Group window, provide a Name and Description for the group and click Add.
5. In the Select Users or Groups window, select the user—who should already have been
configured—you want to add to the group and click Add.
6. Repeat this for every user you want to add.
7. When you have completed adding all users, click OK.
8. In the New Group window, verify that the users you added in step 4 appear in the Members field and
then click Create to create this group.
The new groups are created for each login type (admin, switchAdmin, user).
Configuring the RADIUS server
1. From the Windows Start menu, select Programs > Administrative Tools > Internet Authentication
Service to open the Internet Authentication Service window.
2. In the Internet Authentication Service window, right-click the Clients folder and select New Client from
the pop-up menu.
NOTE: A client is the device that uses the RADIUS server; in this case, it is the switch.
3. In the Add Client window, provide the following:
• Friendly name: The friendly name should be an alias that is easily recognizable as the switch to
which you are connecting.
• Protocol: Select RADIUS as the protocol.
4. In the Add RADIUS Client window, provide the following:
• Client address (IP or DNS): Enter the IP address of the switch.
• Client-Vendor: Select RADIUS Standard.
• Shared secret: Provide a password. Shared secret is a password used between the client device
and server to prevent IP address spoofing by unwanted clients. Keep your shared secret password
in a safe place. You must enter this password in the switch configuration.
5. Click Finish and repeat step 2 through step 4 for all switches on which RADIUS authentication is to be
used.
6. In the Internet Authentication Service window, right-click the Remote Access Policies folder, and then
select New Remote Access Policy from the pop-up window.
7. A remote access policy must be created for each login role (root, admin, factory, switchAdmin, and
user) for which you want to use RADIUS, so apply this policy to the user groups that you already
created.
8. In the Add Remote Access Policy window, enter an easily identifiable Policy friendly name that
enables you to see the switch login for which the policy is being created, and then click Next.
9. After the Add Remote Access Policy window refreshes, click Add.
10.In the Select Attribute window, select Windows Groups and click Add.
11.In the Groups window, click Add.
12.In the Select Groups window, select the user-defined group for which you are creating a policy and
click Add.
13.After adding all appropriate groups, click OK.
14.In the Groups window, click OK.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 49
Page 50

15.In the Add Remote Access Policy window, confirm that the Conditions section displays the groups that
you selected and click Next.
16.After the Add Remote Access Policy window refreshes, select the Grant remote access permission
radio button and click Next.
17. After the Add Remote Access Policy window refreshes again, click Edit Profile.
18.In the Edit Dial-in Profile window, select the Authentication tab and then select only the Encrypted
Authentication (CHAP) and Unencrypted Authentication (PAP, SPAP) check boxes.
19. Select the Advanced tab and click Add.
20.In the Add Attributes window, select Vendor-Specific and click Add.
21.In the Multivalued Attribute Information window, click Add.
22.In the VSA Information window, select the Enter Vendor Code radio button and enter the value 1588.
23.Select the Yes. It conforms radio button, and then click Configure Attribute.
24.In the Configure VSA (RFC compliant) window, enter the following:
a. For the vendor-assigned attribute number, enter the value 1.
b. For the attribute format, enter String.
c. For the attribute value, enter the login role (root, admin, factory, switchAdmin, or user) the
user group must use to log in to the switch.
d. Click OK.
25.In the Multivalued Attribute Information window, click OK.
26. In the Edit Dial-in Profile window, remove all additional parameters (except the one you just added,
Vendor-Specific) and click OK.
27. In the Add Remote Access Policy window, click Finish.
28.After returning to the Internet Authentication Service window, repeat step 6 through step 27 to add
additional policies for all login types you want to use the RADIUS server. After this is done, you can
configure the switch.
Configuring the switch
RADIUS configuration of the switch is controlled by the aaaConfig command.
NOTE: On dual-CP switches (Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director), the
switch sends its RADIUS request using the IP address of the active CP. When adding clients, add both the
active and standby CP IP addresses so that users can still log in to the event of a failover.
The following procedures show how to use the aaaConfig command to set up a switch for
RADIUS service.
Displaying the current RADIUS configuration
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --show
If a configuration exists, its parameters are displayed. If RADIUS service is not configured, only the
parameter heading line is displayed. Parameters include:
• Position: The order in which servers are contacted to provide service
• Server: The server names or IP addresses
• Port: The server ports
• Secret: The shared secrets
• Timeouts: The length of time servers have to respond before the next server is contacted
• Authentication: The type of authentication being used on servers
50 Configuring standard security features
Page 51

Adding a RADIUS server to the switch configuration
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --add server [-p port] [-s secret] [-t timeout]
[-a pap | chap]
where:
server Is either a server name or an IP address. Avoid duplicating server listings
(that is, listing the same server once by name and again by IP address).
Up to five servers can be added to the configuration.
-p port Is an optional argument; enter a server port. The default is port 1812.
-s secret Is an optional argument; enter a shared secret. The default is
sharedsecret. Secrets can be 8 to 40 alphanumeric characters. Make
sure that the secret matches that configured on the server.
-t timeout Is an optional argument; enter the length of time (in seconds) that the
server has to respond before the next server is contacted. The default is 3
seconds. Timeout values can range from 1 to 30 seconds.
-a[pap|chap] Specifies PAP or CHAP as the authentication protocol.
Enabling or disabling RADIUS service
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --radius on | off
Specifying on enables the service; specifying off disables it.
At least one RADIUS server must be configured before you can enable RADIUS service.
If no RADIUS configuration exists, turning it on triggers an error message. When the command succeeds,
the event log indicates that the configuration is enabled or disabled.
Deleting a RADIUS server from the configuration
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --remove server | all
where server is a list of servers by either name or IP address. Enter either the name or IP address of
the server to be removed.
3. At the prompt, enter y to complete the command.
When the command succeeds, the event log indicates that the server is removed.
Changing a RADIUS server configuration
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --change server [-p port] [-s secret] [-t timeout]
[-a pap | chap]
where:
server Is a list of servers by either name or IP address. Enter either the name or IP
address of the server to be changed.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 51
Page 52

-p port Is an optional argument; enter a server port.
-s secret Is an optional argument; enter a shared secret.
-t timeout Is an optional argument; enter the length of time (in seconds) the server
has to respond before the next server is contacted.
-a[pap|chap] Specifies PAP or CHAP as authentication protocol.
Changing the order in which RADIUS servers are contacted for service
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --move server to_position
where:
server Is a list of servers by either name or IP address. Enter either the name or IP
address of the server whose position is to be changed.
to_position Is the position number to which the server is to be moved.
When the command succeeds, the event log indicates that a server configuration is changed.
Enabling and disabling local authentication
It is useful to enable local authentication so that the switch can take over authentication locally if the
RADIUS servers fail to respond because of power outage or network problems. To enable or disable local
authentication, issue the following command:
switch:admin> aaaConfig --switchdb on | off
Specifying on enables local authentication; specifying off disables it.
When local authentication is enabled and RADIUS servers fail to respond, you can log in to the default
switch accounts (admin and user) or any user-defined account. You must know the passwords of these
accounts.
RADIUS authentication must be enabled when local database authentication is turned off from the on
state; otherwise, an error is returned.
Because local database authentication might be disabled or enabled when enabling or disabling RADIUS
authentication, set the local database authentication explicitly to enabled or disabled after setting the
desired RADIUS authentication configuration.
When the command succeeds, the event log indicates that local database authentication is disabled
or enabled.
Configuring for the SSL protocol
Fabric OS 4.4.0 and later support SSL protocol, which provides secure access to a fabric through
Web-based management tools like Advanced Web Tools. SSL support is a standard Fabric OS feature; it
is independent of Secure Fabric OS, which requires a license and separate certification.
Switches configured for SSL grant access to management tools through hypertext transfer protocol-secure
links (which begin with https://) instead of standard links (which begin with http://).
SSL uses public key infrastructure (PKI) encryption to protect data transferred over SSL connections. PKI is
based on digital certificates obtained from an Internet Certificate Authority (CA), which acts as the trusted
key agent.
Certificates are based on the switch IP address or fully-qualified domain name (FQDN), depending on the
issuing CA. If you change a switch IP address or FQDN after activating an associated certificate, you
might have to obtain and install a new certificate. Check with the CA to verify this possibility, and plan
these types of changes accordingly.
52 Configuring standard security features
Page 53
Browser and Java support
Fabric OS supports the following web browsers for SSL connections:
• Internet Explorer (Microsoft Windows)
• Mozilla (Solaris and Red Hat Linux)
In countries that allow the use of 128-bit encryption, use the latest version of your browser. For example,
Internet Explorer 6.0 and later supports 128-bit encryption by default. You can display the encryption
support (called cipher strength) using the Internet Explorer Help:About menu option. If you are running an
earlier version of Internet Explorer, you might be able to download an encryption patch from the
Microsoft web site: http://www.microsoft.com
HP recommends that you upgrade to the Java
find the Java version that is currently running, open the Java console and look at the first line of the
window.
For details on levels of browser and Java support, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x Advanced
Web Tools administrator guide.
Summary of SSL procedures
Configure for SSL by obtaining, installing, and activating digital certificates for SSL support. Certificates
are required on all switches that are to be accessed through SSL.
You also need to install a certificate to the Java Plug-in on the management workstation, and you might
need to add a certificate to your web browser.
Configuring for SSL involves these major steps, which are shown in detail in the next sections:
.
TM
1.4.2_03 Plug-in on your management workstation. To
1. Choose a CA.
2. On each switch:
a. Generate a public/private key (secCertUtil genkey command).
b. Generate a certificate signing request (CSR) (secCertUtil gencsr command) and store the
CSR on an FTP server (secCertUtil export command).
3. Obtain the certificates from the CA.
You can request a certificate from a CA through a web browser. After you request a certificate, the
CA either sends certificate files by e-mail (public) or provides access to them on a remote host
(private). Typically, the CA provides the certificate files listed in Table 9.
Table 9 SSL certificate files
Certificate file Description
name.crt The switch certificate.
nameRoot.crt The root certificate. Typically, this certificate is already installed in the
browser, but if not, you must install it.
nameCA.crt The CA certificate. It is not necessary to install this, but you can if you want
the CA name to be displayed in the browser window.
4. On each switch install and activate the certificate.
5. If necessary, install the root certificate to the browser on the management workstation.
6. Add the root certificate to the Java Plug-in keystore on the management workstation.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 53
Page 54
Choosing a CA
To ease maintenance and allow secure out-of-band communication between switches, consider using one
CA to sign all management certificates for a fabric. If you use different CAs, management services
operate correctly, but the Advanced Web Tools Fabric Events button is unable to retrieve events for the
entire fabric.
Each CA (for example, Verisign or GeoTrust) has slightly different requirements; for example, some
generate certificates based on IP address, while others require an FQDN, and most require a 1024-bit
public/private key while some might accept a 2048-bit key. Consider your fabric configuration, check
CA web sites for requirements, and gather all the information that the CA requires.
Generating a public/private key
Perform the following procedure on each switch:
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command to generate a public/private key pair:
switch:admin> seccertutil genkey
The system reports that this process disables secure protocols, deletes any existing CSR, and deletes
any existing certificates.
3. Respond to the prompts to continue and select the key size. For example:
Continue (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Select key size [1024 or 2048]:
Generating new rsa public/private key pair
Done.
1024
Because CA support for the 2048-bit key size is limited, select 1024 in most cases.
Generating and storing a CSR
After generating a public/private key (see ”Generating a public/private key” on page 54), perform this
procedure on each switch:
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> seccertutil gencsr
3. Enter the requested information. For example:
Country Name (2 letter code, eg, US):US
State or Province Name (full name, eg, California):California
Locality Name (eg, city name):San Jose
Organization Name (eg, company name):Brocade
Organizational Unit Name (eg, department name):Eng
Common Name (Fully qualified Domain Name, or IP address): 192.1.2.3
Generating CSR, file name is: 192.1.2.3.csr
Done.
Your CA might require specific codes for Country, State or Province, Locality, Organization, and
Organizational Unit names. Make sure that your spelling is correct and matches the CA requirements.
If the CA requires that the Common Name be specified as an FQDN, make sure that the FQDN is set
on the domain name server.
4. Issue the following command to store the CSR:
switch:admin> seccertutil export
54 Configuring standard security features
Page 55

5. Enter the requested information. For example:
Select protocol [ftp or scp]: ftp
Enter IP address:
Enter remote directory: path_to_remote_directory
Enter Login Name: your account
Enter Password: your password
Success: exported CSR.
6. If you are set up for secure file copy protocol, you can select it; otherwise, select ftp.
7. Enter the IP address of the switch on which you generated the CSR.
8. Enter the remote directory name of the FTP server to which the CSR is to be sent.
9. Enter your account name and password on the server.
Obtaining certificates
Check the instructions on the CA web site and then perform this procedure for each switch:
1. Generate and store the CSR as described in ”Generating and storing a CSR” on page 54.
2. Open a web browser window on the management workstation and go to the CA web site. Follow the
instructions to request a certificate. Locate the area in the request form into which you are to paste
the CSR.
3. Through a telnet window, connect to the switch and log in as admin.
4. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> seccertutil showcsr
The contents of the CSR is displayed.
5. Locate the section that begins with BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST and ends with END
CERTIFICATE REQUEST.
6. Copy and paste this section (including the BEGIN and END lines) into the area provided in the request
form, and then follow the instructions to complete and send the request.
192.1.2.3
It might take several days to receive the certificates. If the certificates arrive by e-mail, save them to an FTP
server. If the CA provides access to the certificates on an FTP server, make note of the path name and
make sure you have a login name and password on the server.
Installing a switch certificate
Perform this procedure on each switch:
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the following command:
switch:admin> seccertutil import
3. Select a protocol, enter the IP address of the host on which the switch certificate is saved, and enter
your login name and password. For example:
Select protocol [ftp or scp]: ftp
Enter IP address:
Enter remote directory: path_to_remote_directory
Enter certificate name (must have “.crt” suffix):
Enter Login Name: your_account
Enter Password: *****
Success: imported certificate [192.1.2.3.crt].
To use this certificate, run the configure command to activate it
The certificate is downloaded to the switch.
192.10.11.12
192.1.2.3.crt
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 55
Page 56
Activating a switch certificate
Issue the configure command and respond to the prompts that apply to SSL certificates:
SSL attributes Enter yes.
Certificate File Enter the name of the switch certificate file, for example,
CA Certificate File If you want the CA name to be displayed in the browser
192.1.2.3.crt.
window, enter the name of the CA certificate file; otherwise, skip
this prompt.
Select length of
crypto key
HTTP attributes Enter yes.
Secure HTTP enabled Enter yes.
For example:
Configure...
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no]
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Certificate File. (filename or none): [10.33.13.182.crt]
CA Certificate File. (filename or none): [none]
Select length of crypto key.
(Valid values are 40, 56, and 128.): (40..128) [128]
http attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
HTTP Enabled (yes, y, no, n): [yes]
Secure HTTP Enabled (yes, y, no, n): [no]
After you exit the configure command, the HTTP daemon restarts to handle HTTPS requests.
Configuring the browser
The root certificate might already be installed on your browser, but if not, you must install it. To determine
whether it is already installed, check the certificate store on your browser.
Enter the encryption key length (40, 56, or 128).
yes
192.1.2.3.crt
yes
no
yes
The following procedures are guides for installing root certificates to Internet Explorer and Mozilla
browsers. For detailed instructions, see the documentation that came with the certificate.
Checking and installing root certificates on Internet Explorer
1. From the browser Tools menu, select Internet Options.
2. Click the Content tab.
3. Click Certificates.
4. Select the various tabs and scroll the lists to see whether the root certificate is listed. If it is listed, you
do not need to install it, and you can omit the remainder of this procedure.
5. If the certificate is not listed, click Import.
6. Follow the instructions in the Certificate Import wizard to import the certificate.
Checking and installing root certificates on Mozilla
1. From the browser Edit menu, select Preferences.
2. In the left pane of the Preferences window, expand the Privacy & Security list and select Certificates.
3. In the right pane, click Manage Certificates.
4. In the next window, select the Authorities tab.
5. Scroll the authorities list to determine whether the root certificate is listed. (For example, its name might
have the form nameRoot.crt.) If it is listed, you do not need to install it; omit the remainder of
this procedure.
6. If the certificate is not listed, click Import.
56 Configuring standard security features
Page 57
7. Browse to the certificate location and select the certificate.
For example, select nameRoot.crt.
8. Click Open and follow the instructions to import the certificate.
Installing a root certificate to the Java Plug-in
For information on Java requirements, see ”Browser and Java support” on page 53.
This procedure is a guide for installing a root certificate to the Java Plug-in on the management
workstation. Install the root certificate, if it is not already installed to the plug-in. For detailed instructions,
see the documentation that came with the certificate and to the Sun Microsystems web site:
www.sun.com
1. Copy the root certificate file from its location on the FTP server to the Java Plug-in bin.
For example, the bin location might be:
C: \program files\java\j2re1.4.2_03\bin
2. Open a Command Prompt window and change to the Java Plug-in bin directory.
3. Issue the keytool command and respond to the prompts. For example:
C:\Program Files\Java\j2re1.4.2_03\bin> keytool -import -alias RootCert -file
RootCert.crt -keystore ..\lib\security\RootCerts
Enter keystore password:
Owner: CN=Brocade, OU=Software, O=Brocade Communications, L=San Jose,
ST=California, C=US
Issuer: CN=Brocade, OU=Software, O=Brocade Communications, L=San Jose,
ST=California, C=US
Serial number: 0
Valid from: Thu Jan 15 16:27:03 PST 2004 until: Sat Feb 14 16:27:03 PST 2004
Certificate fingerprints:
MD5: 71:E9:27:44:01:30:48:CC:09:4D:11:80:9D:DE:A5:E3
SHA1: 06:46:C5:A5:C8:6C:93:9C:FE:6A:C0:EC:66:E9:51:C2:DB:E6:4F:A1
Trust this certificate? [no]:
Certificate was added to keystore
.
changeit
yes
In the example, changeit is the default password and RootCert is an example of a root certificate
name.
Displaying and deleting certificates
Table 10 summarizes the commands that display and delete certificates. For details on these commands,
see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide.
Table 10 Commands to display and delete SSL certificates
Command Description
secCertUtil show Displays the state of the SSL key and a list of installed certificates
secCertUtil show filename Displays the contents of a specific certificate
secCertUtil showcsr Displays the contents of a CSR
secCertUtil delete filename Deletes a specified certificate
secCertUtil delcsr Deletes a CSR
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 57
Page 58

Troubleshooting certificates
If you receive messages in the browser or in a pop-up window when logging in to the target switch using
HTTPS, see Table 11.
Table 11 SSL messages and actions
Message Action
The page cannot be displayed The SSL certificate is not installed correctly or HTTPS is not
enabled correctly. Make sure that the certificate has not
expired, that HTTPS is enabled, and that certificate file names
are configured correctly.
The security certificate was
issued by a company you have
not chosen to trust.
The security certificate has
expired or is not yet valid
The name on the security
certificate is invalid or does
not match the name of the site
file
This page contains both secure
and nonsecure items. Do you
want to display the nonsecure
items?
The certificate is not installed in the browser. Install it as
described in ”Configuring the browser” on page 56.
Either the certificate file is corrupted or it needs to be
updated. Click View Certificate to verify the certificate
content. If it is corrupted or out of date, obtain and install a
new certificate.
The certificate is not installed correctly in the Java Plug-in.
Install it as described in ”Installing a root certificate to the
Java Plug-in” on page 57.
Click No in this pop-up window. The session opens with a
closed lock icon on the lower-right corner of the browser,
indicating an encrypted connection.
Configuring SNMP agent and traps
You can perform a configuration for the transmission of SNMP information to management stations.
SNMPv3 and SNMPv1 are supported.
The configuration process involves configuring the SNMP agent and configuring SNMP traps. The
following commands are used in the process:
• The configure command sets the security level. You can specify no security, authentication only, or
authentication and privacy.
• The snmpConfig command configures the SNMP agent and traps for SNMPv3 or
SNMPv1 configurations.
• If necessary for backward compatibility, you can use these legacy commands for the configuration of
SNMP v1:
•The agtCfgShow, agtCfgset, and agtCfgDefault commands configure the SNMPv1 agent.
•The snmpMibCapSet command filters at the trap level and the snmpMibCapShow command
displays the trap filter values.
The SNMP trap configuration specifies the MIB trap elements to be used to send information to the SNMP
management station. There are two main MIB trap choices:
• HP-specific MIB trap is associated with the HP-specific StorageWorks MIB (SW-MIB); it monitors HP
StorageWorks switches specifically.
• FibreAlliance MIB trap is associated with the FibreAlliance MIB (FA-MIB); it manages SAN switches
and devices from any company that complies with FibreAlliance specifications.
If you use both SW-MIB and FA-MIB, you might receive duplicate information. You can disable the
FA-MIB, but not the SW-MIB.
58 Configuring standard security features
Page 59

You can also use the following MIBs and their associated traps:
• FICON-MIB (for FICON environments)
• HA-MIB (for the Core Switch 2/64 and SAN Director 2/128)
• SW-EXTTRAP, whcih includes the Software Serial Number (swSsn) as a part of HP StorageWorks SW
traps. It is also used with the legacy Integrated/64 SAN Switch fabrics product to provide detailed
group information for a particular trap.
For information on HP StorageWorks MIBs, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x MIB reference
guide. For information on the specific commands used in these procedures, see online help or the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide.
Setting the security level
Use the configure command to set the security level (called SNMP attributes). You can specify no
security, authentication only, or authentication and privacy. For example, to configure for authentication
and privacy:
switch:admin> configure
Not all options will be available on an enabled switch.
To disable the switch, use the “switchDisable” command.
Configure...
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no]
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
http attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
snmp attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
y
Select SNMP Security Level:
(0 = No security, 1 = Authentication only, 2 = Authentication and
Privacy): (0..2) [0] 2
Using the snmpConfig command
Use the snmpConfig --set command to change either the SNMPv3 or SNMPv1 configuration. You
can also change access control, MIB capability, and system group.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 59
Page 60

Sample SNMPv3 configuration:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set snmpv3
SNMPv3 user configuration:
User (rw): [snmpadmin1] adminuser
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3] 1
New Auth Passwd:
Verify Auth Passwd:
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv[2]): (1..2) [2] 1
New Priv Passwd:
Verify Priv Passwd:
User (rw): [snmpadmin2] shauser
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3] 2
New Auth Passwd:
Verify Auth Passwd:
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv[2]): (1..2) [2] 1
New Priv Passwd:
Verify Priv Passwd:
User (rw): [snmpadmin3] nosec
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv[2]): (2..2) [2]
User (ro): [snmpuser1]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (3..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv[2]): (2..2) [2]
User (ro): [snmpuser2]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (3..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv[2]): (2..2) [2]
User (ro): [snmpuser3]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (3..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv[2]): (2..2) [2]
SNMPv3 trap recipient configuration:
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 192.168.45.90
UserIndex: (1..6) [1]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 4
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 192.168.45.92
UserIndex: (1..6) [2]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 2
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Committing configuration...done.
60 Configuring standard security features
Page 61

Sample SNMPv1 configuration:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set snmpv1
SNMP community and trap recipient configuration:
Community (rw): [Secret C0de] admin
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 10.32.225.1
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 1
Community (rw): [OrigEquipMfr]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [10.32.225.2]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [1]
Community (rw): [private]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [10.32.225.3]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [2]
Community (ro): [public]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [10.32.225.4]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [3]
Community (ro): [common]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [10.32.225.5]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [4]
Community (ro): [FibreChannel]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [10.32.225.6]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [5]
Committing configuration...done.
Sample accessControl configuration:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set accessControl
SNMP access list configuration:
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 192.168.0.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 10.32.148.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true] f
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 10.33.0.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true] f
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Committing configuration...done.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 61
Page 62

Sample mibCapability configuration:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show mibCapability
FA-MIB: YES
FICON-MIB: YES
HA-MIB: YES
SW-TRAP: YES
swFCPortScn: YES
swEventTrap: YES
swFabricWatchTrap: YES
swTrackChangesTrap: NO
FA-TRAP: YES
connUnitStatusChange: YES
connUnitEventTrap: NO
connUnitSensorStatusChange: YES
connUnitPortStatusChange: YES
SW-EXTTRAP: NO
FICON-TRAP: NO
HA-TRAP: YES
fruStatusChanged: YES
cpStatusChanged: YES
fruHistoryTrap: NO
Sample systemGroup configuration (default):
switch:admin> snmpconfig --default systemGroup
*****
This command will reset the agent's system group configuration back to
factory default
*****
sysDescr = Fibre Channel Switch
sysLocation = End User Premise
sysContact = Field Support
authTraps = 0 (OFF)
*****
Are you sure? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Using legacy commands for SNMPv1
Use the snmpConfig command to configure the SNMPv1 agent and traps (see ”Using the snmpConfig
command” on page 59). However, if necessary for backward compatibility, you can choose to use legacy
commands.
62 Configuring standard security features
Page 63

Sample SNMP agent configuration information:
switch:admin> agtcfgshow
Current SNMP Agent Configuration
Customizable MIB-II system variables:
sysDescr = FC Switch
sysLocation = End User Premise
sysContact = Field Support.
authTraps = 1 (ON)
SNMPv1 community and trap recipient configuration:
Community 1: Secret C0de (rw)
Trap recipient: 192.168.1.51
Trap recipient Severity level: 4
Community 2: OrigEquipMfr (rw)
Trap recipient: 192.168.1.26
Trap recipient Severity level: 0
Community 3: private (rw)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 4: public (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 5: common (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 6: FibreChannel (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
SNMP access list configuration:
Entry 0: Access host subnet area 192.168.64.0 (rw)]
Entry 1: No access host configured yet
Entry 2: No access host configured yet
Entry 3: No access host configured yet
Entry 4: No access host configured yet
Entry 5: No access host configured yet
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 63
Page 64

Sample modification of the SNMP configuration values:
switch:admin> agtcfgset
Customizing MIB-II system variables ...
At each prompt, do one of the followings:
o <Return> to accept current value,
o enter the appropriate new value,
o <Control-D> to skip the rest of configuration, or
o <Control-C> to cancel any change.
To correct any input mistake:
<Backspace> erases the previous character,
<Control-U> erases the whole line,
sysDescr: [FC Switch]
sysLocation: [End User Premise]
sysContact: [Field Support.]
authTrapsEnabled (true, t, false, f): [true]
SNMP community and trap recipient configuration:
Community (rw): [Secret C0de]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [192.168.1.51]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 3
Community (rw): [OrigEquipMfr]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [192.168.1.26]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0]
Community (rw): [private]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 192.168.64.88
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 1
Community (ro): [public]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Community (ro): [common]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Community (ro): [FibreChannel]
Trap Recipient's IP address in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
SNMP access list configuration:
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 192.168.64.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Committing configuration...done.
value = 1 = 0x1
64 Configuring standard security features
Page 65

Sample reset of the SNMP agent configuration to default values:
switch:admin> agtcfgdefault
*****
This command will reset the agent's configuration back to factory default
*****
Current SNMP Agent Configuration
Customizable MIB-II system variables:
sysDescr = Fibre Channel Switch.
sysLocation = End User Premise
sysContact = sweng
authTraps = 0 (OFF)
SNMPv1 community and trap recipient configuration:
Community 1: Secret C0de (rw)
Trap recipient: 192.168.15.41
Trap recipient Severity level: 4
Community 2: OrigEquipMfr (rw)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 3: private (rw)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 4: public (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 5: common (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 6: FibreChannel (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
SNMP access list configuration:
Entry 0: Access host subnet area 192.168.64.0 (rw)]
Entry 1: No access host configured yet
Entry 2: No access host configured yet
Entry 3: No access host configured yet
Entry 4: No access host configured yet
Entry 5: No access host configured yet
*****
Are you sure? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Committing configuration...done.
agent configuration reset to factory default
Current SNMP Agent Configuration
Customizable MIB-II system variables:
sysDescr = Fibre Channel Switch.
sysLocation = End User Premise
sysContact = Field Support.
authTraps = 0 (OFF)
SNMPv1 community and trap recipient configuration:
Community 1: Secret C0de (rw)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 2: OrigEquipMfr (rw)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 3: private (rw)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 4: public (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 5: common (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
Community 6: FibreChannel (ro)
No trap recipient configured yet
(output truncated)
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 65
Page 66

Sample modification of the options for configuring SNMP MIB traps:
switch:admin> snmpmibcapset
The SNMP Mib/Trap Capability has been set to support
FE-MIB
SW-MIB
FA-MIB
FA-TRAP
FA-MIB (yes, y, no, n): [yes]
FICON-MIB (yes, y, no, n): [no]
HA-MIB (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
SW-TRAP (yes, y, no, n): [no]
swFCPortScn (yes, y, no, n): [no]
swEventTrap (yes, y, no, n): [no]
swFabricWatchTrap (yes, y, no, n): [no]
swTrackChangesTrap (yes, y, no, n): [no]
FA-TRAP (yes, y, no, n): [yes]
connUnitStatusChange (yes, y, no, n): [no]
connUnitEventTrap (yes, y, no, n): [no]
connUnitSensorStatusChange (yes, y, no, n): [no]
connUnitPortStatusChange (yes, y, no, n): [no]
SW-EXTTRAP (yes, y, no, n): [no]
FICON-TRAP (yes, y, no, n): [no]
linkRNIDDeviceRegistration (yes, y, no, n): [no]
linkRNIDDeviceDeRegistration (yes, y, no, n): [no]
linkLIRRListenerAdded (yes, y, no, n): [no]
linkLIRRListenerRemoved (yes, y, no, n): [no]
linkRLIRFailureIncident (yes, y, no, n): [no]
HA-TRAP (yes, y, no, n): [no]
fruStatusChanged (yes, y, no, n): [no]
cpStatusChanged (yes, y, no, n): [no]
fruHistoryTrap (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Avoid-Duplicate-TRAP (yes, y, no, n): [no]
switch:admin>
y
y
y
y
y
y
The following snmpMibCapSet parameters for FA-TRAP appear in the preceding example:
• connUnitStatusChange: Indicates that the overall status of the connectivity unit has changed. Its
variables are:
• connUnitStatus: The status of the connection unit
• connUnitState: The state of the connection unit
• connUnitEventTrap: Indicates that the connectivity unit has generated an event. Its variables are:
• connUnitEventId: The internal event ID
• connUnitEventType: The type of this event
• connUnitEventObject: Used with the connUnitEventType to identify the object to which the
event refers.
• connUnitEventDescr: The description of the event.
• connUnitSensorStatusChange: Indicates that the status of the sensor associated with the
connectivity unit has changed.
• connUnitSensorStatus: The status indicated by the sensor.
• connUnitPortStatusChange: Indicates that the status of the sensor associated with the
connectivity unit has changed.
• connUnitPortStatus: Shows overall protocol status for the port.
• connUnitPortState: Shows the user-specified state of the port hardware.
66 Configuring standard security features
Page 67

Sample view of the SNMP MIB trap setup:
switch:admin> snmpmibcapshow
FA-MIB: YES
FICON-MIB: YES
HA-MIB: YES
SW-TRAP: YES
swFCPortScn: YES
swEventTrap: YES
swFabricWatchTrap: YES
swTrackChangesTrap: YES
FA-TRAP: YES
SW-EXTTRAP: YES
HA-TRAP: YES
fruStatusChanged: YES
cpStatusChanged: YES
fruHistoryTrap: YES
Configuring secure file copy
Use the configure command to specify that secure file copy (scp) be used for configuration uploads
and downloads. For example:
switch:admin> configure
Not all options will be available on an enabled switch.
To disable the switch, use the “switchDisable” command.
Configure...
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no] n
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no] n
http attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no] n
snmp attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no] n
rpcd attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no] n
cfgload attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Enforce secure config Upload/Download (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
switch:admin>
Setting the boot PROM password
The boot PROM password provides an additional layer of security by protecting the boot PROM from
unauthorized use. Setting a recovery string for the boot PROM password enables you to recover a lost
boot PROM password by contacting your switch service provider. Without the recovery string, a lost boot
PROM password cannot be recovered.
Set the boot PROM password and the recovery string on all switches. If your site procedures dictate that
you set the boot PROM password without the recovery string, see ”Without a recovery string” on page 69.
To set the boot PROM password with a recovery string, see the section that applies to your switch model.
NOTE: Setting the boot PROM password requires accessing the boot prompt, which stops traffic flow
through the switch until the switch is rebooted. Perform this procedure during planned down time.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 67
Page 68

4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32
Follow this procedure to set the boot PROM password with a recovery string:
1. Connect to the serial port interface as described in ”Connecting through the serial port” on page 21.
2. Reboot the switch.
3. Press ESC within four seconds after the message Press escape within 4 seconds... is
displayed.
The following options are available:
Option Description
1 Start system Continues the system boot process.
2 Recovery password Lets you set the recovery string and the boot PROM
password.
3 Enter command shell Provides access to boot parameters.
4. Enter 2.
If no password was previously set, the following message is displayed:
Recovery password is NOT set. Please set it now.
If a password was previously set, the following messages are displayed:
Send the following string to Customer Support for password recovery:
afHTpyLsDo1Pz0Pk5GzhIw==
Enter the supplied recovery password.
Recovery Password:
5. Enter the recovery password (string).
The recovery string must be between 8 and 40 alphanumeric characters. HP recommends a random
string that is 15 characters or longer for higher security. The firmware prompts for this password only
once. It is not necessary to remember the recovery string because it is displayed the next time you enter
the command shell.
The New password prompt is displayed.
6. Enter the boot PROM password, and reenter it when prompted. The password must be eight
alphanumeric characters (any additional characters are not recorded). Record this password for
future use.
The new password is saved (the saveEnv command is not required).
7. Reboot the switch.
Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
The boot PROM and recovery passwords must be set for each CP blade on the Core Switch 2/64, SAN
Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director as follows:
1. Connect to the serial port interface on the standby CP blade, as described in ”Connecting through the
serial port” on page 21.
2. Connect to the active CP blade by serial or telnet and issue the haDisable command to prevent
failover during the remaining steps.
3. For the Core Switch 2/64: Reboot the standby CP blade by pressing the yellow ejector buttons at the
top and bottom of the CP blade, and then press both ejector handles back towards the switch to lock
the blade back into the slot.
For the SAN Director 2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director: Reboot the standby CP blade by sliding the
On/Off switch on the ejector handle of the standby CP blade to Off, and then back to On.
4. Press ESC within four seconds after the message Press escape within 4 seconds... is
displayed.
68 Configuring standard security features
Page 69

The following options are available:
Option Description
1 Start system Continues the system boot process.
2 Recovery password Lets you set the recovery string and the boot PROM
password.
3 Enter command shell Provides access to boot parameters.
5. Enter 2.
If no password was previously set, the following message is displayed:
Recovery password is NOT set. Please set it now.
If a password was previously set, the following messages are displayed:
Send the following string to Customer Support for password recovery:
afHTpyLsDo1Pz0Pk5GzhIw==
Enter the supplied recovery password.
Recovery Password:
6. Enter the recovery password (string).
The recovery string must be between 8 and 40 alphanumeric characters. HP recommends a random
string that is 15 characters or longer for higher security. The firmware prompts for this password only
once. It is not necessary to remember the recovery string because it is displayed the next time you
enter the command shell.
The New password prompt is displayed.
7. Enter the boot PROM password, and then reenter it when prompted. The password must be eight
alphanumeric characters (any additional characters are not recorded). Record this password for
future use.
The new password is saved (the saveEnv command is not required).
8. Connect to the active CP blade serially or by telnet and issue the haEnable command to restore HA,
and then fail over the active CP blade by issuing the haFailover command.
Traffic flow through the active CP blade resumes when the failover is complete.
9. Connect the serial cable to the serial port on the new standby CP blade (previously the active
CP blade).
10.Repeat step 2 through step 7 for the new standby CP blade (each CP blade has a separate boot
PROM password).
11.Connect to the active CP blade serially or by telnet and issue the haEnable command to restore
high availability.
Without a recovery string
Although you can set the boot PROM password without also setting the recovery string, HP strongly
recommends that you set both the password and the string. If your site procedures dictate that you must
set the boot PROM password without the string, follow the procedure that applies to your switch model.
NOTE: Setting the boot PROM password requires accessing the boot prompt, which stops traffic flow
through the switch until the switch is rebooted. Perform this procedure during planned down time.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 69
Page 70

4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32
Follow this procedure to set the boot PROM password without a recovery string:
1. Create a serial connection to the switch as described in ”Connecting through the serial port” on
page 21.
2. Reboot the switch by issuing the reboot command.
3. Press ESC within four seconds after the message Press escape within 4 seconds... is
displayed.
The following options are available:
Option Description
1 Start system. Continues the system boot process.
2 Recovery password. Lets you set the recovery string and the boot PROM
password.
3 Enter command shell. Provides access to boot parameters.
4. Enter 3.
5. At the shell prompt, issue the passwd command.
NOTE: The passwd command applies only to the boot PROM password when it is entered from the
boot interface.
6. Enter the boot PROM password at the prompt, and then reenter it when prompted. The password must
be eight alphanumeric characters (any additional characters are not recorded). Record this password
for future use.
7. Issue the saveEnv command to save the new password.
8. Reboot the switch by issuing the reset command.
Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
On the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, set the password on the
standby CP blade, fail over, and then set the password on the previously active (now standby) CP blade
to minimize disruption to the fabric:
1. Determine the active CP blade by opening a telnet session to either CP blade, connecting as admin,
and entering the haShow command.
2. Connect to the active CP blade serially and by telnet and issue the haDisable command to prevent
failover during the remaining steps.
3. Create a serial connection to the standby CP blade as described in ”Connecting through the serial
port” on page 21.
4. For the Core Switch 2/64: Reboot the standby CP blade by pressing the yellow ejector buttons at top
and bottom of the CP blade, and then press both ejector handles back towards the switch to lock the
blade back into the slot.
SAN Director 2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director: Reboot the standby CP blade by sliding the On/Off
switch on the ejector handle of the standby CP blade to Off, and then back to On.
This causes the blade to reset.
5. Press ESC within four seconds after the message Press escape within 4 seconds... is
displayed.
70 Configuring standard security features
Page 71
The following options are available:
Option Description
1 Start system. Continues the system boot process.
2 Recovery password. Lets you set the recovery string and the boot PROM
password.
3 Enter command shell. Provides access to boot parameters.
6. Enter 3.
7. Issue the passwd command at the shell prompt.
NOTE: The passwd command applies only to the boot PROM password when it is entered from the boot
interface.
8. Enter the boot PROM password at the prompt, and then reenter it when prompted. The password must
be eight alphanumeric characters (any additional characters are not recorded). Record this password
for future use.
9. Issue the saveEnv command to save the new password.
10.Reboot the standby CP blade by issuing the reset command.
11.Connect to the active CP blade serially and by telnet and issue the haEnable command to restore
HA, and then fail over the active CP blade by issuing the haFailover command.
Traffic resumes flowing through the newly active CP blade after it has completed rebooting.
12.Connect the serial cable to the serial port on the new standby CP blade (previously the active
CP blade).
13.Repeat step 3 through step 10 for the new standby CP blade.
14.Connect to the active CP blade serially and by telnet and issue the haEnable command to restore
HA.
Recovering forgotten passwords
If you know the root password, you can use this procedure to recover the user, admin, and
factory passwords:
1. Open a CLI connection (serial or telnet) to the switch. If secure mode is enabled, connect to the
primary FCS switch.
2. Log in as root.
3. Issue the command for the type of password that was lost:
•
passwd user
• passwd admin
•
passwd factory
4. Enter the requested information at the prompts.
To recover a lost root password, contact your switch service provider.
To recover a lost boot PROM password, contact your switch service provider. You must have previously
set a recovery string to recover the boot PROM password.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 71
Page 72

72 Configuring standard security features
Page 73

4 Maintaining configurations and firmware
This chapter contains procedures for maintaining switch configurations and maintaining firmware.
Maintaining configurations
It is important to maintain consistent configuration settings on all switches in the same fabric, because
inconsistent parameters (such as inconsistent PID formats) can cause fabric segmentation. As part of
standard configuration maintenance procedures, HP recommends that you back up all important
configuration data for every switch on a host computer server for emergency reference.
The following sections contain procedures for basic switch configuration maintenance.
Displaying configuration settings
The switch configuration file contains four sections:
• The Boot Parameters section contains variables, such as the switch's name and IP address.
• The Licenses section lists the licenses that are active on the switch.
• The Chassis Configuration section contains configuration variables, such as diagnostic settings, fabric
configuration settings, and SNMP settings.
• The Configuration section contains licensed option configuration parameters.
To display configuration settings, connect to the switch, log in as admin, and issue the configShow
command. The configuration settings vary depending on switch model and configuration.
Backing up a configuration
If the configuration is lost or unintentional changes are made, keep a backup copy of the configuration
file (or a backup copy of both configuration files, one for each logical switch—if you are using a Core
Switch 2/64 or SAN Director 2/128 with two domains). The configuration file is what gets saved when
you issue the configUpload command. Keep individual backup files for all switches in the fabric. Do
not copy configurations from one switch to another.
The following information is not saved in a backup file:
• dnsconfig information
• Passwords
You must have a valid account on the FTP server where the backup file is stored.
You can specify the use of secure file copy (scp) during the procedure. For instructions on configuring the
use of scp by default, see ”Configuring secure file copy” on page 67.
Before beginning, verify that you can reach the FTP server from the switch. Using a telnet connection, save
a backup copy of the configuration file from a logical switch to a host computer as follows:
1. Verify that the FTP service is running on the host computer.
2. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
3. Issue the configUpload command.
The command becomes interactive and you are prompted for the required information.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 73
Page 74

4. Respond to the prompts as follows:
Protocol If your site requires the use of Secure Copy, specify scp. Otherwise,
specify ftp.
Server
Name or IP
Address
Enter the name or IP address of the server where the file is to be stored;
for example, 192.1.2.3. You can enter a server name if DNS is
enabled. For details about the dnsConfig command, see the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide.
User name Enter the user name of your account on the server, for example,
JohnDoe.
File name Specify a file name for the backup file, for example, config.txt.
Absolute path names can be specified using forward slash (/). Relative
path names create the file in the user’s home directory on UNIX servers,
and in the directory where the FTP server is running on Windows servers.
Password Enter your account password for the server.
For example:
switch:admin> configupload
Protocol (scp or ftp) [ftp]: ftp
Server Name or IP Address [host]: 192.1.2.3
User Name [user]: JohnDoe
File Name [config.txt]: /pub/configurations/config.txt
Password: xxxxx
Upload complete
switch:admin>
Restoring a configuration
Restoring a configuration involves overwriting the configuration on the switch by downloading a
previously saved backup configuration file. Perform this procedure during a planned down time.
Make sure that the configuration file you are downloading is compatible with your switch model;
configuration files from other model switches might cause your switch to fail.
You must have a user ID on the FTP server where the backup file is stored.
Use the following procedure:
1. Verify that the FTP service is running on the server where the backup configuration file is located.
2. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
3. Disable the switch by issuing the switchDisable command.
4. Issue the configDownload command.
The command becomes interactive and you are prompted for the required information.
5. Respond to the prompts as follows:
Protocol If your site requires the use of Secure Copy, specify scp. Otherwise, specify
ftp.
Server
Name or IP
Address
User name Enter the user name of your account on the server, for example, JohnDoe.
Enter the name or IP address of the server where the file is stored; for
example, 192.1.2.3. You can enter a server name if DNS is enabled.
File name Specify the full path name of the backup file, for example,
/pub/configurations/config.txt.
Password Enter your account password for the server.
74 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 75

6. At the Do you want to continue [y/n] prompt, enter y.
7. Wait for the configuration to be restored.
8. When the process is finished, issue the switchEnable command.
For example:
switch:admin> configdownload
Protocol (scp or ftp) [ftp]: ftp
Server Name or IP Address [host]: 192.1.2.3
User Name [user]: JohnDoe
File Name [config.txt]: /pub/configurations/config.txt
Password: xxxxx
*** CAUTION ***
This command is used to download a backed-up configuration
for a specific switch. If using a file from a different
switch, this file's configuration settings will override
any current switch settings. Downloading a configuration
file, which was uploaded from a different type of switch,
may cause this switch to fail.
Do you want to continue [y/n]: y
download complete..
switch:admin> switchenable
NOTE: After you download a configuration file, you must reboot to be sure the parameters are enabled.
Before the reboot, this type of parameter is listed in the configuration file, but it is not effective until after
the reboot.
Restoring configurations in a FICON environment
If the switch is operating in a FICON Control Unit Port (CUP) environment, and the ASM (active=saved)
bit is set on, the switch ignores the initial program load (IPL) file that is downloaded when you restore a
configuration. Table 12 describes this behavior in detail.
Table 12 Backup and restore in a FICON CUP environment
ASM bit Command Description
on or off configupload All the files saved in the file access facility are uploaded to
the management workstation. A section in the uploaded
configuration file labeled FICON_CUP is in an
encoded format.
on configdownload Files saved on the switch that are also present in the
FICON_CUP section of the configuration file
are overwritten.
Files in the FICON section of configuration file that are not
currently present on the switch are saved.
The IPL file is not replaced, because active=saved mode is
on. A message is displayed in the syslog to warn that the
IPL file is not being overwritten.
off configdownload Files saved on the switch that are also present in the
FICON_CUP section of the configuration file
are overwritten.
Files in the FICON section of configuration file that are not
currently present on the switch are saved.
The IPL file is replaced, because active=saved mode is off.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 75
Page 76

If fmsmode is enabled in a configuration file, but is disabled on the switch, the configdownload
command fails and displays an error message. This prevents undesirable conditions that could result from
enabling fmsmode on a switch that does not require it.
Downloading configurations across a fabric
To save time when configuring fabric parameters and software features, you can save a configuration file
from one switch and download it to other switches of the same model type, as shown in the following
procedure. Avoid downloading configuration files to different model switches, because that can cause the
switches to fail.
1. Configure one switch first.
2. Use the configUpload command to save the configuration information.
See ”Backing up a configuration” on page 73.
3. Use the configDownload command to download the file onto each of the remaining switches.
See ”Restoring a configuration” on page 74.
Printing hard copies of switch information
HP recommends that you print a hard copy of all key configuration data, including license key information
for every switch, and store it in a secure place for emergency reference. Print out the information from the
following commands, and store the printouts in a secure location:
• The configShow command displays configuration parameters and setup information, including
license information.
• The ipAddrShow command displays the IP address.
• The licenseShow command displays the license keys you have installed and provides better detail
than the license information from the configShow command.
Depending on the security procedures of your company, you might also want to keep a record of the user
levels and passwords (including any boot ROM passwords) for all switches in the fabric. Access to this
sensitive information should be limited.
Maintaining firmware
This section explains how to obtain and install firmware. Fabric OS 5.0.1x provides nondisruptive
firmware installation.
In most cases, you will be upgrading firmware; that is, installing a later firmware version than the one you
are currently running. However, some circumstances might require installing an earlier version; that is,
downgrading the firmware. The procedures in this section assume that you are upgrading firmware, but
they work for downgrading as well, provided the old and new firmware versions are compatible. Always
reference the latest release notes for updates that may exist regarding downgrades under particular
circumstances.
Using the CLI (or HP Advanced Web Tools), you can upgrade the firmware on one switch at a time. You
can also use the optionally licensed HP Fabric Manager software tool to upgrade firmware simultaneously
on multiple switches. For details on Fabric Manager and other licensed software tools, visit the HP web
site: http://
Obtaining and unzipping firmware
Firmware upgrades are available for customers with support service contracts and partners on the HP
Storage web site: http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/eng/prodserv/storage.html
switches:
h18006.www1.hp.com/storage/saninfrastructure/switches.html.
. For currently sold
1. Locate the Networked storage section under IT storage products and click Storage area networks.
The SAN Infrastructure page is displayed.
2. Click Fibre Channel Switches.
The Fibre Channel switches page is displayed.
3. Go to the B-Series Fabric-Enterprise Class section and select the appropriate switch.
The switch overview page is displayed.
76 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 77

4. In the Product information section on the right side, select Software & drivers.
The download drivers & software page is displayed.
5. Click the appropriate switch in the select your product section.
The specify operating system page is displayed.
6. Click Cross operating system (BIOS, Firmware, Diagnostics, etc.).
The download drivers and software page is displayed.
7. In the Firmware section, click the blue download button to the right of the applicable firmware.
To locate all available switch firmware, start at the HP web site: http://www.hp.com
Downloads.
The Software & Driver Downloads page is displayed. You may search for your product using either of the
following methods:
1. Select the Download drivers and software radio button, enter your product name in the space
provided, and press Enter.
The Product search results page is displayed.
a. Select the appropriate product.
The specify operating system page is displayed.
b. Click Cross operating system (BIOS, Firmware, Diagnostics, etc.).
The download drivers and software page is displayed.
c. In the Firmware section, click the blue download button to the right of the applicable firmware.
2. Click Storage in the Or Select a product category section.
The Storage page is displayed.
a. Click SAN Infrastructure.
The SAN Infrastructure page is displayed.
b. Select the appropriate product family.
The product family page is displayed.
c. Select the appropriate switch.
The specify operating system page is displayed.
d. Click Cross operating system (BIOS, Firmware, Diagnostics, etc.).
The download drivers and software page is displayed.
e. In the Firmware section, click the blue download button to the right of the applicable firmware.
and select Driver
Before you can use the firmwareDownload command to update the firmware on your equipment, you
must unzip the firmware (using the UNIX tar or gzip command or a Windows unzip program).
When you unpack the downloaded firmware it expands into a directory that is named according to the
version of Fabric OS it contains. For example, if you download and unpack Fabric OS 5.0.1.zip, it
expands into a directory called 5.0.1. When you use the firmwaredownload command, you specify
the path to the version 5.0.1 directory and append the keyword release.plist to the path.
Checking connected switches
If the switch to be upgraded is running version 4.1.0 firmware or later, HP recommends that all switches
directly connected to it be running versions no earlier than 2.6.1, 3.1.0, or 4.1.0. If some connected
switches are running earlier firmware versions, upgrade them to at least the earliest recommended version
(shown in Table 13) before upgrading firmware on your switch. HP recommends that you download the
latest firmware; to download firmware, see ”Obtaining and unzipping firmware” on page 76.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 77
Page 78

Table 13 Recommended firmware
Switch model
1
Earliest recommended Fabric OS version
4/8 SAN Switch and 4/16 SAN
5.0.1
Switch
1 GB Switches 2.6.1
SAN Switch 2/8-EL, SAN Switch
3.1.0
2/16-EL, and SAN Switch 2/16
SAN Switch 2/8V and SAN
4.2.0
Switch 2/16V
SAN Switch 2/32 4.1.0
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP
5.0.1
p-Class BladeSystem
SAN Switch 4/32 4.4.0
Core Switch 2/64 4.1.0
SAN Director 2/128 4.2.0
4/256 SAN Director 5.0.1
1. During code activation on the SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, or SAN Switch 2/32 running Fabric OS 4.1.0
or later, data continues to flow between hosts and storage devices; however, fabric services are unavailable for a
period of approximately 50–55 seconds. Possible disruption of the fabric can be minimized by ensuring that
switches logically adjacent to these models (directly connected via an ISL) are running at the minimum Fabric OS
2.6.1 or later, 3.1.0 or later, or 4.1.0 or later.
If the SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class
BladeSystem, or SAN Switch 4/32 are adjacent and you start firmware downloads on them at same time, there
might be I/O disruption.
To determine whether you need to upgrade connected switches before upgrading your switch, use the
following procedure on each connected switch to display firmware information and build dates.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the version command.
The following information is displayed:
• Kernel displays the version of switch kernel operating system.
• Fabric OS displays the version of switch Fabric OS.
• Made on displays the build date of firmware running in switch.
• Flash displays the installation date of firmware stored in nonvolatile memory.
• BootProm displays the version of the firmware stored in the boot PROM.
About the download process
The firmwareDownload command downloads unzipped switch firmware from an FTP server to the
switch’s nonvolatile storage area.
In the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, this command (when not using
any options flags) by default downloads the firmware image to a standby CP, if there is one, to prevent
disruption to application services. This operation depends on HA support. If HA is not available,
experienced technicians can upgrade the CPs one at a time, using the -s option.
78 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 79

CAUTION: To ensure a nondisruptive download, for each nondirector class switch in your fabric,
complete all firmware download changes before issuing the firmwareDownload command on the next
switch.
HP StorageWorks fixed-port models and each CP blade of the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128,
and 4/256 SAN Director have two partitions of nonvolatile storage areas (a primary and a secondary) to
store two firmware images. The firmwareDownload command always loads the new image into the
secondary partition and swaps the secondary partition to be the primary. It then reboots the partition and
activates the new image. Finally, it performs the firmwareCommit procedure, to copy the new image to
the other partition.
Effects of firmware changes on accounts and passwords
Table 14 describes what happens to accounts and passwords when you replace the switch firmware with
a different version. Upgrading means installing a later version of firmware. Downgrading means installing
an earlier version.
Table 14 Effects of firmware changes on accounts and passwords
Change First time Subsequent times (after upgrade, then
downgrade, and then upgrade)
Upgrading Default accounts and their passwords
are preserved.
Downgrading User-defined accounts are no longer
valid. Default accounts and their
passwords are preserved. If a default
account was disabled, it is reenabled
after the downgrade.
Upgrading to
version 3.2.0
(You might upgrade a switch in the fabric as part of ”Checking connected switches”
on page 77.) Earlier versions allowed you to change the default account names. You
cannot add user-defined accounts until you change the names back to default with the
passwdDefault command.
Considerations for downgrading firmware
The following items must be considered before attempting to downgrade to an earlier version of
Fabric OS:
• If your fabric is set to the extended edge PID format and you want to downgrade to an earlier Fabric
OS version that does not support extended edge, you must change the PID to a supported format. For
more information, see ”Configuring the PID format” on page 213.
• Downgrading a SAN Director 2/128 that is configured for two domains from Fabric OS 4.4.0 to
Fabric OS 4.2.0 is not supported.
• If you are running Fabric OS 4.0.2 firmware on a SAN Switch 2/32, you cannot downgrade to an
earlier version.
User-defined and default accounts and
their passwords are preserved.
User-defined and default accounts and
their passwords are preserved, including
accounts added after the first upgrade.
Considerations for FICON CUP environments
To prevent channel errors during nondisruptive firmware installation, the switch CUP port must be taken
offline from all host systems.
Upgrading HP StorageWorks switches
The 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32,
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32 maintain primary and
secondary partitions for firmware. The firmwareDownload command defaults to an autocommit option
that copies the firmware from one partition to the other.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 79
Page 80

Do not override an autocommit under normal circumstances; use the default. See ”Upgrading firmware in
single-CP mode” on page 239 for details about overriding the autocommit option.
As an alternative, before starting a firmware download, you can connect the switch with a serial console
cable to a computer that is running a session capture. The information collected might be useful for
troubleshooting.
Summary of the upgrade process
The following summary describes the default behavior of the firmwareDownload command (without
options) on the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN
Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32:
1. Issue the firmwareDownload command.
2. Fabric OS downloads firmware to the secondary partition.
3. The system performs an HA reboot (haReboot). After the haReboot, the former secondary partition
is the primary partition.
4. The system replicates the firmware from the primary to the secondary partition.
You can issue the firmwareDownloadStatus command to view the firmware process.
Upgrading 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN
Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32
The upgrade process first downloads and then commits the firmware to the switch. While the upgrade is
proceeding, you can start another telnet session on the switch and observe the upgrade progress.
NOTE: After you start the process, do not enter any disruptive commands (such as reboot) that interrupt
the process. The entire firmware download and commit process takes approximately 17 minutes. If there
is a problem, wait for the timeout (30 minutes for network problems; 10 minutes for incorrect IP address).
Disrupting the process can render the switch inoperable and require you to seek help from Customer
Support.
Do not disconnect the switch from power during the process; the switch could become inoperable upon
reboot.
Use this procedure to upgrade firmware for the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V,
SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and
SAN Switch 4/32:
1. Verify that the FTP service is running on the host server and that you have a user ID on that server.
2. Obtain the firmware file from the HP web site:
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/prodserv/storage.html
Verify that the FTP service is running and unpack the compressed files preserving directory structures.
3. Use the firmwareShow command to check the current firmware version on connected switches.
Upgrade their firmware, if necessary, before upgrading this switch.
See ”Checking connected switches” on page 77.
4. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
5. Use the firmwareShow command to check the current firmware version of the switch to verify
compatibility with the version of firmware you are going to download.
and store the file on the FTP server.
NOTE: For the SAN Switch 2/8V and SAN Switch 2/16V: If you are running Fabric OS 4.2.0
firmware, you cannot downgrade to earlier versions.
For the SAN Switch 2/32: If you are running Fabric OS 4.0.2 firmware, you cannot downgrade to
earlier versions.
80 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 81

6. Issue the firmwareDownload command.
7. At the Do you want to continue [y/n] prompt, enter y.
8. Respond to the prompts as follows:
Server
Name or IP
Address
Enter the name or IP address of the server where the firmware file is
stored, for example, 192.1.2.3. You can enter a server name if DNS is
enabled.
User name Enter the user name of your account on the server, for example,
JohnDoe.
File name Specify the full path name of the firmware directory, appended by
release.plist, for example, /pub/v5.0.1/release.plist.
For version 4.x and 5.x switches only, do not attempt to locate the
release.plist file in the top level directory; there is a
release.plist file for each platform, and the correct one is selected.
Password Enter your account password for the server.
After the firmware is downloaded, the switch reboots and starts the firmware commit.
9. After the reboot, connect to the switch and log in again as admin.
10.If you want to watch the upgrade progress, issue the firmwareDownloadStatus command.
11.After the firmware commit finishes, issue the firmwareShow command to display the firmware level
for both partitions.
For example:
switch:admin> firmwaredownload
You can run firmwareDownloadStatus to get the status of this command.
This command will cause the switch to reset and will require that existing
telnet, secure telnet or SSH sessions be restarted.
Do you want to continue [Y]: y
Server Name or IP Address: 192.1.2.3
User Name: JohnDoe
File Name: /pub/v5.0.1/release.plist
Password: xxxxx
Firmwaredownload has started.
0x8fd (Fabric OS): Switch: 0, Warning SULIB-FWDL_START, 3, Firmwaredownload
command has started.
.
.
.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 81
Page 82

Log in again to view the upgrade progress:
switch:admin> firmwaredownloadstatus
[0]: Tue Apr 20 10:32:34 2004
cp0: Firmwaredownload has started.
[1]: Tue Apr 20 10:36:07 2004
cp0: Firmwaredownload has completed successfully.
[2]: Tue Apr 20 10:57:09 2004
cp0: Firmwarecommit has started.
[3]: Tue Apr 20 10:36:07 2004
cp0: Firmwarecommit has completed successfully.
[4]: Tue Apr 20 11:03:28 2004
cp0: Firmwaredownload command has completed successfully.
switch:admin> firmwareshow
Primary partition: v5.0.1
Secondary Partition: v5.0.1
switch:admin>
CAUTION: To successfully download firmware to a director you must have an active Ethernet connection
on both CPs.
Upgrading HP StorageWorks directors
You can download firmware to the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
without disrupting the overall fabric if the two CP blades are installed and fully synchronized. Use the
haShow command to confirm synchronization. If only one CP blade is powered on, the switch must
reboot to activate firmware, which is disruptive to the overall fabric.
If there is an error during the firmware download, the system ensures that the two partitions of a CP blade
contain the same version of firmware. However, the two CP blades might contain different versions of
firmware; in that event, repeat the firmware download process.
During the upgrade process, the director fails over to its standby CP blade and the IP addresses for the
two logical switches move to that CP blade's Ethernet port. This might cause informational ARP address
reassignment messages to appear on other switches in the fabric. This is normal behavior, because the
association between the IP addresses and MAC addresses has changed.
Summary of the upgrade process
The following summary describes the default behavior of the firmwareDownload command (without
options) on Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director:
1. Issue the firmwareDownload command on the active CP blade.
2. The standby CP blade downloads firmware.
3. The standby CP blade reboots and comes up with the new Fabric OS.
4. The active CP blade synchronizes its state with the standby CP blade.
5. The active CP blade forces a failover and reboots to become the standby CP blade.
6. The new standby CP blade (the active CP blade before the failover) downloads firmware.
7. The new standby CP blade reboots and comes up with the new Fabric OS.
8. The new active CP blade synchronizes its state with the new standby CP blade.
9. The firmwareCommit command runs on both CP blades.
82 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 83

NOTE: After you start the process, do not issue any disruptive commands (such as reboot) that will
interrupt the process. The entire firmware download and commit process takes approximately 15 minutes.
If there is a problem, wait for the timeout (30 minutes for network problems; 10 minutes for incorrect IP
address). Disrupting the process can render the switch inoperable and require you to seek help from
Customer Support.
Do not disconnect the switch from power during the process, because the switch could become inoperable
upon reboot.
Upgrading the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
Core Switch 2/64 directors have four IP addresses: one for each of the two logical switches (switch 0 and
switch 1) and one for each of the two CP blades (CP0 in slot 5 and CP1 in slot 6). The SAN Director
2/128 in its default configuration has three IP addresses, but can be configured for four. The 4/256 SAN
Director does not support two domains; hence, you can use only three IP addresses.
NOTE: By default, the firmwareDownload command upgrades both the active CP blade and the
standby CP blade. When upgrading a Core Switch 2/64 that is running 4.0.0c or earlier, you must
upgrade each CP blade separately, as described in ”Upgrading a single Core Switch 2/64 or SAN
Director 2/128 blade” on page 240. (Do not use the following procedure under normal circumstances.)
Follow this procedure to upgrade the firmware on Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256
SAN Director:
1. Verify that the FTP service is running on the host server and that you have a user ID on that server.
2. Obtain the firmware file from the HP web site:
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/prodserv/storage.html
and store the file on the FTP server.
Verify that the FTP service is running and unpack the compressed files preserving directory structures.
3. Use the firmwareShow command to check the current firmware version on connected switches.
Upgrade the firmware, if necessary, before proceeding with upgrading this switch.
See ”Checking connected switches” on page 77.
4. Using a telnet session, connect to the switch and log in as admin.
5. For the Core Switch 2/64, use the firmwareShow command to check the current firmware version of
the switch.
6. Issue the haShow command to confirm that the two CP blades are synchronized.
CP blades must be synchronized and running Fabric OS 4.2.0 or later to provide a nondisruptive
download. If the two CP blades are not synchronized, and the current firmware version is 4.2.0 or later,
issue the haSyncStart command to synchronize the two CP blades. In the following example, the
active CP blade is CP1 and the standby is CP0:
switch:admin> hashow
Local CP (Slot 6, CP1): Active
Remote CP (Slot 5, CP0): Standby
HA Enabled, Heartbeat up, HA State is in Sync
switch:admin>
7. Log in to either of the logical switches (sw0 for the 4/256 SAN Director and SAN Director 2/128
configured with a single domain).
8. Issue the firmwareDownload command.
9. At the Do you want to continue [y/n] prompt, enter y.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 83
Page 84

10.Respond to the prompts as follows:
Server
Name or IP
Address
Enter the name or IP address of the server where the firmware file is
stored, for example, 192.1.2.3. You can enter a server name if DNS is
enabled.
User name Enter the user name of your account on the server, for example,
JohnDoe.
File name Specify the full path name of the firmware directory, appended by
release.plist, for example, /pub/v5.0.1/release.plist.
Password Enter your account password for the server.
The firmware is downloaded to one CP blade at a time, beginning with the standby CP blade. During
the process, the active CP blade is failed over. After the firmware is downloaded, a firmware commit
starts on both CP blades. The entire firmware download and commit process takes approximately 35
minutes.
11.Optional: After the failover, connect to the switch and log in again as admin.
12.Using a separate telnet session, issue the firmwareDownloadStatus command to monitor the
firmware download status.
13.Issue the firmwareShow command to display the new firmware versions.
For example:
switch:admin> firmwaredownload
This command will upgrade both CPs in the switch. If you
what to upgrade a single CP only, please use -s option.
You can run firmwareDownloadStatus to get the status
of this command.
This command will cause the active CP to reset and will
require that existing telnet, secure telnet, or SSH sessions
be restarted.
Do you want to continue [Y]: y
Server Name or IP Address: 192.1.2.3
User Name: JohnDoe
File Name: /pub/v5.0.1/release.plist
Password:*****
FirmwareDownload has started on Standby CP. It may take up to 30 minutes.
Firmwaredownload has completed successfully on Standby CP.
.
.
.
Standby CP reboots.
Standby CP booted up.
Standby CP booted up with new firmware.
cp1: Firmwarecommit has started on both Active and Standby CPs.
cp1: Firmwarecommit has completed successfully on Active CP.
cp1: Firmwaredownload command has completed successfully.
switch:admin>
84 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 85
Start a new session to view the upgrade progress:
switch:admin> firmwaredownloadstatus
[0]: Tue Apr 20 15:18:56 2003
cp0: Firmwaredownload has started on Standby CP. It may take up to 10 minutes.
[1]: Tue Apr 20 15:24:17 2003
cp0: Firmwaredownload has completed successfully on Standby CP.
[2]: Tue Apr 20 15:24:19 2003
cp0: Standby CP reboots.
[3]: Tue Apr 20 15:27:06 2003
cp0: Standby CP booted up.
[4]: Tue Apr 20 15:29:01 2003
cp1: Active CP forced failover succeeded. Now this CP becomes Active.
[5]: Tue Apr 20 15:29:05 2003
cp1: Firmwaredownload has started on Standby CP. It may take up to 30 minutes.
[6]: Tue Apr 20 15:34:16 2003
cp1: Firmwaredownload has completed successfully on Standby CP.
[7]: Tue Apr 20 15:34:19 2003
cp1: Standby CP reboots.
[8]: Tue Apr 20 15:36:59 2003
cp1: Standby CP booted up with new firmware.
[9]: Tue Apr 20 15:37:04 2003
cp1: Firmwarecommit has started on both Active and Standby CPs.
[10]: Tue Apr 20 15:42:48 2003
cp1: Firmwarecommit has completed successfully on Active CP.
[11]: Tue Apr 20 15:42:49 2003
cp1: Firmwaredownload command has completed successfully.
Troubleshooting firmware downloads
A firmware download can fail for many reasons, such as a power failure, a failed network connection, a
failed FTP server, or an incorrect path to unpacked firmware files. In most cases, the firmware is not
affected. You can make necessary corrections (for example, check the Ethernet cables and check the file
path names) and then rerun the firmwareDownload command.
NOTE: Under firmware versions earlier than 4.1.0, do not perform a firmware download while the
switch is running POST. If a firmware download is attempted on a Core Switch 2/64 while POST is
running, the download might fail because the CP blades cannot synchronize with each other.
Issue the firmwareShow command to see whether both CP blades have the same firmware. In the
following example, the active and standby CP blades have the same version:
switch: admin> firmwareshow
Local CP (Slot 6, CP1): Standby
Primary partition: v5.0.1d
Secondary Partition: v5.0.1d
Remote CP (Slot 5, CP0): Active
Primary partition: v5.0.1d
Secondary Partition: v5.0.1d
Note: If Local CP and Remote CP have different versions
of firmware, please retry firmwaredownload command.
switch: admin>
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 85
Page 86

Decide which firmware version you want to be applied to each CP blade. If you want the version on the
standby CP, issue the haFailover command on the active CP. If you want the version from the active CP,
issue the firmwareDownload -s command on the standby CP. After entering the haFailover
command, you must issue the firmwareDownload -s command on the new standby CP.
86 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 87

5 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director
2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
This chapter contains procedures that are specific to the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and
4/256 SAN Director.
Because directors contain interchangeable 16-port blades (32-port blades in the 4/256 SAN Director),
their procedures differ from those for the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN
Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN
Switch 4/32 fixed-port switches. For example, fixed-port models identify ports by domain,port number,
while director models identify ports by slot/port number.
Also, because the Core Switch 2/64 director comprises two logical switches (domains), and the SAN
Director 2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director in their default configurations have only one domain (the
4/256 SAN Director supports only one domain), procedures for the directors sometimes differ from one
another.
For detailed information about the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director,
see the installation guide for the switch.
Identifying ports
The Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director have slots and can have a
variable number of ports within a given domain. Ports are identified by their combined slot number and
port number.
There are 10 slots that contain port blades:
• Slot 5 and 6 contain CP blades.
• Slot 1 through 4 and 7 through 10 contain port blades.
On each port blade, there are 16 or 32 ports (counted from the bottom, 0 to 15, or 0 to 31). A particular
port must be represented by both slot number (1 through 4 and 7 through 10) and port number (0 through
15).
When you have port blades with different port counts in the same director (for example, 16-port blade
and 32-port blades), the area IDs no longer match the port numbers. Following are the port numbering
schemes for the 4/256 SAN Director:
• For the FC4-16 port blade, ports are numbered from 0 through 15 from bottom to top.
• For the FC-32 port blade, ports are numbered from 0 through 15 from bottom to top on the left set of
ports and 16 through 31 from bottom to top on the right set of ports.
The Core Switch 2/64 is divided into two logical switches, where slots 1 through 4 constitute logical
switch 0 (sw0) and slots 7 through 10 constitute logical switch 1 (sw1). You must be connected to the
logical switch that represents the slot where you want to execute a command.
In the SAN Director 2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director default configuration, all the ports are part of a
single logical switch. With Fabric OS 4.4.0 and later, you can configure the SAN Director 2/128 as two
logical switches (domains).
The following sections tell how to identify ports on the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and
4/256 SAN Director, and how to identify ports for zoning commands.
By slot and port number
The port number is assigned to an external port to give it a unique identifier in a switch.
To select a specific port in the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, you
must identify both the slot number and the port number using the format slot number/port number. No
spaces are allowed between the slot number, the slash (/), and the port number.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 87
Page 88
The following example shows how to enable port 4 on a blade in slot 2:
switch:admin> portenable 2/4
By port area ID
Zoning commands require that you specify ports using the area ID method. In Fabric OS 4.0.0 and later,
each port on a particular domain is given a unique area ID. The relationship between the port number
and area ID depends upon the PID format used in the fabric:
• When Core PID format is in effect, the area ID for port 0 is 0, for port 1, it is 1, and so forth.
When using Core PID mode on the Core Switch 2/64 (two logical 64-port switches), 4/256 SAN
Director (one domain only), and the SAN Director 2/128 configured with two domains, the area IDs
for both logical switches (domains) range from 0 to 63. This means that both logical switch 0 and
logical switch 1 have a port that is referenced with area ID 0.
For 32-port blades in the 4/256 SAN Director (using FC4-32), the numbering is contiguous up to port
15; from port 16, the numbering is still contiguous, but you must add 128 to each port number. For
example, port 16 in slot 1 has a port number and area ID of 128; port number 15 has a port number
and area ID of 15.
• When Extended Edge PID format is in effect, the area ID is the port number plus 16 for ports 0 to 111.
For port numbers greater than 111, the area ID wraps around so that port 112 has an area ID of 0,
and so on. Each 64-port logical switch (domain) has area IDs ranging from 16 to 79. Port numbers
greater than 128 are mapped directly to the core PID.
For details about port area IDs in Extended Edge PID mode, see ”Changing to Extended Edge PID
format” on page 220.
• If you perform a port swap operation, the port number and area ID no longer match.
To determine the area ID of a particular port, issue the switchShow command. This command displays
all ports on the current (logical) switch and their corresponding area IDs.
Basic blade management
This section provides procedures for powering a port blade off and on and for disabling and enabling a
port blade.
Powering port blades off and on
Port blades are powered on by default.
Powering off a port blade
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the slotPowerOff command with the slot number of the port blade you want to power off.
The slot must exist in the logical switch where you are logged in. For example:
switch:admin> slotpoweroff 3
Slot 3 is being powered off
switch:admin>
Providing power to a port blade
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the slotPowerOn command with the slot number of the port blade you want to power on.
The slot must exist in the logical switch where you are logged in. For example:
switch:admin> slotpoweron 3
Powering on slot 3
switch:admin>
88 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
Page 89

Disabling and enabling port blades
Port blades are enabled by default.
You might need to disable a port blade to perform diagnostics. When diagnostics are executed manually
(from the Fabric OS command line), many commands require the port blade to be disabled. This ensures
that diagnostic activity does not interfere with normal fabric traffic.
Disabling a port blade
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the slotOff command with the slot number of the port blade you want to disable.
For example:
switch:admin> slotoff 3
Slot 3 is being disabled
switch:admin>
Enabling a port blade
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the slotOn command with the slot number of the port blade you want to enable.
For example:
switch:admin> sloton 3
Slot 3 is being enabled
switch:admin>
Conserving power
To conserve power and ensure that more critical components are the least affected by a power
fluctuation, you can power off components in a specified order, using the powerOffListSet command.
The available power is compared to the power demand to determine whether there is enough power to
operate. If there is less power available than the demand, the power-off list is processed until there is
enough power for operation. By default, the processing proceeds from slot 1 to the last slot in the chassis.
As power becomes available, slots are powered up in the reverse order.
NOTE: Some FRUs in the chassis may use significant power, yet they cannot be powered off through
software. For example, a missing blower FRU may change the power computation enough to affect how
many slots can be powered up.
The powerOffListShow command displays the power-off order.
Blade terminology and compatibility
Before configuring a chassis, familiarize yourself with the director CP blade and port blade nomenclature,
as well as the port blade compatibilities. Often in procedures, only the abbreviated names for CP and
port blades are used (for example, the FC4-16 blade). Table 15 provides CP and port blade abbreviations
and descriptions.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 89
Page 90

Table 15 HP StorageWorks director terminology and abbreviations
Term Abbreviation Blade ID Definition
Core Switch 2/64 CP blade CP1 1 The first-generation CP blade provided with the Core
Switch 2/64. This CP supports 1- and 2-Gbit/sec port
speeds. It supports only the dual domain configuration
within the chassis.
SAN Director 2/128 CP blade CP2 5 The second-generation CP blade provided with the SAN
Director 2/128. This CP supports 1- and 2-Gbit/sec
port speeds. It supports both the dual domain and a
single domain configuration within the chassis.
4/256 SAN Director CP blade CP4 16 The second-generation CP blade provided with the
4/256 SAN Director. This CP supports 1-, 2-, and
4-Gbit/sec port speeds, as well as 16 and 32-port
blades.
16-port 2-Gbit/sec port blade FC-16 2 The first-generation HP StorageWorks director 16-port
blade supporting 2-Gbit/sec port speeds. This port
blade is compatible only with the Core Switch 2/64 or
SAN Director 2/128 CP blades.
16-port 2-Gbit/sec port blade FC2-16 4 The second-generation HP StorageWorks director 16
port blade supporting 1- and 2-Gbit/sec port speeds.
This port blade is compatible only with the SAN Director
2/128 or 4/256 SAN Director CP blades.
16-port 4-Gbit/sec port blade FC4-16 17 The third-generation HP StorageWorks director 16 port
blade supporting 1-, 2-, and 4-Gbit/sec port speeds.
This port blade is compatible only with the SAN Director
2/128 and 4/256 SAN Director CP blades. FC4-16
blades do not support private devices.
32-port 4-Gbit/sec port blade FC4-32 18 A 32-port HP StorageWorks director port blade
supporting 1-, 2-, and 4-Gbit/sec port speeds.This port
blade is compatible only with the 4/256 SAN Director
CP blades. FC4-32 blades do not support private
devices.
CP blades
CP blades determine the director type:
• If CP1 blades are installed, the director is a Core Switch 2/64.
• If CP2 blades are installed, the director is a SAN Director 2/128.
• If CP4 blades are installed, the director is a 4/256 SAN Director.
HP recommends that each HP StorageWorks director have only one type of CP blade installed and that
each CP (primary and secondary partition) maintains the same firmware version.
90 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
Page 91

Port blade compatibility
Table 16 indicates which blades are supported for each HP StorageWorks director.
Table 16 Blades supported by each HP StorageWorks director
Director Port Blades
FC-16 FC2-16 FC4-16 FC4-32
Core Switch 2/64
(CP1)
SAN Director
2/128 (CP2)
4/256 SAN
Director (CP4)
Supported N/A N/A N/A
Supported Supported Supported N/A
N/A Supported Supported Supported
Setting chassis configurations
The chassisConfig command allows you to set the chassis configuration for products that support both
single-switch (one domain) and dual-switch (two domains) operation.
Table 17 lists the supported configurations options for Fabric OS 5.x.
Table 17 Supported configuration options
Option Number of
domains
1 1 128 FC2-16, FC4-16 CP2 or CP4 CP4 fits all chassis
Maximum number
of ports per switch
Supported port
blades
Supported
CP blades
Notes Results
except the D2
chassis. Option 1
is the default
configuration for
the SAN Director
2/128.
One 128-port
switch (Blade
IDs 4, 17 on
slots 1–4, 7–10.
Blade ID 5 and
16 on slots 5, 6)
22 64/64 FC2-16 CP2 N/A Two 64-port
switches (Blade
ID 4 on slots
1–4, 7–10.
Blade ID 5 on
slots 5, 6)
32 64/64 Left side: FC2-16
Right side: FC-16
CP2 N/A Two 64-port
switches (Blade
ID 4 on slots
1–4; ID 2 on
slots 7–10.
Blade ID 5 on
slots 5, 6)
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 91
Page 92

Table 17 Supported configuration options (continued)
Option Number of
domains
42 64/64 Left side: FC-16
5 1 256 FC4-16, FC4-32 CP4 CP4 fits all chassis
Maximum number
of ports per switch
Supported port
blades
Right side: FC2-16
Supported
Notes Results
CP blades
CP2 N/A Two 64-port
except the D2
chassis. Option 5
is the default
configuration
option for 4/256
SAN Director.
The following sections contain procedures for obtaining chassis information and for configuring director
domains using the chassisConfig command.
Obtaining slot information
For a Core Switch 2/64 or SAN Director 2/128 configured as two logical switches, the chassis-wide
commands display or control both logical switches. In the default configuration, the SAN Director 2/128
and 4/256 SAN Director are configured as one logical switch, so the chassis-wide commands display
and control the single logical switch.
switches (Blade
ID 2 on slots
1–4; ID 4 on
slots 7–10.
Blade ID 5 on
slots 5, 6)
One 256-port
switch (Blade
IDs 4, 17, and
18 on slots 1–4,
7–10. Blade ID
16 on slots 5, 6)
Displaying the status of all slots in the chassis
1. Connect to the switch and log in as user or admin.
2. Issue the slotShow command to display the current status of each slot in the system.
The format of the display includes a header and four fields for each slot. The fields and their possible
values are:
Field Value
Slot Displays the physical slot number.
Blade Type Displays the blade type:
• SW BLADE: The blade is a switch.
• CP BLADE: The blade is a CP.
• UNKNOWN: The blade is not present or its type is not recognized.
ID Displays the hardware ID of the blade type.
92 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
Page 93

Field Value
Status Displays the status of the blade:
• VACANT: The slot is empty.
• INSERTED, NOT POWERED ON: The blade is present in the slot
but is turned off.
• DIAG RUNNING POST1: The blade is present, powered on, and
running the post-initialization POST.
• DIAG RUNNING POST2: The blade is present, powered on, and
running the POST.
• ENABLED: The blade is on and enabled.
• ENABLED (User Ports Disabled): The blade is on, but external ports
have been disabled with the bladeDisable command.
• DISABLED: The blade is powered on but disabled.
• FAULTY: The blade is faulty because an error was detected. The
reason code numbers displayed are for debugging purposes.
• UNKNOWN: The blade is inserted but its state cannot be determined.
Configuring a new SAN Director 2/128 with two domains
By factory default, the SAN Director 2/128 is configured as one 128-port switch (one domain). The
following procedure assumes that the new director:
• Has been installed and connected to power, but is not yet attached to the fabric.
• Has been given an IP address, but is otherwise running factory defaults. If this is not the case, back up
the current configuration before starting, so that you can restore it later if necessary.
• Is running Fabric OS 4.4.0 or later.
• Is running in configuration option one (one switch, FC2-16 cards installed).
Use the following procedure to add a factory-new SAN Director 2/128 to a fabric and configure it as
two 64-port switches (two domains).
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the chassisconfig command without options to verify that the switch is configured with one
domain.
For example:
chassisconfig
Current Option: 1
3. Issue the chassisconfig command to configure two domains. Use the -f option to suppress
prompting for uploading the configuration.
This command reboots the system. For example:
chassisconfig -f 2
Current Option changed to 2
Restoring switch 0 configuration to factory defaults...
All account passwords have been successfully set to factory default.
Restoring switch 1 configuration to factory defaults...
All account passwords have been successfully set to factory default.
4. After the system reboots, log in again to the first logical switch (sw0) as admin.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 93
Page 94

5. Use the configure command to configure the sw0 to match your fabric specifications.
If the director is to be merged into an existing fabric, do not configure zoning parameters; these are
propagated when you merge the director into the fabric.
6. Log in to the second logical switch (sw1) as admin.
7. Use the configure command to configure the sw1 to match your fabric specifications.
If the director is to be merged into an existing fabric, do not configure zoning parameters; these are
propagated when you merge the director into the fabric.
8. If the fabric is in secure mode, perform the following steps; otherwise, proceed to step 9.
(See the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator guide for specific instructions.)
a. Optional: To configure sw0 and sw1 in one operation, connect them with an ISL link to form a
temporary fabric.
b. If you want sw0 and sw1 to be FCSs, update the overall fabric’s FCS policy to include them. If not,
skip this step.
c. On sw0, enable security mode and use the secModeEnable command to create an FCS list that
matches your overall fabric’s FCS policy.
d. Reset the version stamp on sw0.
e. If you connected sw0 and sw1 in step 8a and you do not want them connected, disconnect the ISL
link between them. If you did not connect them, repeat step 8b through step 8d on sw1.
9. Optional: Connect the new two-domain SAN Director 2/128 to the fabric.
10.Issue the fabricShow command to verify that sw0 and sw1 have been merged with the fabric.
11.Issue the cfgShow command to verify that zoning parameters were propagated.
Converting an installed SAN Director 2/128 to support two domains
Fabric OS versions earlier than 4.4.0 supported only one domain for SAN Director 2/128s (one
128-port logical switch). When you upgrade a SAN Director 2/128 to Fabric OS 4.4.0 or later, you can
use the chassisConfig command to specify two domains for the director (two 64-port logical switches,
sw0 and sw1). This conversion is for SAN Director 2/128s using configuration option one (one switch,
FC2-16 cards installed).
NOTE: This procedure restores most configuration parameters to factory defaults. After performing this
procedure, you must check the new configuration and reconfigure those parameters that you customized
in the old configuration.
During this procedure, power is reset and the CP blades are rebooted, so traffic on the fabric is disrupted.
If the fabric is in secure mode, enabling security on the new domains is a complicated task. Do not
convert existing core switches.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. If the director is already in a fabric, minimize disruption by removing the director from the fabric using
one of the following methods:
• Physically disconnect the director.
•Use the portCfgPersistentDisable command on all connected remote switches to
persistently disable their ports that are connected to the director, or remove ISLs that connect the
SAN Director 2/128 to the current fabric.
3. Issue the chassisConfig command to change the configuration from the default (one domain) to
two domains. The following command reboots the system:
chassisconfig 2
During the conversion, you are prompted to save the configuration of sw0. Follow the prompts to save
the configuration file.
94 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
Page 95

4. Issue the ipAddrSet command to set and confirm the IP address of sw1 (sw1 takes on a default that
must be corrected).
The IP address of sw0 is already set.
5. After the system reboots, log in again as admin to each logical switch and issue the switchName
command to assign a name to the new switch.
6. Using the configuration file saved in step 3 as a guide, manually reconfigure sw0 and sw1.
Do not configure zoning parameters; these are propagated when you merge the director into the
fabric.
7. If the fabric is in secure mode, perform the following steps; otherwise, proceed to step 8.
a. Optional: to configure sw0 and sw1 in one operation, connect them with an ISL link to form a
temporary fabric.
b. If you want sw0 and sw1 to be FCSs, update the overall fabric’s FCS policy to include them. If not,
skip this step.
c. On sw0, enable security mode and use the secModeEnable command to create an FCS list that
matches your overall fabric’s FCS policy.
d. Reset the version stamp on sw0.
e. If you connected sw0 and sw1 in step 7a and you do not want them connected, disconnect the ISL
link between them. If you did not connect them, repeat step 7b through step 7d on sw1.
8. If you physically disconnected the switch in step 2, reconnect it to the fabric.
If you used the portCfgPersistentDisable command in step 2, use the
portCfgPersistentEnable command to persistently enable all ports that connect the switch to
other switches in the fabric.
9. Issue the fabricShow command to verify that sw0 and sw1 have been merged with the fabric.
10.Issue the configShow command to verify that zoning parameters were propagated.
Setting the blade beacon mode
When beaconing mode is enabled, the port LEDs flash amber in a running pattern from port 0 through
port 15 and back again. The pattern continues until you turn beaconing mode off. Use the flashing LEDs
to locate a particular blade.
Setting the blade beacon mode on:
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the bladeBeacon command:
bladebeacon slotnumber, mode
The slotnumber is the blade on which you want to enable beacon mode; this slot number must exist
on the logical switch. A mode value or 1 turns beaconing on, and 0 turns beaconing off. For example:
switch:admin> bladebeacon 3, 1
switch:admin>
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 95
Page 96

96 Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
Page 97

6 Routing traffic
This chapter describes HP StorageWorks switch routing features and procedures.
About data routing and routing policies
Data moves through a fabric from switch to switch and from storage to server along one or more paths
that make up a route. Routing policies determine the correct path for each frame of data.
CAUTION: For most configurations, the default routing policy is optimal, and provides the best
performance. Change the policy only if there is a performance issue that is of concern, or a particular
fabric configuration requires it.
The following routing policies are available to tune routing performance:
• Exchange-based routing: The choice of routing path is based on the source ID (SID), destination ID
(DID), and Fibre Channel originator exchange ID (OXID), optimizing path utilization for the best
performance. Thus, every exchange can take a different path through the fabric
• Device-based routing: The choice of routing path is based on the Fibre Channel addresses of the SID
and the DID, improving path utilization for better performance. Thus, the same route is always used
and the sequence of exchanges is guaranteed.
• Port-based routing: The choice of routing path is based only on the incoming port and the destination
domain. To optimize port-based routing, the Dynamic Load Sharing feature (DLS) can be enabled to
balance the load across the available output ports within a domain.
Device-based and exchange-based routing require the use of DLS; when these policies are in effect, you
cannot disable the DLS feature.
Using port-based routing, you can assign a static route, in which the path chosen for traffic never
changes. In contrast, device-based and exchange-based routing policies always employ dynamic path
selection. Port-based routing is supported by all HP StorageWorks models (except the 4/256 SAN
Director using configuration option 5; see Table 17 on page 91).
Specifying the routing policy
The following routing policies are supported:
• Port-based path selection: The default on SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, and SAN Switch
2/32, Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director (using configuration
options 1 through 4). These switches support the port-based policy only; you cannot change the
routing policy for these switches. The 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP
p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32 can also use port-based routing.
• Device-based path selection: Available on 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, Brocade 4Gb SAN
Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, and 4/256 SAN Director (using
configuration option 5). If there are devices in your fabric that cannot accommodate out-of-order
exchanges, use the device-based policy. In FICON environments device-based routing is
recommended.
• Exchange-based path selection: The default on the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, Brocade 4Gb
SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, and 4/256 SAN Director (using
configuration option 5).
See ”Configuring Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director” on page 87 for
details about 4/256 SAN Director configuration options.
You can use the aptPolicy command to display and specify a different routing policy. Note that if you
attempt to set the policy when the 4/256 SAN Director uses configuration options 1–4, an error message
is returned. See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide for details on the
aptPolicy command.
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 97
Page 98

You must disable the switch before changing the routing policy, and reenable it afterward.
In the following example, the routing policy for a SAN Switch 4/32 is changed from exchange-based to
device-based:
switch:admin> aptpolicy
Current Policy: 3
3: Default Policy
1: Port Based Routing Policy
2: Device Based Routing Policy
3: Exchange Based Routing Policy
switch:admin> switchdisable
switch:admin> aptpolicy 2
Policy updated successfully.
switch:admin> switchenable
switch:admin> aptpolicy
Current Policy: 2
Assigning a static route
A static route can be assigned only when the active routing policy is port-based. When device-based or
exchange-based routing is active, you cannot assign static routes. Thus, the 4/256 SAN Director using
configuration option 5 does not support static routing.
To assign a static route, use the uRouteConfig command. To remove a static route, use the
uRouteRemove command.
NOTE: For the SAN Switch 2/32, Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director
(using configuration options 1 through 4):
When you issue the uRouteConfig command, two similar warning messages might be displayed if a
platform conflict occurs. The first message is displayed when the static routing feature detects the conflict.
The second message is displayed when the DLS feature detects the condition as it tries to rebalance the
route.
A platform conflict occurs if a static route was configured with a destination port that is currently down.
The static route is ignored in this case, in favor of a normal dynamic route. When the configured
destination port comes back up, the system attempts to reestablish the static route, potentially causing a
conflict.
Specifying frame order delivery
The order of delivery of frames is maintained within a switch and determined by the routing policy in
effect. Following are the frame delivery behaviors for each routing policy.
• Port-based routing: All frames received on an ingress port destined for a destination domain are
guaranteed to exit the switch in the same order in which they were received.
• Device-based routing: All frames received on an ingress port between the same two fabric devices are
guaranteed to exit the switch in the same order in which they were received. This policy maintains the
order of frames across exchanges between the fabric devices as well.
• Exchange-based routing: All frames received on an ingress port for a given exchange are guaranteed
to exit the switch in the same order in which they were received. Because different paths are chosen
for different exchanges, this policy does not maintain the order of frames across exchanges.
If even one switch in the fabric delivers out-of-order exchanges, exchanges are then delivered to the target
out-of-order, regardless of the policy configured on other switches in the fabric.
98 Routing traffic
Page 99

In a stable fabric, frames are always delivered in order, even when the traffic between switches is shared
among multiple paths. However, when topology changes occur in the fabric (for example, if a link goes
down), traffic is rerouted around the failure, and some frames could be delivered out of order. Most
destination devices tolerate out-of-order delivery, but some do not.
By default, out-of-order frame-based delivery is allowed to minimize the number of frames dropped. Force
in-order frame delivery only across topology changes if the fabric contains destination devices that cannot
tolerate occasional out-of-order frame delivery.
Forcing in-order frame delivery across topology changes
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the iodSet command.
NOTE: This command can cause a delay in the establishment of a new path when a topology change
occurs; use it with care.
Restoring out-of-order frame delivery across topology changes
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the iodReset command.
Using DLS
The device-based and exchange-based routing policies depend on the Fabric OS DLS feature for dynamic
routing path selection. When these policies are in force, DLS is by default enabled and cannot be
disabled.
When the port-based policy is in force, you can enable DLS to optimize routing. When DLS is enabled, it
shares traffic among multiple equivalent paths between switches. DLS recomputes load sharing when a
switch boots up, each time an E_Port goes offline and online, or when an Fx_Port goes offline.
Checking and setting DLS
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the dlsShow command to view the current DLS setting.
One of the following messages appears:
• DLS is set, which indicates that DLS is turned on.
• DLS is not set, which indicates that DLS is turned off.
3. Issue the dlsSet command to enable DLS or issue the dlsReset command to disable it.
You cannot disable DLS when device-based or exchange-based routing policies are in effect.
For example:
switch:admin> dlsshow
DLS is not set
switch:admin> dlsset
switch:admin> dlsshow
DLS is set
switch:admin> dlsreset
switch:admin> dlsshow
DLS is not set
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide 99
Page 100

Viewing routing path information
The topologyShow and uRouteShow commands provide information about the routing path.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Issue the topologyShow command to display the fabric topology, as it appears to the local switch.
The following entries appear:
Local Domain ID Domain number of the local switch
Domain Domain number of the destination switch
Metric Cost of reaching the destination domain
Name The name of the destination switch
Path Count The number of currently active paths to the destination domain
Hops The maximum number of hops to reach the destination domain.
Out Port The Port to which the incoming frame will be forwarded in order
to reach the destination domain
In Ports Input ports that use the corresponding Out Port to reach the
destination domain
Total Bandwidth The maximum bandwidth of the out port
Bandwidth Demand The maximum bandwidth demand of the in ports
Flags Always D, indicating a dynamic path
For example:
switch:admin> topologyshow
2 domains in the fabric; Local Domain ID: 1
Domain: 6
Metric: 500
Name: switch
Path Count: 4
Hops: 1
Out Port: 60
In Ports: None
Total Bandwidth: 2 Gbps
Bandwidth Demand: 0%
Flags: D
Hops: 1
Out Port: 61
In Ports: None
Total Bandwidth: 2 Gbps
Bandwidth Demand: 0%
Flags: D
Hops: 1
Out Port: 62
In Ports: None
Total Bandwidth: 2 Gbps
Bandwidth Demand: 0%
Flags: D
Hops: 1
Out Port: 58
In Ports: None
Total Bandwidth: 2 Gbps
Bandwidth Demand: 0%
Flags: D
100 Routing traffic
 Loading...
Loading...