Page 1

ProCurve 5400zl Switches
Installation and Getting Started Guide
CLI Reference Guide for HP ProCurve MSM3xx / MSM4xx Access Points
ProCurve MSM3xx / MSM4xx Access Points
CLI Reference Guide
Page 2

Page 3

HP ProCurve
MSM3xx / MSM4xx Access Points
CLI Reference Guide
Page 4

Copyright and Disclaimer Notices
© Copyright 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The
information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
This document contains proprietary information, which is
protected by copyright. No part of this document may be
photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language
without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard.
Publication Number
5992-5947
May 2009
Applicable Products
MSM310 Access Point J9374A J9379A
MSM310-R Access Point J9380A J9383A
MSM320 Access Point J9360A J9364A
MSM320-R Access Point J9365A J9368A
MSM325 Access Point with Sensor J9369A J9373A
MSM335 Access Point with Sensor J9356A J9357A
MSM410 Access Point J9426A J9427A
MSM422 Access Point J9358A J9359A
USA part WW part
Disclaimer
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF
ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors
contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this
material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth
in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or
reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished by
Hewlett-Packard.
Trademark Credits
Windows NT®, Windows®, and MS Windows® are US
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Hewlett-Packard Company
8000 Foothills Boulevard
Roseville, California 95747-5552
www.procurve.com
Page 5

Contents
In this Contents section, new to 5.3.x contexts and commands are preceded with an asterisk
“*” and formatted in green like this:
* new context
* new command
1 Introduction
About this guide ...........................................................................................................1-2
Products covered................................................................................................... 1-2
HP ProCurve Product Naming............................................................................. 1-2
Important terms..................................................................................................... 1-3
Typographical conventions ..................................................................................1-3
Command syntax ............................................................................................1-3
Management tool ............................................................................................1-4
HP ProCurve Networking support.............................................................................1-4
Before contacting support .............................................................................1-4
Online documentation .................................................................................................1-5
CLI support in autonomous and controlled modes .................................................1-5
Controlled mode ....................................................................................................1-5
Autonomous mode ................................................................................................ 1-5
Configuring CLI support.............................................................................................. 1-6
SSH client support.................................................................................................1-7
Entering strings ............................................................................................................1-7
Context hierarchy ........................................................................................................1-7
Sample CLI session ......................................................................................................1-8
CLI commands
2
View context .................................................................................................................2-2
arping ......................................................................................................................2-2
enable......................................................................................................................2-2
iperf .........................................................................................................................2-2
nslookup .................................................................................................................2-2
iii
Page 6

ping..........................................................................................................................2-2
ps .............................................................................................................................2-3
quit...........................................................................................................................2-3
show license........................................................................................................... 2-3
show logging filtered.............................................................................................2-3
top............................................................................................................................ 2-3
traceroute ...............................................................................................................2-3
Enable context..............................................................................................................2-4
reboot device..........................................................................................................2-4
show certificate .....................................................................................................2-4
show certificate binding .......................................................................................2-4
iperf .........................................................................................................................2-4
ping..........................................................................................................................2-4
arping ......................................................................................................................2-5
arp............................................................................................................................ 2-5
end ...........................................................................................................................2-5
quit...........................................................................................................................2-5
rcapture...................................................................................................................2-5
show arp .................................................................................................................2-5
show bridge ............................................................................................................2-5
show bridge forwarding........................................................................................ 2-6
show dns cache...................................................................................................... 2-6
show interfaces......................................................................................................2-6
* show ip.................................................................................................................2-6
show ip route .........................................................................................................2-6
show system info ...................................................................................................2-6
factory reset ...........................................................................................................2-6
switch operational mode ......................................................................................2-6
show dot11 associations.......................................................................................2-7
show dot11 statistics client-traffic ......................................................................2-7
show local mesh ....................................................................................................2-7
show wireless neighborhood ............................................................................... 2-7
show wireless rogue-ap ........................................................................................2-7
show client log .......................................................................................................2-7
show discrete pin...................................................................................................2-7
config.......................................................................................................................2-7
show all config .......................................................................................................2-8
iv
Page 7

Config context ..............................................................................................................2-9
certificate................................................................................................................ 2-9
certificate binding..................................................................................................2-9
certificate revocation ............................................................................................2-9
end ...........................................................................................................................2-9
factory settings ......................................................................................................2-9
interface ethernet ..................................................................................................2-9
reboot device........................................................................................................2-10
show certificate ...................................................................................................2-10
show certificate binding .....................................................................................2-10
show config factory.............................................................................................2-10
username ..............................................................................................................2-10
interface ip............................................................................................................2-10
interface wireless ................................................................................................2-10
local mesh profile ................................................................................................2-11
interface gre .........................................................................................................2-11
virtual ap............................................................................................................... 2-11
* admin local authentication..............................................................................2-11
* admin radius authentication ...........................................................................2-11
* admin radius authentication server ...............................................................2-12
ip http port............................................................................................................ 2-12
ip https port.......................................................................................................... 2-12
snmp-server trap certificate-expired.................................................................2-12
snmp-server trap certificate-expires-soon .......................................................2-12
snmp-server trap web-fail...................................................................................2-13
snmp-server trap web-login................................................................................ 2-13
snmp-server trap web-logout .............................................................................2-13
web admin kickout.............................................................................................. 2-13
web allow..............................................................................................................2-13
world-mode dot11 country code........................................................................2-14
web access port-1 ................................................................................................2-14
web access port-2 ................................................................................................2-14
web access wireless ............................................................................................2-14
web access interface vlan................................................................................... 2-14
web access interface gre ....................................................................................2-14
web access local mesh........................................................................................2-15
clock......................................................................................................................2-15
* clock auto adjust dst........................................................................................ 2-15
clock timezone..................................................................................................... 2-15
v
Page 8

* clock use custom dst rules..............................................................................2-15
ntp protocol..........................................................................................................2-16
ntp server..............................................................................................................2-16
* clock custom dst begins ..................................................................................2-16
* clock custom dst begins format .....................................................................2-16
* clock custom dst ends .....................................................................................2-17
* clock custom dst ends format ........................................................................2-17
ntp server..............................................................................................................2-17
ntp server failure trap .........................................................................................2-17
config-update automatic.....................................................................................2-18
config-update operation......................................................................................2-18
config-update time............................................................................................... 2-18
config-update uri..................................................................................................2-18
config-update weekday.......................................................................................2-18
snmp-server trap config-change ........................................................................2-18
snmp-server trap config-update.........................................................................2-19
logging destination ..............................................................................................2-19
snmp-server trap syslog-severity .......................................................................2-19
snmp-server.......................................................................................................... 2-19
snmp-server access port-1.................................................................................. 2-19
snmp-server allow ...............................................................................................2-20
snmp-server chassis-id........................................................................................2-20
snmp-server contact............................................................................................2-20
snmp-server heartbeat period............................................................................2-20
snmp-server location........................................................................................... 2-20
snmp-server port..................................................................................................2-21
snmp-server readonly..........................................................................................2-21
snmp-server readwrite ........................................................................................2-21
snmp-server trap..................................................................................................2-21
snmp-server trap community .............................................................................2-21
snmp-server trap destination .............................................................................2-22
snmp-server trap heartbeat ................................................................................2-22
snmp-server trap link-state.................................................................................2-22
snmp-server trap snmp-authentication.............................................................2-22
* snmp-server version 1......................................................................................2-22
* snmp-server version 2c....................................................................................2-23
* snmp-server version 3......................................................................................2-23
snmp-server access interface vlan ....................................................................2-23
snmp-server access local mesh..........................................................................2-23
vi
Page 9

snmp-server access interface gre ......................................................................2-23
snmp-server access wireless.............................................................................. 2-24
snmp-server access port-2.................................................................................. 2-24
* snmp-server user ..............................................................................................2-24
* snmp-server notification receiver ..................................................................2-24
soap-server ...........................................................................................................2-24
soap-server access interface vlan......................................................................2-25
soap-server access port-1 ...................................................................................2-25
soap-server access port-2 ...................................................................................2-25
soap-server allow................................................................................................. 2-25
soap-server http authentication.........................................................................2-25
soap-server http authentication password....................................................... 2-26
soap-server http authentication username....................................................... 2-26
soap-server port................................................................................................... 2-26
soap-server ssl......................................................................................................2-26
soap-server ssl with client certificate ...............................................................2-26
soap-server access interface gre........................................................................2-26
soap-server access wireless ...............................................................................2-27
soap-server access local mesh........................................................................... 2-27
snmp-server trap low-snr.................................................................................... 2-27
snmp-server trap low-snr interval .....................................................................2-27
snmp-server trap low-snr level ..........................................................................2-27
snmp-server trap new-association.....................................................................2-27
snmp-server trap new-association interval ......................................................2-28
snmp-server trap vpn-connection...................................................................... 2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-association-fail.......................................................2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-association-success...............................................2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-fail .................................................2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-success .........................................2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-fail .............................................2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-success .....................................2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-fail.................................................. 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-success.......................................... 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-fail ...................................................2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-success ...........................................2-29
snmp-server trap syslog-matches ...................................................................... 2-30
snmp-server trap syslog-matches regex ...........................................................2-30
snmp-server trap syslog-severity level..............................................................2-30
snmp-server trap network-trace ........................................................................ 2-30
vii
Page 10

firmware-update automatic................................................................................2-30
firmware-update start .........................................................................................2-31
firmware-update time..........................................................................................2-31
firmware-update uri ............................................................................................2-31
firmware-update weekday..................................................................................2-31
snmp-server trap firmware-update.................................................................... 2-31
access-controller restrict location.....................................................................2-32
service-sensor ......................................................................................................2-32
service-sensor ......................................................................................................2-32
service-sensor poll............................................................................................... 2-32
service-sensor retry............................................................................................. 2-33
service-sensor timeout........................................................................................2-33
ip name-server......................................................................................................2-33
ip name-server cache ..........................................................................................2-33
ip name-server dynamic...................................................................................... 2-34
ip name-server interception ............................................................................... 2-34
ip name-server switch-on-servfail .....................................................................2-34
ip name-server switch-over ................................................................................2-34
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap ....................................................................2-34
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap interval ......................................................2-35
wireless-scan........................................................................................................ 2-35
wireless-scan period............................................................................................2-35
wireless-scan url ..................................................................................................2-35
access controller shared secret .........................................................................2-35
radius-server profile ............................................................................................2-36
ip-qos profile ........................................................................................................2-36
dot11 igmp snooping-helper...............................................................................2-36
discovery protocol............................................................................................... 2-36
discovery protocol device-id..............................................................................2-36
bridge priority ......................................................................................................2-37
bridge protocol ieee ............................................................................................2-37
bridge protocol ieee vlan ....................................................................................2-37
ip route gateway ..................................................................................................2-37
dot1x reauth .........................................................................................................2-38
dot1x reauth period.............................................................................................2-38
dot1x reauth terminate .......................................................................................2-38
dot1x supplicant timeout.................................................................................... 2-38
dynamic key .........................................................................................................2-38
dynamic key interval ...........................................................................................2-39
viii
Page 11

add wireless ip-qos profile..................................................................................2-39
delete wireless ip-qos profile all ........................................................................2-39
delete wireless ip-qos profile .............................................................................2-39
wireless link qos ..................................................................................................2-39
sensor discovery mode .......................................................................................2-39
sensor network detector.....................................................................................2-40
sensor server id.................................................................................................... 2-40
sensor server name .............................................................................................2-40
config-version.......................................................................................................2-40
Port-2 interface context.............................................................................................2-41
end .........................................................................................................................2-41
duplex ...................................................................................................................2-41
speed .....................................................................................................................2-41
vlan ........................................................................................................................2-41
vlan compatibility mode .....................................................................................2-42
vlan-management filter .......................................................................................2-42
interface vlan........................................................................................................2-42
Port-1 interface context.............................................................................................2-43
end .........................................................................................................................2-43
duplex ...................................................................................................................2-43
speed .....................................................................................................................2-43
vlan ........................................................................................................................2-43
vlan compatibility mode .....................................................................................2-44
vlan-management filter .......................................................................................2-44
interface vlan........................................................................................................2-44
WAN IP interface context..........................................................................................2-45
pppoe client user .................................................................................................2-45
ip address mode...................................................................................................2-45
ip address..............................................................................................................2-45
ip default-gateway ...............................................................................................2-45
ip address dhcp client-id..................................................................................... 2-46
end .........................................................................................................................2-46
pppoe auto-reconnect .........................................................................................2-46
pppoe mru ............................................................................................................2-46
pppoe mtu............................................................................................................. 2-46
pppoe unnumbered .............................................................................................2-47
ix
Page 12

Wireless context......................................................................................................... 2-48
end .........................................................................................................................2-48
radio active........................................................................................................... 2-48
rts threshold .........................................................................................................2-48
distance.................................................................................................................2-48
dot11...................................................................................................................... 2-49
transmit power..................................................................................................... 2-49
antenna bidirectionnal ........................................................................................2-50
antenna gain .........................................................................................................2-50
autochannel skip..................................................................................................2-50
beacon interval ....................................................................................................2-50
dot11 automatic frequency.................................................................................2-50
dot11 automatic frequency period ....................................................................2-51
dot11 automatic frequency time ........................................................................2-51
dot11 automatic transmit-power .......................................................................2-51
dot11 automatic transmit-power period........................................................... 2-51
multicast rate .......................................................................................................2-51
station distance....................................................................................................2-51
dot11 mode........................................................................................................... 2-52
spectralink view................................................................................................... 2-52
dot11n channel extension...................................................................................2-52
dot11n channel width.......................................................................................... 2-52
dot11n guard interval ..........................................................................................2-52
dot11n multicast rate ..........................................................................................2-52
bandwidth.............................................................................................................2-53
bandwidth max .................................................................................................... 2-53
Virtual AP context...................................................................................................... 2-54
virtual ap name ....................................................................................................2-54
ingress interface ..................................................................................................2-54
guest-mode ...........................................................................................................2-54
max-association ...................................................................................................2-54
ssid name ..............................................................................................................2-55
vlan ........................................................................................................................2-55
encryption key 1 ..................................................................................................2-55
encryption key format.........................................................................................2-55
transmit key..........................................................................................................2-56
authentication server access controller ...........................................................2-56
authentication server accounting...................................................................... 2-56
x
authentication server accounting radius profile .............................................2-56
Page 13

authentication server radius ..............................................................................2-56
dot1x authentication ...........................................................................................2-56
wpa-psk.................................................................................................................2-57
authentication server accounting radius stationid case.................................2-57
authentication server accounting radius stationid delimiter.........................2-57
wireless filters......................................................................................................2-57
wireless filters mac .............................................................................................2-57
wireless filters rule input....................................................................................2-58
wireless filters rule output .................................................................................2-58
wireless filters type .............................................................................................2-58
mac-filters local ...................................................................................................2-59
mac-filters.............................................................................................................2-60
mac-filters mode ..................................................................................................2-60
mac authentication accounting .........................................................................2-60
mac authentication accounting radius profile ................................................. 2-60
mandatory authentication .................................................................................. 2-60
mac authentication radius profile .....................................................................2-61
mac authentication radius stationid case.........................................................2-61
mac authentication radius stationid delimiter.................................................2-61
mac authentication..............................................................................................2-61
add ip filter ...........................................................................................................2-61
delete ip filter .......................................................................................................2-62
delete ip filter all..................................................................................................2-62
ip filters................................................................................................................. 2-62
active .....................................................................................................................2-62
beacon dtim count...............................................................................................2-62
beacon transmit power .......................................................................................2-63
data rate ................................................................................................................2-63
public forwarding ................................................................................................ 2-63
fast authentication............................................................................................... 2-63
layer3 mobility .....................................................................................................2-63
add ip-qos profile .................................................................................................2-63
delete ip-qos profile all........................................................................................2-64
delete ip-qos profile.............................................................................................2-64
qos .........................................................................................................................2-64
upstream diffserv tagging ...................................................................................2-65
wmm advertising .................................................................................................2-65
location-aware group ..........................................................................................2-65
end .........................................................................................................................2-65
xi
Page 14

security .................................................................................................................2-66
VLAN interface context .............................................................................................2-67
end .........................................................................................................................2-67
ip address..............................................................................................................2-67
ip address mode...................................................................................................2-67
vlan name..............................................................................................................2-68
Local mesh context.................................................................................................... 2-69
end .........................................................................................................................2-69
active .....................................................................................................................2-69
interface................................................................................................................ 2-69
local mesh name ..................................................................................................2-69
remote mac........................................................................................................... 2-69
security .................................................................................................................2-70
security mode....................................................................................................... 2-70
security psk ..........................................................................................................2-70
security wep .........................................................................................................2-70
speed .....................................................................................................................2-70
interface vlan........................................................................................................2-70
accept forced links ..............................................................................................2-71
allowed downtime ...............................................................................................2-71
dynamic local mesh.............................................................................................2-71
dynamic mode......................................................................................................2-71
initial discovery time...........................................................................................2-71
mesh id..................................................................................................................2-71
minimum snr ........................................................................................................2-71
preserve master link............................................................................................ 2-72
promiscuous mode ..............................................................................................2-72
promiscuous mode startup delay ......................................................................2-72
snr cost per hop ...................................................................................................2-72
RADIUS context .........................................................................................................2-73
end .........................................................................................................................2-73
radius-server accounting port............................................................................ 2-73
radius-server alternate hosts.............................................................................. 2-73
radius-server authentication method................................................................ 2-73
radius-server authentication port...................................................................... 2-73
radius-server deadtime .......................................................................................2-74
radius-server host ................................................................................................2-74
xii
radius-server key 2 ..............................................................................................2-74
Page 15

radius-server message-authenticator ................................................................2-74
radius-server name ..............................................................................................2-74
radius-server nasid ..............................................................................................2-75
radius-server timeout ..........................................................................................2-75
radius-server timeout ..........................................................................................2-75
IP_QOS context ..........................................................................................................2-76
end .........................................................................................................................2-76
end-port.................................................................................................................2-76
priority ..................................................................................................................2-76
profile name .........................................................................................................2-76
protocol.................................................................................................................2-76
start-port ...............................................................................................................2-76
GRE interface context ...............................................................................................2-78
end force............................................................................................................... 2-78
gre name ...............................................................................................................2-78
ip address..............................................................................................................2-78
peer ip address.....................................................................................................2-78
remote ip address ................................................................................................2-78
Syslog destination context........................................................................................ 2-79
active .....................................................................................................................2-79
logging facility......................................................................................................2-79
logging host ..........................................................................................................2-79
logging prefix .......................................................................................................2-79
name...................................................................................................................... 2-79
end .........................................................................................................................2-80
level .......................................................................................................................2-80
level .......................................................................................................................2-80
matches.................................................................................................................2-80
message.................................................................................................................2-80
message.................................................................................................................2-81
process.................................................................................................................. 2-81
process.................................................................................................................. 2-81
* SNMP user context..................................................................................................2-82
* access level .......................................................................................................2-82
* end......................................................................................................................2-82
* password ...........................................................................................................2-82
* security ..............................................................................................................2-82
xiii
Page 16

* user name ..........................................................................................................2-82
* SNMP notification receiver context...................................................................... 2-83
* community ........................................................................................................2-83
* end......................................................................................................................2-83
* port..................................................................................................................... 2-83
* receiver ..............................................................................................................2-83
* user..................................................................................................................... 2-83
* version ...............................................................................................................2-83
xiv
Page 17

Alphabetical list of commands
In this alphabetical list, new to 5.3.x commands are preceded
by an asterisk “*” and formatted in green like this:
* command 2-xxx
accept forced links 2-71
access controller shared secret 2-35
* access level 2-82
access-controller restrict location 2-32
active 2-62
active 2-69
active 2-79
add ip filter 2-61
add ip-qos profile 2-63
add wireless ip-qos profile 2-39
* admin local authentication 2-11
* admin radius authentication 2-11
* admin radius authentication server 2-12
allowed downtime 2-71
antenna bidirectionnal 2-50
antenna gain 2-50
arp 2-5
arping 2-2
arping 2-5
authentication server access controller 2-56
authentication server accounting 2-56
authentication server accounting radius profile 2-56
authentication server accounting radius stationid case 2-57
authentication server accounting radius stationid delimiter
2-57
authentication server radius 2-56
autochannel skip 2-50
bandwidth 2-53
bandwidth max 2-53
beacon dtim count 2-62
beacon interval 2-50
beacon transmit power 2-63
bridge priority 2-37
bridge protocol ieee 2-37
bridge protocol ieee vlan 2-37
certificate 2-9
certificate binding 2-9
certificate revocation 2-9
clock 2-15
* clock auto adjust dst 2-15
* clock custom dst begins 2-16
* clock custom dst begins format 2-16
* clock custom dst ends 2-17
* clock custom dst ends format 2-17
clock timezone 2-15
* clock use custom dst rules 2-15
* community 2-83
config 2-7
config-update automatic 2-18
config-update operation 2-18
config-update time 2-18
config-update uri 2-18
config-update weekday 2-18
config-version 2-40
data rate 2-63
delete ip filter 2-62
delete ip filter all 2-62
delete ip-qos profile 2-64
delete ip-qos profile all 2-64
delete wireless ip-qos profile 2-39
delete wireless ip-qos profile all 2-39
discovery protocol 2-36
discovery protocol device-id 2-36
distance 2-48
dot11 2-49
dot11 automatic frequency 2-50
dot11 automatic frequency period 2-51
dot11 automatic frequency time 2-51
dot11 automatic transmit-power 2-51
dot11 automatic transmit-power period 2-51
dot11 igmp snooping-helper 2-36
dot11 mode 2-52
dot11n channel extension 2-52
dot11n channel width 2-52
dot11n guard interval 2-52
dot11n multicast rate 2-52
dot1x authentication 2-56
dot1x reauth 2-38
dot1x reauth period 2-38
dot1x reauth terminate 2-38
dot1x supplicant timeout 2-38
duplex 2-41
duplex 2-43
dynamic key 2-38
dynamic key interval 2-39
dynamic local mesh 2-71
dynamic mode 2-71
enable 2-2
encryption key 1 2-55
encryption key format 2-55
end force 2-78
end-port 2-76
factory reset 2-6
factory settings 2-9
fast authentication 2-63
firmware-update automatic 2-30
firmware-update start 2-31
firmware-update time 2-31
firmware-update uri 2-31
firmware-update weekday 2-31
gre name 2-78
guest-mode 2-54
ingress interface 2-54
initial discovery time 2-71
interface 2-69
interface ethernet 2-9
interface gre 2-11
interface ip 2-10
interface vlan 2-42
interface vlan 2-44
interface vlan 2-70
interface wireless 2-10
ip address 2-45
ip address 2-67
ip address 2-78
ip address dhcp client-id 2-46
ip address mode 2-45
ip address mode 2-67
ip default-gateway 2-45
ip filters 2-62
xv
Page 18

ip http port 2-12
ip https port 2-12
ip name-server 2-33
ip name-server cache 2-33
ip name-server dynamic 2-34
ip name-server interception 2-34
ip name-server switch-on-servfail 2-34
ip name-server switch-over 2-34
ip route gateway 2-37
iperf 2-2
iperf 2-4
ip-qos profile 2-36
layer3 mobility 2-63
level 2-80
level 2-80
local mesh name 2-69
local mesh profile 2-11
location-aware group 2-65
logging destination 2-19
logging facility 2-79
logging host 2-79
logging prefix 2-79
mac authentication 2-61
mac authentication accounting 2-60
mac authentication accounting radius profile 2-60
mac authentication radius profile 2-61
mac authentication radius stationid case 2-61
mac authentication radius stationid delimiter 2-61
mac-filters 2-60
mac-filters local 2-59
mac-filters mode 2-60
mandatory authentication 2-60
matches 2-80
max-association 2-54
mesh id 2-71
message 2-80
message 2-81
minimum snr 2-71
multicast rate 2-51
name 2-79
nslookup 2-2
ntp protocol 2-16
ntp server 2-16
ntp server 2-17
ntp server failure trap 2-17
* password 2-82
peer ip address 2-78
ping 2-2
ping 2-4
* port 2-83
pppoe auto-reconnect 2-46
pppoe client user 2-45
pppoe mru 2-46
pppoe mtu 2-46
pppoe unnumbered 2-47
preserve master link 2-72
priority 2-76
process 2-81
process 2-81
profile name 2-76
promiscuous mode 2-72
promiscuous mode startup delay 2-72
protocol 2-76
ps 2-3
public forwarding 2-63
qos 2-64
quit 2-3
quit 2-5
radio active 2-48
radius-server accounting port 2-73
radius-server alternate hosts 2-73
radius-server authentication method 2-73
radius-server authentication port 2-73
radius-server deadtime 2-74
radius-server host 2-74
radius-server key 2 2-74
radius-server message-authenticator 2-74
radius-server name 2-74
radius-server nasid 2-75
radius-server profile 2-36
radius-server timeout 2-75
radius-server timeout 2-75
rcapture 2-5
reboot device 2-10
reboot device 2-4
* receiver 2-83
remote ip address 2-78
remote mac 2-69
rts threshold 2-48
security 2-66
security 2-70
* security 2-82
security mode 2-70
security psk 2-70
security wep 2-70
sensor discovery mode 2-39
sensor network detector 2-40
sensor server id 2-40
sensor server name 2-40
service-sensor 2-32
service-sensor 2-32
service-sensor poll 2-32
service-sensor retry 2-33
service-sensor timeout 2-33
show all config 2-8
show arp 2-5
show bridge 2-5
show bridge forwarding 2-6
show certificate 2-10
show certificate 2-4
show certificate binding 2-10
show certificate binding 2-4
show client log 2-7
show config factory 2-10
show discrete pin 2-7
show dns cache 2-6
show dot11 associations 2-7
show dot11 statistics client-traffic 2-7
show interfaces 2-6
* show ip 2-6
show ip route 2-6
show license 2-3
show local mesh 2-7
show logging filtered 2-3
show system info 2-6
show wireless neighborhood 2-7
show wireless rogue-ap 2-7
snmp-server 2-19
snmp-server access interface gre 2-23
snmp-server access interface vlan 2-23
snmp-server access local mesh 2-23
snmp-server access port-1 2-19
xvi
Page 19

snmp-server access port-2 2-24
snmp-server access wireless 2-24
snmp-server allow 2-20
snmp-server chassis-id 2-20
snmp-server contact 2-20
snmp-server heartbeat period 2-20
snmp-server location 2-20
* snmp-server notification receiver 2-24
snmp-server port 2-21
snmp-server readonly 2-21
snmp-server readwrite 2-21
snmp-server trap 2-21
snmp-server trap certificate-expired 2-12
snmp-server trap certificate-expires-soon 2-12
snmp-server trap community 2-21
snmp-server trap config-change 2-18
snmp-server trap config-update 2-19
snmp-server trap destination 2-22
snmp-server trap firmware-update 2-31
snmp-server trap heartbeat 2-22
snmp-server trap link-state 2-22
snmp-server trap low-snr 2-27
snmp-server trap low-snr interval 2-27
snmp-server trap low-snr level 2-27
snmp-server trap network-trace 2-30
snmp-server trap new-association 2-27
snmp-server trap new-association interval 2-28
snmp-server trap snmp-authentication 2-22
snmp-server trap syslog-matches 2-30
snmp-server trap syslog-matches regex 2-30
snmp-server trap syslog-severity 2-19
snmp-server trap syslog-severity level 2-30
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap 2-34
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap interval 2-35
snmp-server trap vpn-connection 2-28
snmp-server trap web-fail 2-13
snmp-server trap web-login 2-13
snmp-server trap web-logout 2-13
snmp-server trap wireless-association-fail 2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-association-success 2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-fail 2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-success 2-28
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-fail 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-success 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-fail 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-success 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-fail 2-29
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-success 2-29
* snmp-server user 2-24
* snmp-server version 1 2-22
* snmp-server version 2c 2-23
* snmp-server version 3 2-23
snr cost per hop 2-72
soap-server 2-24
soap-server access interface gre 2-26
soap-server access interface vlan 2-25
soap-server access local mesh 2-27
soap-server access port-1 2-25
soap-server access port-2 2-25
soap-server access wireless 2-27
soap-server allow 2-25
soap-server http authentication 2-25
soap-server http authentication password 2-26
soap-server http authentication username 2-26
soap-server port 2-26
soap-server ssl 2-26
soap-server ssl with client certificate 2-26
spectralink view 2-52
speed 2-41
speed 2-43
speed 2-70
ssid name 2-55
start-port 2-76
station distance 2-51
switch operational mode 2-6
top 2-3
traceroute 2-3
transmit key 2-56
transmit power 2-49
upstream diffserv tagging 2-65
* user 2-83
* user name 2-82
username 2-10
* version 2-83
virtual ap 2-11
virtual ap name 2-54
vlan 2-41
vlan 2-43
vlan 2-55
vlan compatibility mode 2-42
vlan compatibility mode 2-44
vlan name 2-68
vlan-management filter 2-42
vlan-management filter 2-44
web access interface gre 2-14
web access interface vlan 2-14
web access local mesh 2-15
web access port-1 2-14
web access port-2 2-14
web access wireless 2-14
web admin kickout 2-13
web allow 2-13
wireless filters 2-57
wireless filters mac 2-57
wireless filters rule input 2-58
wireless filters rule output 2-58
wireless filters type 2-58
wireless link qos 2-39
wireless-scan 2-35
wireless-scan period 2-35
wireless-scan url 2-35
wmm advertising 2-65
world-mode dot11 country code 2-14
wpa-psk 2-57
xvii
Page 20

xviii
Page 21

Chapter 1: Introduction
Introduction
Contents
About this guide ...........................................................................................................1-2
Products covered................................................................................................... 1-2
HP ProCurve Product Naming............................................................................. 1-2
Important terms..................................................................................................... 1-3
Typographical conventions ..................................................................................1-3
HP ProCurve Networking support.............................................................................1-4
1
Online documentation .................................................................................................1-5
CLI support in autonomous and controlled modes .................................................1-5
Controlled mode ....................................................................................................1-5
Autonomous mode ................................................................................................ 1-5
Configuring CLI support.............................................................................................. 1-6
SSH client support.................................................................................................1-7
Entering strings ............................................................................................................1-7
Context hierarchy ........................................................................................................1-7
Sample CLI session ......................................................................................................1-8
Page 22
Introduction
About this guide
About this guide
This guide explains how to work with the Command Line Interface (CLI) on HP ProCurve
Networking MSM3xx and MSM4xx APs.
Products covered
This guide covers the following products:
Part number
USA
Model
MSM310 Access Point J9374A J9379A
MSM310-R Access Point J9380A J9383A
MSM320 Access Point J9360A J9364A
MSM320-R Access Point J9365A J9368A
MSM325 Access Point with Sensor J9369A J9373A
MSM335 Access Point with Sensor J9356A J9357A
MSM410 Access Point J9426A J9427A
version
Worldwide
version
MSM422 Access Point J9358A J9359A
HP ProCurve Product Naming
As of October 1st, 2008, Colubris Networks was acquired by HP ProCurve. HP ProCurve has
begun integrating the Colubris product line into the HP ProCurve Networking product
portfolio (www.procurve.com/news/colubris-10-01-08.htm).
In the online help and this manual, Colubris product names have been changed to their
equivalent HP ProCurve product names.
Note SOAP and SNMP MIBs retain the Colubris naming so you do not need to change your existing
SOAP and MIB usage.
The Colubris Networks product names and their corresponding new HP ProCurve product
names are as follows:
Colubris name HP ProCurve name
MSC-5100 MultiService Controller MSM710 Controller
MSC-5200 MultiService Controller MSM730 Controller
1-2
MSC-5500 MultiService Controller MSM750 Controller
Page 23
Colubris name HP ProCurve name
Introduction
About this guide
MAP-320 MultiService Access Point MSM310 Access Point
MAP-320R MultiService Access Point MSM310-R Access Point
MAP-330 MultiService Access Point MSM320 Access Point
MAP-330R MultiService Access Point MSM320-R Access Point
MAP-330 AP+Sensor MultiService Access Point MSM325 Access Point with Sensor
MAP-625 MultiService Access Point MSM422 Access Point
MAP-630 AP+Sensor MultiService Access Point MSM335 Access Point with Sensor
WCB-200 Wireless Client Bridge M111 Client Bridge
Visitor Management Tool Guest Management Software
RF Manager 1500 Enterprise RF Manager 100 IDS/IPS system
RF Manager 1300 Basic RF Manager 50 IDS/IPS system
RF Planner RF Planner
Important terms
The following terms are used in this guide.
Term Description
AP Refers to any HP ProCurve Networking MSM3xx or MSM4xx
Access Point.
service controller Refers to any HP ProCurve Networking MSM7xx Controller,
including both Access Controller and Mobility Controller
variants.
VSC, Virtual ap, VAP These terms are used interchangeably to refer to VSC (Virtual
Service Community).
Typographical conventions
Command syntax
Command syntax is formatted in a monospaced font as follows:
Example Description
web admin kickout
ip http port <number>
Items in plain text must be entered as shown.
Items in italics and enclosed in < > are parameters for
which you must supply a value. In this example, you
must supply a value for <number>.
1-3
Page 24
Introduction
HP ProCurve Networking support
Example Description
end [force]
firewall mode (high|low|none)
Items enclosed in square brackets are optional. You
can either include them or not. Do not include the
brackets. In this example you can either include
“force” or omit it.
Items enclosed in parenthesis and separated by a
vertical line indicate a choice. Specify only one of the
items. In this example, you must specify ’high’, ’low’, or
’none’.
Management tool
When referring to the management tool interface, the Main menu name is presented first
followed by a right angle-bracket and then the sub-menu name, as in Network > Ports.
HP ProCurve Networking support
HP ProCurve Networking offers support 24 hours a day, seven days a week through a number
of automated electronic services. See the Customer Support/Warranty booklet included with
your product.
The HP ProCurve Networking Web site, www.procurve.com/customercare provides up-to-
date support information.
Additionally, your HP-authorized network reseller can provide you with assistance, both with
services that they offer and with services offered by HP.
Before contacting support
To make the support process most efficient, before calling your networking dealer or HP
Support, you first should collect the following information:
Collect this information Where to find it
Product identification. On the rear of the product.
Software version. The service controller management tool
Network topology map, including the
addresses assigned to all relevant devices.
Login page.
Your network administrator.
1-4
Page 25

Introduction
Online documentation
Online documentation
For the latest documentation, visit the HP ProCurve Networking manuals Web page at:
www.procurve.com/manuals.
CLI support in autonomous and controlled modes
An AP operates in either controlled mode or autonomous mode.
Controlled mode
Controlled mode is the factory default mode for all APs.
When in controlled mode, an AP establishes a control channel with a service controller. The
service controller manages the AP and provides all configuration settings. Discovery of the
service controller is automatic if default settings are used on all devices.
Note In controlled mode, access to the CLI is possible only before any control channel is
established, which can occur in the following scenarios:
Network failures prevent a control channel from being created.
After an AP is restarted, prior to establishment of the control channel (during the brief
service controller discovery process).
When the AP is in controlled mode, a reduced number of CLI commands are available. The
most notable command is switch operational mode, which enables you to switch the AP to
autonomous mode. The config context is not available.
Autonomous mode
When in autonomous mode, the AP operates as a stand-alone unit. You can configure and
manage the AP using the AP management tool, SNMP, CLI, or SOAP. Autonomous mode
supports all CLI commands.
1-5
Page 26
Introduction
Configuring CLI support
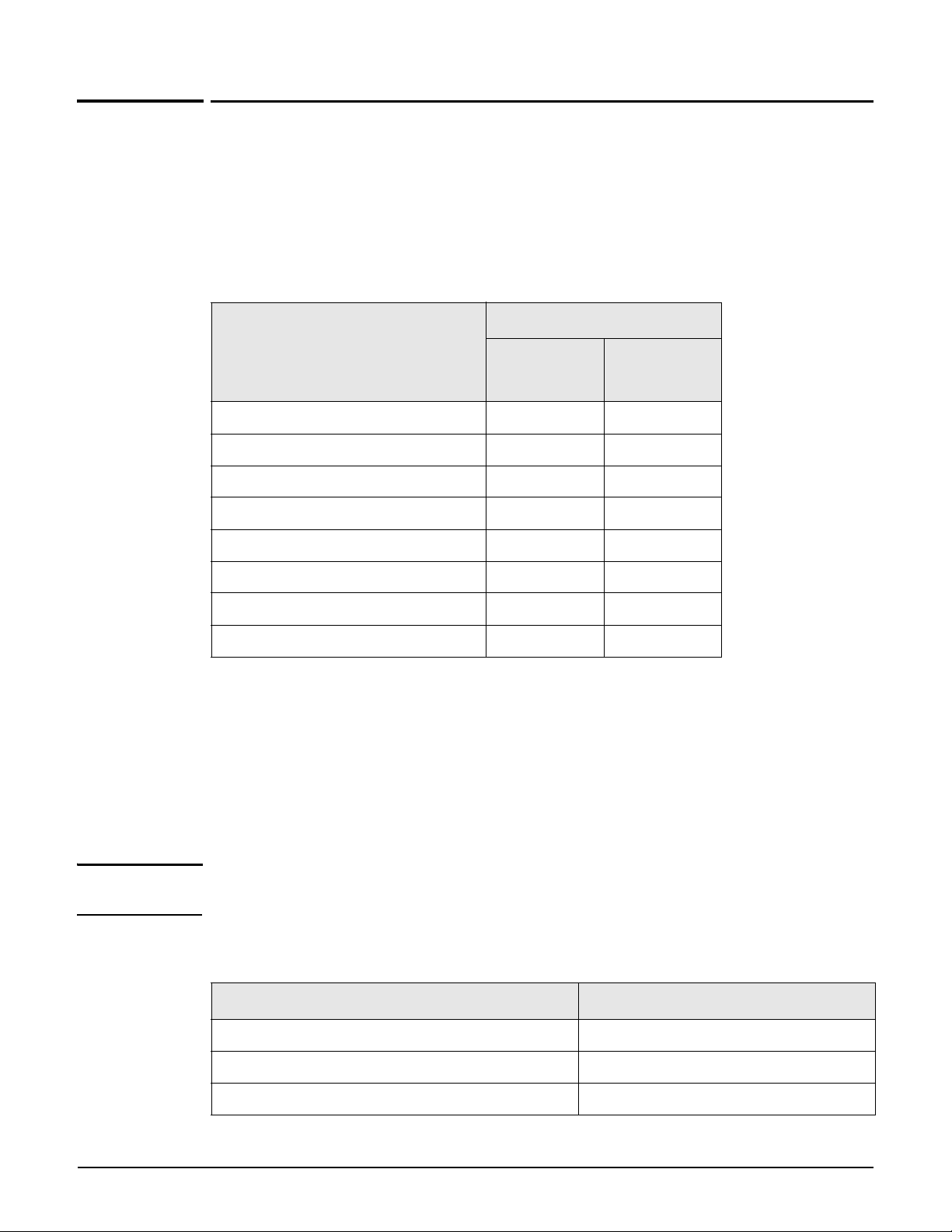
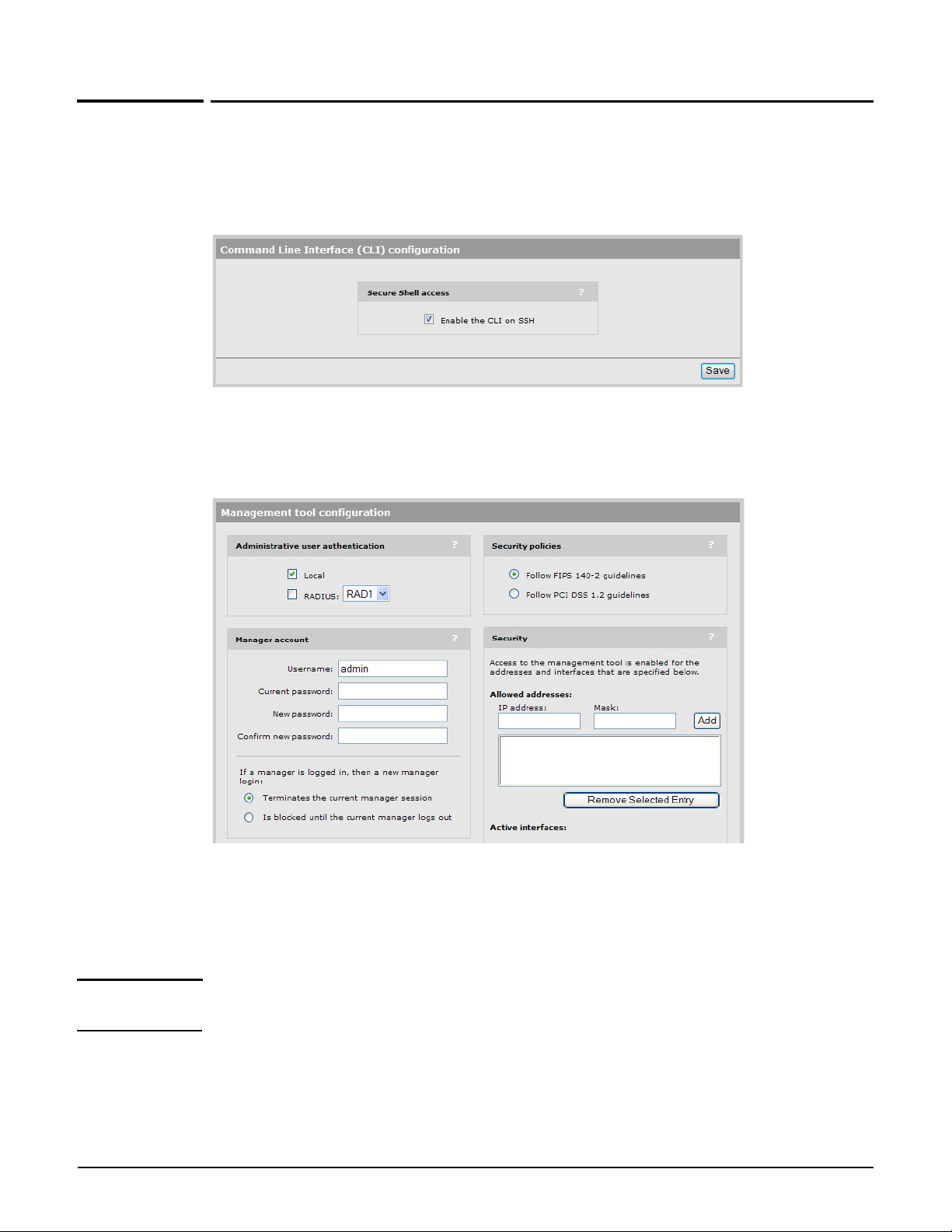
Configuring CLI support
Using the AP management tool, open the page Management > CLI. Use this page to enable/
disable CLI support via an SSH or serial connection. A maximum of three concurrent CLI
sessions are supported regardless of the connection type.
The CLI supports SSH on the standard TCP port (22).
Connectivity and login credentials for SSH connections use the same settings as defined for
the management tool manager on the Management > Management tool page.
SSH connections to the CLI can be made on any active interface. Support for each
interface must be explicitly enabled under Security.
The login credentials for SSH connections are the same as those defined under Manager
account. By default, both username and password are set to admin.
Note SSH logins always use the local manager username and password, even if Administrative
user authentication is set to use a RADIUS server.
1-6
Page 27
SSH client support
Introduction
Entering strings
The following SSH clients have been tested with the CLI. Others may work as well:
OpenSSH
Tectia
SecureCRT
Putty
Entering strings
When entering a value that contains spaces, you must enclose it in quotation marks. For
example, if the command syntax is:
ssid <name>
you must specify one of the following:
ssid ANameWithNoSpaces
ssid "A name with spaces"
Context hierarchy
CLI commands are grouped into functional contexts. The following table shows the context
hierarchy and the command used to switch from the parent context.
Context hierarchy Command to switch from parent context
View context (This is the first context. No command is needed.)
Enable context enable
Config context config
WAN IP interface context interface ip
Port-2 interface context interface ethernet port-2
VLAN interface context interface vlan <id>[-<id2>]
Port-1 interface context interface ethernet port-1
VLAN interface context interface vlan <id>[-<id2>]
Wireless context interface wireless <number>
Local mesh context local mesh profile <name>
VLAN interface context interface vlan <number>
GRE interface context interface gre <name>
Virtual AP context virtual ap <name>
Syslog destination context logging destination <name>
SNMP user context snmp-server user <name>
SNMP notification receiver context snmp-server notification receiver <host>
RADIUS context radius-server profile <name>
IP_QOS context ip-qos profile <name>
1-7
Page 28

Introduction
Sample CLI session
Sample CLI session
This sample CLI session shows you how to set the wireless port to support 802.11a on
channel 60 with medium distance between access points. (The CLI prompt is shown in bold.)
CLI> enable
CLI# config
CLI(config)# interface wireless
CLI(config-if-wlan)# dot11 a 60
CLI(config-if-wlan)# distance medium
CLI(config-if-wlan)# end
CLI(config)# end
CLI# quit
1-8
Page 29

Chapter 2: CLI commands
CLI commands
2
Page 30

CLI commands
View context
Path: View
This is the root of the command tree.
arping
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
arping [ -AbDfhqUV] [ -c <count>] [ -w <deadline>] [ -s <source>] -I <interface>
<destination>
Pings a destination on a device interface using ARP packets.
enable
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
enable
Switches to the enable context.
iperf
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
iperf -c host [-t time]
Runs a performance throughput test.
Parameters
<-c host> The IP address or DNS name of the iperf server to connect to.
<-t length> Length of the throughput test in seconds.
nslookup
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
nslookup [ -option authentication ] [ <host-to-find> | - [< server> ]]
Queries DNS servers for information on hosts or domains.
ping
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ping <host> [-c <count>] [-s <length>] [-q]
Determines if the specified remote IP address is active.
Parameters
<-c host> The IP address or DNS name of the host to ping.
<-c count> Number of pings.
<-s length> Length of the ping datagram.
<-q> Quiet mode. No output.
2-2
Page 31

ps
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ps
Displays all running processes.
quit
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
quit
Quits the CLI.
show license
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show license (eula | gpl | other)
CLI commands
Displays license information.
show logging filtered
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show logging [filtered]
Displays the system log.
top
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
top
Displays all running processes.
traceroute
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
traceroute [-n] [-r] [-v] [-m <max_ttl>] [-p <port#>] [-q <nqueries>] [-s
<src_addr>] [-t <tos>] [-w <wait>] <host> [<data size>]
Show the hosts that are traversed to reach the specified IP address.
2-3
Page 32

CLI commands
Enable context
Path: View > Enable
This context provides access to various utilities.
reboot device
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
reboot device
Restarts the system.
show certificate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show certificate
Display current certificates.
show certificate binding
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show certificate binding
Display how the certificates are used.
iperf
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
iperf -c host [-t time]
Runs a performance throughput test.
Parameters
<-c host> The IP address or DNS name of the iperf server to connect to.
<-t length> Length of the throughput test in seconds.
ping
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ping <host> [-c <count>] [-s <length>] [-q]
Determines if the specified remote IP address is active.
Parameters
<-c host> The IP address or DNS name of the host to ping.
<-c count> Number of pings.
<-s length> Length of the ping datagram.
<-q> Quiet mode. No output.
2-4
Page 33

CLI commands
arping
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
arping [ -AbDfhqUV] [ -c <count>] [ -w <deadline>] [ -s <source>] -I <interface>
<destination>
Pings a destination on a device interface using ARP packets.
arp
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
arp [-evn] [-H <type>] [-i if] ?- [<hostname>] arp [-v] [-i if] -d <hostname>
[pub] arp [-v] [-H <type>] [-i if] -s <hostname> <hw_addr> [temp] arp [-v] [-H
<type>] [-i if] -s <hostname> <hw_addr> [<netmask> <nm>] <pub> arp [-v] [-H
<type>] [-i if] -Ds <hostname> ifa [<netmask> <nm>] <pub>
Displays and modifies the Internet-to-Ethernet address translation tables used by the address
resolution protocol.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
Switches to parent context.
quit
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
quit
Exit the enable context.
rcapture
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
rcapture [<a>] [<b>] [<c>] [<d>] [<e>] [<f>] [<g>] [<h>]
Sends port capture to an FTP server.
Refer to Linux documentation for a complete description of this command and its options.
show arp
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320
show arp
Show the ARP table.
MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show bridge
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320
show bridge
MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
Show bridge information.
2-5
Page 34

CLI commands
show bridge forwarding
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show bridge forwarding
Show bridge forwarding information.
show dns cache
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show dns cache [<serial>]
Show DNS cache entries. Specify a serial number to display detailed information.
show interfaces
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show interfaces
Show networking interfaces.
show ip
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show ip
Show all IP addresses, mask, MTU, and MAC addresses.
show ip route
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show ip route
Show all IP routes.
show system info
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show system info
2-6
Show basic system information.
factory reset
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
factory reset
Resets the unit to factory default settings.
switch operational mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
switch operational mode
Switches the unit operational mode.
Page 35

show dot11 associations
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show dot11 associations
CLI commands
Show all current wireless associations.
show dot11 statistics client-traffic
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show dot11 statistics client-traffic
Show current client matrix statistics.
show local mesh
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show local mesh
Show current local mesh interfaces.
show wireless neighborhood
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show wireless neighborhood
Show all access points detected nearby.
show wireless rogue-ap
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show wireless rogue-ap
Show all rogue access points detected nearby.
show client log
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show client log [<macaddr>]
Display client station log. Enter the MAC address to display more details for a specific client
station.
show discrete pin
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show discrete pin
Display the state of the discrete pin.
config
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config
Switches to the config context.
2-7
Page 36

CLI commands
show all config
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show all config
Print all configuration that applies to this device.
2-8
Page 37

Config context
Path: View > Enable > Config
This is the root context for all configuration commands.
certificate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
CLI commands
certificate (authority | local) <uri> <certname> [<password>]
Add a new certificate to the store, using the friendly name.
certificate binding
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
certificate binding (web-management | html-auth | soap | eap) <certname>
Assign a certificate to a service.
no certificate binding (web-management | html-auth | soap | eap) <certname>
Unassign a certificate from a service.
certificate revocation
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
certificate revocation <uri> <certname>
Add a Certificate Revocation List to an existing authority certificate.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
Switches to parent context.
factory settings
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
factory settings
Resets the system configuration to factory default settings.
interface ethernet
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface ethernet (port-1|port-2)
Switches to the specified Ethernet interface context.
2-9
Page 38

CLI commands
reboot device
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
reboot device
Restarts the system.
show certificate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show certificate
Display current certificates.
show certificate binding
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show certificate binding
Display how the certificates are used.
show config factory
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
show config [factory]
Generates a list of CLI commands that can be used to define the currently loaded configuration.
username
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
username <user> <password>
Changes the current administrator username and password.
Parameters
<user> New administrator username.
<password> New administrator password.
interface ip
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface ip
2-10
Switches to the specified IP interface context.
interface wireless
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface wireless <interface number>
Switches to the specified wireless interface context.
Page 39

local mesh profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
local mesh link <name>
CLI commands
Switches to the specified local mesh link context.
Parameters
<name> Number of the local mesh link to configure.
interface gre
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface gre <name>
Switches to the specified GRE interface or creates a new GRE interface with the specified name.
no interface gre <name>
Deletes the specified GRE interface.
virtual ap
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
virtual ap <name>
Creates a new VAP (VSC) profile or switches to the existing VAP (VSC) context with the specified
name.
no virtual ap <name>
Deletes the specified Virtual AP profile.
Parameters
name Name of an existing or new VAP (VSC) profile.
admin local authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
admin local authentication
Enable the authentication of administrator logins to occur using local account.
no admin local authentication
Disable administrator authentication via local account.
admin radius authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
admin radius authentication
Sets the authentication of administrator logins to occur using RADIUS.
no admin radius authentication
Disable administrator authentication via RADIUS.
2-11
Page 40

CLI commands
admin radius authentication server
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
admin radius authentication server <name>
Sets the authentication of administrator logins to occur using RADIUS.
ip http port
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip http port <number>
Sets the port number to use for HTTP access to the AP.
Parameters
<number> Port number. Range: 1 - 65535.
Description
HTTP connections made to this port are met with a warning and the browser is redirected to the
secure web server port. By default. this parameter is set to port 80.
ip https port
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip https port <number>
Sets the port number used for HTTPS access to the AP.
Parameters
<number> Port number. Range: 1 - 65535.
snmp-server trap certificate-expired
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap certificate-expired
Send a trap when the SSL certificate has expired. A trap is sent every 12 hours.
no snmp-server trap certificate-expired
Do not send a trap when the SSL certificate has expired.
snmp-server trap certificate-expires-soon
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap certificate-expires-soon
Send a trap when the SSL certificate is about to expire. A trap is sent every 12 hours starting 15
days before the certificate expires.
no snmp-server trap certificate-expires-soon
Do not send a trap when the SSL certificate is about to expire.
2-12
Page 41

snmp-server trap web-fail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap web-fail
Send a trap each time an administrator login is refused.
no snmp-server trap web-fail
CLI commands
Do not send a trap each time an administrator login is refused.
snmp-server trap web-login
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap web-login
Send a trap each time an administrator login is accepted.
no snmp-server trap web-login
Do not send a trap each time an administrator login is accepted.
snmp-server trap web-logout
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap web-logout
Send a trap each time an administrator logs out.
no snmp-server trap web-logout
Do not send a trap each time an administrator logs out.
web admin kickout
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web admin kickout
Enables a new administrator login to terminate an existing administrator session.
no web admin kickout
Stops a new administrator from logging in until an existing administrator logs out.
web allow
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web allow <ip address>/<mask>
Adds an address to the list of hosts that can access the management tool.
no web allow <ip address>/<mask>
Removes the specified address from the list of hosts that can access the management tool.
Parameters
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
2-13
Page 42

CLI commands
world-mode dot11 country code
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
world-mode dot11 country code <code>
Specifies the country the AP is operating in.
Parameters
<code> An ISO3166 three-letter country code.
web access port-1
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web access port-1
Enables access to the management tool via Port-2.
no web access port-1
Blocks access to the management tool via Port-2.
web access port-2
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320
web access port-2
Enables access to the management tool via Port-1.
no web access port-2
Blocks access to the management tool via Port-1.
web access wireless
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web access wireless
Enables access to the management tool via the wireless port.
no web access wireless
Blocks access to the management tool via the wireless port.
web access interface vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web access interface vlan <name>
Enables access to the management tool via the specified VLAN.
no web access interface vlan <name>
Removes access to the management tool for the specified VLAN.
web access interface gre
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web access interface gre <name>
Enables access to the management tool via the specified GRE tunnel.
2-14
Page 43

CLI commands
no web access interface gre <name>
Disables access to the management tool via the specified GRE tunnel.
web access local mesh
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
web access local mesh <name>
Enables access to the management tool via the specified local mesh.
no web access local mesh <name>
Disables access to the management tool via the specified local mesh.
clock
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock <time> <date>
Sets the system time and date.
Parameters
<time> Time as hh:mm:ss. For example: 15:44:00.
<date> Date as dd Month yyyy. For example: 17 Oct 2004.
clock auto adjust dst
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock auto adjust dst
Automatically adjust clock for daylight savings changes.
no clock auto adjust dst
Do not automatically adjust clock for daylight savings changes.
clock timezone
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock timezone <gmtdiff>
Sets the time zone the AP is operating in.
Parameters
<gmtdiff> Offset from GMT as follows: +-HOUR:MIN. For example, Eastern Standard
time is -5:00.
clock use custom dst rules
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock use custom dst rules
Use custom DST rules instead of default ones.
no clock use custom dst rules
Do not use custom DST rules, use default ones.
2-15
Page 44

CLI commands
ntp protocol
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ntp protocol (ntp | sntp)
Sets the network time protocol to use.
ntp server
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ntp server
Enable this option to have the AP periodically contact a network time server to update its internal
clock.
no ntp server
Disables the use of a network time server.
clock custom dst begins
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock custom dst begins <day> <weekday> <month> <time>
Set parameters of the rule defining the beginning of daylight savings time.
Parameters
<day> Day of the month. Range 1 - 31.
<weekday> Weekday. Valid values are: "sun", "mon", "tue", "wed", "thu", "fri", "sat".
<month> Month. Valid values are: "jan", "feb", "mar", "apr", "may", "jun", "jul", "aug",
<time> Time as hh:mm[:ss]. For example: 15:44:00.
If a parameter does not apply to the configured DST rule format, simply set this parameter to any
valid value.
"sep", "oct", "nov", "dec".
2-16
clock custom dst begins format
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock custom dst begins format (fixed | last-weekday | following-date |
preceding-date)
Set the format of the custom DST rule.
Parameters
<fixed> Rule of the form: The [Day]th of [Month] at [Time].
<last-weekday> Rule of the form: The last [Weekday] of [Month] at [Time].
<following-date> Rule of the form: The first [Weekday] on or after the [Day]th of [Month] at
<preceding-date> Rule of the form: The first [Weekday] on or before the [Day]th of [Month]
[Time].
at [Time].
Page 45

CLI commands
clock custom dst ends
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock custom dst end <day> <weekday> <month> <time>
Set parameters of the rule defining the end of daylight savings time.
Parameters
<day> Day of the month. Range 1 - 31.
<weekday> Weekday. Valid values are: "sun", "mon", "tue", "wed", "thu", "fri", "sat".
<month> Month. Valid values are: "jan", "feb", "mar", "apr", "may", "jun", "jul", "aug",
<time> Time as hh:mm[:ss]. For example: 15:44:00.
If a parameter does not apply to the configured DST rule format, simply set this parameter to any
valid value.
"sep", "oct", "nov", "dec".
clock custom dst ends format
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
clock custom dst ends format (fixed | last-weekday | following-date | precedingdate)
Set the format of the custom DST rule.
Parameters
<fixed> Rule of the form: The [Day]th of [Month] at [Time].
<last-weekday> Rule of the form: The last [Weekday] of [Month] at [Time].
<following-date> Rule of the form: The first [Weekday] on or after the [Day]th of [Month] at
<preceding-date> Rule of the form: The first [Weekday] on or before the [Day]th of [Month]
[Time].
at [Time].
ntp server
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ntp server <index><host>
Adds a network time server.
Parameters
<index> Index of the time server in the list. Up to 20 time servers are supported.
<host> DNS name or IP address of the time server.
Time servers are checked in the order that they appear in the list.
ntp server failure trap
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ntp server failure trap
Send a trap each time a time server synchronization failed.
no ntp server failure trap
Do not send a trap each time a time server synchronization failed.
2-17
Page 46

CLI commands
config-update automatic
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config-update automatic
Enables scheduled configuration restore or backup.
no config-update automatic
Disables scheduled configuration restore or backup.
The AP can automatically download the configuration file from a local or remote URL (restore). It
is also possible to upload the current configuration to a given URL (backup). Theses operations
can be done at preset times.
config-update operation
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config-update operation (restore | backup)
Sets the type of operation that will take place at the preset time.
config-update time
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config-update time <time>
Sets the time of day when the scheduled configuration operation (backup or restore) will take
place.
Parameters
<time> Time as hh:mm:ss. For example: 15:44:00.
config-update uri
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config-update uri <uri>
Sets the URI where the AP will download or upload the configuration file.
no config-update uri
Clears the configuration file URI.
config-update weekday
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config-update weekday (everyday | monday | tuesday | wednesday | thursday |
friday | saturday | sunday)
Sets the day when the scheduled configuration operation (backup or restore) will take place.
snmp-server trap config-change
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap config-change
Send a trap whenever the configuration is changed.
2-18
Page 47

CLI commands
no snmp-server trap config-change
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap config-update
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap config-update
Send a trap whenever the firmware is updated.
no snmp-server trap config-update
Do not send this trap.
logging destination
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
logging destination <name>
Creates a new remote destination for syslog.
no logging destination <name>
Deletes the specified syslog destination.
Parameters
<name> Name of syslog destination. Use the name "local" to edit your local log file
settings. Any other name will edit/create a remote log destination.
snmp-server trap syslog-severity
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap syslog-severity
Set the severity level of syslog messages that will trigger a trap.
no snmp-server trap syslog-severity
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server
Enables the SNMP agent.
no snmp-server
Disables the SNMP agent.
snmp-server access port-1
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server access port-1
Enables SNMP access on the downstream port.
no snmp-server access port-1
Blocks SNMP access on the downstream port.
2-19
Page 48

CLI commands
snmp-server allow
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server allow <ip address>/<mask>
Adds a host to the list of IP address from which access to the SNMP interface is permitted.
no snmp-server allow <ip address>/<mask>
Removes a host from the list of IP address from which access to the SNMP interface is permitted.
Parameters
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
snmp-server chassis-id
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server chassis-id <name>
Specifies a name to identify the AP. By default, this is set to the serial number of the AP.
no snmp-server chassis-id
Deletes the system name.
snmp-server contact
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server contact <email>
Specifies contact information.
no snmp-server contact
Deletes contact information.
Parameters
<email> Email address.
snmp-server heartbeat period
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server heartbeat period <seconds>
Sets the interval between sending heartbeat traps.
Parameters
<seconds> Heartbeat interval in seconds.
snmp-server location
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server location <name>
Specifies the location where the AP is installed.
no snmp-server location
Deletes location information.
2-20
Page 49

Parameters
<name> Location where the AP is installed.
snmp-server port
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server port <port number>
CLI commands
Sets the port the AP will use to respond to SNMP requests.
Parameters
<port number> SNMP port number. Range 1 - 65535.
snmp-server readonly
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server readonly <community>
Sets the read-only community string.
no snmp-server readonly
Deletes the read-only community string.
snmp-server readwrite
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server readwrite <community>
Sets the read-write community string.
no snmp-server readwrite
Deletes the read-write community string.
snmp-server trap
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap
Enables support for SNMP traps.
no snmp-server trap
Disables support for SNMP traps.
snmp-server trap community
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap community <str>
Sets the password required by the remote host that will receive the trap.
no snmp-server trap community
Deletes the password required by the remote host that will receive the trap.
2-21
Page 50

CLI commands
snmp-server trap destination
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap destination <host> <[port number]>
Add a new trap destination.
no snmp-server trap destination <host> [<port>]
Deletes the specified trap destination.
Parameters
<host> Sets the IP address or domain name of the host that the AP will send traps
<[port number]> SNMP port number. Range 1 - 65535. By default port 162 is used
to.
snmp-server trap heartbeat
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap heartbeat
Enables sending of heartbeat traps at regular intervals.
no snmp-server trap heartbeat
Disables sending of heartbeat traps at regular intervals.
snmp-server trap link-state
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap link-state
Send a trap when the link state changes on any interface.
no snmp-server trap link-state
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap snmp-authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap snmp-authentication
Send a trap each time an SNMP request fails to supply the correct community name.
snmp-server version 1
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server version 1
2-22
Enable version 1
no snmp-server version 1
Disable version 1
Page 51

snmp-server version 2c
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335
snmp-server version 2c
CLI commands
MSM410 MSM422
Enable version 2c
no snmp-server version 2c
Disable version 2c
snmp-server version 3
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335
snmp-server version 3
Enable version 3
no snmp-server version 3
Disable version 3
MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server access interface vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server access interface vlan <name>
Enables access to SNMP via the specified VLAN.
no snmp-server access interface vlan <name>
Disables access to SNMP via the specified VLAN.
Parameters
<name> Specifies the name of the VLAN.
snmp-server access local mesh
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server access local mesh <profile>
Enables access to SNMP via the specified local mesh.
no snmp-server access local mesh <profile>
Enables access to SNMP via the specified local mesh.
snmp-server access interface gre
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server access interface gre <name>
Enables access to SNMP via the specified GRE tunnel.
no snmp-server access interface gre <name>
Removes access to SNMP via the specified GRE tunnel.
2-23
Page 52

CLI commands
snmp-server access wireless
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server access wireless
Enables SNMP access on the wireless port.
no snmp-server access wireless
Blocks SNMP access on the wireless port.
snmp-server access port-2
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320
snmp-server access port-2
Enables SNMP access on the upstream port.
no snmp-server access port-2
Blocks SNMP access on the upstream port.
snmp-server user
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server user <name>
Creates a new SNMP user or switches to the SNMP user context with the specified user name.
no snmp-server user <name>
Deletes the specified SNMP user.
snmp-server notification receiver
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server notification receiver <host>
Creates a new SNMP notification receiver or switches to the SNMP notification receiver context
with the specified IP address.
no snmp-server notification receiver <host>
Deletes the specified SNMP notification receiver.
soap-server
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server
Enables the SOAP server.
no soap-server
Disables the SOAP server.
2-24
Page 53

soap-server access interface vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server access interface vlan <name>
Enables access to SOAP via this VLAN.
CLI commands
no soap-server access interface vlan <name>
Disables access to SOAP via this VLAN.
soap-server access port-1
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server access port-1
Enables SOAP access on the downstream port.
no soap-server access port-1
Blocks SOAP access on the downstream port.
soap-server access port-2
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server access port-2
Enables SOAP access on the upstream port.
no soap-server access port-2
Blocks SOAP access on the upstream port.
soap-server allow
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server allow <ip address>/<mask>
Adds a host to the list of IP address from which access to the SOAP interface is permitted.
no soap-server allow <ip address>/<mask>
Removes a host from the list of IP address from which access to the SOAP interface is permitted.
Parameters
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
soap-server http authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server http authentication
Enable the SOAP server HTTP authentication.
no soap-server http authentication
Disable the SOAP server HTTP authentication.
2-25
Page 54

CLI commands
soap-server http authentication password
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server http authentication password
Set the SOAP server HTTP authentication password.
soap-server http authentication username
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server http authentication username
Set the SOAP server HTTP authentication username.
soap-server port
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server port <port number>
Sets the port the AP will use to respond to SOAP requests.
Parameters
<port number> SOAP port number. Range 1 - 65535.
soap-server ssl
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server ssl
SSL enabled for SOAP server.
no soap-server ssl
SSL disabled for SOAP server.
soap-server ssl with client certificate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server ssl with client certificate
Enable the use of client certificate with SSL for SOAP server.
no soap-server ssl with client certificate
Disable the use of client certificate with SSL for SOAP server.
soap-server access interface gre
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server access interface gre <name>
Enables access to SOAP via the specified GRE tunnel.
no soap-server access interface gre <name>
Removes access to SOAP via the specified GRE tunnel.
2-26
Page 55

soap-server access wireless
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server access wireless
Enables SOAP access on the wireless port.
no soap-server access wireless
CLI commands
Blocks SOAP access on the wireless port.
soap-server access local mesh
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
soap-server access local mesh <profile>
Enables access to the management tool via the specified local mesh.
no soap-server access local mesh <profile>
Disables access to the management tool via the specified local mesh.
snmp-server trap low-snr
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap low-snr
Send a trap when the average signal to noise ratio on a VAP (VSC) exceeds a specified level.
no snmp-server trap low-snr
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap low-snr interval
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap low-snr interval <number>
Sets the interval at which the average SNR level is checked for each VAP (VSC).
snmp-server trap low-snr level
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap low-snr level <number>
Sets the SNR level that will trigger a trap.
snmp-server trap new-association
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap new-association
Send trap on when a new wireless client station associates with any VAP (VSC).
no snmp-server trap new-association
Do not send this trap.
2-27
Page 56

CLI commands
snmp-server trap new-association interval
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap new-association interval <number>
Interval, in minutes, between notifications.
snmp-server trap vpn-connection
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap vpn-connection
Send a trap when a user establishes a VPN connection with the AP.
no snmp-server trap vpn-connection
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-association-fail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-association-fail
Send a trap when a wireless client station fails to associate with the AP.
no snmp-server trap wireless-association-fail
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-association-success
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-association-success
Send a trap when a wireless client station successfully associates with the AP.
no snmp-server trap wireless-association-success
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-fail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-fail
Send a trap when a wireless client station fails to authenticate.
no snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-fail
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-success
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-success
Send a trap when a wireless client station is successfully associated.
no snmp-server trap wireless-authentication-success
2-28
Do not send this trap.
Page 57

snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-fail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-fail
Send a trap when a wireless client station fails to deauthenticate from the AP.
CLI commands
no snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-fail
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-success
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-success
Send a trap when a wireless client station deauthenticates from the AP.
no snmp-server trap wireless-deauthentication-success
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-fail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-fail
Send a trap when a wireless client station fails to disassociate from the AP.
no snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-fail
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-success
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-success
Send a trap when a wireless client station disassociates from the AP.
no snmp-server trap wireless-disassociation-success
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-fail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-fail
Send a trap when a wireless client station fails to reassociate with the AP.
no snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-fail
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-success
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-success
Send a trap when a wireless client station reassociates with the AP.
2-29
Page 58

CLI commands
no snmp-server trap wireless-reassociation-success
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap syslog-matches
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap syslog-matches
Send a trap when syslog messages matches a specified regular expression.
no snmp-server trap syslog-matches
Do not send this trap.
snmp-server trap syslog-matches regex
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap syslog-matches regex <regex>
Sets the regular expression used to match the syslog messages.
snmp-server trap syslog-severity level
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap syslog-severity level (debug | info | notice | warning | error
| critical | alert | emergency)
Set the severity level of syslog messages that will trigger a trap.
snmp-server trap network-trace
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap network-trace
Send a trap when a network trace is started or stopped.
no snmp-server trap network-trace
Do not send this trap.
firmware-update automatic
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
firmware-update automatic
Enables scheduled firmware upgrades.
no firmware-update automatic
Disables scheduled firmware upgrade.
The AP can automatically retrieve and install firmware from a local or remote URL at preset
times. By placing AP firmware on a web or ftp server, you can automate the update process for
multiple units.
When the update process is triggered the AP retrieves the first 2K of the firmware file to determine
if it is different from the active version. If different, the entire firmware file is then downloaded
and installed.
2-30
Page 59

CLI commands
(Different means older or newer. This enables you to return to a previous firmware version if
required).
Configuration settings are preserved during the update unless stated otherwise in the release
notes for the firmware. However, all active connections will be terminated. Users will have to log
in again after the AP restarts
firmware-update start
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
firmware-update start
Upload the firmware based on a specified URI. This URI can be set with the command: firmwareupdate uri.
firmware-update time
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
firmware-update time <time>
Sets the time of day the scheduled firmware upgrade will take place.
Parameters
<time> Time as hh:mm:ss. For example: 15:44:00.
firmware-update uri
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
firmware-update uri <uri>
Sets the URI where the AP will retrieve new firmware.
no firmware-update uri
Clears the firmware URI.
firmware-update weekday
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
firmware-update weekday (everyday | monday | tuesday | wednesday | thursday |
friday | saturday | sunday)
Sets the day when the scheduled firmware upgrade will take place.
snmp-server trap firmware-update
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap firmware-update
Send a trap on firmware update.
no snmp-server trap firmware-update
Do not send a trap on firmware update.
2-31
Page 60

CLI commands
access-controller restrict location
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
access-controller restrict location (gateway | mac <mac address>)
Identifies the access controller the AP will communicate with.
Parameters
gateway Use the default gateway as the service controller.
mac Use the specified MAC address as the gateway.
<mac address> MAC address. Specify 6 pairs of hexadecimal numbers separated by
colons, with the values a to f in lowercase. For example: 00:00:00:0a:0f:01
service-sensor
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
service-sensor
Enables the service sensor. The service sensor polls a target device at present intervals. If the
device does not respond, the radio is shut off.
no service-sensor
Disables the service sensor.
service-sensor
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
service-sensor (gateway | address<ip address>)
Sets the target device the service sensor will poll. This can be the default gateway or a specific IP
address.
no service-sensor
Disables the service sensor.
Parameters
gateway The service sensor will poll the default gateway.
address The service sensor will poll another device.
<ip address> IP address of the other device. For example: 192.168.10.10
service-sensor poll
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
service-sensor poll <seconds>
Sets the poll frequency.
Parameters
<seconds> Poll frequency. Range: 1 - 3600 seconds.
2-32
Page 61

service-sensor retry
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
service-sensor retry <retries>
CLI commands
Specify how many retries the service sensor will attempt when polling the target device.
When the retry limit is reached, the radio on the AP is turned off.
Parameters
<retires> Number of retries. Range: 0 - 100.
service-sensor timeout
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
service-sensor timeout <seconds>
Sets how long the service sensor will wait for a response to a poll before timing out.
Parameters
<seconds> Length of timeout. Range: 1 - 5 seconds.
ip name-server
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip name-server <primary> [<secondary>] [<third>]
Sets the primary and secondary DNS servers overriding dynamically assigned ones.
Parameters
<primary> IP address of the primary DNS server.
<secondary> IP address of the secondary DNS server.
<third> IP address of the third DNS server.
ip name-server cache
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip name-server cache
Enables the DNS cache.
no ip name-server cache
Disables the DNS cache.
Once a host name has been successfully resolved to an IP address by a remote DNS server, it is
stored in the cache. This speeds up network performance, as the remote DNS server now does not
have to be queried for subsequent requests for this host.
The entry stays in the cache until:
an error occurs when connecting to the remote host
the time to live (TTL) of the DNS request expires
the AP is restarted.
2-33
Page 62
CLI commands
ip name-server dynamic
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip name-server dynamic
Enables dynamic assignment of DNS servers.
no ip name-server dynamic
Disables dynamic DNS assignment.
ip name-server interception
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip name-server interception
Intercepts all DNS requests from users and relays them to configured servers.
no ip name-server interception
Process DNS requests addressed to this device only.
ip name-server switch-on-servfail
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip name-server switch-on-servfail
Switch to next server when server failure is received.
no ip name-server switch-on-servfail
Do not switch to next server when server failure is received.
ip name-server switch-over
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip name-server switch-over
Switch over to primary when active.
no ip name-server switch-over
Do not switch over to primary when active.
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap
Send a trap when a rogue access point is detected.
no snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap
Do not send this trap.
2-34
Page 63

snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap interval
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snmp-server trap unauthorized-ap interval <number>
CLI commands
If set to 0, then traps are only sent when a rogue access point is detected. If set to 0, the entire list
of rogue access points is sent each time the interval expires.
wireless-scan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless-scan
Enables wireless neighborhood scanning.
no wireless-scan
Disables wireless neighborhood scanning.
wireless-scan period
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless-scan period <seconds>
Specifies the interval between wireless neighborhood scans.
Parameters
<seconds> Scanning interval. Range: 10 - 600 seconds.
wireless-scan url
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless-scan url <location>
Sets the URL of the file that contains a list of all authorized access points.
no wireless-scan url
Deletes the URL of the file that contains a list of all authorized access points.
The format of this file is XML. Each entry in the file is composed of two items: MAC address and
SSID. Each entry should appear on a new line.
For example:
00:00:00:07:f5:11 "AP_1"
00:00:00:07:f5:23 "AP_2"
00:00:00:07:f5:12 "AP_3"
access controller shared secret
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
access controller shared secret <secret>
Sets the shared secret used to communicate with the service controller.
no access controller shared secret
Sets the shared secret used to communicate with the access controller.
2-35
Page 64

CLI commands
The service controller will only accept authentication/location-aware information from satellites
that have a matching shared secret to its own.
radius-server profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
radius-server profile <name>
Creates a new RADIUS profile or switches to the RADIUS context with the specified profile name.
no radius-server profile <name>
Deletes the specified RADIUS profile.
ip-qos profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip-qos profile <name>
Creates a new IP QoS profile or switches to the IP QoS context with the specified profile name.
no ip-qos profile <name>
Deletes the specified IP QoS profile.
dot11 igmp snooping-helper
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 igmp snooping-helper
Enables IGMP snooping helpers which ensure that the AP correctly delivers multicast packets to
roaming client stations that are part of a multicast group.
no dot11 igmp snooping-helper
Disable IGMP snooping helpers.
discovery protocol
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
discovery protocol
Enables broadcast of device information for interoperability with CDP-enabled networking
hardware.
no discovery protocol
Disable broadcast of device information.
discovery protocol device-id
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
discovery protocol device-id <name>
Overwrite the device-id field of information packets (the AP serial number is not used).
no discovery protocol device-id
2-36
Do not overwrite the device-id field of information packets (use the AP serial number).
Page 65

CLI commands
bridge priority
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
bridge priority <number>
Sets the bridge priority for the spanning tree.
The spanning tree uses the bridge ID to elect the root bridge and the designated bridges. The
bridge ID is built with the MAC address of the bridge and the bridge priority. The first 2 most
significant bytes are the bridge priority and the next 6 bytes are the MAC address. To control
which bridge will become the root bridge, you can configure the bridge priority parameter on the
bridges. The root will be the bridge with the lowest bridge ID. The Bridge priority has a valid range
of 0 to 0xFFFF. The default value is the middle value: 0x8000.
bridge protocol ieee
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
bridge protocol ieee
Enable the bridge spanning tree protocol to prevent undesirable loops from occurring in the
network that may result in decreased throughput.
no bridge protocol ieee
Disable the bridge spanning tree protocol.
bridge protocol ieee vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
bridge protocol ieee vlan
Enable the bridge spanning tree protocol for VLANs.
no bridge protocol ieee vlan
Disable the bridge spanning tree protocol for VLANs.
ip route gateway
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip route gateway<destination>/<mask> <gateway> <[metric]>
Adds a static route.
no ip route gateway <destination>/<mask> <gateway> <[metric]>
Removes the specified static route.
Parameters
<destination> Traffic addressed to this IP address will be routed.
<mask> Indicates the number of bits in the destination address that is checked for a
match.
<gateway> Indicates the IP address of the gateway the AP will forward routed traffic
to. The gateway address must be on the same subnet as one of the
available interfaces (Internet port or LAN port).
<metrix> Indicates the priority of a route. If two routes exist for a destination
address then the AP chooses the one with the lower metric.
2-37
Page 66
CLI commands
dot1x reauth
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot1x reauth
Enable this option to force 802.1X client stations to reauthenticate.
no dot1x reauth
Disables 802.1X reauthentication.
dot1x reauth period
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot1x reauth period (15m | 30m | 1h | 2h | 4h | 8h | 12h)
Sets the 802.1X reauthentication interval. Client stations must reauthenticate when this interval
expires.
dot1x reauth terminate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot1x reauth terminate
Enable this option to allow client stations to remain connected during re-authentication. Client
traffic is blocked only when re-authentication fails.
no dot1x reauth terminate
Disabled this option to block client traffic during re-authentication and only activate traffic again
if authentication succeeds.
dot1x supplicant timeout
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
802.1x supplicant time-out <seconds>
Sets the 802.1X supplicant time-out.
Parameters
<seconds> time-out in seconds.
dynamic key
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dynamic key
Enables dynamic key support for 802.1X and WPA.
no dynamic key
Disables dynamic key support for 802.1X and WPA.
2-38
Page 67

CLI commands
dynamic key interval
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dynamic key interval (5m | 10m | 15m | 30m | 1h | 2h | 4h | 8h | 12h)
Specifies how often (in minutes or hours) that the group (broadcast) key is changed for 802.1X
and WPA.
add wireless ip-qos profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
add wireless ip-qos profile <name>
Adds the specified profile to the list of IP QoS profiles in effect for the wireless links.
<profile-name> Name of an existing IP QoS profile.
delete wireless ip-qos profile all
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
delete wireless ip-qos profile all
Clears the list of IP QoS profiles currently in effect for the wireless links.
delete wireless ip-qos profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
delete wireless ip-qos profile <name>
Removes the specified profile from the list of IP QoS profiles in effect for the wireless links.
<profile-name> Name of an existing IP QoS profile currently in the profile list for the
wireless links.
wireless link qos
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless link qos (disabled | 802.1p | wme | very-high | high | normal | low |
tos | diffsrv)
Sets the wireless link QoS policy.
sensor discovery mode
Supported on: MSM320 MSM335
sensor discovery mode (id | ip)
Sets the method the AP will use to communicate with the RF Manager Server.
Parameters
id Connect using the Server ID of the RF Manager Server.
ip Connect using the IP address or hostname of the RF Manager Server.
Description
For these methods to work, the following must be true:
2-39
Page 68

CLI commands
The AP must be able to reach the RF Manager Server via a network connected to port 1 or
port 2. For example, you should be able to ping the RF Manager Server IP address from the
AP.
If there are any firewalls between the AP and the RF Manager Server, then TCP and UDP ports
3851 must be open bidirectionally.
If using the hostname option, an entry must be created on the network DNS server that points
to the IP address of the RF Manager Server.
If using the Server ID option, support for multicast traffic must be enabled on all routers and
switches connected between the AP and the RF Manager Server.
sensor network detector
Supported on: MSM320 MSM335
sensor network detector
Enable the Network Detector.
no sensor network detector
Disable the Network Detector.
sensor server id
Supported on: MSM320 MSM335
sensor server id <id>
Sets the server ID of the the RF Manager Server to connect to.
Parameters
ID Specify the Server ID of the RF Manager Server to connect to. Set the
Server ID to 0 to have the AP send a discovery request to all active RF
Manager Servers. The AP will connect to the first server that responds to
the discovery request.
sensor server name
Supported on: MSM320 MSM335
sensor server name <name>
Sets the IP address or hostname of the the RF Manager Server to connect to.
Parameters
Name Specify the IP address of the the RF Manager Server or its hostname. If a
config-version
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
config-version <string>
hostname is specified, the AP must be able to resolve it via DNS, that is, an
entry must be created on the network DNS server that points to the IP
address of the RF Manager Server.
2-40
Sets a string to identify the user configuration version.
Page 69

Port-2 interface context
Path: View > Enable > Config > Port-2 interface
This context provides commands for configuring Port-2.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
CLI commands
Switches to parent context.
duplex
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
duplex (auto | half | full)
Sets the duplex mode on Port-2.
Parameters
auto Lets the AP automatically set duplex mode based on the type of equipment
half Forces the port to operate in half duplex mode.
full Forces the port to operate in full duplex mode.
it is connected to.
speed
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
speed (auto | 10 | 100)
Sets the speed of Port-2.
Parameters
auto Lets the AP automatically set port speed based on the type of equipment it
100 Forces the port to operate at 100 mbps.
10 Forces the port to operate at 10 mbps.
is connected to.
vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan <id>
Sets the default VLAN ID. Range: 1 - 4094. All outgoing traffic that does not have a VLAN already
assigned to it, is sent on this VLAN.
no vlan
Deletes the default VLAN ID.
2-41
Page 70

CLI commands
vlan compatibility mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan compatibility mode
When this option is enabled, the AP sends all management traffic AND all untagged traffic on both
the default VLAN and untagged.
no vlan compatibility mode
Disable VLAN and untagged compatibility mode.
vlan-management filter
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan-management filter
Restricts the default VLAN to carry management traffic only.
no vlan-management filter
Does not restrict the default VLAN to carry management traffic only.
Management traffic includes:
all traffic that is exchanged by the AP and the access controller
all communications with RADIUS servers
HTTPS sessions to the management tool
SNMP traffic
interface vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface vlan <id>[-<id2>]
Switches to the specified VLAN interface or create a new VLAN interface with the specified ID.
no interface vlan <id>[-<id2>]
Deletes the specified VLAN.
Parameters
<id> VLAN ID. Range: 1 - 4094.
<id2> VLAN ID. When specified, this is the last value in a range.
2-42
Page 71

Port-1 interface context
Path: View > Enable > Config > Port-1 interface
This context provides commands for configuring Port-1.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
CLI commands
Switches to parent context.
duplex
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
duplex (auto | half | full)
Sets the duplex mode on Port-1.
Parameters
auto Lets the AP automatically set duplex mode based on the type of equipment
half Forces the port to operate in half duplex mode.
full Forces the port to operate in full duplex mode.
it is connected to.
speed
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
speed (auto | 10 | 100)
Sets the speed of Port-1.
Parameters
auto Lets the AP automatically set port speed based on the type of equipment it
100 Forces the port to operate at 100 mbps.
10 Forces the port to operate at 10 mbps.
is connected to.
vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan <id>
Sets the default VLAN ID. Range: 1 - 4094. All outgoing traffic that does not have a VLAN already
assigned to it, is sent on this VLAN.
no vlan
Deletes the default VLAN ID.
2-43
Page 72

CLI commands
vlan compatibility mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan compatibility mode
When this option is enabled, the AP sends all management traffic AND all untagged traffic on both
the default VLAN and untagged.
no vlan compatibility mode
Disable VLAN and untagged compatibility mode.
vlan-management filter
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan-management filter
Restricts the default VLAN to carry management traffic only.
no vlan-management filter
Does not restrict the default VLAN to carry management traffic only.
Management traffic includes:
all traffic that is exchanged by the AP and the access controller
all communications with RADIUS servers
HTTPS sessions to the management tool
SNMP traffic
interface vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface vlan <id>[-<id2>]
Switches to the specified VLAN interface or create a new VLAN interface with the specified ID.
no interface vlan <id>[-<id2>]
Deletes the specified VLAN interface.
Parameters
<id> VLAN ID. Range: 1 - 4094.
<id2> VLAN ID. When specified, is the last value in a range.
2-44
Page 73

CLI commands
WAN IP interface context
Path: View > Enable > Config > WAN IP interface
This context provides commands for configuring various IP-networking related settings.
pppoe client user
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
pppoe client user <username> <password>
Sets the PPPoE username and password.
no pppoe client user
Deletes the PPPoE username.
Parameters
<username> The username assigned to you by your ISP. The AP will use this username
to log on to your ISP when establishing a PPPoE connection.
<password> The password assigned to you by your ISP. The AP will use this username
to log on to your ISP when establishing a PPPoE connection.
ip address mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip address mode (dhcp | pppoe | static)
Sets the IP addressing mode for Port-2.
Parameters
dhcp Dynamic host configuration protocol. The DHCP server will automatically
pppoe Point-to-point protocol over Ethernet. The PPPoE server will automatically
static This option enables you to manually assign an IP address to the AP.
assign an address to the AP, which functions as a DHCP client.
assign an IP address to the AP. You need to supply a username and
password so the AP can log on.
ip address
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip address <ip address>/<mask>
Sets a static IP address for the port.
Parameters
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
ip default-gateway
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip default-gateway <ip address>
Sets the IP address of the default gateway.
2-45
Page 74

CLI commands
no ip default-gateway
Deletes the default gateway IP address.
Parameters
<address> IP address.
ip address dhcp client-id
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip address dhcp client-id <id>
Specifies an ID to identify the AP to a DHCP server. This parameter is not required by all ISPs.
no ip address dhcp client-id
Deletes the specified DHCP client id.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
Switches to parent context.
pppoe auto-reconnect
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
pppoe auto-reconnect
The AP will automatically attempt to reconnect if the connection is lost.
no pppoe auto-reconnect
The AP will not automatically attempt to reconnect if the connection is lost.
pppoe mru
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
pppoe mru <bytes>
2-46
Specifies the maximum receive unit.
Changes to this parameter should only be made according to the recommendations of your ISP.
Incorrectly setting this parameter can reduce the throughput of your Internet connection.
Parameters
<bytes> Maximum size (in bytes) of a PPPoE packet when receiving. Range: 500 -
1500 bytes.
pppoe mtu
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
pppoe mtu <bytes>
Specifies the maximum transmit unit.
Changes to this parameter should only be made according to the recommendations of your ISP.
Incorrectly setting this parameter can reduce the throughput of your Internet connection.
Page 75

CLI commands
Parameters
<bytes> Maximum size (in bytes) of a PPPoE packet when transmitting. Range: 500
- 1500 bytes.
pppoe unnumbered
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
pppoe unnumbered
Enable unnumbered mode.
no pppoe unnumbered
Disable unnumbered mode.
This feature is useful when the AP is connected to the Internet and NAT is not being used. Instead
of assigning two IP addresses to the AP, one to the Internet port and one to the LAN port, both
ports can share a single IP address. This is especially useful when a limited number of IP
addresses are available to you.
2-47
Page 76

CLI commands
Wireless context
Path: View > Enable > Config > Wireless
This context provides commands for configuring the wireless network.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
Switches to parent context.
radio active
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
radio active
Enables the radio.
no radio active
Disables the radio.
rts threshold
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
rts threshold <value>
Sets the RTS threshold.
no rts threshold
Deletes the RTS threshold value.
Parameters
< value> Threshold value in the range 128 and 1540.
Description
Use this parameter to control collisions on the link that can reduce throughput. If the Status
Wireless page on the management tool shows increasing values for Tx multiple retry frames or Tx
single retry frames, you should adjust this value until the errors clear up. Start with a value of 1024
and then decrease to 512 until errors are reduced or eliminated.
Using a small value for RTS threshold can affect throughput.
2-48
If a packet is larger than the threshold, the AP will hold it and issue a request to send (RTS)
message to the client station. Only when the client station replies with a clear to send (CTS)
message will the AP send the packet. Packets smaller than the threshold are transmitted without
this handshake.
distance
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
distance (small | medium | large)
Sets the distance between access points.
Page 77

CLI commands
Use this parameter to adjust the receiver sensitivity of the AP. This parameter should only be
changed if:
you have more than one wireless access point installed in your location
you are experiencing throughput problems
In all other cases, use the default setting of Large.
If you have installed multiple APs, reducing the receiver sensitivity of the AP from its maximum
will help to reduce the amount of crosstalk between the wireless stations to better support
roaming clients. By reducing the receiver sensitivity, client stations will be more likely to connect
with the nearest access point.
dot11
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 <mode> <frequency>
Sets the wireless mode and the frequency the AP will operate at.
Parameters
<mode> Sets the transmission speed and frequency band. The available options are
a: Selects 802.11a providing 54 Mbps in the 5 GHz frequency band.
b: Selects 802.11b providing 11 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
determined by the wireless card installed in the AP, and may include:
g: Selects 802.11g providing 54 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
bg: Selects 802.11b + 802.11g providing 11 and 54 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
n: Selects 802.11n.
an: Selects 802.11n + 802.11a, on the 5Ghz frequency band.
gn: Selects 802.11n + 802.11g, on the 2.4Ghz frequency band.
bgn: Selects 802.11n + 802.11g + 802.11b, on the 2.4Ghz frequency band.
<frequency> Sets the operating frequency by specifying a number in GHz or by
specifying a channel number. The frequencies that are available are
determined by the radio installed in the AP and the regulations that apply
in your country.
For optimum performance when operating in 802.11b or 802.11g modes,
choose a frequency that differs from other wireless access points operating
in neighboring cells by at least 25 MHz.
If operating in 802.11a mode, all channels are non-overlapping.
transmit power
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
transmit power (DB | max)
Sets the maximum transmission power of the wireless radio.
Parameters
<db> Power is specified in steps of 1dBm. The maximum setting is 18 dBm.
2-49
Page 78

CLI commands
Note: The actual transmit power used may less than the value specified. The AP determines the
power to used based on the settings you made for regulatory domain, wireless mode, and
operating frequency.
antenna bidirectionnal
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
antenna bidirectionnal (diversity | main | auxiliary)
Sets the antenna to transmit and receive on. Select diversity to transmit and receive on both
antennas.
Parameters
diversity In this mode both antennas are used to transmit and receive. The AP
supports both transmit and receive diversity.
main Transmit and receive on the main antenna only.
aux Transmit and receive on the aux antenna only.
antenna gain
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
antenna gain <number>
Used only for Radar detection, records gain (in 5GHz band) of external antenna installed on
device. Does not affect output power.
autochannel skip
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
autochannel skip <chan>
Adds the specified channel to the list of channels that are not allowed to be selected by the Auto
Channel algorithm.
no autochannel skip <chan>
Removes the specified channel to the list of channels that are not allowed to be selected by the
Auto Channel algorithm.
beacon interval
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
beacon interval <value>
Sets the beacon interval.
Parameters
< value> Beacon interval value in the range 20 and 500 time units (TU) (1 TU =
1024us).
dot11 automatic frequency
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 automatic frequency
Enable this option to have the AP automatically determine the best operating frequency.
2-50
Page 79

no dot11 automatic frequency
CLI commands
Disable automatic frequency selection.
dot11 automatic frequency period
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 automatic frequency period (disabled | 1h | 2h | 4h | 8h | 12h | 24h)
Specify how often the frequency setting is re-evaluated when automatic frequency selection is
enabled.
dot11 automatic frequency time
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 automatic frequency time <time>
Specify when the channel should be re-evaluated.
dot11 automatic transmit-power
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 automatic transmit-power
Enables automatic transmit power selection.
no dot11 automatic transmit-power
Disables automatic transmit power selection.
dot11 automatic transmit-power period
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 automatic transmit-power period (1h | 2h | 4h | 8h | 12h | 24h)
Sets the interval at which the transmit power setting is re-evaluated when automatic power
selection is enabled.
multicast rate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
multicast rate (1 | 2 | 5.5 | 6 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 54)
Sets the transmit rate for multicast traffic.
This is a fixed rate, which means that if a station is too far away to receive traffic at this rate, then
the multicast will not be seen by the station. By rasing the multicast rate you can increase overall
throughput significantly.
station distance
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
station distance (0km | 5km | 10km | 15km | 20km | 25km | 30km | 35km)
Fine tunes internal timeout settings to account for the distance that wireless links span. For
normal operation, the AP is optimized for links of less than 1 km.
2-51
Page 80

CLI commands
This is a global setting that is useful when creating wireless links to remote sites. However, it also
applies to all wireless connection made with the radio, not just for wireless links. Therefore, if you
are also using the radio to serve local wireless client stations, adjusting this setting may lower the
performance for clients with marginal signal strength or when interference is present.
(Essentially, it means that if a frame needs to be retransmitted it will take longer before the actual
retransmit takes place.)
dot11 mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot11 mode (monitor | ap+wds | ap-only | wds-only | sensor)
Sets the operating mode for the radio.
spectralink view
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
spectralink view
Enable the use of spectralink view.
no spectralink view
Disable the use of spectralink view.
dot11n channel extension
Supported on: MSM410 MSM422
dot11n channel extension (above | below)
Select the 802.11n channel extension. Applicable only in the 2.4 GHz band with a 40 MHz channel
width.
dot11n channel width
Supported on: MSM410 MSM422
dot11n channel width (40 | 20 | auto)
2-52
Select the 802.11n channel width.
dot11n guard interval
Supported on: MSM410 MSM422
dot11n guard interval (short | long)
Select the 802.11n guard interval.
dot11n multicast rate
Supported on: MSM410 MSM422
dot11n multicast rate <rate>
Set the multicast rate for use with 802.11n networks.
Page 81

bandwidth
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
bandwidth
CLI commands
Enables bandwidth control.
no bandwidth
Disables bandwidth control.
bandwidth max
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
bandwidth max <rate>
Set the maximum data rate on the wireless port in kbps.
Parameters
<rate> Maximum data rate. Range: 50 - 500000 kbps.
2-53
Page 82

CLI commands
Virtual AP context
Path: View > Enable > Config > Virtual AP
This context provides commands for configuring Virtual AP profiles (VAP (VSC)s).
By default one profile exists with the name "". This is the default profile and cannot be deleted.
The following example shows how to add a new VAP (VSC) with egress mapped to an existing
VLAN named "hongkong":
CLI(config)# virtual ap newap
CLI(virtual-ap)# access control
CLI(virtual-ap)# egress any vlan hongkong
CLI(virtual-ap)# ssid name "newap"
CLI(virtual-ap)# ingress ssid
CLI(virtual-ap)# bandwidth high
CLI(virtual-ap)# end
CLI(config)#
virtual ap name
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
virtual ap name <name>
Change the VAP (VSC) name.
ingress interface
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ingress interface (wireless | wireless) <name>
Sets the specified interface as the ingress interface traffic will be accepted on.
no ingress interface (wireless | wireless) <name>
Removes the specified interface as an ingress interface.
guest-mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
guest-mode
Enables broadcast of the wireless network name (SSID).
no guest-mode
Disables broadcast of the wireless network name (SSID).
2-54
max-association
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
max-association <stations>
Sets the maximum number of clients stations that can associate with this VAP (VSC).
<stations> Number of client stations. Range: 1 - 255.
Page 83

ssid name
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ssid name <name>
Specifies the WLAN name (SSID) for the profile.
vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan <id>
Assigns a VLAN ID to this VAP (VSC).
no vlan
CLI commands
Deletes the VLAN ID for this VAP (VSC).
Parameters
<id> VLAN ID. Range: 1 - 4094.
encryption key 1
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
encryption key <key> <value>
Sets WEP key 1.
no encryption key <key>
Deletes WEP key 1.
Parameters
<key> WEP key number. Range: 1 - 4. Keys 2 to 4 are only supported on the first
<value> Key value. The number of characters you specify for a key determines the
WLAN profile.
level of encryption the AP will provide.
For 40-bit encryption, specify 5 ASCII characters or 10 HEX digits.
For 128-bit encryption, specify 13 ASCII characters or 26 HEX digits.
encryption key format
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
encryption key format (hex | ascii)
Specify the WEP key format.
Parameters
hex Hex keys should only include the following digits: 0-9, a-f, A-F
ascii ASCII keys are much weaker than carefully chosen hex keys. You can
include ASCII characters between 32 and 126, inclusive, in the key.
However, note that not all client stations support non-alphanumeric
characters such as spaces, punctuation, or special symbols in the key.
2-55
Page 84

CLI commands
transmit key
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
transmit key <key number>
Sets the key the AP will use to encrypt transmitted data. All four keys are used to decrypt received
data.
Parameters
<key number> Transmit key number. Range: 1 -4.
authentication server access controller
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
authentication server access controller
Use the access controller to authenticate 802.1X or WPA logins.
authentication server accounting
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
authentication server accounting
Enables RADIUS accounting for this VAP (VSC).
no authentication server accounting
Disables RADIUS accounting for this VAP (VSC).
authentication server accounting radius profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
authentication server accounting radius profile <name>
Sets RADIUS accounting to use the specified RADIUS profile.
no authentication server accounting radius profile
Removes accounting support for 802.1x.
authentication server radius
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
authentication server radius <name>
Sets the RADIUS profile to use for 802.1X or WPA authentication.
dot1x authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dot1x authentication (local | radius | active-directory)
2-56
Sets the authentication for 802.1X and WPA.
Page 85

CLI commands
wpa-psk
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wpa-psk <key>
Sets the WPA preshared key.
no wpa-psk
Deletes the WPA preshared key.
Parameters
<key> Specify a key that is between 8 and 63 alphanumeric characters in length. It
Description
The AP uses the key you specify to generate the TKIP keys that encrypt the wireless data stream.
Since this is a static key, it is not as secure as the RADIUS option.
is recommended that the preshared key be at least 20 characters long, and
be a mix of letters and numbers. The double quote character should not be
used
authentication server accounting radius stationid case
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
authentication server accounting radius stationid case (uppercase | lowercase)
Specifies the case applied to the station delimiter if it is a letter.
authentication server accounting radius stationid delimiter
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
authentication server accounting radius stationid delimiter (null | colon |
dash | dot | space | comma | under)
Specifies the one-character delimiter that will be used to format both the calling station ID and the
called station ID attributes in RADIUS packets.
wireless filters
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless filters
Enables the wireless security filters which only allow traffic to flow between the AP and a specific
upstream device (such as a service controller).
no wireless filters
Do not limit traffic flow between the AP and an upstream device.
This prevents wireless users from accessing resources on the backbone LAN that interconnects
the AP and the upstream device.
wireless filters mac
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless filters mac <mac>
Sets the MAC address of the upstream device to send traffic to.
2-57
Page 86
CLI commands
no wireless filters mac <mac>
Deletes the MAC address of the upstream device to send traffic to.
wireless filters rule input
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless filters rule input <rule>
Adds a custom filter definition for incoming wireless traffic.
Use this command to define custom security filters for incoming wireless traffic. Filters are
specified using standard pcap syntax (http://www.tcpdump.org/tcpdump_man.html) with the
addition of a few -specific placeholders. These placeholders can be used to refer to specific MAC
addresses and are expanded by the AP when the filter is activated. Once expanded, the filter must
respect the pcap syntax. The pcap syntax is documented in the tcpdump man page:
Placeholders
%a - MAC address of the access controller.
%b - MAC address of the bridge.
%g - Mac address of the default gateway assigned to the AP.
%w - MAC address of wireless port.
wireless filters rule output
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless filters rule output <rule>
Adds a custom filter definition for outgoing wireless traffic.
Use this command to define custom security filters for outgoing wireless traffic. Filters are
specified using standard pcap syntax (http://www.tcpdump.org/tcpdump_man.html) with the
addition of a few -specific placeholders. These placeholders can be used to refer to specific MAC
addresses and are expanded by the AP when the filter is activated. Once expanded, the filter must
respect the pcap syntax. The pcap syntax is documented in the tcpdump man page:
Placeholders
%a - MAC address of the access controller.
%b - MAC address of the bridge.
%g - Mac address of the default gateway assigned to the AP.
%w - MAC address of wireless port.
wireless filters type
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wireless filters type (mac | gateway | rules)
2-58
Sets the type of wireless security filter to use.
Parameters
mac Traffic is forwarded to an upstream device with a specific MAC address.
Wireless security filters use the default definitions.
gateway Traffic is forwarded to the default gateway assigned to the AP. Wireless
security filters use the default definitions.
Page 87

CLI commands
custom
Lets you define custom security filters and address for the upstream
device.
Description
The AP features an intelligent bridge which can apply security filters to safeguard the flow of
wireless traffic. The filters limit both incoming and outgoing traffic as defined below, and force
the AP to exchange traffic with a specific upstream device. If the AP is configured to use the
services of a access controller, then the default security filters are automatically enabled and all
traffic is sent to the access controller.
Default filters for incoming wireless traffic
Applies to traffic sent from wireless client stations to the AP.
Accepted
Any IP traffic addressed to the access controller.
PPPoE traffic (The PPPoe server must be the upstream device.)
IP broadcast packets, except NetBIOS
Certain address management protocols (ARP, DHCP) regardless of their source address.
Any traffic addressed to the AP, including 802.1x.
Blocked
All other traffic is blocked. This includes NetBIOS traffic regardless of its source/destination
address. TTPS traffic not addressed to the AP (or upstream device) is also blocked, which
means wireless client stations cannot access the management tool on other products.
Default filters for outgoing wireless traffic
Applies to traffic sent from the AP to wireless client stations.
Accepted
Any IP traffic coming from the upstream device, except NetBIOS packets.
PPPoE traffic from the upstream device.
IP broadcast packets, except NetBIOS
ARP and DHCP Offer and ACK packets.
Any traffic coming from the AP itself, including 802.1x.
Blocked
All other traffic is blocked. This includes NetBIOS traffic regardless of its source/destination
address.
mac-filters local
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac-filters local
Enables the MAC filter list.
no mac-filters local
Disables the MAC filter list.
2-59
Page 88

CLI commands
mac-filters
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac-filters <address>
Adds an address to the MAC filter list.
no mac-filters <address>
Remove the specified address from the MAC filter list.
Parameters
<address> MAC address. Specify 6 pairs of hexadecimal numbers separated by
colons, with the values a to f in lowercase. For example: 00:00:00:0a:0f:01
Description
This feature enables you to control access to the AP based on the MAC address of client stations.
You can either block access or allow access, depending on your requirements. When both this
option and the MAC-based authentication options are enabled, the following applies: if a user
MAC address does not appear in the MAC filtering list, then MAC-based authentication takes place
for that user.
mac-filters mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac-filters mode (allow | block)
Either allow or block access to the wireless network for client stations whose addresses appear in
the MAC filter list.
mac authentication accounting
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac authentication accounting
Enables RADIUS accounting for this VAP (VSC).
no mac authentication accounting
Disables RADIUS accounting for this VAP (VSC).
mac authentication accounting radius profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac authentication accounting radius profile <name>
Sets RADIUS accounting to use the specified RADIUS profile.
no mac authentication accounting radius profile
Disables accounting support for MAC authentication.
mandatory authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mandatory authentication
MAC-based authentication is mandatory.
2-60
Page 89

no mandatory authentication
CLI commands
MAC-based authentication is not mandatory.
mac authentication radius profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac authentication radius profile <radiusname>
Specifies the name of the RADIUS profile to use for MAC-based authentication.
no mac authentication radius profile
Do not use a RADIUS profile.
mac authentication radius stationid case
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac authentication radius stationid case (uppercase | lowercase)
Specifies the case applied to the station delimiter if it is a letter.
mac authentication radius stationid delimiter
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac authentication radius stationid delimiter (null | colon | dash | dot | space
| comma | under)
Specifies the one-character delimiter that will be used to format both the calling station ID and the
called station ID attributes in RADIUS packets.
mac authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mac authentication
Enables support for MAC-based authentication.
no mac authentication
Disable support for MAC-based authentication.
add ip filter
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
add ip filter <ip address>/<mask>
Adds an IP filter to the list of destination addresses that traffic will be accepted for. All other
traffic will be blocked.
If the list is empty, then all wireless-to-wired LAN traffic is permitted.
Where:
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
2-61
Page 90
CLI commands
delete ip filter
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
delete ip filter <ip address>/<mask>
Deletes the specified address from the IP filter list.
If the list is empty, then all wireless-to-wired LAN traffic is permitted.
Where:
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
delete ip filter all
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
delete ip filter all
Deletes all addresses from the IP filter list.
ip filters
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip filters
Activates the IP filter which enables you to block wireless-to-wired LAN traffic on this profile
based on its destination address.
no ip filters
Disables the IP filter for this profile.
active
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
active
Enable this VAP (VSC).
no active
Disable this VAP (VSC).
beacon dtim count
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
beacon dtim count <number>
2-62
Defines the DTIM period in the beacon.
Client stations use the DTIM to wake up from low-power mode to receive multicast traffic. The AP
transmits a beacon every 100 ms. The DTIM counts down with each beacon that is sent, therefore
if the DTIM is set to 5, then client stations in low-power mode will wake up every 500 ms (.5
second) to receive multicast traffic.
Page 91

beacon transmit power
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
beacon transmit power
CLI commands
Advertise the current transmit power setting in the beacon.
no beacon transmit power
Do not advertise the current transmit power setting in the beacon.
data rate
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
data rate (a | b | g | bg | n) <rate>
Enable the given data rate for a particular PHY type.
no data rate (a | b | g | bg | n) <rate>
Disable the given data rate for a particular PHY type.
public forwarding
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
public forwarding (any | 802.1x | none | ipv6)
Enables support for traffic exchange between wireless client stations.
fast authentication
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
fast authentication
Enables WPA2 opportunistic key caching.
no fast authentication
Disables WPA2 opportunistic key caching.
layer3 mobility
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
layer3 mobility
Enables Layer 3 mobility.
no layer3 mobility
Disables Layer 3 mobility.
add ip-qos profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
add ip-qos profile <name>
Adds the specified profile to the list of IP QoS profiles in effect for this VAP (VSC).
<profile-name> Name of an existing IP QoS profile.
2-63
Page 92

CLI commands
delete ip-qos profile all
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
delete ip-qos profile all
Clears the list of IP QoS profiles currently in effect for this VAP (VSC).
delete ip-qos profile
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
delete ip-qos profile <name>
Removes the specified profile from the list of IP QoS profiles in effect for this VAP (VSC).
<profile-name> Name of an existing IP QoS profile currently in the profile list for this VAP
(VSC).
qos
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
qos ( 802.1p | very-high | high | normal | low | diffsrv | tos | default | vap0
| vap1 | vap2 | vap3)
Sets the QoS level for this profile.
no qos
Disables QoS for this profile.
Four traffic queues are provided based on the WME standard. In order of priority, these queues
are:
1: Voice traffic
2: Video traffic
3: Best effort data traffic
4: Background data traffic
Each QoS priority mechanism maps traffic to one of the four traffic queues. Client stations that do
not support the QoS mechanism for the profile they are connected to are always assigned to queue
3.
2-64
Important: Traffic delivery is based on strict priority (per the WME standard). Therefore, if
excessive traffic is present on queues 1 or 2, it will reduce the flow of traffic on queues 3 and 4.
802.1p Traffic from 802.1p client stations is classified based on the VLAN priority
field present within the VLAN header. When this mechanism is selected,
the AP will advertise WME capabilities, enabling WME clients to associate
and take advantage of them. This setting has no effect on legacy clients.
Note: To support 802.1p, the wireless profile must have a VLAN assigned to
it, which means that client station traffic is forwarded onto the LAN port
only.
Page 93

CLI commands
vap0 to vap3
Allows a specific priority level to be specified for all traffic on a VAP (VSC)
profile. This enables client stations without a QoS mechanism to set traffic
priority by connecting to the appropriate SSID.
If you enable this priority mechanism, it takes precedence regardless of the
priority mechanism supported by associated client stations. For example,
if you set SSID-based low priority for a profile, all devices that connect to
the profile have their traffic set at this priority
Mapping to the traffic queues is as follows: vap0 or very-high=queue 1,
vap1 or high=queue 2, vap2 or normal=queue 3, vap3 or low=queue 4
diffsrv Differential services is a method for defining IP traffic priority on a per-hop
basis. The Differential Service bits are defined in RFC2474 and are
composed of the six most significant bits of the IP TOS field. These bits
define the class selector code points which the CN320 maps to the
appropriate traffic queue. (default setting)
tos The IP TOS (type of service) field can be used to mark prioritization or
special handling for IP packets.
upstream diffserv tagging
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
upstream diffserv tagging
Enables upstream diffserv tagging.
no upstream diffserv tagging
Disables upstream diffserv tagging.
wmm advertising
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
wmm advertising
Enables WMM information element advertising.
no wmm advertising
Disables WMM information element advertising.
location-aware group
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
location-aware group <name>
Sets the specified group name for the access point.
no location-aware group
Deletes the specified group name for the access point.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
Switches to parent context.
2-65
Page 94

CLI commands
security
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
security (none | wep | 802.1x [wep | static-wep] | wpa (psk | radius) [ v1 | v2
] )
Sets the current wireless security policy.
Parameters
none No wireless security.
wep This option enables support for wireless users with WEP client software.
802.1x This option enables support for wireless users with 802.1X client software.
wep Enables the use of dynamic WEP keys for all 802.1X sessions. Dynamic key
static-wep Support client stations using static WEP keys.
wpa This option enables support for wireless users with WPA client software.
psk Enables support for a preshared key:
radius The AP obtains the MPPE key from the RADIUS server. This is a dynamic
v1,v2 Specify which version of WPA to use. None will use both versions (mixed
The AP supports 802.1x client software that uses EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS,
EAP-SIM, and PEAP.
rotation occurs on key 1, which is the broadcast key. Key 0 is the pairwise
key. It is automatically generated by the AP.
key that changes each time the user logs in and is authenticated. The
MPPE key is used to generate the TKIP keys that encrypt the wireless data
stream.
mode).
2-66
Page 95

CLI commands
VLAN interface context
Path: View > Enable > Config > Port-2 interface > VLAN interface
View > Enable > Config > Port-1 interface > VLAN interface
View > Enable > Config > Local mesh > VLAN interface
This context provides commands for configuring Virtual LANs (VLANs). In this context, VLANs
can be added or edited.
For example, to create a new VLAN interface named "hongkong" on the LAN port with VLAN id 88,
do the following:
CLI(config)# interface lan
CLI(if-lan)# interface vlan 88
CLI(if-vlan)# vlan name hongkong
CLI(if-vlan)# ip address mode dhcp
CLI(if-vlan)# no nat
CLI(if-vlan)# end
CLI(if-lan)#
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
Switches to parent context.
ip address
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip address <ip address>/<mask>
Sets a static IP address for the VLAN.
Parameters
<address> IP address.
</mask> Subnet mask in CIDR format. Specifies the number of bits in the mask.
ip address mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
ip address mode (dhcp | static | none)
Sets the IP addressing mode for this VLAN interface.
Parameters
dhcp Dynamic host configuration protocol. The DHCP server will automatically
static This option enables you to manually assign an IP address to the AP.
none This VLAN does not have an IP address.
assign an address to the AP, which functions as a DHCP client.
2-67
Page 96

CLI commands
vlan name
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
vlan name <name>
Change the name of this VLAN interface.
2-68
Page 97

Local mesh context
Path: View > Enable > Config > Local mesh
This context provides commands for configuring local meshes.
end
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
end
CLI commands
Switches to parent context.
active
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
active
Activates the local mesh.
no active
Deactivates the local mesh.
interface
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface (radio1 | radio2 | radio3)
Select the interface to which this local mesh link applies.
no interface (radio1 | radio2 | radio3)
Select the interface to remove for this local mesh link.
local mesh name
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
local mesh name <name>
Renames the current local mesh link.
remote mac
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
remote mac <address>
Sets the MAC address of the remote access point.
no remote mac
Deletes the MAC address of the remote access point.
Parameters
<address> MAC address. Specify 6 pairs of hexadecimal numbers separated by
colons, with the values a to f in lowercase. For example: 00:00:00:0a:0f:01
2-69
Page 98

CLI commands
security
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
security
Enables wireless security.
no security
Disables wireless security.
security mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
security mode (wep | tkip | ccmp)
Set the security mode.
security psk
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
security psk <secret>
Sets the PSK secret.
no security psk
Clears the PSK secret.
security wep
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
security wep <key>
Sets the WEP key.
no security wep
Deletes the WEP key.
speed
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
2-70
speed (auto | 1 | 2 | 5.5 | 6 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 54)
Sets the speed of the wireless link in Mbps.
interface vlan
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
interface vlan <id>
Switches to the specified VLAN interface or create a new VLAN interface with the specified Id.
no interface vlan <number>
Removes the specified VLAN interface.
Parameters
<id> VLAN ID. Range: 1 - 4094.
Page 99

CLI commands
accept forced links
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
accept forced links
May accept master orders for selection.
no accept forced links
ignore master orders for selection.
allowed downtime
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
allowed downtime <number>
Set the allowed downtime for a connection (or a link) to a peer.
dynamic local mesh
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dynamic local mesh
Use dynamic local mesh.
no dynamic local mesh
Use static local mesh.
dynamic mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
dynamic mode (master | alt-master | slave)
Selects the dynamic operation mode.
initial discovery time
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
initial discovery time <number>
Slave: Set the group’s initial discovery time in seconds.
mesh id
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
mesh id <id>
Set the local mesh group id.
minimum snr
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
minimum snr <number>
Slave: Set the group’s minimum SNR.
2-71
Page 100

CLI commands
preserve master link
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335
preserve master link
Preserve master link across reboots.
no preserve master link
Do not preserve master link across reboots.
MSM410 MSM422
promiscuous mode
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320
promiscuous mode
Slave: Accept any group.
no promiscuous mode
Slave: Use only the slave’s group.
MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
promiscuous mode startup delay
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
promiscuous mode startup delay <number>
Set delay in seconds before promiscuous mode starts (if enabled).
snr cost per hop
Supported on: MSM310 MSM320 MSM335 MSM410 MSM422
snr cost per hop <number>
Slave: Set the group’s SNR cost per hop.
2-72
 Loading...
Loading...