Page 1

HP-UX Directory Server configuration, command, and file reference
HP-UX Directory Server Version 8.1
HP Part Number: 5900-0313
Published: September 2009
Edition: 1
Page 2

© Copyright 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computersoftware. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor's standard commercial license.
The informationcontained hereinis subject to change without notice. Theonly warranties for HPproducts andservices are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Introduction...................................................................................................................15
1.1 Directory Server configuration........................................................................................................15
1.2 Directory Server instance file reference...........................................................................................15
1.3 Using Directory Server command-line utilities..............................................................................15
1.4 Using Directory Server command-line scripts................................................................................16
2 Core server configuration reference...........................................................................17
2.1 Overview of the Directory Server configuration.............................................................................17
2.1.1 LDIF and schema configuration files......................................................................................17
2.1.2 How the server configuration is organized............................................................................19
2.1.2.1 Configuration attributes..................................................................................................19
2.1.2.2 Configuration of plug-in functionality...........................................................................19
2.1.2.3 Configuration of databases.............................................................................................20
2.1.2.4 Configuration of indexes.................................................................................................20
2.2 Accessing and modifying server configuration..............................................................................20
2.2.1 Access control for configuration entries..................................................................................20
2.2.2 Changing configuration attributes..........................................................................................21
2.2.2.1 Modifying configuration entries using LDAP................................................................21
2.2.2.2 Restrictions to modifying configuration entries and attributes......................................22
2.2.2.3 Configuration changes requiring server restart..............................................................22
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference...............................................................................22
2.3.1 cn=config.................................................................................................................................23
2.3.1.1 nsslapd-accesslog (Access log)........................................................................................23
2.3.1.2 nsslapd-accesslog-level (Access log level)......................................................................24
2.3.1.3 nsslapd-accesslog-list (List of access log files)................................................................24
2.3.1.4 nsslapd-accesslog-logbuffering (Log buffering).............................................................24
2.3.1.5 nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtime (Access log expiration time)................................25
2.3.1.6 nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtimeunit (Access log expiration time unit)..................25
2.3.1.7 nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled (Access log enable logging)...................................25
2.3.1.8 nsslapd-accesslog-logmaxdiskspace (Access log maximum disk space).......................26
2.3.1.9 nsslapd-accesslog-logminfreediskspace (Access log minimum free disk space)...........26
2.3.1.10 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsync-enabled (Access log rotation sync enabled)..........27
2.3.1.11 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsynchour (Access log rotation sync hour).....................27
2.3.1.12 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsyncmin (Access log rotation sync minute)...................27
2.3.1.13 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime (Access log rotation time)......................................28
2.3.1.14 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtimeunit (Access log rotation time unit)........................28
2.3.1.15 nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsize (Access log maximum log size)....................................28
2.3.1.16 nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir (Access log maximum number of log files)............29
2.3.1.17 nsslapd-accesslog-mode (Access log file permission)...................................................29
2.3.1.18 nsslapd-attribute-name-exceptions...............................................................................30
2.3.1.19 nsslapd-auditlog (Audit log).........................................................................................30
2.3.1.20 nsslapd-auditlog-list......................................................................................................31
2.3.1.21 nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtime (Audit log expiration time).................................31
2.3.1.22 nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtimeunit (Audit log expiration time unit)...................31
2.3.1.23 nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled (Audit log enable logging)....................................32
2.3.1.24 nsslapd-auditlog-logmaxdiskspace (Audit log maximum disk space)........................32
2.3.1.25 nsslapd-auditlog-logminfreediskspace (Audit log minimum free disk space)............33
2.3.1.26 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled (Audit log rotation sync enabled).............33
2.3.1.27 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsynchour (Audit log rotation sync hour)........................33
2.3.1.28 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsyncmin (Audit log rotation sync minute).....................34
Table of Contents 3
Page 4

2.3.1.29 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime (Audit log rotation time)........................................34
2.3.1.30 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtimeunit (Audit log rotation time unit)..........................34
2.3.1.31 nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsize (Audit log maximum log size).......................................35
2.3.1.32 nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir (Audit log maximum number of log files)...............35
2.3.1.33 nsslapd-auditlog-mode (Audit log file permission).....................................................35
2.3.1.34 nsslapd-certdir (Certificate and key database directory)..............................................36
2.3.1.35 nsslapd-certmap-basedn (Certificate map search base)................................................36
2.3.1.36 nsslapd-config...............................................................................................................37
2.3.1.37 nsslapd-conntablesize...................................................................................................37
2.3.1.38 nsslapd-counters............................................................................................................37
2.3.1.39 nsslapd-csnlogging........................................................................................................38
2.3.1.40 nsslapd-ds4-compatible-schema...................................................................................38
2.3.1.41 nsslapd-enquote-sup-oc (Enable superior object class enquoting)...............................38
2.3.1.42 nsslapd-errorlog (Error log)..........................................................................................39
2.3.1.43 nsslapd-errorlog-level (Error log level).........................................................................39
2.3.1.44 nsslapd-errorlog-list......................................................................................................40
2.3.1.45 nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtime (Error log expiration time)..................................41
2.3.1.46 nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtimeunit (Error log expiration time unit)....................41
2.3.1.47 nsslapd-errorlog-logging-enabled (Enable error logging)............................................41
2.3.1.48 nsslapd-errorlog-logmaxdiskspace (Error log maximum disk space)..........................41
2.3.1.49 nsslapd-errorlog-logminfreediskspace (Error log minimum free disk space)..............42
2.3.1.50 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsync-enabled (Error log rotation sync enabled)..............42
2.3.1.51 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsynchour (Error log rotation sync hour).........................43
2.3.1.52 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsyncmin (Error log rotation sync minute).......................43
2.3.1.53 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime (Error log rotation time)..........................................43
2.3.1.54 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtimeunit (Error log rotation time unit)............................44
2.3.1.55 nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsize (Maximum error log size)..............................................44
2.3.1.56 nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir (Maximum number of error log files)......................44
2.3.1.57 nsslapd-errorlog-mode (Error log file permission).......................................................45
2.3.1.58 nsslapd-groupevalnestlevel...........................................................................................45
2.3.1.59 nsslapd-idletimeout (Default idle timeout)...................................................................45
2.3.1.60 nsslapd-instancedir (Instance directory).......................................................................46
2.3.1.61 nsslapd-ioblocktimeout (IO block time out).................................................................46
2.3.1.62 nsslapd-lastmod (Track modification time)..................................................................46
2.3.1.63 nsslapd-ldapifilepath (LDAPI socket file path)............................................................47
2.3.1.64 nsslapd-ldapilisten (Enable LDAPI socket)..................................................................47
2.3.1.65 nsslapd-listenhost (Listen to IP address)......................................................................47
2.3.1.66 nsslapd-localhost (Local host).......................................................................................48
2.3.1.67 nsslapd-localuser (Local user).......................................................................................48
2.3.1.68 nsslapd-lockdir (Server lock file directory)...................................................................48
2.3.1.69 nsslapd-maxbersize (Maximum message size).............................................................49
2.3.1.70 nsslapd-maxdescriptors (Maximum file descriptors)...................................................49
2.3.1.71 nsslapd-max-filter-nest-level (Maximum search filter nesting level)...........................50
2.3.1.72 nsslapd-maxsasliosize (Maximum SASL packet size)..................................................50
2.3.1.73 nsslapd-maxthreadsperconn (Maximum threads per connection)...............................51
2.3.1.74 nsslapd-nagle.................................................................................................................51
2.3.1.75 nsslapd-outbound-ldap-io-timeout...............................................................................52
2.3.1.76 nsslapd-plugin...............................................................................................................52
2.3.1.77 nsslapd-port (Port number)...........................................................................................52
2.3.1.78 nsslapd-privatenamespaces..........................................................................................52
2.3.1.79 nsslapd-pwpolicy-local (Enable subtree- and user-level password policy).................53
2.3.1.80 nsslapd-readonly (Read only).......................................................................................53
2.3.1.81 nsslapd-referral (Referral).............................................................................................53
2.3.1.82 nsslapd-referralmode (Referral mode)..........................................................................54
2.3.1.83 nsslapd-reservedescriptors (Reserved file descriptors)................................................54
4 Table of Contents
Page 5

2.3.1.84 nsslapd-return-exact-case (Return exact case)..............................................................55
2.3.1.85 nsslapd-rewrite-rfc1274.................................................................................................55
2.3.1.86 nsslapd-rootdn (Manager DN)......................................................................................56
2.3.1.87 nsslapd-rootpw (Root password)..................................................................................56
2.3.1.88 nsslapd-rootpwstoragescheme (Root password storage scheme)................................57
2.3.1.89 nsslapd-saslpath............................................................................................................57
2.3.1.90 nsslapd-schema-ignore-trailing-spaces (Ignore trailing spaces in object class
names)........................................................................................................................................57
2.3.1.91 nsslapd-schemacheck (Schema checking).....................................................................58
2.3.1.92 nsslapd-schemadir.........................................................................................................58
2.3.1.93 nsslapd-schemareplace..................................................................................................59
2.3.1.94 nsslapd-securelistenhost...............................................................................................59
2.3.1.95 nsslapd-securePort (Encrypted port number)...............................................................59
2.3.1.96 nsslapd-security (Security)............................................................................................60
2.3.1.97 nsslapd-sizelimit (Size limit).........................................................................................60
2.3.1.98 nsslapd-ssl-check-hostname (Verify host name for outbound connections)................61
2.3.1.99 nsslapd-threadnumber (Thread number).....................................................................61
2.3.1.100 nsslapd-timelimit (Time limit).....................................................................................61
2.3.1.101 nsslapd-tmpdir............................................................................................................62
2.3.1.102 nsslapd-versionstring..................................................................................................62
2.3.1.103 nsslapd-workingdir.....................................................................................................62
2.3.1.104 passwordChange (Password change)..........................................................................62
2.3.1.105 passwordCheckSyntax (Check password syntax).......................................................63
2.3.1.106 passwordExp (Password expiration)...........................................................................63
2.3.1.107 passwordGraceLimit (Password expiration)...............................................................64
2.3.1.108 passwordHistory (Password history)..........................................................................64
2.3.1.109 passwordInHistory (Number of passwords to remember).........................................64
2.3.1.110 passwordIsGlobalPolicy (Password policy and replication).......................................65
2.3.1.111 passwordLockout (Account lockout)..........................................................................65
2.3.1.112 passwordLockoutDuration (Lockout duration)..........................................................65
2.3.1.113 passwordMaxAge (Password maximum age).............................................................66
2.3.1.114 passwordMaxFailure (Maximum password failures).................................................66
2.3.1.115 passwordMaxRepeats (Password syntax)...................................................................66
2.3.1.116 passwordMin8Bit (Password syntax)..........................................................................67
2.3.1.117 passwordMinAge (Password minimum age)..............................................................67
2.3.1.118 passwordMinAlphas (Password syntax).....................................................................68
2.3.1.119 passwordMinCategories (Password syntax)...............................................................68
2.3.1.120 PasswordMinDigits (Password syntax).......................................................................68
2.3.1.121 passwordMinLength (Password minimum length)....................................................68
2.3.1.122 PasswordMinLowers (Password syntax)....................................................................69
2.3.1.123 PasswordMinSpecials (Password syntax)...................................................................69
2.3.1.124 PasswordMinTokenLength (Password syntax)...........................................................69
2.3.1.125 PasswordMinUppers (Password syntax)....................................................................70
2.3.1.126 passwordMustChange (Password must change)........................................................70
2.3.1.127 passwordResetFailureCount (Reset password failure count after).............................70
2.3.1.128 passwordStorageScheme (Password storage scheme)................................................70
2.3.1.129 passwordUnlock (Unlock account).............................................................................71
2.3.1.130 passwordWarning (Send warning)..............................................................................71
2.3.2 cn=changelog5,cn=config.........................................................................................................72
2.3.2.1 nsslapd-changelogdir......................................................................................................72
2.3.2.2 nsslapd-changelogmaxage (Max changelog age)...........................................................73
2.3.2.3 nsslapd-changelogmaxentries (Max changelog records)................................................73
2.3.3 cn=encryption,cn=config.........................................................................................................73
2.3.3.1 nssslsessiontimeout.........................................................................................................73
2.3.3.2 nssslclientauth.................................................................................................................74
Table of Contents 5
Page 6

2.3.3.3 nsSSL2.............................................................................................................................74
2.3.3.4 nsSSL3.............................................................................................................................74
2.3.3.5 nsssl3ciphers....................................................................................................................75
2.3.4 cn=features,cn=config..............................................................................................................75
2.3.5 cn=mapping tree,cn=config.....................................................................................................75
2.3.6 Suffix configuration attributes under cn="suffixName".........................................................75
2.3.6.1 nsslapd-state....................................................................................................................76
2.3.6.2 nsslapd-backend..............................................................................................................76
2.3.7 Replication attributes under cn=replica, cn="suffixDN", cn=mapping tree, cn=config..........76
2.3.7.1 nsDS5Flags......................................................................................................................77
2.3.7.2 nsDS5ReplicaBindDN.....................................................................................................77
2.3.7.3 nsDS5ReplicaChangeCount............................................................................................77
2.3.7.4 nsDS5ReplicaId...............................................................................................................78
2.3.7.5 nsDS5ReplicaLegacyConsumer......................................................................................78
2.3.7.6 nsDS5ReplicaName.........................................................................................................78
2.3.7.7 nsDS5ReplicaPurgeDelay................................................................................................78
2.3.7.8 nsDS5ReplicaReferral......................................................................................................79
2.3.7.9 nsDS5ReplicaRoot...........................................................................................................79
2.3.7.10 nsDS5ReplicaTombstonePurgeInterval.........................................................................79
2.3.7.11 nsDS5ReplicaType.........................................................................................................80
2.3.7.12 nsDS5ReplicaReapActive..............................................................................................80
2.3.7.13 nsState............................................................................................................................80
2.3.7.14 nsDS5ReplConflict.........................................................................................................81
2.3.8 Replication attributes under cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica, cn="suffixName",
cn=mapping tree, cn=config.............................................................................................................81
2.3.8.1 cn.....................................................................................................................................81
2.3.8.2 description.......................................................................................................................81
2.3.8.3 nsDS5ReplicaBindDN.....................................................................................................82
2.3.8.4 nsDS5ReplicaBindMethod..............................................................................................82
2.3.8.5 nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime...........................................................................................82
2.3.8.6 nsDS5ReplicaChangesSentSinceStartup.........................................................................83
2.3.8.7 nsDS5ReplicaCredentials................................................................................................83
2.3.8.8 nsDS5ReplicaHost...........................................................................................................83
2.3.8.9 nsDS5ReplicaLastInitEnd................................................................................................84
2.3.8.10 nsDS5ReplicaLastInitStart.............................................................................................84
2.3.8.11 nsDS5ReplicaLastInitStatus...........................................................................................84
2.3.8.12 nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateEnd.......................................................................................85
2.3.8.13 nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStart......................................................................................85
2.3.8.14 nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStatus....................................................................................85
2.3.8.15 nsDS5ReplicaPort..........................................................................................................85
2.3.8.16 nsDS5ReplicaPriority....................................................................................................86
2.3.8.17 nsDS5ReplicaReapActive..............................................................................................86
2.3.8.18 nsDS5BeginReplicaRefresh...........................................................................................87
2.3.8.19 nsDS5ReplicaRoot.........................................................................................................87
2.3.8.20 nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime...................................................................................87
2.3.8.21 nsDS5ReplicatedAttributeList.......................................................................................88
2.3.8.22 nsDS5ReplicaTimeout...................................................................................................88
2.3.8.23 nsDS5ReplicaTransportInfo...........................................................................................89
2.3.8.24 nsDS5ReplicaUpdateInProgress....................................................................................89
2.3.8.25 nsDS5ReplicaUpdateSchedule......................................................................................89
2.3.8.26 nsDS50ruv.....................................................................................................................90
2.3.9 Synchronization attributes under cn=syncAgreementName, cn=Replica,cn="suffixName",
cn=mapping tree, cn=config.............................................................................................................90
2.3.9.1 nsds7DirectoryReplicaSubtree........................................................................................91
2.3.9.2 nsds7DirsyncCookie........................................................................................................91
6 Table of Contents
Page 7

2.3.9.3 nsds7NewWinGroupSyncEnabled.................................................................................91
2.3.9.4 nsds7NewWinUserSyncEnabled.....................................................................................91
2.3.9.5 nsds7WindowsDomain...................................................................................................92
2.3.9.6 nsds7WindowsReplicaSubtree........................................................................................92
2.3.9.7 winSyncInterval..............................................................................................................92
2.3.10 cn=monitor.............................................................................................................................92
2.3.11 cn=replication........................................................................................................................94
2.3.12 cn=SNMP,cn=config...............................................................................................................94
2.3.12.1 nssnmpenabled..............................................................................................................94
2.3.12.2 nssnmpname.................................................................................................................94
2.3.12.3 nssnmporganization......................................................................................................95
2.3.12.4 nssnmplocation..............................................................................................................95
2.3.12.5 nssnmpcontact...............................................................................................................95
2.3.12.6 nssnmpdescription........................................................................................................95
2.3.12.7 nssnmpmasterhost.........................................................................................................96
2.3.12.8 nssnmpmasterport.........................................................................................................96
2.3.13 SNMP statistic attributes.......................................................................................................96
2.3.14 cn=tasks,cn=config.................................................................................................................97
2.3.14.1 Task invocation attributes for entries under cn=tasks...................................................98
2.3.14.2 cn=import,cn=tasks,cn=config.....................................................................................100
2.3.14.3 cn=export,cn=tasks,cn=config......................................................................................103
2.3.14.4 cn=backup,cn=tasks,cn=config.....................................................................................106
2.3.14.5 cn=restore,cn=tasks,cn=config.....................................................................................107
2.3.14.6 cn=index,cn=tasks,cn=config.......................................................................................108
2.3.14.7 cn=schema reload task,cn=tasks,cn=config..................................................................109
2.3.14.8 cn=memberof task,cn=tasks,cn=config........................................................................110
2.3.15 cn=uniqueid generator,cn=config........................................................................................111
3 Plug-in implemented server functionality reference................................................113
3.1 Server plug-in functionality reference...........................................................................................113
3.1.1 7-bit check plug-in.................................................................................................................113
3.1.2 ACL plug-in...........................................................................................................................114
3.1.3 ACL preoperation plug-in.....................................................................................................114
3.1.4 Attribute uniqueness plug-in................................................................................................114
3.1.5 Binary syntax plug-in............................................................................................................115
3.1.6 Boolean syntax plug-in..........................................................................................................115
3.1.7 Case exact string syntax plug-in............................................................................................116
3.1.8 Case ignore string syntax plug-in.........................................................................................116
3.1.9 Chaining database plug-in....................................................................................................116
3.1.10 Class of service plug-in........................................................................................................117
3.1.11 Country string syntax plug-in.............................................................................................117
3.1.12 Distinguished name syntax plug-in....................................................................................117
3.1.13 Distributed numeric assignment plug-in............................................................................118
3.1.14 Generalized time syntax plug-in.........................................................................................118
3.1.15 HTTP client plug-in.............................................................................................................119
3.1.16 Integer syntax plug-in..........................................................................................................119
3.1.17 Internationalization plug-in................................................................................................119
3.1.18 JPEG syntax plug-in.............................................................................................................120
3.1.19 ldbm database plug-in.........................................................................................................120
3.1.20 Legacy replication plug-in...................................................................................................120
3.1.21 MemberOf plug-in...............................................................................................................121
3.1.22 Multi-master replication plug-in.........................................................................................121
3.1.23 Octet string syntax plug-in..................................................................................................122
3.1.24 OID syntax plug-in..............................................................................................................122
Table of Contents 7
Page 8

3.1.25 Password Storage Schemes..................................................................................................122
3.1.26 Postal address string syntax plug-in...................................................................................123
3.1.27 PTA plug-in..........................................................................................................................124
3.1.28 Referential integrity postoperation plug-in.........................................................................124
3.1.29 Retro Changelog plug-in.....................................................................................................125
3.1.30 Roles plug-in........................................................................................................................125
3.1.31 Schema reload plug-in.........................................................................................................126
3.1.32 Space insensitive string syntax plug-in...............................................................................126
3.1.33 State change plug-in............................................................................................................126
3.1.34 Telephone syntax plug-in....................................................................................................127
3.1.35 URI syntax plug-in...............................................................................................................127
3.1.36 Views plug-in.......................................................................................................................127
3.1.37 Account policy plug-in........................................................................................................128
3.2 List of attributes common to all plug-ins......................................................................................128
3.2.1 nsslapd-pluginPath................................................................................................................128
3.2.2 nsslapd-pluginInitfunc..........................................................................................................129
3.2.3 nsslapd-pluginType...............................................................................................................129
3.2.4 nsslapd-pluginEnabled..........................................................................................................129
3.2.5 nsslapd-pluginId...................................................................................................................129
3.2.6 nsslapd-pluginVersion..........................................................................................................130
3.2.7 nsslapd-pluginVendor...........................................................................................................130
3.2.8 nsslapd-pluginDescription....................................................................................................130
3.3 Attributes allowed by certain plug-ins..........................................................................................130
3.3.1 nsslapd-pluginLoadNow......................................................................................................130
3.3.2 nsslapd-pluginLoadGlobal....................................................................................................131
3.3.3 nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-type..........................................................................................131
3.3.4 nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-named......................................................................................131
3.4 Database plug-in attributes...........................................................................................................132
3.4.1 Database attributes under cn=config, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config................132
3.4.1.1 nsLookthroughLimit.....................................................................................................132
3.4.1.2 nsslapd-cache-autosize..................................................................................................133
3.4.1.3 nsslapd-cache-autosize-split.........................................................................................133
3.4.1.4 nsslapd-dbcachesize......................................................................................................134
3.4.1.5 nsslapd-db-checkpoint-interval....................................................................................134
3.4.1.6 nsslapd-db-circular-logging..........................................................................................135
3.4.1.7 nsslapd-db-debug..........................................................................................................135
3.4.1.8 nsslapd-db-durable-transactions...................................................................................135
3.4.1.9 nsslapd-db-home-directory...........................................................................................136
3.4.1.10 nsslapd-db-idl-divisor.................................................................................................136
3.4.1.11 nsslapd-db-logbuf-size................................................................................................137
3.4.1.12 nsslapd-db-logdirectory..............................................................................................137
3.4.1.13 nsslapd-db-logfile-size................................................................................................138
3.4.1.14 nsslapd-db-page-size...................................................................................................138
3.4.1.15 nsslapd-db-private-import-mem.................................................................................138
3.4.1.16 nsslapd-db-spin-count.................................................................................................139
3.4.1.17 nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-val................................................................................139
3.4.1.18 nsslapd-db-trickle-percentage.....................................................................................140
3.4.1.19 nsslapd-db-verbose......................................................................................................140
3.4.1.20 nsslapd-dbncache........................................................................................................140
3.4.1.21 nsslapd-directory.........................................................................................................141
3.4.1.22 nsslapd-exclude-from-export......................................................................................141
3.4.1.23 nsslapd-idl-switch.......................................................................................................141
3.4.1.24 nsslapd-idlistscanlimit.................................................................................................142
3.4.1.25 nsslapd-import-cachesize............................................................................................142
3.4.1.26 nsslapd-import-cache-autosize....................................................................................142
8 Table of Contents
Page 9

3.4.1.27 nsslapd-mode..............................................................................................................143
3.4.1.28 nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test.................................................................................144
3.4.1.29 nsslapd-search-use-vlv-index......................................................................................144
3.4.1.30 nsslapd-serial-lock.......................................................................................................144
3.4.2 Database attributes under cn=monitor, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config..............144
3.4.3 Database attributes under cn=NetscapeRoot, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config and
cn=userRoot, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config...............................................................144
3.4.3.1 nsslapd-cachesize..........................................................................................................145
3.4.3.2 nsslapd-cachememsize..................................................................................................145
3.4.3.3 nsslapd-directory...........................................................................................................145
3.4.3.4 nsslapd-readonly...........................................................................................................146
3.4.3.5 nsslapd-require-index...................................................................................................146
3.4.3.6 nsslapd-suffix................................................................................................................146
3.4.4 Database attributes under cn=database, cn=monitor, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,
cn=config........................................................................................................................................147
3.4.5 Database attributes under cn=default indexes, cn=config, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,
cn=config........................................................................................................................................148
3.4.5.1 cn...................................................................................................................................148
3.4.5.2 description.....................................................................................................................148
3.4.5.3 nsSystemIndex...............................................................................................................148
3.4.5.4 nsIndexType..................................................................................................................149
3.4.5.5 nsMatchingRule.............................................................................................................149
3.4.6 Database attributes under cn=monitor, cn=NetscapeRoot, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,
cn=config........................................................................................................................................149
3.4.7 Database attributes under cn=index, cn=NetscapeRoot, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,
cn=config and cn=index, cn=UserRoot, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config......................150
3.4.7.1 nsSubStrBegin................................................................................................................150
3.4.7.2 nsSubStrEnd..................................................................................................................151
3.4.7.3 nsSubStrMiddle.............................................................................................................151
3.4.8 Database Attributes under cn=attributeName, cn=encrypted attributes, cn=database_name,
cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config.....................................................................................152
3.4.8.1 nsEncryptionAlgorithm................................................................................................153
3.5 Database link plug-in attributes (chaining attributes)..................................................................153
3.5.1 Database link attributes under cn=config, cn=chaining database, cn=plugins, cn=config....153
3.5.1.1 nsActiveChainingComponents.....................................................................................153
3.5.1.2 nsMaxResponseDelay...................................................................................................154
3.5.1.3 nsMaxTestResponseDelay.............................................................................................154
3.5.1.4 nspossiblechainingcomponents....................................................................................154
3.5.1.5 nsTransmittedControls..................................................................................................155
3.5.2 Database link attributes under cn=default instance config, cn=chaining database, cn=plugins,
cn=config........................................................................................................................................155
3.5.2.1 nsAbandonedSearchCheckInterval...............................................................................155
3.5.2.2 nsBindConnectionsLimit...............................................................................................155
3.5.2.3 nsBindRetryLimit..........................................................................................................156
3.5.2.4 nsBindTimeout..............................................................................................................156
3.5.2.5 nsCheckLocalACI..........................................................................................................156
3.5.2.6 nsConcurrentBindLimit.................................................................................................157
3.5.2.7 nsConcurrentOperationsLimit......................................................................................157
3.5.2.8 nsConnectionLife...........................................................................................................157
3.5.2.9 nsOperationConnectionsLimit......................................................................................157
3.5.2.10 nsProxiedAuthorization..............................................................................................158
3.5.2.11 nsReferralOnScopedSearch.........................................................................................158
3.5.2.12 nsSizeLimit..................................................................................................................158
3.5.2.13 nsTimeLimit.................................................................................................................159
Table of Contents 9
Page 10

3.5.3 Database link attributes under cn=database_link_name, cn=chaining database, cn=plugins,
cn=config........................................................................................................................................159
3.5.3.1 nsBindMechanism.........................................................................................................159
3.5.3.2 nsFarmServerURL.........................................................................................................160
3.5.3.3 nsMultiplexorBindDN...................................................................................................160
3.5.3.4 nsMultiplexorCredentials..............................................................................................161
3.5.3.5 nshoplimit......................................................................................................................161
3.5.3.6 nsUseStartTLS...............................................................................................................161
3.5.4 Database link attributes under cn=monitor, cn=database instance name, cn=chaining
database, cn=plugins, cn=config....................................................................................................161
3.6 Retro changelog plug-in attributes................................................................................................162
3.6.1 nsslapd-changelogdir............................................................................................................162
3.6.2 nsslapd-changelogmaxage (Max changelog age)..................................................................163
3.7 Distributed numeric assignment plug-in attributes......................................................................163
3.7.1 dnaFilter.................................................................................................................................163
3.7.2 dnaMagicRegen.....................................................................................................................163
3.7.3 dnaMaxValue.........................................................................................................................164
3.7.4 dnaNextRange.......................................................................................................................164
3.7.5 dnaNextValue........................................................................................................................164
3.7.6 dnaPrefix................................................................................................................................165
3.7.7 dnaRangeRequestTimeout....................................................................................................165
3.7.8 dnaScope................................................................................................................................166
3.7.9 dnaSharedCfgDN..................................................................................................................166
3.7.10 dnaThreshold.......................................................................................................................166
3.7.11 dnaType...............................................................................................................................167
3.8 MemberOf plug-in attributes........................................................................................................167
3.8.1 memberofattr.........................................................................................................................167
3.8.2 memberofgroupattr...............................................................................................................167
3.9 Account policy plug-in attributes..................................................................................................168
4 Server instance file reference...................................................................................169
4.1 Overview of Directory Server files................................................................................................169
4.2 Backup files....................................................................................................................................169
4.3 Configuration files.........................................................................................................................169
4.4 Database files.................................................................................................................................169
4.5 LDIF files.......................................................................................................................................171
4.6 Lock files........................................................................................................................................171
4.7 Log files..........................................................................................................................................171
4.8 PID files..........................................................................................................................................171
4.9 Tools...............................................................................................................................................172
4.10 Scripts...........................................................................................................................................172
5 Log file reference.......................................................................................................173
5.1 Access log reference.......................................................................................................................173
5.1.1 Access logging levels.............................................................................................................173
5.1.2 Default access logging content..............................................................................................174
5.1.2.1 Connection number.......................................................................................................174
5.1.2.2 File descriptor................................................................................................................174
5.1.2.3 Slot number...................................................................................................................175
5.1.2.4 Operation number.........................................................................................................175
5.1.2.5 Method type..................................................................................................................175
5.1.2.6 Version number.............................................................................................................175
5.1.2.7 Error number.................................................................................................................175
10 Table of Contents
Page 11

5.1.2.8 Tag number....................................................................................................................175
5.1.2.9 Number of entries..........................................................................................................176
5.1.2.10 Elapsed time................................................................................................................176
5.1.2.11 LDAP request type......................................................................................................176
5.1.2.12 LDAP response type....................................................................................................177
5.1.2.13 Unindexed search indicator.........................................................................................177
5.1.2.14 VLV-related entries......................................................................................................177
5.1.2.15 Search scope.................................................................................................................177
5.1.2.16 Extended operation OID..............................................................................................178
5.1.2.17 Change sequence number...........................................................................................178
5.1.2.18 Abandon message........................................................................................................178
5.1.2.19 Message ID..................................................................................................................179
5.1.2.20 SASL multi-stage bind logging....................................................................................179
5.1.3 Access log content for additional access logging levels........................................................179
5.1.3.1 Connection description.................................................................................................180
5.1.3.2 Options description.......................................................................................................180
5.1.4 Common connection codes...................................................................................................180
5.2 Error log reference.........................................................................................................................181
5.2.1 Error log logging levels.........................................................................................................181
5.2.2 Error log content....................................................................................................................182
5.2.3 Error log content for other log levels.....................................................................................183
5.3 Audit log reference........................................................................................................................186
5.4 LDAP result codes.........................................................................................................................187
6 Command-line utilities...............................................................................................189
6.1 Finding and executing command-line utilities.............................................................................189
6.2 Using special characters................................................................................................................189
6.3 Command-line utilities quick reference........................................................................................189
6.4 ldapsearch......................................................................................................................................190
6.4.1 ldapsearch syntax..................................................................................................................190
6.4.2 Commonly-used ldapsearch options....................................................................................190
6.4.3 Persistent search options.......................................................................................................192
6.4.4 ldapsearch SSL options..........................................................................................................192
6.4.5 ldapsearch SASL options.......................................................................................................193
6.4.6 Additional ldapsearch options..............................................................................................199
6.5 ldapmodify....................................................................................................................................201
6.5.1 ldapmodify syntax.................................................................................................................201
6.5.2 Commonly-used ldapmodify options...................................................................................201
6.5.3 ldapmodify SSL options........................................................................................................202
6.5.4 ldapmodify SASL options.....................................................................................................203
6.5.5 Additional ldapmodify options.............................................................................................204
6.6 ldapdelete......................................................................................................................................204
6.6.1 ldapdelete syntax...................................................................................................................205
6.6.2 Commonly-used ldapdelete options.....................................................................................205
6.6.3 ldapdelete SSL options..........................................................................................................205
6.6.4 ldapdelete SASL options.......................................................................................................206
6.6.5 Additional ldapdelete options...............................................................................................207
6.7 ldappasswd....................................................................................................................................207
6.7.1 ldappasswd syntax................................................................................................................207
6.7.2 ldappasswd-specific options.................................................................................................208
6.7.3 General ldappasswd options.................................................................................................208
6.7.4 ldappasswd SASL options.....................................................................................................209
6.7.5 ldappasswd examples...........................................................................................................210
6.8 ldif..................................................................................................................................................211
Table of Contents 11
Page 12

6.8.1 ldif syntax..............................................................................................................................212
6.8.2 ldif options.............................................................................................................................212
6.9 dbscan............................................................................................................................................212
6.9.1 dbscan syntax........................................................................................................................212
6.9.2 dbscan options.......................................................................................................................213
6.9.3 dbscan examples....................................................................................................................213
7 Command-line scripts................................................................................................215
7.1 Finding and executing command-line scripts...............................................................................215
7.2 Command-line scripts quick reference..........................................................................................215
7.3 Shell scripts....................................................................................................................................216
7.3.1 bak2db (Restores a database from backup)...........................................................................217
7.3.2 cl-dump (Dumps and decodes the changelog).....................................................................217
7.3.3 dbverify (Checks for corrupt databases)...............................................................................218
7.3.4 db2bak (Creates a backup of a database)..............................................................................219
7.3.5 db2ldif (Exports database contents to LDIF).........................................................................219
7.3.6 db2index (Reindexes database index files)...........................................................................220
7.3.7 ldif2db (Import).....................................................................................................................220
7.3.8 ldif2ldap (Performs import operation over LDAP)...............................................................221
7.3.9 pwdhash (Prints encrypted passwords)................................................................................221
7.3.10 monitor (Retrieves monitoring information).......................................................................222
7.3.11 repl-monitor (Monitors replication status)..........................................................................222
7.3.12 restart-slapd (Restarts the Directory Server).......................................................................224
7.3.13 restoreconfig (Restores Administration Server configuration)...........................................224
7.3.14 saveconfig (Saves Administration Server configuration)....................................................224
7.3.15 start-slapd (Starts the Directory Server)..............................................................................225
7.3.16 stop-slapd (Stops the Directory Server)...............................................................................225
7.3.17 suffix2instance (Maps a suffix to a backend name).............................................................225
7.3.18 vlvindex (Creates virtual list view indexes)........................................................................225
7.4 Perl scripts.....................................................................................................................................226
7.4.1 bak2db.pl (Restores a database from backup)......................................................................226
7.4.2 cl-dump.pl (Dumps and decodes the changelog).................................................................227
7.4.3 db2bak.pl (Creates a backup of a database)..........................................................................227
7.4.4 db2index.pl (Creates and generates indexes)........................................................................228
7.4.5 db2ldif.pl (Exports database contents to LDIF).....................................................................228
7.4.6 fixup-memberof.pl (Regenerate memberOf attributes)........................................................229
7.4.7 ldif2db.pl (Import).................................................................................................................230
7.4.8 logconv.pl (Log converter).....................................................................................................231
7.4.9 ns-accountstatus.pl (Establishes account status)...................................................................233
7.4.10 ns-activate.pl (Activates an entry or group of entries)........................................................234
7.4.11 ns-inactivate.pl (Inactivates an entry or group of entries)..................................................234
7.4.12 ns-newpwpolicy.pl (Adds attributes for fine-grained password policy)............................234
7.4.13 repl-monitor.pl (Monitors replication status)......................................................................235
7.4.14 schema-reload.pl (Reload schema files dynamically).........................................................237
7.4.15 verify-db.pl (Check for corrupt databases).........................................................................237
8 Support and other resources....................................................................................239
8.1 Contacting HP...............................................................................................................................239
8.1.1 Information to collect before contacting HP.........................................................................239
8.1.2 How to contact HP technical support...................................................................................239
8.1.3 HP authorized resellers.........................................................................................................239
8.1.4 Documentation feedback.......................................................................................................239
8.2 Related information.......................................................................................................................240
12 Table of Contents
Page 13

8.2.1 HP-UX Directory Server documentation set.........................................................................240
8.2.2 HP-UX documentation set.....................................................................................................241
8.2.3 Troubleshooting resources....................................................................................................241
8.3 Typographic conventions..............................................................................................................241
A Using the ns-slapd command-line utilities...............................................................243
A.1 Overview of ns-slapd....................................................................................................................243
A.2 Finding and executing the ns-slapd command-line utilities........................................................243
A.3 Utilities for exporting databases: db2ldif.....................................................................................243
A.4 Utilities for restoring and backing up databases: ldif2db............................................................244
A.5 Utilities for restoring and backing up databases: archive2db......................................................245
A.6 Utilities for restoring and backing up databases: db2archive......................................................245
A.7 Utilities for creating and regenerating indexes: db2index...........................................................245
Glossary.........................................................................................................................247
Index...............................................................................................................................257
Table of Contents 13
Page 14

14
Page 15

1 Introduction
The HP-UX Directory Server is based on an open-systems server protocol called the Lightweight
Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). The Directory Server is a robust, scalable server designed to
manage large scale directories to support an enterprise-wide directory of users and resources,
extranets, and e-commerce applications over the Internet. The Directory Server runs as the
ns-slapd process or service on the machine. The server manages the directory databases and
responds to client requests.
This reference covers the server configuration and the command-line utilities. It is designed
primarily for directory administrators and experienced directory users who want to use the
command-line to access the directory. After configuring the server, use this reference to help
maintain it.
The Directory Server can also be managed through the Directory Server Console, a graphical
user interface. The HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide describes how to do this and
explains individual administration tasks more fully.
The major components of Directory Server include:
• An LDAP server
The LDAP v3-compliant network daemon.
• Directory Server Console
A graphical management console that dramatically reduces the effort of setting up and
maintaining your directory service.
• SNMP agent
Can monitor theDirectory Server using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
• Administration Server
Required for managing the Directory Server using the Directory Server Console.
1.1 Directory Server configuration
The format and method for storing configuration information for Directory Server and a listing
for all server attributes are found in two chapters, Chapter 2 “Core server configuration reference”
and Chapter 3 “Plug-in implemented server functionality reference”.
1.2 Directory Server instance file reference
Chapter 4 “Server instance file reference” has an overview of the files and configuration
information stored in each instance of Directory Server. This reference helps administrators
understand the changes or absence of changes in the course of directory activity. From a security
standpoint, this also helps users detect errors and intrusion by highlighting normal changes and
abnormal behavior.
1.3 Using Directory Server command-line utilities
Directory Server comes with a set of configurable command-line utilities that can search and
modify entries in the directory and administer the server. Chapter 6 “Command-line utilities”
describes these command-line utilities and contains information on where the utilities are stored
and how to access them. In addition to thesecommand-line utilities, Directory Server also provides
ns-slapd command-line utilities for performing directory operations, as described in
Appendix A “Using the ns-slapd command-line utilities”.
1.1 Directory Server configuration 15
Page 16

1.4 Using Directory Server command-line scripts
In addition to command-line utilities, several non-configurable scripts are provided with the
Directory Server that make it quick and easy to perform routine server administration tasks from
the command-line. Chapter 7 “Command-line scripts” lists the most frequently used scripts and
contains information on where the scripts are stored and how to access them.
16 Introduction
Page 17
2 Core server configuration reference
The configuration information for the HP-UX Directory Server is stored as LDAP entries within
the directory itself. Therefore, changes to the server configuration must be implemented through
the use of the server itself rather than by simply editing configuration files. The principal
advantage of this method of configuration storage is that it allows a directory administrator to
reconfigure the server using LDAP while it is still running, thus avoiding the need to shut the
server down for most configuration changes.
This chapter gives details on how the configuration is organized and how to alter it. The chapter
also provides an alphabetical reference for all attributes.
2.1 Overview of the Directory Server configuration
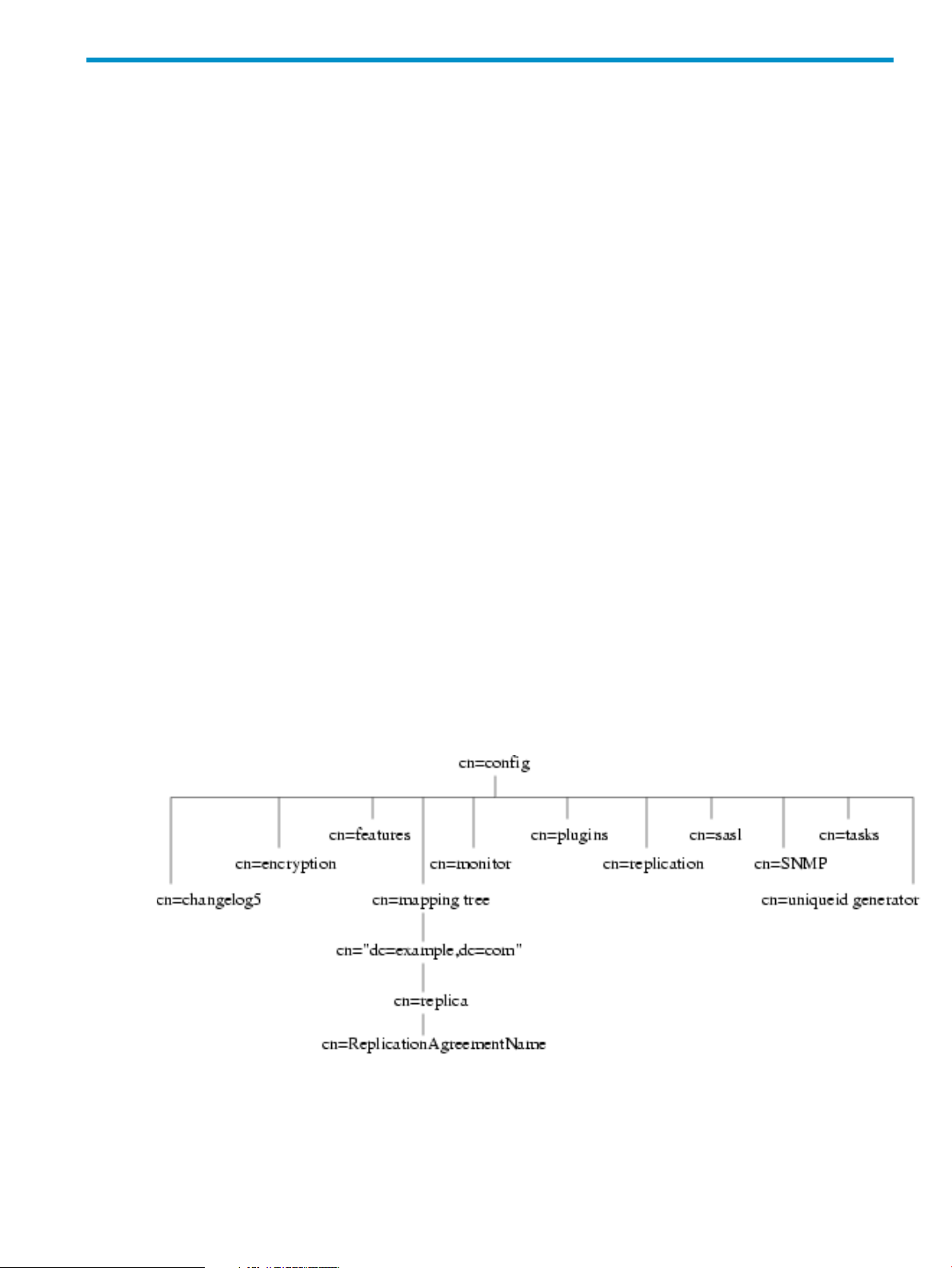
When the Directory Server is set up, its default configuration is stored as a series of LDAP entries
within the directory, under the subtree cn=config. When the server is started, the contents of
the cn=config subtree are read from a file (dse.ldif) in LDIF format. This dse.ldif file
contains all the server configuration information. The latest version of this file is called dse.ldif,
the version prior to the last modification is called dse.ldif.bak, and the latest file with which
the server successfully started is called dse.ldif.startOK.
Many of the features of the Directory Server are designed as discrete modules that plug into the
core server. The details of the internal configuration for each plug-in are contained in separate
entries undercn=plugins,cn=config. For example, the configuration of the Telephone Syntax
Plug-in is contained in this entry:
cn=Telephone Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config
Similarly, database-specific configuration is stored under cn=ldbm
database,cn=plugins,cn=config for local databases and cn=chaining
database,cn=plugins,cn=config for database links.
The following diagram illustrates how the configuration data fits within the cn=config directory
information tree.
Figure 2-1 Directory information tree showing configuration data
2.1.1 LDIF and schema configuration files
The Directory Server configuration data is automatically output to files in LDIF format that are
located in the /etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name directory. Thus, if a server identifier
is phonebook, then for a Directory Server, the configuration LDIF files are all stored under
/etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-phonebook.
2.1 Overview of the Directory Server configuration 17
Page 18

This directory also contains other server instance-specific configuration files.
Schema configuration is also stored in LDIF format. The master schema directory is /etc/opt/
dirsrv/schema, and the instance-specific schema directory is
/etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/schema.
The following table lists all the configuration files that are supplied with the Directory Server,
including those for the schema of other compatible servers. Each file is preceded by a number
which indicates the order in which they should be loaded (in ascending numerical, then
alphabetical order).
Table 2-1 Directory Server LDIF configuration files
PurposeConfiguration file name
dse.ldif
00core.ldif
01common.ldif
05rfc2247.ldif
05rfc2927.ldif
10presence.ldif
10rfc2307.ldif
Contains front-end Directory Specific Entries created by the directory at server
startup. These include the Root DSE ("") and the contents of cn=config and
cn=monitor (acis only).
Contains only those schema definitions necessary for starting the server with the
bare minimum feature set (no user schema, no schema for any non-core features).
The rest of the schema used by users, features, and applications is found in
01common.ldif and the other schema files. Do not modify this file.
Contains LDAPv3 standard operational schema, such as subschemaSubentry,
LDAPv3 standard user and organization schema defined in RFC 2256 (based on
X.520/X.521), inetOrgPersonand other widely-used attributes, and the operational
attributes used by Directory Server configuration. Modifying this file causes
interoperability problems. User-defined attributes should be added through the
Directory Server Console.
Schema from RFC 2247 and related pilot schema, from "Using Domains in
LDAP/X500 Distinguished Names."
Schema from RFC 2927, "MIME Directory Profile for LDAP Schema." Contains the
ldapSchemas operational attribute required for the attribute to show up in the
subschema subentry.
Legacy. Schema for instant messaging presence (online) information; the file lists
the default object classes with the allowed attributes that must be added to a user's
entry in order for instant-messaging presence information to be available for that
user.
Schema from RFC 2307, "An Approach for Using LDAP as a Network Information
Service." Thismay be superseded by 10rfc2307bis, the new version of rfc2307,
when that schema becomes available.
20subscriber.ldif
25java-object.ldif
28pilot.ldif
30ns-common.ldif
50ns-admin.ldif
50ns-certificate.ldif
50ns-directory.ldif
18 Core server configuration reference
Contains new schema elements and the Nortel subscriber interoperability
specification. Also contains the adminRole and memberOfattributes and
inetAdmin object class, previously stored in the 50ns-delegated-admin.ldif
file.
Schema from RFC 2713, "Schema for Representing Java®Objects in an LDAP
Directory."
Contains pilot directory schema from RFC 1274, which is no longer recommended
for new deployments. Future RFCs which succeed RFC 1274 may deprecate some
of or all 28pilot.ldif attribute types and classes.
Schema that contains objects classes and attributes common to the Directory Server
Console framework.
Schema used by the Administration Server.
Schema for Dogtag Certificate System.
Contains additional configuration schema used by DirectoryServer 4.16 and earlier
versions of the directory, which is no longer applicable to current releases of
Directory Server. This schema is required for replicating between Directory Server
4.16 and current releases.
Page 19

Table 2-1 Directory Server LDIF configuration files (continued)
PurposeConfiguration file name
50ns-mail.ldif
50ns-value.ldif
50ns-web.ldif
60pam-plugin.ldif
99user.ldif
Schema used by Netscape Messaging Server to define mail users and mail groups.
Schema for servers' value item attributes.
Schema for Netscape Web Server.
Reserved for future use.
User-defined schema maintained by Directory Server replication consumers which
contains the attributes and object classes from the suppliers.
2.1.2 How the server configuration is organized
The dse.ldif file contains all configuration information including directory-specific entries
created by the directory at server startup, such as entries related tothe database. The file includes
the root Directory Server entry (or DSE, named by "") and the contents of cn=config and
cn=monitor.
When the server generates the dse.ldif file, it lists the entries in hierarchical order in the order
that the entries appear in the directory under cn=config, which is usually the same order in
which an LDAP search of subtree scope for base cn=config returns the entries.
dse.ldif also contains the cn=monitor entry, which is mostly read-only, but can have ACIs
set on it.
NOTE:
The dse.ldif file does not contain every attribute in cn=config. If the attribute has not been
set by the administrator and has a default value, the server will not write it to dse.ldif. To see
every attribute in cn=config, use the ldapsearch command.
2.1.2.1 Configuration attributes
Within a configuration entry, each attribute is represented as an attribute name. The value of the
attribute corresponds to the attribute's configuration.
The following code sample is an example of part of the dse.ldif file for a Directory Server.
The example shows, among other things, that schema checking has been enabled; this is
represented by the attribute nsslapd-schemacheck, which takes the value on.
dn: cn=config
objectclass: top
objectclass: extensibleObject
objectclass: nsslapdConfig
nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled: on
nsslapd-enquote-sup-oc: off
nsslapd-localhost: phonebook.example.com
nsslapd-schemacheck: on
nsslapd-port: 389
nsslapd-localuser: www
...
2.1.2.2 Configuration of plug-in functionality
The configuration for each part of Directory Server plug-in functionality has its own separate
entry and set of attributes under the subtree cn=plugins,cn=config. The following code
sample is an example of the configuration entry for an example plug-in, the Telephone Syntax
plug-in.
dn: cn=Telephone Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config
objectclass: top
2.1 Overview of the Directory Server configuration 19
Page 20

objectclass: nsSlapdPlugin
objectclass: extensibleObject
cn: Telephone Syntax
nsslapd-pluginType: syntax
nsslapd-pluginEnabled: on
Some of these attributes are common to all plug-ins, and some may be particular to a specific
plug-in. Check which attributes are currently being used by a given plug-in by performing a
search with the ldapsearch utility on the cn=config subtree.
For a list of plug-ins supported by Directory Server, general plug-in configuration information,
the plug-in configuration attribute reference, and a list of plug-ins requiring restart for
configuration changes, see Chapter 3 “Plug-in implemented server functionality reference”.
2.1.2.3 Configuration of databases
The cn=NetscapeRoot and cn=UserRoot subtrees under the database plug-in entry contain
configuration data for the databases containing the o=NetscapeRoot suffix and the default
suffix created during setup, such as dc=example,dc=com.
These entries and their children have many attributes used to configure different database settings,
like the cache sizes, the paths to the index files and transaction logs, entries and attributes for
monitoring and statistics; and database indexes.
2.1.2.4 Configuration of indexes
Configuration information for indexing is stored as entries in the Directory Server under the
following information-tree nodes:
• cn=index,cn=backend_instance,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
• cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
For more information about indexes in general, see the HP-UX Directory Server administrator
guide. For information about the index configuration attributes, see “Database attributes under
cn=config, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config”.
2.2 Accessing and modifying server configuration
This section discusses access control for configuration entries and describes the various ways in
which the server configuration can be viewed and modified. It also covers restrictions to the
kinds of modification that can be made and discusses attributes that require the server to be
restarted for changes to take effect.
2.2.1 Access control for configuration entries
When the Directory Server is installed, a default set of access control instructions (ACIs) is
implemented for all entries under cn=config. The following code sample is an example of these
default ACIs.
aci: (targetattr = "*")(version 3.0; acl "Configuration Administrators Group"; allow (all)
groupdn = "ldap:///cn=Configuration Administrators,u=Groups, ou=TopologyManagement, o=NetscapeRoot";)
aci: (targetattr = "*")(version 3.0; acl "Configuration Administrator"; allow (all)
userdn = "ldap:///uid=admin, ou=Administrators, ou=TopologyManagement, o=NetscapeRoot";)
aci: (targetattr = "*")(version 3.0; acl "Local Directory Administrators Group"; allow (all)
groupdn = "ldap:///ou=Directory Administrators, dc=example,dc=com";)
aci: (targetattr = "*")(version 3.0; acl "SIE Group"; allow(all)
groupdn = "ldap:///cn=slapd-phonebook, cn=HP-UX Directory Server,
cn=Server Group, cn=phonebook.example.com, dc=example,dc=com, o=NetscapeRoot";)
These default ACIs allow all LDAP operations to be carried out on all configuration attributes
by the following users:
• Members of the Configuration Administrators group.
• The user acting as the administrator, the admin account that was configured at setup. By
default, this is the same user account which is logged into the Console.
20 Core server configuration reference
Page 21

• Members of local Directory Administrators group.
• The SIE (Server Instance Entry) group, usually assigned using the Set Access Permissions
process the main console.
For more information on access control, see the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
2.2.2 Changing configuration attributes
Server attributes can be viewed and changed in one of three ways: through the Directory Server
Console, by performing ldapsearch and ldapmodify commands, or by manually editing the
dse.ldif file.
NOTE:
You must stop the server before editing the dse.ldif file; otherwise, the changes are lost.
Editing the dse.ldif file is recommended only for changes to attributes which cannot be altered
dynamically. See “Configuration changes requiring server restart” for further information.
The following sections describe how to modify entries using LDAP (both by using Directory
Server Console and by using the command line), the restrictions that apply to modifying entries,
the restrictions that apply to modifying attributes, and the configuration changes requiring
restart.
2.2.2.1 Modifying configuration entries using LDAP
The configuration entries in the directory can be searched and modified using LDAP either
through the Directory Server Console or by performing the ldapsearch and ldapmodify
operations in the same way as other directory entries. The advantage of using LDAP to modify
entries is changes can be made while the server is running.
For further information, see the chapter titled “Creating Directory Entries” in the HP-UX Directory
Server administrator guide. However, certain changes do require the server to be restarted before
they are taken into account. See “Configuration changes requiring server restart” for further
information.
NOTE:
As with any set of configuration files, care should be taken when changing or deleting nodes in
the cn=config subtree as this risks affecting Directory Server functionality.
The entire configuration, including attributes that are set to default values, can be viewed by
performing an ldapsearch operation on the cn=config subtree:
# ldapsearch -b cn=config -D bindDN -w password
Where:
bindDN
is the DN chosen for the Directory Manager when the server was installed
(cn=Directory Manager by default).
password
is the password chosen for the Directory Manager.
For more information on using the ldapsearch command, see “ldapsearch”.
To disable a plug-in, use the ldapmodify command to edit the nsslapd-pluginEnabled
attribute:
# ldapmodify -D "cn=directory manager" -w password
dn: cn=Telephone Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config
changetype: modify
replace: nsslapd-pluginEnabled
nsslapd-pluginEnabled: off
2.2 Accessing and modifying server configuration 21
Page 22

2.2.2.2 Restrictions to modifying configuration entries and attributes
Certain restrictions apply when modifying server entries and attributes:
• The cn=monitor entry and its child entries are read-only and cannot be modified, except
to manage ACIs.
• If an attribute is added to cn=config, the server ignores it.
• If an invalid value is entered for an attribute, the server ignores it.
• Because the ldapdelete command is used for deleting an entire entry, use the ldapmodify
command to remove an attribute from an entry.
2.2.2.3 Configuration changes requiring server restart
Some configuration attributes cannot be altered while the server is running. In these cases, for
the changes to take effect, the server needs to be shut down and restarted. The modifications
should bemade either through the Directory Server Console or by manually editing the dse.ldif
file. Some of the attributes that require a server restart for any changes to take effect are listed
below.
nsslapd-certdirnsslapd-cachesize
nsslapd-dbncachensslapd-dbcachesize
nsslapd-changelogdirnsslapd-plugin
nsslapd-changelogmaxentriesnsslapd-changelogmaxage
nsslapd-schemadirnsslapd-port
nsslapd-secureportnsslapd-saslpath
nsSSL2nsslapd-tmpdir
nsSSLclientauthnsSSL3
nsslapd-conntablesizensSSLSessionTimeout
nsslapd-maxdescriptorsnsslapd-lockdir
nsslapd-listenhostnsslapd-reservedescriptors
nsslapd-securelistenhostnsslapd-schema-ignore-trailing-spaces
nsslapd-return-exact-casensslapd-workingdir
This list is not exhaustive; to see a complete list, run the ldapsearch command and search for
the nsslapd-requiresrestart attribute. For example:
# ldapsearch -p 389 -D "cn=directory manager" \
-w password -s sub -b "cn=config" \
"(objectclass=*)" | grep nsslapd-requiresrestart
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference
This section contains reference information on the configuration attributes that are relevant to
the core server functionality. For information on changing server configuration, see “Accessing
and modifying server configuration”. For a list of server features that are implemented as plug-ins,
see “Server plug-in functionality reference”. For help with implementing custom server
functionality, contact HP support.
The configuration information stored in the dse.ldif file is organized as an information tree
under the general configuration entry cn=config, as shown in . Figure 2-1
22 Core server configuration reference
Page 23

Figure 2-2 Directory information tree showing configuration data
Most of these configuration tree nodes are covered in the following sections.
The cn=plugins node is covered in Chapter 3 “Plug-in implemented server functionality
reference”. The description of each attribute contains details such as the DN of its directory entry,
its default value, the valid range of values, and an example of its use.
NOTE:
Some of the entries and attributes described in this chapter may change in future releases of the
product.
2.3.1 cn=config
General configuration entries are stored in the cn=config entry. The cn=config entry is an
instance of the nsslapdConfig object class, which in turn inherits from extensibleObject
object class.
2.3.1.1 nsslapd-accesslog (Access log)
This attribute specifies the path and file name of the log used to record each LDAP access. The
following information is recorded by default in the log file:
• IP address of the client machine that accessed the database.
• Operations performed (for example, search, add, and modify).
• Result of the access (for example, the number of entries returned or an error code).
The following table describes the attribute parameters:
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any valid file name.ValidValues
Default Value
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/log/access
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog: /var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-example/log/accessExample
For more information on turning access logging off, see the "Monitoring Server and Database
Activity" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 23
Page 24

For access logging to be enabled, the nsslapd-accesslog attribute must contain a valid path,
and the nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled configuration attribute must be switched
to on. Table 2-2 lists the four possible combinations of values for these two configuration attributes
and their outcome in terms of disabling or enabling of access logging.
Table 2-2 Attribute values for enabling or disabling access logging
Value of the
Value of the nsslapd-accesslog
attribute
nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled
attribute
Resulting logging state
empty string
empty string
2.3.1.2 nsslapd-accesslog-level (Access log level)
This attribute controls what is logged to the access log.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
0 No access logging
4 Logging for internal access operations
256 Logging for connections, operations, and results
512 Logging for access to an entry and referrals
131072 Provides microsecond operation timing
These values can be added together to provide the exact type of logging required; for
example, 516 (4 + 512) to obtain internal access operation, entry access, and referral logging.
256Default Value
on
onfilename
off
offfilename
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-level: 256Example
2.3.1.3 nsslapd-accesslog-list (List of access log files)
This read-only attribute, which cannot be set, provides a list of access log files used in access log
rotation.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
NoneDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-list: accesslog2,accesslog3Example
2.3.1.4 nsslapd-accesslog-logbuffering (Log buffering)
When set to off, the server writes all access log entries directly to disk. Buffering allows the
server to use access logging even when under a heavy load without significantly impacting
performance. However, when debugging, it is sometimes useful to disable buffering in order to
see the operations and their results right away instead of having to wait for the log entries to be
24 Core server configuration reference
Page 25

flushed to the file. Disabling log buffering can severely impact performance in heavily loaded
servers.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
on or off
onDefault Value
Directory StringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logbuffering: offExample
2.3.1.5 nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtime (Access log expiration time)
This attribute specifies the maximum age that a log file is allowed to reach before it is deleted.
This attribute supplies only the number of units. The units are provided by the
nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtimeunit attribute.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Range
cn=config
–1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)
A value of -1 or 0 means that the log never expires.
–1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtime: 2Example
2.3.1.6 nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtimeunit (Access log expiration time unit)
This attribute specifies the units for nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtime attribute. If
the unit is unknown by the server, then the log never expires.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
month |week|dayValid Values
monthDefault Value
Directory StringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logexpirationtimeunit: weekExample
2.3.1.7 nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled (Access log enable logging)
Disables and enables accesslog logging but only in conjunction with the nsslapd-accesslog
attribute that specifies the path and parameter of the log used to record each database access.
The following table describes the attribute parameters.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 25
Page 26

DescriptionParameter
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled: offExample
For access logging to be enabled, this attribute must be switched to on, and the
nsslapd-accesslog configuration attribute must have a valid path and parameter. Table 2-3
lists the four possible combinations of values for these two configuration attributes and their
outcome in terms of disabling or enabling of access logging.
Table 2-3 Attribute values for enabling or disabling access logging
Value of the
nsslapd-accesslog-logging-enabled
attribute
Value of the nsslapd-accesslog
attribute
Resulting logging state
on
filenameon
off
filenameoff
2.3.1.8 nsslapd-accesslog-logmaxdiskspace (Access log maximum disk space)
This attribute specifies the maximum amount of disk space in megabytes that the access logs are
allowed to consume. If this value is exceeded, the oldest access log is deleted.
When setting a maximum disk space, consider the total number of log files that can be created
due to log file rotation. Also, remember that there are three different log files (access log, audit
log, and error log) maintained by the Directory Server, each of which consumes disk space.
Compare these considerations to the total amount of disk space for the access log.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntryDN
Valid Range
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means that the
disk space allowed to the access log is unlimited in size.
500Default Value
IntegerSyntax
Disabledempty string
Enabled
Disabledempty string
Disabled
nsslapd-accesslog-logmaxdiskspace: 200Example
2.3.1.9 nsslapd-accesslog-logminfreediskspace (Access log minimum free disk space)
This attribute sets the minimum allowed free disk space in megabytes. When the amount of free
disk space falls below the value specified on this attribute, the oldest access logs are deleted until
enough disk space is freed to satisfy this attribute.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntryDN
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
5Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logminfreediskspace: 4Example
26 Core server configuration reference
Page 27

2.3.1.10 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsync-enabled (Access log rotation sync enabled)
This attribute sets whether access log rotation is to be synchronized with a particular time of the
day. Synchronizing log rotation this way can generate log files at a specified time during a day,
such as midnight to midnight every day. This makes analysis of the log files much easier because
they then map directly to the calendar.
For access log rotation to be synchronized with time-of-day, this attribute must be enabled with
the nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsynchour and
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsyncmin attribute values set to the hour and minute of
the day for rotating log files.
For example, to rotate access log files every day at midnight, enable this attribute by setting its
value to on, then set the values of the nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsynchour and
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsyncmin attributes to 0.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=config
on or off
off
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsync-enabled: onExample
2.3.1.11 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsynchour (Access log rotation sync hour)
This attribute sets the hour of the day for rotating access logs. This attribute must be used in
conjunction with nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsync-enabled and
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsyncmin attributes.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 through 23Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsynchour: 23Example
2.3.1.12 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsyncmin (Access log rotation sync minute)
This attribute sets the minute of the day for rotating access logs. This attribute must be used in
conjunction with nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsync-enabled and
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsynchour attributes.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 through 59Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationsyncmin: 30Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 27
Page 28
2.3.1.13 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime (Access log rotation time)
This attribute sets the time between access log file rotations. The access log is rotated when this
time interval is up, regardless of the current size of the access log. This attribute supplies only
the number of units. The units (day, week, month, and so forth) are given by the
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtimeunit attribute.
Although it is not recommended for performance reasons to specify no log rotation because the
log grows indefinitely, there are two ways of specifying this. Either set the
nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir attribute value to 1 or set the
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime attribute to -1. The server checks the
nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir attribute first,and, if this attribute value islarger than
1, the server then checks the nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime attribute. See
“nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir (Access log maximum number of log files)” for more
information.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Range
cn=config
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means that the
time between access log file rotation is unlimited.
1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime: 100Example
2.3.1.14 nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtimeunit (Access log rotation time unit)
This attribute sets the units for the nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime attribute.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
month | week | day | hour | minuteValid Values
dayDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtimeunit: weekExample
2.3.1.15 nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsize (Access log maximum log size)
This attribute sets the maximum access log size in megabytes. When this value is reached, the
access log is rotated. That means the server starts writing log information to a new log file. If the
nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir attribute is set to 1, the server ignores this attribute.
When setting a maximum log size, consider the total number of log files that can be created due
to log file rotation. Also, remember that there are three different log files (access log, audit log,
and error log) maintained by the Directory Server, each of which consumes disk space. Compare
these considerations to the total amount of disk space for the access log.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
28 Core server configuration reference
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means the log
file is unlimited in size.
100DefaultValue
Page 29

DescriptionParameter
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsize: 100Example
2.3.1.16 nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir (Access log maximum number of log files)
This attribute sets the total number of access logs that can be contained in the directory where
the access log is stored. Each time the access log is rotated, a new log file is created. When the
number of files contained in the access log directory exceeds the value stored in this attribute,
then the oldest version of the log file is deleted.
NOTE: For performance reasons, HP recommends not setting this value to 1 because the server
does not rotate the log, and it grows indefinitely.
If the value for this attribute is higher than 1, then check the
nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime attribute to establish whether log rotationis specified.
If the nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime attribute has a value of -1, then there is no
log rotation. See “nsslapd-accesslog-logrotationtime (Access log rotation time)” for more
information.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
10DefaultValue
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-maxlogsperdir: 10Example
2.3.1.17 nsslapd-accesslog-mode (Access log file permission)
This attribute sets the access mode or file permission with which access log files are to be created.
The valid values are any combination of 000 to 777 (these mirror the numbered or absolute
UNIX file permissions). The value must be a 3-digit number, the digits varying from 0 through
7:
0
1
2
3
None
Execute only
Write only
Write and execute
DescriptionDigitDescriptionDigit
4
5
6
7
Read only
Read and execute
Read and write
Read, write, and execute
In the 3-digit number, the first digitrepresents the owner's permissions, the second digit represents
the group's permissions, and the third digit represents everyone's permissions. When changing
the default value, remember that 000 prevents access to the logs and that allowing write
permissions to everyone can result in the logs being overwritten or deleted by anyone.
The newly configured access mode takes effect immediately for any open log file, as well as for
any log files that are created subsequently.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 29
Page 30

NOTE:
Any umask set for the runtime user of the Directory Server causes the effective mode to be more
restrictive.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
000 through 777ValidRange
600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-accesslog-mode: 600Example
2.3.1.18 nsslapd-attribute-name-exceptions
This attribute allows non-standard characters in attribute names to be used for backwards
compatibility with older servers, such as "_" in schema-defined attributes.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-attribute-name-exceptions: onExample
2.3.1.19 nsslapd-auditlog (Audit log)
This attribute sets the path and file name of the log used to record changes made to each database.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=config
Any valid file nameValid Values
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/log/audit
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog: /var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-example/log/auditExample
For audit logging to be enabled, this attribute must have a valid path and parameter, and the
nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled configuration attribute must be switched to on.
Table 2-4 lists the four possible combinations of values for these two configuration attributes
and their outcome in terms of disabling or enabling of audit logging.
Table 2-4 Attribute values for enabling or disabling audit logging
Value of the
nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled
Resulting logging state
Disabled
Enabled
empty string
AttributeValue of the nsslapd-auditlog Attribute
on
onfilename
30 Core server configuration reference
Page 31

Table 2-4 Attribute values for enabling or disabling audit logging (continued)
Value of the
nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled
AttributeValue of the nsslapd-auditlog Attribute
Resulting logging state
empty string
off
offfilename
2.3.1.20 nsslapd-auditlog-list
Provides a list of audit log files.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
NoneDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-list: auditlog2,auditlog3Example
2.3.1.21 nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtime (Audit log expiration time)
This attribute sets the maximum age that a log file is allowed to be before it is deleted. This
attribute supplies only the number of units. The units (day, week, month, and so forth) are given
by the nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtimeunit attribute.
Disabled
Disabled
DescriptionParameter
EntryDN
ValidRange
cn=config
-1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)
A value of -1 or 0 means that the log never expires.
-1DefaultValue
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtime: 1Example
2.3.1.22 nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtimeunit (Audit log expiration time unit)
This attribute sets the units for the nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtime attribute. If
the unit is unknown by the server, then the log never expires.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
month | week | dayValid Values
weekDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logexpirationtimeunit: dayExample
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 31
Page 32

2.3.1.23 nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled (Audit log enable logging)
Turns audit logging on and off.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled: offExample
For audit logging to be enabled, this attribute must have a valid path and parameter and the
nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled configuration attribute must be switched to on.
Table 2-5 lists the four possible combinations of values for these two configuration attributes
and their outcome in terms of disabling or enabling of audit logging.
Table 2-5 Attribute values for enabling or disabling audit logging
Value of the
nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled
Attribute
on
filenameon
off
filenameoff
Resulting logging stateValue of the nsslapd-auditlog Attribute
2.3.1.24 nsslapd-auditlog-logmaxdiskspace (Audit log maximum disk space)
Disabledempty string
Enabled
Disabledempty string
Disabled
This attribute sets the maximum amount of disk space in megabytes that the audit logs are
allowed to consume. If this value is exceeded, the oldest audit log is deleted.
When setting a maximum disk space, consider the total number of log files that can be created
due to log file rotation. Also remember that there are three different log files (access log, audit
log, and error log) maintained by the Directory Server, each of which consumes disk space.
Compare these considerations with the total amount of disk space for the audit log.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means that the
disk space allowed to the audit log is unlimited in size.
500Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logmaxdiskspace: 500Example
32 Core server configuration reference
Page 33

2.3.1.25 nsslapd-auditlog-logminfreediskspace (Audit log minimum free disk space)
This attribute sets the minimum permissible free disk space in megabytes. When the amount of
free disk space falls below the value specified by this attribute, the oldest audit logs are deleted
until enough disk space is freed to satisfy this attribute.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
5Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logminfreediskspace: 3Example
2.3.1.26 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled (Audit log rotation sync enabled)
This attribute sets whether audit log rotation is to be synchronized with a particular time of the
day. Synchronizing log rotation this way can generate log files at a specified time during a day,
such as midnight to midnight every day. This makes analysis of the log files much easier because
they then map directly to the calendar.
For audit log rotation to be synchronized with time-of-day, this attribute must be enabled with
the nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsynchour and
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsyncmin attribute values set to the hour and minute of
the day for rotating log files.
For example, to rotate audit log files every day at midnight, enable this attribute by setting its
value to on, then set the values of the nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsynchour and
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsyncmin attributes to 0.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled: onExample
2.3.1.27 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsynchour (Audit log rotation sync hour)
This attribute sets the hour of the day for rotating audit logs. This attribute must be used in
conjunction with nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled and
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsyncmin attributes.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=config
0 through 23Valid Range
None (because nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled is off)
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsynchour: 23Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 33
Page 34

2.3.1.28 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsyncmin (Audit log rotation sync minute)
This attribute sets the minute of the day for rotating audit logs. This attribute must be used in
conjunction with nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled and
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsynchour attributes.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=config
0 through 59Valid Range
None (because nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsync-enabled is off)
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationsyncmin: 30Example
2.3.1.29 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime (Audit log rotation time)
This attribute sets the time between audit log file rotations. The audit log is rotated when this
time interval is up, regardless of the current size of the audit log. This attribute supplies only the
number of units. The units (day, week, month, and so forth) are given by the
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtimeunit attribute. If the
nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir attribute is set to 1, the server ignores this attribute.
Although it is not recommended for performance reasons to specify no log rotation, as the log
grows indefinitely, there are two ways of specifying this. Either set the
nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir attribute value to 1 or set the
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime attribute to -1. The server checks the
nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir attribute first, and, if this attribute value is larger than
1, the server then checks the nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime attribute. See
“nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir (Audit log maximum number of log files)” for more information.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Range
cn=config
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means that the
time between audit log file rotation is unlimited.
1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime: 100Example
2.3.1.30 nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtimeunit (Audit log rotation time unit)
This attribute sets the units for the nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime attribute.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
month | week | day | hour | minuteValid Values
weekDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtimeunit: dayExample
34 Core server configuration reference
Page 35

2.3.1.31 nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsize (Audit log maximum log size)
This attribute sets the maximum audit log size in megabytes. When this value is reached, the
audit log is rotated. That means the server starts writing log information to a new log file. If
nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir to 1, the server ignores this attribute.
When setting a maximum log size, consider the total number of log files that can be created due
to log file rotation. Also, remember that there are three different log files (access log, audit log,
and error log) maintained by the Directory Server, each of which consumes disk space. Compare
these considerations to the total amount of disk space for the audit log.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Range
cn=config
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means the log
file is unlimited in size.
100Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsize: 50Example
2.3.1.32 nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir (Audit log maximum number of log files)
This attribute sets the total number of audit logs that can be contained in the directory where
the audit log is stored. Each time the audit log is rotated, a new log file is created. When the
number of files contained in the audit log directory exceeds the value stored on this attribute,
then the oldest version of the log file is deleted. The default is 1 log. If this default is accepted,
the server will not rotate the log, and it grows indefinitely.
If the value for this attribute is higher than 1, then check the
nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime attribute to establish whether log rotation is specified.
If the nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime attribute has a value of -1, then there is no log
rotation. See “nsslapd-auditlog-logrotationtime (Audit log rotation time)” for more information.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-maxlogsperdir: 10Example
2.3.1.33 nsslapd-auditlog-mode (Audit log file permission)
This attribute sets the access mode or file permissions with which audit log files are to be created.
The valid values are any combination of 000 to 777 because they mirror numbered or absolute
UNIX file permissions. The value must be a combination of a 3-digit number, the digits varying
from 0 through 7:
0
1
None
Execute only
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 35
DescriptionDigitDescriptionDigit
4
5
Read only
Read and execute
Page 36

DescriptionDigitDescriptionDigit
2
3
Write only
Write and execute
6
7
Read and write
Read, write, and execute
In the 3-digit number, the first digitrepresents the owner's permissions, the second digit represents
the group's permissions, and the third digit represents everyone's permissions. When changing
the default value, remember that 000 does not allow access to the logs and that allowing write
permissions to everyone can result in the logs being overwritten or deleted by anyone.
The newly configured access mode takes effect immediately for any open log file, as well as for
any log files that are created subsequently.
NOTE:
Any umask set for the runtime user of the Directory Server causes the effective mode to be more
restrictive.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
000 through 777Valid Range
600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-auditlog-mode: 600Example
2.3.1.34 nsslapd-certdir (Certificate and key database directory)
This is the full path to the directory holding the certificate and key databases for a Directory
Server instance. This directory must contain only the certificate and key databases for this instance
and no other instances. This directory must be owned and allow read-write access for the server
user ID. No other user should have read or right access to this directory. The default location is
the configuration file directory, /etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name.
Changes to this value will not take effect until the server is restarted.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
Absolute path to any directory which is owned by the server user ID and only allows read
and write access to the server user ID
/etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name
DirectoryStringSyntax
/etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-phonebookExample
2.3.1.35 nsslapd-certmap-basedn (Certificate map search base)
This attribute can be used when client authentication is performed using SSL certificates in order
to avoid limitations of the security subsystem certificate mapping, configured in the
certmap.conf file. Depending on the certmap.conf configuration, the certificate mapping
may be done using a directory subtree search based at the root DN. If the search is based at the
root DN, then the nsslapd-certmap-basedn attribute may force the search to be based at
some entry other than the root. The valid value for this attribute is the DN of the suffix or subtree
36 Core server configuration reference
Page 37

to use for certificate mapping. For further information on configuring for SSL, see the "Managing
SSL" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
2.3.1.36 nsslapd-config
This read-only attribute is the config DN.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any valid configuration DNValid Values
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-config: cn=configExample
2.3.1.37 nsslapd-conntablesize
This attribute sets the connection table size, which determines the total number of connections
supported by the server.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
Default Value
Increase the value of this attribute if Directory Server is refusing connections because it is out of
connection slots. When this occurs, the Directory Server's error log file records the message Not
listening for new connections -- too many fds open.
A server restart is required for the change to take effect.
You might have to do the following:
• Increase the operating system limits for the number of open files and number of open files
per process
• Edit the Directory Server environment configuration file /etc/opt/dirsrv/config/
dirsrv to increase the ulimit for the number of open files (ulimit -n)
For more information, see “nsslapd-maxdescriptors (Maximum file descriptors)”.
2.3.1.38 nsslapd-counters
cn=configEntry DN
Operating-system dependentValid Values
The default value is the process max descriptors, which can be configured using the
“nsslapd-maxdescriptors (Maximum file descriptors)” attribute.
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-conntablesize: 4093Example
Enables or disables some counters.
This version of Directory Server uses 64-bit numbers to avoid wrapping for some performance
and operational counters, such as entrycachetries and entriessent. However, arithmetic
operations on 64-bit numbers can impact performance in some situations. Turning off the counters
can provide a minimal improvement to performance, while negatively affecting long-term
statistics tracking.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 37
Page 38

This parameter is enabled by default. To disable statistics tracking, stop the Directory Server,
edit the dse.ldif file directly, and restart Directory Server.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
on or off
on
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-counters: onExample
2.3.1.39 nsslapd-csnlogging
This attribute sets whether change sequence numbers (CSNs), when available, are to be logged
in the access log. By default, CSN logging is turned on.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-csnlogging: onExample
2.3.1.40 nsslapd-ds4-compatible-schema
Makes the schema in cn=schema compatible with 4.x versions of Directory Server.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-ds4-compatible-schema: offExample
2.3.1.41 nsslapd-enquote-sup-oc (Enable superior object class enquoting)
This attribute is deprecated and will be removed in a future version of Directory Server.
This attribute controls whether quoting in the objectclass attributes contained in the
cn=schema entry conforms to the quoting specified by Internet draft RFC 2252. By default, the
Directory Server conforms to RFC 2252, which indicates that this value should not be quoted.
Only very old clients need this value set to on, so leave it off.
Turning this attribute on or off does not affect Directory Server Console.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
38 Core server configuration reference
Page 39

DescriptionParameter
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-enquote-sup-oc: offExample
2.3.1.42 nsslapd-errorlog (Error log)
This attribute sets the path and file name of the log used to record error messages generated by
the Directory Server. These messages can describe error conditions, but more often they contain
informative conditions, such as:
• Server startup and shutdown times.
• The port number that the server uses.
This log contains differing amounts of information depending on the current setting of the Log
Level attribute. See “nsslapd-errorlog-level (Error log level)” for more information.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any valid file nameValid Values
Default Value
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/log/errors
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog: /var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-example/log/errorsExample
For error logging to be enabled, this attribute must have a valid path and file name, and the
nsslapd-errorlog-logging-enabled configuration attribute must be switched to on.
Table 2-6 lists the four possible combinations of values for these two configuration attributes
and their outcome in terms of disabling or enabling of error logging.
Table 2-6 Attribute values for enabling or disabling error logging
Value of the
nsslapd-errorlog-logging-enabled
AttributeValue of the nsslapd-errorlog Attribute
empty string
empty string
2.3.1.43 nsslapd-errorlog-level (Error log level)
This attribute sets the level of logging for the Directory Server. The log level is additive; that is,
specifying a value of 3 includes both levels 1 and 2.
on
onfilename
off
offfilename
Resulting logging state
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 39
Page 40

The default value for nsslapd-errorlog-level is 16384.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
1 Trace function calls. Logs a message when the server enters and exits a function.
2 Debug packet handling.
4 Heavy trace output debugging.
8 Connection management.
16 Print out packets sent/received.
32 Search filter processing.
64 Config file processing.
128 Access control list processing.
1024 Log communications with shell databases.
2048 Log entry parsing debugging.
4096 Housekeeping thread debugging.
8192 Replication debugging.
16384 Default levelof logging used for critical errors and other messages that are always
written to the error log; for example, server startup messages. Messages at this
level are always included in the error log, regardless of the log level setting.
32768 Database cache debugging.
65536 Server plug-in debugging. It writes an entry to the log file when a server plug-in
calls slapi-log-error.
131072 Microsecond resolution for timestamps instead of the default seconds.
262144
Access control summary information, much less verbose than level 128. This
value is recommended for use when a summary of access control processing is
needed. Use 128 for very detailed processing messages.
2.3.1.44 nsslapd-errorlog-list
This read-only attribute provides a list of error log files.
Valid Values
16384Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-level: 8192Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
NoneDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-list: errorlog2,errorlog3Example
40 Core server configuration reference
Page 41

2.3.1.45 nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtime (Error log expiration time)
This attribute sets the maximum age that a log file is allowed to reach before it is deleted. This
attribute supplies only the number of units. The units (day, week, month, and so forth) are given
by the nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtimeunit attribute.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
-1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)
A value of -1 or 0 means that the log never expires.
-1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtime: 1Example
2.3.1.46 nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtimeunit (Error log expiration time unit)
This attribute sets the units for the nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtime attribute. If
the unit is unknown by the server, then the log never expires.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
month | week | dayValid Values
monthDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logexpirationtimeunit: weekExample
2.3.1.47 nsslapd-errorlog-logging-enabled (Enable error logging)
Turns error logging on and off.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logging-enabled: onExample
2.3.1.48 nsslapd-errorlog-logmaxdiskspace (Error log maximum disk space)
This attribute sets the maximum amount of disk spacein megabytes that the error logs are allowed
to consume. If this value is exceeded, the oldest error log is deleted.
When setting a maximum disk space, consider the total number of log files that can be created
due to log file rotation. Also, remember that there are three different log files (access log, audit
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 41
Page 42

log, and error log) maintained by the Directory Server, each of which consumes disk space.
Compare these considerations to the total amount of disk space for the error log.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means that the
disk space allowed to the error log is unlimited in size.
500Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logmaxdiskspace: 500Example
2.3.1.49 nsslapd-errorlog-logminfreediskspace (Error log minimum free disk space)
This attribute sets the minimum allowed free disk space in megabytes. When the amount of free
disk space falls below the value specified on this attribute, the oldest error log is deleted until
enough disk space is freed to satisfy this attribute.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
5Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logminfreediskspace: 5Example
2.3.1.50 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsync-enabled (Error log rotation sync enabled)
This attribute sets whether error log rotation is to be synchronized with a particular time of the
day. Synchronizing log rotation this way can generate log files at a specified time during a day,
such as midnight to midnight every day. This makes analysis of the log files much easier because
they then map directly to the calendar.
For error log rotation to be synchronized with time-of-day, this attribute must be enabled with
the nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsynchour and
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsyncmin attribute values set to the hour and minute of
the day for rotating log files.
For example, to rotate error log files every day at midnight, enable this attribute by setting its
value to on, then set the values of the nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsynchour and
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsyncmin attributes to 0.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
on or off
off
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsync-enabled: onExample
42 Core server configuration reference
Page 43

2.3.1.51 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsynchour (Error log rotation sync hour)
This attribute sets the hour of the day for rotating error logs. This attribute must be used in
conjunction with nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsync-enabled and
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsyncmin attributes.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 through 23Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsynchour: 23Example
2.3.1.52 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsyncmin (Error log rotation sync minute)
This attribute sets the minute of the day for rotating error logs. This attribute must be used in
conjunction with nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsync-enabled and
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsynchour attributes.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 through 59Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationsyncmin: 30Example
2.3.1.53 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime (Error log rotation time)
This attribute sets the time between error log file rotations. The error log is rotated when this
time interval is up, regardless of the current size of the error log. This attribute supplies only the
number of units. The units (day, week, month, and so forth) are given by the
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtimeunit (Error Log Rotation Time Unit) attribute.
Although it is not recommended for performance reasons to specify no log rotation, as the log
grows indefinitely, there are two ways of specifying this. Either set the
nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir attribute value to 1 or set the
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime attribute to -1. The server checks the
nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir attribute first, and, if this attribute value is larger than
1, the server then checks the nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime attribute. See
“nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir (Maximum number of error log files)” for more information.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647), where a value of -1 means that the
time between error log file rotation is unlimited).
1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime: 100Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 43
Page 44

2.3.1.54 nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtimeunit (Error log rotation time unit)
This attribute sets the units for nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime (Error Log Rotation
Time). If the unit is unknown by the server, then the log never expires.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
month | week | day | hour | minuteValid Values
weekDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtimeunit: dayExample
2.3.1.55 nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsize (Maximum error log size)
This attribute sets the maximum error log size in megabytes. When this value is reached, the
error log is rotated, and the server starts writing log information to a new log file. If
nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir is set to 1, the server ignores this attribute.
When setting a maximum log size, consider the total number of log files that can be created due
to log file rotation. Also, remember that there are three different log files (access log, audit log,
and error log) maintained by the Directory Server, each of which consumes disk space. Compare
these considerations to the total amount of disk space for the error log.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
-1 | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647) where a value of -1 means the log
file is unlimited in size.
100Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsize: 100Example
2.3.1.56 nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir (Maximum number of error log files)
This attribute sets the total number of error logs that can be contained in the directory where the
error log is stored. Each time the error log is rotated, a new log file is created. When the number
of files contained in the error log directory exceeds the value stored on this attribute, then the
oldest version of the log file is deleted. The default is 1 log. If this default is accepted, the server
does not rotate the log, and it grows indefinitely.
If the value for this attribute is higher than 1, then check the
nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime attribute to establish whether log rotation is specified.
If the nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime attribute has a value of -1, then there is no log
rotation. See “nsslapd-errorlog-logrotationtime (Error log rotation time)” for more information.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
1Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-maxlogsperdir: 10Example
44 Core server configuration reference
Page 45

2.3.1.57 nsslapd-errorlog-mode (Error log file permission)
This attribute sets the access mode or file permissions with which error log files are to be created.
The valid values are any combination of 000 to 777 because they mirror numbered or absolute
UNIX file permissions. That is, the value must be a combination of a 3-digit number, the digits
varying from 0 through 7:
DescriptionDigitDescriptionDigit
0
1
2
3
None
Execute only
Write only
Write and execute
4
5
6
7
Read only
Read and execute
Read and write
Read, write, and execute
In the 3-digit number, the first digitrepresents the owner's permissions, the second digit represents
the group's permissions, and the third digit represents everyone's permissions. When changing
the default value, remember that 000 does not allow access to the logs and that allowing write
permissions to everyone can result in the logs being overwritten or deleted by anyone.
The newly configured access mode takes effect immediately for any open log file, as well as for
any log files that are created subsequently.
NOTE:
Any umask set for the runtime user of the Directory Server causes the effective mode to be more
restrictive.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
000 through 777Valid Range
600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-errorlog-mode: 600Example
2.3.1.58 nsslapd-groupevalnestlevel
This attribute is deprecated, and documented here only for historical purposes.
The Access Control Plug-in does not use the value specified by the
nsslapd-groupevalnestlevel attribute to set the number of levels of nesting that access
control performs for group evaluation. Instead, the number of levels of nesting is hard-coded as
5.
2.3.1.59 nsslapd-idletimeout (Default idle timeout)
This attribute sets the amount of time in seconds after which an idle LDAP client connection is
closed by the server. A value of 0 means that the servernever closes idle connections. This setting
applies to all connections and all users. Idle timeout is enforced when the connection table is
walked, when poll() does not return zero. Therefore, a server with a single idle connection
never enforces the idle timeout.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 45
Page 46

Use the nsIdleTimeout operational attribute, which can be added to user entries, to override
the value assigned to this attribute. For details, see the "Setting Resource Limits Based on the
Bind DN" section in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-idletimeout: 0Example
2.3.1.60 nsslapd-instancedir (Instance directory)
This attribute is deprecated. There are now separate configuration parameters for instance-specific
paths, such as nsslapd-certdir and nsslapd-lockdir. See the documentation for the
specific directory path that is set.
2.3.1.61 nsslapd-ioblocktimeout (IO block time out)
This attribute sets the amount of time in milliseconds after which the connection to a stalled
LDAP client is closed. An LDAP client is considered to be stalled when it has not made any I/O
progress for read or write operations.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
1800000Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-ioblocktimeout: 1800000Example
2.3.1.62 nsslapd-lastmod (Track modification time)
This attribute sets whether the Directory Server maintains the modification attributes for Directory
Server entries. These are operational attributes. These attributes include:
modifiersname
modifytimestamp
creatorsname
createtimestamp
Valid Values
The distinguished name of the person who last modified the entry.
The timestamp, in GMT format, for when the entry was last modified.
The distinguished name of the person who initially created the entry.
The timestamp for when the entry was created in GMT format.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-lastmod: onExample
46 Core server configuration reference
Page 47

CAUTION:
This attribute should never be turned off. If the nsslapd-lastmod is set to off, then generating
nsUniqueIDs is also disabled, replication does not work, and other issues may arise.
If for some reason this attribute were set to off, the solution is to export the database to ldif
(db2ldif or db2ldif.pl or from the console), set the value to on, and import the data. The
import process assigns each entry a unique id.
2.3.1.63 nsslapd-ldapifilepath (LDAPI socket file path)
This attribute is applicable only if nsslapd-ldapilisten is enabled. This attribute indicates
the path to the socket file used for communicating using LDAP over UNIX domains (LDAPI).
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=config
Any valid file nameValid Values
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/slapd-instance_name.socket
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-ldapifilepath: /var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-example/slapd-example.socketExample
2.3.1.64 nsslapd-ldapilisten (Enable LDAPI socket)
This attribute is applicable only if nsslapd-ldapilisten is enabled. This attribute indicates
the path to the socket file used for communicating using LDAP over UNIX domains (LDAPI).
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=config
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-ldapilisten: offExample
2.3.1.65 nsslapd-listenhost (Listen to IP address)
This attribute allows multiple Directory Server instances to run on a multihomed machine (or
makes it possible to limit listening to one interface of a multihomed machine). There can be
multiple IP addresses associated with a single host name, and these IP addresses can be a mix
of both IPv4 and IPv6. This parameter can be used to restrict the Directory Server instance to a
single IP interface.
If a host name is given as the nsslapd-listenhost value, then the Directory Server responds
to requests for every interface associated with the host name. If a single IP interface (either IPv4
or IPv6) is given as the nsslapd-listenhost value, Directory Server only responds to requests
sent to that specific interface. Either an IPv4 or IPv6 address can be used.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=config
Any local host name, IPv4 or IPv6 addressValid Values
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 47
Page 48

DescriptionParameter
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-listenhost: ldap.example.comExample
NOTE:
The host name value can be a relocatable IP address.
2.3.1.66 nsslapd-localhost (Local host)
This attribute specifies the host machine on which the Directory Server runs. This attribute is
used to create the referral URL that forms part of the MMR protocol. In a high-availability
configuration with failover nodes, that referral should point to the virtual name of the cluster,
not the local host name.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any fully qualified host name.Valid Values
Host name of installed machine.Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-localhost: phonebook.example.comExample
2.3.1.67 nsslapd-localuser (Local user)
This attribute sets the user as whom the Directory Server runs. The group as which the user runs
is derived from this attribute by examining the user's primary group. Should the user change,
then all the instance-specific files and directories for this instance need to be changed to be owned
by the new user, using a tool such as the chown command.
The value for the nsslapd-localuser is set initially when the server instance is configured.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any valid userValid Values
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-localuser: wwwExample
2.3.1.68 nsslapd-lockdir (Server lock file directory)
This is the full path to the directory the server uses for lock files. The default value is
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/lock. Changes to this value willnot take effect
until the server is restarted.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Absolute path to a directory owned by the server user ID with write access to the server IDValid Values
48 Core server configuration reference
Page 49

DescriptionParameter
Default Value
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/lock
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-lockdir: /var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-example/lockExample
2.3.1.69 nsslapd-maxbersize (Maximum message size)
Defines the maximum size in bytes allowed for an incoming message. This limits the size of
LDAP requests that can be handled by the Directory Server. Limiting the size of requests prevents
some kinds of denial of service attacks.
The limit applies to the total size of the LDAP request. For example, if the request is to add an
entry and if the entry in the request is larger than two megabytes, then the add request is denied.
Be cautious before changing this attribute.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
0 - 2 gigabytes (2,147,483,647 bytes)
Zero 0 means that the default value should be used.
2097152Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-maxbersize: 2097152Example
2.3.1.70 nsslapd-maxdescriptors (Maximum file descriptors)
This attribute sets the maximum, platform-dependent number of file descriptors that the Directory
Server tries to use. A file descriptor is used whenever a client connects to the server and also for
some server activities, such as index maintenance. File descriptors are also used by access logs,
error logs, audit logs, database files (indexes and transaction logs), and as sockets for outgoing
connections to other servers for replication and chaining.
The number of descriptors available for TCP/IP to serve client connections is determined by
nsslapd-conntablesize, and is equal to the nsslapd-maxdescriptors attribute minus
the number of file descriptors used by the server as specified in the
nsslapd-reservedescriptors attribute for non-client connections, such as index management
and managing replication. The nsslapd-reservedescriptors attribute is the number of file
descriptors available for other uses as described above. See “nsslapd-reservedescriptors (Reserved
file descriptors)”.
The number given here should not be greater than the total number of file descriptors that the
operating system allows the ns-slapd process to use. This number differs depending on the
operating system.
If this value is set too high, the Directory Server queries the operating system for the maximum
allowable value, then use that value. It also issues a warning in the error log. If this value is set
to aninvalid value remotely, by usingthe Directory Server Console or the ldapmodify command,
the server rejects the new value, keep the old value, and respond with an error.
Some operating systems let users configure the number of file descriptors available to a process.
See the operating system documentation for details on file descriptor limits and configuration.
The dsktune program (explained in the HP-UX Directory Server installation guide) can be used
to suggest changes to the system kernel or TCP/IP tuning attributes, including increasing the
number of file descriptors if necessary. Increased the value on this attribute if the Directory Server
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 49
Page 50

is refusing connections because it is out of file descriptors. When this occurs, the following
message is written to the Directory Server's error log file:
Not listening for new connections -- too many fds open
See “nsslapd-conntablesize” for more information about increasing the number of incoming
connections.
NOTE:
UNIX shells usually have configurable limits on the number of file descriptors. See the operating
system documentation for further information about limit and ulimit, as these limits can
often cause problems.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to 65535Valid Range
1024Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-maxdescriptors: 1024Example
2.3.1.71 nsslapd-max-filter-nest-level (Maximum search filter nesting level)
This attribute sets the level of nesting allowed in search filters. Setting this parameter to 0 or a
negative number removes any limit on the depth of the nested filters.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
-1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
40Default Value
IntegerSyntax
Example
nsslapd-max-filter-nest-level: 1
This would cause the following filter to be rejected:
"(&(&(uid=jsmith)(sn=smith))(objectclass=person))"
2.3.1.72 nsslapd-maxsasliosize (Maximum SASL packet size)
When a user is authenticated to the Directory Server over SASL GSS-API, the server must allocate
a certain amount of memory to the client to perform LDAP operations, according to how much
memory the client requests. It is possible for an attacker to send such a large packet size that it
crashes the Directory Server or ties it up indefinitely as part of a denial of service attack.
The packet size which the Directory Server will allow for SASL clients can be limited using the
nsslapd-maxsasliosize attribute. This attribute sets the maximum allowed SASL IO packet
size that the server will accept.
When an incoming SASL I/O packet is larger than the nsslapd-maxsasliosize limit, the
server immediately disconnects the client and logs a message to the error log, so that an
administrator can adjust the setting if necessary.
50 Core server configuration reference
Page 51

This attribute value is specified in bytes.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
-1 (unlimited) to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647) on 32-bit systems
-1 (unlimited) to the maximum 64-bit integer value (9223372036854775807) on 64-bitsystems
2097152 (2MB)Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-maxsasliosize: 5000000Example
2.3.1.73 nsslapd-maxthreadsperconn (Maximum threads per connection)
Defines the maximum number of threads that a connection can use. For normal operations where
a client binds and only performs one or two operations before unbinding, use the default value.
For situations where a client binds and simultaneously issues many requests, increase this value
to allow each connection enough resources to perform all the operations. This attribute is not
available from the server console.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to maximum operation threads (nsslapd-threadnumber)Valid Range
5Default Value
IntegerSyntax
2.3.1.74 nsslapd-nagle
When the value of this attribute is off, the TCP_NODELAY option is set so that LDAP responses
(such as entries or result messages) are sent back to a client immediately. When the attribute is
turned on, default TCP behavior applies; specifically, sending data is delayed so that additional
data can be grouped into one packet of the underlying network MTU size, typically 1500 bytes
for Ethernet.
Valid Values
nsslapd-maxthreadsperconn: 5Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-nagle: offExample
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 51
Page 52

2.3.1.75 nsslapd-outbound-ldap-io-timeout
This attribute limits the I/O wait time for all outbound LDAP connections such as those established
for replication. The default is 300000 milliseconds (5 minutes). A value of 0 means that the
server does not impose a limit on I/O wait time.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
300000Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-outbound-ldap-io-timeout: 300000Example
2.3.1.76 nsslapd-plugin
This read-only attribute lists the DNs of the plug-in entries for the syntax and matching rule
plug-ins loaded by the server.
2.3.1.77 nsslapd-port (Port number)
This attribute gives the TCP/IP port number used for standard LDAP communications. To run
TLS/SSL over this port, use the Start TLS extended operation. This selected port must be unique
on the host system; make sure no other application is attempting to use the same port number.
Specifying a port number of less than 1024 means the Directory Server has to be started as root.
The server sets its effective user to the nsslapd-localuser value after startup.
When changing the port number for a configuration directory, the corresponding server instance
entry in the configuration directory must be updated.
The server has to be restarted for the port number change to be taken into account.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to 65535Valid Range
389Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-port: 389Example
NOTE:
Set the port number to zero (0) to disable the LDAP port if the LDAPS port is enabled.
2.3.1.78 nsslapd-privatenamespaces
This read-only attribute contains the list of the private naming contexts cn=config, cn=schema,
and cn=monitor.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
cn=config, cn=schema, and cn=monitorValid Values
Default Value
52 Core server configuration reference
Page 53

DescriptionParameter
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-privatenamespaces: cn=configExample
2.3.1.79 nsslapd-pwpolicy-local (Enable subtree- and user-level password policy)
Turns fine-grained (subtree- and user-level) password policy on and off.
If this attribute has a value of off, all entries (except for cn=Directory Manager) in the
directory is subjected to the global password policy; the server ignores any defined subtree/user
level password policy.
If this attribute has a value of on, the server checks for password policies at the subtree- and
user-level and enforces those policies.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-pwpolicy-local: offExample
2.3.1.80 nsslapd-readonly (Read only)
This attribute sets whether the whole server is in read-only mode, meaning that neither data in
the databases nor configuration information can be modified. Any attempt to modify a database
in read-only mode returns an error indicating that the server is unwilling to perform the operation.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-readonly: offExample
2.3.1.81 nsslapd-referral (Referral)
This multi-valued attribute specifies the LDAP URLs to be returned by the suffix when the server
receives a request for an entry not belonging to the local tree; that is, an entry whose suffix does
not match the value specified on any of the suffix attributes. For example, assume the server
contains only entries:
ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
but the request is for this entry:
ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com
In this case, the referral would be passed back to the client in an attempt to allow the LDAP client
to locate a server that contains the requested entry. Although only one referral is allowed per
Directory Server instance, this referral can have multiple values.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 53
Page 54

NOTE:
To use SSL and TLS communications, the referral attribute should be in the form
ldaps://server-location.
Start TLS does not support referrals.
For more information on managing referrals, see the "Configuring Directory Databases" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
Any valid LDAP URL in the form ldap://server-location
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-referral: ldap://ldap.example.comExample
2.3.1.82 nsslapd-referralmode (Referral mode)
When set, this attribute sends back the referral for any request on any suffix.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
Any valid LDAP URL in the form >ldap://server-location
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-referralmode: ldap://ldap.example.comExample
2.3.1.83 nsslapd-reservedescriptors (Reserved file descriptors)
This attribute specifies the number of file descriptors that Directory Server reserves for managing
non-client connections, such as index management and managing replication. The number of
file descriptors that the server reserves for this purpose subtracts from the total number of file
descriptors available for servicing LDAP client connections (See “nsslapd-maxdescriptors
(Maximum file descriptors)”).
Most installations of Directory Server should never need to change this attribute. However,
consider increasing the value on this attribute if all the following are true:
• The server is replicating to a large number of consumer servers (more than 10), and/or the
server is maintaining a large number of index files (more than 30).
• The server is servicing a large number of LDAP connections.
• There are error messages reporting that the server is unable to open file descriptors (the
actual error message differs depending on the operation that the server is attempting to
perform), but these error messages are not related to managing client LDAP connections.
Increasing the value on this attribute may result in more LDAP clients being unable to access
the directory. Therefore, the value on this attribute is increased, also increase the value on the
nsslapd-maxdescriptors attribute. It may not be possible to increase the
nsslapd-maxdescriptors value if the server is already using the maximum number of file
descriptors that the operating system allows a process to use; see the operating system
documentation for details. If this is the case, then reduce the load on the server by causing LDAP
54 Core server configuration reference
Page 55

clients to search alternative directory replicas. See “nsslapd-conntablesize” for information about
file descriptor usage for incoming connections.
To assist in computing the number of file descriptors set for this attribute, use the following
formula:
nsslapd-reservedescriptor = 20 + (NldbmBackends * 4) + NglobalIndex +
ReplicationDescriptor + ChainingBackendDescriptors + PTADescriptors + SSLDescriptors
Where:
• NldbmBackends is the number of ldbm databases.
• NglobalIndex is the total number of configured indexes for all databases including system
indexes. (By default 8 system indexes and 17 additional indexes per database).
• ReplicationDescriptor is eight (8) plus the number of replicas in the server that can
act as a supplier or hub (NSupplierReplica).
• ChainingBackendDescriptors is NchainingBackend times the
nsOperationConnectionsLimit (a chaining or database link configuration attribute;
10 by default).
• PTADescriptors is 3 if the Pass Through Authentication plug-in (PTA) is configured and
0 if PTA is not configured.
• SSLDescriptors is 5 (4 files + 1 listensocket) if SSL is configured and 0 if SSL is not
configured.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to 65535Valid Range
64Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-reservedescriptors: 64Example
2.3.1.84 nsslapd-return-exact-case (Return exact case)
Returns the exact case of attribute type names as requested by the client. Although
LDAPv3-compliant clients must ignore the case of attribute names, some client applications
require attribute names to match exactly thecase of the attribute as it is listed in the schema when
the attribute is returned by the Directory Server as the result of a search or modify operation.
This attribute is enabled by default. However, HP recommends that client applications do not
set expectations regarding the case of attributes returned from the server, as this violates LDAPv3.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-return-exact-case: offExample
2.3.1.85 nsslapd-rewrite-rfc1274
This attribute is deprecated and will be removed in a later version.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 55
Page 56

This attribute is used only for LDAPv2 clients that require attribute types to be returned with
their RFC 1274 names. Set the value to on for those clients. The default is off.
2.3.1.86 nsslapd-rootdn (Manager DN)
This attribute sets the distinguished name (DN) of an entry that is not subject to access control
restrictions, administrative limit restrictions for operations on the directory, or resource limits
in general. There does not have to be an entry corresponding to this DN, and by default there is
not an entry for this DN, thus values like cn=Directory Manager are acceptable.
For information on changing the root DN, see the "Creating Directory Entries" chapter in the
HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any valid distinguished nameValid Values
Default Value
DNSyntax
nsslapd-rootdn: cn=Directory ManagerExample
2.3.1.87 nsslapd-rootpw (Root password)
This attribute sets the password associated with the Manager DN. When the root password is
provided, it is hashed according to the hashing method selected for the
nsslapd-rootpwstoragescheme attribute. When viewed from the server console, thisattribute
shows the value *****. When viewed from the dse.ldif file, this attribute shows the hashing
method followed by the hashed string of the password. The example shows the password as
displayed in the dse.ldif file, not the actual password.
CAUTION:
When the root DN is configured at server setup, a root password is required. However, you can
delete the root password from dse.ldif by directly editing the file. In this situation, the root
DN obtains unauthenticated (anonymous) access only. When a root DN is configured for the
database, always make sure that a root password is defined in dse.ldif. The pwdhash
command-line utility can create a new root password. For more information, see “pwdhash
(Prints encrypted passwords)”.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
Any valid password encrypted by any one of the encryption methods which are described
in “passwordStorageScheme (Password storage scheme)”.
Syntax
56 Core server configuration reference
DirectoryString {encryption_method }encrypted_Password
nsslapd-rootpw: {SSHA}9Eko69APCJfFExample
Page 57

2.3.1.88 nsslapd-rootpwstoragescheme (Root password storage scheme)
This attribute sets the encryption method used for the root password.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
2.3.1.89 nsslapd-saslpath
Sets the absolute path to the directory containing the Cyrus-SASL SASL2 plug-ins. Normally,
the HP-UX Directory Server cannot use the system SASL libraries because they may not be
provided or they may be the wrong version. Setting this attribute allows the server to use custom
or non-standard SASL plug-in libraries. This is usually set correctly during installation, and HP
strongly recommends not changing this attribute.
If this parameter is set, the server uses the specified path for loading SASL plugins. If this
parameter is not set, the server uses the SASL_PATH environment variable. If neither
nsslapd-saslpath or SASL_PATH are set, the server attempts to load SASL plugins from the
default location, /opt/dirsrv/lib/sasl2.
Changes made to this attribute will not take effect until the server is restarted.
Any encryption method as described in “passwordStorageScheme (Password storage
scheme)”.
SSHADefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-rootpwstoragescheme: SSHAExample
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Path to plugins directory.Valid Values
/opt/dirsrv/lib/sasl2Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-saslpath: /opt/dirsrv/lib/sasl2Example
2.3.1.90 nsslapd-schema-ignore-trailing-spaces (Ignore trailing spaces in object class names)
Ignores trailing spaces in object class names. By default, the attribute is turned off. If the directory
contains entries with object class values that end in one or more spaces, turn this attribute on. It
is preferable to remove the trailing spaces because the LDAP standards do not allow them.
For performance reasons, a server restart is required for changes to take effect.
An error is returned by default when object classes that include trailing spaces are added to an
entry. Additionally, during operations such as add, modify, and import (when object classes are
expanded and missing superiors are added) trailing spaces are ignored, if appropriate. This
means that even when nsslapd-schema-ignore-trailing-spaces is on, a value such as
top is not added if top is already there. An error message is logged and returned to the client
if an object class is not found and it contains trailing spaces.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 57
Page 58

DescriptionParameter
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-schema-ignore-trailing-spaces: onExample
2.3.1.91 nsslapd-schemacheck (Schema checking)
This attribute sets whether the database schema is enforced when entries are added or modified.
When this attribute has a value of on, Directory Server will not check the schema of existing
entries until they are modified. The database schema defines the type of information allowed in
the database. The default schema can be extended by adding object class and attribute type
definitions. For information on how to extend the schema using the Directory Server Console,
see the "Extending the Directory Schema" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator
guide.
CAUTION:
HP strongly discourages turning off schema checking. This can lead to severe interoperability
problems. This is typically used for very old or nonstandard LDAP data that must be imported
into the Directory Server. If there are not a lot of entries that have this problem, consider using
the extensibleObject object class in those entries to disable schema checking on a per entry
basis.
NOTE:
Schema checking works by default when database modifications are made using an LDAP client,
such as ldapmodify, or when importing a database from LDIF using ldif2db. If schema
checking is turned off, every entry has to be verified manually to see that they conform to the
schema. If schema checking is turned on, the server sends an error message listing the entries
which do not match the schema. Ensure that the attributes and object classes created in the LDIF
statements are both spelled correctly and identified in dse.ldif. Either create an LDIF file in
the schema directory or add the definitions to 99user.ldif.
Valid Values
2.3.1.92 nsslapd-schemadir
This is the absolute path to the directory containing the Directory Server instance-specific schema
files. When the server starts up, it reads the schema files from this directory, and when the schema
is modified through LDAP tools, the schema files in this directory are updated. This directory
must be owned by the server user ID, and that user must have read and write permissions to
the directory. The default value is the schema subdirectory of the Directory Server instance-specific
configuration directory, /etc/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/schema.
Changes made to this attribute will not take effect until the server is restarted.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-schemacheck: onExample
58 Core server configuration reference
Page 59

2.3.1.93 nsslapd-schemareplace
Determines whether modify operations that replace attribute values are allowed on the
cn=schema entry.
The default setting allows only the replication protocol to perform a complete schemareplacement;
normal clients are limited to adding and deleting individualschema definitions. HP recommends
that the default setting not be modified.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off or replication-only
replication-onlyDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-schemareplace: replication-onlyExample
2.3.1.94 nsslapd-securelistenhost
This attribute allows multiple Directory Server instances to run on a multihomed machine (or
makes it possible to limit listening to one interface of a multihomed machine). There can be
multiple IP addresses associated with a single host name, and these IP addresses can be a mix
of both IPv4 and IPv6. This parameter can be used to restrict the Directory Server instance to a
single IP interface; this parameter also specifically sets what interface to use for TLS/SSL traffic
rather than regular LDAP connections.
If a host name is given as the nsslapd-securelistenhost value, then the Directory Server
responds to requests for every interface associated with the host name. If a single IP interface
(either IPv4 or IPv6) is given as the nsslapd-securelistenhost value, Directory Server only
responds to requests sent to that specific interface. Either an IPv4 or IPv6 address can be used.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any secure host name, IPv4 or IPv6 addressValid Values
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-securelistenhost: ldaps.example.comExample
2.3.1.95 nsslapd-securePort (Encrypted port number)
This attribute sets the TCP/IP port number used for TLS/SSL communications. This selected port
must be unique on the host system; make sure no other application is attempting to use the same
port number. Specifying a port number of less than 1024 requires that Directory Server be started
as root. The server sets its effective user to the nsslapd-localuser value after startup.
The server only listens to this port if it has been configured with a private key and a certificate,
and nsslapd-security is set to on; otherwise, it does not listen on this port.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 59
Page 60

The server has to be restarted for the port number change to be taken into account.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to 65535Valid Range
636Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-securePort: 636Example
2.3.1.96 nsslapd-security (Security)
This attribute sets whether the Directory Server is to accept TLS/SSL communications on its
encrypted port. This attribute should be set to on for secure connections. To run with security
on, the server must be configured with a private key and server certificate in addition to the
other TLS/SSL configuration.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-security: offExample
2.3.1.97 nsslapd-sizelimit (Size limit)
This attribute sets the maximum number of entries to return from a search operation. If this limit
is reached, ns-slapd returns any entries it has located that match the search request, as well as
an exceeded size limit error.
When no limit is set, ns-slapd returns every matching entry to the client regardless of the
number found. To set a no limit value whereby the Directory Server waits indefinitely for the
search to complete, specify a value of -1 for this attribute in the dse.ldif file.
This limit applies to everyone, regardless of their organization.
NOTE:
A value of -1 on this attribute in dse.ldif file is the same as leaving the attribute blank in the
server console, in that it causes no limit to be used. This cannot have a null value in dse.ldif
file, as it is not a valid integer. It is possible to set it to 0, which returns size limit exceeded
for every search.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
-1 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Range
2000Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-sizelimit: 2000Example
60 Core server configuration reference
Page 61

2.3.1.98 nsslapd-ssl-check-hostname (Verify host name for outbound connections)
This attribute determines whether an SSL-enabled Directory Server should verify authenticity
of peer servers by matching their host name against the value assigned to the common name
(cn) attribute of the subject name (subjectDN field) in the certificate being presented. By default,
the attribute is set to on. If it is on and if the host name does not match the cn attribute of the
certificate, appropriate error messages are logged.
For example, in a replicated environment, messages similar to the following are logged in the
supplier server's log files if it finds that the peer server's host name does not match the name
specified in its certificate:
[DATE] - SSL alert: ldap_sasl_bind("",LDAP_SASL_EXTERNAL) 81 (Netscape runtime error -12276 Unable to communicate securely with peer: requested domain name does not
match the server's certificate.)
[DATE] NSMMReplicationPlugin - agmt="cn=SSL Replication Agreement to host1" (host1.example.com:636):
Replication bind with SSL client authentication failed:
LDAP error 81 (Can't contact LDAP server)
HP recommends turning this attribute on to protect Directory Server's outbound SSL connections
against a man in the middle (MITM) attack.
NOTE:
DNS and reverse DNS must be set up correctly in order for this to work; otherwise, the server
cannot resolve the peer IP address to the host name in the subject DN in the certificate.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-ssl-check-hostname: onExample
2.3.1.99 nsslapd-threadnumber (Thread number)
Defines the number of operation threads that the Directory Server creates at startup. The
nsslapd-threadnumber value should be increased if there are many directory clients
performing time-consuming operations such as add or modify, as this ensures that there are
other threads available for servicing short-lived operations such as simple searches. This value
may also need increased if there are many replication agreements or chained backends (database
links). This attribute is not available from the server console.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum number of threads supported by the systemValid Range
30Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-threadnumber: 60Example
2.3.1.100 nsslapd-timelimit (Time limit)
This attribute sets the maximum number of seconds allocated for a search request. If this limit
is reached, Directory Server returns any entries it has located that match the search request, as
well as an exceeded time limit error.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 61
Page 62

When no limit is set, ns-slapd returns every matching entry to the client regardless of the time
it takes. To set a no limit value whereby Directory Server waits indefinitely for the search to
complete, specify a value of -1 for this attribute in the dse.ldif file. A value of zero (0) causes
no time to be allowed for searches. The smallest time limit is 1 second.
NOTE:
A value of -1 on this attribute in thedse.ldif is the same as leaving the attribute blank in the
server console in that it causes no limit to be used. However, a negative integer cannot be set in
this field in the server console, and a null value cannot be used in the dse.ldif entry, as it is
not a valid integer.
2.3.1.101 nsslapd-tmpdir
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
-1 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
3600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-timelimit: 3600Example
This is the absolute path of the directory the server uses to cache SSL session ID.. The directory
must be owned by the server user ID and the user must have read and write access. No other
user ID should have read or write acces to the directory. The default value is /tmp.
Changes made to this attribute will not take effect until the server is restarted.
2.3.1.102 nsslapd-versionstring
This attribute sets the server version number. The build data is automatically appended when
the version string is displayed.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Any valid server version number.Valid Values
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-versionstring: HP-UX Directory/8.1.0Example
2.3.1.103 nsslapd-workingdir
This is the absolute path of the directory that the server uses as its current working directory
after startup. This is the value that the server would return as the value of the getcwd() function,
and the value that the system process table shows as its current working directory. This is the
directory a core file is generated in. The server user ID must have read and write access to the
directory, and no other user ID should have read or write access to it. The default value for this
attribute is the same directory containing the error log, which is usually
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/log.
Changes made to this attribute will not take effect until the server is restarted.
2.3.1.104 passwordChange (Password change)
Indicates whether users may change their passwords.
62 Core server configuration reference
Page 63

For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordChange: onExample
2.3.1.105 passwordCheckSyntax (Check password syntax)
This attribute sets whether the password syntax is checked before the password is saved. The
password syntax checking mechanism checks that the password meets or exceeds the password
minimum length requirement and that the string does not contain any trivial words, such as the
user's name or user ID or any attribute value stored in the uid, cn, sn, givenName, ou, or mail
attributes of the user's directory entry.
Password syntax includes several different categories for checking:
• Minimum number of digit characters (0-9)
• Minimum number of ASCII alphabetic characters, both upper- and lower-case
• Minimum number of uppercase ASCII alphabetic characters
• Minimum number of lowercase ASCII alphabetic characters
• Minimum number of special ASCII characters, such as !@#$
• Minimum number of 8-bit characters
• Maximum number of times that the same character can be immediately repeated, such as
aaabbb
• Minimum number of character categories required per password; a category can be upper-
or lower-case letters, special characters, digits, or 8-bit characters
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordCheckSyntax offExample
2.3.1.106 passwordExp (Password expiration)
Indicates whether user passwords expire after a given number of seconds. By default, user
passwords do not expire. After password expiration is enabled, set the number of seconds after
which the password expires using the passwordMaxAge attribute.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 63
Page 64

For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordExp: onExample
2.3.1.107 passwordGraceLimit (Password expiration)
This attribute is only applicable if password expiration is enabled. After the user's password has
expired, the server allows the user to connect for the purpose of changing the password. This is
called a grace login. The server allows only a certain number of attempts before completely
locking out the user. This attribute is the number of grace logins allowed. A value of 0 means
the server does not allow grace logins.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 (off) to any reasonable integerValid Values
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordGraceLimit: 3Example
2.3.1.108 passwordHistory (Password history)
Enables password history. Password history refers to whether users are allowed to reuse
passwords. By default, password history is disabled, and users can reuse passwords. If this
attribute is set to on, the directory stores a given number of old passwords and prevents users
from reusing any of the stored passwords. Set the number of old passwords the Directory Server
stores using the passwordInHistory attribute.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordHistory: onExample
2.3.1.109 passwordInHistory (Number of passwords to remember)
Indicates the number of passwords the Directory Server stores in history. Passwords that are
stored in history cannot be reused by users. By default, the password history feature is disabled,
meaning that the Directory Server does not store any old passwords, and so users can reuse
passwords. Enable password history using the passwordHistory attribute.
64 Core server configuration reference
Page 65

To prevent users from rapidly cycling through the number of passwords that are tracked, use
the passwordMinAge attribute.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
2 to 24 passwordsValid Range
6Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordInHistory: 7Example
2.3.1.110 passwordIsGlobalPolicy (Password policy and replication)
This attribute controls whether password policy attributes are replicated.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordIsGlobalPolicy: offExample
2.3.1.111 passwordLockout (Account lockout)
Indicates whether users are locked out of the directory after a given number of failed bind
attempts. By default, users are not locked out of the directory after a series of failed bind attempts.
If account lockout is enabled, set the number of failed bind attempts after which the user is locked
out using the passwordMaxFailure attribute.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordLockout: offExample
2.3.1.112 passwordLockoutDuration (Lockout duration)
Indicates the amount of time in seconds during which users are locked out of the directory after
an account lockout. The account lockout feature protects against hackers who try to break into
the directory by repeatedly trying to guess a user's password. Enable and disable the account
lockout feature using the passwordLockout attribute.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 65
Page 66

For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
3600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordLockoutDuration: 3600Example
2.3.1.113 passwordMaxAge (Password maximum age)
Indicates the number of seconds after which user passwords expire. To use this attribute, password
expiration has to be enabled using the passwordExp attribute.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
8640000 (100 days)Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMaxAge: 100Example
2.3.1.114 passwordMaxFailure (Maximum password failures)
Indicates the number of failed bind attempts after which a user is locked out of the directory. By
default, accountlockout is disabled. Enableaccount lockout by modifyingthe passwordLockout
attribute.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to maximum integer bind failuresValid Range
3Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMaxFailure: 3Example
2.3.1.115 passwordMaxRepeats (Password syntax)
Maximum number of times the same character can appear sequentially in the password. Zero
(0) is off. Integer values reject any password which used a character more than that number of
66 Core server configuration reference
Page 67

times; for example, 1 rejects characters that are used more than once (aa) and 2 rejects characters
used more than twice (aaa).
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMaxRepeats: 1Example
2.3.1.116 passwordMin8Bit (Password syntax)
This sets the minimum number of 8-bit characters the password must contain.
NOTE:
For the userPassword attribute to use this password policy constraint, the 7-bit checking plug-in
must be disabled.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMin8Bit: 0Example
2.3.1.117 passwordMinAge (Password minimum age)
Indicates the number of seconds that must pass before a user can change their password. Use
this attributein conjunction with the passwordInHistory (number ofpasswords to remember)
attribute to prevent users from quickly cycling through passwords so that they can use their old
password again. A value of zero (0) means that the user can change the password immediately.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to valid maximum integerValid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinAge: 150Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 67
Page 68

2.3.1.118 passwordMinAlphas (Password syntax)
This attribute sets the minimum number of alphabetic characters password must contain.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinAlphas: 4Example
2.3.1.119 passwordMinCategories (Password syntax)
This sets the minimum number of character categories that are represented in the password. The
categories are lower, upper, digit, special, and 8-bit. For example, if the value of this attribute
were set to 2, and the user tried to change the password to aaaaa, the server would reject the
password because it contains only lower case characters, and therefore contains characters from
only one category. A password of aAaAaA would pass because it contains characters from two
categories, uppercase and lowercase. The default is 3, which means that if password syntax
checking is enabled, valid passwords have to have three categories of characters.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 5Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinCategories: 2Example
2.3.1.120 PasswordMinDigits (Password syntax)
This sets the minimum number of digits a password must contain.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinDigits: 3Example
2.3.1.121 passwordMinLength (Password minimum length)
This attribute specifies the minimum number of characters that must be used in Directory Server
user password attributes. In general, shorter passwords are easier to crack. By default, Directory
Server enforces a minimum password of eight characters.
68 Core server configuration reference
Page 69

For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
2 to 512 charactersValid Range
8Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinLength: 6Example
2.3.1.122 PasswordMinLowers (Password syntax)
This attribute sets the minimum number of lower case letters password must contain.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinLowers: 1Example
2.3.1.123 PasswordMinSpecials (Password syntax)
This attribute sets the minimum number of special, or nonalphanumeric, characters a password
must contain.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinSpecials: 1Example
2.3.1.124 PasswordMinTokenLength (Password syntax)
This attribute sets the smallest attribute value length that is used for trivial words checking. For
example, if the PasswordMinTokenLength is set to 3, then a givenName of DJ does not result
in a policy that rejects DJ from being in the password, but the policy rejects a password containing
the givenName of Bob.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to 64Valid Range
3Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinTokenLength: 3Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 69
Page 70

2.3.1.125 PasswordMinUppers (Password syntax)
This sets the minimum number of uppercase letters password must contain.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
0 to 64Valid Range
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordMinUppers: 2Example
2.3.1.126 passwordMustChange (Password must change)
Indicates whether users must change their passwords when they first bind to the Directory Server
after the password has been created or reset by the Directory Manager.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordMustChange: offExample
2.3.1.127 passwordResetFailureCount (Reset password failure count after)
Indicates the amount of time in seconds after which the password failure counter resets. Each
time an invalid password is sent from the user's account, the password failure counter is
incremented. If the passwordLockout attribute is set to on, users are locked out of the directory
when thecounter reaches the numberof failures specified bythe passwordMaxFailure attribute
(within 600 seconds by default). After the amount of time specified by the
passwordLockoutDuration attribute, the failure counter is reset to zero (0).
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordResetFailureCount: 600Example
2.3.1.128 passwordStorageScheme (Password storage scheme)
This attribute sets the type of encryption used to store Directory Server passwords.
70 Core server configuration reference
Page 71

The following encryption types are supported by the Directory Server:
• CLEAR means the password is stored in cleartext, with no hashing or encryption. This
scheme must be used in order to use SASL DIGEST-MD5.
• SSHA (Salted Secure Hash Algorithm), the default, is the recommended method because it
is the most secure. There are several bit sizes available: 140 bits (the default), 256, 384, and
512.
• SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) is included only for backward compatibility with 4.x Directory
Servers; do not use this algorithm.
• MD5 (Message Digest algorithm 5) is a commonly used standard hashing algorithm.
• CRYPT, the UNIX crypt algorithm, is provided for compatibility with UNIX passwords.
NOTE:
Passwords cannot be encrypted using the NS-MTA-MD5 password storage scheme. The storage
scheme is still present but only for reasons of backward compatibility.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
2.3.1.129 passwordUnlock (Unlock account)
Indicates whether users are locked out of the directory for a specified amount of time or until
the administrator resets the password after an account lockout. The account lockout feature
protects against hackers who try to break into the directory by repeatedly trying to guess a user's
password. If this passwordUnlock attribute is set to off and the operational attribute
accountUnlockTime has a value of 0, then the account is locked indefinitely.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
passwordUnlock: offExample
2.3.1.130 passwordWarning (Send warning)
Indicates the number of seconds before a user's password is due to expire that the user receives
a password expiration warning control on their next LDAP operation. Depending on the LDAP
client, the user may also be prompted to change their password at the time the warning is sent.
For more information on password policies, see the "Managing Users and Passwords" chapter
in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=configEntry DN
1 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
86400 (1 day)Default Value
IntegerSyntax
passwordWarning: 86400Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 71
Page 72

2.3.2 cn=changelog5,cn=config
Replication changelog configuration is stored in the cn=changelog5,cn=config entry. The
changelog behaves much like a database, and it has many of attributes also used by the ldbm
databases. The changelog entry supports the following attributes with the same meaning as for
databases:
The default values for the cache-related memory parameters (tuned for a single backend replicated
to a single consumer) are as follows:
• nsslapd-cachesize: 3000 (3000 entries)
• nsslapd-cachememsize: 10000000 (10 Mbyte)
When morebackends are replicated orwhen one backend is replicated to more than one consumer,
tune the parameters as below:
nsslapd-cachesize = 2000*#repl_agreements_initiated_from_this_server
nsslapd-cachememsize = 5000000*#repl_agreements_initiated_from_this_server
Also, the relationship between the values assigned to the nsslapd-dbcachesize and
nsslapd-cachememsize parameters should be the same as the relationship that is described
in the database-tuning section.
The cn=changelog5,cn=config entry is an instance of the extensibleObject object class.
NOTE:
Two different types of changelogs are maintained by Directory Server. The first type, which is
stored here and referred to as the changelog, is used by multi-master replication; the second
changelog, which is actually a plug-in and referred to as the retro changelog, is for
compatibility with some legacy applications. See “Retro Changelog plug-in” for further
information about the Retro Changelog Plug-in.
2.3.2.1 nsslapd-changelogdir
This required attribute specifies the name of the directory in which the changelog database is
created. Whenever a changelog configuration entry is created, it must contain a valid directory;
otherwise, the operation is rejected. The GUI proposes by default that this database be stored in
/var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/changelogdb.
NOTE:
If the cn=changelog5,cn=config entry is removed, any changelog database files that reside
in the directory specified in the nsslapd-changelogdir parameter are automatically removed.
If removal of these database files leaves the directory empty, the directory itself is also removed.
NOTE:
For performance reasons, store this database on a different physical disk.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=changelog5,cn=configEntry DN
Any valid path to the directory storing the changelogValid Values
NoneDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-changelogdir: /var/opt/dirsrv/slapd-example/changelogdbExample
72 Core server configuration reference
Page 73

2.3.2.2 nsslapd-changelogmaxage (Max changelog age)
This attribute sets the maximum age of any entry in the changelog. The changelog contains a
record for each directory modification and is used when synchronizing consumer servers. Each
record contains a timestamp. Any record with a timestamp that is older than the value specified
in this attribute is removed. If this attribute is absent, there is no age limit on changelog records.
For information on the changelog, see “nsslapd-changelogdir”.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=changelog5,cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
Syntax
0 (meaning that entries are not removed according to their age) to maximum 32-bit integer
(2147483647)
0Default Value
DirectoryString IntegerAgeID where AgeID is s for seconds, m for minutes, h for hours,
d for days, and w for weeks
nsslapd-changelogmaxage: 30dExample
2.3.2.3 nsslapd-changelogmaxentries (Max changelog records)
This attribute sets the maximum number of records the changelog may contain. If this attribute
is absent, there is no maximum number of records the changelog can contain. For information
on the changelog, see “nsslapd-changelogdir”.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=changelog5,cn=configEntry DN
Valid Range
0 (meaning that the only maximum limit is the disk size) to maximum 32-bit integer
(2147483647)
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsslapd-changelogmaxentries: 5000Example
2.3.3 cn=encryption,cn=config
Encryption related attributes are stored under the cn=encryption,cn=config entry. The
cn=encryption,cn=config entry is an instance of the nsslapdEncryptionConfig object
class.
2.3.3.1 nssslsessiontimeout
This attribute sets the lifetime duration of a TLS/SSL. The minimum timeout value is 5 seconds.
If a smaller value is set, then it is automatically replaced by 5 seconds. A value greater than the
maximum value in the valid range below is replaced by the maximum value in the range.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=encryption,cn=configEntry DN
5 seconds to 24 hoursValid Range
0, which means use the maximum value in the valid range above.Default Value
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 73
Page 74

2.3.3.2 nssslclientauth
This attribute sets how clients may use certificates to authenticate to the Directory Server for SSL
connections. If this attribute is set to required, which enforces clients to use authentication
certification, you cannot set the Console to require SSL. Certificate-based authentication is not
supported with the Console
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
IntegerSyntax
nssslsessiontimeout: 5Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=encryption,cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
2.3.3.3 nsSSL2
Supports SSL version 2. SSLv2 is deprecated, and HP strongly discourages using it.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
Valid Values
Any of the following:
off
allowed
required
allowedDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssslclientauth: allowedExample
DescriptionParameter
cn=encryption,cn=configEntry DN
on or off
offDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsssl2: offExample
Means disallow certificate-based authentication
Means clients may use certificates or other forms of authentication
Means clients must use certificates for authentication
2.3.3.4 nsSSL3
Supports SSL version 3.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
DescriptionParameter
cn=encryption,cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
74 Core server configuration reference
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsssl3: onExample
Page 75

2.3.3.5 nsssl3ciphers
This multi-valued attribute specifies the set of encryption ciphers the Directory Server uses during
SSL communications. For more information on the ciphers supported by the Directory Server,
see the "Managing SSL" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
DescriptionParameter
cn=encryption,cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
Syntax
For SSLv3:
• rsa_null_md5
• rsa_rc4_128_md5
• rsa_rc4_40_md5
• rsa_rc2_40_md5
• rsa_des_sha
• rsa_fips_des_sha
• rsa_3des_sha
• rsa_fips_3des_sha
For TLS:
• tls_rsa_export1024_with_rc4_56_sha
• tls_rsa_export1024_with_des_cbc_sha
DirectoryString
Use the plus (+) symbol to enable or minus (-) symbol to disable, followed by the ciphers.
Blank spaces are not allowed in the list of ciphers.
To enable all ciphers (except rsa_null_md5, which must be specifically called) specify
+all.
nsslapd-SSL3ciphers: +RSA_NULL_MD5,+RC4_56_SHA,-RC4_56_SHAExample
For more information, see the "Managing SSL" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator
guide
2.3.4 cn=features,cn=config
There are no relevant attributes for this entry. This entry is only used as a parent container entry.
See the documentation on the child entries for more information.
2.3.5 cn=mapping tree,cn=config
• Configuration attributes for suffixes, replication, and Windows synchronization are stored
under cn=mapping tree,cn=config. Configuration attributes related to suffixes are
found under the suffix subentry cn=suffix, cn=mapping tree,cn=config.
For example, a suffix is the root entry in the directory tree, such as dc=example,dc=com.
• Replication configuration attributes are stored under cn=replica, cn=suffix,
cn=mapping tree,cn=config.
• Replication agreement attributes are stored under cn=replicationAgreementName,
cn=replica, cn=suffix,cn=mapping tree,cn=config.
• Windows synchronizationagreement attributes are stored under cn=syncAgreementName,
cn=replica, cn=suffix,cn=mapping tree,cn=config.
2.3.6 Suffix configuration attributes under cn="suffixName"
Suffix configuration attributes are stored under the cn=suffix entry. The cn=suffix entry is
an instance of the nsMappingTree object class which inherits from the extensibleObject
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 75
Page 76

object class. For suffix configuration attributes to be taken into account by the server, these object
classes (in addition to the top object class) must be present in the entry.
The suffix DN should be quoted because the suffix DN contains characters such as equals signs
(=), commas (,), and space characters that must be quoted or escaped to appear as a value in
another DN.
2.3.6.1 nsslapd-state
Determines how the suffix handles operations.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
2.3.6.2 nsslapd-backend
Gives the name of the database or database link used to process requests. This attribute can be
multi-valued, with one database or database link per value. This attribute is required when the
value of the nsslapd-state attribute is set to backend or referral on update. The value
should be the name of the backend database entry instance under cn=ldbm
database,cn=plugins,cn=config. For example, a database name of NetscapeRoot should
be used for the backend database instance:
cn=NetscapeRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config.
cn=suffix, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any of the following:
backend
disabled
referral
referral on update
backendDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-state: backendExample
Means the backend (database) is used toprocess all operations.
Means the database is not available for processing operations.
The server returns a "No such search object" error in response
to requests made by client applications.
Means a referral is returned for requests made to this suffix.
Means the database is used for all operations except update
requests, which receive a referral.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=suffix, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any valid partition nameValid Values
NoneDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsslapd-backend: userRootExample
2.3.7 Replication attributes under cn=replica, cn="suffixDN", cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Replication configuration attributes are storedunder cn=replica, cn=suffix, cn=mapping
tree, cn=config. The cn=replica entry is an instance of the nsDS5Replica object class.
For replication configuration attributes to be taken into account by the server, this object class
(in addition to the top object class) must be present in the entry. For further information about
replication, see the "Managing Replication" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator
guide.
76 Core server configuration reference
Page 77

2.3.7.1 nsDS5Flags
This attribute sets replica properties that were previously defined in flags. At present only one
flag exists, which sets whether the log changes.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
One of the following:
0
1
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5Flags: 0Example
2.3.7.2 nsDS5ReplicaBindDN
This multi-valued attribute specifies the DN to use when binding. Although there can be more
than one value in this cn=replica entry, there can only be one supplier bind DN per replication
agreement. Each value should be the DN of a local entry on the consumer server. If replication
suppliers are using client certificate-based authentication to connect to the consumers, configure
the certificate mapping on the consumer to map the subjectDN in the certificate to a local entry.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any valid DNValid Values
Means no changes are logged.
Means changes are logged.
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaBindDN: cn=replication manager, cn=configExample
2.3.7.3 nsDS5ReplicaChangeCount
This read-only attribute shows the total number of entries in the changelog and whether they
still remain to be replicated. When the changelog is purged, only the entries that are still to be
replicated remain.
See “nsDS5ReplicaPurgeDelay”and “nsDS5ReplicaTombstonePurgeInterval” for more information
about purge operation properties.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
-1 to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647)Valid Range
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaChangeCount: 675Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 77
Page 78

2.3.7.4 nsDS5ReplicaId
This attribute sets the unique ID for suppliers and consumers in a given replication environment.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
1 to 65534 for suppliers, and 65535 for consumersValid Range
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaId: 1Example
2.3.7.5 nsDS5ReplicaLegacyConsumer
If this attribute is absent or has a value of false, then it means that the replica is not a legacy
consumer.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
true | falseValid Values
falseDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaLegacyConsumer: falseExample
2.3.7.6 nsDS5ReplicaName
This attribute specifies the name of the replica with a unique identifier for internal operations.
If it is not specified, this unique identifier is allocated by the server when the replica is created.
NOTE:
It is recommended that the server be permitted to generate this name. However, in certain
circumstances, for example, in replica role changes (master to hub etc.), this value needs to be
specified. Otherwise, the server will not use the correct changelog database, and replication fails.
This attribute is destined for internal use only.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
DirectoryString (a UID identifies the replica)Syntax
nsDS5ReplicaName: 66a2b699-1dd211b2-807fa9c3-a58714648Example
2.3.7.7 nsDS5ReplicaPurgeDelay
This attribute controls the maximum age of deleted entries (tombstone entries) and state
information.
The Directory Server stores tombstone entries and state information so that when a conflict occurs
in a multi-master replication process, the server resolves the conflicts based on the timestamp
and replica ID stored in the change sequence numbers.
78 Core server configuration reference
Page 79

An internal Directory Server housekeeping operation periodically removes tombstone entries
which are older than the value of this attribute (in seconds). State information which is older
than the nsDS5ReplicaPurgeDelay value is removed when an entry which contains the the
state information is modified.
Not every tombstone and state information may be removed because, with multi-master
replication, the server may need to keep a small number of the latest updates to prime replication,
even if they are older than the value of the attribute.
This attribute specifies the interval, in seconds, to perform internal purge operations on an entry.
When setting this attribute, ensure that the purge delay is longer than the longest replication
cycle in the replication policy to preserve enough information to resolve replication conflicts and
to prevent the copies of data stored in different servers from diverging..
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
2.3.7.8 nsDS5ReplicaReferral
This multi-valued attribute specifies the user-defined referrals. This should only be defined on
a consumer. User referrals are only returned when a client attempts to modify data on a read-only
consumer. This optional referral overrides the referral that is automatically configured by the
consumer by the replication protocol.
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
0 (keep forever) to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647)Valid Range
604800 [1 week (60x60x24x7)]Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaPurgeDelay: 604800Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any valid LDAP URLValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaReferral: ldap://ldap.example.comExample
2.3.7.9 nsDS5ReplicaRoot
This attribute sets the DN at the root of a replicated area. This attribute must have the same value
as the suffix of the database being replicated and cannot be modified.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Suffix of the database being replicated, which is the suffix DNValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaRoot: "dc=example,dc=com"Example
2.3.7.10 nsDS5ReplicaTombstonePurgeInterval
This attribute specifies the time interval in seconds between purge operation cycles.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 79
Page 80

Periodically, the server runs an internal housekeeping operation to purge old update and state
information from the main database. For more information, see “nsDS5ReplicaPurgeDelay”.
When setting this attribute, remember that the purge operation is time-consuming, especially if
the server handles many delete operations from clients and suppliers.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
2.3.7.11 nsDS5ReplicaType
Defines the type of replication relationship that exists between this replica and the others.
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
0 to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
86400 (1 day)Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaTombstonePurgeInterval: 86400Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
One of the following:
Means unknown
0
Means primary (not yet used)
1
Means consumer (read-only)
2
Consumer/supplier (updateable)
3
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaType: 2Example
2.3.7.12 nsDS5ReplicaReapActive
This read-only attribute specifies whether the background task that removes old tombstones
(deleted entries) from the database is active. See “nsDS5ReplicaTombstonePurgeInterval” for
more information about this task. A value of 0 means that the task is inactive, and a value of 1
means that the task is active. The server ignores the modify request if this value is set manually.
DescriptionParameter
cn=replica,cn="suffixDN”,cn=mapping tree,cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
0 or 1
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaReapActive: 0Example
2.3.7.13 nsState
This attribute stores information on the state of the clock. It is designed only for internal use to
ensure that the server cannot generate a change sequence number (csn) inferior to existing ones
required for detecting backward clock errors.
80 Core server configuration reference
Page 81

2.3.7.14 nsDS5ReplConflict
Although this attribute is not in the cn=replica entry, it is used in conjunction with replication.
This multi-valued attribute is included on entries that have a change conflict that cannot be
resolved automatically by the synchronization process. To check for replication conflicts requiring
administrator intervention, performan LDAP search for (nsDS5ReplConflict=*). For example:
# ldapsearch -D cn=directory manager \
-w password -s sub -b dc=example,dc=com \
"(|(objectclass=nsTombstone)(nsDS5ReplConflict=*))" \
dn nsDS5ReplConflict nsUniqueID
Using the search filter "(objectclass=nsTombstone)" also show tombstone (deleted) entries.
The value of the nsDS5ReplConflict contains more information about which entries are in
conflict, usually by referring to them by their nsUniqueID. It is possible to search for a tombstone
entry by its nsUniqueID. For example:
# ldapsearch -D cn=directory manager \
-w password -s sub -b dc=example,dc=com \
"(|(objectclass=nsTombstone)(nsUniqueID=66a2b699-1dd211b2-807fa9c3-a58714648))"
2.3.8 Replication attributes under cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica, cn="suffixName", cn=mapping tree, cn=config
The replication attributes that concern the replication agreement are stored under
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree,
cn=config.
The cn=ReplicationAgreementName entry is an instance of the
nsDS5ReplicationAgreement object class. Replication agreements are configured only on
master (supplier) replicas.
2.3.8.1 cn
This attribute is used for naming. After this attribute has been set, it cannot be modified. This
attribute is required for setting up a replication agreement.
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
2.3.8.2 description
Free form text description of the replication agreement. This attribute can be modified.
DescriptionParameter
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any valid cn
DirectoryStringSyntax
cn: MasterAtoMasterBExample
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any stringValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
description: Replication Agreement between Server A and Server B.Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 81
Page 82

2.3.8.3 nsDS5ReplicaBindDN
This attribute sets the DN to use when binding to the consumer during replication. The value of
this attribute must be the same as the one in cn=replica on the consumer replica. This may be
empty if certificate-based authentication is used, in which case the DN used is the subject DN
of the certificate, and the consumer must have appropriate client certificate mapping enabled.
This can also be modified.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any valid DN (can be empty if client certificates are used)Valid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaBindDN: cn=replication manager, cn=configExample
2.3.8.4 nsDS5ReplicaBindMethod
This attribute sets the method to use for binding. This attribute can be modified.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=ReplicationAgreementName , cn=replica, cn=suffixDN,cn=mapping tree,cn=config
SIMPLE, SSLCLIENTAUTH, SASL/DIGEST-MD5, or SASL/GSSAPI
The SIMPLE and SASL/DIGEST-MD5 bind methods require a DN and password.
SIMPLEDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaBindMethod: SIMPLEExample
2.3.8.5 nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime
This attribute sets the amount of time in seconds a supplier should wait after a consumer sends
back a busy response before making another attempt to acquire access. The default value is three
(3) seconds. If the attribute is set to a negative value, Directory Server sends the client a message
and an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error code.
The nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime attribute works in conjunction with the
nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime attribute. The two attributes are designed so that the
nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime interval is always at least one second longer than the
interval specified fornsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime. The longer interval gives waiting suppliers
a better chance to gain consumer access before the previous supplier can re-access the consumer.
Set the nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime attribute at any time by using changetype:modify
with the replace operation. The change takes effect for the next update session if one is already
in progress.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any valid integerValid Values
3Default Value
82 Core server configuration reference
Page 83

DescriptionParameter
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime: 3Example
2.3.8.6 nsDS5ReplicaChangesSentSinceStartup
This read-only attribute shows the number of changes sent to this replica since the server started.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
0 to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647)Valid Range
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaChangesSentSinceStartup: 647Example
2.3.8.7 nsDS5ReplicaCredentials
This attribute sets the credentials for the bind DN (specified in the nsDS5ReplicaBindDN
attribute) on the remote server containing the consumer replica. The value for this attribute can
be modified. When certificate-based authentication is used, this attribute may not have a value.
The example shows the dse.ldif entry, not the actual password. If this value is updated over
LDAP or using the Console, set it to the cleartext credentials, and let the server encrypt the value.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
Syntax
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any valid password, which is then encrypted using the DES reversible password encryption
schema.
DirectoryString {DES} encrypted_password
2.3.8.8 nsDS5ReplicaHost
This attribute sets the host name for the remote server containing the consumer replica. After
this attribute has been set, it cannot be modified.
Entry DN
Default Value
nsDS5ReplicaCredentials:{DES} 9Eko69APCJfF08A0aD0CExample
DescriptionParameter
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any valid host server nameValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaHost: ldap2.example.comExample
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 83
Page 84

2.3.8.9 nsDS5ReplicaLastInitEnd
This optional, read-only attribute states when the initialization of the consumer replica ended.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ is the date/timein GeneralizedTime format whichthe connection was
opened. This value gives the time in relation to Greenwich Mean Time. The hours are set
with a 24-hour clock. The Z at the end indicates that the time is relative to Greenwich Mean
Time.
GeneralizedTimeSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaLastInitEnd: 20090504121603ZExample
2.3.8.10 nsDS5ReplicaLastInitStart
This optional, read-only attribute states when the initialization of the consumer replica started.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ is the date/timein GeneralizedTime format whichthe connection was
opened. This value gives the time in relation to Greenwich Mean Time. The hours are set
with a 24-hour clock. The Z at the end indicates that the time is relative to Greenwich Mean
Time.
GeneralizedTimeSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaLastInitStart: 20090503030405Example
2.3.8.11 nsDS5ReplicaLastInitStatus
This optional, read-only attribute provides status for the initialization of the consumer. There is
typically a numeric code followed by ashort string explaining the status. Zero (0) means success.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
An internal error code followed by a status message.Valid Values
StringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaLastInitStatus: 0 Total update succeededExample
84 Core server configuration reference
Page 85

2.3.8.12 nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateEnd
This read-only attribute states when the most recent replication schedule update ended.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ is the date/timein GeneralizedTime format whichthe connection was
opened. This value gives the time in relation to Greenwich Mean Time. The hours are set
with a 24-hour clock. The Z at the end indicates that the time is relative to Greenwich Mean
Time.
GeneralizedTimeSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateEnd: 20090502175801ZExample
2.3.8.13 nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStart
This read-only attribute states when the most recent replication schedule update started.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ is the date/timein GeneralizedTime format whichthe connection was
opened. This value gives the time in relation to Greenwich Mean Time. The hours are set
with a 24-hour clock. The Z at the end indicates that the time is relative to Greenwich Mean
Time.
GeneralizedTimeSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStart: 20090504122055ZExample
2.3.8.14 nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStatus
This read-only attribute provides the status for the most recent replication schedule updates.
The format is a numeric code followed by a short string. Zero (0) means success.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
An internal error code followed by a status message.Valid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsds5replicaLastUpdateStatus: 0 Incremental update succeededExample
2.3.8.15 nsDS5ReplicaPort
This attribute sets the port number for the remote server containing the replica. After this attribute
has been set, it cannot be modified.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Port number for the remote server containing the replicaValid Values
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 85
Page 86

DescriptionParameter
Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaPort:389Example
2.3.8.16 nsDS5ReplicaPriority
This attribute assigns a priority to replication agreements, controlling their rate of updates relative
to peer agreements.
Prioritizing agreements is useful for a set of replicas that need to be updated in a particular order.
For example, a replication topology might include a primary master replica with replication
agreements configured for two replicas:
• A geographically distant backup master replica connected by WAN, intended for disaster
recovery
• A local consumer replica that is accessed by client applications.
By default, or if equal priorities are assigned to the two replication agreements, the backup master
replica and the consumer replica receive updates from the primary master concurrently. The
relatively slower WAN connection to the backup master replica may eventually cause its update
to fall behind relative to the consumer replica's update. If the primary master replica fails while
the backup master update is behind, then some downtime for reinitialization would be required
before the backup master replica could take over the role of the primary master replica.
To avoid this undesirable situation, you can use the replication agreement attribute
nsds5ReplicaPriority to control the flow of updates so that the backup master replica is
always equally or more updated than the consumer replica. Assigning a higher priority to the
backup master relative to the consumer replica causes the agreement to the consumer to pause
before sending any update that has not yet been sent to the backup master replica. When the
pending updates are successfully sent to the backup master, the agreement to the consumer
continues where it left off.
You can configure replication agreements in a priority hierarchy. An agreement with priority 0
transmits updates at an unlimited rate. An agreement with priority 1 depends on the progress
of any agreement with priority 0; the priority 1 agreement pauses transmission whenever a
priority 0 agreement update falls behind. Likewise, an agreement with priority 2 depends on
the progress of all agreements with priority 0 and 1.
NOTE:
When assigning priority values, remember that the highest priority is 0, while lower priority
values are any integers greater than 0 and up to 2147483647.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
0 to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647)Valid Range
0, which means the agreement does not pause to wait for other agreementsDefault Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaPriority: 1Example
2.3.8.17 nsDS5ReplicaReapActive
This read-only attribute specifies whether the background task that removes old tombstones
(deleted entries) from the database is active. See “nsDS5ReplicaTombstonePurgeInterval” for
86 Core server configuration reference
Page 87

more information about this task. A value of zero (0) means that the task is inactive, and a value
of 1 means that the task is active. If this value is set manually, the server ignores the modify
request.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
0 or 1
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaReapActive: 0Example
2.3.8.18 nsDS5BeginReplicaRefresh
Initializes the replica. This attribute is absent by default. However, if this attribute is added with
a value of start, then the server initializes the replica and removes the attribute value. To
monitor the status of the initialization procedure, poll for this attribute. When initialization is
finished, the attribute is removed from the entry, and the other monitoring attributes can be used
for detailed status inquiries.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
stop or start
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5BeginReplicaRefresh: startExample
2.3.8.19 nsDS5ReplicaRoot
This attribute sets the DN at the root of a replicated area. This attribute must have the same value
as the suffix of the database being replicated and cannot be modified.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Suffix of the database being replicated - same as suffixDN specified in the Entry DN
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaRoot: "dc=example,dc=com"Example
2.3.8.20 nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime
This attribute sets the amount of time in seconds a supplier should wait between update sessions.
The default value is 0. If the attribute is set to a negative value, Directory Server sends the client
a message and an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error code.
The nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime attribute works in conjunction with the
nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime attribute. The two attributes are designed so that the
nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime interval is always at least one second longer than the
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 87
Page 88

interval specified fornsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime. The longer interval gives waiting suppliers
a better chance to gain consumer access before the previous supplier can re-access the consumer.
• If either attribute is specified but not both, nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime is set
automatically to 1 second more than nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime.
• If both attributes are specified, but nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime is less than or
equal to nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime, nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime is set
automatically to 1 second more than nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime.
When setting thevalues, ensure that the nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime interval is at least
1 second longer than the interval specified for nsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime. Increase the
interval as needed until there is an acceptable distribution of consumer access among the suppliers.
Set the nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime attribute at any time by usingchangetype:modify
with the replace operation. The change takes effect for the next update session if one is already
in progress.
If Directory Server has to reset the value of nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime automatically,
the value is changed internally only. The change is not visible to clients, and it is not saved to
the configuration file. From an external viewpoint, the attribute value appears as originally set.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Any valid integerValid Values
0Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTime: 0Example
2.3.8.21 nsDS5ReplicatedAttributeList
This allowed attribute specifies any attributes that are not replicated to a consumer server.
Fractional replication allows databases to be replicated across slow connections or to less secure
consumers while still protecting sensitive information. By default, all attributes are replicated,
and this attribute is not present. For more information on fractional replication, see the "Managing
Replication" chapter in the HP-UX Directory Server administrator guide.
NOTE:
To maintain data integrity, the consumer server must be a read-only server.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Range
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicatedAttributeList: (objectclass=*) $ EXCLUDE salary userPassword managerExample
2.3.8.22 nsDS5ReplicaTimeout
This allowed attribute specifies the number of seconds outbound LDAP operations waits for a
response from the remote replica before timing out and failing. If the server writes Warning:
timed out waiting messages in the error log file, then increase the value of this attribute.
88 Core server configuration reference
Page 89

Find out the amount of time the operation actually lasted by examining the access log on the
remote machine, then set the nsDS5ReplicaTimeout attribute accordingly to optimize
performance.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
0 to maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647) in secondsValid Range
600Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaTimeout: 600 secondsExample
2.3.8.23 nsDS5ReplicaTransportInfo
This attribute sets the type of transport used for transporting data to and from the replica. The
attribute values can be either SSL, which means that the connection is established over SSL, or
LDAP, which means that regular LDAP connections are used. If this attribute is absent, then
regular LDAP connections are used. This attribute cannot be modified after it is set.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
SSL | LDAPValid Values
absentDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaTransportInfo: LDAPExample
2.3.8.24 nsDS5ReplicaUpdateInProgress
This read-only attribute states whether or not a replication update is in progress.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
true or false
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaUpdateInProgress: trueExample
2.3.8.25 nsDS5ReplicaUpdateSchedule
This multi-valued attribute specifies the replication schedule and can be modified. Changes
made to this attribute take effect immediately. Modifying this value can be useful to pause
replication and resume it later. For example, if this value to 0000-0001 0, this in effect causes
the server to stop sending updates for this replication agreement. The server continues to store
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 89
Page 90

them for replay later. If the value is later changed back to 0000-2359 0123456, this makes
replication immediately resume and sends all pending changes.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Range
cn=ReplicationAgreementName, cn=replica,cn=suffixDN, cn=mappingtree, cn=config
Time schedule presented as XXXX-YYYY 0123456, where XXXX is the starting hour, YYYY
is the finishing hour, and the numbers 0123456 are the days of the week starting with
Sunday.
0000-2359 0123456 (all the time)Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nsDS5ReplicaUpdateSchedule: 0000-2359 0123456Example
2.3.8.26 nsDS50ruv
This attribute stores the last replica update vector (RUV) read from the consumer of this replication
agreement. It is always present and must not be changed.
2.3.9 Synchronization attributes under cn=syncAgreementName, cn=Replica,cn="suffixName", cn=mapping tree, cn=config
The synchronization attributes that concern the synchronization agreement are stored under
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=Replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config.
The cn=syncAgreementName entry is an instance of the
nsDSWindowsReplicationAgreement object class. For synchronization agreement
configuration attributes to be taken into account by the server, this object class (in addition to
the top object class) must be present in the entry. Synchronization agreements are configured
only on databases that are enabled to synchronize with Windows Active Directory servers.
Table 2-7 List of attributes shared between replication and synchronization agreements
nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateEndcn
nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStartdescription
nsDS5ReplicaLastUpdateStatusnsDS5ReplicaBindDN (the Windows sync manager ID)
nsDS5ReplicaPortnsDS5ReplicaBindMethod
nsDS5ReplicaRootnsDS5ReplicaBusyWaitTime
nsDS5ReplicaSessionPauseTimensDS5ReplicaChangesSentSinceStartup
nsDS5ReplicaTimeoutnsDS5ReplicaCredentials (the Windows sync manager
password)
nsDS5ReplicaTransportInfonsDS5ReplicaHost (the Windows host)
nsDS5ReplicaUpdateInProgressnsDS5ReplicaLastInitEnd
nsDS5ReplicaUpdateSchedulensDS5ReplicaLastInitStart
nsDS50ruvnsDS5ReplicaLastInitStatus
90 Core server configuration reference
Page 91

2.3.9.1 nsds7DirectoryReplicaSubtree
The suffix or DN of the Directory Server subtree that is being synchronized.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
2.3.9.2 nsds7DirsyncCookie
This string is created by Active Directory DirSync and gives the state of the Active Directory
Server at the time of the last synchronization. The old cookie is sent to Active Directory with
each Directory Server update; a new cookie is returned along with the Windows directory data.
This means only entries which have changed since the last synchronization are retrieved.
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any valid suffix or subsuffixValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS7DirectoryReplicaSubtree: ou=People,dc=example,dc=comExample
DescriptionParameter
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any stringValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS7DirsyncCookie::khDKJFBZsjBDSCkjsdhIU74DJJVBXDhfvjmfvbhzxjExample
2.3.9.3 nsds7NewWinGroupSyncEnabled
This attribute sets whether a new group created in the Windows sync peer is automatically
synchronized by creating a new group on the Directory Server.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
on or off
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS7NewWinGroupSyncEnabled: onExample
2.3.9.4 nsds7NewWinUserSyncEnabled
This attribute sets whether a new entry created in the Windows sync peer is automatically
synchronized by creating a new entry on the Directory Server.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
on or off
Default Value
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 91
Page 92

DescriptionParameter
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS7NewWinUserSyncEnabled: onExample
2.3.9.5 nsds7WindowsDomain
This attribute sets the name of the Windows domain to which the Windows sync peer belongs.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any valid domain nameValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS7WinndowsDomain: DOMAINWORLDExample
2.3.9.6 nsds7WindowsReplicaSubtree
The suffix or DN of the Windows subtree that is being synchronized.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
Any valid suffix or subsuffixValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nsDS7WindowsReplicaSubtree: cn=Users, dc=domain, dc=comExample
2.3.9.7 winSyncInterval
This attribute sets how frequently, in seconds, the Directory Server polls the Windows sync peer
to look for changes in the Active Directory entries. If this entry is not set, the Directory Server
checks the Windows server every five (5) minutes, meaning the default value is 300 (300 seconds).
This value can be set lower to write Active Directory changes over to the Directory Server faster
or raised if the directory searches are taking too long.
Entry DN
2.3.10 cn=monitor
Information used to monitor the server is stored under cn=monitor. This entry and its children
are read-only; clients cannot directly modify them. The server updates this information
automatically. This section describes the cn=monitor attributes. The only attribute that can be
changed by a user to set access control is the aci attribute.
DescriptionParameter
cn=syncAgreementName, cn=replica, cn=suffixDN, cn=mapping tree, cn=config
1 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Values
300Default Value
IntegerSyntax
winSyncInterval: 600Example
92 Core server configuration reference
Page 93

If the nsslapd-counters attribute in cn=config is set to on (the default setting), then all the
counters kept by the Directory Server instance increment using 64-bit integers, even on 32-bit
machines or with a 32-bit version of Directory Server. For the cn=monitor entry, the 64-bit
integers are used with the opsinitiated, opscompleted, entriessent, bytessent, and
totalconnections counters.
NOTE:
The nsslapd-counters attribute enables 64-bit support for these specific database and server
counters. The counters which use 64-bit integers are not configurable; the 64-bit integers are
either enabled for all the allowed counters or disabled for all allowed counters.
connection This attribute lists open connections. These are given in the following format:
connection: A:YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ:B:C:D:E
For example:
connection: 31:20010201164808Z:45:45::cn=directory manager
A
This is the connection number, which is the number of the slot in the
connection table associated with this connection. This is the number
logged as slot=A in the access log message when this connection was
opened, and usually corresponds to the file descriptor associated with
the connection. The attribute dTableSize shows the total size of the
connection table.
YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ
This is the date and time, in GeneralizedTime form, at which the
connection was opened. This value gives the time in relation to
Greenwich Mean Time.
B
C
This is the number of operations received on this connection.
This is the number of completed operations.
D This is r if the server is in the process of reading BER from the network,
empty otherwise. This value is usually empty (as in the example).
E This is the bind DN. This may be empty or have value of NULLDN for
anonymous connections.
currentConnections This attribute shows the number of currently open and active Directory
Server connections.
totalConnections This attribute shows the total number of Directory Server connections. This
number includes connections that have been opened and closed since the server was last started
in addition to the currentConnections.
dTableSize This attribute shows the size of the Directory Server connection table. Each
connection is associated with a slot in this table, and usually corresponds to the file descriptor
used by this connection. See “nsslapd-conntablesize” for more information.
readWaiters This attribute shows the number of connections where some requests arepending
and not currently being serviced by a thread in Directory Server.
opsInitiated This attribute shows the number of Directory Server operations initiated.
opsCompleted This attribute shows the number of Directory Server operations completed.
entriesSent This attribute shows the number of entries sent by Directory Server.
bytesSent This attribute shows the number of bytes sent by Directory Server.
currentTime This attribute shows the current time, given in Greenwich Mean Time (indicated
by generalizedTime syntax Z notation; for example, 20090202131102Z).
startTime This attribute shows the Directory Server start time given in Greenwich Mean Time,
indicated by generalizedTime syntax Z notation. For example, 20090202131102Z.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 93
Page 94

version This attribute shows the Directory Server vendor, version, and build number. For
example, HP-UX-Directory/8.1.0 B2009.176.2042.
threads This attribute shows the number of threads used by the Directory Server. This should
correspond to nsslapd-threadnumber in cn=config.
nbackEnds This attribute shows the number of Directory Server database backends.
backendMonitorDN This attribute shows the DN for each Directory Server database backend.
For further information on monitoring the database, see the following sections:
• “Database Attributes under cn=attributeName, cn=encrypted attributes, cn=database_name,
cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins, cn=config”
• “Database attributes under cn=database, cn=monitor, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,
cn=config”
• “Database attributes under cn=monitor, cn=NetscapeRoot, cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,
cn=config”
• “Database link attributes under cn=monitor, cn=database instance name, cn=chaining
database, cn=plugins, cn=config”
2.3.11 cn=replication
This entry has no attributes. When configuring legacy replication, thoe entries are stored under
this cn=replication node, which serves as a placeholder.
2.3.12 cn=SNMP,cn=config
SNMP configuration attributes are stored under cn=SNMP,cn=config. The cn=SNMP entry is
an instance of the nsSNMP object class.
2.3.12.1 nssnmpenabled
This attribute sets whether SNMP is enabled.
Valid Values
2.3.12.2 nssnmpname
This attribute sets the name of the Directory Server being monitored by SNMP.
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
on or off
onDefault Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmpenabled: offExample
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
94 Core server configuration reference
Directory Server instance_name
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmpname: exampleExample
Page 95

2.3.12.3 nssnmporganization
This attribute sets the organization to which the Directory Server belongs.
Default Value
2.3.12.4 nssnmplocation
This attribute sets the location within the company or organization where the Directory Server
resides.
Default Value
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
Organization nameValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmporganization: Example, Inc.Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
LocationValid Values
2.3.12.5 nssnmpcontact
This attribute sets the email address of the person responsible for maintaining the Directory
Server.
Default Value
2.3.12.6 nssnmpdescription
Provides a unique description of the Directory Server instance.
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmplocation: B14Example
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
Contact email addressValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmpcontact: jerome@example.comExample
DescriptionParameter
Default Value
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
DescriptionValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmpdescription: Employee directory instanceExample
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 95
Page 96

2.3.12.7 nssnmpmasterhost
nssnmpmasterhost is deprecated. This attribute is deprecated with the introduction of
net-snmp. The attribute still appears in dse.ldif but without a default value.
2.3.12.8 nssnmpmasterport
The nssnmpmasterport attribute was deprecated with the introduction of net-snmp. The
attribute still appears in dse.ldif but without a default value.
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
machine host name or localhostValid Values
<blank>Default Value
DirectoryStringSyntax
nssnmpmasterhost: localhostExample
DescriptionParameter
cn=SNMP, cn=configEntry DN
Valid Values
Operating system dependent port number. See the operating system documentation for
further information.
<blank>Default Value
IntegerSyntax
nssnmpmasterport: 199Example
2.3.13 SNMP statistic attributes
Table 2-8 “SNMP statistic attributes” contains read-only attributes which list the statistics available
for LDAP and SNMP clients. Unless otherwise noted, the value for the given attribute is the
number of requests received by the server or results returned by the server since startup. Some
of these attributes are not used by or are not applicable to the Directory Server but are still
required to be present by SNMP clients.
If the nsslapd-counters attribute in cn=config is set to off, the SNMP statistics will not
be maintained.
Table 2-8 SNMP statistic attributes
DescriptionAttribute
This shows the number of anonymous bind requests.AnonymousBinds
This shows the number of unauthenticated (anonymous) binds.UnAuthBinds
This shows the number of LDAP simple bind requests (DN and password).SimpleAuthBinds
This shows the number of LDAP SASL bind requests, for all SASL mechanisms.StrongAuthBinds
This shows the number of number of times aninvalid password wasgiven in a bind request.BindSecurityErrors
This shows the total number of all requests received by the server.InOps
ReadOps
96 Core server configuration reference
Not used. This value is always 0.
This shows the number of LDAP compare requests.CompareOps
This shows the number of LDAP add requests.AddEntryOps
Page 97

Table 2-8 SNMP statistic attributes (continued)
DescriptionAttribute
This shows the number of LDAP delete requests.RemoveEntryOps
This shows the number of LDAP modify requests.ModifyEntryOps
This shows the number of LDAP modify RDN (modrdn) requests.ModifyRDNOps
ListOps
Chainings
SecurityErrors
ConnectionSeq
MasterEntries
Not used. This value is always 0.
This shows the number of LDAP search requests.SearchOps
This shows the number of one-level search operations.OneLevelSearchOps
This shows the number of subtree-level search operations.WholeSubtreeSearchOps
This shows the number of LDAP referrals returned.Referrals
Not used. This value is always 0.
This shows the number of errors returned that were security related, such as invalid
passwords, unknown or invalid authentication methods,or stronger authentication required.
This shows the number of errors returned.Errors
This shows the number of currently open connections.Connections
This shows the total number of connections opened, including both currently open and
closed connections.
This shows the number of bytes received.BytesRecv
This shows the number of bytes sent.BytesSent
This shows the number of entries returned as search results.EntriesReturned
This provides information on referrals returned as search results (continuation references).ReferralsReturned
Not used. This value is always 0.
CopyEntries
CacheEntries
CacheHits
SlaveHits
1
CacheEntries and CacheHits are updated every ten (10) seconds. HP strongly encourages using the database
backend specific monitor entries for this and other database information.
1
1
Not used. This value is always 0.
If the server hasonly one database backend, this is the number ofentries cached in the entry
cache. If the server has more than one database backend, this value is 0, and see the monitor
entry for each one for more information.
If the server has only one database backend, this is the number of entries returned from the
entry cache, rather than from the database, for search results. If the server has more than
one database backend, this value is 0, and see the monitor entry for each one for more
information.
Not used. This value is always 0.
2.3.14 cn=tasks,cn=config
Some core Directory Server tasks can be initiated by editing a directory entry using LDAP tools.
These task entries are contained in cn=tasks. Each task can be invoked by updating an entry
such as the following:
dn: cn=task_id, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config ...
In deployments before Directory Server 8.0, many Directory Server tasks were managed by the
Administration Server. These tasks were moved to the core Directory Server configuration in
version 8.0 and are invoked and administered by Directory Server under the cn=tasks entry.
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 97
Page 98

There are seven tasks that are managed under the cn=tasks entry:
• cn=import
• cn=export
• cn=backup
• cn=restore
• cn=index
• cn=schema reload task
• cn=memberof task
The common attributes for these tasks are listed in “Task invocation attributes for entries under
cn=tasks”.
The cn=tasks entry itself has no attributes and serves as the parent and container entry for the
individual task entries.
IMPORTANT:
Task entries are not permanent configuration entries. They only exist in the configuration file
for as long as the task operation is running or until the ttl period expires. Then, the entry is
deleted automatically by the server.
2.3.14.1 Task invocation attributes for entries under cn=tasks
Five tasks which administer Directory Server instances have configuration entries which initiate
and identify individual operations. These task entries are instances of the same object class,
nsDirectoryServerTask, and have certain common attributes which describe the state and
behavior of Directory Server tasks. The task types can be import, export, backup, restore, index,
schema reload, and memberof.
cn The cn attribute is used to identify a new task operation to initiate. The cn attribute value
can be anything, as long as it defines a new task.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
Any stringValid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
cn: example task entry nameExample
nsTaskStatus This attribute contains changing information about the status of the task, such as
cumulative statistics or its current output message. The entire contents of the attribute may be
updated periodically for as long as the process is running.
This attribute value is set by the server and should not be edited.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
Any stringValid Values
Default Value
case-exact stringSyntax
nsTaskStatus: Loading entries....Example
98 Core server configuration reference
Page 99

nsTaskLog This entry contains all the log messages for the task, including bothwarning and
information messages. New messages are appended to the end of the entry value, so this attribute
value grows larger, without erasing the original contents, by default.
Successful task operations, which have an nsTaskExitCode of 0, are only recorded in the
nsTaskLog attribute. Any non-zero response, which indicates an error, may be recorded in the
error log as an error, but the error message is only recorded in the nsTaskLog attribute. For this
reason, use the information in the nsTaskLog attribute to find out what errors actually occurred.
This attribute value is set by the server and should not be edited.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
Any stringValid Values
Case-exact stringSyntax
nsTaskLog: example...Example
nsTaskExitCode This attribute contains the exit code for the task. This attribute only exists after
the task is completed and any value is only valid if the task is complete. The result code can be
any LDAP exit code, as listed in “LDAP result codes”, but only a 0 value equals success; any
other result code is an error.
This attribute value is set by the server and should not be edited.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
1
Any response other than 0 is an error.
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
0 (success) to 97
IntegerSyntax
nsTaskExitCode: 0Example
1
nsTaskCurrentItem This attribute shows the number of subtask which the task operation has
completed, assuming the task can be broken down into subtasks. If there is only one task, then
nsTaskCurrentItem is 0 while the task is running, and 1 when the task is complete. In this
way, the attribute is analogous to a progress bar. When the nsTaskCurrentItem attribute has
the same value as nsTaskTotalItems, then the task is completed.
This attribute value is set by the server and should not be edited.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
0 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Values
IntegerSyntax
nsTaskCurrentItem: 148Example
2.3 Core server configuration attributes reference 99
Page 100

nsTaskTotalItems This attributes shows the total number of subtasks that must be completed
for the task operation. When the nsTaskCurrentItem attribute has the same value as
nsTaskTotalItems, then the task is completed.
This attribute value is set by the server and should not be edited.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
0 to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Values
IntegerSyntax
nsTaskTotalItems: 152Example
nsTaskCancel This attribute allows a task to be aborted while in progress. This attribute can
be modified by users.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Valid Values
Default Value
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
true | false
Case-insensitive stringSyntax
nsTaskCancel: trueExample
ttl This attribute sets the amount of time (in seconds) the task entry will remain in the DSE
after the task has finished or aborted. Setting a ttl attribute allows the task entry to be polled
for new status information without missing the exit code. Setting the ttl attribute to 0 means
that the entry is not cached.
DescriptionParameter
Entry DN
Default Value
cn=task_name, cn=task_type, cn=tasks, cn=config
0 (cannot be cached) to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647)Valid Values
DirectoryStringSyntax
ttl: 120Example
2.3.14.2 cn=import,cn=tasks,cn=config
An LDIF file or multiple LDIF files can be imported through the command line by creating a
special task entry which defines the parameters of the task and initiates the task. As soon as the
task is complete, the task entry it removed from the directory.
The cn=import entry is a container entry for import task operations. The cn=import entry
itself has no attributes, but each of the task entries within this entry, such as cn=task_ID,
cn=import, cn=tasks, cn=config, uses the following attributes to define the import task.
An import task entry under cn=import must contain the LDIF file to import (in the “nsFilename”
attribute) and the name of the instance into which to import the file (in the “nsInstance” attribute).
Additionally, it must contain a unique cn to identify the task. For example:
100 Core server configuration reference
 Loading...
Loading...