Page 1

Configuring and Troubleshooting MS DFS links in an HP
CIFS Server (Samba) Environment
Executive summary............................................................................................................................... 2
What IS MS DFS? ............................................................................................................................ 2
Configuring MS DFS on HP CIFS Server ................................................................................................. 2
Test environment .............................................................................................................................. 2
Configuration details ........................................................................................................................ 3
Modifying the smb.conf file: .......................................................................................................... 3
Creating the MS DFS links: ............................................................................................................ 4
New to SAMBA 3.x:..................................................................................................................... 5
Testing our MS DFS environment........................................................................................................ 6
How it works ................................................................................................................................... 9
Redundant MS DFS links ................................................................................................................. 11
Troubleshooting MS DFS on HP CIFS Server.......................................................................................... 13
Problem 1: The network path was not found...................................................................................... 13
Problem 2: Logon failure: unknown username or password. ................................................................ 18
Summary .......................................................................................................................................... 19
For more information.......................................................................................................................... 19
Page 2

Executive summary
HP CIFS Server (Samba) has the ability to host Microsoft Distributed File System (MS DFS). With
careful planning, this can enable you to create a virtual smb file and directory tree spanning multiple
servers and file systems. This whitepaper presents a sample configuration of MS DFS on an HP CIFS
Server and discusses several potential pitfalls encountered in a MS DFS environment.
What IS MS DFS?
MS DFS, put simply, is an agreed upon set of protocols implemented within the CIFS (Common
Internet File System) protocol to enable links to be created within a CIFS Share that point to shares on
OTHER CIFS Servers, and for those links to be followed by a client accessing them. For the purposes
of this paper, we will configure an HP CIFS Server (version 2.2k), available from
http://software.hp.com
MS DFS links to shares on a WIN2k and WIN2k3 server. All of the information contained in this
paper is equally applicable to HP CIFS Server revisions based on 2.2.x OR 3.x versions of Samba
unless otherwise specified. This information should also be applicable to these versions of Samba
running on Linux. We will use a Windows/XP client for testing.
, with a single share, with files and directories LOCAL to the server as well as
Configuring MS DFS on HP CIFS Server
Test environment
We will be using a combination of HP CIFS Server, Win2k and Win2k3 servers, and a Windows/XP
client for the examples in this paper.
Table 1: Test Environment
HP CIFS Server name rkm-nt
MS DFS enabled share name Dfsroot
MS DFS link linka -> \\ceres\shared_stuff
MS DFS link linkb -> \\mccall\shared_stuff
Win2k server name Ceres
Win2k Share name shared_stuff
Win2k3 server name Mccall
Win2k3 Share name shared_stuff
Windows Xp client name Mccallevo
Xp Username FreddieTheFish
Page 3
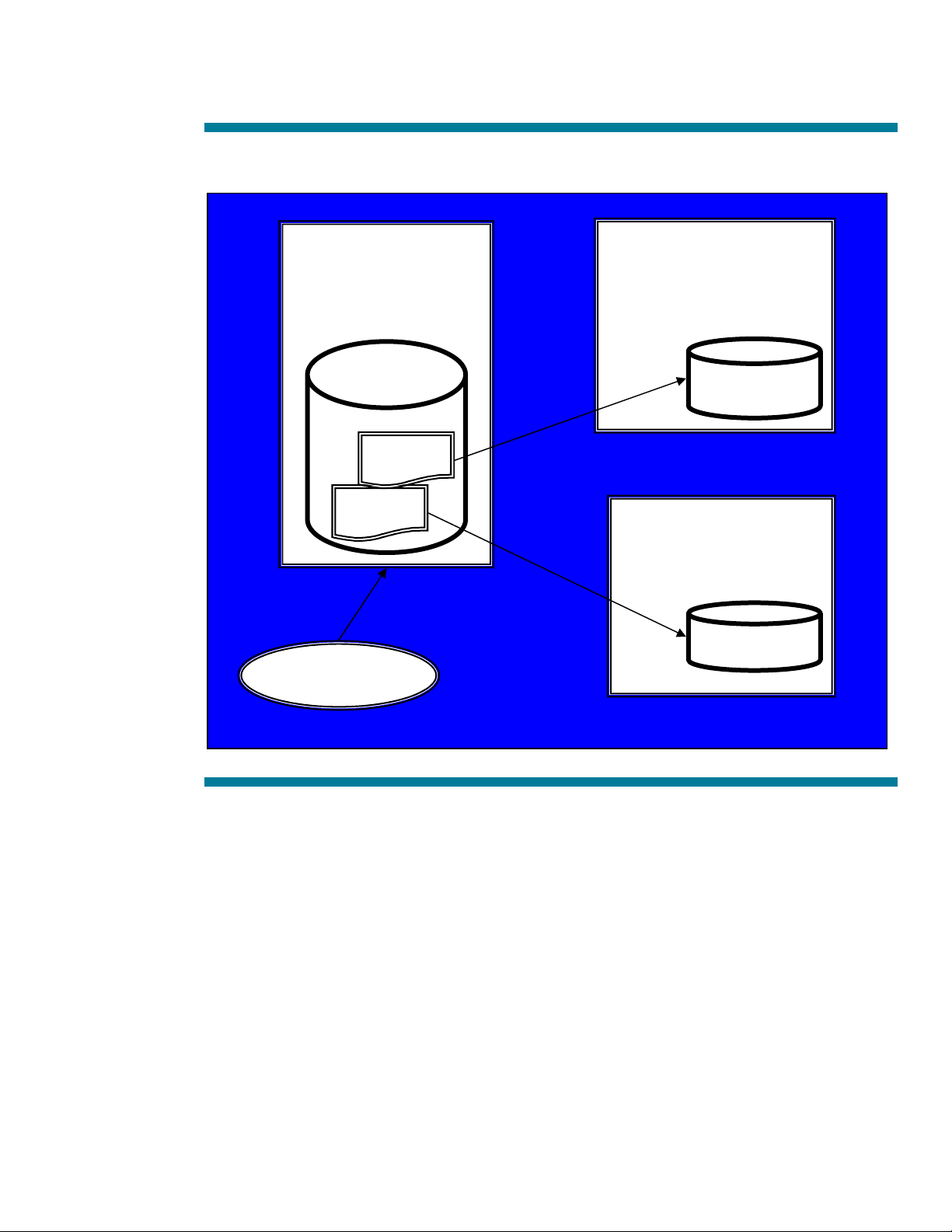
Figure 1 gives us a picture of our test environment.
Figure 1: MS DFS Test Environment
Server:rkm-nt
Dfsroot
linkb
Client:mccallevo
Server:ceres
Shared_stuff
linka
Server:mccall
Shared_stuff
Configuration details
There are three steps to configuring MS DFS on an HP CIFS Server. Two modifications to the
/etc/opt/samba/smb.conf file and the actual creation of the MS DFS links in the HP-UX file system
directory that is hosting the MS DFS root. Notice that ALL of the modifications are done on the HP
CIFS Server – the windows servers that contain the actual shares being linked to require no special
attention.
Modifying the smb.conf file:
[global]
workgroup = DON1
NetBIOS name = RKM-NT
server string = Samba Server
security = DOMAIN
encrypt passwords = Yes
Page 4
password server = ceres
log level = 10
syslog = 0
log file = /var/opt/samba/log.%m
max log size = 1000
host msdfs = Yes
read only = No
[dfsroot]
path = /dfsroot
msdfs root = Yes
Note the two red colored parameters above in [global] and [dfsroot],
respectively:
‘Host msdfs = yes’: This parameter must be set to yes to enable samba to
host MS DFS links in individual shares.
‘msdfs root = yes’: This parameter is set to yes in any share that will
contain MS DFS links to other servers. In this case, we have defined a
single share with this property, called ‘dfsroot’. It points to the HP-UX
directory ‘/dfsroot’.
Creating the MS DFS links:
# cd /dfsroot
# ln -s msdfs:ceres\\shared_stuff linka
# ln -s msdfs:mccall\\shared_stuff linkb
# ll
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root sys 23 Nov 2 12:35 linka -> msdfs:ceres\shared_stuff
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root sys 25 Nov 2 12:35 linkb -> msdfs:mccall\shared_stuff
NOTE: Compare the format of the ‘ll’ output to the ‘ln –s’ command – we
had to ‘escape’ the ‘\’ in the ‘ln’ command. One of the more commonly
made mistakes while setting up DFS links for samba is NOT having the
appropriate number of backslashes in the ‘ln –s’ command. A properly
formatted MS DFS link will take the form:
msdfs:<servername>\<sharename>
Page 5
NOTE: Currently the symbolic names used in MS DFS links must be in
lowercase.
New to SAMBA 3.x:
A new version of HP CIFS Server, A.02.01.01, was released in February 2005. The information in
this paper is equally applicable to this release, which includes ADDITIONAL MS DFS functionality,
enabled by the share level option ‘msdfs proxy’. This option effectively allows an entire SHARE to be
redirected vi MS DFS referral to a share on another server. For instance, consider the following
share definition in the smb.conf file:
[dfsproxy]
msdfs root = yes
msdfs proxy = \ceres.alf.cpqcorp.net\shared_stuff
When a user connects to THIS share, he will get an MS DFS referral to the share named ‘shared_stuff’
on the server ‘ceres.alf.cpqcorp.net’. This is in contrast to having a share that points to a local
directory which has MS DFS LINKS defined IN the local directory. NOTE the use of the FQDN (fully
qualified domain name) in the server portion of the proxy definition. This allows for clients who may
not be able to find the referred server via NetBIOS to resolve the name via DNS.
Page 6
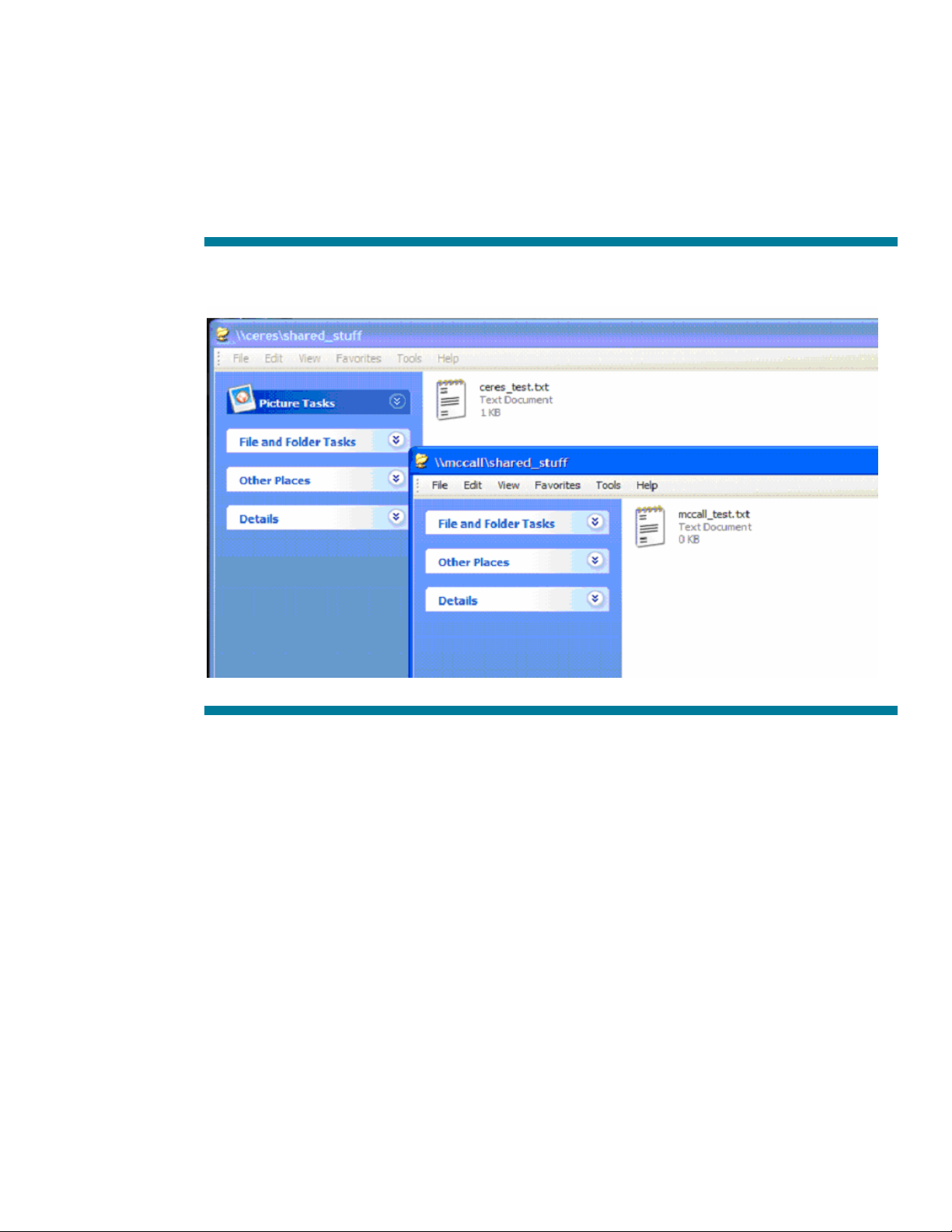
Testing our MS DFS environment
Now that we have configured the HP CIFS Server to offer a couple of MS DFS links, let ’s see it in
action. For this purpose, we have created a single file on each of the linked shares:
\\ceres\shared_stuff: filename=ceres_test.txt
\\mccall\shared_stuff: filename = mccall_test.txt
Figure 2: Shares and files on CERES and MCCALL
Page 7
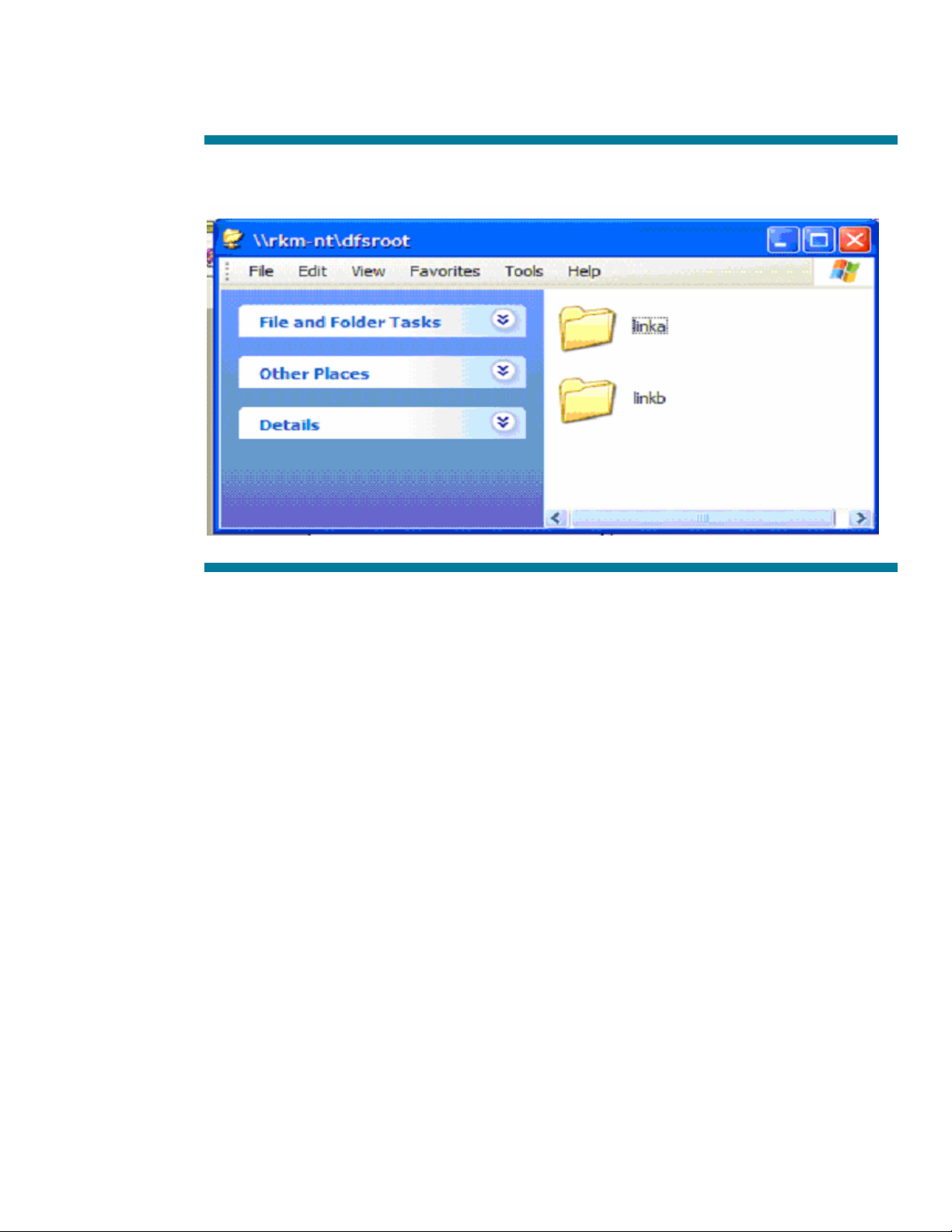
Let’s use our Windows/XP client ‘mccallevo’ to connect to these shares THROUGH the MS DFS links
we have set up on the share \\rkm-nt\dfsroot.
Figure 3: MS DFS links 'linka' & 'linkb'
Notice from Figure 3 that these links show up as standard folders.
Page 8

When we click on the ‘linkb’ folder, we get:
Figure 4: Contents of 'linkb'
And we can see in Figure 4 that, indeed, the file we put on the \\mccall\shared_stuff directory DOES
show up. So the redirection through the MS DFS link was successful. We clicked on a ‘directory’ in
our \\rkm-nt\dfsroot share, and ended up on the ‘shared_stuff’ share on the ‘ceres’ server.
Page 9
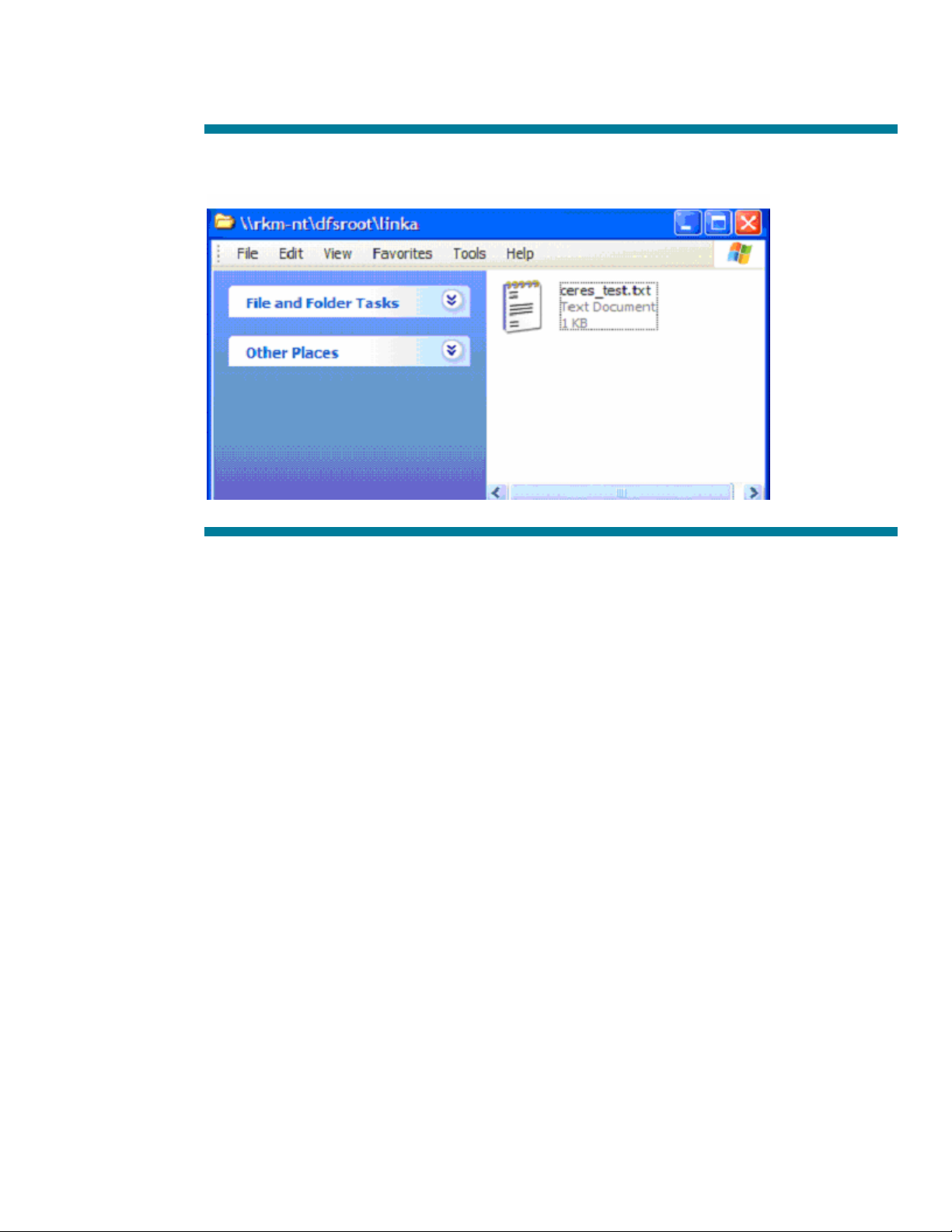
If we click on the folder ‘linka’, we are also successful.
Figure 5: Contents of 'linka'
So, we have demonstrated that by connecting to a single HP CIFS Server, ‘rkm-nt’ we are able to
actually access files on completely independent servers.
How it works
The mechanism behind this is interesting. What actually happens behind the scenes is this.
Client connects to a HP CIFS Server share that is hosting MS DFS links, and attempts to access one of
these links for the first time (for instance, clicking on ‘linka’ in the Explorer window open to the
‘dfsroot’ share on rkm-nt).
HP CIFS Server recognizes that this is a MS DFS link, and returns an ERROR to the client. The error
that is returned is NT_STATUS_PATH_NOT_COVERED. An MS DFS aware client (such as
Windows/XP) recognizes this special error code as a signal that the resource is a MS DFS link. This
triggers the client to send an NT_TRANSACT2 request for a MS DFS referral.
HP CIFS Server responds to this NT_TRANSACT2 request with a MS DFS referral which contains the
server and share name the client should refer to.
The client uses this information to make a direct connection to the \\server\sharename in the referral,
and from that point on the client works directly with the referred server.
The following two screen snapshots from an Ethereal4 trace of the client ‘mccallevo’. Clicking on the
‘linkb’ directory in the ‘dfsroot’ share on the HP CIFS Server ‘rkm-nt’ illustrates the network traffic
which supports this transaction.
Page 10

Figure 6: Highlighted line shows client request for info on linka, the MS DFS link. Note the response immediately after, with the
Error: STATUS_PATH_NOT_COVERED
Page 11

Figure 7: Highlighted line shows response to the MS DFS referral request from the client - note the 'Node: \ceres\shared_stuff'
field in the detail window. This is the actual referral to the 'shared_stuff' share on the server 'ceres'.
Redundant MS DFS links
You can build some redundancy into your MS DFS links by referencing two or more server\share
referrals with the same link. If the FIRST link is unavailable, the client will then attempt to connect to
the SECOND link and so forth. Of course, for this to be effective, you must have some method of
keeping the shares in sync in terms of the data stored on each. The syntax for this is as follows:
ln –s msdfs:\\server1\share1,server2\\share2 linkname
For example, if we set up our ‘linka’ to point to ‘ceres’ first, and then to ‘mccall’:
Ln –s msdfs:ceres\\shared_stuff,mccall\\shared_stuff linka
Page 12

And then, take ‘ceres’ offline. Note the results in the following screen snapshot.
Figure 8: Note that the file 'mccall_test.txt' is the file from \\mccall\shared_stuff, since the 1st referral to \\ceres\shared_stuff
was unavailable. The failure to find \\ceres\shared_stuff was transparent to the user.
NOTE: Both the client AND the server hosting the MS DFS root do some
form of caching in regards to links that have been followed. Because of
this, if you change a share such that it no longer hosts MS DFS links, or visa
versa, you may have to reboot your clients that have accessed this share. It
is also recommended that you restart samba after changing a share
to/from a MS DFS root. Terpstra and Kalele in Chapter 16 of ‘The Official
Samba-3 HOWTO and Reference Guide ’ recommend creating a NEW
share when introducing a MS DFS root, rather than converting an existing
share.
Page 13

Troubleshooting MS DFS on HP CIFS Server
So, now that we know what it looks like when it WORKS, let’s step through troubleshooting a couple
of common problems you might run into.
Problem 1: The network path was not found.
I have followed the above configuration steps, and my users can connect to the SHARE, but when
they click on the MS DFS link, they get the following error.
Figure 9: Client Error returned when referral fails
One way to troubleshoot this would be with a network trace using Ethereal, an Open source software
network sniffer. You can download this excellent utility from
The following screenshot shows a partial trace of the network activity resulting from the user clicking
on the MS DFS link ‘linka’:
http://www.ethereal.com.
Page 14

Figure 10: Trace of a failing MS DFS referral due to client being unable to resolve node name in referral response.
In the screen shot for Figure 10, we see the ‘STATUS_PATH_NOT_COVERED’, followed by the
‘GET_DFS_REFERRAL’. THEN we see a number of packets involving name lookup for the server
‘ceres’, who is the server we got a MS DFS referral for. Note the highlighted line ‘Name Query
Response’. In the detail window of the above screenshot, you see that this is a NEGATIVE response –
‘ Requested name does not exist’. SO – the referral functioned properly – the client is trying to find
the server we referred it to, but is unsuccessful. From the trace, it clearly cannot find the server named
‘ceres’. Why?
First, let’s check to make sure that the server and share we are setting the link up to is correct. On the
HP CIFS Server ‘rkm-nt’ we will do this using the ‘smbclient’ utility.
# /opt/samba/bin/smbclient //ceres/shared_stuff -U FreddieTheFish
added interface ip=16.113.9.137 bcast=16.113.63.255 nmask=255.255.192.0
Password:
Domain=[DON1] OS=[Windows 5.0] Server=[Windows 2000 LAN Manager]
smb: \> dir
. D 0 Tue Nov 2 14:42:02 2004
.. D 0 Tue Nov 2 14:42:02 2004
ceres_test.txt A 29 Mon May 24 09:06:10 2004
34717 blocks of size 524288. 32348 blocks available
smb: \>quit
Ok, so WE can find the server and share just fine from the HP CIFS Server making the MS DFS
referral.
Page 15

But what about the CLIENT? We will use the command prompt window to try to directly attach to the
server and share we are being referred to.
Figure 11: Using cmd window to check direct access to a server and share
As we can see from the above screenshot, the client is not able to get to the referred
server/sharename DIRECTLY. The error received is similar to that returned when we tried to follow the
MS DFS link. All of the symptoms above (the error messages about network path not found, the
ethereal trace showing the NetBIOS server name not found, but the server proven available from at
least one other source) are typically indicative of a name resolution issue.
Let’s take a look at the server again, and see if we can figure out where this server is. We’ll use the
HP-UX utility ‘nslookup’.
# nslookup ceres
Name Server: fwd2.cca.mycompany.net
Address: 55.155.155.55
Trying DNS
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: ceres.alf.mycompany.net
Address: 16.113.9.139
Ok! Now that we have an address for ceres, we can address this problem in several ways.
We could set up a wins server and make sure that everyone is using the same source for name
resolution.
We could set up our clients and servers to use the same DNS source for name resolution.
Page 16

We could add the ‘ceres’ server and its ip address to the local lmhosts file on the client.
Choice # 3 is the simplest from a testing standpoint. So we add the following line to the
/windows/system32/drivers/etc/lmhosts file on the client
16.113.9.139 ceres #PRE
and reload the remote cache name table on the client from the command prompt.
c:\>nbtstat –R
Page 17
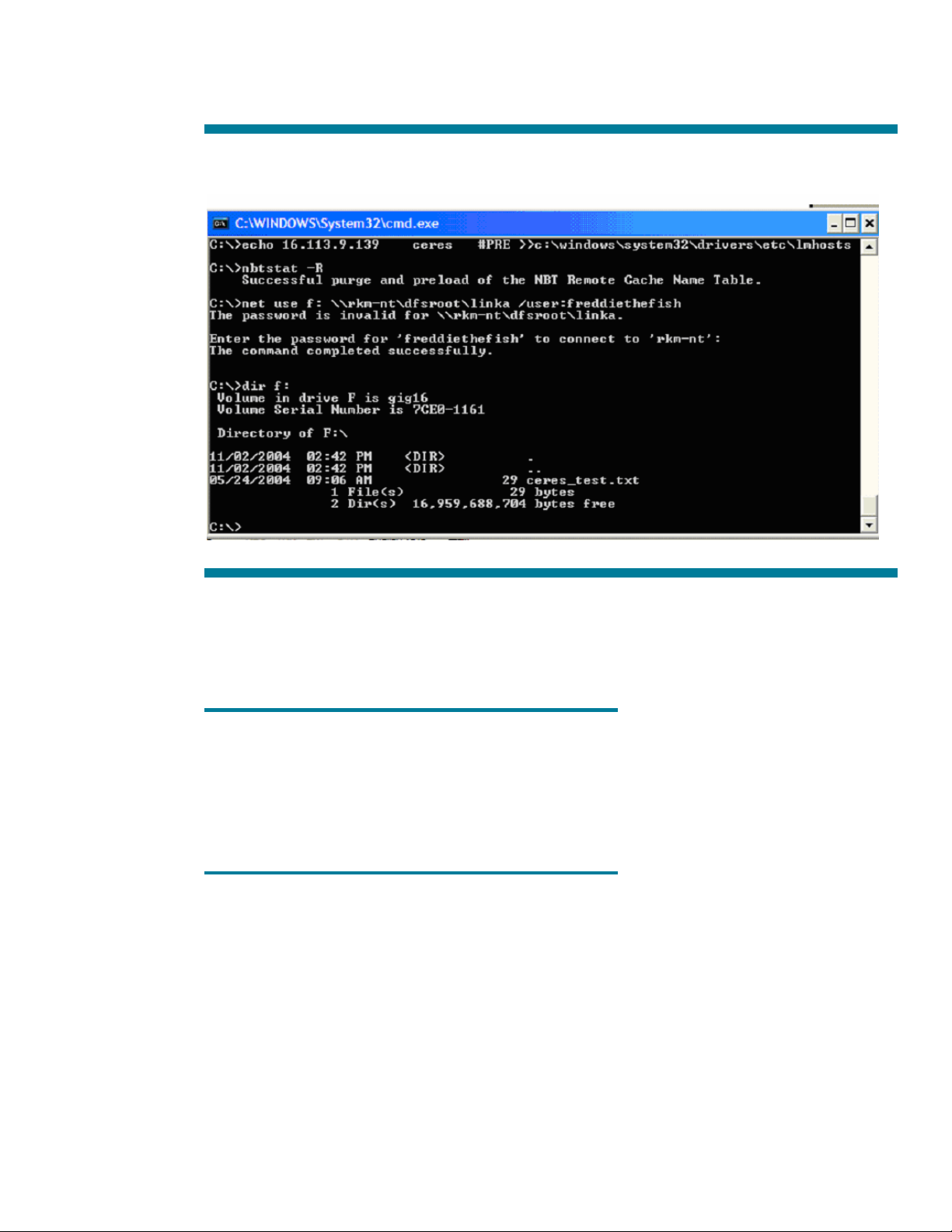
And NOW, as the screenshot below shows, we are able to successfully follow the MS DFS link.
Figure 12: Adding an lmhosts entry and reloading the NetBIOS name cache from the cmd window
Naturally, in a production environment, you would want to either use WINS or DNS, to globally
resolve name issues across your enterprise rather than having to add entries to the lmhosts file of
every client needing to follow this link. But this simple method is very useful for troubleshooting.
NOTE: Since it is the client’s responsibility to directly connect to the node
(server) and share name that the MS DFS referral response returns, it is
entirely possible to create MS DFS links on your HP CIFS Server share that
the server itself is unable to resolve or connect to so long as the CLIENT can
resolve the name and has the appropriate credentials to connect to the
share on the referred server. There is no check on the HP CIFS Server side
to verify that a MS DFS link is reachable.
Page 18
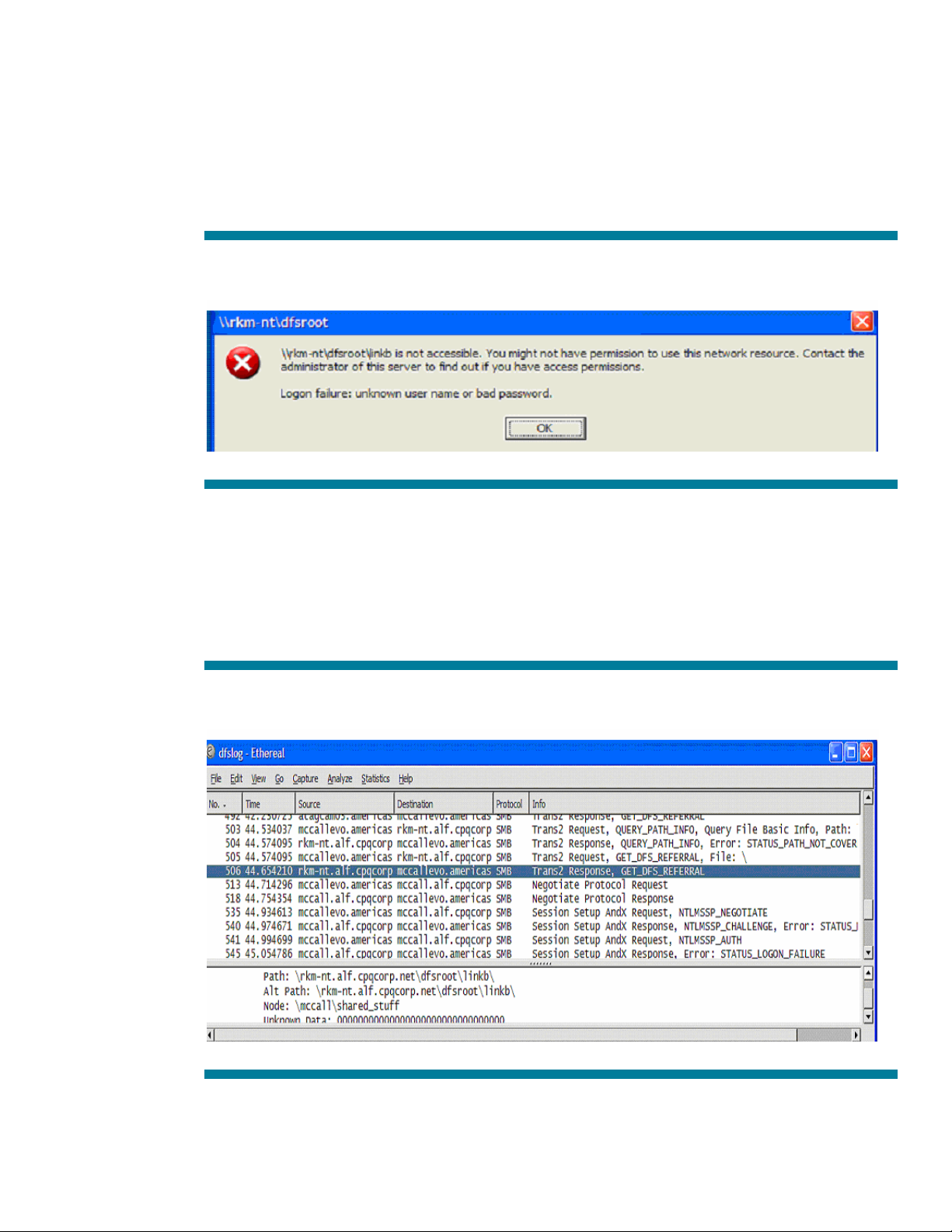
Problem 2: Logon failure: unknown username or password.
I have followed the above configuration steps and my users can connect to the SHARE but when they
click on the MS DFS link, they get the following error.
Figure 13: Error returned to the client as a result of a bad username or password on the referred server
To begin troubleshooting this, we must first remember that the user having access to the HP CIFS
Server HOSTING the MS DFS root doesn’t guarantee that that same user will have access to the
server that the MS DFS link will refer him to!
And in fact, the following screen shot of a partial Ethereal trace of the network traffic involved clearly
shows the authentication failure, not at the HP CIFS Server ‘rkm-nt’, but when trying to set up a session
to the ‘referred’ server, ‘mccall’:
Figure 14: Trace showing the result of a MS DFS referral to a link where the client username/password is not recognized
This tells us that either the username or the password that the client is using to connect to the HP CIFS
Server share hosting the MS DFS root is not recognized by the referred server ‘mccall’. You can
Page 19

verify this by having the client attempt to directly connect to the referred server and share returned in
the trace, i.e. ‘mccall\shared_stuff’ as shown below using the command prompt window on the client.
Figure 15: Using the cmd window to test for valid username/password directly to the referred server
At this point, you should have the client contact the administrator of the ‘mccall’ server to set up the
necessary username and password for appropriate access to this server.
Summary
HP CIFS Server (Samba) is capable of hosting MS DFS roots. The links in these roots can be used to
create a single share that will allow clients to access shares on multiple discrete servers across the
Windows enterprise. Since the HP CIFS server does not participate in connecting the client directly to
the referred shares other than to provide the client with the server (node) name and sharename, the
clients availing themselves of this share must be able both to resolve the server name provided in the
MS DFS referral and possess the appropriate credentials, username/password to connect to the share
on the referred server. If your clients have difficulties following a MS DFS link you have set up,
oftentimes a network trace of the attempt will be helpful in determining the reason for the failure.
MS DFS also provides some possibility of redundancy by configuring referrals to multiple servers from
the same MS DFS link. Remember that in using this it is your responsibility to keep the data on the
various shares in-sync. This is important since from a client standpoint, there is no simple way of
telling WHICH referral in a multi-referral MS DFS link was followed.
Finally, in versions of HP CIFS Server based on Samba 3.x (A.02.01 and above) new MS DFS
functionality has been introduced with the smb.conf parameter ‘msdfs proxy’. This parameter will
allow you to set up a SHARE that will be treated as a MS DFS link to a share on another CIFS server.
For more information
The Official Samba-3 HOWTO and Reference Guide, by Terpstra and Vernooij (Prentice Hall) also
available online at:
Page 20

http://us1.samba.org/samba/docs/man/Samba-HOWTO-Collection/
Using Samba 2nd Edition, by Ts, Eckstein and Collier-Brown (O'REILLY Press) also available online at:
http://us1.samba.org/samba/docs/using_samba/toc.html
Implementing CIFS, by Christopher Hertel (Prentice Hall) also available online at:
http://www.ubiqx.org/cifs/
Ethereal Users Guide, available online at:
http://www.ethereal.com/docs/user-guide/
In addition, there are numerous articles available from Microsoft on MS DFS. While these are not
specifically applicable to MS DFS on Samba, they do give useful background and implementation
information. Some useful articles in this category:
Distributed File System (DFS): Best Practices and Troubleshooting Guide
812487 - Overview of DFS in Windows 2000
Distributed File System: Frequently Asked Questions
Distributed File System White paper
This white paper was written by Don McCall.
Don McCall is a Master software support engineer with the GSE WTEC organization, and has been
with HP for 23 years. He currently supports versions of Samba on HP-UX, MPE/iX, and Linux.
Page 21

© 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained
herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and
services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein.
Itanium is a trademark or registered trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and
other countries and is used under license.
XXXX-XXXXEN, 3/2005
 Loading...
Loading...