Page 1

Using Microsoft®
Baseline Security
Analyzer 2.2
®
and WindowS
Update
For HP Thin Clients running Microsoft
Windows Embedded Standard 7
Table of Contents:
Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer 2.2 .............................................................. 2
Preface ........................................................................................................... 2
Introduction .................................................................................................... 2
Background .................................................................................................... 2
Installation on WES 7 ...................................................................................... 3
Scanning Options ............................................................................................ 6
Key Options for Thin Clients: ................................................................... 6
Features .......................................................................................................... 7
Enhanced Reporting: ............................................................................... 7
Using Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer 2.2 ................................................ 7
Using the MBSA GUI with WES 7 ............................................................. 7
Using MBSA Command-line with WES 7 ................................................ 11
Using MBSA in OFF-line Mode with WES 7 ............................................ 14
Localizations ................................................................................................. 18
Issues ........................................................................................................... 18
Using Windows Update on WES 7 ..................................................................... 18
Introduction .................................................................................................. 18
Audience ...................................................................................................... 19
Overview ...................................................................................................... 19
RAM Drive Considerations ............................................................................. 19
Good News about WES 7 Quick Fix Engineering (QFE) Releases ..................... 20
Disk Space Concerns ..................................................................................... 20
Page 2

HP Windows Update Perspective ................................................................... 20
How to Enable Windows Update ................................................................... 21
HKEY Local Machine ............................................................................. 21
HKEY Current User ................................................................................ 21
Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer 2.2
Preface
The scope of this document is focused on how customers can identify the most
current Microsoft Quick Fix Engineering (QFE) releases and Security Updates that
are applicable to their Golden Master image and is not concerned with the process
of downloading and deploying these items.
The Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) solution presents a Microsoftsupported method for discovering and identifying security updates, on-demand,
without the customer having to wait for the same update to be packaged, tested,
and then delivered to http://www.hp.com/
for identifying necessary security updates.
Introduction
. This process is recommended by HP
This white paper describes the application of MBSA on HP thin clients with WES 7
for the purpose of assessing the security state and detecting missing security
updates for this platform.
Background
To easily assess the security state of Windows machines, Microsoft offers the free
Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) scan tool. MBSA includes a graphical
and command line interface that can perform local or remote scans of Microsoft
Windows systems.
®
MBSA 2.2 runs on Windows Server
2008, Windows Vista™, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP and Windows
2000 systems and will scan for missing security updates, rollups, and service packs
using Microsoft Update technologies. MBSA also scans for common security
misconfigurations (also called Vulnerability Assessment checks) using a known list of
less secure settings and configurations for all versions of Windows; Internet
Information Server (IIS) 5.0, 6.0, and 6.1; SQL Server 2000 and 2005; Internet
Explorer
To assess missing security updates, MBSA only scans for missing security updates,
update rollups, and service packs available from Microsoft Update. MBSA does not
scan or report missing non-security updates, tools, or drivers.
®
(IE) 5.01 and later; and Office 2000, 2002, and 2003 only.
2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server
2
Page 3
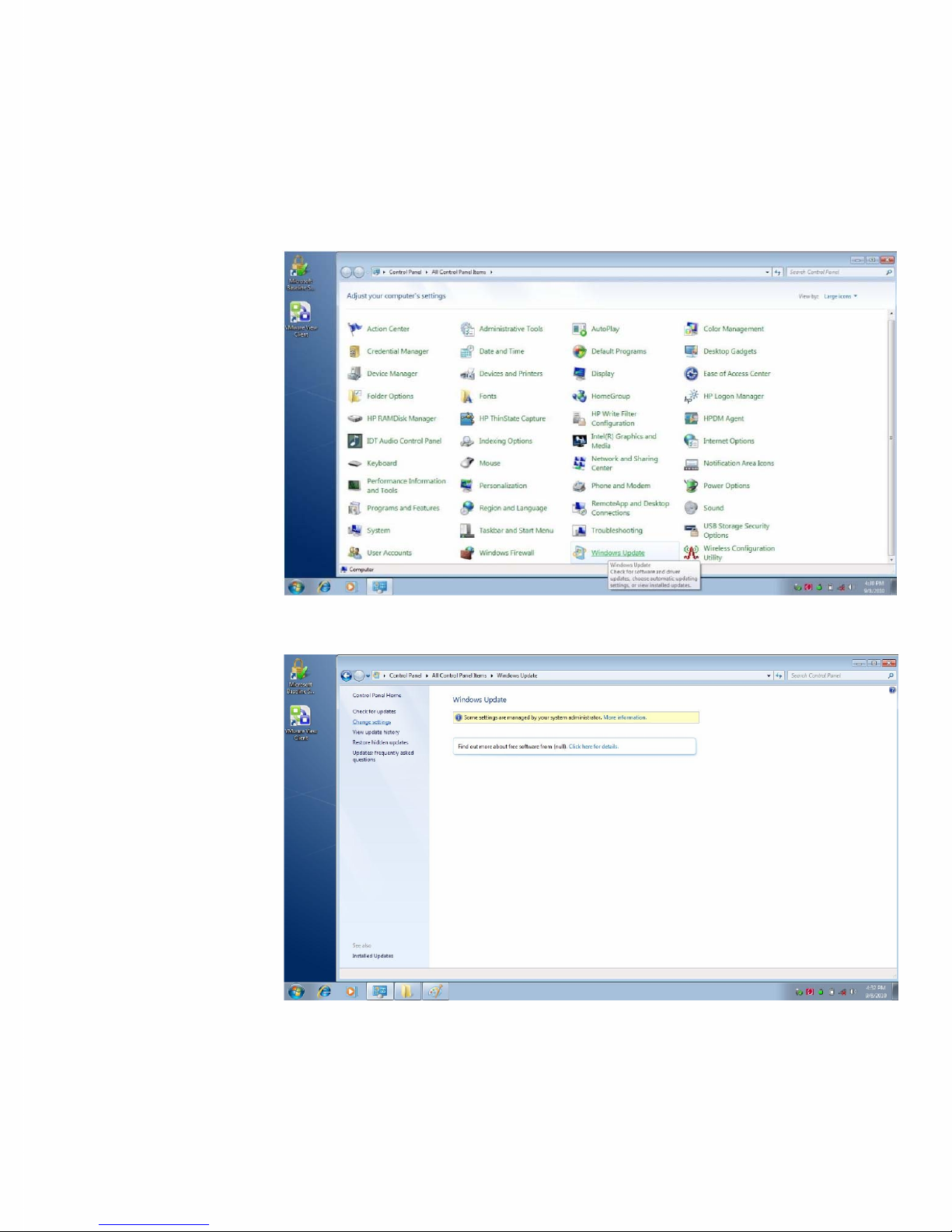
Installation on WES 7
The MBSA graphical user interface (GUI) is a simple and seamless installation
process for WES 7 that only takes approximately 2 Mb of disk space.
Windows Update must be enabled first, go to Control Panel and open Windows
Update:
1. Click Change Settings.
3
Page 4
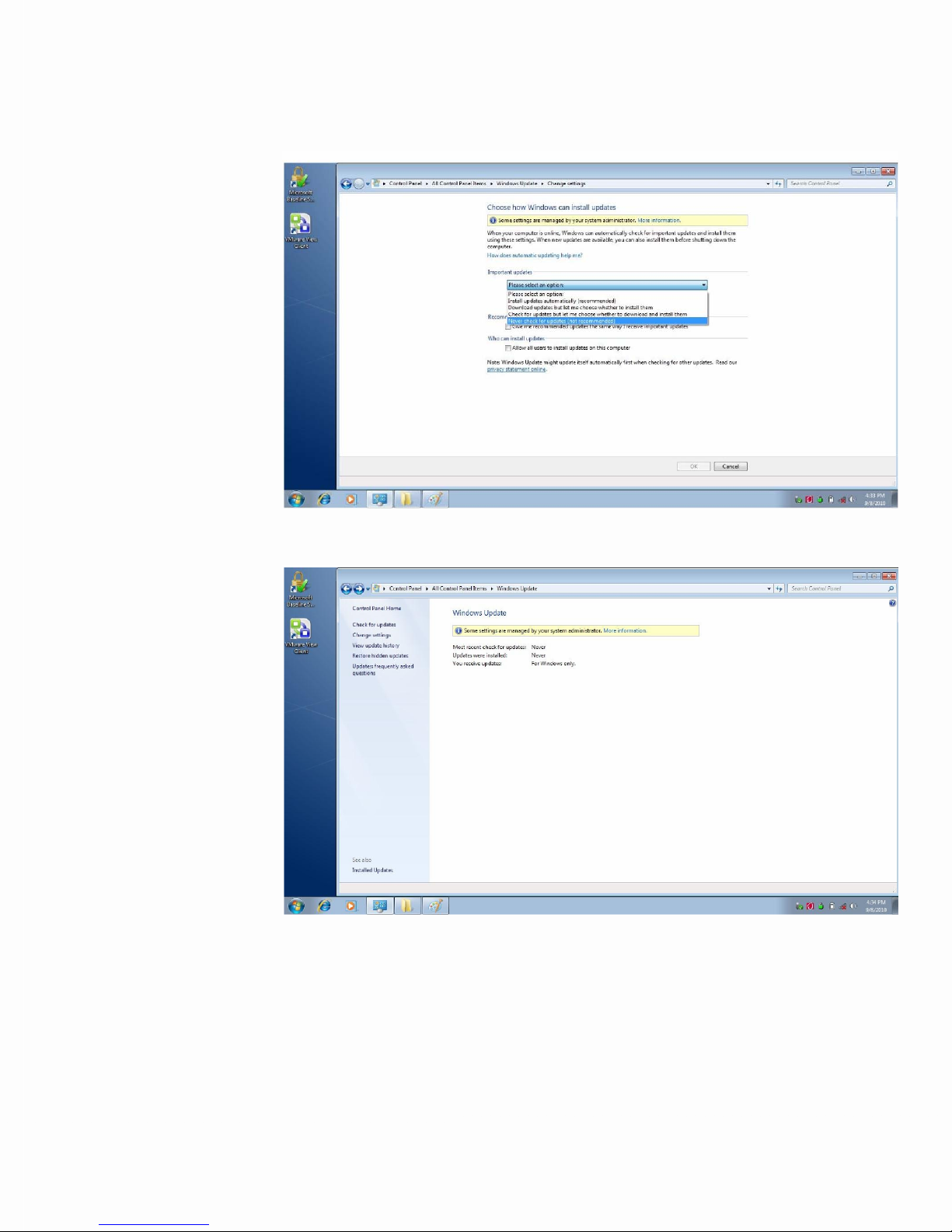
2. Under Important Updates, choose Never check for updates..., then click OK.
Windows Update is now active:
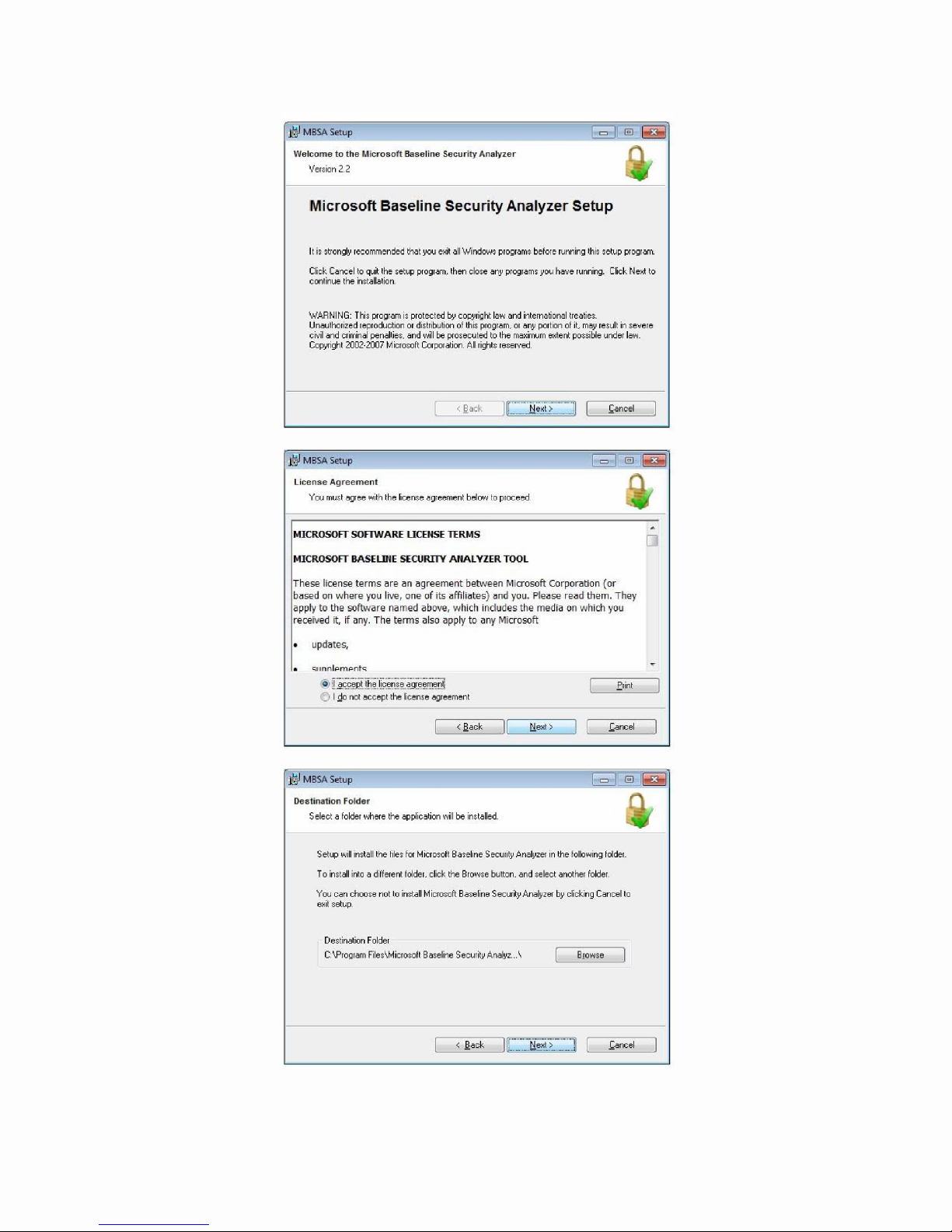
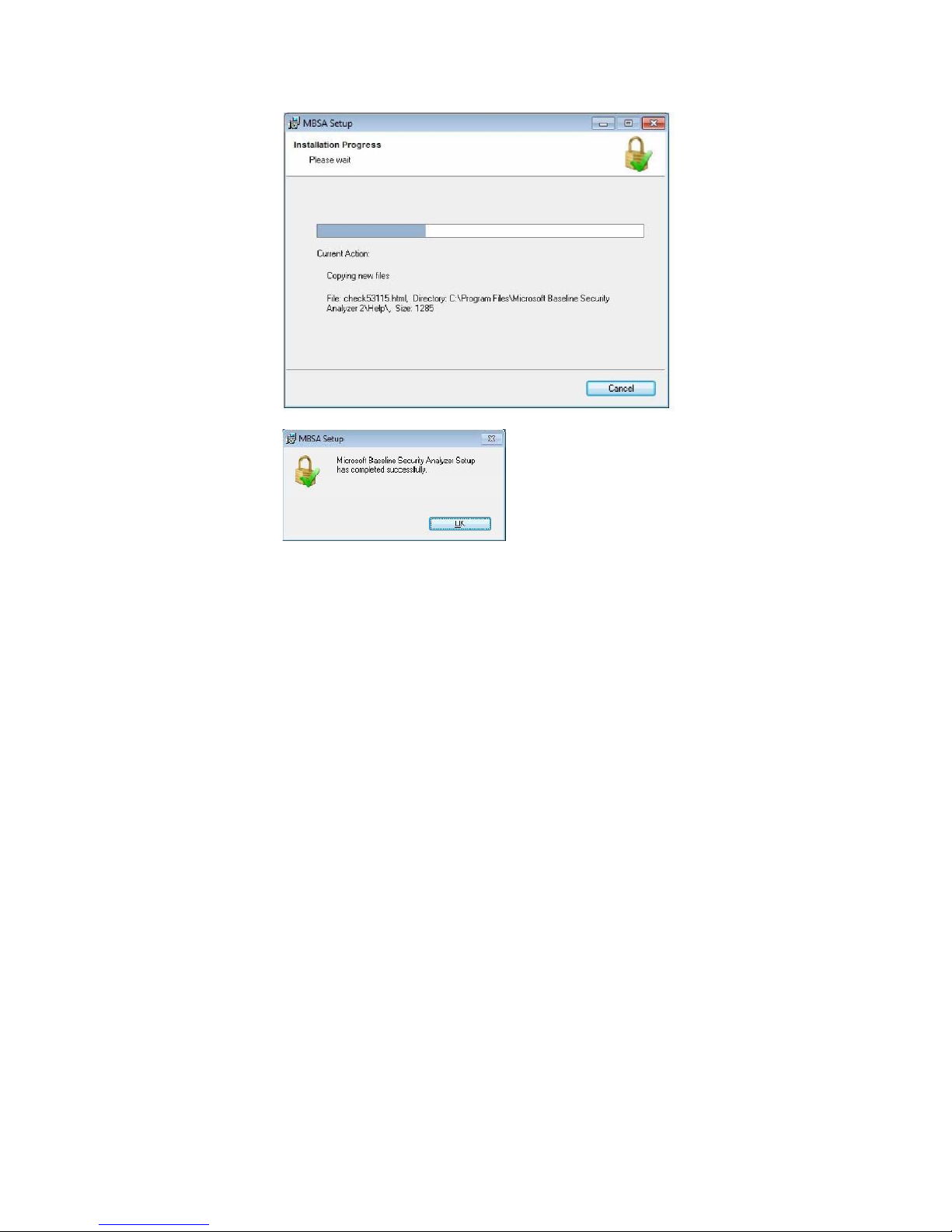
3. Install MBSA 2.2. Once finished, the Write Filter must be committed and the
system rebooted:
4
Page 5
5
Page 6
Scanning Options
Key Options for Thin Clients:
Check for Security Updates
Select this option to check the target computer for missing Microsoft Windows
updates. When you select this option, you can also specify the following options:
Configure Computers for Microsoft Update and Scanning
Prerequisites
Select this option to install the current version of the Windows Update Agent on the
target computer, if it is absent or out of date, and to configure the target computer
to meet other requirements for scanning for security updates.
Scan Using Update Services Servers Only
Select this option to scan only for those security updates that are approved on the
computer's assigned Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server. The
Microsoft Update website or an offline catalog is not used.
Scan using Microsoft Update Only
Select this option to use only the security update catalog downloaded from the
Microsoft Update website to determine the updates to be checked. Updates that are
not approved on the computer's WSUS server are reported as though they were
approved. If the Microsoft Update website cannot be reached by the client, an error
is reported.
6
Page 7
Features
Enhanced Reporting:
• Current Update Compliance appears in the report; installed and needed
updates are reported together in a single scan report.
• Maximum bulletin severity and update package download links are now
available in report details.
• Access to the live Microsoft Update site for published content for live (online)
security update assessment, as well as an off line catalog for customers with
limited or secure internet access are provided.
• Command-line option to redirect reports to a user-selected directory or network
share using /rd option is available.
• Reports can now be easily shared and viewed.
• Multiple copies of MBSA can be run for increased scanning performance.
• Structured XML output offers simplified integration for update scanning.
• Specific web links are available for locating updates and taking necessary
actions.
Using Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer 2.2
Using the MBSA GUI with WES 7
The target system must be connected to the Internet in order to download the current
Microsoft Security Update database.
1. Click Scan a computer.
7
Page 8

2. Select options and click Start Scan.
MBSA downloads the current Security Update Database and scans the target
system.
8
Page 9

After scanning is complete, the report is immediately generated.
3. In the Security Update Scan Results, select the top Security Update listed (MS1
0-046).
9
Page 10

The Microsoft webpage for the Security Update (MS1 0-046) appears.
4. Scroll down and select the applicable operating system. For WES 7, it is
Windows 7 for 32-bit Systems.
10
Page 11

You can then download the Security Update in .msu or .exe format for later
use.
Using MBSA Command-line with WES 7
Having completed the process for installing the MBSA GUI, the Command-line
utility can also be used to scan a target system or systems for security updates,
generating a report in .mbsa (rich format report viewable in MBSA), .xml or .txt
format as needed to then be used on Microsoft Security Bulletin Search website:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/current.aspx
11
Page 12

12
Page 13

13
Page 14

Using MBSA in OFF-line Mode with WES 7
MBSA uses files that it downloads from the Internet, but the computer I want to use
to scan my network doesn't have Internet access. How can I use MBSA in an offline
and secure environment?
You can either perform the scan using the mbsacli command-line utility with the /nd
(do not download) parameter, or you can perform the scan using the GUI. Before
scanning you must copy the necessary files to the computer performing the scan.
Four types of files are required:
• Security update catalog (wsusscn2.cab), available from the Microsoft website:
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=74689
• Windows Update Redistribution Catalog (wu redist.cab) at
http://update.microsoft.com/redist/wuredist.cab
• Authorization catalog (muauth.cab) for Windows Update site access, available
from the Microsoft website or by examining the contents of the wuredist.cab file
at http://update.microsoft.com/redist/wuredist.cab
• Windows Update Agent standalone installers (if not already installed)
The latest versions are available by examining the contents of the wuredist.cab file
at http://update.microsoft.com/redist/wuredist.cab
After downloading the files from the Microsoft website, copy all files listed above to
the following folder on the computer performing the security update scan:
C :\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local
Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\MBSA\2.1 \Cache
.
Important
To ensure that MBSA has access to the most current
versions of these files, you should download them on a
weekly basis or after any release of security bulletins from
14
Page 15

Microsoft. This is especially important in the case of the
security update catalog (Wsusscn2.cab), because
Microsoft releases an updated version of this file whenever
a new security bulletin is released or updated.
When you run MBSA to perform security update checks on remote computers,
MBSA deploys the Windows Update Agent to the remote computer.
Example:
c:\Program Files\Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
2\mbsaci /target "target computer name" /wi /nd /catalog
c:\temp\wsusscn2.cab /rd c:\temp /qt
(Generates an .mbsa rich format, detailed report inside the MBSA utility)
OFF-line mode Scanning:
15
Page 16

And the resulting report sent to C:\Temp:
MBSACLI Switches:
• MBSACLI [/target | /r | /d domain] [/n option] [/o file] [/qp] [/qe] [/qr]
[/qt] [/listfile file] [/xmlout] [/wa | /wi] [/catalog file] [/nvc] [/ia] [/mu]
[/nd] [/rd directory] [/?]
• MBSACLI [/l] [/ls] [/lr file] [/ld file] [/unicode] [/nvc] [/?]
Description: This is a command line interface for Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
Parameter List:
/target domain\computer Scan named computer.
/target IP Scan named IP address.
/r IP-IP Scan named IP addresses range.
/listfile file Scan named IP address or computer listed in the
specified file.
/d domain Scan named domain (Use NetBIOS compatible
domain name (Ex: MyDomain) instead of Fully
Qualified Domain Name (Ex:Mydomain.com) ).
/n option Select which scans to NOT perform. All checks are
performed by default.
Valid values: "OS", "SQL", "IIS", "Updates",
“Password", Can be concatenated with "+" (no
spaces).
/wa Show only updates approved on the WSUS server.
/wi Show all updates even if not approved on the
WSUS server.
/nvc Do not check for a new version of MBSA.
16
Page 17

/o filename Output XML file name template.
Default: %D% - %C% (%T%).
/qp Do not display scan progress.
/qt Do not display the report by default following a
single-computer scan.
/qe Do not display error list.
/qr Do not display report list.
/q Do not display any of the preceding items.
/unicode Output Unicode.
/u username Scan using the specified username.
/p password Scan using the specified password.
/catalog filename Specify the data source that contains the available
security update information.
/ia Update the prerequisite Windows Update Agent
components during a scan.
/mu Configure computers to use the Microsoft Update
website for scanning.
/nd Do not download any files from the Microsoft
website when scanning.
/xmlout Run in updates only mode using only mbsacli.exe
and wusscan.dll. Only these switches can be used
with this option: /catalog, /wa, /wi, /nvc,
/unicode
/l List all reports available.
/ls List reports from the latest scan.
/lr filename Display overview report.
/ld filename Display detailed report.
/rd directory Save or Retrieve reports from the specified
directory.
/? Display this help/usage.
Executing MBSACLI with no parameters scans the local computer for all checks and
displays the report in text-mode.
Examples:
MBSACLI
MBSACLI /n Password+IIS+OS+SQL
MBSACLI /d MyDomain MBSACLI /target 200.0.0.1 MBSACLI /r 200.0.0.1-
MBSACLI /ld "Domain - Computer (03-01 -2002 1 2-00 AM)"
MBSACLI >c:\results.txt
MBSACLI /catalog c:\wsusscn2.cab /ia /nvc
MBSACLI /wa
200.0.0.50 MBSACLI /listfile export.txt
17
Page 18

MBSACLI /xmlout /catalog c:\temp\wsusscn2.cab /unicode >results.xml
MBSACLI /l /rd c:\scanreports
Localizations
MBSA releases are available for German, Japanese, and French.
The WSUSSCN2.CAB file is localized to all supported languages and is
automatically downloaded and used by the tool for any client language or locale
being scanned. Results are stored in the report based on the MBSA installation
language.
Issues
Problems discovered during the scoping of this project:
• Microsoft is not supporting the Nobackup feature for WES 7 Security Updates.
This is a crucial and impacting change, as the addition of monthly Security
Updates expands the Image footprint from month to month.
• The current catalog files must be downloaded from the Internet before an OFF-
line mode scan. It is strongly recommended that these files be downloaded on
a weekly basis to ensure that the current security database is being used for
scanning.
• Installation history (explicitly installed/effectively installed) no longer reflects
those updates that have been superseded by another update. The behavior of
this feature follows the behavior for missing updates, where only the most
recent non-superseded update is shown.
• Workaround: Refer to the bulletin, fixlist, or TechNet search page to identify
each previous bulletin that has been included in the update in question from the
Current Update Compliance listing.
Using Windows Update on WES 7
Introduction
This section discusses the pros and cons of enabling Windows Update on
HP Windows Embedded Standard 7 (WES 7) images.
The section also covers the level of support Microsoft and HP have for Windows
Update and what the customer can expect if Windows Update is enabled on
HP thin clients.
It concludes with some special notes regarding installing WES 7 QFEs with a write
filter enabled.
18
Page 19

Audience
This section is intended for technical audiences and implies a working knowledge
of editing the system registry, reconfiguring HP thin client utilities, and modifying
aspects of the WES 7 operating system.
The section does not include detailed instructions needed to complete each
modification, as ample information is available in the public domain to achieve the
desired results.
Overview
Microsoft has included full support for Windows Update in WES 7. In prior versions
of Windows Embedded operating systems, the Windows Update website would not
always recognize Windows XP Embedded clients and some, but not all, QFEs or
updates would be available for download.
One drawback to Windows Update on WES 7 is that the in-box Windows Update
client is not write filter-aware, and it does not know to manage the write filers if they
are enabled.
This presents a serious challenge for HP thin client users that wish to take advantage
of Windows Update support for QFE servicing. Microsoft provides no native
solution or workaround for this situation, which leaves it up to the users to
implement an end-to-end solution.
RAM Drive Considerations
A possible blocking issue for HP thin client users is the RAM Drive. Implemented as
a performance enhancement, HP redirects the TEMP, TMP, and Temporary Internet
Files environment variables to the Z:\ RAM Drive. These redirected folders are
commonly used during installation of software applications and QFEs.
As a matter of best practices, HP strongly recommends that users change the
redirected folders to the C:\ drive before downloading and installing QFEs and
feature updates from Windows Update. This may prevent the system from running
out of disk space on the RAM Drive and causing unexpected errors when updating
the system.
If users see unexpected installation failures or odd errors during QFE installation,
modifying the RAM Drive size or even redirecting the folder to the C: drive for
installation may be required to complete the installation successfully. This may occur
when installing any of the following:
®
• New versions of Internet Explorer or Windows Media
• New .Net Framework revisions or service packs
• New WES 7 Service Packs (SP1, SP2, etc…)
• Large numbers of QFEs installing simultaneously
Player
19
Page 20

Good News about WES 7 Quick Fix Engineering (QFE)
Releases
Fortunately, most WES 7 QFEs download and install from the
C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download folder. This means that it
may not be necessary to modify the environment variables for monthly QFE
updates.
No data is available from Microsoft about the requirements for available TEMP
space for any given QFE, so individual QFEs may behave differently, depending on
how the feature team at Microsoft developed and delivered the package to the
Windows Update team.
The rule of thumb is that most monthly QFEs do not require modification of
environment variables in HP thin clients, but watch out for large packages and
feature upgrades such as IE, WMP, or .Net Framework.
Disk Space Concerns
A flaw in the Microsoft QFE strategy for WES 7 is the lack of a nobackup switch for
QFEs. In XP Embedded, Microsoft QFEs could be passed a /nobackup argument
that would prevent the QFE from creating a backup folder on the disk (typically in
the C:\Windows folder). This was helpful in preventing the limited disk space on
thin clients from filling up over time.
It is unclear if Microsoft will implement the /nobackup switch option for individual
WES 7 QFEs, or if QFEs downloaded and installed via Windows Update will
automatically have the /nobackup option enabled. HP will continue to engage
Microsoft to improve this scenario in WES 7.
Because the nobackup switch is not available, QFEs can also be uninstalled. This is
also a major change in behavior in Windows Embedded QFEs. HP will not test and
qualify all of the permutations of the install/uninstall scenarios around MS QFEs. It
is recommended that QFEs only be uninstalled if there is cause to believe a
regression or issue is a direct result of a QFE installation.
HP Windows Update Perspective
HP officially discourages customers from using Windows Update because of the
known limitations with the Microsoft implementation.
The client pull servicing schema that Windows Update offers is not consistent with
the way thin clients are typically serviced industry wide. A server push schema is
the more deterministic and successful way to manage thin clients in the enterprise
environment.
For all the virtues of the client pull servicing scenario, risks are still involved with
user managed devices. Best examples are:
• Users can opt to not install QFEs for vulnerabilities, if they don’t want to
(disable WU or change settings to ignore availability notices).
• Microsoft does not guarantee that QFEs and updates will not harm or conflict
with your system or configuration.
• Administrator rights and privileges are required.
20
Page 21

• The device is end user-managed—not IT-managed.
• More than one reboot may be required to complete full installation of QFEs on
WES 7.
• Modifications of system environment variables may be required to install QFEs
and the restore system to prior state.
• The Windows Update agent will be disabled via system policies by default in
the HP WES 7 image.
HP recommends that HP customers use the Microsoft Base Line Security Analyzers to
identify needed QFEs, and then utilize a server push model to deliver QFEs and
updates to deployed units. Preferably, all QFEs and updates would be pretested
and qualified against a Golden Master image before being mass deployed. HP
strongly recommends this model to prevent QFEs and updates from corrupting or
adversely modifying deployed images.
See Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer 2.2 for more information.
How to Enable Windows Update
The following section explains how to enable Windows Update on HP WES 7
images.
Two OS policies need to be disabled before Windows Update website will
recognize and communicate with the client system. One policy is a global system
policy in HKEY Local Machine and the other is user profile-specific that needs to be
disabled on each user profile on the system:
HKEY Local Machine
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersio
n\Policies\WindowsUpdate
1. DisableWindowsUpdateAccess = REG_DWORD 0x00000001
2. Change DWORD to 0 to disable.
3. Change DWORD to 1 to enable.
HKEY Current User
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
\Policies\Explorer
1. NoWindowsUpdate = REG_DWORD 0x00000001
2. Change DWORD to 0 to disable.
3. Change DWORD to 1 to enable.
A reboot is required after changing registry settings to enable support.
If the File-Based Write Filer (FBWF) is enabled, remember to disable to the write
filer before making any registry changes.
If the Enhanced Write Filter (EWF) is enabled, either disable the write filter before
making registry modifications or commit the overlay after making registry changes
so the settings are persisted.
21
Page 22

Note
In order to manage the Enhanced or File-Based Write
Filter in WES 7, the user must have Administrator’s
privileges. Without Administrator’s privileges, the write
filters cannot be disabled, enabled, or committed.
© 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein
is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services
are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and
services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows Vista, Windows Media Player, and
Internet Explorer are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
643369-001, December 2010
22
 Loading...
Loading...