Page 1

HP ProLiant Lights-Out 100 Remote Management
J
User Guide
for HP ProLiant DL140 G2, DL145 G2, ML110 G3, and ML150 G2 Servers
Part Number 436853-001
anuary 2007 (First Edition)
Page 2

© Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212,
Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S.
Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Windows Server 2003 is a U.S. trademark of Microsoft
Corporation. Java is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Audience assumptions
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems.
HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards
in products with hazardous energy levels.
Page 3

Contents
Operational overview ................................................................................................................... 5
User guide overview.................................................................................................................................. 5
Server management................................................................................................................................... 5
Server management features....................................................................................................................... 5
Installation ................................................................................................................................... 7
Remote management card kit contents.......................................................................................................... 7
Pre-installation procedures ..........................................................................................................................7
Installing the remote management card on ProLiant ML110 G3 servers ............................................................8
Installing the remote management card on ProLiant ML150 G2 servers ............................................................9
Post-installation procedures......................................................................................................................... 9
Configuration............................................................................................................................. 11
Configuring network access...................................................................................................................... 11
Establishing user accounts ........................................................................................................................ 11
Using the serial port ................................................................................................................................ 12
Enabling serial access to the LO100 ................................................................................................ 12
LO100 serial port configuration ...................................................................................................... 13
Using TCP/IP over Ethernet management port ............................................................................................. 13
Selecting an Ethernet management port............................................................................................ 14
Obtaining a DHCP IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility................................................................... 14
Setting up a static IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility .................................................................... 15
Enabling telnet and HTTP services.................................................................................................... 15
Updating the firmware ............................................................................................................................. 16
Updating the firmware remotely ......................................................................................................16
TFTP settings .................................................................................................................................17
Using LO100 ............................................................................................................................. 19
SSL overview .......................................................................................................................................... 19
SSH overview ......................................................................................................................................... 20
Importing a certificate.............................................................................................................................. 21
Creating a certificate .....................................................................................................................21
Installing a certificate or private key through the CLP.......................................................................... 21
CLP overview.......................................................................................................................................... 22
Using CLP..................................................................................................................................... 22
Base commands ............................................................................................................................ 23
Specific commands........................................................................................................................ 27
IPMI 2.0 support ..................................................................................................................................... 27
Logging in to LO100 ............................................................................................................................... 28
Logging in through a web browser ..................................................................................................28
Logging in through the CLP ............................................................................................................. 29
Browser main menu options...................................................................................................................... 29
Hardware Inventory page ........................................................................................................................ 30
Controlling server power remotely ............................................................................................................. 30
Controlling server power from a browser.......................................................................................... 31
Controlling server power through the CLP .........................................................................................31
Controlling server power through the BIOS Setup Utility...................................................................... 32
Contents 3
Page 4

Monitoring sensors .................................................................................................................................. 32
Viewing sensors data from a web browser ....................................................................................... 32
Viewing sensors data from the BIOS Setup Utility............................................................................... 32
Platform event filtering configuration ................................................................................................ 33
Using the system event log........................................................................................................................ 34
Accessing the system event log from a web browser ..........................................................................34
Accessing the system event log from the CLP .....................................................................................35
Accessing the system event log from the BIOS Setup Utility.................................................................. 35
Network settings .....................................................................................................................................36
Configuring network settings using a web browser ............................................................................ 36
Configuring network settings using the CLP .......................................................................................36
Configuring network settings using the BIOS Setup Utility.................................................................... 37
Using the virtual floppy feature.................................................................................................................. 38
Configuring the TFTP Server............................................................................................................ 39
Configuring virtual floppy from a Web browser................................................................................. 39
Configuring the virtual floppy from the BIOS setup............................................................................. 40
Configuring virtual floppy from the CLP ............................................................................................ 40
Rebooting the server ...................................................................................................................... 41
Platform event trap configuration ............................................................................................................... 41
User administration.................................................................................................................................. 42
Changing user settings through a web browser ................................................................................. 42
Changing user settings through the CLP ............................................................................................ 43
Accessing the remote console through telnet ............................................................................................... 43
BIOS console text redirection through telnet ...................................................................................... 43
Linux console redirection ................................................................................................................44
Microsoft Windows® EMS management .......................................................................................... 45
HP SIM support....................................................................................................................................... 46
Acronyms and abbreviations........................................................................................................ 47
Index......................................................................................................................................... 50
Contents 4
Page 5

Operational overview
In this section
User guide overview................................................................................................................................. 5
Server management.................................................................................................................................. 5
Server management features...................................................................................................................... 5
User guide overview
This guide covers the standard and optional operational features of the LO100 used in HP ProLiant DL140
G2, DL145 G2, ML150 G2, and ML110 G3 servers.
This guide is an update to the HP ProLiant DL140 G2, DL145 G2, ML150 G2, and ML110 G3 LO100
remote management user guides.
Server management
HP ProLiant Lights-Out 100 delivers basic remote control of vital server resources, supports IPMI 2.0, and
provides system administrators with access to the server at any time, even before an operating system is
installed on the server.
HP ProLiant Lights-Out 100 provides text mode console redirection, DMTF SMASH compliant command
line interface, and browser access to many of the same system management functions. You can access
LO100 through a dedicated Ethernet port or through the server serial port.
Server management features
Using the Lights-Out 100 Remote Management processor, you can:
• Switch between console redirection and the command line using either the dedicated management
or serial port
• Communicate securely using SSL and SSH
• Remotely power up and power down the server
• Perform warm or cold server reboots
• Reboot the server to a virtual floppy
• Remotely monitor server-state voltage, fan speed, and system state (S0 or S5)
• Access the System Event log
• Configure TCP/IP settings for the NIC
• Change user passwords
• Access the BMC and server controls using a standard browser or new industry standard SMASH CLP
command-line interface
Operational overview 5
Page 6

• Access command-line help
• Manage the server with IPMI 2.0-compliant applications
Operational overview 6
Page 7

Installation
In this section
Remote management card kit contents ........................................................................................................ 7
Pre-installation procedures......................................................................................................................... 7
Installing the remote management card on ProLiant ML110 G3 servers........................................................... 8
Installing the remote management card on ProLiant ML150 G2 servers........................................................... 9
Post-installation procedures........................................................................................................................ 9
Remote management card kit contents
The remote management card kit is required only on ProLiant ML110 G3 and ProLiant ML150 G2 servers.
ProLiant ML110 G3
• HP ProLiant ML110 G3 Remote Management Card
• Spacer support
• HP Lights-Out 100 Remote Management Card Installation Instructions for HP ProLiant ML110
Generation 3 Servers
ProLiant ML150 G2
• HP ProLiant ML150 G2 Remote Management Card
• Hexnut screw
• HP Lights-Out 100 Remote Management Card Installation Instructions for HP ProLiant ML150
Generation 2 Servers
Pre-installation procedures
The installation procedures in this document are intended for individuals who are qualified in the servicing
of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards in products with hazardous energy levels.
WARNING: Failure to properly turn off the server before you open the server may cause
serious damage to the equipment as well as bodily harm.
CAUTION: Follow the ESD precautions listed in your server guide when handling the remote
management card.
IMPORTANT: Observe the pre- and post-configuration procedures described in later sections
when installing the remote management card.
NOTE: The procedures described in this section assume that the server is positioned on a flat,
stable surface.
1. Back up the server data.
Installation 7
Page 8
2.
Shut down the operating system as outlined in the operation system instructions.
3. Power off the server and all the peripherals connected to it.
4. Unplug all cables from the power outlets to avoid exposure to high energy levels that can cause
burns when parts are short-circuited by metal objects such as tools or jewelry.
5. Label each cable, if not already labeled, to expedite reassembly.
6. Disconnect telecommunication cables to avoid exposure to shock hazard from ringing voltages.
7. Open the server according to the instructions described in your server manual.
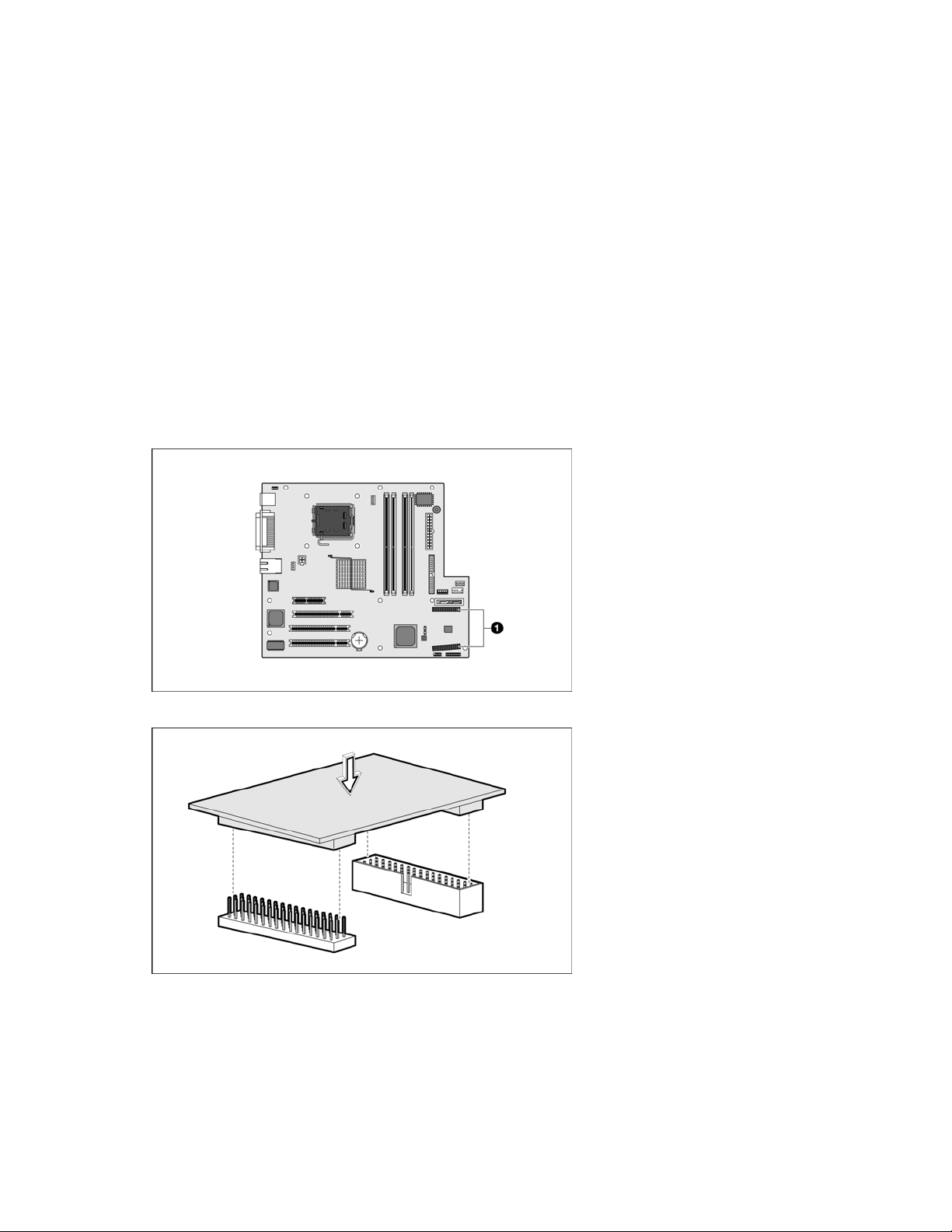
Installing the remote management card on ProLiant ML110 G3 servers
1. Remove the access panel.
2. Lay the server on its unexposed side to access the system board.
3. Locate the remote management card connectors on the system board.
4. Install the remote management card in the connectors on the system board.
5. Reinstall the system covers following the "Post-installation procedures (on page 9)".
Installation 8
Page 9
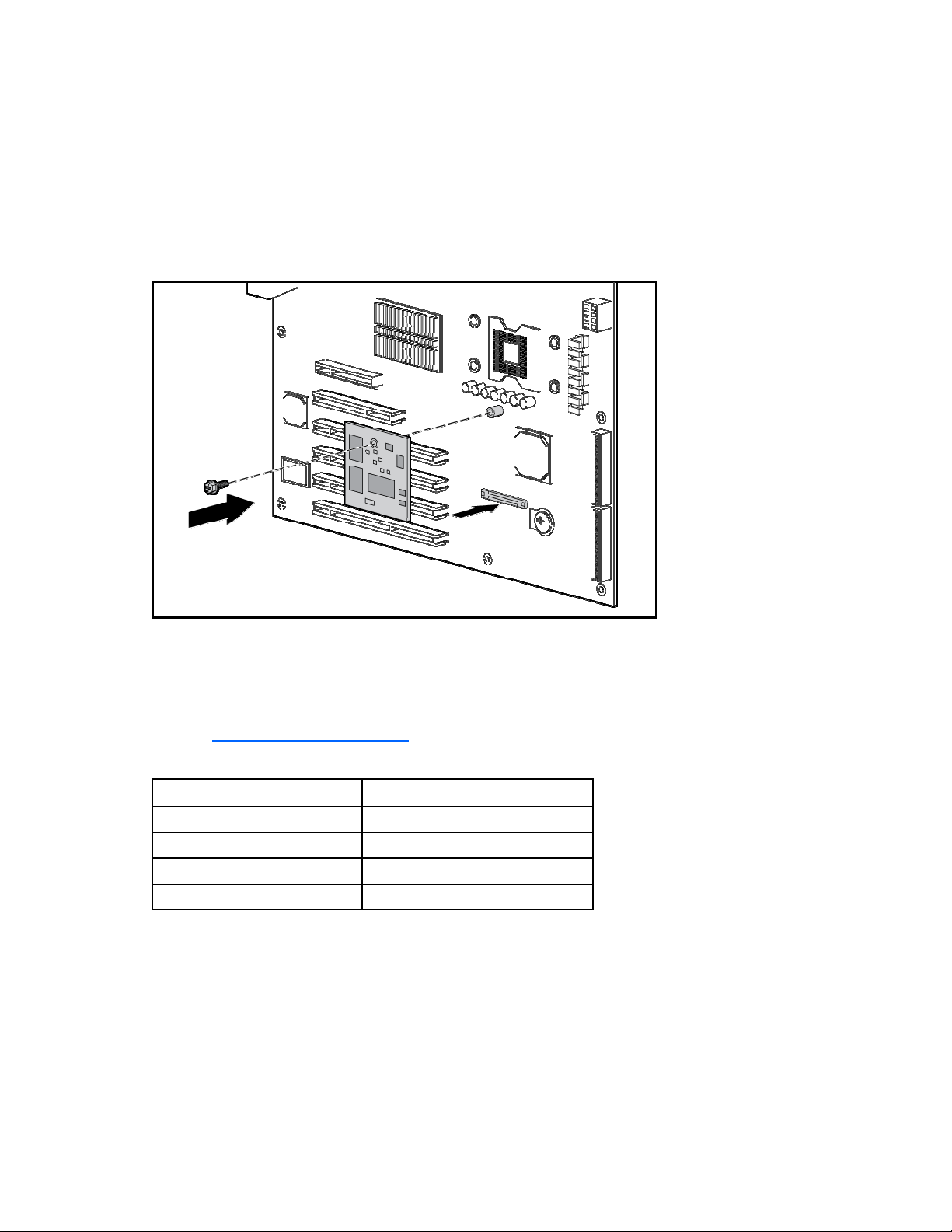
Installing the remote management card on ProLiant ML150 G2 servers
1. Remove the access panel.
2. Lay the server on its unexposed side to access the system board.
3. Locate the remote management card connectors on the system board.
4. Install the remote management card in the connectors on the system board.
5. Reinstall the system covers following the "Post-installation procedures (on page 9)".
6. Verify BIOS version and switch settings for the card.
To ensure proper operation of the ProLiant ML150 G2 Lights-Out 100 remote management processor, the
server BIOS must be version 0.28 or later. You can download the latest BIOS for your server on the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/support
The remote management card switches must be set to factory default settings.
).
Switch Setting
SW1 Off
SW2 On
SW3 On
SW4 Off
Post-installation procedures
1. Be sure all components are installed according to the "Pre-installation procedures (on page 7)."
2. Be sure you have not left any loose tools or parts inside the server.
3. Reinstall any expansion boards, peripherals, board covers, and system cables previously removed.
4. Reinstall the system covers.
5. Connect all external cables and the AC power cord to the system.
Installation 9
Page 10

6.
Press the power button on the front panel to turn on the server.
Installation 10
Page 11

Configuration
In this section
Configuring network access..................................................................................................................... 11
Establishing user accounts ....................................................................................................................... 11
Using the serial port ............................................................................................................................... 12
Using TCP/IP over Ethernet management port............................................................................................ 13
Updating the firmware............................................................................................................................ 16
Configuring network access
The server is connected to the network by a standard Ethernet cable. Using this connection, you can
access the remote management CLP, verify POST remotely, and access the BIOS Setup Utility remotely.
To configure network access:
1. Connect a standard Ethernet cable from the LO100 to a network jack.
2. Obtain the DHCP IP address by using one of the following methods:
o Look at the DHCP clients table.
o Press the F10 key during POST, and read the IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility under
Advanced/IPMI/LAN Setting. See "Obtaining a DHCP IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility (on
page 14)" for more information.
3. Using the DHCP IP address, use telnet to log into the remote management CLP, or use a web
browser to access the HTML interface.
To set up a static IP address, see "Setting up a static IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility (on page 15)"
for more information.
Establishing user accounts
LO100 supports three types of user accounts, with varying levels of permissions to view and control
features. For more information about user accounts, see the "User administration (on page 42)" section.
Two accounts are available by default, one of type administrator and one of type operator. While one
user account always has the administrator privilege, the other user account is customizable.
The administrator account enables the user to execute the full set of CLP commands and change
management processor configuration. The default name for the administrator account is admin, and the
default password is admin.
The operator account enables the user to execute common commands and functions, but restricts access to
specific functions, such as adding and changing user account information and changing the configuration
of the management processor. Log in with the operator account to perform common functions. The default
name for the operator account is Operator, and the default password is Operator.
For more information about how to log in to LO100, see the "Logging in to LO100 (on page 28)"
section.
Configuration 11
Page 12
Using the serial port
The server serial port provides basic serial port functionality and serves as an interface to LO100. You
can configure the system serial port for exclusive use with LO100.
CAUTION: After enabling the serial port for use with LO100, legacy serial devices might not
You must configure the LO100 serial port hardware parameters to work with your respective serial port
communications software. LO100 serial port configuration is controlled through the BIOS Setup Utility.
Enabling serial access to the LO100
1. Power on the server by pressing the Power On/Off button on the front panel.
2. When POST displays the message, ROM-Based Setup, press the F10 key. If the server has an
3. On HP ProLiant ML150 G2 servers:
function correctly if attached to the serial port.
administrator password configured, the system prompts you to enter the password. If the server does
not have a password configured, the main screen of the BIOS Setup Utility appears.
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IO Device Configuration. Press the Enter key.
c. Select Serial Port A, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Select
Enabled.
d. Press the Esc key to return to the Advanced menu.
e. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
f. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Settings submenu. Press the Enter key.
g. Confirm the following settings:
Ping Response: [Enabled]
Telenet Access: [Enabled]
HTTP Access: [Enabled}
4. On HP ProLiant ML110 G3 servers:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to navigate to the SuperIO Configuration menu. Press the Enter key.
c. Select Serial Port1 Address, and press the Enter key to toggle between Disabled, 3F8/IRQ4,
3E8/IRQ4, and 2E8/IRQ3. Select 3F8/IRQ4.
d. Review the serial port settings, and ensure that the settings match the serial port communications
software settings used to connect to LO100.
5. On HP ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to I/O Device Configuration. Press the Enter key.
c. Press the down arrow key (↓) to scroll to the Serial Port menu. Press the Enter key to toggle
between SIO COM Port and BMC COM Port. Select BMC COM Port.
d. Press the Esc key to return to the Advanced menu.
e. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
Configuration 12
Page 13

f.
Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
g. Confirm the following settings:
BMC Telnet Service: [Enabled]
BMC Ping Response: [Enabled]
BMC HTTP Service: [Enabled]
6. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
LO100 serial port configuration
1. Power on the server by pressing the Power On/Off button on the front panel.
2. When POST displays the message, ROM-Based Setup, press the F10 key. If the server has an
administrator password configured, the system prompts you to enter the password. If the server does
not have a password configured, the main screen of the BIOS Setup Utility appears.
3. On ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Console Redirection menu. Press Enter.
c. Press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Select Enabled for the console
redirection option.
d. Review the serial port settings, and ensure that the settings match the serial port communications
software settings used to connect to LO100.
4. On ProLiant ML150 G2 servers:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Console Redirection menu. Press Enter.
c. Press the Enter key to toggle between Disabled, On-board Com A, and On-board BMC/VSI.
Select On-Board BMC/VSI for the console redirection option.
d. Review the serial port settings, and ensure that the settings match the serial port communications
software settings used to connect to LO100.
5. On ProLiant ML110 G3 servers:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the BIOS Serial Console Configuration menu. Press the
Enter key. Select Bios Serial Console, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and
Disabled. Select Enabled.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to and select Serial Over LAN (SOL). Press the Enter key to
toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Select Enabled.
6. Press the Esc key to return to the previous screen, or press the F10 key to save the changes and exit
Setup.
Using TCP/IP over Ethernet management port
The LO100 LAN port can be accessed from two different Ethernet ports: the dedicated 10/100 LO100
management port or through a side-band connection with the second LOM (NIC2).
Configuration 13
Page 14

Selecting an Ethernet management port
The Ethernet management port is only available on ProLiant ML150 G2 and ML110 G3 servers.
To select either the LO100 or side-band connection:
1. Power on the server by pressing the Power On/Off button on the front panel.
2. When POST displays the message, ROM-Based Setup, press the F10 key. If the server has an
administrator password configured, the system prompts you to enter the password. If the server does
not have a password configured, the main screen of the BIOS Setup Utility appears.
3. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to NIC Option. Press the Enter key to select between the
dedicated or side-band connection.
5. Press the Esc key to return to the previous screen, or press the F10 key to save the changes and exit
Setup.
The dedicated TCP/IP over Ethernet management port, whether dedicated or shared, is a standard
Ethernet 10/100Mb interface that is connected to the network using a standard Ethernet cable. Before
using the dedicated management port, you must determine the DHCP IP address, set a static IP address,
or use the default static IP address.
Obtaining a DHCP IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility
By default, LO100 has DHCP enabled and automatically negotiates an IP address. To view the DHCP IP
address, run the BIOS Setup Utility or retrieve the DHCP IP address using CLP through the serial port
connection.
To view the DHCP IP address using the BIOS Setup Utility:
1. Power on the server by pressing the Power On/Off button on the front panel.
2. When POST displays the message, ROM-Based Setup, press the F10 key. If the server has an
administrator password configured, the system prompts you to enter the password. If the server does
not have a password configured, the main screen of the BIOS Setup Utility appears.
3. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
5. On HP ProLiant ML110 G3 and ML150 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Configuration (ML110 G3) submenu or LAN
Interface (ML150 G2). Press the Enter key.
b. Note the DHCP assigned IP address for future reference.
6. On HP ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Note the DHCP assigned IP address for future reference.
7. Press the Esc key to return to the previous screen, or press the F10 key to save the changes and exit
Setup.
To configure or change your network settings, see "Network settings (on page 36)" for more information.
Configuration 14
Page 15

Setting up a static IP address from the BIOS Setup Utility
By default, LO100 has DHCP enabled and automatically negotiates an IP address.
To disable DHCP and enable a static IP address:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. On the ProLiant ML150 G2 server:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Select IP Address Source, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Set
DHCP IP Source to Disabled.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the IP Address setting.
d. Enter a valid IP address. Press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields.
e. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to the Subnet Mask submenu. Press the Enter key.
f. Enter a valid subnet mask. Press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields.
5. On the ProLiant ML110 G3 server:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Set LAN Configuration submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Select DHCP IP Source, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Set
DHCP IP Source to Disabled.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the IP Address submenu. Press the Enter key.
d. Enter a valid IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address. Press the Tab or period (.) key to
move between address fields.
e. Press the Esc key to return to the Set LAN Configuration submenu.
f. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Subnet Mask submenu. Press the Enter key.
g. Enter a valid subnet mask. Press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields.
6. On the ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Settings submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Set the IP Address Assignment to Static. This setting enables you to modify a static IP address
through the BIOS setup menu.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down and enter a valid IP address, subnet mask, and
gateway address (press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields).
7. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
To restore DHCP, see "Configuring network settings using the BIOS Setup Utility (on page 37)."
Enabling telnet and HTTP services
On the ProLiant ML110 G3 server, HTTP and telnet are automatically enabled.
To enable HTTP and telnet on ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
Configuration 15
Page 16
4.
Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
5. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the following settings, and set the parameters as needed
(the following example shows configuring for LO100 access using telnet and a web page):
o BMC Telnet Service: [Enabled]
o BMC Ping Response: [Enabled]
o BMC HTTP Service: [Enabled]
To enable HTTP and telnet on ProLiant ML150 G2 servers:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the following settings, and set the parameters as needed
(the following example shows configuring for LO100 access using telnet and a web page):
o Ping Response: [Enabled]
o Telnet Access: [Enabled]
o HTTP Access: [Enabled]
Updating the firmware
To update LO100 firmware, use the ROMPaq utility. ROMPaq downloads are available on the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/support
website (http://www.hp.com/servers/manage
NOTE: LO100 does not support ROMPaq flashing or flashing LO100 from a virtual floppy.
NOTE: Firmware upgrade packages for ProLiant ML150 G2 servers contain firmware images
for LO100 standard and advanced functionality. When updating the firmware, only the active
LO100 device is flashed. If an HP Lights-Out 100c Remote Management Card is installed in
the system when flashing the firmware, only the HP Lights-Out 100c Remote Management Card
firmware is updated. If an HP Lights-Out 100c Remote Management Card is not installed, only
the standard (basic) LO100 functionality is updated.
After the ROMPaq utility flashes the selected device, cycle power manually to reboot the operating
system.
). For more information about using the ROMPaq utility, see the HP
).
Updating the firmware remotely
If you want to update the LO100 firmware remotely, you can use the load command. The firmware file
must be an uncompressed firmware image file which you can create using the DOS ROMPAQ utility
found on the Lights-Out 100 Firmware Upgrade Diskette Utility, available for download from the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
To create an uncompressed image file, enter the following command at the DOS prompt:
ROMPAQ /D <infile> <outfile>
where <infile> is the ROMPAQ firmware image file and <outfile> is the file name for the
uncompressed binary image file. For example:
).
Configuration 16
Page 17

ROMPAQ /D cpqq0801.D14 ldrImage.bin
ROMPAQ Firmware Upgrade Utility, Version 5.02 (R)
Copyright (c) Hewlett-Packard Corporation, 1994-2006
Input file: CPQQ0801.D14
Output file: LDRIMAGE.BIN
The load command is used to take a binary image from a specific source location (specified as a URL)
and place it at the specified target address. The load command can download and flash a ldr firmware
image file using TFTP from the specified location.
To update the firmware, log in to LO100 as administrator through the CLP interface and issue the load
command to upload and install the firmware from the map1/firmware directory.
1. Start a CLP session. To access the CLP in Windows®:
a. Click Start>All Programs>Accessories>Command Prompt.
b. At the command prompt, enter telnet <IP address> where IP address is the IP Address
of the server to which you want to connect.
2. At the CLP prompt, enter: cd/map1/firmware
3. At the CLP prompt, enter load -source <URI> -oemhpfiletype csr
where:
o <URI> is the //tftpserver IP/path/filename to be downloaded.
o tftp server IP is the URL or IP address of the TFTP server containing the firmware.
o filename is the file name of the image file (LdrImage.bin in this example).
For example, enter: load -source //10.141.38.157/LdrImage.bin - oemhpfiletype
csr
NOTE: After using the load command LO100 will reset ending your CLP interface session.
You must reconnect to the CLP interface.
NOTE: When you use the CLP load command with TFTPD32, HP recommends using a 30-
second timeout and 6 retries.
TFTP settings
When using a TFTP server, the settings vary by on different operating systems. Use the following settings:
Flashing the firmware image file using TFTP on Microsoft Windows®
1. Copy the BMC firmware into a directory on the server.
2. Run TFTP by launching the executable file tftpd32.exe.
3. Navigate to TFTP Configuration>Settings, and set Timeout to 30 seconds and Max Retransmit to 6.
4. Enter File Name and TFTP Server IP Address. File Name is the path where the BMC firmware is
residing. TFTP Server IP Address is the IP address of the TFTP server. For example, 10.141.38.157.
Flashing the firmware image file using TFTP on Linux
1. Navigate to Applications>Systems Settings>Server Settings>Services, and ensure that tftp and
xinetd are running.
Configuration 17
Page 18

Open the file /etc/xinetd.d/tftp and modify the parameter server_args to include -T
2.
15000000. For example, server_args = -c -s /tftpboot -T 15000000
3. The firewall that is built into some Linux systems might not allow the TFTP server to send and receive
information. You might first have to disable the firewall to allow these connections. If you are
experiencing firewall issues, change the firewall settings to allow connections on port 69 (the default
port for TFTP servers). See your firewall documentation for additional information.
If a firewall is enabled, disable it or modify the settings to allow the firewall to connect to the TFTP
port. To change the firewall settings, navigate to Applications>System Settings>Security Level, and
enter 69:udp in other ports.
Configuration 18
Page 19

Using LO100
In this section
SSL overview ......................................................................................................................................... 19
SSH overview ........................................................................................................................................ 20
Importing a certificate............................................................................................................................. 21
CLP overview......................................................................................................................................... 22
IPMI 2.0 support .................................................................................................................................... 27
Logging in to LO100 .............................................................................................................................. 28
Browser main menu options..................................................................................................................... 29
Hardware Inventory page ....................................................................................................................... 30
Controlling server power remotely............................................................................................................ 30
Monitoring sensors................................................................................................................................. 32
Using the system event log ...................................................................................................................... 34
Network settings .................................................................................................................................... 36
Using the virtual floppy feature ................................................................................................................ 38
Platform event trap configuration.............................................................................................................. 41
User administration................................................................................................................................. 42
Accessing the remote console through telnet.............................................................................................. 43
HP SIM support...................................................................................................................................... 46
SSL overview
SSL is an advanced feature that is available on ProLiant ML150 G2 and ProLiant ML110 G3 servers by
installing the Lights-Out 100 Remote Management Card, or on ProLiant DL140 G2 servers and ProLiant
DL145 G2 servers by purchasing the Lights-Out 100i Select Pack or the Lights-Out 100i Advanced Pack.
SSL is a protocol used to transmit private documents through the Internet. SSL uses a private key or
certificate to encrypt data transferred over the SSL connection. The Lights-Out 100 remote management
processor provides strong security for remote management in distributed IT environments by using 128-bit
SSL encryption of HTTP data transmitted across the network. SSL encryption ensures that the HTTP
information is secure as it travels across the network.
LO100 comes preinstalled with a certificate. To install a user-specific certificate, see the one-time
"Importing a certificate (on page 21)" setup procedure.
If you cannot access the login page, you must verify the SSL encryption level of your browser is set to 128
bits. The SSL encryption level within the management processor is set to 128 bits and cannot be changed.
The browser and management processor encryption levels must be the same.
To use the preinstalled certificate, enter https://ipaddress in the address line of the browser, which
uses SSL-encrypted communication. Enter http://ipaddress to use non-SSL encrypted communication.
Using LO100 19
Page 20

SSH overview
SSH is an advanced feature that is available on ProLiant ML150 G2 and ProLiant ML110 G3 servers by
installing the Lights-Out 100 Remote Management Card, or on ProLiant DL140 G2 servers and ProLiant
DL145 G2 servers by purchasing the Lights-Out 100i Select Pack or the Lights-Out 100i Advanced Pack.
SSH is a telnet-like program for logging in to and executing commands on a remote machine, which
includes security with authentication, encryption, and data-integrity features. The Lights-Out 100 remote
management processor can support simultaneous access from two SSH clients. After SSH is connected
and authenticated, the command line interface is available.
LO100 supports the following protocols:
• SSH protocol version 2
• PuTTY 0.54, which is a free version of telnet and SSH protocols available for download on the
Internet. When using PuTTY, versions earlier than 0.54 might display two line feeds instead on a
single line feed, when the Enter key is pressed. To avoid this issue, and for best results, use version
0.54 or later.
• OpenSSH, which is a free version of the SSH protocol available for download on the Internet.
NOTE: Logging in to an SSH session could take up to 90 seconds. Depending on the client
used, you might not see on-screen activity during this time.
LO100 comes preinstalled with a certificate. To install a user-specific certificate, see the one-time
"Importing a certificate (on page 21)" setup procedure.
Using SSH
When using a Secure Shell utility to connect to a server for the first time, the utility will prompt you to
accept the server's public key, sometimes referred to as a host key. Accepting this key authorizes the
utility to store a copy of the public key in its own database. The utility will automatically recognize the
server when future connections are attempted, by comparing the public key to the one stored in its
database.
To access the remote management processor using SSH:
1. Open an SSH window.
2. When prompted, enter the IP address or DNS name, login name, and password.
Using OpenSSH
To start an OpenSSH client in Linux, use:
ssh -l loginname ipaddress/dns name
Using PuTTY
• To start a PuTTY session, double-click the PuTTY icon in the directory in which PuTTY is installed.
• To start a PuTTY session from the command line:
o To start a connection to a server called host:
putty.exe [-ssh | -telnet | -rlogin | -raw] [user@]host
o For telnet sessions, the following alternative syntax is supported:
putty.exe telnet://host[:port]/
o To start an existing saved session called sessionname:
Using LO100 20
Page 21

o
putty.exe -load "session name"
Importing a certificate
If you do not want to use the preinstalled public key (certificate), create and install your own private key
(certificate). Importing a key or certificate is a one-time procedure that supports both SSH and SSL. The
key must be generated using external third-party software, placed on a TFTP server, and uploaded to the
LO100. For Microsoft® Windows®, if you do not have a TFTP software package, use TFTPD32.EXE,
which is available on the Internet. Linux generally has a TFTP server installed with the operating system. If
it is not, see your Linux documentation for more information.
NOTE: When you use the CLP load command with TFTPD32, HP recommends using a 30-
second timeout and 6 retries.
NOTE: When using the CLP load command in Linux set the timeout to 15000000. The
firewall built into some Linux systems might not allow the TFTP server to send and receive
information. You might have to disable the firewall to allow these connections. If you are
experiencing firewall issues, change the firewall settings to allow connections on port 69 (the
default port for TFTP servers). See your firewall documentation for additional information.
Creating a certificate
LO100 requires a 1,024-bit DSA key stored in PEM (Base64-encoded) format to be located on a TFTP
server. For example, the following process uses Win32 OpenSSL, downloaded from the Shining Light
Productions website (http://www.slproweb.com/products/Win32OpenSSL.html
issued in a DOS window to generate the certificate. To generate a certificate using Win32 OpenSSL:
1. Download Win32 OpenSSL.
2. Install and set up OpenSSL.
3. Using OpenSSL, generate a DSA parameters file:
openssl dsaparam -out server_dsaparam.pem 1024
4. Generate the DSA private key file, called server_privkey.pem:
openssl gendsa -out server_privkey.pem server_dsaparam.pem
5. Generate the DSA certificate (public key) file, called server cacert.pem:
openssl req -new -x509 -key server_privkey.pem -out server_cacert.pem days 1095
6. When prompted for a distinguished name, enter an appropriate domain name for the servers
receiving the certificate.
7. After creating the certificate, copy it to a TFTP server that is accessible on the same network as
LO100.
), with the commands
Installing a certificate or private key through the CLP
To install the certificate, log in to LO100 as administrator through the CLP interface and issue the load
command to upload and install the certificate. For example:
load -source <URI> -oemhpfiletype cer
where:
Using LO100 21
Page 22

<URI> is the //tftpserver IP/path/filename to be downloaded.
o
o tftpserver is the URL or IP address of the TFTP server containing the certificate.
o Path is the path of the file relative to the TFTP server root.
o filename is the name of the certificate (server_privkey.pem in this example).
You can also find these commands in /map1/firmware directory.
To install a private key, log in to LO100 as administrator through the CLP interface, and issue the load
command to upload and install the certificate. For example:
load -source <URI> -oemhpfiletype key
where:
o <URI> is the //tftpserver IP/path/filename to be downloaded.
o tftpserver is the URL or IP address of the TFTP server containing the private key file.
o Path is the path of the file relative to the TFTP server root.
o filename is the file name of the private key file (server_privkey.pem in this example.)
You can also find these commands in /map1/firmware directory.
NOTE: After using the load command LO100 will reset ending your CLP interface session.
You must reconnect to the CLP interface.
CLP overview
HP has worked with key industry partners within Distributed Management Task Force, Inc. to define an
industry-standard set of commands. The SMASH suite will standardize manageability interfaces for
servers. The Lights-Out 100 remote management processor implements the command set defined in the
Server Management Command Line Protocol Specification, 1.00 Draft. The CLP replaces the simple CLI
that was released previously and is no longer supported.
The management processor functionality accessible from the SMASH CLP is a low-bandwidth interface
and provides similar functionality to the web interface. The CLP is designed for users who prefer a
nongraphical interface. The CLP is accessible through the following methods:
• Telnet
• SSH connection
Using CLP
• Physical serial port
The general syntax of CLP command is:
<verb> <target> <option> <property>
• Verbs—The following verbs are supported:
o cd
o help
o load
o reset
o set
Using LO100 22
Page 23

show
o
o start
o stop
o exit
o version
• Target—The default target is the /. The target can be changed by the cd command or by specifying
a target on the command line.
• Options—The following options are valid:
o -help/-h
o -all/-a
• Properties are the attributes of the target that can be modified.
• Output—The output syntax is text.
The valid Boolean values for any command are true and false.
General notes
If the commands on the CLP command span more than one line, you cannot navigate between different
lines.
Operating system-specific notes
• The Microsoft® Windows® 2000 telnet client does not support the Functions keys F1 through F12,
Insert, Home, and End keys. These keys will not work in a Lights-Out 100 command line session.
• The Backspace key in the Lights-Out 100 CLP implementation is mapped to the value 0x8. Some
client operating systems, Novell Linux Desktop and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 Desktop, map the
Backspace key to the value 0x7f, which is used for the Delete key in the Windows® telnet client.
The Backspace key will not work from a client from which it has value of 0x7f. For the Linux clients,
using the Home or the End key enables the Lights-Out 100 CLP service to remap the Backspace key
to use the value 0x7f, making the key functional.
In the Windows® PuTTY client, the Backspace key can be mapped to a value of 0x8 by changing the
setting for Terminal Keyboard to Control-H.
Base commands
• The help command displays context-sensitive help.
Entering help displays all the supported commands. Entering <command help/?> displays the
help message specific to that command.
o Help for verbs
Calling help for a verb returns the general syntax and usage associated with issuing that verb.
Calling help for a verb that is not present in the current directory returns an Unsupported
Command message. The following are all valid ways to call help for a verb.
/./-> help show
Usage: show [<target>][<options>][<properties>]
/./-> show -h
Usage: show [<target>][<options>][<properties>]
Using LO100 23
Page 24

/./-> show -help
Usage: show [<target>][<options>][<properties>]
/./->
o Help for targets
Calling help for a target returns any information about the target and what it contains. You can
call help for any target that is not contained in the current directory (help map1 can be called
from system1).
/./-> system1 -h
Invalid command
/./-> system1 -help
Invalid command
/./-> help system1
Host System Directory
/./-> help map1
Management Service Processor Directory
/./-> cd system1
/./system1/-> help map1
Management Service Processor Directory
o Help for properties
Calling help for a property or any other option for which there is no help information returns an
Unsupported Command or Invalid command message. For example:
/./system1/-> show
/./system1
Targets
log1
Properties
name=Hewlett-Packard
enabledstate=enabled
Verbs
cd
version
exit
show
reset
start
Using LO100 24
Page 25

stop
help
/./system1/-> help name
Unsupported Command
/./system1/-> help enabledstate
Unsupported Command
/./system1/-> help properties
Unsupported Command
/./system1/-> name -h
Invalid command
/./system1/->
• The exit command terminates the CLP session.
• The cd command sets the current default target. The context works like a directory path. The root
context for the server is /. which is the starting point for a CLP system. By changing the context, you
can shorten commands.
For example:
o cd changes the directory.
o cd .. moves up the tree one directory.
o cd folder moves to folder assuming folder is in the current directory.
If you want to move to a directory not in the current directory, you must enter the full path. Root in
the command line is /./
If you are in system1 and want to move to map1, issue the command cd /./map1. Neither cd
/map1 nor cd map1 works. The filename is not case-sensitive, whereas the command is casesensitive (cd MaP1 works while CD map1 does not).
• The show command displays values of a property or contents of a collection target. For example:
/./> show
/./
Targets
system1/
map1/
Properties
Verbs
cd
version
exit
show
help
Using LO100 25
Page 26

The first line of information returned by the show command is the current context. In the example, /
is the current context. Following the context is a list of subtargets (Targets) and properties (Properties)
applicable to the current context. The verbs (Verbs) section shows what commands are available in
this context.
The show command can also be specified with an explicit or implicit context and a specific
property. An explicit context is /map1/firmware and is not dependent on the current context. An
implicit context assumes that the context specified is a child of the current context. If the current
context is /map1, then a show firmware command displays the /map1/firmware data. If a
property is not specified, then all properties are shown.
• The load command moves a binary image from a URL to the map. The load command is used to
take a binary image from a specific source location (specified as a URL) and place it at the specified
target address. In a remote management processor implementation, the firmware downloads a full
image file using TFTP from the specified location and programs flash with the image.
In a remote management processor implementation, /map1/firmware is a valid target.
The load command supports usage only with the following options.
o -source <location>—This option must be specified.
o (h)elp—this option appears on the command line, the command ignores all options and
properties except -output (for terse or verbose output). These options are only valid for this
command when the -help option is used.
o source <value>—This option specifies the target from which it will transfer the binary image.
The value specified must be a valid URL. The expected format is
//tftpserverip/path/filename. This option is required in the command line every time
the load command is executed unless -help is used. The file must be an uncompressed firmware
image file that you create using the DOS ROMPAQ utility found on the Lights-Out 100 Firmware
Upgrade Diskette Utility available for download from the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
To create the uncompressed image file, enter the following command from DOS:
ROMPAQ /D <infile> <outfile>
where <infile> is the ROMPAQ firmware image file and <outfile> is the filename for the
uncompressed binary image file.
The load command returns any status data on the first lines. After the status data appears, one of
the following lines of text displays on the next line:
<URL> transferred to <target address> (if the file is transferred)
<URL> not transferred (if the file is not transferred)
Example:
load -source //192.168.2.1/pub/firmwareimage.bin -oemhpfiletype csr
//192.168.2.1/pub/firmwareimage.bin transferred to
/map1/firmware/fullimage
).
• The reset command causes a target to cycle from enabled to disabled and back to enabled.
• The set command sets a property or set of properties to a specific value. set property = new
value is the standard syntax for the set command.
The set command is used to change any changeable property. If the current directory does not
contain the property you want to change, the target of the property must be specified before entering
the property you want to change.
Using LO100 26
Page 27

• The start command causes a target to change state to a higher run level.
• The stop command causes a target to change state to a lower run level.
• The version command queries the version of the CLP implementation or other CLP elements. For
example:
/./map1/-> version
Version 1.00
/./map1/-> cd firmware
/./map1/firmware/-> version
Version 1.00
/./map1/firmware/-> show
/./map1/firmware
Targets
Properties
fwversion=0.59
Verbs
cd
version
exit
show
reset
load
help
/./map1/firmware/-> show fwversion
fwversion=0.59
/./map1/firmware/-> fwversion
Invalid command
/./map1/firmware/->
Specific commands
CLP syntax for specific commands is found in the sections that also describe the functionality through the
Web interface.
IPMI 2.0 support
LO100 supports the industry-standard IPMI 2.0. The IPMI specification defines standardized, abstracted
interfaces that can be used for monitoring and control functions that are built in to the platform hardware.
In addition to supporting the mandatory commands for IPMI 2.0, the following additional IPMI 2.0
features are supported by LO100:
• Additional IPMI 2.0 commands
o Get Channel Cipher Suites
o Set/Get Channel Security Keys
o Suspend/Resume Payload Encryption
Using LO100 27
Page 28

• Payload types
o IPMI Message
o RMCP+ Open Session Request/Response
o RAKP Message 1 / 2
o RAKP Message 3 / 4
• Authentication algorithms
o RAKP-none
o RAKP-HMAC-SHA1
• Integrity algorithms
o None
o HMAC-SHA1-96
• Confidentiality algorithms
o None
o AES-CBC-128
Logging in to LO100
You can log in to the remote management processor through a web browser ("Logging in through a web
browser" on page 28) or through the CLP ("Logging in through the CLP" on page 29). If you are unsure of
Logging in through a web browser
your DHCP IP address, refer to the "Configuring network access (on page 11)" section.
1. Browse to the IP address of the remote management processor to access the login screen.
2. Enter your user name and password. The default user name for the Administrator account is admin,
and the default password is admin. The default user name for the Operator account is Operator,
and the default password is Operator.
Using LO100 28
Page 29

Logging in through the CLP
To log in to the remote management processor through the CLP and enter Terminal mode:
1. Establish a connection to the remote management processor by launching a telnet session or an SSH
session.
2. Enter the user name at the login: prompt. The default user name for the Administrator account is
admin. The default user name for the Operator account is Operator.
3. Enter the password at the password: prompt. The default password for the Administrator account is
admin. The default password for the Operator account is Operator.
To exit the CLP and enter Console mode, enter the exit command at the command prompt.
Browser main menu options
The main menu provides access to all basic remote management capabilities of the remote management
processor.
Option Description
Home Accesses or returns you to the main menu
navigation bar
Virtual Power Accesses system power control options
Monitoring Sensors Lists all sensor information, including type,
name, status, reading, and PEF settings
System Event Log Displays the system event log
Virtual Floppy Accesses the virtual floppy screen
Hardware Inventory Displays system hardware
User Administration Accesses the user configuration screen
Network Settings Accesses the network parameter settings
screen
Using LO100 29
Page 30

Option Description
IPMI PET Configuration Accesses the PET destinations and alert policy
table
Hardware Inventory page
The Hardware Inventory page enables you to remotely identify the presence of processors on a target
server. To access this page from a web browser, click Hardware Inventory on the main menu navigation
bar.
Controlling server power remotely
LO100 enables you to remotely operate the power button of a host server using a web browser or the
CLP. LO100 virtual power support enables you to power up, power down, and power cycle the host
server. This virtual power support operates independently of the state of the operating system.
Using LO100 30
Page 31

Controlling server power from a browser
The Virtual Power screen displays current power status, how long the server has been powered up, and
reason for the last server restart. To display the Virtual Power screen, click Virtual Power on the main
menu navigation bar.
To modify Chassis Actions, select the desired Power Control Option in the Chassis Actions section, and
click Apply to initiate the action.
To identify the server in the rack and illuminate the UID (LED on the front panel of the server), select the
length of time you want the UID to stay illuminated on the Chassis Locator list, and click Identify.
NOTE: The UID is only available on HP ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers.
Controlling server power through the CLP
1. Log in to LO100 CLP as described in the "Logging in to LO100 (on page 28)" section.
2. Change to the system1 target by entering cd system1.
3. To power on the server, enter start /system1. For example:
/./system1/> start /system1
System1 started.
4. To power off the server, enter stop /system1. For example:
/./system1/> stop /system1
System1 stopped.
The -force option can also be used with the stop command. This option forces the
implementation to stop the target, ignoring any policy that might cause the implementation to
normally not execute the command. In remote management processor implementation, this process is
equivalent to a hard power down.
5. To reset the server, enter reset /system1. For example:
/./system1/> reset
System1 reset.
Using LO100 31
Page 32

Controlling server power through the BIOS Setup Utility
To control how the system responds after a power failure through the BIOS Setup Utility:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Power Tab of the BIOS Setup Utility.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to After Power Failure. Press the Enter key.
4. On the ProLiant ML150 G2, or ML110 G3 servers: Use the arrow keys to navigate between Stay
Off, Last State, and Power On. Select your power control option, and press the Enter key.
5. On ProLiant DL140 G2 or ProLiant DL145 G2 servers: Use the arrow keys to navigate between
Always Off, Previous State, and Always On. Select your power control option, and press the Enter
key.
6. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
Monitoring sensors
LO100 provides operating system-independent remote monitoring of the current status of major sensors of
a target server including system temperature, fans, and voltage. You can view the data for this feature on
Viewing sensors data from a web browser
the Monitoring Sensors Page through a web browser or through the BIOS Setup Utility.
The Monitoring Sensors screen displays a snapshot of the temperature, fans, and voltage sensor data
including sensor type, name, status, and current reading. To access this page from a web browser, click
Monitoring Sensors on the main menu navigation bar.
To update the display, click the Refresh button on the web browser. To view or add a PEF action, click
PEF. See "Platform Event Filtering configuration (on page 33)" for more information.
Viewing sensors data from the BIOS Setup Utility
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
Using LO100 32
Page 33

2.
On ProLiant ML150 G2 servers:
a. To navigate to the Monitor menu, press the right arrow (→) key.
b. Scroll down to view the different sensors. Data is real-time and updated periodically.
3. On ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to Realtime Sensor Data. Press the Enter key.
The Loading data. Please wait… message appears. After this message disappears, the
Temperature and Voltage sensor data appears. Data is displayed in real-time and updated
periodically.
4. On the ProLiant ML110 G3 server:
a. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to Hardware Health Configuration menu. Press the Enter
key. The real-time sensor data displays.
Platform event filtering configuration
The PEF Configuration screen enables you to configure LO100 to take selected actions on received or
internally generated event messages. These actions include powering down the system, system reset, and
triggering the generation of an alert.
To configure a PEF for a particular sensor, click the PEF button to the far right of that sensor on the
Monitoring Sensors screen. The PEF button adjacent to each sensor opens a PEF Configuration page for
that sensor.
The PEF Configuration screen contains two sections: Current PEF Entries and Add PEF Entry. The Current
PEF Entries section includes Sensor Type, Sensor Name, PEF Action, and PEF Control information. The
Add PEF Entry section enables you set an action.
Initially, there are no entries in the Current PEF Entries section because no PEFs are defined. When PEF
entries are defined, the PEF Control field is active and allows individual entries to be enabled, disabled,
or deleted.
Using LO100 33
Page 34

To configure an action (PEF entry) select the desired Event Offsets and PEF Action settings and click Add.
• Event Offsets are trip points (movements across thresholds) that define what type of sensor event
triggers an action. The information in the Events Offsets section varies with the type of sensor. Not all
options are available for all sensors. You can select any of the available options.
• PEF Action displays the same information for all sensors:
o Sensor Type displays the type of sensor selected.
o Sensor Name displays the name of the sensor.
o PEF Action enables you to select from Power Off, Power Cycle, Hard Reset, and Send Alert
(requires a systems management console supporting IPMI 1.5 or later.)
o PEF Control enables or disables the sensor.
o Alert Policy (dropdown list adjacent to the Add button) enables you to select an alert policy (if
defined.) Alert policies are defined on the PET Configuration screen. See "Platform event trap
configuration (on page 41)" for more information.
If alert policies are not defined (default), the Alert Policy dropdown list displays No Alert Policy.
The Alert Policy dropdown list will populate after alert policies are defined and configured. After
configuring your alert policies, you can select from the defined alert policies for this sensor and
PEF.
o Add adds the new entry to the PEF Current Entry table at the top of the page.
Using the system event log
LO100 captures and stores the IPMI event log for access through a browser, CLP, BIOS Setup Utility, and
RBSU even when the server is not operational. The system event log lists a short description of each
system event. Recorded events include abnormal temperature, fan and voltage events, system resets,
Accessing the system event log from a web browser
system power loss, user login, and unsuccessful login attempts.
The System Event Log screen displays a brief description of the event including event type, date, time,
source, description, and direction.
Using LO100 34
Page 35

To access the System Event Log from a web browser, click System Event Log on the main menu navigation
bar. To clear the system event log, click Clear Event Log.
Accessing the system event log from the CLP
1. Log in to the CLP as described in the "Logging in to LO100 (on page 28)" section.
2. Enter cd /./system1/log1
3. Enter show to display the total number of system event records.
4. Enter show record<n> to display the details of a specific record. For example:
/system1/log1/record1
Targets
Properties
number=1
date=12/20/2004
time=15:22:05
sensordescription= Backplane +12V
eventdescription= Upper Critical-going high
eventdirection=Assertion
Verbs
cd
version
exit
show
reset
oemhp
help
Accessing the system event log from the BIOS Setup Utility
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. On ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to System Event log submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll the following setup options: Clear System Event Log and
View System Event Log.
If you select View System Event log, use the PG UP, PG DOWN keys, or spacebar to scroll
through the entries.
5. On ProLiant ML150 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the System Event log submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to through the following setup options including Date
Format to show, Date Separator, System Event Logging, Sys Firmware Progress, and BIOS POST
Errors.
6. On ProLiant ML110 G3 servers:
Using LO100 35
Page 36

a.
Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the View BMC System Event Log submenu. Press the
Enter key.
b. Use the plus (+) or minus (-) keys to scroll through the events.
7. Press the Esc key to return to the previous screen, or press the F10 key to save the changes and exit
Setup.
Network settings
You can view and modify network settings for LO100 using a web browser, CLP, or the BIOS Setup
Utility. If you change the IP address, the connection to the server terminates. You must reconnect to the
Configuring network settings using a web browser
server using the new IP address.
The Network Settings screen displays IP address, subnet mask, and other TCP/IP-related settings. From the
Network Settings screen, you can enable or disable DHCP, and you can configure a static IP address for
servers not using DHCP. You can view and modify the network settings when logged in as either OEM or
administrator (admin).
To modify the network settings, click Network Settings on the browser main menu navigation bar, enter
the new settings, and click Apply.
Configuring network settings using the CLP
1. Log in to LO100 CLP as described in the "Logging in to LO100 (on page 28)" section.
2. At the command prompt, enter cd map1/nic1.
3. Configure the network settings by entering the following: set <network property>=<new
setting>. Configurable valid network properties are:
o networkaddress specifies the IP address for the NIC. This setting is dynamic.
o oemhp_nonvol_networkaddress specifies the IP address stored in non-volatile memory.
o oemhp_mask specifies the subnet mask for NIC. This setting is dynamic.
Using LO100 36
Page 37

oemhp_nonvol_mask specifies the subnet mask stored in non-volatile memory.
o
o oemhp_gateway specifies the gateway IP address for the NIC. This setting is dynamic.
o oemhp_nonvol_gateway specifies the gateway IP address stored in non-volatile memory.
o oemhp_dhcp_enable specifies whether DHCP is enabled for the NIC. Boolean values are
accepted
o oemhp_nonvol_dhcp_enable specifies whether DHCP is enabled for the NIC and address
stored in non-volatile memory.
Configuring network settings using the BIOS Setup Utility
To enable a static IP address:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. On the ProLiant ML150 G2 server:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Select IP Address Source, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Set
DHCP IP Source to Disabled.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the IP Address setting.
d. Enter a valid IP address. Press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields.
e. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to the Subnet Mask submenu. Press the Enter key.
f. Enter a valid subnet mask. Press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields.
5. On the ProLiant ML110 G3 server:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Set LAN Configuration submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Select DHCP IP Source, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Set
DHCP IP Source to Disabled.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the IP Address submenu. Press the Enter key.
d. Enter a valid IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address. Press the Tab or period (.) key to
move between address fields.
e. Press the Esc key to return to the Set LAN Configuration submenu.
f. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Subnet Mask submenu. Press the Enter key.
g. Enter a valid subnet mask. Press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields.
6. On the ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Settings submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Set the IP Address Assignment to Static. This setting enables you to modify a static IP address
through the BIOS setup menu.
c. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down and enter a valid IP address, subnet mask, and
gateway address (press the Tab or period (.) key to move between address fields).
7. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
To enable a DHCP assigned address:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
Using LO100 37
Page 38

2.
Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. On the ProLiant ML150 G2 server:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Set LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Select DHCP IP Source, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enable and Disabled. Select
Enabled.
5. On the ProLiant ML110 G3 server:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the Set LAN Configuration submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Select DHCP IP Source, and press the Enter key to toggle between Enable and Disabled. Select
Enabled.
6. On HP ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Settings submenu. Press the Enter key.
b. Set the IP Address Assignment to DHCP.
7. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
On the ProLiant ML110 G3 server, HTTP and telnet are automatically enabled.
To enable HTTP and telnet on ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the LAN Interface submenu. Press the Enter key.
5. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the following settings, and set the parameters as needed
(the following example shows configuring for LO100 access using telnet and a web page):
o BMC Telnet Service: [Enabled]
o BMC Ping Response: [Enabled]
o BMC HTTP Service: [Enabled]
To enable HTTP and telnet on ProLiant ML150 G2 servers:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to the following settings, and set the parameters as needed
(the following example shows configuring for LO100 access using telnet and a web page):
o Ping Response: [Enabled]
o Telnet Access: [Enabled]
o HTTP Access: [Enabled]
Using the virtual floppy feature
The virtual floppy feature enables you to boot the server with a boot image residing on a remote server.
To boot using a virtual floppy on a remote system:
1. Configure the TFTP server ("Configuring the TFTP Server" on page 39).
Using LO100 38
Page 39

2.
Configure the virtual floppy on the server using one of the following methods:
o BIOS Setup ("Configuring the virtual floppy from the BIOS setup" on page 40)
o Web browser ("Configuring virtual floppy from a Web browser" on page 39)
o CLP ("Configuring virtual floppy from the CLP" on page 40)
3. Reboot the server ("Rebooting the server" on page 41).
Configuring the TFTP Server
The virtual floppy feature enables you to boot the server with a boot image residing on a remote server.
To boot using a virtual floppy on a remote system:
1. Install a TFTP server on a remote system and ensure that it is running. (TFTP servers are typically
included with Linux and are available for other operating systems as well. Consult your TFTP server
documentation for further details. If you do not have a TFTP software package, use TFTPD32.EXE,
which is available on the Internet.)
2. Create the remote boot image of the boot floppy using flimage.exe. The flimage.exe utility
application is used to create a binary image of a 1.44-MB floppy disk. The floppy image is stored
as 80 sequentially-numbered binary files starting with 0. Each file represents the contents of the
corresponding cylinder from the floppy disk. You can find flimage.exe on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support
3. Place the boot image in a subfolder (for this example, rboot is the folder containing the boot image)
under the folder where the TFTP server executable program resides. For example, if the TFTP server
program TFTP.exe is in C:\tftp, then place the boot image in the folder c:\tftp\rboot.
4. Launch the executable file TFTP.exe and run TFTP.
).
Configuring virtual floppy from a Web browser
1. Log in to the remote management processor as described previously in the "Logging in to the remote
management processor ("Logging in to LO100" on page 28)" section.
2. Click the Virtual Floppy link from the main menu navigation bar.
3. Enter the IP address of the TFTP server that you configured in the previous section.
4. Enter the path to the folder containing the floppy boot image. This path is relative to where the TFTP
server program TFTP.exe resides. For example, if the TFTP server program TFTP.exe is in C:\tftp and
the floppy boot image is in the folder c:\tftp\rboot, then the path would be rboot.
Using LO100 39
Page 40

5.
Click the Apply button.
Configuring the virtual floppy from the BIOS setup
1. On the target server, press the F10 key during POST to enter BIOS setup.
2. In the BIOS Setup Utility, press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to VSI configuration. Press the Enter key.
5. Select Virtual Floppy, and press the Enter key.
6. Select Enabled.
7. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to TFTP Server IP Address, and enter the IP address of the TFTP
server that you configured in the "Configuring the TFTP server (on page 39)" section of this guide.
8. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to Floppy Timeout to change the default value.
9. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to Image Directory Name. Press the Enter key.
10. In the Enter new Address Path box, enter the path to the folder containing the floppy boot image.
This path is relative to where the TFTP server program, TFTP.exe, resides. For example, if TFTP.exe is
in C:\tftp and the floppy boot image in C:\tftp\rboot, then the path would be rboot.
11. Press the F10 key to save the changes and exit Setup.
Configuring virtual floppy from the CLP
1. Open a CLP window on the remote system, and enter cd map1/nic1 at the command prompt.
2. Configure the TFTP server path by entering the following: set oemhp_vsi_tftpserver=<path>
where <path> is the remote TFTP server IP address. For example:
set oemhp_vsi_tftpserver=10.12.52.142
3. Configure the VSI path by entering the following: set oemhp_vsi_path=<path>, where <path> the
path to the folder containing the floppy boot image. This path is relative to where the TFTP server
program TFTP.exe resides. For example, if the TFTP server program TFTP.exe is in C:\tftp and the
floppy boot image in the folder c:\tftp\rboot, then the path would be rboot. For example:
Using LO100 40
Page 41

set oemhp_vsi_path=rboot
4. Configure the remote file permission by entering the following: set
oemhp_vsi_permission=<permission>, where <permission> is the file permission default RW (Read
Write.) For example:
set oemhp_vsi_permission=rw
Rebooting the server
After the TFTP server and the virtual floppy are properly configured, the server can be rebooted using the
remote floppy boot image that resides on the TFTP server. The methods for rebooting the server are
described in "Controlling server power remotely (on page 30)." The server continues to reboot to the
virtual floppy until the virtual floppy is disabled using the following procedure:
1. Ensure the target server is configured for network access. See "Network settings (on page 36)."
2. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
3. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
4. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to IPMI. Press the Enter key.
5. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll to VSI Configuration. Press the Enter key.
6. Select Virtual Floppy, and press the Enter key.
7. Select Enabled.
8. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
Platform event trap configuration
The PET Configuration screen enables you to set an alarm or specified condition originating on the server
to alert an IPMI 2.0 supported systems management console. To access this page from a browser, click
PET Configuration on the main menu navigation bar.
The PET Destinations section indicates where LO100 sends the PET (if configured.) This section has up to
four entries specifying IP and MAC addresses. Enter either an IP address or a MAC address and click
Apply. If both the a MAC and an IP address are entered, the IP address is used.
Using LO100 41
Page 42

To set a policy, do the following:
1. Select the Policy Enable state and enter the Policy Number and Destination Selector information.
o The Policy Enable field enables you to selectively enable and disable trap forwarding.
o The Policy Number field enables you to select a policy that will be used in PEF configuration.
o The Destination Selector field specifies where to send the PET trap from the destinations defined
in the PET Destination section.
2. Click Apply.
User administration
The User Configuration option on the main menu navigation bar enables you (if authorized) to edit the
username and password for existing users. You must be logged in as a user with administrative privileges
to modify the user configuration. You cannot create a new user. The user password is stored in nonvolatile
memory and can be changed through a web browser ("Changing user settings through a web browser"
on page 42) or the through the CLP ("Changing user settings through the CLP" on page 43).
When using CLP, if you do not have the correct privileges you are not prompted to log in with the correct
credentials. You are warned if you have insufficient access. If you receive a warning message, you must
end the telnet connection and re-establish a connection. There are no restrictions when logged in as
administrator (admin). The second user always has the administrator privilege. User and operator
accounts have the following access:
Option User Operator
Hardware Inventory Yes Yes
Virtual Power No Yes
Monitoring Sensors View only Yes
System Event Log Yes Yes
Network Settings No No
IPMI PET Configuration No No
User Configuration No No
Changing user settings through a web browser
The User Configuration screen displays user information and enables you to modify user settings. To
access the User Configuration screen through a web browser, click User Configuration on the main menu
navigation bar.
To modify user settings, do the following:
1. Click User Configuration on the main menu navigation bar.
2. Enter the password in the Password and Confirm Password fields.
3. Select the User Privilege level from the dropdown list. See "User administration (on page 42)" for
more information on user privileges and access rights.
4. Change the user name if needed.
5. Click the Set button to save the changes.
Using LO100 42
Page 43

Changing user settings through the CLP
1. Log in to the CLP as described in the "Logging in to LO100 (on page 28)" section.
2. At the command prompt, enter cd map1/accounts.
3. Select a user by entering cd user1 or cd user2.
4. To change the user name, enter set username=<new username>. For example:
/./map1/accounts/user1/> set username=testuser1
5. To change the user password, enter set password=<new password> and enter the new
password when prompted. For example:
/./map1/accounts/user1/> set password=testpswd1
Passwords are case-sensitive and can contain up to 16 characters.
6. To change the group name enter, set group=<new group name>. Valid group settings are
admin, user, OEM, and operator. For example:
/./map1/accounts/user1/> set group=user
Accessing the remote console through telnet
You can access the remote console through either the BIOS console text-redirection functionality or a
Microsoft® Windows Server™ 2003 text-based console. Only one Remote Console window can be open
at a time.
To start a remote console session, press the Esc+Q keys. To end a remote console session and return to the
CLP press the Esc+( keys.
BIOS console text redirection through telnet
BIOS console text-redirection functionality enables you to view the entire boot process remotely and make
changes in the BIOS Setup Utility from a remote computer. This tool is valuable in troubleshooting and
managing servers remotely.
To configure the BIOS Setup Utility on the target system:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. Press the right arrow (→) key to navigate to the Advanced menu.
3. On ProLiant ML110 G3 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to the BIOS Serial Console Configuration option, and
press Enter.
b. Verify the following settings:
— BIOS Serial Console: Enabled
— Serial Over LAN (SOL): Enabled
4. On ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers, press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down
to the Console Redirection option, and press the Enter key to access the submenu.
Verify the following settings:
o Console Redirection: Enabled
o Baud Rate: 9600
o Terminal Type: VT100+
Using LO100 43
Page 44

o
Flow Control: None
o Redirection After BIOS POST: On
5. On HP ProLiant ML150 G2 servers, press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to the Console
Redirection option, and press the Enter key to access the submenu.
Verify the following settings:
o Baud Rate: 9600
o Console Type: VT100+
o Flow Control: None
o Continue C.R. after POST: On
6. Press the Esc key to return to the previous screen.
7. Scroll to the I/O Device Configuration option, and press the Enter key.
8. On the ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers, verify that Serial Port is set to BMC
COM PORT.
9. Follow the instructions in the "Network settings (on page 36)" section to set or obtain a valid IP
address.
10. Press the F10 key to save and exit.
After completing the console redirection process, view the boot process remotely from a client computer
through an established telnet session to the IP address of LO100. See your operating system
documentation for instructions on establishing telnet sessions.
When a telnet session is first established, an EMS> prompt appears. If the system is currently booting, the
boot process is displayed. If you do not want to view boot, press the Esc+( keys. If the system is in the
Operating System or off, the EMS> prompt appears, but disappears after pressing Enter.
To redirect the console to the telnet session and view the boot process, press the Esc+Q keys in the telnet
session during server boot. If you reset the server using the telnet connection and press the Esc+Q keys,
the boot process might not appear immediately. The boot process appears after the server resets. To end
the session, press the Esc+( keys.
NOTE: If you encounter problems logging in to the remote console, be aware that some telnet
programs might require you to enable their send line feed at end of line option. If
the remote console does not respond to the Enter key, try setting this option in your telnet
program.
NOTE: You must follow the instructions in the "Network settings (on page 36)" section to
configure the network access properly.
Linux console redirection
In the remote console and servers with the Linux operating system, you can enable a remote login on
ttyS0 by making the following changes to the BIOS Setup Utility and boot documents.
1. On the ProLiant DL140G2, ProLiant DL145G2, and ML150 G2 servers, verify or change the
following:
Console Redirection:
Verify the following settings:
o Baud Rate: 9600
Using LO100 44
Page 45

o
Console Type: VT100+
o Flow Control: None
o Continue C.R. after POST: On
o Serial Port: BMC COM PORT (on the ProLiant DL140 G2 and ProLiant DL145 G2 servers only)
NOTE: To customize the examples for your server, do the following:
• On DL140 G2 servers, replace ttyS0 with ttyS3
2. In the /boot/grub/menu.lst file, append the following to the kernel startup instruction:
• On DL145 G2 servers, replace ttyS0 with ttyS2
console=ttyS0 115200
Comment out the line GRAPHICAL DISPLAY LINE
# splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz
3. Add an entry to allow serial console login in /etc/inittab. For example:
S0:12345:respawn:/sbin/agetty -L 115200 ttyS0 vt102
4. In /etc/securetty enable root access to ttyS0 by adding the ttyS0.
5. In /etc/sysconfig/kudzu, set kudzu to not perform serial port probing during boot. For example:
SAFE=yes
6. After modifying and saving the following files, reboot the server. You can now log in to the
operating system through remote console.
After POST, in the remote console, the server prompts you with a login. Enter a valid login and use the
server as you normally would. Use the ESC+Q keys to start remote console through the telnet and the
ESC+( keys to exit the remote console in telnet.
Microsoft Windows® EMS management
Microsoft® Windows Server™ 2003 provides text-based console access. You can connect a laptop to the
LO100 to perform basic management tasks on the target system. The Windows® EMS Console, if
enabled, displays the processes that are running and enables administrators to halt processes. This
capability is important in cases where video, device drivers, or other operating system features have
prevented normal operation and normal corrective actions.
To enable Windows® EMS management on the target system:
1. Press the F10 key during POST to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
2. On ProLiant ML110 G3 servers:
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to the BIOS Serial Console Configuration option,
and press Enter.
b. Verify the following settings:
— BIOS Serial Console: Enabled
— Serial Over LAN (SOL): Enabled
3. On ProLiant 140 G2, ProLiant DL145 G2, and ProLiant ML150 G2 servers, press the right arrow
(→) key to scroll down to Advanced>Console Redirection menu.
a. Press the down arrow (↓) key to scroll down to EMS Console option, and press the Enter key to
access the submenu.
b. Verify the following settings:
Using LO100 45
Page 46

— Console Redirection: Enabled
— Baud Rate: 9600
— Terminal Type: VT100+
— Flow Control: None
— Redirection After BIOS POST: On
4. Press the Esc key to return to the previous screen, or press the F10 key to save the changes and exit
Setup.
After enabling Windows® EMS management, you can view the Windows® EMS management console
remotely from a client computer through an established telnet session to the IP address of the target server
by pressing the Esc+Q keys. To end an EMS session press the Esc+( keys. See your operating system
documentation for instructions on establishing telnet sessions.
NOTE: If you encounter problems logging in to the remote console, be aware that some telnet
programs might require you to enable their send line feed at end of line option. If
the remote console does not respond to the Enter key, try setting this option in your telnet
program.
HP SIM support
HP SIM discovers LO100 and enables you to identify and launch LO100. See your HP SIM user guide for
more information on using HP SIM with LO100.
Using LO100 46
Page 47

Acronyms and abbreviations
BIOS
Basic Input/Output System
BMC
baseboard management controller
CLI
Command Line Interface
CLP
command line protocol
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DSA
Digital Signature Algorithm
EMS
Emergency Management Services
HP SIM
HP Systems Insight Manager
HTTP
hypertext transfer protocol
IP
Internet Protocol
IPMI
Intelligent Platform Management Interface
JVM
Java Virtual Machine
Acronyms and abbreviations 47
Page 48

KCS
Keyboard Controller Style
KVM
keyboard, video, and mouse
LO100
HP Lights-Out 100 Remote Management processors
MAC
medium access control
NIC
network interface controller
OS
operating system
PEF
Platform Event Filtering
PEM
Privacy Enhanced Mail
PET
Platform Event Trap
POST
Power-On Self Test
RBSU
ROM-Based Setup Utility
SLES
SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server
SMASH
System Management Architecture for Server Hardware
SSH
Secure Shell
Acronyms and abbreviations 48
Page 49

SSL
Secure Sockets Layer
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol
URL
uniform resource locator
VNC
virtual network computing
Acronyms and abbreviations 49
Page 50

Index
A
access options 28
accessing software, browser 28
administration 11
alert messages 41
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) 11,
14, 15, 28, 36, 37
DHCP addresses 14
DHCP, disabling 15
DHCP, enabling 14
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 11,
14, 15, 28, 36, 37, 47
B
base management controller (BMC) 11
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) 16, 32
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) 16, 32
BIOS console, text redirection 43
BIOS upgrade 16
BMC (base management controller) 11
browser-based setup 36
C
certificates, generating 21
certificates, installing 21
CLP (Command Line Protocol) 5, 11, 14, 16, 21,
22, 23, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 34, 35, 36, 38,
40, 42, 43
CLP overview 22
CLP, base commands 23
CLP, commands 31, 35, 36, 40, 43
CLP, connection options 22
CLP, general syntax 22, 23
CLP, specific commands 27
CLP, using 22
Command Line Protocol (CLP) 5, 11, 14, 16, 21,
22, 23, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 34, 35, 36, 38,
40, 42, 43
configuration procedures 11
configuration, network 11, 36
configuring the LOM processor 11
connectors, illustrated 8, 9
console redirection 13
console redirection, Linux 44
D
data protection methods 19
dedicated management port 13
E
Emergency Management Services (EMS) 45
EMS (Emergency Management Services) 45
EMS Console 45
encryption 19, 20
Ethernet connections 14
event log 34
event log entries 34
event log, BIOS setup access 35
event log, browser access 34
event log, CLP access 35
F
features, CLP 22
features, IPMI 2.0 27
features, overview 5
features, SSL 19
firmware, updating 16
flash ROM 16
H
hardware inventory 30
HP Systems Insight Manager, support 46
HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol) 11, 12, 15, 19
hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) 11, 12, 15, 19
I
importing 21
installation instructions 7, 9
installation requirements 7
installation, management card 7, 9
installing management card 8, 9
Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) 5,
11, 27, 29, 33, 34, 40, 41, 42
Index 50
Page 51

Internet Protocol (IP) 11
IP (Internet Protocol) 11
IP address assignment 15
IPMI (Intelligent Platform Management Interface) 5,
11, 27, 29, 33, 34, 40, 41, 42
IPMI support 27
K
key, public 21
kit contents 7
L
Linux, console redirection 44
LO100 settings 19
LO100, logging in through browser 28
LO100, remote management 19
LO100c connectors 8, 9
logging in 28, 29
logging in, through a browser 28
logging in, through the CLP 29
M
main menu functions 29
manangement card, installing 8, 9
medium access control (MAC) 41
monitoring sensors 32
N
network access 11
network access, configuring 11
network interface controller (NIC) 5, 7, 12, 13, 36,
40, 48
network settings 11, 36
network settings, configuring through the BIOS
setup 37
network settings, configuring through the CLP 36
NIC (network interface controller) 5, 7, 12, 13, 36,
40
O
operational overview 5
overview, CLP 22
overview, server management 5
overview, SSH 20
overview, SSL 19
P
password, changing through a browser 42
password, changing through the CLP 43
passwords 42
PEF entires, 33
Platform Event Filtering (PEF) 33, 41
POST (Power-On Self Test) 9, 11
post-installation procedures 9
power control options 31
power cycle server 30
powering on/off 30, 31, 32
Power-On Self Test (POST) 9, 11
preinstallation, guidelines 7
priveleges, user 42
processors 30
public key 21
R
RBSU (ROM-Based Setup Utility) 34
reboot, server 41
remote console, using 43
remote management card connectors 8, 9
remote management processor, logging in through
CLP 29
remote management, browser main menu 29
remote server power, controlling 31, 32
requirements, SSH 20
ROM-Based Setup Utility (RBSU) 34
ROMPaq utility 16
S
safety considerations 7
Secure Shell (SSH) 20, 21, 22, 29
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) 21
sensor data, BIOS access 32
sensor data, browser access 32
sensor data, viewing 32
serial port 12
serial port, BIOS console configuration 13
serial port, enabling 12
server management 5
settings, network 36
settings, PEF 33
settings, power options 31
side-band connection 14
SMASH (System Management Architecture for Server
Hardware) 5, 22
SSH (Secure Shell) 20, 21, 22, 29
SSL, (Secure Sockets Layer) 21
Index 51
Page 52

SSL, importing key and certificate 21
SSL, overview 19
SSL, using 19
static IP addresses 15
support, HP Systems Insight Manager 46
support, IPMI 27
system event log, access through the BIOS 35
system event log, access through the CLP 35
system event log, using 34
System Management Architecture for Server
Hardware (SMASH) 5, 22
T
telnet 15, 43
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) 16, 17, 21, 23,
38, 39, 40, 41
TFTP, configuration 17, 39
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) 16, 17, 21, 23,
38, 39, 40, 41
U
UID (unit identification) 5, 22
unit identification (UID) 5, 22
user access 11, 42
user account, modifying 11, 42
user and configuration settings 11, 42
user guide updates 5
V
virtual devices 38
virtual floppy, configuring from BIOS setup 40
virtual power 30
virtual storage interface (VSI) 13, 39, 40, 41
VSI (virtual storage interface) 13, 39, 40, 41
W
Windows® EMS Console, enabling 45
Index 52
 Loading...
Loading...