Page 1

HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Win32 Edition Best Practices
October 2005 (Fourth Edition)
Part Number 370971-004
Page 2

© Copyright 2004, 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212,
Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S.
Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
October 2005 (Fourth Edition)
Part Number 370971-004
Page 3

Contents
Introduction.................................................................................................................................. 4
Win32 Toolkit overview............................................................................................................................. 4
Toolkit changes......................................................................................................................................... 4
Minimum requirements............................................................................................................................... 4
Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment................................................................................ 5
Overview of the Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment ..................................................................... 5
Windows PE build process ......................................................................................................................... 5
Building a Windows PE base image ..................................................................................................5
Customizing the Windows PE image using the Toolkit driver component................................................. 6
Booting Windows PE from a USB drive key ..................................................................................................7
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE ........................................................................... 8
Overview of configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE....................................................................... 8
Unattended configuration using startnet.cmd................................................................................................. 8
Creating required data files with Windows PE .............................................................................................. 9
Capturing and storing data files using physical media........................................................................ 10
Capturing data files over a network .................................................................................................10
Creating script files.................................................................................................................................. 10
CD-based Windows PE deployment........................................................................................................... 16
PXE-based Windows PE deployment .......................................................................................................... 17
Network-based Windows PE deployment ...................................................................................................17
Technical support........................................................................................................................ 19
Reference documentation ......................................................................................................................... 19
Toolkit support ........................................................................................................................................ 19
HP contact information............................................................................................................................. 19
Acronyms and abbreviations........................................................................................................ 20
Index......................................................................................................................................... 22
Contents 3
Page 4

Introduction
In this section
Win32 Toolkit overview............................................................................................................................ 4
Toolkit changes........................................................................................................................................ 4
Minimum requirements.............................................................................................................................. 4
Win32 Toolkit overview
This document describes how to best utilize the Win32 edition of the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit to
configure HP ProLiant servers. It also contains information about using the Toolkit utilities in an unattended
environment. This document does not include information about installing the operating system.
The best practices also include suggestions about how to organize utilities and data files by following a
set of operational procedures that standardize configuration procedures and help reduce errors.
CAUTION: Because of the potential risk of data loss, be sure that all necessary precautions are taken so
that mission-critical systems are not disrupted if a failure occurs.
Toolkit changes
Previous versions of the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit utilities were designed for the MS-DOS environment.
However, limitations in MS-DOS have become a significant problem as hardware and software have
evolved. In response to this issue, HP has migrated the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit to a Win32
environment to provide better scripting and better hardware support using Win32 drivers and to take
advantage of built-in Win32 features, such as integrated network support.
The Win32 edition of the Toolkit provides the same functionality as the earlier MS-DOS version. However,
tools, arguments, and data files are different in the Win32 edition of the Toolkit, so you must update your
customized scripts to work in a Win32 environment. Data files have been migrated to industry-standard
XML format to provide improved extensibility. For more information about the Toolkit utilities, refer to the
HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Linux and Win32 Editions User Guide on the Toolkit website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/sstoolkit
).
Minimum requirements
Before beginning the deployment process, be sure to have the following items available:
• HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Linux and Win32 Editions User Guide
• SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Win32 Edition
• Microsoft® Windows® PE Build Tools 2005
• Microsoft® Windows® Server 2003, Service Pack 1 (SP1)
Introduction 4
Page 5

Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment
In this section
Overview of the Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment.................................................................... 5
Windows PE build process ........................................................................................................................ 5
Booting Windows PE from a USB drive key................................................................................................. 7
Overview of the Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment
Microsoft® Windows® Preinstallation Environment 2005 is a small footprint of the Microsoft®
Windows® Server 2003 environment that replaces MS-DOS and enables you to run tools in a 32-bit
Windows® environment. However, Windows® PE 2005 is based on the Windows® Server 2003 SP1
kernel running in protected mode. Therefore, only a subset of features and APIs are available in this
environment. This document is applicable to Windows® PE 2005 only. It is not backward compatible
with previous versions of Windows® PE.
Windows® PE enables you to install the Windows® operating system, establish a connection with
network servers, and perform hardware configuration using the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit. You can use
Windows® PE to customize and configure your servers before the operating system is installed.
A bootable image of Windows® PE is available from Microsoft® through the Open Value program. You
can also obtain tools, scripts, and documentation that enable you to create and customize your own
Windows® PE image. However, customers are required to have the Microsoft EA or SAM to gain access
to Windows® PE. For more information, refer to the Microsoft® Windows® PE website
(http://www.microsoft.com/licensing/programs/sa/support/winpe.mspx
Windows PE build process
Microsoft® provides a collection of scripts and tools to help you build your own Windows® PE image.
You must customize your Windows® PE image to include the latest HP drivers and the SmartStart
Scripting Toolkit utilities, data files, and customized scripts. The latest ProLiant drivers are available on the
HP support website (http://www.hp.com/support/files
The following sections, "Building a Windows PE base image (on page 5)" and "Customizing the
Windows PE image using the Toolkit driver component (on page 6)," give an overview of the Windows®
PE build process with HP drivers and tools and should be executed in the Windows® command prompt
Building a Windows PE base image
(CMD.EXE) environment.
).
).
This section describes how to build a Windows® PE base image. The base image can then be
customized as described in "Customizing the Windows PE image using the Toolkit driver component (on
page 6)." For detailed information about customizing a Windows® PE base image, refer to the
Windows® PE documentation.
Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment 5
Page 6
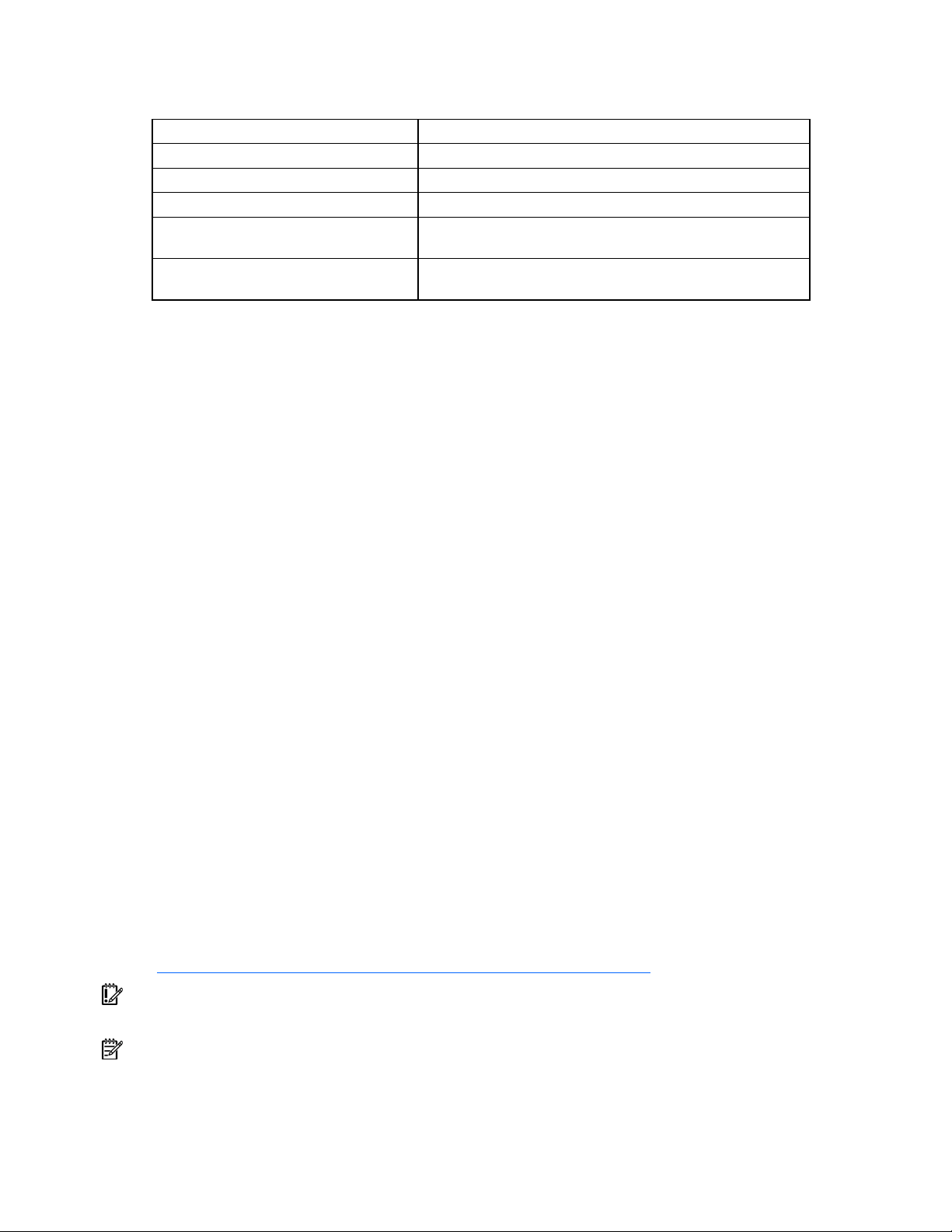
The following table describes the directories and paths that you must define for the Windows® PE base
image build procedure.
Directory or path Description
WinPEBuildTools Build location for the Windows® PE tools
PathToWinPEFiles Path to the original Windows® PE files
PathToOSFiles Path to the operating system CD or directory
WinPE_Directory
OptionalComponentsDirectory
Target directory where the flat Windows® PE image will be
created
Target directory where the Windows optional components will
be stored
To build a Windows® PE base image:
1. Set an environment variable for the platform (x86 or i386):
set platform = x86
2. Copy the Windows® PE Build Tools and files for the appropriate target server platform to a
temporary directory:
a. Create the temporary build directory:
mkdir WinPEBuildTools
b. Copy the files to the temporary build directory:
xcopy /s /e PathToWinPEFiles\WinPE\*.* WinPEBuildTools
xcopy /s /e PathToWinPEFiles\Tools\%Platform%\*.* WinPEBuildTools
3. Run the mkimg batch file to build the folder structure of Windows® PE image with PnP and WMI
support enabled:
cd WinPEBuildTools
mkimg.cmd PathToOSFiles WinPE_Directory /PnP /WMI
4. If needed, build Windows® PE optional components. Optional components include support for
ADO, HTA, and WSH:
a. Build the optional components:
Buildoptionalcomponents.vbs /s:PathToOSFiles
/d:OptionalComponentDirectory /ADO /HTA /WSH /X
b. Copy the optional component files to the Windows® PE flat image folder:
xcopy /e OptionalComponentDirectory WinPE_Directory
c. Edit startnet.cmd to include the string oc.bat:
echo oc.bat >> WinPE_Directory\%Platform%\system32\startnet.cmd
Customizing the Windows PE image using the Toolkit driver component
Windows® PE contains a set of drivers and other files imported from Windows® XP that are critical
during the boot process of Windows® PE. In addition to the drivers imported from Windows® XP,
additional WDM compliance drivers can be added to the Windows® PE image during customization.
Use the Windows® PE tools available from Microsoft® to help you update drivers to the Windows® PE
image. For more information, refer to the Microsoft® Windows® PE website
(http://www.microsoft.com/licensing/programs/sa/support/winpe.mspx
IMPORTANT: HP ProLiant drivers must be added during Windows® PE customization to ensure the
Toolkit utilities function properly.
NOTE: Tools and data files are not required during the boot process, so they do not need to be stored on
the Windows® PE CD. These files can reside on a diskette, a USB drive key, or a network share.
Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment 6
).
Page 7

To simplify the process of customizing the Windows® PE image with the latest ProLiant drivers, the Win32
edition of the Toolkit provides a driver component that automatically registers and copies the drivers to the
appropriate folders. User interaction is still required to set up the Windows® command prompt
(CMD.EXE) environment.
To extract the component:
• Locate the compressed file, which is a self-extracting executable.
• Double-click the self-extracting executable, and select Extract to extract all of the files and drivers to
a temporary directory.
The component uses drivers shipped with the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit to customize the Windows® PE
image. The component must be run after the Windows® PE base image is built but before other
modifications are made to the Windows® PE image.
Booting Windows PE from a USB drive key
Some applications, such as the firmware update components, require the use of a writable medium. A
writable file system allows for the expansion of the contents of the components and provides a scratch
area for the backup firmware image copied from the device under flash. While using Windows® PE on
CD is not suitable for this purpose, a USB drive key provides the ideal medium for this type of activity.
NOTE: Booting from a USB drive key is supported only on the HP ProLiant BL20p G3 Server and ProLiant
G4 and later servers.
To boot Windows® PE from a USB drive key, refer to the Microsoft Windows® PE documentation
(http://www.microsoft.com/licensing/programs/sa/support/winpe.mspx
). This information is also
available with the Windows® PE build tools documentation.
Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment 7
Page 8

Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE
In this section
Overview of configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE.....................................................................8
Unattended configuration using startnet.cmd ............................................................................................... 8
Creating required data files with Windows PE............................................................................................. 9
Creating script files................................................................................................................................. 10
CD-based Windows PE deployment.......................................................................................................... 16
PXE-based Windows PE deployment......................................................................................................... 17
Network-based Windows PE deployment.................................................................................................. 17
Overview of configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE
This section describes how to perform an unattended configuration using a batch file. It also describes
three ways to use Windows® PE to configure HP ProLiant systems using captured data files:
• CD-based Windows PE deployment (on page 16)
• PXE-based Windows PE deployment (on page 17)
• Network-based Windows PE deployment (on page 17)
You can also perform an attended configuration. For more information about using the Toolkit utilities in
an attended configuration, refer to the HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Linux and Win32 Editions User
Guide, located on the Toolkit website (http://www.hp.com/servers/sstoolkit
).
Unattended configuration using startnet.cmd
In an unattended configuration, a batch file is launched automatically at the end of the Windows® PE
boot process to perform the configuration tasks. There are several ways to start a batch file for custom
routines, but the simplest is by using startnet.cmd.
Startnet.cmd, located in the WinPE_Directory\Platform\system32 directory, is a command batch file that
Windows® PE automatically loads at the end of the boot process. The content of startnet.cmd varies
depending on usage. In the following example, startnet.cmd is used to map drives to a network file server
and execute files located on a remote server.
Sample contents for startnet.cmd:
factory -winpe
net use f: \\fileserver\share
x:\startdeploy.cmd
a:\custom.cmd
For more information about the startnet.cmd command and other methods of starting a batch file,
refer to the Microsoft Windows® PE documentation
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 8
Page 9

(http://www.microsoft.com/licensing/programs/sa/support/winpe.mspx). For more information about
the net use command, enter net help use at the command prompt.
Because startnet.cmd is stored in the WinPE_Directory\Platform\system32 directory, command files listed
in startnet.cmd are relative to the directory. Use the default system variables SystemDrive and SystemRoot
to specify paths to the utilities. Be sure that the contents of the file are accurate and tested before using it
widely.
Creating required data files with Windows PE
Some Toolkit utilities require data files as input arguments to provide detailed settings for the system. You
can build data files manually to use with the utilities, but Toolkit utilities can also capture existing
configuration data files from a server that can then be customized to use with other servers.
NOTE: For more information about using the Toolkit utilities and building data files manually, refer to the
HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Linux and Win32 Editions User Guide, located on the Toolkit website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/sstoolkit
SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Win32 Edition utilities are only supported in a Win32 environment. They can
run in either Windows® or Windows® PE. To use the Toolkit utilities in a Windows® PE environment,
Windows® PE must be built with the latest HP drivers to ensure the utilities can access the hardware. For
more information, refer to "Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment (on page 5)."
).
No restrictions are placed on file naming. However, if data files for various servers are placed on an
installation CD-ROM, store each server profile in its own directory. The data files include:
• HWCONFIG.XML—Hardware configuration data file generated by CONREP
• ARRAYCFG.INI—Array configuration data file generated by CPQACU. You can also use one of the
automatic configuration sample files provided with the Toolkit:
• PL-R0.INI—Configures all controllers as RAID 0 with all physical drives allocated to a single
logical drive.
• PL-R1.INI—Configures all controllers as RAID 1 with all physical drives on each controller
allocated to separate RAID 1 logical drives. Assumes two or more physical drives.
• PL-R5.INI—Configures all controllers as RAID 5 with all physical drives on each controller
allocated to a single logical drive. Assumes three or more physical drives.
• PL-RD1.INI—Configures the first controller as RAID 1 with all physical drives allocated to a
single logical drive.
• PL-RD.INI—Automatically configures all controllers to the most appropriate RAID level, based
on the number of drives.
• PL-R1R5.INI—Configures the first two controllers as RAID 1 and the remaining controllers as
RAID 5. Assumes 5 or more drives.
• ERASE.INI—Clears all controllers of all configurations.
• DISKPART0.TXT—Partition configuration data file created by the user to configure a bootable
partition. This file is used by the DISKPART utility.
• HWDISC.XML—Hardware discovery data file generated by HWDISC.EXE and used at runtime
• ILOCFG.XML—RILOE II or iLO configuration data file created by the user (optional). This file is used
by the HPONCFG utility.
The following examples assume a floppy disk, but other media (CD, PXE, USB drive key) are also
acceptable. To generate the data files on the source server:
1. Generate the hardware configuration data file with the following command:
CONREP /S A:\HWCONFIG.XML
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 9
Page 10

This command reads the current configuration on the source server and writes the hardware
configuration data file to A:\HWCONFIG.XML.
2. Generate the array configuration data file with the following command:
CPQACUXE /C A:\PL-RD.INI
This command reads the array configuration on the source server and writes the array configuration
data file to A:\PL-RD.INI.
3. Create the partition configuration data file. A sample DISKPART0.TXT file is provided with the Toolkit
in the samples directory. For more information on using DISKPART, refer to the Microsoft®
documentation.
4. If needed, create the RILOE II or iLO configuration data file. For examples of the command line
parameters, refer to the "Using HPONCFG" section of the HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit Linux and
Win32 Editions User Guide.
Use a text editor as necessary to make changes to the configuration files so that they conform to the target
server.
Now, data files can be captured and stored in either of the following ways:
• Capturing and storing data files using physical media (on page 10)
• Capturing data files over a network (on page 10)
Capturing and storing data files using physical media
HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit utilities and scripts can be stored on physical media, such as a diskette or
a driverless USB storage device.
NOTE: Windows® PE supports USB natively, but USB devices must be connected to the system before
Windows® PE boots to be recognized. Be sure the proper device driver is loaded if you are using a nondriverless USB device for storage.
After Windows® PE boots, you can execute the utilities to capture data files and store them on the USB
storage device. These data files can then be modified as needed and used for deploying configurations
on other systems.
Capturing data files over a network
For Windows® PE to support network access, the driver for the networking device must be on the
Windows® PE image. To update drivers to the Windows® PE image, refer to "Microsoft Windows
Preinstallation Environment (on page 5)."
Windows® PE does not support access to files or folders on Windows® PE servers from another location
on the network.
After Windows® PE boots, you can access files and folders stored on other servers on the network. Map
the proper drive to the file server where the utilities are stored and the data files will reside, and execute
the utilities to capture data files. These data files can then be modified as needed and used for deploying
configurations on other systems.
Creating script files
After the server data files are generated and modified for the target server, modify and save a copy of the
script files to the appropriate location. Refer to the operating system documentation for a complete
description of the options that can be modified in the unattended installation file to customize the
installation.
Using a standard text editor, create the following additional Toolkit files for the unattended install.
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 10
Page 11

1.
STARTDEPLOY.CMD is a script file that is executed by STARTNET.CMD in Windows PE. Edit the
STARTDEPLOY.CMD file to modify the environment variables to match the locations of the utilities
and data files specific to your deployment infrastructure. You must customize this file for your
environment. In the following example, bold lines indicate information that must be modified for your
environment.
The STARTDEPLOY.CMD file is similar to the following:
rem @echo off
REM
REM This is the first Script called from Startnet.cmd stub in the WinPE
REM
REM Make sure that the network is fully started...
REM Sometimes it requires a bit of time
ipconfig
REM Map a drive to the share you are working from.
REM If none ignore this step and set the drive letter in
REM the following statements to appropriate drive
REM============================================================
set Tools=s:\tkdemoarea\HP\Tools
set MSTools=X:\i386\system32
set GlobalData=s:\tkdemoarea\HP\DeploymentScripts\datafiles
set MSDistribution=s:\tkdemoarea\w2k3entsp1
set HPQFlatFiles=s:\tkdemoarea\hpqflatfiles
set HPQComponents=s:\tkdemoarea\ntcsp
set SystemScripts=s:\tkdemoarea\HP\DeploymentScripts
REM============================================================
net start sysmgmt
REM Call the first Script
call %SystemScripts%\ServerDetect.cmd
echo Done!
2. If needed, modify the SERVERDETECT.CMD file for your specific environment. This file is provided in
the samples subdirectory. SERVERDETECT.CMD does not accept any arguments. It runs the
HWDISCOVERY utility to determine the server type and then executes a typical deployment script
(DEPLOYSERVER.CMD).
3. Edit the DEPLOYSERVER.CMD file for your specific environment.
NOTE: The IFHW and HWQUERY utilities can be used to assist in customizing the DEPLOYSERVER.CMD
script for your environment. For more information about these utilities, refer to the HP SmartStart Scripting
Toolkit Linux and Win32 Editions User Guide.
The DEPLOYSERVER.CMD file is similar to the following:
rem @echo off
cls
echo [ SCRIPT FOR REMOTE INSTALL OF W2K3 ON TYPICAL SERVER ]
pause
echo Retrieving State Information...
%Tools%\System\statemgr /r phase
if errorlevel 3 goto State3
if errorlevel 2 goto State2
if errorlevel 1 goto State1
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 11
Page 12

if errorlevel 0 goto State0
:State0
REM *** Configure the target server hardware by reading the configuration
REM *** information in the script file
echo Running Configuration Replication Utility...
%Tools%\System\conrep -l -f%GlobalData%\HardwareSettings\hwconfig.xml x%Tools%\System\conrep.xml
echo Setting State Information...
%Tools%\System\statemgr /w Phase 1
:State1
REM========================================================================
REM *** Configure the array controllers by reading the configuration
REM *** information in the script file and stamping it onto the array
REM *** controllers of the target server
REM========================================================================
echo Configuring the Array Controllers...
%Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml PCI:"Smart
Array 5i Controller"
if errorlevel 1 GOTO NEXT1
%Tools%\ACU\bin\hpacubin.exe -i %GlobalData%\ArraySettings\pl-r0.ini
GOTO NEXT6
:NEXT1
%Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml PCI:"Smart
Array 6i Controller"
if errorlevel 1 GOTO NEXT2
%Tools%\ACU\bin\hpacubin.exe -i %GlobalData%\ArraySettings\pl-r1.ini
GOTO NEXT6
:NEXT2
%Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml PCI:"Smart
Array 5312"
if errorlevel 1 GOTO NEXT3
%Tools%\ACU\bin\hpacubin.exe -i %GlobalData%\ArraySettings\pl-r1.ini
GOTO NEXT6
:NEXT3
%Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml PCI:"Smart
Array 640X Controller"
if errorlevel 1 GOTO NEXT4
%Tools%\ACU\bin\hpacubin.exe -i %GlobalData%\ArraySettings\pl-r5.ini
GOTO NEXT6
:NEXT4
%Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml PCI:"Smart
Array P600 Controller"
if errorlevel 1 GOTO NEXT5
%Tools%\ACU\bin\hpacubin.exe -i %GlobalData%\ArraySettings\pl-r1r5.ini
GOTO NEXT6
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 12
Page 13

:NEXT5
%Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml PCI:"HP 6 Port
SATA RAID Controller"
if errorlevel 1 GOTO NEXT6
.\Adaptec\bin\arcconf.exe ***Fill in command options***
:NEXT6
pause
REM========================================================================
REM *** Configure the iLO if iLo Present
REM *** echo configuring iLO is present
REM========================================================================
rem %Tools%\System\ifhw .\hwdisc.xml %Tools%\System\allboards.xml
PCI:"Integrated Lights-Out Controller"
rem if errorlevel 1 GOTO State2
rem .\iLo\hponcfg -f %GlobalData%\iLoSettings\iloconfig.xml
REM========================================================================
echo Setting State Information... Due to Problems with diskpart not picking
up new logical volumes
REM========================================================================
%Tools%\System\statemgr /w Phase 2
REM *** REBOOT if necessary
%Tools%\System\reboot PXE
:State2
REM========================================================================
REM *** Create partition by reading content of the script file and
REM *** stamping the configuration onto the hard drive in the target server
REM========================================================================
echo Creating Disk Partition...
%MsTools%\DiskPart /s %GlobalData%\diskPart0.txt
echo Formatting Disk Partition...
%MsTools%\format c: /FS:NTFS /Q /y
pause
%Tools%\System\statemgr /w Phase 3
echo Creating Driver Directory and Copying Drivers...
mkdir c:\ntcsp
rem xcopy %HPQFlatFiles%\$oem$ c:\$oem$ /s /e
xcopy %HPQComponents% c:\ntcsp /s /e
pause
REM *** Copy the customized UNATTEND.TXT file from the system
REM *** configuration area to the root directory of the target server's
REM *** hard drive
:State3
copy %GlobalData%\unattend.txt c:\
REM========================================================================
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 13
Page 14

REM *** Start installation of the operating system from the hard drive of
REM *** the target system, reading unattended installation instructions from
REM *** the C:\UNATTEND.TXT file
REM========================================================================
%MSDistribution%\i386\winnt32 /s:%MSDistribution%\i386
/unattend:c:\unattend.txt /syspart:c
%Tools%\System\reboot c:
:State4
4. Modify the Windows Server 2003 SP1 UNATTEND.TXT sample file to fit your deployment
requirements. In the following example, bold lines indicate modifications made to fully automate the
installation of the operating system.
Refer to the operating system documentation for a complete description of the options that can be
modified in the unattended installation file to customize the installation of Microsoft® Windows® PE.
For more information, refer to the Microsoft® website
(http://www.microsoft.com/resources/documentation/WindowsServ/2003/all/techref/en-
us/default.asp).
UNATTEND.TXT example script:
; Base Server Unattended Install Script for Windows Server 2003
;
[Unattended]
DriverSigningPolicy=Ignore
ExtendOemPartition=1
; FileSystem=ConvertNTFS
KeyboardLayout="US"
NtUpgrade=No
; OemFilesPath=C:
OemPnPDriversPath=drivers\net;drivers\scsi
OemPreinstall=Yes
OemSkipEula=Yes
DisableVirtualOemDevices=yes
OverwriteOemFilesOnUpgrade=No
TargetPath=\WINDOWS
UnattendMode=FullUnattended
Win9xUpgrade=No
[MassStorageDrivers]
"Adaptec Ultra160 Family Manager Set"=OEM
"Compaq Smart Array Controllers"=OEM
"Smart Array 5x and 6x Controllers"=OEM
"Integrated Ultra ATA-100 IDE RAID Controller (Windows 2000)"=OEM
"LSI Logic Ultra320 1020/1030 Driver (Windows Server 2003)"=OEM
"LSI Logic C8100 PCI SCSI Host Adapter"=RETAIL
"LSI Logic C896 PCI SCSI Host Adapter"=RETAIL
"LSI Logic C8xx PCI SCSI Host Adapter"=RETAIL
"IDE CD-ROM (ATAPI 1.2)/PCI IDE Controller"=RETAIL
"CSB-6 Ultra ATA-100 IDE RAID Controller (Windows Server 2003)"=OEM
"Smart Array SAS/SATA Controllers"=OEM
"Adaptec RAID Controller"=OEM
[OEMBootFiles]
ADPU160M.SYS
CPQARRY2.SYS
CPQCISSM.SYS
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 14
Page 15

MegaIDE.sys
Symmpi.sys
LsiCsb6.sys
HPCISSs2.sys
AAC.sys
TXTSETUP.OEM
[GuiUnattended]
AdminPassword=password
AutoLogon=Yes
AutoLogonCount=1
OEMSkipRegional=1
OemSkipWelcome=1
TimeZone=20
[UserData]
ComputerName=TEST
FullName=HP
OrgName=HPQ
ProductID=xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx
[Proxy]
Proxy_Enable=0
Use_Same_Proxy=0
[LicenseFilePrintData]
AutoMode=PerServer
AutoUsers=999
[GuiRunOnce]
"c:\ntcsp\setupex.exe /smartstart"
[RegionalSettings]
Language=00000409
LanguageGroup=1
[Components]
iis_pwmgr=Off
iis_inetmgr=Off
iis_www=Off
iis_ftp=Off
TSClients=On
TSEnable=On
[Networking]
InstallDefaultComponents=Yes
[Identification]
JoinWorkgroup=WORKGROUP
[NetOptionalComponents]
SNMP=1
WBEMSNMP=1
SimpTCP=1
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 15
Page 16

[SNMP]
Community_Name=Public
Traps=Localhost
Accept_CommunityName=public
Send_Authentication=yes
[TerminalServices]
ApplicationServer=0
PermissionsSetting=0
[Display]
AutoConfirm=1
BitsPerPel=16
ConfigureAtLogon=0
VRefresh=60
Xresolution=800
Yresolution=600
[OEM_Ads]
Logo=Compaq.bmp
5. Use the latest version of SmartStart to obtain supported drivers for new hardware devices. Also, add
lines to copy the new devices and add the new devices to the UNATTEND.TXT and TXTSETUP.OEM
files.
6. If needed, edit the TEXTSETUP.OEM file. The TEXTSETUP.OEM file provided with the Toolkit does not
need to be modified unless you want to add mass storage drivers. For more information, refer to the
Microsoft website
(http://www.microsoft.com/resources/documentation/WindowsServ/2003/all/techref/en-
us/default.asp).
CD-based Windows PE deployment
This section assumes all scripts, utilities, and data files are stored on the Windows® PE CD.
The Windows® PE CD image must contain the utilities, data files, latest device drivers from HP, and at
least one customized batch file to initiate the system configuration. For information about building a
customized Windows® PE image, refer to "Microsoft Windows Preinstallation Environment (on page 5)."
To build a Windows® PE CD image that automatically configures an HP ProLiant system:
1. Build the Windows® PE folder structure as described in "Microsoft Windows Preinstallation
Environment (on page 5)."
2. Modify WinPE_Directory\Platform\system32\startnet.cmd to include the following:
factory -winpe
startdeploy.cmd
For more information about using a batch file, refer to "Unattended configuration using startnet.cmd
(on page 8)."
3. Use the edited STARTDEPLOY.CMD file to begin the deployment process. Be sure that the
STARTDEPLOY.CMD script is located in the directory that will be used to create the Windows® PE
ISO image. If STARTDEPLOY.CMD is used to create a connection to a network resource, the file must
exist on the CD.
4. Build an ISO image using the Windows® PE folder as the source.
5. Create a Windows® PE CD using the ISO image.
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 16
Page 17

PXE-based Windows PE deployment
This section describes how to use a PXE server to boot Windows® PE through a network. Review the
server specification to determine whether PXE is supported on the target server. Currently, the Microsoft®
RIS server is the only PXE server officially supported by Microsoft® with Windows® PE. Third-party PXE
servers have not been validated with Windows® PE. Refer to RIS documentation for information about
setting up and using RIS.
NOTE: Using a PXE server to boot Windows® PE through a network is only supported when used in
conjunction with RIS.
Using PXE to boot Windows® PE eliminates the need to create a physical Windows® PE CD. Because the
Windows® PE image files reside in the RIS server, files can easily be modified if needed. With network
access, scripts, utilities, and data files can be stored on the RIS server or on other file servers on the
network. For detailed information about using RIS with Windows® PE, refer to the Windows® PE tools
documentation.
To build a Windows® PE image for use with a PXE server to automatically configure an HP ProLiant
system:
1. Build the Windows® PE folder structure as described in "Microsoft Windows Preinstallation
Environment (on page 5)."
2. Store the command batch file on RIS or on other servers on network. In the following example, the
customized command batch file is located on \\fileserver\share.
factory -winpe
net use f: \\fileserver\share
f:\startdeploy.cmd
For more information about using a batch file, refer to "Unattended configuration using startnet.cmd
(on page 8)."
3. Use the edited STARTDEPLOY.CMD file to begin the deployment process. Be sure that the
STARTDEPLOY.CMD script is located in the directory that will be used to create the Windows® PE
ISO image. If STARTDEPLOY.CMD is used to create a connection to a network resource, the file must
exist on the CD.
To use the Windows® PE image with RIS, refer to the Windows® PE tools documentation.
Network-based Windows PE deployment
This section assumes that the scripts, data files, and utilities are stored on a file server. Windows® PE runs
startnet.cmd at the end of the boot process and launches the customized command batch file
automatically.
To build a Windows® PE image to automatically configure an HP ProLiant system through a network:
1. Build the Windows® PE folder structure as described in "Microsoft Windows Preinstallation
Environment (on page 5)."
2. Modify WinPE_Directory\Platform\system32\startnet.cmd to include the following:
factory -winpe
net use f: \\fileserver\share
f:\startdeploy.cmd
For more information about using a batch file, refer to "Unattended configuration using startnet.cmd
(on page 8)."
3. Use the edited STARTDEPLOY.CMD file to begin the deployment process. Be sure that the
STARTDEPLOY.CMD script is located in the directory that will be used to create the Windows® PE
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 17
Page 18

ISO image. If STARTDEPLOY.CMD is used to create a connection to a network resource, the file must
exist on the CD.
4. Build an ISO image using the Windows® PE folder.
5. Create a Windows® PE CD using the ISO image.
Configuring HP ProLiant systems with Windows PE 18
Page 19

Technical support
In this section
Reference documentation ........................................................................................................................ 19
Toolkit support ....................................................................................................................................... 19
HP contact information............................................................................................................................ 19
Reference documentation
For issues or problems not addressed by this guide, refer to the following resources for more information:
• The SmartStart Scripting Toolkit website (http://www.hp.com/servers/sstoolkit)
• The Microsoft® website (http://www.microsoft.com)
Toolkit support
E-mail support for the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit is available from the HP support website
(http://atwnt947.external.hp.com/fd2/email_form.cfm?countrycode=US&langcode=en&sni=437764&la
ng=en&cc=us).
HP contact information
For the name of the nearest HP authorized reseller:
• In the United States, refer to the HP US service locator webpage
(http://www.hp.com/service_locator
• In other locations, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
For HP technical support:
• In North America:
• Call 1-800-HP-INVENT (1-800-474-6836). This service is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a
week. For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
• If you have purchased a Care Pack (service upgrade), call 1-800-633-3600. For more
information about Care Packs, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com
• Outside North America, call the nearest HP Technical Support Phone Center. For telephone numbers
for worldwide Technical Support Centers, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com
).
).
).
Technical support 19
Page 20

Acronyms and abbreviations
ADO
ActiveX Data Objects
API
application program interface
EA
Enterprise Agreement
HTA
HTML applications
iLO
Integrated Lights-Out
MBR
master boot record
OEM
original equipment manufacturer
PnP
plug and play
PXE
Preboot Execution Environment
RILOE II
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition II
RIS
Remote Installation Services
SAM
Software Assurance Membership
Acronyms and abbreviations 20
Page 21

WDM
Windows Driver Module
WMI
Windows Management Instrumentation
WSH
Windows Script Host
Acronyms and abbreviations 21
Page 22

Index
A
additional information 19
authorized reseller 19
B
base image 5
batch file 8
booting Windows PE from a USB drive key 7
build process 5
building a Windows PE base image 5
C
capturing data files over a network 10
capturing data files using physical media 10
capturing data files, overview 9
caution, data loss 4
CD-based deployment 16
customizing Windows PE with a script file 6
D
data file 9
data loss 4
deployment methods 8
O
overview, capturing data files 9
overview, unattended configuration 8
overview, Win32 Toolkit 4
overview, Win32 Toolkit environment 5
overview, Windows PE build process 5
P
PXE-based deployment 17
R
references 19
Remote Installation Services (RIS) 17
requirements, minimum 4
S
startnet.cmd 8
support 19
T
technical support 19
telephone numbers 19
E
e-mail 19
environment variables 6
I
image, Windows PE 5
M
minimum requirements 4
N
network-based deployment 17
U
unattended configuration, overview 8
W
Win32 Toolkit environment, overview 5
Win32 Toolkit overview 4
Index 22
 Loading...
Loading...