Page 1

Release Notes: Version M.10.72 Software
for the HP ProCurve Series 3400cl Switches
"M” software versions are supported on these switches:
ProCurve Switch M.08.51 through
M.08.95
ProCurve Switch 3400cl-24G (J4905A)
ProCurve Switch 3400cl-48G (J4906A)
ProCurve Switch 6400cl-6XG 10-GbE CX4(J8433A)
ProCurve Switch 6410cl-6XG 10-GbE X2(J8474A)
✔
✔
✔
✔
M.08.99.x
and newer
✔
✔
M.08.96, M.08.97,
M.10.01
and newer
✔
✔
Release M.10.41 supports the ProCurve Switch 3400cl-24G (J4905A), and 3400cl-48G (J4906A).
These release notes include information on the following:
■ Downloading switch software and documentation from the Web (page 1)
■ Clarification of operating details for certain software features (page 20)
■ A listing of software enhancements in recent releases (page 25)
■ A listing of software fixes included in releases M.08.51 through M.10.72 (page 145)
IMPORTANT:
3400cl switches MUST be running ROM version I.08.12 prior to loading M.10.20 or newer software. If your
switch is using a software version earlier than M.10.10, you need to install and boot the M.10.10 software
(included in the M.10.41 software package) to load the I.08.12 ROM version, before installing M.10.20 or
newer.
Security Note:
Downloading and booting software release M.08.89 or greater for the first time automatically enables
SNMP access to the hpSwitchAuth MIB objects. If this is not desirable for your network, ProCurve
recommends that you disable it after downloading and rebooting with the latest switch software. For more
information, refer to “Enforcing Switch Security” on page 10 and “Using SNMP To View and Configure
Switch Authentication Features” on page 35.
Configuration Compatibility Caution:
Configuration files created or saved using version M.10.65 or higher are NOT backward-compatible with
previous software versions. The user is advised to save a copy of the pre-M.10.65 startup-config file
BEFORE UPDATING to M.10.68 or greater, in case there is ever a need to revert back to an earlier version
of software.
i
Page 2

© Copyright 2004 - 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development
Company, LP. The information contained herein is subject
to change without notice.
Publication Number
5991-4764
May, 2009
Applicable Product
ProCurve Switch 3400cl-24G (J4905A)
ProCurve Switch 3400cl-48G (J4906A)
Trademark Credits
Microsoft®, Windows®, and Windows NT® are US
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems
Incorporated. Java™ is a US trademark of Sun
Microsystems, Inc.
Software Credits
SSH on ProCurve Switches is based on the OpenSSH software toolkit. This product includes software developed by
the OpenSSH Project for use in the OpenSSH Toolkit. For
more information on OpenSSH, visit
Disclaimer
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not
be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or
reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished
by Hewlett-Packard.
Warranty
See the Customer Support/Warranty booklet included with
the product.
A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your
Hewlett-Packard products and replacement parts can be
obtained from your HP Sales and Service Office or
authorized dealer.
http:// www.openssh.com
SSL on ProCurve Switches is based on the OpenSSL software toolkit. This product includes software developed by
the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit. For
more information on OpenSSL, visit
http://www.openssl.org.
This product includes cryptographic software written by
Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). This product includes
software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com)
.
Hewlett-Packard Company
8000 Foothills Boulevard, m/s 5551
Roseville, California 95747-5551
www.procurve.com
Page 3

Contents
Software Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Software Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Download Switch Documentation and Software from the Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
View or Download the Software Manual Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Downloading Software to the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Downloading Software to the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
TFTP Download from a Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Xmodem Download From a PC or Unix Workstation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Saving Configurations While Using the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Install Recommendations for I.08.12 Boot ROM Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
ProCurve Switch, Routing Switch, and Router Software Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Minimum Software Versions for Series 3400cl Switch Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
OS/Web/Java Compatibility Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Enforcing Switch Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Switch Management Access Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Default Settings Affecting Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Local Manager Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Inbound Telnet Access and Web Browser Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Secure File Transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
SNMP Access (Simple Network Management Protocol) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Physical Access to the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Other Provisions for Management Access Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Network Access Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Access Control Lists (ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Web and MAC Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Secure Shell (SSH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Secure Socket Layer (SSLv3/TLSv1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Traffic/Security Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
802.1X Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Port Security, MAC Lockdown, MAC Lockout, and IP Lockdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Key Management System (KMS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
iii
Page 4

Connection-Rate Filtering Based On Virus-Throttling Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Identity-Driven Management (IDM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Clarifications and Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Operating Notes for Jumbo Traffic-Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Non-Genuine Mini-GBIC Detection and Protection Initiative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Publication Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
IGMP Command Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
General Switch Traffic Security Guideline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
The Management VLAN IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Interoperating with 802.1s Multiple Spanning-Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Rate-Limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Known Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Release M.10.17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Release M.08.69 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Release M.08.70 through M.08.72 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Release M.08.73 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Release M.08.74 through M.08.77 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Release M.08.78 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Using Fastboot To Reduce Boot Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Release M.08.79 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
CLI Port Rate Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Release M.08.80 through M.08.83 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Release M.08.84 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Release M.08.85 through M.08.88 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Release M.08.89 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
DNS Resolver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Using SNMP To View and Configure Switch Authentication Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
MSTP Default Path Cost Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
iv
Page 5

QoS Pass-Through Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Release M.08.94 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
DHCP Option 82: Using the Management VLAN IP Address for the Remote ID . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Releases M.08.95 through M.10.01 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Release M.08.96 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Releases M.08.97 through M.10.01 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Release M.10.02 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
RADIUS-Assigned Access Control Lists (ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
SFlow Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Release M.10.04 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Instrumentation Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
TCP/UDP Port Closure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Spanning Tree Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Release M.10.05 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Release M.10.06 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Release M.10.07 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Release M.10.08 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Release M.10.09 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Uni-Directional Link Detection (UDLD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Release M.10.10 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Spanning Tree Per-Port BPDU Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Releases M.10.11 through M.10.12 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Release M.10.13 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Releases M.10.14 through M.10.16 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Release M.10.17 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Spanning Tree BPDU Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Example of BPDU Protection Additions to Show Spanning Tree Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Release M.10.21 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Release M.10.22 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Release M.10.23 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Release M.10.24 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Release M.10.25 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
v
Page 6

Release M.10.26 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Release M.10.27 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Release M.10.28 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Release M.10.29 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Release M.10.30 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Release M.10.31 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Release M.10.32 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Scheduled Reload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Release M.10.33 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
How RADIUS-Based Authentication Affects VLAN Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
VLAN Assignment on a ProCurve Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Example of Untagged VLAN Assignment in a RADIUS-Based Authentication Session . . . . . 104
Enabling the Use of GVRP-Learned Dynamic VLANs in Authentication Sessions . . . . . . . . . . 107
Release M.10.34 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Concurrent TACAS+ and SFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Release M.10.35 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Dynamic ARP Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Release M.10.36 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Release M.10.37 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Configuring MSTP Port Connectivity Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Release M.10.38 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Send SNMP v2c Informs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Release M.10.39 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
RADIUS Server Unavailable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
ARP Age Timer Increase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Release M.10.40 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Release M.10.41 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Release M.10.42 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Release M.10.43 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Dynamic IP Lockdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Release M.10.44 through M.10.64 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
vi
Page 7

Release M.10.65 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
MSTP VLAN Configuration Enhancement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Release M.10.66 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Configure Logging via SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Release M.10.67 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Release M.10.68 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
LACP and Link Traps Global Disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Release M.10.69 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Release M.10.70 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Release M.10.71 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Release M.10.72 Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Software Fixes in Release M.08.51 - M.10.72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Release M.08.52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Release M.08.53 (Never Released) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Release M.08.54 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Release M.08.55 - Release M.08.60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Release M.08.61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Release M.08.62 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Release M.08.63 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Release M.08.64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Release M.08.65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Release M.08.66 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Release M.08.67 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Release M.08.68 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Release M.08.69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Release M.08.70 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Release M.08.71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Release M.08.72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Release M.08.73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Release M.08.74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Release M.08.75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
vii
Page 8

Release M.08.76 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Release M.08.77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Release M.08.78 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Release M.08.79 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Release M.08.80 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Release M.08.81 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Release M.08.82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Release M.08.83 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Release M.08.84 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Release M.08.85 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Release M.08.86 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Release M.08.87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Release M.08.88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Release M.08.89 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Release M.08.90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Release M.08.91 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Release M.08.92 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Release M.08.93 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Release M.08.94 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Release M.08.95 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Release M.08.96 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Release M.08.97 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Release M.10.01 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Release M.10.02 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Release M.10.03 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Release M.10.04 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Release M.10.05 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Release M.10.06 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Release M.10.07 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Release M.10.08 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Release M.10.09 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
viii
Page 9

Release M.10.10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Release M.10.11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Release M.10.12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Release M.10.13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Release M.10.14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Release M.10.15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Release M.10.16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Release M.10.17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Release M.10.18 - Release M.10.19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Release M.10.20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Release M.10.21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Release M.10.22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Release M.10.23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Release M.10.24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Release M.10.25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Release M.10.26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Release M.10.27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Release M.10.28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Release M.10.29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Release M.10.30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Release M.10.31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Release M.10.32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Release M.10.33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Release M.10.34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Release M.10.35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Release M.10.36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Release M.10.37 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Release M.10.38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Release M.10.39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Release M.10.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Release M.10.41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
ix
Page 10

Release M.10.42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Release M.10.43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Release M.10.44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Release M.10.45 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Release M.10.46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Release M.10.47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Release M.10.48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Release M.10.49 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Release M.10.50 through M.10.64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Release M.10.65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Release M.10.66 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Release M.10.67 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Release M.10.68 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Release M.10.69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Release M.10.70 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Release M.10.71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Release M.10.72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
x
Page 11

Software Management
Software Updates
Software Management
Software Updates
Check the ProCurve Networking Web site frequently for free software updates for the various
ProCurve switches you may have in your network.
Download Switch Documentation and Software from the Web
You can download software updates and the corresponding product documentation from the
ProCurve Networking Web site as described below.
View or Download the Software Manual Set
Go to: www.procurve.com/manuals
You may want to bookmark this Web page for easy access in the future.
You can also register on the My ProCurve portal to receive a set of ProCurve switch manuals on CDROM. To register and request a CD, go to www.procurve.com and click on My ProCurve Sign In. After
registering and entering the portal, click on My Manuals.
Downloading Software to the Switch
ProCurve Networking periodically provides switch software updates through the ProCurve
Networking Web site (www.procurve.com). After you acquire the new software file, you can use one
of the following methods for downloading it to the switch:
■ For a TFTP transfer from a server, do either of the following:
• Select Download OS in the Main Menu of the switch’s menu interface and use the (default)
TFTP option.
•Use the copy tftp command in the switch’s CLI (see below).
■ For an Xmodem transfer from a PC or Unix workstation, do either of the following:
• Select Download OS in the Main Menu of the switch’s menu interface and select the
Xmodem option.
•Use the copy xmodem command in the switch’s CLI (page 3).
■ Use the USB port to download a software file from a USB flash drive.
■ Use the download utility in ProCurve Manager Plus.
1
Page 12
Software Management
Downloading Software to the Switch
Note
Downloading new software does not change the current switch configuration. The switch configuration is contained in a separate file that can also be transferred, for example, for archive purposes
or to be used in another switch of the same model.
This section describes how to use the CLI to download software to the switch. You can also use the
menu interface for software downloads. For more information, refer to the Management and
Configuration Guide for your switch.
Downloading Software to the Switch
ProCurve Networking periodically provides switch software updates through the ProCurve
Networking Web site (www.procurve.com
of the following methods for downloading it to the switch:
■ For a TFTP transfer from a server, do either of the following:
• Click on Download OS in the Main Menu of the switch’s menu interface and use the
(default) TFTP option.
). After you acquire the new software file, you can use one
•Use the copy tftp command in the switch’s CLI (see below).
■ For an Xmodem transfer from a PC or Unix workstation, do either of the following:
• Click on Download OS in the Main Menu of the switch’s menu interface and select the
Xmodem option.
•Use the copy xmodem command in the switch’s CLI (page 3).
■ Use the download utility in ProCurve Manager Plus.
Note
Downloading new software does not change the current switch configuration. The switch configuration is contained in a separate file that can also be transferred, for example, for archive purposes
or to be used in another switch of the same model.
This section describes how to use the CLI to download software to the switch. You can also use the
menu interface for software downloads. For more information, refer to the Management and
Configuration Guide for your switch.
2
Page 13

Downloading Software to the Switch
Software Management
TFTP Download from a Server
Syntax: copy tftp flash <ip-address> <remote-os-file> [ < primary | secondary > ]
Note that if you do not specify the flash destination, the TFTP download defaults to the primary flash.
For example, to download a software file named M_08_8x.swi from a TFTP server with the IP address
of 10.28.227.103:
1. Execute the copy command as shown below:
ProCurve switch # copy tftp flash 10.28.227.103 M_08_8x.swi
The primary OS image will be deleted. continue [y/n]? Y
03125K
2. When the switch finishes downloading the software file from the server, it displays the progress
message shown in Figure 1. When the CLI prompt re-appears, the switch is ready to reboot to
activate the downloaded software:
When this message appears, the switch has finished
downloading the software file from the server.
When the CLI prompt appears, the switch is ready for
rebooting to activate the downloaded software.
ProCurve switch #
Figure 1. Message Indicating the Switch Is Ready To Activate the Downloaded Software
3. Reboot the switch.
After the switch reboots, it displays the CLI or Main Menu, depending on the Logon Default setting
last configured in the menu’s Switch Setup screen.
Xmodem Download From a PC or Unix Workstation
This procedure assumes that:
■ The switch is connected via the Console RS-232 port to a PC operating as a terminal. (Refer
to the Installation and Getting Started Guide you received with the switch for information
on connecting a PC as a terminal and running the switch console interface.)
■ The switch software is stored on a disk drive in the PC.
3
Page 14
Software Management
Downloading Software to the Switch
■ The terminal emulator you are using includes the Xmodem binary transfer feature. (For
example, in the HyperTerminal application included with Windows NT, you would use the
Send File option in the Transfer dropdown menu.)
Using Xmodem and a terminal emulator, you can download a switch software file to either primary
or secondary flash using the CLI.
Syntax: copy xmodem flash [< primary | secondary >]
1. To reduce the download time, you may want to increase the baud rate in your terminal emulator
and in the switch to a value such as 115200 bits per second. (The baud rate must be the same
in both devices.) For example, to change the baud rate in the switch to 115200, execute this
command:
ProCurve (config)# console baud-rate 115200
(If you use this option, be sure to set your terminal emulator to the same baud rate.)
Changing the console baud-rate requires saving to the Startup Config with the "write memory"
command. Alternatively, you can logout of the switch and change your terminal emulator speed
and allow the switch to AutoDetect your new higher baud rate (i.e. 115200 bps)
2. Execute the following command in the CLI:
ProCurve # copy xmodem flash primary
The primary OS image will be deleted. continue [y/n]? Y
Press ‘Enter’ and start XMODEM on your host...
3. Execute the terminal emulator commands to begin the Xmodem transfer. For example, using
HyperTerminal:
a. Click on Transfer, then Send File.
b. Type the file path and name in the Filename field.
c. In the Protocol field, select Xmodem.
d. Click on the
Send button.
The download can take several minutes, depending on the baud rate used in the transfer.
4. If you increased the baud rate on the switch (step 1), use the same command to return it to its
previous setting. (HP recommends a baud rate of 9600 bits per second for most applications.)
Remember to return your terminal emulator to the same baud rate as the switch.)
5. Reboot the switch.
After the switch reboots, it displays the CLI or Main Menu, depending on the Logon Default setting
last configured in the menu’s Switch Setup screen.
4
Page 15
Saving Configurations While Using the CLI
Software Management
Saving Configurations While Using the CLI
The switch operates with two configuration files:
■ Running-Config File: Exists in volatile memory and controls switch operation. Rebooting
the switch erases the current running-config file and replaces it with an exact copy of the
current startup-config file. To save a configuration change, you must save the running
configuration to the startup-config file.
■ Startup-Config File: Exists in flash (non-volatile) memory and preserves the most recently-
saved configuration as the “permanent” configuration. When the switch reboots for any
reason, an exact copy of the current startup-config file becomes the new running-config file
in volatile memory.
When you use the CLI to make a configuration change, the switch places the change in the runningconfig file. If you want to preserve the change across reboots, you must save the change to the startupconfig file. Otherwise, the next time the switch reboots, the change will be lost. There are two ways
to save configuration changes while using the CLI:
■ Execute write memory from the Manager, Global, or Context configuration level.
■ When exiting from the CLI to the Main Menu, press [Y] (for Yes) when you see the “save
configuration” prompt:
Do you want to save current configuration [y/n] ?
5
Page 16
Software Management
Install Recommendations for I.08.12 Boot ROM Update
Install Recommendations for I.08.12 Boot ROM Update
When installing the M.10.17 software to load the I.08.12 ROM version, ProCurve recommends that
you use the “fastboot” feature and the “reload” command after updating to M.10.17, as shown below.
ProCurve3400cl#config
ProCurve3400cl(config)# fastboot
ProCurve3400cl(config)# copy tftp flash <ip address of tftp server> M_10_17.swi
The Primary OS Image will be deleted, continue [y/n]? y Validating and Writing System
Software to FLASH...
ProCurve3400cl(config)# reload
Device will be rebooted, do you want to continue [y/n]? y
Rebooting the System
Then reconnect and run the show flash command:
ProCurve3400cl# show flas
Image Size(Bytes) Date Version
----- ---------- -------- ------Primary Image : 3576793 09/26/06 M.10.17
Secondary Image : 3506627 05/26/06 M.10.07
Boot Rom Version: I.08.12
Current Boot : Primary
Please also refer to “Known Issues” on page 24 for additional information regarding updating to the
M.10.20 software release.
6
Page 17

ProCurve Switch, Routing Switch, and Router Software Keys
Software Management
ProCurve Switch, Routing Switch, and Router Software Keys
Software
Letter
CY Switch 8100fl Series (8108fl and 8116fl)
ProCurve Networking Products
C 1600M, 2400M, 2424M, 4000M, and 8000M
E Switch 5300xl Series (5304xl, 5308xl, 5348xl, and 5372xl)
F Switch 2500 Series (2512 and 2524), Switch 2312, and Switch 2324
G Switch 4100gl Series (4104gl, 4108gl, and 4148gl)
H Switch 2600 Series, Switch 2600-PWR Series: H.07.81 and earlier, or H.08.55 and greater,
Switch 2600-8-PWR requires H.08.80 or greater.
Switch 6108: H.07.xx and earlier
I Switch 2800 Series (2824 and 2848)
J Secure Router 7000dl Series (7102dl and 7203dl)
K Switch 3500yl Series (3500yl-24G-PWR and 3500yl-48G-PWR), Switch 6200yl-24G, 5400zl Series (5406zl,
5406zl-48G, 5412zl, 5412zl-96G), Switch 8212zl and Switch 6600 Series (6600-24G, 6600-24G-4XG, 660024XG).
L Switch 4200vl Series (4204vl, 4208vl, 4202vl-72, and 4202vl-48G)
M Switch 3400cl Series (3400-24G and 3400-48G): M.08.51 though M.08.97, or M.10.01 and greater;
Series 6400cl (6400cl-6XG CX4, and 6410cl-6XG X2 ): M.08.51 though M.08.95, or M.08.99 to M.08.100 and
greater.
N Switch 2810 Series (2810-24G and 2810-48G)
PA/PB Switch 1800 Series (Switch 1800-8G – PA.xx; Switch 1800-24G – PB.xx)
Q Switch 2510 Series (2510-24)
R Switch 2610 Series (2610-24, 2610-24/12PWR, 2610-24-PWR, 2610-48 and 2610-48-PWR)
T Switch 2900 Series (2900-24G and 2900-48G)
U Switch 2510-48
W Switch 2910al Series (2910al-24G, 2910al-24G-PoE+, 2910al-48G, and 2910al-48G-PoE+)
VA/VB Switch 1700 Series (Switch 1700-8 - VA and 1700-24 - VB)
WA ProCurve Access Point 530
WS ProCurve Wireless Edge Services xl Module and the ProCurve Redundant Wireless Services xl Module
WT ProCurve Wireless Edge Services zl Module and the ProCurve Redundant Wireless Services zl Module
Y Switch 2510G Series (2510G-24 and 2510G-48)
7
Page 18

Software Management
ProCurve Switch, Routing Switch, and Router Software Keys
Software
Letter
numeric Switch 9408sl, Switch 9300 Series (9304M, 9308M, and 9315M), Switch 6208M-SX and Switch 6308M-SX
ProCurve Networking Products
(Uses software version number only; no alphabetic prefix. For example 07.6.04.)
8
Page 19
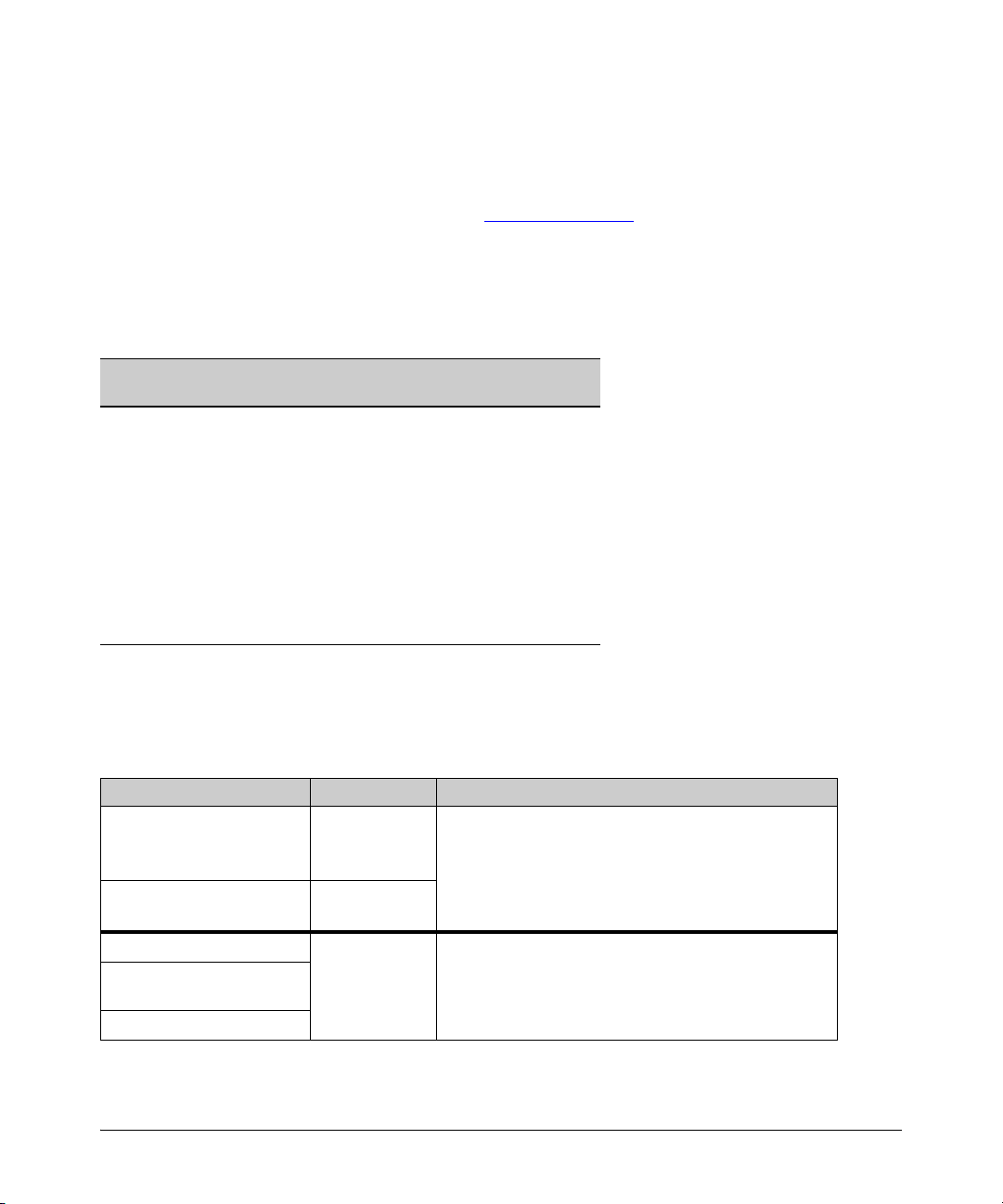
Minimum Software Versions for Series 3400cl Switch Features
Software Management
Minimum Software Versions for Series 3400cl Switch Features
For Software Features. To view a tabular listing of major switch software features and the
minimum software version each feature requires:
1. Visit the ProCurve Networking Web site at w
ww.procurve.com.
2. Click on Software updates.
3. Click on Minimum Software Version Required by Feature.
For Switch 3400cl Hardware Accessories.
ProCurve Device Minimum Supported
J8434A ProCurve 10-GbE Copper Module M.08.54
J8435A ProCurve 10-GbE Media Flex Module M.08.54
J8436A ProCurve 10-GbE X2-SC SR Optic M.08.51
J8437A ProCurve 10-GbE X2-SC LR Optic M.08.54
J8438A ProCurve 10 GbE X2-SC ER Optic M.08.75
J8439A ProCurve 10-GbE CX4 Media Converter M.08.54
J8440A ProCurve 10-GbE X2-CX4 Transceiver M.08.54
J8440B ProCurve 10-GbE X2-CX4 Transceiver M.10.06
Software Version
OS/Web/Java Compatibility Table
The switch Web agent supports the following combinations of OS browsers and Java Virtual
Machines:
Operating System Internet Explorer Java
Windows NT 4.0 SP6a 5.00, 5.01
5.01, SP1
6.0, SP1
Windows 2000 Pro SP4 5.05, SP2
Sun Java 2 Runtime Environment:
– Version 1.3.1.12
– Version 1.4.2.05
6.0, SP1
Windows XP Pro SP2 6.0, SP2
Windows Server SE 2003
and 7.0
Sun Java 2 Runtime Environment:
– Version 1.5.0_11, Version 1.6.0
SP2
Windows Vista
9
Page 20

Enforcing Switch Security
Switch Management Access Security
Enforcing Switch Security
ProCurve switches are designed as “plug and play” devices, allowing quick and easy installation in
your network. However, when preparing the switch for network operation, ProCurve strongly
recommends that you enforce a security policy to help ensure that the ease in getting started is not
used by unauthorized persons as an opportunity for access and possible malicious actions. Since
security incidents can originate with sources inside as well as outside of an organization, your switch
and network access security provisions must protect against internal and external threats while
preserving the necessary network access for authorized clients and uses.
This section provides an overview of switch management and network access security features and
applications. For information on specific features, refer to the software manuals provided for your
switch model.
Caution:
In its default configuration, the switch is open to unauthorized access of various types. ProCurve
recommends that you review this section to help ensure that you recognize the potential for
unauthorized switch and network access and are aware of the features available to help prevent
such access.
Switch Management Access Security
This section outlines provisions for protecting access to the switch’s status information configuration
settings. For more detailed information on these features, refer to the indicated manuals.
Default Settings Affecting Security
In the default configuration, switch management access is available through the following methods:
■ Telnet
■ Web-browser interface (including the ability to launch Telnet access)
■ SNMP access
■ Front-Panel access (serial port access to the console, plus resets and clearing the pass-
word(s) or current configuration)
10
Page 21

Switch Management Access Security
Enforcing Switch Security
It is important to evaluate the level of management access vulnerability existing in your network and
take steps to ensure that all reasonable security precautions are in place. This includes both
configurable security options and physical access to the switch hardware.
Local Manager Password
In the default configuration, there is no password protection. Configuring a local Manager password
is a fundamental step in reducing the possibility of unauthorized access through the switch’s web
browser and console (CLI and Menu) interfaces. The Manager password can easily be set using the
CLI password manager command, the Menu interface Console Passwords option, or the password
options under the Security tab in the web browser interface.
Inbound Telnet Access and Web Browser Access
The default remote management protocols enabled on the switch are plain text protocols, which
transfer passwords in open or plain text that is easily captured. To reduce the chances of unauthorized
users capturing your passwords, secure and encrypted protocols such as SSH and SSL must be used
for remote access. This enables you to employ increased access security while still retaining remote
client access.
■ SSHv2 provides Telnet-like connections through encrypted and authenticated transactions
■ SSLv3/TLSv1 provides remote web browser access to the switch via encrypted paths
between the switch and management station clients capable of SSL/TLS operation.
(For information on SSH and SSL/TLS, refer to the chapters on these topics in the Advanced Traffic
Management Guide for your switch.)
Also, access security on the switch is incomplete without disabling Telnet and the standard web
browser access.Among the methods for blocking unauthorized access attempts using Telnet or the
Web browser are the following two commands:
■ no telnet-server: This CLI command blocks inbound Telnet access.
■ no web-management: This CLI command prevents use of the web browser interface
through http (port 80) server access.
If you choose not to disable Telnet and web browser access, you may want to consider using RADIUS
accounting to maintain a record of password-protected access to the switch. Refer to the chapter
titled “RADIUS Authentication and Accounting” in the Access Security Guide for your switch.
Secure File Transfers
Secure Copy and SFTP provide a secure alternative to TFTP and auto-TFTP for transferring sensitive
information such as configuration files and log information between the switch and other devices.
For more on these features, refer to the section titled “Using Secure Copy and SFTP” in the “File
Transfers” appendix of the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch.
11
Page 22

Enforcing Switch Security
Switch Management Access Security
SNMP Access (Simple Network Management Protocol)
In the default configuration, the switch is open to access by management stations running SNMP
management applications capable of viewing and changing the settings and status data in the switch’s
MIB (Management Information Base). Thus, controlling SNMP access to the switch and preventing
unauthorized SNMP access should be a key element of your network security strategy.
General SNMP Access to the Switch. The switch supports SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3, including
SNMP community and trap configuration. The default configuration supports versions 1 and 2c
compatibility, which uses plain text and does not provide security options. ProCurve recommends
that you enable SNMP version 3 for improved security. SNMPv3 includes the ability to configure
restricted access and to block all non-version 3 messages (which blocks version 1 and 2c unprotected
operation). SNMPv3 security options include:
• configuring device communities as a means for excluding management access by
unauthorized stations
• configuring for access authentication and privacy
• reporting events to the switch CLI and to SNMP trap receivers
• restricting non-SNMPv3 agents to either read-only access or no access
• co-existing with SNMPv1 and v2c if necessary
For more on SNMPV3, refer to the next subsection and to the chapter titled “Configuring for Network
Management Applications” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch.
SNMP Access to the Switch’s Authentication Configuration MIB . A management station
running an SNMP networked device management application such as ProCurve Manager Plus
(PCM+) or HP OpenView can access the switch’s management information base (MIB) for read access
to the switch’s status and read/write access to the switch’s configuration. In earlier software versions,
SNMP access to the switch’s authentication configuration (hpSwitchAuth) MIB was not allowed.
However, beginning with software release M.08.89, the switch’s default configuration allows SNMP
access to security settings in hpSwitchAuth. If SNMP access to the hpSwitchAuth MIB is considered
a security risk in your network, then you should implement the following security precautions when
downloading and booting from software release M.08.89 or greater:
1. If SNMP access to the authentication configuration (hpSwitchAuth) MIB described above and
in the section titled “Using SNMP To View and Configure Switch Authentication Features” (page
35) is not desirable for your network, then immediately after downloading and booting from
the M.08.89 or greater software for the first time, use the following command to disable this
feature:
snmp-server mib hpswitchauthmib excluded
12
Page 23

Switch Management Access Security
Enforcing Switch Security
Caution:
Downloading and booting from the M.08.89 or greater software version for the first time enables
SNMP access to the authentication configuration MIB (the default action). If SNMPv3 and other
security safeguards are not in place, the switch’s authentication configuration MIB is exposed to
unprotected SNMP access and you should use the above command to disable this access.
2. If you choose to leave the authentication configuration MIB accessible, then you should do the
following to help ensure that unauthorized workstations cannot use SNMP tools to access the
MIB:
• Configure SNMP version 3 management and access security on the switch.
• Disable SNMP version 2c on the switch.
Refer to “Using SNMP Tools To Manage the Switch” in the chapter titled “Configuring for Network
Management Applications” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch. .
Physical Access to the Switch
Physical access to the switch allows the following:
■ use of the console serial port (CLI and Menu interface) for viewing and changing the current
configuration and for reading status, statistics, and log messages.
■ use of the switch’s Clear and Reset buttons for these actions:
• clearing (removing) local password protection
• rebooting the switch
• restoring the switch to the factory default configuration (and erasing any nondefault
configuration settings)
Keeping the switch in a locked wiring closet or other secure space helps to prevent unauthorized
physical access. As additional precautions, you can do the following:
■ Disable or re-enable the password-clearing function of the Clear button.
■ Configure the Clear button to reboot the switch after clearing any local usernames and
passwords.
■ Modify the operation of the Reset+Clear button combination so that the switch reboots, but
does not restore the switch’s factory default settings.
■ Disable or re-enable password recovery.
13
Page 24

Enforcing Switch Security
Switch Management Access Security
For the commands to implement the above actions, refer to “Front-Panel Security” in the chapter
titled “Configuring Usernames and Passwords” in the Access Security Guide for your switch.
Other Provisions for Management Access Security
Authorized IP Managers. This feature uses IP addresses and masks to determine whether to allow
management access to the switch through the network, and covers access through the following:
■ Telnet and other terminal emulation applications
■ The switch’s web browser interface
■ SNMP (with a correct community name)
Refer to the chapter titled “Using Authorized IP Managers” in the Access Security Guide for your
switch.
Secure Management VLAN. This feature creates an isolated network for managing the ProCurve
switches that offer this feature. When a secure management VLAN is enabled, CLI, Menu interface,
and web browser interface access is restricted to ports configured as members of the VLAN.
Refer to the chapter titled “Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide
for your switch.
RADIUS Authentication. For each authorized client, RADIUS can be used to authenticate operator
or manager access privileges on the switch via the serial port (CLI and Menu interface), Telnet, SSH,
and Secure FTP/Secure Copy (SFTP/SCP) access methods.
Refer to the chapter titled “RADIUS Authentication and Accounting” in the Access Security Guide
for your switch.
TACACS+ Authentication. This application uses a central server to allow or deny access to
TACACS-aware devices in your network. TACACS+ uses username/password sets with associated
privilege levels to grant or deny access through either the switch’s serial (console) port or remotely,
with Telnet. If the switch fails to connect to a TACACS+ server for the necessary authentication
service, it defaults to its own locally configured passwords for authentication control. TACACS+
allows both login (read-only) and enable (read/write) privilege level access.
Refer to the chapter titled “TACACS+ Authentication” in the Access Security Guide for your switch
model.
Access Control Lists (ACLs) for Management Access Protection. ACLs can be used to secure
access to the management interface of the switch by blocking inbound IP traffic that has the switch
itself as the destination address. (Refer also to “Access Control Lists” in the next section.)
14
Page 25
Enforcing Switch Security
Network Access Security
Network Access Security
This section outlines provisions for protecting access through the switch to the network. For more
detailed information on these features, refer to the indicated manuals.
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
ACLs enable the switch to permit or deny the following:
■ any inbound IP traffic on a port
■ specific types of TCP or UDP traffic
While ACLs do not provide user or device authentication, or protection from malicious manipulation
of data in IP packet transmissions, ACLs can enhance network security by blocking selected IP traffic
types. This functionality can be utilized to:
■ permit or deny in-band management access by limiting or preventing the use of designated
TCP or UDP protocols
■ permit or deny unwanted IP traffic to or from specific hosts
Refer to the chapter titled “Access Control Lists (ACLs) for the Series 3400cl and Series 6400cl
Switches” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide for your switch model.
Web and MAC Authentication
These options are designed for application on the edge of a network to provide port-based security
measures for protecting private networks and the switch itself from unauthorized access. Because
neither method requires clients to run any special supplicant software, both are suitable for legacy
systems and temporary access situations where introducing supplicant software is not an attractive
option. Both methods rely on using a RADIUS server for authentication. This simplifies access
security management by allowing you to control access from a master database in a single server. It
also means the same credentials can be used for authentication, regardless of which switch or switch
port is the current access point into the LAN. Web authentication uses a web page login to
authenticate users for access to the network. MAC authentication grants access to a secure network
by authenticating device MAC address for access to the network.
Refer to the chapter titled “Web and MAC Authentication” in the Access Security Guide for your
switch model.
15
Page 26

Enforcing Switch Security
Network Access Security
Secure Shell (SSH)
SSH provides Telnet-like functions through encrypted, authenticated transactions of the following
types:
■ client public-key authentication: uses one or more public keys (from clients) that must
be stored on the switch. Only a client with a private key that matches a stored public key
can gain access to the switch.
■ switch SSH and user password authentication: this option is a subset of the client public-
key authentication, and is used if the switch has SSH enabled without a login access
configured to authenticate the client’s key. In this case, the switch authenticates itself to
clients, and users on SSH clients then authenticate themselves to the switch by providing
passwords stored on a RADIUS or TACACS+ server, or locally on the switch.
■ secure copy (SC) and secure FTP (SFTP): By opening a secure, encrypted SSH session,
you can take advantage of SC and SFTP to provide a secure alternative to TFTP for
transferring sensitive switch information.
Refer to the chapter titled “Configuring Secure Shell (SSH)” in the Access Security Guide for your
switch model. For more on SC and SFTP, refer to the section titled “Using Secure Copy and SFTP”
in the “File Transfers” appendix of the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch model.
Secure Socket Layer (SSLv3/TLSv1)
This feature includes use of Transport Layer Security (TLSv1) to provide remote web access to the
switch via authenticated transactions and encrypted paths between the switch and management
station clients capable of SSL/TLS operation. The authenticated type includes server certificate
authentication with user password authentication.
Refer to the chapter titled “Configuring Secure Socket Layer (SSL) in the Access Security Guide for
your switch model.
Traffic/Security Filters
These statically configured filters enhance in-band security (and improve control over access to
network resources) by forwarding or dropping inbound network traffic according to the configured
criteria. Filter options and the devices that support them are listed in the following table:
16
Page 27
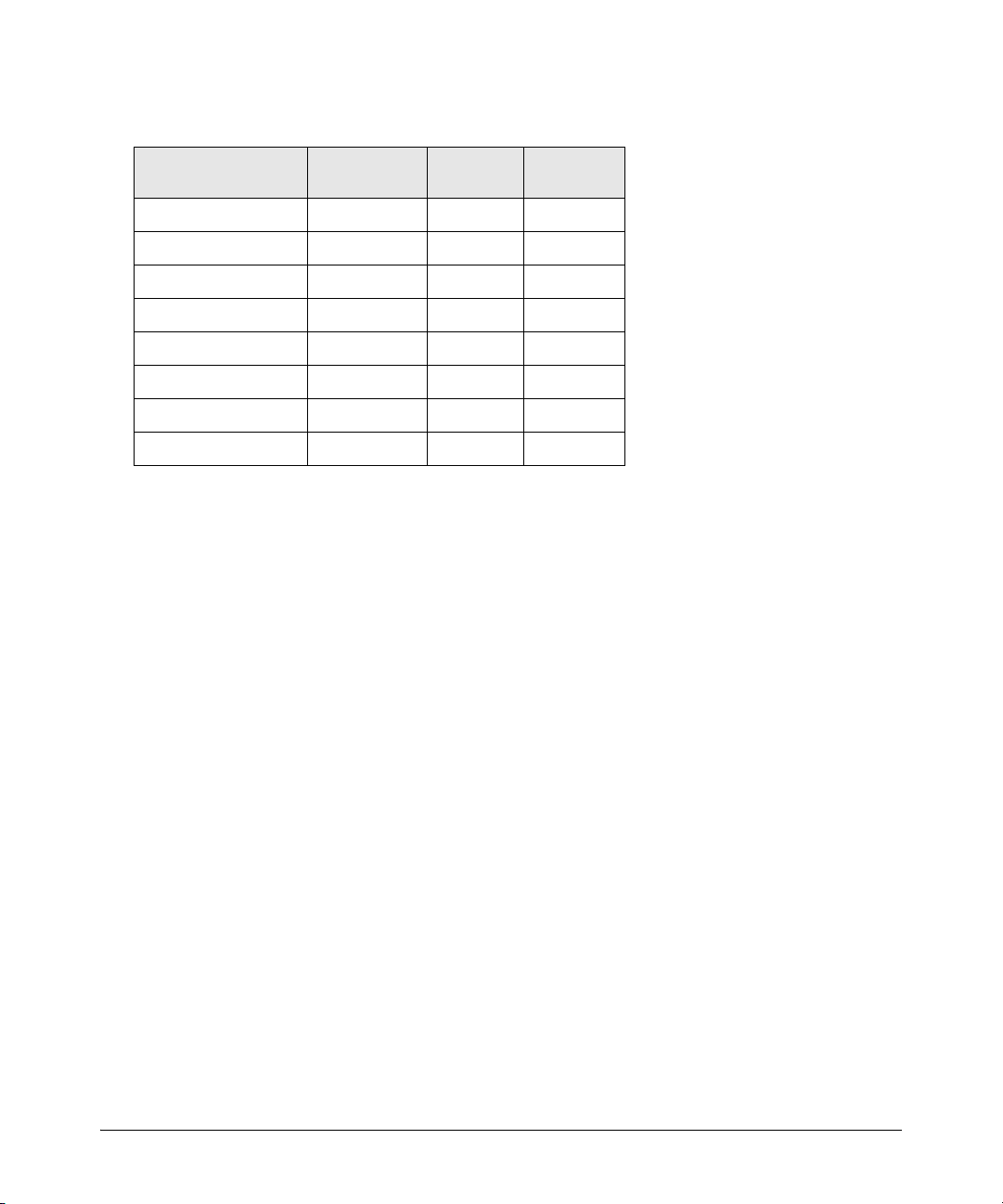
Enforcing Switch Security
Network Access Security
Switch Model Source-Port
Filters
Series 6400cl X -- --
Series 5400zl X X X
Series 5300xl X X X
Series 4200vl X -- --
Series 3500yl X X X
Series 3400cl X -- --
Series 2800 X -- --
Series 2600 X -- --
■ source-port filters: Inbound traffic from a designated, physical source-port will be
Protocol
Filters
Multicast
Filters
forwarded or dropped on a per-port (destination) basis.
■ multicast filters: Inbound traffic having a specified multicast MAC address will be
forwarded to outbound ports or dropped on a per-port (destination) basis.
■ protocol filters: Inbound traffic having the selected frame (protocol) type will be forwarded
or dropped on a per-port (destination) basis.
Refer to the chapter titled “Traffic/Security Filters” in the Access Security Guide for your switch
model.
802.1X Access Control
This feature provides port-based or client-based authentication through a RADIUS server to protect
the switch from unauthorized access and to enable the use of RADIUS-based user profiles to control
client access to network services. Included in the general features are the following:
■ client-based access control supporting up to 32 authenticated clients per-port
■ port-based access control allowing authentication by a single client to open the port
■ switch operation as a supplicant for point-to-point connections to other 802.1X-aware
switches
The following table shows the type of access control available on the various ProCurve switch
models:
17
Page 28
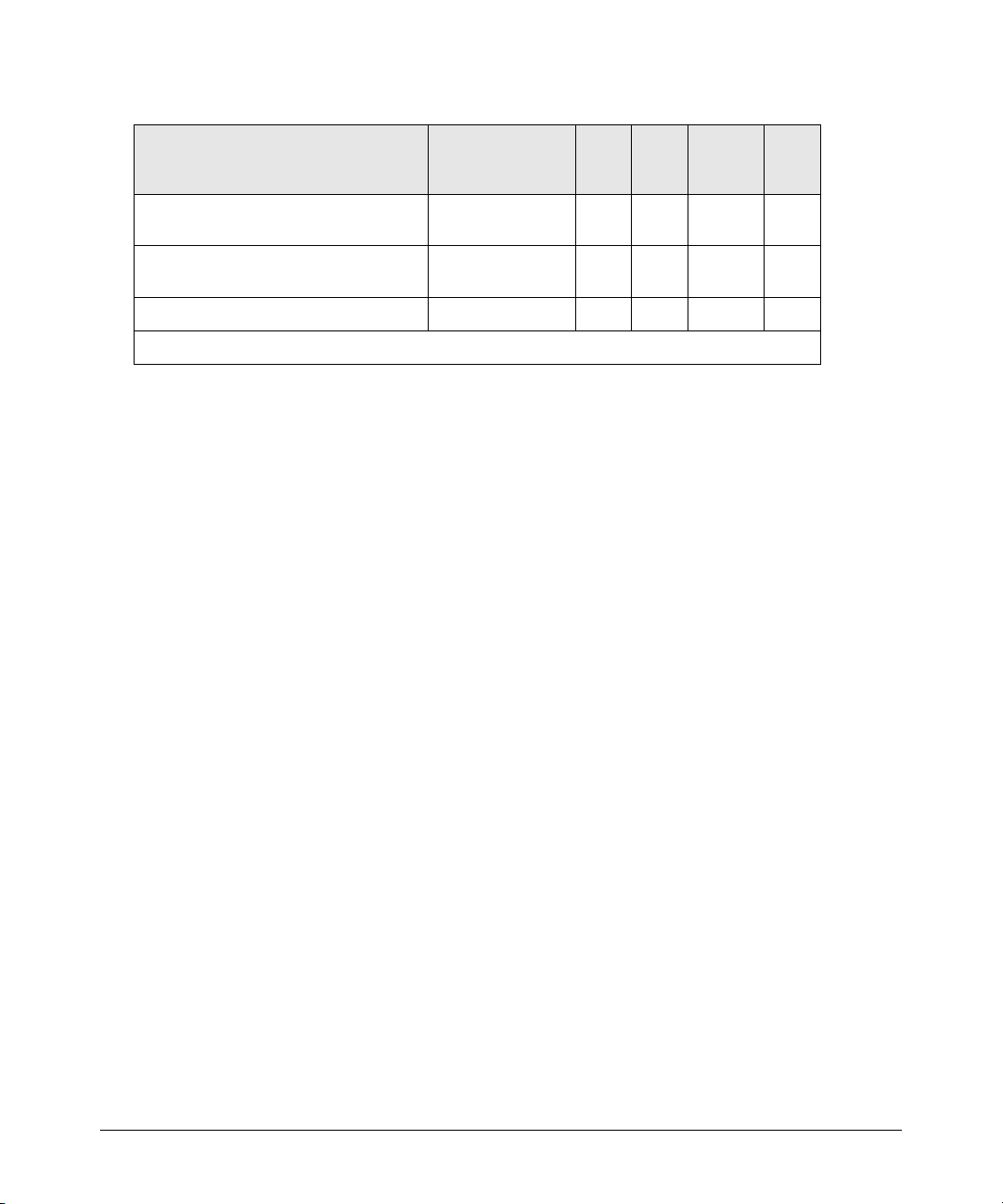
Enforcing Switch Security
Network Access Security
Access Control Types 6200yl 5400zl 3500yl 5300xl
client-based access control
(up to 32 authenticated clients per port)
port-based access control
(one authenticated client opens the port)
switch operation as a supplicant X X X X X
* On the 5300xl switches, this feature is available with software release E.09.02 and greater.
XX*------
X XXX X
4200vl
3400cl
6400cl
2800
2600
2600-pwr
4100gl
Refer to the chapter titled “Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control” in the Access
Security Guide for your switch model.
Port Security, MAC Lockdown, MAC Lockout, and IP Lockdown
These features provide device-based access security in the following ways:
■ port security: Enables configuration of each switch port with a unique list of the MAC
addresses of devices that are authorized to access the network through that port. This
enables individual ports to detect, prevent, and log attempts by unauthorized devices to
communicate through the switch. Some switch models also include eavesdrop prevention
in the port security feature.
■ MAC lockdown: This “static addressing” feature is used as an alternative to port security
for to prevent station movement and MAC address “hijacking” by allowing a given MAC
address to use only one assigned port on the switch. MAC lockdown also restricts the client
device to a specific VLAN.
■ MAC lockout: This feature enables blocking of a specific MAC address so that the switch
drops all traffic to or from the specified address.
■ IP lockdown: Available on Series 2600 and 2800 switches only, this feature enables restric-
tion of incoming traffic on a port to a specific IP address/subnet, and denies all other traffic
on that port.
Refer to the chapter titled “Configuring and Monitoring Port Security” in the Access Security Guide
for your switch model.
Key Management System (KMS)
KMS is available in several ProCurve switch models and is designed to configure and maintain key
chains for use with KMS-capable routing protocols that use time-dependent or time-independent
keys. (A key chain is a set of keys with a timing mechanism for activating and deactivating individual
18
Page 29

Enforcing Switch Security
Network Access Security
keys.) KMS provides specific instances of routing protocols with one or more Send or Accept keys
that must be active at the time of a request.
Refer to the chapter titled “Key Management System” in the Access Security Guide for your switch
model.
Connection-Rate Filtering Based On Virus-Throttling Technology
While not specifically a tool for controlling network access, this feature does help to protect the
network from attack and is recommeded for use on the network edge. It is primarily focused on the
class of worm-like malicious code that tries to replicate itself by taking advantage of weaknesses in
network applications behind unsecured ports. In this case, the malicious code tries to create a large
number of outbound IP connections on a routed interface in a short time. Connection-Rate filtering
detects hosts that are generating routed traffic that exhibits this behavior, and causes the switch to
generate warning messages and (optionally) to either throttle routed traffic from the offending hosts
or drop all traffic from the offending hosts.
Refer to the chapter titled “Virus Throttling” in the Access Security Guide for your switch model.
Identity-Driven Management (IDM)
IDM is a plug-in to ProCurve Manager Plus (PCM+) and uses RADIUS-based technologies to create
a user-centric approach to network access management and network activity tracking and monitoring. IDM enables control of access security policy from a central management server, with policy
enforcement to the network edge, and protection against both external and internal threats.
Using IDM, a system administrator can configure automatic and dynamic security to operate at the
network edge when a user connects to the network. This operation enables the network to distinguish
among different users and what each is authorized to do. Guest access can also be configured without
compromising internal security. This means that users can be identified and either approved or denied
at the edge of the network instead of in the core.
Criteria for enforcing RADIUS-based security for IDM applications includes classifiers such as:
■ authorized user identity
■ authorized device identity (MAC address)
■ software running on the device
■ physical location in the network
■ time of day
Responses can be configured to support the networking requirements, user (SNMP) community,
service needs, and access security level for a given client and device.
For more information on IDM, visit the ProCurve web site at http://www.procurve.com
and click on
Products and Solutions, then Identity Driven Management (under Network Management).
19
Page 30

Clarifications and Updates
Operating Notes for Jumbo Traffic-Handling
Clarifications and Updates
Operating Notes for Jumbo Traffic-Handling
In the Management and Configuration Guide, (Oct., 2005 version) on page 14-33 ( page 347 of the .pdf
file) where it states:
When a port is not a member of any jumbo-enabled VLAN, it drops all jumbo traffic. If the port
is receiving “excessive” inbound jumbo traffic, the port generates an Event Log message to notify
you of this condition. This same condition generates a Fault-Finder message in the Alert log of
the switch’s web browswer interface, and also increments the switch’s “Giant Rx” counter.
Note that it is the “Total Rx Errors” counter that is incremented, not the “Giant Rx” counter. On the
3400cl and 6400cl series switches, when the switch applies the jumbo MTU to a VLAN, all frames
with jumbo MTU sizes (1523 to 9220 bytes) are incremented to “Total Rx Errors”.
Non-Genuine Mini-GBIC Detection and Protection Initiative
Non-genuine ProCurve Transceivers and Mini-GBICs have been offered for sale in the marketplace.
To protect customer networks from these unsupported products, ProCurve switch software includes
the capability to detect and disable non-genuine transceivers and mini-GBICs discovered in Series
3400cl Switch ports. When a non-genuine device is discovered, the switch disables the port and
generates an error message in the Event Log.
Publication Updates
Table 1 lists updates to the manual set dated January, 2005.
Table 1. Publication Updates for Manual Set Dated January, 2005
Management and Configuration Guide
for the 3400cl, 5300xl, & 6400cl
Switches, p/n 5990-6050, January 2005
Edition
Chapter 14: “Configuring for Network
Management Applications”
Pages 14-44 and 14-49
Update
show lldp info stats is an invalid command.
The
The correct syntax is: show lldp stats.
20
Page 31

Clarifications and Updates
IGMP Command Update
IGMP Command Update
The following information updates and clarifies information in Chapter 4, “Multimedia Traffic Control
with IP Multicast (IGMP)” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide—part number 5990-6051,
September 2004 edition. Please refer to this chapter for a detailed explanation of IGMP operation.
The 3400cl switches support the following standards and RFCs:
■ RFC2236 (IGMP V.2, with backwards support for IGMP V.1)
■ Interoperability with RFC3376 (IGMPv3)
■ IETF draft for IGMP and MLD snooping switches (for IGMP V1, V2 V3)
The 3400cl switches:
■ Provide full IGMPv2 support as well as full support for IGMPv1 Joins.
■ Forward packets for the joined group from all sources, including IGMPv3 Joins.
■ Do not support IGMPv3 “Exclude Source” or “Include Source” options in the Join Reports.
■ Can operate in IGMPv2 Querier mode on VLANs with an IP address.
IGMP is supported in the HP MIB, rather than the standard IGMP MIBs, as the latter reduce Group
Membership detail in switched environments.
Using Delayed Group Flush. This feature continues to filter IGMP groups for a specified additional
period of time after IGMP leaves have been sent. The delay in flushing the group filter prevents
unregistered traffic from being forwarded by the server during the delay period. In practice, this is
rarely necessary on switches such as the Series 3400cl switches, which support data-driven IGMP.
(Data-Driven IGMP, which is enabled by default, prunes off any unregistered streams detected on the
switch.)
Syntax: igmp delayed-flush < time period >
Where leaves have been sent for IGMP groups, enables the switch to continue
to flush the groups for a specified period of time (0 - 255 seconds). This
command is applied globally to all IGMP-configured VLANs on the switch.
A setting of 0 (zero) disables the feature. (Default: Disabled.)
Syntax: show igmp delayed-flush
Displays the current setting for the switch.
21
Page 32

Clarifications and Updates
General Switch Traffic Security Guideline
Setting Fast-Leave and Forced Fast-Leave from the CLI. In earlier switch models, including
the 5300xl switches, fast-leave and forced fast-leave options for a port were configured with a lengthy
setmib command.
The following commands now allow a port to be configured for fast-leave or forced
fast-leave operation with a conventional CLI command instead of the setmib command. Note that
these commands must be executed in a VLAN context.
Syntax: [no] ip igmp fastleave < port-list >
Enables IGMP fast-leaves on the specified ports in the selected VLAN. In the
Config context, use the VLAN specifier, for example, vlan < vid > ip igmp
fastleave < port-list >. The no form of the command disables IGMP fast-leave.
(Default: Enabled)
[no] ip igmp forcedfastleave < port-list >
Forces IGMP Fast-Leaves on the specified ports in the selected VLAN, even
if they are cascaded. (Default: Disabled)
To view a non-default IGMP forced fast-leave configuration on a VLAN, use the show running-config
command. (The show running-config output does not include forced fast-leave if it is set to the default
of 0.)
Note
In a future version of the 3400cl switch software, the show running-config command output will include
any non-default fast-leave settings configured. However, this information is not included in the output
for the M.08.53 software release.
IGMP Operating Notes.
■ On the Series 3400cl switches, the delayed group flush feature offers little additional benefit
over the IGMP data-driven feature (which is enabled by default).
■ Forced fast-leave can be used when there are multiple devices attached to a port.
General Switch Traffic Security Guideline
Where the switch is running multiple security options, it implements network traffic security based
on the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection model) precedence of the individual options, from the
lowest to the highest. The following list shows the order in which the switch implements configured
security features on traffic moving through a given port.
1. Disabled/Enabled physical port
2. MAC lockout (Applies to all ports on the switch.)
3. MAC lockdown
22
Page 33

The Management VLAN IP Address
4. Port security
5. Authorized IP Managers
6. Application features at higher levels in the OSI model, such as SSH.
(The above list does not address the mutually exclusive relationship that exists among some security
features.)
Clarifications and Updates
The Management VLAN IP Address
The optional Management VLAN, if used, must be configured with a manual IP address. It does not
operate with DHCP/Bootp configured for the IP address.
Interoperating with 802.1s Multiple Spanning-Tree
The ProCurve implementation of Multiple Spanning-Tree (MSTP) complies with the IEEE 802.1s
standard and interoperates with other devices running compliant versions of 802.1s. Note that the
ProCurve Series 9300 routing switches do not offer 802.1s-compliant MSTP. Thus, to support a
connection between a 9300 routing switch and a 3400cl switch running MSTP, configure the 9300
with either 802.1D (STP) or 802.1w (RSTP). For more information on this topic, refer to the chapter
titled “Spanning-Tree Operation” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide for your 3400cl switch.
Rate-Limiting
The configured rate limit on a port reflects the permitted forwarding rate from the port to the switch
fabric, and is visible as the average rate of the outbound traffic originating from the rate-limited port.
(The most accurate rate-limiting is achieved when using standard 64-byte packet sizes.) Also, ratelimiting reflects the available percentage of a port’s entire inbound bandwidth. The rate of inbound
flow for traffic of a given priority and the rate of flow from a rate-limited port to a particular queue
of an outbound port are not measures of the actual rate limit enforced on a port. Also, rate-limiting
is byte-based and is applied to the available bandwidth on a port, and not to any specific applications
running through the port. If the total bandwidth requested by all applications together is less than
the available, configured maximum rate, then no rate-limit can be applied. This situation occurs with
a number of popular throughput-testing software applications, as well as most regular network
applications.
As a performance consideration, implementing rate-limiting in heavy traffic situations involving QoS,
can affect overall performance. For more information on rate-limiting operation, refer to “Operating
Notes for Rate-Limiting” in the chapter titled “Port Traffic Controls ” of the Management and
Configuration Guide for your ProCurve Series 3400cl switch. (To download switch documentation,
refer to “Software Updates” on page 1.)
23
Page 34

Known Issues
Rate-Limiting
Known Issues
Release M.10.17
The following is a known issue related to installation of Release M.10.17 software, which includes a
required update to ROM version I.08.12.
When there is an active 10-GbE link in port 26 of the ProCurve 3400cl-24G switch, or port 50 of the
ProCurve 3400cl-48G switch, there may be a problem with that link initializing following a software
update into the required M.10.17 software version. For customers with a console connection to the
switch during the boot process, there may also be a false report with one or more of the following
messages:
This switch needs replacement during next scheduled downtime ? or,
Module selftest failure or,
Port [26 or 50] selftest failure. ?
Workarounds: If this is a mission-critical switch and the software is being updated remotely through
a 10-GbE link in port 26 or 50, it is recommended that you have someone onsite with the switch able
to directly communicate with the switch from another port or the console connection. The issue may
be avoided by enabling the “fastboot” feature and using the “reload” command after updating to
M.10.17 ( refer to “Install Recommendations for I.08.12 Boot ROM Update” on page 6)
If the problem persists, it may also be possible to re-initialize the link by administratively disabling
and re-enabling both the affected port and the port that is directly connected to it. If those steps fail
to resolve the problem, try disconnecting the media from the potentially affected port until after the
switch is running M.10.17. The port should then initialize.
Fix: There is a fix associated with software version M.10.20. Once the switch has been updated to
software version M.10.17, update to software version M.10.20 and reboot.
Note that M.10.10 does not have the same issue related to installation of Release M.10.17 software.
24
Page 35

Release M.08.69 Enhancements
Enhancements
Enhancements
Enhancments are listed in chronological order, oldest to newest software release. To review the list
of enhancements included since the last general release that was published, begin with “Release
M.10.21 Enhancements” on page 95.
Release M.08.69 Enhancements
Release M.08.69 included the following enhancements:
■ Support for Web RADIUS authentication with CLI.
■ A new scripting mode.
■ Source Port Filter user interface, described in Chapter 9. “Traffic/Security Filters” in the
Access Security Guide for the switch.
Information on these features is included in the current documentation for the switch, available on
the web at: http://www.hp.com/rnd/support/manuals/
.
Release M.08.70 through M.08.72 Enhancements
Software fixes only; no new enhancements.
Release M.08.73 Enhancements
Release M.08.73 included the following enhancements:
■ Support for the new I.08.07 Boot ROM version.
(The 2800/3400/6400 series switches all share the same ROM code)
Release M.08.74 through M.08.77 Enhancements
Software fixes only; no new enhancements.
25
Page 36

Enhancements
Release M.08.78 Enhancements
Release M.08.78 Enhancements
Using Fastboot To Reduce Boot Time
The fastboot command allows a boot sequence that skips the internal power-on self-tests, resulting
in a faster boot time.
Syntax: [no] fastboot
Used in the global configuration mode to enable the fastboot
option. The no version of the command disables fastboot
operation.
Syntax: show fastboot
Shows the status of the fastboot feature, either enabled or
disabled.
For example:
ProCurve(config)# show fastboot
Fast Boot: Disabled
Release M.08.79 Enhancements
CLI Port Rate Display
Beginning with release M.08.79 the CLI “show interface [port list]” command includes the port rate
in the display. The rate displayed is the average for a period of 5 minutes, given in bps for 1G ports,
or in Kbps for 10G ports. You can also use the CLI command: show interface port-utilization to display
port-rate over a period of 5 minutes.
26
Page 37

Release M.08.80 through M.08.83 Enhancements
The following shows a sample output from this new command.
ProCurve# show interface port-utilization
Enhancements
Port
Mode
|
|
-------
|
KBits/s
Rx
------Pkts/s
-----Util
------KBits/s
Tx
-----Pkts/s
-----Util
---- ---- + ------- ------- ------ ------- ------ ------
1 100FDx | 100000 525 12 100000 400 10
2 1000FDx | 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 100FDx | 536 44 00.53 504 0 00.50
4 1000FDx | 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 1000FDx | 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 1000FDx | 0 0 0 0 0 0
7 1000FDx | 0 5 0 0 0 0
8 1000FDx | 0 5 0 0 0 0
9 100FDx | 0 30 0 0 0 0
Figure 2. Example rate display output for ports
Operating Notes
■ For each port on the switch, the command provides a real-time display of the rate at which
data is received (Rx) and transmitted (Tx) in terms of kilobits per second (KBits/s), number
of packets per second (Pkts/s), and utilization (Util) expressed as a percentage of the total
bandwidth available.
■ As in previous software versions, the show interfaces <port-list> command can be used to
display the current link status and the port rate average over a 5 minute period. Port rates
are shown in bits per second (bps) for ports up to 1 Gigabit, and are shown in kilobits per
second (Kbps) for 10 Gigabit ports.
Release M.08.80 through M.08.83 Enhancements
Software fixes only; no new enhancements.
27
Page 38

Enhancements
Release M.08.84 Enhancements
Release M.08.84 Enhancements
Release M.08.84 includes the following enhancement:
Added the show tech transceivers command to allow removable transceiver serial numbers to be
read without removal of the transceivers from the switch. :
Release M.08.85 through M.08.88 Enhancements
Software fixes only; no new enhancements.
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Release M.08.89 includes the following enhancements:
• DNS Resolver for using DNS names for Ping and Traceroute
• RADIUS Configuration via SNMP (see “Using SNMP To View and Configure Switch
Authentication Features” on page 35)
DNS Resolver
The Domain Name System (DNS) resolver is designed for use in local network domains where it
enables use of a host name or fully qualified domain name to perform ping and traceroute operations
from the switch.
Ter mi no lo gy
Domain Suffix — Includes all labels to the right of the unique host name in a fully qualified domain
name assigned to an IP address. For example, in the fully qualified domain name “device53.evergreen.trees.org”, the domain suffix is “evergreen.trees.org”, while “device53” is the unique (host)
name assigned to a specific IP address.
Fully Qualified Domain Name — The sequence of labels in a domain name identifying a specific
host (host name) and the domain in which it exists. For example, if a device with an IP address
of 10.10.10.101 has a host name of device53 and resides in the evergreen.trees.org domain, then
the device’s fully qualified domain name is device53.evergreen.trees.org and the DNS resolution
of this name is 10.10.10.101.
Host Name — The unique, leftmost label in a domain name assigned to a specific IP address in a
DNS server configuration. This enables the server to distinguish a device using that IP address
from other devices in the same domain. For example, in the evergreen.trees.org domain, if an
28
Page 39

Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Enhancements
IP address of 10.10.100.27 is assigned a host name of accounts015 and another IP address of
10.10.100.33 is assigned a host name of sales021, then the switch configured with the domain
suffix evergreen.trees.org and a DNS server that resolves addresses in that domain can use the
host names to reach the devices with ping and traceroute commands:
ping accounts015
traceroute sales021
Basic Operation
■ When the switch is configured with only the IP address of a DNS server available to the
switch, then a ping or traceroute command, executed with a fully qualified domain name, can
reach a device found in any domain accessible through the configured DNS server.
■ When the switch is configured with both of the following:
• the IP address of a DNS server available to the switch
• the domain suffix of a domain available to the configured DNS server
then:
•A ping or traceroute command that includes the host name of a device in the same domain
as the configured domain suffix can reach that device.
•A ping or traceroute command that includes a fully qualified domain name can reach a
device in any domain that is available to the configured DNS server.
Example. Suppose the switch is configured with the domain suffix mygroup.procurve.net and the IP
address for an accessible DNS server. If an operator wants to use the switch to ping a host using the
DNS name “leader” assigned to an IP address used in that domain, then the operator can use either
of the following commands:
ProCurve# ping leader
10.28.229.220 is alive, time = 1 ms
ProCurve# ping leader.mygroup.procurve.net
10.28.229.220 is alive, time = 1 ms
Host Name for the Desired Host
Ping Response
Fully Qualified Domain Name for the
Desired Host
Ping Response
Figure 3. Example of Using Either a Host Name or a Fully Qualified Domain Name
In the preceeding example, if the DNS server’s IP address is configured on the switch, but a domain
suffix is not configured, then the fully qualified domain name must be used.
Note that if the target host is in a domain other than the domain configured on the switch, then:
29
Page 40

Enhancements
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
■ The host’s domain must be reachable from the switch. This requires that the DNS server for
the switch must be able to communicate with the DNS server(s) in the path to the domain
in which the target host operates.
■ The fully qualified domain name must be used, and the domain suffix must correspond to
the domain in which the target host operates, regardless of the domain suffix configured in
the switch.
Example. Suppose the switch is configured with the domain suffix mygroup.procurve.net and the IP
address for an accessible DNS server. This time, the operator wants to use the switch to trace the
route to a host named “remote-01” in another domain named common.group.net. A s l on g a s t h is do ma in
is accessible to the DNS server configured on the switch, a traceroute command using the target’s
fully qualified DNS name should succeed.
ProCurve# traceroute remote-01.common.group.net
traceroute to 10.22.240.73
Fully Qualified Host Name for
the Target Host
1 hop min, 30 hops max, 5 sec. timeout, 3 probes
1 10.28.229.3 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms
2 10.71.217.1 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms
3 10.0.198.2 1 ms 0 ms 0 ms
4 10.22.240.73 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms
IP Address for Target Host
“remote-01”
Figure 4. Example Using the Fully Qualified Domain Name for an Accessible Target in Another Domain
Configuring and Using DNS Resolution with Ping and Traceroute Commands
1. Determine the following:
a. the IP address for a DNS server operating in a domain in your network
b. the domain name for an accessible domain in which there are hosts you want to reach with
ping and/or traceroute commands. (This is the domain suffix in the fully qualified domain
name for a given host operating in the selected domain. Refer to “Terminology” on page 28.)
Note that if a domain suffix is not configured, fully qualified domain names can be used to
resolve ping and traceroute commands.
c. the host names assigned to target IP addresses in the DNS server for the specified domain
2. Use the data from steps 1a and 1b to configure the DNS entry on the switch.
3. Use either ping or traceroute with the host names for the target devices whose connectivity you
are testing or troubleshooting.
30
Page 41

Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Enhancements
Configuring a DNS Entry
The switch allows one DNS server entry, which includes the DNS server IP address and the chosen
domain name suffix. Configuring the entry enables the use of ping and traceroute with a target’s host
name instead of the target’s IP address.
Syntax: [no] ip dns server-address < ip-addr >
Configures the IP address of a DNS server accessible to the switch. This setting
identifies the server to use for DNS resolution to the target IP address, and must be
configured before ping or traceroute can be executed with host name criteria.
The switch supports one DNS server entry. Configuring another IP address for this
value replaces the current IP address with the new one.
The no form of the command replaces the configured IP address with the null setting,
which disables host name resolution. (Default: null)
Syntax: [no] ip dns domain-name < domain-name-suffix >
Configures the domain suffix that is automatically appended to the host name
entered with the ping or traceroute command. When the domain suffix and the DNS
server IP address are both configured on the switch, you can execute ping and
traceroute with only the host name of the desired target within the domain. In either
of the following two instances, you must manually provide the domain identification by using a fully qualified DNS name with each ping and traceroute command:
• If the DNS server IP address is configured on the switch, but the domain suffix
is not configured (null)
• The domain suffix configured on the switch is not the domain in which the target
host exists
The switch supports one domain suffix entry. Configuring a new entry for this value
replaces the current suffix.
The no form of the command replaces the configured domain suffix with the null
setting. (Default: null)
Example Using DNS Names with Ping and Traceroute
In the network illustrated in Figure 5, the switch at 10.28.192.1 is configured to use DNS names for
ping and traceroute in the pubs.outdoors.com domain. The DNS server has been configured to assign
the host name docservr to the IP address used by the document server (10.28.229.219).
31
Page 42

Enhancements
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Switch “A” Configured
with DNS Resolver
Domain: pubs.outdoors.com
10.28.192.1
Router “B”
10.28.192.2
10.28.229.1
DNS Server for pubs.outdoors.com
10.28.229.10
Host Name for IP address
10.28.229.219 = “docservr”
Document
Server
docservr
(10.28.229.219)
Figure 5. Example Network Domain
Configuring switch “A” with the domain name and the IP address of a DNS server for the domain
enables the switch to use host names assigned to IP addresses in the domain to perform ping and
traceroute actions on the devices in the domain. To summarize:
Entity: Identity:
DNS Server IP Address
Domain Name (and Domain Suffix for Hosts in
the Domain)
Host Name Assigned to 10.28.229.219 by the
10.28.229.10
pubs.outdoors.com
docservr
DNS Server
Fully Qualified Domain Name for the IP address
Used By the Document Server (10.28.229.219)
Switch IP Address
Document Server IP Address
docservr.pubs.outdoors.com
10.28.192.1
10.28.229.219
With the above already configured, the following commands enable ping and traceroute with the host
name docserver to reach the document server at 10.28.229.219.
ProCurve(config)# ip dns server-address 10.28.229.10
ProCurve(config)# ip dns domain-name pubs.outdoors.com
Figure 6. Configuring Switch “A” in Figure 5 To Support DNS Resolution
32
Page 43

ProCurve# ping docservr
10.28.229.219 is alive, time = 1 ms
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Enhancements
ProCurve# traceroute docservr
First-Hop Router (“B”)
traceroute to 10.28.229.219
1 hop min, 30 hops max, 5 sec. timeout, 3 probes
1 10.28.192.2 1 ms 0 ms 0 ms
2 10.28.229.219 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms
Traceroute Target
Figure 7. Example of Ping and Traceroute Execution for the Network in Figure 5 on Page 32
As mentioned under “Basic Operation” on page 29, if the DNS entry configured in the switch includes
only the DNS server’s IP address, you must use the target host’s fully qualified domain name with
ping and traceroute. For example, using the document server in Figure 5 as a target:
ProCurve# ping docservr.pubs.outdoors.com
10.28.229.219 is alive, time = 1 ms
Target’s Fully Qualified
Domain Name
ProCurve# traceroute docservr.pubs.outdoors.com
traceroute to 10.28.229.219
1 hop min, 30 hops max, 5 sec. timeout, 3 probes
1 10.28.192.2 1 ms 0 ms 0 ms
2 10.28.229.219 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms
Figure 8. Example of Ping and Traceroute Execution When Only the DNS Server IP Address Is Configured
Viewing the Current DNS Configuration
The show ip command displays the current DNS configuration along with other IP configuration
information. If the switch configuration currently includes a nondefault (non-null) DNS entry, it will
also appear in the show run command output.
33
Page 44

Enhancements
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
ProCurve# show ip
Internet (IP) Service
IP Routing : Disabled
Default Gateway : 10.28.192.2
Default TTL : 64
Arp Age : 20
Domain Suffix : pubs.outdoors.com
DNS server : 10.28.229.10
DNS Resolver Configuration in the
show ip command output
VLAN | IP Config IP Address Subnet Mask
------------ + ---------- --------------- -------------- DEFAULT_VLAN | Manual 10.28.192.1 255.255.255.0
Figure 9. Example of Viewing the Current DNS Configuration
Operating Notes
■ The DNS server must be accessible to the switch, but it is not necessary for any intermediate
devices between the switch and the DNS server to be configured to support DNS operation.
■ A DNS configuration must include the IP address for a DNS server that is able to resolve host
names for the desired domain. If a DNS server has limited knowledge of other domains, then
its ability to resolve ping or traceroute requests is also limited.
■ If the DNS configuration includes a DNS server IP address but does not also include a domain
suffix, then any ping or traceroute command should include the target host’s fully qualified
domain name. Refer to Figure 3 on page 29.
■ The switch supports one DNS entry; that is, one DNS server IP address and the corresponding
domain name suffix.
■ Switch-Initiated DNS packets go out through the VLAN having the best route to the DNS
server, even if a Management VLAN has been configured.
■ The traceroute command output shows only IP addresses.
■ The DNS server address must be manually input. It is not be automatically determined via
DHCP.
■ Operation with IPv4 DNS servers has been verified and, while no problems with servers
supporting both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are expected, testing has not been performed with
such servers. (IPv6 AAAA-style queries are not supported.)
34
Page 45

Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Enhancements
Event Log Messages
Message Meaning
DNS server address not configured The switch does not have an IP address configured for the DNS
server.
DNS server not responding The DNS server failed to respond or is unreachable. An incorrect
server IP address can produce this result.
Unknown host < host-name > The host name did not resolve to an IP address. Some reasons for
this occurring include:
• The host name was not found.
• The named domain was not found.
• The domain suffix was expected, but has not been configured. (If
the server’s IP address has been configured in the switch but the
domain name has not been configured, then the host’s fully
qualified domain name must be used.)
Using SNMP To View and Configure Switch Authentication Features
In earlier software releases, SNMP MIB object access has not been available for switch authentication
configuration (hpSwitchAuth) features. Beginning with software release M.08.89, the 3400cl and
6400cl switches allow, by default, manager-only SNMP read/write access to a subset of the authentication MIB objects for the following features:
■ number of primary and secondary login and enable attempts
■ TACACS+ server configuration and status
■ RADIUS server configuration
■ selected 802.1X settings
■ key management subsystem chain configuration
■ key management subsystem key configuration
■ OSPF interface authentication configuration
With SNMP access to the hpSwitchAuth MIB enabled, a device with management access to the switch
can view the configuration for the authentication features listed above (excluding passwords and
keys). Using SNMP sets, a management device can change the authentication configuration
(including changes to passwords and keys). Operator read/write access to the authentication MIB
is always denied.
35
Page 46

Enhancements
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Security Notes
Passwords and keys configured in the hpSwitchAuth MIB are not returned via SNMP, and the
response to SNMP queries for such information is a null string. However, SNMP sets can be used to
configure password and key MIB objects.
To help prevent unauthorized access to the switch’s authentication MIB, ProCurve recommends
enhancing security according to the guidelines under “Enforcing Switch Security” on page 10.
If you do not want to use SNMP access to the switch’s authentication configuration MIB, then you
should use the snmp-server mib hpswitchauthmib excluded command to disable this access, as
described in the next section.
If you choose to leave SNMP access to the security MIB open (the default setting), ProCurve
recommends that you configure the switch with the SNMP version 3 management and access security
feature, and disable SNMP version 2c access. (Refer to “Enforcing Switch Security” on page 10.)
Changing and Viewing the SNMP Access Configuration
Syntax: snmp-server mib hpswitchauthmib < excluded | included >
included: Enables manager-level SNMP read/write access to the switch’s authentication configuration (hpSwitchAuth) MIB.
excluded: Disables manager-level SNMP read/write access to the switch’s authentication configuration (hpSwitchAuth) MIB.
(Default: included )
Syntax: show snmp-server
The output for this command has been enhanced to display the current access status
of the switch’s authentication configuration MIB in the Excluded MIBs field.
36
Page 47

Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Enhancements
For example, to disable SNMP access to the switch’s authentication MIB and then display the result
in the Excluded MIB field, you would execute the following two commands.
ProCurve(config)# snmp-server mib hpswitchauthmib excluded
ProCurve(config)# show snmp-server
SNMP Communities
This command disables
SNMP security MIB access.
Community Name MIB View Write Access
---------------- -------- ----------- public Manager Unrestricted
Trap Receivers
Link-Change Traps Enabled on Ports [All] : All
Send Authentication Traps [No] : No
Address Community Events Sent in Trap
---------------------- ---------------- -------------------
Excluded MIBs
Indicates that SNMP security MIB access is
disabled, which is the nondefault setting.
hpSwitchAuthenticationMIB
Figure 10. Disabling SNMP Access to the Authentication MIB and Displaying the Result
An alternate method of determining the current Authentication MIB access state is to use the show
run command.
37
Page 48

Enhancements
Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements
ProCurve(config)# show run
Running configuration:
; J4905A Configuration Editor; Created on release #M.10.05
hostname "ProCurve"
snmp-server mib hpSwitchAuthMIB excluded
ip default-gateway 10.10.24.55
snmp-server community "public" Operator
Indicates that SNMP access
to the authentication
configuration MIB
(hpSwitchAuth) is disabled.
vlan 1
name "DEFAULT_VLAN"
untagged 1-26
ip address 10.10.24.100 255.255.255.0
exit
password manager
Figure 11. Using the show run Command to View the Current Authentication MIB Access State
Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements
■ The MSTP enhancement implementing the CLI command for spanning-tree legacy-path-cost
was included in releaseM.08.90
■ The MSTP enhancement implementing the CLI command for spanning-tree legacy-mode
was included in release M.08.91
■ QoS Pass-Through Mode enhancement, a new command that allows the configuration of the
Quality of Service (QoS) queues to be selected.
MSTP Default Path Cost Controls
Summary: 802.1D and 802.1t specify different default path-cost values (based on interface speed).
These are used if the user hasn't configured a "custom" path-cost for the interface. The default of this
toggle is to use 802.1t values. The reason one might set this control to 802.1D would be for better
interoperability with legacy 802.1D STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) bridges.
To support legacy STP bridges, the following commands (options) have been added to CLI:
spanning-tree legacy-path-cost - Use 802.1D values for default path-cost
no spanning-tree legacy-path-cost - Use 802.1t values for default path-cost (default setting)
38
Page 49

Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements
Enhancements
The “legacy-path-cost” CLI command does not affect or replace functionality of the “spanningtree force-version” command. The “spanning-tree force-version” controls whether MSTP will
send and process 802.1w RSTP, or 802.1D STP BPDUs. Regardless of what the “legacy-path-cost”
parameter is set to, MSTP will interoperate with legacy STP bridges (send/receive Config and
TCN BPDUs).
spanning-tree legacy-mode - A “macro” that is the equivalent of executing the “spanning-tree legacy-
path-cost” and “spanning-tree force-version stp-compatible” commands.
no spanning-tree legacy-mode - A “macro” that is the equivalent of executing the “no spanning-tree
legacy-path-cost” and “spanning-tree force-version mstp-compatible” commands.
When either legacy-mode or legacy-path-cost control is toggled, all default path costs will be
recalculated to correspond to the new setting, and spanning tree is recalculated if needed.
QoS Pass-Through Mode
Release M.08.91 introduced a new command that allows the configuration of the Quality of Service
(QoS) queues to be selected. By better matching the configuration of the QoS queues to the amount
of prioritized and non-prioritized traffic being transferred, performance can be improved and packet
loss due to over-subscription can be minimized.
In previous software versions, the 3400cl and the 6400cl switches had four QoS queues of equal size.
Depending on the mix of prioritized and non-prioritized traffic, this configuration might not always
optimize performance and could result in dropped packets when resources were over-subscribed.
Starting with this software version, four QoS Pass-Through modes are available for use. The number
of queues and the size of the memory buffer used by each queue differs in each mode. Table 2 below
summarizes the QoS queue configuration of each mode
Table 2. QoS Pass-Through Modes
QoS Pass-Through Mode Number of
Queues
typical (default) 4 One large queue for Priority 0
balanced 4 All queues are the same size. Equal amounts of prioritized and
one-queue 1 One large queue.
optimized 2 One small queue for Priority 6
1
This mode has a small queue used exclusively for Priority 7 management and control traffic.
QoS Queue Memory Buffer
Configuration
and 3 traffic and three other
queues for the remaining traffic.
1
and 7 traffic; one large queue for
all other traffic.
Description
A mix of prioritized and nonprioritized traffic. This is the
default mode, used when QoS
Pass-Through is disabled.
non-prioritized traffic. This is the
same mode used in pre-M.08.78
software versions.
No traffic is prioritized.
Most traffic is not prioritized.
39
Page 50

Enhancements
Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements
Note
Changing the QoS Pass-Through Mode can be done without rebooting the switch. However, the switch
ports are toggled down and back up, allowing the QoS queues to be reconfigured. This may affect
routing and spanning tree operation. ProCurve Networking recommends that QoS queues be reconfigured during periods of non-peak traffic.
Configuring QoS Pass-Through Mode
Syntax: qos-passthrough-mode [ balanced | one-queue | optimized | typical ]
Specifies the QoS queue mode to be used by the switch. The number of queues and the
size of each queue is determined by the mode selected. If no mode is specified the optimized
mode is used. QoS Pass-Through is disabled using the no qos-pass-through command.
balanced: Configures four QoS queues of the same size. This configuration is the
same as was used by software versions prior to M.08.78.
one-queue: Configures one QoS queue. By consolidating packet buffer memory, line-
rate flows with no loss of data may be achieved.
Note: This mode has a small queue used exclusively by Priority 7 management
and control packets.
optimized: Configures two QoS queues: a small queue for Priority 6 and 7 traffic
and a large queue for all other traffic.
typical: Configures four QoS queues: a large queue for Priority 0 and 3 traffic, and
three other queues for the remaining traffic. This is the default configuration
on the switch and is used when QoS Pass-Through is disabled.
Syntax: [no] qos-passthrough-mode
Specifies the optimized QoS queue mode for the switch.
The no qos-pass-through command returns the QoS queue mode to typical, the default
setting.
Configuring QoS Pass-Through Mode Through the CLI. The following example changes the
QoS Pass-Through Mode to balanced. A show command verifies the new mode.
ProCurve(config)# qos-passthrough-mode balanced
This requires a temporary shut-down of logical ports. Continue (y/n) y
ProCurve(config)# show qos-passthrough-mode
Qos passthrough mode : balanced
ProCurve(config)#
Reconfiguring the
QoS queues toggles
the switch ports,
which may affect
routing and spanning
tree operation.
Choose
n to cancel
this operation.
Figure 1. Example Showing QoS Pass-Through Mode Set Using the CLI
40
Page 51

Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements
Enhancements
QoS Pass-Through Mode SNMP MIB Object. A read-write MIB object,
1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.5.1.7.1.24.1, has been added to the ProCurve switch MIB. The QoS Pass-Through
Mode can be changed using either an SNMP network management application or the CLI setmib
command.
Syntax: setMIB hpSwitchQosPassThroughModeConfig.0 -i [ 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 ]
Specifies the QoS queue mode to be used by the switch. The number of queues and
the size of each queue is determined by the mode selected.
1 optimized: Configures two QoS queues: a small queue for Priority 6 and
7 traffic and a large queue for all other traffic.
2 typical: Configures four QoS queues: a large queue for Priority 0 and 3
traffic, and three other queues for the remaining traffic. This is the
default configuration on the switch and is used when QoS PassThrough is disabled.
3 balanced: Configures four QoS queues of the same size. This configura-
tion is the same as was used by software versions prior to M.08.xx.
4 one-queue: Configures one QoS queue. By consolidating packet buffer
memory, line-rate flows with no loss of data may be achieved.
Note: This mode has a small queue used exclusively by Priority 7
management and control packets.
The following example changes the QoS Pass-Through Mode to one-queue. A show command verifies
the new mode.
ProCurve(config)# setMIB hpSwitchQosPassThroughModeConfig.0 -i 4
hpSwitchQosPassThroughModeConfig.0 = 4
ProCurve(config)# show qos-passthrough-mode
Qos passthrough mode : one-queue
ProCurve(config)#
Figure 2. Example Showing QoS Pass-Through Mode Set Using the setMIB Command
Displaying the Current QoS Pass-Through Mode on the Switch
The following command indicates the current QoS Pass-Through Mode on the switch.
Syntax: show qos-passthrough-mode
This command displays the current QoS Pass-Through Mode configured on the switch. The
default mode is typical.
41
Page 52

Enhancements
Release M.08.94 Enhancements
The current QoS Pass-Through Mode also is displayed in the show running-config command output.
Operating Notes
■ To use the same QoS queue structure used in pre-M.08.78 software, set the QoS Pass-Through
Mode to balanced.
■ The optimized mode matches the QoS Pass-through mode on the ProCurve Series 2800
switches. This mode is used when the QoS Pass-Through Mode command is entered with no
arguments, qos-passthrough-mode.
Release M.08.94 Enhancements
Release M.08.94 includes the following enhancements:
■ Added DHCP Option 82 functionality for 3400cl series.
■ UDP broadcast forwarding feature is now supported on the 3400cl series.
DHCP Option 82: Using the Management VLAN IP Address for the Remote ID
This section describes the Management VLAN enhancement to the DHCP option 82 feature. For more
information on DHCP option 82 operation, refer to “Configuring DHCP Relay” in the chapter titled
“IP Routing Features” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide.
When the routing switch is used as a DHCP relay agent with Option 82 enabled, it inserts a relay agent
information option into client-originated DHCP packets being forwarded to a DHCP server. The
option automatically includes two suboptions:
■ Circuit ID: the identity of the port through which the DHCP request entered the relay agent
■ Remote ID: the identity (IP address) of the DHCP relay agent
Using earlier software releases, the remote ID can be either the routing switch’s MAC address (the
default option) or the IP address of the VLAN or subnet on which the client DHCP request was
received. Beginning with software release M.08.xx, if a Management VLAN is configured on the
routing switch, then the Management VLAN IP address can be used as the remote ID.
42
Page 53

Release M.08.94 Enhancements
Enhancements
Syntax: dhcp-relay option 82 < append | replace | drop > [ validate ] [ ip | mac | mgmt-vlan ]
[ ip | mac | mgmt-vlan ] : Specifies the remote ID suboption the routing switch will use
in Option 82 fields added or appended to DHCP client packets. The choice depends
on h o w y o u w a n t t o define DHCP policy areas in the client requests sent to the DHCP
server. If a remote ID suboption is not configured, then the routing switch defaults
to the mac option.
mgmt-vlan: Specifies the IP address of the (optional) Management VLAN configured
on the routing switch. Requires that a Management VLAN is already configured on
the switch. If the Management VLAN is multinetted, then the primary IP address
configured for the Management VLAN is used for the remote ID.
ip: Specifies the IP address of the VLAN on which the client DHCP packet enters the
routing switch. In the case of a multinetted VLAN, the remote ID suboption uses the
IP address of the subnet on which the client request packet is received.
mac: Specifies the routing switch’s MAC address. (The MAC address used is the same
MAC address that is assigned to all VLANs configured on the routing switch.)
(Default: mac)
Example
In the routing switch shown below, option 82 has been configured with mgmt-vlan for the Remote ID.
ProCurve(config)# dhcp-relay option 82 append mgmt-vlan
The resulting effect on DHCP operation for clients X, Y, and Z is shown inTable 3.
Routing Switch
Management VLAN
VLAN 300
DHCP Server “A”
DHCP Server “B”
DHCP Server “C”
10.39.10.1 (secondary IP)
10.38.10.1 (primary IP)
VLAN 200
10.29.10.1
10.28.10.1
VLAN 100
10.15.10.1
Client “X”
Client “Y”
Client “Z”
On a routing switch that is
the primary DHCP relay
agent for a given client, if
the (optional) Management
VLAN is selected as the
Remote ID suboption and is
also multinetted, then the
Remote ID for the client
DHCP requests is the
primary IP address of the
Management VLAN.
Figure 12. DHCP Option 82 When Using the Management VLAN as the Remote ID Suboption
43
Page 54

Enhancements
Release M.08.94 Enhancements
Table 3. DHCP Operation for the Topology in Figure 12
Client Remote ID giaddr* DHCP
X 10.38.10.1 10.39.10.1 A only If a DHCP client is in the Management VLAN, then its DHCP requests
Y 10.38.10.1 10.29.10.1 B or C Clients outside of the Management VLAN can send DHCP requests
Z 10.38.10.1 10.15.10.1 B or C
*The IP address of the primary DHCP relay agent receiving a client request packet is automatically added to the packet,
and is identified as the giaddr (gateway interface address). This is the IP address of the VLAN on which the request
packet was received from the client. For more information, refer to RFC 2131 and RFC 3046.
Server
can go only to a DHCP server that is also in the Management VLAN.
Routing to other VLANs is not allowed.
only to DHCP servers outside of the Management VLAN. Routing to
the Management VLAN is not allowed.
Operating Notes
■ Routing is not allowed between the Management VLAN and other VLANs. Thus, a DHCP
server must be available in the Management VLAN if there are clients in the Management
VLAN that require a DHCP server.
■ If the Management VLAN IP address configuration changes after mgmt-vlan has been config-
ured as the remote ID suboption, the routing switch dynamically adjusts to the new IP
addressing for all future DHCP requests.
■ The Management VLAN and all other VLANs on the routing switch use the same MAC address.
UDP Broadcast Forwarding
Beginning with software release M.08.94, UDP Broadcast Forwarding is available on the ProCurve
3400cl and 6400cl switches. For further information, refer to the section titled “UDP Broadcast
Forwarding on 5300xl Switches” in the “IP Routing Features” chapter of the Advanced Traffic
Management Guide for your switch. (Note that this manual covers multiple switches and the
description of UDP Broadcast Forwarding is no longer restricted to just the 5300xl switches.)
Some applications rely on client requests sent as limited IP broadcasts addressed to a UDP application port. If a server for the application receives such a broadcast, the server can reply to the client.
Since typical router behavior, by default, does not allow broadcast forwarding, a client’s UDP
broadcast requests cannot reach a target server on a different subnet unless the router is configured
to forward client UDP broadcasts to that server.
A switch with routing enabled includes optional per-VLAN UDP broadcast forwarding that allows up
to 256 server and/or subnet entries on the switch (16 entries per-VLAN). If an entry for a particular
UDP port number is configured on a VLAN and an inbound UDP broadcast packet with that port
number is received on the VLAN, then the switch routes the packet to the appropriate subnet. (Each
entry can designate either a single device or a single subnet. The switch ignores any entry that
designates multiple subnets.)
44
Page 55

Releases M.08.95 through M.10.01 Enhancements
Enhancements
Releases M.08.95 through M.10.01 Enhancements
Software fixes only; no new enhancements.
Release M.08.96 Enhancements
■ Enabled use of login "Message of the Day" (MOTD) banner. For details on using this feature,
refer to “Custom Login Banners for the Console and Web Browser Interfaces” in Chapter 2
of the Management and Configuration Guide for 3400cl and 6400cl switches.
Releases M.08.97 through M.10.01 Enhancements
No new enhancements in release M.08.97. The M code software for the 3400cl then branched to
M.10.01, which has software fixes only, no enhancements.
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Release M.10.02 includes the following enhancements:
■ Support for RADIUS assigned ACLs (access control lists).
■ Added new "show sFlow" commands.
RADIUS-Assigned Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Introduced with software release M.10.xx on the 3400cl switches, this feature uses RADIUS-assigned,
per-port ACLs for Layer-3 filtering of inbound IP traffic from authenticated clients. A given RADIUSassigned ACL is identified by a unique username/password pair or client MAC address, and applies
only to traffic from clients that authenticate with the same unique credentials. The ACL is applied to
the switch port used by the client and remains in force for the duration of the client session. ACL
services for an authenticated client include filtering inbound IP traffic based on destination and/or
IP traffic type (such as TCP and UDP traffic) and traffic counter options. Implementing the feature
for a given client requires the following:
■ RADIUS authentication of the client must be available on the switch through either 802.1X,
Web authentication, or MAC authentication.
45
Page 56

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
■ An ACL must be configured on the RADIUS server (instead of the switch) by creating and
assigning one or more Access Control Entries to the username/password pair or MAC
address of the client for which you want ACL support.
■ Where 802.1X is used for client authentication, then either the client device must be running
802.1X supplicant software or the capability must exist for the client to download this
software from the network through use of the 802.1X Open VLAN mode available on the
switch. (If authentication is achieved through Web or MAC Authentication, then 802.1X
supplicant software is not required.)
A RADIUS-assigned ACL is a type of extended ACL that filters IP traffic inbound on a port from any
source (and, optionally, of any specific IP application or protocol type) to a single destination IP
address, a group of contiguous IP addresses, an IP subnet, or any IP destination.
This feature is designed to accept dynamic configuration of a RADIUS-based ACL on an individual
port on the network edge to filter traffic from an authenticated end-node client. Using RADIUS to
apply per-port ACLs to edge ports enables the switch to filter IP traffic coming from outside the
network, thus removing unwanted traffic as soon as possible and helping to improve system
performance. Also, applying RADIUS-assigned ACLs to ports on the network edge is likely to be less
complex than using ACLs in the network core to filter unwanted traffic that could have been filtered
at the edge.
This feature enhances network and switch management access security by permitting or denying
authenticated client access to specific network resources and to the switch management interface.
This includes preventing clients from using TCP or UDP applications (such as Telnet, SSH, Web
browser, and SNMP) if you do not want their access privileges to include these capabilities.
Note
A RADIUS-assigned ACL filters all inbound IP traffic from an authenticated client on a port, regardless
of whether the traffic is to be switched or routed.
ACLs enhance network security by blocking selected IP traffic, and can serve as one aspect of
network security. However, because ACLs do not protect from malicious manipulation of data carried
in IP packet transmissions, they should not be relied upon for a complete edge security solution.
The ACLs described in this section do not screen non-IP traffic such as AppleTalk and IPX.
Table 4, highlights several key differences between the static ACLs configurable on 3400cl switch
ports and the dynamic ACLs that can be assigned to individual ports by a RADIUS server. (The switch
supports either one RADIUS-based ACL or one port-based ACL at a time on a given port. It does not
support having both ACL types on the same port at the same time.)
46
Page 57

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
Table 4. Contrasting Dynamic and Static ACLs
RADIUS-Based (Dynamic) ACLs Port-Based (Static) ACLs
Operates on the 3400cl switches. Operates on both the 3400cl and 6400cl switches.
Configured in client accounts on a RADIUS server. Configured in the switch itself.
Designed for use on the edge of the network where
filtering of inbound traffic is most important and where
clients with differing access requirements are likely
Designed for general use where the filtering needs for
the traffic to the switch from connected devices is
predictable and largely static.
to use the same port at different times.
Implementation requires client authentication. Client authentication not a factor.
Instead of an ACL name or number, the ACL is defined
by the credentials (username/password pair or the
Identified by a number in the range of 1-199 or an
alphanumeric name.
MAC address) of the specific client the ACL is
intended to service. Thus, all ACEs configured in the
RADIUS server with the same client identifiers
comprise the ACL for the specified client.
Supports dynamic assignment to filter only the
inbound IP traffic from an authenticated client on the
port to which the client is connected. (Traffic can be
routed or switched, and includes traffic having a DA
Supports static assignments to filter traffic from a
connected device, and operates in applictions that
may or may not include 802.1X or other types of client
authentication.
on the switch itself.)
When the authenticated client session ends, the
switch removes the RADIUS-assigned ACL from the
client port.
Remains statically assigned to the ports unless
removed by a no interface < port-list > access-group
CLI command.
Supports one RADIUS-based ACL on a port. Supports one inbound ACL per-port.
The ACL filters the IP traffic received inbound from the
client whose authentication resulted in the ACL
An ACL applied inbound on a port filters all IP traffic
received.
assignment. Inbound traffic from any other source is
denied.
Requires client authentication by a RADIUS server
configured to dynamically assign an ACL to the client
Configured in the switch and statically applied to filter
all inbound IP traffic on the specified ports.
port, based on client credentials.
ACEs allow a counter (cnt) option that causes a
counter to increment when there is a packet match.
ACEs allow a log option that generates a log message
whenever there is a packet match with a “deny” ACE.
47
Page 58

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Terminology
ACE: See Access Control Entry, below.
Access Control Entry (ACE): An ACE is a policy consisting of a packet-handling action and criteria
to define the packets on which to apply the action. For RADIUS-based ACLs, the elements
composing the ACE include:
• permit or drop (action)
•in < ip-packet-type > from any (source)
• to < ip-address [/ mask ] | any > (destination)
• [ port-# ] (optional TCP or UDP application port numbers used when the packet type is TCP
or UDP)
• [ cnt ] (optional counter that increments when there is a packet match)
ACL: See Access Control List, below.
Access Control List (ACL): A list (or set) consisting of one or more explicitly configured Access
Control Entries (ACEs) and terminating with an implicit “deny” default which drops any packets
that do not have a match with any explicit ACE in the named ACL.
ACL Mask: Follows a destination IP address listed in an ACE. Defines which bits in a packet’s
corresponding IP addressing must exactly match the IP addressing in the ACE, and which bits
need not match (wildcards).
DA: The acronym for Destination IP Address. In an IP packet, this is the destination IP address
carried in the header, and identifies the destination intended by the packet’s originator.
Deny: An ACE configured with this action causes the switch to drop a packet for which there is a
match within an applicable ACL.
Deny Any Any: An abbreviated form of deny in ip from any to any, which denies any inbound IP traffic
from any source to any destination.
Extended ACL: This type of Access Control List uses layer-3 IP criteria composed of source and
destination IP addresses and (optionally) TCP or UDP port criteria to determine whether there
is a match with an IP packet. On the 3400cl switches, the source IP address is always defined as
“any”, and extended ACLs apply only to inbound bridged or routed traffic. For a RADIUS-based,
extended ACL assigned to a port, only the inbound traffic from the client whose authentication
caused the ACL assignment is filtered. Inbound traffic from any other sources is denied.
Implicit Deny: If the switch finds no matches between an inbound packet and the configured criteria
in an applicable ACL, then the switch denies (drops) the packet with an implicit “deny IP any/
any” operation. You can preempt the implicit “deny IP any/any” in a given ACL by configuring
permit in ip from any to any as the last explicit ACE in the ACL. Doing so permits any inbound IP
48
Page 59

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
packet (from the authenticated client) that is not explicitly permitted or denied by other ACEs
configured sequentially earlier in the ACL. Unless otherwise noted, “implicit deny IP any” refers
to the “deny” action enforced by both standard and extended ACLs.
Inbound Traffic: For the purpose of defining where the switch applies ACLs to filter traffic, inbound
traffic is any IP packet that enters the switch from a given client on a given port.
NAS (Network Attached Server): In this context, refers to a ProCurve switch configured for
RADIUS operation.
Permit: An ACE configured with this action allows the switch to forward an inbound packet for
which there is a match within an applicable ACL.
Permit Any Any: An abbreviated form of permit in ip from any to any, which permits any inbound IP
traffic from the authenticated source to any destination. Inbound traffic from any other sources
is denied. (Inbound traffic from a client other than the client whose authentication caused in the
ACL assignment will be denied.)
VSA (Vendor-Specific-Attribute): A value used in a RADIUS-based configuration to uniquely
identify a networking feature that can be applied to a port on a given vendor’s switch during an
authenticated client session.
Wildcard: The part of a mask that indicates the bits in a packet’s IP addressing that do not need to
match the corresponding bits specified in an ACL. See also ACL Mask on page 48.
Enhancements
Caution Regarding the Use of Source Routing
Source routing is enabled by default on the switch and can be used to override ACLs. For this reason,
if you are using ACLs to enhance network security, the recommended action is to use the no ip source-
route command to disable source routing on the switch. (If source routing is disabled in the runningconfig file, the show running command includes “no ip source-route” in the running-config file listing.)
General Operation
An ACL is a list of one or more Access Control Entries (ACEs), where each ACE consists of a matching
criteria and an action (permit or deny). These ACEs are designed to control the network access
privileges of an authenticated client. A RADIUS-based ACL applies only to the inbound traffic from
the client whose authentication triggers the ACL assignment to the client port.
How a RADIUS Server Applies a RADIUS-Based ACL to a Switch Port. A RADIUS-based
ACL configured on a RADIUS server is identified and invoked by the unique credentials (username/
password pair or a client MAC address) of the specific client the ACL is designed to service. Where
the username/password pair is the selection criteria, the corresponding ACL can also be used for a
group of clients that all require the same ACL policy and use the same username/password pair. Where
49
Page 60

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
the client MAC address is the selection criteria, only the client having that MAC address can use the
corresponding ACL. When a RADIUS server authenticates a client, it also assigns the ACL configured
with that client’s credentials to the port. The ACL then filters the client’s inbound IP traffic and denies
(drops) any such traffic from the client that is not explicitly permitted by the ACL. (Every ACL ends
with an implicit deny in ip from any to any (“deny any any”) ACE that denies IP traffic not specifically
permitted by the ACL.) When the client session ends, the switch removes the RADIUS-based ACL
from the client port.
When multiple clients supported by the same RADIUS server use the same credentials, they will all
be serviced by different instances of the same ACL. (The actual traffic inbound from any client on
the switch carries a source MAC address unique to that client. The RADIUS-based ACL uses this MAC
address to identify the traffic to be filtered.)
Notes
On any ACL assigned to a port, there is an implicit deny in ip from any to any (“deny any any”) command
that results in a default action to deny any inbound IP traffic that is not specifically permitted by the
ACL. To reverse this default, use an explicit “permit any” as the last ACE in the ACL.
On a given port, RADIUS-based ACL filtering occurs only for the inbound traffic from the client whose
authentication caused a RADIUS-based ACL assignment. Inbound traffic from any other source,
including a second, authenticated client (on the same port) will be denied.
The Packet-filtering Process
Sequential Comparison and Action. When an ACL filters a packet from an authenticated client,
it sequentially compares each ACE’s filtering criteria to the corresponding data in the packet until it
finds a match. The action indicated by the matching ACE (deny or permit) is then performed on the
packet.
Implicit Deny. If a packet from the authenticated client does not have a match with the criteria in
any of the ACEs in the ACL, the ACL denies (drops) the packet. If you need to override the implicit
deny so that a packet (from the authenticated client) that does not have a match will be permitted,
then you can use the “permit any” option as the last ACE in the ACL. This directs the ACL to permit
(forward) packets that do not have a match with any earlier ACE listed in the ACL, and prevents
these packets from being filtered by the implicit “deny any”. (Note that the “permit any” option applies
only to packets from the client whose authentication caused the assignment of the ACL to the port.)
50
Page 61

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
Example. Suppose the ACL in Figure 3 is assigned to filter the traffic from an authenticated client
on a given port in the switch:
For an inbound packet with a destination
IP address of 18.28.156.3, the ACL:
1. Compares the packet to this ACE first.
2. Since there is not a match with the first
ACE, the ACL compares the packet to the
second ACE, where there is also not a
match.
3. The ACL compares the packet to the third
ACE. There is an exact match, so the ACL
denies (drops) the packet.
4. The packet is not compared to the fourth
ACE.
Permit in ip from any to 18.28.136.24
Permit in ip from any to 18.28.156.7
Deny in ip from any to 18.28.156.3
Deny in tcp from any to any 23
Permit in ip from any to any
(Deny in ip from any to any)
This line demonstrates the “deny any any” ACE implicit in every
RADIUS-based ACL. Any inbound ip traffic from the authenticated
client that does not have a match with any of the five explicit ACEs
in this ACL will be denied by the implicit “deny any any”.
Figure 3. Example of Sequential Comparison
As shown above, the ACL tries to apply the first ACE in the list. If there is not a match, it tries the
second ACE, and so on. When a match is found, the ACL invokes the configured action for that entry
(permit or drop the packet) and no further comparisons of the packet are made with the remaining
ACEs in the list. This means that when an ACE whose criteria matches a packet is found, the action
configured for that ACE is invoked, and any remaining ACEs in the ACL are ignored. Because of this
sequential processing, successfully implementing an ACL depends in part on configuring ACEs
in the correct order for the overall policy you want the ACL to enforce.
Note
Because only one ACL is allowed on a port, if a statically configured ACL already exists on a port, a
RADIUS-based ACL cannot be assigned to that port. In this case, if a client authenticates and the
RADIUS server is configured to assign a dynamic ACL to the port for that client, the client will then
be de-authenticated.
51
Page 62

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Test packet against
criteria in first ACE.
Test the packet against
criteria in second ACE.
Test packet against
criteria in Nth ACE.
Is there a
match?
No
Is there a
match?
No
Is there a
match?
Yes
Yes
Yes
Perform action
(permit or deny).
Perform action
(permit or deny).
Perform action
(permit or deny).
End
End
End
1. If a match is not found with
the first ACE in an ACL, the
switch proceeds to the next
ACE and so on.
2. If a match with an explicit
ACE is subsequently found,
the packet is either permitted (forwarded) or denied
(dropped), depending on
the action specified in the
matching ACE. In this case
the switch ignores all subsequent ACEs in the ACL.
3. If a match is not found with
any explicit ACE in the ACL,
the switch invokes the
implicit deny IP any at the
end of every ACL, and
drops the packet.
Note: If the list includes a
permit IP any entry, no
packets can reach the
implicit deny IP any at the
end of the list. Also, a
permit IP any ACE at any
point in an ACL defeats the
purpose of any subsequent
ACEs in the list.
No
Deny the packet
(invoke implicit
deny any).
End
Figure 4. The Packet-Filtering Process in an ACL with N Entries (ACEs)
Note
The order in which an ACE occurs in an ACL is significant. For example, if an ACL contains six ACEs,
but the first ACE is a “permit IP any”, then the ACL permits all IP traffic from the authenticated client,
and the remaining ACEs in the list do not apply, even if they specify criteria that would make a match
with any of the traffic permitted by the first ACE.
52
Page 63

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
For example, suppose you want to configure a RADIUS-based ACL to invoke these policies in the
11.11.11.0 network:
1. Permit inbound client traffic with a DA of 11.11.11.42.
2. Permit inbound Telnet traffic for DA 11.11.11.101.
3. Deny inbound Telnet traffic for all other IP addresses in the 11.11.11.0 network.
4. Permit inbound HTTP traffic for any IP address in the 11.11.11.0 network.
5. Deny all other inbound traffic.
The following ACL model, when invoked by a client authenticating with the credentials configured
in the RADIUS server for this ACL, supports the above case:
Permit in ip from any to 11.11.11.42
1
Permit in tcp from any to 11.11.11.101 23
2
Deny in tcp from any to 11.11.11.0/24 23
3
Permit in tcp from any to 11.11.11.1/24 80
4
(implicit deny in ip any to any)
5
1. Permits inbound IP traffic from the authenticated client to the
destination address 11.11.11.42. Packets matching this criterion
are forwarded and are not compared to any later ACE in the list.
Packets not matching this criterion will be compared to the next
entry in the list.
2. Permits inbound Telnet traffic from the authenticated client to
the destination address 11.11.11.101. Packets matching this
criterion are forwarded and are not compared to any later ACE
in the list. Packets not matching this criterion will be compared
to the next entry in the list.
3. Denies inbound Telnet traffic from the authenticated client to
any IP address in the 11.11.11.0 network. Since packets
matching entry “2” will never reach this ACE, the Telnet traffic
permitted by entry “2” will not be affected. Packets matching
this criterion will be denied and will not be compared to any
later criteria in the list. Packets not matching this criterion will
be compared to the next entry in the list.
4. Permits inbound HTTP traffic from the authenticated client to
any address in the 11.11.11.1 network. Packets matching this
criterion are permitted and are not compared to any later
criteria in the list. Packets not matching this criterion are
compared to the next entry in the list.
5. This entry does not appear in an actual ACL, but is implicit as
the last entry in every ACL. Any inbound traffic from the
authenticated client that does not match any of the criteria in
the ACL’s preceding ACE entries will be denied (dropped).
Figure 5. Example of How a RADIUS-Based ACL Filters Packets
Overriding the Implicit “deny IP any any”. RADIUS-based ACLs include an implicit “deny IP
any any”. That is, packets received inbound from an authenticated client that the ACL does not
explicitly permit or deny will be implicitly denied, and therefore dropped instead of forwarded. If
you want the port to permit all inbound IP traffic (from the authenticated client) that the ACL does
not explicitly permit or deny, insert a permit in ip from any to any (“permit any any”) as the last explicit
entry in the ACL. (Inbound traffic from a client other than the client whose authentication caused
the ACL assignment to the port is dropped.)
53
Page 64

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
General Steps
These steps suggest a process for using ACLs to establish client access policies. The topics following
this section provide details.
1. Determine the polices you want to enforce for client traffic inbound on the switch.
2. Plan ACLs to execute traffic policies:
• Apply ACLs on a per-client basis where individual clients need different traffic policies
or where each client must have a different username/password pair or will authenticate
using MAC authentication.
• Apply ACLs on a client group basis where all clients in a given group can use the same
traffic policy and the same username/password pair.
3. Configure the ACLs on a RADIUS server accessible to the intended clients.
4. Configure the switch to use the desired RADIUS server and to support the desired client
authentication scheme. Options include 802.1X, Web authentication, or MAC authentication.
(Note that the switch supports the option of simultaneously using 802.1X with either Web or
MAC authentication.)
5. Test client access on the network to ensure that your RADIUS-based ACL application is properly
enforcing your policies.
Determining Traffic Policies
This section assumes that the RADIUS server needed by a client for authentication and ACL
assignments is accessible from any switch that authorized clients may use.
Begin by defining the policies you want an ACL to enforce for a given client or group of clients. This
includes the type of IP traffic permitted or not permitted from the client(s) and the areas of the
network the client(s) are authorized or not authorized to use.
■ What traffic should you permit for the client? In some cases you will need to explicitly identify
permitted traffic. In other cases, depending on your policies, you can insert a permit in ip from
any to any entry at the end of the ACL so that all IP traffic (from the authenticated client) that
is not specifically matched by earlier entries in the list will be permitted. This may be the
best choice for an ACL that begins by defining the inbound client IP traffic that should be
dropped.
■ What traffic must be explicitly blocked for the client or group? This can include requests to
access to “off-limits” subnets, unauthorized access to the internet, access to sensitive data
storage or restricted equipment, and preventing the use of specific TCP or UDP applications
such as Telnet, SSH, and web browser access to the switch.
■ What traffic can be blocked simply by relying on the implicit deny in ip from any to any that is
automatically included at the end of every ACL? This can reduce the number of entries
needed in an ACL.
54
Page 65

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
■ Is it important to keep track of the number of matches for a particular client or ACE? If so,
Enhancements
you can use the optional cnt (counter) feature in ACEs where you want to know this
information. This is especially useful if you want to verify that the switch is denying
unwanted client packets. (Note that configuring a high number of counters can exhaust the
counter resources. Refer to Table 5 on page 57.)
Caution
ACLs can enhance network security by blocking selected IP traffic, and can serve as one aspect of
maintaining network security. However, because ACLs do not provide user or device authentication,
or protection from malicious manipulation of data carried in IP packet transmissions, they should
not be relied upon for a complete security solution.
Planning the ACLs Needed To Enforce Traffic Policies
This section can help in understanding how to order the ACEs in a RADIUS-based ACL and in
understanding how clients and the switch operate in this dynamic environment.
Guidelines for Structuring a RADIUS-Based ACL.
■ The sequence of ACEs is significant. When the switch uses an ACL to determine whether to
permit or deny a packet on a particular port, it compares the packet to the criteria specified
in the individual Access Control Entries (ACEs) in the ACL, beginning with the first ACE in
the list and proceeding sequentially until a match is found. When a match is found, the switch
applies the indicated action (permit or deny) to the packet. This is significant because, when
a match is found for a packet, subsequent ACEs in the same ACL will not be used for that
packet, regardless of whether they match the packet.
■ Inbound Traffic Only: RADIUS-based ACLs filter only the inbound IP traffic from an
authenticated client for which an ACL has been configured on the appropriate RADIUS
server.
■ Result of an ACE/Packet Match: The first match of a given packet to an ACE dictates the
action for that packet. Any subsequent match possibilities are ignored.
■ Explicitly Permitting Any IP Traffic from the Authenticated Client: Entering a permit
in ip from any to any (permit any any) ACE in a RADIUS-based ACL permits all IP traffic (from
the authenticated client) that is not previously permitted or denied by that ACL. Any ACEs
listed after that point do not have any effect. (While a RADIUS-based ACL is applied to a
port, traffic inbound from sources other than the client whose authentication caused the
ACL assignment is denied.)
55
Page 66

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
■ Explicitly Denying Any IP Traffic: Entering a deny in ip from any to any ACE in an ACL
denies all IP traffic not previously permitted or denied by that ACL. Any ACEs listed after
that point have no effect.
■ Implicitly Denying Any IP Traffic: For any packet being filtered by an ACL, there will
always be a match. Included in every ACL is an implicit deny in ip from any to any. This means
that the ACL denies any IP packet it filters that does not have a match with an explicitly
configured ACE. Thus, if you want an ACL to permit any packets that are not explicitly
denied, you must configure permit in ip from any to any as the last explicit ACE in the ACL.
Because, for a given packet, the switch sequentially applies the ACEs in an ACL until it finds
a match, any packet that reaches the permit in ip from any to any entry will be permitted, and
will not reach the implicit deny in ip from any to any ACE that is included at the end of the ACL.
For an example, refer to Figure 5 on page 53.
■ Determine the order in which you want the individual ACEs in the ACL to filter inbound
traffic from a client. A general guideline is to arrange the ACEs in the expected order of
decreasing application frequency. This will result in the most prevalent traffic types finding
a match earlier in the ACL than traffic types that are more infrequent, thus saving processing
cycles.
Operating Rules for RADIUS-Based ACLs
■ ACL Assignments Per-Port: One RADIUS-assigned ACL is allowed per-port.
■ Port Trunks Excluded: RADIUS-assigned ACLs cannot be assigned to a port trunk.
■ Relating a Client to a RADIUS-Based ACL: A RADIUS-based ACL for a particular client
must be configured in the RADIUS server under the authentication credentials the server
should expect for that client. (If the client must authenticate using 802.1X and/or Web
Authentication, the username/password pair forms the credential set. If authentication is
through MAC Authentication, then the client MAC address forms the credential set.) For
more on this topic, refer to “Configuring an ACL in a RADIUS Server” on page 58.
■ Multiple Clients Using the Same Username/Password Pair: Multiple clients using the
same username\password pair will use duplicate instances of the same ACL.
■ RADIUS-Based ACL Not Allowed on a Port that has a Statically-Configured ACL:
Where a RADIUS server is configured to assign an ACL when a given client authenticates, if
the port used by that client is already statically configured with a port-based ACL in the
switch configuration, then the RADIUS-based ACL is not accepted and the client is deauthenticated.
■ A RADIUS-Based ACL Affects Only the Inbound Traffic from a Specific, Authenti-
cated Client: A RADIUS-based ACL assigned to a port as the result of a client authenticating
on that port applies only to the inbound traffic received on that port from that client. It does
not affect the traffic received from any other authenticated clients on that port, and does not
affect any outbound traffic on that port.
56
Page 67

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
Limits for RADIUS-Based ACLs, Associated ACEs, and Counters
Table 5 describes limits the switch supports in ACLs applied by a RADIUS server. Exceeding a limit
causes the related client authentication to fail.
Table 5. Limits Affecting RADIUS-Based ACL Applications
Item Limit Notes
Maximum Number of
Authenticated Client
Sessions Per-Port Using
RADIUS-based ACLs
Maximum Number of
(internal) ACEs Per-Port,
and Maximum Number of
(internal) ACEs Per-ACL
*Uses shared internal resources, which can affect the per-port availability of internal ACEs. Refer to the section
titled “Planning an ACL Application on a Series 3400cl or 6400cl Switch” in the chapter titled “Access Control Lists
(ACLs) for the Series 3400cl and 6400cl Switches” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide for your switch model.
Use the show access-list resources command to view the current resources available for the ports on the switch.
Maximum Number of
Characters in an ACE
Maximum Number of
(optional) Internal Counters Used Per-ACL
1 One RADIUS-based ACL can operate on a given port at a time. If an authenticated
client is already using a RADIUS-based ACL on a port and a second client
requiring a RADIUS-based ACL attempts to authenticate on the same port, the
attempt by the second client will fail.
Up to
Depending on how a RADIUS-assigned ACE is formed, it can consume multiple
120*
internal ACEs. A RADIUS-assigned ACE that does not specify TCP or UDP port
numbers uses one internal ACE. However, an ACE that includes TCP or UDP port
numbers uses one or more internal ACE resources, depending on the port number
groupings. A single TCP or UDP port number or a series of contiguous port
numbers comprise one group. For example, “80” and “137-146” each form one
group. “135, 137-140, 143” in a given ACE form three groups. The following ACE
examples illustrate how the switch applies internal ACE usage.
Examples of Single and Multiple (Internal) ACEs Per-Port
deny in ip from any to any
deny in tcp from any to any
deny in tcp from any to any 80
permit in tcp from any to any 135, 137-146, 445
permit in tcp from any to any 135-137, 139, 141, 143, 146, 445
permit in tcp from any to any 135-146, 445Note:
80 —
32 Depending on how an ACE is formed, using the cnt (counter) option consumes
one or more internal counters. Using a counter in an ACE that does not specify
TCP or UDP port numbers uses one counter. Using a counter in an ACE that
includes TCP or UDP port numbers uses one or more counters, depending on the
port number groupings. A single TCP or UDP port number or a series of contiguous port numbers comprise one group. For example, “80” and “137-146” each
form one group. “135, 137-140, 143” in a given ACE form three groups. The ACE
examples below show how the switch calculates internal counter groups.
Examples of ACE Usage of Internal Counters Counters
deny in ip from any to any cnt
deny in tcp from any to any cnt
deny in tcp from any to any 80 cnt
permit in tcp from any to any 135, 137-146, 445 cnt
permit in tcp from any to any 135-137, 139, 141, 143, 146, 445 cnt
permit in tcp from any to any 135-146, 445 cnt
Internal
ACEs
1
1
1
3
6
2
1
1
1
3
6
2
57
Page 68

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Item Limit Notes
Per-Port Mask Usage ACLs consume per-port (internal) mask resources rapidly and can be affected by
IGMP usage on the same switch. For more on this topic, refer to the “ACL
Resource Usage and Monitoring” and “Extended ACLs” subsections in the
chapter titled “Access Control Lists (ACLs) for the Series 3400cl and Series 6400cl
Switches” of the Advanced Traffic Management Guide for your 3400cl switch.
Configuring an ACL in a RADIUS Server
This section provides general guidelines for configuring a RADIUS server to specify RADIUS-based
ACLs. Also included is an example configuration for a FreeRADIUS server application. However, to
configure support for these services on a specific RADIUS server application, please refer to the
documentation provided with the application.
Elements in a RADIUS-Based ACL Configuration. A RADIUS-based ACL configuration in a
RADIUS server has the following elements:
■ vendor and ACL identifiers:
• ProCurve (HP) Vendor-Specific ID: 11
• Vendor-Specific Attribute for ACLs: 61 (string = HP-IP-FILTER-RAW)
• Setting: HP-IP-FILTER-RAW = < “permit” or “deny” ACE >
(Note that the “string” value and the “Setting” specifier are identical.)
■ ACL configuration, including:
• one or more explicit “permit” and/or “deny” ACEs created by the system operator
•implicit deny in ip from any to any ACE automatically active after the last operator-created
ACE
■ ACEs define the ACL for a given client:
• A given ACE configuration on a RADIUS server includes the identity of the client to
which it applies. That is, the ACE includes the client username/password pair or the
client device’s MAC address.
• All ACEs configured on a RADIUS server for the same client are interpreted as belonging
to the same ACL. (There is no ACL name or number configured on the RADIUS server.)
Example of Configuring a RADIUS-based ACL Using the FreeRADIUS Application. This
example illustrates one method for configuring RADIUS-based ACL support for two different client
identification methods (username/password and MAC address). For information on how to configure
this functionality on other RADIUS server types, refer to the documentation provided with the server.
1. Enter the HP vendor-specific ID and the ACL VSA in the FreeRADIUS dictionary file:
58
Page 69

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
VENDOR HP 11
ProCurve (HP) Vendor-Specific ID
BEGIN-VENDOR HP
ATTRIBUTE HP-IP-FILTER-RAW 61 STRING
END-VENDOR HP
ProCurve (HP) Vendor-Specific
Attribute for RADIUS-Based ACLs
Figure 6. Example of Configuring the VSA for RADIUS-Based ACLs in a FreeRADIUS Server
2. Enter the switch IP address, NAS (Network Attached Server) type, and the key in the FreeRADIUS clients.conf file. For example, if the switch IP address is 10.10.10.125 and the key is “1234”,
you would enter the following in the server’s clients.conf file:
client 10.10.10.125
nastype = other
secret = 1234
Note: The key configured in the switch and the secret configured in
the RADIUS server supporting the switch must be identical. Refer to
the chapter titled “RADIUS Authentication and Accounting” in the
Access Security Guide for your switch.
Figure 7. Example of Configuring the Switch’s Identity Information in a FreeRADIUS Server
3. For a given client username/password pair or MAC address, create an ACL by entering one or
more ACEs in the FreeRADIUS “users” file. Enter the ACEs in an order that promotes optimum
traffic management and conservation of system resources, and remember that every ACL you
create automatically includes an implicit deny in ip from any to any ACE. (Refer to “Guidelines for
Structuring a RADIUS-Based ACL” on page 55.) For example, suppose that you wanted to create
identical ACL support for the following:
• a client having a username of “mobile011” and a password of “run101112”
• a client having a MAC address of 08 E9 9C 4F 00 19
The ACL in this example must achieve the following:
• permit http (TCP port 80) traffic from the client to the device at 10.10.10.101
• deny http (TCP port 80) traffic from the client to all other devices
• permit all other traffic from the client to all other devices
To configure the above ACL, you would enter the username/password and ACE information
shown in Figure 8 into the FreeRADIUS users file.
Note
For syntax details on RADIUS-based ACLs, refer to “Format Details for ACEs Configured in a
RADIUS-Based ACL” on page 60.
59
Page 70

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Client’s Username (802.1X or Web Authentication)
Client’s Password (802.1X or Web Authentication)
mobile011 Auth-Type:= Local, User-Password == run101112
HP-IP-FILTER-RAW = “permit in tcp from any to 10.10.10.101”,
HP-IP-FILTER-RAW += “deny in tcp from any to any”,
HP-IP-FILTER-RAW += “permit in ip from any to any”
Client’s Password (MAC Authentication)
Client’s Username (MAC Authentication)
Client’s Password (MAC Authentication)
08E99C4F0019 Auth-Type:= Local, User-Password == 08E99C4F0019
HP-IP-FILTER-RAW = “permit in tcp from any to 10.10.10.101”,
HP-IP-FILTER-RAW += “deny in tcp from any to any”,
HP-IP-FILTER-RAW += “permit in ip from any to any”
Note that when the client MAC address is used for authentication, this address is used
in both the username and password spaces in the entry.
Figure 8. Example of Configuring the FreeRADIUS Server To Support ACLs for the Indicated Clients
Format Details for ACEs Configured in a RADIUS-Based ACL.
Any instance of a RADIUS-Based ACL is structured to filter authenticated client traffic as follows:
■ Applies only to inbound client traffic on the switch port the authenticated client is using.
■ Allows only the “any” source address (for any authenticated IP device connected to the port).
■ Applies to all IP traffic from the authenticated client or to a specific type of IP traffic type
from the client. Options include TCP, UDP, or any other type of IP traffic that is identified by
an IP protocol number. (More information on protocol numbers is provided in the following
ACL syntax description.)
■ Has one of the following destination types:
• A specific IP address
• A contiguous series of IP address or an entire subnet
• Any IP address
■ Where the traffic type is either TCP or UDP, the ACE can optionally include one or more TCP
or UDP port numbers.
60
Page 71

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
The following syntax and operating information refers to ACLs configured in a RADIUS server
.
ACE Syntax:
< permit | deny >: Specifies whether to forward or drop the identified IP traffic type from the
authenticated client.
in: Required keyword specifying that the ACL applies only to the traffic inbound from the
authenticated client.
< ip | ip-protocol-value >: Options for specifying the type of traffic to filter.
from any: Required keywords specifying the (authenticated) client source. (Note that a
RADIUS-Based ACL assigned to a port filters only the inbound traffic having a source
MAC address that matches the MAC address of the client whose authentication invoked the
ACL assignment.)
to : Required destination keyword.
[ tcp/udp-ports]: Optional TCP or UDP port specifier. Used when the ACL is intended to filter
client TCP or UDP traffic with one or more specific TCP or UDP destination port numbers.
You can specify port numbers as individual values and/or ranges. For example, the
following ACE denies any UDP traffic from an authenticated client that has a DA of any
IP address and a UDP destination port of 135, 137-139, or 445:
< permit | deny > in < ip | ip-protocol-value > from any to < ip-addr > [/< mask > ] | any > [ tcp/udp-ports] [cnt ]
ip: This option applies the ACL to all IP traffic from the authenticated client.
ip-protocol-value: This option applies the ACL to the type of IP traffic specified by either
a protocol number or by
tcp or udp. The range of protocol numbers is 0-255, and you
can substitute 6 for TCP or 17 for UDP. (Protocol numbers are defined in RFC 2780.
For a complete listing, refer to “Protocol Numbers” under “Protocol Number Assignment Services” on the Web site of the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority at
www.iana.com.) Some examples of protocol numbers include:
1 = ICMP 6 = TCP 41 = IPv6
2 = IGMP 17 = UDP
< ip-addr >: Specifies a single destination IP address.
< ip-addr /< mask >: Specifies a series of contiguous destination IP addresses or all
destination IP addresses in a subnet. The < mask > is CIDR notation for the number
of leftmost bits in a packet’s destination IP address that must match the corresponding bits in the destination IP address listed in the ACE. For example, a
destination of 10.100.17.1/24 in the ACE means that a match occurs when an
inbound packet (of the designated IP type) from the authenticated client has a
destination IP address where the first three octets are 10.100.17. (The fourth octet is
a wildcard, and can be any value up to 255.)
any: Specifies any IP destination address. Use this option when you want the ACL
action to apply to all traffic of the designated type, regardless of destination.
deny in udp from any to any 135, 137-139, 445
.
61
Page 72

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
[ cnt ]: Optional counter specifier for a RADIUS-based ACL. When used in an ACL, the
counter increments each time there is a “match” with a permit or deny ACE. (Refer to the
entry describing the maximum number of (optional) internal counters in the table on
page 57.) Counter values appear in RADIUS accounting log for client if RADIUS
networking accounting is configured on the switch.
Configuring the Switch To Support RADIUS-Based ACLs
An ACL configured in a RADIUS server is identified by the authentication credentials of the client or
group of clients the ACL is designed to support. When a client authenticates with credentials
associated with a particular ACL, the switch applies that ACL to the switch port the client is using.
To enable the switch to forward a client’s credentials to the RADIUS server, you must first configure
RADIUS operation and an authentication method on the switch.
1. Configure RADIUS operation on the switch:
Syntax: radius-server host < ip-address > key < key-string >
[auth-port < udp-dest-port > acct-port < udp-dest-port >]
This command configures the IP address and encryption key of a RADIUS server. The server
should be accessible to the switch and configured to support authentication requests from
clients using the switch to access the network. For more on RADIUS configuration, including
the auth-port and acct-port options, refer to the chapter titled “RADIUS Authentication and
Accounting” in the Access Security Guide for your switch.
2. Configure RADIUS network accounting on the switch (optional). RADIUS network accounting
is necessary to retrieve counter information if the cnt (counter) option (described on page 62)
is included in any of the ACEs configured on the RADIUS server.
Syntax: aaa accounting network < start-stop | stop-only > radius
For more on RADIUS accounting, refer to the chapter titled “RADIUS Authentication and
Accounting” in the Access Security Guide for your switch.
Note
Refer to the documentation provided with your RADIUS server for information on how the server
receives and manages network accounting information, and how to perform any configuration
steps necessary to enable the server to support network accounting data from the switch.
62
Page 73

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
3. Configure an authentication method. Options include 802.1X, Web authentication, and MAC
authentication. (You can configure 802.1X and either Web or MAC authentication to operate
simultaneously on the same ports.)
802.1X Option:
Syntax: aaa port-access authenticator < port-list >
aaa authentication port-access chap-radius
aaa port-access authenticator active
These commands configure 802.1X port-based access control on the switch, and activates
this feature on the specified ports. For more on 802.1X configuration and operation, refer to
the chapter titled “Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control” in the Access
Security Guide for your switch.
MAC Authentication Option:
Syntax: aaa port-access mac-based < port-list >
This command configures MAC authentication on the switch and activates this feature on
the specified ports. For more on MAC authentication, refer to the chapter titled “Web and
MAC Authentication” in the Access Security Guide for your switch.
Web Authentication Option:
Syntax: aaa port-access web-based < port-list >
This command configures Web authentication on the switch and activates this feature on the
specified ports. For more on Web authentication, refer to the chapter titled “Web and MAC
Authentication” in the Access Security Guide for your switch.
63
Page 74

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Displaying the Current RADIUS-Based ACL Activity on the Switch
These commands output data indicating the current ACL activity imposed per-port by RADIUS server
responses to client authentication.
Syntax: show access-list radius < port-list >
For the specified ports, this command lists the explicit ACEs, switch port, and client MAC
address for the ACL dynamically assigned by a RADIUS server as a response to client
authentication. If cnt (counter) is included in an ACE, then the output includes the current
number of inbound packet matches the switch has detected in the current session for that
ACE.
Note: If there are no ACLs currently assigned to any port in < port-list >, executing this
command returns the following message:
Port < port-# >, No RADIUS ACLs applied on this port.
If a client authenticates but the server does not return a RADIUS-based ACL to the client
port, then the server does not have a valid ACL configured and assigned to that client’s
authentication credentials.
For example, the following output shows that a RADIUS server has assigned an ACL to port 10 to
filter inbound traffic from an authenticated client identified by a MAC address of 00-11-85-C6-54-7D.
ProCurve# show access-list radius 10
Radius-configured Port-based ACL for
Port 10, Client -- 001185C6547D
deny in tcp from any to 10.15.240.184 23 cnt
Packet Hit Counter : 0
deny in tcp from any to 10.15.240.184 80 cnt
Packet Hit Counter : 0
permit in tcp from any to 10.15.240.184 7
permit in udp from any to 10.15.240.184 7
deny in tcp from any to 10.15.240.184 161 cnt
Packet Hit Counter : 0
deny in udp from any to 10.15.240.184 161 cnt
Packet Hit Counter : 0
permit in ip from any to any
Indicates MAC address identity of the
authenticated client on the specified port. This
data identifies the client to which the ACL
applies.
Lists “deny” ACE for Inbound Telnet (23 = TCP
port number) traffic, with counter configured to
show the number of matches detected.
Lists current counter for the preceeding
“Deny” ACE.
Lists “permit” ACE for inbound TCP and UDP
traffic, with no counters configured.
Note that the implicit “deny any/any” included
automatically at the end of every ACL is not
visible in ACL listings generate by the switch.
Figure 9. Example Showing a RADIUS-Based ACL Application to a Currently Active Client Session
64
Page 75

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Syntax: show port-access authenticator < port-list >
For ports,in < port-list > that are configured for authentication, this command indicates
whether there are any RADIUS-assigned features active on the port(s). (Any ports in
< port-list > that are not configured for authentication do not appear in this listing.)
Port: Port number of port configured for authentication.
Status: Port connection status:
Open = active connection with an external device
Closed = no active connection with an external device
Current VLAN ID: VLAN ID (VID) of the VLAN currently supporting the active connection.
Current Port CoS: Indicates the status of the current 802.1p priority setting for inbound traffic.
No-override: Indicates that no RADIUS-assigned 802.1p priority is currently active on
the indicated port. (For more on traffic prioritization for the 5300xl switches, refer to
the chapter titled “Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively” in
the Advanced Traffic Management Guide
for your switch.)
0 - 7: Indicates that the displayed 802.1p priority has been assigned by a RADIUS server
to inbound traffic on the indicated port for a currently active, authenticated client
session. This assignment remains active until the session ends.
% Curr.Rate Limit Inbound: Indicates the status of the current rate-limit setting for inbound
traffic.
No-override: No RADIUS-assigned rate-limit is currently active on the indicated port.
(For more on rate-limiting, refer to the chapter titled “Port Traffic Controls” in the
Management and Configuration Guide
for your switch.)
0 - 100: Indicates that the displayed rate-limit has been assigned by a RADIUS server to
inbound traffic on the indicated port for a currently active, authenticated client session.
This assignment remains active until the session ends.
RADIUS ACL Applied?: Indicates whether a RADIUS-assigned ACL is currently active on the
port.
Yes : An ACL has been assigned by a RADIUS server to inbound traffic on the indicated
port for a currently active, authenticated client session. This assignment remains
active until the session ends.
No: There is no RADIUS-assigned ACL currently active on the indicated port.
Enhancements
65
Page 76

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
ProCurve(config)# show port-access authenticator 10-11
Port Access Authenticator Status
Port-access authenticator activated [No] : No
Current Current % Curr. Rate RADIUS ACL
Port Status VLAN ID Port COS Limit Inbound Applied?
---- ------ -------- ----------- -------------- ---------- 10 Open 1 7 No-override Yes
11 Closed 1 No-override No-override No
Figure 10. Example of Output Showing Current RADIUS-Applied Features
Event Log Messages
Message Meaning
ACE parsing error, permit/deny
keyword < ace-# > client < mac-address >
port < port-# >.
Could not add ACL entry.
Could not create ACL entry.
Could not add ACL, client mac < mac-
address >
port < port-# >, at max per-port
ACL quantity.
ACE parsing error, IN keyword,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
ACE parsing error, protocol field,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
ACE parsing error, FROM keyword,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
ACE parsing error, ANY keyword,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
ACE parsing error, TO keyword,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
Notifies of a problem with the permit/deny keyword in
the indicated ACE included in the access list for the indicated client on the indicated switch port.
Notifies that the ACE entry could not be added to the internal
ACL storage.
Notifies that the ACL could not be added to the internal ACL
storage.
Notifies that the ACL could not be added because the perport ACL quantity would be exceeded.
Notifies of a problem with the IN keyword in the indicated
ACE of the access list for the indicated client on the indicated switch port.
Notifies of a problem with the protocol field in the indicated
ACE of the access list for the indicated client on the indicated switch port.
Notifies of a problem with the FROM keyword in the indicated ACE of the access list for the indicated client on the
indicated switch port.
Notifies of a problem with the ANY keyword in the indicated
ACE of the access list for the indicated client on the indicated switch port.
Notifies of a problem with the TO keyword in the indicated
ACE of the access list for the indicated client on the indicated switch port.
Indicates a RADIUS ACL is
currently applied as part of
an active session with an
authenticated client.
66
Page 77

Message Meaning
ACE parsing error, destination IP,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
ACE parsing error, tcp/udp ports,
< ace-# > client < mac-address > port
< port-# >.
Port < port-# >, No RADIUS ACLs applied
on this port.
Rule limit per ACL exceeded. < ace-# >
client < mac-address > port < port-# >.
Duplicate mac. An ACl exists for
Notifies of a problem with the destination IP field in the
indicated ACE of the access list for the indicated client on
the indicated switch port.
Notifies of a problem with the TCP/UDP port field in the
indicated ACE of the access list for the indicated client on
the indicated switch port.
Appears in response to the CLI show access-list radius
< port-# > command when there is not currently a RADIUS
ACL assigned to the port.
Notifies that an ACL has too many rules. A maximum of 30
(internal) ACEs are allowed per ACL. Refer to Table 5 on
page 57.
Notifies that an ACL for this mac on this port already exists.
client. Deauthenticating second.
client < mac-address > port < port-# >.
Invalid Access-list entry length,
client < mac-address > port < port-# >.
Memory allocation failure for IDM
ACL.
ACE limit per port exceeded. client
< mac-address > port < port-# >.
Exceeded counter per port limit.
client < mac-address > port < port-# >.
Notifies that the string configured for an ACE entry on
the Radius server exceeds 80 characters.
Notifies of a memory allocation failure for a RADIUS-based
ACL.
User Action?
Notifies that the maximum number of ACEs (30) allowed on
the port was exceeded.
Notifies that the internal counter (cnt) limit of 32 per port
was exceeded on port < port-# >. Refer to Table 5 on page 57.
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
Causes of Client Deauthentication Immediately After Authenticating
■ ACE formatted incorrectly in the RADIUS server
• “from”, “any”, or “to” keyword missing
• An IP protocol number in the ACE exceeds 255.
• An optional UDP or TCP port number is invalid.
■ A RADIUS-Based ACL limit has been exceeded. (Refer to Table 5, “Limits Affecting RADIUS-
Based ACL Applications” on page 57.)
• The allowed maximum of one RADIUS-assigned ACL has already been reached on the
port through which the deauthenticated client is trying to access the network. (Each
client requiring a RADIUS-assigned ACL is a separate instance, even if multiple clients
are assigned the same ACL.)
• For a given port, the latest client authentication includes a RADIUS-Based ACL assign-
ment exceeding the maximum number of ACEs allowed on the port (30).
67
Page 78

Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
• An ACE in the ACL for a given authenticated client exceeds 80 characters.
• An ACL assigned to an authenticated client causes the number of optional counters
needed on the ACL to exceed the per-ACL maximum (32).
SFlow Show Commands
In earlier software releases, the only method for checking whether sFlow is enabled on the switch
was via an snmp request. Beginning with software release M.10.02, the 3400cl switches have added
the following show sFlow commands that allow you to see sFlow status via the CLI.
Syntax: show sflow agent
Displays sFlow agent information. The agent address is normally the ip address of
the first vlan configured.
Syntax: show sflow destination
Displays information about the management station to which the sFlow samplingpolling data is sent.
Syntax: show sflow sampling-polling <port-list/range>
Displays status information about sFlow sampling and polling.
Syntax: show sflow all
Displays sFlow agent, destination, and sampling-polling status information for all
the ports on the switch.
Ter mi no lo gy
sFlow — An industry standard sampling technology, defined by RFC 3176, used to continuously
monitor traffic flows on all ports providing network-wide visibility into the use of the network.
sFlow agent — A software process that runs as part of the network management software within a
device. The agent packages data into datagrams that are forwarded to a central data collector.
sFlow destination — The central data collector that gathers datagrams from sFlow-enabled switch
ports on the network. The data collector decodes the packet headers and other information to
present detailed Layer 2 to Layer 7 usage statistics.
Viewing SFlow Configuration
The show sflow agent command displays read-only switch agent information. The version information
shows the sFlow MIB support and software versions; the agent address is typically the ip address of
the first vlan configured on the switch.
68
Page 79

Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Enhancements
ProCurve# show sflow agent
Version 1.3;HP;M.10.03
Agent Address 10.0.10.228
Figure 13. Viewing sFlow Agent Information
The show sflow destination command includes information about the management-station’s destination address, receiver port, and owner.
ProCurve# show sflow destination
sflow Enabled
Datagrams Sent 221
Destination Address 10.0.10.41
Receiver Port 6343
Owner admin
Timeout (seconds) 333
Max Datagram Size 1400
Datagram Version Support 5
Figure 14. Example of Viewing sFlow Destination Information
Note the following details:
■ Destination Address remains blank unless it has been configured on the switch via SNMP.
■ Datagrams Sent shows the number of datagrams sent by the switch agent to the manage-
ment station since the switch agent was last enabled.
■ Timeout displays the number of seconds remaining before the switch agent will automati-
cally disable sFlow (this is set by the mangement station and decrements with time).
■ Max Datagram Size shows the currently set value (typically a default value, but this can
also be set by the management station).
The show sflow sampling-polling command displays information about sFlow sampling and polling on
the switch. You can specify a list or range of ports for which to view sampling information.
69
Page 80

Enhancements
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
ProCurve# show sflow sampling-polling 1-5
sflow destination Enabled
Port | Sampling Dropped | Polling
Enabled Rate Header Samples | Enabled Interval
----- + ------- -------- ------ ---------- + ------- ------- 1 | Yes 6500000 128 5671234 Yes 60
2 | No 50 128 0 Yes 300
3 | Yes 2000 100 24978 No 30
4 | Yes 200 100 4294967200 Yes 40
5 | Yes 20000 128 34 Yes 500
Figure 15. Example of Viewing sFlow Sampling and Polling Information
The show sflow all command combines the outputs of the preceding three show commands including
sFlow status information for all the ports on the switch.
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Release M.10.04 includes the following enhancements:
■ Enhancement (PR_1000330743) - Instrumentation Monitor, which includes Denial of Service
(DoS) logging enhancement.
■ Enhancement (PR_1000331027) - TCP/UDP port closure enhancement.
■ Enhancement (PR_1000330532) - Improved the "show" command display of STP port detail
information to assist in monitoring and troubleshooting of the spanning tree protocol.
Instrumentation Monitor
The 3400cl switches have instrumentation to monitor many operating parameters at pre-determined
intervals. Beginning with software release M.10.04, this capability can be used to detect anomalies
caused by security attacks or other irregular operations on the switch. The following table shows the
parameters that can be monitored, and the possible security attacks that may trigger an alert:
Parameter Name Description
pkts-to-closed-ports The count of packets per minute sent to closed TCP/UDP ports. An excessive amount
arp-requests The count of ARP requests processed per minute. A large amount of ARP request
70
of packets could indicate a port scan, in which an attacker is attempting to expose a
vulnerability in the switch.
packets could indicate an host infected with a virus that is trying to spead itself.
Page 81

Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Enhancements
Parameter Name Description
ip-address-count The number of destination IP addresses learned in the IP forwarding table. Some
attacks fill the IP forwarding table causing legitimate traffic to be dropped.
system-resource-usage
(Denial of Service logging)
The percentage of system resources in use. Some Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks
will cause excessive system resource usage, resulting in insufficient resources for
legitimate traffic.
login-failures/min The count of failed CLI login attempts or SNMP management authentication failures.
This indicates an attempt has been made to manage the switch with an invalid login
or password. Also, it might indicate a network management station has not been
configured with the correct SNMP authentication parameters for the switch.
port-auth-failures/min The count of times a client has been unsuccessful logging into the network
system-delay The response time, in seconds, of the CPU to new network events such as BPDU
packets or packets for other network protocols. Some DoS attacks can cause the
CPU to take too long to respond to new network events, which can lead to a
breakdown of Spanning Tree or other features. A delay of several seconds indicates
a problem.
mac-address-count The number of MAC addresses learned in the forwarding table. Some attacks fill the
forwarding table so that new conversations are flooded to all parts of the network.
mac-moves/min The average number of MAC address moves from one port to another per minute.
This usually indicates a network loop, but can also be caused by DoS attacks.
learn-discards/min Number of MAC address learn events per minute discarded to help free CPU
resources when busy.
Operating Notes
■ To generate alerts for monitored events, you must enable the instrumentation monitoring
log and/or SNMP trap. The threshold for each monitored parameter is configurable and can
be adjusted to minimize false alarms (see “Configuring Instrumentation Monitor” on page 73).
■ When a parameter exceeds its threshold, an alert (event log message and/or SNMP trap) is
generated to inform network administrators of this condition. The following example shows
an event log message that occurs when the number of MAC addresses learned in the
forwarding table exceeds the configured threshold:
Standard Date/Time Prefix
for Event Log Messages
“inst-mon” label indicates an
Instrumentation Monitor event
Monitored
Parameter
W 05/27/06 12:10:16 inst-mon: Limit for MAC addr count (300) is exceeded (321)
Figure 16. Example of Event Log Message generated by Instrumentation Monitor
Threshold
Valu e
Current
Valu e
71
Page 82

Enhancements
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
■ Alerts are automatically rate limited to prevent filling the log file with redundant information.
The following is an example of alerts that occur when the device is continually subject to
the same attack (too many MAC addresses in this instance):
W 01/01/90 00:05:00 inst-mon: Limit for MAC addr count (300) is exceeded (321)
W 01/01/90 00:10:00 inst-mon: Limit for MAC addr count (300) is exceeded (323)
W 01/01/90 00:15:00 inst-mon: Limit for MAC addr count (300) is exceeded (322)
W 01/01/90 00:20:00 inst-mon: Limit for MAC addr count (300) is exceeded (324)
W 01/01/90 00:20:00 inst-mon: Ceasing logs for MAC addr count for 15 minutes
Figure 17. Example of the rate limiting that occurs when multiple messages are generated
In the preceding example, if a condition is reported 4 times (persists for more than 15 minutes)
then alerts cease for 15 minutes. If after 15 minutes the condition still exists, the alerts cease for
30 minutes, then for 1 hour, 2 hours, 4 hours, 8 hours, and after that the persisting condition is
reported once a day. Note that ProCurve switches also have the ability to send event log entries
to a syslog server.
Known Limitations
As of release M.10.06, the instrumentation monitor runs once every five minutes. The current
implementation does not track information such as the port, MAC, and IP address from which an
attack is received.
72
Page 83

Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Enhancements
Configuring Instrumentation Monitor
The following commands and parameters are used to configure the operational thresholds that are
monitored on the switch. By default, the instrumentation monitor is disabled.
Syntax: [no] instrumentation monitor [parameterName|all] [<low|med|high|limitValue>]
[log] : Enables/disables instrumentation monitoring log so that event log messages
are generated every time there is an event which exceeds a configured threshold.
(Default threshold setting when instrumentation monitoring is enabled: enabled)
[all] : Enables/disables all counter types on the switch but does not enable/disable
instrumentation monitor logging.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: see parameter lisings below)
[arp-requests] : The number of arp requests that are processed each minute.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 1000 (med))
[ip-address-count]: The number of destination IP addresses learned in the IP
forwarding table.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 1000 (med))
[learn-discards] : The number of MAC address learn events per minute discarded to
help free CPU resources when busy.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 100 (med))
[login-failures] : The count of failed CLI login attempts or SNMP management authen-
tication failures per hour.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 10 (med))
[mac-address-count] : The number of MAC addresses learned in the forwarding table.
You must enter a specific value in order to enable this feature.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 1000 (med))
[mac-moves] : The average number of MAC address moves per minute from one port
to another.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 100 (med))
[pkts-to-closed-ports] : The count of packets per minute sent to closed TCP/UDP ports.
(Default threshold setting when enabled:
[port-auth-failures] : The count of times per minute that a client has been unsuccessful
logging into the network.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 10 (med))
[system-resource-usage]: The percentage of system resources in use.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 50 (med)))
[system-delay] : The response time, in seconds, of the CPU to new network events such
as BPDU packets or packets for other network protocols.
(Default threshold setting when enabled: 3 seconds (med))
[trap] : Enables or disables SNMP trap generation.
(Default setting when instrumentation monitoring is enabled: disabled)
10 (med))
To enable instrumentation monitor using the default parameters and thresholds, enter the general
instrumentation monitor command. To adjust specific settings, enter the name of the parameter that
you wish to modify, and revise the threshold limits as needed.
73
Page 84

Enhancements
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Examples
To turn on monitoring and event log messaging with the default medium values:
ProCurve(config)# instrumentation monitor
To turn off monitoring of the system delay parameter:
ProCurve(config)# no instrumentation monitor system-delay
To adjust the alert threshold for the MAC address count to the low value:
ProCurve(config)# instrumentation monitor mac-address-count low
To adjust the alert threshold for the MAC address count to a specific value:
ProCurve(config)# instrumentation monitor mac-address-count 767
To enable monitoring of learn discards with the default medium threshold value:
ProCurve(config)# instrumentation monitor learn-discards
To disable monitoring of learn discards:
ProCurve(config)# no instrumentation monitor learn-discards
To enable or disable SNMP trap generation:
ProCurve(config)# [no] instrumentation monitor trap
Viewing the Current Instrumentation Monitor Configuration
The show instrumentation monitor configuration command displays the configured thresholds for
monitored parameters, as shown in Figure 18 on the next page.
An alternate method of determining the current Instrumentation Monitor configuration is to use the
show run command. However, the show run command output does not display the threshold values
for each limit setting.
74
Page 85

ProCurve# show instrumentation monitor configuration
PARAMETER LIMIT
------------------------- -------------- mac-address-count 1000 (med)
ip-address-count 1000 (med)
system-resource-usage 50 (med)
system-delay 5 (high)
mac-moves/min 100 (med)
learn-discards/min 100 (med)
ip-port-scans/min 10 (med)
arp-requests/min 100 (low)
login-failures/min 10 (med)
port-auth-failures/min 10 (med)
SNMP trap generation for alerts: enabled
Instrumentation monitoring log : enabled
Figure 18. Viewing the Instrumentation Monitor Configuration
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Enhancements
TCP/UDP Port Closure
In earlier software releases, certain UDP ports were always open. Beginning with software release
M.10.04, all TCP/UDP ports on the 3400cl switches will remain closed until the associated services
are enabled on the switch.
The following ports and services are affected by this change:
Port Service
69 TFTP
161 SNMP
520 RIP
1507 Stacking (SNMP)
To open any of these ports, the respective services must first be enabled on the switch. For
information on how to enable/disable these services, refer to the following command listings . For
details on each service, refer to the latest version of the switch’s software documentation available
on the ProCurve Networking Web site.
75
Page 86

Enhancements
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Enabling/Disabling TFTP
The TFTP server and client can be enabled and/or disabled independently.
Syntax: [no] tftp < client | server >
Enables or disables the TFTP client.
client: Enables or disables the TFTP client.
(Default: disabled)
server: Enables or disables the TFTP server.
(Default: disabled)
Note: Both the tftp command (with no arguments) and the tftp client command can be used to enable
or disable the tftp client.
Enabling/Disabling SNMP
To enable/disable SNMP, use the following commands.
Syntax: [no] snmp-server enable
Enables or disables SNMP v1/v2.
(Default: disabled)
Syntax: [no] snmpv3 enable
Enables or disables SNMP v3.
(Default: disabled)
Notes
■ The SNMP port (161) will be opened if either SNMP v1/2 or SNMP v3 are enabled, or remain
closed if both are disabled.
■ The snmp-server enable command takes precedence over the snmp-server enable traps
command that is used to enable or disable authentication traps to be sent when a management station attempts an unauthorized access.
■ If SNMP is disabled, both the SNMP port (161) and the stacking port (1507) will remain
closed.
Enabling/Disabling RIP
To enable/disable RIP, use the following command.
Syntax: [no] router rip
Enables, disables, or configures Routing Internet Protocol (RIP) on the switch.
(Default: disabled)
76
Page 87

Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Enhancements
Note
The router rip command exists in previous software versions. In this implementation, however, RIP
must be enabled in order to open the port on the switch.
Enabling/Disabling Stacking
To enable/disable stacking, use the following command.
Syntax: [no] stack
Enables stacking (SNMP) on the switch. (Default: disabled)
Note
The stack command exists in previous software versions. In this implementation, however, both
stacking and SNMP must be enabled to open the port on the switch. If either feature is disabled, the
port will remain closed.
Spanning Tree Show Commands
The show spanning-tree detail command previously displayed 802.1D (STP) and 802.1w (RSTP) status
and counters for all ports on the switch. Beginning with software release M.10.04, this command
provides 802.1s (MSTP) multi-instance spanning tree details and displays additional parameters to
enhance spanning-tree reporting via the CLI.
77
Page 88

Enhancements
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
The following shows RSTP sample output from the enhanced command.
ProCurve# show spanning-tree detail
Status and Counters - RSTP Port(s) Detailed Information
Port : 1
Status : Up
Role : Root
State : Forwarding
Priority : 128
Path Cost : 200000
Root Path Cost : 10
Root Bridge ID : 1:0001e7-215e00
Designated Bridge ID : 32768:0001e7-3d0080
Designated Port ID : 128:75
AdminEdgePort : Yes
OperEdgePort : No
AdminPointToPointMAC : Force-True
OperPointToPointMAC : Yes
Aged BPDUs Count : 0
Loop-back BPDUs Count : 0
TC Detected : 1
TC Flag Transmitted : 0 TC ACK Flag Transmitted : 0
TC Flag Received : 0 TC ACK Flag Received : 47
RSTP RSTP CFG CFG TCN TCN
BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- 3 0 0 256654 47 0
Figure 19. Example of Show Spanning-Tree Detail
Operating Notes
■ TC refers to a Topology Change detected on the given port. Note the following details:
• TC Detected counter shows when a port identifies a topology change (increments when
the particular non-Edge port goes into forwarding). For RSTP and MSTP, this would be
due to the switch’s link going to forwarding.
• TC Flag Transmitted counter shows the number of TC notifications sent out of the port.
This refers to propagating a topology change that occurred on another port (that is, a
TC Detected increment) or to propagating a topology change received on another port
(that is, TC Flag Received).
78
Page 89

Release M.10.05 Enhancements
• TC Flag Received counter shows the number of TC notifications (RSTP or MSTP style
BPDU with the TC flag set) received on the port.
• TC ACK Flag Transmitted is an 802.1D mode counter. It will only increment when the port
is operating in 802.1D mode and an 802.1D style PDU is sent out of the port.
• TC ACK Flag Received is an 802.1D mode counter. It will only increment when the port is
operating in 802.1D mode and an 802.1D style PDU is received on the port.
■ With STP and RSTP activated:
•The show spanning tree detail command shows all active RSTP port by port.
•The show spanning-tree <port-list> detail command shows the specified port-list RSTP
port by port detail.
■ With MSTP activated:
•The show spanning tree detail command shows all active MSTP port by port. This
command only gives information concerning the common spanning tree (CST) ports. To
view counters pertaining to a specific spanning-tree instance, you must use the show
spanning-tree instance <inst> detail command. The show spanning-tree <port-list> detail
command shows the specified port-list MSTP port by port detail.
•The show spanning-tree instance <inst> detail command shows all ports active for a
specific instance of MSTP.
Enhancements
•The show spanning-tree <port-list> instance <inst> detail shows the specified port-list for
the specified instance of MSTP.
• TC ACK Flag Transmitted and TC ACK Flag Received are part of the CST counters displayed
by the show spanning tree detail command. TC Detected, TC Flag Transmitted, and TC Flag
Received are included only with the instance parameter due to the nature of MSTP.
Release M.10.05 Enhancements
Release M.10.05 includes the following enhancement:
■ Ping functionality now in conformance with RFC 2925 specification.
Release M.10.06 Enhancements
Release M.10.06 includes the following enhancement:
■ Enhancement (PR_1000330704) - Added RADIUS Command Authorization and Accounting
for the Command Line Interface on 3400cl switch. Please refer to Chapter 6, RADIUS
Authentication and Accounting in the Access Security Guide for the ProCurve Series 6400cl/
5300xl/4200vl/3400cl Switches (October 2005) for additional information.
79
Page 90

Enhancements
Release M.10.07 Enhancements
Release M.10.07 Enhancements
Release M.10.07 includes the following enhancement:
■ Added support for PIM Dense Mode. For details, refer to Chapter 5, “PIM-DM (Dense Mode)
on the 5300xl Switches” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide for the ProCurve Series
6400cl/5300xl/4200vl/3400cl Switches.
Release M.10.08 Enhancements
Software fixes only, no new enhancements.
Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Release M.10.09 includes the following enhancement:
■ Added support for Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD). See “Uni-Directional Link Detec-
tion (UDLD)” on page 80 for details.
Uni-Directional Link Detection (UDLD)
Uni-directional Link Detection (UDLD) monitors a link between two ProCurve switches and blocks
the ports on both ends of the link if the link fails at any point between the two devices. This feature
is particularly useful for detecting failures in fiber links and trunks.
In the example shown in Figure 20, each ProCurve switch load balances traffic across two ports in
a trunk group. Without the UDLD feature, a link failure on a link that is not directly attached to one
of the ProCurve switches remains undetected. As a result, each switch continues to send traffic on
the ports connected to the failed link. When UDLD is enabled on the trunk ports on each ProCurve
switch, the switches detect the failed link, block the ports connected to the failed link, and use the
remaining ports in the trunk group to forward the traffic.
80
Page 91

Scenario 1 (No UDLD): Without UDLD, the switch ports
remain enabled despite the link failure. Traffic continues to
be load-balanced to the ports connected to the failed link.
Scenario 2 (UDLD-enabled): When UDLD is enabled, the
feature blocks the ports connected to the failed link.
Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Enhancements
Tr un k
ProCurve
Switch
Third Party
Switch
ProCurve
Switch
Link Failure
Figure 20. UDLD Example
Similarly, UDLD is effective for monitoring fiber optic links that use two uni-direction fibers to
transmit and receive packets. Without UDLD, if a fiber breaks in one direction, a fiber port may
assume the link is still good (because the other direction is operating normally) and continue to send
traffic on the connected ports. UDLD-enabled ports, however, prevent traffic from being sent across
a bad link by blocking the ports in the event that either the individual transmitter or receiver for that
connection fails.
Ports enabled for UDLD exchange health-check packets once every five seconds (the link-keepalive
interval). If a port does not receive a health-check packet from the port at the other end of the link
within the keepalive interval, the port waits for four more intervals. If the port still does not receive
a health-check packet after waiting for five intervals, the port concludes that the link has failed and
blocks the UDLD-enabled port.
When a port is blocked by UDLD, the event is recorded in the switch log or via an SNMP trap (if
configured); and other port blocking protocols, like spanning tree or meshing, will not use the bad
link to load balance packets. The port remains blocked until the link is unplugged, disabled, or fixed.
The port can also be unblocked by disabling UDLD on the port.
81
Page 92

Enhancements
Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Configuration Considerations
■ UDLD is configured on a per-port basis and must be enabled at both ends of the link. See the
note below for a list of ProCurve switches that support UDLD.
■ To configure UDLD on a trunk group, you must configure the feature on each port of the
group individually. Configuring UDLD on a trunk group’s primary port enables the feature
on that port only.
■ Dynamic trunking is not supported. If you want to configure a trunk group that contains
ports on which UDLD is enabled, you must remove the UDLD configuration from the ports.
After you create the trunk group, you can re-add the UDLD configuration.
Note
UDLD interoperates with the following ProCurve switch series: 2600, 2800, 3400, 3500, 4200, 5300,
5400, 6200, 6400, and 9300. Consult the release notes and current manuals for required software
versions.
Configuring UDLD
The following commands allow you to configure UDLD via the CLI.
Syntax: [no] interface <port-list> link-keepalive
Enables UDLD on a port or range of ports.
To disable the feature, enter the no form of the command.
Default: UDLD disabled
Syntax: link-keepalive interval <interval>
Determines the time interval to send UDLD control packets. The <interval> parameter specifies how often the ports send a UDLD packet. You can specify from 10 –
100, in 100 ms increments, where 10 is 1 second, 11 is 1.1 seconds, and so on.
Default: 50 (5 seconds)
Syntax: link-keepalive retries <num>
Determines the maximum number of retries to send UDLD control packets. The
<num> parameter specifies the maximum number of times the port will try the health
check. You can specify a value from 3 – 10.
Default: 5
Syntax: [no] interface <port-list> link-keepalive vlan <vid>
Assigns a VLAN ID to a UDLD-enabled port for sending of tagged UDLD control
packets.Under default settings, untagged UDLD packets can still be transmitted and
received on tagged only ports—however, a warning message will be logged.
The no form of the command disables UDLD on the specified port(s).
Default: UDLD packets are untagged; tagged only ports will transmit and receive
untagged UDLD control packets
82
Page 93

Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Enhancements
Enabling UDLD. UDLD is enabled on a per port basis. For example, to enable UDLD on port a1,
enter:
ProCurve(config)#interface al link-keepalive
To enable the feature on a trunk group, enter the appropriate port range. For example:
ProCurve(config)#interface al-a4 link-keepalive
Note
When at least one port is UDLD-enabled, the switch will forward out UDLD packets that arrive on
non-UDLD-configured ports out of all other non-UDLD-configured ports in the same vlan. That is,
UDLD control packets will “pass through” a port that is not configured for UDLD. However, UDLD
packets will be dropped on any blocked ports that are not configured for UDLD.
Changing the Keepalive Interval. By default, ports enabled for UDLD send a link health-check
packet once every 5 seconds. You can change the interval to a value from 10 – 100 deciseconds,
where 10 is 1 second, 11 is 1.1 seconds, and so on. For example, to change the packet interval to
seven seconds, enter the following command at the global configuration level:
ProCurve(config)# link-keepalive interval 70
Changing the Keepalive Retries. By default, a port waits five seconds to receive a health-check
reply packet from the port at the other end of the link. If the port does not receive a reply, the port
tries four more times by sending up to four more health-check packets. If the port still does not
receive a reply after the maximum number of retries, the port goes down.
You can change the maximum number of keepalive attempts to a value from 3 – 10. For example, to
change the maximum number of attempts to 4, enter the following command at the global configuration level:
ProCurve(config)# link-keepalive retries 4
Configuring UDLD for Tagged Ports. The default implementation of UDLD sends the UDLD
control packets untagged, even across tagged ports. If an untagged UDLD packet is received by a
non-ProCurve switch, that switch may reject the packet. To avoid such an occurrence, you can
configure ports to send out UDLD control packets that are tagged with a specified VLAN.
To enable ports to receive and send UDLD control packets tagged with a specific VLAN ID, enter a
command such as the following at the interface configuration level:
ProCurve(config)#interface l link-keepalive vlan 22
83
Page 94

Enhancements
Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Notes
■ You must configure the same VLANs that will be used for UDLD on all devices across the
network; otherwise, the UDLD link cannot be maintained.
■ If a VLAN ID is not specified, then UDLD control packets are sent out of the port as untagged
packets.
■ To re-assign a VLAN ID, re-enter the command with the new VLAN ID number. The new
command will overwrite the previous command setting.
■ When configuring UDLD for tagged ports, you may receive a warning message if there are
any inconsistencies with the port’s VLAN configuration (see page 87 for potential problems).
Viewing UDLD Information
The following show commands allow you to display UDLD configuration and status via the CLI.
Syntax: show link-keepalive
Displays all the ports that are enabled for link-keepalive.
Syntax: show link-keepalive statistics
Displays detailed statistics for the UDLD-enabled ports on the switch.
Syntax: clear link-keepalive statistics
Clears UDLD statistics. This command clears the packets sent, packets received, and
transitions counters in the show link-keepalive statistics display.
84
Page 95

Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Enhancements
Displaying Summary UDLD Information. To display summary information on all UDLD-enabled
ports, enter the show link-keepalive command. For example:
ProCurve(config)# show link-keepalive
Total link-keepalive enabled ports: 4
Keepalive Retries: 3 Keepalive Interval: 1 sec
Port 1 is UDLD-enabled, and
Port Enabled Physical Keepalive Adjacent UDLD
tagged for a specific VLAN.
Status Status Switch VLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------ 1 Yes up up 00d9d-f9b700 200
2 Yes up up 01560-7b1600 untagged
3 Yes down off-line
4 Yes up failure
5 No down off-line
Port 4 is connected, but is blocked
due to a link-keepalive failure
Port 5 has been disabled by
the System Administrator.
Port 3 is UDLD-enabled, but
has no physical connection.
Figure 21. Example of UDLD Information displayed using Show Link-Keepalive Command
85
Page 96

Enhancements
Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Displaying Detailed UDLDP Status Information. To display detailed UDLD information for
specific ports, enter enter the show link-keepalive statistics command. For example:
Ports 1 and 2 are UDLD-enabled and show
the number of health check packets sent
ProCurve(config)# show link-keepalive statistics
Port: 1
Current State: up Neighbor MAC Addr: 0000a1-b1c1d1
Udld Packets Sent: 1000 Neighbor Port: 5
Udld Packets Received: 1000 State Transitions: 2
Port Blocking: no Link-vlan: 1
Port: 2
Current State: up Neighbor MAC Addr: 000102-030405
Udld Packets Sent: 500 Neighbor Port: 6
Udld Packets Received: 450 State Transitions: 3
Port Blocking: no Link-vlan: 200
Port: 3
Current State: off line Neighbor MAC Addr: n/a
Udld Packets Sent: 0 Neighbor Port: n/a
Udld Packets Received: 0 State Transitions: 0
Port Blocking: no Link-vlan: 1
and received on each port.
Port 4 is shown as blocked
due to a link-keepalive failure
Port: 4
Current State: failure Neighbor MAC Addr: n/a
Udld Packets Sent: 128 Neighbor Port: n/a
Udld Packets Received: 50 State Transitions: 8
Port Blocking: yes Link-vlan: 1
Figure 22. Example of Detailed UDLD Information displayed using Show Link-Keepalive Statistics
Command
Clearing UDLD Statistics. To clear UDLD statistics, enter the following command:
ProCurve# clear link-keepalive statistics
This command clears the Packets sent, Packets received, and Transitions counters in the show link
keepalive statistics display (see Figure 22 for an example).
86
Page 97

Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Enhancements
Configuration Warnings and Event Log Messages
Warning Messages. The following table shows the warning messages that may be issued and their
possible causes, when UDLD is configured for tagged ports.
Table 6. Warning Messages caused by configuring UDLD for Tagged Ports
CLI Command Example Warning Message Possible Problem
link-keepalive 6 Possible configuration
link-keepalive 7
vlan 4
no vlan 22 tagged 20Possible configuration
Note: If you are configuring the switch via SNMP with the same problematic VLAN configuration choices, the above
warning messages will also be logged in the switch’s event log.
problem detected on port
6. UDLD VLAN
configuration does not
match the port's VLAN
configuration.
Possible configuration
problem detected on port
7. UDLD VLAN
configuration does not
match the port's VLAN
configuration.
problem detected on port
18. UDLD VLAN
configuration does not
match the port's VLAN
configuration.
You have attempted to enable UDLD on a port that is
a tagged only port, but did not specify a configuration
for tagged UDLD control packets. In this example, the
switch will send and receive the UDLD control
packets untagged despite issuing this warning.
You have attempted to configure tagged UDLD
packets on a port that does not belong to the specified
VLAN. In this example, if port 7 belongs to VLAN 1 and
22, but the user tries to configure UDLD on port 7 to
send tagged packets in VLAN 4, the configuration will
be accepted. The UDLD control packets will be sent
tagged in VLAN 4, which may result in the port being
blocked by UDLD if the user does not configure VLAN
4 on this port.
You have attempted to remove a VLAN on port that is
configured for tagged UDLD packets on that VLAN. In
this example, if port 18, 19, and 20 are transmitting and
receiving tagged UDLD packets for Vlan 22, but the
user tries to remove Vlan 22 on port 20, the
configuration will be accepted. In this case, the UDLD
packets will still be sent on Vlan 20, which may result
in the port being blocked by UDLD if the users do not
change the UDLD configuration on this port.
Event Log Messages. The following table shows the event log messages that may be generated once
UDLD has been enabled on a port.
Table 7. UDLD Event Log Messages
Message Event
I 01/01/06 04:25:05 ports: port 4 is
deactivated due to link failure.
I 01/01/06 06:00:43 ports: port 4 is
up, link status is good.
A UDLD-enabled port has been blocked due to part of the link
having failed.
A failed link has been repaired and the UDLD-enabled port is no
longer blocked.
87
Page 98

Enhancements
Release M.10.10 Enhancements
Release M.10.10 Enhancements
Release M.10.10 includes the following enhancement:
Spanning Tree Per-Port BPDU Filtering
The STP BPDU filter feature allows control of spanning-tree participation on a per-port basis. It can
be used to exclude specific ports from becoming part of spanning tree operations. A port with the
BPDU filter enabled will ignore incoming BPDU packets and stay locked in the spanning-tree
forwarding state. All other ports will maintain their role.
Here are some sample scenarios in which this feature may be used:
■ To have STP operations running on selected ports of the switch rather than every port of the
switch at a time.
■ To prevent the spread of errant BPDU frames.
■ To eliminate the need for a topology change when a port's link status changes. For example,
ports that connect to servers and workstations can be configured to remain outside of
standard spanning-tree operations.
■ To protect the network from denial of service attacks with spoofing spanning-tree BPDUs
by dropping incoming BPDU frames.
Note
BPDU protection imposes a more secure mechanism that implements port shut down and a detection
alert when an errant BPDU frame is received ( see page 91 for details). BPDU protection will take
precedence over BPDU filtering if both features have been enabled on the same port.
Configuring STP BPDU Filters
The following commands allow you to configure BPDU filters via the CLI.
Syntax: [no] spanning-tree <port-list | all> bpdu-filter
Enables/disables the BPDU filter feature on the specified port(s).
For example, to configure BPDU filtering on port a9, enter:
ProCurve(config)# spanning-tree a9 bpdu-filter
88
Page 99

Release M.10.10 Enhancements
Enhancements
Caution
Ports configured with the BPDU filter mode remain active (learning and forward frames); however,
spanning-tree cannot receive or transmit BPDUs on the port. The port remains in a forwarding state,
permitting all broadcast traffic. This can create a network storm if there are any loops (that is, trunks
or redundant links) using these ports. If you suddenly have a high load, disconnect the link and
remove ("no") the bpdu-filter.
Viewing Status of BPDU Filtering
The show spanning-tree <port-list> detail command has been extended to show per-port BPDU filter
mode as shown below.
ProCurve# show spanning-tree a9 detail
Status and Counters - CST Port(s) Detailed Information
Port : A1
Status : Up
BPDU Filtering : Yes
Errant BPUDUs received : 65
MST Region Boundary : Yes
External Path Cost : 200000
External Root Path Cost : 420021
Administrative Hello Time : Use Global
Operational Hello Time : 2
AdminEdgePort : No
OperEdgePort : No
AdminPointToPointMAC : Force-True
OperPointToPointMAC : Yes
Aged BPDUs Count : 0
Loop-back BPDUs Count : 0
TC ACK Flag Transmitted : 0
TC ACK Flag Received : 0
Rows indicating BPDU filtering
has been enabled and number of
errant BPDUs received.
Column indicating BPDU frames
accepted for processing when
permitted by BPDU filter.
MST MST CFG CFG TCN TCN
BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- 8 28 0 0 0 0
Figure 23. Example of BPDU Filter Fields in Show Spanning Tree Detail Command
89
Page 100

Enhancements
Release M.10.10 Enhancements
The show spanning-tree command has also been extended to display BPDU filtered ports.
ProCurve# show spanning-tree
Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) Information
STP Enabled : Yes
Force Version : MSTP-operation
IST Mapped VLANs : 1-7
Row showing ports with BPDU filters enabled
...
Protected Ports :
Filtered Ports : A6-A7
....
Figure 24. Example of BPDU Filtered Ports Field in Show Spanning Tree Command
Viewing Configuration of BPDU Filtering
The BPDU filter mode adds an entry to the spanning tree category within the configuration file.
ProCurve(config)# show configuration
. . .
spanning-tree
spanning-tree A7 bpdu-filter
spanning-tree C9 bpdu-filter
spanning-tree Trk2 priority 4
. . .
Rows showing ports with BPDU filters enabled
Figure 25. Example of BPDU Filters in the Show Configuration Command
The spanning-tree show < port> configuration command displays the BPDU’s filter state.
ProCurve(config)# show spanning-tree a8 config
...
BPDU
Port Type | Cost Priority Edge Point-to-Point MCheck Filter
---- --------- + --------- -------- ---- -------------- ------ ----- A8 100/1000T | Auto 128 Yes Force-True Yes No
Column showing BPDU filter status
Figure 26. Example of BPDU Filter Status in Show Spanning Tree Configuration Command
90
 Loading...
Loading...