Honeywell VRN Dynamic Pressure-Regulating Control Valves and Actuators Installation Instructions
Page 1

38-00005EFS-04
VRN Dynamic Pressure-Regulating Control Valves and Actuators
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
Oversized valves can cause excessive cycling and the seat
and ball can be damaged because of the restricted
opening.
Proper Use
VRN valves are intended for use in chilled water and hot
water closed loop applications only, with a temperature
range of 35 to 250°F, and pressures up to 360psig.
Water should be properly filtered, treated and conditioned
for good operating performance, and according to
recommendations of the boiler or chiller manufacturers.
The installation of strainers and filters is recommended.
Do not use with manual balancing valves.
IMPORTANT
The presence of excessive iron oxide (red rust) in
the system voids the valve warranty.
APPLICATION
The VRN2 two-way dynamic pressure-regulating control
valves maintain constant flow of hot or chilled water with
glycol solutions up to 50% in closed-loop heating,
ventilating, and air conditioning systems, within the
specified pressure drop ranges of each model number.
These valve assemblies can be ordered with or without
factory-mounted actuators.
Application Notes
Valve sizing is important for correct system operation.
Undersized valves do not have sufficient capacity at
maximum load. Oversized valves do not have sufficient
authority over the load in modulating applications.
Effective Flow Rate
The built-in differential pressure regulator makes fluid
flow through the valve independent of changes in supply.
The pressure regulator virtually eliminates cavitation in
the valve, and decouples the control valve from the effects
of piping components such as reducers and elbows.
Pressure independent control valves are sized to match
design coil flow regardless of coil connection size. VRN2
valves eliminate the need to balance the system for proper
flow, and allow chillers to be operated at design
temperature differential for maximum efficiency at every
load condition. When used in a system with variable speed
pump drives, 3-way valves and coil bypass lines are not
required.
Required Operating Torque
Both Honeywell fail in place and fail-safe low torque direct
coupled actuators can be used with the VRN valves.
VRN valves use a patented seat design that reduces the
torque needed from the actuator.
Actuators with 27 lb-in torque, (for valves up to 1-1/4 in
size), and 35 lb-in torque (for 1-1/2 in size and above)
provide sufficient torque to operate the valve at rated
close-off. (See Table 1).
Maximum safe operating torque is 44 lb-in.
Page 2
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
CAUTION
M34979A
FLOW FLOW
CLOSED
OPEN
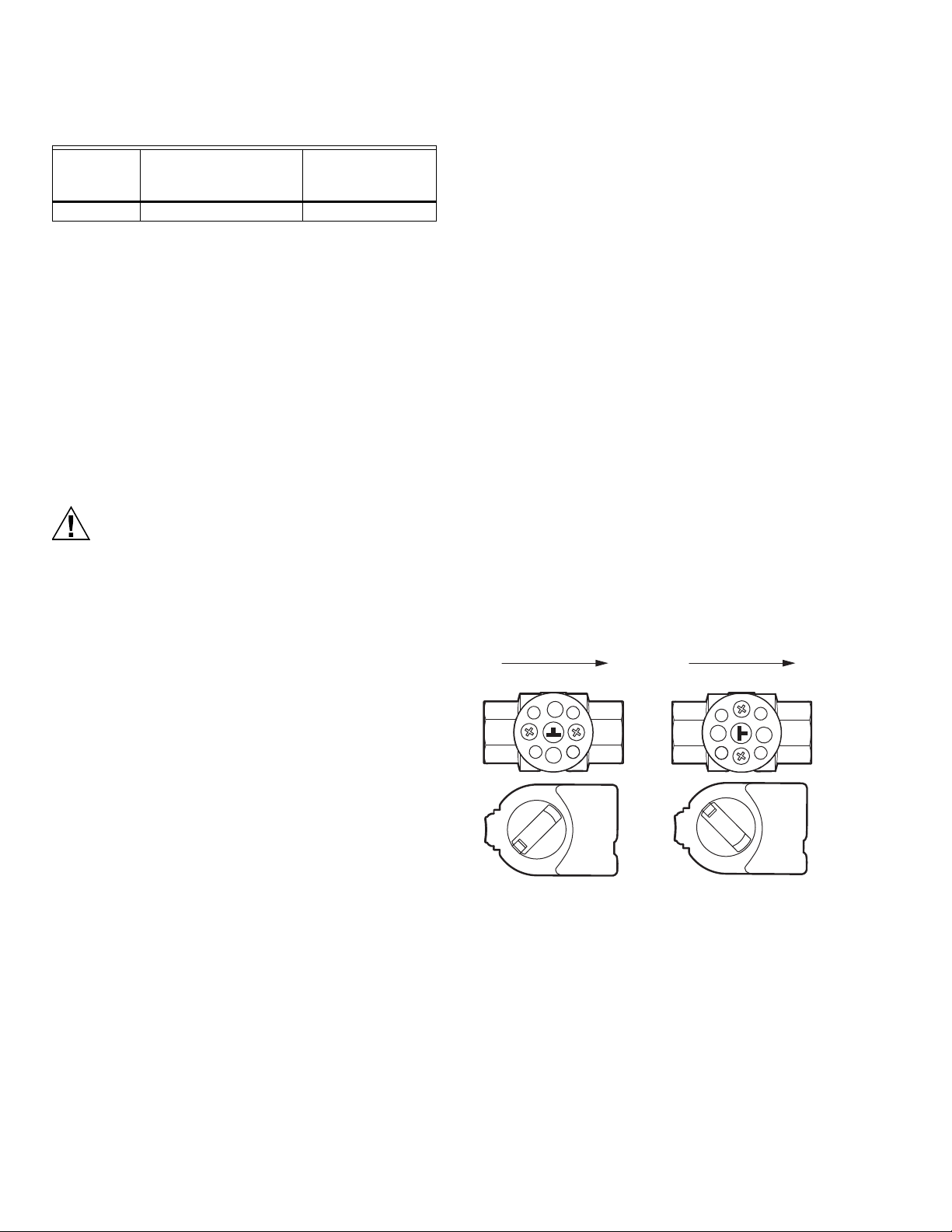
NOTES: TO MOUNT ACTUATOR ON OPEN VALVE, TURN ACTUATOR FULLY
COUNTER CLOCKWISE AS SHOWN. TO MOUNT ACTUATOR ON
CLOSED VALVE, TURN ACTUATOR FULLY CLOCKWISE AS SHOWN.
The valves are tapped in NPT and should be sealed with an
Table 1. Close-off, Differential Pressure Ratings.
Close-off
Pressure Rating
Valve Type Valve Size
2 way 1/2 in. to 3 in. 100
(psi)
INSTALLATION
When installing this product...
1. Read these instructions carefully. Failure to follow
them could damage the product or cause a hazardous condition.
2. Check ratings given in instructions and on the prod-
uct to ensure the product is suitable for your application.
3. Installer must be a trained, experienced service
technician.
4. After installation is complete, check out product
operation as provided in these instructions.
approved pipe sealant. Torque should not exceed 75 lb-ft.
Refer to actuator literature for actuator dimensions.
1. Clean the lines upstream of particles larger than
1/16 in. diameter (welding slag, pipe scale and other
contaminants).
2. Proceed with installation once the system specifics
(expansion/contraction of the system and its
medium as well as operating pressures) are within
tolerances.
3. Eliminate air from system.
4. Valves are marked to show flow direction.
IMPORTANT
Flow arrows must point in the direction of the flow
for proper operation.
5. Stem rotation:
a. Clockwise to close.
b. Counterclockwise to open.
NOTE: After valves have been installed in the pip-
Preparation
Equipment Damage Hazard
Foreign particles like dirt and metal chips can
damage the ball seals.
For trouble-free operation of the product, good
installation practice must include initial system
flushing, and chemical water treatment. Clean the
lines upstream of particles larger than 1/16 inch
diameter (welding slag, pipe scale, sand and other
suspended particulate). Use of a 50 micron (or
finer) system side stream filter is suggested.
Remove all filters before flushing.
Do not use boiler additives, solder flux and wetted
materials which are petroleum based or contain
mineral oil, hydrocarbons, or ethylene glycol
acetate. Compounds which can be used, with
minimum 50% water dilution, are diethylene
glycol, ethylene glycol, and propylene glycol
(antifreeze solutions).
If installing these valves in an addition to, or
retrofitting an existing building, do not assume
that the fluid in the existing piping meets these
criteria.
6. Valve must be mounted with the actuator/bracket
above the valve body. Do not install the valve with
the stem below horizontal or upside down. (See
Fig. 3 and 4.)
ing, the installer can determine the ball orientation within the valve from the notches
in the top of the valve stem. For VRN valves,
the lengthwise direction of the notch indicates the flow through the ball (i.e. when the
notch is parallel to the axis of the valve
between A and B ports, the ball will allow
flow through the valve).
Mechanical Installation
IMPORTANT:
38-00005EFS—04 2
Hold valve with pipe wrench by hexagonal fitting
ONLY. Do NOT handle the valve body with the pipe
wrench; product damage may result.
Fig. 1. Orientation of valve.
Page 3
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
M13738A
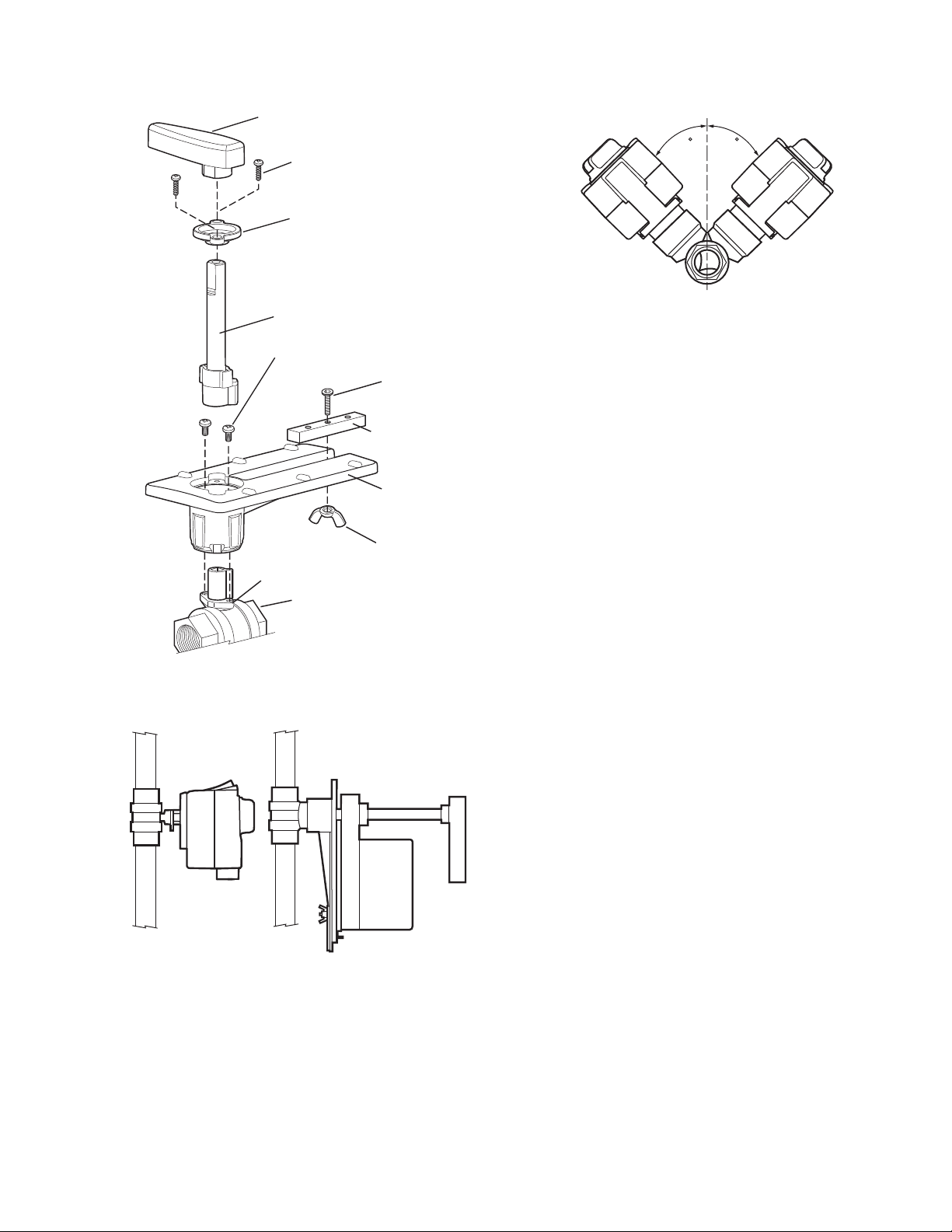
VALVE BODY
VALVE STEMCOUPLER
WING NUT**
MOUNTING
PLATE**
ANTI-ROTATION
BRACKET**
BOLT**
STEM ASSEMBLY COVER**
SCREWS (2)**
HANDLE (REMOVABLE) FOR
MANUALLY ROTATING SHAFT**
STEM ASSEMBLY**
**INCLUDED IN REPLACEMENT KIT (PART NO. 5112-11)
SCREWS (2)**
M34954
45
45
M33091
Fig. 4. Acceptable valve angle from vertical
Mounting Plate Adjustment
The Actuator Mounting Plate can be rotated to a different
position for installation in confined spaces. This is
accomplished as follows:
1. Remove the handle from the shaft and set it aside.
2. Remove the two screws that hold the stem assembly
to the mounting plate and set them aside.
3. Remove and set aside the stem assembly.
4. Remove and set aside the two screws that attach the
mounting plate to the valve.
5. Remove and set aside hold-down ring from mount-
ing plate.
6. Rotate mounting plate around valve top to the
desired position.
Fig. 2. Valve assembly exploded view.
Fig. 3. Vertical valve installation.
NOTE: Take note of the screw hole positions on the valve.
They limit the mounting plate positions.
7. Lower ring down to valve body and engage it in the
new position relative to the mounting plate.
8. Tighten screws to valve body securing the mounting
plate.
9. Reattach the stem assembly to the mounting plate.
10. If desired, replace the handle on the shaft.
NOTE: See Fig. 2 for valve exploded view.
Electrical Installation
1. If necessary, remove actuator wiring cover.
2. Wire actuator using Figures 5 through 28 for the
application required.
3. Replace cover.
3 38-00005EFS—04
Page 4
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
4
3
2
FLOATING ACTUATOR
24 VAC
Direct
Reverse
Service/Off
1
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
FLOATING
CONTROLLER
M18946A
24 VAC
1
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
PROPORTIONAL
CONTROLLER
+
–
FEEDBACK
1
325
PROPORTIONAL ACTUATOR
FEEDBACK
+
0(2)-10 VDC OF 0(4)-20 mA CONTROL SIGNAL ACCEPTABLE.
SET CONTROL SIGNAL DIP SWITCH TO “OFF” FOR VOLTAGE.
SET TO “ON” FOR CURRENT.
2
2
2 -10 Vdc
2 -10 Vdc
0 -10 Vdc
0 -10 Vdc
M18947B
4
5°
85°
S1 S2
S3 S5 S6
M25214A
END SWITCHES (CLASS II-ONLY)
Wiring
FLOATING ACTUATOR
DIRECT
SERVICE/OFF
REVERSE
432
1
3
24 VAC
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
2
CONNECTION REQUIRED FOR SPST CONTROL.
CONTROLLER
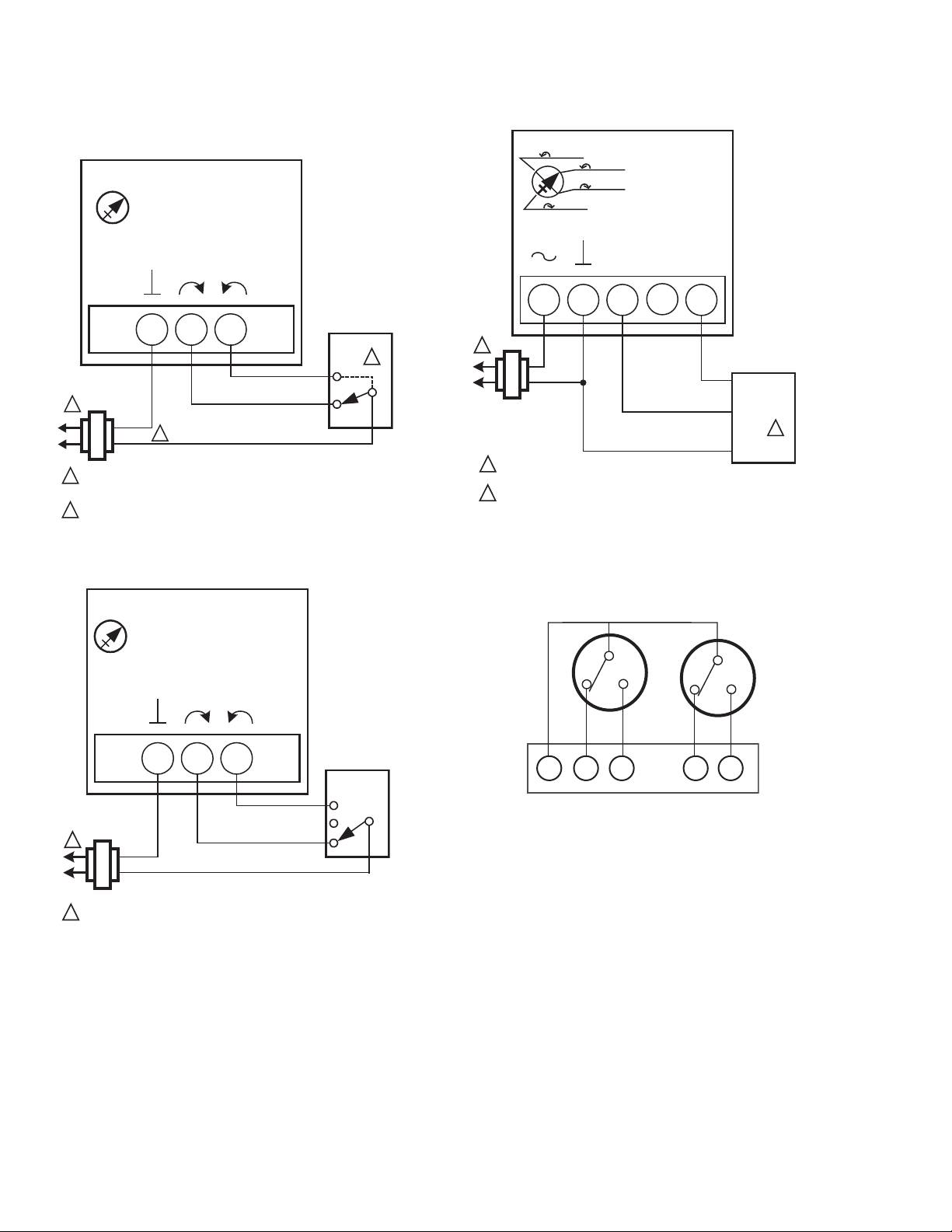
Fig. 5. MN6105 with On/Off SPDT Control.
2
M34869A
Fig. 7. MN7505 with 0(2)-10 Vdc Control.
Fig. 6. MN6105 with Floating Control.
38-00005EFS—04 4
Fig. 8. Wiring for MN6105 and MN7505 models with
aux./end switches.
Page 5
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
FLOATING ACTUATOR
24 VAC
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
FLOATING
CONTROLLER
M33137D
2
3
4
1
BLACK
WHITE
BROWN
2
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
FLOATING ACTUATOR
24 VAC
1
FLOATING
CONTROLLER
2
3
4
1
M33138C
BLACK
WHITE
BROWN
2
M33557C
FLOATING ACTUATOR
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
2
3
4
1
24 VAC
BLACK
BROWN
WHITE
SPST
PROPORTIONAL ACTUATOR
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
4-20mA
CONTROLLER
M33141C
1
2
3
+
+
–
DIP SWITCH POSITION
1 2 MODE
OFF OFF 2-10V
OFF ON 0-10V
ON OFF 10-2V
ON ON 10-0V
PROPORTIONAL/MODULATING: 4-20mA CONTROLLER OUTPUT WITH
500Ω SERIES RESISTOR
TO OTHER
ACTUATORS
500 OHMS,
1/2 W
MINIMUM
24 VAC
RED
BLACK
WHITE
1
PROPORTIONAL ACTUATOR
24 VAC
1
POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
0 (2)-10 VDC
CONTROLLER
M33140A
1
2
3
+
+
–
DIP SWITCH POSITION
1 2 MODE
OFF OFF 2-10V
OFF ON 0-10V
ON OFF 10-2V
ON ON 10-0V
PROPORTIONAL/MODULATING: 0(2)...10 VDC OR 10...0(2) VDC CONTROLLER OUTPUT
2
RED
BLACK
WHITE
2
1
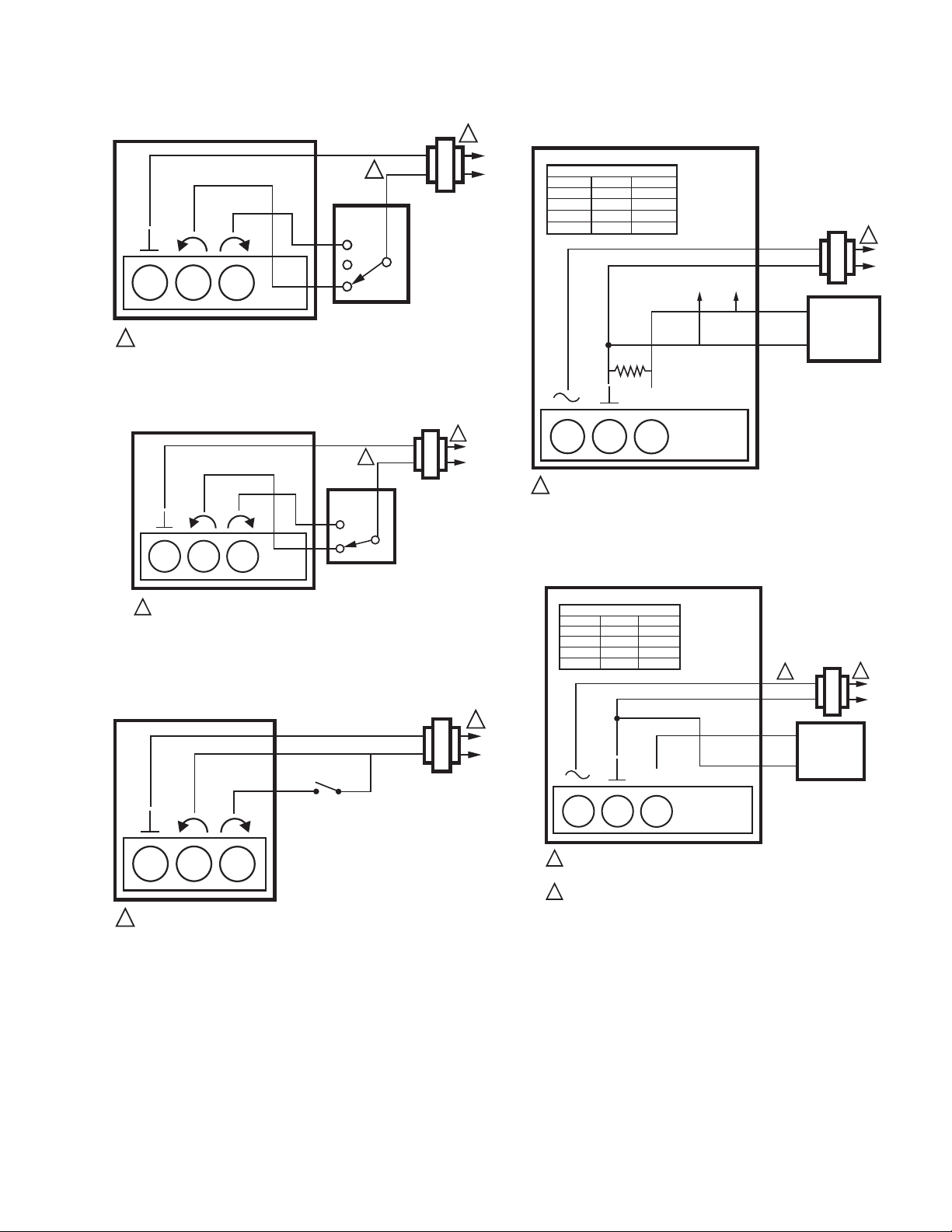
Fig. 9. MVN613 with Floating Control.
Fig. 10. MVN613 or MVN643 with Two Position SPDT
Control.
Fig. 11. MVN643 with Two Position SPST Control.
Fig. 12. MVN713 with 4-20mA Control.
Fig. 13. MVN713 with 0(2)-10 Vdc Control.
5 38-00005EFS—04
Page 6
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
SPDT
24 VAC
1
1
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
SET SWITCH TO FLOATING.
M37304
ACTUATOR
V
0°-90°/MODULATING
90°-0°/FEEDBACK
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
FLOATING, FWD
FLOATING, REV
2
RED
BLACK
BROWN
WHITE
CLASS 2
24 VAC
1
1
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
SET SWITCH TO FLOATING.
M37319
ACTUATOR
V
4
3
1
2
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
FLOATING, FWD
FLOATING, REV
2
0°-90°/MODULATING
90°-0°/FEEDBACK
RED
BLACK
BROWN
WHITE
CLASS 2
ACTUATOR
4 TO 20 mA
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
24 VAC
1
1
2
3
2
490 TO 510
OHMS,
1/2 W
MINIMUM
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING IF AVAILABLE.
V
–
+
FEEDBACK
4
3
1
2
M37321
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
FLOATING, FWD
FLOATING, REV
3
0°-90°/MODULATING
90°-0°/FEEDBACK
RED
BLACK
BROWN
WHITE
CLASS 2
ACTUATOR
0/2 TO 10 VDC
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
24 VAC
1
1
2
3
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION
AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING
IF AVAILABLE.
V
–
+
FEEDBACK
4
3
1
2
M37322
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
FLOATING
, FWD
FLOATING
, REV
3
ACTUATOR
V
4
3
1
2
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
FLOATING
, FWD
FLOATING
, REV
3
0°-90°/MODULATING
90°-0°/FEEDBACK
RED
BLACK
BROWN
WHITE
0°-90°/MODULATING
90°-0°/FEEDBACK
RED
BLACK
BROWN
WHITE
CLASS 2
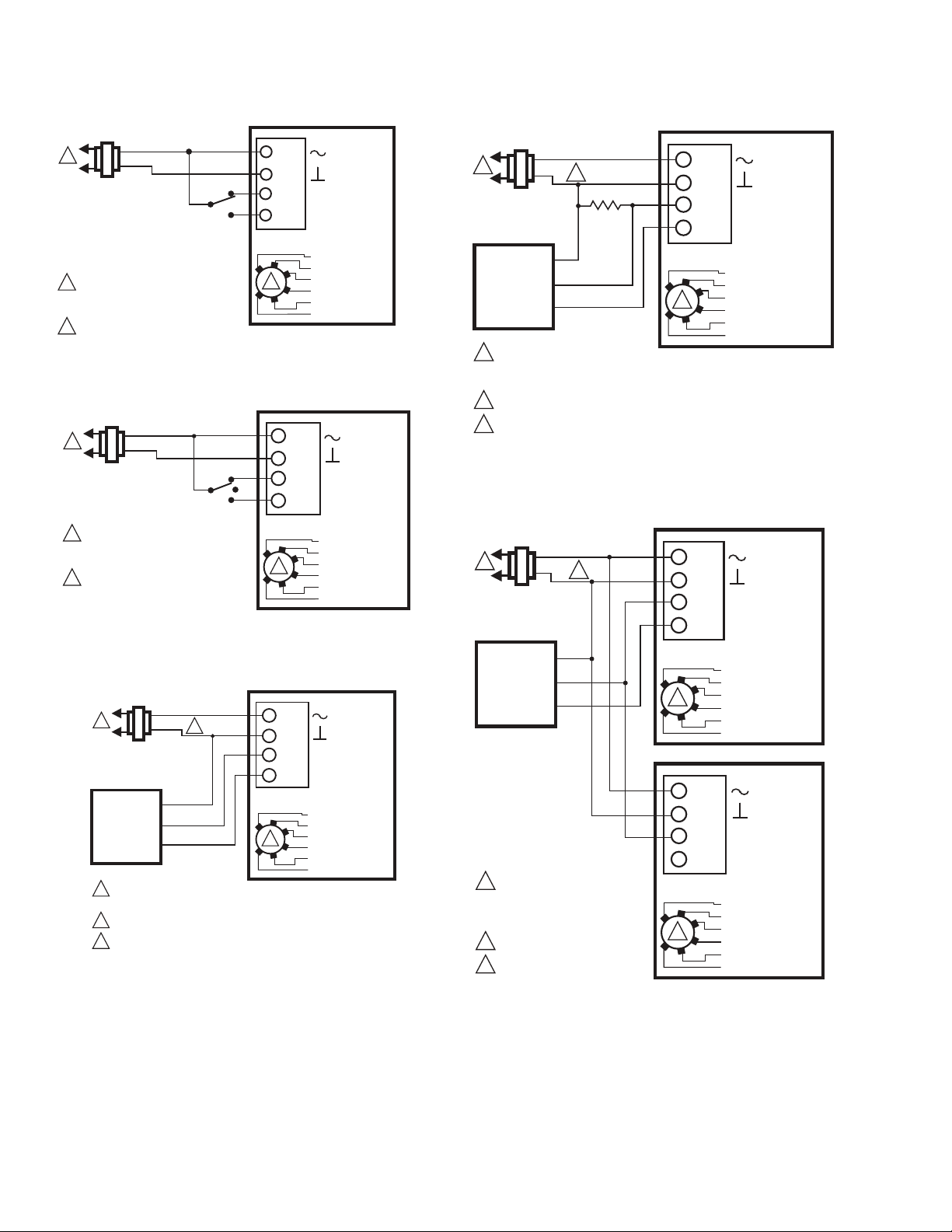
Fig. 14. MS7505 with Two Position SPDT Control.
Fig. 17. MS7103 with 4-20 mA Control (MS7503 shown,
ignore selection switch).
Fig. 15. MS7505 with Floating Control.
CLASS 2
1
0/2 TO 10 VDC
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
FEEDBACK
1
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
2
3
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING IF AVAILABLE.
Fig. 16. MS7103 with 2-10 Vdc Control (MS7503 shown,
38-00005EFS—04 6
RED
24 VAC
–
+
2
1
2
BLACK
3
WHITE
4
BROWN
3
ignore selection switch).
ACTUATOR
0°-90°/MODULATING
90°-0°/FEEDBACK
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
FLOATING
FLOATING
V
, FWD
, REV
M37320
Fig. 18. MS7103 with 2-10 Vdc Control using two
actuators (MS7503 shown, ignore selection switch).
Page 7
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
ACTUATOR
SPST
24 VAC
1
1
2
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
V
1
2
M34973
3
ACTUATOR
SPST
1
1 LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
V
1
2
M34974
2
ACTUATOR
0/2 TO 10 VDC
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
24 VAC
1
1
2
3
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING.
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
–
+
FEEDBACK
5
4
3
1
2
M19576A
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
SPDT
ACTUATOR
0/2 TO 10 VDC
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
24 VAC
1
1
2
3
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING.
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
–
+
FEEDBACK
5
4
3
1
2
M19577A
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
SPST
ACTUATOR
0/2 TO 10 VDC
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
24 VAC
1
1
2
3
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING.
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
–
+
FEEDBACK
5
4
3
1
2
M34976
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
RED
BLACK
ACTUATOR
SPST SWITCHES
MAIN
CABLE
WHITE
BROWN
+ OR 0˚−90˚
FEEDBACK OR 90˚−0˚
BLUE
BROWN
GRAY
SWITCHES
CABLE
BLACK
M37303A
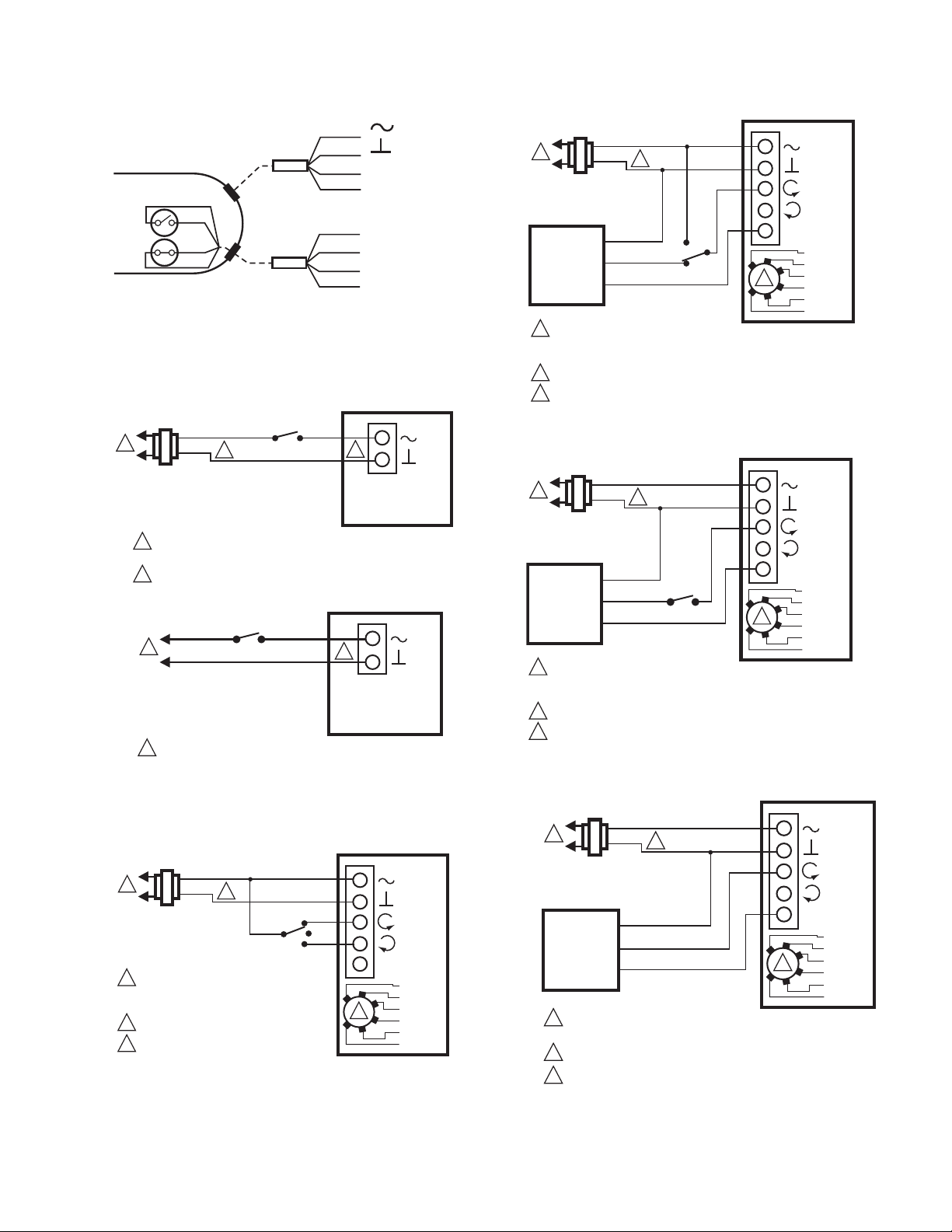
Fig. 19. Wiring for MS7103 and MS3103 Auxiliary
Switches. Gray/Black = Normally Open. Closed in range
80 degrees to Fully Open. Blue/Brown = Normally
Closed. Open in range 10 degrees to Fully Open.
Fig. 22. MS7505 with override to full open.
Fig. 20. MS8105 with Two Position SPDT Control.
1
1
2
3
24 VAC
2
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO FLOATING.
Fig. 21. MS7505 with Floating Control.
1
2
3
4
5
3
ACTUATOR
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
Fig. 23. MS7505 with override to full closed.
M34975
Fig. 24. MS7505 with 0(2)-10 Vdc Controllers.
7 38-00005EFS—04
Page 8
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
ACTUATOR
4 TO 20 mA
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
24 VAC
1
1
2
3
2
490 TO 510
OHMS,
1/2 W
MINIMUM
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING.
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
–
+
FEEDBACK
5
4
3
1
2
M34977
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
S1S3
S2
M35813
1
2
3
HOT
COM
CONTROLLER
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
ADDRESS SELECTOR
S-BUS
S-BUS
24 VAC
CLASS 2
S-BUS
S-BUS
RED
BLACK
BROWN
BROWN
ACTUATOR
ADDRESS 11
ADDRESS 12
ADDRESS 13
ADDRESS 14
ADDRESS 15
TEST
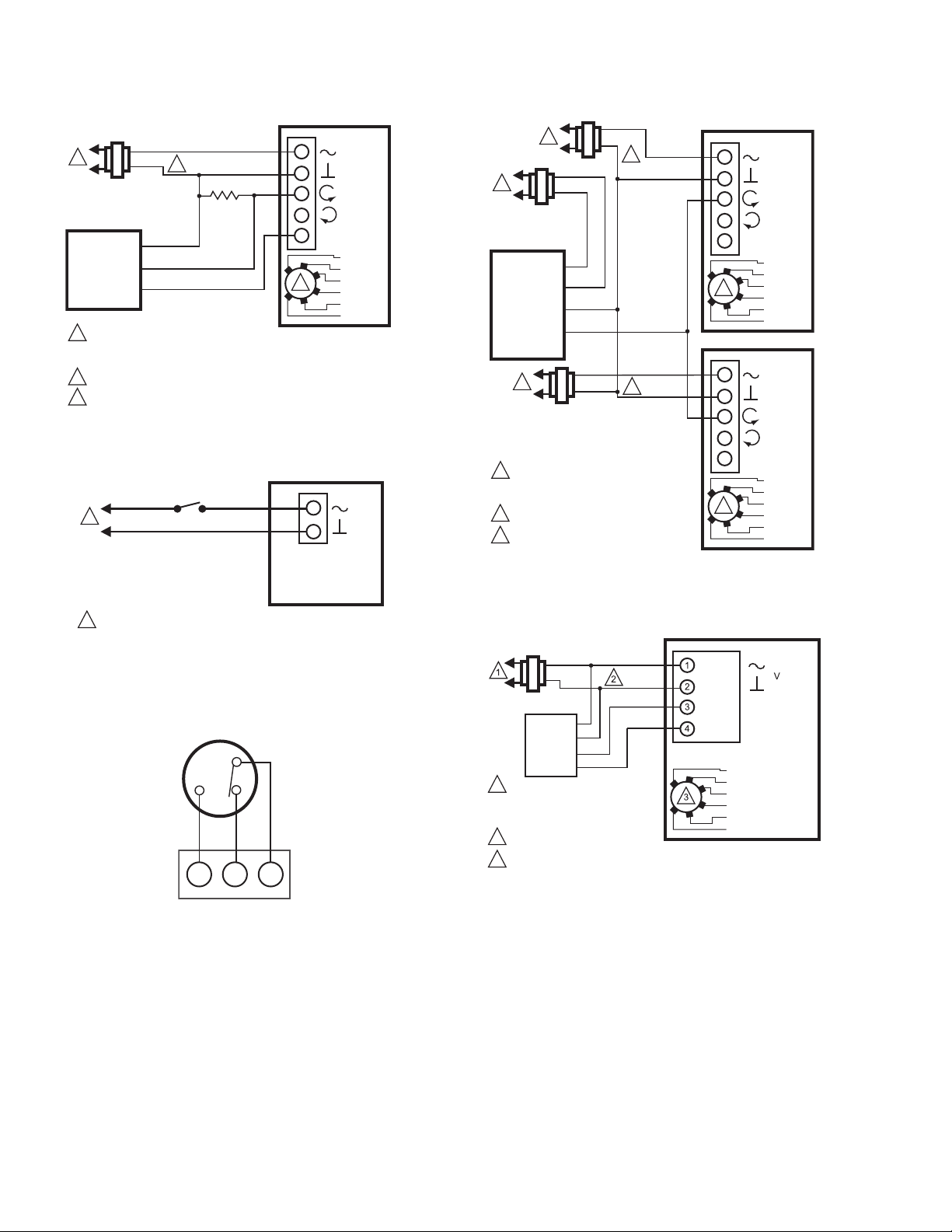
Fig. 25. MS7505 with 4-20mA Controllers.
1
1 LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY. PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS
AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
SPST
1
2
ACTUATOR
V
M29122
24 VAC
24 VAC
ACTUATOR
2
2
1
2
3
4
5
3
1
2
3
4
5
3
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
ACTUATOR
V
OR +
OR N/A
FEEDBACK
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
M34978
1
1
0/2 TO 10 VDC
PROPORTIONING
CONTROLLER
1
LINE VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY.
PROVIDE DISCONNECT MEANS AND
OVERLOAD PROTECTION AS REQUIRED.
2
24 VDC SUPPLY ACCEPTABLE.
SET SWITCH TO MODULATING.
3
24 VAC
HOT
COM
–
+
1
Fig. 28. MS7505 with 0(2)-10 Vdc controller operating
multiple actuators.
Fig. 26. MS4105 with 120 Vac Two Position SPDT
Fig. 27. Wiring for MS4105, MS7505, and MS8105
models with aux./end switches.
38-00005EFS—04 8
control.
Fig. 29. MS3103 with Sylk Bus control.
OPERATION AND CHECKOUT
Once both the mechanical and electrical installations are
complete:
1. Cycle the actuator to verify that the direction of rota-
tion suits the control sequence.
2. If the rotation direction is incorrect:
a. For 2-position and Sylk-enabled spring return
actuators: Remove, flip over, and replace actuator on the bracket.
b. For floating control actuators: Reverse two con-
trol signal wires (CW/CCW), or change position
of selector switch.
Page 9
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
M27714
A
0
FLOW
RATE
(GPM)
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE (PSID)
12
10
6
4
5.8
8
16
22
28
50
M29707A
8
12
34 40
60
100% OPEN
80% OPEN
60% OPEN
40% OPEN
20% OPEN
c. For analog control actuators either:
(1) Change setting of reverse/direct-acting
switch, or
(2) To change spring return direction: remove,
flip over, and replace actuator on bracket.
3. If the control scheme requires fail-safe operation,
ensure that, upon removal of power, the fail position
coincides with the control sequence.
4. Spring return actuators are factory-configured for
normally-closed, fail-safe operation on power loss.
To change this action to normally-open, remove and
reinstall the actuator in the opposite orientation as
follows:
a. Loosen the shaft coupling bolt using a 10 mm
wrench.
b. Loosen all other mounting bolts connecting the
actuator to the mounting bracket, and set aside.
c. Remove the actuator from the valve shaft.
d. Move the Self-Centering Shaft Adaptor to the
opposite side of the actuator, as displayed in
Fig. 30.
M29908
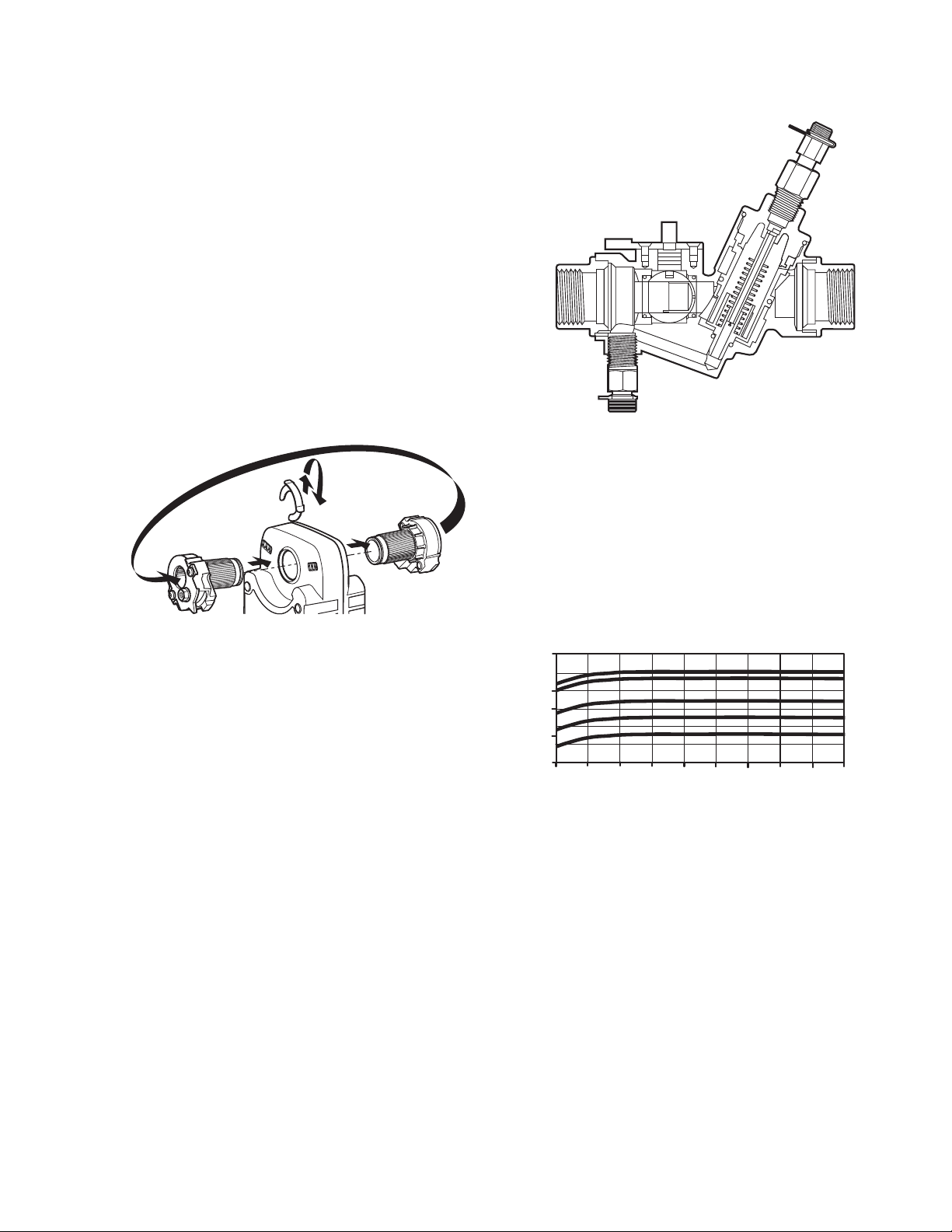
Fig. 31. VRN2 cross section showing fitting, control ball,
and pressure regulator.
At full flow in a 2-position control application, a VRN2
behaves as a flow limiter.
The pressure regulator takes a minimum pressure to
operate, and has a maximum differential regulation
capability. See Fig. 32. The high pressure drop across a
VRN2 Valve is comparable to the pressure drop across a
control valve and balancing valve in a conventional
system design.
Fig. 30. Change actuator to normally open.
(1) Remove the retainer clip from the Self-Cen-
tering Shaft Adapter and set it aside for later
use.
(2) Remove SCSA from actuator.
(3) Reinstall SCSA on the opposite side of the
actuator, aligning it based on the stroke label-
ing.
(4) Replace the retainer clip on the shaft cou-
pling using the groove of the coupling.
e. Reconnect the actuator to the valve mounting
bracket by replacing the screws previously
Fig. 32. Pressure regulation, large body models.
removed (step b).
f. Tighten the shaft coupling bolt using a 10 mm
wrench or socket using maximum 120 lb-in
torque.
Operation
PIN changes constantly in a multi-zone system as other
valves open and close, changing system flow and head
pressure according to the characteristics of the supply
pump curve. Reaction of the mechanical pressure
regulator is instantaneous, eliminating changes in room
temperature due to changes in fluid flow, and reducing the
need for the control system to constantly operate the
control portion of the valve to correct for the non-load
related temperature changes that occur in a system with
standard control valves.
SETTINGS AND ADJUSTMENTS
At the full open position, VRN2 valves will maintain flow in
the loop. Flow rates are listed in the Specification Data
form 62-3115EFS. Under steady state operation, the
control system will only require the valve to open enough
to satisfy load conditions. During morning recovery from
night setback, the controller will usually command the
valve to 100%. For optimum performance, choose only the
next larger valve size needed to satisfy design load. Do not
oversize valves—reduced rangeability and may result in
less accurate temperature control.
9 38-00005EFS—04
Page 10
VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
CAUTION
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
0° 30° 60° 90°
VALVE STEM STROKE
FLOW
M29551A
10°
20°
40° 50°
70°
80°
FULL PORT
BALL
2-WAY
CHARACTERIZED
FLOW
STEM
ASSEMBLY
COUNTERSUNK
SCREWS
STEM RETAINER
PLATE
“T” SYMBOL
STEM
UPPER PACKING
GLAND
O-RING
LOWER PACKING
GLAND
M34994
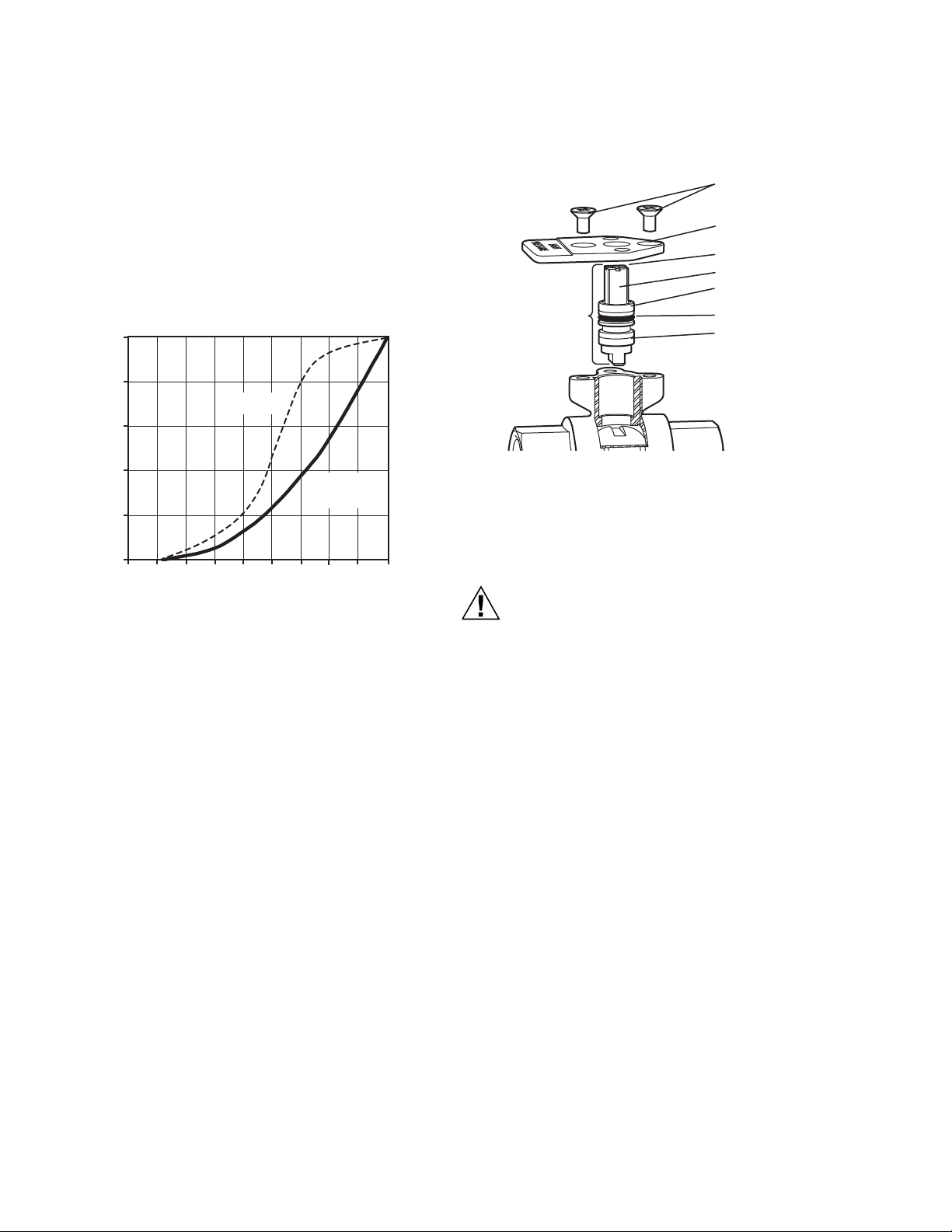
Ball valves close between 10 and 15% of stroke, to ensure
full seal engagement. If desired, modulating actuators can
be set to 0-10 V response so that 2 V of a 2-10 V control
signal more closely corresponds to minimum flow. The
valve will still close with signal loss.
If desired, maximum flow may be trimmed to a lesser value
in one of two ways:
1. With modulating actuator, limit span of control volt-
age issued by the building automation controller.
Valves with flow control inserts have an equal percentage flow characteristic (See Fig. 33). Each 10%
reduction in maximum control voltage will result in a
10% reduction in flow.
Service and Repair
The valve stem can be replaced in-line, if necessary. See
Fig. 34.
Fig. 34. Replacing the valve stem in-line.
Follow steps 1 to 6 of “Mounting Plate Adjustment” on
page 3, then:
1. If the lower packing gland is stuck, remove it with
gland removal tool or rubber-tipped dental tool.
Fig. 33. Typical flow characteristics.
2. To mechanically limit stroke, set DCA to full open
position. Loosen shaft coupling and rotate valve
shaft to desired maximum flow position, as confirmed by pressure measurement across coil, using
coil manufacturer's data. Retighten shaft coupling.
Use Fig. 33 as a guide to setting actuator stroke.
If using mechanical adjustment technique with
MN/MS7505 modulating actuators, the stroke autoadaption feature will automatically scale the 2–
10 Vdc signal to the mechanical rotation of the ball.
See actuator literature for details.
Coil flow can be confirmed by reading pressures at the coil
inlet and coil outlet (not across control valve as with
conventional balancing—this pressure drop will be
constant), and using the manufacturer's data to calculate
flow.
Note that the pressure regulator in this valve guarantees
that the flow through the coil will not be affected by
upstream changes in pressure. Unlike conventional
balancing valves, it is not necessary to reconfirm coil flow
after adjusting other valves. Any overflow during morning
recovery due to oversized pressure regulated valves will
not affect other valves in the system, provided pumps are
capable of required flow.
Avoid scratching the inside of the valve neck.
This may cause a leak when re-assembled.
2. Carefully remove any fouling or corrosion from
inside of valve.
3. Align arrow with short leg of “T” symbol on new stem
assembly.
NOTE: “T” symbol will vary.
4. Insert the new stem assembly. Be sure to line up the
stem key with the ball slot.
5. Fasten stem retainer high pressure plate to the valve
using the new countersunk screws. Then fasten the
mounting plate to the valve.
6. Repressurize valve and confirm stem does not leak
before proceeding.
7. Slide the sub shaft over the stem with the tab ori-
ented as shown in Fig. 34.
8. Replace the thermal break, shaft, and shaft cover. If
shaft has come loose from thermal break, push
firmly on end of shaft until blade in shaft snaps into
thermal break.
9. Replace actuator and secure it to shaft and mount-
ing plate.
10. Snap handle onto top of shaft.
Any other service to valve such as seat seal replacement
requires removal of valve from piping.
38-00005EFS—04 10
Page 11

VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
11 38-00005EFS—04
Page 12

VRN DYNAMIC PRESSURE-REGULATING CONTROL VALVES AND ACTUATORS
By using this Honeywell literature, you agree that Honeywell will have no liability for any damages arising out of your use or
modification to, the literature. You will defend and indemnify Honeywell, its affiliates and subsidiaries, from and against any
liability, cost, or damages, including attorneys’ fees, arising out of, or resulting from, any modification to the literature by you.
Honeywell Building Technologies
In the U.S.:
Honeywell
® U.S. Registered Trademark
© 2019 Honeywell International Inc.
38-00005EFS—04 M.S. Rev. 12-19
Printed in United States
Page 13

Clapets et actionneurs de régulation
de pression dynamique VRN
NOTICE D’INSTALLATION
Les clapets trop grands peuvent causer des cycles trop
fréquents, et le siège et la bille peuvent être endommagés
en raison de l'ouverture restreinte.
Utilisation correcte
Les clapets VRN sont uniquement conçus pour les circuits
à boucle fermée d’eau chaude ou refroidie dans une plage
de températures de 1,7 à 121 °C (35 à 250 °F) et à une
pression maximale de 2 482 kPa (360 lb/po²).
L’eau doit être correctement filtrée, traitée et conditionnée
pour fournir un bon rendement opérationnel,
conformément aux recommandations des fabricants de
chaudières et refroidisseurs.
Il est recommandé de poser des crépines et des filtres.
Ne pas utiliser avec des robinets d'équilibrage manuels.
APPLICATION
Les clapets de régulation dynamique à deux voies VRN2
permettent de maintenir un débit constant d'eau chaude
ou refroidie avec concentrations de glycol pouvant
atteindre 50 % dans les circuits de chauffage, de
ventilation et de climatisation (CVC) à boucle fermée, dans
les plages de chute de pression de chaque numéro de
modèle.
Ces clapets peuvent être commandés avec ou sans les
actionneurs montés en usine.
Notes d’application
Le dimensionnement des clapets est important pour que
le système fonctionne correctement. Les clapets trop
petits n'ont pas une capacité suffisante pour la charge
maximale. Les clapets trop grands n'ont pas une autorité
suffisante sur la charge dans les applications à
modulation.
IMPORTANT
La présence d’oxyde de fer (rouille rouge) en excès
dans le système annule la garantie du clapet.
Débit efficace
Le régulateur de pression différentielle intégré assure
l'écoulement du liquide dans le clapet sans égard aux
changements de l'alimentation. Le régulateur de pression
élimine virtuellement la cavitation dans le clapet, et libère
le régulateur des effets des organes de tuyauterie, tels que
les réducteurs et les coudes.
Les clapets indépendants de la pression sont
dimensionnés pour convenir au débit du serpentin, peu
importe son diamètre de raccordement. Les clapets VRN2
éliminent le besoin d’équilibrer le système pour assurer un
débit adéquat et permettent d’utiliser les refroidisseurs à
la température différentielle prévue lors de la conception
pour une efficacité maximale dans toutes les conditions
de charge. Lorsque le système est utilisé avec des
entraînements de pompe à vitesse variable, des clapets à
trois voies et des lignes de dérivation de serpentin ne sont
pas requis.
Couple de fonctionnement requis
Les actionneurs à accouplement direct à maintien de
position en cas de panne et à sécurité intégrée Honeywell
peuvent être utilisés avec les clapets VRN.
Les clapets VRN utilisent un siège de conception brevetée
qui réduit le couple requis de l'actionneur.
Page 14

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
MISE EN GARDE
Actionneurs fournissant un couple de 305 Ncm (27 lb-po)
(pour clapets jusqu’à 1,25 po de diamètre) et de 395 Ncm
(35 lb-po) (pour les clapets de 1,5 po de diamètre et plus)
qui suffit à fermer le clapet à son taux nominal. (Reportezvous au Table 1.)
Couple de fonctionnement maximal sécuritaire : 500 Ncm
(44 lb-po).
Tableau 1. Valeurs nominales de pression différentielle
pour la fermeture.
Type de
clapet Taille de clapet
2voies 1/2po à 3po 100
Pression de fermeture
nominale (psi)
INSTALLATION
Lors de l’installation de ce produit...
1. Lire attentivement ces instructions. Le non-respect
des instructions peut endommager le produit ou
provoquer une situation dangereuse.
2. Vérifier les caractéristiques nominales indiquées
dans les instructions et sur le produit, et s’assurer
que celui-ci correspond bien à l’application prévue.
3. L’installateur doit être un technicien expérimenté
ayant reçu la formation adéquate.
4. Une fois l’installation terminée, vérifier que le pro-
duit fonctionne comme indiqué dans ces instructions.
Préparation
Risque de dommages de l'équipement
Les particules étrangères telles que la poussière et
les copeaux métalliques peuvent endommager les
joints des billes.
Pour un fonctionnement sans problème du produit,
les bonnes pratiques d’installation doivent inclure
une vidange initiale du système et un traitement de
l’eau chimique. Nettoyer les conduits en amont des
particules d’un diamètre supérieur à 1/16 po
(scories de soudage, dépôts calcaires de conduits,
sable et autres particules en suspension). Il est
recommandé d’utiliser un filtre en dérivation de
50 microns ou plus fin. Retirer tous les filtres avant
de procéder à la vidange.
Ne pas utiliser d'additifs pour chaudières, de flux à
soudure, ou de matériaux humides à base de pétrole
ou qui contiennent des huiles minérales, des
hydrocarbures ou du monoacétate d'éthylène
glycol. Les composés qui peuvent être employés,
dilués avec au moins la moitié d'eau, sont le
diéthylène glycol, l'éthylène glycol et le propylène
glycol (solutions antigel).
Si ces clapets sont installés dans un
agrandissement ou pour la modernisation d’une
installation existante, envisager la possibilité que le
liquide présent dans la tuyauterie existante ne soit
pas conforme à ces critères.
Installation mécanique
IMPORTANT
Tenir le clapet avec une clé à tuyau par le raccord
hexagonal UNIQUEMENT. NE PAS tenir le clapet
par le corps avec une clé à tuyau; ceci pourrait
endommager le produit.
Les clapets ont un filetage NPT et doivent être
étanchéifiés avec un produit d’étanchéité pour tuyauterie
approuvé. Le couple ne doit pas dépasser 75 lb-pi.
Consulter la documentation de l’actionneur pour les
dimensions de l’actionneur.
1. Nettoyer les conduits en amont des particules d’un
diamètre supérieur à 1/16 po (scories de soudage,
dépôts calcaires de conduits et autre contaminants).
2. Procéder à l’installation une fois que les spécifica-
tions du système (expansion/contraction du système et du fluide, et pressions de fonctionnement)
sont dans les tolérances indiquées.
3. Éliminer l’air du système.
4. Les clapets à sont marqués pour montrer la direc-
tion du débit.
IMPORTANT
Les flèches de débit doivent pointer dans la direction du débit pour assurer un fonctionnement
adéquat.
5. Rotation de la tige :
a. Sens horaire pour fermer.
b. Sens antihoraire pour ouvrir.
REMARQUE : Une fois les clapets installés dans la
tuyauterie, l’installateur peut déterminer
l’orientation de la bille dans le clapet grâce
aux encoches en haut de la tige du clapet.
Pour les clapets VRN, la direction longitudinale de l'encoche indique un débit par la
bille (c'est-à-dire que lorsque l'encoche est
parallèle à l'axe du clapet entre les ports A et
B, la bille permet le débit par le clapet).
6. Le clapet doit être monté avec l’actionneur/support
au-dessus du corps du clapet. Ne pas installer le clapet avec la tige sous l’horizontale ou inversée. (Voir
les Fig. 3 et 4.)
38-00005EFS—04 2
Page 15

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
MF34979
DÉBIT DÉBIT
FERMÉ
OUVERT
REMARQUES :
POUR MONTER L'ACTIONNEUR SUR UN CLAPET OUVERT, TOURNER
COMPLÈTEMENT L’ACTIONNEUR DANS LE SENS ANTIHORAIRE COMME ILL
POUR MONTER L'ACTIONNEUR SUR UN CLAPET FERMÉ, TOURNER
COMPLÈTEMENT L’ACTIONNEUR DANS LE SENS HORAIRE COMME ILLUST
MF13738A
CORPS DU CLAPET
TIGE DU CLAPET COUPLEUR
ÉCROU À
AILETTES**
PLAQUE DE
MONTAGE**
COUVERCLE DE TIGE**
VIS (2)**
POIGNÉE (AMOVIBLE) POUR LA
ROTATION MANUELLE DE L’ARBRE**
TIGE**
**INCLUS DANS LE NÉCESSAIRE DE RECHANGE (RÉF. N° 5112-11)
VIS (2)**
SUPPORT
ANTIROTATION**
BOULON**
M34954
45
45
M33091
Fig. 1. Orientation du clapet.
Fig. 3. Installation verticale du clapet.
Fig. 2. Vue éclatée du clapet.
Fig. 4. Angle de clapet acceptable par rapport à la
verticale
Ajustement de la plaque de montage
La plaque de montage de l’actionneur peut être tournée à
une position différente pour les installations en espace
réduit. Ceci s’accomplit de la façon suivante :
1. Retirer la poignée de l'arbre et la mettre de côté.
2. Retirer les deux vis fixant la tige à la plaque de mon-
tage et les mettre de côté.
3. Retirer la tige et la mettre de côté.
4. Retirer les deux vis fixant la plaque de montage au
clapet et les mettre de côté.
5. Retirer la bague de retenue de la plaque de montage
et la mettre de côté.
6. Faire tourner la plaque de montage autour de la par-
tie supérieure du clapet à la position désirée.
REMARQUE : Noter la position des trous de vis sur le cla-
pet. Ils limitent les positions de la plaque de
montage.
7. Abaisser la bague sur le corps du clapet et l'engager
dans la nouvelle position par rapport à la plaque de
montage.
8. Serrer les vis du corps du clapet fixant la plaque de
montage.
9. Rattacher la tige à la plaque de montage.
10. Si cela est souhaité, replacer la poignée sur l'arbre.
REMARQUE : Voir la Fig. 2 pour la vue éclatée du clapet.
3 38-00005EFS—04
Page 16

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
432
ACTIONNEUR FLOTTANT
24 V c.a.
1
1 ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
CONNEXION REQUISE POUR COMMANDE UNIPOLAIRE
BIDIRECTIONNELLE.
2
RÉGULATEUR
2
DIRECT
SERVICE/ARRÊT
INVERSE
MF34869B
3
4
3
2
ACTIONNEUR FLOTTANT
24 V c.a.
1
1
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
RÉGULATEUR
FLOTTANT
MF18946
DIRECT
SERVICE/ARRÊT
INVERSE
24 V c.a.
1
1
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
CONTRÔLEUR
PROPORTIONNEL
+
–
RETOUR
1
325
ACTIONNEUR PROPORTIONNEL
RETOUR
+
SIGNAL DE COMMANDE 0(2)-10 V c.c. OU 0(4)-20 mA ACCEPTABLE.
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR DIP DU SIGNAL DE COMMANDE SUR
ARRÊT POUR LA TENSION ET SUR MARCHE POUR LE COURANT.
2
2
2 -10 V c.c.
2 -10 V c.c.
0 -10 V c.c.
0 -10 V c.c.
MF18947B
4
5°
85°
S1 S2
S3 S5 S6
MF25214A
INTERRUPTEURS D'EXTRÉMITÉ (CLASSE II UNIQUEMENT)
Installation électrique
1. Si nécessaire, retirer le couvercle de câblage de
l'actionneur.
2. Câbler l’actionneur en consultant les Fig. 5 à 28 pour
l’application requise.
3. Replacer le couvercle.
Câblage
Fig. 5. MN6105 avec commande SPDT marche/arrêt.
38-00005EFS—04 4
Fig. 6. MN6105 avec commande flottante.
Fig. 7. MN7505 avec commande 0(2)-10 V CC.
Fig. 8. Câblage pour modèles MN6105 et MN7505 avec
contacteurs aux./de fin de course.
Page 17

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ACTIONNEUR FLOTTANT
24 V c.a.
1
2
3
4
1
MF33138C
NOIR
BLANC
MARRON
2
RÉGULATEUR
MF33557B
ACTIONNEUR FLOTTANT
1
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
2
3
4
1
24 V c.a.
NOIR
MARRON
BLANC
SPST
(UNIPOLAIRE
UNIDIRECTIONNEL)
É
ACTIONNEUR PROPORTIONNEL
24 V c.a.
1
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
CONTRÔLEUR
0 (2)-10 V c.c.
MF33140
1
2
3
+
+
–
POSITION DU COMMUTATEUR DIP
1 2 MODE
ARRÊT ARRÊT 2-10V
ARRÊT MARCHE 0-10V
MARCHE ARRÊT 10-2V
MARCHE MARCHE 10-0V
PROPORTIONNEL/MODULATION : SORTIE DE CONTRÔLEUR 0(2)...10 V c.c. OU 10...0(2) V c.c.
2
ROUGE
NOIR
BLANC
2
1
ACTIONNEUR FLOTTANT
NOIR
BLANC
MARRON
3
2
1
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
4
24 V c.a.
2
RÉGULATEUR
Fig. 9. MVN613 avec commande flottante
1
MF33137B
PROPORTIONNEL/MODULATION : SORTIE DE R
AVEC RÉSISTANCE 500
ACTIONNEUR PROPORTIONNEL
POSITION DU COMMUTATEUR DIP
1 2 MODE
ARRÊT ARRÊT 2-10V
ARRÊT MARCHE 0-10V
MARCHE ARRÊT 10-2V
MARCHE MARCHE 10-0V
ROUGE
NOIR
VERS D’AUTRES
ACTIONNEURS
BLANC
500 OHMS,
1/2 W
MINIMUM
+
2
1
1
ALIMENTATION. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
3
GULATEUR 4-20mA
24 V c.a.
RÉGULATEUR
4-20 mA
Fig. 12. MVN713 avec régulateur 4-20mA.
1
+
–
MF33141D
Fig. 10. MVN613 ou MVN643 à commande SPDT à deux
positions.
Fig. 11. MVN643 avec commande unipolaire
unidirectionnelle à deux positions.
Fig. 13. MVN713 avec régulateur 0(2)-10 V c.c.
5 38-00005EFS—04
Page 18

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
SPDT
1
2
MF37304
ACTIONNEUR
V
4
3
1
2
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
ROUGE
NOIR
BRUN
BLANC
CLASSE 2
24 V CA
1
2
TENSION D’ALIMENTATION.
AU BESOIN, PLACEZ UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION
CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
RÉGLEZ LE COMMUTATEUR AU
MODE « FLOTTANT ».
ACTIONNEUR
0/2 À 10 V CC
RÉGULATEUR À
COMMANDE
PROPORTIONNELLE
24 V CA
1
1
2
3
2
490 À 510
OHMS,
1/2 W
MINIMUM
TENSION D’ALIMENTATION. AU
BESOIN, PLACEZ UN DISPOSITIF DE
COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V CC ACCEPTÉE.
RÉGLEZ LE COMMUTATEUR À MODULATION, SI POSSIBLE.
V
–
+
RÉTROACTION
4
3
1
2
MF37321
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
3
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
ROUGE
NOIR
BRUN
BLANC
CLASSE 2
Fig. 14. MS7505 à commande SPDT à deux positions.
CLASSE 2
1
1
2
24 V CA
TENSION D’ALIMENTATION.
AU BESOIN, PLACEZ UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION
CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
RÉGLEZ LE COMMUTATEUR AU
MODE « FLOTTANT ».
Fig. 15. MS7505 à commande à flotteur.
CLASSE 2
1
0/2 À 10 V CC
RÉGULATEUR À
COMMANDE
PROPORTIONNELLE
RÉTROACTION
1
2
3
Fig. 16. MS7103 avec commande 2-10 V CC (MS7503
38-00005EFS—04 6
24 V CA
2
–
+
TENSION D’ALIMENTATION. AU BESOIN, PLACEZ UN DISPOSITIF DE COUPURE
ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V CC ACCEPTÉE.
RÉGLEZ LE COMMUTATEUR À MODULATION, SI POSSIBLE.
montré, ignorez le sélecteur).
1
2
3
4
2
NOIR
BLANC
BRUN
V
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
ACTIONNEUR
ROUGE
ACTIONNEUR
ROUGE
1
2
NOIR
3
BLANC
4
BRUN
3
V
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
MF37319
MF37320
Fig. 17. MS7103 avec commande 4-20 mA (MS7503
montré, ignorez le sélecteur).
CLASSE 2
1
RÉGULATEUR À
COMMANDE
PROPORTIONNELLE
0/2 À 10 V CC
24 V CA
2
–
+
RÉTROACTION
TENSION D’ALIMENTATION.
1
AU BESOIN, PLACEZ UN
DISPOSITIF DE COUPURE ET
UNE PROTECTION CONTRE
LES SURCHARGES.
2
ALIMENTATION 24 V CC
ACCEPTÉE.
3
RÉGLEZ LE COMMUTATEUR À
MODULATION, SI POSSIBLE.
1
2
3
4
3
1
2
3
4
3
ACTIONNEUR
ROUGE
NOIR
BLANC
BRUN
V
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
ACTIONNEUR
ROUGE
NOIR
BLANC
BRUN
V
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
Fig. 18. MS7103 avec commande 2-10 V CC utilisant
deux actionneurs (MS7503 montré, ignorez le
sélecteur).
MF37322
Page 19

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
ACTIONNEUR
SPST
24 V c.a.
1
1
2
2
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
V
1
2
MF34973
3
ACTIONNEUR
SPST
1
1 ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
V
1
2
MF34974
2
24 V c.a.
1
1
2
3
2
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE
UN DISPOSITIF DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION
CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR SUR FLOTTANT.
MF34975
ACTIONNEUR
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
5
4
3
1
2
2-10 V c.c.
10-2 V c.c.
0-10 V c.c.
10-0 V c.c.
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
ACTIONNEUR
RÉGULATEUR
PROPORTIONNEL
0/2 À 10 V C.C.
24 V c.a.
1
1
2
3
2
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR SUR MODULANT.
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
–
+
RETOUR
5
4
3
1
2
MF19576
2-10 V c.c.
10-2 V c.c.
0-10 V c.c.
10-0 V c.c.
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
SPDT
ACTIONNEUR
RÉGULATEUR
PROPORTIONNEL
0/2 À 10 V C.C.
24 V c.a.
1
1
2
3
2
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR SUR MODULANT.
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
–
+
RETOUR
5
4
3
1
2
MF34976
2-10 V c.c.
10-2 V c.c.
0-10 V c.c.
10-0 V c.c.
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
ROUGE
NOIR
ACTIONNEUR
INTERRUPTEURS SPST
CÂBLE
PRINCIPAL
BLANC
BRUN
+ OU 0°−90°
RÉTROACTION OU 90°-0°
BLEU
BRUN
CÂBLE DES
INTERRUPTEURS
GRIS
NOIR
MF37303A
Fig. 19. Câblage pour interrupteurs auxiliaires MS7103
et MS3103). Gray/Black = Normally Open. Closed in
range 80 degrees to Fully Open. Blue/Brown = Normally
Closed. Open in range 10 degrees to Fully Open.
Fig. 20. MS8105 à commande SPDT à deux positions.
Fig. 22. MS7505 avec dérivation pour ouverture
complète.
ACTIONNEUR
1
RÉGULATEUR
PROPORTIONNEL
0/2 À 10 V C.C.
1
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
2
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
3
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR SUR MODULANT.
RETOUR
24 V c.a.
–
+
2
SPST
1
2
3
4
5
3
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
2-10 V c.c.
10-2 V c.c.
0-10 V c.c.
10-0 V c.c.
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
MF19577
Fig. 23. MS7505 avec dérivation pour fermeture
complète.
Fig. 21. MS7505 pour action flottante.
Fig. 24. MS7505 avec régulateurs 0(2)-10 V CC.
7 38-00005EFS—04
Page 20

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
ACTIONNEUR
SPST
1
1 ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. FOURNIR AU BESOIN UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
V
1
2
MF29122A
S1S3
S2
M35813
ACTIONNEUR
RÉGULATEUR
PROPORTIONNEL
0/2 À 10 V C.C.
1
2
3
2
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI
NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF DE COUPURE ET
UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR SUR MODULANT.
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
5
4
3
1
2
MF34978
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
ACTIONNEUR
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
5
4
3
1
2
2-10 VDC
10-2 VDC
0-10 VDC
10-0 VDC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
24 V c.a.
1
24 V c.a.
1
2
24 V c.a.
1
SOUS TENSION
COMMON
–
+
1
2
3
CHAUD
COM
CONTRÔLEUR
ALIMENTATION DE TENSION DE
LIGNE. FOURNIR DES MOYENS
DE DÉCONNEXION ET UNE
PROTECTION CONTRE LES
SURCHARGES, SI NÉCESSAIRE.
ALIMENTATION 24 V CC ACCEPTÉE.
SÉLECTEUR D'ADRESSE
S-BUS
S-BUS
24 V CA
CLASSE 2
S-BUS
S-BUS
ROUGE
NOIR
BRUN
BRUN
ACTIONNEUR
ADRESSE 11
ADRESSE 12
ADRESSE 13
ADRESSE 14
ADRESSE 15
TEST
ACTIONNEUR
1
RÉGULATEUR
PROPORTIONNEL
4 À 20 mA
1
2
3
24 V c.a.
2
490 À
510 OHMS,
1/2 W
–
+
RETOUR
ALIMENTATION SECTEUR. PLACER SI NÉCESSAIRE UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
ALIMENTATION 24 V c.c. ACCEPTABLE.
RÉGLER LE COMMUTATEUR SUR MODULANT.
MINIMUM
1
2
3
4
5
3
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETOUR
2-10 V c.c.
10-2 V c.c.
0-10 V c.c.
10-0 V c.c.
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
MF34977
Fig. 25. MS7505 avec régulateurs 4-20 mA.
Fig. 26. MS4105 à commande SPDT 120 V CA à deux
positions.
d’extrémité/auxiliaire.
Fig. 27. Câblage pour les modèles avec interrupteurs
38-00005EFS—04 8
Fig. 28. MS7505 avec régulateur 0(2)-10 V CC
actionnant plusieurs actionneurs.
Fig. 29. MS3103 with Sylk Bus control.
Page 21

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
M27714
A
FONCTIONNEMENT ET VÉRIFICATION
Une fois les installations mécanique et électrique
terminées :
1. Actionner l’actionneur pour vérifier que le sens de
rotation correspond à la séquence de commande.
2. Si le sens de rotation est incorrect :
a. For 2-position and Sylk-enabled spring return
actuators : Retirer, inverser et replacer l’actionneur sur le support.
b. Pour les actionneurs de commande flottants :
Inverser les deux fils de signal de commande
(sens horaire/antihoraire) ou modifier la position
de la commande du sélecteur.
c. Pour les actionneurs analogiques :
(1) Modifier le réglage de l’interrupteur à action
directe/inverse, ou
(2) Pour changer le sens du ressort de rappel :
déposer, inverser et poser l’actionneur de
nouveau sur le support.
3. Si la configuration de commande nécessite un
fonctionnement avec sécurité intégrée, s’assurer
que la position de sécurité coïncide avec la
séquence de commande lors de l’interruption de
l’alimentation.
4. Les actionneurs à ressort de rappel sont configurés
en usine pour un fonctionnement normalement
fermé à sécurité intégrée lors des coupures d’alimentation. Pour changer cette action pour un
fonctionnement en position normalement ouvert,
retirer et réinstaller l’actionneur dans le sens opposé
de la façon suivante :
a. Desserrer le boulon d’accouplement de l’arbre
avec une clé de 10 mm.
b. Desserrer tous les autres boulons de montage
connectant l’actionneur au support de montage
et les mettre de côté.
c. Retirer l’actionneur de l’arbre du clapet.
d. Déplacer l’adaptateur d’arbre à centrage
automatique du côté opposé à l’actionneur,
comme illustré dans la Fig. 30.
(1) Retirer l’attache de fixation de l’adaptateur
d’arbre à centrage automatique et la mettre
de côté pour une utilisation ultérieure.
(2) Retirer l’adaptateur d’arbre à centrage
automatique de l’actionneur.
(3) Reposer l’adaptateur d’arbre à centrage
automatique du côté opposé de l’actionneur
en l’alignant conformément à l’étiquetage de
course.
(4) Replacer l’attache de fixation sur l’accouple-
ment de l’arbre en utilisant la rainure de
l’accouplement.
e. Reconnecter l’actionneur au support de montage
du clapet en remplaçant les vis précédemment
déposées (étape b).
f. À l’aide d’une clé ou d'une douille de 10 mm, ser-
rez fermement le boulon d'accouplement d'arbre
à un couple de 13,6 Nm (120 lb-po).
Fonctionnement
PIN change constamment dans un système multi-zones
lors de l’ouverture et de la fermeture d’autres clapets,
modifiant le débit et la pression de refoulement du
système conformément aux caractéristiques de la courbe
de la pompe d’alimentation. La réaction du régulateur de
pression mécanique est instantanée, éliminant les
modifications de température de la pièce dus aux
changements de débit de liquide, et réduisant la nécessité
d’un fonctionnement continu du système de commande
du clapet pour corriger les changements de température
non liés à la charge se produisant dans les systèmes avec
clapets de commande standard.
Fig. 30. Placer l’actionneur en position normalement
ouvert.
M29908
Fig. 31. VRN2 Vue en coupe du VRN2 illustrant le
raccord, la bille de contrôle et le régulateur de pression.
Pour une application à commande à deux positions à plein
débit, le VRN2 agit comme un limiteur de débit.
Le régulateur de débit ne nécessite qu’une pression
minimale pour fonctionner, et a une capacité de
régulation différentielle maximale. Consulter la Fig. 32. La
chute de pression élevée d’un clapet VRN2 est comparable
à la chute de pression d’un régulateur et d’un clapet
d’équilibrage d’un système conventionnel.
9 38-00005EFS—04
Page 22

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
MISE EN GARDE
0
DÉBIT
GAL./MIN)
PRESSION DIFFÉRENTIELLE (PSID)
12
10
6
4
5.8
8
16
22
28
50
MF29707
8
12
34 40
60
100 % OUVERT
80 % OUVERT
60 % OUVERT
40 % OUVERT
20 % OUVERT
TIGE
VIS À TÊTE
FRAISÉE
PLAQUE DE
FIXATION DE TIGE
SYMBOLE « T »
TIGE
FOULOIR
SUPÉRIEUR
JOINT TORIQUE
FOULOIR INFÉRIEUR
MF34994
2. Pour limiter mécaniquement la course, régler
l’actionneur à accouplement direct en position complètement ouverte. Desserrer l’accouplement de
l’arbre et faire tourner l’arbre du clapet à la position
de débit maximum désirée, telle que confirmée par
la mesure de pression du serpentin, en utilisant les
données du fabricant du serpentin. Resserrer
l’accouplement de l’arbre. Utiliser la Fig. 33 comme
guide de réglage de la course de l’actionneur.
Si une technique d’ajustement mécanique est util-
Fig. 32. Régulation de pression, modèles à grand corps.
isée avec les actionneurs modulants MN/MS7505,
la fonction d’auto-adaptation de la course règle
automatiquement le signal de 2-10 V c.c. en
RÉGLAGES ET AJUSTEMENTS
En position d'ouverture complète, les clapets VRN2
maintiennent le débit dans la boucle. Les débits sont
indiqués dans le document de spécifications
62-3115EFS. En fonctionnement stable, le système de
commande ne requiert qu'une ouverture du clapet
suffisante pour répondre aux conditions de charge. Lors
de la récupération matinale du décalage de nuit, le
contrôleur commande généralement le clapet à 100 %.
Pour une performance optimale, ne choisir que la taille de
clapet immédiatement supérieure pour satisfaire à la
charge de conception. Ne pas utiliser de clapets trop
grands : une gamme réduite pourrait entraîner une
régulation de température moins précise.
Les clapets à bille se ferment entre 10 et 15 % de leur
course pour assurer un engagement complet du dispositif
fonction de la rotation mécanique de la bille. Voir la
documentation de l’actionneur pour les détails.
Le débit du serpentin peut être confirmé en lisant les
pressions d’entrée et de sortie du serpentin (et non pas sur
le régulateur comme c’est le cas avec un équilibrage
traditionnel : cette chute de pression est constante) et en
utilisant les données du fabricant pour calculer le débit.
Noter que le régulateur de pression de ce clapet garantit
que le débit dans le serpentin ne sera pas affecté pas les
changements de pression en amont. Contrairement aux
clapets d’équilibrage traditionnels, il n’est pas nécessaire
de reconfirmer le débit du serpentin après le réglage
d’autres clapets. Tout débit excessif ayant lieu lors de la
récupération matinale dû à des régulateurs de pression
surdimensionnés n’affecte pas les autres clapets du
système, à condition que les pompes soient d’une
capacité suffisante pour le débit requis.
d’étanchéité. Le cas échéant, les actionneurs modulants
peuvent être réglés à une réponse de 0-10 V pour que les
2 V d’un signal de commande de 2-10 V assurent une
meilleure correspondance au débit minimum. Le clapet
continuera à se fermer en cas de perte de signal.
Réparations et entretien
La tige de clapet peut être remplacée dans le système, si
nécessaire. Voir la Fig. 34.
Le cas échéant, le débit maximum peut être ajusté à une
valeur moindre de l’une des deux façons suivantes :
1. Avec l’actionneur modulant, limiter la plage de ten-
sion de commande du contrôleur d’automatisation
de bâtiment. Les clapets avec inserts de commande
de débit ont des caractéristiques d’égal pourcentage
(voir la Fig. 33). Chaque réduction de 10 % de la tension de commande maximale entraîne une réduction de 10 % du débit.
100%
80%
60%
DÉBIT
40%
20%
0%
0° 30° 60° 90°
38-00005EFS—04 10
10°
Fig. 33. Caractéristiques de débit types.
BILLE À ORIFICE
INTÉGRAL
20°
40° 50°
COURSE DE TIGE DE CLAPET
DÉBIT
CARACTÉRISÉ
À DEUX VOIES
80°
70°
Fig. 34. Remplacement dans le système de la tige de
clapet.
Suivre les étapes 1 à 6 de la section «Ajustement de la
plaque de montage» à la page 3, puis :
1. Si le fouloir inférieur est coincé, le retirer avec un
outil d’extraction de fouloir ou un outil dentaire à
extrémité en caoutchouc.
MF29551
Éviter d’érafler l’intérieur du cou du clapet.
Ceci pourrait causer une fuite lors du remontage.
Page 23

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
2. Retirer avec précaution toute saleté ou corrosion à
l’intérieur du clapet.
3. Aligner la flèche avec la patte courte du symbole
« T » de la tige neuve.
REMARQUE : Le symbole « T » varie.
4. Insérer la tige neuve. Veiller à bien aligner la clavette
de la tige avec la fente de la bille.
5. Attacher la plaque haute pression de fixation de la
tige au clapet en utilisant les vis à tête fraisée
neuves. Attacher ensuite la plaque de montage sur
le clapet.
6. Remettre le clapet sous pression et vérifier que la
tige ne fuit pas avant de continuer.
7. Glisser le sous-arbre sur la tige avec la languette ori-
entée comme indiqué dans la Fig. 34.
8. Replacer le coupe-circuit thermique, l’arbre et le
couvercle de l’arbre. Si l’arbre s’est desserré du disjoncteur thermique, pousser fermement sur
l’extrémité de l’arbre jusqu’à ce que la lame dans
l’arbre s’enclenche sur le coupe-circuit thermique.
9. Remplacer l’actionneur et l’attacher à l’arbre et à la
plaque de montage.
10. Enclencher la poignée sur la partie supérieure de
l’arbre.
Tout autre entretien du clapet, tel que le remplacement du
joint de siège, nécessite le retrait du clapet de la
tuyauterie.
11 38-00005EFS—04
Page 24

CLAPETS ET ACTIONNEURS DE RÉGULATION DE PRESSION DYNAMIQUE VRN
Par l'utilisation de la présente documentation Honeywell, vous consentez à ce qu'Honeywell ne possède aucune responsabilité
pour tous dommages résultant de votre utilisation ou modification de ladite documentation. Vous défendrez et indemniserez
Honeywell, ses sociétés affiliées, filiales pour et contre toute responsabilité, frais ou dommages, y compris les honoraires
d'avocats, résultant de quelque manière, ou survenant en connexion avec toute modification à la documentation de votre part.
Honeywell Building Technologies
Aux États-Unis :
Honeywell
® Marque de commerce déposée aux États-Unis
© 2019 Honeywell International Inc.
38-00005EFS—04 M.S. Rev. 12-19
Imprimé aux États-Unis
Page 25

Válvulas de control y actuadores
VRN con regulación de presión
dinámica
INSTRUCCIONES PARA LA INSTALACIÓN
Las válvulas de mayor tamaño pueden ocasionar ciclos
excesivos y el asiento y la bola se pueden dañar debido a
la abertura restringida.
Uso correcto
Las válvulas VRN están diseñadas para usar solamente en
aplicaciones de circuito cerrado de agua fría y caliente,
con un rango de temperatura de 35 °F a 250 °F (2 °C a
120 °C) y presiones de 360 psig (25 kg/cm²).
El agua debe estar bien filtrada, tratada y acondicionada
para un buen rendimiento operativo, y de acuerdo con las
recomendaciones del fabricante de la caldera o del
enfriador.
Se recomienda la instalación de tamices y filtros.
No utilizar con válvulas de equilibrado manual.
APLICACIÓN
Las válvulas de control bidireccionales VRN2 con
regulación de presión dinámica mantienen el flujo
constante de agua caliente y fría con soluciones de glicol
de hasta el 50 % en sistemas de calefacción, ventilación y
aire acondicionado de circuito cerrado, dentro de los
rangos de variación de presión especificados de cada
número de modelo.
Estos ensambles de válvula se pueden pedir con o sin
actuadores de montaje en fábrica.
Notas sobre la aplicación
El tamaño de la válvula es importante para el
funcionamiento adecuado del sistema. Las válvulas de
menor tamaño no tienen suficiente capacidad a la carga
máxima. Las válvulas de mayor tamaño no tienen
suficiente control sobre la carga en aplicaciones
modulantes.
IMPORTANTE
La presencia de óxido de hierro (oxidación de color
rojo) en exceso en el sistema anula la garantía de
la válvula.
Caudal efectivo
El regulador de presión diferencial incorporado hace fluir
el líquido a través de la válvula, independientemente de
los cambios de presión de suministro. El regulador de
presión prácticamente elimina la cavitación en la válvula y
libera la válvula de control de los efectos de los
componentes de la tubería, como los reductores y los
codos.
Las válvulas de control independientes de presión están
diseñadas para adaptarse al flujo de diseño en el
serpentín, independientemente del tamaño del serpentín.
Con las válvulas VRN2 no es necesario compensar el
sistema para obtener un flujo adecuado, ya que permiten
hacer funcionar los enfriadores según el diferencial de
temperatura de diseño a fin de obtener una eficacia
máxima en cualquier condición de carga. Cuando las usa
en un sistema con impulsores de bomba de velocidad
variable, las válvulas de 3 vías y las líneas con derivación
de serpentín no son necesarias.
Par de torsión operativo necesario
Tanto los actuadores de acoplamiento directo de poco par
de torsión a prueba de fallas como de falla en la posición
de Honeywell se pueden utilizar con las válvulas VRN.
Page 26

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
PRECAUCIÓN
Las válvulas VRN utilizan un diseño de asiento patentado
que disminuye el par de torsión necesario del actuador.
Los actuadores con un par de torsión de 27 lb-in (3 Nm)
(para válvulas de hasta 1-1/4" [32 mm] de tamaño) y
35 lb-in (4 Nm) (para válvulas mayores de 1-1/2" [38 mm]
de tamaño) ofrecen par de torsión suficiente para operar
la válvula en el cierre nominal. (Consulte la Table 1).
El par de torsión máximo para una operación segura es
44 lb-in (5 Nm).
Tabla 1. Especificaciones de cierre-apagado, presión
diferencial.
Tipo de
válvula Tamaño de la válvula
2 vías 1/2 in. a 3 in. 100
Especificación de
presión de cierre-
apagado (psi)
INSTALACIÓN
Cuando instale este producto...
1. Lea detenidamente estas instrucciones. De no
seguirlas, se podría dañar el producto o provocar
una situación peligrosa.
2. Revise los valores nominales especificados en las
instrucciones y en el producto, para asegurarse que
el producto sea adecuado para la aplicación.
3. El instalador debe ser un técnico de servicio capacit-
ado y experimentado.
4. Después de terminar la instalación, compruebe el
funcionamiento del producto tal como se indica en
estas instrucciones.
Preparación
No emplee aditivos para calderas, fundente para
soldar ni materiales húmedos a base de petróleo o
que contengan aceites minerales, hidrocarburos o
acetato de etilenglicol. Los compuestos que se
pueden utilizar, con un mínimo de 50% de
disolución en agua, son: dietilenglicol, etilenglicol y
propilenglicol (soluciones anticongelantes).
Si instala estas válvulas en la ampliación o
modernización de un edificio existente, no dé por
hecho que el líquido en las tuberías existentes
cumple con estos requisitos.
Instalación mecánica
IMPORTANTE:
Sujete la válvula con una llave para tubería por el
conector hexagonal ÚNICAMENTE. NO manipule
el cuerpo de la válvula con la llave para tubería; el
producto se puede dañar.
Las válvulas se roscan en el conector NPT y se deben
sellar con un sellador aprobado para tuberías. La fuerza
de torsión no debe exceder 75 lb-pies.
Consulte los documentos del actuador para conocer las
dimensiones del actuador.
1. Limpie los conductos de manera ascendente para
quitar partículas de más de 1/16 in (1.6 mm) de
diámetro (escorias de soldadura, sarro en las
tuberías y otros agentes contaminantes).
2. Continúe con la instalación una vez que las condi-
ciones específicas del sistema (expansión/contrac-
ción del sistema y su medio, así como también las
presiones de funcionamiento) estén dentro de las
tolerancias.
3. Elimine el aire del sistema.
4. Las válvulas están marcadas para mostrar la direc-
ción del flujo.
Riesgo de daño en el equipo
Las partículas extrañas, como los restos de metal y
la suciedad, pueden dañar los sellos de la bola.
Para que el producto funcione sin complicaciones,
el proceso de instalación adecuado debe incluir el
drenado inicial del sistema y el tratamiento
químico del agua. Limpie los conductos de manera
ascendente para quitar partículas de más de
1/16 in (1.6 mm) de diámetro (escorias de
soldadura, sarro en las tuberías, arena y otras
partículas suspendidas). Se sugiere utilizar un
filtro de corriente lateral para el sistema de
50 micrones (o más fino). Retire todos los filtros
antes de realizar el drenaje.
38-00005EFS—04 2
IMPORTANTE
Las flechas del flujo deben estar orientadas en la
dirección del flujo para un funcionamiento
correcto.
5. Rotación del vástago:
a. En sentido horario para cerrar.
b. En sentido antihorario para abrir.
NOTA: Después de instalar las válvulas en las tuberías, el
instalador puede determinar la orientación de la
bola dentro de la válvula por las muescas que se
encuentran en la parte superior del vástago de la
válvula. Para las válvulas VRN, la dirección en
sentido longitudinal de la muesca indica el flujo a
través de la bola (es decir, cuando la muesca se
encuentra paralela al eje de la válvula entre los
puertos A y B, la bola permitirá el flujo a través de
la válvula).
6. La válvula se debe montar con el actuador/soporte
por encima del cuerpo de la válvula. No instale la
válvula con el vástago por debajo de la línea hori-
zontal o en forma invertida. (Consulte las Fig. 3 y 4).
Page 27

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
MS34979
FLUJO FLUJO
CERRADO
ABIERTO
NOTAS: PARA MONTAR EL ACTUADOR EN UNA VÁLVULA ABIERTA, GIRE EL
ACTUADOR COMPLETAMENTE EN SENTIDO ANTIHORARIO COMO SE MUESTRA.
PARA MONTAR EL ACTUADOR EN UNA VÁLVULA CERRADA, GIRE EL
ACTUADOR COMPLETAMENTE EN SENTIDO HORARIO COMO SE MUESTRA.
M34954
45
45
M33091
Fig. 1. Orientación de la válvula.
MANIJA (DESMONTABLE)
PARA ROTACIÓN MANUAL**
Fig. 3. Instalación vertical de la válvula.
** INCLUIDOS EN EL KIT DE REEMPLAZO (PIEZA 5112-11).
Fig. 2. Vista en despiece del ensamble de la válvula.
ACOPLADOR DEL VÁSTAGO DE LA VÁLVULA
TORNILLOS (2)**
CUBIERTA DEL ENSAMBLE
DE VÁSTAGO**
ENSAMBLE DE VÁSTAGO**
TORNILLOS (2)**
CUERPO DE LA VÁLVULA
PERNO**
SOPORTE
ANTIRROTACIÓN**
PLACA DE MONTAJE**
TUERCA MARIPOSA**
MS13738A
Fig. 4. Ángulo aceptable de la válvula desde la línea
vertical.
Ajuste de la placa de montaje
La placa de montaje del actuador se puede girar hacia una
posición diferente para la instalación en espacios
reducidos. Esto se realiza de la siguiente manera:
1. Quite la manija del eje y déjela a un lado.
2. Quite los dos tornillos que sujetan el ensamble del
vástago a la placa de montaje y déjelos a un lado.
3. Quite y deje a un lado el ensamble del vástago.
4. Quite y deje a un lado los dos tornillos que sujetan la
placa de montaje a la válvula.
5. Quite y aparte el aro de sujeción de la placa de mon-
taje.
6. Gire la placa de montaje alrededor de la parte supe-
rior de la válvula a la posición deseada.
NOTA: Tenga en cuenta las posiciones de los agujeros
para los tornillos en la válvula. Estos limitan las
posiciones de la placa de montaje.
7. Baje el aro hasta el cuerpo de la válvula y engánch-
elo en la nueva posición con relación a la placa de
montaje.
8. Apriete los tornillos al cuerpo de la válvula para fijar
la placa de montaje.
9. Vuelva a fijar el ensamble del vástago a la placa de
montaje.
10. Si lo desea, reemplace la manija en el eje.
NOTA: Consulte la Fig. 2 para ver la vista en despiece de
la válvula.
3 38-00005EFS—04
Page 28

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
24 V CA
1
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN
Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
+
–
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
1
325
ACTUADOR PROPORCIONAL
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
+
0(2)-10 V CC DE 0(4)-20 mA SEÑAL DE CONTROL ACEPTABLE. CONFIGURE
EL INTERRUPTOR DIP DE CONTROL DE SEÑAL EN “OFF” (APAGADO) PARA
VOLTAJE. CONFIGURE EN “ON” (ENCENDIDO) PARA CORRIENTE.
2
2
2 -10 V CC
2 -10 V CC
0 -10 V CC
0 -10 V CC
MS18947B
4
5°
85°
S1 S2
S3 S5 S6
MS25214A
INTERRUPTORES TERMINALES (CLASE II ÚNICAMENTE)
Instalación eléctrica
1. Si fuera necesario, retire la cubierta del cableado del
actuador.
2. Conecte el actuador usando las Figuras 5 a 28 como
guía para la aplicación requerida.
3. Vuelva a colocar la cubierta.
Cableado
ACTUADOR FLOTANTE
DIRECTO
SERVICIO/APAGADO
INVERSO
CONTROLADOR
432
FLOTANTE
2
1
24 V CA
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
1
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN
SE REQUIERA.
SE REQUIERE CONEXIÓN PARA CONTROL SPST.
2
3
Fig. 5. MN6105 con control SPDT de
encendido/apagado.
ACTUADOR FLOTANTE
DIRECTO
SERVICIO/APAGADO
INVERSO
3
2
4
CONTROLADOR
FLOTANTE
Fig. 7. MN7505 con control de 0(2)-10 V CC.
MS34869B
Fig. 8. Cableado para los modelos MN6105 y MN7505
con interruptores auxiliar/fin.
1
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN
Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
Fig. 6. MN6105 con control flotante.
38-00005EFS—04 4
24 V CA
MS18946
Page 29

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
ACTUADOR FLOTANTE
24 V CA
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN
SE REQUIERA.
CONTROLADOR
MS33137B
2
3
4
1
NEGRO
BLANCO
MARRÓN
2
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN
SE REQUIERA.
ACTUADOR FLOTANTE
24 V CA
1
2
3
4
1
MS33138C
NEGRO
BLANCO
MARRÓN
2
CONTROLADOR
MS33557C
ACTUADOR FLOTANTE
1
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN
SE REQUIERA.
2
3
4
1
24 V CA
NEGRO
MARRÓN
BLANCO
SPST
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS
SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
CONTROLADOR
DE 4-20mA
MS33141B
1
2
3
+
+
–
ACTUADOR PROPORCIONAL
POSICIÓN DEL INTERRUPTOR DIP
1 2 MODO
OFF (apagado) OFF (apagado) 2-10V
OFF (apagado) ON (encendido 0-10V
ON (encendido) OFF (apagado) 10-2V
ON (encendido) ON (encendido) 10-0V
PROPORCIONAL/DE MODULACIÓN: SALIDA DEL CONTROLADOR DE
4-20mA CON RESISTENCIA DE LA SERIE 500
A OTROS
ACTUADORES
500OHMIOS,
MÍNIMO
DE 1/2W
24VCA
ROJO
NEGRO
BLANCO
1
ACTUADOR PROPORCIONAL
24 V CA
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN
Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
CONTROLADOR
DE 0 (2)-10 V CC
MS33140
1
2
3
+
+
–
POSICIÓN DEL INTERRUPTOR DIP
1 2 MODO
OFF (apagado) OFF (apagado) 2-10V
OFF (apagado) ON (encendido) 0-10V
ON (encendido) OFF (apagado) 10-2V
ON (encendido) ON (encendido) 10-0V
PROPORCIONAL/DE MODULACIÓN: SALIDA DEL CONTROLADOR DE 0(2)...10 V CC O 10...0(2) V CC
2
ROJO
NEGRO
BLANCO
2
1
Fig. 9. MVN613 con control flotante.
Fig. 10. MVN613 o MVN643 con control SPDT de dos
posiciones.
Fig. 11. MVN643 con control SPST de dos posiciones.
Fig. 12. MVN713 con control de 4-20 mA.
Fig. 13. MVN713 con control de 0(2)-10 V CC.
5 38-00005EFS—04
Page 30

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
SPDT
1
2
MF37304
ACTIONNEUR
V
4
3
1
2
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTTANT, MARCHE AVANT
FLOTTANT, MARCHE ARRIÈRE
0°-90°/MODULATION
90°-0°/RÉTROACTION
ROUGE
NOIR
BRUN
BLANC
CLASSE 2
24 V CA
1
2
TENSION D’ALIMENTATION.
AU BESOIN, PLACEZ UN DISPOSITIF
DE COUPURE ET UNE PROTECTION
CONTRE LES SURCHARGES.
RÉGLEZ LE COMMUTATEUR AU
MODE « FLOTTANT ».
1
MS37319
V
4
3
1
2
2
ACTUADOR
0° a 90°/MODULANTE
90° a 0°/RETROALIMENTACIÓN
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTANTE, ADELANTE
FLOTANTE, REVERSA
ROJO
NEGRO
MARRÓN
BLANCO
1
2
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN DE LA
LÍNEA DE TENSIÓN. PROPORCIONE
MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y
PROTECCIÓN DE SOBRECARGA
SEGÚN SEA NECESARIO.
INSTALE EL INTERRUPTOR EN LA
POSICIÓN FLOTANTE.
24 V CA
CLASE 2
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
1
1
2
3
2
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN DE LA LÍNEA DE TENSIÓN. PROPORCIONE
MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y PROTECCIÓN DE SOBRECARGA SEGÚN SEA
NECESARIO.
SUMINISTRO DE 24 V CC ACEPTABLE.
COLOQUE EL INTERRUPTOR EN MODULANTE SI ESTÁ DISPONIBLE.
V
–
+
RETROALI-
MENTACIÓN
4
3
1
2
MS37320
3
ACTUADOR
0° a 90°/MODULANTE
90° a 0°/RETROALIMENTACIÓN
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTANTE, ADELANTE
FLOTANTE, REVERSA
ROJO
NEGRO
MARRÓN
BLANCO
24 V CA
CLASE 2
1
2
V
–
+
RETROALI-
MENTACIÓN
4
3
1
2
MS37322
3
V
4
3
1
2
3
ACTUADOR
0° a 90°/MODULANTE
90° a 0°/RETROALIMENTACIÓN
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTANTE, ADELANTE
FLOTANTE, REVERSA
ROJO
NEGRO
MARRÓN
BLANCO
ACTUADOR
0° a 90°/MODULANTE
90° a 0°/RETROALIMENTACIÓN
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTANTE, ADELANTE
FLOTANTE, REVERSA
ROJO
NEGRO
MARRÓN
BLANCO
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
24 V CA
CLASE 2
1
2
3
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN DE
LA LÍNEA DE TENSIÓN. PROPORCIONE
MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y
PROTECCIÓN DE SOBRECARGA
SEGÚN SEA NECESARIO.
SUMINISTRO DE 24 V CC ACEPTABLE.
COLOQUE EL INTERRUPTOR EN
MODULANTE SI ESTÁ DISPONIBLE.
Fig. 14. MS7505 con control SPDT de dos posiciones.
CLASE 2
ROJO
1
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
24 V CA
2
1
2
NEGRO
BLANCO
3
4
MARRÓN
–
+
RETROALI-
MENTACIÓN
1
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN DE LA LÍNEA DE TENSIÓN. PROPORCIONE
MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y PROTECCIÓN DE SOBRECARGA SEGÚN SEA
NECESARIO.
2
SUMINISTRO DE 24 V CC ACEPTABLE.
3
COLOQUE EL INTERRUPTOR EN MODULANTE SI ESTÁ DISPONIBLE.
3
ACTUADOR
V
0° a 90°/MODULANTE
90° a 0°/RETROALIMENTACIÓN
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
FLOTANTE, ADELANTE
FLOTANTE, REVERSA
MS37321
Fig. 17. MS7103 con control de 4-20 mA (se muestra
MS7503, ignore el interruptor de selección).
Fig. 15. MS7505 con control flotante.
Fig. 16. MS7103 con control de 2-10 V CC (se muestra
MS7503, ignore el interruptor de selección).
38-00005EFS—04 6
Fig. 18. MS7103 con control de 2-10 V CC que usa dos
actuadores (se muestra MS7503, ignore el interruptor
de selección).
Page 31

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
ACTUADOR
INTERRUPTORES DE SPST
CABLE
PRINCIPAL
MS37303A
ROJO
NEGRO
BLANCO
MARRÓN
CABLE DE LOS
INTERRUPTORES
AZUL
MARRÓN
GRIS
NEGRO
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
O 90° a 0°
+ O 0° a 90°
ACTUADOR
SPST
1
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
V
1
2
MS34974
2
Fig. 19. Cableado para los interruptores auxiliares de
MS7103 y MS3103. Gray/Black = Normally Open.
Closed in range 80 degrees to Fully Open. Blue/Brown =
Normally Closed. Open in range 10 degrees to Fully
Open.
1
1
2
24 V CA
2
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
SPST
1
2
ACTUADOR
V
MS34973
3
ACTUADOR
1
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
1
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
2
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
3
CONFIGURE EL INTERRUPTOR EN EL MODO DE MODULACIÓN.
24 V CA
–
+
2
SPDT
1
2
3
OR +
OR N/A
4
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
5
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
3
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
Fig. 22. MS7505 con control de sobrecomando
para la posición completamente abierta.
ACTUADOR
1
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
1
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
2
3
CONFIGURE EL INTERRUPTOR EN EL MODO DE MODULACIÓN.
24 V CA
–
+
2
SPST
1
V
2
3
OR +
OR N/A
4
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
5
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
3
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
V
MS19576
MS19577
Fig. 20. MS8105 con control SPDT de dos posiciones.
1
1
2
3
24 V CA
2
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA.
PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y
DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN
SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
CONFIGURE EL INTERRUPTOR EN EL MODO FLOTANTE.
Fig. 21. MS7505 con control flotante.
ACTUADOR
1
V
2
3
OR +
OR N/A
4
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
5
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
3
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
MS34975
Fig. 23. MS7505 con control de sobrecomando
para la posición completamente cerrada .
ACTUADOR
1
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
2
CONFIGURE EL INTERRUPTOR EN EL MODO DE MODULACIÓN.
3
24 V CA
–
+
2
1
2
3
4
5
3
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
MS34976
Fig. 24. MS7505 con controladores de 0(2)-10 V CC.
7 38-00005EFS—04
Page 32

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
ACTUADOR
SPST
1
1 SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA.
PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y DE
PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
V
1
2
MS29122
S1S3
S2
M35813
ACTUADOR
0/2 A 10 V CC
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
1
2
3
2
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE
LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA
SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
CONFIGURE EL INTERRUPTOR EN EL MODO DE
MODULACIÓN.
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
5
4
3
1
2
MS34978
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
ACTUADOR
V
OR +
OR N/A
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
5
4
3
1
2
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
3
24 V CA
1
24 V CA
1
2
24 V CA
1
CON CORRIENTE
COMÚN
–
+
1
2
3
CALIENTE
COM
CONTROLADOR
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN DE
TENSIÓN DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE
LOS MEDIOS DE DESCONEXIÓN Y
LA PROTECCIÓN CONTRA
SOBRECARGA NECESARIOS.
SUMINISTRO DE 24 V CC ACEPTABLE.
SELECTOR DE DIRECCIONES
BUS S
BUS S
24 V CA
CLASE
2
BUS S
BUS S
ROJO
NEGRO
MARRÓN
MARRÓN
ACTUADOR
DIRECCIÓN 11
DIRECCIÓN 12
DIRECCIÓN 13
DIRECCIÓN 14
DIRECCIÓN 15
PRUEBA
ACTUADOR
1
4 A 20 mA
CONTROLADOR
PROPORCIONAL
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
1
SUMINISTRO ELÉCTRICO DEL VOLTAJE DE LÍNEA. PROPORCIONE LOS MEDIOS DE
DESCONEXIÓN Y DE PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGAS SEGÚN SE REQUIERA.
SUMINISTRO ACEPTABLE: 24 V CC.
2
CONFIGURE EL INTERRUPTOR EN EL MODO DE MODULACIÓN.
3
24 V CA
–
+
2
490 A 510
OHMIOS,
MÍNIMO
DE 1/2 W
1
V
2
3
OR +
OR N/A
4
RETROALIMENTACIÓN
5
2-10 V CC
10-2 V CC
0-10 V CC
3
10-0 V CC
Fltg, fwd
Fltg, rev
MS34977
Fig. 25. MS7505 con controladores de 4-20 mA.
Fig. 26. MS4105 con control SPDT de dos posiciones de
120 V CA.
38-00005EFS—04 8
Fig. 27. Cableado para el modelo
con interruptores aux./terminales.
Fig. 28. MS7505 con controlador de 0(2)-10 V CC que
pone en funcionamiento varios actuadores.
Fig. 29. MS3103 with Sylk Bus control.
FUNCIONAMIENTO Y VERIFICACIÓN
Una vez que se hayan completado las instalaciones
eléctrica y mecánica, haga lo siguiente:
1. Realice un ciclo del actuador para verificar que la
dirección de rotación sea adecuada para la secuencia de control.
2. Si la dirección de rotación es incorrecta, debe tomar
estas medidas:
Page 33

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
M27714
A
a. For 2-position and Sylk-enabled spring return
actuators: haga lo siguiente: quite, dé vuelta y
vuelva a colocar el actuador sobre el soporte.
b. Para los actuadores de control flotante, haga lo
siguiente: invierta los dos cables de la señal de
control (en sentido horario/antihorario) o cambie
la posición del interruptor de selección.
c. Para los actuadores de control análogo, haga lo
siguiente:
(1) cambie la configuración del interruptor de
acción directa/inversa; o bien,
(2) Para cambiar la dirección del muelle de recu-
peración: retire, voltee y reemplace el actuador en el soporte.
3. Si el esquema de control requiere un funciona-
miento a prueba de fallas, asegúrese de que, al interrumpir el suministro eléctrico, la posición de falla
coincida con la secuencia de control.
4. Los actuadores con muelle de retorno están config-
urados de fábrica para un funcionamiento a prueba
de fallas, con configuración normalmente cerrada, al
producirse una falla eléctrica. Para cambiar esta
acción a la configuración normalmente abierta,
quite y vuelva a instalar el actuador en la orientación
opuesta, de la siguiente manera:
a. Afloje el perno de acoplamiento del eje con una
llave de 10 mm.
b. Afloje todos los demás pernos de montaje que
conectan el actuador al soporte de montaje y
déjelos a un lado.
c. Quite el actuador del eje de la válvula.
d. Desplace el adaptador de eje autocentrante
(Self-Centering Shaft Adaptor, SCSA) hacia el
lado opuesto del actuador, tal como se muestra
en la Fig. 30.
e. Vuelva a conectar el actuador al soporte de mon-
taje de la válvula y a colocar los tornillos que
retiró anteriormente (paso b).
f. Ajuste el perno del acoplador del eje con una
llave o un casquillo de 10 mm aplicando un par
máximo de 120 lb-in (13.5 Nm).
Funcionamiento
La presión de entrada (Pressure Input, PIN) cambia
constantemente en un sistema de zonas múltiples, ya que
otras válvulas se abren y cierran. Esto cambia el flujo en el
sistema y la presión en el cabezal, según las
características de la curva de suministro de la bomba. La
reacción del regulador de presión mecánica es
instantánea, lo que elimina los cambios en la temperatura
ambiente debido a cambios en el flujo de líquido, y reduce
la necesidad de que el sistema de control haga funcionar
de manera constante la parte de control de la válvula, a fin
de corregir los cambios de temperatura por falta de carga
que se producen en un sistema con válvulas de control
estándar.
Fig. 30. Cambio del actuador a la configuración
normalmente abierta.
(1) Quite el sujetador de retención del adaptador
de eje autocentrante y déjelo a un lado para
usarlo más adelante.
(2) Quite el SCSA del actuador.
(3) Vuela a instalar el SCSA en el lado opuesto
del actuador y alinéelo según la etiqueta de
desplazamiento.
(4) Vuelva a ubicar el sujetador de retención en el
acoplador del eje usando la ranura del acop-
lador.
M29908
Fig. 31. Corte transversal de la VRN2, donde se
observan los conectores, la bola de control y el
regulador de presión.
Con flujo completo en una aplicación de control de
2 posiciones, una VRN2 funciona como un limitador de
flujo.
El regulador de presión toma un mínimo de presión para
funcionar y tiene una capacidad de regulación diferencial
máxima. Consulte la Fig. 32. La caída de presión alta en
una válvula VRN2 es comparable a la caída de presión en
una válvula de control y en una válvula de compensación
en un diseño de sistema convencional.
9 38-00005EFS—04
Page 34

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
0
CAUDAL
(GPM)
PRESIÓN DIFERENCIAL (PSID)
12
10
6
4
5.8
8
16
22
28
50
MS29707
8
12
34 40
60
100% ABIERTA
80% ABIERTA
60% ABIERTA
40% ABIERTA
20% ABIERTA
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
0° 30° 60° 90°
CARRERA DEL VÁSTAGO DE LA VÁLVULA
FLUJO
MS29551
10°
20°
40° 50°
70°
80°
BOLA DE
PASO TOTAL
FLUJO
CARACTERIZADO
DE 2 VÍAS
Fig. 32. Modelos de cuerpo grande con regulación de
presión.
CONFIGURACIONES Y AJUSTES
En la posición completamente abierta, las válvulas VRN2
mantienen el flujo en el circuito. Los caudales se
enumeran en el formulario de Datos de especificación
62-3115EFS. En funcionamiento de estado continuo, el
sistema de control solo requiere que la válvula se abra lo
suficientemente como para cumplir con las condiciones
de carga. Durante la retorno matutina del reajuste del
modo de funcionamiento nocturno, el controlador
generalmente hará que la válvula esté a 100%. Para lograr
un rendimiento óptimo, elija únicamente el siguiente
tamaño de válvula más grande necesario para cumplir con
la carga de diseño. No se exceda en el tamaño de las
válvulas, ya que la reducción en la capacidad de rango
puede dar como resultado un control de temperatura
menos preciso.
Las válvulas de bola se cierran entre 10% y 15% de
carrera, a fin de asegurar el enganche del sello completo.
Si lo desea, puede configurar los actuadores de
modulación en una respuesta de 0 a 10 V para que 2 V de
una señal de control de 2 a 10 V se correspondan más con
un flujo mínimo. Aún así, la válvula se cerrará con la
pérdida de señal.
Si lo desea, el flujo máximo se puede reducir a un valor
menor siguiendo uno de los siguientes dos métodos:
1. Con el actuador de modulación, limite el intervalo de
voltaje de control que emite el controlador de
automatización de edificios. Las válvulas con insertos de control de flujo tienen una característica de
flujo de igual porcentaje (consulte la Fig. 33). Cada
38-00005EFS—04 10
reducción del 10% en el voltaje de control máximo
dará como resultado una reducción del 10% en el
flujo.
Fig. 33. Características de flujo típico.
2. Para limitar mecánicamente la carrera, configure el
actuador de acoplamiento directo (Direct Coupling
Actuator, DCA) en la posición completamente abierta. Afloje el acoplador del eje y gire el eje de la válvula hacia la posición de flujo máximo deseada,
según lo confirme la medición de presión en el serpentín, usando la información del fabricante de serpentines. Vuelva a ajustar el acoplador del eje. Use la
Fig. 33 como guía para configurar la carrera del
actuador.
Si usa una técnica de ajuste mecánico con los actuadores de modulación MN/MS7505, la característica de adaptación automática de la carrera
convertirá, de manera automática, la señal de
2-10 V CC para la rotación mecánica de la bola.
Consulte la documentación del actuador para
obtener más información detallada.
El flujo en el serpentín se puede confirmar mediante la
lectura de presiones en la entrada y la salida del serpentín
(no en la válvula de control debido a que, con
compensación convencional, esta caída de presión será
constante) y con la información del fabricante para
calcular el flujo.
Observe que el regulador de presión de esta válvula
garantiza que el flujo que pasa a través del serpentín no se
verá afectado por los cambios de flujo ascendente en la
presión. A diferencia de las válvulas de compensación
convencionales, no es necesario volver a confirmar el flujo
en el serpentín después de ajustar otras válvulas.
Cualquier desborde durante la retorno matutina debido al
gran tamaño de las válvulas de regulación de presión no
afectará a otras válvulas del sistema, siempre y cuando las
bombas proporcionadas tengan capacidad para el flujo
necesario.
Page 35

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
PRECAUCIÓN
ENSAMBLE DE
VÁSTAGO
TORNILLOS
AVELLANADOS
PLACA RETENEDORA
DE VÁSTAGO
SÍMBOLO “T”
VÁSTAGO
CASQUILLO
SUPERIOR DE
EMPAQUETADURA
JUNTA TÓRICA
CASQUILLO
INFERIOR DE
EMPAQUETADURA
MS34994
Servicio técnico y reparación
El vástago de la válvula se puede reemplazar en línea, si es
necesario. Consulte la Fig. 34.
Fig. 34. Reemplazo del vástago de la válvula en línea.
Siga los pasos del 1 al 6 detallados en la sección “Ajuste
de la placa de montaje” en la página 3; luego proceda de
la siguiente forma:
1. Si el casquillo inferior de empaquetadura se atasca,
quítelo con la herramienta para quitar casquillos o
con la herramienta con dientes y punta de goma.
2. Quite con cuidado cualquier obstrucción o corrosión
del interior de la válvula.
3. Alinee la flecha con la pata más corta del símbolo “T”
en el ensamble de vástago nuevo.
NOTA: El símbolo “T” variará.
4. Inserte el ensamble de vástago nuevo. Asegúrese de
alinear la llave del vástago con la ranura de la bola.
5. Fije la placa retenedora de alta presión del vástago a
la válvula con los tornillos avellanados nuevos.
Luego, fije la placa de montaje a la válvula.
6. Vuelva a presurizar la válvula y, antes de continuar,
compruebe que el vástago no tenga filtraciones.
7. Deslice el subeje por el vástago, con la lengüeta ori-
entada como se indica en la Fig. 34.
8. Vuelva a ubicar el disyuntor térmico, el eje y la cubi-
erta del eje. Si el eje se desconectó del disyuntor térmico, empuje con firmeza el extremo del eje hasta
que la hoja del eje encaje en el disyuntor térmico.
9. Vuelva a ubicar el actuador y asegúrelo al eje y a la
placa de montaje.
10. Coloque a presión la manija en la parte superior del
eje.
Para realizar cualquier otra tarea de servicio técnico en la
válvula, como reemplazar el sello del asiento, es necesario
quitar la válvula de la tubería.
Evite raspar el interior del cuello de la válvula.
Esto puede provocar una filtración al ensamblarla
nuevamente.
11 38-00005EFS—04
Page 36

VÁLVULAS DE CONTROL Y ACTUADORES VRN CON REGULACIÓN DE PRESIÓN DINÁMICA
Con la utilización de la presente documentación, usted acepta que Honeywell no tendrá responsabilidad alguna por los daños que
pudieren surgir del uso o la modificación que usted haga de la documentación. Usted exime a Honeywell, sus afiliadas y
subsidiarias de toda responsabilidad, costos o daños, incluyendo las tarifas de abogados, que pudieren surgir o resultar de
cualquier modificación que usted realice a esta documentación.
Honeywell Building Technologies
En los EE. UU.:
Honeywell
® Marca Registrada en los Estados Unidos
© 2019 Honeywell International Inc.
38-00005EFS—04 M.S. Rev. 12-19
Impreso en Estados Unidos
 Loading...
Loading...