Honeywell SmartDrive Compact User Manual

Ho
Honeywell
Complete User Manual
SmartDrive Compact
Constan and variable torque
Variable Frequency Drives
for Induction motors
Subject to changes without notice

Honeywell 1
User’s Manual
Index
1. SAFETY ..........................................................................................3
1.1 Warnings ................................................................................3
1.2 Safety instructions .................................................................. 5
1.3 Grounding and earth fault protection......................................5
1.4 Before running the motor........................................................6
2. RECEIPT OF DELIVERY ................................................................ 7
2.1 Type designation code ........................................................... 7
2.2 Storage................................................................................... 7
2.3 Maintenance........................................................................... 7
2.4 Warranty................................................................................. 8
3. INSTALLATION ..............................................................................9
3.1 Mechanical installation ........................................................... 9
3.1.1 SmartDrive Compact dimensions ................................10
3.1.2 Cooling......................................................................... 10
3.1.3 EMC-levels...................................................................11
3.1.4 Changing the EMC protection class.............................12
3.2 Cabling and connections ........................................................13
3.2.1 Power cabling .............................................................. 13
3.2.2 Control cabling .............................................................14
3.2.3 Cable and fuse specifications ...................................... 16
3.2.4 General cabling rules ...................................................17
3.2.5 Stripping lengths of motor and mains cables...............18
3.2.6 Cable installation and the UL standards ......................18
3.2.7 Cable and motor insulation checks ..............................19
4. COMMISSIONING........................................................................... 20
4.1 Commissioning steps of SmartDrive Compact....................... 20
5. FAULT TRACING ........................................................................... 22
6. SMARTDRIVE COMPACT CONTROL CONNECTIONS ...............25
6.1 Introduction.............................................................................25
6.2 Control I/O ..............................................................................26
7. CONTROL PANEL..........................................................................27
7.1 General...................................................................................27
7.2 Display....................................................................................27
7.3 Keypad ...................................................................................28
7.4 Navigation on the SmartDrive Compact control panel ...........29
7.4.1 Main menu ...................................................................29
7.4.2 Reference menu .......................................................... 30
7.4.3 Monitoring menu ..........................................................30

2 Honeywell
7.4.4 Parameter menu...........................................................32
7.4.5 Fault history menu ........................................................33
8. PARAMETERS................................................................................34
8.1 Quick setup parameters (Virtual menu, shows when par. 3.1 = 1)
..............................................................................................35
8.2 Motor settings (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P1) ...................37
8.3 Start/stop setup (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P2).................38
8.4 Frequency references (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P3).......38
8.5 Ramps and brakes setup (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P4)..39
8.6 Digital inputs (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P5) .....................39
8.7 Analogue inputs (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P6)................40
8.8 Digital and analogue outputs (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P7)
..............................................................................................41
8.9 Protections (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P9)........................42
8.10 Autorestart parameters (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P10).42
8.11 PI control parameters (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P12) ...43
8.12 Easy usage menu (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P0)..........44
8.13 System parameters ..............................................................44
9. PARAMETER DESCRIPTIONS ......................................................46
9.1 Motor settings (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P1) ...................46
9.2 Start/Stop setup (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P2)................50
9.3 Frequency references (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P3).......53
9.4 Ramps & brakes setup (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P4) .....54
9.5 Digital inputs (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P5) .....................58
9.6 Analoque inputs (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P6)................59
9.7 Digital and analoque outputs (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P7)
..............................................................................................59
9.8 Motor thermal protection (parameters 9.7 - 9.10)...................60
9.9 Autorestart parameters (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P10)..63
9.10 PI control parameters (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P12) ...63
9.11 Easy usage menu (Control panel: Menu PAR -> P9)...........65
9.12 Fieldbus parameters (Control panel: Menu PAR -> S2).......66
9.12.1 Modbus process data .................................................67
10. TECHNICAL DATA .......................................................................70
10.1 SmartDrive Compact technical data .....................................70
10.2 Power ratings........................................................................72
10.2.1 SmartDrive Compact - Mains voltage 208 - 240 V.....72
10.2.2 SmartDrive Compact - Mains voltage 380 - 480 V.....73
Honeywell Safety 3
ONLY A COMPETENT ELECTRICIAN IS ALLOWED TO
CARRY OUT THE ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION!
1. SAFETY
This manual contains clearly marked cautions and warnings which are intended for
your personal safety and to avoid any unintentional damage to the product or connected appliances.
Please read the information included in cautions and warnings carefully:
= Dangerous voltage
Risk of death or severe injury
= General warning
Risk of damage to the product or connected appliances
1.1 WARNINGS
The components of the power unit of the inverter are live when
SmartDrive Compact is connected to mains potential. Coming into
contact with this voltage is extremely dangerous and may cause
1
death or severe injury. The control unit is isolated from the mains
potential.
The motor terminals U, V, W (T1, T2, T3) and the possible brake
resistor terminals -/+ are live when inverter is connected to mains,
2
even if the motor is not running.
The control I/O-terminals are isolated from the mains potential.
However, the relay output terminals may have a dangerous control
3
voltage present even when inverter is disconnected from mains.
The earth leakage current of SmartDrive Compact inverters
exceeds 3.5mA AC. According to standard EN61800-5-1, a rein-
4
forced protective ground connection must be ensured.
If the inverter is used as a part of a machine, the machine manufacturer is responsible for providing the machine with a main
5
switch (EN 60204-1).
1
1
4 Safety Honeywell
If SmartDrive Compact is disconnected from mains while running
the motor, it remains live if the motor is energized by the process.
In this case the motor functions as a generator feeding energy to
6
the inverter.
After disconnecting the inverter from the mains, wait until the fan
stops and the indicators on the display go out. Wait 5 more min-
7
utes before doing any work on power connections.
Honeywell Safety 5
1.2 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
The SmartDrive Compact inverter has been designed for fixed
1
installations only.
Do not perform any measurements when the inverter is connected
2
to the mains.
Do not perform any voltage withstand tests on any part of Smart-
3
Drive Compact. The product safety is fully tested at factory.
Prior to measurements on the motor or the motor cable, disconnect
4
the motor cable from the inverter.
Do not open the cover of SmartDrive Compact. Static voltage discharge from your fingers may damage the components. Opening
5
the cover may also damage the device. If the cover of SmartDrive
Compact is opened, warranty becomes void.
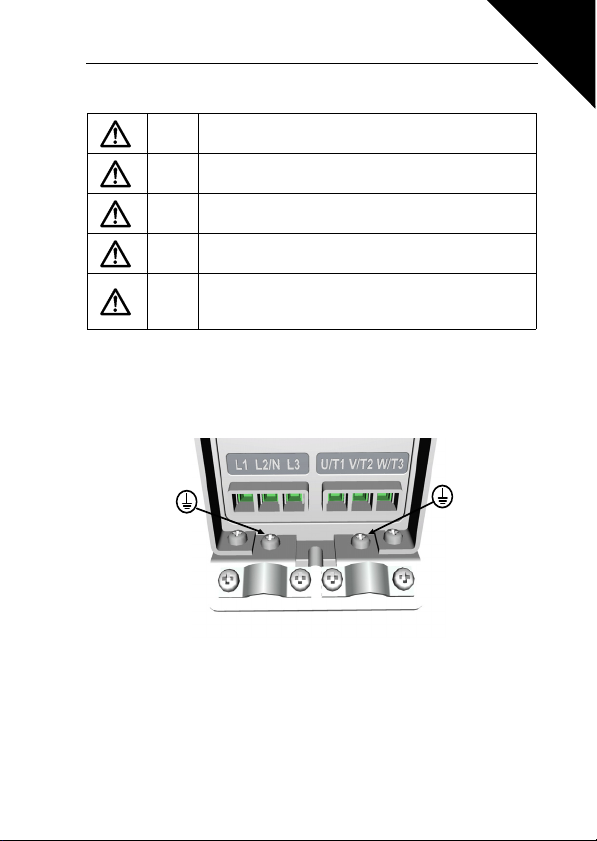
1.3 GROUNDING AND EARTH FAULT PROTECTION
The SmartDrive Compact inverter must always be earthed with an grounding conductor connected to the grounding terminal. See figure below:
1
• The earth fault protection inside the inverter protects only the con-
verter itself against earth faults.
• If fault current protective switches are used they must be tested
with the drive with earth fault currents that are possible to arise in
fault situations.
1
6 Safety Honeywell
1.4 BEFORE RUNNING THE MOTOR
Checklist:
Before starting the motor, check that the motor is mounted
properly and ensure that the machine connected to the motor
allows the motor to be started.
Set the maximum motor speed (frequency) according to the
motor and the machine connected to it.
Before reversing the motor shaft rotation direction make sure
that this can be done safely.
Make sure that no power correction capacitors are connected
to the motor cable.
Honeywell Receipt of Delivery 7
COMP400-1P1-20
Product range:
COMP = SmartDrive Compact
Nominal voltage:
230 = 208-240 Vac (1~ input, 3~ output)
400 = 380-500 Vac
Nominal power:
P75 = 0.75 kW
1P1 = 1.1 kW
Etc.
Enclosure class:
20 = IP20
COMP400-1P1-20
Product range:
COMP = SmartDrive Compact
Nominal voltage:
230 = 208-240 Vac (1~ input, 3~ output)
400 = 380-500 Vac
Nominal power:
P75 = 0.75 kW
1P1 = 1.1 kW
Etc.
Enclosure class:
20 = IP20
2. RECEIPT OF DELIVERY
After unpacking the product, check that no signs of transport damages are to be
found on the product and that the delivery is complete (compare the type designation
of the product to the code below).
Should the drive have been damaged during the shipping, please contact primarily
the cargo insurance company or the carrier.
If the delivery does not correspond to your order, contact the supplier immediately.
2.1 TYPE DESIGNATION CODE
Figure 2.1: SmartDrive Compact type designation code
2.2 STORAGE
If the inverter is to be kept in store before use make sure that the ambient conditions
are acceptable:
Storing temperature-40…+70°C
Relative humidity < 95%, no condensation
2.3 MAINTENANCE
In normal operating conditions, SmartDrive Compact inverters are maintenancefree.
2

8 Receipt of Delivery Honeywell
2.4 WARRANTY
Honeywell’s time of warranty is 30 months from the delivery or 24 months from the
commissioning whichever expires first (General Conditions NL92/Orgalime S92 ).
2
Honeywell Installation 9
MI2-3MI1
=M 4
=M 5
12
3. INSTALLATION
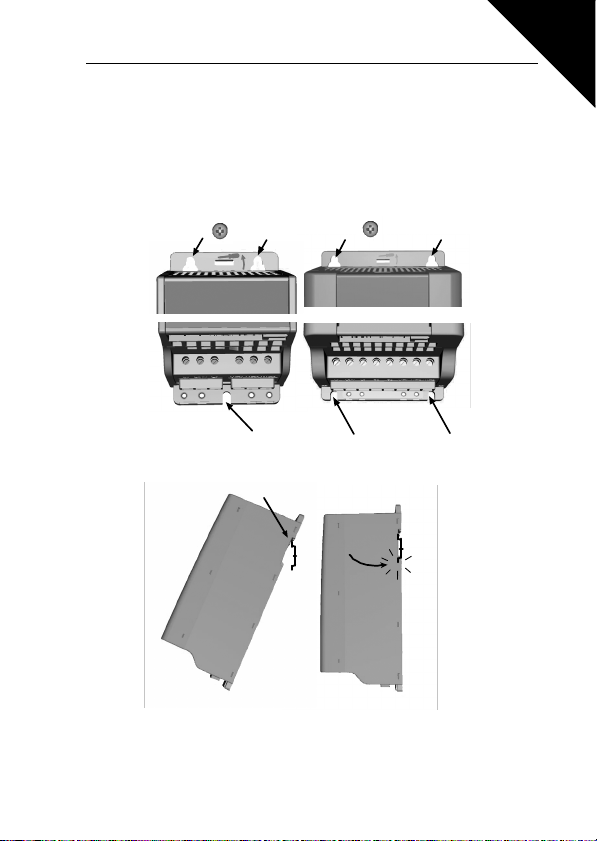
3.1 MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
There are two possible ways to mount SmartDrive Compact in the wall; either screw
or DIN-rail mounting. The mounting dimensions are given on the back of the drive
and on the following page.
Figure 3.1: Screw mounting
3
Figure 3.2: DIN-rail mounting

3
W1
W2
W3
H1
H2D1H3
D2
10 Installation Honeywell
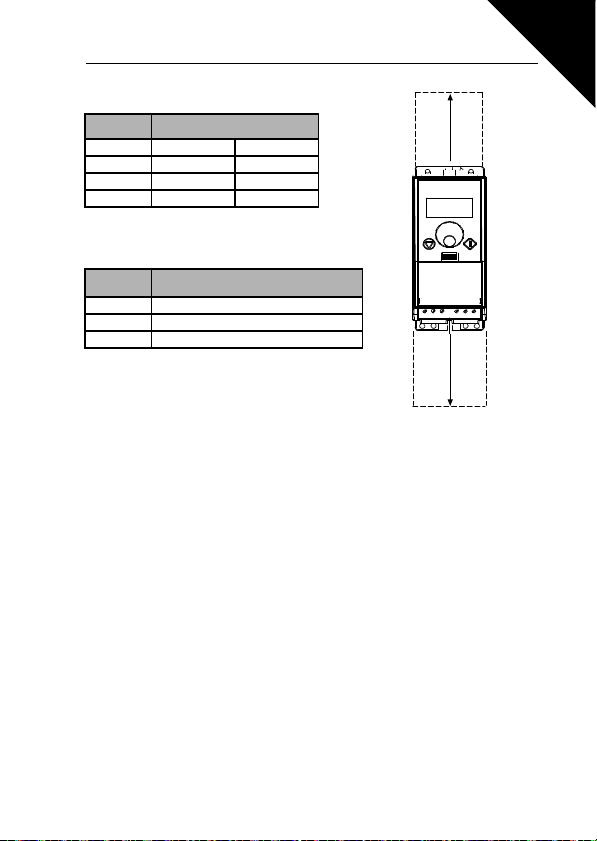
3.1.1 SmartDrive Compact dimensions
Figure 3.3: SmartDrive Compact dimensions, MI1-MI3
Typ e H1 H2 H3 W1 W2 W3 D1 D2
MI1 156,5 147 137,3 65,5 37,8 4,5 98,5 7
MI2 195 183 170 90 62,5 5,5 101,5 7
MI3 262,5 252,3 241,3 100 75 5,5 108,5 7
Table 3.1 : SmartDrive Compact dimensions in millimetres
3.1.2 Cooling
Forced air flow cooling is used in all SmartDrive Compact drives.
Enough free space shall be left above and below the inverter to ensure sufficient air
circulation and cooling. You will find the required dimensions for free space in the table below:
Honeywell Installation 11
A
B
Typ e Dimensions (mm)
AB
MI1 100 50
MI2 100 50
MI3 100 50
Table 3.2 : Dimensions required for cooling
3
Typ e
MI1 10
MI2 10
MI3 30
Table 3.3 : Required cooling air
Note! Side-to-side installation allowed only if the ambient temperature is below 40
degrees Celsius.
Cooling air required (m3/h)
3.1.3 EMC-levels
SmartDrive Compact inverters are divided into three classes according to the level
of electromagnetic disturbances emitted, the requirements of a power system network and the installation environment (see below). The EMC class of each product
is defined in the type designation code.
Category C1 (Honeywell EMC class C): Inverters of this class comply with the requirements of category C1 of the product standard EN 61800-3 (2004). Category C1
ensures the best EMC characteristics and it includes converters the rated voltage of
which is less than 1000V and which are intended for use in the 1st environment. This
EMC class is meant for highly sensitive areas and can be sometimes required in installations in e.g. hospitals or airport control towers.
NOTE: The requirements of class C1 are fulfilled only as far as the conducted emissions are concerned with an external EMC-filter.
Category C2 (Honeywell EMC class H): All Honeywell SmartDrive Compact inverters comply with the requirements of category C2 of the product standard EN 618003 (2004). Category C2 includes converters in fixed installations and the rated voltage
of which is less than 1000V. The class H inverters can be used both in the 1st and
the 2nd environment. This category fulfills the requirements with normal installations
in buildings.
3
12 Installation Honeywell
IT networks (Honeywell EMC class T): Inverters of this class fulfil the product
standard EN 61800-3 (2004) if intended to be used in IT systems. In IT systems, the
networks are isolated from earth, or connected to earth through high impedance to
achieve a low leakage current. NOTE: if inverters are used with other supplies, no
EMC requirements are complied with. SmartDrive Compact inverters can be easily
modified to the requirements of the T-class. This class is very typical requirement
also in installations in ships.
Environments in product standard EN 61800-3 (2004)
First environment: Environment that includes domestic premises. It also includes
establishments directly connect ed without intermediate transformers to a low-voltage
power supply network which supplies buildings used for domestic purposes.
NOTE: houses, apartments, commercial premises or offices in a residential building
are examples of first environment locations.
Second environment: Environment that includes all establishments other than
those directly connected to a low-voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for domestic purposes.
NOTE: industrial areas, technical areas of any building fed from a dedicated transformer are examples of second environment locations.
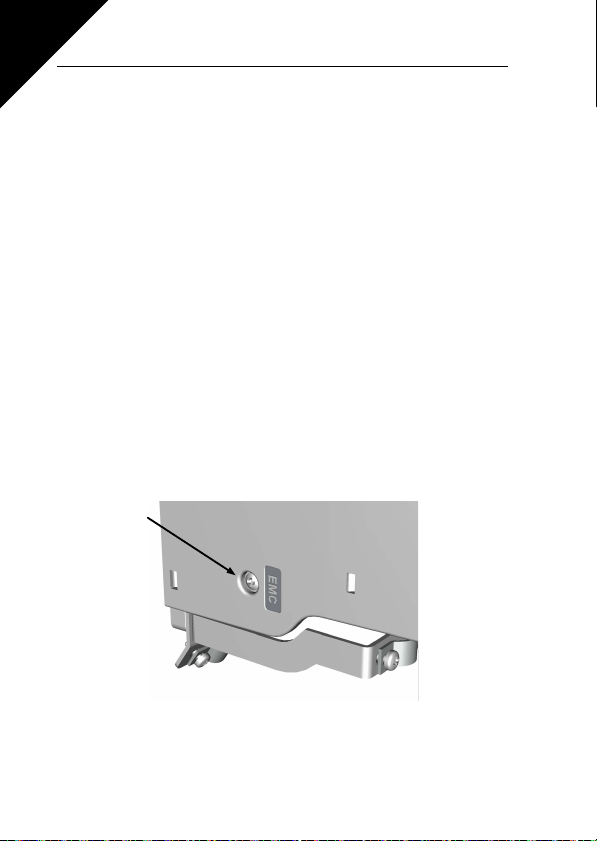
3.1.4 Changing the EMC protection class
The EMC protection class of SmartDrive Compact inverters can be changed from
class H by removing the EMC-capacitor disconnecting screw, see figure below.
Note! Do not attempt to change the EMC level back to class H. Even if the proce-
dure above is reversed, the inverter will no longer fulfil the EMC requirements of
class H!
Honeywell Installation 13
3.2 CABLING AND CONNECTIONS
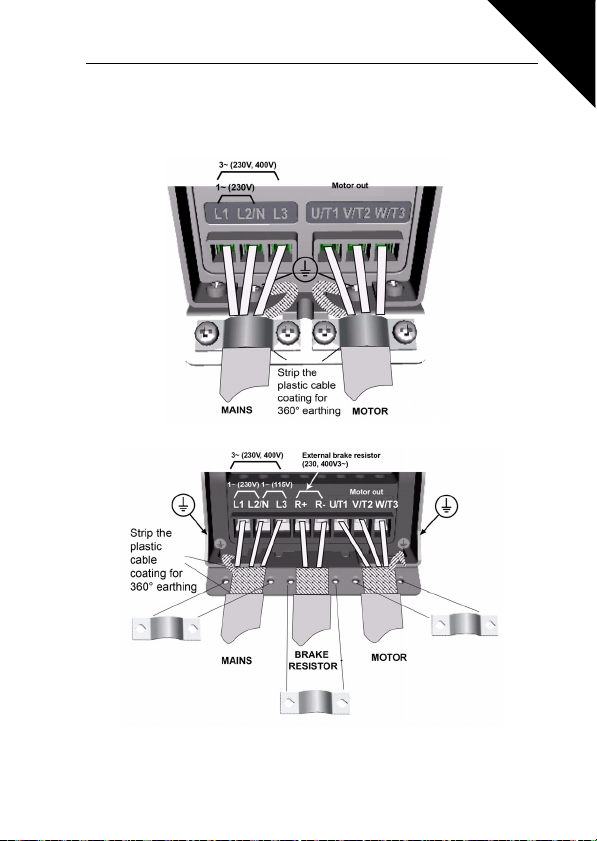
3.2.1 Power cabling
Note! Tightening torque for power cables is 0.5 - 0.6 Nm
Figure 3.4: SmartDrive Compact power connections, MI1
3
Figure 3.5: SmartDrive Compact power connections, MI2 - MI3
3
14 Installation Honeywell
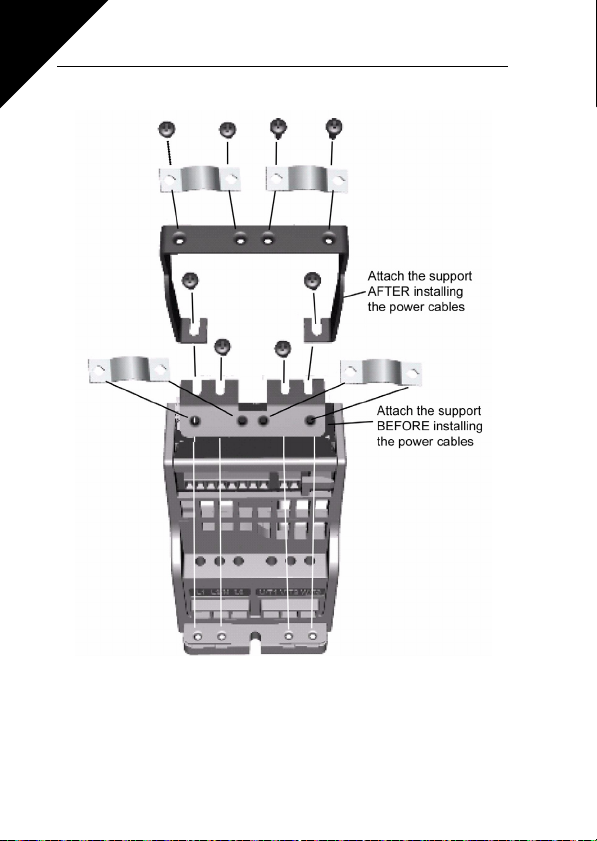
3.2.2 Control cabling
Figure 3.6: Mount the PE- plate and control cable support
Honeywell Installation 15
Strip the p lastic
cable coating for
360
°
Control cable
tightening
torque: 0.4 Nm
grounding
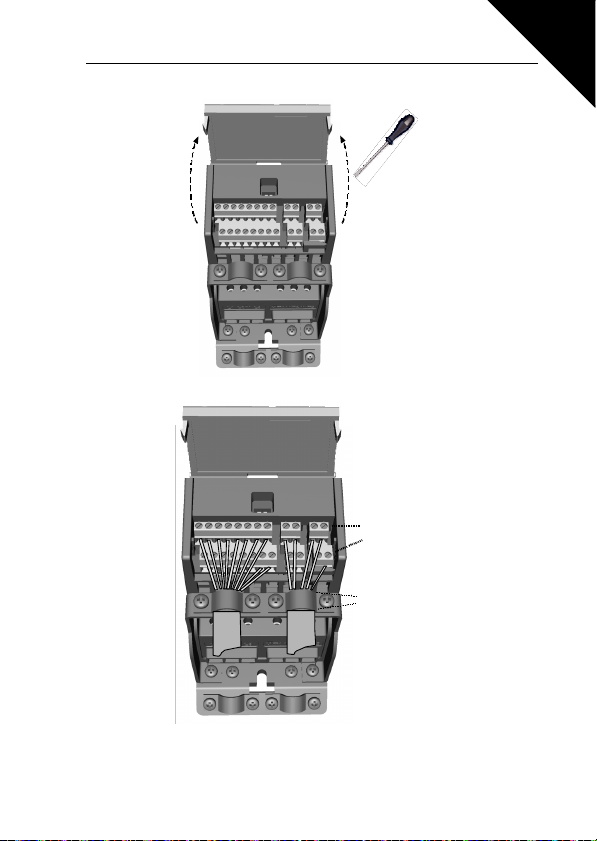
Figure 3.7: Open the cover
3
Figure 3.8: Install the control cables. See Chapter 6.2
3
16 Installation Honeywell
3.2.3 Cable and fuse specifications
Use cables with heat resistance of at least +70 C. The cables and the fuses must be
dimensioned according to the tables below. Installation of cables according to UL
regulations is presented in Chapter 3.2.6.
The fuses function also as cable overload protection.
These instructions apply only to cases with one motor and one cable connection from
the inverter to the motor. In any other case, ask the factory for more information.
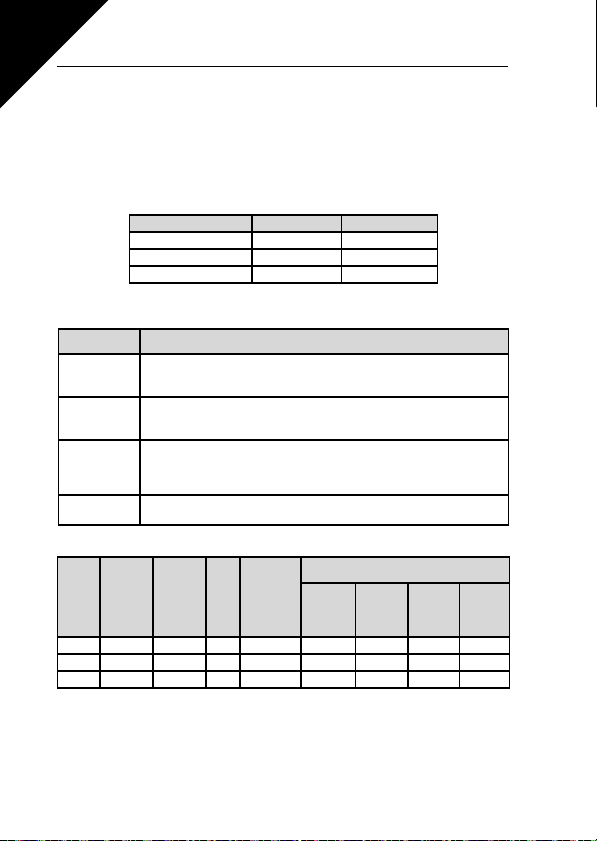
EMC class Level H (C2) Level C (C1)
Mains cable types 1 1
Motor cable types 3 3
Control cable types 4 4
Table 3.4 : Cable types required to meet standards. EMC levels are
described in Chapter 3.1.3.
Cable type Description
Power cable intended for fixed installation and the specific mains voltage.
Shielded cable not required.
1
(NKCABLES/MCMK or similar recommended)
Power cable equipped with concentric protection wire and intended for the
specific mains voltage.
2
(NKCABLES /MCMK or similar recommended).
Power cable equipped with compact low-impedance shield and intended
for the specific mains voltage.
3
(NKCABLES /MCCMK, SAB/ÖZCUY-J or similar recommended).
*360º grounding of both motor and FC connection r equired to meet the standard
Screened cable equipped with compact low-impedance shield (NKCA-
4
Table 3.5 : Cable type descriptions
BLES /Jamak, SAB/ÖZCuY-O or similar).
Fuse
[A]
Mains
cable
Cu [mm2]
I
Frame Type
MI1 P25-P75 1.7-3.7 10 2*1.5+1.5 1.5-4 1.5-4 0.5-1.5 0.5-1.5
MI2 1P1-1P5 4.8-7.0 20 2*2.5+2.5 1.5-4 1.5-4 0.5-1.5 0.5-1.5
MI3 2P2 9.6 32 2*6+6 1.5-6 1.5-6 0.5-1.5 0.5-1.5
[A]
N
Terminal cable size (min/max)
Main
Earth
terminal
2
[mm
]
Control
terminal
2
[mm
]
terminal
2
[mm
]
Table 3.6 : Cable and fuse sizes for SmartDrive Compact, 208 - 240V
Relay
terminal
2
[mm
]
Honeywell Installation 17
3
Terminal cable size (min/max)
Main
Earth
terminal
2
[mm
]
Control
terminal
2
[mm
]
terminal
2
[mm
]
Relay
terminal
[mm
Fuse
[A]
Mains
cable
Cu [mm2]
I
Frame Ty pe
MI1 P37-1P1 1.9-3.3 6 3*1.5+1.5 1.5-4 1.5-4 0.5-1.5 0.5-1.5
MI2 1P5-2P2 4.3-5.6 10 3*1.5+1.5 1.5-4 1.5-4 0.5-1.5 0.5-1.5
MI3 3P0-5P5 7.6-12 20 3*2.5+2.5 1.5-6 1.5-6 0.5-1.5 0.5-1.5
[A]
N
Table 3.7 : Cable and fuse sizes for SmartDrive Compact, 380 - 480V
Note! To fulfil standard EN61800-5-1, the protective conductor should be at least
10mm2 Cu or 16mm Al. Another possibility is to use an additional protective con-
ductor of at least the same size as the original one.
3.2.4 General cabling rules
Before starting the installation, check that none of the components of the inverter
1
is live.
Place the motor cables sufficiently far from other cables:
• Avoid placing the motor cables in long parallel lines with other cables
• If the motor cable runs in parallel with other cables, the minimum distance
between the motor cable and other cables is
2
3
4
0,3 m.
• The given distance also applies between the motor cables and signal cables
of other systems.
• The maximum length of the motor cables is 30 m
• The motor cables should cross other cables at an angle of 90 degrees.
If cable insulation checks are needed, see Chapter 3.2.7.
Connecting the cables:
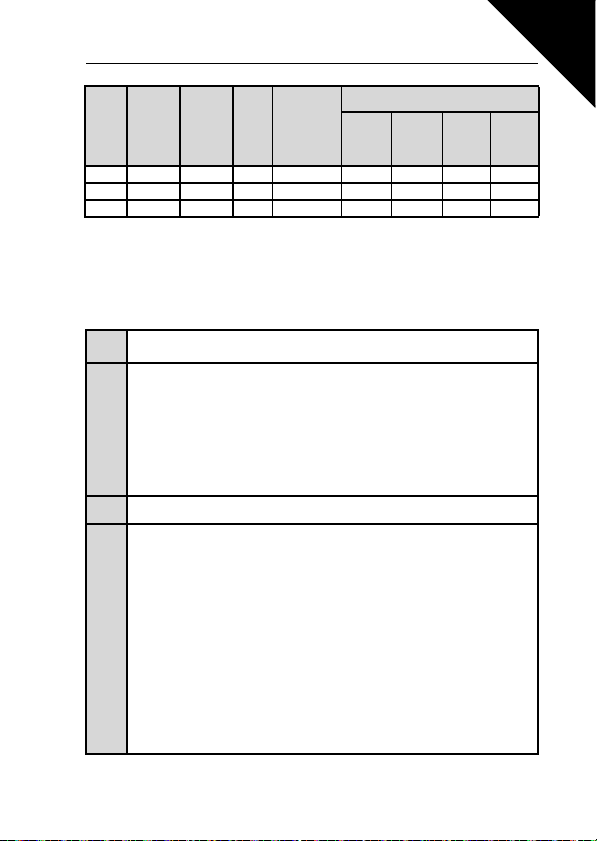
• Strip the motor and mains cables as advised in Figure 3.9.
• Connect the mains, motor and control cables into their respective terminals,
see Figures 3.4 - 3.8.
• Note the tightening torques of power cables and control cables given in
page 13 and page 15.
• For information on cable installation according to UL regulations see Chapter
3.2.6 .
• Make sure that the control cable wires do not come in contact with the electronic components of the unit
• If an external brake resistor (option) is used, connect its cable to the appropriate terminal.
• Check the connection of the earth cable to the motor and the inverter terminals marked with
• Connect the separate shield of the motor cable to the earth plate of the
inverter, motor and the supply centre
2
]
3
20 mm
35 mm
8 mm
Earth conduct or
8 mm
18 Installation Honeywell
3.2.5 Stripping lengths of motor and mains cables
Figure 3.9: Stripping of cables
Note! Strip also the plastic cover of the cables for 360 degree grounding. See Figures 3.4, 3.5 and 3.8.
3.2.6 Cable installation and the UL standards
To meet the UL (Underwriters Laboratories) regulations, a UL-approved copper cable with a minimum heat-resistance of +60/75 0C must be used.

Honeywell Installation 19
3.2.7 Cable and motor insulation checks
These checks can be performed as follows if motor or cable insulations are suspected to be faulty.
1. Motor cable insulation checks
Disconnect the motor cable from terminals U/T1, V/T2 and W/T3 of the inverter and
from the motor. Measure the insulation resistance of the motor cable between each
phase conductor as well as between each phase conductor and the protective
ground conductor.
The insulation resistance must be >1MOhm.
2. Mains cable insulation checks
Disconnect the mains cable from terminals L1, L2/N and L3 of the inverter and from
the mains. Measure the insulation resistance of the mains cable between each phase
conductor as well as between each phase conductor and the protective ground conductor.The insulation resistance must be >1MOhm.
3. Motor insulation checks
Disconnect the motor cable from the motor and open the bridging connections in the
motor connection box. Measure the insulation resistance of each motor winding. The
measurement voltage must equal at least the motor nominal voltage but not exceed
1000 V. The insulation resistance must be >1MOhm.
3
20 Commissioning Honeywell
4. COMMISSIONING
Before commissioning, note the warnings and instructions listed in
Chapter 1!
4.1 COMMISSIONING STEPS OF SMARTDRIVE COMPACT
Read carefully the safety instructions in Chapter 1 and follow them.
1
After the installation, make sure that:
• both the inverter and the motor are grounded
• the mains and motor cables comply with the requirements given in Chapter
3.2.3.
2
3
4
5
6
• the control cables are located as far as possible from the power cables
(see Chapter, step 2) and the shields of the shielded cables are connected
to protective earth.
Check the quality and quantity of cooling air (Chapter 3.1.2).
Check that all Start/Stop switches connected to the I/O terminals are in Stop-
position.
Connect the inverter to mains.
Run the Start Up Wizard (The Wizard is explained fully in chapter 9.11)
1. Activate the wizard by pressing STOP for 5 seconds
2. Tune the motor nominal speed
3. Tune the motor nominal current
4. Select the mode (0 = basic, 1 = Fan, 2 = Pump, 3 = Conveyor)
Or if the setting is done manually set the parameters of group 1 according to the
requirements of your application. At least the following parameters should be set:
• motor nominal voltage (par. 1.1)
• motor nominal frequency (par. 1.2)
• motor nominal speed (par. 1.3)
• motor nominal current (par. 1.4)
You will find the values needed for the parameters on the motor rating plate.
4
Honeywell Commissioning 21
Perform test run without motor. Perform either Test A or Test B:
A) Control from the I/O terminals:
• Turn the Start/Stop switch to ON position.
• Change the frequency reference (potentiometer).
• Check in the Monitoring Menu that the value of Output frequency changes
according to the change of frequency reference.
• Turn the Start/Stop switch to OFF position.
7
B) Control from the keypad:
• Move to keypad control by pressing the navigation wheel for 5 seconds.
You can also select the keypad as the control place with par. 2.1.
• Push the Start button on the keypad.
• Check in the Monitoring Menu that the value of Output frequency changes
according to the change of frequency reference.
• Push the Stop button on the keypad.
Run the no-load tests without the motor being connected to the process, if possible. If this is not possible, secure the safety of each test prior to running it. Inform
your co-workers of the tests.
• Switch off the supply voltage and wait up until the drive has stopped.
• Connect the motor cable to the motor and to the motor cable terminals of
8
9
the inverter.
• See to that all Start/Stop switches are in Stop positions.
• Switch the mains ON.
• Repeat test 7A or 7B.
Connect the motor to the process (if the no-load test was run without the motor
being connected).
• Before running the tests, make sure that this can be done safely.
• Inform your co-workers of the tests.
• Repeat test 7A or 7B.
4
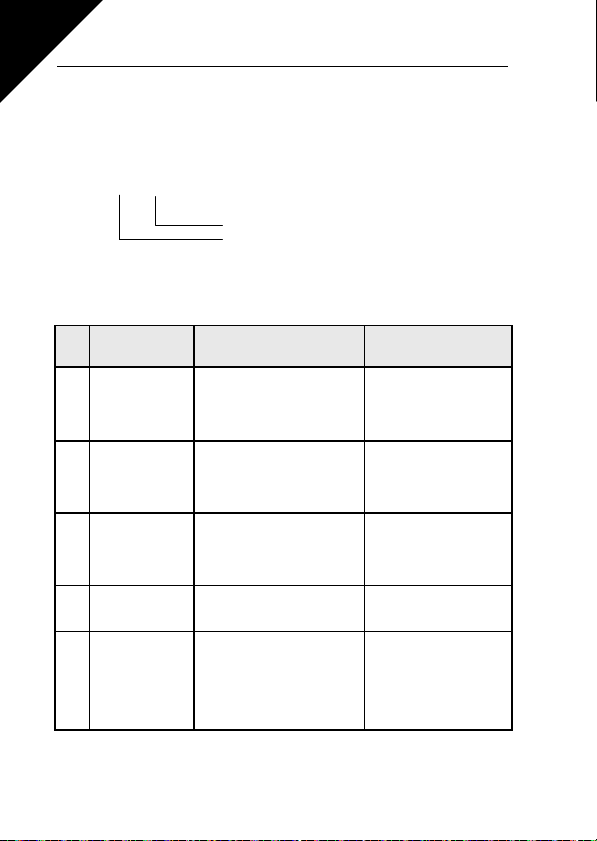
5
F1 02
Fault code (02 = overvoltage)
Fault ordinal number (F1 = latest fault)
22 Fault Tracing Honeywell
5. FAULT TRACING
When a fault is detected by the inverter control electronics, the drive is stopped and
the symbol F together with the ordinal number of the fault and the fault code appear
on the display in the following format, e.g:
The fault can be reset by pressing the Stop button on the control keypad or via the I/
O terminal or fieldbus. The faults with time labels are stored in the Fault history menu
which can be browsed. The different fault codes, their causes and correcting actions
are presented in the table below.:
Fault
Fault name Possible cause Correcting actions
code
Overcurrent
1
Overvoltage
2
Earth fault
3
System fault
8
Undervoltage
9
Table 5.1 : Fault codes
Inverter has detected too high a
current (>4*I
The DC-link voltage has
exceeded the internal safety limit:
Current measurement has
detected extra leakage current at
start:
The DC-link voltage has
exceeded the internal safety limit:
) in the motor cable:
N
• Sudden heavy load increase
• Short circuit in motor cables
• Unsuitable motor
• Too short a deceleration time
• High overvoltage spikes in
mains
• Insulation failure in cables or
motor
• Component failure
• Faulty operation
• Most probable cause: too low
a supply voltage
• Inverter internal fault
• Power outages
Check loading.
Check motor size.
Check cables.
Increase the deceleration
time (P.4.3).
Check motor cables and
motor.
Reset the fault and restart.
Should the fault recur, contact technical support.
In case of temporary supply
voltage break reset the fault
and restart the inverter.
Check the supply voltage. If
it is adequate, an internal
failure has occurred.
Contact technical support.
 Loading...
Loading...