Hill-Rom MetaNeb System User Manual
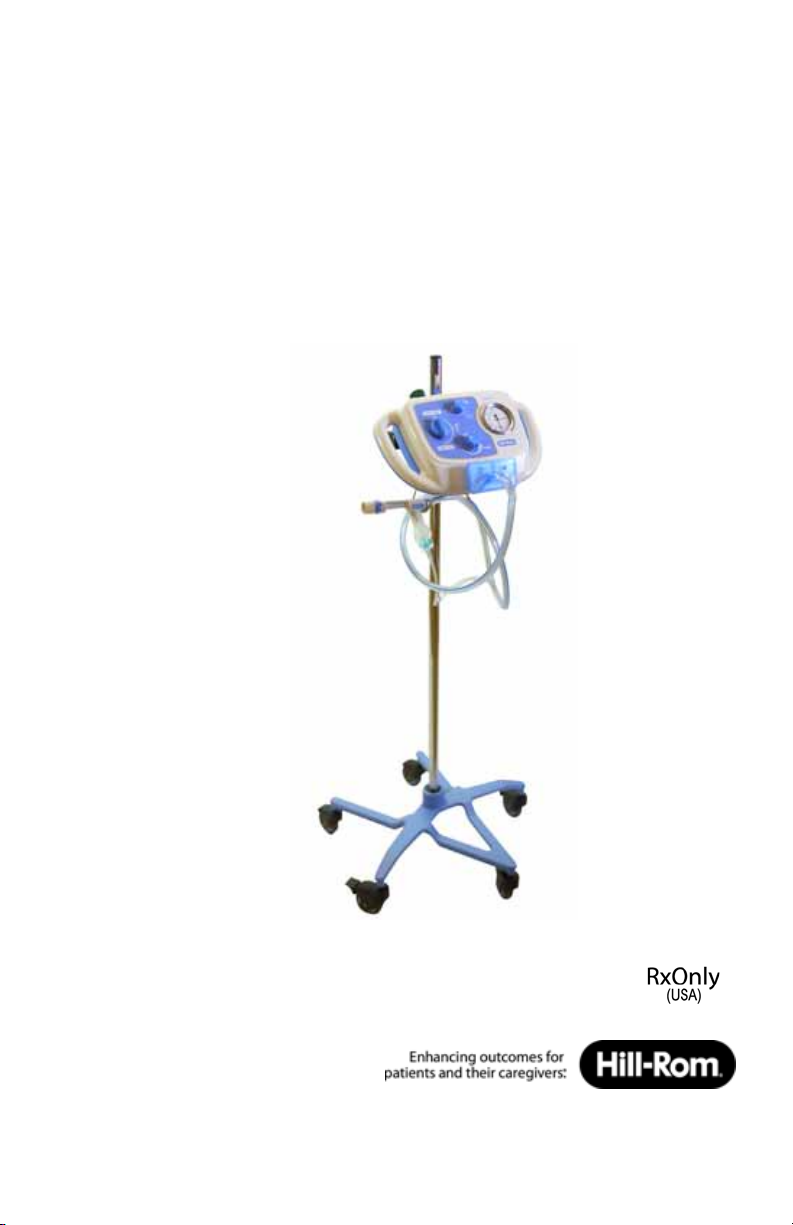
The MetaNeb® System
User Manual
Product No. PMN4
174432 REV 7


REVISION
© 2016 by Hill-Rom Services PTE Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Manufactured by:
HILL-ROM SERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED
1 YISHUN AVENUE 7
SINGAPORE 768923
Authorized European Union Representative:
HILL-ROM SAS
B.P. 14 - Z.I. du Talhouet
56330 PLUVIGNER
FRANCE
Tel: +33 (0)2 97 50 92 12
Authorized Brazilian Representative:
VR MEDICAL—MEDICAL DEVICES IMPORTER & DISTRIBUTOR, LTDA.
391 BATATAES STREET
CJ 11-13, 8TH FLOOR
SÃO PAULO, SP-BRAZIL
CNJP: 04.718.143/0001-94
No part of this text shall be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording,
or by any information or retrieval system without written permission from
Hill-Rom Services, Inc. (Hill-Rom).
The information in this manual is confidential and may not be disclosed to
third parties without the prior written consent of Hill-Rom.
The information in this manual is subject to change without notice. HillRom makes no commitment to update or keep current, the information in
this manual.
Hill-Rom reserves the right to make changes without notice in design,
specifications, and models. The only warranty Hill-Rom makes is the
express written warranty extended on the sale or rental of its products.
The MetaNeb® System may be covered by one or more patents. For a list
of applicable patents, go to www.hill-rom.com/patents.
This manual (174432) was originally released and supplied in English. For
a list of available translations, contact Hill-Rom Technical Support.
Seventh Edition, August 2016
First Printing, 2013
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) i

Hill-Rom® is a registered trademark of Hill-Rom Services, Inc.
MetaNeb® and MetaTherapy® are registered trademarks of Comedica, Inc.
Replace this manual (174432) if it is damaged and/or can not be read.
For product support or to order additional copies of this manual (174432),
contact your distributor, local Hill-Rom representative, or go to www.hillrom.com.
Reference Documents
MetaNeb® System Service Manual, North America (174508)
MetaNeb® System Service Manual, International (187293)
183808 (Stand) Assembly (182920)
ii The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7)

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Revision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . i
Document Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Indications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Indications for Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Patient Population . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Absolute Contraindications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Relative Contraindications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Possible Adverse Reactions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Theory of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Normal Mucus Clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Mucociliary Escalator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Cough . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Autocephalad Flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
The MetaNeb® System and Bronchial Hygiene. . . . . . . . . 6
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Assemble the Controller System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Stand Assembly and Controller Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Connect the Oxygen Hose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Assemble the Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Typical Mouthpiece Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Other Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Mask. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Tracheostomy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
In-Line with Ventilator Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Add Medication to the Nebulizer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Pre-Use Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Pre-Use Check For In-Line Use with a ventilator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) 1

Table of Contents
MetaTherapy® Treatment Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Assessment of Outcome . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Re-Evaluation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
The MetaNeb® System In-Line with Ventilator Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Assessment of Outcome . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Re-Evaluation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Move the Stand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Cleaning the Controller and Stand. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Cleaning the Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Troubleshooting and Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Shipping and Packaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Product symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Controller Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Stand Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Classification and Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Technical Specification for Performance—Breathing Simulator . . . 31
CHFO Pulses—Airway Pressure Reading . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
CPEP—Airway Pressure Reading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Hi Pressure CHFO Pulses—Airway Pressure Reading . 33
Hi Pressure CPEP—Airway Pressure Reading. . . . . . . . . 33
Bench Performance Checks—Breathing Simulator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Nebulizer Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Circuit Part Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Particle Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2 The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7)

Document Symbols
DOCUMENT SYMBOLS
This manual contains different typefaces and symbols to make the
content easier to read and understand:
• Standard text—used for regular data.
• Boldface text—emphasizes a word or phrase.
• NOTE:—sets apart special data or important instruction clarification.
• WARNING or CAUTION
– A WARNING identifies situations or actions that may have an
effect on patient or user safety. To ignore a warning could
cause patient or user injury.
– A CAUTION identifies special procedures or precautions that
persons must obey to help prevent equipment damage.
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) 1

Indications
INDICATIONS
Indications for Use
The MetaNeb® System is indicated for mobilization of secretions, lung
expansion therapy, the treatment and prevention of pulmonary
atelectasis, and also has the ability to provide supplemental oxygen when
used with compressed oxygen.
Patient Population
• Adult and children over the age of 2
Absolute Contraindications
• Untreated tension pneumothorax
• Untrained or unskilled operator
Relative Contraindications
• History of pneumothorax
• Pulmonary air leak
• Recent pneumonectomy
• Pulmonary hemorrhage
• Myocardial infarction
• Vomiting
Possible Adverse Reactions
• Hyperventilation
• Gastric distension
• Decreased cardiac output
• Increased intracranial pressure
• Increased air trapping
• Hyperoxygenation
• Pneumothorax
• Pulmonary air leak
• Pulmonary hemorrhage
2 The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7)

Indications
Precautions
• Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a
physician.
• Circuits are for single patient use, multiple treatment sessions.
• Do not occlude entrainment orifices.
• Do not use on uncooperative patients.
• Read the User Manual before use.
• Use only with the supplied nebulizer.
• To be used only by individuals familiar with its use.
• Failure to discard the circuit in accordance with facility protocol could
cause patient injury due to cross-contamination.
• Care should be taken to appropriately suction secretions as they
mobilize into the upper airways.
• Use only with hospital grade 50 psi oxygen sources that meet local,
state, and government regulations.
• Continuous Positive Expiratory Pressure (CPEP) is a therapy and is
never to be used for life support.
• Monitor the patient, patient lines, and circuit lines during therapy
and/or bed articulation.
• Make sure you connect the nebulizer to the nebulizer tubing only.
• Only persons trained to use the The MetaNeb® System and ventilators
should perform therapy on ventilated patients.
• Unlock the brake casters during transport. Lock the brake casters
during therapy or when not being transported.
• Let the unit stabilize to room conditions for 1 hour after storage or
transport in a cold or humid environment.
• Keep away from all ignition sources.
• Do not use near flammable anesthetics.
• This device is not suitable for use with anesthetic breathing systems.
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) 3

Introduction
INTRODUCTION
The MetaNeb® System supplies a therapy that enhances secretion removal
and helps prevent or resolve patchy atelectasis.
Description
The MetaNeb® System is a therapeutic device that uses a systematic
approach to enhance normal mucus clearance and resolve or prevent
patchy atelectasis.
The system has three modes:
• CHFO (Continuous High Frequency Oscillation)—a pneumatic form of
chest physiotherapy that delivers medicated aerosol while oscillating
the airways with continuous pulses of positive pressure.
• CPEP (Continuous Positive Expiratory Pressure)—supplies medicated
aerosol combined with continuous positive pressure to help hold
open and expand the airways.
• Aerosol—for the delivery of aerosol only. In this mode CHFO and
CPEP are not available.
The MetaNeb® System supplies a platform from which both CHFO and
CPEP can be administered contiguously. This composite therapy is
referred to as “MetaTherapy® Treatment.” MetaTherapy® Treatment is a
combination therapy that seamlessly alternates between CPEP and CHFO
modes. CPEP is a therapy and is never to be used for life support.
There are three major components to The MetaNeb® System:
• Circuit—includes a mouthpiece, handset, nebulizer, tubing, and biofilter/tri-connector. It is a single patient use, latex-free assembly that is
intended for multiple treatment sessions.
• Controller—contains the controls to select the three different modes.
It also has a manometer to monitor pressure. Power is supplied by a
hose connected to a minimum 50 psi oxygen source.
• Stand—lets you easily move the The MetaNeb® System from room to
room.
4 The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7)

Introduction
Theory of Operation
Normal Mucus Clearance
Normal mucus clearance in the lungs is accomplished in three unique
ways. It must be understood that these mechanisms complement each
other and none are mutually exclusive. The three mechanisms are:
1. Mucociliary Escalator
2. Cough
3. Autocephalad Flow
Mucociliary Escalator
The respiratory tract consists of approximately twenty-four generations,
each lined with a mucus secretion that has two layers. The top layer is a
hydrated gel layer. The bottom layer is a thin, less viscous sol layer. Cilia
line the entire surface of the respiratory tract down to the terminal
bronchiole (16th generation). These cilia beat continuously at a rate of
approximately 10-20 times per second and propel mucus in a cephalad
fashion 1-3 mm per second. The mucus with any entrapped particles is
swallowed or coughed to the atmosphere.
Cough
A cough can be voluntary or stimulated as part of a reflex and is an
effective way to remove even large quantities of secretions from the upper
airways (6th-7th generations). This is accomplished by creating high
velocity flow rates at high lung volumes through the generation of
intrapleural pressures >100 mmHg, then releasing this pressure
explosively to the atmosphere. Air can be expelled in excess of 100 miles
per hour. These high airflows create shear forces, which in turn, cause
mucus to be expelled. Past the 6th generation, airways begin to lose their
cartilaginous support, and at the high pressures the small airways tend to
collapse, which prevents secretion removal. Thus, the rationale behind the
HUFF cough and FET maneuvers is that when you teach patients to cough
at lower lung volumes, high pressures are minimized and small airway
collapse is reduced.
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) 5

Introduction
Autocephalad Flow
When gas flows over a thickly lined mucus layer, a shear force directly
proportional to the velocity of the gas is produced. If this airflow velocity
is maintained and exceeds the cohesive forces of the mucus, the mucus
will move in the direction of the gas flow. Essentially, autocephalad flow is
comparable to a cough, except that lower gas velocities are generally
present. To further understand, it is helpful to examine normal tidal
breathing. During normal inspiration the diaphragm contracts and is
displaced caudally. Concomitantly, the intercostal muscles contract to lift
the ribs. These actions together increase the anterior-posterior dimension
(volume) of the thoracic cavity which causes a decrease in alveolar
pressure as compared to atmospheric. This pressure gradient causes a
flow of gas into the lungs.
It is important to understand that as the pressure gradient rises, so do the
flow rate and the velocity. The highest flow rates can be expected to be in
the upper airways during inspiration because the gradient begins at the
mouth and ends at the alveoli. During exhalation the process is reversed
and the alveolar pressure is greater than atmospheric. The flow gradient is
now from the alveoli to the mouth, and therefore, the greatest flow rates
will be in the smaller airways. Since the normal I:E (inspiratory to
expiratory) ratio is 1:1.5 to 1:2, secretions from these airways are
transported to the larger airways by way of asymmetric periodic gas flow.
The MetaNeb® System and Bronchial Hygiene
The MetaNeb® System supplies aerosol, CHFO, and CPEP therapy modes.
CHFO is a pneumatic form of chest physiotherapy that uses a systematic
approach to enhance normal mucus clearance and resolve patchy
atelectasis. CHFO—
• Supplies aerosolized medication and humidification to relax
bronchial smooth muscle so that airway resistance is decreased, and
at the same time hydrates thickened retained secretions.
• Uses specifically calibrated frequency and I:E ratio to create a mean
airway pressure in order to maintain airway caliber, prevent
premature closure, and expand collapsed lung regions.
• Maintains continuous high frequency oscillation during both
inspiration and expiration to form a pressure gradient to the small
airways where secretions are trapped. This pressure gradient creates
an accelerated expiratory airflow that can be manipulated to help
move the secretions to the upper airways.
• Aids in the mobilization of retained secretions.
6 The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7)

Introduction
CPEP is a therapy which supplies a continuous, clinician-set airway
pressure above atmospheric by use of a venturi, a fixed orifice resistor, and
flow during both inspiration and expiration. CPEP—
• Prevents or reverses atelectasis.
• Delivers hyperinflation therapy through positive expiratory pressure
that will help patients deeply breathe and cough.
• Reduces the incidence of air trapping.
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) 7
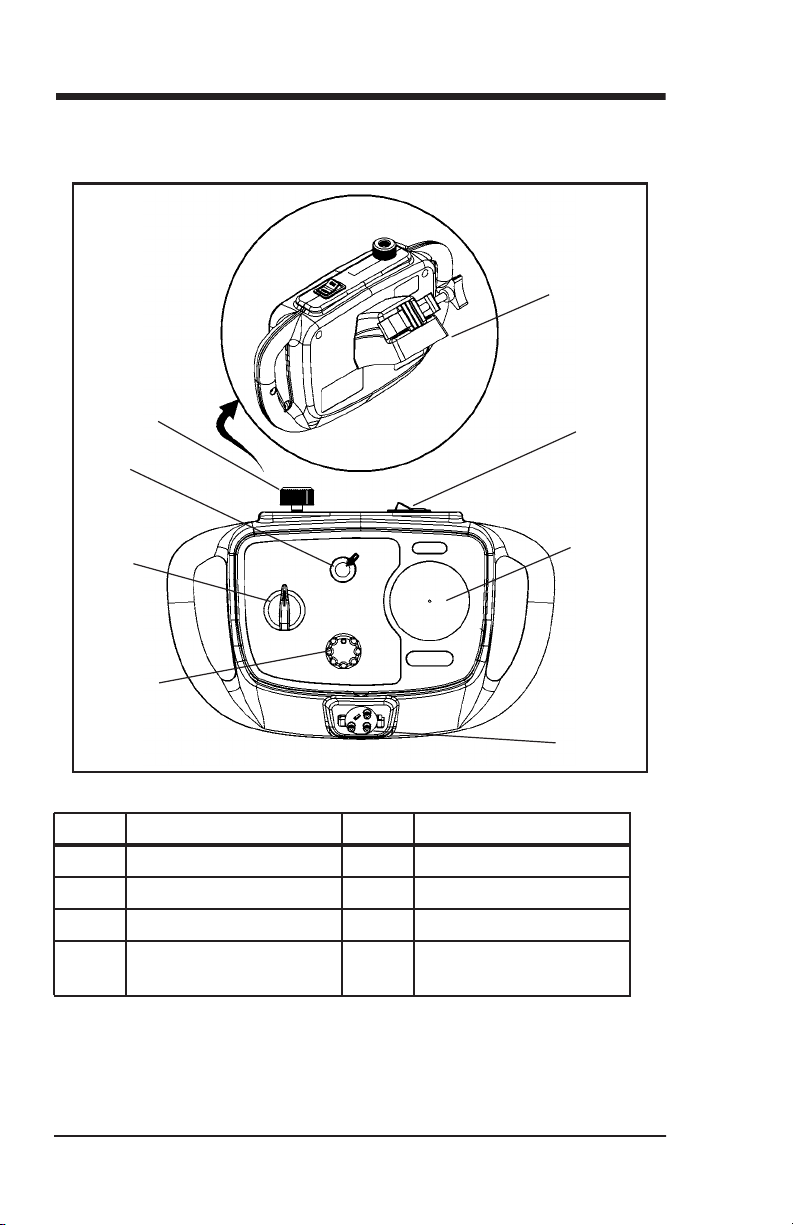
Features
FEATURES
Controller
H
G
F
B
A
C
E
D
Item Description Item Description
A Pressure manometer E CPEP flow adjuster
B Higher/lower switch F Master on/off switch
C Mode selector G Oxygen gas connector
D Circuit tri-connector
port
H Mount bracket
8 The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7)

Features
Circuit
Item Description Item Description
A Mouthpiece G Orifice indicators
B Selector ring H Adapter, 22 mm x 15 mm
C Handset I Adapter, 22 mm x 22 mm
D Circuit tri-connector/
J Occlusion ring
bio-filter
E Tubing K Silicon adapter
F Nebulizer L Nebulizer tubing
The MetaNeb® System User Manual (174432 REV 7) 9
 Loading...
Loading...