Page 1

TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual
Document version: 2.2 - 2013-04-02
Page 2

1. Grass Valley Product Support ......................................................................................................................... 3
2. About this document ........................................................................................................................................ 3
3. TX/MAM functions and syntax......................................................................................................................... 3
4. Defines ............................................................................................................................................................. 4
5. Initializing the library ....................................................................................................................................... 6
5.1 Initializing the library to use a local playout database ............................................................................ 6
5.2 Initializing the library to use a remote database ..................................................................................... 7
6. Database search functions .............................................................................................................................. 8
6.1 Clearing all criteria used in a previous search ......................................................................................... 8
6.2 Adding a criterion that defines a restriction for integer database fields ................................................... 9
6.3 Adding a criterion that defines a restriction for int64 (='long long') database fields .............................. 10
6.4 Adding a criterion that defines a restriction for string database fields ................................................... 11
6.5 Adding a criterion that contains a SQL-query ....................................................................................... 12
6.6 Adding a criterion that contains a parameter for a previously added SQL-query .................................. 13
6.7 Retrieving the list of IDs that are the result of evaluating the previously added criteria ....................... 14
7. Retrieve functions ......................................................................................................................................... 15
7.1 Clearing all requests for fields that may have been used in a previous retrieve call ............................. 15
7.2 Adding a field request for an integer database field ............................................................................. 16
7.3 Adding a field request for an int64 (= long long) database field ............................................................ 17
7.4 Adding a field request for a string database field ................................................................................. 18
7.5 Adding a field request for a text blob database field .............................................................................. 19
7.6 Retrieving the requested fields for the record with id == id and from the table == table ....................... 20
8. Update functions ........................................................................................................................................... 21
8.1 Adding a field update for an integer database field ............................................................................... 21
8.2 Adding a field update for an int64 (= long long) database field ............................................................. 22
8.3 Adding a field update for a string database field.................................................................................... 23
8.4 Adding a field update for a text blob database field ............................................................................... 24
8.5 Updating the record (from table with ID) with the previously added field values .................................. 25
8.6 Creating a record in the table with previously added fieldvalues .......................................................... 26
8.7 Creating the assetjobs, asset_index and group_access records for an asset in the
database ............................................................................................................................................................ 27
8.8 Deleting a record (indicated by the ID) from a table .............................................................................. 28
9. Finalization functions .................................................................................................................................... 29
9.1 Cleaning up the library ........................................................................................................................... 29
10. Date & time functions ................................................................................................................................. 30
10.1 Converting a Cobalt time field to two strings containing resp. the time and date part .......................... 30
10.2 Converting human readable time and date string to a Cobalt time field ............................................... 31
10.3 Getting the current system time and converting to a Cobalt time field .................................................. 32
11. Scheduling functions ................................................................................................................................. 33
11.1 Creating a new main event with import fields and formats ....................................................................... 33
11.2 Checking if the asset indicated by asset_id is in a schedule with the time indicated by
start_timedate and end_timedate ...................................................................................................................... 36
12. Utility functions........................................................................................................................................... 37
12.1 Returning the current library version ...................................................................................................... 37
Copyright © Grass Valley USA, LLC. All rights reserved. This product may be covered by one or
more U.S. and foreign patents.
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 2
Page 3

1. Grass Valley Product Support
Contact information: http://www.grassvalley.com/support/contact
U.S Technical Support: +1 800-547-4989 or +1 530 478 4148 or E-mail: Please use our online
form
All other countries Technical Support: +800 80 80 20 20 or +33 1 48 25 20 20 or E-mail:
callcentre@grassvalley.com
FAQ: http://grassvalley.novosolutions.net/
Training: https://grassvalley.csod.com/LMS/catalog/Main.aspx?tab_page_id=-67&tab_id=6
2. About this document
This document applies to TX/MAM version 2.2, nexos version 3.0 and Channel Composer version
1.6 and higher.
The K2 Edge Protocol Manual describes how to launch Channel Composer templates on nexos.
3. TX/MAM functions and syntax
Applets are written in C. The extension for applet files is .app. To be able to retrieve information from
the TX/MAM database, a library (libcolbalt.so) and a header file (cobalt.h) are available on request.
Following functions are available in the library:
Initialize the library
Database search functions
Retrieve functions
Update functions
Finalization functions
Date & time functions
Scheduling functions
Utility functions
When defining an applet in Channel Composer, make sure to specify the parameters that are used
by the applet.
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 3
Page 4
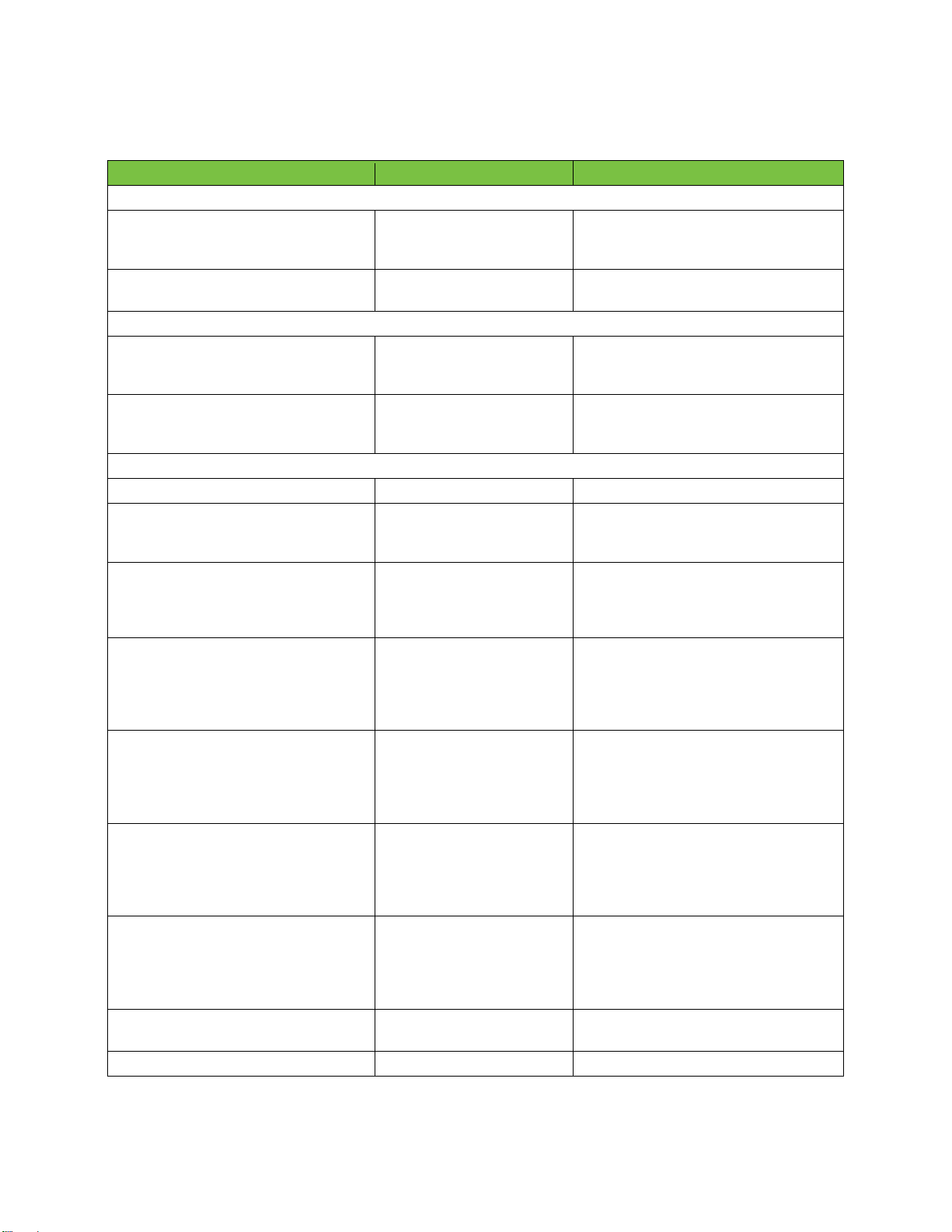
Name
Value
Description
Maximum values
MAX_IDS
1024
The maximum number of rows that
can be retrieved from the database in
one call.
SMALL_BLOB
1024
The size for a small text blob
database field.
Logical Search operators
LOP_AND
“AND”
This criterion will use the
'AND' operator with the next
criterion.
LOP_OR
“OR”
This criterion will use the 'OR'
operator with the next
criterion.
Criterion types
COP_GET_ALL
“GET_ALL”
Get all records from a table.
COP_EQUALS
“EQUALS”
Get all records where the
provided value equals the field
value.
COP_CONTAINING
“CONTAINING”
Get all records where the
provided value is part of the
field value. Can only be used
with string or text blob fields.
COP_GREATER_THAN
“GREATER_THAN”
Get all records where the field
value is greater than the
provided value; usually
applied for integer or int64
fields.
COP_SMALLER_THAN
“SMALLER_THAN”
Get all records where the field
value is smaller than the
provided value; usually
applied for integer or int64
fields.
COP_GREATER_THAN_OR
_EQUALS
“GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ
UALS”
Get all records where the field
value is greater than or equals
the provided value; usually
applied for integer or int64
fields.
COP_SMALLER_THAN_OR
_EQUALS
“SMALLER_THAN_OR_EQU
ALS”
Get all records where the field
value is smaller than or equals
the provided value; usually
applied for integer or int64
fields.
COP_ORDER_BY
“ORDER_BY”
Order the results by the
indicated field.
CRIT_ORDER_ASCENDING
“ASCENDING“
Use the ascending sort order.
4. Defines
The following defines are used within the library:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 4
Page 5
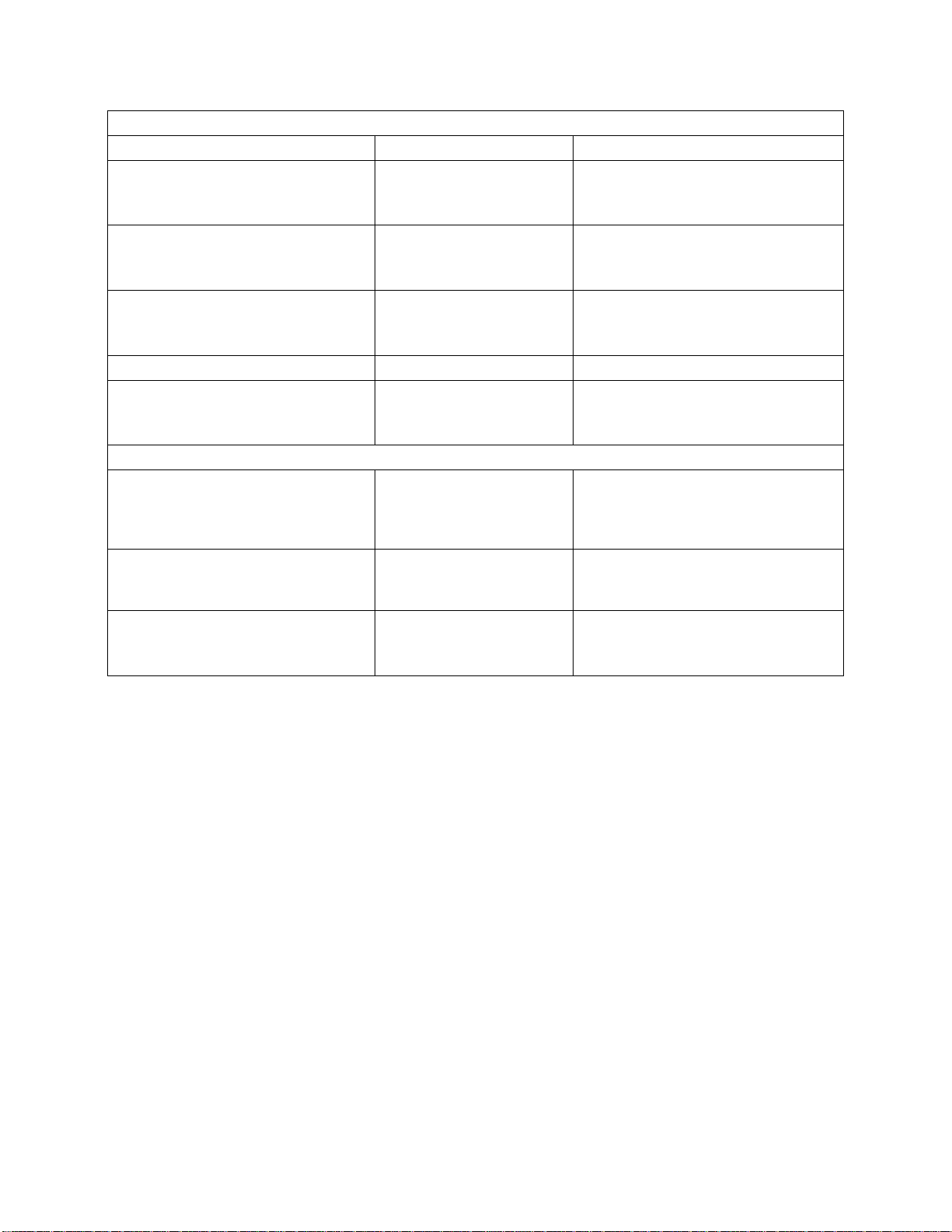
FIELD Origins
ORIGINAL_DATA
0
The field is a database field.
CUSTOM_DATA
1 The field is stored within the
'custom_metadata' field in the
'asset_element' table.
TYPE_DATA
2 The field is stored within the
'type_metadata' field in the
'asset_element' table.
TRANSFER_DATA
3 The field is stored within the
'transfer_metadata' field in the
'asset_element' table.
BLOB_DATA
4
The field is a text blob field.
IMPORT_DATA
5 The field is stored within the
'import_fields' field in the
'main_event' table.
File Transfer types
LOCAL_TRANSFER
Only used for demo systems.
1
The asset files are stored locally in
the
/system/objects/cobassets/media
directory.
FTP_TRANSFER
2
The files are stored on a ftp-server as
indicated in the
'transfer_metadata' field.
FMS_TRANSFER
Not used anymore.
3 The files are stored on an fms-system
as indicated in the
'transfer_metadata' field.
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 5
Page 6

Name
Description
char *channel_name
Not used, can be used with "no_name".
Value
Description
0
Success, the library can now be used to retrieve information from the local
Playout database.
-1
Failure, setting up a connection to the local playout database failed.
5. Initializing the library
The following functions are used to configure the library.
5.1 Initializing the library to use a local playout database
Use this function to verify if the local playout database can be accessed.
int cob_init( char *channel_name );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
if ( cob_init("no_name")==0 ){
/* continue with the rest of the applet */
} else {
/* not possible to connect to database, report error and stop...*/
return -1;
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 6
Page 7

Name
Description
char *database_ip
The ip-address of the machine with the remote database, e.g. "192.168.7.186".
int port
The port on the remote machine to connect to, default 5020.
Value
Description
0
Success, the library can now be used to retrieve information from the
remote database.
-1
Failure, setting up a connection to the remote database failed.
5.2 Initializing the library to use a remote database
Use this function to verify if a remote database can be accessed.
int cob_init_remote( char *database_ip, int port );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
if ( cob_init_remote("192.168.7.186",5020) == 0 ) {
/* continue with the rest of the applet */
} else {
/* not possible to connect to database, report error and stop... */
return -1;
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 7
Page 8

Value
Description
0
Success, all criteria cleared.
-1
Failure.
6. Database search functions
Use the functions described in this section to search the database.
A search command consists of a number (>=1) of criteria that constitute the query that will be used to
match the records. Criteria can be used with the 'and' and 'or' logical operators. The result of a search
command is a list of IDs of records that matched the criteria.
Most criteria can only use fields that reside in the same table. SQL-criteria are an exception to this
rule.
Restrict the number of records in the result list as much as possible, especially when retrieving a
main_event from a Playlist. Too many records will result in a failure on the call. Returning a great
number of records can have a negative effect on system performance.
6.1 Clearing all criteria used in a previous search
int cob_criteria_clear( void );
Parameters
No parameters required
Result
The result of the function is an integer with the following values:
Example
cob_criteria_clear(); /* continue with the rest of the applet */
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 8
Page 9

Name
Description
char *table
The table from which to use the field, e.g. “main_event".
char *logical
Which logical operator to use, e.g. LOP_AND.
char *criteria
The criterion type to use, e.g. COP_EQUALS.
char *field
The field to compare, e.g. "status".
int value
The value to compare, e.g. 2048.
Value
Description
0
Success, the criterion has been added.
-1
Failure, the criterion could not be added.
6.2 Adding a criterion that defines a restriction for integer database
fields
int cob_criteria_add_integer( char *table, char *logical, char *criteria,
char *field , int value );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer with the following values:
Example
This example will retrieve all asset_elements with status_int == 1:
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_criteria_add_integer( "asset_element", LOP_AND, COP_EQUALS, "status_int" , 1 );
number_of_ids = cob_get_id_list( id_array, max_id_size );
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 9
Page 10

Name
Description
char *table
The table from which to use the field, e.g. "main_event".
char *logical
Which logical operator to use, e.g. LOP_AND.
char *criteria
The criterion type to use, e.g. COP_EQUALS.
char *field
The field to compare, e.g. "status".
long long value
The value to compare e.g. 2048.
Value
Description
0
Success, the criterion has been added.
-1
Failure, the criterion could not be added.
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_criteria_add_long( "main_event", LOP_AND, COP_EQUALS, "id_Playlist" , 1 );
cob_criteria_add_integer( "main_event", LOP_AND, COP_EQUALS, "status" , 2048 );
number_of_ids = cob_get_id_list( id_array, max_id_size );
6.3 Adding a criterion that defines a restriction for int64 (='long long')
database fields
int cob_criteria_add_long( char *table, char *logical, char *criteria,
char *field, long long value );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example will retrieve all main events for id_Playlist = 1 and status = 2048:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 10
Page 11

Name
Description
char *table
The table from which to use the field, e.g."asset_element".
char *logical
Which logical operator to use, e.g. LOP_AND.
char *criteria
The criteria type to use, e.g. COP_EQUALS.
char *field
The field to compare, e.g. "asset_string".
long long value
The value to compare e.g. "Clips".
Value
Description
0
Success, the criterion has been added.
-1
Failure, the criterion could not be added.
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_criteria_add_integer( "asset_element", LOP_AND, COP_EQUALS, "status_int" , 1 );
cob_criteria_add_string( "asset_element", LOP_AND, COP_EQUALS, "asset_string" , "Clips" );
number_of_ids = cob_get_id_list( id_array, max_id_size );
6.4 Adding a criterion that defines a restriction for string database
fields
int cob_criteria_add_string( char *table, char *logical, char *criteria,
char *field , char *value );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example will retrieve a list of all asset_elements with an asset_string value that equals to "Clips"
and with status_int value that equals to 1:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 11
Page 12

Name
Description
char *table
The table from which to use the field, e.g. "asset_element".
char *value
The SQL-query e.g. "select id, save_stamp from asset_element where
status_int = 1".
Value
Description
0
Success, the criterion has been added
-1
Failure, the criterion could not be added
6.5 Adding a criterion that contains a SQL-query
The SQL-query can only be a 'read only' query and should always return the fields 'ID' and
'SAVE_STAMP'. For a reference on the SQL 'select' statement, please refer to
http://www.ibphoenix.com/downloads/60LangRef.zip
The values to compare the fields with can be put directly into the SQL-statement (e.g. “where
id_Playlist = 1”), except when the field is a string field. In this case the value should be passed using
a parameter. This means that the SQL-statement will contain for example “where asset_string
= :asset_string” and the cob_criteria_add_sqlparam function will be used to provide the
value, for example cob_criteria_add_sqlparam( “asset_element”, “asset_string”,
”Clips” ).
A cob_criteria_add_sqlquery() should only be executed once for every
cob_get_id_lis()call. Multiple parameters can be added per cob_get_id_list()call.
int cob_criteria_add_sqlquery( char *table, char *value );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example will retrieve a list of all asset_elements with an asset_string value that equals "Clips"
and with status_int value that equals 1:
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_criteria_add_sqlquery( "asset_element","select id,savestamp from asset_element where ”
"asset_string = :asset_string and status_int=1" );
cob_criteria_add_sqlparam( "asset_element", "asset_string", "Clips" );
number_of_ids = cob_get_id_list( id_array, max_id_size );
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 12
Page 13

Name
Description
char *table
The table from which to use the field, e.g."asset_element".
char *field
The parameter name, e.g "asset_string".
char *value
The value of the parameter e.g. "Clips".
Value
Description
0
Success, the criterion has been added.
-1
Failure, the criterion could not be added.
6.6 Adding a criterion that contains a parameter for a previously added
SQL-query
Only required for string fields
int cob_criteria_add_sqlparam( char *table, char *field, char *value );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example will retrieve a list of all asset_elements with an asset_string value that equals "Clips"
and with status_int value that equals 1:
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_criteria_add_sqlquery( "asset_element","select id,savestamp from asset_element where "
"asset_string = :asset_string and status_int =1" );
cob_criteria_add_sqlparam( "asset_element" , "asset_string", "Clips" );
number_of_ids = cob_get_id_list( id_array, max_id_size );
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 13
Page 14

Name
Description
long long *id_list
The pointer to the list in which the resulting list will be placed. This list is an
array of 'long long', e.g. 'long long asset_element_array [ MAX_IDS ];'
int max_ids
The maximum number of rows to return, e.g 1024.
Value
Description
>=0
Success, the number indicates the number of rows that were returned.
-1
Failure, retrieving the list failed.
6.7 Retrieving the list of IDs that are the result of evaluating the
previously added criteria
int cob_get_id_list( long long *id_list, int max_ids );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example will retrieve a list of all asset_elements with an asset_string value that equals "Clips"
and with status_int value that equals 1:
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_criteria_add_sqlquery( "asset_element","select id, save_stamp from asset_element where "
"asset_string = :asset_string and status_int = 1" );
cob_criteria_add_sqlparam( "asset_element" , "asset_string", "Clips" );
number_of_ids = cob_get_id_list( id_array, max_id_size );
if ( number_of_ids >= 0 ){
/* continue with the rest of the applet by looping through the array */
} else {
/* failure, log the error and stop */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 14
Page 15

Value
Description
0
Success, all criteria cleared.
7. Retrieve functions
Retrieving fields is performed on individual records. To retrieve details of all records that have been
returned by the cob_get_id_list call, loop through the resulting array and retrieve the required
fields.
To retrieve fields of database records, the following functions are available.
7.1 Clearing all requests for fields that may have been used in a
previous retrieve call
int cob_fieldlist_clear( void );
Parameters
No parameters required.
Result
The result of the function is an integer with only one possible value:
Example
cob_fieldlist_clear(); /* continue with the rest of the applet */
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 15
Page 16

Name
Description
char *field
The field to get, e.g. "status".
int **result_target
The pointer to the pointer that contains the result, e.g. _status_int with
the declaration int *_status_int;.
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. ORIGINAL_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
7.2 Adding a field request for an integer database field
The result is temporarily placed in a library variable. Copy to a local variable to save this value even
after a cob_fieldlist_clear call.
int cob_fieldlist_get_integer( char *field, int **result_target, int data_type );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer and has following possible values:
Example
This example will retrieve details for the asset_element record with id == 1035:
char *_artist;
int *_status_int;
long long *_id_category;
char artist[256];
int status_int;
long long category_id;
[..]
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_get_long( "id_category", &_id_category,ORIGINAL_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_string( "artist", &_artist, CUSTOM_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_integer( "status_int", &_status_int, ORIGINAL_DATA );
result = cob_get_field_values( "asset_element", 1035 );
if ( result == -1 ) {
printf( "Can't find asset_element: %Ld -> exit \n", 1035 );
return -1;
}
category_id = *_id_category;
strcpy( _artist, artist );
status_int = *_status_int;
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 16
Page 17

int cob_fieldlist_get_long( char *field, long long **result_target, int data_type );
Value
Description
char *field
The field to retrieve, e.g. "status".
long long **result_target
The pointer to the pointer that contains the result, e.g.
_id_asset_element with the declaration long long
*_id_asset_element;.
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. ORIGINAL_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
7.3 Adding a field request for an int64 (= long long) database field
The result is temporarily placed in a library variable. Copy this to a local variable to save the value
even after a cob_fieldlist_clear call.
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example retrieves details for asset_element record with id == 1035:
char *_artist;
int *_status_int;
long long *_id_category;
char artist[256];
int status_int;
long long category_id;
[..]
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_get_long( "id_category", &_id_category,ORIGINAL_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_string( "artist", &_artist, CUSTOM_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_integer( "status_int", &_status_int, ORIGINAL_DATA );
result = cob_get_field_values( "asset_element", 1035 );
if ( result == -1 ) {
printf( "Can't find asset_element: %Ld -> exit \n", 1035 );
return -1;
}
category_id = *_id_category;
strcpy( _artist, artist );
status_int = *_status_int;
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 17
Page 18

int cob_fieldlist_get_string( char *field, char **result_target, int data_type );
Name
Description
char *field
The field to get, e.g. "artist".
char **result_target
The pointer to the pointer that contains the result, e.g. _artist with the
declaration char *_artist;.
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. CUSTOM_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
7.4 Adding a field request for a string database field
The result is temporarily placed in a library variable. Copy this to a local variable to save the value
even after a cob_fieldlist_clear call.
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example retrieves details for asset_element record with id == 1035:
char *_artist;
int *_status_int;
long long *_id_category;
char artist[256];
int status_int;
long long category_id;
[..]
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_get_long( "id_category", &_id_category, ORIGINAL_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_string( "artist", &_artist, CUSTOM_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_integer( "status_int", &_status_int, ORIGINAL_DATA );
result = cob_get_field_values( "asset_element", 1035 );
if ( result == -1 ) {
printf( "Can't find asset_element: %Ld -> exit \n", 1035 );
return -1;
}
category_id = *_id_category;
strcpy( _artist, artist );
status_int = *_status_int;
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 18
Page 19

Name
Description
char *field
The field to get, e.g. "transfer_metadata".
char **result_target
The pointer to the pointer that contains the result, e.g. _artist with the
declaration char *_artist;
int **result_size The pointer to the pointer that contains the size of the
resulting text, e.g. _charcount with the declaration int *_charcount;.
int content_type
The origin of the data, e.g. CUSTOM_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
char *_transfer_metadata;
int *_charcount;
char transfer_metadata[ SMALL_BLOB ];
int charcount;
[..]
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_get_small_blob( "transfer_metadata", &_transfer_metadata,
&_charcount, SMALL_BLOB);
result = cob_get_field_values( "asset_element", 1035 );
if ( result == -1 ) {
printf( "Can't find asset_element: %Ld -> exit \n", 1035 );
return -1;
}
charcount = *_charcount;
memcpy( transfer_metadata, _transfer_metadata, charcount );
7.5 Adding a field request for a text blob database field
The result is temporarily placed in a library variable. Copy this to a local variable to save the value
even after a cob_fieldlist_clear call.
int cob_fieldlist_get_small_blob( char *field, char **result_target,
int **result_size, int content_type );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer and has following possible values:
Example
This function retrieves transfer_metadata for the asset_element record with id == 1035:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 19
Page 20

Name
Description
char *table
The table to get the record from, e.g. "asset_element".
long long id
The id of the record, e.g. 1035.
Value
Description
0
Success, the fields have been retrieved.
-1
Failure, the fields could not be retrieved.
7.6 Retrieving the reque sted fields for the record with id == id and from
the table == table
The resulting field values are temporarily placed in library variables. Copy this to a local variable to
save the values even after a cob_fieldlist_clear call.
int cob_get_field_values( char *table, long long id );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer and has following possible values:
Example
This example retrieves details for the asset_element record with id == 1035:
char *_artist;
int *_status_int;
long long *_id_category;
char artist[256];
int status_int;
long long category_id;
[..]
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_get_long( "id_category", &_id_category, ORIGINAL_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_string( "artist", &_artist, CUSTOM_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_get_integer( "status_int", &_status_int, ORIGINAL_DATA );
result = cob_get_field_values( "asset_element", 1035 );
if ( result == -1 ) {
printf( "Can't find asset_element: %Ld -> exit \n", 1035 );
return -1;
}
category_id = *_id_category;
strcpy( _artist, artist );
status_int = *_status_int;
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 20
Page 21

int cob_fieldlist_set_integer( char *field, int value, int data_type );
Name
Description
char *field
The field to set, e.g. "status_int".
int value
The new value, e.g. 12.
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. ORIGINAL_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_integer( "status", 12, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_adjust_field_values( "asset_element", 1035 ) != 0 ){
/* Log error */
}
8. Update functions
Fields are updated for individual records. Multiple fields can be set in one update by using multiple
cob_fieldlist_set_[x] functions before calling the cob_adjust_field_values call.
8.1 Adding a field update for an integer database field
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example sets the status_int field for the asset_element record with id == 1035 to
12:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 21
Page 22

int cob_fieldlist_set_long( char *field, long long value, int data_type );
Value
Description
char *field
The field to set, e.g. "id_category".
long long value
The new value, e.g. 12.
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. ORIGINAL_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_long( "id_category", 345, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_adjust_field_values("asset_element", 1035) != 0 ){
/* Log error */
}
8.2 Adding a field update for an int64 (= long long) database field
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example sets the id_category field to 345 for asset_element record with id ==
1035:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 22
Page 23

Name
Description
char *field
The field to get, e.g. "name".
char *value
The new value, e.g. "adjusted".
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. ORIGINAL_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_string( "name", "adjusted", ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_adjust_field_values("main_event", 1035) != 0 ){
/* Log error */
}
8.3 Adding a field update for a string database field
int cob_fieldlist_set_string( char *field, char * value, int data_type );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example sets the name field to "adjusted" for main_event record with id == 1035:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 23
Page 24

int cob_fieldlist_set_small_blob( char *field, char *value, int size,
int content_type );
Name
Description
char *field
The field to get, e.g. "transfer_metadata".
char *value
The new value, e.g. "adjusted" The new value, e.g. "<XML></XML>".
int size
The size of the value, e.g. 11.
int data_type
The origin of the data, e.g. ORIGINAL_DATA.
Value
Description
0
Success, the field has been added.
-1
Failure, the field could not be added.
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_small_blob( "transfer_metadata", "<XML></XML>",11, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if (cob_adjust_field_values( "asset_element", 345 ) != 0 ) {
/* Log error */
}
8.4 Adding a field update for a text blob database field
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example sets the transfer_metadata field to "<XML></XML>" for asset_element record
with id == 345:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 24
Page 25

Name
Description
char *table
The table to update, e.g. "asset_element".
long long id
The ID of the record.
Value
Description
0
Success, the fields have been updated.
-1
Failure, the fields could not be updated.
8.5 Updating the record (from table with ID) with the previously added
field values
int cob_adjust_field_values( char *table, long long id );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer and has following possible values:
Example
This example will update the id_category field and the transfer_metadata for the asset_element record
with id == 1035:
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_long( "id_category", 345, ORIGINAL_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_set_small_blob( "transfer_metadata", "<XML></XML>", 11, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_adjust_field_values("asset_element", 1035) != 0 ) {
/* Log error */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 25
Page 26

Name
Description
char *table
The table to update, e.g. "asset_element".
long long *id
The resulting id of the new record.
Value
Description
0
Success, the record has been created.
-1
Failure, the record could not be created.
8.6 Creating a record in the table with previously added fieldvalues
int cob_create_table_element( char *table, long long *id );
The new id will be returned in id.
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer and has following possible values:
Example
This example will create a new asset_element record with the id_category field and the
transfer_metadata already filled in:
cob_fieldlist_clear ();
cob_fieldlist_set_long( "id_category", 345, ORIGINAL_DATA );
cob_fieldlist_set_small_blob( "transfer_metadata", "<XML></XML>",11, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_create_table_element ( "asset_element", &new_id ) != 0){
/* Log error */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 26
Page 27

Name
Description
assetId
The asset ID.
userGroupId
ID of the user group the asset belongs to.
logUserGroupId
ID of the log user group the application belongs to
Value
Description
0
Success, the asset references have been created.
-1
Failure, the asset references have not been created.
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_criteria_clear();
if ( cob_create_asset_references( assetId, userGroupId, logUserGroupId ) != 0 ) {
/* Log error */
}
8.7 Creating the assetjobs, asset_index and group_access records for
an asset in the database
int cob_create_asset_references( const long long assetId, const long long userGroupId, const long
long logUserGroupId );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example sets the name field to "adjusted" for main_event record with id == 1035:
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 27
Page 28

int cob_delete_table_element( char *table, long long id );
Name
Description
char *table
The table to update, e.g. "asset_element".
long long id
The id of the record to delete, e.g. 123.
Value
Description
0
Success, the record has been deleted.
-1
Failure, the record could not be deleted.
8.8 Deleting a record (indicated by the ID) from a table
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example deletes the asset_element record with id== 123:
if ( cob_create_table_element("asset_element", 123) != 0 ) {
/* Log error */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 28
Page 29

Value
Description
0
Success, the library has been cleaned up.
9. Finalization functions
The following function is used to close the link created with the local- or remote database with an
earlier call to cob_init() or cob_init_remote(), and clean up associated resources.
9.1 Cleaning up the library
int cob_clear( void );
Parameters
No parameters required.
Result
The result of the function is an integer with only one possible value:
Example
cob_clear();
return 0;
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 29
Page 30

Name
Description
long long
time_date_msec
The Cobalt time field to convert.
char *time
The time part as a string, e.g. "13:00:00:00".
char *date
The date part as a string, e.g. "2006-10-06".
Value
Description
0
Success, the time could be converted.
-1
Failure, the time could not be converted.
10. Date & time functions
Use following functions to work with the time and date formats as used in Cobalt.
10.1 Converting a Cobalt time field to two strings containing resp. the
time and date part
int cob_msec_to_timedate( long long time_date_msec, char *time, char *date );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
Converting a start time to human readable format:
cob_msec_to_timedate( mainevent_datetime, time, date );
printf( "Main Event starts at %s,
%s", time, date );
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 30
Page 31

Name
Description
char *time
The time part as a string, e.g. "13:00:00:00".
char *date
The date part as a string, e.g. "2006-10-06".
long long
*time_date_msec
The resulting Cobalt time field.
Value
Description
0
Success, the time could be converted.
-1
Failure, the time could not be converted.
10.2 Converting human readable time and date string to a Cobalt time
field
int cob_timedate_to_msec( char *time, char *date, long long *time_date_msec );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
Converting a human readable time and date to a Cobalt time field:
cob_msec_to_timedate( "13:00:00:00", "2006-10-06" , mainevent_datetime );
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_long( "start_datetime", mainevent_datetime, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_adjust_field_values( "main_event", 1035 ) != 0 ){
/* Log error */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 31
Page 32

Name
Description
long long
*time_date_msec
The resulting Cobalt time field.
Value
Description
0
Success, time converted
-1
Failure, the time could not be converted
10.3 Getting the current system time and converting to a Cobalt time
field
int cob_get_current_timedate_msec( long long *time_date_msec );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
Setting the current system time to the start time of a main event:
cob_get_current_timedate_msec( mainevent_datetime );
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_fieldlist_set_long( "start_datetime", mainevent_datetime, ORIGINAL_DATA );
if ( cob_adjust_field_values("main_event", 1035) != 0 ){
/* Log error */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 32
Page 33

Name
Description
long long AssetId
The main asset id, e.g. 302.
long long StartTimeDate
The starttime of the main_event as Cobalt time field.
int Duration
The duration in milliseconds (-1 if the asset duration can be used).
long long ChannelId
Asset ID of the Channel Asset specifying the actual playout server
to schedule to.
int OptOut
The optout to use (reserved for future use), e.g. 0.
MainEventType
0=Follow, 1=Manual, 2=Fixed.
BlockId
ID of the scheduled block. If a new Block is started (i.e. event type
has fixed starttime) this can be -1 to create a new block.
char* PlayoutAddress
The ip-address of the playout machine.
int PlayoutPort
The ip-port of the playout machine.
char *AssetAddress
The virtual ip-address of the TX/MAM database, e.g.
"192.168.7.210".
int AssetPort
The port of the TX/MAM database, e.g. 5020.
char* ImportFields
XML-structure with Import fields e.g.
<XML>
<FIELD name="ranking">nr 5</FIELD>
<FIELD name="rating">PG</FIELD>
</XML>
11. Scheduling functions
To manipulate the current schedule, following functions are provided.
11.1 Creating a new main event with import fields and formats
This function creates a new main event at the time indicated by StartTimeDate, with the main
asset AssetId and applying Formats. If Duration is other than -1, this duration is used as the
duration of the resulting main event. Otherwise the use_duration of the asset is applied.
The resulting main event is added to the playlist using OptOut. All asset information is taken from
the asset database at AssetAddress / AssetPort.
No precautions are taken with regards to any items present at the same StartTimeDate. The
caller is responsible for schedule under runs and over runs.
long long
cob_create_main_event_dyn_format( long long AssetId, long long StartTimeDate, int Duration,
long long ChannelId, int OptOut, int MainEventType,
long long BlockId, char *PlayoutAddress, int PlayoutPort,
char *AssetAddress, int AssetPort, char *ImportFields,
char *Formats, char *MainEventName, long long iLockID,
char *TcIn, char *TcOut );
Parameters
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 33
Page 34

char* Formats
XML structure with Formats and import field values (Italic
values are optional) e.g.
<XML>
<FORMAT name=”formatName” offset=”00:00:30:00”
duration=”00:00:10:00”>
<FIELD name=”importFieldName”>value</FIELD>
</FORMAT>
</XML>
The import field is transformed to a Main Event import field
by the name of: “[formatIndex]_[fieldName]”. If [value] of an
format import field is empty, the value ‘empty’ will be used.
char* MainEventName
Main Event name.
long long iLockID
0 (is not used).
char* TcIn
Specifies timecode in in hh:mm:ss:ff.
char* TcOut
Specifies timecode out in hh:mm:ss:ff.
Value
Description
>=0
Success, the main_event is created. The result is the id of the new
main_event.
-1
Failure, the main_event could not be created.
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
This example creates a main event with an import field (test) and format (PGM).
// Constants
const string8 externalRefSt = “test”;
const string8 playoutIpSt = “192.168.0.1”;
const int playoutPortNm = 5020;
const string8 assetIpSt = “192.168.0.2”;
const int assetPortNm = 5020;
const long long channelIdNm = 1;
// Connect to asset database
int result = cob_init_remote ( assetIpSt.c_str(), assetPortNm );
if (result == 0 ) return;
// Find external reference in asset database
cob_criteria_clear();
cob_fieldlist_clear();
cob_criteria_add_sqlquery( "asset_element" , "SELECT first 1 id, save_stamp FROM
asset_element WHERE external_ref = :external_ref" );
cob_criteria_add_sqlparam( "asset_element", "external_ref", externalRefSt.c_str() );
long long assetIdNm;
result = cob_get_id_list( &assetIdNm, 1 );
if ( result <= 0 ) return;
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 34
Page 35

// Start cache on asset database
cob_start_cache( assetIpSt.c_str(), assetPortNm );
// Connect to playout dataserver
int result = cob_init_remote ( playoutIpSt.c_str(), playoutPortNm );
if (result == 0 ) return;
// Get current playout datetime
long long startDateTimeNm;
result = cob_get_current_timedate_msec( &startDateTimeNm );
if ( result <= 0 ) return;
// Create event
long long mainEventIx = cob_create_main_event_dyn_format(
assetIdNm,
startDateTimeNm,
10000, // duration
channelIdNm,
0,
2, // event type
-1, // block id
playoutIpSt.c_str(), // playout ip
playoutPortNm, // playout port
assetIpSt.c_str(), // asset database ip
assetPortNm, // asset database port
“<XML><FIELD name=\”test\”></FIELD></XML>”,
“<XML><FORMAT name=\”PGM\”></FORMAT></XML>”,
“Name”, // event name
0,
NULL, // tc-in
NULL, // tc-out
);
cob_flush_cache( assetIpSt.c_str(), assetPortNm );
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 35
Page 36

Name
Description
long long
asset_id
The main asset id, e.g. 302.
long long
start_timedate
The start time of the period to check as Cobalt time field.
long long
end_timedate
The end time of the period to check as Cobalt time field.
Name
Description
-1
Failure, the check could not be performed.
0
The asset is not scheduled within this time period.
>0
The asset is scheduled, the result is the id of the first main event to use
this asset.
11.2 Checking if the asset indicated by asset_id is in a schedule with
the time indicated by start_timedate and end_timedate
long cob_check_asset_scheduled( long long asset_id, long long start_timedate,
long long end_timedate );
Parameters
Result
The result of the function is an integer that can have following values:
Example
To check if an asset is scheduled within now and now + 1 hour:
long cob_init( "no name" );
cob_msec_to_timedate( start_datetime );
mainevent_id = cob_check_asset_scheduled( 302, mainevent_datetime,
mainevent_datetime + (60 *60 * 1000));
if ( mainevent_id < 0 ){
/* Log error */
} else if ( mainevent_id > 0 ) {
/* asset is scheduled */
} else {
/* asset is not scheduled */
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 36
Page 37

12. Utility functions
12.1 Returning the current library version
int cob_library_version( void );
Parameters
No parameters required.
Result
The result of the function is an integer with the library version.
Example
Checking if the library has (at least) the required version:
if ( cob_library_version() < (REQUIRED_LIB_VERSION) ){
printf( "applet needs at least version %d of libcobalt (current version: %d), "
"execution stopped.", REQUIRED_LIB_VERSION, cob_library_version() );
return -1;
}
TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 37
Page 38

TX/MAM Database Protocol Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 38
 Loading...
Loading...