Page 1

TX/MAM User Manual
Document version: 2.2 - 12/20/2012
Page 2

Contents
1. Grass Valley Product Support .......................................................................................................... 5
2. About his document .......................................................................................................................... 5
3. The K2 Edge Workflow ..................................................................................................................... 6
3.1 Overview .................................................................................................................................. 6
3.2 Assets ...................................................................................................................................... 6
3.3 Channel Packs......................................................................................................................... 8
4. TX/MAM Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 9
4.1 Assets ...................................................................................................................................... 9
4.1.1 Metadata ............................................................................................................................ 10
4.1.2 Essences ........................................................................................................................... 10
4.1.3 Spotcheck .......................................................................................................................... 11
4.1.4 Jobs ................................................................................................................................... 11
4.1.5 Sharing and Export ............................................................................................................ 12
4.1.6 History ................................................................................................................................ 13
4.2 Asset Types ........................................................................................................................... 14
5. Starting the TX/MAM Browser ........................................................................................................ 15
6. The TX/MAM Interface ................................................................................................................... 16
7. Configuring TX/MAM ...................................................................................................................... 17
7.1 Users and User groups .......................................................................................................... 17
7.1.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 17
7.1.2 Administrator and superuser ............................................................................................. 18
7.1.3 Creating or modifying a User Group .................................................................................. 19
7.1.4 Deleting a User group ........................................................................................................ 19
7.1.5 Creating or modifying a User ............................................................................................. 20
7.1.6 Deleting a User .................................................................................................................. 20
7.1.7 Assigning superuser or administrator rights ...................................................................... 20
7.2 Folders ................................................................................................................................... 21
7.2.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 21
7.2.2 Adding a Folder ................................................................................................................. 22
7.3 Menu items ............................................................................................................................ 24
7.3.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 24
7.3.2 Adding or editing a menu item ........................................................................................... 25
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 2
Page 3

7.3.3 Deleting a menu item ......................................................................................................... 25
7.4 Jobs, TX Values and Statuses .............................................................................................. 26
7.4.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 26
7.4.2 Statuses and values .......................................................................................................... 27
7.4.3 Workflow values and statuses ........................................................................................... 29
7.4.4 Creating or modifying TX Values ....................................................................................... 30
7.4.5 Deleting a TX Value ........................................................................................................... 30
7.4.6 Creating or modifying Asset jobs ....................................................................................... 30
7.4.7 Creating or modifying TX Statuses .................................................................................... 30
7.5 Asset Types ........................................................................................................................... 31
7.5.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 31
7.5.2 Creating an Asset Type ..................................................................................................... 33
7.5.3 Customizing the Asset Type’s metadata definition ............................................................ 34
8. Asset Management with TX/MAM .................................................................................................. 37
8.1 Creating and editing Assets ................................................................................................... 37
8.1.1 Creating Assets ................................................................................................................. 37
8.1.2 Editing Assets. ................................................................................................................... 37
8.2 Ingest ..................................................................................................................................... 38
8.2.1 Automatic ........................................................................................................................... 38
8.3 Sharing Assets....................................................................................................................... 38
8.4 Search ................................................................................................................................... 40
8.5 Deleting Assets ...................................................................................................................... 40
8.6 Profile ..................................................................................................................................... 40
8.7 About ..................................................................................................................................... 40
8.8 Editing an Asset's metadata information ............................................................................... 40
8.9 Spotcheck and soft parts ....................................................................................................... 41
8.9.1 Quality Check (QC) ............................................................................................................ 41
8.9.2 Creating Segments ............................................................................................................ 41
8.10 Checking and modifying Job status ....................................................................................... 41
8.11 Exporting Assets and Files .................................................................................................... 43
8.12 History .................................................................................................................................... 43
8.13 Adding comments to Assets .................................................................................................. 43
8.14 Customizing the Asset list ..................................................................................................... 44
9. Quick Reference ............................................................................................................................. 45
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 3
Page 4

9.1 Toolbar ................................................................................................................................... 45
9.2 Export options in the Assets list ............................................................................................. 45
9.3 Assets .................................................................................................................................... 45
9.3.1 Info, technical and other metadata tabs ............................................................................ 45
9.3.2 Essences tab ..................................................................................................................... 46
9.3.3 Spotcheck tab .................................................................................................................... 46
9.3.4 Jobs tab ............................................................................................................................. 47
9.3.5 Sharing tab ........................................................................................................................ 47
9.3.6 History tab .......................................................................................................................... 47
9.4 Asset Type window ................................................................................................................ 48
9.5 User group window ................................................................................................................ 49
9.6 Users window ........................................................................................................................ 50
9.7 Menu items window ............................................................................................................... 52
9.8 Folders window ...................................................................................................................... 53
9.9 TX Values window ................................................................................................................. 55
9.10 TX Statuses window .............................................................................................................. 56
9.11 Asset jobs window ................................................................................................................. 57
Copyright © Grass Valley USA, LLC. All rights reserved. This product may be covered by one or more
U.S. and foreign patents.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 4
Page 5

1. Grass Valley Product Support
Contact information: http://www.grassvalley.com/support/contact
U.S Technical Support: +1 800-547-4989 or +1 530 478 4148 or E-mail: Please use our online form
All other countries Technical Support: +800 80 80 20 20 or +33 1 48 25 20 20 or E-mail:
callcentre@grassvalley.com
FAQ: http://grassvalley.novosolutions.net/
Training: https://grassvalley.csod.com/LMS/catalog/Main.aspx?tab_page_id=-67&tab_id=6
2. About his document
This document describes TX/MAM version 2.2. Information in this manual may at some points differ
from your TX/MAM application due to differences in version.
This manual starts with a short description of the K2 Edge workflow, followed by an introduction to
TX/MAM concepts. Then the TX/MAM Interface is explained. Next, this manual is divided in three
sections:
• Configuring TX/MAM
• Asset Management with TX/MAM
• a Quick Reference
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 5
Page 6
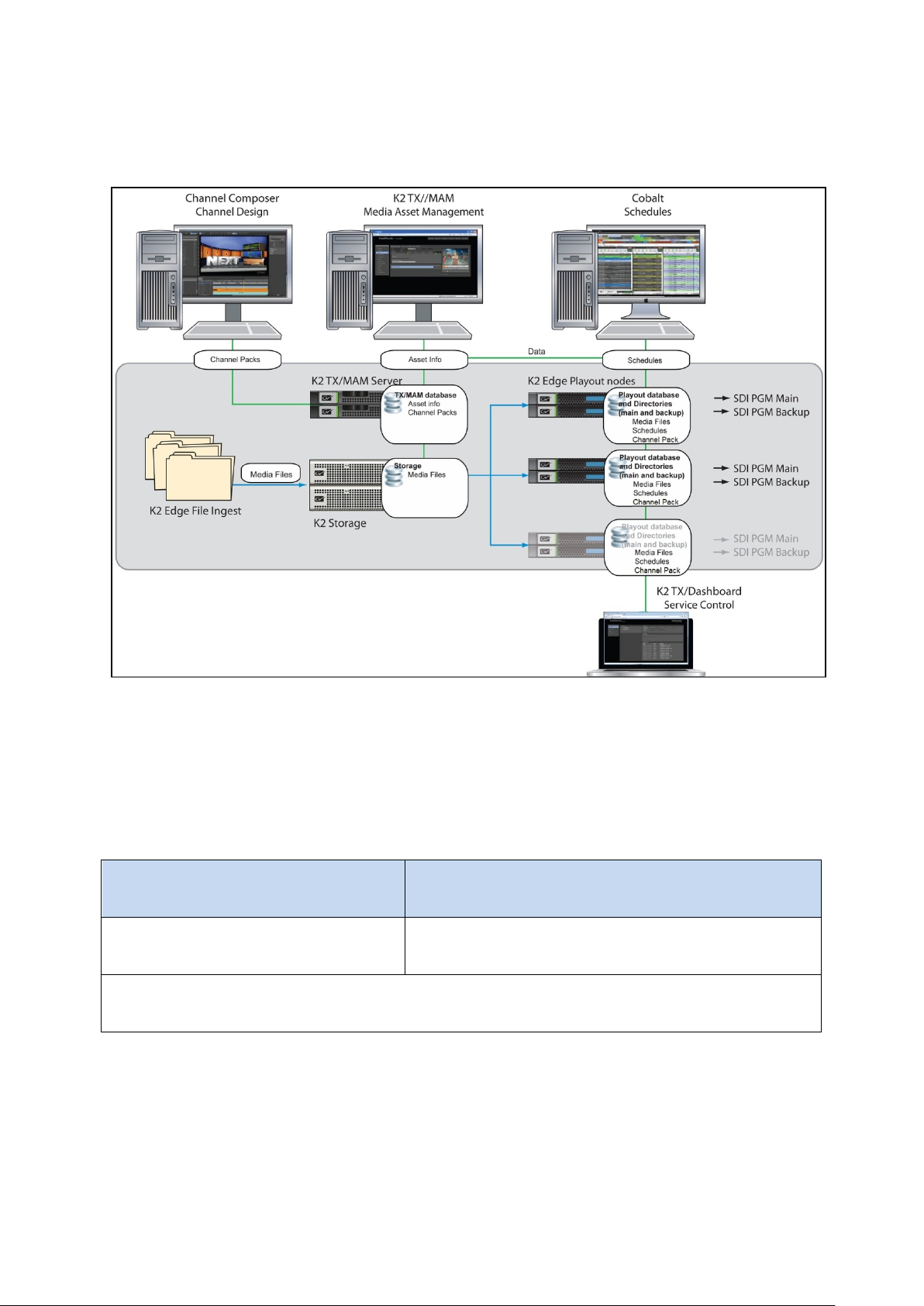
3. The K2 Edge Workflow
Files (Essences) are ingested via Inboxes
Essence
Metadata and info that describes the
Media file(s).
Essence(s) are media files which belong to the Asset. Mostly, these Essences are linked via the
3.1 Overview
3.2 Assets
• Assets are created in TX/MAM. Asset info is stored in the TX/MAM database. Assets can also
be created by the Schedule Importer or Asset Importer.
• Files (Essences) are ingested via Inboxes on the Storage Server.
on the Storage Server. Asset Info
Asset.
Asset’s External reference.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 6
Page 7
Asset info:
Filename
Asset (external reference)
abc123.mpg
abc123
Example Asset
Original
External reference
AssetID
Filename in txmam-media folder
• Metadata
Assets have fixed metadata like file type, external reference, duration and customizable
metadata, for instance artist, title, and episode.
• Jobs and statuses
Assets can have configurable jobs and statuses, which are visible in TX/MAM. Jobs can be
executed automatically and/or manually.
• Workflow
Workflow steps can be defined using the status of an Asset or Asset Job.
Files and Assets are linked based on the filename (the first part before the file extension) and the
Asset’s External reference, as shown in the two examples below:
(essence)
abc123_eng.stl English subtitle belonging to the Asset with ext. reference abc123
During ingest, the file extension for clip files is renamed to .avf (default).
Example: a0000153.avf
Filename
abc123.mpg abc123
When a Schedule is imported and Assets in the Schedule do not yet exist, empty Assets are created.
You can also create empty Assets (Assets for which the file has not yet been ingested in TX/MAM).
Note that empty Assets can be scheduled, but cannot be played out. Before playout, the Essence
must be available.
153 a0000153.avf
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 7
Page 8
Scene Parameter
Event ID
Scene Parameter Value when scheduled
clip
12345
a0000548.avf
clip
12346
a0000978.avf
clip
12347
a0000564.avf
3.3 Channel Packs
Channels are designed in Channel Composer. All the fixed files that belong to a Channel design are
added to the Channel Composer Project as Assets. These Assets are included in the Channel Pack
when the Project is exported to the TX/MAM database. Thus, all the fixed design elements needed for
playout - logos, straps, and so on - are available in the Channel Pack.
To refer to dynamic content (Essences), Scene Parameters are defined. These parameters are
dynamically updated with the Assets’ filename when Events are scheduled. Dynamic content
(Essences) is fetched from Storage for playout.
Example:
The K2 Edge Smart Playout Center Commissioning and Engineering Manuals describe the Ingest
process in more detail.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 8
Page 9
4. TX/MAM Introduction
TX/MAM is a tool for managing Assets. Functionality includes:
• Create Assets and Asset types.
• Automatic file ingest.
• Trim, soft part segments.
• Low-res proxy quality control.
• User management.
• Edit metadata.
• Asset jobs.
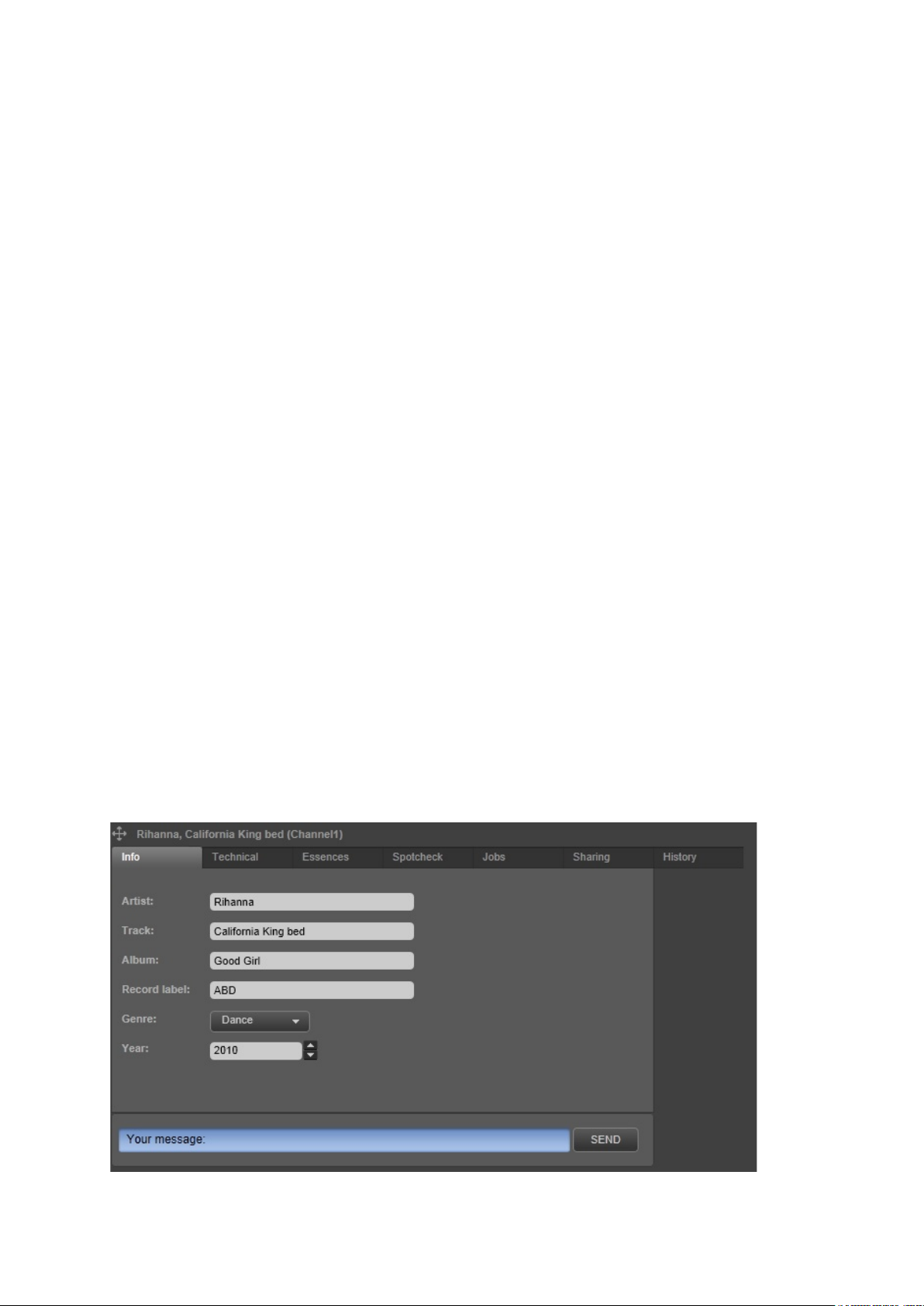
This chapter explains TX/MAM basic concepts using an example Asset, a music video California King
Bed.
4.1 Assets
In TX/MAM each Asset is described on several tabs:
• Configurable metadata tab pages. In the default setup:
o Info: Asset info such as Artist and Track.
o Technical: Asset info such as Media Type and Aspect ratio.
o Images: shows the graphic (only for TGA-Assets).
• Essences: the file(s) linked to an Asset and their status (only for video Assets).
• Spotcheck: file quality check and segments (only for video Assets).
• Jobs: the Jobs linked to an Asset and their status.
• Sharing: Assets are linked to a User Group, Channel1 in the example below. This group has
access to the Asset. To give other Groups access, Assets can be shared.
• History: lists all actions performed for this Asset.
Example Asset (video) in TX/MAM.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 9
Page 10
4.1.1 Metadata
The Asset contains the metadata that describes the Asset, such as External reference, Artist and
Track. This Asset info is displayed on the Asset’s Info and Technical tabs, as well as in the columns in
the Assets list.
Example Assets list with Asset info (External reference, Artist, track, ID …)
Asset info can be used for scheduling (for example schedule clips based on Genre) and for playout
(for example playout Artist and Track info with a clip).
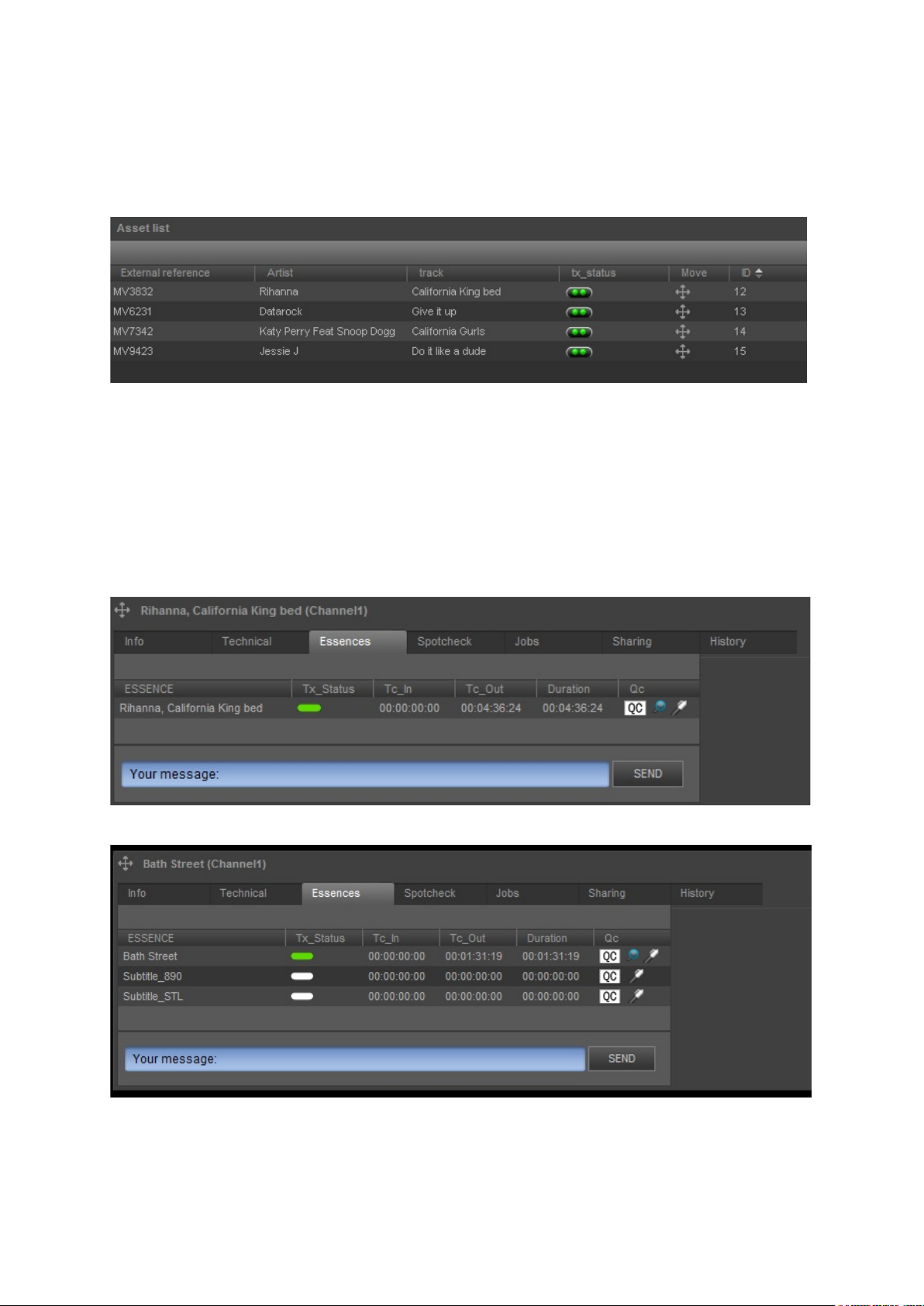
4.1.2 Essences
The media file(s) linked to an Asset are named Essences. The Tx-Status column on the Essences tab
shows the status of file ingest.
Example Essences tab for a Music Video.
Example Essences tab for Asset Bath Street. Three Essences (files) are linked to this Asset.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 10
Page 11
Note that you can create empty Assets; Assets for which Essences have not been ingested yet. Empty
Assets can be scheduled, but cannot be played out. Before playout, the Essence file(s) must be
ingested.
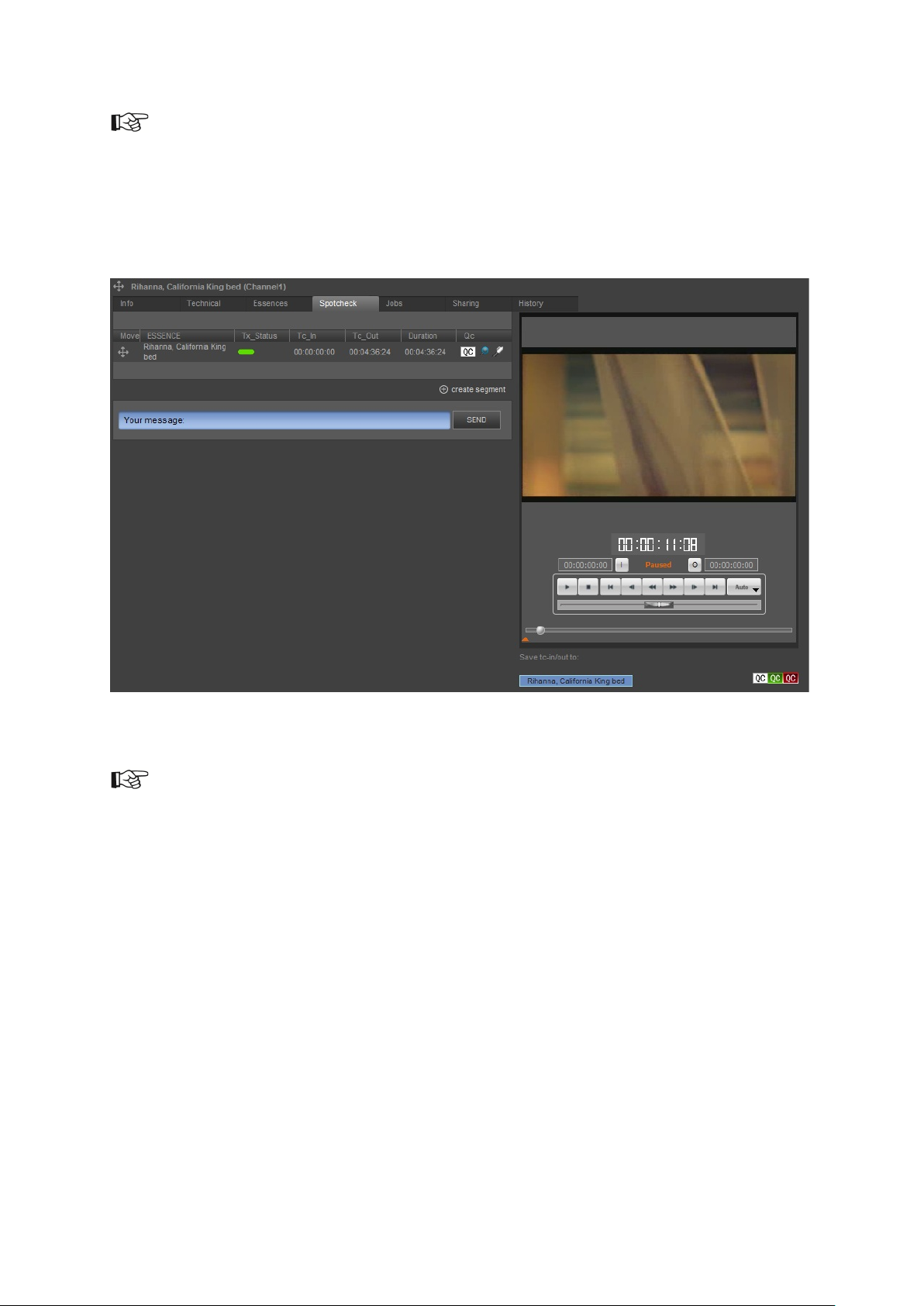
4.1.3 Spotcheck
TX/MAM’s Spotcheck functionality lets you verify the Essences’ quality. You can also define
Segments- using Tc-in and Tc-out (time code in and out) - when only part of a file is used.
Segments can be scheduled (drag into POC), but are not listed in the Assets list.
4.1.4 Jobs
Jobs and procedures can be defined and linked to Asset Types and will then automatically be
executed for all Assets of that type. Example jobs:
A job Browse copy to create a low resolution copy of files. The status Browse created is displayed
in the Asset list’s tx_status column.
A job Get media info, used to retrieve info about file duration and type. This info can then be
displayed in the Asset list.
The Jobs tab shows the status of Jobs for an Asset. You can change this status or in some cases
manually execute Jobs.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 11
Page 12
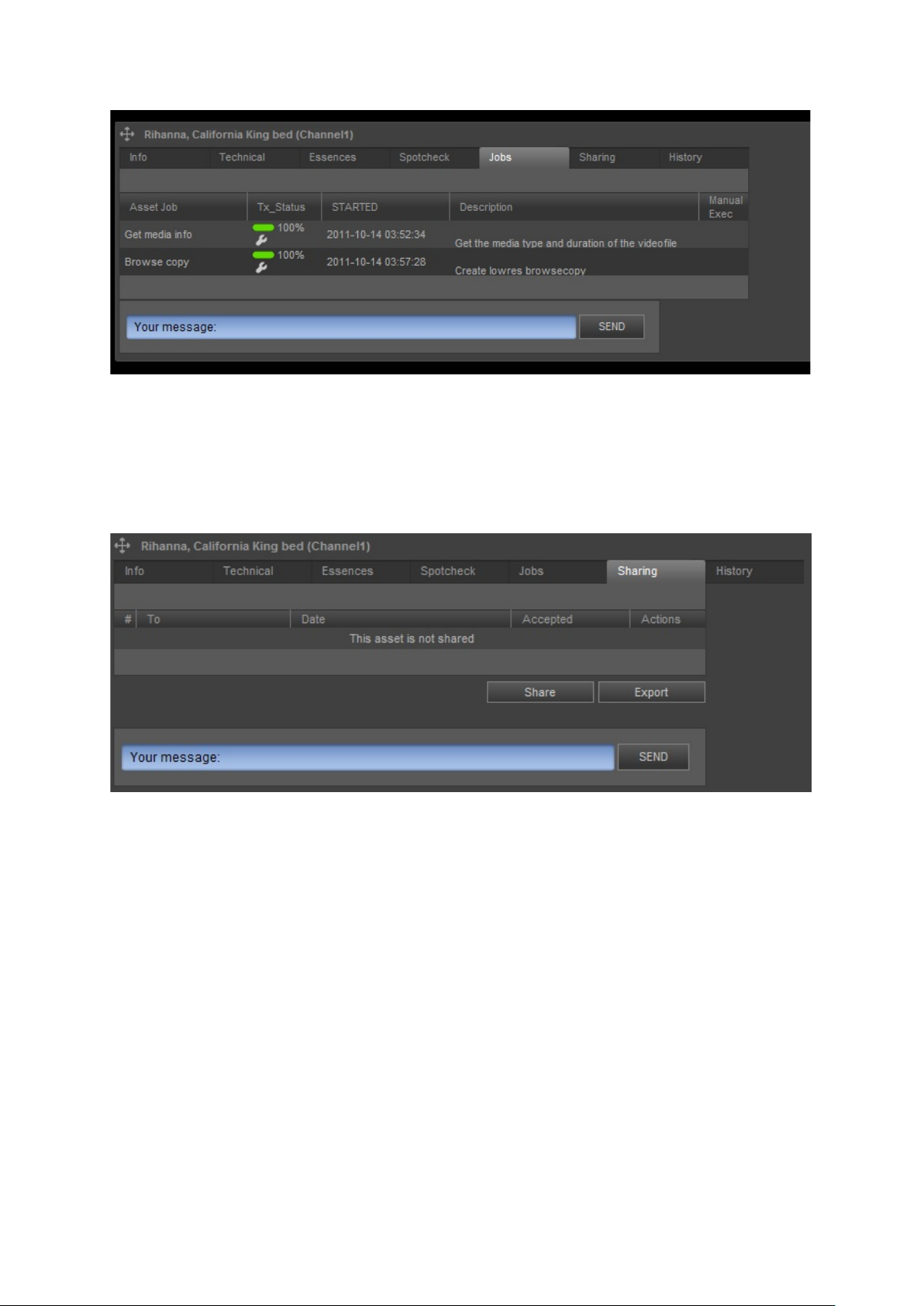
Example Jobs tab.
4.1.5 Sharing and Export
Assets are linked to a User Group. Only this User Group has access to the Asset. To enable access
for other user Groups, the Asset can be shared. Assets can also be exported to a predefined Folder.
Example Sharing tab; the Asset is not shared with other User Groups.
Note how ‘Channel1’ in the Asset’s title refers to the User Group that has access to this Asset.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 12
Page 13
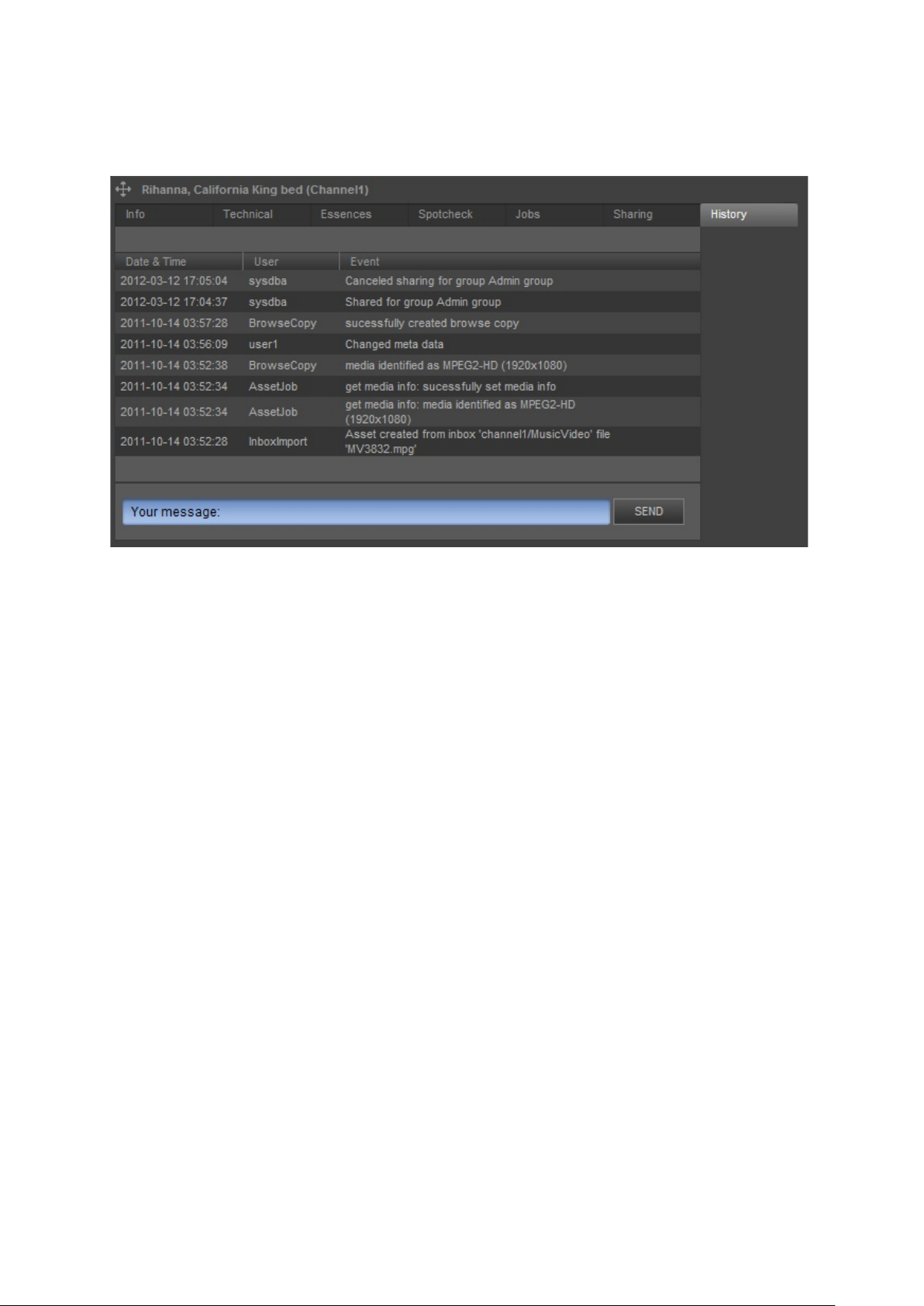
4.1.6 History
The Asset’s History describes all Asset Jobs or user actions performed for the Asset.
Example History tab.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 13
Page 14
4.2 Asset Types
Asset Types define groups of Assets with the same file type and metadata definition.
• Example file types are: AVF (for video files), TGA (for graphics) and WAV.
• Metadata fields such as External reference and Duration are fixed for all Asset Types. Custom
metadata can be configured per Asset Type.
Below you find the custom metadata definition for Asset Type Music Videos. The name attribute
defines the custom metadata fields for Assets of this type: Artist, Track, Album, and so on.
<XML>
<WINDOW width="535" height="220">
<PAGE name="Info">
<LABEL x="10" y="27" height="16" width="80">Artist:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="artist" x="100" y="25" height="20" width="200" search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="10" y="57" height="16" width="80">Track:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="track" x="100" y="55" height="20" width="200" search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="10" y="87" height="16" width="80">Album:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="album" x="100" y="85" height="20" width="200" search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="10" y="117" height="16" width="80">Record label:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="record" x="100" y="115" height="20" width="200"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="10" y="147" height="16" width="80">Genre:</LABEL>
<COMBOBOX name="genre" x="100" y="145" height="20" width="100"
search="true">None#13Disco#13Dance#13Launce#13Rap</COMBOBOX>
<LABEL x="10" y="177" height="20" width="80">Year:</LABEL>
<SPINEDIT name="year" x="100" y="175" height="20" width="90" search="true">2010</SPINEDIT>
</PAGE>
<PAGE name="Technical">
<LABEL x="10" y="27" height="16" width="80">Media type:</LABEL>
<COMBOBOX name="media_type" x="100" y="25" height="20" width="120" search="true">#13MPEG2SD#13MPEG2-HD#13MXF-SD#13MXF-HD</COMBOBOX>
<LABEL x="10" y="57" height="16" width="80">Aspect ratio:</LABEL>
<COMBOBOX name="aspect_ratio" x="100" y="55" height="20" width="120"
search="true">#134:3#1316:9 Anamorphic#1316:9 Letterbox</COMBOBOX>
<LABEL x="10" y="87" height="16" width="80">Loudness:</LABEL>
<LABEL x="20" y="107" height="16" width="100">Integrated:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="integrated_loudness" x="120" y="105" height="20" width="45"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="20" y="127" height="16" width="100">Max Momentary:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="momentary_loudness" x="120" y="125" height="20" width="45"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="20" y="147" height="16" width="100">Max Short term:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="shortterm_loudness" x="120" y="145" height="20" width="45"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="20" y="167" height="16" width="100">Range:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="loudness_range" x="120" y="165" height="20" width="45"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="10" y="197" height="16" width="100">Parental guide:</LABEL>
<COMBOBOX name="parental_guide_age" x="100" y="195" width="51" height="20"
search="true">#13AL#136#139#1312#1316#1318</COMBOBOX>
<COMBOBOX name="parental_guide_icon1" x="190" y="195" width="100" height="20"
search="true">#13fear#13sex#13violence#13drugs#13language#13discrimination</COMBOBOX>
<COMBOBOX name="parental_guide_icon2" x="300" y="195" width="100" height="20"
search="true">#13fear#13sex#13violence#13drugs#13language#13discrimination</COMBOBOX>
<COMBOBOX name="parental_guide_icon3" x="410" y="195" width="100" height="20"
search="true">#13fear#13sex#13violence#13drugs#13language#13discrimination</COMBOBOX>
</PAGE>
</WINDOW>
</XML>
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 14
Page 15

5. Starting the TX/MAM Browser
Open a web browser on your workstation.
Enter the K2 TX/MAM servers’ virtual IP-address and press [Enter].
Enter the credentials for the TX/MAM database and press [Enter]. This will open the TX/MAM
application.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 15
Page 16
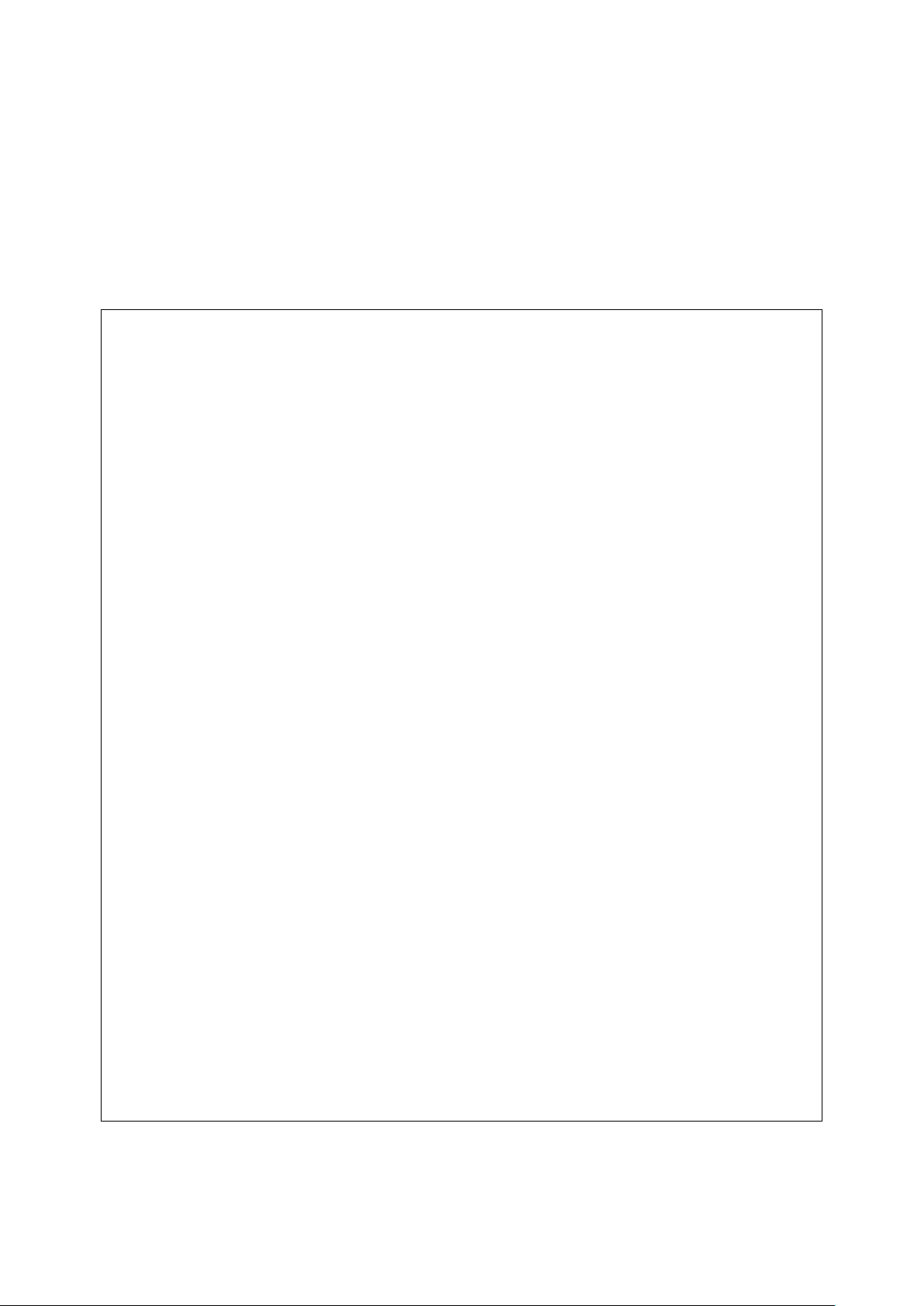
6. The TX/MAM Interface
A
C
The main window shows the information as selected in the left hand menu. In the example
D
The refresh option.
F
Example TX/MAM Interface (including superuser and administrator tabs).
Use the left hand menu to select the information that you want to display in the main window
(C). While a number of items are fixed, this menu can be customized. Items can be added via
the Menu items option [see also paragraph 7.3].
B
The toolbar in the top right corner shows a number of basic options such as ‘Create’, ‘Search’
and ‘Profile’. Options available differ depending on the contents of the main window.
Click the ‘About’ option to view the TX/MAM version and release notes.
above ‘Music videos’ are listed. This is a customized menu item that shows all Assets that
match the query for ‘music videos’.
E
Page and Export Assets options.
Select the number of items to be listed.
The TX/MAM interface is described in more detail in the Quick Reference in chapter 9.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 16
Page 17
7. Configuring TX/MAM
TX/MAM configuration options include:
• Define Users and User groups to manage access and authorization levels for Folders, Asset
Types and Assets.
• Modify the TX/MAM menu to specify customized views on your Assets.
• Define Folders for automatic ingest, asset sharing and export.
• Link jobs to Asset Types.
7.1 Users and User groups
7.1.1 Introduction
TX/MAM lets you define Users and User groups as a means to manage access and authorization
levels for Folders, Asset types and Assets.
• Example Users: Operator, Supervisor and Administrator.
• Example User groups (for a service provider): Customer1 and Customer2.
The table below shows different authorization levels that can be set for Users and User groups.
User group
User
• allowed Asset types;
• allowed Assets (defined when creating an Asset as a property of the Asset,
Assets can be shared with other groups);
• allowed Folders (defined when creating a Folder);
• assign administrator and superuser rights.
• set rights for TX/Dashboard
• allowed applications (Cobalt, TX/MAM);
• authorization levels (create, read, delete, …);
• allowed tabs (Metadata, Essences, …);
• allowed menu items (Inbox and Outbox).
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 17
Page 18

7.1.2 Administrator and superuser
Administrator and superuser rights can be assigned to Groups.
Administrator
and Superuser
Superuser
Read/write rights for:
• Menu Item List;
• User groups;
• Users;
• Categories.
Read/write rights for:
• Folders;
• Options;
• TX-statuses and values;
• Asset Types;
• Asset Jobs.
Example User Group.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 18
Page 19

Example User.
You need superuser or administrator rights to work with Users and User Groups.
7.1.3 Creating or modifying a User Group
Click the User groups menu item.
Click the Add button.
Specify a Name for the group.
Add a short description of the Group in the Description field.
Activate the Administrators option if you want to assign administrator rights to the group [see
paragraph 7.1.2].
Activate the Superuser option if you want to assign superuser rights to the group [see paragraph
7.1.2].
Select the Asset type(s) this group is allowed to work with.
Set rights for TX/Dashboard.
Click Save to save changes, Cancel to discard.
7.1.4 Deleting a User group
Click the User groups menu item.
Select the User group you want to delete.
The Edit group window opens, now click the Delete button. Click OK to delete the group, Cancel
to discard.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 19
Page 20

7.1.5 Creating or modifying a User
Click the Users menu item.
Click the Create button.
Specify a Username.
Specify a Password.
Specify the user’s Real name.
Specify the user’s E-Mail address.
Specify a Secret question.
Specify the user’s Secret answer.
Don’t display metadata tabs: If applicable, specify metadata tabs this user is not allowed to see.
You can specify a Date and Time Format for the User. The ‘a’ (for example hh;mm:ss a)stands
for: AM.
Select the applications the user will be given access to.
Select the User groups the User belongs to.
Specify Authorization level, Tabs allowed to mutate (only visible when the Authorization level
> Mutate option has been activated) and Allowed menu items. See also the Quick reference,
paragraph 9.6 for an explanation of these options.
Click Save to save changes, Cancel to discard.
7.1.6 Deleting a User
Click the Users tab.
Select the user you want to delete.
The View user window opens, now click the Delete button. Click OK to delete the user, Cancel to
discard.
7.1.7 Assigning superuser or administrator rights
Create a Group with superuser or administrator rights: go to User groups > Add > define a group
and select the Administrators or Superuser option > click Save, or Cancel to discard.
Add the User to the Group with superuser/administrator rights: go to Users > select the user >
User groups > add the user to the group with superuser/administrator rights.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 20
Page 21

7.2 Folders
Filename
Asset (external reference)
abc123.mpg
abc123
You need superuser rights to work with Folders.
7.2.1 Introduction
In TX/MAM, Inboxes and Outboxes can be configured. Inboxes (watch folders) are automatically
checked for files. Based on a number of options described in more detail in paragraph 7.2.2, files in
the Inbox are then automatically ingested.
Each Folder is linked to a User Group and Asset Type. Files imported from the Folder are linked to
Assets for the specified User group and Asset Type. Assets are automatically related to the Folder
Asset Type. When ingest has completed, files are moved from the Inbox.
Files and Assets are linked based on the filename (the first part before the file extension) and the
Asset’s external reference. Please find two examples below:
abc123_eng.stl English subtitle belonging to the Asset with ext. reference abc123
Outboxes are used to export files or Assets to an outbox directory on the FTP server. Outboxes are
linked to a User Group. Only Users in the specified User Group are allowed to export to that Folder.
Both Inboxes and Outboxes can be configured on the K2 Storage Server (FTP watch folder), or are
locally available on the TX/MAM server, mostly via a mount on the K2 Storage Server. Both Inboxes
and Outboxes are linked to a User group.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 21
Page 22

Example Folder definition
The Unregistered box is not used at the moment.
How to configure the FTP-server is described in more detail in the FTP-server User Manual.
7.2.2 Adding a Folder
Specify the Folder Name.
Select the appropriate Folder type. Use one of the Local options
Select the User group that has access to the Folder.
Specify the Folder path, either on the K2 Storage server or locally on the TX/MAM server. For
example: endclient\Program.
Allowed extensions: file types that will be imported. Other file types will be moved to a failed
directory.
Specify the File check interval in seconds.
Select applicable Folder options:
Create new Assets: when a file is ingested (automatic ingest via an Inbox) and the related
Asset (based on external reference) does not exist yet, an Asset is created if this option is
activated.
The Asset will have following properties:
• the Asset Type defined for the Folder
• transfer metadata is filled in
• the external reference is set
If this option is not activated, no Asset is created and the file will not be ingested.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 22
Page 23

Allow reingest: when a file is ingested and the related Asset (based on external reference)
already exists, the file will be ingested if this option is activated.
If this option is not activated, the file will not be ingested.
Allow update Assettype: when a file is ingested and the related Asset (based on external
reference) already exists but as a different Asset Type than the folder Asset Type, the file
can be ingested as the folder Asset Type if this option is activated. The Asset Type is
updated to the Folder’s Asset Type.
If this option is not activated, the file will not be ingested.
The imported directory contains files for all Assets that have been ingested. Note that the
Create imported file option should be activated in TX/MAM for the folder to enable this
functionality.
When a file is ingested, a file is created in the imported directory with a name that contains
the Asset’s external reference, size, time and date of ingest if this option I activated. When
this option is not activated, the imported file is not created. By default, these ‘imported’ files
are deleted after 48 hours.
Asset type: Assets are automatically added to the Asset Type specified here.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 23
Page 24

7.3 Menu items
You need superuser or administrator rights to work with Menu items.
7.3.1 Introduction
Custom menu items can be added to the left hand menu. Custom menu items define a view on the
Assets in the TX/MAM database, based on a query. The example below shows a Menu item Music
video, followed by a number of example queries.
Example query showing Assets with Asset Type ID 14.
select id from asset_element where asset_element_type-id=14
Explanation:
• asset_element_type-id=10 means Asset Type with ID=10.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 24
Page 25

Example query showing video files that have not been ingested yet:
select id from Asset_element where updated_date > :today
select id from Asset_element where status_int<>1 and file_extension='avf'
select id from Asset_element where status_int<>1 and file_extension='avf'
Explanation:
• status_int = 1 means that the file has been ingested;
• avf is the default file_extension for video files in TX/MAM.
Example query showing the Assets that are scheduled in the future.
Explanation: the field updated_date corresponds with the last scheduled date, so this query will show
Assets that are scheduled in the future.
Example query showing video files that have not been ingested and are scheduled in the future:
and updated_date > :today
7.3.2 Adding or editing a menu item
In the left hand menu, click Menu items. The Menu items list opens.
To add an item, click the Add button, to edit an item click the menu item you want to edit.
Specify the Menu name as will be displayed in the menu.
In the Insert query.. field, specify a query to filter the Assets you want show.
Specify where to place the new item in the menu in Add after...
Select the Focus tab, this is the tab that will be active when opening the menu item.
Select the tabs that will be visible when opening the menu item in Visible tabs.
Sort Assets by the metadata field selected here.
Specify a Sort direction for the Assets, ascending or descending.
Click Save to save changes.
7.3.3 Deleting a menu item
In the left hand menu, click Menu items. The Menu items list opens.
Click the item you want to delete.
Click the Delete button.
Click OK to delete, Cancel to discard.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 25
Page 26

7.4 Jobs, TX Values and Statuses
7.4.1 Introduction
TX/MAM lets you define Asset jobs and procedures, for example:
• a job to create a low resolution browse copy of files
• a procedure to retrieve information about the Asset’s file transfer status
Jobs and procedures can be linked to Asset Types and will then automatically be executed for all
Assets of that type.
The picture below shows the jobs and statuses linked to Asset Type ‘Music Video’:
• A job Browse copy to create a low resolution copy of files.
The status Browse created will be displayed in the Asset list’s tx_status column.
• A job Get media info, used to retrieve info about file duration and type.
This info can then be displayed in the Asset list.
• A status Asset ingested that uses a procedure to retrieve information about Assets’ file
transfer status.
The status Asset ingested will be displayed in the Asset list’s tx_status column.
Example Asset Type with linked jobs and statuses
TX Statuses are displayed in the Asset list’s tx_status column. The example below shows the Asset
list for Asset Type Music Video. The tx_status column shows the statuses Browse created and Asset
ingested for each Asset. Info retrieved with the Get media info job is displayed in the DURATION
column.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 26
Page 27

The Jobs- tab for an Asset of the list shows the status of jobs Get media info and Browse copy. Note
that the Job status can be manually changed. Jobs can be manually executed if this option is enabled
in the job configuration.
Example Jobs tab
A number of jobs and procedures are configured by default in TX/MAM.
Job configuration is described in more detail in the FTP-server User Manual.
7.4.2 Statuses and values
Each status is linked to a procedure or job and can have a number of values. Values can be
customized. Each value has an ID. Jobs and procedures refer to these IDs. This is explained in more
detail on the next pages.
Example values in TX/MAM
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 27
Page 28

The example below shows the configuration of status Browse created. This status is linked to job
Browse copy. Possible values for this status are Ok, Failed and New.
The status Asset ingested? uses a procedure STATUS_ASSET_INGESTED to retrieve information
about Asset file’s status (Empty, OK or Failed). Procedures can be used to retrieve Asset status
information from the TX/MAM database.
RECREATE PROCEDURE STATUS_ASSET_INGESTED (
ID Integer
)
RETURNS (
CODE Integer,STATUSINT Integer
)
AS
BEGIN
FOR SELECT STATUS_INT FROM ASSET_ELEMENT WHERE ID = :ID INTO :STATUSINT
DO
BEGIN
IF ((STATUSINT = 3) OR (STATUSINT = 0)) THEN
CODE = 1;
ELSE IF ((STATUSINT = 1) OR (STATUSINT = 100)) THEN
CODE = 2;
ELSE
CODE = 3;
END
END
Note how the codes refer to the TX values: code 1=empty, 2=Ok and 3=failed.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 28
Page 29

7.4.3 Workflow values and statuses
1. Define custom TX Values, if applicable.
2. Define an Asset job, if applicable.
3. Add a TX Status and link to the Asset job or specify a procedure.
4. Link Asset types, jobs and statuses.
You need superuser rights to work with Jobs, TX Values and Statuses.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 29
Page 30

7.4.4 Creating or modifying TX Values
In the left hand menu, click TX Values. The TX Values list opens.
To add an item, click the Add button, to edit an item click the value you want to edit.
In the Title field, specify the name for the value.
To change or select an image, click the Browse button to select a TX Image and/or ES Image.
You can use .gif and .png images.
o The TX Image is displayed in the tx_status column.
o The ES Image is displayed on the Essences tab.
Click Save to save changes.
7.4.5 Deleting a TX Value
In the left hand menu, click TX Values. The TX Values list opens.
In the Values list, select the Value you want to delete.
Click the Delete button.
Click OK to delete, Cancel to discard.
7.4.6 Creating or modifying Asset jobs
In the left hand menu, click Asset jobs. The Asset jobs list opens.
To add an item, click the Add button, to edit an item click the job you want to edit.
In the Name field, specify the name for the job.
Job definition: job configuration is described in the FTP-server User Manual.
Under Manual exec select Yes if it should be possible to manually execute the Job.
Add a short job description in the Description field.
Select Possible values this job can have.
Select the Default TX-status value.
Click Save to save changes, Cancel to discard.
7.4.7 Creating or modifying TX Statuses
In the left hand menu, click TX Statuses. The TX Statuses list opens.
To add an item, click the Add button, to edit an item click the status you want to edit.
In the Title field, specify the name for the status.
Now either;
o Select an Asset job config.
o Select a status procedure.
o Select the New procedure option and define a procedure in the Procedure content field.
The usage of procedures and jobs is explained in paragraph 7.4.1.
You can add a description of the status in the Description field.
In the Order field you can specify in which order you want to display statuses in the tx_status
column.
Select Possible values for this status.
Click Save to save changes, Cancel to discard.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 30
Page 31

7.5 Asset Types
You need superuser rights to work with Asset Types.
7.5.1 Introduction
Asset Types group Assets with the same file type and metadata definition.
The metadata definition consists of a default and custom part. In addition to custom metadata fields,
custom TX/MAM tabs can be added. The default tabs are Info and Technical.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 31
Page 32

Example Asset Type in TX/MAM.
Note that Channels are defined in Asset Manager.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 32
Page 33

7.5.2 Creating an Asset Type
To create an Asset Type:
Specify the Asset Type name in the Title field.
Link as essence to type: if applicable, link this Asset Type as an essence to an Asset Type.
For example link subtitles to a Program Asset Type..
Definition XML: to add custom metadata fields for this Asset Type, add the metadata
definition here [see paragraph 7.5.3 for an explanation].
• Transfer protocol: Specify a transfer protocol for files of this Asset Type. Transfer settings
specify amongst others the storage location and are used by the playout_distri process when
fetching files from storage for playout.
o use global config: transfer metadata in
/system/objects/cobassets/bin/transfer_ftp.xml (as set with the
/system/objects/cobassets/bin/set.sh script) is used. Leave the Transfer metadata
field as is: <XML></XML>
o FTP: select this option if you do not want to use the global settings, but specific
transfer settings for this Asset Type:
Example:
<XML>
<FIELD name="username">delta</FIELD>
<FIELD name="password">delta</FIELD><FIELD
name="ip">10.250.51.20</FIELD>
<FIELD name="port">21</FIELD>
<FIELD name="path">/system/ftp-mount/txmam-media/</FIELD>
</XML>
A warning when specifying the value for the path field in the transfer xml:
Paths that start with a slash will be interpreted as an absolute path. Be sure that when specifying an
absolute path that this path is accessible by a FTP-client and the given user/password. This can be
tested using the standard FTP command-line client by trying to change the directory to the desired
absolute path after logging in (e.g. “cd /mydata/media”). (The standard FTP command-line client is
called “ftp”.)
o LOCAL: files are stored on the TX/MAM server.
Leave the Transfer metadata field as is: <XML></XML>
The K2 Edge Smart Playout Center Commissioning and Engineering Manuals describe the Ingest
process and configuration of the Storage Server in more detail.
Required: not implemented yet.
Quality Check Required: activate if a quality check (spotcheck, QC) for Assets of this type is
required. To be implemented.
Select the File extension for Assets of this type. This file extension will be added to files that
are added to this Asset Type.
Select the TX Statuses and Asset jobs that you want to link to this Asset Type.
Note that Asset jobs and TX Statuses should match.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 33
Page 34

Specify the Format that will be linked to Events when an Asset is Plain/CTRL/SHIFT/ALT-
dragged into a POC-Playlist. Use the dummy DFLT format when you do not want to link a
fixed Format.
In TX/MAM, Formats are linked to Asset Types. A dummy Format is available in the Smart Playout
Center installation: DFLT. This Format can be used if you do not want to link a fixed Format to an
Asset Type. Events will initially be scheduled with this dummy Format. Then Format Control can be
used to apply Formats when the Playlist is activated.
Formats can also be linked to Events in the Schedule [see the Schedule Importer User Manual]. The
Format defined in the Schedule will overwrite the Format linked to the Event’s main Asset Type, if
applicable.
7.5.3 Customizing the Asset Type’s metadata definition
The example below shows the custom metadata fields for an Asset Type:
<XML>
<WINDOW width="535" height="200">
<PAGE name="Info">
<LABEL x="10" y="27" height="20" width="80">Title:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="title" x="100" y="25" height="20" width="200"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="10" y="57" height="20" width="80">Description:</LABEL>
<TEXTAREA name="description" x="100" y="55" height="40"
width="400"></TEXTAREA>
</PAGE>
<PAGE name="Technical">
<LABEL x="10" y="27" height="16" width="80">Media type:</LABEL>
<COMBOBOX name="media_type" x="100" y="25" height="20" width="120"
search="true">#13MPEG2-SD#13MPEG2-HD</COMBOBOX>
<LABEL x="10" y="57" height="16" width="80">Aspect ratio:</LABEL>
<COMBOBOX name="aspect_ratio" x="100" y="55" height="20" width="120"
search="true">#134:3#1316:9 Anamorphic#1316:9 Letterbox</COMBOBOX>
<LABEL x="10" y="87" height="16" width="80">Loudness:</LABEL>
<LABEL x="20" y="107" height="16" width="80">Momentary:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="momentary_loudness" x="100" y="105" height="20"
width="45" search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="20" y="127" height="16" width="80">Integrated:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="integrated_loudness" x="100" y="125" height="20"
width="45" search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
<LABEL x="20" y="147" height="16" width="80">Range:</LABEL>
<TEXTFIELD name="loudness_range" x="100" y="145" height="20" width="45"
search="true"></TEXTFIELD>
</PAGE>
</WINDOW>
</XML>
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 34
Page 35

Following tags and attributes are available:
XML
These tags are obligatory and start and end the xml-definition. Example:
WINDOW
Defines the window size (obligatory).
PAGE
Use to define custom tab pages. The default TX/MAM tabs are Info and
Controls
CHECKBOX
Defines a checkbox. Example:
width="100" search="false">label</CHECKBOX>
• <XML>
• <WINDOW>
• <PAGE>
• <CHECKBOX>
• <COMBOBOX>
• <DATETIMEPICKER>
• <LABEL>
• <SPINEDIT>
• <TEXTAREA>
• <TEXTFIELD>
• <TIMECODE>
Attributes
• x,y, width, height
• max
• name
• searchable
• id
Tags and attributes are described below:
<XML> <WINDOW width="400" height="300" scrollwidth="300"
scrollheight="250">controls</WINDOW> </XML>
A scrollbox can be defined (optional).
Example:
<WINDOW width="400" height="300" scrollwidth="300"
scrollheight="250">controls</WINDOW>
Technical. Example:
<WINDOW width="400" height="300" scrollwidth="300"
scrollheight="250" > <PAGE name="tab1">controls</PAGE>
<PAGE name="tab2">controls</PAGE> </WINDOW>
<CHECKBOX name="checkbox" x="90" y="90" height="100"
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 35
Page 36

COMBOBOX
Defines a combobox. Items in the definition must be separated by "#13" (see
the example below). Default, the first item is selected. Example:
DATETIMEPICKER
Defines a date or time picker depending on mode (0=date, 1=time). The format
LABEL
SPINEDIT
Defines a counter spin. Example:
TEXTAREA
Defines a text input box. Max can be used to limit the amount of characters that
width="255" search="false" max="20"></TEXTAREA>
TEXTFIELD
Text input field (single line). Max can be used to limit the amount of characters
TIMECODE
Timecode is a specific time format hh:mm:ss:ff, hours, minutes, seconds and
Attributes
x,y, width, height
These attributes define position and size of metadata fields.
max
Defines the maximum number of characters allowed for text inputs.
name
Defines the column title in TX/MAM.
searchable
Metadata fields are only searchable if "search=true".
id
<COMBOBOX name="combobox" x="90" y="155" height="20"
width="62"
search="true">line1#13line2#13line3#13line4</COMBOBOX>
is optional and depends on the mode used (date or time). Default modes are
"yyyy-MM-dd" for dates and "HH:mm:ss" for time. Example:
<DATETIMEPICKER name="datetimepicker" x="90" y="70"
height="20" width="50"
search="false"format="hh:mm:ss">1</DATETIMEPICKER>
Defines a text label. Example:
<LABEL name="label" x="71" y="2" height="20"
width="40">label</LABEL>
<SPINEDIT name="spinedit" x="90" y="50" height="20"
width="62" search="false"></SPINEDIT>
can be used. Example:
<TEXTAREA name="textarea" x="90" y="0" height="100"
that can be used. Example:
<TEXTFIELD name="textfield" x="90" y="0" height="20"
width="40" search="true" max="20"></TEXTFIELD>
frames. Example:
<TIMECODE name="timecode" x="90" y="90" height="100"
width="100" search="false"></TIMECODE>
Defines the drag order of columns: the attribute: id="0", id="1", id="2" etc.
defines the order of columns when dragging Assets to Playout Control or
Weekplanner.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 36
Page 37

8. Asset Management with TX/MAM
All Assets
To create an Asset, open the All Assets or a custom Asset list.
Create
User group
Select the User group that will have access to this Asset.
Type
Category
Create
Click Create to create the Asset, Cancel to discard.
All Assets
Asset
Click the Asset you want to edit. This will open the Asset.
TX/MAM basic concepts are explained in chapter 4.
You need appropriate user rights to work with Assets. Only superuser or administrator can assign
these rights.
8.1 Creating and editing Assets
8.1.1 Creating Assets
External
reference
Click the
Select the Asset Type the Asset belongs to.
Note that only the Asset Types linked to the User group selected in the previous
field are listed here.
Optional, select a Category.
Note that only Categories linked to the User group and Asset Type selected in
the previous fields are listed here.
Specify the Asset’s external reference.
Assets and essences are linked based on external reference, see also
paragraph 4.1.2.
button.
8.1.2 Editing Assets.
To edit an Asset, select the Asset on the All Assets or a custom Asset tab.
The next paragraphs describe how you can edit Assets.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 37
Page 38

8.2 Ingest
8.2.1 Automatic
Files are automatically ingested via predefined Inboxes. This is a superuser or administrator task
described in more detail in chapter 7.2.
8.3 Sharing Assets
Assets are linked to a User Group, but can be shared with other Groups.
Example Asset being shared with User Group Customer2.
To share Assets with a User Group:
Open the Asset and go to the Sharing tab.
Select the User Group you want to share the Asset with and click Share.
The status of the Asset changes to: Pending.
Example Asset pending for acceptance.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 38
Page 39

Example Asset pending for acceptance in the Customer1's share Outbox.
To accept an Asset that has been shared with your User Group:
Go to the Inbox > share Inbox.
Click the icon to accept the Asset, click the icon to decline.
Once accepted, the Asset disappears from the Inbox and is added to the Asset list.
Example Asset pending for acceptance in Customer2's share Inbox.
Example Asset accepted as shown in Customer1's share Outbox.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 39
Page 40

You can remove an Asset from the share Outbox with the icon.
Delete option.
8.4 Search
To search for specific Assets, click the Search option in the top right corner toolbar.
.
Several filter options are available, including search by Asset Type, metadata field
or status
8.5 Deleting Assets
This option will delete both the Asset's metadata and related files (Essences).
To delete an Asset, select the Asset, then in the top right corner toolbar click the
8.6 Profile
Use this option to modify your user's credentials or email address. To edit:
Log in with the user you want to edit.
Click the Profile option, then modify properties. Note that credentials are
case sensitive.
Click Save to save changes.
8.7 About
Show versions and release notes.
8.8 Editing an Asset's metadata information
To view or edit an Asset's metadata fields:
Double-click the Asset, then select the applicable metadata tab.
Edit the metadata fields.
To save changes, click Save.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 40
Page 41

8.9 Spotcheck and soft parts
This file has not been checked.
This file has been checked and quality was not good.
Use the Spotcheck function to preview the quality of clips and to create soft part segments.
Example Spotcheck tab.
8.9.1 Quality Check (QC)
Double-click the Asset you want to view, then select the Spotcheck tab.
Click the icon for the clip or segment you want to preview.
Use the control buttons, shuttle control and timeline to navigate through the clip.
When finished, click the appropriate QC status icon (the default icons are listed below):
This file has been checked and quality was good.
8.9.2 Creating Segments
Double-click the Asset you want to trim, then select the Spotcheck tab.
If you want to trim the main Asset you can skip the next two steps.
If you want to create a Segment from the main Asset, click the create segment
button.
Specify the external reference and click Save.
Click the icon for the clip or segment you want to edit.
Use the control buttons, shuttle control and timeline to navigate through the clip.
Click the tc-in and tc-out buttons to set timecode in and out.
Save tc-in/out to: select the main Asset or Segment you want to save time codes to.
Segments can be scheduled (drag and drop into POC), but are not listed in the Assets list.
8.10 Checking and modifying Job status
To view the Jobs linked to an Asset:
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 41
Page 42

Double click the Asset, then select the Jobs tab. Information on the Jobs tab includes status
(configurable), job start date and time and description.
To manually change the status of a Job;
Click the icon and select the appropriate status.
Example Change Job status window.
Click Ok to confirm changes, Cancel to discard.
This option changes a Job's status, but does not restart the Job. This can be done by manually
executing a Job, if this option is configured for that Job.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 42
Page 43
8.11 Exporting Assets and Files
To export Essence files to the FTP-server:
Go to the Asset's Sharing tab > Export.
Files will be exported to the specified outbox on the FTP-server. The Outbox menu shows the
assets which are exported. Assets are removed from the Outbox when transfer has
completed.
To export Asset info as a CSV-file:
Open the applicable Assets list.
Click the Export Part option to export the current page to a given location.
Click the Export All option to export the list to a given location.
Note: The columns which are shown in the asset list are exported to the csv-file.
8.12 History
Use this option to view an Asset's history, or to add comments to an Asset. To display:
Double click the Asset, then select the History tab.
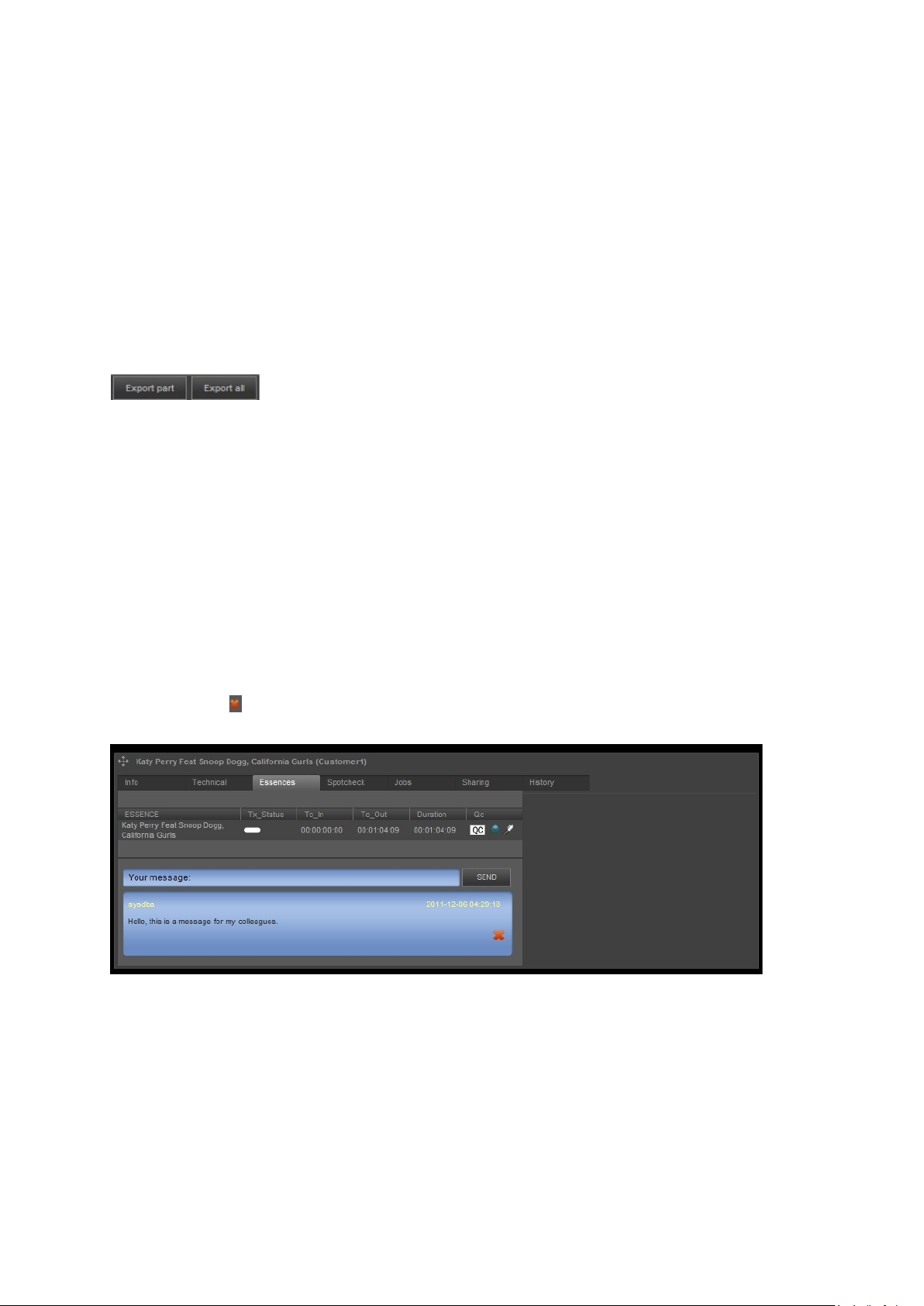
8.13 Adding comments to Assets
To add comments to an Asset:
Enter information in the message box, then click SEND.
Comments will be displayed in the Asset window.
Click the icon to remove a message.
Example message displayed in Asset window.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 43
Page 44

8.14 Customizing the Asset list
The columns in an Asset list show the metadata fields defined for Assets of that type. To display
additional columns:
Right-click the list.
Select the columns you want to add.
Example customize columns.
To change the number of items listed or go to another page, use the options at the bottom of
the list.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 44
Page 45

9. Quick Reference
9.1 Toolbar
Create item.
Add item.
Save item.
Close item.
Delete item.
Search option.
Edit profile (current user).
Logout.
9.2 Export options in the Assets list
Export all Assets in the list to a CSV-file.
Export Assets on the current page to a CSV-file.
9.3 Assets
9.3.1 Info, technical and other metadata tabs
These tabs show metadata info as defined in the metadata definition.
To edit, edit fields, then click Save.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 45
Page 46

9.3.2 Essences tab
Tx-status
The status of file ingest. Note that these status icons can be customized.
Tc_in
Timecode in.
Tc_out
Timecode out.
Duration
File duration in hh:mm:ss:ff.
Filesize
File size
Indicates the status of a file’s quality check (spotcheck).
Note that these status icons can be customized. The default icons are:
This file has not been checked.
Drag file or segment into POC to schedule an Event. The Event is scheduled with
the default Format.
External_ref
External reference, click to edit.
Tx-status
The status of file ingest. Note that these status icons can be customized.
Tc_in
Timecode in.
Tc_out
Timecode out.
Duration
File duration in hh:mm:ss:ff.
Note that these status icons can be customized. The default icons are:
Click to edit the essence.
9.3.3 Spotcheck tab
This file has been checked and quality was good.
This file has been checked and quality was not good.
Use the control buttons, shuttle control and timeline to navigate through the clip.
Indicates the status of a file’s quality check (spotcheck).
This file has not been checked.
This file has been checked and quality was good.
This file has been checked and quality was not good.
Click to start a (low-res) preview.
Click to edit an essence or segment.
Save tc-in/out
to:
Click the tc-in button to set timecode in.
Click the tc-out button to set timecode out.
Select the main Asset or Segment you want to save time codes to.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 46
Page 47
Click to add a segment.
Click to set a QC-status for the selected file or segment.
Tx-status
Job status. Note that Job statuses can be customized.
Click to manually change the Job status. Note that status is changed, but the Job is
not re-executed.
STARTED
Start date and time for this Job.
Manual Exec
Jobs can only be manually executed if this option is configured. If so, the tool-icon is
Export an Asset’s Essence files to the FTP-server, see chapter 8.11 for an
9.3.4 Jobs tab
Shows the Jobs linked to an Asset and their status.
listed in this column. Click to execute the Job.
9.3.5 Sharing tab
Assets can be shared or exported on the Sharing tab. When shared, this tab shows if the Asset has
been accepted.
Share an Asset with another User Group, see chapter 8.3 for an explanation.
explanation.
9.3.6 History tab
The Asset’s History describes all Asset Jobs or user actions performed for the Asset.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 47
Page 48

9.4 Asset Type window
Option
Description
Title
Definition XML
The Asset Type’s custom metadata definition.
Transfer protocol
Specify a transfer protocol for files of this Asset Type. Transfer settings
Required
Not implemented yet.
Quality Check Required
Activate if a quality check for Assets of this type is required.
TX Statuses
Plain/CTRL/SHIFT/ALT
Specify the Format that will be linked to Events when an Asset is
Save
Example Asset Type window.
Link as essence to type
Asset jobs
The Asset Type name.
If applicable, link this Asset Type as an Essence to an Asset Type. For
example link voice overs or subtitles to a clip.
specify amongst others the storage location and are used when fetching
files from storage.
Select the TX Statuses and Jobs that apply for Assets of the type
defined here. Note that Asset jobs and TX Statuses should match.
drag format
Plain/CTRL/SHIFT/ALT-dragged into a POC-Playlist. If you do not want
to link a fixed Format, use the DFLT dummy Format.
Click to save changes.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 48
Page 49

9.5 User group window
Name
Description
Description of the User Group.
Administrators
Activate to assign administrator rights to the Group.
Superuser
Asset Type
Select the Asset Type(s) this User Group has access to.
TX/Dashboard
Select the TX/Dashboard options this User Group has access to.
Save
Click to save changes.
Example User group
Option Description
User group name.
Activate to assign superuser rights to the Group.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 49
Page 50

9.6 Users window
Option
Description
Username
Username.
Password
E-Mail
The user’s e-mail address.
Secret question
Secret question.
Secret Answer
Secret answer.
Don’t display metadata..
Date Format
Select a data format for this User.
Time Format
Select a time format for this User.
Applications
Example User window.
Real name
Password.
The user’s real name.
If applicable, specify metadata tabs this user is not allowed to see,
comma separated.
Applications the user is authorized for:
• Channel Composer
• Weekplanner
• Cobalt
• TX-MAM
• POC
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 50
Page 51

• TX/Dashboard
User groups
Authorization level
Create
The user is allowed to create Assets.
Read
The user has read rights for the Asset folders.
Delete
Download
The user is allowed to export files.
Upload
The user is allowed to accept shared Assets.
Allow Drag&Drop
The user is allowed to drag Assets into POC.
List Export
Allowed menu items (list)
<Menu items>
Select the Menu items the User has access to.
Tabs allowed to mutate (only available when the Mutate option is active)
Metadata
Spotcheck
The user is allowed to perform Quality Checks and soft parting.
Jobs
The user is allowed to view and change job statuses.
Sharing
Save
Select the User Group(s) the User belongs to.
The user is allowed to delete Assets.
Mutate
Essences
The user can edit allowed tabs [see below].
The user is allowed to export Assets from an Asset list.
The user is allowed to edit metadata.
The user is allowed to view essences.
The user is allowed to share Assets.
Click to save changes.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 51
Page 52
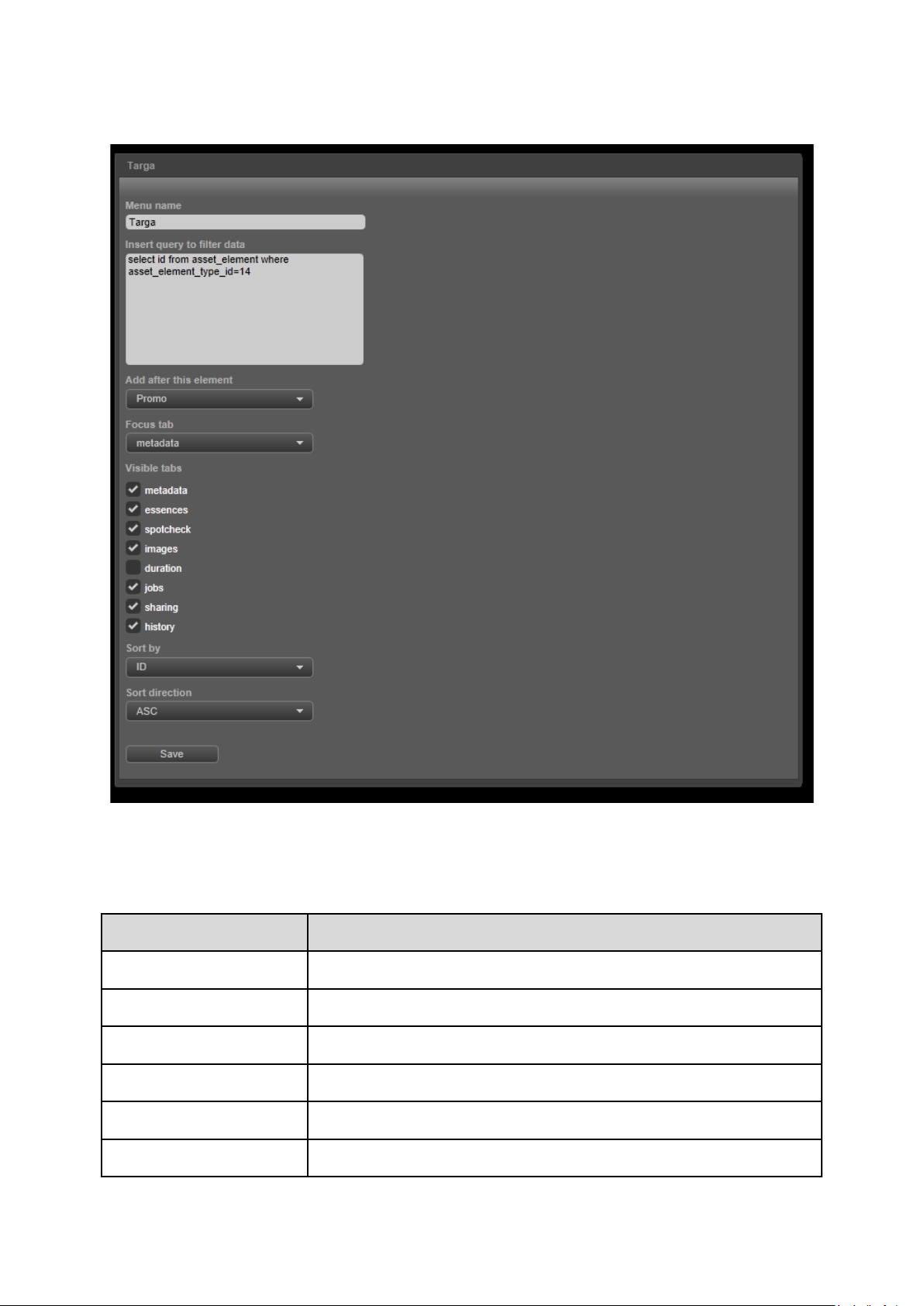
9.7 Menu items window
Option
Description
Menu name
Name of the menu item (as will be displayed in the menu).
Insert query ..
Specify a filter query here.
Add after ..
Visible tabs
The tabs that will be visible when opening the menu item.
Sort by
Sort Assets by the property selected here.
Example.
Focus tab
Specify the menu order here.
The tab that will be active when opening the menu item.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 52
Page 53

Sort direction
Save
Click to save changes.
Name
The Folder name.
Folder type
The Folder type:
9.8 Folders window
Assets sort order; ascending or descending.
Example Folder window.
Option Description
• (Inbox) FTP watch folder: not implemented.
• (Inbox) Local FTP folder
• (Outbox) FTP push folder: not implemented.
• (Outbox) Local push folder
Explanation:
• Watch folder: this folder is automatically checked for files for
ingest.
• Push folder: files can be (manually) exported to this folder.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 53
Page 54

FTP: folder on the K2 Storage Server.
User group
The User Group that has access to the folder.
Folder path
Folder path.
Allowed extensions
Folder options
Create new Assets
When a file is ingested (automatic ingest via an Inbox) and the
Allow reingest
Allow update Assettype
Create imported file
Select to create ‘imported’ files.
Asset type
Assets are automatically added to the Asset Type specified here.
Save
Click to save changes.
• Local: folder on the TX/MAM server, mostly via a mount on
the K2 Storage Server.
File types allowed in this folder.
File check interval
Interval in seconds at which the folder is checked for files.
related Asset does not exist yet, an Asset is created if this option
is activated.
(Files and Assets are linked based on the Asset’s external
reference. This is the filename without extension.)
The Asset will have following properties:
• the Asset Type defined for the folder;
• transfer metadata is filled in;
• the external reference is set.
If this option is not activated, no Asset is created and the file will
only be ingested if the Asset already exists.
When a file is ingested and the related Asset (based on external
reference) already exists and has content, if this option is
activated the file will be ingested.
If this option is not activated, the file will not be ingested.
When a file is ingested and the related Asset (based on external
reference) already exists but has a different Asset Type than the
folder Asset Type, if this option is activated the file can be
ingested with the folder Asset Type.
If this option is not activated, the file will not be ingested.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 54
Page 55

9.9 TX Values window
Option
Description
Image
Select the image you want to link to this status.
TX Image
To change or select an image, click the Browse button to select a
Save
Click to save changes.
Example TX Values window.
Title
ES Image
The value’s name.
TX Image and/or ES Image. You can use .gif and .png images.
The TX Image is displayed in the tx_status column.
The ES Image is displayed on the Essences tab.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 55
Page 56

9.10 TX Statuses window
Option
Description
Title
Specifies the name for the status.
Asset job config
Either:
Description
Status description.
Order
Possible values
Possible values for this status.
Save
Click to save changes.
Status procedure
Procedure content
Select an Asset job config.
Select a status procedure.
Select the New procedure option and define a procedure in
the Procedure content field.
Specifies in which order statuses are displayed in the tx_status
column.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 56
Page 57

9.11 Asset jobs window
Option
Description
Name
Specifies the name for the Job.
Job definition
Manual exec.
Select Yes if the job should be manually executable.
Description
A short Job description.
Possible values
Select the values this Job can have. These possible values are
Save
Click to save changes.
Example Asset jobs window.
Select Possible values this job can have.
Select the Default TX-status value.
Click Save to save changes, Cancel to discard.
In the left hand menu, click TX Statuses. The TX Statuses list opens.
Job configuration is described in the FTP-server User Manual.
shown when editing the job status.
Default TX-status value Select the default TX-status value. The default is used when a
new asset is created.
TX/MAM User Manual - document version: 2.2 – Page 57
 Loading...
Loading...