GE Consumer & Industrial
Power Protection
High Speed DC Circuit Breaker
Gerapid 2607, 4207, 6007, 8007
with arc chutes 1X2, 1X4, 2X2, 2X3, 2X4
USER MANUAL
2010-06-07 S47183-E rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 1

2 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

INDEX
1. WARNINGS........................................................................................... 4
2. GENERAL USAGE CONDITIONS................................................... 4
2.1 Transportation and storing ..................................................... 4
2.2 Installation....................................................................................... 5
2.2.1 Operational environment................................................. 5
2.2.2 Installation and interfaces............................................... 5
2.3 Usage................................................................................................. 5
2.3.1 Supply and load ...................................................................5
2.3.2 Adjusting the over current release.............................. 5
3. TECHNICAL INFORMATION ........................................................... 6
3.1 Introduction.................................................................................... 6
3.2 Components and accessories................................................6
3.2.1 Contact system ....................................................................6
3.2.2 Arc chute (Code 2)................................................................ 6
3.2.3 Mechanism ............................................................................. 7
3.2.4 Over current release (Code 7)....................................... 7
3.2.5 ED impulse coil release (Code 12).................................8
3.2.6 Auxiliary tripping devices (Code 11)............................8
3.2.7 Forced tripping release (Code 13)................................ 8
3.2.8 Lever for manual operating (Code 16)...................... 9
3.2.9 Auxiliary switch (Code 9) ................................................10
3.2.10 Indicators............................................................................10
3.2.11 Solenoid closing drive (Code 3).................................10
3.2.12 Current measurement system (Code 6) ...............11
3.2.13 Electronic control system............................................11
3.3 Technical data tables...............................................................13
4. ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS...................................................................15
4.1 Controls layout............................................................................15
4.2 Terminals wiring system ........................................................16
4.3 Electrical diagrams....................................................................17
4.3.1 Wiring code...........................................................................17
4.3.2 Controls supply circuit.....................................................18
4.3.3 ED coil with external capacity bank .........................19
4.3.4 NEKO control circuit .........................................................20
4.3.5 SU control circuit................................................................21
4.3.6 Shunt trip control circuit.................................................22
4.3.7 Zero voltage release control circuit..........................24
4.3.8 Indicators...............................................................................25
4.3.9 Auxiliary switch...................................................................26
4.3.10 SEL measuring system.................................................27
5. DIMENSIONS & SAFETY DISTANCES........................................28
5.1 Safety distances.........................................................................29
5.2 Outlined dimensions.................................................................30
5.2.1 Gerapid 2607,4207, 6007 with arc chute 1x_......30
5.2.2 Gerapid 2607, 4207, 6007with arc chute 2x_......31
5.2.3 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 1x_...............................32
5.2.4 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 2x_...............................33
5.2.5 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with H / H terminals...............34
5.2.6 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with V / V terminals................35
5.2.7 Gerapid 6007 terminals..................................................36
5.2.8 Gerapid 8007 terminals..................................................37
6. INSPECTIONS AND MAINTENANCE.........................................38
6.1 List of inspections......................................................................38
6.1.1 General visual inspection...............................................39
6.1.2 General functional inspection......................................39
6.1.3 Inspection of the arc chute...........................................39
6.1.4 Inspection of the contact system..............................40
6.1.5 Inspection of contacts’ tilt and gap ..........................41
6.1.6 Inspection of the screw connections.......................41
6.1.7 Inspection of the mechanical components ..........41
6.2 List of maintenance works....................................................42
6.2.1 Contact system (after 11/2003)..................................43
6.2.2. Contact system (before 11/2003). .............................44
6.2.3 Layout of control PCB inside control box...............46
6.2.4 Replacement of the control boards..........................46
6.2.5 Adjusting the auxiliary switch......................................48
6.3 Spare parts lists..........................................................................49
6.3.1 Mechanical spare parts..................................................49
6.3.2 Electrical spare parts.......................................................50
6.3.3 Recommend materials for selected works............50
7. CUSTOMER SUPPORT....................................................................51
7.1 Options overview. ......................................................................51
7.2 Ordering. ........................................................................................52
7.2.1 Example of order no. 1....................................................53
7.2.2 Example of order no. 2....................................................54
7.2.3 Example of order no. 3....................................................55
7.3 Glossary .........................................................................................56
7.4 Troubleshooting..........................................................................57
7.5 GE service teams........................................................................58
7.6 Notes................................................................................................59
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 3

1. Warnings
Warnings:
During operation, electrical equipment carries
dangerous voltages. In addition, circuit breaker
emits hot, ionized gases when switching
currents, especially short circuit currents.
Installing, commissioning, maintaining, changing
or refitting of this equipment must be carried out
only by qualified and suitably trained personnel
and under strict observation of national and
international applicable safety regulations.
During their operation, circuit breakers must be
equipped with appropriately fitted covers, e.g. in
suitable enclosures or panel boards. Safety
distances must be preserved. Suitably trained
service personnel shall only carry out certain
works.
Non-compliance with these warnings may result
in death, and/or severe physical damage and
extensive damage to equipment.
Prior to carrying out maintenance, inspection or
checks, the circuit breaker must be open, the
both terminals must be grounded, the circuit
breaker must be switched off and the control
plugs removed.
Manual activation of the breaker while energized
is forbidden. Manual activation must only be
used for maintenance and inspection purposes,
when breaker power is off and grounded.
The circuit breaker consists of high energy
moving components. Do not touch the circuit
breaker while it is being switched ON (closing) or
OFF (opening). There is a high risk of major injury.
The control circuits may include capacitor banks,
which can be charged with dangerous voltages.
Work on this section must be carried out
carefully.
2. General usage conditions
2.1 Transportation and storing
• The breaker is transported on wooden palette. It is fixed
by shrunken plastic film. A cardboard box covers the
breaker on the palette. Truck, railway, airplane and ship
transport is possible. In case of sea transport, special
protection against salty and humid environment is
provided.
• The circuit breaker must always be transported to the
installation site vertically and fully packed. The packaging
protects the device against damage and dust; it should
only be removed prior to installation.
• If the packaging is damaged, the breaker and the arc
chute must be inspected for damage. Ensure that all
packaging materials have been carefully removed prior to
breaker installation.
• For handling the unpacked breaker use canvas slings and
position them below the closing drive (a) and below the
lower terminal (b) [Fig. 1].
Fig. 1 Handling the breaker
• WARNING: Breaker and arc chute must be transported
separately. Never handle the breaker with arc chute
installed at!
• Take care that the bottom isolation plate of the unpacked
breaker is not damaged during handling. Do not push the
breaker back and forth on any rough surface.
• The breaker’s weight, including arc chute is listed in Table
1, page 13. Arc chute’s weight is ca. 30 kG (66 lb) for “1x_”
type, and ca. 60 kG (132 lb) for “2x_” type
WARNING:
• Store in original packaging!
• Do not store outdoors!
• Use protection against crush and blow!
• Do not store the breaker in a damp area!
• Storing temperature-range –25 °C…+55 °C!
4 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

2.2 Installation
2.3 Usage
2.2.1 Operational environment
• The breaker, as delivered, is IP00 (NEMA 1) protected. It is
intended to work in indoor applications, without
pollutions, with non-conductive dust, protected against
high humidity and condensation. Low conductivity dust
deposit due to frequent condensation of humidity is
acceptable. General environmental conditions refer to EN
50123-1 - annex B, and IEC 60947, class PD3.
• The breaker can operate at rated current within ambient
temperature range of –5 °C to +40 °C (23 to 104 °F).
Maximum operating ambient temperature is +55 °C
(130 °F) with continuous current derated by 10 %.
• The breaker can operate at altitude up to 2000 m
(~6500 ft) without derating.
• The breaker shall not be subjected to strong vibrations.
Maximum vibrations of 0.5 g per 30 sec in vertical and
horizontal directions are allowed.
• Air shall be clean and its relative humidity shall be not
more than 50 % r.h. at the maximum temperature of
+40 °C (104 °F). Relative humidity may be higher if the
temperatures are lower, for example, 90 %r.h. at +20 °C
(68 °F). Slight condensation might occur during variations
of temperature
2.2.2 Installation and interfaces
• The lower and upper main terminals (Code 4) must be
connected directly to the main cables or bus bars.
• WARNING: The breaker must only be used in an upright
operation position with the arc chute in place and fully
secured.
• After arc chute installation check for tightness both
connections to the arc runners. See drawing 49, item 3.
• The safety distances as listed in section 5.1 shall be
maintained to grounded or insulated parts. Suitable
measures must be taken to protect personnel from arcs.
• Strong, external magnetic fields, caused by improperly
located supply conductors or stray fields from other
devices, can lead to a shift of the trip setting thresholds.
This may result in premature tripping, or no tripping at all
during low-level short circuit current events. This has to
be accounted for when installing and operating the
device with shielding added if appropriate.
• The control wires must be connected to the control
terminals (Code 19), as shown in the schematic circuit
diagrams in section 4. The protective grounding wire must
be connected at the marked contact [Fig. 2].
2.3.1 Supply and load
• In accordance with its type, the breaker has been
designed for the current and voltage listed in Table 1,
section 3.3.
• During continuous operation, breaker must only be
loaded up to its maximum rated current. Load currents in
excess of breaker nameplate rating are allowable for brief
periods. Refer to the short time currents listed in Table 1.
• Do not exceed the rated operating voltage shown on the
breaker’s nameplate.
• Supply voltage for the drive and the auxiliary-tripping
devices (Code 8) shall be within the specified control
voltage range. Maximum current values for the auxiliarytripping devices are listed in Table 2a.
• WARNING: Plugging in or unplugging of the auxiliary
connectors (-X2 :1/:2) (-X3 :4/:5) is only allowed with
disconnected primary (mains) and secondary voltages.
2.3.2 Adjusting the over current release
• OCT is an over-current tripping release (Code 7), which
trips and releases the breaker in case of overload or short
circuit currents. This is an instantaneous and direct acting
device.
• If equipped with an adjustable OCT, the response
threshold can be easily adjusted [Fig.3], by turning the
adjustment nut 1 with a SW6 hexagon wrench 2.
• The adjustment must only be carried out after the breaker
has been disconnected from the main circuit. For fixed
installations breaker’s main terminals shall be grounded.
• Turning the adjustment screw clockwise increases the trip
threshold, turning the screw counter-clockwise decreases
the tripping threshold.
• Align the arrow and the desired marking 3, to perform
adjustment.
SW 6
Fig. 3 Setting of the OCT unit
Fig. 2 Termination for grounding wire
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 5
3. Technical information
3.2 Components and accessories
3.1 Introduction
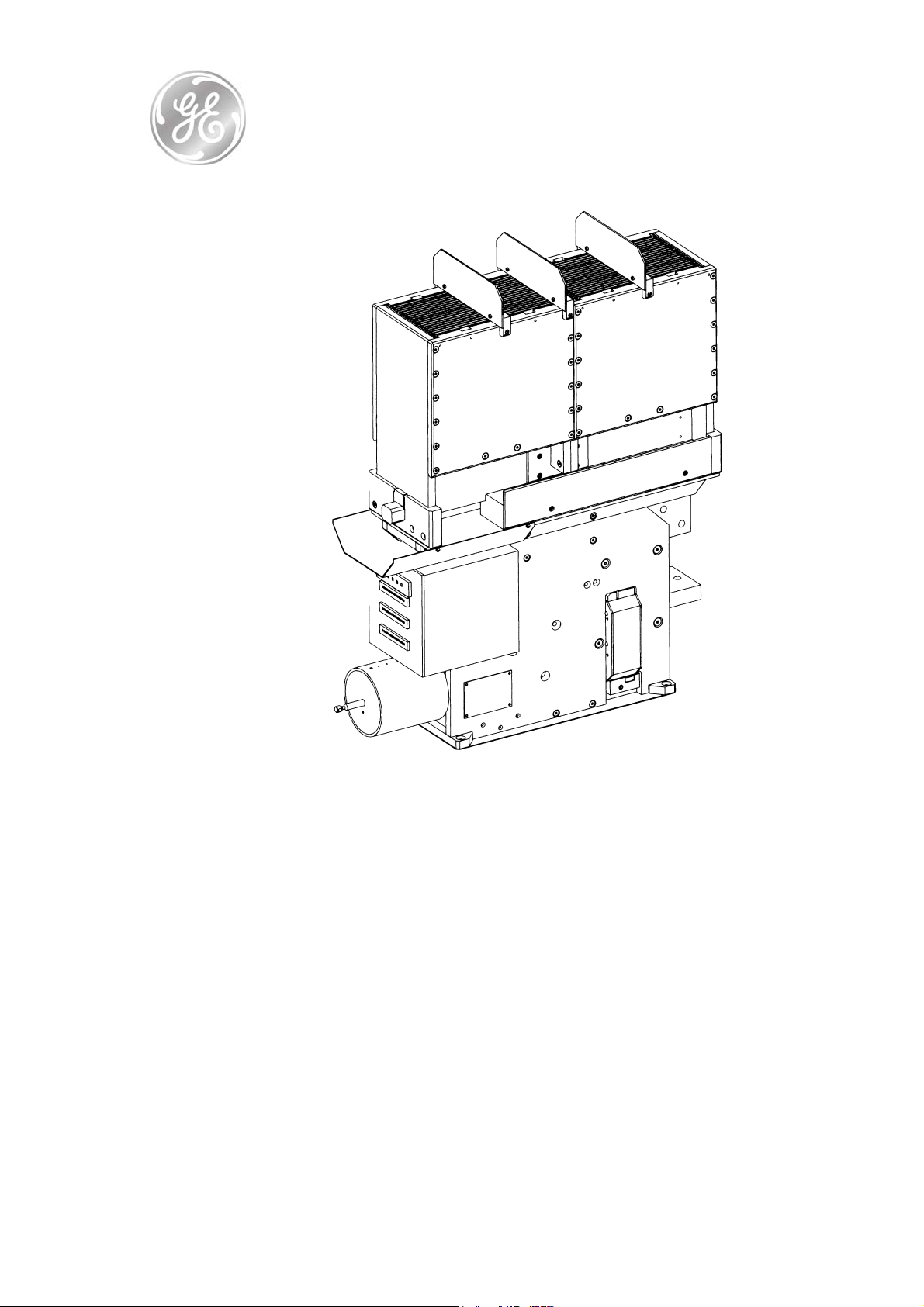
• Gerapid is a high-speed DC circuit breaker. This is a
single-pole DC breaker, primarily designed for use in
railway power distribution systems with operating
currents up to 8000 A (Code 1) and operating voltages up
to 3600 V (Code 2). Additional applications are special
industrial plants such as electrolysis, mining or steel mills.
• Gerapid breaker has a very high interruption capacity
combined with a current limiting characteristic. The arc
chute works on the basis of an asbestos-free arc splitting
principle.
• A wide variety of accessories and spares are available for
maintenance, repair, or as a possible enhancement.
• Use the catalogue coding system described in section 7.1
to configure the breaker. Each rating, option or accessory
has own code.
• Closing of the circuit breaker is performed through a highpower solenoid drive (Code 3).
• During inspections, opening and closing may be carried
out by means of a hand lever (Code 16), which is mounted
onto the armature of the closing drive.
• Overload tripping and release is obtained directly by
means of the OCT release (Code 7), or optionally by ED
impulse release (Code 12). Indirect remote tripping can be
achieved by means of a shunt trip, or optionally by a zero
voltage release (Code 11).
• Gerapid breakers have a compact and enclosed
construction [Fig. 4]. Gerapid is IP 00 protected. All parts
are mounted on thick-walled, non-breakable and
fireproof insulation panels.
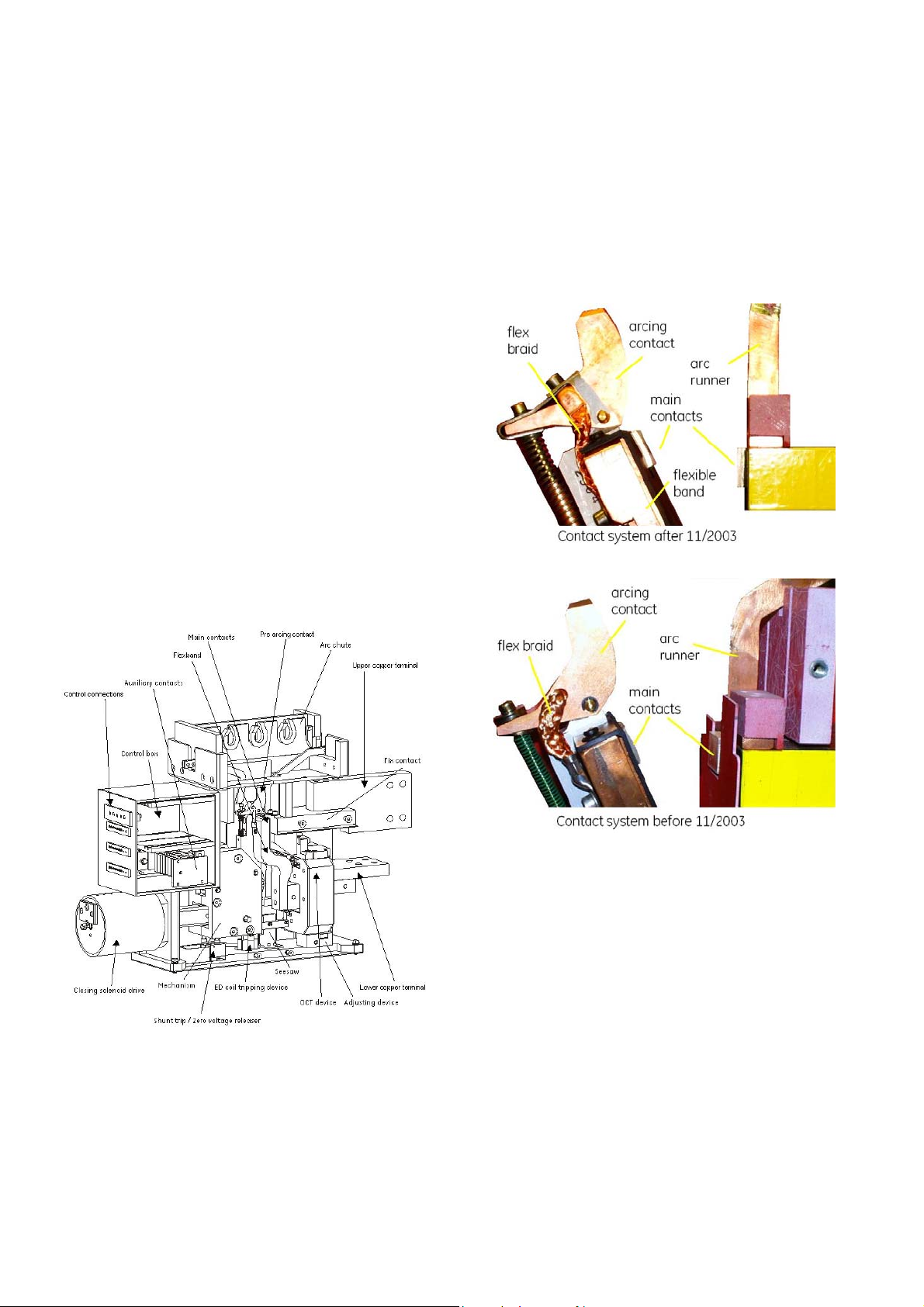
3.2.1 Contact system
• All Gerapid breakers are equipped with a two-stage
contact system [Fig. 5], consisting of a main contact and
an arcing contact. With this proven design, the main
contact is not subjected to any appreciable wear or tear.
• The main contact is made of a silver composite material.
The arcing contact and link braid are made of copper and
can be easily replaced.
• The flexible bend is linked to the arcing contact by means
of very tight braid.
Fig. 5 Two types of the contact system
3.2.2 Arc chute (Code 2)
• Compact and modular design of the arc system requires
no additional magnetic support and allows small safety
distances with high breaking capacity.
• Because of the compact dimensions, these breakers can
be installed in extremely small enclosures (from 500 mm;
Fig. 4 Modular construction overview
6 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
1.65 ft) and offers a cost-effective solution for
replacements.
• An adaptor [Fig.43] is used to mount the various arc
chutes for different operating voltages on the breakers.
• The arc chutes consist of a highly durable, arc-proof
material, in which the arc plates have been integrated.
• The arc plates split the arc into partial arcs and increase
the arcing voltage by multiplying the anode and cathode
voltage drop. Because of their high heat capacity, the
plates and arc chute walls absorb a large amount of the
arc’s energy.
3.2.3 Mechanism
• The Gerapid is equipped with a modular designed
mechanism, which is wear-resistant and nearly
maintenance-free. This mechanism ensures an extended
electrical and mechanical endurance of the breaker as
well as a high level of safety under all operation
conditions.
• Breaker can operate 20 000 cycles when opened by the
shunt trip or zero voltage release, and 1 000 operations
by means of ED impulse coil or OCT releases.
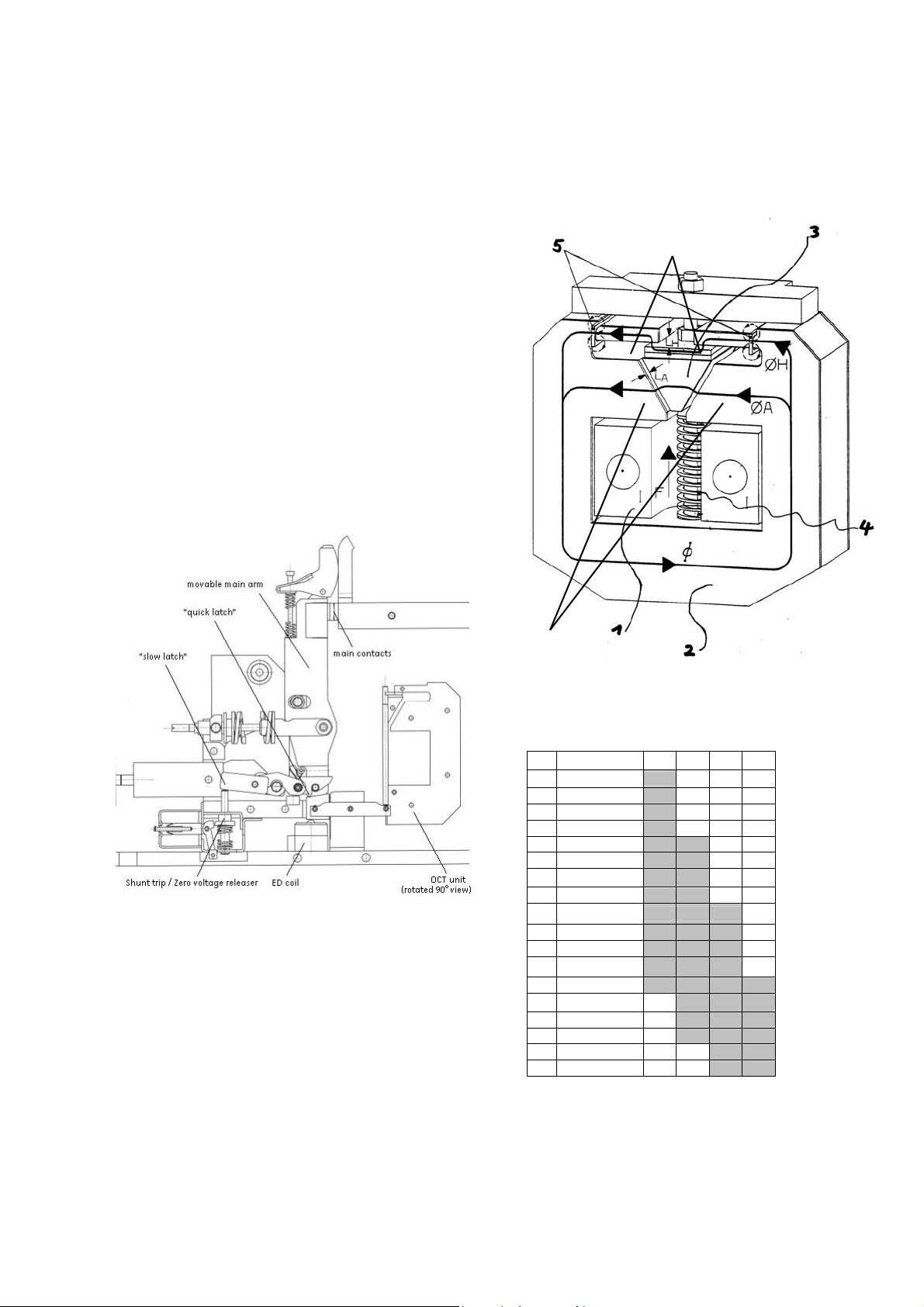
• This mechanism is mechanically latched in the CLOSED
position. The principle of a mechanically latched
mechanism offers a big advantage compared to often
used electro magnet holding system. No auxiliary control
power source is required to keep breaker closed.
• The mechanism is provided with two tripping latches
[Fig. 6]. First latch, called “slow latch”, is used for opening
under normal conditions, like actuation of shunt trip or
zero-voltage release. The second one, “quick latch”, declutches the main contact arm from the mechanism and
opens the contacts with an extremely short delay. This is
used when interrupting short-circuit or overloads. All
safety releases operate onto “quick latch” latch.
• Different main springs are used in mechanisms for
different breaker frames. Therefore mechanisms cannot
be exchange between breakers of different frame.
which releases the quick latch in the mechanism. The
latch and contacts are opened immediately.
• The response threshold can be easily adjusted by turning
the adjustment nut with a SW6 hexagon wrench. The
available ranges are described in the table below. Other
ranges might be possible on request.
• When supplied with the optional transparent side
protection covers (Code 15), a fixed mounted insulated
knob is provided to enable OCT adjustment [Fig. 16].
6
Fig. 6 Latching and tripping system
3.2.4 Over current release (Code 7)
• The OCT release is a magnet with two magnetic circuits,
optimizing the twin magnetic field principle [Fig. 7]. This
technology ensures equally fast tripping in both current
directions. This system does not require an auxiliary
control voltage to operate. It is a direct acting and
instantaneous tripping device.
• The OCT consists of the holding circuit [6], the movable
armature [3] and the tripping circuit [7]. The holding and
the tripping magnetic circuits are both excited by load
current [1]. Until the static overload release’s response
threshold has been reached, the armature [3] is held in
position by the holding flux (ΦH) [2] and the counter
spring’s force [4]. Once the load current exceeds the set
static response threshold, the attraction flux (ΦA) [2] takes
over and rapidly pulls down the flexible armature [3].
During this operation, the armature hits the seesaw,
7
Fig. 7 OCT device.
Default tripping bands for the OCT release 1).
No
OCT band 2607 4207 6007 8007
1 1,5 kA - 2,5 kA
2 1,5 kA – 3 kA
3 1,5 kA – 4 kA
4 1,5 kA – 5 kA
5 2 kA – 6 kA
6 2 kA – 7 kA
7 2 kA – 8 kA
8 2,5 kA - 5,5 kA
9 3 kA – 7 kA
10 3 kA – 8 kA
11 3 kA – 9 kA
12 3 kA – 12 kA
13 5 kA – 10 kA
14 6 kA – 14 kA
15 7 kA – 15 kA
16 8 kA – 18 kA
17 10 kA – 16 kA
18 12 kA – 24 kA
1) Customer specific bands on request.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 7
3.2.5 ED impulse coil release (Code 12)
• ED impulse release requires an external protective relay
for monitoring a current increase. This relay must be
provided and installed by the customer.
• If a fault occurs, an external relay signal wired into the
capacitors’ control unit (internal NEKO or external C-bank),
causes NEKO unit to discharge its energy into ED coil [Fig.
8]. The coil trips the breaker’s quick latch and opens
breaker’s contacts in less 3ms.
• ED impulse release is an optional accessory. Complete set
consists of ED coil and electronic control unit with C-bank
called NEKO. The external release signal shall be 6 V to
24 V DC, and shall be connected at terminals (-X2 :10 /
:11) in standard wiring scheme.
• Customer supplied capacitor trip unit may be used. Rated
voltage of 300 V and capacity of 2 000 µF is required. In
this case only ED coil will be installed in the breaker.
• WARNING: Firing signal voltage level is between 6 V and
24 V. There should be no spikes on the signal of duration
less 3 ms. This can lead to defect of the NEKO board!
• WARNING: Maximum duration of the firing signal must
not exceed ~1 sec. Longer signal can lead to NEKO
overheat! It is recommended to use an auxiliary contact
in serial connection with firing circuit (-X2 :10/:11). It will
automatically cut off the firing circuit after breaker
opening.
• The UVR [Fig. 9] is used for remote actuation and, in
combination with an internal electronic control, for
voltage control.
• The UVR releases at voltage interruption or supply voltage
drop below 20 V. In these cases UVR trips the breaker. It is
therefore possible to use this device in combination with
the electronic trip unit for voltage monitoring, where an
unintended re-start of machines after a temporary
voltage breakdown is to be prevented.
• The UVR is intended for continuous operation. Its rated
power is 10 W.
• Due to its operational mode, the UVR is a self-monitoring
device, i.e. when the breaker is tripped upon a break of
the pilot wire (EMERGENCY-OFF principle).
• NOTE: Manual closing of the breaker with ST installed,
while pushbutton OPEN is pressed and control power
applied, might lead to ST coil’s overheating and damage.
Fig. 8 ED impulse coil with seesaw interface
3.2.6 Auxiliary tripping devices (Code 11)
• The breaker can be equipped with either a shunt trip (ST)
or a zero voltage release (UVR). It is not possible to have
both devices installed in the same breaker. Both devices
are interchangeable.
• In standard configuration, internal voltage converter
(Code 8) transforms external voltage into 24 V DC, which
is required by ST or UVR. Both devices are tripped by a
potential free contact connected as shown in section 4.2.
• Optionally, ST can be connected directly to external
voltage. In this case extinguish capacitors and diode is
used to improve switching of the shunt trip’s coil [Fig 194c]. Double winding shunt trip is available with this option
for 110/125/220 V DC external control supply.
• Optionally, it’s possible to supply both devices directly to
external 24 V DC ( ± 5%). In this case the release signal for
ST shall not be longer 100 ms.
• The ST is used for remote actuation. It is designed for
short time operation with max. duty cycle of 9 %. ST’s
supply is connected through auxiliary contacts, which cut
off supply voltage after opening. This protects ST against
overheating.
Fig. 9 Zero voltage release
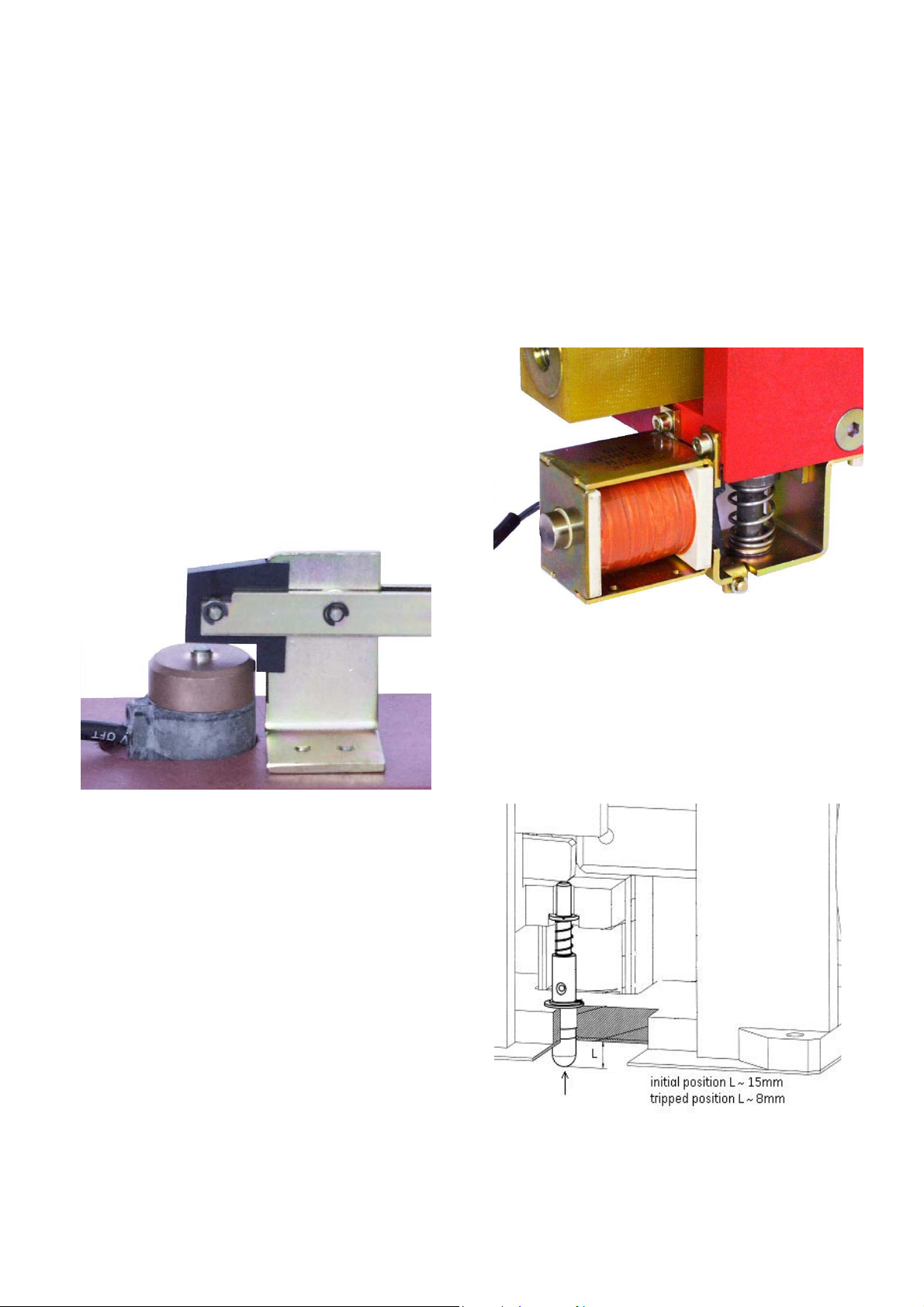
3.2.7 Forced tripping release (Code 13)
• Optionally, the forced tripping release (FT) can be installed
in the breaker [Fig. 10a]. This unit mechanically trips the
breaker, by pressing the pin against the bottom plate.
Force required to trip the breaker is about 30 N (~7 ft-lb).
The tripping pin position is as on Fig. 10b.
F~30 N
Fig. 10a Forced tripping release
(~0.6 in)
(~0.3 in)
8 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
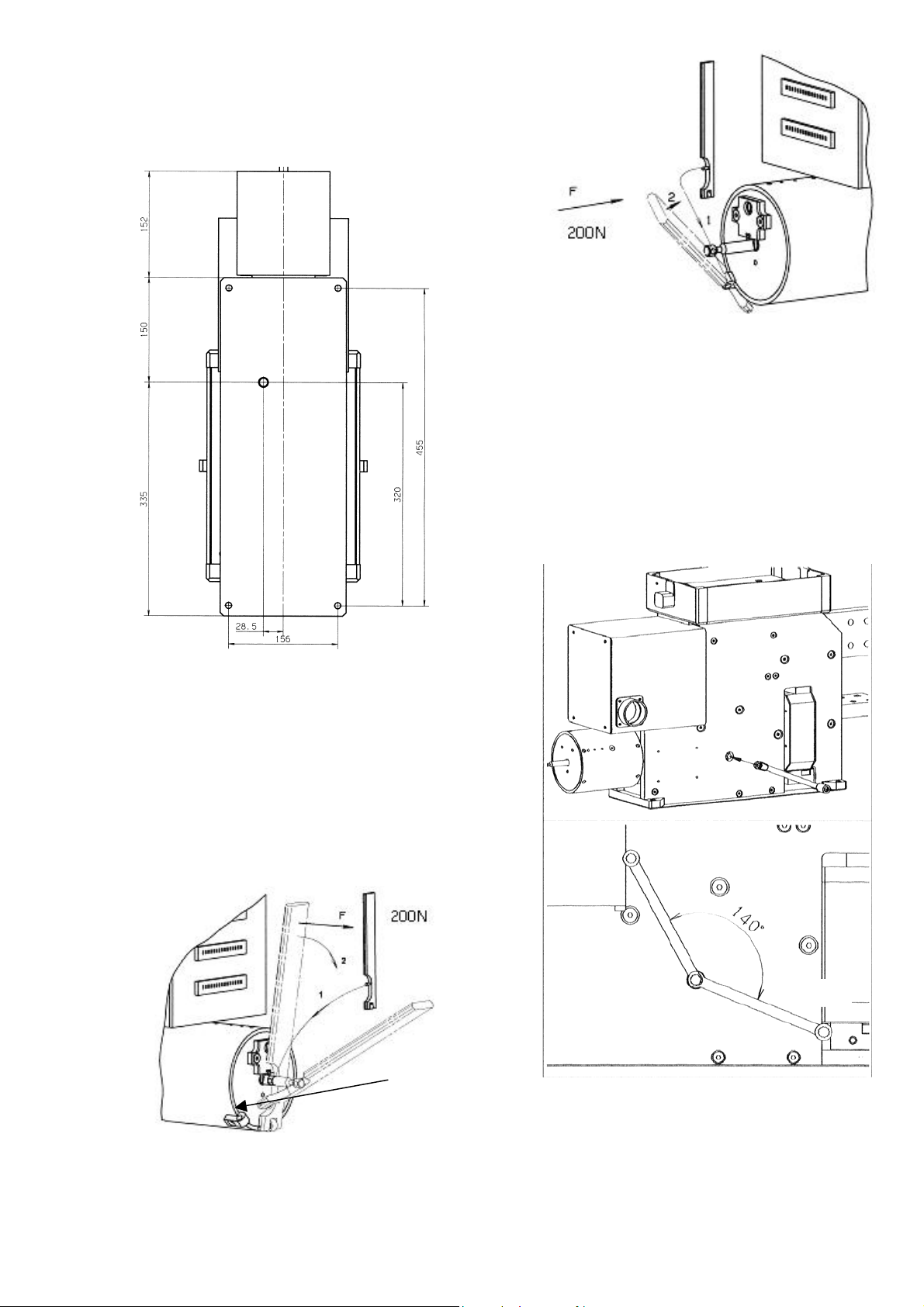
• With a correctly designed interlock in an enclosure, FT
g
provides safety-tripping function. During withdrawal
operation of the trolley, the breaker is tripped BEFORE its
main terminals disconnect from the mains.
Bottom view
Fig. 10b Positioning of the forced tripping pin
3.2.8 Lever for manual operating (Code 16)
• Optionally, a hand lever for manual closing and opening
operation during maintenance is available. This tool must
not be use while breaker is energized!
• To close the contacts, install hand lever on the drive’s rod,
and pull it out smoothly until latches snap [Fig. 11a].
• To open the contacts, install the tool into the ring and
push it hard against the drive’s rod until breaker opens
[Fig. 11b].
WARNING: Manual closing and opening – only during
maintenance!
Fig. 11b Opening operation by using hand lever
• Alternative manual closing and opening operation is
possible by rotating the main shaft of the breaker
mechanism, which is accessible from the side. Use
10 mm hexagon-socket wrench to OPEN/CLOSE [Fig. 11c].
• WARNING: Pay attention to control rotation speed of the
shaft during manual opening. Impede the wrench to
avoid hitting it to the ground, which may lead to a hand
injury.
CLOSE
(~45 ft-lb)
OPEN
rin
WARNING: Manual closing and opening – only during
maintenance!
WARNING: Manual closing and opening – only during
maintenance!
Fig. 11a Closing operation by using hand lever
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 9
Fig. 11c ON/OFF operation by using a 10 mm wrench

3.2.9 Auxiliary switch (Code 9)
• Standard breaker can be equipped with 3, 5 or 10
isolated, form C, invertible auxiliary contacts (1 NO/NC
each). The movable main arm activates the contacts.
• The contacts are wired to 15-pin control terminals: -X4
and -X5, with 5 switches to each terminal [Fig. 21].
• Conventional thermal current Ith=10 A. Maximum
electrical ratings for switches are 1 A/230 V for AC15. For
DC13 are 0.5 A/110 V and 0.3 A/220 V.
Fig. 12 Auxiliary contacts layout in control box
3.2.10 Indicators
Optionally, the circuit breaker can be equipped with
following indicators:
• POSITION INDICATOR (Code 14) - mounted at the front of
the closing drive. Mechanically switched by means of
drive’s rod. Indicates position of the main contacts.
“O” – means contacts are open
“I” – means contacts are closed
• ARC CHUTE INDICATOR (Code 17) – a potential free, NO
contact mounted on the sidewall. Locks electrically the
closing drive when arc chute is not installed on [Fig. 15].
Fig. 15 Arc chute indicator
3.2.11 Solenoid closing drive (Code 3)
• A high power solenoid is used to perform fast closing
operation. This drive is mounted at the front of the
breaker and is encased in a grounded casing [Fig. 16].
• Closing drive is supplied independently from other
controls (-X2 :1/:2), directly from external power source.
Voltage level must be defined at order placement. Rated
power, depends on breaker type, but is between 1.8 kW
and 2.6 kW.
• CLOSING command is enable by external potential free
contact at (-X2 :4/:5). Signal duration shall be ~300 ms.
• The closing drive system always includes a self-interrupt
control circuit (SU PCB). This circuit enables short
activation with a time of ~150 ms. SU switches power to
the solenoid and automatically disconnects it after
~400 ms.
• The SU unit also prevents repeated drive closing, due to
an existing and continuous short circuit conditions and
provides an “anti-pumping” safety feature.
Fig. 13 Position indicator
• OC TRIP TARGET (Code 10) – a potential free, NO contact
mounted at the top of the OCT [Fig. 14]. Provides a signal
when OCT trips.
Fig. 16 Solenoid closing drive and control box
• After closing attempt, the switch-in mechanism is
Fig. 14 OCT trip target
10 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
electrically blocked for approximately 8 sec. Lock time
increases to 14 sec, if internal C-bank (NEKO) is present.
This prevents premature closing following a short circuit.

3.2.12 Current measurement system (Code 6)
• The SEL current measurement system consists of the
sensing component (1) and signal-processing unit (2)
[Fig.17]. SEL sensor is integrated into a specially shaped
upper terminal of the breaker and is connected by a
shielded cable to the signal-processing unit. SEL control
unit is placed in the control-box [Fig. 18].
Fig. 17 SEL current measurement system
• SEL may be used for recording DC currents in selected
measurement ranges of 6 kA or 12 kA. Measurement of
rated current values and of the current rise may now be
made directly at the breaker.
• The sensor includes Hall-probes and delivers a
proportional signal-output to the SEL control. The signalprocessing unit transforms input signal, into standard
output signals shown in the table below.
• The outputs are insulated from the main voltage. The
insulation withstands voltages up to 4 kV RMS and up to
40 kV in peak.
• Two versions are available. Standard model (T35) for
ambient temperature –5 °C…+35 °C and the model for
higher temperature (T55) –5 °C…+55 °C.
• More details can be found in separate instruction for SEL
usage.
Type SEL 06-1 06-2 06-4 12-1 12-2 12-4
Input - 6 kA…+6 kA -12 kA…+12 kA
U
[V] 1000 2000 4000 1000 2000 4000
Ne
T35 for ambient temperature of the breaker
-5 °C…+35 °C / +23 °F…+95 °F
3.2.13 Electronic control system
All the control PCBs are installed in control box [Fig. 18].
Starting from the left, these are:
Fig. 18 Control box with control units
• (1) NEKO control unit [Fig. 19-1] (Code 12) – internal
control unit with capacitor bank. Releases firing signal for
ED coil (-X2 :10/:11) and provides indication of the
capacitors charging (-X3 :6/:7). NEKO control unit also
blocks the firing signal until C-bank is fully charged
(~15 sec).
• WARNING: NEKO unit requires a high quality firing signal.
Be sure, that voltage level is between 6 V…24 V DC and
there are no short spikes on signal (<3 ms). This might
lead to major defect of the NEKO control unit!
Fig. 19-1 NEKO control unit
• (2) Internal voltage converter (Code 8) - converts
external supply voltage (-X3 :4/:5) to the internal
24 V DC. Required by controls (except for the drive
supply).
T55 for ambient temperature of the breaker
INe Relating to the rated current of the breaker
Output 4...20 mA
U
[kV] 12 18 40 12 18 40
Ni
-5 °C…+55 °C / +23 °F...+131 °F
-20...20 mA
-10...10 V
Fig. 19-2 Voltage converter 110 V/24 V DC.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 11
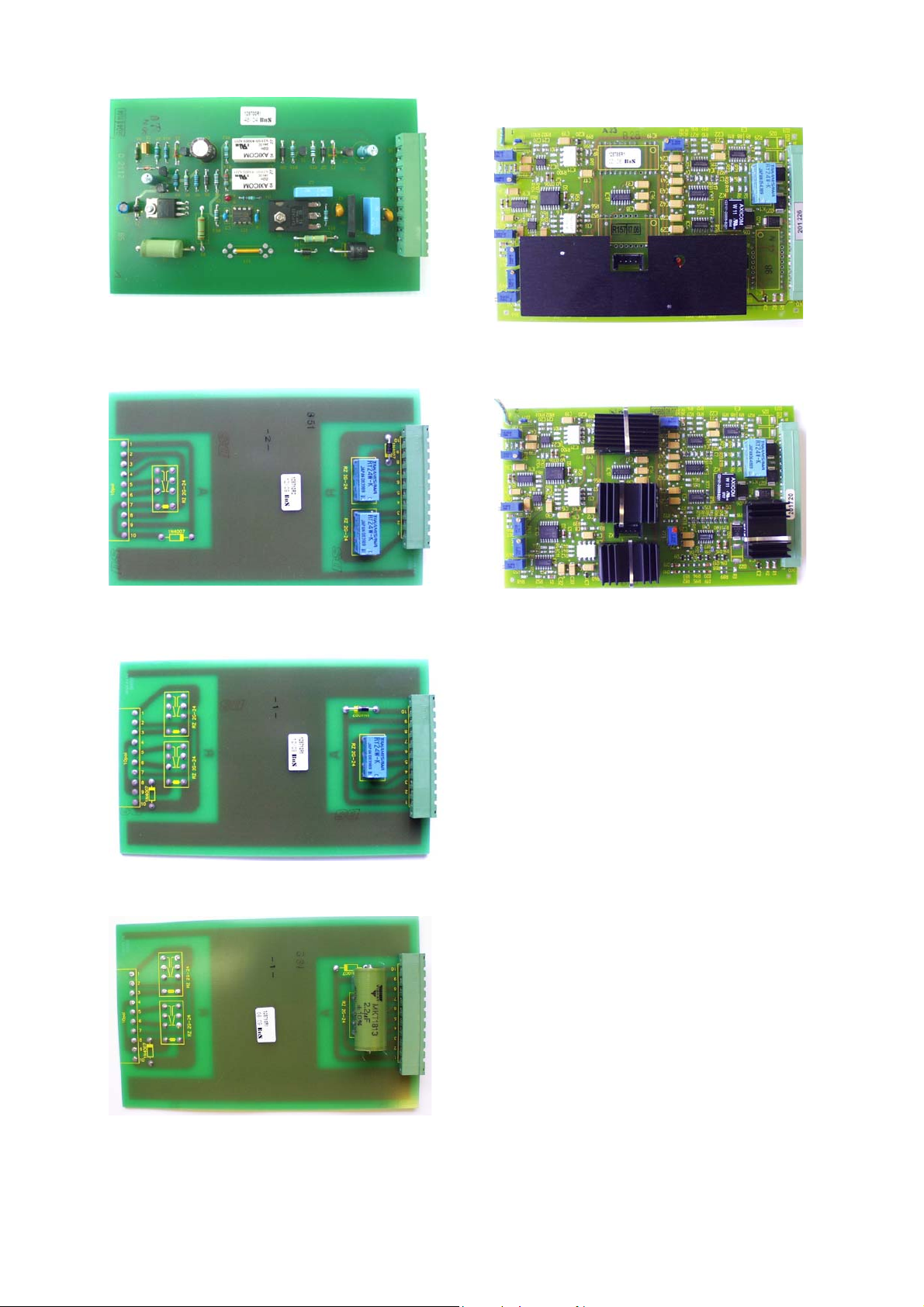
• (3) SU control unit – see point 3.2.11
• (5) EMPTY SLOT. – not used.
• (6) SEL control unit – see point 3.2.12
Fig. 19-3 SU control unit.
• (4) ST/UVR control unit – simple relay system. It controls
operation of shunt trip or zero voltage release.
Fig. 19-4a UVR control unit
Fig. 19-6a SEL control unit (T 35)
Fig. 19-6b SEL control unit (T 55)
Fig. 19-4b- ST control unit
Fig. 19-4c Extinguish capacitor for direct ST supply.
12 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
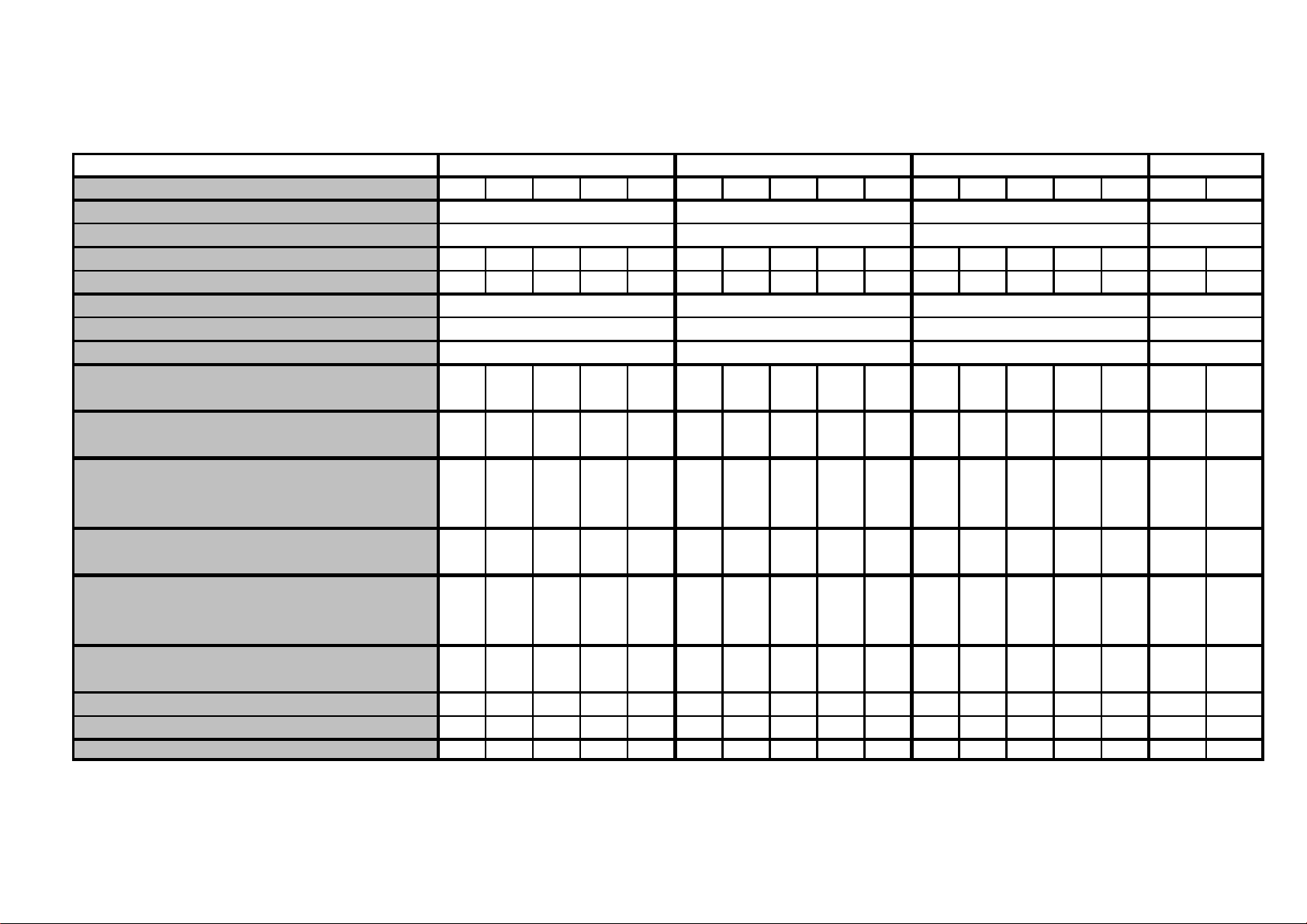
3.3 Technical data tables
Breaker type
Gerapid 2607
Arc chute type 1X2 1X4 2X2 2X3 2X4 1X2 1X4 2X2 2X3 2X4 1X2 1X4 2X2 2X3 2X4 1X2 2X2
Conventional thermal current I
[A] (IEC/EN)
th
2600 4200 6000
Rated current [A] (ANSI/IEEE C37.14) 2600 4150 -1)
Rated voltage U
Rated insulation voltage U
Short time current 120 min [A]
Short time current 2 min [A]
Short time current 20 sec [A]
e
[V]
1000 2000 2000 3000 3600 1000 2000 2000 3000 3600 1000 2000 2000 3000 3600 1000 2000
[V]
i
2000 2000 2000 3000 4000 2000 2000 2000 3000 4000 1000 2000 2000 3000 4000 1000 2000
3150
5200
7800 12600
Impulse withstand voltage 1,2/50 µs Ui [kV] 18 18 18 30 30 18 18 18 30 30 12 18 18 30 -1) 12 18
according to EN 50124-1:1997
Power frequency withstand voltage 50 Hz Ua [kVeff] 10 10 10 15 15 10 10 10 15 15 7 10 10 15 -1) 7 10
according to EN 50124-1:1997
Rated short circuit making capacity Î
Rated short circuit breaking capacity I
Nss
Nss
[kA]
[kA]
70 50 100 50 42 70 50 100 50 42 70 50 80 50 -1) 70 - 1)
50 35 71 35 30 50 35 71 35 30 50 35 56 35 -1) 50 50
according to EN 50123-2
Rated service short circuit breaking current Ics [kA] 60 40 50 40 40 60 40 50 40 40 60 40 50 40 -1) 60 - 1)
according to IEC 947-2
Short circuit current according to IEEE C37.14 [kA] 120 -1) 120 60 -1) 120 -1)
Peak current according to IEEE C37.14 [kA] 200 -1) 200 100 -1) 200 -1)
Gerapid 4207 Gerapid 6007
5000
8500
7200
12000
18000
Gerapid 8007
8000
6000
9600
16000
24000
Maximum short circuit current [kA] 244 120 100 52 244 120 100 52 200 240
tested at customer request
Maximum arc voltage Uarc [kV] 2445,672445,672445,67 2 4
Weight ca. [kg] 120 120 160 160 160 120 120 160 160 160 150 150 165 165 165 190 210
Weight ca. [lbs] 265 265 352 352 352 265 265 352 352 352 331 331 364 364 364 419 463
1) Rating tests at customer request
Table 1: Technical data of Gerapid 2607, 4207, 6007, 8007.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 13
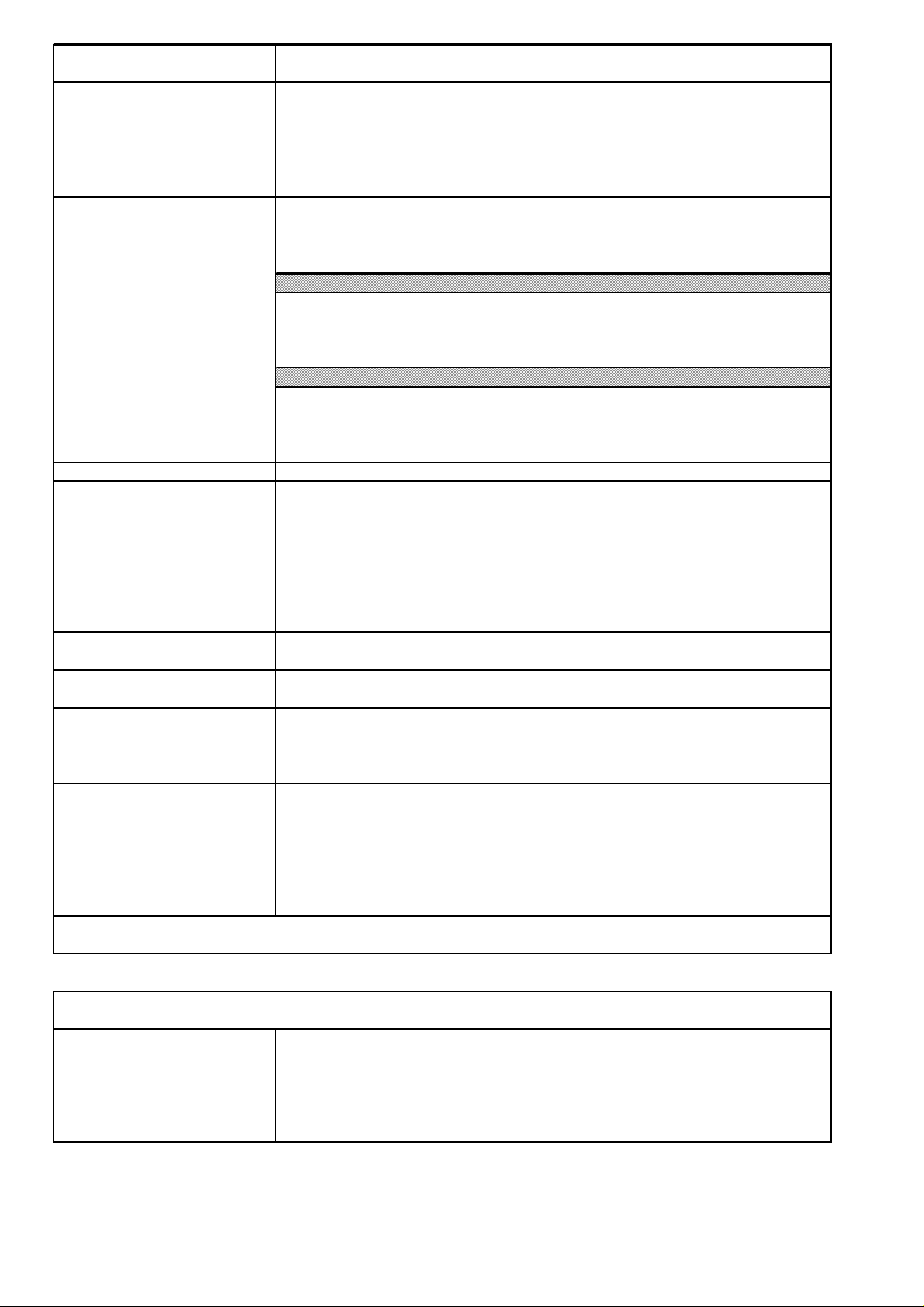
Control box terminals
Closing solenoid drive
Internal voltage converter
1)
1)
for Gerapid 2607, 4207, 6007, 8007
External power supply
Aux. contact HS 1…HS 10,
OC trip target (code 10)
Arc chutes indicator (code 17)
1x12-pole AC 400 V, 20 A
4x15-pole AC 250 V, 8 A
Rated voltage AC 48 V - 230 V and DC 48 V - 220 V
Operating range 80 % - 115 % of rated voltage
Power consumption Gerapid 2607 / 4207 1750 W / 2000 W
Power consumption Gerapid 6007 / 8007 2600 W / 2600 W
Minimal CLOSING command duration 100 ms
min.interval between two "CLOSE" operations ~8 s w/o NEKO installed; ~14 s with NEKO
Input: Voltage range DC 33 - 85 V
Output: Voltage range DC 24 V (±5%)
Current 6 A permanent
Model description PCMD 150 48 S24W-GE
Input: Voltage range DC 88 - 145 V
Output: Voltage range DC 24 V (±5%)
Current 6 A permanent
Model description PCMD 150 110 S24W-GE
Input: Voltage range AC 115 - 240 V, DC 125 - 353 V
Output: Voltage range DC 24 V (±5%)
Current 3 A permanent, 5 A/100 ms
Model description PCMA 70 S24W-GE
with plug and socket unit requires extrnal 24 V (±5%) DC
Rated operational voltage Ue/AC 230 V
Rated operational current Ie/AC-15 1 A
Conventional thermal current Ie/AC-12 (Ith) 10 A
Rated operational voltage Ue/DC 110 V / 220 V
Rated operational current Ie/DC-13 0.5 A / 0.3 A
Minimum current/voltage ratings 0,1 mA / 6 V DC
Contact duty (min. value) DC 10 V / 2 mA
Shunt trip standard
Rated voltage/power Uc/Pc 24 V / 100 W
Operating range: OFF 21.6 V - 26.4 V
Shunt trip double winded
Rated voltage/power Uc DC 110 V/ DC 125 V/ DC 220 V
Rated power for a single winding Pc 230 W
UVR
Rated voltage Uc 24 V
(Zero voltage release) Operating range: OFF < 4 V
Operating range: ON 24 V (±10%)
Power consumption ~ 10 W
ED impulse release
Energie source: Capacity 2000 µF
Charging voltage 300 V
Switching interval max. 2/min with 10 consecutive operations
Endurance 1 000 operations with 1 operation per 180 s
Firing signal level / duration
6 - 24 V / 100 - 1000 ms
Charging signalization relay AC duty : AC 250 V/ 0.5 A - AC 120 V /1 A
DC duty : DC 220V/0.1A - DC 125V/0.3A - DC 10V/3A
1)
Standard ambient conditions acc. to EN 50123-1 Attachement B. For meeting outside of this standard range, please call back.
Table 2a: Technical data of auxiliary circuits
Components Technical datas of control circuits
Us / In
SU-Control
ST releasing
UVR releasing
CLOSE-push-button -S1 DC 24 V / approx. 10 mA
push-button-S2 DC 24 V / approx. 4 A
push-button -S2 ( -X2 :6 / :7) DC 24 V / approx. 10 mA
push-button -S2 ( -X2 :8 / :9 ) DC 24 V / approx. 450 mA
ED-coil tripping w/o NEKO
ED-coil tripping with NEKO
push-button -S3 DC 300 V / 750 A / 3 ms
Connect "Firing signal" at ( -X2 :10 / :11 ) DC 6 V…24 V / approx.20 mA
Table 2b: Control circuits ( directional values to rate the components )
14 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
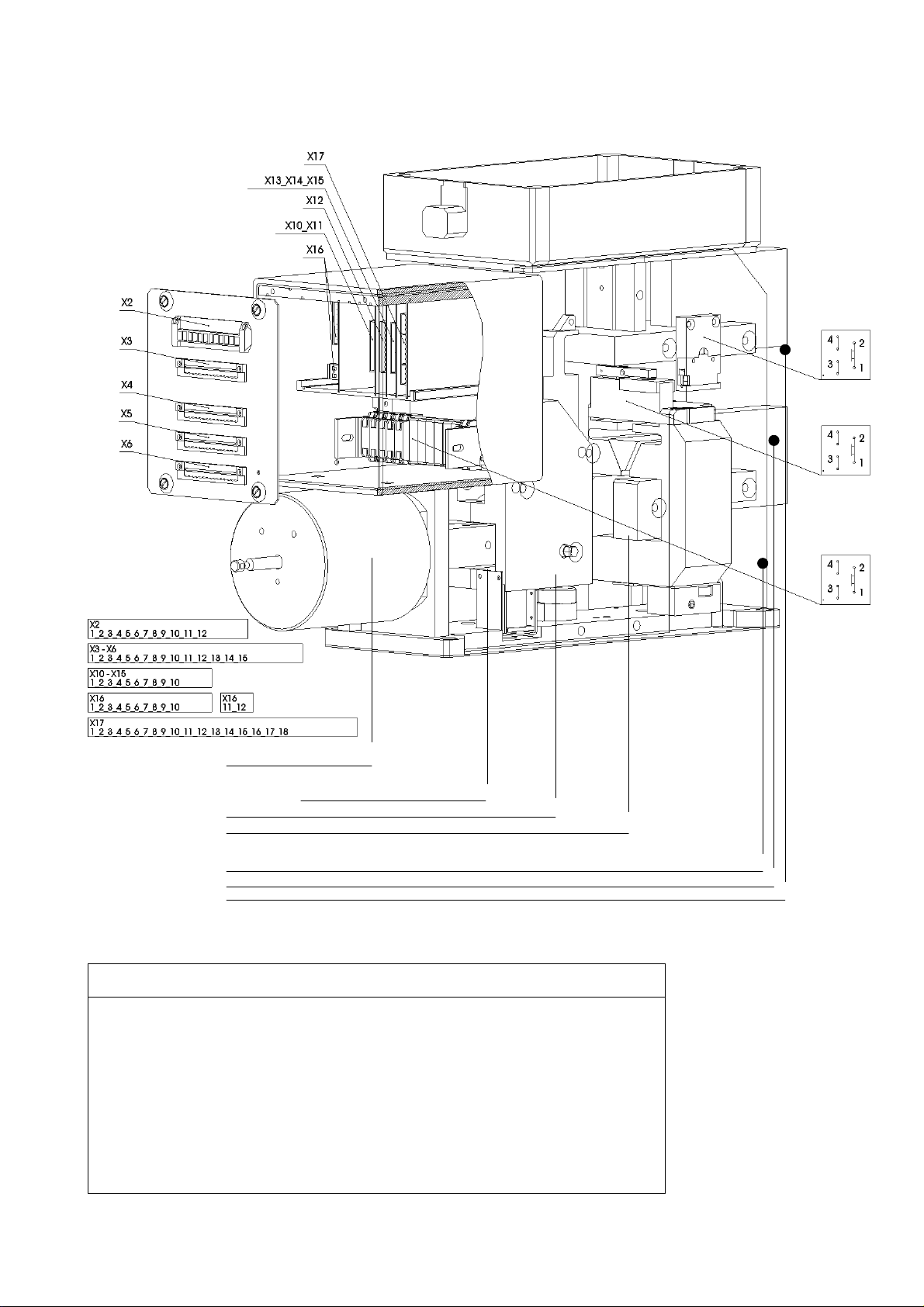
4. Electrical circuits
4.1 Controls layout
Closing solenoid drive
Shunt trip / Zero voltage release
ED coil
OCT device
HS 1...HS 10
OCT trip target
Arc chute-indicator
Description
X2 1.Connector: Auxiliary- and control circuits
X3 2.Connector: Auxiliary- and control circuits
X4 3.Connector: Auxiliary contacts HS1...HS5
X5 4.Connector: Auxiliary contacts HS6...HS10
X6 5.Connector: Current measure system SEL
X10 Control board: Voltage converter
X11 Control board: Interface for external DC 24V supply (OPTION)
X12 Control board: SU control unit
X13 Control board: Shunt trip control unit
X14 Control board: Zero voltage release
X16 Control board: NEKO control unit for ED coil control
X17 Control board: Current measure system SEL
Designation
Fig. 20 Control system’s layout
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 15
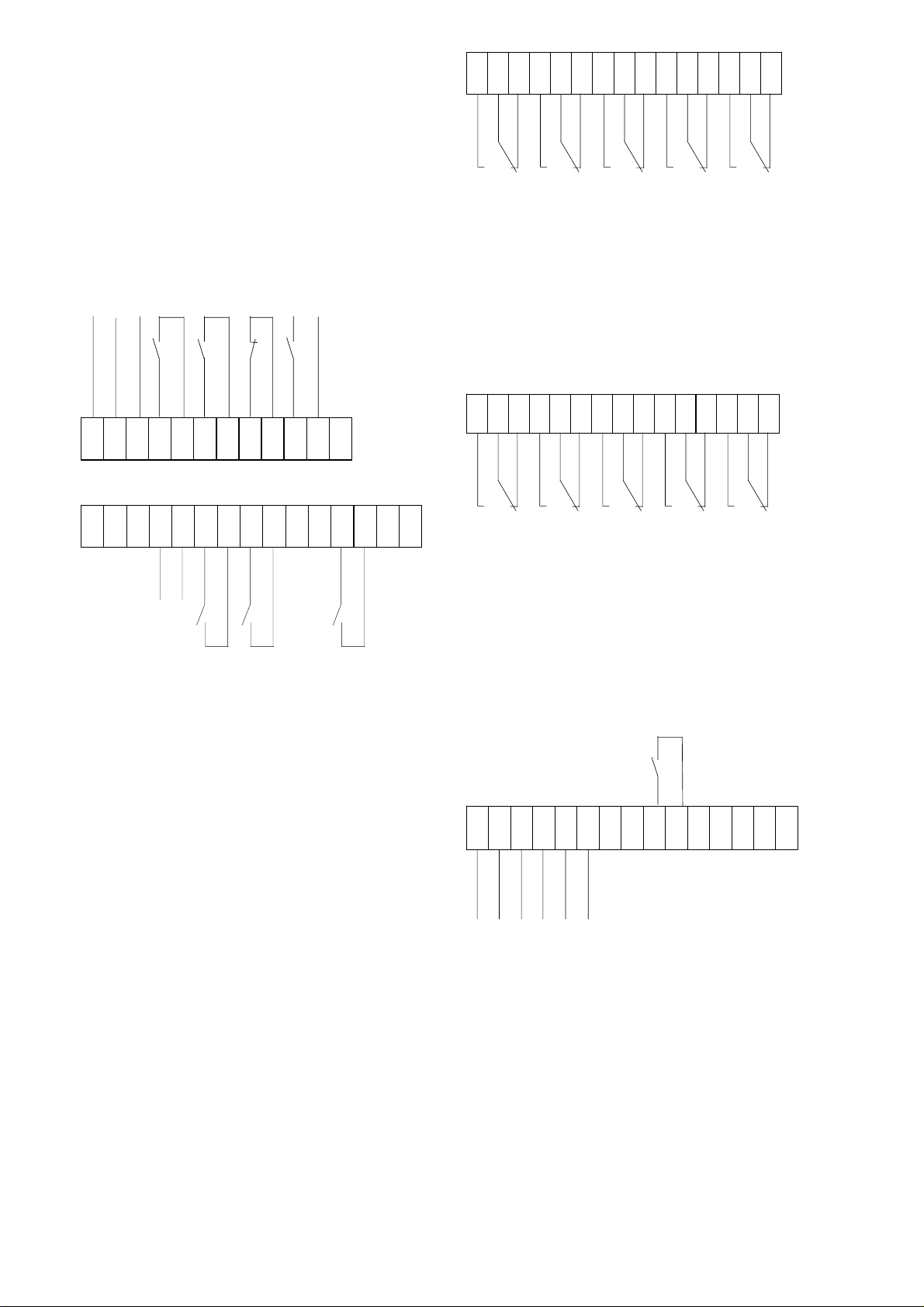
4.2 Terminals wiring system
X
123456789101112131415
X4
Closing drive supply (~,+) (S3)
Closing drive supply (N,-)
PE
S1 ( CLOSE-Command)
S2 ( OPEN by ST command)
S2 (OPEN by UVR command )
S3 ed-trip firing signal 6…24Vdc
(+) (-)
123456789101112
X2
123456789101112131415
X3
HS 1
HS 2
HS 3
HS 4
HS 5
123456789101112131415
5
HS 6
HS 7
HS 8
HS 9
HS 10
SEL (self check)
External Control Voltage Supply (+)
External Control Voltage Supply (-)
NEKO charging indicator
(indicates C-bank charging)
with OCT indicator
(Indicates tripping by OCT)
Fig. 21 Typical terminals wiring system, external customer connections.
123456789101112131415
Arc chute indicator
(Indicator switch)
X6
+
+
SEL (4…20 mA)
-
-
SEL (4…20 mA)
SEL ( +/- 20 mA)
SEL ( +/- 20 mA)
-
+
SEL ( +/- 10V )
SEL ( +/- 10 V )
16 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
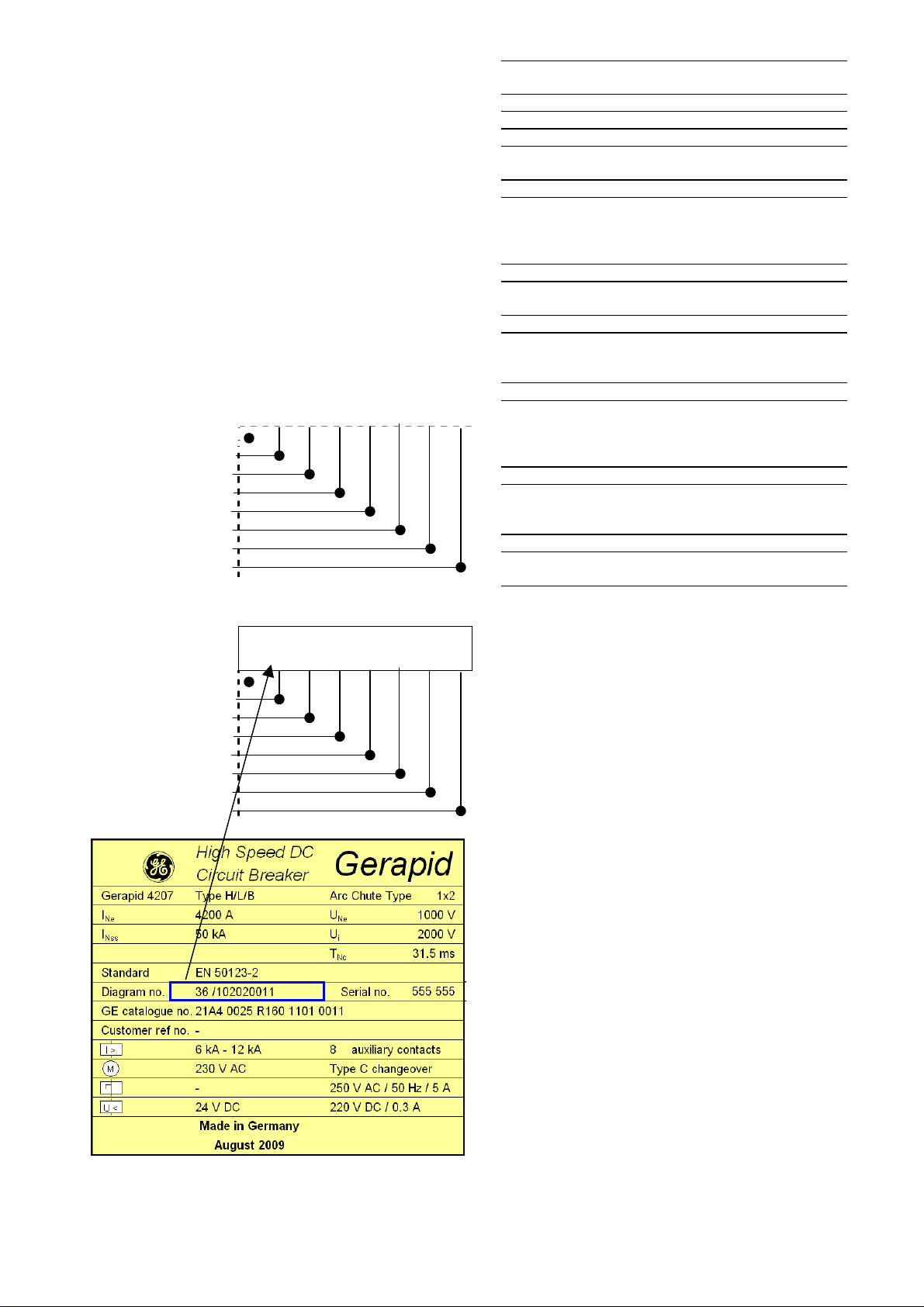
4.3 Electrical diagrams
4.3.1 Wiring code
• The main circuits are not shown in the wiring diagrams
for transparency. The control circuit is presented as a
typical circuit diagram and is a combination of numbered
basic diagrams for drives, trips and indicators.
• Using the key numbers of the basic plan, you can derive
the number of the complete diagram.
• WARNING: Some non standard electrical circuits do not
comply with the diagrams in this instruction. Such circuits
are coded with unique numbers i.e 36/0033. In such a
case an appendix to this instruction is delivered, which
contains relevant electrical diagrams.
Coding positions:
Breaker type
Aux. voltage supply
ED impulse release
Closing drive
Aux. tripping device
Indicators
Aux. switches
SEL system
EXAMPLE:
Key position:
Gerapid
With voltage converter
Without ED and NEKO
With closing drive
With UVR release
With OCT trip target
With 3 aux. switches
Without SEL system
Key number:
1 / 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
36 / 1 0 20 20 01 1
Key
position
Type
1 36 Gerapid
Auxiliary voltage
2 1 Voltage converter
2 DC 24 V external supply
Tripping coil
3 0 Without ed-trip coil
1 With ed-trip coil
2 With ed-trip coil and NEKO
Drive
4 20 Solenoid drive with
Tripping device
5 00 Without trip unit
10 With shunt trip
20 With zero voltage release
Indication device
6 00 Without indicators
01 OCT trip target
02 Arc chute indicator
03 OCT + arc chute indicator
Auxiliary contacts
7 1 3 auxiliary contacts
2 5 auxiliary contacts
3 10 auxiliary contacts
Current-measurement system
8 S with SEL
Indication of components
Q1 Impulse ED coil
Q2 Closing drive coil
S1 Push button „CLOSE“
S2 Push button „OPEN“, type NO
S3 Push button “OPEN”, type NC
SU control PCB:
K1 Closing relay
K2 Internal closing stop relay
Shunt trip, zero voltage release PCB:
K1 Internal closing stop relay
K2 Tripping relay
HS11 Shunt trip self cut-off auxiliary contact
ED-tripping device with internal NEKO PCB:
K1 Voltage monitoring relay
Internal closing stop relay
K2
1) These relays are part of internal closing stop circuit.
It is a 24 V DC closed circuit, through all PCBs in the box,
except SEL. Serial connection of all relays is realized
through connections ( :5/:6) in each PCB. This circuit
provides priority of a tripping signal over a closing signal.
Additionally it prevents from closing the internal supply
24 V DC lost at UVR PCB or NEKO PCB.
Key
number
Designation
control unit
SU control unit
1)
1)
1)
Fig. 22 Example code shown on the nameplate.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 17
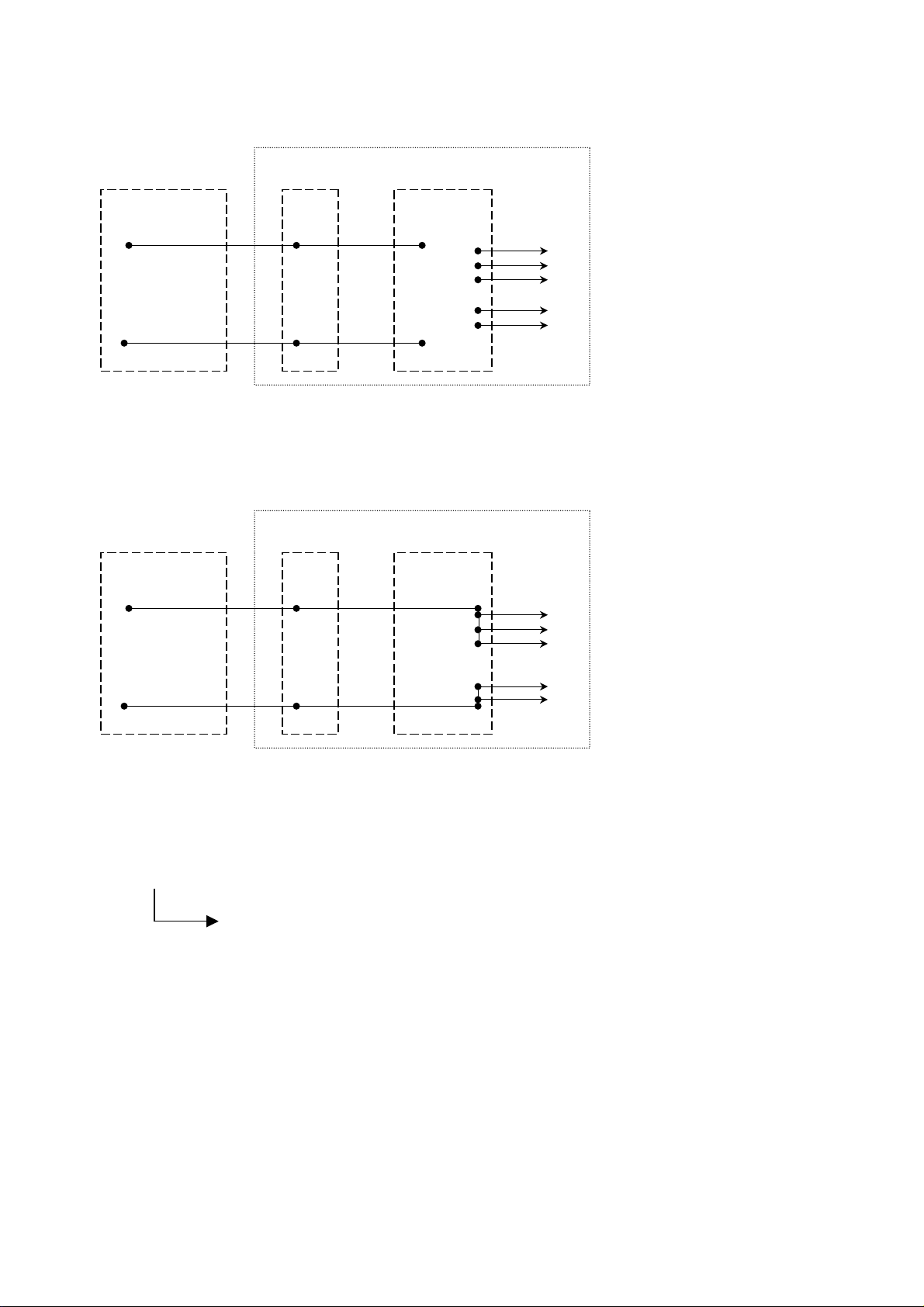
4.3.2 Controls supply circuit
y
External
power supply
+ / ~
AC 115-240V ±10%
DC 35-350V ±10%
- / N
External
power supply
+
DC 24 V ±5%
-
36/ X _ _ _ _ _ _
Key position - 2
Key number – 1: Voltage converter DC 35-85 V ; DC 88-145 V ; DC 125-353 V ;AC 115-240 V
Ke
Breaker
-X3
[ 4 ]
[ 5 ]
-X10
[ 1 ]
[ 3 ]
[ 10 ]
[ 9 ]
[ 8 ]
[ 7 ]
[ 6 ]
+DC 24 V ±2%
GND
Breaker
-X3
[ 4 ]
[ 5 ]
number – 2: Interface for direct external voltage DC 24 V +/- 5% connection.
-X11
[ 1 ]
[ 3 ]
[ 10 ]
[ 9 ]
[ 8 ]
[ 7 ]
[ 6 ]
+DC 24 V ±2%
GND
Fig. 23 Supply with voltage converter or with direct external 24 V DC ±5%.
18 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

4.3.3 ED coil with external capacity bank
y
• In this option customer provides his own solution for releasing of the ED coil, by means of external capacitor
trip device. The NEKO control unit is not furnished, and coil is connected directly to front panel of control box (X2 :10/:11).
-S2
External
C-bank
U=300 V
C=2000 uF
Breaker
-X2
[ 10 ]
[ 11 ]
-Q1
ED
impulse
coil
36/ _ X _ _ _ _ _
Key position - 3
Key number – 0: Without ED coil.
number – 1: With ED coil and external C-bank.
Ke
Fig. 24 ED coil with external Capacitor trip device
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 19

4.3.4 NEKO control circuit
_
Cut-off
contact
i.e. HS 10
provided
by user !
-X10/11
[ 8 ]
(+)
24 Vdc
[ 6 ]
(-)
-X3
[ 6 ]
C-bank
charging
signalization
[ 7 ]
Closing
STOP relay
-X2
[ 10 ]
Tripping
signal
6V...24V
[ 11 ]
-Q1
ED impulse
coil
-X16: NEKO PCB
[ 1 ]
(+)
(-)
[ 2 ]
[ 9 ]
[ 10 ]
[ 5 ]
[ 6 ]
[ 3 ]
Signals
-K1
-K2
(+)
(-)
[ 4 ]
[ 11]
[ 12 ]
Impulse switching
Input circuit for firing signal
C-bank and output circuit
Isolating Transformer
Charging Control
Charging Voltage
Control
Firing signal
control
36/ _ X _ _ _ _
Key position - 3
Key number - 2: With ED coil and internal NEKO control unit.
• Firing signal at (-X2 :10/:11) is processed by opto-coupler. Pay attention to the polarity!
• Closing STOP signal is provided to lock CLOSE command, until capacitors are fully charged.
• Be sure that voltage level is between DC 6 V - 24 V and there are no transient spikes (<3 ms) on firing signal.
This can lead to major defect of the NEKO control unit!
• Maximum duration of the firing command must not exceed ~1 sec. Longer signal might cause NEKO failure! It is
recommended to use one of HS auxiliary contacts connected in series with firing circuit (-X2 :10). It will
automatically cut off the firing circuit after breaker opening.
Fig. 25 ED coil with internal NEKO control unit
20 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

4.3.5 SU control circuit
Power
supply
+ / ~
AC 110-250V
DC 48-220V
- / N
-S1
-X10/11
[ 9 ]
24 V DC
36/ _ _ X _ _ _ _
-Q1 Closing drive
-X12: SU PCB
-X2
[ 1 ]
[ 2 ]
-X2
[ 4 ]
[ 5 ]
(+)
-
Key position - 4
Key number – 20: Closing solenoid drive with SU control unit.
[ 3 ]
[ 4 ]
[ 8 ]
[ 9 ]
[ 10 ]
[ 7 ]
[ 5 ]
[ 6 ]
Transforming of CLOSE signal
-K1
Closing
STOP
-K2
[1]
[2]
Closing
control
circuit
-K1
Fig. 26 SU-control circuit
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 21

4.3.6 Shunt trip control circuit
y
Standard DC 24 V shunt trip with control PCB.
-S2
-X2
[ 6 ]
[ 7 ]
-X13: ST PCB
[ 4 ]
[ 3 ]
]
-X10/11
[ 7 ](-)
24 V DC
[ 9 ] (+)
ST coil
Cut-off
contact
-HS11
[ 8 ]
[ 7 ]
[ 10 ]
[ 9 ]
[ 1 ]
[ 2 ]
-K1
-K1
[ 5
[ 6
]
Closing
STOP relay
36/ _ _ _ X _ _ _
Key position - 5
Key number - 00: Without shunt trip or zero voltage release.
number - 10: With shunt trip.
Ke
• The closing STOP signal is provided for resetting K2 on the SU-control circuit. It effects with priority in switching
OFF (by ST or UVR) before switching ON. Once switching ON and OFF signals are simultaneous, switching OFF
command will stay longer than switching ON. It means, that OFF command is master command.
• The shunt trip operates for short time period only. After main contacts open, switch HS 11 cuts off shunt trip
coil.
• Manual closing of the breaker, while –S2 contact is closed, leads to overheating of ST coil and will damage coil.
Fig. 27a ST control circuit
22 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

• Below, non-standard shunt trip with single winding, directly supplied from external DC voltage.
-
7
-
Breaker’s
aux.
10 2 4 8 3 5 6
-X2:7 -
• Below, non-standard shunt trip with double winding, directly supplied from external DC voltage.
1st winding
2nd winding
-
-
7
-
7
-
10 2 4 8 3 5 6
10 2 4 8 3 5 6
1
Breaker’s
aux.
3
2
4
Breaker’s
aux.
-X2:7 -
-X2:9 -
• Double winding shunt trip coil is available for external DC 110 V, DC 125 V and DC 220 V.
• User shall provide fused means for safe switching the voltage to the coil. See table 2a for coil parameters.
• Auxiliary contacts used for cutting off shunt trip coils are internal breaker’s components.
Fig. 27b Special versions of shunt trip with a single and double winding coils, directly supplied from external DC source.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 23

4.3.7 Zero voltage release control circuit
y
-S3
-S2
-X2
[ 9 ]
[ 8 ]
[ 7 ]
[ 6 ]
-X10/11
[ 7 ](-)
DC 24 V
UVR coil
U<
-X14: UVR PCB
[ 1 ]
[ 2 ]
[ 3 ]
[ 4 ]
[ 7 ]
[ 8 ]
[ 9 ]
[ 10 ]
-K2
-K1
-K2
-K1
[ 5 ]
[ 6 ]
Closing
STOP relay
36/ _ _ _ X _ _ _
Key position - 5
Key number - 00: Without shunt trip or zero voltage release.
number - 20: With zero voltage release.
Ke
• The closing STOP signal is provided for resetting K2 on the SU-control circuit. It effects with priority in switching
OFF (by ST or UVR) before switching ON. Once switching ON and OFF signals are simultaneous, switching OFF
command will stay longer than switching ON. It means, that OFF command is master command.
• -S2 (-X2 :6/:7) is NO contact, utilized for indirect releasing of the UVR by relay -K2
• -S2 (-X2 :8/:9) is NC contact utilized for direct releasing of the UVR. If it’s not used, please short this connection
permanently.
Fig. 28 UVR control circuit
24 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

4.3.8 Indicators
y
36/ _ _ _ _ X _ _
-X3
[ 8]
[ 9]
[ 12 ]
[ 13 ]
OCT trip target
Arc chute
indicator
Key position - 6
Key number - 00: Without indicators.
Key number - 01: With OCT trip target only.
Key number - 02: With arc chute indicator only.
number - 03: With OCT trip target and arc chute indicator.
Ke
Fig. 29 OCT trip target and arc chute indicator
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 25

4.3.9 Auxiliary switch
123456789101112131415
X4
HS 1
HS 2
HS 3
HS 4
HS 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
X5
HS 6
HS 7
HS 8
HS 9
HS 10
36/ _ _ _ _ _ X _
Key position - 7
Key number - 1: With 3 switches (HS1 thru HS3).
Key number - 2: With 5 switches (HS1 thru HS5).
Key number - 3: With 10 switches (HS1 thru HS10).
Fig. 30 Auxiliary switch
26 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

4.3.10 SEL measuring system
Signal
Processing
Unit
Voltage
stabilizer
DC 24 V
1)
max. 500 Ω
Self check control
2)
max. 500 Ω
36/ _ _ _ _ _ _ X
Key position - 8
Key number - S: With SEL measurement system.
3)
min. 300 kΩ
DC 24 V
Fig. 31 SEL current measurement system
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 27

5. Dimensions & safety distances
Warnings
During operation, all metallic parts of the breaker, except
control box and closing solenoid drive, may carry
dangerous voltages.
Insulation covers are available as an option.
For installation of the breaker into cubicle, top and side
openings shall be provided, in order to reduce internal
pressure rise during clearing short circuit.
Ventilation openings in the breaker cubicle top cover
shall not be less than 50% of total surface area.
28 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

5.1 Safety distances.
Units call in mm (inches)
Type Arc chute Main- Additional Deflector Safety distances / Insulated plates Safety distances / Earthed plates
Gerapid Connection isolation
EABCDABCD
2607 / 4207
1x2
1x3
1x4
all
all
all
10 (0,4) 700 (27,6) 150 (5,9) 150 (5,9) 120 (4,7) 1000 (39,4) 300 (11,8) 300 (11,8) 300 (11,8)
1) 1) 1) 1) 1) - - - -
150 (5,9) 700 (27,6) 150 (5,9) 150 (5,9) 120 (4,7) 1350 (53,2) 450 (17,7) 450 (17,7) 200 (7,9)
2x2
2x3
2x4
2x4
2x4
6007
8007
2) 2x2
2) 2x3
1)
will be checked by customers order 2) acc. IEC 947-2 / ks-setting <12 kA
1x2
1x3
1x4
2x2
2x3
2x4
1x2
1x3
1x4
2x4
all
all
H / H Plate
H / H Sidewalls
SEL / H Pan
V / V Heat sink
1) 1)
V / V Heat sink
V / V Heat sink
V / V Heat sink
1) 1)
V / V Heat sink
1) 1)
1) 1)
V / V Heat sink
V / V Heat sink
1) 1)
80 (3,15) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 1350 (53,2) 450 (17,7) 450 (17,7) 300 (11,8)
80 (3,15) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - 150 (5,9) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - 150 (5,9) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - 150 (5,9) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - -
10 (0,4) 1000 (39,4) 300 (11,8) 300 (11,8) 180 (7,1) - - - -
1) 1) 1) 1) 1) - - - -
150 (5,9) 1000 (39,4) 300 (11,8) 300 (11,8) 180 (7,1) - - - -
80 (3,15) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - 80 (3,15) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - -
1) 1) 1) 1) 1) - - - -
10 (0,4) 1000 (39,4) 300 (11,8) 300 (11,8) 180 (7,1) - - - -
1) 1) 1) 1) 1) - - - -
1) 1) 1) 1) 1) - - - -
80 (3,15) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) - - - 80 (3,15) 1000 (39,4) 180 (7,1) 180 (7,1) 300 (11,8) - - - -
1) 1) 1) 1) 1) - - - -
H
…Horizontal terminal V...Vertical terminal
Legend for dimensional drawings
K Heat sink (for Gerapid 6007)
L All openings respectively free areas on the top of the cubical shall be not less than 50%
M Solenoid drive
P Diameter 9 mm [0,35 in], Countersunk screw M8
S Control box
Z Connector
SEL
...Current measurement system type SEL
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 29

5.2 Outlined dimensions
5.2.1 Gerapid 2607,4207, 6007 with arc chute 1x_
Pay attention to legend, warnings and safety distances pages 26/27!
Fig. 32 Gerapid 2607- 6007, arc chute 1X (dimensions in mm and inches)
30 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

5.2.2 Gerapid 2607, 4207, 6007with arc chute 2x_
Pay attention to legend, warnings and safety distances pages 26/27!
Fig. 33 Gerapid 2607- 6007, arc chute 2x (dimensions in mm and inches)
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 31

5.2.3 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 1x_
Pay attention to legend, warnings and safety distances pages 26/27!
Fig. 34 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 1x (dimensions in mm and inches)
32 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

5.2.4 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 2x_
Pay attention to legend, warnings and safety distances pages 26/27!
Fig. 35 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 2x (dimensions in mm and inches)
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 33

5.2.5 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with H / H terminals
It’s possible to combine horizontal and vertical connectors. Dimensions are corresponding. Note with
SEL option, top connector is vertical only
Fig. 36 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with horizontal terminals (dimensions in mm and inches)
34 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

5.2.6 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with V / V terminals
It’s possible to combine horizontal and vertical connectors. Dimensions are corresponding.
Fig. 37 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with vertical terminals (dimensions in mm and inches)
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 35

5.2.7 Gerapid 6007 terminals
Gerapid 6007 is available only with V / V terminals !
Fig. 38 Gerapid 6007 with vertical terminals (dimensions in mm)
36 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

5.2.8 Gerapid 8007 terminals
Gerapid 8007 is available only with V / V terminals !
Fig. 39 Gerapid 8007 with vertical terminals (dimensions in mm and inches)
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 37

6. Inspections and maintenance
6.1 List of inspections
TYPE OF THE
INSPECTION
A. General visual
inspection
B. General functional
inspection
C. Inspection of the arc
chute and contact
system
D. Inspection of the
screw/bolt connections
E. Inspection of the
mechanic components
Required tools:
Cleaning tissue; abrasive paper; manual closing lever; hexagon wrenches SW5, SW6; Torx® wrenches size 30, 40, 45; small and
medium screwdrivers; ratchet with 10 mm hex cap; pliers; tongs.
Dispose of the breakers if required:
Pay attention to the national and local regulations of disposal!
BY WHOM HOW OFTEN WHAT TO DO/CHECK
-Customer
-Trained technician
-Customer
-Trained technician
-Customer
-Trained technician
-Customer
-Trained technician
-GE
-Service technician
Every 6-12 months
Every 6-12 months
Every 6-12 months
or after:
• high short circuit
opening at >25 kA
• >300 openings at load
current
• >100 openings at over
current load (2-3 x In)
It is recommend to carry
out inspection of contact
system after breaking of
equivalent of 150MA
let through energy.
Every 6-12 months
or after every inspection:
• of the arc runners
• of the contacts
• of the arc chute
Every 5 years
or
After 5.000 openings
2
s total
• Check for damages or cracks of the
frame, adapter or arc chute
• Check for missing screws or caps
• Check for damaged labels
• Check for corrosion
• Check for distinct manifestations of flame
or smoke at the frame
• Clean the breaker from dirt and dust
• Clean and degrease the copper terminals
• Manually close and open the breaker to
check the drive and mechanism
• Close the breaker electrically and open by
trip unit(s) releasing, to check controls
• Check for wear of the arc runners; shall
not exceed 30 % of its cross section
• Check for wear of the pre-arcing contact.
It shall not exceed 2 mm [0.08 in].
• Check for wear of the main contacts at
fixed and flexible sides; shall not exceed
1.5 mm [0.06 in] of its depth.
• Check for wear of the arc chute plates;
check for deposits inside of arc chute, this
area shall be free of deposits.
• Check for wear of protective walls; shall
not exceed 1 mm [0.04 in].
• Check for contact tilt and gaps.
Check the position of the countersunk screws
in the sidewalls.
Check for tightness or use torque tool (torque
in SI and Imperial units):
• M8 ~20 Nm [~ 177 in-lbs]
• M6 ~10 Nm [~ 88 in-lbs]
• M5 ~5 Nm [~ 44 in-lbs]
• M4 ~3 Nm [~ 26 in-lbs]
• Carry out inspection “B” above
• Check out settings of the main contacts
and auxiliary switch
• Check out upper dumper of the
mechanism; no cracks, deformation or
heavy discoloration; hard consistency;
without punctures
• Check out main flexband breakage; shall
not exceed 30 % of its cross section
• Check out wear of mini flexband; shall not
exceed 30 % of its cross section
• Clean and degrease UVR latch and quick
latch of the mechanism. Apply dash of
Beacon EP2 grease afterwards.
38 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

6.1.1 General visual inspection
• Check out for damages or cracks of the frame, the
adapter or the arc chute.
• Check out the black marks on the countersunk screws.
These marks shall be aligned together. If any screw is
loosening, shall be replaced with new one, using Loctite
222. Afterwards, mark the screw with black line to sign
its position in nest.
• Check out for missing screws or caps.
• Check out for damaged labels. Clean and repair.
• Check out for corrosion. In case of significant corrosion,
please contact GE representative for assistance.
• Check out for distinct manifestations of flame or smoke
at the frame. Especially in lower area of the breaker.
Please document and contact GE representative for
assistance.
• Clean the breaker of dirt and dust. Remove all dirt with a
dry cloth. No particularly high signs of abrasion (rough
chips) should be visible anywhere.
• Clean and degrease the copper terminals.
6.1.2 General functional inspection
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
• In order to check the latch mechanism, the breaker can
be opened and closed with a hand lever.
• Re-energize the control circuits and switch the breaker
ON and OFF several times using ST or UVR, and using
closing drive. The contacts must close after the CLOSE
command and must open following the OPEN command
• The breaker mechanism must not appear sluggish nor
must ON/OFF be unduly delayed.
6.1.3 Inspection of the arc chute
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
A) Remove the arc chute
• [Fig. 41]. Take off isolation caps (6). Loosen the clamping
screws (3) and (4), using SW5 hexagon wrench and take
off the arc chute (1) from the adapter (2).
B) Check the arc chute
• [Fig. 42]. Check the arc chute’s interior, as far as possible,
for deposits (1). There should be no copper pearls on the
metal-plates, which could partially short the plates.
• [Fig. 42]. Check the general condition of the insulation
plates (4). These shall not be bent or burned. Also other
insulation shall not be heavily damaged.
• [Fig. 42]. Check the arc horns (2). The cross section shall
not be reduced more than ~30 %.
• [Fig. 42] Check the splitting plates (3). These shall not be
burned more than ~20 mm [~0,8 in].
C) Install the arc chute
• [Fig. 41]. Put arc chute (1) into adapter (2).
• [Fig. 41]. Tighten front and backside connections of the
arc runners (3), including lock washer. Use a torque of 10
Nm [88 in-lbs].
• [Fig. 41]. Tighten front- and backside of the arc chute
connections (4), including flat washers. Use a torque of
5 Nm [44 in-lbs].
• [Fig. 41]. Put on isolation caps (6).
1
Fig. 40 Using of the hand lever
6
2
4
3
5
Fig. 41 Arc chute and arc runners fixing
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 39

4
1
2
Fig. 42 Inspection of the arc chute
6.1.4 Inspection of the contact system
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
A) Remove the arc chute
• [Fig. 41]. Loosen the clamping screws (3) and (4), using
SW5 hexagon wrench and take off the arch chute (1)
from the adapter (2).
B) Remove the arc chute adapter
• [Fig. 43]. To dismantle the arc chute adapter, loosen and
pull out the four upright screws (1) using SW5 tool. Pay
attention that no screws or washers fall inside the
breaker!
• [Fig. 43]. Draw aside and lift off both parings of adapter
(2). Then pull out two protective walls (3).
3
1
2
Fig. 44 Checking the contact system
C) Check the protective walls
1
• [Fig. 44]. The material burn out on the protective walls (5)
shall not exceed 1 mm [0.04 in] at any place.
D) Check the arc runners
• [Fig. 44]. The arc runners should not be burned more
than 30 % of its total cross section. Pay particular
attention to the area around arc runner bend (3) and at
contact point with arcing contact (2).
E) Check the arcing contact
• [Fig. 44]. Wear of the arcing contact (1) must not exceed
2 mm [0.08 in] of its depth. Replace the arcing contact in
that case. If contact erosion exceeds 4 mm [0.16 in],
major contact system failure is possible.
F) Check the main contacts
• [Fig. 44]. The main contacts (4) shall not show any
particular signs of material erosion, since the arc is
ignited between the arcing contacts. It means, that for
rated and overload currents there should be no erosion
of main contacts.
• Erosion of main contacts can take place only in case of
excessively worn, highly burned arcing contact or during
very high short circuit currents. In that case wear must
not exceed 1.5 mm [0.06 in].
G) Install the adapter
• [Fig. 43]. Install the two protective walls (3). Use new ones
if necessary. Install two parings of adapter (2) and
tighten screws (1) use 10 Nm [88 in-lbs].
H) Install the arc chute
• [Fig. 41]. Put arc chute (1) into adapter (2).
• [Fig. 41]. Tighten front and backside connections of the
arc runners (3), including lock washer; use 10 Nm [88 inlbs].
• [Fig. 41]. Tighten front and backside of the arc chute
connections (4), including flat washers; use 5 Nm [44 inlbs]. Put on isolation caps (6).
Fig. 43 Adapter and protective walls
40 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

6.1.5 Inspection of contacts’ tilt and gap
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
A) Remove the arc chute and adapter
• See 6.1.4-A/B.
B) Check the tilt of the main contacts
• [Fig. 45]. Use the hand lever for slowly closing the main
contacts.
• [Fig. 46]. Once the arcing contact touches arc runner,
check the air gap between main contacts. The gap
between main contacts shall have more than 1 mm
[0.04 in].
• In case of insufficient tilt (gap), replace the arcing contact
with new one. See 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 for details.
• If required gap is not available, even after component
replacing, please contact GE Service Team.
C) Check the air gap of arcing contact
• Close the breaker and secure the solenoid drive against
unintended opening. See 1.2.1.
• [Fig. 47]. Check the air gap between the arcing contact
and main arm. It shall be minimum 1 mm [0.04 in].
• In case of insufficient gap, replace the arcing contact
with new one. See 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 for details.
• If required gap is not available, even after contact
replacing, please contact GE Service Team.
D) Install back adapter and arc chute
• See 6.1.4-G/H.
Fig. 45 Closing operation by using hand lever
6.1.6 Inspection of the screw connections
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
• [Fig. 41]. Tighten front and backside of the arc runner
screw connections (3) and (5). Use torque of 10 Nm
[88 in-lbs].
• [Fig. 41]. Tighten arc chute connections (4). Use torque of
5 Nm [44 in-lbs].
• [Fig. 41]. The arc runner’s screw connections (3) must be
secured by means of lock washer.
• [Fig. 41]. The arc chute’s screw connections (4) must be
secured by means of flat washer.
• Any other screws shall be tightening with applied
torques from Table 3-D.
• Ensure that the screws are in good condition, that
thread and nest are not damaged. Surface shall be free
from rust. Replaced any screw, which does not fulfill
above conditions.
• This check must be carried out prior to commissioning
and after maintenance.
6.1.7 Inspection of the mechanical components
Only GE Service Team or its representative shall perform this
inspection. These require major disassembly and adjustment
of the breaker. Customer, without supervision of trained
specialist, shall not execute these.
Fig. 46 Inspection of the main contacts’ tilt
Fig. 47 Inspection of the arcing contact’s air gap
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 41

6.2 List of maintenance works
TYPE OF THE WORK BY WHOM WHEN REQUIRED RECOMMENDATIONS
A. Arc chute changing -Customer
-Trained technician
B. Arcing contact and arc
runners changing
C. Protective walls changing -Customer
D. Adjustment of the
contacts
E. Replacement of the
control board
F. Adjustment of the
mechanism
G. Flexband or fixed contact
changing
H. Mechanism changing -GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection B,E
I. Dumper(s) changing -GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection E Replace upper and lower dumper at
J. Trip unit changing &
adjustment
K. Auxiliary contacts
adjustment and changing
L. Drive changing -GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection B,E
M. Accessories changing -GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection B,E
Table 4
Required tools:
• Cleaning tissue
• Pocket lamp
• Hand lever
• Hexagon wrench SW 4, SW 5, SW 6
• Screw wrench SW 10, SW 13
• Torx® wrench size 30, 40 and 45
• Small and medium screwdriver
• Pliers
• Wire cutter
• File
• Steel brush
Safety hints:
Securing against falling parts
Hint 1 Place a cloth into the lower area of the arcing
contact [Fig. a]. Remember to secure the closing drive
according to Hint 3.
-Customer
-Trained technician
-Trained technician
-GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection C Only when replacement of the arcing
-Customer
-Trained technician
-GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection B,E
-GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection C,E
-GE Service Engr As a result of the inspection B,E
-Customer
-Trained technician
As a result of the inspection C
As a result of the inspection C Replace complete arcing set.
As a result of the inspection C
contact results with incorrect gaps.
See point 6.1.5.
As a result of the inspection B,E
the same time.
As a result of the inspection B,E In case of improper operation of the
switches, adjustment might be
necessary.
Maintenance with zero voltage release
Hint 2 If an optional zero voltage release is installed, it
must be energized to enable closing of the breaker. Only
then maintenance of the arcing contacts is possible.
To prevent the risk of injury, it is recommended
Hint 3
to secure the breaker in the closed position with a simple
mechanical interlock device [Fig. b]. A piece of tubing
having ~50 mm [~2 in] length and inner diameter of
minimum 14 mm [0,55 in] works well. The outer diameter
of the locking rod shall be less 8 mm [0,3 in]. GE does not
offer this locking device.
Fig. b Securing closing drive against opening
Fig. a Protecting of the arcing area against falling parts
42 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

6.2.1 Contact system (after 11/2003).
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
This section is valid for breakers manufactured after
11/2003.
This section refers to maintenance works A, B, C from Table 4.
A) Remove the arc chute
• [Fig. 49]. Loosen the screws (3) and (4), using SW5
hexagon wrench and take off the arch chute (1) from the
adapter (2).
B) Remove the arc chute adapter
• [Fig. 48]. To dismantle the arc chute adapter, loosen and
pull out the four upright screws (1) using SW5 tool. Pay
attention that no screws or washers fall inside the
breaker!
• [Fig. 48]. Draw aside and lift off both parings of adapter
(2). Then pull out two protective walls (3).
C) Changing the protective walls, arc runners and arcing contacts
• [Fig. 48]. Pull out two protective walls (3).
• [Fig. 50]. Loosen screws (6a) with tool (SW4) and take out
front wall (6).
• [Fig. 50]. Loosen screw (5a) with tool (SW5) and take out
the front arc runner (5).
• [Fig. 50]. Take out the back arc runner (4) by loosening
two screws (4a) with tool (SW5). Don’t remove the
protective cap (4b).
• [Fig. 50]. Loosen and take out screw (7) including locking
plate (8). Don’t split up screw and locking plate!
• [Fig. 50]. Pull out axis pin (9). Pull out arcing contact (10)
and put in new arcing contact.
• [Fig. 50]. Put in axis pin (9) and protect it by the locking
plate (8). Tighten screw (7) with torque of 10 Nm [88 inlbs].
• [Fig. 50]. Install front-arc runner (5) and back-arc runner
(4). Tighten it using torque of 10 Nm [88 in-lbs].
• [Fig. 50]. Install front wall (6) and adjust it by positioning
the protective wall. Tighten with torque of 10 Nm [88 inlbs].
• [Fig. 48]. Put in two protective walls (3).
D) Install the adapter
• [Fig. 48]. Install two protective walls (3). Use new ones if
necessary. Install two parings of adapter (2) and tighten
screws (1); use 5 Nm [44 in-lbs].
E) Install the arc chute
• [Fig. 49]. Put in arc chute (1) into adapter (2).
• [Fig. 49]. Tighten front- and backside connections of the
arc runners (3), including lock washer; use 10 Nm [88 inlbs].
• [Fig. 49]. Tighten front- and backside of the arc chute
connections (4), including flat washers; use 5 Nm [44 inlbs].
1
2
Fig. 48 Adapter and protective walls
Fig. 49 Arc chute and arc runners fixing
1
2
4
3
5
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 43

4
4
4a
5
6
5a
6.2.2. Contact system (before 11/2003).
Pay attention to the warnings, Section 1!
This section is valid for breakers manufactured
before 11/2003.
This section refers to maintenance works A, B, C from Table 4.
A) Remove the arc chute and adapter
• See 6.2.1-A/B.
C) Changing the protective walls and arc runners
• [Fig. 48]. Pull out two protective walls (3).
• [Fig. 50]. Loosen screws (6a) with Torx® 30 and take out
front wall (6).
• [Fig. 50]. Loosen screw (5a) with tool (SW5).
• [Fig. 50]. Take out the front arc runner as it’s shown.
• [Fig. 50]. Take out the back arc runner (4) by loosening
two screws (4a) with tool (SW5). Don’t remove the
protective cap (4b).
• [Fig. 50]. Install new front-arc runner (5) and new backarc runner (4). Tighten it using torque of 10 Nm [88 inlbs].
• [Fig. 50]. Install front wall (6) and adjust it by positioning
the protective wall (3) [Fig. 48]. Tighten it using torque of
10 Nm [88 in-lbs]
• [Fig. 48]. Put in two new protective walls (3).
6a
7
8
10
Fig. 50 Changing arcing contact.
Fig. 51 Taking out the front arc runner of old design
44 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

D) Changing the arcing contact
• Remove front and back arc runner. See 6.2.2-C.
• Close the breaker and secure the solenoid drive against
unintended opening. See 1.2.2.
• Secure the contact area against parts falling inside
the breaker. See 1.2.1.
• [Fig. 52-1]. Initially loosen two braid’s screws with tool,
and unbolt them finally by hand.
• [Fig. 52-2]. Remove the safety ring from axis pin end.
• [Fig. 52-3]. Pull out the axis pin from contact.
• [Fig. 52-4]. Replace arcing contact with new one. Use old
contact to lift up two washers, and slip the new contact
under these. Remove old contact and rotate the new one
by 180 ° to its normal orientation.
• [Fig. 52-2/3]. Re-install the axis pin and safety ring.
• [Fig. 52-5]. Initially screw in braid’s screws by hand.
• [Fig. 52-6]. Tighten these by torque of 10 Nm [88 in-lbs].
• Install back the arc runners. See 6.2.2-C.
• Check the adjustments according to point 6.1.5-C.
• Install back adapter and arc chute. See 6.2.1-D/E.
Fig. 52-1 Unscrew cooper braid
Fig. 52-2 Remove safety ring
Fig. 52-4 Replace arcing contact
Fig. 52-5 Tighten braid’s screws by means of hand
Fig. 52-3 Remove axis pin
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 45
Fig. 52-6 Tighten braid’s screws with torque of 10Nm

6.2.3 Layout of control PCB inside control box
Slot numbers:
1 2 3 4 5 6
Fig. 53 Control box inside (w/o SEL unit)
Slot Control board Z-No. Orientation
1
---
2
NEKO unit (ED trip) 128 750 R1 equipment to left
3
Voltage converter 128 730 R2-R4 equipment to left
4
SU-control unit 128 700 equipment to right
5
---
6
ST/UVR control unit 128 710 R1, R2 equipment to left
Table 5 Layout of control PCBs inside the box w/o SEL
Slot numbers:
1 2 3 4 5 6
6.2.4 Replacement of the control boards
1. OPEN the breaker.
2. Disconnect power supply, and pull out all
the plugs from control box’s terminals.
3. If a NEKO control unit is installed, wait 1
minute until capacitors discharge.
Fig. 55-1 Unscrew and remove all the external plugs
Fig. 54 Control box inside (with SEL unit)
Slot Control board Z-No. Orientation
1
NEKO unit (ED trip) 128 750 R1 equipment to right
2
Voltage converter 128 730 R2-R4 equipment to right
3
SU-control unit 128 700 equipment to left
4
ST/UVR control unit 128 710 R1, R2 equipment to right
5
---
6
SEL control unit 128 785 R1-R2 equipment to left
Table 6 Layout of control PCBs inside the box with SEL
• Warning: The isolation plates between the control
boards and at the wall of the box must always be
present!
• Hint: In older systems, the control boards may be
installed turned 180 °!
46 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
Fig. 55-2 Unscrew four bolts of the box cover
Fig. 55-3 Carefully lower the box cover

Fig. 55-4 Unscrew all the plugs from control boards
Fig. 55-5 Pull out the plugs of the control boards. Pull out
selected control board. Insert new control board
• Listen that both, the isolation plate at the side of
equipment and the isolation plate at the side of
soldering, were inserted!
Fig. 55-7 Pay attention, that no cables will be pinched
between box and front cover during closing!
Fig. 55-8 Carefully replace the control box front cover and
attach the with the four screws
• Put on plugs X2…X6, fix the screws of the plugs and
switch on control voltage.
Checking the breaker:
• Open and Close the breaker 3 times while it is
disconnected from the system (in the “Test-position“ of
the draw out version/the installation). The breaker must
open and close without a time delay over 400 ms.
• If the test succeeds, reconnect the breaker to the main
circuit.
Fig. 55-6 Plug in all control plugs and tighten it by the
screws.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 47

6.2.5 Adjusting the auxiliary switch
536
21
1. OPEN the breaker.
2. Disconnect power supply, and pull out all the
plugs from control box’s terminals.
3. In case of NEKO control unit inside, wait 1
minute until capacitors discharge.
• Adjustment of the switches may be required if they fail
to provide correct position indication. This condition can
be caused by misalignment of the actuating plate (6)
[Fig. 56-3], represented by dashed line.
• If only 3 or 5 switches are installed in the center of the
block, plate misalignment will not occur (breakers built
after 2003).
• In the case of 10 switches or when switches are
mounted at the far left position, it might be needed
(breaker before 2003). In most cases, only far left or far
right mounted switches might need to be re-adjusted.
• Check all the switches operation to establish which need
to be re-adjusted (left or right side).
• OPEN the breaker.
• [Fig. 56-1] Loosen four screws (2). Move the front cover
(1) slowly down. The auxiliary switch block (3) is
accessible now, in the bottom of the compartment.
• [Fig. 56-2] Loosen screw (4) on the side (left or right),
which needs to be re-adjusted. Turn the proper adjusting
screw (5) clockwise, until all contacts switch properly.
Warning! Adjusting screw (5) too far in may over
compress the switches’ pin and cause breakdown.
• [Fig. 56-1] Check the correct signalization of all switches
at the connecting plug terminations X4, X5! If necessary
re-adjust the switches from other side.
• Now tighten solid the screws (4).
• [Fig. 56-1] Close the control box with front cover (1) by
fixing the four screws (2). Pay attention, that no cables
will be pinched between box and front plate.
• CLOSE the breaker several times. Check if the auxiliary
contacts are switching over correctly.
• Finally check the electrical functions in the “TESTposition” of the draw-out version after installing the
breaker into the substation.
If re-adjustment does not help, please contact GE Service
Team. It might be required to install switch block again or to
move switches to center of the block for better performance.
Fig. 56-1 Control box with auxiliary switch block
Fig. 56-2 Auxiliary switch block
Gerapid in “ON“ position:
Main contacts closed.
Aux. switches not actuated
Fig. 56-3 Actuating plate for auxiliary switch block
Gerapid in "OFF“ position:
Main contacts open.
Auxiliary
switches actuated
48 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

1
6.3 Spare parts lists.
6.3.1 Mechanical spare parts.
n
NNOOTTEE:: GGrraayy--sshhaaddeedd ppaarrttss aarree rreeccoommmmeennddeedd ffoorr aa mmaaiin
aapppplliiccaabbllee ttoo yyoouurr ssppeecciiffiicc bbrreeaak
Component Type Arc chute Part no. Ver.
Service kit for replacing
arcing components.
(Before 11/2003).
Service kit for replacing
arcing components.
(After 11/2003).
Arcing contact
Arc runner back side
Arc runner front side
Fixed main contact
Movable main contact
Set of protection walls
Ground insulation
Additional ground insulation
Spring bar cap ALL N/A 128 058
Upper damper ALL N/A 128 018
Lower damper ALL N/A 128 019
Adapter
Probe protection cap ALL ALL 128 529
Arc chute
Forced tripping release ALL N/A 128 640
1) Check the nameplate to define type
keerr ccoonnffiigguurraattiioonn..
2607 / 4207 / 6007 1x_ APN340110 R01
2607 / 4207 / 6007 2x_ APN340110 R02
8007 1x_ APN340110 R03
8007 2x_ APN340110 R04
ALL EF4-12 APN340110 R05
2607 / 4207 / 6007 1x_ APN340110 R06
2607 / 4207 / 6007 2x_ APN340110 R07
8007 1x_ APN340110 R08
8007 2x_ APN340110 R09
ALL EF4-12 APN340110 R10
ALL (after 11/2003) N/A 128 122 R02
ALL (before 11/2003) N/A 128 121
ALL 1x_ 128 521 R01
ALL 2x_ 128 521 R02
ALL EF4-12 128 810
2607 / 4207 / 6007 1x_ 128 525 R01
8007 1x_ 128 525 R02
2607 / 4207 / 6007 2x_ 128 525 R03
8007 2x_ 128 525 R04
ALL EF4-12 128 815
2607 / 4207 / 6007 N/A 128 110 R01
8007 with triple terminals N/A 128 110 R04
8007 with single terminals
2607 N/A 128 108 R01
4207 N/A 128 108 R02
6007 N/A 128 108 R03
8007 N/A 128 108 R04
ALL 1x / EF4-12 128 515/516 R01
ALL 2x_ 129 515/516 R02
2607 / 4207 / 6007 ALL 128 203 R01
8007 ALL 128 203 R02
2607 / 4207 / 6007 2x3/2x4/EF4 128 203 R04
8007 2x3/2x4/EF4
2607 / 4207 / 6007 1x_ 128 500 R01
8007 1x_ 128 500 R02
2607 / 4207 / 6007 2x_ 128 500 R03
8007 2x_ 128 500 R04
ALL EF4-12 128 500 R05
1X2 (1000V) 1x_ 128 550 R01
1X3 (1500V) 1x_ 128 550 R02
1X4 (2000V) 1x_ 128 550 R03
2X2 (2000V) 2x_ 128 550 R11
2X3 (3000V) 2x_ 128 550 R12
2X4 (3600V) 2x_ 128 550 R13
2X2S (2000V) 2x_ 128 550 R15
EF4-12 (3900V) EF4-12 124 900 R17
tteennaannccee ssttoocckk,, aass
N/A 128 110 R02
128 203 R05
Hints for parts identification:
128 122 R02 128 121
128 810 128 521 R01, R02
128 525 R01, R02
128 525 R03, R04
128 815
128 515 R01, R02
128 529 128 058
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 49

6.3.2 Electrical spare parts.
SU control PCB ALL N/A 128 700
ST control PCB ALL N/A 128 710 R01
UVR control PCB ALL N/A 128 710 R02
Interface plug External supply 24 V DC ±5% N/A 128 730 R01
PCMD 150 24 S24W-GE N/A 128 730 R02
Voltage converter
Standard NEKO PCB ALL N/A 128 750 R01
External NEKO 3C PCB ALL (obsolete) N/A 128 755 R01
External NEKO 4C PCB ALL (obsolete) N/A 128 755 R02
SEL control PCB
Auxiliary contact ALL N/A 174 349
Shunt trip 24 V DC ±5% ALL N/A 128 300 R01
Shunt trip 24 V DC ±20% ALL N/A 128 300
Shunt trip 220 V DC ALL N/A 128 300 R03
Shunt trip 125 V DC ALL N/A 128 300 R04
Shunt trip 110 V DC ALL N/A 128 300 R05
Zero-voltage release ALL N/A 128 320 R01
Solenoid closing drive ALL N/A 128 070 1)
Connector X2 ALL N/A DFK-PC 4/12-GF-7.62
Connector X3, X4, X5 ALL N/A DFK-MSTB 2.5/15-GF
PCMD 150 48 S24W-GE N/A 128 730 R03
PCMD 150 110 S24W-GE N/A 128 730 R04
PCMA 150 70 S24W-GE N/A 128 730 R05
2607/4207 for 35 °C ambient N/A 128 785 R01
2607/4207 for 55 °C ambient N/A 128 785 R02
R02
128 018 128 019
6.3.3 Recommend materials for selected works.
Standard parts, glues, pastes and greases are recommended for a maintenance stock.
Work to do. Spare parts.
Arc chute change Correct version of arc chute 128 550. Screws & Washers: M6x16 – 8.8 (ISO 4762); M6
Arcing contact, arc
runners and protective
walls change.
Correct version of the service kit APN340110
consist of:
- Arcing contact;
- Two arc runners;
- Two protection sheets;
Optional:
- Mini flexible braid 128 123;
Wiring modifications
and control PCB
Correct control PCBs or prepared wiring
harness.
change.
Dumpers change. - Damper 128 018;
- Damper 128 019;
Optional:
- Spring bar cap 128 058;
Changing of zero
voltage release / shunt
trip
- UV release 128 320;
- Correct shunt trip;
Optional:
- Spring bar cap 128 058;
1) For substitute materials please consult GE representative.
Standard parts, materials and optional
components 1).
toothed Rip-Lock, M6 conical spring (DIN 6796).
Screws & Washers: M6x16 A4 (DIN 4762); M6
toothed Rip-Lock; Retain ring 4 (DIN 6799); Disc
spring 12.5 type A (DIN 2093)
Others: Conductivity grease Alvania RL3 by Shell.
Hint: Replace 128 123 or 128 150 only if recognize
these parts are broken. Replace all the parts from
service kit APN340110.
Wires: 1 mm2, 1.5 mm2, 2.5 mm2; 500 V polymer
insulation type up to +100 C; RoHS compliant;
black.
Plugs: MSTBC 2.5-5.08;
Terminations: Crimp MSTBC-MT 0.5-1.0; Crimp
MSTBC-MT 1.5-2.5; Receptacles 2.8 mm DIN 46247
with insulation cap;
Screws & Washers: M6x25, M6x30, M8x25, M8x30 -
8.8 (ISO14581);
Materials: Transparent silicone E-COLL 310ML; glue
Locktite 222; thermo paste WLP500;
Screws & Washers: M6x25, M6x30, M8x25, M8x30 -
8.8 (ISO14581); M4x10 – 8.8 (DIN912); M4 ribbed
lock washer (BN791 by Bossard);
Others: Polyamide clip bands 25x100mm.
Materials: Transparent silicone E-COLL 310ML; glue
Locktite 222; thermo paste WLP500; grease Beacon
EP3 by ESSO.
50 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

7. Customer support
7.1 Options overview.
• The coding system,
introduced in 2008, is a
catalog configuration tool
based on Excel®.
• The catalogue code consists
of 20 digits. Each digit
represents specific rated
value or component.
• Table 7 shows all available
values, components and
accessories for the Gerapid
breaker family. Detailed
descriptions are available in
section 3. Please contact GE
Sales representative in case of
any questions.
• The coding system is valid for
Gerapid feeder type (F),
rectifier type (R) and
disconnector type (DS). This
User Manual relates only to
standard, feeder type
breakers (F).
• Not all of the options from
Table 7 are compatible. To
avoid improper configurations
use the “Gerapid
configuration tool” for
ordering.
• This Excel® based tool
provides a quick and mistake
proof configuration with
automatic generating of the
proper catalogue code and
set of characteristics helpful
for order description. Ask your
GE Representative for details.
The number of this tool is:
APN460437.
Table 7. General options overview for Gerapid breakers.
Breaker type Code number: 123 4567891011121314151617181920 Relevant standards
1 Gerapid 2607 5 Gerapid 8007R LV DC acc. IEC60947-2 4 Railway DC acc. EN50123-2 1
2 Gerapid 4207 6 Gerapid 10007R On Request R LV DC acc. IEEEC37.14 2
3 Gerapid 6007 7 Gerapid 8007DS China acc. IEC947-2 & GB14048.2 3
4 Gerapid 8007
Arc chute type Code 2 Gearapid SE retrofit 3 Railway & Industry applications 1
1 1X2 (1000 V) 4 2X2 (2000 V) S 2X2 S (1500 V) Heavy Industry type 4 Military type acc. MIL-C-5015G 2
2 1X3 (1500 V) 5 2X3 (3000 V) E EF4-12 (3600 V) R
3 1X4 (2000 V) 6 2X4 (3600 V)
Closing solenoid supply voltage Code 3 Mechanical Counter 1 Without 0
1 48 V DC 5 220 V DC 9 125 V AC
2 60 V DC 6 250 V DC A 230 V AC
3 110 V DC 7 110 V AC B 240 V AC Code 17 Arc chute presence signal
4 125 V DC 8 120 V AC R On Request With 1 Without 0
1 H/H - (H)orizontal 4 V/V B Special type B With 1 Without 0
2 H/V - (V)ertical 5 For SEL 6 kA S Special type S
3V/H 6For SEL 12 kA ROn Request
Main terminals polarization Code 5 Sidewalls protection panels 1 Without 0
1 Top connector '+' 2 Top connector '-' 0 Not apply Rodent proofing 2
SEL operation temperature Code 6 Code 14 Contacts position indicator
1 Ta = 35 °C 0 without SEL With 1 Without 0
2 Ta = 55 °C
Over current release (OCT) Code 7 With 1 Without 0
1 Fixed setting up to 15 kA 5 Polarized adj. 0,4-1,2 kA 0
2 Adjustable up to 15 kA 6 Polarized adjust. 0,8-2,5 kA Code 12 Impulse coil release
3 Fixed setting up to 24 kA 7 Polarized adjust. 2-6 kA Impulse coil with internal C-bank (NEKO) 2 Without 0
4 Adjustable up to 24 kA 8 Polarized adjust. 4-8 kA - 3 Impulse coil w/o internal C-bank 1
Control circuits supply voltage Code 8 Code 11 Auxiliary tripping device
1 external 24 V DC±5% 4 88 .. 145 V DC Shunt Trip - external 125 V DC 4 Without 0
2 24 V/24 V (DC stabilizer) 5 125 .. 353 V DC / 115 .. 240 V AC Shunt Trip - external 220 V DC 5 - 1
3 33 .. 85 V DC R On request Standard Zero Voltage Release 6 Standard Shunt Trip 2
Auxiliary contacts quantity - changeover type Code 9 Code 10 OC trip target
1 3 convertible contacts 3 9 convertible contacts R On Request With 1 Without 0
2 5 convertible contacts 4 10 convertible contacts
Main terminals layout (Top / Bottom) Code 4 Code 16 Lever for manual operating
Code 15 Protection options
Code 13 Forced tripping release
Without
OCT
code 19 Control conn ectors type
Code 18 Counter
0 R Shunt Trip - external 110 V DC 3
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 51

7.2 Ordering.
Gerapid with arc chute APN460437 rev03 09/2009
Quantity
Catalogue no:
=>
Diagram no:
Customer's reference no.
Breaker type
1
Code Name
Opt Code Code
2
3
4
[BAU]: code 1
5
6
Arc chute type
7
8
[LIC]: code 2
9
10
Closing solenoid supply voltage
11
12
13
14
[STE]: code 3
15
16
Main terminals layout
Top/Bottom
17
18
19
20
[ANS]: code 4
21
22
Main terminals polarization
[POL]: code 5
23
24
SEL operation temperature
[TSEL]: code 6
25
26
OC release
Threshold [kA]
27
28
[KSA]: code 7
29
30
Requested marks on the scale
31
32
Control circuits supply voltage
33
[NET]: code 8
34
35
Auxiliary contacts quantity
36
[HIS]: code 9
37
38
OC trip target
[KSM]: code 10 1
39
40
Auxiliary tripping releases
41
42
[HIL]: code 11
43
44
ED impulse coil release
[EDA]: code 12 13
45
46
Forced tripping release
[ZWA]: code 13 1
47
48
Contact position indicator
[STA]: code 14 1
49
50
Protection options
[SCH]: code 15 1
51
52
Lever for manual operating
[HAN]: code 16 1
53
54
Arc chute presence
[LBM]: code 17 1
55
56
Counter
[ZAL]: code 18 1
57
58
Control connectors type
59
[SST]: code 19 R
60
61
Relevant standard
62
[CUS]: code 20 3R
63
64
Documentation Language
[LNG]:
65
=> =>
Name
Gerapid 2607
Gerapid 4207
Gerapid 6007
Gerapid 8007
1X2 (1000 V)
1X3 (1500 V)
1X4 (2000 V)
2X2 S (1500 V)
48 V DC
60 V DC
110 V DC
125 V DC
220 V DC
250 V DC
H/H - (H)orizontal
H/V - (V)ertical
V/H
V/V
Special type B
Special type S
Top connector '+'
Top connector '-'
Ta = 35 °C
Ta = 55 °C
Fixed setting up to 15 kA
Adjustable up to 15 kA
Fixed setting up to 24 kA
Adjustable up to 24 kA
kA kA kA
kA kA kA
external 24 V DC±5%
24 V/24 V (DC stabilizer)
33 .. 85 V DC
3 convertible contacts
5 convertible contacts
9 convertible contacts
Without
With
Without
Standard Shunt Trip
Shunt Trip - external 110 V DC
Without
Impulse coil w/o internal C-bank
Without
With
Without
With
Without
Sidewalls protection panels
Without
With
Without
With
Without
Mechanical Counter
Railway & Industry applications
Military type acc. MIL-C-5015G
Railway DC acc. EN50123-2
LV DC acc. IEEEC37.14
China acc. IEC947-2 & GB14048.2
English
German
Unlock "On Request" options.
Special ratings tested by customer.
kA
kA
Breaker number:
Gerapid 8007R
15
Gerapid 10007R
26
Gerapid 8007DS
37
4
2X2 (2000 V)
14
2X3 (3000 V)
25
2X4 (3600 V)
36
EF4-12 (3600 V)
SE
17
110 V AC
120 V AC
28
125 V AC
39
230 V AC
4A
240 V AC
5B
On Request
6R
For SEL 6 kA
15
For SEL 12 kA
26
On Request
3R
4
B
S
10
Not apply
2
1
without SEL
20
Polarized adj. 0,4 kA - 1,2 kA
15
Polarized adjust. 0,8 kA - 2,5 kA
26
Polarized adjust. 2 kA - 6 kA
37
Polarized adjust. 4 kA - 8 kA
48
kA kA 0
kA kA
14
88 .. 145 V DC
125 .. 353 V DC / 115 .. 240 V AC
25
On request
3R
14
10 convertible contacts
On Request
2R
3
0
Shunt Trip - external 125 V DC
04
Shunt Trip - external 220 V DC
15
Standard Zero Voltage Release
26
3
02
Impulse coil with internal C-bank (NEKO)
-
0
0
02
Rodent proofing
0
0
0
Gearapid SE retrofit
13
Heavy Industry type
24
On Request
LV DC acc. IEC60947-2
14
2
On Request
Chinese
En Ch
On Request
De R
Name
to
Without OCT
52 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

7.2.1 Example of order no. 1
Line feeder breaker for LRT substation in Europe; comply with EN50123, with breaking
capacity of 50 kA, configured as follows:
1. Load current of 4000 A.
2. Nominal voltage of 1500 V; 2x2 arc chute chosen due to high breaking
capacity up to 70 kA.
3. Auxiliary supply voltage of 230 VAC for closing solenoid;
4. Vertical layout of both main terminals (V/V);
5. Breaker polarization not important;
6. Without SEL unit (not available with special terminals);
7. With OC release, adjustable in range of 6 kA…12 kA, with 7 marks on the scale
every 1 kA, set at 9 kA;
8. Auxiliary supply voltage of 230 VAC for controls;
9. With 8 auxiliary contacts;
10. With OC trip target;
11. With zero voltage release (UVR);
12. Without electrodynamic tripping device;
13. With forced tripping release for withdrawal operations;
14. With contacts’ position indicator;
15. Without sidewalls’ protection;
16. With hand lever;
17. Without arc chute indicator;
18. Counter not available;
19. With standard control connectors;
20. Test report according to EN50123-2 standard.
Correct catalogue code shall be: 2233AA4400002255RR1166001111001100001111
General remarks:
• Please check the “Unlock On Request options” checkbox to enable entering values,
which are not listed in this form.
• Please always define the markings number and values for OC release.
• Please choose the “On Request” option to define own OC tripping range.
• Use “On Request” option if available to define own, not standard ratings.
• Any other than first option for connector type are usually dedicated for retrofit
purposes. Please refer to special type of connectors’ options 2,3,4,R before
choosing these. Option 1 is suitable for most applications.
2010-06-07 S47183-E rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 53

7.2.2 Example of order no. 2
USA customer wants to buy Gerapid for DC drive application. The customer used to
buy Gerapid 8007 according to company special ID code “GE80071x2R3”. The breaker
shall comply with standard IEEE C37.14. Breaking capacity of 200 kA is required and
configuration as follows:
1. Load current of 6000 A;
2. Nominal voltage of 800 V;
3. Available auxiliary voltage of 125 V DC;
4. With special design of main terminals as per customer drawing number
“GE8007terR3”. Customer tested breaker in this configuration and test report and
drawings were sent to GE for confirmation.
5. Breaker polarization not important;;
6. Without SEL measurement system;
7. With OC release, w/o adjustment possibility. Threshold set at 24 kA;
8. Auxiliary supply voltage of 125 V DC for controls;
9. With maximum possible number of auxiliary contacts.
10. With OC trip target;
11. Shunt trip, with double winding, directly supply from external 125 V DC;
12. With electrodynamic coil and internal C-bank (NEKO control PCB);
13. Without forced tripping release;
14. With contacts’ position indicator;
15. Without additional protection covers;
16. With hand lever;
17. With arc chute indicator;
18. Counter not available;
19. With standard terminals for controls connection;
20. According to IEEE C37.14 standard.
Correct catalogue code shall be:
General remarks:
• “Special wiring!” indicates, that dedicated electrical diagram will be created for this
order. The diagram will be attached to the User Manual as an appendix. Diagrams
from the User Manual are not applicable here.
• Customer may call any special identification code that has been used in the past.
This will be additional reference number and will be placed on the breaker’s
nameplate beside of the actual, 20-digit catalogue code.
• Modifications of main terminals according to customer’s drawings are possible
after agreement with GE and after positive tests results.
Choosing a double winded shunt trip will limit your available auxiliary contacts
•
number to maximum 8 units.
441144RR0000334444114422001100111100112
2
54 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

7.2.3 Example of order no. 3
Customer wants to use Gerapid as a field discharge breaker to commutate current
from excitation system of synchronous machine to the discharge resistor circuit.
Customer has previously tested one Gerapid breaker in a special test sequence using
special ratings and internal standard “XXX 123”. Customer requests to put on the
nameplate rated parameters that have been tested. After agreement with GE both
parties decided to create special version of the breaker and assign to it a letter “a” as
extension of standard name. These breakers will be a retrofit units replacing old
Gearapid SE type.
1 Load current of 3200 A;
2 Operating voltage of 2750 V;
3 High power, low stability, source 220 V AC available for closing solenoid;
4 Terminals suitable to install SEL current measurement system.
5 Plus pole connected to the TOP terminal;
6 With SEL measurement system;
7 Without OC release;
8 Low power, high stability, 24 V DC source available for control supply;
9 With maximum possible number of auxiliary contacts.
10 Without OC trip target;
11 Zero voltage release;
12 With ED impulse release supply directly from external C-bank;
13 Without forced tripping release;
14 With contacts’ position indicator;
15 With side insulation panels;
16 With hand lever;
17 Without arc chute indicator;
18 Counter not available;
19 Special retrofit connectors for Gearapid SE breakers;
20 According to IEC 60947-2 standard.
21 User Manual must be in Polish.
Correct catalogue code shall be:
General remarks:
• Customer’s special solution with non-typical ratings. Additional letter “a” will be
assign to this configuration exclusively. Later customer can use this letter to call
the same configuration.
• It is possible to supply closing drive and controls from two separate source of
power.
22aa55RR551122001144006611001111110000334
4
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 55

7.3 Glossary
A
a-release – see Shunt trip device;
Activating magnet – see Closing drive;
Anti-pumping device – see SU control PCB. Prevents
reclosing after a close-open operation, as long as the device
initiating closing is maintained in the position for closing
Arc runners – (also: arc probes; arc horns). Provide safe arc
leading into the arc chute. There are two arc runners
mounted in Gerapid breaker, front and back.
Arcing contact – – (also: pre-contact; arcing pre-contact). An
arcing contact on which the arc is intended to be established,
to avoid wearing and burning of the main contacts. It is
mounted at the top of flexible band. It is easy to replace.
Spring loaded to maintain proper contact force.
Auxiliary contact – (also: make/break contact; a-/b-contact,
changeover contact, convertible contact). A contact included
in an auxiliary circuit and mechanically operated by the
breaker.
Auxiliary switch – (also: auxiliary switch; make/break contact;
a-/b-contact). A switch block containing up to 10 auxiliary
contacts,. Mechanically operated by the mechanism of the
breaker during switching operations. Auxiliary switch block is
mounted in lower compartment of the control box. Every
contact can be either NO or NC, configured by appropriate
wiring.
C
Closing drive – (also: activating magnet; closing solenoid;
solenoid drive). High power, black solenoid coil, mounted at
the front of the breaker, below the control box. Use for
electric and remote closing of the main contacts. Power
consumption is up to 2.6kW. Closing time is ~150ms.
Closing operation – (also: switching ON; CLOSE operation). It
is operation, by which the breaker is brought from the OPEN
position to the CLOSED position.
Closing solenoid - see Closing drive;
Control circuit terminals – (also: control sockets/plugs). Fully
insulated sockets at the front cover of control box. Intended
for external connection to the auxiliary and control circuits.
E
ED coil – (also: electro-dynamic coil). An impulse coil release.
Actuating element of ED impulse release, mounted on the
base, under the mechanism.
Electro-Dynamic impulse release – (also: ED tripping;
impulse release). Release device, consist of actuator (ED coil)
and control circuit (NEKO PCB with C-bank). This is an
auxiliary release, activated by high-energy impulse of
current. The impulse is shaped by internal (NEKO) or external
C-bank. Opening time is less 3ms. Time to charge capacitors
is ~15sec.
H
Lever for manual operating – (also: hand lever). Hand lever
can be used for both, closing and opening manual operation.
It is intend for use only during maintenance.
M
Main circuit – (also: mains; primary circuit; current path). All
the conductive parts of the breaker included in the circuit,
which is intend to close or open. It consists of: main terminals
(upper and lower), fixed contact, flexible band and lower bus
bar.
Main terminals – (also: main connections). Two conductive
bars provided for electrical connection to external main
circuit. Different configurations are avaiable.
N
NEKO control PCB – (also: ED coil control unit; internal C-bank
control). Control circuit PCB to supervise the operation of the
ED coil. It consists of control circuit and bank of capacitors.
Required to energize the ED impulse coil.
O
OCT – see Over-Current release;
Opening operation – (also: switching OFF; OPEN operation).
An operation by which the breaker is brought from the
CLOSED
Over-Current release – (also: OCT). An instantaneous and
direct acting mechanical release. Tripping the breaker in case
of overloads and short circuits. Is adjustable within
predetermined range. Opening time depends on short circuit
conditions and shall not exceed 5ms. Oct is activated be
means of magnetic energy from main circuit. Requires no
external control power.
P
Position indicator – (also: position indicating device). A
mechanical device mounted at the front of closing drive.
Indicates whether the breaker is in the open or closed
position.
CLOSED position is marked as “I”.
OPEN position is marked as “O”.
Pre-contact – see Arcing contact;
R
r-release – see Zero voltage release;
S
SEL – Current measurement system, consisting of sensing
element and control circuit. The sensor is an insulated tube,
mounted on the top terminal of the breaker. Utilizes two Hall’s
probes for sensing the current and direction. The proportional
voltage signal is transmitted to control circuit, placed in
control box. The SEL control PCB is an opto-isolated
transducer, which generates standard output signals
proportional to measured current.
SEL control PCB – a control circuit PCB. Controls and
transforms current measurement signal from SEL sensor.
Self cut-off function– A safety feature provided to avoid
overstressing of the closing drive and shunt trip release.
Closing drive is automatically cut-off from power source after
500ms. Shunt trip coil is connected in series with auxiliary
contact(s), which cause cut-off after breaker’s opening.
Shunt trip release – (also: ST; shunt release; a-release).
Instantaneous release energized by means of voltage signal.
Within 50ms trips the breaker’s mechanism. Use for remote
OPEN operation. ST can be activated by potential free contact
or by directly applied voltage from external source. ST can
have a single or double winding.
Solenoid drive - see Closing drive;
ST control PCB – control circuit PCB supervising the operation
of shunt trip release.
SU control PCB – control circuit PCB supervising the remote
closing operation by means of solenoid drive. Presents in
every breaker, and placed in control box. Provides also anti-
pumping and self cut-off functions.
Switching ON – see Closing operation;
Switching OFF – see Opening operation;
T
Trip-free device – A mechanical switching device, the moving
contacts of which return to and remain in the open position
when the opening operation is initiated after the initiation of
the closing operation, even if the closing command is
maintained. To ensure proper breaking of the current, which
may have been established, it may be necessary that the
contacts momentarily reach the closed position.
U
UVR control PCB - control circuit, designed as a single PCB,
for supervising the zero-voltage release device.
Z
Zero-voltage release – (also: under-voltage; UVR; r-release).
An auxiliary tripping device. Trips the breaker open on control
voltage loss. Opening time is less 75ms. It is used for remote
OPEN operation or control voltage supervision.
Interchangeable option with shunt trip release. Activated by
means of auxiliary “potential free”, NO or NC contact.
56 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07

7.4 Troubleshooting
Breaker does not CLOSE.
A) Closing drive doesn't operate electrically but it is still possible to close the breaker manually by mean of the hand lever.
1) Check the supply voltage of the drive (-X2 :1/:2). The
voltage shall not be less than 80% of drive’s rated
voltage.
2) Check the supply voltage of the controls (-X3 :4/:5).
The voltage shall not be less than minimum input voltage
required for installed voltage converter
3) Calculate the voltage drop at both supply lines and
check for adequate wire size.
4) Check the polarity of the supply connections.
5) Check continuity of the control connections.
Open the control box:
WARNING ! Following operations are done with control
voltage connected. Only trained specialist or GE Service
representative shall perform them. Risk of electric shock!
6) Check if the PCBs’ plugs are connected and
screwed.
7) Check if there is 24 V DC available at output of the
voltage converter. Check -X10 (:8:9:10) / (:6:7).
8) Check the status of the red LED diode on the SU
PCB.
- Does not light – power supply failure;
- Weak light – system ready to CLOSE;
- Intensive red light – system not ready to
CLOSE. Closing STOP circuit is active, or NEKO PCB is
not charged, or “anti-pumping” is active for 15 sec.
9) Check if the Closing STOP circuit is not open.
Measure voltage at SU PCB, (-X12 5:/:6). There shall
be ~24 V DC available for actuation of “closing stop
relay”. If there is no 24 V DC, check continuity of
closing STOP circuit. Check relays at ST/UVR/NEKO
PCBs, by controlling state of contacts at points :5/:6
of each.
10) Replace any ST/UVR/NEKO if necessary.
11) Replace the SU control PCB.
12) Switch OFF the power at control box! Check
continuity and resistance of solenoid winding. Replace
the solenoid in case of winding breakage.
Contact GE Service in case the problem is not solved.
B) Closing drive operates electrically, but it is not possible to keep contacts closed.
1) Check the forced tripping release (if installed). A
permanently blocked tripping device, during closing
operation, will cause closing failure and force contact
opening.
2) Check contact system area. Look for any parts that
may be stuck between contacts or into mechanism
module.
3) If the zero voltage release is installed, check
connection of (–S2) pushbutton. If only NO type (-X2 :6/:7)
is used, be sure that (–X2 :8/:9) is shorted.
Open the control box (only when UVR is installed).
4) Check the wiring connections for UVR PCB.
5) Check supply of the UVR control PCB (-X13 :7/:8)
Contact GE Service in case the problem is not solved.
Breaker does not OPEN.
WARNING! Below operations are done with control voltage
connected. Only trained specialist or GE Service
representative shall perform them. Risk of electric shock!
A) Shunt trip does not operate. Breaker is able to CLOSE and OPEN by means of hand lever.
1) Check points A2 to A5.
2) Check the self cut off contact HS11 (-X14 :1/:2).
3) Check the wiring connections and supply line of ST
PCB (-X14 :7/:8).
4) Check the continuity of shunt trip coil (-X14 :9/:10).
5) Replace the ST PCB or ST coil if necessary.
Contact GE Service in case of problem is not solved.
B) Zero voltage release does not operate. Breaker is able to CLOSE and OPEN by means of hand lever.
1) Check points A2 to A5.
2) Check point B3 to B5.
3) Check the continuity of UVR’s coil (-X13 :9/:10).
4) Replace the UVR PCB or UVR coil if necessary.
Contact GE Service in case the problem is not solved.
C) ED impulse releasedoes not operate. Breaker is able to CLOSE and OPEN by means of hand lever.
1) Check points A2 to A5.
2) Check the wiring connections and supply line for NEKO
PCB (-X16 :1/:2).
3) Check the voltage level and timing of firing signal for
releasing the C-bank energy (-X16 :3/:4). Voltage signal
shall be between 6-24 V DC and duration of minimum
3 ms.
4) Check if the NEKO is signaling C-bank charging correctly
(-X16 :9/:10). Relay is closed when NEKO is ready to
operate.
5) Check the continuity of ED coil (-X16 :11/:12).
6) Replace the NEKO PCB if necessary.
Contact GE Service in case the problem is not solved.
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 57

7.5 GE service teams
2010-06-07 S47183-E rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 58

7.6 Notes
2010-06-07 S47183e rev.03 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 59

GE Consumer & Industrial GmbH
Berliner Platz 2-6
D-24534 Neumünster
Germany
Phone: ++49 4321-201-0
Fax : ++49 4321-201-444 S47183e rev.03 09/2009
60 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183e rev.03 2010-06-07
 Loading...
Loading...