Page 1

™
models: 500, 510, 550, 560
Pilot's Guide
Page 2

Page 3

OVERVIEW
GPS NAVIGATION
FLIGHT PLANNING
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
ADDITIONAL FEATURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
Page 4

Page 5

Copyright © 2009 Garmin Ltd. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
This manual reflects the operation of System Software version 0002.0 or later. Some differences
in operation may be observed when comparing the information in this manual to earlier or later
software versions.
Garmin International, Inc., 1200 East 151st Street, Olathe, Kansas 66062, U.S.A.
Tel: 913/397.8200 Fax: 913/397.8282
Garmin AT, Inc., 2345 Turner Road SE, Salem, OR 97302, U.S.A.
Tel: 503/391.3411 Fax 503/364.2138
Garmin (Europe) Ltd, Liberty House, Bulls Copse Road, Hounsdown Business Park,
Southampton, SO40 9RB, U.K.
Tel: 44/0870.8501241 Fax: 44/0870.8501251
Garmin Corporation, No. 68, Jangshu 2nd Road, Shijr, Taipei County, Taiwan
Tel: 886/02.2642.9199 Fax: 886/02.2642.9099
Web Site Address: www.garmin.com
Except as expressly provided herein, no part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, transmitted,
disseminated, downloaded or stored in any storage medium, for any purpose without the express
written permission of Garmin. Garmin hereby grants permission to download a single copy of this
manual and of any revision to this manual onto a hard drive or other electronic storage medium to
be viewed for personal use, provided that such electronic or printed copy of this manual or revision
must contain the complete text of this copyright notice and provided further that any unauthorized
commercial distribution of this manual or any revision hereto is strictly prohibited.
®
and SafeTaxi® are registered trademarks of Garmin Ltd. or its subsidiaries. aera™ is
Garmin
a trademark of Garmin Ltd. or its subsidiaries. These trademarks may not be used without the
express permission of Garmin.
®
Jeppesen
XM
is a registered trademark of Jeppesen, Inc.
®
is a registered trademark of XM Satellite Radio, Inc.
October 2009 190-01117-02 Rev. A Printed in the United States or Taiwan
Page 6

Warnings, Cautions & Notes
WARNING: When installing the aera™, place the unit so it does not obstruct
the field of view or interfere with operating controls.
WARNING: The indicators represented on the Panel are based on GPS-derived
data and may differ from the instruments in the aircraft.
WARNING: Navigation and terrain separation must NOT be predicated upon
the use of the terrain function. The aera Terrain Proximity feature is NOT
intended to be used as a primary reference for terrain avoidance and does not
relieve the pilot from the responsibility of being aware of surroundings during
flight. The Terrain Proximity feature is only to be used as an aid for terrain
avoidance and is not certified for use in applications requiring a certified
terrain awareness system. Terrain data is obtained from third party sources.
Garmin is not able to independently verify the accuracy of the terrain data.
WARNING: The displayed minimum safe altitudes (MSAs) are only advisory
in nature and should not be relied upon as the sole source of obstacle and
terrain avoidance information. Always refer to current aeronautical charts
for appropriate minimum clearance altitudes.
WARNING: The altitude calculated by aera GPS receivers is geometric height
above Mean Sea Level and could vary significantly from the altitude displayed
by pressure altimeters. Always use pressure altitude displayed by the aircraft
altimeter when determining or selecting aircraft altitude.
WARNING: Do not use outdated database information. Databases used in the
aera system must be updated regularly in order to ensure that the information
remains current. Pilots using any outdated database do so entirely at their
own risk.
WARNING: XM Weather should not be used for hazardous weather
penetration. Weather information is approved only for weather avoidance,
not penetration.
WARNING: NEXRAD weather data is to be used for long-range planning
purposes only. Due to inherent delays in data transmission and the relative
age of the data, NEXRAD weather data should not be used for short-range
weather avoidance.
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 7
Warnings, Cautions & Notes
WARNING: The illustrations in this guide are only examples. Never use the
aera to attempt to penetrate a thunderstorm. Both the FAA Advisory Circular,
Subject: Thunderstorms, and the Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM)
recommend avoiding “by at least 20 miles any thunderstorm identified as
severe or giving an intense radar echo.”
WARNING: To reduce the risk of unsafe operation, carefully review and
understand all aspects of the aera Pilot’s Guide documentation and the Pilot’s
Operating Handbook of the aircraft. Thoroughly practice basic operation
prior to actual use. During flight operations, carefully compare indications
from the aera to all available navigation sources, including the information
from other NAVAIDs, visual sightings, charts, etc. For safety purposes, always
resolve any discrepancies before continuing navigation.
WARNING: The Garmin aera has a very high degree of functional integrity.
However, the pilot must recognize that providing monitoring and/or self-test
capability for all conceivable system failures is not practical. Although unlikely,
it may be possible for erroneous operation to occur without a fault indication
shown by the aera. It is thus the responsibility of the pilot to detect such
an occurrence by means of cross-checking with all redundant or correlated
information available in the cockpit.
WARNING: For safety reasons, aera operational procedures must be learned
on the ground.
WARNING: The United States government operates the Global Positioning
System and is solely responsible for its accuracy and maintenance. The GPS
system is subject to changes which could affect the accuracy and performance
of all GPS equipment. Portions of the Garmin aera utilize GPS as a precision
electronic NAVigation AID (NAVAID). Therefore, as with all NAVAIDs,
information presented by the aera can be misused or misinterpreted and,
therefore, become unsafe.
WARNING: The data contained in the terrain and obstacle databases comes
from government agencies. Garmin accurately processes and cross-validates
the data, but cannot guarantee the accuracy and completeness of the data.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
Page 8

Warnings, Cautions & Notes
WARNING: Do not use basemap (land and water data) information for
primary navigation. Basemap data is intended only to supplement other
approved navigation data sources and should be considered as an aid to
enhance situational awareness.
CAUTION: Avoid using any chemical or abrasive cleaners on the touchscreen
and/or plastic casing. Clean the touchscreen with a soft, clean, lint-free cloth.
Use water, isopropyl alcohol, or eyeglass cleaner, if needed.
CAUTION: The Garmin aera does not contain any user-serviceable parts.
Repairs should only be made by an authorized Garmin service center.
Unauthorized repairs or modifications could void both the warranty and the
pilot’s authority to operate this device under FAA/FCC regulations.
NOTE: All visual depictions contained within this document, including screen
images of the aera panel and displays, are subject to change and may not
reflect the most current aera system and aviation databases. Depictions of
equipment may differ slightly from the actual equipment.
NOTE: This product, its packaging, and its components contain chemicals
known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or reproductive
harm. This notice is being provided in accordance with California’s Proposition
65. If you have any questions or would like additional information, please
refer to our web site at www.garmin.com/prop65.
NOTE: Interference from GPS repeaters operating inside nearby hangars can
cause an intermittent loss of attitude and heading displays while the aircraft
is on the ground. Moving the aircraft more than 100 yards away from the
source of the interference should alleviate the condition.
NOTE: Use of polarized eyewear may cause the flight displays to appear dim
or blank.
NOTE: Temporary Flight Restriction (TFR) data is provided by the FAA and
may not be updated outside of normal business hours. Confirm data currency
through alternate sources and contact your local FSS for interpretation of TFR
data.
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 9

Table of Contents
Section 1 Overview ........................................................................................ 1
1.1 Unit Overview ............................................................................................................1
1.2 Getting Started .........................................................................................................2
Battery Installation ............................................................................................................... 2
Charging the Battery ............................................................................................................ 3
Mounting the aera in the Aircraft .......................................................................................... 3
Turning the Unit On/Off ........................................................................................................ 4
Changing Modes .................................................................................................................. 4
GPS Receiver Status ............................................................................................................. 5
1.3 Operation ...................................................................................................................7
Basic Navigation Controls ..................................................................................................... 7
‘Home’ Screen ...................................................................................................................... 8
Selecting a Function ........................................................................................................... 14
Scrolling ............................................................................................................................. 14
1.4 Accessing System Functionality .............................................................................15
Option Menus .................................................................................................................... 15
Data Entry .......................................................................................................................... 15
Waypoint Information Tabs ................................................................................................. 17
1.5 Using Map Displays .................................................................................................17
Map Range ........................................................................................................................ 18
Map Panning ..................................................................................................................... 19
Map Overlays ..................................................................................................................... 21
Map Symbols ..................................................................................................................... 22
1.6 System Settings ......................................................................................................23
Display ............................................................................................................................... 23
Sound ................................................................................................................................ 24
Additional Settings ............................................................................................................. 26
1.7 Nearest Airport Criteria Settings ..........................................................................27
1.8 Present Position ......................................................................................................28
Position .............................................................................................................................. 28
New Location ..................................................................................................................... 29
Simulator Mode ................................................................................................................. 29
Section 2 GPS Navigation ............................................................................ 31
2.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................31
Data Fields ......................................................................................................................... 32
Numeric Flight Data ...........................................................................................................35
Compass Arc ...................................................................................................................... 36
2.2 HSI/Panel ..................................................................................................................37
Changing the CDI Scale ...................................................................................................... 38
Setting the Bug Indicator .................................................................................................... 38
Manually Setting a Course .................................................................................................. 39
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
i
Page 10

Table of Contents
2.3 Vertical Navigation (VNAV) ....................................................................................40
Using the VNAV Feature ..................................................................................................... 41
2.4 Map Display Setup ..................................................................................................43
Map Orientation................................................................................................................. 43
Airports, Navaids, Cities & Roads ........................................................................................ 44
Airways .............................................................................................................................. 45
2.5 Waypoints ................................................................................................................46
Nearest Information ........................................................................................................... 49
Weather Information .......................................................................................................... 51
Accessing Additional information ........................................................................................ 52
2.6 Direct-to Navigation ...............................................................................................64
Section 3 Flight Planning ............................................................................. 67
3.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................67
Data Fields ......................................................................................................................... 67
3.2 Flight Plan Creation ................................................................................................68
Adding Waypoints to an Existing Flight Plan ........................................................................ 70
3.3 Flight Plan Storage .................................................................................................71
3.4 Flight Plan Activation .............................................................................................72
Editing Speed and Fuel Flow ............................................................................................... 72
Copying Flight Plans ........................................................................................................... 73
Deleting Flight Plans .......................................................................................................... 73
Inverting a Flight Plan ........................................................................................................ 74
3.5 Approaches ..............................................................................................................75
Selecting an Approach ........................................................................................................ 76
Activating Vectors-to-Final .................................................................................................. 78
Section 4 Hazard Avoidance ......................................................................... 79
4.1 XM® Weather (aera 510 & 560) ...............................................................................79
Activating Services .............................................................................................................79
XM Satellite Weather Products ............................................................................................ 80
Using XM Satellite Weather Products .................................................................................. 91
4.2 Terrain ......................................................................................................................94
Terrain Information ............................................................................................................. 95
Obstacle Information .......................................................................................................... 95
Terrain and Obstacle Color Code......................................................................................... 96
Terrain Views ...................................................................................................................... 97
Terrain Alerts & Setup ......................................................................................................... 98
4.3 Traffic Information Service (TIS) ..........................................................................101
TIS Symbology .................................................................................................................. 101
TIS Alerts ......................................................................................................................... 102
Traffic Ground Track ......................................................................................................... 103
Displaying Traffic Data ...................................................................................................... 103
ii
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 11

Table of Contents
Section 5 Additional Features ................................................................... 105
5.1 SafeTaxi ..................................................................................................................105
SafeTaxi Cycle Number and Revision ................................................................................. 106
5.2 AOPA Data (aera 500 & 560 Americas) ................................................................107
5.3 XM® Radio (aera 510 & 560) .................................................................................109
Activating XM Satellite Radio Services .............................................................................. 110
Using XM Radio ............................................................................................................... 111
Section 6 Appendices ................................................................................. 119
Appendix A: Messages, Alerts & Data Field Options ...............................................119
Miscellaneous Message Advisories .................................................................................... 119
Airspace Messages ........................................................................................................... 121
Data Field & Numeric Data Options ..................................................................................121
Aural Alerts ...................................................................................................................... 123
Appendix B: Abnormal Operation ..............................................................................125
Loss of GPS Position ......................................................................................................... 125
Hazard Display with Loss of GPS Position .......................................................................... 125
Appendix C: Managing Files and Databases .............................................................127
Connecting to a Computer ............................................................................................... 127
Managing Files ................................................................................................................ 128
MicroSD™ Card Use (Optional) ......................................................................................... 130
Databases ........................................................................................................................ 131
Appendix D: Installation and Interfacing .................................................................135
Mounting the aera in the Aircraft ...................................................................................... 135
Connecting to a Garmin VHF Comm Radio ........................................................................ 139
Information about USB Drivers ......................................................................................... 141
Connecting the GXM 40 Antenna (aera 510 & 560) .......................................................... 141
Connecting to a GTX 330 Mode S Transponder ................................................................. 142
Interfacing ....................................................................................................................... 143
Using an external GPS Antenna (Optional) ........................................................................ 145
Appendix E: Battery and Care Information ..............................................................147
Battery Information .......................................................................................................... 147
Changing the Fuse ........................................................................................................... 147
Cleaning the Casing ......................................................................................................... 148
Cleaning the Touchscreen ................................................................................................. 148
Protecting the Unit ........................................................................................................... 148
Avoiding Theft .................................................................................................................. 149
Registering the Unit ......................................................................................................... 149
Appendix F: General TIS Information ........................................................................151
TIS vs. TAS/TCAS ............................................................................................................... 151
TIS Limitations ................................................................................................................. 151
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
iii
Page 12

Table of Contents
Appendix G: Utilities ...................................................................................................155
Flight Log ......................................................................................................................... 155
Track Log ......................................................................................................................... 156
Heading Line .................................................................................................................... 159
E6B Calculator ................................................................................................................. 160
Aircraft Profile .................................................................................................................. 162
Weight & Balance ............................................................................................................163
EPE Circle ........................................................................................................................ 164
Proximity Waypoints ......................................................................................................... 165
Appendix H: Display Symbols ....................................................................................167
VFR Symbols .................................................................................................................... 167
IFR Symbols ..................................................................................................................... 168
Airspace Symbols ............................................................................................................. 170
Appendix I: Map Datum and Location Formats ........................................................173
Map Datums .................................................................................................................... 173
Location Formats .............................................................................................................. 173
Appendix J: Glossary ...................................................................................................175
Appendix K: License Agreement and Warranty ........................................................181
Contact Garmin................................................................................................................ 181
Software License Agreement ............................................................................................. 181
Limited Warranty .............................................................................................................. 181
AOPA Airport Directory Notice ..........................................................................................182
XM Satellite Radio Service Agreement ............................................................................... 182
Weather Data Warranty .................................................................................................... 183
FCC Compliance............................................................................................................... 184
Industry Canada Compliance ............................................................................................ 184
iv
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 13

Overview
SECTION 1 OVERVIEW
1.1 UNIT OVERVIEW
In aviation mode the aera presents GPS-derived analog flight instrumentation,
position, navigation, and hazard avoidance information to the pilot using a 4.3”
QWVGA color display with Touch Screen.
Power Button
Headphone/audio-out Jack
(Under Weather Cap)
External Antenna Connec-
tor (Under Weather Cap)
Microphone
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
MicroSD™ Slot
Battery Contacts
Release Key: Slide and
Release to Open the Battery
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Cover
Mini-USB Connector
Serial Number (Under
the Battery)
Unit Overview
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
GPS Antenna
Speaker
1
Page 14

Overview
1.2 GETTING STARTED
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
BATTERY INSTALLATION
NOTE: Refer to Appendix E for additional battery information.
CAUTION: Always keep the battery installed when the unit is on.
WARNING: The product contains a lithium-ion battery. To prevent damage,
remove the unit from the aircraft or vehicle when exiting or store it out of
direct sunlight.
Installing the battery:
1)
Locate the lithium-ion battery that came in the product box.
2)
Slide the release key until the battery cover on the back of the aera opens
up.
3)
Remove the battery cover.
4)
Locate the metal contacts on the end of the lithium-ion battery.
5)
Insert the battery so that the metal contacts on the battery line-up with the
metal contacts inside the battery compartment.
6)
Slide the top of the battery cover into the groove on the inside of the
battery compartment, and press down.
Installing the Battery
2
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 15
Overview
CHARGING THE BATTERY
NOTE: While in Charge Mode, the unit draws a current from the aircraft. To
avoid discharging the aircraft’s battery, disconnect the external power cable
from the unit when not in use for several days.
Charge the aera for at least 4 hours before using on battery power. Charge the
battery by connecting the vehicle or aviation power cable, the USB cable, an AC adapter
(optional accessory), or use a battery charger (optional accessory).
Plug the unit into a 12-Volt or 24-Volt connector to charge. The unit can be used
while it is charging. Charge the unit within the following temperature range
104°F (0° to 40°C).
Charging the unit’s battery using the aircraft's power outlet:
1)
Mount the aera in the aircraft (refer to Appendix D 'Installation and
Interfacing'), and connect the power cable to the aircraft power outlet
(cigarette lighter receptacle).
2)
Route the power cable so that it does not interfere with aircraft operation.
The unit begins charging as soon as external power is applied.
USING CHARGE MODE
: 32° to
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Applying external power to the aera automatically turns on the unit for full operation.
If the battery is present and needs to be charged, the external power source charges
the battery while the unit is in use.
If you do not want to use the unit, but you would like to charge the battery, you can
put the unit into Charge Mode. Connect the unit to an external power supply. Press
and hold the POWER Button. Instead of completely turning off, the unit now goes
into Charge Mode.
The unit will run cooler and may allow more current to be available while in Charge
Mode, when XM is unplugged, the backlight is turned down, etc.
MOUNTING THE aera IN THE AIRCRAFT
Refer to Appendix D 'Installation & Interfacing' for information on mounting the
aera in the aircraft.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
3
Page 16
Overview
TURNING THE UNIT ON/OFF
Press and hold the POWER Button to turn the unit on or off.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
The first time the unit is turned on, the receiver must collect satellite data and
establish its present location. To ensure proper initialization, the aera is shipped from
the factory in AutoLocate mode, which allows the receiver to “find itself” anywhere in
the world.
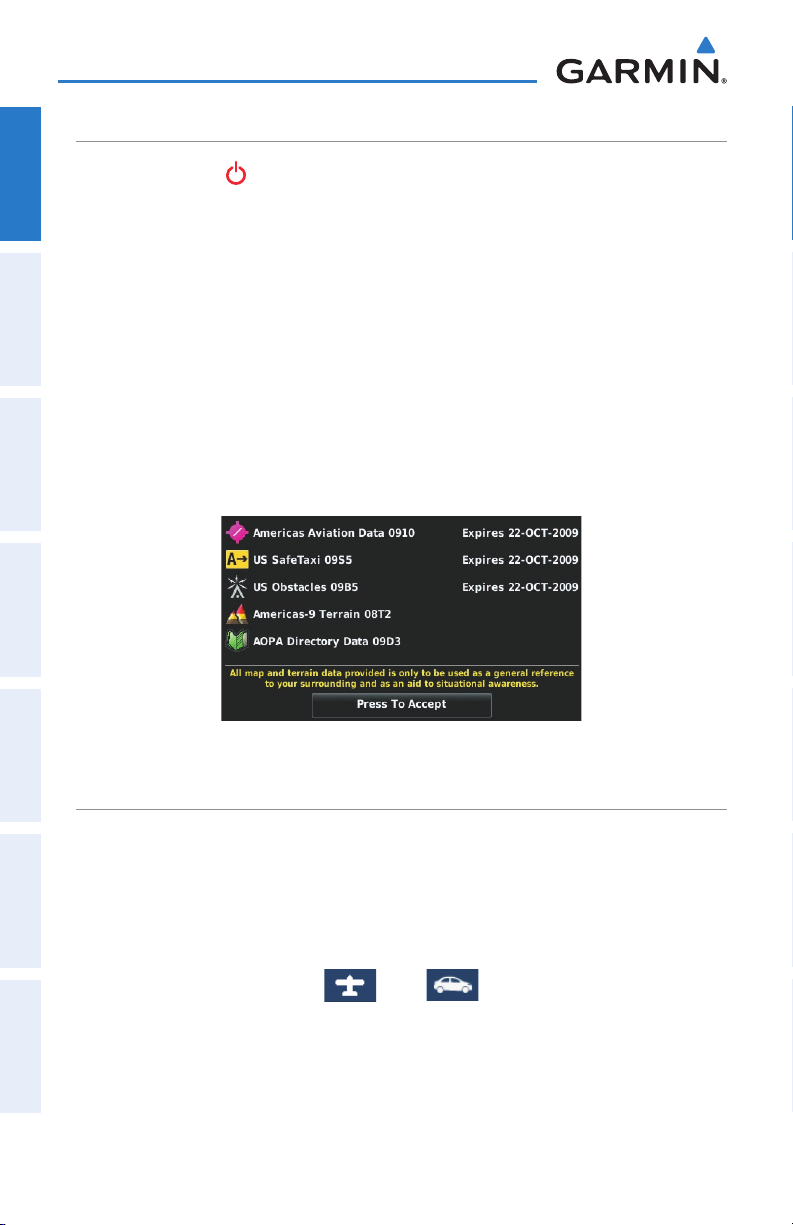
During initialization, current database information is displayed. Database information
includes valid operating dates, cycle number, and database type. When this information
has been reviewed for currency (to ensure that no databases have expired), the pilot
is prompted to continue.
Touching the Press To Accept Button acknowledges this information, and the
'Home' Screen is displayed.
Database Initialization
CHANGING MODES
The aera offers two modes for transportation: automotive and aviation.
Changing modes:
1)
Touch the automotive or aviation icon at the top of the 'Home' Screen.
2)
Touch Yes.
AutomotiveAviation
Or:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Automotive or Aviation (from
automotive mode).
2)
4
Touch Yes.
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 17
Overview
GPS RECEIVER STATUS
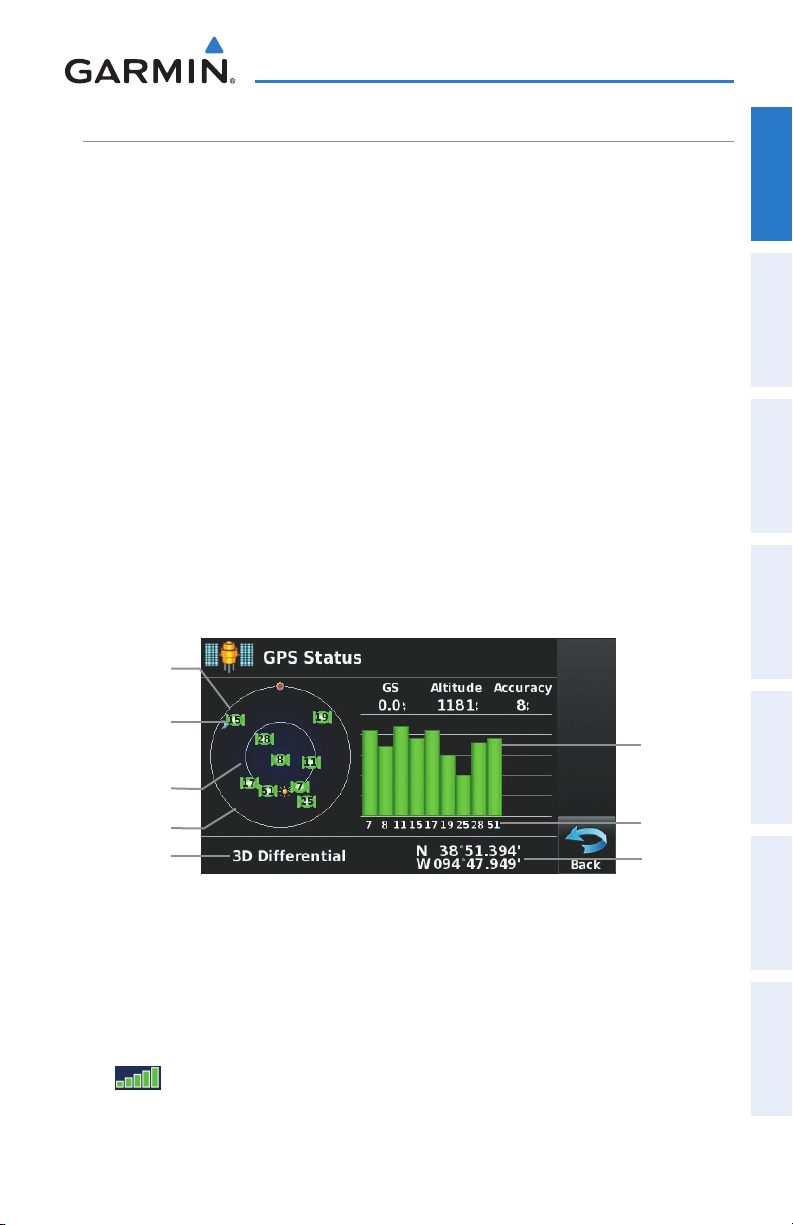
The receiver status displays one of the following conditions:
•Autolocate—Receiver is looking for any satellite whose almanac has been
collected, which can take up to 5 minutes
•Searching the Sky—Receiver is looking for satellites
•Acquiring Satellites—Receiver is looking for and collecting data from satellites
visible at its last known or initialized location, but has not acquired a fix
•2D GPS Location—At least three satellites have been acquired and a two-
dimensional location fix has been calculated. “2D Differential” appears when
you are receiving DGPS corrections in 2D mode
•3D GPS Location—At least four satellites have been acquired and a three-
dimensional fix has been calculated. “3D Differential” appears when you are
receiving DGPS corrections in 3D mode
•Lost Satellite Reception—the receiver is no longer tracking enough satellites for a
2D or 3D fix
Constellation
Diagram
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
PRN Number
45° Above
Horizon
Horizon
Receiver Status
GPS Status
Viewing the GPS status:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > GPS Status.
ACQUIRING SATELLITES
The bars on the 'Home' Screen indicate the GPS signal strength.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
Signal
Strength Bar
PRN Number
Location
(Lat/Long)
5
Page 18

Overview
When the receiver is in the process of acquiring enough satellite signals for
navigation, the receiver uses satellite orbital data (collected continuously from the
satellites) and last known position to determine the satellites that should be in view.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
‘Acquiring Satellites’ is indicated as the solution until a sufficient number of satellites
have been acquired for computing a solution.
When the receiver is in the process of acquiring a 3D differential GPS solution, ‘3D
GPS Location’ is indicated as the solution until the 3D differential fix has finished
acquisition.
SATELLITE INFORMATION
Satellites currently in view are shown at their respective positions on a satellite
constellation diagram. The outer circle of the constellation diagram represents the
horizon, the inner circle represents 45° above the horizon, and the center point shows
the position directly overhead. Each satellite is represented by a square containing the
Pseudo-Random Noise (PRN) number (i.e., satellite identification number).
GPS Status can be helpful in troubleshooting weak (or missing) signal levels
due to poor satellite coverage or installation problems. As the GPS receiver locks
onto satellites, a signal strength bar is displayed for each satellite in view, with the
appropriate satellite PRN number (01-32 or 33-64 for WAAS) below each bar. The
progress of satellite acquisition is shown in three stages, as indicated by signal bar
appearance:
- No bar—Receiver is looking for the indicated satellite
- Gray bar—Receiver has collected the necessary data and the satellite signal can
be used
- Green bar—Satellite is being used for the GPS solution
6
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 19
Overview
1.3 OPERATION
BASIC NAVIGATION CONTROLS
The controls on the touchscreen change dynamically depending on the function
displayed.
Touch the following icons to perform the associated function:
Home Returns to the ‘Home’ screen.
Back Displays the previous page; Returns ‘Home’ (touch and hold).
OK Commits a value edited or selected.
Menu Displays the context sensitive option menu.
Menu/ Displays the menu; Displays the Direct-to function (touch and hold).
Up Scrolls up.
Down Scrolls down.
Direct-to Displays the Direct-to function.
Out Zooms out.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
In Zooms in.
KEYPAD CONTROLS
OK Exits the keypad function and accepts the changes.
BKSP Erases the current data.
Numeric Displays the numeric only keypad.
Alpha Displays the alpha and numeric keypads.
Cancel Cancels a value that has been edited.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
7
Page 20
Overview
‘HOME’ SCREEN
Touch the
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
icon at any time to access the ‘Home’ Screen.
‘HOME’ SCREEN ICONS
Touch the following icons to perform the associated function:
Map Displays the Navigation Map.
Terrain Displays the Terrain Map.
HSI/Panel Displays the Panel Mode.
Nearest Displays the second-level Nearest Icons.
Numbers Displays flight data.
Active FPL Displays the Active Flight Plan.
WPT Info Displays the Waypoint Information.
Direct To Displays the 'Direct To' function.
Position Displays the aircraft's Present Position.
Weather Displays second-level Weather Icons (aera 510 & 560).
XM Radio Displays XM Radio (aera 510 & 560).
Tools Displays second-level Tools Icons.
8
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 21
Overview
NEAREST ICONS
From the ‘Home‘ Screen, touch the Nearest Icon to access the second-level
Nearest Icons.
Touch the following icons to perform the associated function:
Airport Displays nearest airports.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Airport WX Displays nearest airport weather.
VOR Displays nearest VORs.
NDB Displays nearest NDBs.
Intersection Displays nearest intersections.
VRP Displays nearest Visual Reporting Point (VRP) (Atlantic).
User WPT Displays nearest user waypoints.
City Displays nearest cities.
ARTCC Displays nearest ARTCCs.
FSS Displays nearest Flight Service Stations (FSS).
Airspace Displays nearest airspace.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
9
Page 22
Overview
WEATHER ICONS (aera 510 & 560)
From the ‘Home‘ Screen, touch the Weather Icon to access the second-level
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Weather Icons.
Touch the following second-level Weather Icons to display the weather product on
the Weather Map:
NEXRAD Displays NEXRAD (NEXt-generation RADar).
Satellite Displays Satellite Mosaic cloud cover.
Echo Tops Displays Echo Tops.
Winds Displays Winds Aloft.
Lightning Displays Lightning.
Storm Cells Displays Storm Cells.
METAR Displays METARs.
10
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 23
Overview
AIRMET Displays AIRMETs.
SIGMET Displays SIGMETs.
TFR Displays TFRs (Temporary Flight Restrictions).
PIREP Displays PIREPs.
Freeze Lvl Displays Freezing Levels.
Turb Fcst Displays the Turbulence Forecast.
Icing Fcst Displays the Icing Forecast.
WX Frst Displays Forecast Information (current, 12, 24, 36, & 48).
Pressure Displays Surface Pressure.
Sea Temp Displays Water Temperature.
TOOLS
From the ‘Home‘ Screen, touch the Tools Icon to access the second-level Tools
Icons.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
11
Page 24
Overview
Touch the following second-level icons to perform the associated function:
Setup Displays third-level Setup Icons.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
User WPT Displays User Waypoints and Proximity Waypoints.
Flight Log Displays Flight Logs.
Track Log Displays Track Logs.
FPL List Displays the Flight Plan List.
VNAV Displays Vertical Navigation.
Profile Displays Aircraft Profiles.
E6B Calc Displays the E6B Calculator.
Weight/Bal Displays the Weight & Balance.
Database Displays database and software version information.
Automotive Activates automotive mode.
GPS Status Displays GPS status information.
12
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 25
Overview
Se t u p Ic o n S
From the ‘Home‘ Screen, touch the Tools > Setup to access the third-level Setup
Icons.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Touch the following third-level icons to perform the associated function:
Display Displays backlight intensity/timeout and color mode settings.
Sound Displays sound settings.
Units Displays unit settings.
Date/Time Displays date & time settings.
Map Displays Navigation Map settings.
Position Displays position settings.
Interface Displays interface settings.
Alarms Displays alarm settings.
SUA Alarms Displays Special Use Airspace alarm settings.
Power Displays power settings
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
13
Page 26
Overview
SELECTING A FUNCTION
Selecting a function:
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Touch the desired icon. The icon will momentarily turn blue when selected.
Terrain Icon Selected (‘Home’ Screen)
SCROLLING
Scrolling up/down on the touchscreen:
Touch the Up or Down Arrow Icons (if available).
Or:
If the arrow icons are present, touch and drag your finger up or down.
14
Scrolling (Weather Icons)
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 27
Overview
1.4 ACCESSING SYSTEM FUNCTIONALITY
OPTION MENUS
The aera has a dedicated Menu Icon that displays a context-sensitive list of options
for the function displayed.
The Option Menu allows the user to access additional features or make setting
changes which specifically relate to the currently displayed function.
Navigating the option menu:
➊
I
f available, touch the Menu or Menu/ Icon
➋
T
ouch the Up/Down Icons if necessary to scroll through the Option Menu.
➌
T
ouch the desired menu option.
➋
➌
➊
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
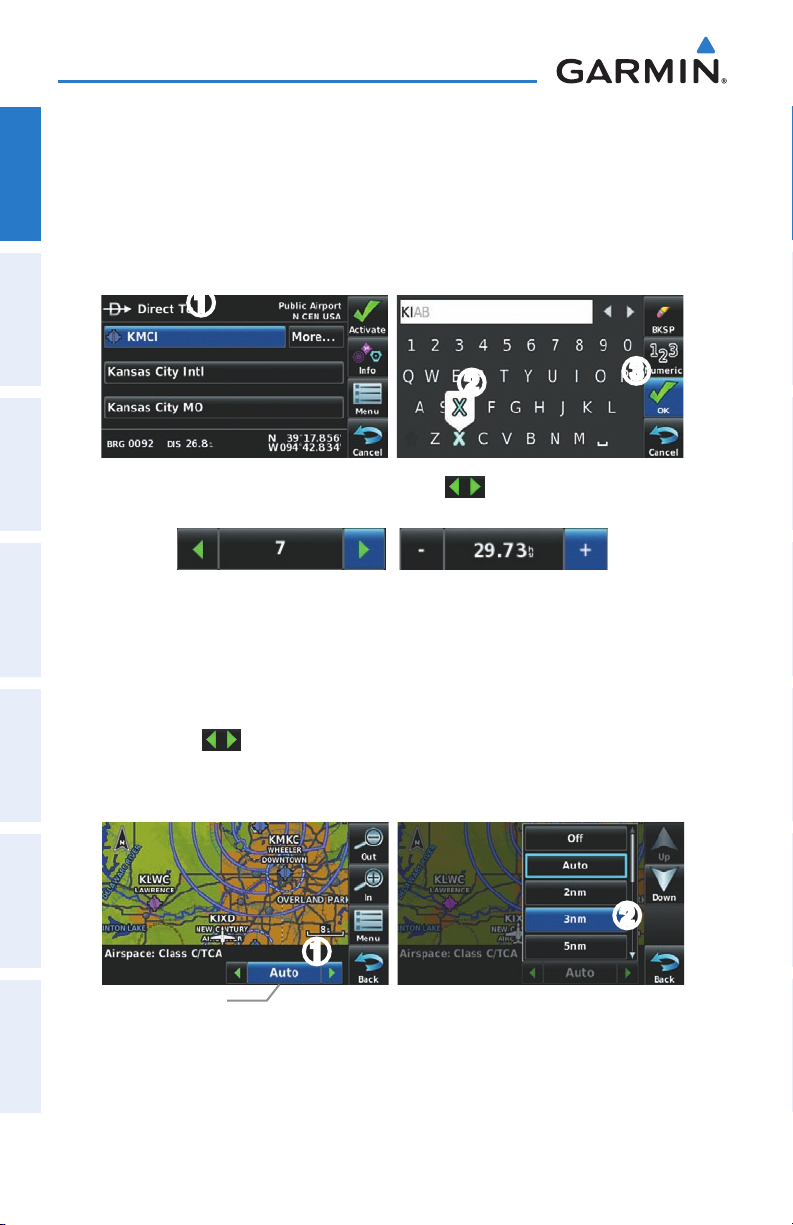
DATA ENTRY
Alphanumeric data can be entered using the keypad. In some instances, such as
when entering an identifier, the aera tries to predict the desired identifier based on the
characters being entered. In this case, if the desired identifier appears, use the OK Icon
to confirm the entry without entering the rest of the identifier manually. This can save
the pilot from having to enter all the characters of the identifier.
Predetermined data options are entered by touching the
horizontal list, or by touching the button to display a vertical list (if only two options
are available, touching the button will toggle the two data options).
Besides character-by-character data entry using the keypad and predetermined
data entry, the aera also provides a shortcut for entering ‘Flight Plan’, ‘Nearest’, and
‘Recent’ waypoint identifiers.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
to cycle through a
15
Page 28
Overview
Entering alphanumeric data:
➊
W
hen alphanumeric data can be entered, a keypad will appear after
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
touching the desired button.
➋
T
ouch the keypad to enter the desired data.
➌
T
ouch OK.
➊
➋
Nu
meric data may also be entered using or '+/-' buttons (if
applicable).
Entering predetermined data options:
➊
T
ouch the Data Option Button to display a vertical list of data options (if
applicable), or to toggle two data options
Or
:
To
uch the buttons to cycle through a horizontal list (if more than two
data options are available).
➋
I
f using the vertical list, touch the desired data option from the list.
(i.e., On/Off)
.
➌
➋
Data Option Button
16
➊
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 29
Overview
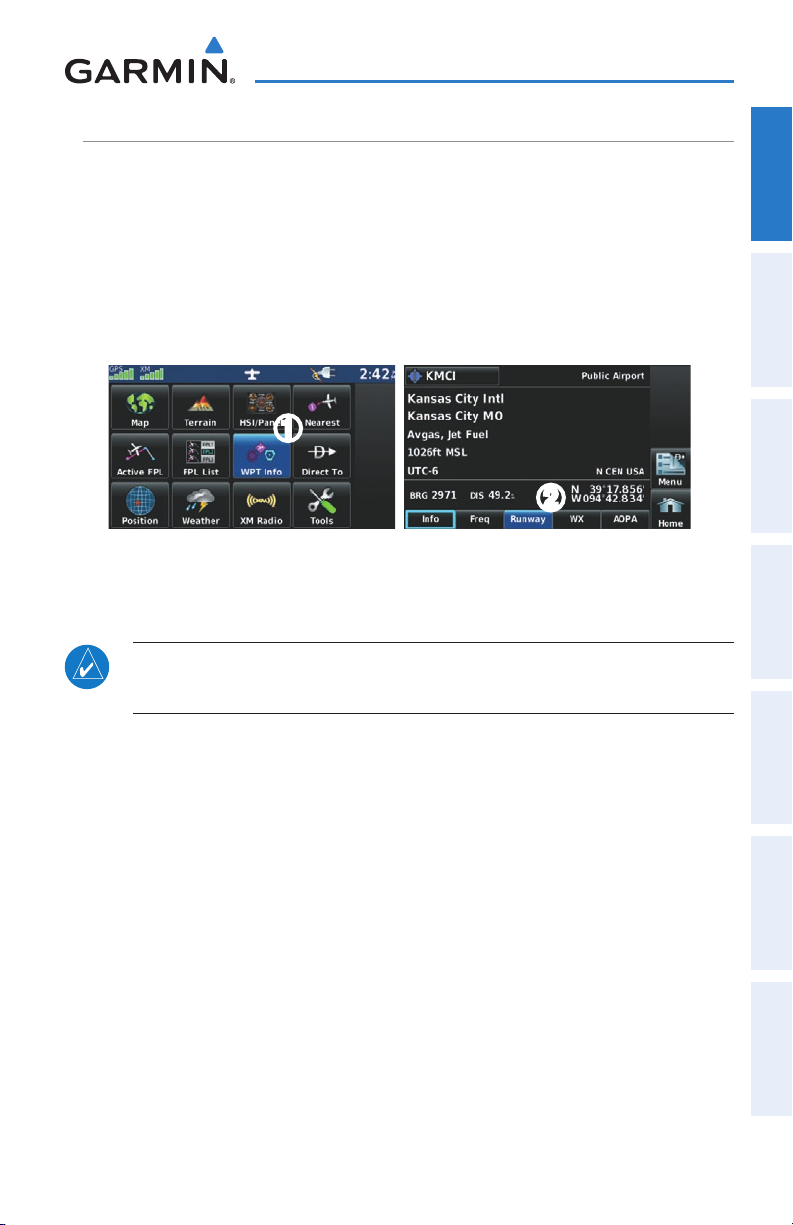
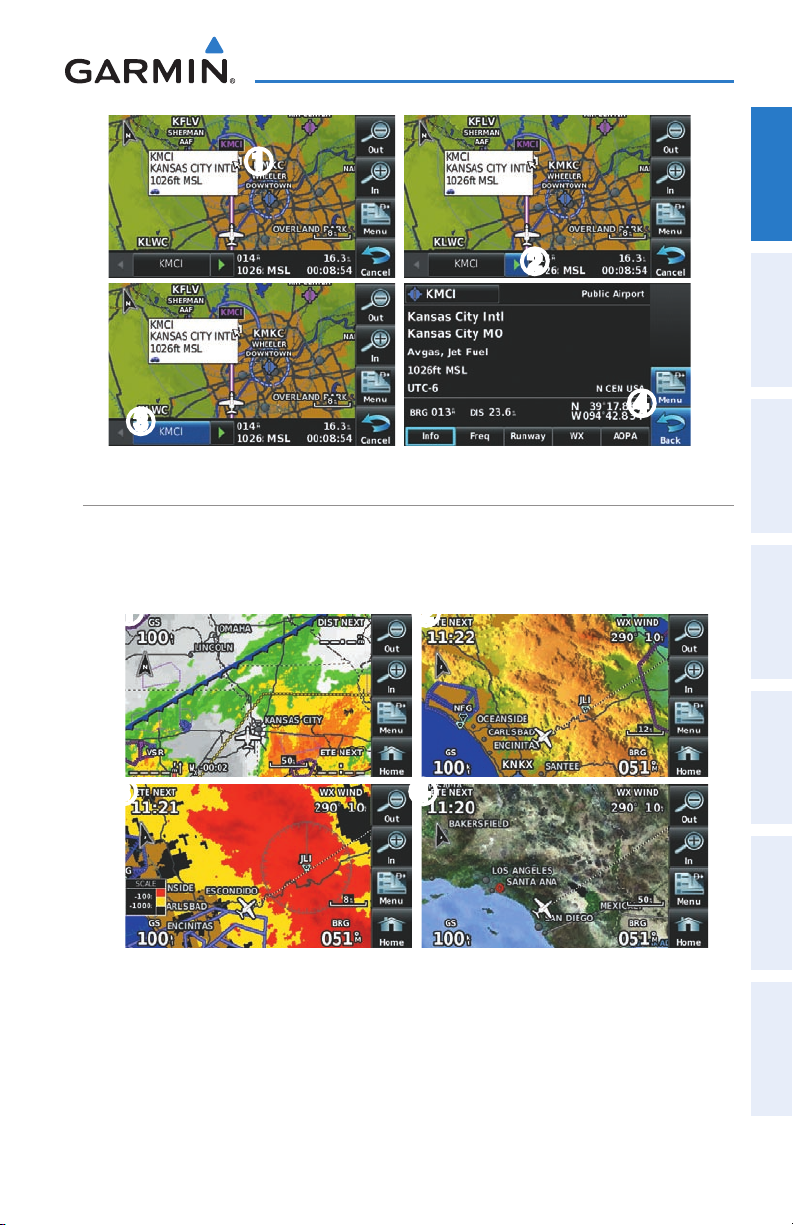
WAYPOINT INFORMATION TABS
Waypoint information is broken down into 5 tabs (
510 & 560 only), and
Waypoint Information Tabs:
➊
F
rom the 'Home' Screen, touch the WPT Info Icon.
➋
T
ouch the desired Tab (Info, Freq, Runway, WX
(optional)
).
AOPA
(aera 550 & 560 Americas only)).
➊
1.5 USING MAP DISPLAYS
NOTE: Refer to the GPS Navigation section for more information on Map
Display Setup.
Info, Freq, Runway, WX
(optional)
, AOPA
➋
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
(aera
Map displays are used extensively in the aera to provide situational awareness in
flight. Most aera maps can display the following information:
•
Airports, NAVAIDs, airspaces, airways, land data (highways, cities, lakes, rivers,
borders, etc.) with names
•Map Pointer information (distance and bearing to pointer, location of pointer,
name, and other pertinent information)
•Maprange
•Aircrafticon(representingpresentposition)
•Flightplanlegs
•Userwaypoints
•Trackvector
•Topographydata
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
17
Page 30
Overview
MAP RANGE
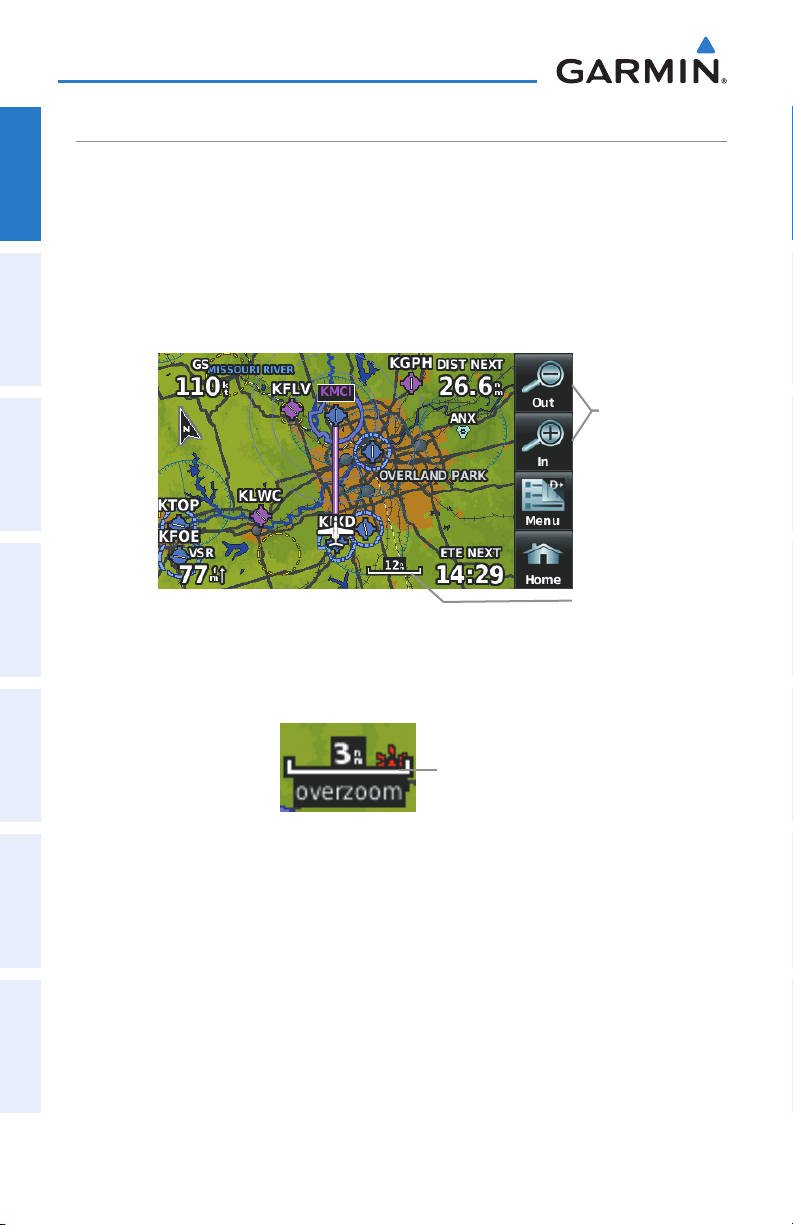
There are 23 different map ranges available, from 200 feet to 800 nm. The current
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
map range is indicated in the lower right. The scale bar represents the map scale. To
change the map range on any map, use the Out or In Icons to zoom ‘out’ (increasing),
or zoom ‘in‘ (decreasing).
Adjusting the map range:
While viewing a Map Display, touch the In or Out Icons.
Range
Icons
Map Range
Navigation Map
When the selected range exceeds the resolution of the map data, ‘overzoom’ appears
below the map range scale.
Scale Bar Representing a Map
Scale of 3 nm Per
Scale Width.
Map Range/Overzoom
AUTO ZOOM
Auto Zoom allows the aera to change the map display range to the smallest range
clearly showing the active waypoint. Auto Zoom can be overridden by adjusting the
range and remains that way until the active waypoint changes, a terrain or traffic alert
occurs, or the aircraft takes off.
18
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 31

Overview
Enabling/disabling auto zoom:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map.
2)
Touch the buttons to select the 'General' Category.
3)
Touch 'Autozoom'.
4)
Touch the 'On/Off' Data Option Button.
MAP PANNING
Map panning allows the pilot to:
•Viewpartsofthemapoutsidethedisplayedrangewithoutadjustingthemap
range
•Highlightandselectlocationsonthemap
•Reviewinformationforaselectedairport,NAVAIDoruserwaypoint
•Designatelocationsforuseinightplanning
•Viewairspaceandairwayinformation
When the panning function is selected by touching anywhere on the Map, the Map
Pointer is displayed. An Information Window also appears at the bottom of the map
display showing the the bearing, distance and time to the pointer from the aircraft’s
present position, the elevation of the land at the position of the pointer, or the object’s
(airports, obstacles, etc) elevation, if known.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
When the Map Pointer is over a map feature, the map feature is highlighted, an
information box appears on the map, and the highlighted map feature is displayed
on the Map Feature Button at the bottom of the screen (even if the name was not
originally displayed on the map).
Touching the Map Feature Button displays additional information for the highlighted
map feature. If multiple features are present at the Map Pointer position, green arrows
will appear on the Map Feature Button. Touching the
will cycle through the list
of map features present at that position.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
19
Page 32

Overview
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Information
Box
Map Feature
Button
Green Arrow
Indicating
Multiple
Features are
Present at the
Map Pointer
Location.
Activating the map pointer:
While viewing a Map Display, touch anywhere on the map to activate the
map pointer. Touch the Cancel Icon to remove the map pointer.
Panning the map:
While viewing a Map Display, touch anywhere on the map and drag. Touch
the Cancel icon to remove the map pointer.
Map Pointer
Map Panning (Navigation Map)
- Bearing,
Distance, and
Time En Route
to the Pointer
from the Aircraft's Present
Position.
- Elevation
at the Pointer
location.
Reviewing information for a map feature:
➊
W
hile viewing a Map Display, touch anywhere on the map to activate the
map pointer. When the Map Pointer is over a map feature, the map feature
is highlighted, an information box appears on the map, and the highlighted
map feature is displayed on the Map Feature Button at the bottom of the
screen. If multiple features are present at the Map Pointer position, green
arrows will appear on the Map Feature Button.
➋
I
f necessary, touch the buttons to cycle through the list of map
features present at that position.
➌
T
ouch the Map Feature Button to review information for the Map Feature.
➍
T
ouch the Back Icon to return to the map or touch and hold the Menu/
Icon to navigate to the map feature. Touch the Cancel Icon to remove the
map pointer.
20
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 33
➊
Overview
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
➋
➌
➍
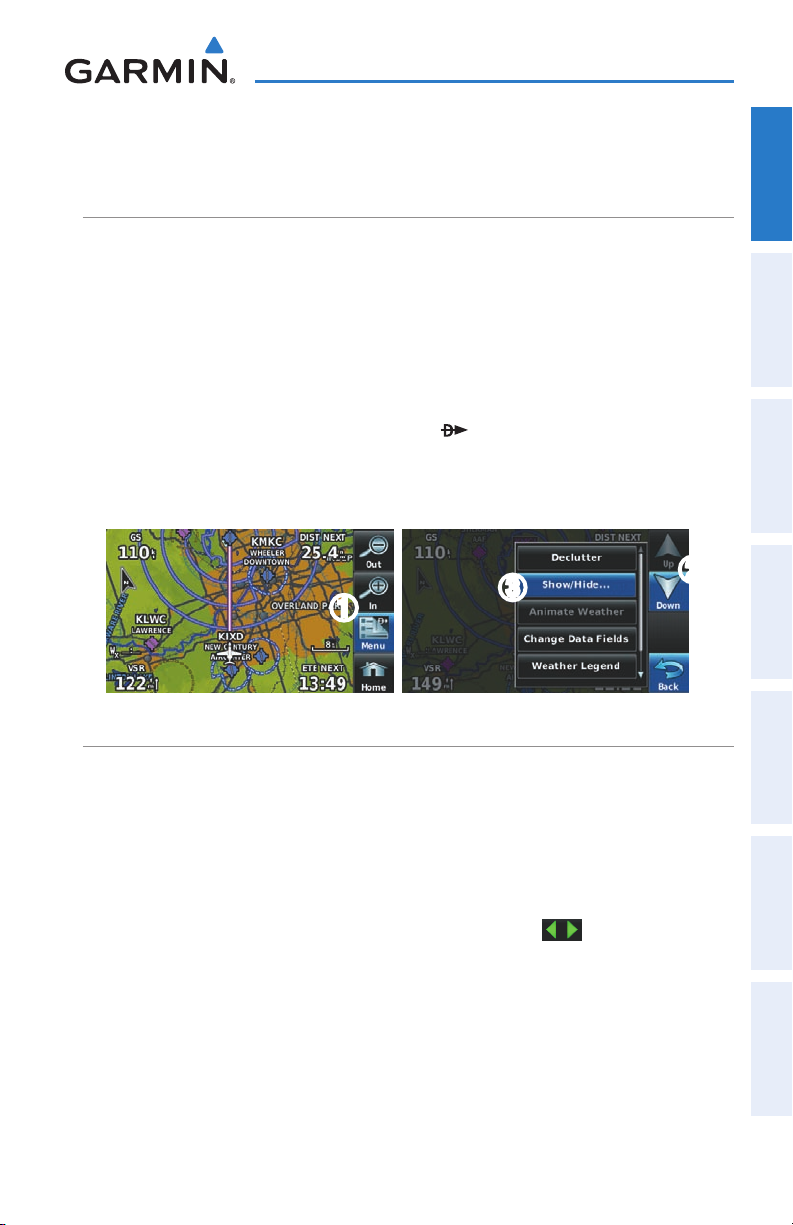
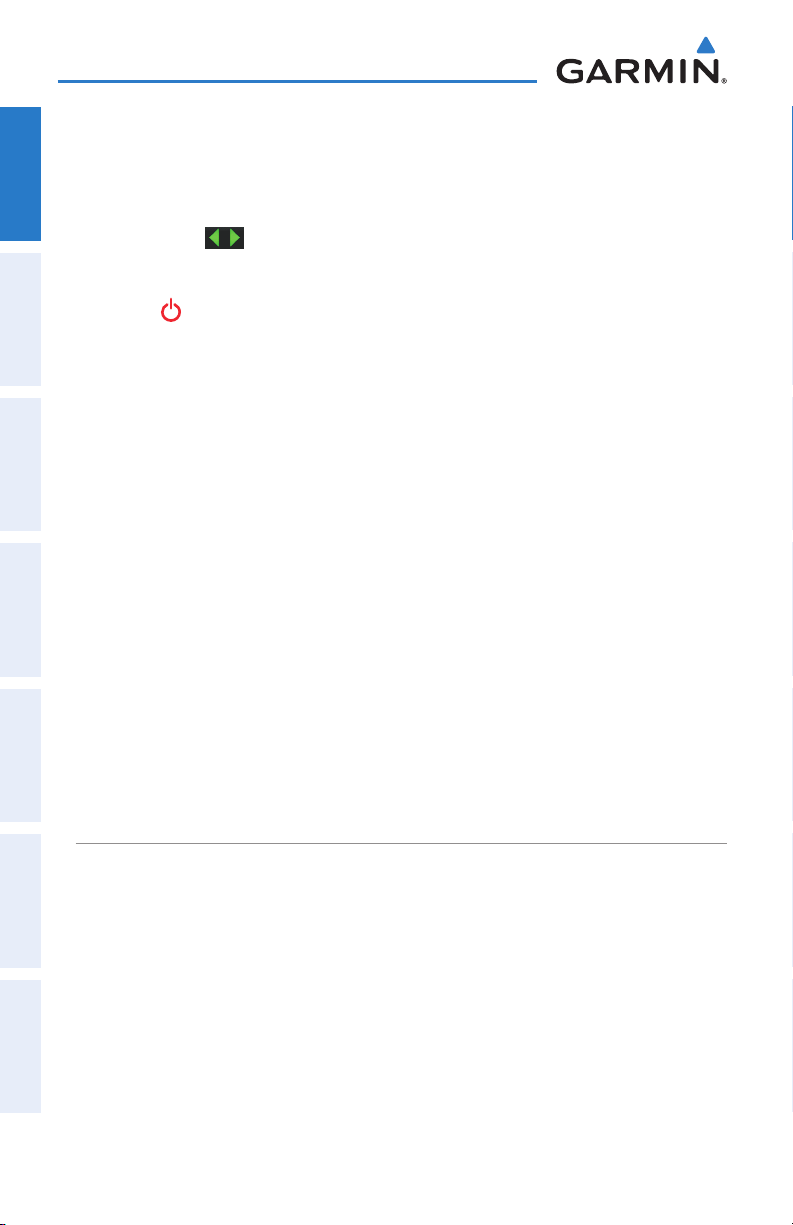
MAP OVERLAYS
The ➊Weather, ➋Topography, ➌Terrain, and ➍Satellite Imagery map overlays
can be displayed or removed.
➊
➌
Displaying/removing map overlays:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Show/Hide.
2)
Touch the 'Show/Hide' Data Option Button for the desired overlay.
➋
➍
Satellite View only displays satellite imagery at and above the 20nm range. Below
the 20nm range, 'no sat view' is displayed below the map range.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
21
Page 34

Overview
MAP SYMBOLS
Refer to Appendix H for a list of map symbols.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
DECLUTTER
The map can be adjusted to declutter (remove unwanted items, such as highways)
on the map.
Adjusting the declutter level of the navigation map:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Declutter.
2)
Touch the desired level (-1, -2, -3) on the right side of the screen. The
currently selected level is highlighted blue.
3)
Touch the Back Icon to remove the detail options.
Declutter
MAP DETAIL
The map detail can also be adjusted. Map detail changes the amount of detail with
respect to the zoom scale.
Adjusting the map detail:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map.
2)
Touch the buttons to select the 'General' Category.
3)
Touch Detail Level.
4)
Touch the Data Option Button, and touch the desired option from the list
(Least, Less, Normal, More, or Most).
22
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 35

Overview
1.6 SYSTEM SETTINGS
The third-level Setup Icons allow management of the following system
parameters:
•Display
•Sound
•Units
•Date&Time
•Map
Restoring system setting defaults:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup.
2)
Touch the desired Setup Icon (Display, Sound, Units, Date & Time,
Map, Position, Interface, Alarms, SUA Alarms, or Power).
3)
Touch Menu > Restore Default.
Or
:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup > Menu > Restore All
Settings.
•Position
•Interface
•Alarms
•SUAAlarms
•Power
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
DISPLAY
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Display Setup
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
23
Page 36
Overview
BACKLIGHT INTENSITY
Adjusting backlight intensity:
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup > Display.
2)
Touch the buttons to adjust the backlight intensity.
Or:
Press the POWER Button and enter the desired backlight intensity.
BACKLIGHT TIMEOUT
After a specified period of inactivity the backlight will turn off to save battery
power.
Adjusting backlight timeout:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup > Display.
2)
Touch the 'Backlight Timeout' Data Option Button, and touch the desired
option from the list (Stays On, 15 Seconds, 30 Seconds, 1 Minute, or
2 Minutes).
TOUCHSCREEN
Calibrating the touchscreen:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup > Display > Menu >
Calibrate.
2)
Follow the onscreen instructions, and touch OK. The unit will restart.
SOUND
Sound is broken down into ‘Master’, ‘Alerts’, and ‘Media’. 'Master’ controls ALL
sound. ‘Alerts’ and ‘Media’ are a percentage of the ‘Master’ sound. ‘Alerts’ refers to
navigation phrases (e.g. "Pull Up"), and ‘Media’ refers to the XM radio volume. The
Terrain Alerts, TIS Alerts, and Key Tones can also be toggled On/Off.
24
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 37

Sound Setup
Adjusting the sound:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup > Sound.
2)
Touch the buttons to adjust the sound.
Or
:
Touch the
Icon to mute the Master, Alerts, or Media audio. A blue
'X' will appear over the icon.
Or
:
Touch the 'On/Off' Data Option Button to toggle Terrain Audio, TIS Audio,
or Key Tones on or off.
Or:
Overview
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
1)
Press the POWER Button to quickly access the Master volume/mute.
2)
Touch Menu > Sound Setup to access ALL volume settings.
Muting sound:
See the ‘Adjusting the Sound’ procedure above.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
25
Page 38

Overview
ADDITIONAL SETTINGS
Changing settings (Units, Date & Time, Position, Interface, Alarms,
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
SUA Alarms, and Power):
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup.
2)
Touch the desired Settings Icon (Units, Date/Time, Position, Interface,
Alarms, SUA Alarms, or Power).
3)
Touch the desired setting to change. If only two options are available,
touching the field will toggle the two settings. If more than two options are
available, a vertical list is displayed with a blue outline around the current
setting. Touch the '+' or '-' buttons to increase/decrease the numerical
values (if necessary).
4)
Touch and hold the Back Icon to return to the ‘Home’ Screen.
Icon Available Settings
Display
Sound
Units
Date/Time
Position
Interface
Alarms
SUA Alarms
Power
Backlight Intensity, Backlight Timeout, Color Mode, Screenshot,
Calibration (from Option Menu)
Master (0-10), Alerts (0-10), Media (0-10), Key Tone, Terrain Audio,
TIS Audio
Distance, Speed, Direction Display, Temperature, Altitude, Vertical
Speed, Pressure, Fluid Volume
Time Format, Auto UTC Offset
Location Format, Map Datum, Heading, Magnetic Variation
Serial Data Format
Arrival, Next WPT, Proximity, Fuel Tank Reminder
Class B/TMA, Class C/TCA, Class D, Restricted, MOA, Other/ADIZ,
Parachute Area
Power Loss Warning
26
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 39

Overview
1.7 NEAREST AIRPORT CRITERIA SETTINGS
The Nearest Airports Option Menu allows the pilot to filter out airports that do not
meet a defined criteria. Specific surface types and runway lengths can be defined, as
well as the option to include private airports and/or heliports.
Runway Surface—allows you to set criteria for the type of surface on the runway:
•
Hard Only—shows only runways with a concrete, asphalt, or similar sealed
surface.
•
Hard or Soft—shows all runways except water landing facilities.
•
Water Only—shows only water landing facilities.
•
Any—shows any runway, regardless of surface type, including water landing
facilities.
Minimum Runway Length—allows the pilot to enter a specific length for the shortest
runway allowed.
Entering airport criteria:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > Airport > Menu > Set
Airport Criteria.
2)
Touch the desired setting to change ('Runway Surface', 'Include
Private Apts', 'Include Heliports') or touch the '+' or '-' buttons to
increase/decrease the Minimum Runway Length.
Or
:
To restore defaults, touch Menu > Restore Default.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Restoring airport criteria defaults:
See the ‘Entering Airport Criteria’ procedure above.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
27
Page 40

Overview
1.8 PRESENT POSITION
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
POSITION
The Present Position function displays latitude, longitude, GPS altitude, reference
waypoint, type, distance, direction, and bearing. The reference waypoint is designed to
display the current position in relation to a prominent landmark. The pilot can change
the reference waypoint ‘Nearest Type’ using the ‘Change Nearest Type’ menu option.
By default the Nearest Type is set to ‘Automatic’, which will display the nearest large
airport, enroute VOR, or city (in that order).
Present Position
Changing the Nearest Type:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Position > Menu > Change Nearest
Type.
2)
Touch the desired nearest type ('Automatic', 'Airport', 'VOR', 'NDB',
'Intersection', 'City', or 'Waypoint').
Viewing the present position:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Position.
28
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 41

Overview
NEW LOCATION
The ‘New Location’ menu option is used when the GPS Receiver is having trouble
finding the satellites it expects to be there.
Entering a new location:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Position > Menu > New Location.
2)
Touch 'Use Map', or 'Use Identifier'.
3)
After selecting your approximate position using the map pointer or entering
an identifier, touch OK.
4)
The GPS Receiver will begin a new search based on the location entered.
SIMULATOR MODE
Simulator Mode is helpful for practicing with the unit indoors or when no satellite
or XM signals are available. All waypoints and routes created in Simulator Mode are
retained in memory for future use.
NOTE: Do not attempt to navigate using Simulator Mode. When the unit is
set to Simulator Mode, the GPS receiver is turned off. Any Satellite Signal
Strength Bars shown are only simulations and do not represent the strength
of actual satellite signals.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Starting/Stopping Simulator Mode:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Position > Menu > Start/Stop Simulator.
Adjusting the simulated altitude, track, speed, waypoint, & position:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Position > Menu > Start Simulator.
2)
Touch the 'GPS simulator is on (for use indoors)' message to remove it.
3)
Touch Menu > Drive Simulator.
4)
Enter the desired data by touching the fields or using the +/- buttons.
Refer to Section 1.4 'Data Entry' for more information.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
29
Page 42
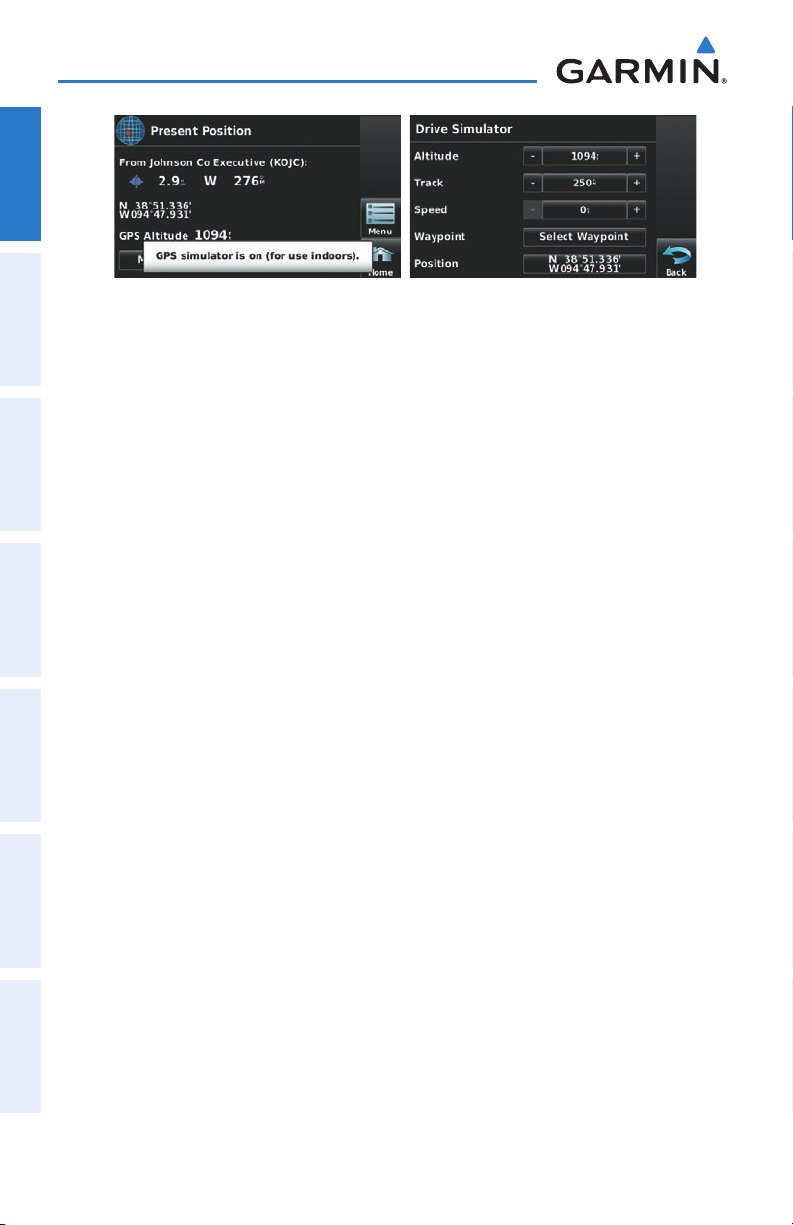
Overview
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Simulator Mode
30
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 43

GPS Navigation
SECTION 2 GPS NAVIGATION
2.1 INTRODUCTION
The Navigation Map displays aviation data (e.g., airports, VORs, airways, airspaces),
geographic data (e.g., cities, lakes, highways, borders), topographic data (map shading
indicating elevation). The Navigation Map can be oriented three different ways: North
Up (NORTH UP), Track Up (TRK UP) or Desired Track Up (DTK UP).
An aircraft icon is placed on the Navigation Map at the location corresponding
to the calculated present position. The aircraft position and the flight plan legs are
accurately based on GPS calculations. The basemap upon which these are placed are
from a source with less resolution, therefore the relative position of the aircraft to map
features is not exact. The leg of the active flight plan currently being flown is shown as
a magenta line on the navigation map. The other legs are shown in white.
Inactive Leg
(White)
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Flight Plan Legs (Navigation Map)
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
Active Leg
(Magenta)
Aircraft Icon
31
Page 44

GPS Navigation
DATA FIELDS
The data fields on the Navigation Map can be independently configured by the
user.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Data Fields
Data Fields (Navigation Map)
By default, the Data Bar Fields are set to display Ground Speed (GS), Distance - Next
(DIST NEXT), Vertical Speed Required (VSR), and Time En Route - Next (ETE NEXT).
These four data fields can be changed to display any of the Data Field Options.
32
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 45
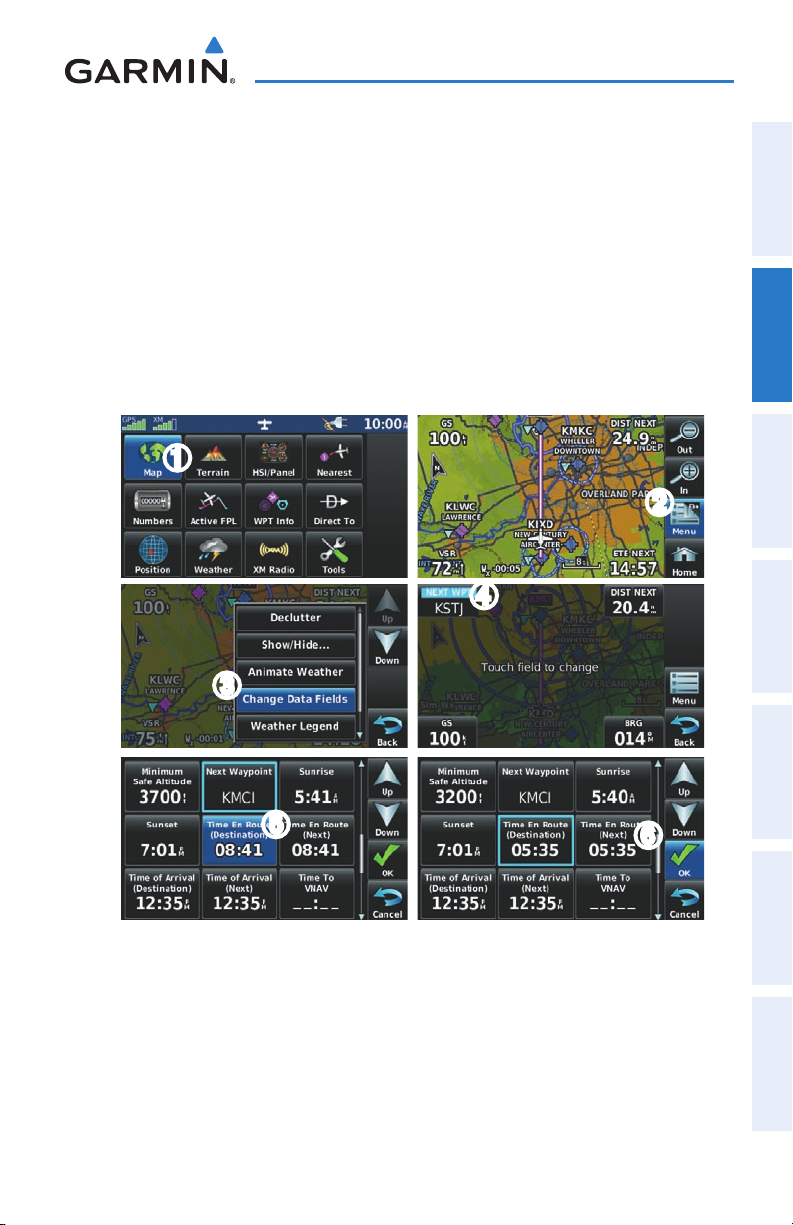
GPS Navigation
Changing the information shown in the data fields:
➊ From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Map Icon.
➋ Touch the Menu Icon.
➌ Touch the 'Change Data Fields' menu option.
➍ Touch the desired Data Field to change. A list of available Data Field Options
is displayed.
➎ Touch the desired Data Field Option.
➏ Touch the OK Icon.
➊
➋
➍
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
➌
➎
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
➏
33
Page 46

GPS Navigation
DATA FIELD OPTIONS
•Accuracy
•Altitude
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
•Bearing(BRG)
•CoursetoSteer(CTS)
•DesiredTrack(DTK)
•Distance(Destination)(DISTDEST)
•Distance(Next)(DISTNEXT)
•EnRouteSafeAltitude(ESA)
•ExternalVoltage(EXTVOLTS)
•FlightTimer(FLTTIMER)
•FuelTimer
•GlideRatio(G/R)
•GroundSpeed(GS)
•GroundTrack(TRK)
•MinimumSafeAltitude(MSA)
•NextWaypoint(NEXTWPT)
•Sunrise
•Sunset
•Time En Route (Destination) (ETE
DEST)
•TimeEnRoute(Next)(ETENEXT)
•Timeof Arrival (Destination) (ETA
DEST)
•TimeofArrival(NEXT)(ETANEXT)
•TimetoVNAV(VNAVTIME)
•Time(Local)
•Time(UTC)
•VerticalSpeed(VS)
•VerticalSpeedRequired(VSR)
•Wx(Altimeter)(WXALTIM)
•Wx(DewPoint)(WXDEWPT)
•Wx(Rel.Humidity)(WXHUMIDI)
•Wx(Temperature)(WXTEMP)
•Wx(Wind)(WXWIND)
34
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 47

GPS Navigation
NUMERIC FLIGHT DATA
The numeric flight data can be independently configured by the user.
Accessing numeric flight data:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Numbers.
Changing numeric flight data fields:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Numbers.
2)
Touch the desired data field to change. The available data fields are
displayed.
3)
Touch the desired data field.
4)
Touch OK.
Restoring default numeric flight data:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Numbers > Menu > Restore Default.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Numeric Flight Data
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
35
Page 48

GPS Navigation
COMPASS ARC
A compass arc appears by default on the Navigation Map. The route line represents
the course and the magenta bug indicator (similar to the bug indicator on the HSI)
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
can be set to ‘Bearing’ (default), ‘Course to Steer’, a specific heading reference (‘User
Selected’), or ‘Off’.
Magenta Bug Indicator
Compass Arc
Compass Arc (Navigation Map)
Displaying/Removing the Compass Arc from the Navigation Map:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map
2)
Touch the buttons to select the 'General' Category (if necessary).
3)
Touch Compass Arc.
4)
Touch the On/Off Button.
Setting the Compass Arc Bug Indicator:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Bug Indicator (only
available when the compass arc is displayed).
2)
Touch the desired menu option ('User Selected', 'Bearing', 'Course to
Steer', or 'Off').
36
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 49
GPS Navigation
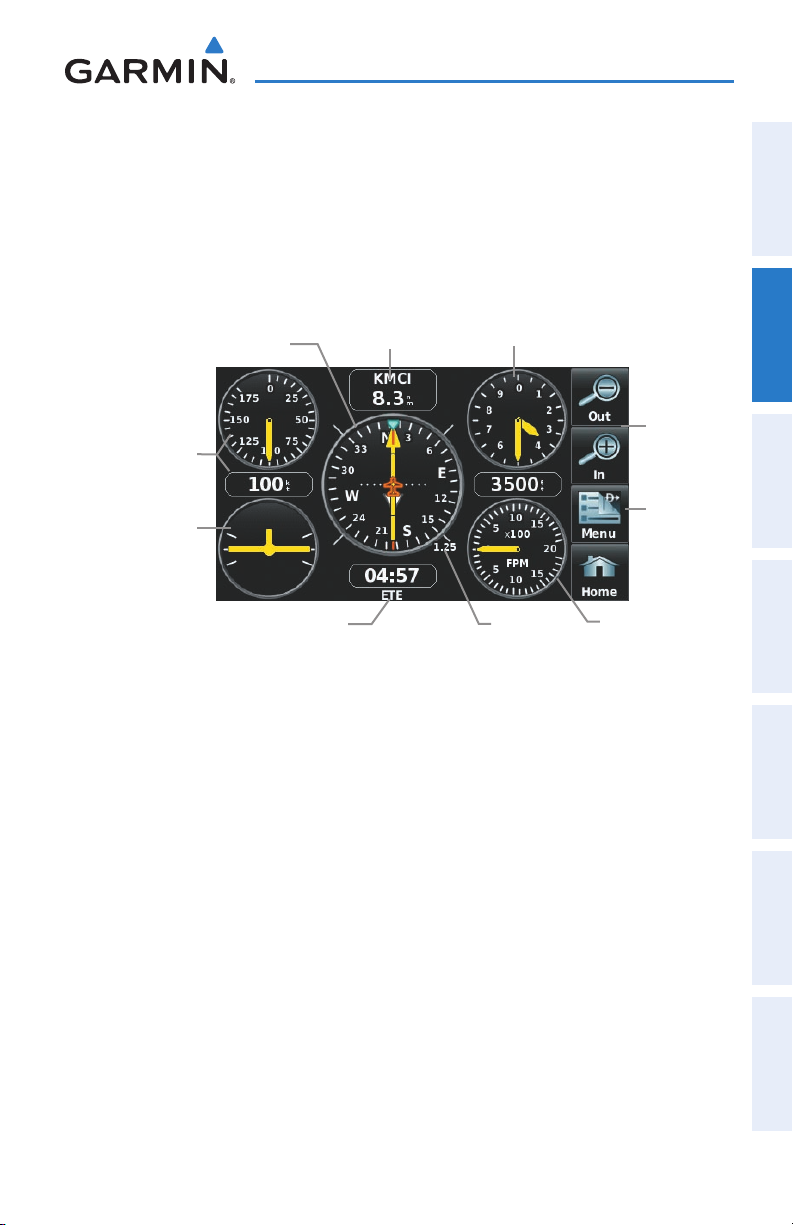
2.2 HSI/PANEL
The HSI/Panel shows GPS-derived data in a graphical format. Keep in mind the
differences between the GPS-derived panel and mechanical instruments, as mechanical
panel instruments use sensors that provide information different from that derived
using GPS.
HSI
Ground Speed
Turn Rate Indicator
- Next Waypoint
-Distance
HSI/Panel
The Panel shows a graphic Horizontal Situation Indicator (HSI) surrounded by
additional indicators.
Altitude
CDI Scale
Adjustment
Option
Menu
Vertical SpeedCDI ScaleEstimated Time Enroute
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
The graphic HSI depicts the course to the destination or the next waypoint in a flight
plan, current ground track, off course error, and a To/From indication. The rotating
compass indicates your current ground track.
The course pointer and course deviation needle indicate the course and whether you
are on the course. The Bug Indicator can be set to ‘Bearing’ (default), ‘Course to Steer’,
a specific heading reference (‘User Selected’), or ‘Off’.
Bearing is the compass direction from the present position to a destination waypoint.
Course to Steer is the recommended direction to steer in order to reduce cross-track
error and return to the course line.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
37
Page 50

GPS Navigation
The Course Deviation Indicator, or needle, indicates how far off course, left or right,
based on its placement along the course deviation scale.
The course deviation scale setting is adjustable for Auto, ±0.25, 1.25 or 5.0 (nautical
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
mile, statute mile, or kilometer) full-scale deflection. The course deviation scale appears
on the lower right corner of the HSI. The default setting is Auto, which uses three
factors to determine the distance from the center of the CDI to full left or right limits:
CDI scale = 1.25 - within 30 nm of any airport in the active route.•
CDI scale = 0.25 - on an approach leg or within 2 nm of the FAF or MAP.•
CDI scale = 5.0 - if the previous two conditions do not exist.•
Displaying the HSI/Panel:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch the HSI/Panel Icon.
CHANGING THE CDI SCALE
The CDI scale can be set by touching the In or Out Icons from the HSI/Panel Screen
(if the CDI scale is NOT set to 'Automatic') or from the HSI/Panel option menu.
Changing the CDI scale:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch HSI/Panel > Menu > Set CDI Scale.
2)
Touch the desired CDI Scale (' Automatic', ' 0.25 nm', ' 1.25 nm', or
'5.00 nm').
SETTING THE BUG INDICATOR
The Bug Indicator can be set from the HSI/Panel option menu.
Setting the Bug Indicator:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch HSI/Panel > Menu > Set Bug
Indicator.
2)
Touch the desired menu option ('User Selected', 'Bearing', 'Course to
Steer', or 'Off').
38
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 51

GPS Navigation
MANUALLY SETTING A COURSE
Use the ‘Set OBS and Hold’ menu option to manually set your course to the
destination.
Manually setting a course to the destination waypoint:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the HSI/Panel or the Active FPL Icon.
2)
Touch the Menu Icon
3)
Touch the ' Set OBS and Hold' menu option (only available when
navigating a Direct To or Flight Plan).
4)
Touch the '+' or '-' Buttons to increase/decrease the value
Or
:
Touch the Radial Button to enter the desired radial using the keypad and
touch the OK Icon.
Radial Button
HSI/Panel Option Menu
Set OBS
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Returning to automatic sequencing of route waypoints:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the HSI/Panel or the Active FPL Icon.
2)
Touch the Menu Icon
3)
Touch the 'Release Hold' menu option (only available when navigating a
Direct To or Flight Plan).
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
39
Page 52

GPS Navigation
VNAV Profile
Glide Ratio to Target
Distance to Target
Distance to Profile
Target Altitude
Airport
2.3 VERTICAL NAVIGATION (VNAV)
The VNAV function provides settings for the vertical navigation. These settings create
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
a three-dimensional profile from the present location and altitude to a final (target)
altitude at a specified location.
When the VNAV profile is defined, the pilot is informed of the progress by message
alerts. The teal bar on the HSI (when displayed) shows the VNAV profile.
The Vertical Navigation feature is only available when navigating a Direct To or flight
plan, and the ground speed is greater than 35 knots.
The “Approaching VNAV Profile” message appears one minute prior to the initial
descent point. The descent angle locks to prevent changes in speed from altering the
profile. The VNAV feature does not take into account any changes in groundspeed that
occur during the transition from level flight to descent or climb.
At 500 ft above the target altitude, the “Approaching Target Altitude” message
appears, the ‘Estimated Time To VNAV’ goes blank, and the VNAV indicator disappears
from the HSI.
40
CAUTION: The aera is a VFR navigation tool and should not be used to perform
instrument approaches.
CAUTION: VNAV is only a VFR navigation aid and is not intended for
instrument approaches.
Visual Representation of VNAV
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 53

GPS Navigation
USING THE VNAV FEATURE
Use the VNAV (Vertical Navigation) feature to ensure the aircraft is at the proper
altitude. The VNAV Indicator appears on the HSI (when displayed) as a horizontal teal
bar. A message appears when approaching the VNAV Profile. When the bar is in the
vertical center of the HSI, the aircraft is at the proper altitude for the VNAV Profile.
Enabling/disabling the VNAV indicator:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the HSI/Panel Icon.
2)
Touch the Menu Icon
3)
Touch the 'Enable VNAV Indicator' or 'Disable VNAV Indicator' menu
option (only available when navigating a Direct To or Flight Plan).
Capturing/cancelling VNAV profile:
1)
Enter a valid VNAV profile (see 'Configuring a VNAV Profile' below) and
begin navigation.
2)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the HSI/Panel Icon.
3)
Touch the 'Capture VNAV Profile' or 'Cancel Capture' menu option
(only available when navigating a Direct To or Flight Plan).
VNAV Indicator
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
VNAV Indicator (Panel)
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
41
Page 54
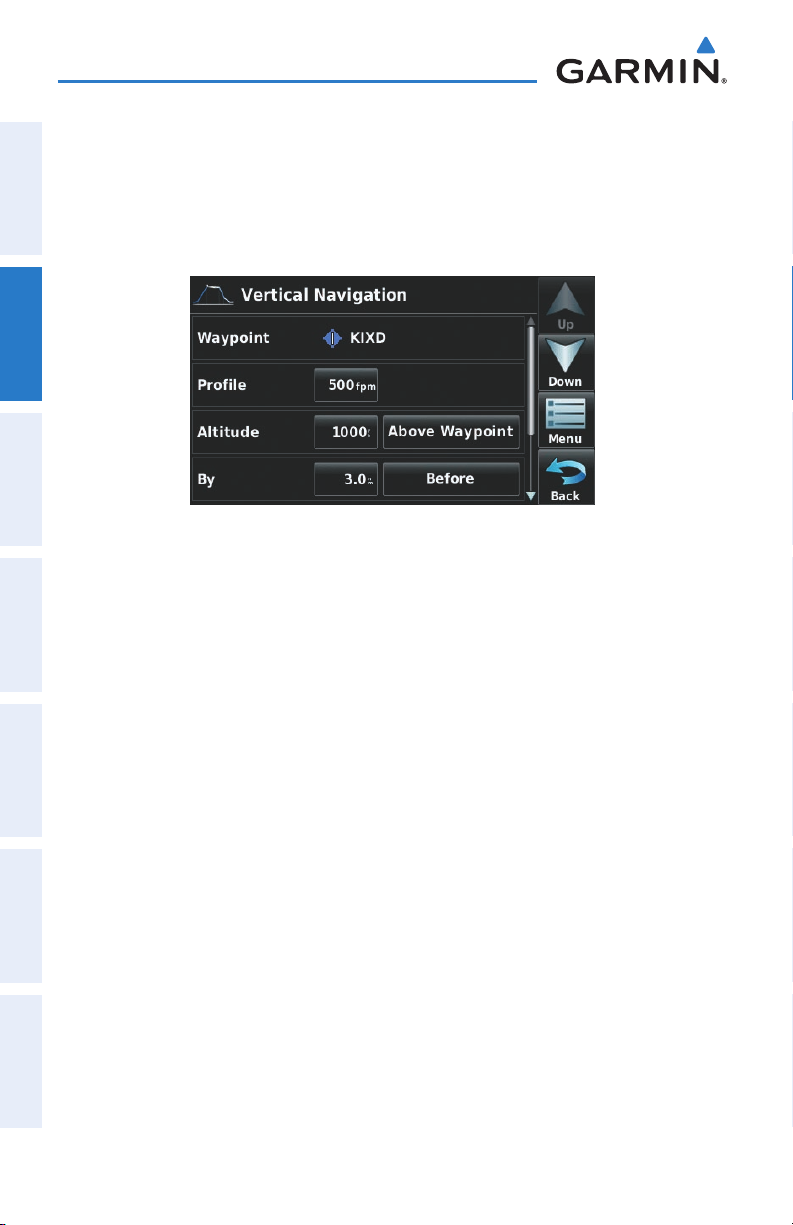
GPS Navigation
Configuring a VNAV profile:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > VNAV
2)
Touch the desired fields ('Profile', 'Altitude', etc) to enter the VNAV
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
profile.
3)
Touch and hold the Back Icon to return to the ‘Home’ Screen.
•
Waypoint—Enter any waypoint along the currently active route as the
reference waypoint. The reference waypoint defines the target location.
•
Profile—Enter the descent rate.
Vertical Navigation
•
Altitude—Enter the desired reference waypoint altitude. Select ‘Above
Waypoint’ to use field elevation for airports in the Jeppesen database or ‘MSL’
to specify an exact MSL altitude target.
•
By—Enter the target location with settings of distance ‘Before’ or ‘After’ a
reference waypoint. To set a target location at a reference waypoint, enter a
distance of zero.
•
VNAV Messages—Select ‘On’ or ‘Off’ to enable/disable VNAV alert messages.
42
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 55

GPS Navigation
2.4 MAP DISPLAY SETUP
Map displays are used extensively in the aera to provide situational awareness in
flight. Most aera maps can display the following information:
•
Airports, NAVAIDs, airspaces, airways, land data (highways, cities, lakes, rivers,
borders, etc.) with names
•Map Pointer information (distance and bearing to pointer, location of pointer,
name, and other pertinent information)
•Maprange
•Aircrafticon(representingpresentposition)
•Flightplanlegs
•Userwaypoints
•Trackvector
•Topographydata
MAP ORIENTATION
Maps are shown in one of three different orientation options, allowing flexibility
in determining aircraft position relative to other items on the map (North Up) or for
determining where map items are relative to where the aircraft is going (Track Up), or
desired track up (DTK UP)).
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
•NorthUpalignsthetopofthemapdisplaytonorth(defaultsetting).
•TrackUpalignsthetopofthemapdisplaytothecurrentgroundtrack.
•DesiredTrack(DTK)Upalignsthetopofthemapdisplaytothedesiredcourse.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
43
Page 56
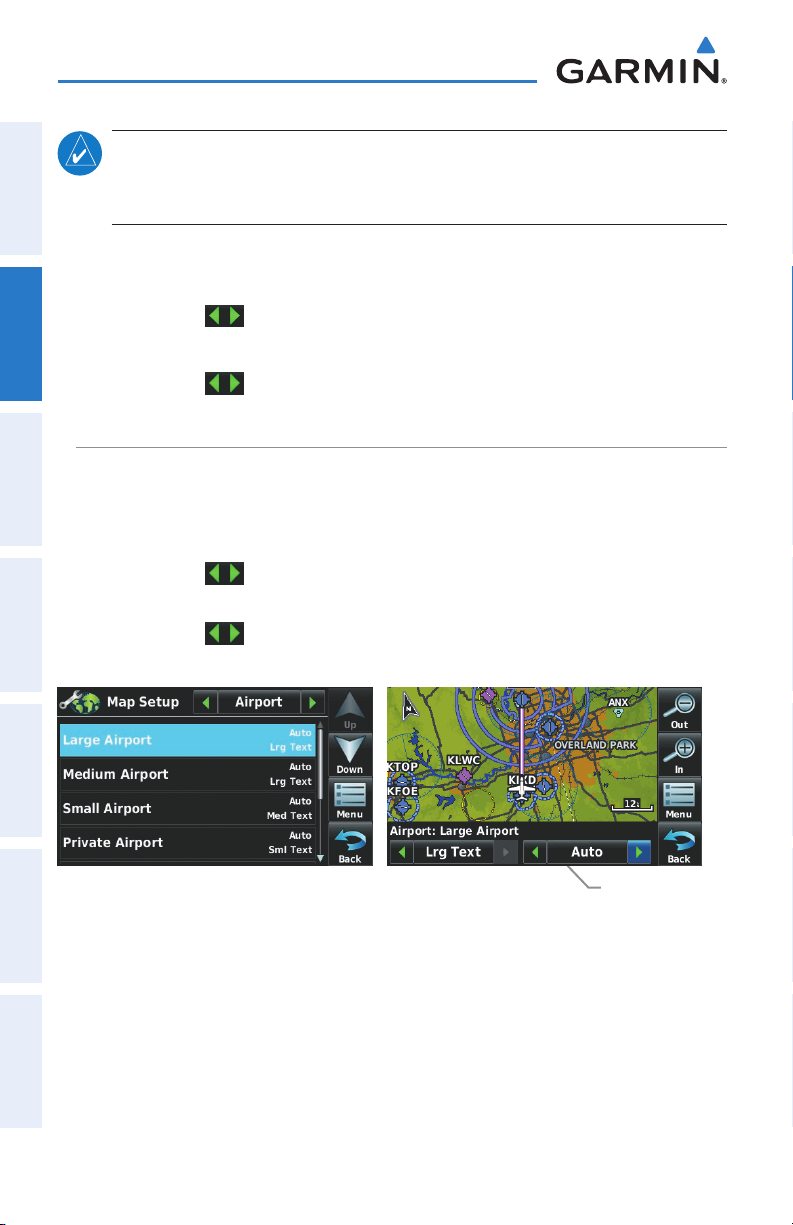
GPS Navigation
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
NOTE:
Menu. All other maps (except weather maps) that show navigation data reflect
the orientation selected for the Navigation Map.
Map orientation can only be changed from the Navigation Map Option
Changing the Navigation Map orientation:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map
2)
Touch the buttons to select the 'General' Category (if necessary).
3)
Touch Orientation.
4)
Touch the buttons to select 'North Up', 'Track Up', or 'DTK Up'.
AIRPORTS, NAVAIDS, CITIES & ROADS
Setting up and customizing airports, NAVAIDs, cities & roads for
the navigation map:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map
2)
Touch the buttons to select the 'Airport', 'Navaid', 'City', or 'Road'
Category.
3)
Touch the buttons to select the desired settings, or touch the Data
Option Button to toggle on option On/Off.
44
Map Setup (Airport Category Example)
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
Data Option Button
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 57

GPS Navigation
AIRWAYS
Low Altitude Airways (or Victor Airways) primarily serve smaller piston-engine,
propeller-driven airplanes on shorter routes and at lower altitudes. Airways are eight
nautical miles wide and start 1,200 feet above ground level (AGL) and extend up
to but not including 18,000 feet mean sea level (MSL). Low Altitude Airways are
designated with a “V” before the airway number (hence the name “Victor Airways”)
since they run primarily between VORs.
High Altitude Airways (or Jet Routes) primarily serve airliners, jets, turboprops, and
turbocharged piston aircraft operating above 18,000 feet MSL. Jet Routes start at
18,000 feet MSL and extend upward to 45,000 feet MSL (altitudes above 18,000 feet
are called “flight levels” and are described as FL450 for 45,000 feet MSL). Jet Routes
are designated with a “J” before the route number.
Low Altitude Airways are drawn in gray. High Altitude Airways are drawn in green.
When both types of airways are displayed, high altitude airways are drawn on top of
Low Altitude Airways.
When airways are selected for display on the map, the airway waypoints (VORs,
NDBs and Intersections) are also displayed.
Displaying/removing airways:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map
2)
Touch the buttons to select the 'Navaid' Category.
3)
Touch Airways.
4)
Touch the buttons to select the desired setting ('Off', 'Low', 'High',
or 'Both').
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Airways
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
45
Page 58
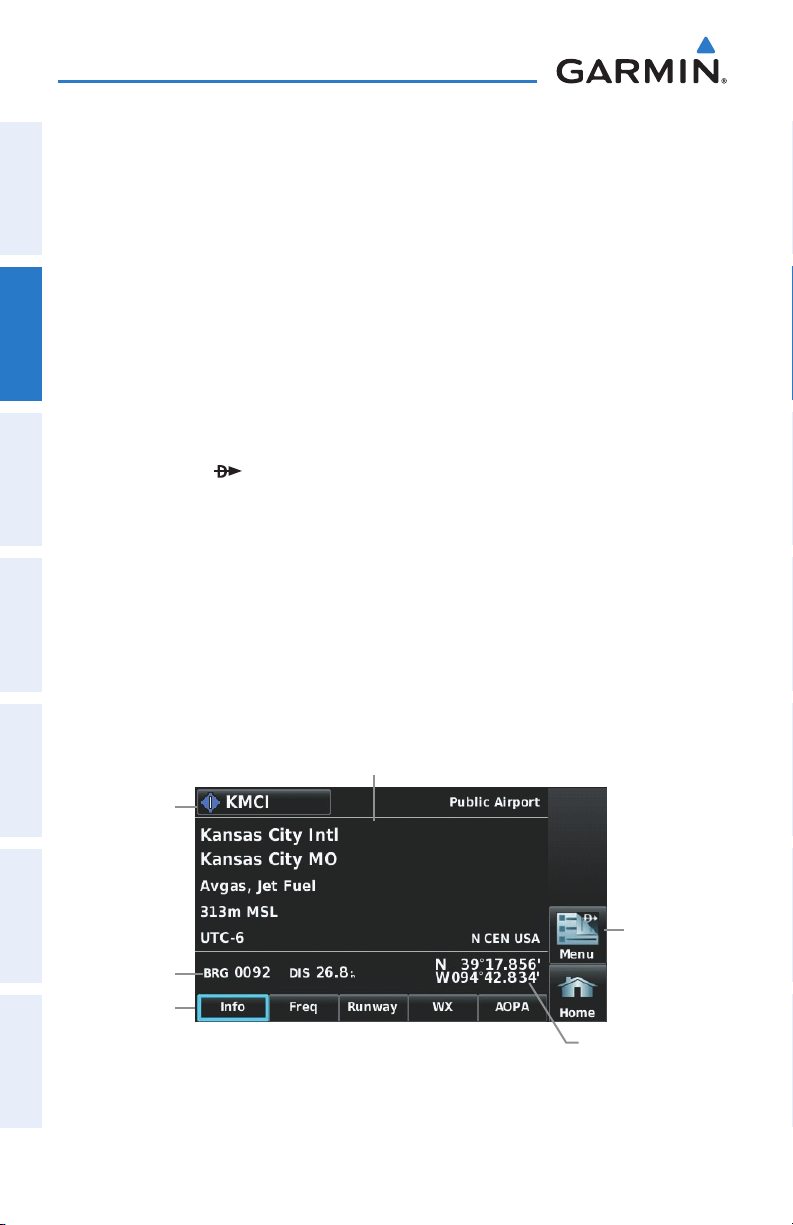
GPS Navigation
2.5 WAYPOINTS
The WPT INFO (Waypoint Information) function provides airport and waypoint
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
information.
Waypoints are predetermined geographical positions (internal database) or pilot-
entered positions, and are used for all phases of flight planning and navigation.
Waypoints can be selected by entering the ICAO identifier, entering the name of
the facility, or by entering the city name. As a waypoint identifier, facility name, or
location is entered, the aera’s Spell’N’Find™ feature scrolls through the database,
displaying those waypoints matching the characters which have been entered up to
that point. A direct-to navigation leg to the selected waypoint can be initiated by
pressing the Menu/ Icon.
The waypoint function allows the pilot to review airport information, runway
information, frequencies, AOPA information (if available), and weather information
(if available) by touching the desired tab. The pilot can manually enter the identifier
or the aera will choose the most appropriate identifier based on the current position
and phase of flight.
-Waypoint Identifier/Symbol/Type
-Facility Name
-City/State
-Fuel Available
-Elevation
Time Zone (UTC Offset)
-Region
Waypoint
Identifier
Button
46
Bearing/
Distance
Info Tab
Waypoint Information (Info Tab)
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
Option
Menu
Lat/Long
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 59

GPS Navigation
The following descriptions and abbreviations are used:
•Usagetype:Public,Military,orPrivate
•Runwaysurfacetype:Hard,Turf,Sealed,Gravel,Dirt,Soft,Unknown,orWater
•Runwaylightingtype:NoLights,PartTime,FullTime,Unknown,orPCLFreq(for
pilot-controlled lighting)
•COMAvailability:TX(transmitonly),RX(receiveonly),PT(parttime),* (additional
information available)
Selecting an airport for review by identifier, facility name, or city:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch WPT Info > Info Tab (if necessary).
2)
Touch the Waypoint Identifier Button.
3)
Enter the desired waypoint:
a)
Touch the buttons to 'Search by Identifier', 'Search by
Facility Name', or 'Search by City' using the keypad.
b)
Enter the desired waypoint.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
Or
:
a)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the waypoint categories
('Flight Plan Waypoints', 'Nearest Airports', or 'Recent
Waypoints'.)
b)
Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
4)
If duplicate entries exist for the entered facility name or location, duplicate
waypoints are displayed. Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Selecting a runway:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch WPT Info > Runway Tab.
2)
Touch the Waypoint Identifier Button.
3)
Enter the desired waypoint:
a)
Touch the buttons to 'Search by Identifier', 'Search by
Facility Name', or 'Search by City' using the keypad.
b)
Enter the desired waypoint.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
Or:
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
47
Page 60

GPS Navigation
a)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the waypoint categories
('Flight Plan Waypoints', 'Nearest Airports', or 'Recent
Waypoints'.)
b)
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
4)
5)
Or
Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
If duplicate entries exist for the entered facility name or location, duplicate
waypoints are displayed. Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
If multiple runways exist, touch the Runway Button, and touch the desired
runway from the vertical list.
:
Touch the buttons to cycle through the runways.
Waypoint
Identifier
Button
-Length/Width
-Surface
-Lighting
-Traffic Pattern
Runway
Button
-Wind
Option
Menu
Runway Tab
Waypoint Information (Runway Tab)
Selecting additional information for a frequency:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch WPT Info > Freq Tab.
2)
Touch the frequency denoted with an *.
Waypoint Information (Freq Tab)
48
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 61

GPS Navigation
The Frequencies Box uses the descriptions and abbreviations listed in the follow-
ing table:
Communication Frequencies Navigation
Frequencies
Approach *
Arrival *
ASOS
ATIS
AWOS
Center
Class B *
Class C *
Control
CTA *
Departure *
Gate
Ground
Helicopter
Multicom
Other
Pre-Taxi
Radar
Ramp
Terminal*
TMA *
Tower
TRSA *
Unicom
ILS
LOC
Clearance
* May include Additional Information
Frequency Abbreviations
NEAREST INFORMATION
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
The aera provides a Nearest function which gives the pilot quick access to nearest
airport, weather, VOR, NDB, intersection, user waypoint, city, ARTCC, FSS, and airspace
information. If there are none available, “None Within 200 NM” is displayed.
The Nearest functions contain the following information.
Airport• —identifier, bearing, distance, length of the longest runway, and common
traffic advisory (CTAF) or tower frequency.
Airport WX (Airport Weather)• —identifier, bearing, distance, METAR text (aera 510 &
560 only), and ATIS, AWOS, or ASOS frequency.
VOR (VHF Omnidirectional Radio Beacon)• —identifier, facility type (symbol), bearing,
distance, and frequency.
NDB (Non Directional Beacons)• —identifier, facility, type (symbol), bearing, distance,
and frequency.
Intersection• —identifier, bearing, and distance.
VRP (Visual Reporting Point) (Atlantic Unit Only)• —identifier, bearing, and distance.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
49
Page 62

GPS Navigation
USR WPT (User Waypoints)• —name, bearing, and distance.
City• —name, bearing, and distance.
ARTCC (Air Route Traffic Control Center)• —bearing, distance, and frequency.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
FSS (Flight Service Station)• —name, bearing, distance, frequency, and VOR (if
applicable).
Airspace• —name, time to entry (when applicable), and status.
Viewing nearest information:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Nearest Icon to display the second
level Nearest Icons.
2)
Touch the desired Nearest Icon (Airport, Airport WX, VOR, NDB,
Intersection, User WPT, City, ARTCC, FSS, or Airspace).
3)
Touch the desired nearest option from the list for additional information.
Or
:
If viewing Nearest ARTCCs or FSSs, touch the buttons to cycle through
the list.
4)
If desired, touch Menu > Show Map (except for ARTCC, FSS, or Airspace).
5)
Touch the Back Icon to return to the second level Nearest Icons.
Or
:
Touch the Direct Icon (if applicable), then the Activate Button to navigate
Direct-to the selected waypoint.
50
Nearest VORs List Additional VOR Information
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 63

GPS Navigation
NEAREST AIRPORT CRITERIA
The pilot can define the minimum runway length and surface type used when
determining the 15 nearest airports to display. A minimum runway length and/or
surface type can be entered to prevent airports with small runways or runways that
are not appropriately surfaced from being displayed. Default settings are 0 feet (or
meters) for runway length and "Any" for runway surface type. Private airports and
Heliports can also be included.
The Nearest Airports Option Menu also allows the pilot to choose between displaying
the facility names, city names, bearing, or direction arrows.
Setting nearest airport criteria:
Refer to Section 1.4 'Airport Criteria Settings'.
WEATHER INFORMATION
Textual weather information can be viewed several different ways.
Viewing airport weather information:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the WPT Info Icon.
2)
Enter the desired waypoint identifier.
3)
Touch the WX Tab.
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Nearest > Airport WX.
2)
Touch the desired Nearest Airport Weather from the list.
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Weather > METAR.
2)
Touch the desired METAR flag.
3)
Touch the Map Feature Button with the desired identifier displayed (refer to
'Map Panning' in the Overview Section for more information). The weather
information is displayed.
Or
:
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
51
Page 64

GPS Navigation
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Map Icon.
2)
Touch the desired METAR Flag (If the METAR flags are not displayed, adjust
the settings from the 'Set Up Map' menu option).
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
3)
Touch the Map Feature Button with the desired identifier displayed (refer to
'Map Panning' in the Overview Section for more information). The weather
information is displayed.
METAR Selected
Map
Feature
Button
Weather Information
ACCESSING ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
In addition to airport and weather information, additional information for VORs,
NDBs, Intersections, User Waypoints, Cities, ARTCCs, FSSs, and Airspace can be viewed
using the Waypoint Information function, the Nearest function, or the Map Panning
function.
52
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 65

GPS Navigation
Identifier
Frequency
Name
City
State
Type
Morse Code
Radial
Region
Bearing
Distance
Lat/Long
Elevation (MSL)
Fuel Available
Time Zone (UTC Offset)
Runway Information
AO PA
Weather
Controlling Agency
Vertical Boundaries
Class
Additional Information
VOR
Airport
NDB
Intersection
+ + + + +
+ + + + + +
+ + + + + +
+ + + + +
+ + + +
+ + +
+ +
+
+ + + + +
+ + + + + + + +
+ + + + + + + + +
+ + + + + +
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
User Wpt
City
ARTCC
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
FSS
Airspace
+
+
+
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
53
Page 66

GPS Navigation
INTERSECTIONS
Intersection information can be viewed using the Waypoint Information function, the
Nearest function, or the Map Panning function.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
The Nearest Intersection function can be used to quickly find an intersection close to
the flight path. The list only includes Intersections that are within 200nm. If there are
no Intersections within the range, text indicating that there are no nearest intersections
is displayed.
Select an intersection:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the WPT Info Icon.
2)
Touch the Waypoint Identifier Field to begin entering the desired
intersection. Refer to the Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more
information.
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Nearest > Intersection.
2)
Touch the desired Nearest Intersection from the list.
3)
If desired, touch Menu > Show Map.
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Map Icon.
2)
Touch the desired Intersection on the map.
3)
Touch the Map Feature Button with the desired intersection displayed (refer
to the Overview Section on 'Map Panning' for more information). The
intersection information is displayed.
NDBS
NDB information can be viewed using the Waypoint Information function, the
Nearest function, or the Map Panning function.
The Nearest NDB function can be used to quickly find a NDB close to the flight path.
The list only includes NDBs that are within 200nm. If there are no NDBs in the list, text
indicating that there are no nearest NDBs is displayed.
54
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 67

GPS Navigation
Select an NDB:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the WPT Info Icon.
2)
Touch the Waypoint Identifier Field to begin entering the desired NDB.
Refer to the Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, Nearest > NDB.
2)
Touch the desired Nearest Intersection from the list.
3)
If desired, touch Menu > Show Map.
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Map Icon.
2)
Touch the desired NDB on the map.
3)
Touch the Map Feature Button with the desired NDB displayed (refer to
the Overview Section on 'Map Panning' for more information). The NDB
information is displayed.
VORS
VOR information can be viewed using the Waypoint Information function, the
Nearest function, or the Map Panning function.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
The Nearest VOR function can be used to quickly find a VOR close to the flight path.
The list only includes VORs that are within 200nm. If there are no VORs in the list, text
indicating that there are no nearest VORs is displayed.
Localizer information cannot be viewed for the VOR. If a VOR station is combined
with a TACAN station it is listed as a VORTAC, and if it includes only DME it is displayed
as VOR-DME.
Select an VOR:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the WPT Info Icon.
2)
Touch the Waypoint Identifier Field to begin entering the desired VOR.
Refer to the Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
Or
:
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
55
Page 68

GPS Navigation
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Nearest > VOR.
2)
Touch the desired Nearest VOR from the list.
3)
If desired, touch Menu > Show Map.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Or
:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Map Icon.
2)
Touch the desired VOR on the map.
3)
Touch the Map Feature Button with the desired VOR displayed (refer to
the Overview Section on 'Map Panning' for more information). The VOR
information is displayed.
USER WAYPOINTS
The aera can create and store up to 3,000 user-defined waypoints. Once a waypoint
has been created, it can be renamed, deleted, or moved.
Creating user waypoints:
1)
To create a new user waypoint at the current location or using the Map
Pointer:
a)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > User WPT > Menu.
b)
Touch 'Create Waypoint'.
Or:
With a map displayed, touch an empty area without any map features.
a)
b)
Touch the Map Feature Button.
c)
Touch 'Save'.
Or:
56
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
User Waypoints
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 69
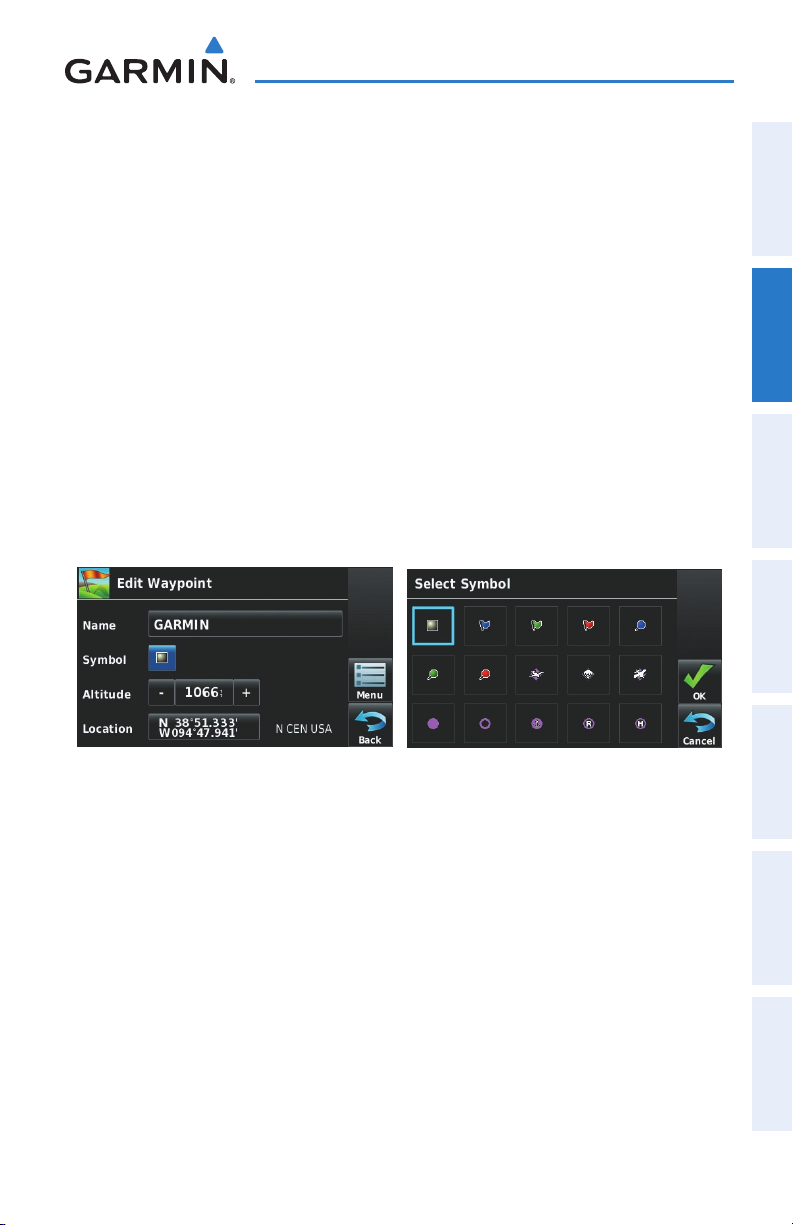
GPS Navigation
a)
With a map displayed, touch a map feature.
b)
Touch the Menu Icon.
c)
Touch 'Create Waypoint'.
Or:
a)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Position Icon.
b)
Touch the Mark Waypoint Button.
2)
Enter the desired user waypoint name (up to 10 characters). Refer to the
Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
3)
Touch the OK Icon. If changing the User Waypoint settings (symbol,
altitude, location, or reference waypoints) continue with Step 4.
4)
If desired, touch the Symbol Field to change the symbol that will appear
on the map.
a)
Touch the desired symbol.
b)
Touch the OK Icon.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
5)
If desired, touch the Altitude Field
a)
b)
6)
If desired, touch the Location Field.
a)
b)
190-01117-02 Rev. A
User Waypoint Symbols
Enter the desired altitude using the keypad or the +/- buttons. Refer to
the Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
Touch the OK Icon.
Enter the desired latitude and longitude by touching the left/right
arrows to move the cursor, and the up/down arrows to change the
value.
Touch the OK Icon.
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
57
Page 70

GPS Navigation
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
7)
If desired, touch the Menu Icon and touch 'Reference Waypoints' to enter a
bearing and distance from another waypoint or the bearing from two other
waypoint to define a new waypoint location.
a)
Touch the Waypoint Field(s) to enter the desired waypoint.
b)
Touch the Bearing and/or Distance Fields to enter the desired values.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
8)
Touch and hold the Back Icon to return to the 'Home' Screen.
User Waypoint Location
Reference Waypoints
Selecting and viewing nearest user waypoints:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > User WPT.
2)
Touch the desired User Waypoint. The User Waypoint information is
displayed.
3)
If desired, touch the Menu Icon and the 'Show Map' menu option to view
the User Waypoint on the map.
Editing or renaming a user waypoint:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > User WPT.
2)
Touch the desired User Waypoint. The option menu automatically displays.
58
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 71

3)
Touch the 'Edit Waypoint' menu option.
4)
Touch the desired field to edit:
a)
Touch the Name Button.
b)
Enter the desired user waypoint name (up to 10 characters). Refer to
the Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
Or:
a)
Touch the Symbol Button.
b)
Touch the desired symbol.
Or:
a)
Touch the Altitude Button.
b)
Enter the desired altitude. Refer to the Overview Section on 'Data
Entry' for more information.
Or:
a)
Touch the Location Button.
b)
Enter the desired latitude and longitude by touching the left/right
arrows to move the cursor, and the up/down arrows to change the
value.
5)
Touch the OK Icon.
GPS Navigation
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Deleting user waypoints:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > User WPT.
2)
Delete a single waypoint, delete all waypoints, delete by symbol or delete
by distance:
a)
Touch the desired User Waypoint. The option menu automatically
displays
b)
Touch the 'Delete Waypoint' menu option. The confirmation window
will appear.
Or:
a)
Touch the Menu Icon.
b)
Touch the 'Delete All' menu option. The confirmation window will
appear.
Or:
a)
Touch the Menu Icon.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
59
Page 72

GPS Navigation
b)
Touch the 'Delete by Symbol' menu option.
c)
Touch the desired symbol to delete. The symbol will be highlighted
blue.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
d)
Touch the OK icon. The confirmation window will appear.
Or:
a)
Touch the Menu Icon.
b)
Touch the 'Delete by Distance' menu option.
c)
If desired, touch the From Field and touch 'Current Location'
(default), 'Use Identifier', or 'Use Map' from the option menu.
d)
If desired, touch the 'Less Than/More Than' Button, and touch the
Distance Field to enter the desired distance.
e)
Touch the OK icon. The confirmation window will appear.
3)
Touch Yes.
CITIES
City information can be viewed using the Waypoint Information function, the Nearest
function, or the Map Panning function.
The Nearest City function can be used to quickly find a city close to the flight path.
The list only includes cities that are within 200nm. If there are no cities in the list, text
indicating that there are no nearest cities is displayed.
Select a city:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch WPT Info > Info Tab.
2)
Touch the Waypoint Identifier Field.
3)
Touch the buttons until the 'Search by City' option is displayed, and
touch the button.
4)
Enter the desired city using the keypad and touch OK. Refer to the
Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
Or
:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > City.
2)
Touch the desired Nearest City from the list.
3)
If desired, touch Menu > Show Map.
Or
:
60
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 73

GPS Navigation
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Map Icon.
2)
Touch the desired city symbol on the map.
3)
Touch the Map Feature Button with the desired city displayed (refer to
the Overview Section on 'Map Panning' for more information). The city
information is displayed.
ARTCC
ARTCC information can be viewed using the Nearest function.
The Nearest ARTCC function can be used to quickly find a ARTCC close to the flight
path. The list only includes ARTCC that are within 200nm. If there are no ARTCCs in
the list, text indicating that there are no nearest ARTCCs is displayed.
Select an ARTCC:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > ARTCC.
2)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the list. The associated bearing,
distance, and frequencies are displayed.
FSS
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
FSS information can be viewed using the Nearest function.
The Nearest FSS function can be used to quickly find a FSS close to the flight path.
The list only includes FSS that are within 200nm. If there are no FSSs in the list, text
indicating that there are no nearest FSSs is displayed.
FSS frequencies and phone numbers can also be found using the AOPA Tab when
reviewing information for an airport. Refer to the Additional Features Section on
'AOPA' for more information.
Select an FSS:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > FSS.
2)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the list. The associated bearing,
distance, and frequencies are displayed.
AIRSPACE
The Nearest Airspace function and Airspace Alerts provide information about
airspaces and the location of the aircraft in relationship to them. The Nearest Airspace
function can be used to quickly find airspaces close to the flight path.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
61
Page 74

GPS Navigation
The Nearest Airspace function displays the class of airspace, controlling agency,
vertical boundaries, and status.
Selecting and viewing nearest airspaces:
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > Airspace.
2)
Touch the desired airspace from the list. The airspace information is
displayed.
3)
If desired, touch 'Frequencies' to view frequencies associated with that
airspace.
Nearest Airspace
AI r S p A c e Al e r t Me S S A g e S
If airspace alarms are set to 'On' (default is 'Off'), the aera will display a message
which includes the airspace name, time to entry (if applicable), and status. Touch the
message to acknowledge it.
There are four types of status information:
Ahead• —Projected to enter the airspace within the next 10 minutes or less
Near• —Within two nautical miles of an airspace but not projected to enter it.
Near & Ahead• —Project to enter the airspace within two nautical miles.
Inside Airspace• —Within the boundaries of the airspace.
Airspace alert setup:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Tools > Setup > SUA Alarms.
2)
Touch the desired On/Off Button(s).
62
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 75

GPS Navigation
Airspace Alert Message
SM A r t AI r S p A c e
Smart Airspace shows airspace at and immediately surrounding the aircraft’s current
altitude in bold. Airspaces at all other altitudes are de-emphasized.
Bold Airspace
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
De-emphasized
Airspace
Smart Airspace setup:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Map > Menu > Set Up Map.
2)
Touch the buttons to select the Airspace Category.
3)
Touch the Smart Airspace.
4)
Touch the On/Off Button.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Smart Airspace
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
63
Page 76

GPS Navigation
2.6 DIRECT-TO NAVIGATION
The Direct-to method of navigation, initiated by pressing the Direct To Icon is
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
quicker to use than a flight plan when the desire is to navigate to a single point such
as a nearby airport.
The Direct To Icon is available from the 'Home' Screen, or 'touch and hold' the
Menu/ Icon when available.
Once a direct-to is activated, the aera establishes a point-to-point course line from
the present position to the selected direct-to destination. Course guidance is provided
until the direct-to is replaced with a new direct-to or flight plan, or cancelled.
Direct To
Entering a waypoint identifier, facility name, or city as a direct-to
destination:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Direct To Icon.
Or
:
Touch and hold the Menu/ Icon (when available).
2)
Touch Menu > Resume Navigation.
Or
:
a)
Touch the 'Search by Identifier', 'Search by Facility Name', or
'Search by City' fields.'.
b)
Enter the desired Identifier, Facility Name, or City using the keypad.
Refer to the Overview Section on 'Data Entry' for more information.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
64
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 77

GPS Navigation
Or
:
a)
Touch 'More...'.
b)
Touch the buttons to view 'Flight Plan Waypoints', 'Nearest
Airports', or 'Recent Waypoints'.
c)
Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
4)
Touch the Activate Icon (if necessary).
Selecting a nearby airport as a direct-to destination:
1)
From the 'Home' Screen, touch Nearest > Airport.
2)
Touch the desired nearest airport.
3)
Touch and hold the Menu/ Icon.
4)
Touch the Activate Icon.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Direct To Shortcut
Selecting a waypoint as a direct-to destination using the pointer:
1)
With a map displayed, activate the map pointer by touching the desired
waypoint. If no airport, NAVAID, or User Waypoint exists at the desired
location, a temporary waypoint named 'MAP' is automatically created at
the location of the map pointer.
2)
Touch and hold the Direct Icon.
3)
Touch the Activate Icon.
Cancelling a direct-to:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Direct To Icon.
Or
:
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
65
Page 78

GPS Navigation
Fr
om the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
Or
:
Touch and hold the Menu/ Icon (when available).
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
2)
Touch the Menu Icon.
3)
Touch 'Stop Navigation'.
66
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 79

Flight Planning
SECTION 3 FLIGHT PLANNING
3.1 INTRODUCTION
Flight planning on the aera consists of building a flight plan by entering waypoints
one at a time and inserting approaches as needed. The flight plan is displayed on
maps using different line widths, colors, and types, based on the type of leg and the
segment of the flight plan currently being flown.
Up to 50 flight plans with up to 300 waypoints each can be created and stored
in memory. One flight plan can be activated at a time and becomes the active flight
plan. The active flight plan is erased when the destination is reached and the system
is turned off. When storing flight plans with an approach, the aera uses the waypoint
information from the current database to define the waypoints. If the database is
changed or updated, the aera automatically updates the information if the procedure
has not been modified. If an approach is no longer available, the procedure is deleted
from the affected stored flight plan(s), and an alert is displayed.
Whenever an approach is loaded into the active flight plan it replaces the destination
airport with a sequence of waypoints for the selected approach. The airport must have
a published instrument approach and only the final course segment (usually from final
approach fix to missed approach point) of the published approach is available in the
aera.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
DATA FIELDS
The Active and Saved Flight Plan Data Fields can be changed by touching the Data
Field Buttons at the top of the flight plan.
Changing the information shown in the flight plan data fields:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
Or:
a)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List.
b)
Touch the desired Saved Flight Plan from the list. An option menu
appears.
c)
Touch the 'Review Flight Plan' menu option.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
67
Page 80

Flight Planning
2)
Touch the desired Data Field Button at the top of the Flight Plan.
3)
Touch the desired Data Field. The currently selected Data Field is outlined
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
blue.
4)
Touch the OK Icon.
5)
If desired, repeat Steps 2-4 for the remaining Data Field.
Data Field Button
Flight Plan Data Fields
3.2 FLIGHT PLAN CREATION
The active flight plan is the flight plan to which the aera is currently providing
guidance, and is shown on the navigation maps. Stored flight plans are flight plans
available for activation (becomes the active flight plan).
Data Fields
Active
Leg
Option
Menu
Active Flight Plan
68
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 81

Flight Planning
Creating an active flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
2)
Touch the 'Touch to add Waypoint' Button.
3)
Enter the desired waypoint:
a)
Touch the buttons to 'Search by Identifier', 'Search by
Facility Name', or 'Search by City' using the keypad.
b)
Enter the desired waypoint.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
Or:
a)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the waypoint categories
('Flight Plan Waypoints', 'Nearest Airports', or 'Recent
Waypoints'.)
b)
Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
4)
If duplicate entries exist for the entered facility name or location, duplicate
waypoints are displayed. Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
5)
Repeat Steps 2-5 to enter each additional waypoint.
Creating a stored flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List > Menu > New Flight
Plan.
2)
Touch the 'Touch to add Waypoint' Button.
3)
Enter the desired waypoint:
a)
Touch the buttons to 'Search by Identifier', 'Search by
Facility Name', or 'Search by City' using the keypad.
b)
Enter the desired waypoint.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
Or:
a)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the waypoint categories
('Flight Plan Waypoints', 'Nearest Airports', or 'Recent
Waypoints'.)
b)
Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
4)
If duplicate entries exist for the entered facility name or location, duplicate
waypoints are displayed. Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
5)
Repeat Steps 2-5 to enter each additional waypoint.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
69
Page 82

Flight Planning
ADDING WAYPOINTS TO AN EXISTING FLIGHT PLAN
Waypoints can be added to the active flight plan or any stored flight plan. Choose
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
the flight plan, select the desired point of insertion, enter the waypoint, and it is added
in front of the selected waypoint. Flight plans are limited to 300 waypoints (including
approach waypoints).
Adding a waypoint to an active or stored flight plan:
1)
With an active or saved flight plan displayed, touch the desired point
of insertion. The new waypoint will be added in front of the selected
waypoint. An option menu will appear.
2)
Touch the 'Insert Waypoint' menu option.
3)
Enter the desired waypoint:
a)
Touch the buttons to 'Search by Identifier', 'Search by
Facility Name', or 'Search by City' using the keypad.
b)
Enter the desired waypoint.
c)
Touch the OK Icon.
Or:
a)
Touch the buttons to cycle through the waypoint categories
('Flight Plan Waypoints', 'Nearest Airports', or 'Recent
Waypoints'.)
b)
Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
4)
If duplicate entries exist for the entered facility name or location, duplicate
waypoints are displayed. Touch the desired waypoint from the list.
Loading an approach procedure into a stored flight plan:
An Approach Procedure can be loaded at any airport that has an approach available.
Only one approach can be loaded at a time in a flight plan. The route for a selected
approach is defined by designating transition waypoints.
1)
With an active or saved flight plan displayed, touch the Menu Icon
2)
Touch the 'Select Approach' menu option. A vertical list of available
approaches is displayed.
3)
Touch the desired approach. The designated transition waypoints are
added to the flight plan.
70
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 83
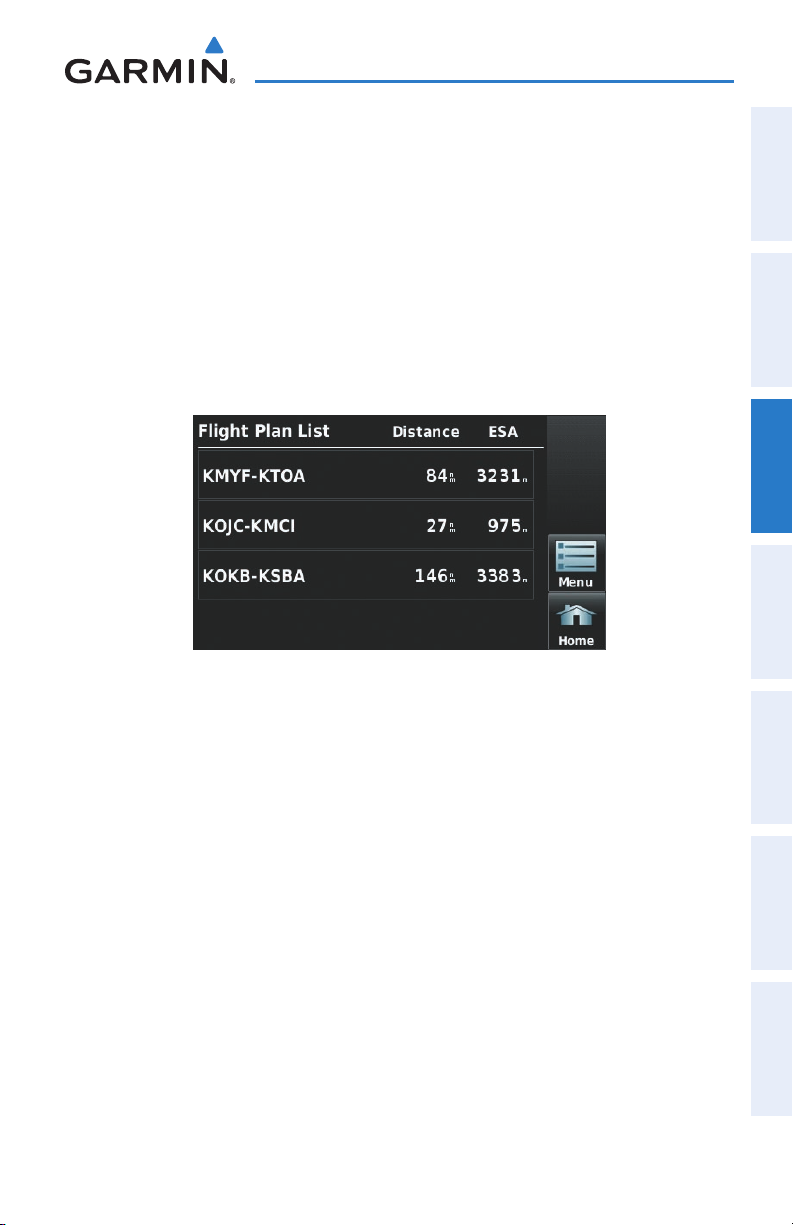
Flight Planning
3.3 FLIGHT PLAN STORAGE
The aera can store up to 50 flight plans. The active flight plan is erased when
another flight plan is activated. Details about each stored flight plan can be viewed
using the Flight Plan List function.
Viewing information about a stored flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List
2)
Touch the desired saved flight plan. An option menu is displayed.
3)
Touch the 'Review Flight Plan' menu option.
Flight Plan List
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Storing an active flight plan:
1)
With the Active Flight Plan displayed, touch the Menu Icon.
2)
Touch the 'Save Flight Plan' menu option. A confirmation window
appears.
3)
Touch Yes. A copy of the flight plan is stored in the next available position
in the Flight Plan List.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
71
Page 84
Flight Planning
3.4 FLIGHT PLAN ACTIVATION
Activating a stored flight plan erases the active flight plan and replaces it with a copy
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
of the flight plan being activated. Inverting a stored flight plan reverses the waypoint
order and activates it.
Activating a stored flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List
2)
Touch the desired saved flight plan. An option menu is displayed.
3)
Touch the 'Activate Flight Plan' menu option. A confirmation window
appears.
4)
Touch Yes.
Activating a Flight Plan Leg:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
2)
While navigating an active flight plan, touch the desired leg to be activated.
An option menu automatically appears.
3)
Touch the 'Activate Leg' menu option.
4)
Touch Yes.
3.5 FLIGHT PLAN EDITING
EDITING SPEED AND FUEL FLOW
Adjusting the Flight Plan cruise speed and fuel flow:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > Profile.
2)
If necessary, touch the Aircraft Button, and touch the desired aircraft from
the vertical list.
3)
Touch the Cruise Speed and/or Fuel Flow Fields to enter the desired
value using the keypad or by touching the '+' or '-' Buttons.
72
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 85
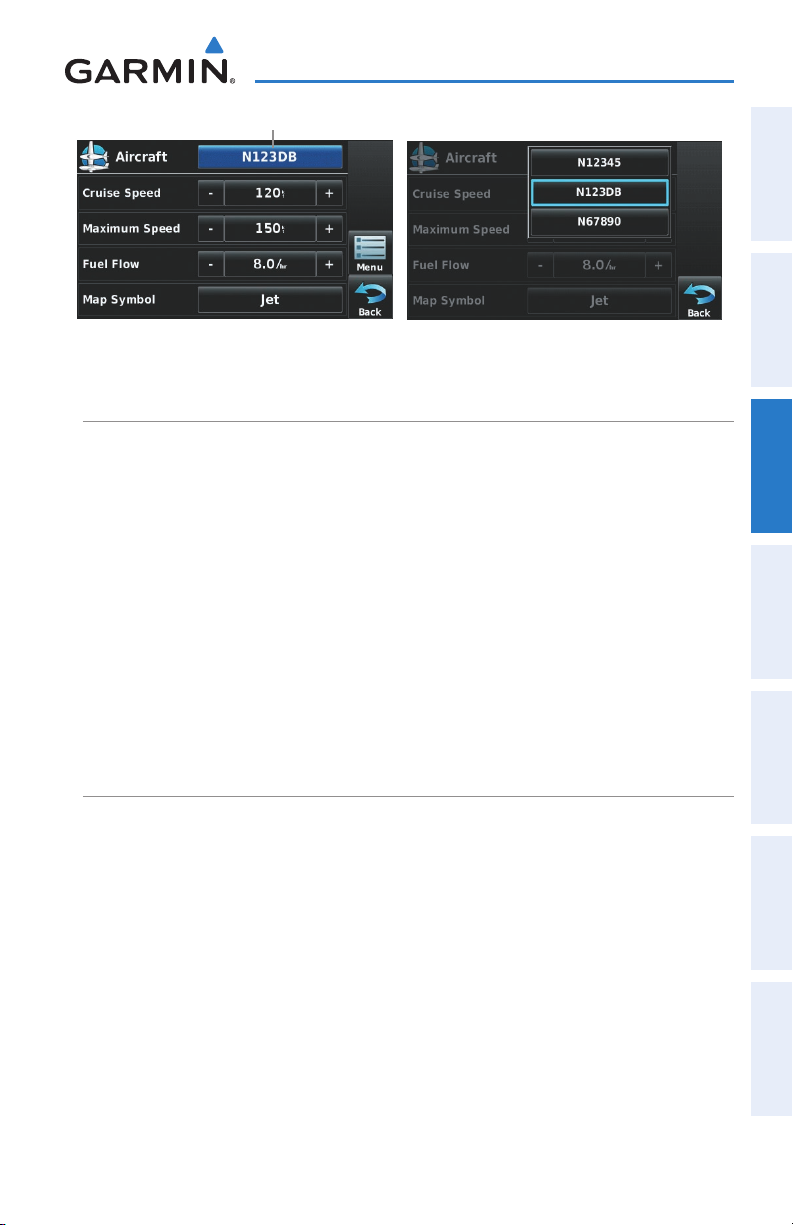
Flight Planning
Aircraft Button
Flight Plan Data Fields
COPYING FLIGHT PLANS
The aera allows copying a flight plan into a new flight plan memory slot, allowing
editing, etc., without affecting the original flight plan. This can be used to duplicate an
existing stored flight plan for use in creating a modified version of the original stored
flight plan.
Copying a stored flight plan:
With the desired Stored Flight Plan displayed, touch the Menu > Copy
Flight Plan > Yes.
Or
:
With the Flight Plan List displayed, touch the desired flight plan to copy,
and touch Copy Flight Plan.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
DELETING FLIGHT PLANS
Individual or all stored flight plans can be deleted from the aera memory.
Deleting a stored flight plan:
With the desired Stored Flight Plan displayed, touch the Menu > Delete
Flight Plan > Yes
Or
:
With the Flight Plan List displayed, touch the desired flight plan to delete,
and touch Delete Flight Plan > Yes.
Deleting all stored flight plans:
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List > Menu > Delete All >
Yes.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
73
Page 86
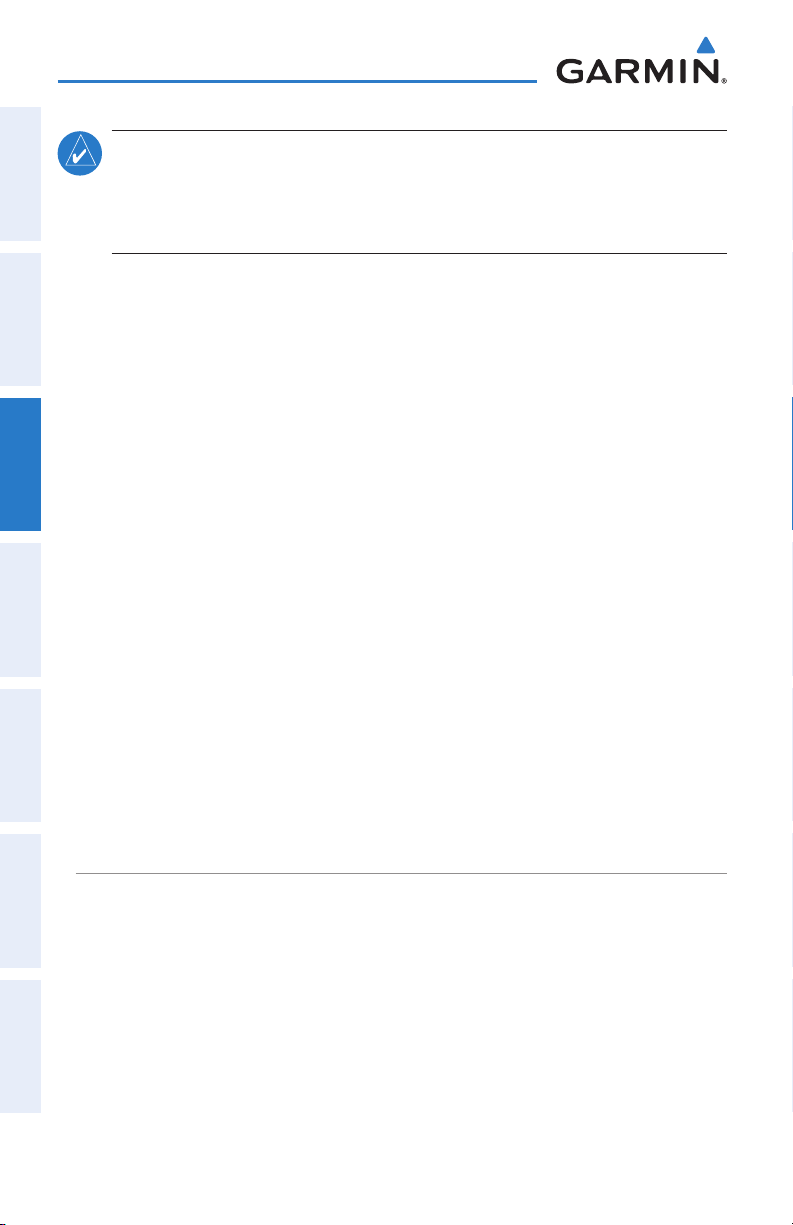
Flight Planning
NOTE:
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
The changes made to the active flight plan affect navigation as soon as
they are entered. Editing the active flight plan does not affect any saved flight
plans. Waypoints in the final approach segment (such as the FAF or MAP) can
not be deleted individually.
Deleting the Active Flight Plan:
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Active FPL > Menu > Stop Navigation.
Deleting an individual waypoint from the active flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
2)
While navigating an active flight plan, touch the waypoint to be deleted.
An option menu appears.
3)
Touch the 'Remove Waypoint' menu option. A confirmation window
appears.
4)
Touch Yes.
Deleting an individual waypoint from a saved flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List.
2)
Touch the desired saved flight plan. An option menu is displayed.
3)
Touch the 'Review Flight Plan' menu option.
4)
Touch the desired waypoint to be deleted. An option menu appears.
5)
Touch the 'Remove Waypoint' menu option.
6)
Touch the desired waypoint to be deleted. A confirmation window appears.
7)
Touch Yes.
INVERTING A FLIGHT PLAN
Any flight plan may be inverted (reversed) for navigation back to the original
departure point.
Inverting the active flight plan:
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Active FPL > Menu > Invert Flight
Plan > Yes.
Inverting a saved flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Tools > FPL List
2)
Touch the desired saved flight plan. An option menu is displayed.
74
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 87

Flight Planning
3)
Touch the 'Review Flight Plan' menu option.
4)
Touch the Menu Icon
5)
Touch the 'Invert Flight Plan' menu option. A confirmation window
appears.
6)
Touch Yes.
3.5 APPROACHES
WARNING: The aera is not designed to be independently used for flight
into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) or other conditions in which
aircraft control is based solely upon flight instruments. The approaches
provided are for monitoring purposes only. Only the final course segment
(final approach fix (FAF) to missed approach point (MAP)) of the published
approach is available for monitoring.
An approach can be loaded at any airport that has one available, and provides
guidance for non-precision and precision approaches to airports with published
instrument approach procedures. Only one approach can be loaded at a time in a
flight plan. If an approach is loaded when another approach is already in the active
flight plan, the new approach replaces the previous approach. Only the final course
segment (Final Approach Fix (FAF) to Missed Approach Point (MAP)) of the published
approach is available for monitoring.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Whenever an approach is selected the aera automatically activates the approach.
The procedure is added to the end of the flight plan and immediately begins to provide
guidance to the first waypoint in the approach.
Select Approach
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
75
Page 88

Flight Planning
SELECTING AN APPROACH
When selecting an approach, it replaces the destination airport with the sequence
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
of waypoints for the selected approach. Keep in mind that the airport must have a
published approach (GPS, RNAV, VOR, NDB, localizer, or ILS) and only the final course
segment (final approach fix to missed approach point) of the published approach is
available in the aera. If the airport does not have a published approach, the 'Select
Approach' menu option is not available.
An approach can be selected using the Direct-to, Active Flight Plan, and the Saved
Flight Plan functions.
Selecting an approach from the active or saved flight plan:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
Or:
a)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Tools Icon.
b)
Touch the FPL List Icon.
c)
Touch the desired Saved Flight Plan from the list. An option menu
appears.
d)
Touch the 'Review Flight Plan' menu option.
2)
With the flight plan displayed, touch the Menu Icon.
3)
Touch the 'Select Approach' menu option (only available if the
destination airport has a published approach). A vertical list of available
approaches is displayed.
4)
Touch the desired approach. The 'Vectors to Final?' window appears.
5)
Touch 'Yes' or 'No'. The procedure is added to the end of the flight plan.
If activating an approach from the Active Flight Plan, the aera immediately
begins to provide guidance to the first waypoint in the approach.
Selecting an approach using the Direct To function:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Direct To Icon.
2)
Touch the Menu Icon.
3)
Touch the 'Select Approach' menu option (only available when
navigating a flight plan. A vertical list of available approaches is displayed.
76
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 89

Flight Planning
4)
Touch the desired approach. The 'Vectors to Final?' window appears.
5)
Touch 'Yes' or 'No'. The procedure is added to the end of the Active Flight
Plan and the aera immediately begins to provide guidance to the first
waypoint in the approach.
Resuming the Flight Plan after selecting an approach:
Whenever an approach is selected the aera automatically activates the approach.
The procedure is added to the end of the flight plan and immediately begins to provide
guidance to the first waypoint in the approach. Follow the steps below to resume the
flight plan after activating the approach.
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
Or
:
From the 'Home' Screen, touch the Direct To Icon.
Or
:
Touch and hold the Menu
2)
With a flight plan and an approach loaded, touch the Menu Icon.
3)
Touch the 'Resume Flight Plan' menu option.
/
Icon (when available).
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Removing an approach:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
Or
:
a)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Tools Icon.
b)
Touch the FPL List Icon.
c)
Touch the desired Saved Flight Plan from the list. An option menu
appears.
d)
Touch the 'Review Flight Plan' menu option.
2)
Press the Menu Icon.
3)
Touch the 'Remove Approach' menu option (only available if an
approach is loaded).
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
77
Page 90

Flight Planning
ACTIVATING VECTORS-TO-FINAL
After an approach has been activated, the 'Activate Vectors-to-Final' menu option is
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
used when being vectored to the final approach course by Air Traffic Control (ATC).
When Vectors-to-Final are activated, the aera creates an extension of the final
course, beyond the final approach waypoint in the database (final approach fix [FAF]).
A Vector to Final symbol appears beside the first approach waypoint in the Active Flight
Plan.
Activating/Cancelling Vectors-to-Final:
1)
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch the Active FPL Icon.
2)
While navigating an Active Flight Plan (with an approach activated), touch
the Menu Icon.
3)
Touch the 'Activate Vectors-to-Final' or 'Cancel Vectors-to-Final'
menu option.
Vectors-to-
Final Symbol
Final Course
Extension
Vectors-to-Final (Active Flight Plan)
Vectors-to-Final (Map)
The aera provides no guidance to the inbound course. The course deviation needle
on the graphic HSI remains off-center until established on the final approach course.
The map shows an extension of the final approach course using a bold magenta line.
If Vectors-to-Final are not activated, the aera creates a straight-line course directly to
the first waypoint in the approach.
Loading the approach cancels the Direct-to and initiates a route to the FAF.
78
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 91

Hazard Avoidance
SECTION 4 HAZARD AVOIDANCE
4.1 XM® WEATHER (aera 510 & 560)
NOTE:
NOTE:
ACTIVATING SERVICES
Before XM Satellite Weather can be used, the service must be activated. Service
is activated by providing XM Satellite Radio with a Radio ID unique to the GXM 40
antenna.
XM Satellite Radio uses the Radio ID to send an activation signal that allows the
aera to display weather data and/or entertainment programming provided through the
GXM 40 antenna.
You MUST have a GXM 40 smart antenna connected to your aera 510
or aera 560 and a subscription to XM Weather to use XM Weather features.
The weather products displayed on the aera are dependant on the XM
Weather Data Service Package (Aviator LT, Aviator, Aviator Pro) purchased.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Refer to the GXM 40 Owner’s Manual for more information on activating XM
Satellite Radio.
XM WEATHER INFORMATION
•Radio ID—Eight-digit ID number used for activation.
•ServiceLevel—XMWeathersubscriptionplanpurchased.
•Weather Products—List of weather features and age of weather data in
minutes.
Accessing the Radio ID:
From the ‘Home’ Screen, touch Weather > Menu > Information.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
79
Page 92

Hazard Avoidance
Radio ID
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Accessing the XM Radio ID
XM SATELLITE WEATHER PRODUCTS
NEXRAD
NEXRAD (NEXt-generation RADar), is a network of 158 high-resolution Doppler
radar systems that are operated by the National Weather Service (NWS). NEXRAD data
provides centralized meteorological information for the continental United States and
selected overseas locations. The maximum range of a single NEXRAD radar site is 250
nm. In addition to a wide array of services, the NEXRAD network provides important
information about severe weather and air traffic safety.
NEXRAD data is not real-time. The lapsed time between collection, processing, and
dissemination of NEXRAD images can be significant and may not reflect the current
radar synopsis. Due to the inherent delays and the relative age of the data, it should
be used for long-range planning purposes only. Never use NEXRAD data or any radar
data to penetrate hazardous weather. Rather, use it in an early-warning capacity of
pre-departure and enroute evaluation.
Composite data from all the NEXRAD radar sites in the United States is shown. This
data is composed of the maximum reflectivity from the individual radar sweeps. The
display of the information is color-coded to indicate the weather severity level.
The display of radar coverage is always active when NEXRAD is selected. Areas
where NEXRAD radar coverage is not currently available or is not being collected are
indicated in grayish-purple. Radar capability exists in these areas, but it is not active
or is off-line.
80
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 93

Hazard Avoidance
neXrAD Ab n o r M A l I t I e S
There are possible abnormalities regarding displayed NEXRAD images. Some, but
not all, of those include:
•Groundclutter
•Strobesandspuriousradardata
•Sunstrobes,whentheradarantennapointsdirectlyatthesun
•Militaryaircraftdeploymetallicdust(chaff)whichcancausealterationsinradar
scans
•Interferencefrombuildingsormountains,whichmaycauseshadows
neXrAD lI M I tAt I o n S
Certain limitations exist regarding the NEXRAD radar displays. Some, but not all, are
listed for the user’s awareness:
•NEXRAD base reectivity does not provide sufcient information to determine
cloud layers or precipitation characteristics (hail vs. rain). For example, it is not
possible to distinguish between wet snow, wet hail, and rain.
•NEXRADbasereectivityissampledattheminimumantennaelevationangle.An
individual NEXRAD site cannot depict high altitude storms at close ranges, and
has no information about storms directly over the site.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
•Radarcoverageonlyextendsto55°N.
•Anyprecipitationdisplayedbetween52°Nand55°Nisunknown.
neXrAD In t e n S I t y
Colors are used to identify the different NEXRAD echo intensities (reflectivity)
measured in dBZ (decibels of Z). “Reflectivity” (designated by the letter Z) is the
amount of transmitted power returned to the radar receiver. The dBZ values increase
as returned signal strength increases. Precipitation intensity is displayed using colors
corresponding to the dBZ values.
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
81
Page 94
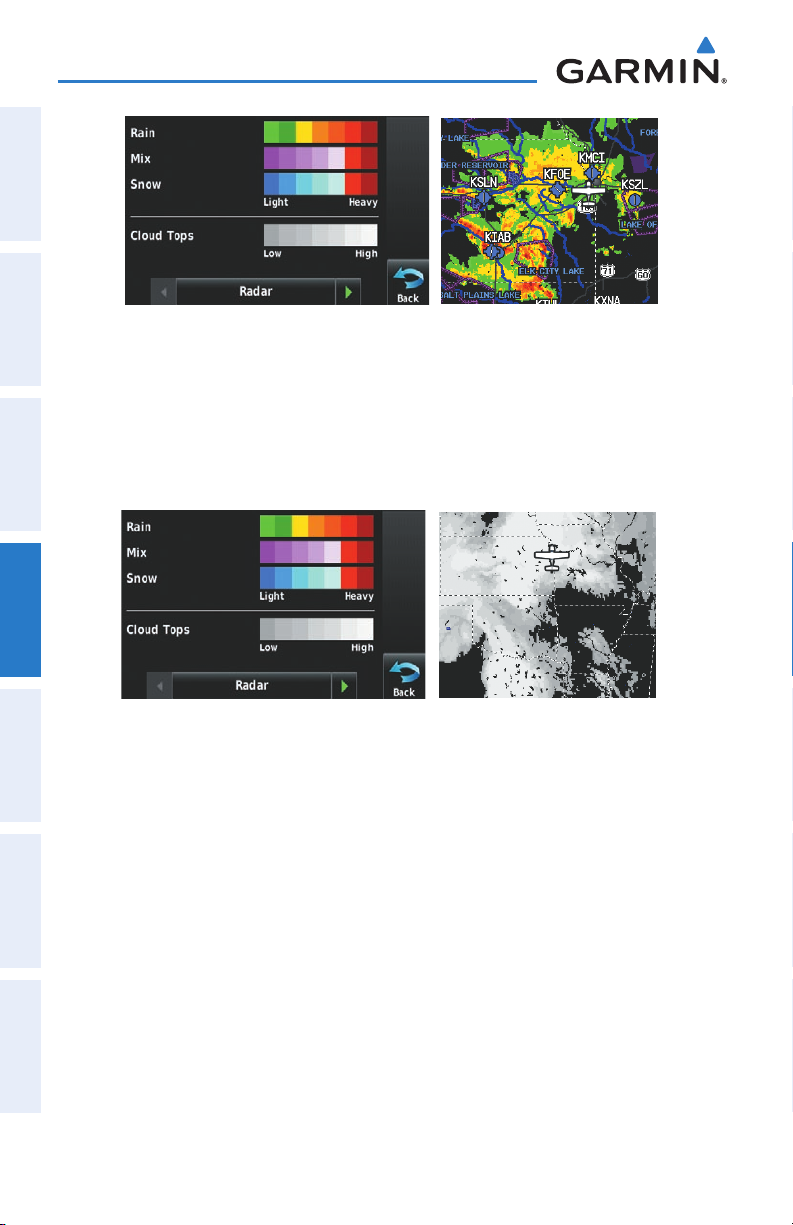
Hazard Avoidance
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
NEXRAD DataRADAR Legend
SATELLITE MOSAIC
Satellite Mosaic displays infrared composite images of cloud cover taken by
geostationary weather satellites. The Satellite Mosaic provides up to seven levels of
cloud cover.
RADAR Legend Satellite Mosaic/Cloud Tops Data
ECHO TOPS
Echo Tops are derived from NEXRAD radar and indicate the highest altitude at which
precipitation is falling. Echo Tops at or above the altitude you select are displayed, in
5,000 foot increments up to 70,000 ft. Echo Tops can be helpful in determining the
severity of thunderstorms.
82
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 95

Hazard Avoidance
Echo Tops Data Echo Tops Altitudes
WINDS ALOFT
Winds Aloft data shows the forecasted wind speed and direction at the surface
and at selected altitudes. Altitudes can be displayed in 3,000-foot increments up to
42,000 feet MSL.
Winds Aloft are displayed using wind barbs or a wind streamline depending on
the selected range. The wind barbs indicate wind speed and direction. The wind
streamline indicates wind direction with arrows.
The wind barbs always point in the direction that the wind is coming from. The wind
speed is depicted using flags at the end of the wind barb. A short wind flag is 5 knots,
a long wind flag is 10 knots, and a triangle flag is 50 knots.
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Winds Aloft Data Winds Aloft Altitudes
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
83
Page 96

Hazard Avoidance
Wind Direction
Calm
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
5 Knots
10 Knots
15 Knots
20 Knots
Wind Flag
50 Knots
Winds Barbs
XM LIGHTNING
Lightning data shows the approximate location of cloud-to-ground lightning strikes.
A strike icon represents a strike that has occurred within a two-kilometer region
and within the last seven minutes. The exact location of the lightning strike is not
displayed.
Lightning Data
STORM CELLS
The Storm Cells feature displays storms as well as the storm’s projected path in the
immediate future.
The direction of the storm is displayed by an arrow. The map range at which the
arrow is displayed depends on the storm cell's speed. The tip of the arrow indicates
where the storm should be in 15 minutes. Critical information about the storm cell
(tops and intensity) can be viewed by selecting the storm cell with the map pointer.
Touching the Map Feature Button will display additional information.
84
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 97
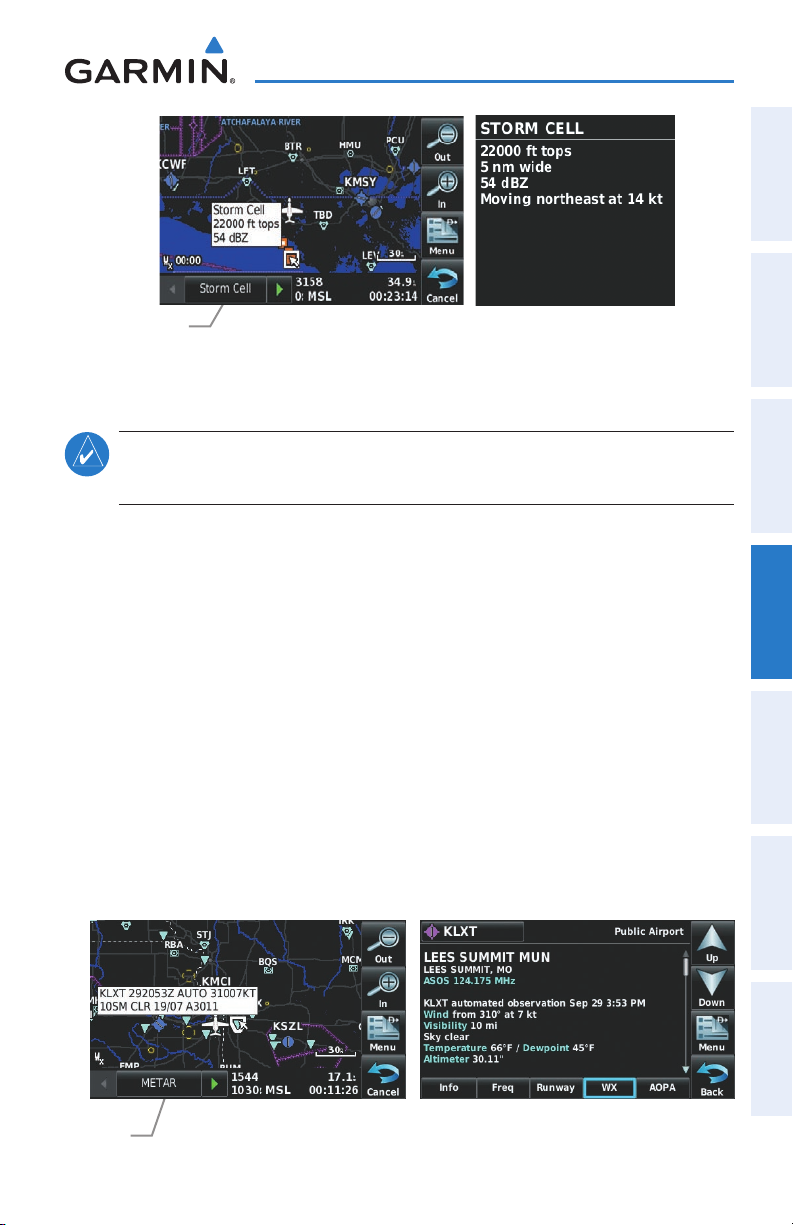
Hazard Avoidance
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Map Feature
Button
Storm Cell Data (Map) Additional Storm Cell Information
METARS AND TAFS
NOTE:
database service area.
METAR (METeorological Aerodrome Report) is an international code used for
reporting weather observations. METARs are updated hourly or as needed. METARs
typically contain information about the temperature, dewpoint, wind, precipitation,
cloud cover, cloud heights, visibility, and barometric pressure. They can also contain
information on precipitation amounts, lightning, and other critical data. If METAR data
is available for an airport, a color-coded flag is shown next to the airport.
TAF (Terminal Area Forecast) is the standard format for 24-hour weather forecasts.
TAFs may contain some of the same code as METAR data. It typically forecasts
significant weather changes, temporary changes, probable changes, and expected
changes in weather conditions.
An abbreviated version can be viewed by selecting the METAR flag with the map
pointer. Touching the Map Feature Button will display additional information. METAR
and TAF data can be displayed as raw or decoded text.
METAR information is only displayed within the installed aviation
Map
Feature
Button
190-01117-02 Rev. A
METAR Data (Map) Additional METAR Data
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
85
Page 98

Hazard Avoidance
The METAR flag color is determined by the information in the METAR text.
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
VFR (ceiling greater than 3000 feet AGL and visibility greater than 5
miles)
Marginal VFR (ceiling 1000-3000 feet AGL and/or visibility 3-5 miles)
IFR (ceiling 500 to below 1000 feet AGL and/or visibility 1 mile to less
than 3 miles)
Low IFR (ceiling below 500 feet AGL or visibility less than 1 mile)
METAR text does not contain adequate information to determine
flight conditions
AIRMETS
An AIRMET (AIRmen’s METeorological Information) can be especially helpful for
pilots of light aircraft that have limited flight capability or instrumentation. An AIRMET
must affect or be forecast to affect an area of at least 3,000 square miles at any one
time. AIRMETs are routinely issued for six-hour periods and are amended as necessary
due to changing weather conditions. AIRMETs are displayed as colored, dashed lines.
SIGMETS
A SIGMET (SIGnificant METeorological Information) advises of weather that is
potentially hazardous to all aircraft. In the contiguous United States, the following
items are covered: severe icing, severe or extreme turbulence, volcanic ash, dust storms,
and sandstorms that lower visibility to less than three statute miles.
A Convective SIGMET is issued for the following conditions: thunderstorms, isolated
severe thunderstorms, embedded thunderstorms, hail at the surface, and tornadoes.
A SIGMET is widespread and must affect or be forecast to affect an area of at least
3,000 square miles. SIGMETs are displayed as a yellow-dashed line.
86
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Page 99

Hazard Avoidance
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
Map
Feature
Button
AIRMET Selected Additional AIRMET Data
TEMPORARY FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS (TFRS)
Temporary Flight Restrictions or TFRs temporarily restrict all aircraft from entering
the selected airspace unless a waiver has been issued. TFRs are routinely issued for
occurrences such as sporting events, dignitary visits, military depots and forest fires.
TFRs are represented as an area highlighted by red (active) or yellow (not yet active).
Map Feature
Button
TFR Data Selected Additional TRF Information
PIREPS
Pilot Weather Reports (PIREPs) provide timely weather information for a particular
route of flight. When significant weather conditions are reported or forecast, Air Traffic
Control (ATC) facilities are required to solicit PIREPs. A PIREP may contain unforecast
adverse weather conditions, such as low in-flight visibility, icing conditions, wind shear,
and turbulence. PIREPs are issued as either Routine (UA) (blue) or Urgent (UUA)
(yellow).
190-01117-02 Rev. A
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
87
Page 100

Hazard Avoidance
OverviewGPS NavigationFlight PlanningHazard AvoidanceAdditional FeaturesAppendicesIndex
Map
Feature
Button
PIREP Selected Additional PIREP Data
FREEZING LEVELS
Freezing Level shows contours for the lowest forecast altitude where icing conditions
are likely to occur.
Freezing Level Data
TURBULENCE FORECAST
Turbulence data identifies the potential for erratic movement of high-altitude air
mass associated winds. Turbulence is classified as light, moderate, severe, or extreme.
Turbulence data is intended to supplement AIRMETs and SIGMETs.
88
Turbulence Forecast Legend Light Turbulence Selected
Garmin aera 500 Series Pilot’s Guide
190-01117-02 Rev. A
 Loading...
Loading...