Page 1

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
Overview
The Fujitsu MBF200 Solid-State Fingerprint Sensor is a direct
contact, fingerprint acquisition device. It is a high performance,
low power, low cost, capacitive sensor composed of a twodimensional array of metal electrodes in the sensing array.
Each metal electrode acts as one plate of a capacitor and the
contacting finger acts as the second plate. A passivation layer on the
device surface forms the dielectric between these two plates. Ridges
and valleys on the finger yield varying capacitor values across the
array, and the resulting varying discharge voltages are read to form
an image of the fingerprint.
The MBF200 is manufactured in standard CMOS technology.
The 256 X 300 sensor array has a 50 µm pitch and yields a 500-dpi
image. The sensor surface is protected by a patented, ultra-hard,
abrasion and chemical resistant coating.
Features
• Capacitive solid-state device
Packages
Applications
• Secure access for databases, networks, local storage
• 500-dpi resolution (50 µm pitch)
• 1.28 cm x 1.50 cm (0.5” x 0.6”) sensor area
• 256 x 300 sensor array
• Smart Cards
• 3.3V to 5V operating range
• Exceptionally hard protective coating
• Integrated 8-bit analog to digital converter
• One of three bus interfaces:
8-bit microprocessor bus interface
Integrated USB Full-Speed Interface
Integrated Serial Peripheral Interface
• Standard CMOS technology
• Low power, less than 70 mW operating at 5V
• Automatic finger detection
• Portable fingerprint acquisition
• Smart Cards
• Identity verification for ATM transactions
• Cellular phone-based security access
• Access control and monitoring (home, auto, office, etc.)
Page 2

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
Table of Contents
Chip Operation .....................................................................................................................................................................1
Block Diagram......................................................................................................................................................................1
Connection Diagram..............................................................................................................................................................2
Pin List................................................................................................................................................................................3
Pin Descriptions....................................................................................................................................................................4
Device Bus Operation.............................................................................................................................................................7
Microprocessor Bus Interface............................................................................................................................................7
Serial Peripheral Bus Interface (SPI) Slave ................................................................................................................................8
SPI Bus Mode.................................................................................................................................................................8
SPI Slave Mode...............................................................................................................................................................8
Register Read Command in SPI Slave Mode ........................................................................................................................8
Register Write Command for SPI Slave Mode......................................................................................................................8
USB Interface Mode, Using Internal ROM ................................................................................................................................8
Endpoint 0 ....................................................................................................................................................................8
Endpoint 1 ....................................................................................................................................................................8
Endpoint 2 ....................................................................................................................................................................8
USB Interface Mode, Using External ROM ...............................................................................................................................8
SPI Master Mode ............................................................................................................................................................9
Function Register Descriptions ...............................................................................................................................................9
Function Register Map...........................................................................................................................................................9
RAH 0x00 .....................................................................................................................................................................9
RAL 0x01....................................................................................................................................................................10
CAL 0x02....................................................................................................................................................................10
REH 0x03....................................................................................................................................................................10
REL 0x04....................................................................................................................................................................10
CEL 0x05 ....................................................................................................................................................................10
DTR 0x06....................................................................................................................................................................11
DCR 0x07....................................................................................................................................................................11
CTRLA 0x08 ...............................................................................................................................................................11
CRTLB 0x09................................................................................................................................................................13
CTRLC 0x0A ...............................................................................................................................................................14
SRA 0x0B....................................................................................................................................................................14
PGC 0x0C ...................................................................................................................................................................15
ICR 0x0D ....................................................................................................................................................................15
ISR 0x0E.....................................................................................................................................................................16
THR 0x0F ...................................................................................................................................................................16
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
-1
Page 3

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
CIDH 0x10 ................................................................................................................................................................. 17
CIDL 0x11.................................................................................................................................................................. 17
TST 0x12.................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Sensor Initialization............................................................................................................................................................ 18
Image Retrieval .................................................................................................................................................................. 18
Microprocessor Interface ............................................................................................................................................... 18
Get Row ............................................................................................................................................................... 18
Get Whole Image ................................................................................................................................................... 19
Get Sub-Image ...................................................................................................................................................... 20
Serial Peripheral Interface ...................................................................................................................................... 21
Get Image............................................................................................................................................................. 21
USB Interface........................................................................................................................................................ 22
Get Image............................................................................................................................................................. 22
Absolute Maximum Ratings ................................................................................................................................................. 23
Operating Range ................................................................................................................................................................ 23
DC Characteristics .............................................................................................................................................................. 23
Power Supply Consumption ................................................................................................................................................. 24
AC Characteristics .............................................................................................................................................................. 25
Microprocessor Bus Mode.............................................................................................................................................. 25
Read Cycle............................................................................................................................................................ 25
Write Cycle........................................................................................................................................................... 25
SPI Slave Mode...................................................................................................................................................... 26
SPI Master............................................................................................................................................................ 26
Timing Diagrams................................................................................................................................................................ 27
Physical Dimensions............................................................................................................................................................ 31
Recommended Land Pattern................................................................................................................................................. 32
Array Orientation............................................................................................................................................................... 33
Appendix A ........................................................................................................................................................................ 34
Recommended Power and Ground Connections ................................................................................................................ 34
Appendix B........................................................................................................................................................................ 35
Recommended MBF200 Sensor Orientation..................................................................................................................... 35
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
0
Page 4

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
Chip Operation
The sensor array includes 256 columns and 300 rows of sensor plates.
Associated with each column are two sample-and-hold circuits.
A fingerprint image is sensed or captured one row at a time. This
“row capture” occurs in two phases. In the first phase, the sensor
plates of the selected row are pre-charged to the VDD voltage.
During this pre-charge period, an internal signal enables the first
set of sample-and-hold circuits to store the pre-charged plate
voltages of the row.
In the second phase, the row of sensor plates is discharged with a
current source. The rate at which a cell is discharged is proportional
Block Diagram
P0
P1
D[7:0]
DATA
REGISTER
to the “discharge current.” After a period of time (referred to as
the “discharge time”), an internal signal enables the second set
of sample-and-hold circuits to store the final plate voltages.
The difference between the precharged and discharged plate voltages
is a measure of the capacitance of a sensor cell. After the row capture,
the cells within the row are ready to be digitized.
The sensitivity of the chip is adjusted by changing the discharge
current and discharge time. The nominal value of the current source
is controlled by an external resistor connected between the ISET pin
and ground. The current source is controlled from the Discharge
Current Register (DCR). The discharge time is controlled by the
Discharge Time Register (DTR).
A0
RD
WR
WAIT
CS0
CS1
MOSI
MISO
DP
DM
EXTINT
INTR
TEST
INDEX
REGISTER
CONTROL
SPI
USB
FUNCTION
REGISTERS
SAMPLE AND HOLD
A/D CONVERTER
ANALOG
MULTI-
VIBRATOR
256 X 300
SENSOR
ARRAY
AIN
ISET
FSET
MODE1
MODE0
XTAL
OSC
XTAL1
XTAL2
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
1
Page 5
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
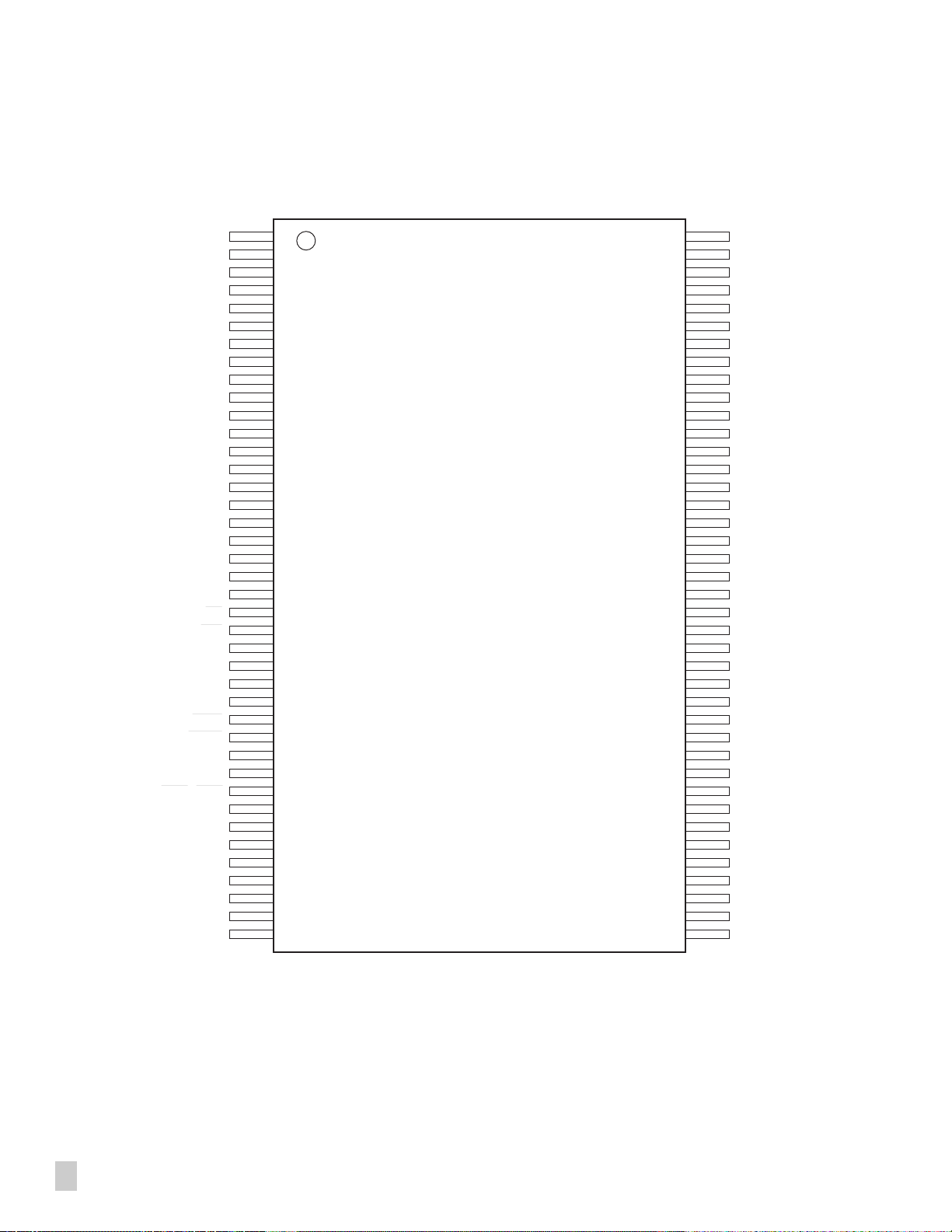
Connection Diagram
VDDA1
VSSA1
ISET
AIN
FSET
VSSA2
VDDA2
TEST
P0
P1
D7
D6
D5
D4
VSS1
VDD1
D3
D2
D1
D0
A0
RD
WR
VSS2
VDD2
XTAL2
XTAL1
INTR
WAIT
EXTINT
CS1/SCLK
CS0/SCS
MOSI
MISO
MODE1
MODE0
DM
DP
VDD3
VSS3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
MBF200
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
2
Page 6

Pin List
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
Pin
Number
1 VDDA1 PWR Analog Power Supply
2 VSSA1 GND Analog Ground
3 ISET O Sets Reference Current
4 AIN I Analog Input
5 FSET O Sets Internal Multi-vibrator Frequency
6 VSSA2 GND Analog Ground
7 VDDA2 PWR Analog Power Supply
8 TEST I Test Mode Enable
9 P0 O 8mA 4mA Output Port 0
10 P1 O 8mA 4mA Output Port 1
11 D7 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 7
12 D6 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 6
13 D5 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 5
14 D4 I/O 8mA Data Bit 4
15 VSS1 GND Digital Ground
16 VDD1 PWR Digital Power Supply
17 D3 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 3
18 D2 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 2
19 D1 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 1
20 D0 I/O 8mA 4mA Data Bit 0
21 A0 I Address Input
22 RD I 8mA 4mA Read Enable, Active Low
23 WR I 8mA 4mA Write Enable, Active Low
24 VSS2 GND Digital Ground
25 VDD2 PWR Digital Power Supply
26 XTAL2 O Internal Oscillator Output
27 XTAL1 I Internal Oscillator Input
28 INTR
29 WAIT O 8mA Wait, Active Low
30 EXTINT I External Interrupt Input
31 CS1/SCLK I/O Chip Select, Active High
32 CS0/SCS I/O Chip Select, Active Low
33 MOSI I/O 8mA 4mA SPI Master Output / Slave Input
34 MISO I/O 8mA 4mA SPI Master Input / Slave Output
35 MODE1 I Mode Select 1
36 MODE0 I Mode Select 0
37 DM I/O USB D-
38 DP I/O USB D+
39 VDD3 PWR Digital Power Supply
40 VSS3 GND Digital Ground
[41:80] N/C No Connect
Name Type IOL (5.0 V) IOH (5.0 V) Description
O 8mA Interrupt Output, Active Low
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
3
Page 7

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
Pin Descriptions
VDDA1, VDDA2 (Pins 1 and 7)
Power Supply to the analog section of the sensor. VDDA1 powers the array, row drivers, column receivers, A/D converter, and sample/hold
amplifier. VDDA2 powers the multi-vibrator and bias circuits.
VSSA1, VSSA2 (Pins 2 and 6)
Ground for the analog section of the sensor. VSSA1 is the ground return for the array, row drivers, column receivers, A/D converter, and
sample hold amplifier. VSSA2 is the ground return for the multi-vibrator and bias circuits.
VDD1, VDD2, VDD3 ( Pins 25, 16, and 39)
Power supply to the digital logic and I/O drivers. VDD2 powers the core digital logic, oscillators, phase-locked loops, and digital inputs.
VDD1 and VDD3 supply power to the digital output circuits and USB transceivers.
VSS1, VSS2, VSS3 (Pins 24, 15, and 40)
Ground for the digital logic and I/O drivers.
VSS2 is the ground connection for the core digital logic, oscillators, phase-locked loops, and digital inputs. VSS1 and VSS3 are the ground
connections for the digital outputs and USB transceivers.
ISET (Pin 3)
Connect a 200k ohm resistor between ISET and analog ground VSSA1 to set the internal reference current. The discharge current is a scalar
function of the internal reference current.
AIN (Pin 4)
Alternate analog input to the A/D converter. Set the AINSEL bit in register CTRLA to select AIN as the input to the A/D converter. Pull this
pin to ground, preferably with a resistor.
FSET (Pin 5)
Connect a resistor between FSET and ground to set the internal multi-vibrator and automatic finger detection frequency. Use a 56k ohm
resistor for standard 12 MHz (±20%) multi-vibrator operation and 120KHz (±20%) automatic finger detection sampling rate.
XTAL1 (Pin 27)
Input to the internal oscillator. To use the internal oscillator, connect a crystal circuit to this pin. If an external oscillator is used, connect its
output to this pin.
XTAL2 (Pin 26)
Output from the internal oscillator. To use the internal oscillator, connect a crystal circuit to this pin. If an external oscillator is used, leave this
pin unconnected.
D[7:0] (Pins 11-14, 17-20)
Bi-directional data bus. D[7:0] have weak latches that hold the bus’s state when not being driven. These pins may be left unconnected in SPI or
USB mode.
A0 (Pin 21)
Address input. Drive A0 low to select the address index register. Drive A0 high to select the data buffer. A0 has a weak latch that holds the pin
state when not being driven. This pin may be left unconnected in SPI or USB mode.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
4
Page 8

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
(Pin 22)
RD
Read enable, active low. To read from the chip, drive RD
resistor and may be left unconnected in SPI or USB mode.
(Pin 23)
WR
Write enable, active low. To write to the chip, drive WR
and may be left unconnected in SPI or USB mode.
/ SCS (Pin 32)
CS0
Chip select, active low. The CS0
USB mode if not using an external serial ROM. The function of the CS0
MODE[1:0] = 00b (Microprocessor Bus Interface Mode)
/SCS functions as an active-low chip select input. Drive CS0/SCS low while CS1 is high to select the chip.
CS0
/SCS pin has a weak latch that holds the pin’s state when not being driven. CS0/SCS may be left unconnected in
low while WR is high and the chip is selected. RD has an internal, weak pull-up
low while RD is high and the chip is selected. WR has an internal, weak pull-up resistor
MBF200
/SCS pin depends on the MODE1 and MODE0 pins.
MODE[1:0] = 01b (SPI Slave Mode)
CS0
/SCS functions as an active-low slave chip select input. Connect a pull-up resistor between CS0/SCS and VDD.
MODE[1:0] = 10b (USB Interface Mode, Using Internal ROM)
CS0
/SCS has no function.
MODE[1:0] = 11b (USB Interface Mode, Using External ROM)
CS0
/SCS functions as the master chip select output, active low to the slave serial ROM chip select. Connect a pullup resistor between
/SCS and VDD.
CS0
CS1 / SCLK (Pin 31)
Chip select, active high. The CS1/SCLK pin has a weak latch that holds the pin’s state when not being driven. CS1/SCLK may be left
unconnected in USB mode if not using an external serial ROM. The function of this pin depends on the MODE1 and MODE0 pins.
MODE[1:0] = 00b (Microprocessor Bus Interface Mode)
CS1/SCLK functions as an active-high chip select input. Drive CS1/SCLK high while CS0-/CSC- is low to select the chip.
MODE[1:0] = 01b (SPI Slave Mode)
CS1/SCLK functions as the slave serial clock input.
MODE[1:0] = 10b (USB Interface Mode, Using Internal ROM)
CS1/SCLK has no function.
MODE[1:0] = 11b (USB Interface Mode, Using External ROM)
CS1/SCLK functions as the master serial clock output to the slave serial ROM clock input. Connect a pull-up resistor between
CS1/SCLK and VDD.
EXTINT (Pin 30)
External Interrupt input. This pin can be programmed to be edge or level sensitive, active-high or active-low. EXTINT has a weak pull-up and
may be left unconnected in MCU, SPI, or USB mode.
INTR
(Pin 28)
Interrupt output, active low. INTR
be enabled if the sensor is in MCU or SPI mode. In USB mode leave this pin unconnected.
is high impedance when it is not active and is driven low when an enabled interrupt event occurs. INTR can
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
5
Page 9

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
AIT (Pin 29)
W
Wait output, active low. W
an A/D conversion is in progress. W
MOSI (Pin 33)
SPI Master Output/Slave input. The MOSI pin has a weak latch that holds the pin’s state when not being driven. MOSI may be left
unconnected in MCU mode or USB mode if not using an external serial ROM. The function of this pin depends on the MODE1 and MODE0
pins.
MODE[1:0] = 00b (Microprocessor Bus Interface Mode)
MOSI has no function.
MODE[1:0] = 01b (SPI Slave Mode)
MOSI functions as the slave serial input.
AIT is driven low when active and high-impedance when not active. WAIT goes low if the A/D converter is read while
AIT will remain low until the A/D conversion is completed.
MODE[1:0] = 10b (USB Interface Mode, Using Internal ROM)
MOSI has no function.
MODE[1:0] = 11b (USB Interface Mode, Using External ROM)
MOSI functions as the master serial data output to the slave serial ROM data input. Unlike standard SPI, MOSI is actively driven high
and low when transmitting data and is high impedance when idle. Connect a pull-up resistor between MOSI and VDD to pull MOSI
high when idle.
MISO (Pin 34)
SPI Master Input/Slave Output. The MISO pin has a weak latch that holds the pin’s state when not being driven. MISO may be left
unconnected in MCU mode or USB mode if not using an external serial ROM. The function of this pin depends on the MODE1 and MODE0
pins.
MODE[1:0] = 00b (Microprocessor Bus Interface Mode)
MISO has no function.
MODE[1:0] = 01b (SPI Slave Mode)
MISO functions as the slave serial data output. Unlike standard SPI, the MISO connection is actively driven high and low when
transmitting data and is high impedance when idle. Connect a pull-up resistor between MISO and VDD to pull MISO high when idle.
MODE1/MODE0 = 10b (USB Interface Mode, Using Internal ROM)
MISO has no function.
MODE1/MODE0 = 11b (USB Interface Mode, Using External ROM)
MISO functions as the master serial data input from the slave serial ROM data output.
P0 (Pin 9)
Port Output 0. This output is controlled by bit 0 of the CTRLC register.
P1 (Pin 10)
Port Output 1. This output is controlled by bit 1 of the CTRLC register.
DP (Pin 38)
USB D+ data line. In USB mode, connect a 1.5k ohm resistor between DP and VDD3, which must be between 3.3V and 3.6V in this mode.
Use a 43 ohm series resistor. In MCU or SPI mode, either pull-up this pin with a resistor or tie it to ground.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
6
Page 10

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
DM (Pin 37)
USB D- data line. Use 43 ohm series resistor. In MCU or SPI mode, either pull-up this pin with a resistor or tie it to ground.
MODE[1:0] (Pins 35 and 36)
Mode Select pins. MODE[1:0] select one of four operating modes.
MBF200
MODE[1:0]
00b Microprocessor Bus Mode
01b SPI Bus Mode
10b USB Mode, Using Internal ROM
11b USB Mode, Using External ROM
Description
TEST (Pin 8)
Test Mode Enable. It is intended for factory use only. Connect this pin to VSS.
No Connect (Pins 41-80)
Unconnected pins.
Device Bus Operation
Microprocessor Bus Interface
The microprocessor bus interface mode uses the following pins:
D[7:0], A0, RD
the internal multi-vibrator or the XTAL1/XTAL2 oscillator can be
selected to provide the clock to the chip. The SPI and USB interfaces
are disabled.
The fingerprint sensor chip uses an indexed addressing scheme to
access its function registers. The chip has eight data lines (D[7:0]) and
one address line (A0). The address line selects between the index
register and the data register. Drive A0 low to select the index
register. Drive A0 high to access the function register selected by the
index register. The index register retains its value until it is rewritten
or the chip is reset.
, WR, CS0, CS1, EXTINT, INTR, and WAIT. Either
The chip has four control inputs: CS0
low and CS1 high to select the chip. Data is latched on the rising edge
of WR-.
The chip has two status lines: INTR
asserted when an interrupt event occurs. The W
when the A/D converter is read while an A/D conversion is in
progress. The W
conversion is completed. Both the W
impedance when they are not active. As a result, they can be activelow WIRE-ORed in conjunction with other interrupts or wait
signals.
The SPI and USB interfaces are disabled when the microprocessor
bus interface is selected. A truth table for the microprocessor bus
interface is shown below:
, CS1, RD, and WR. Drive CS0
and WAIT. The INTR signal is
AIT signal goes low
AIT signal will be high impedance when the A/D
AIT and INTR outputs are high
Truth Table for the Microprocessor Bus Interface
CS0
H X X X X De-selected High Impedance
X L X X X De-selected High Impedance
L H X H H Standby High Impedance
L H L L H Read Index Register Output
L H L H L Write Index Register Input
L H H L H Read Data Register Output
L H H H L Write Data Register Input
CS1 A0 RD WR Mode Data Lines
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
7
Page 11

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Serial Peripheral Bus Interface (SPI)
Slave
SPI Bus Mode
SPI (Slave) bus mode uses the following pins: SCLK, SCS
MISO, and EXTINT. Either the internal multivibrator or the
XTAL1/XTAL2 oscillator can be selected to provide the clock to the
chip. The microprocessor bus and USB interface are disabled.
SPI Slave Mode
In SPI Slave Mode, the sensor can operate in either SPI mode (0, 0)
where CPOL = 0 and CPHA = 0 or SPI mode (1, 1) where CPOL = 1
and CPHA = 1. T he SPI Master may clock in commands and clock out
data up to 12 Mbits per second. The SPI Master can write and read the
registers of the sensor even when the internal 12 MHz multivibrator or
XTAL1/XTAL2 oscillator is halted.
• MOSI bits are sampled on the rising edge of SCK
• MISO bits change on the falling edge of SCK
• SCK can be idle in either a high or low state
• The most significant bits are shifted out first
, MOSI,
USB Interface Mode, Using Internal
ROM
This USB mode uses the following pins: DP, DM, EXTINT, XTAL1,
and XTAL2. XTAL1 must be driven from a 12 MHz source or XTAL1
and XTAL2 must be connected to a 12 MHz crystal circuit. The
internal 12 MHz multivibrator, the microprocessor bus, and SPI
interface are disabled. The internal USB descriptor ROM will be
accessed in response to a USB GET_DESCRIPTOR command.
The sensor’s USB interface uses three endpoints:
Endpoint 0
Endpoint 0 is a control endpoint used for device enumeration and
configuration. The sensor function registers are written and read
using control transfers of vendor specific commands to endpoint 0.
Endpoint 1
Endpoint 1 is a bulk-in endpoint specifically for reading the CTRLA
register, which is the output buffer of the A/D converter. Data is
transmitted in 64-byte packets except for the last packet of a
GETROW operation which may be 64-bytes or less, depending on
the row length.
Register Read Command in SPI Slave Mode
The Register Read command includes a command byte and address
byte. The command sequence begins when the SPI master drives SCS
low and sends the Read Command byte (encoded as 0x03) on the
MOSI pin. Following the command byte, the master sends the
address byte, which is the index to the register to be read. After
receiving the least significant bit (LSB) of the address byte, the SPI
slave sensor sends the contents of the selected register on the MISO
pin. Finally, the master drives SCS
of the data byte. When reading the A/D converter, the Master may
keep SCS
row. A new Register Read command must be issued to read the next
row. The SPI Master must drive SCS
command.
low to read consecutive pixels up to the end of the current
high after it has sampled the LSB
high before beginning another
Register Write Command for SPI Slave Mode
The Register Write command includes a command byte and address
byte followed by the data to be written. The command sequence
begins when the SPI Master drives SCS
Command byte (encoded as 0x02) on the MOSI pin. Then the master
sends the address byte, which is the index to the register to be
written. Finally, the master sends the data byte and thereafter drives
high.
SCS
low and sends the Write
Endpoint 2
Endpoint 2 is an interrupt endpoint. In the event of an interrupt,
the contents of the ISR (Interrupt Status Register) are transfered to
endpoint 2.
USB Interface Mode, Using External
ROM
This USB mode the uses following pins: DP, DM, SCLK, SCS
MOSI, MISO, EXTINT, XTAL1, and XTAL2. XTAL1 must be
driven from a 12 MHz source or a 12 MHz crystal circuit must be
connected to XTAL1 and XTAL2. The internal 12 MHz multivibrator and the microprocessor bus are disabled.
The SPI interface is enabled as an SPI Master. The external SPI serial
ROM will be accessed in response to a USB GET_DESCRIPTOR
command. The internal USB descriptor ROM is disabled. This mode
allows an external serial ROM to override the internal descriptor ROM.
Note: When the MBF200 is directly connected to USB in either of
the modes above, the VDD and VDDA pins must be powered
between 3.3V and 3.6V so that the MBF200 DP and DM pins do
not drive the USB beyond 3.6V.
,
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
8
Page 12

SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
SPI Master Mode
In SPI Master Mode the sensor operates in SPI mode (1,1) where
CPOL = 1, and CPHA = 1. SCK is limited to 1 MHz.
• MOSI bits change on the falling edge of SCK
• MISO bits are sampled on the rising edge of SCK
• SCK is idle in the high state
• The most significant bits are shifted out first
Function Register Map
Index
0x00 RAH Row Address, High R/W
0x01 RAL Row Address, Low R/W
0x02 CAL Column Address, Low R/W
0x03 REH Row Address End, High R/W
0x04 REL Row Address End, Low R/W
0x05 CEL Column Address End, Low R/W
0x06 DTR Discharge Time Register R/W
0x07 DCR Discharge Current Register R/W
0x08 CTRLA Control Register A R/W
0x09 CTRLB Control Register B R/W
0x0A CTRLC Control Register C R/W
0x0B SRA Status Register A R
0x0C PGC Programmable Gain Control Register R/W
0x0D ICR Interrupt Control Register R/W
0x0E ISR Interrupt Status Register R/W
0x0F THR Threshold Register R/W
0x10 CIDH Chip Identification, High R
0x11 CIDL Chip Identification, Low R
0x12 TST Test Mode Register R/W
Name Description Read/Write Access
Function Register Descriptions
The function registers are accessed by indexed addressing. Write the
index register to select a function register. Read or write the data
register to access the contents of the function register. All registers
can be read and written except as noted in the following
descriptions.
Note: In the following descriptions, “sub-image” means a rectangular region of the sensor array, up to and including the entire array.
RAH 0x00
Row Address Register High.
Reset State: 0x00
This register holds the high order bit of the address of the first row of a sub-image.
Bit Number
[7:1] - Reserved. Write 0 to these bits.
0 RA[8] Most Significant Bit of Row Address Register
Bit Name Function
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
9
Page 13

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
RAL 0x01
Row Address Register Low.
Reset State: 0x00
This register holds the low order byte of the address of the first row of a sub-image.
Bit Number
[7:0] RA[7:0] Low eight bits of Row Address Register
Bit Name Function
CAL 0x02
Column Address Register.
Reset State: 0x00
This register holds the address of the first column of a sub-image.
Bit Number
[7:0] CA[7:0] Column Address Register
Bit Name Function
REH 0x03
Row Address End Register High.
Reset State: 0x00
This register holds the most significant bit of the address of the last row of a sub-image.
Bit Number
[7:1] - Reserved. Write 0 to these bits.
0 REND[8] Most Significant Bit of Row Address Register
Bit Name Function
REL 0x04
Row Address End Register Low.
Reset State: 0x00
This register holds the least significant byte of the address of the last row of a sub-image.
Bit Number
[7:0] REND[7:0] Low eight bits of Row Address Register
Bit Name Function
CEL 0x05
Column Address End Register.
Reset State: 0x00
This register holds the address of the last column of a sub-image.
Bit Number Bit Name Function
[7:0] CEND[7:0] Column Address Register
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
10
Page 14

DTR 0x06
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Discharge Time Register
Reset State: 0x00
MBF200
Bit Number
[7] - Reserved. Write 0 to these bits.
[6:0] DT[6:0] Sets the discharge time in oscillator clock periods.
Bit Name Function
DCR 0x07
Discharge Current Register
Reset State: 0x00
Bit Number
[7:5] - Reserved. Write 0 to these bits.
[4:0] DC[4:0] Sets the discharge current rate.
Bit Name Function
CTRLA 0x08
Control Register A.
Reset State: 0x00
Write this register to initiate image conversion. Read this register to read the A/D converter.
Bit Number
7 - Reserved. Write 0 to this bit.
6 - Reserved. Write 0 to this bit.
5 - Reserved. Write 0 to this bit.
4 - Reserved. Write 0 to this bit.
3 AINSEL
2 GETSUB Initiates Auto-increment for sub-image
1 GETIMG Initiates Auto-increment for whole image
0 GETROW Initiates Auto-increment for selected row
Bit Name Function
0=Select Array for Conversion
1=Select External Analog Input Pin and Start Conversion
The GETSUB, GETIMG, and GETROW bits select an image access mode and initiate an A/D conversion sequence. The AINSEL bit selects
the input source to the A/D converter.
Set the GETSUB bit to initiate the capture of a rectangular sub-image defined by the RAH, RAL, CAL, REH, REL, and CEL registers.
In CPU or SPI mode, the sub-image can be an arbitrary rectangle ranging from a single pixel to the entire array. In USB mode, the number of
columns in the sub-image must be an integral multiple of 64.
Set the GETIMG bit to initiate the capture of a whole image starting from row zero and column zero through row 299 and column 255,
regardless of the RAH, RAL, CAL, REH, REL, and CEL registers.
Set the GETROW bit to initiate the capture of a row specified by the RAH and RAL registers.
Writing a 1 to any of GETSUB, GETIMG, or GETROW abandons the current image access operation and restarts at the beginning of the
sub-image, image, or row. Set at most one of these three bits. If more than one these three bits are set, image conversion will not start.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
11
Page 15

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Setting the GETROW bit causes the following events to happen:
• Row address loaded with contents of RAH and RAL register.
• Column address resets to zero
• Row capture automatically starts
• Analog to digital conversion of first pixel automatically starts
Setting the GETIMG bit causes the following events to happen:
• Row address resets to zero
• Column address resets to zero
• Row capture automatically starts
• Analog to digital conversion of first pixel automatically starts
Setting the GETSUB bit causes the following events to happen:
• Row address loaded with contents of RAH and RAL register
• Column address loaded with contents of CAL
• Row capture automatically starts
• Analog to digital conversion of first pixel automatically starts
Set the AINSEL bit along with one of the other three bits to begin the analog to digital conversion of the voltage on the AIN pin instead of the
sensor array.
Writing 0 to the CTRLA register has no effect other than clearing AINSEL; the current image access operation is not abandoned.
Read CTRLA for the result of the A/D conversion. The rising edge of RD
Parameter Description
Rising Edge of WR to First Data Valid 28 + DT[6:0] Clock Cycles
Rising Edge of RD
Note: DT[6:0] refers to the contents of the Discharge Time Register.
to Next Data Valid 6 Clock Cycles
causes the next A/D conversion to start.
Max Units
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
12
Page 16

CRTLB 0x09
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Control Register B.
Reset State: CTRLB[7:6] = state of MODE[1:0].
CTRLB[5] = 1.
CTRLB [4:0] = 0, Chip is disabled, oscillator is stopped.
MBF200
Bit Number
[7:6] MODE[1:0] Reflects the state of the MODE[1:0] pins. These bits are read-only. Writing to these bits has no effect. Write 0 to these bits.
5 RDY
4 - Reserved. Write 0 to this bit.
3 AFDEN
2 AUTOINCEN
1 XTALSEL
0 ENABLE
Bit Name Function
This is a read-only bit that indicates the status of the A/D Converter.
0 = A/D Conversion is in progress.
1 = A/D Converter is idle.
Writing this bit has no effect. Write 0 to this bit.
Set this bit to enable the automatic finger detection circuit.
In USB mode, automatic finger detection will generate an interrupt on endpoint 2.
In CPU or SPI mode, automatic finger detection will generate a finger detect interrupt on the INTR pin as controlled by the Interrupt
Control Register (ICR). In any mode, the automatic finger detection can be combined with ENABLE=0 to save power.
0 = Column and row addresses do not automatically increment after the A/D converter is read.
1 = Column addresses increment and another A/D conversion is initiated after the A/D converter is read. The row address
increments at the end of each column.
In USB mode this bit has no function. In CPU and SPI mode this bit selects the clock source for the digital logic.
0 = Selects the internal 12 MHz multi-vibrator.
1 = Selects the XTAL1 pin.
0 = Place the sensor array, digital, and analog block into low-power state (12 MHz clock is halted, A/D Converter is shut down).
1= Enable the sensor array, digital, and analog blocks (12 MHz clock and A/D Converter are enabled).
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
13
Page 17

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
CTRLC 0x0A
Control Register C. This register controls the behavior of general output port pins P0 and P1.
Reset State: 0x00
Bit Number Bit Name Function
Programs the toggle rate of the P1 pin.
If PT1[2:0] = 000, then the P1 pin follows the state of the P1 bit. Otherwise PT1[2:0] selects the clock divisor to generate a square
wave on the P1 pin.
000 = P1 pin follows state of bit P1.
[7:5] PT1[2:0]
[4:2] PT0[2:0]
1 P1
0 P0
001 = clock divided by 2
010 = clock divided by 223.
011 = clock divided by 222.
100 = clock divided by 221.
101 = Reserved.
110 = Reserved.
111 = Reserved.
Programs the toggle rate of the P0 pin.
If PT0[2:0] = 000, then the P0 pin follows the state of the P0 bit. Otherwise PT0[2:0] selects the clock divisor to generate a square
wave on the P0 pin.
000 = P0 pin follows state of bit P0.
001 = clock divided by 2
010 = clock divided by 223.
011 = clock divided by 222.
100 = clock divided by 221.
101 = Reserved.
110 = Reserved.
111 = Reserved.
General Purpose Output Port. When PT1[2:0] bits are 000, this bit controls the P1 pin.
0 = P1 pin low.
1 = P1 pin high.
General Purpose Output Port. When PT0[2:0] bits are 000, this bit controls the P0 pin.
0 = P0 pin low.
1 = P0 pin high.
24
.
24
.
SRA 0x0B
Status Register A. Read Only. This register shadows the state of CTRLA.
Reset State: 0x00
Bit Number Bit Name Function
7 - Reserved. Returns 0.
6 - Reserved. Returns 0.
5 - Reserved. Returns 0.
4 - Reserved. Returns 0.
3 AINSEL This bit is set or cleared when the AINSEL bit (CTRLA bit 3) is set or cleared by software.
2 GETSUB This bit is set when the GETSUB bit (CTRLA bit 2) is set by software. This bit is cleared after the last byte is read.
1 GETIMG This bit is set when the GETIMG bit (CTRLA bit 1) is set by software. This bit is cleared after the last byte is read.
0 GETROW This bit is set when the GETROW bit (CTRLA bit 0) is set by software. This bit is cleared after the last byte is read.
14 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 18

PGC 0x0C
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Programmable Gain Control Register.
Reset State: 0x00
Bit Number Bit Name Function
[7:4] - Reserved. Write 0 to these bits. Returns 0 when read.
Sets the gain of the amplifier.
0000 = 1.0 (default)
0001 = 0.25
0010 = 0.50
0011 = 0.75
0100 = 1.0
0101 = 1.25
0110 = 1.50
[3:0] PG[3:0]
0111 = 1.75
1000 = 4.0
1001 = 1.0
1010 = 2.0
1011 = 3.0
1100 = 4.0
1101 = 5.0
1110 = 6.0
1111 = 7.0
MBF200
ICR 0x0D
Interrupt Control Register.
Reset State 0x00.
This register controls the behavior of the two interrupt sources of the fingerprint sensor. Interrupt request 0 corresponds to the finger detect
interrupt. Interrupt request 1 corresponds to the external interrupt pin EXTINT.
Set bits IE[1:0] to enable the corresponding interrupt. Disabling an interrupt prevents the interrupt event from causing the chip to assert
or to send a packet on USB endpoint 2. However, the interrupt event is not prevented from setting its corresponding bit in the ISR
INTR
register.
Set bits IM[1:0] to prevent an interrupt event from setting the corresponding bit in the ISR. Setting or clearing IM[1:0] will not clear ISR bits
IR[1:0].
Set bits IT[1:0] to program the interrupts as edge or level sensitive. If IT1 is programmed as edge triggered, then IR1 (interrupt request 1) will
be set by the falling edge of EXTINT.
IP[1:0] select the polarity of the interrupt source. To detect finger down and finger up states with the internal finger detect circuit, set the IP0
bit to detect finger down (rising or high signal). After the finger down interrupt occurs, clear the IP0 bit to detect finger up (falling or low
signal). Similarly, IP1 can be programmed to select the polarity of the EXTINT signal.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 15
Page 19

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Bit Number Bit Name Function
7 IP1
6 IP0
5 IT1
4 IT0
3 IM1
2 IM0
1 IE1
0 IE0
ISR 0x0E
Interrupt Status Register.
Reset State ISR[7:2] = 0.
ISR[1:0] = X. State is indeterminate after reset.
0=EXTINT Interrupt Polarity is Falling Edge or Active Low
1=EXTINT Interrupt Polarity is Rising Edge or Active High
0=Finger Detect Interrupt Polarity is Falling Edge or Active Low
1=Finger Detect Interrupt Polarity is Rising Edge or Active High
0=EXTINT Interrupt is Edge Triggered
1=EXTINT Interrupt is Level Triggered
0=Finger Detect Interrupt is Edge Triggered
1=Finger Detect Interrupt is Level Triggered
0=EXTINT Interrupt Not Masked
1=EXTINT Interrupt Masked
0=Finger Detect Interrupt Not Masked
1=Finger Detect Interrupt Masked
0=EXTINT Interrupt Disabled
1=EXTINT Interrupt Enabled
0=Finger Detect Interrupt Disabled
1=Finger Detect Interrupt Enabled
Read this register to determine source(s) of interrupt(s).
Write a 1 to IR[1:0] to acknowledge and clear the corresponding interrupt bit.
Bits IS[1:0] reflect the state of the finger detect sensor and the EXTINT pin, regardless of the bit settings in the ICR register. When the finger
detect sensor is not triggered, the IS0 bit will be constantly low. However the IS0 bit may not be constantly high when a finger is present; the
bit may be repeatedly changing from a low to high state.
Bit Number Bit Name Function
[7:4] - Reserved. Write 0 to these bits. Returns 0 when read.
3 IS1 Reflects the state of the EXTINT Pin. Write 0 to this bit.
2 IS0 Reflects the state of the Finger Detect Sensor. Write 0 to this bit.
1 IR1 EXTINT Interrupt Request Pending.
0 IR0 Finger Detect Interrupt Request Pending.
THR 0x0F
Threshold Register.
Reset State 0x00.
This register controls the threshold at which a finger is detected by the automatic finger detection circuit.
Bit Number Bit Name Function
7 - Reserved. Write 0 to this bit.
[6:4] THV[2:0] Threshold voltage level.
[3:0] THC[3:0] Sharing capacitor size.
16 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 20

CIDH 0x10
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Chip Identification Register High. This register holds the high order byte of the chip identification word.
Bit Number Bit Name Function
[7:0] CIDH[7:0] Returns 0x20 when read.
CIDL 0x11
Chip Identification Register Low. This register holds the low order byte of the chip identification word.
Bit Number Bit Name Function
[7:0] CIDL[7:0] The return value depends on the Revision of the chip.
TST 0x12
Test Mode Register. Reserved for factory use only.
Reset State 0x00.
Bit Number Bit Name Function
[7:0] TST[7:0] Reserved. Write only 0 to these bits.
MBF200
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 17
Page 21

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Sensor Initialization
The sensor should be enabled and its image parameters adjusted
before beginning a GETIMG, GETROW, or GETSUB operation.
Enable ADC
Write CTRLB with bits
2 and 0 set.
Wait 30 µS.
Sensor Enabled.
If using an external clock,
then set bit 1 also.
Other registers (DTR and
DCR for example) can be
initialized during this time.
Image Retrieval
Microprocessor Interface
Get Row
First load the RAH and RAL registers with the address of the row to
be fetched. Then write the CTRLA register to initiate a GETROW
operation. Finally, read the CTRLA register 256 times to retrieve
the row data.
Setup Row Address
(MCU Mode)
Write RAH.
Write RAL.
Row Selected.
Set Row Address
High Order bit.
Set Row Address
Low Order byte.
Adjust Parameters
Write DTR.
Write DCR.
Write PGC.
Parameters Adjusted.
(MCU Mode)
Write CTRLA with
Wait Row Capture
Read CTRLA.
Conversion Time.
No
of Row was
Row Captured.
GetRow
0x01.
Time.
Wait A/D
Last Cell
Read?
Yes
18 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 22

MBF200
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Get Whole Image
No row or column registers need to be loaded prior to starting a GETIMG operation. The sensor will automatically begin A/D conversion at
row zero, column zero.
Image Capture
(MCU Mode)
Write CTRLA with
0x02.
Wait Row Capture
Time.
Read CTRLA.
Wait A/D
No
Conversion Time.
No
Last Cell
of Row was
Read?
Yes
Last Cell
of Image
was Read?
Yes
Image Captured.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 19
Page 23

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Get Sub-Image
First, load the RAH, RAL, and CAL registers with the starting row and column address of the sensor sub-region. Then load registers REH,
REL, and CEL with the ending row and column address of the sensor sub-region. Write the CTRLA register to initiate a GETSUB operation.
Finally, read CTRLA register until the sub-image has been retrieved. The RAH, RAL, CAL, REH, REL, and CEL registers do not have to be
loaded before each GETIMG operation unless a different sensor sub0region is to be captured.
Setup Sub Region
(MCU Mode)
Write RAH.
Write RAL.
Write CAL.
Write REH.
Write REL.
Write CEL.
Set Starting Row Address,
High Order bit.
Set Starting Row Address,
Low Order byte.
Set Starting Column Address.
Set Ending Row Address,
High Order bit.
Set Ending Row Address,
Low Order byte.
Set Ending Column Address.
No
No
Get Sub Image
(MCU Mode)
Write CTRLA with
0x04.
Wait Row Capture
Time.
Read CTRLA.
Wait A/D
Conversion Time.
Last Cell
of Row was
Read?
Yes
Sub Region Selected.
20 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Last Cell
of Image
was Read?
Yes
Image Captured.
Page 24

MBF200
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Serial Peripheral Interface
The “Get Image,” “Get Sub-Image,” and “Get Row” operations are initiated by writing the same registers as described in the microprocessor
interface, except that the commands are written to the MOSI pin and the data is read back on the MISO pin. However, in SPI mode, an image
or sub-image cannot be retrieved by issuing a single Register Read Command and shifting in the entire image; a separate Register Read
Command must be issued prior to reading each row.
Get Image
Image Capture
(SPI Mode)
Drive SCS- Low.
Send Write Opcode.
Send CTRLA Address.
Send Data 0x02.
Drive SCS- High.
Wait Row Capture
Time.
No
Drive SCS- Low.
Send Read Opcode.
Send CTRLA Address.
Read Data.
No
Converted
Last Cell of
Row?
Yes
Drive SCS- High.
Converted
Last Cell of
Image?
Yes
Image Captured.
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 21
Page 25

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
USB Interface
The “Get Image,” “Get Sub-Image,” and “Get Row” operations are initiated by writing the same registers as described in the microprocessor
interface, except that the registers are written and read on endpoint 0 and the image data is read from endpoint 1.
Get Image
Image Capture
(USB Mode)
At Endpoint 0,
Write CTRLA with
0x02.
From Endpoint 1,
Read 64-byte packet.
No
Final
packet of Image
was Read?
Yes
Image Captured.
22 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 26

MBF200
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Rating Value Unit
VDD Power Supply Voltage +7.0 V
VIN, VOUT Voltage on Any Pin Relative to VSS -0.5V to +7.0V V
IOUT Output Current per I/O 8.0 mA
TSTG Storage Temperature -65°C to +150°C °C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent device failure. Functionality at or above these limits is not
implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Ratings for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Operating Range
Symbol Description Min Max Unit
VDD Supply Voltage
TA Ambient Temperature 0°C 60°C °C
USB Mode 3.3 3.6 V
DC Characteristics
3.3 5.5 V
(VDD=5.0V)
Symbol Description Test Conditions Min Max Units
VIL Input LOW Voltage VDO = 4.5V -0.5 0.8 V
VIH Input HIGH Voltage – 2.0 VDD V
VOL Output LOW Voltage VDD = MIN, IOL = 8 mA - 0.4 V
VOH Output HIGH Voltage VDD = MIN, IOH = -4 mA 2.4 - V
ILI Input Leakage Current VDD = MAX, VIN = VSS to VDD -5.0 5.0 µA
ILO Output Leakage Current VDD = MAX, VOUT = VSS to VDD, CE0- = VIH or CE1 = VIL -5.0 5.0 µA
(VDD=3.3V)
Symbol Description Test Conditions Min Max Units
VIL Input LOW Voltage VDD = 3.0V -0.5 0.6 V
VIH Input HIGH Voltage 2.0 VDD V
V
OL Output LOW Voltage VDD = 3.6V, IOL = 4 mA - 0.4 V
OH Output HIGH Voltage VDD = 3.0V, IOH = -2 mA 2.4 - V
V
ILI Input Leakage Current VDD = 3.6V VIN = VSS to VDD -5.0 5.0 µA
I
LO Output Leakage Current VDD = 3.6V, VOUT = VSS to VDD, CE0- = VIH or CE1 = VIL -5.0 5.0 µA
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 23
Page 27

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Power Supply Consumption
Symbol Description Test Conditions Max Units
(Microprocessor Mode, VDD=5.0V f
I
DD
I
Digital Current, Standby 1 mA
DDSB
I
Digital Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 10 µA
DDPDF
I
Digital Current, Power Down 10 µA
DDPD
I
Analog Current, Dynamic 20 mA
DDA
I
Analog Current, Standby 12 mA
DDASB
I
Analog Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 200 µA
DDAPDF
I
Analog Current, Power Down 10 µA
DDAPD
Digital Current, Dynamic 5 mA
= 20MHz)
OSC
(SPI Slave Mode, VDD=5.0V)
I
DD
Digital Current, Standby 1mA
IDDSB
I
DDPDF
I
DDPD
I
Analog Current, Dynamic 20 mA
DDA
I
Analog Current, Standby 12 mA
DDASB
I
Analog Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 200 µA
DDAPDF
I
Analog Current, Power Down 10 µA
DDAPD
Digital Current, Dynamic 5mA
Digital Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 10 µA
Digital Current, Power Down 10 µA
(Microprocessor Mode, VDD=3.3V)
IDD Digital Current, Dynamic 5mA
I
Digital Current, Standby 1mA
DDSB
I
Digital Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 10 µA
DDPDF
I
Digital Current, Power Down 10 µA
DDPD
I
DDA
I
DDASB
I
DDAPDF
I
DDAPD
Analog Current, Dynamic 15 mA
Analog Current, Standby 8mA
Analog Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 200 µA
Analog Current, Power Down 10 µA
(SPI Slave Mode, VDD=3.3V)
I
DD
I
DDSB
I
DDPDF
I
DDPD
I
DDA
I
DDASB
I
DDAPDF
I
DDAPD
Digital Current, Dynamic 5mA
Digital Current, Standby 1mA
Digital Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 10 µA
Digital Current, Power Down 10 µA
Analog Current, Dynamic 15 mA
Analog Current, Standby 8mA
Analog Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 200 µA
Analog Current, Power Down 10 µA
24 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 28

MBF200
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Power Supply Consumption (continued)
Symbol Description Test Conditions Max Units
(USB Mode, VDD=3.3V)
I
DD
I
DDSB
I
DDPDF
I
DDPD
I
DDSPF
I
DDSP
I
DDA
I
DDASB
I
DDAPDF
I
DDAPD
AC Characteristics
Digital Current, Dynamic 5 mA
Digital Current, Standby 1 mA
Digital Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 10 µA
Digital Current, Power Down 10 µA
Digital Current, USB Suspend with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 10 µA
Digital Current, USB Suspend 10 µA
Analog Current, Dynamic 30 mA
Analog Current, Standby 20 mA
Analog Current, Power Down with Auto Finger Detection Enabled 200 µA
Analog Current, Power Down 10 µA
Microprocessor Bus Mode
Read Cycle
Symbol Description Min Max Units
t
ACC
t
CE
t
OE
t
OH
t
DF
t
DF
Write Cycle
Symbol Description Min Max Units
Address Setup to WR low 0 - ns
t
AS
t
CS
t
CS
t
AH
t
CH
t
CH
t
WP
t
WPH
t
DS
t
DH
Address to Output Delay 5 35 ns
Chip Select to Output Delay 5 35 ns
Read Enable to Output Delay 5 35 ns
Output Hold Time from Address, CS0, CS1, or RD, which ever occurs first 5 - ns
RD high to Output High Z - 10 ns
CS0 high or CS1 low to Output High Z - 10 ns
CS0 Setup to WR low 0 - ns
CS1 Setup to WR low 0 - ns
Address Hold Time from WR high 5 - ns
CS0 Hold Time from WR high 0 - ns
CS1 Hold Time from WR high 0 - ns
WR Pulse Width Low 10 - ns
WR Pulse Width High 10 - ns
Data Setup Time to WR low 8 - ns
Data Hold Time to WR high 0 - ns
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 25
Page 29

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SPI Slave Mode
Symbol Description Min Max Units
f
SCK
t
CSS
t
CSH
t
WL
t
WH
t
CS
t
SU
t
H
t
V
t
HD
t
DIS
SPI Master
Symbol Description Min Max Units
f
SCKM
t
CSSM
t
CSHM
t
WLM
t
WHM
t
CSM
t
SUM
t
HM
t
VM
t
HDM
t
DISM
SCLK Clock Frequency - 12 MHz
SCS Setup Time 40 - ns
SCS Hold Time 40 - ns
SCLK Low 40 - ns
SCLK High 40 - ns
SCS High Time 40 - ns
Data-In Setup Time 20 - ns
Data-In Hold Time 20 - ns
Data-Out Valid Time 20 30 ns
Data-Out Hold Time 0 - ns
Data-Out Disable Time - 100 ns
SCLK Clock Frequency - 2 MHz
SCS Setup Time 250 - ns
SCS Hold Time - 250 ns
SCLK Low - 250 ns
SCLK High - 250 ns
SCS High Time - 250 ns
Data-In Setup Time - 100 ns
Data-In Hold Time - 250 ns
Data-Out Valid Time - 200 ns
Data-Out Hold Time - 200 ns
Data-Out Disable Time - 300 ns
26 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 30

Timing Diagrams
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
A0
CS1
CS0
RD
t
ACC
MBF200
t
CE
t
OE
WR
D[7:0]
Figure 1. Microprocessor Mode Read Cycle
t
OH
t
DF
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 27
Page 31

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
A0
CS1
CS0
RD
WR
D[7:0]
t
AS
t
CS
t
WP
t
AH
t
WPH
t
DS
Figure 2. Microprocessor Mode Write Cycle
t
DH
t
CH
SCS
SCK
MOSI
MISO
28 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
t
CSS
t
SU
t
WL
t
H
data in
Figure 3. SPI Slave Mode Timing
t
V
t
WH
data out
t
CS
t
CSH
t
HD
t
DIS
For read operations only.
Page 32

SCS
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
SCK
MOSI
MISO
SCS
SCK
MOSI
MISO
Command Stage
0
Op Code
00
0
Op Code
x0
Command Stage Data Stage
Op Code Op Code
0
00
0
x0
Address Stage
Register Address
1
10
a4
a3 a2
a1
a0
0
0
Data Stage
Don't Care
x
Data Out
d7 d6 d5
d4
d2
Figure 4. SPI Slave Mode Read Operation
Address Stage
Register Address
0
1
a4
a3
a2
a1
a0
0
0
d7
0
High Impedance
Data In
d4d6 d5
d2
d1
d1
d0d3
d0d3
SCS
SCK
MOSI
MISO
t
CSSM
t
SUM
Figure 5. SPI Slave Mode Write Operation
t
WLM
t
HM
data out
t
VM
Figure 6. SPI Master Timing
t
WHM
data in
t
HDM
t
CSM
t
CSHM
t
DISM
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 29
Page 33

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SCS
SCK
MOSI
MISO
Command Stage Data Stage
Op Code Op Code
0
00
00
0
Address Stage
ROM Address
1
a7 a6 a5 a4 a3
1
Figure 7. SPI Master Read Operation
a2 a1
a0
d7 d6
Data In
d0
d7
d6
d0
30 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 34

Physical Dimensions
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 31
Page 35

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Recommended Land Pattern
P
SEE DETAIL
Z
FULL RADIUS
TYPICAL
L
A
W
DETAIL Z
140
Symbol Description Dimension
N Pin Count 80
A Tip to Tip Dimension 1.074 (27.30)
P Pitch .0197 (.50)
L Pad Length .065 (1.65)
W Pad Width .012 (.30)
Note: Dimensions are in inches (mm)
32 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 36

Array Orientation
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
MBF200
PIN 40 PIN 1
(0, 0) (255, 0)
MBF200
(0, 299)
PIN 41 PIN 80
(255, 299)
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 33
Page 37

Solid State Fingerprint Sensor
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Appendix A
Recommended Power and Ground Connections
The following describes the recommended method for reducing
image noise to get the best image from the sensor.
VDDA1 (Pin 1) and VDDA2 (Pin 7) are the analog power supply
pins. VSSA1 (Pin 2) and VSSA2 (Pin 6) are the ground returns.
Connect one bulk capacitor (4.7µF to 10µF) and two 0.1µF
capacitors in parallel between analog power and ground to provide
filtering of low and high frequency noise. Place the bulk capacitor
near VDDA1. Separate VDDA1 and VDDA2 from the digital power
pins through a 10 ohm resistor.
VDD
0.1 µF 0.1 µF 0.1 µ F 0.1 µF
VSS3
VDD3
VDD2 VSS2
VDD1 VSS1 VDDA2 VSSA2 VSSA1 VDDA1
VDD1 (Pin 16), VDD2 (Pin 25), and VDD3 (Pin 39) are the digital
power supply pins. VSS1 (Pin 15), VSS2 (Pin 24), and VSS3 (Pin
40) are the ground returns. Place 0.1µF capacitors between digital
power and ground, as close to the pins as possible.
Input signals that are to be tied high should not be shorted directly
to VDD, but connected through a 1K to 10K ohm resistor in order
to maximize ESD immunity of the sensor. A single resistor may be
used for all inputs that are tied high.
10Ω
0.1 µF
4.7 to 10 µF
1267151624253940
34 Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc.
Page 38

MBF200
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
APPENDIX B
Recommended MBF200 Sensor Orientation
Mount the MBF200 such that pins 1 through 40 point away the user
and pins 41 through 80 point toward from the user. When a finger is
placed on the sensor, the tip of the finger should be near pins 1
through 40, the cuticle should be centered over the sensor, and the
knuckle should be near pins 41 through 80. This orientation ensures
that fingerprint images will be captured right-side up, not sideways
nor upside down, using Fujitsu’s standard software.
The sensor should be mounted flush with the surrounding surface to
allow the finger to rest flat on the sensor surface and increase the
contact area between the finger and the sensor. If the sensor is
recessed too deeply, only the tip of the finger will be imaged.
It is also recommended that there be a groove or channel to guide the
finger into the proper position so that images are captured with a
uniform orientation.
PIN 1PIN 40
PIN 41 PIN 80
Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 35
Page 39

FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS AMERICA, INC.
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
Corporate Headquarters
1250 E. Arques Ave. Sunnyvale, CA 94088-3470
Tel: (800) 866-8608 Fax: (408) 737-5999
E-mail: inquiry@fma.fujitsu.com Web Site: http://www.fma.fujitsu.com
©2001 Veridicom, Inc. All rights reserved.
All company and product names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective owners.
Printed in U.S.A.
BMS-DS-20886-6/2003
Page 40

SUNST AR商斯达实业集团是集研发、生产、工程、销售、代理经销 、技术咨询、信息服务等为一体的高
SUNSTAR传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
SUNSTAR自动化 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL: 0755-83376489 FAX:0755-83376182 E-MAIL:szss20@163.com
科技企业,是专业高科技电子产品生产厂家,是具有 10 多年历史的专业电子元器件供应商,是中国最早和
最大的仓储式连锁规模经营大型综合电子零部件代理分销商之一,是一家专业代理和分銷世界各大品牌IC
芯片和電子元器件的连锁经营綜合性国际公司。在香港、北京、深圳、上海、西安、成都等全国主要电子
市场设有直属分公司和产品展示展销窗口门市部专卖店及代理分销商,已在全国范围内建成强大统一的供
货和代理分销网络。 我们专业代理经销、开发生产电子元器件、集成电路、传感器、微波光电元器件、工
控机/DOC/DOM电子盘、专用电路、单片机开发、MCU/DSP/ARM/FPGA软件硬件、二极管、三极管、模
块等,是您可靠的一站式现货配套供应商、方案提供商、部件功能模块开发配套商。专业以现代信息产业
(计算机、通讯及传感器)三大支柱之一的传感器为主营业务,专业经营各类传感器的代理、销售生产、
网络信息、科技图书资料及配套产品设计、工程开发。我们的专业网站——
中国传感器科技信息网(全球
传感器数据库) www.SENSOR-IC.COM 服务于全球高科技生产商及贸易商,为企业科技产品开发提供技
术交流
平台。欢迎各厂商互通有无、交换信息、交换链接、发布寻求代理信息。欢迎国外高科技传感器、
变送器、执行器、自动控制产品厂商介绍产品到 中国,共同开拓市场。本网站是关于各种传感器-变送器-
仪器仪表及工业自动化大型专业网站,深入到工业控制、系统工程计 测计量、自动化、安防报警、消费电
子等众多领域,把最新的传感器-变送器-仪器仪表买卖信息,最新技术供求,最新采购商,行业动态,发展方
向,最新的技术应用和市场资讯及时的传递给广大科技开发、科学研究、产品设计人员。本网站已成功为
石油、化工、电力、医药、生物、航空、航天、国防、能源、冶金、电子、工业、农业、交通、汽车、矿
山、煤炭、纺织、信息、通信、IT、安防、环保、印刷、科研、气象、仪器仪表等领域从事科学研究、产
品设计、开发、生产制造的科技人员、管理人员 、和采购人员提供满意服务。 我公司专业开发生产、代
理、经销、销售各种传感器、变送器、敏感元器件、开关、执行器、仪器仪表、自动化控制系统: 专门从
事设计、生产、销售各种传感器、变送器、各种测控仪表、热工仪表、现场控制器、计算机控制系统、数
据采集系统、各类环境监控系统、专用控制系统应用软件以及嵌入式系统开发及应用等工作。如热敏电阻、
压敏电阻、温度传感器、温度变送器、湿度传感器、 湿度变送器、气体传感器、 气体变送器、压力传感
器、 压力变送、称重传感器、物(液)位传感器、物(液)位变送器、流量传感器、 流量变送器、电流
(压)传感器、溶氧传感器、霍尔传感器 、图像传感器、超声波传感器、位移传感器、速度传感器、加速
度传感器、扭距传感器、红外传感器、紫外传感器、 火焰传感器、激光传感器、振动传感器、轴角传感器、
光电传感器、接近传感器、干簧管传感器、继电器传感器、微型电泵、磁敏(阻)传感器 、压力开关、接
近开关、光电开关、色标传感器、光纤传感器、齿轮测速传感器、 时间继电器、计数器、计米器、温控仪、
固态继电器、调压模块、电磁铁、电压表、电流表等特殊传感器 。 同时承接传感器应用电路、产品设计
和自动化工程项目。
更多产品请看本公司产品专用销售网站:
商斯达中国传感器科技信息网:http://www.sensor-ic.com/
商斯达工控安防网:http://www.pc-ps.net/
商斯达电子 元器件网:http://www.sunstare.com/
商斯达微波光电产品网:HTTP://www.rfoe.net/
商斯达消费电子产品网://www.icasic.com/
商斯达军工产品网:http://www.junpinic.com/
商斯达实业科技产品网://www.sunstars.cn/传感器销售热线:
地址:深圳市福田区福华路福庆街鸿图大厦 1602 室
电话:0755-83607652 83376489 83376549 83370250 83370251 82500323
传真:0755-83376182 (0)13902971329 MSN: SUNS8888@hotmail.com
邮编:518033 E-mail:szss20@163.com QQ: 195847376
深圳赛格展销部:深圳华强北路赛格电子市场 2583 号 电话:0755-83665529 25059422
技术支持: 0755-83394033 13501568376
欢迎索取免费详细资料、设计指南和光盘 ;产品凡多,未能尽录,欢迎来电查询。
北京分公司
:北京海淀区知春路 132 号中发电子大厦 3097 号
TEL:010-81159046 82615020 13501189838 FAX:010-62543996
上海分公司
:上海市北京东路 668 号上海賽格电子市场 D125 号
TEL:021-28311762 56703037 13701955389 FAX:021-56703037
西安分公司
:西安高新开发区 20 所(中国电子科技集团导航技术研究所)
西安劳动南路 88 号电子商城二楼 D23 号
TEL:
029-81022619 13072977981 FAX:029-88789382
 Loading...
Loading...