Page 1

High Performance Compact Inverters
MEH531
Page 2
With advanced technology built in, these new
Gentler on the environment
!
Complies with European regulations that limit the use of specific hazardous substances (RoHS).
These inverters are gentle on the environment.
Use of 6 hazardous substances is limited.(except for
interior soldering in the power module.)
<Six Hazardous Substances>
Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium,
Polybrominated biphenyl (PBB), Polybrominated
diphenyl ether (PBDE)
<About RoHS>
The Directive 2002/95/EC, promulgated by the
European Parliament and European Council, limits
the use of specific hazardous substances included in
electrical and electronic devices.
Long-life design!
The design life of each
internal component with
limited life has been
extended to 10 years.
This helps to extend the
maintenance cycle for
your equipment.
Limited Life Component Service Life
Main circuit capacitors 10 years
Electrolytic capacitors
on the printed circuit board
Cooling fan 10 years
Conditions: Ambient temperature is 40 C(104 F) and load
factor is 80% of the inverter's rated current.
10 years
Noise is reduced by the built-in EMC filter.
Use of a built-in EMC filter that reduces noise generated by
the inverter makes it possible to reduce the effect on
peripheral equipment.
Expanded capacity range and abundant model variation
●Standard Series
Input power
supply
3-phase
230V
3-phase
460V
1-phase
230V
●Semi-Standard type
●
EMC filter built-in type
●Option card
●
PG interface card (5V type)(12V type)
●
RS-485 communication card
●
Synchronized operation card
●
Device Net card
●
Profibus-DP card
●
DIO card
●
CC-Link card
1/8 1/4 1/2 1 32107.551520
Nominal applied motor (HP)
!
Capacity
expanded
to 20HP
Page 3
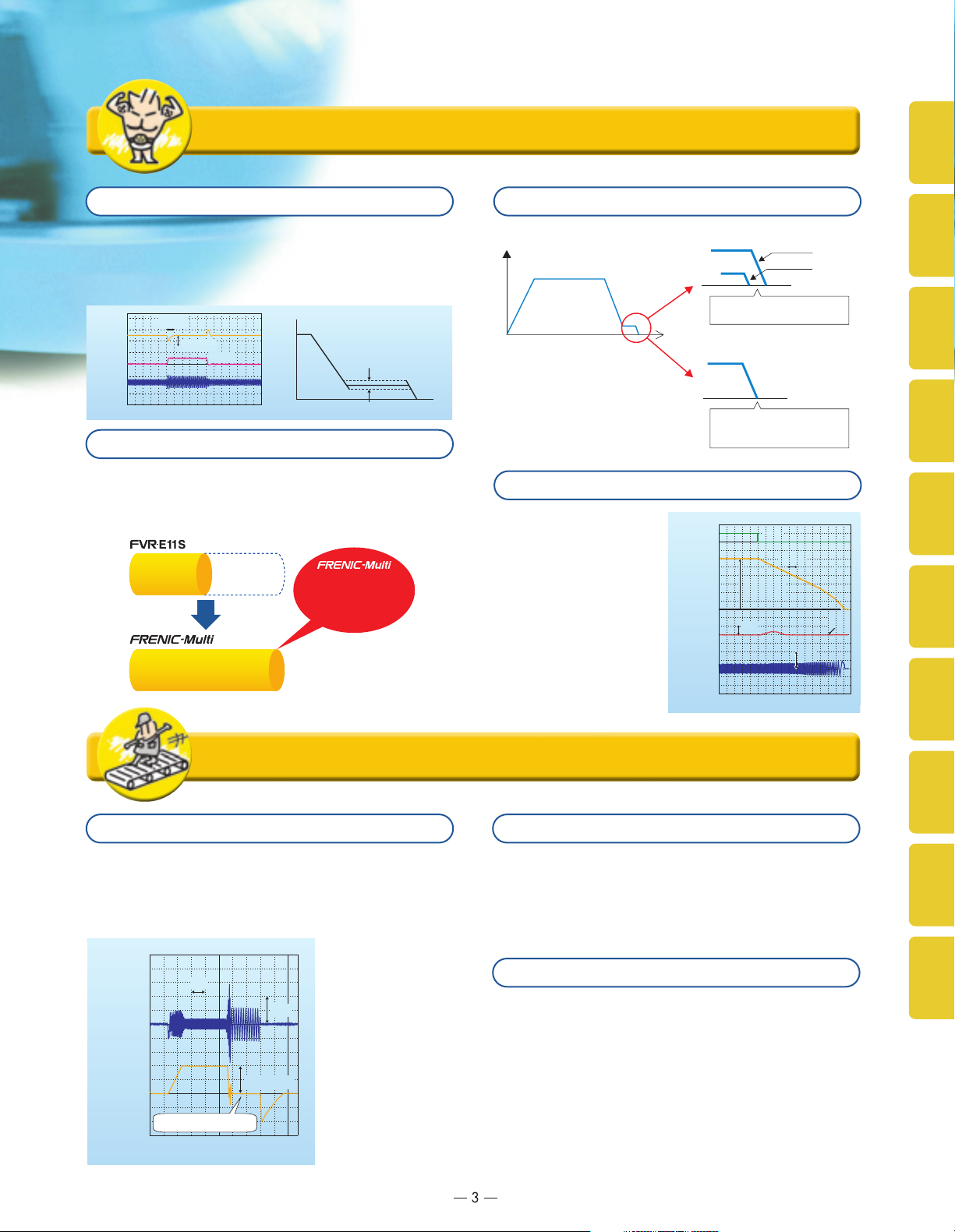
inverters can be used for multiple purposes
!
The highest standards of control and performance in its class
Shortened setting time in slip compensation control
Through "slip compensation control" + "voltage tuning," speed
control accuracy at low speeds is improved. This minimizes
variations in speed control accuracy at times when the load
varies, and since the time at creep speeds is shortened,
single cycle tact times can be shortened.
Rotational
speed
Load
torque
Current
200ms
500r/min
Time
200%
Speed
Creep speed
0
Variations according to load
Conveying distance
Equipped with the highest level CPU for its class!
The highest level CPU of any inverter is used. Computation
and processing capacity is doubled over the previous
inverter, improving speed control accuracy.
●CPU speed comparison
32MHz
64MHz
has doubled processing
capacity compared with
the previous model.
<Example of conveyor operation pattern>
Speed
0
■
Improved speed control accuracy
improves conveyor positioning
accuracy.
■
Positioning time can be shortened.
■
Improves measuring accuracy on a
scale.
The inverter controls the
energy level generated
and the deceleration time,
and so deceleration stop
can be accomplished
without tripping due to
overvoltage.
!
Specifications
Compatible with PG feedback control
■ Without speed feedback
The speed just before positioning
varies, so positioning accuracy drops.
Conveying distance
■ With speed feedback
The speed just before positioning is
stabilized, and so positioning accuracy
is improved.
Tripless deceleration by automatic deceleration control
ON
Run
command
Rotational
speed
DC link
bus voltage
Current
OFF
1500r/min
50V
400ms
20A
Load: Small
Load: Large
540V
External
Dimensions
Keypad
Operations
Basic
Wiring Diagram
Terminal
Functions
Functions
Protective
Optimum for the operations specific to vertical and horizontal conveyance
Hit-and-stop control is realized more easily!
Impacts are detected mechanically and not only can the
inverter's operation pattern be set on coast-to-stop or
deceleration stop, but switching from torque limitation to
current limitation and generating a holding torque (hit-andstop control) can be selected, making it easy to adjust brake
application and
release timing.
2s
Current
Rotational
speed
Holding torque generation
Time
10A
600r/min
Time
Settings
Functions
!
Connection Diagrams
Inclusion of a brake signal makes it even more convenient.
■ At brake release time
After the motor operates, torque generation is detected and
signals are output.
■ At brake application time
Brake application that matches the timing can be done,
and so mechanical brake wear is reduced.
Limit operations can be selected to match your equipment!
Inverters are equipped with two limit operations, "torque
limitation" and "current limitation," so either can be selected to
match the equipment you are using the inverter with.
■ Torque limitation
In order to protect mechanical systems, this function
accurately limits the torque generated by the motor.
(Instantaneous torque cannot be limited.)
■ Current limitation
This function limits the current flowing to the motor to
protect the motor thermally or to provide rough load
limitation. (Instantaneous current cannot be limited. Auto
tuning is not required.)
Peripheral Equipment
Options
Warranty
Page 4
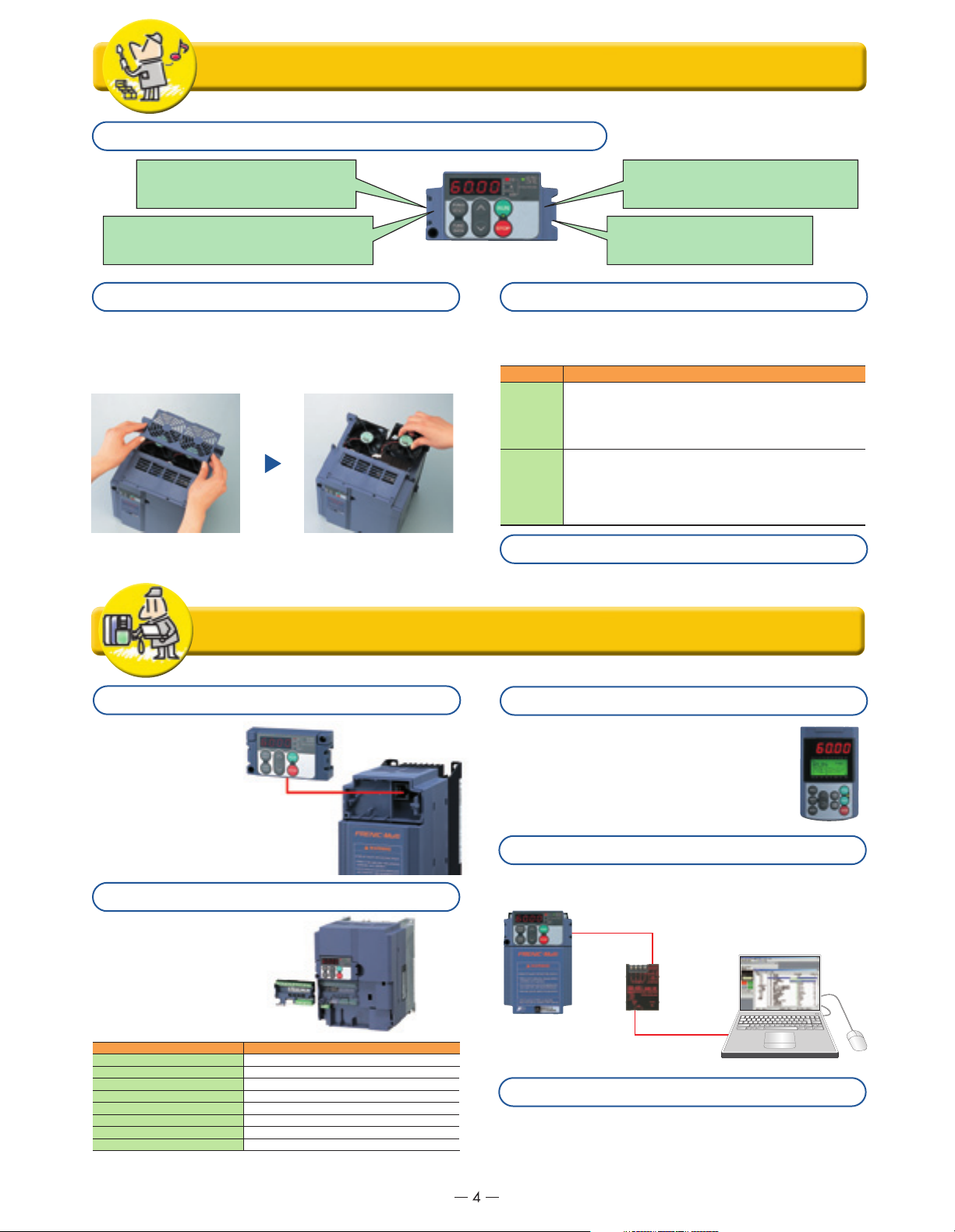
Simple and thorough maintenance
!
The life information on each of the inverter's limited life components is displayed.
Main circuit capacitor capacity
Cumulative running time of the electrolytic
capacitor on the printed circuit board.
Simple cooling fan replacement!
Construction is simple, enabling quick removal of the top
cover and making it easy to replace the cooling fan. (7.5HP or
higher models)
Cooling fan replacement procedure
The cover on top of the inverter can
be quickly removed.
Simply disconnect the power
connector and replace the cooling
fan.
Simple operation, simple connection
Cooling fan cumulative running time
Inverter cumulative running time
Information that contributes to equipment maintenance is displayed!
In addition to inverter maintenance information, data that also
take equipment maintenance into consideration are displayed.
Item
Motor
cumulative
running
time (hr)
Number
of starts
(times)
The actual cumulative running time of the equipment (motor) the
inverter is being used with is calculated.
<Example of use>
If the inverter is used to control a fan, this information is an indication
of the timing for replacing the belt that is used on the pulleys.
The number of times the inverter starts and stops can be counted.
<Example of use>
The number of equipment starts and stops is recorded, and so this
information can be used as a guideline for parts replacement timing
in equipment in which starting and stopping puts a heavy load on the
machinery.
Purpose
The alarm history records the latest four incidents.
Detailed information can be checked for the four most recent
alarms.
!
A removable keypad is standard equipment.
The keypad can be
easily removed and
reset, making remote
operation possible. If the
back cover packed with
the inverter is installed and
a LAN cable is used, the
keypad can be easily mounted
on the equipment's control
panel.
A removable interface card is adapted.
Wiring is quite easy
because the interface card
can be attached and
detached as a terminal
base for control signals.
The following option cards
are available.
Option card names
RS-485 communication card
PG interface card (for 5V)
PG interface card (for 12V)
CC-Link card
DeviceNet card
DIO card
SY (synchronized operation) card
PROFIBUS-DP card
Note) The inverter that can be used with the SY card includes special
specifications. When ordering the SY card, please order together
with the inverter in a set.
Built in the inverter (replaced with the standard interface card)
Built in the inverter (replaced with the standard interface card)
Built in the inverter (replaced with the standard interface card)
Front installation type
Front installation type
Front installation type
Front installation type
Front installation type (Available soon)
Installation method
A multi-function keypad which enables a wide variety of operations is available.
A multi-function keypad is available as an
option. This keypad features a large 7-segment
LED with five digits and large back-lighted liquid
crystal panel. Its view-ability is high, and
guidance is displayed on the liquid crystal panel,
therefore operations can be conducted simply. (A
copy function is included.)
Inverter support loader software is available.
Windows compatible loader software is available to simplify
the setting and management of function codes.
RS-485 communications
(RJ-45 connector)
USB/RS-485 converter
(made by System
Sacom Sales Corp.)
USB cable
(supplied with the converter)
Personal computer
(On sale soon)
Simulated failure enables peripheral device operation checks.
The inverter has the function for outputting dummy alarm
signals, enabling simple checking of sequence operations of
peripheral devices from the control panel where the inverter is
used.
Page 5
Consideration of peripheral equipment, and a full range of protective functions!
Side-by-side mounting saves space!
If your control panel is designed to use multiple inverters,
these inverters make it possible to save space through their
horizontal side-by-side installation. (5HP or smaller models)
!
Resistors for suppressing inrush current are built in, making it
possible to reduce the capacity of peripheral equipment.
When FRENIC-Multi Series (including FRENIC-Mini Series,
FRENIC-Eco Series and 11 Series) is used, the built-in resistor
suppresses the inrush current generated when the motor starts.
Therefore, it is possible to select peripheral equipment with
lower capacity when designing your system than the equipment
needed for direct connection to the motor.
4.72(120)
3.15(80) 3.15(80) 3.15(80)
(The 3-phase 230V, 1HP
model is shown here.)
unit:inch(mm)
Outside panel cooling is also made possible using
the mounting adapter for external cooling (option).
The mounting adapter for external cooling (option) can be
installed easily as an outside panel cooling system.
You can use an inverter equipped with functions like these
First time in
the industry
New system for more energy-efficient operation!
Previous energy saving operation functions worked only to
control the motor's loss to keep it at a minimum in accordance
with the load condition. In the newly developed FRENIC-Multi
Series, the focus has been switched away from the motor
alone to both the motor and the inverter as electrical products.
As a result, we incorporated a new control system (optimum
and minimum power control) that minimizes the power
consumed by the inverter itself (inverter loss) and the loss of
the motor.
Previous
Power
supply
Optimum
motor
control
Way of thinking concerning power used
Power
supply
New control system (FRENIC-Multi)
Optimum
control of the
entire system
Smooth starts through the pick-up function!
In the case where a fan is not
being run by the inverter but
is turning free, the fan's
speed is checked, regardless
of its rotational direction, and
operation of the fan is picked
up to start the fan smoothly.
This function is convenient in
such cases as when
switching instantaneously
from commercial power
supply to the inverter.
Power
supply
voltage
Rotational
speed
Output
frequency
Current
Instantaneous power cut
500ms
1500r/min
50Hz
20A
Equipped with a full range of PID control functions!
Differential alarm and absolute value alarm outputs have been
added for PID adjusters which carry out process controls such as
temperature, pressure and flow volume control. In addition, an
anti-reset windup function to prevent PID control overshoot and
other PID control functions which can be adjusted easily through
PID output limiter, integral hold/reset signals are provided. The
PID output limiter and integral hold/reset signals can also be
used in cases where the inverter is used for dancer control.
Operating signal trouble is avoided by the command loss detection function!
If frequency signals connected to the inverter (0 to 10V, 4 to
20mA, Multi-speed signals, communications, etc.) are
interrupted, the missing frequency commands are detected as a
"command loss." Further, the frequency that is output when
command loss occurs
can be set in
advance, so operation
can be continued
even in cases where
the frequency signal
lines are cut due to
mechanical vibrations
of the equipment, etc.
If the load on equipment
suddenly becomes great
while controlled by the
inverter, the inverter can
be switched to
deceleration stop or to
coast-to-stop operation to
prevent damage to the
equipment.
If foreign matter gets wrapped around a fan or pulley and the
load increases, resulting in a sudden temperature rise in the
inverter or an abnormal rise in the ambient temperature, etc.
and the inverter becomes overloaded, it reduces the motor's
speed, reducing the load and continuing operation.
!
400ms
f1
Analog frequency
command
Command loss
detection
"REF OFF"
Output frequency
x
f1
0.1
f1
x
E65
f1
x
0.1
f1
0
An overload stop function protects equipment from over-operation!
Detection
level
Load
0
Operation
frequency
0
Continuous equipment operation with overload avoidance control!
Load state
Inverter temperature
Output frequency
0
OH trip
f1 x E65
ON
Correct frequency setting
Time
Timer
Deceleration stop Coast-to-stop
Time
Page 6
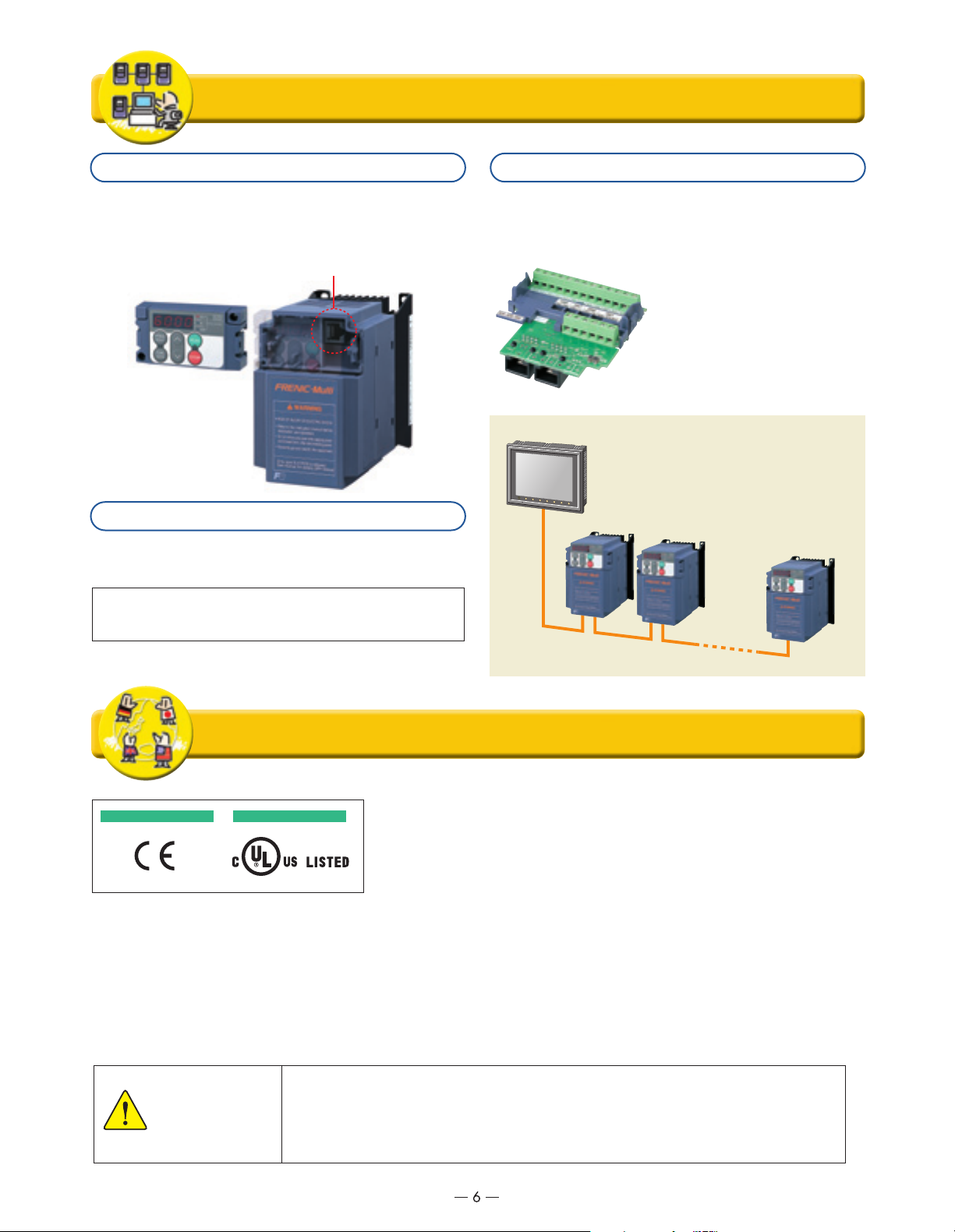
Fully compatible with network operation
!
RS-485 communications (connector) is standard!
A connector (RJ-45) that is compatible with RS-485
communications is standard equipment (1 port, also used for
keypad communications), so the inverter can be connected
easily using a LAN cable (10BASE).
RJ-45 Connector
Wiring is easy with the RS-485 communications card (optional)!
The RS-485 communications card is also available as an
option. When it is installed, you can add a branch connection
that is separate from the communications port provided as
standard equipment (RJ-45 connector), and have two
communications ports.
■
Example of connection configuration with peripheral equipment
Complies with optional networks using option cards.
Installation of special interface cards (option) makes it possible
to connect to the following networks.
●
DeviceNet
●
PROFIBUS-DP
●
CC-Link
POD
■ Important Points
(1) A separate branch adaptor is
not required because of two
ports.
The built-in terminating resistor
(2)
makes provision of a separate
terminating resistor unnecessary.
Global compatibility
Europe North America/Canada
Safety
Precautions
UL Standard (cUL Certified)EC Directives (CE Mark)
1. Use the contents of this catalog only for selecting product types and models. When using a product, read the
Instruction Manual beforehand to use the product correctly.
2. Products introduced in this catalog have not been designed or manufactured for such applications in a system
or equipment that will affect human bodies or lives. Customers, who want to use the products introduced in this
catalog for special systems or devices such as for atomic-energy control, aerospace use, medical use, and
traffic control, are requested to consult the Fuji's Sales Division. Customers are requested to prepare safety
measures when they apply the products introduced in this catalog to such systems or facilities that will affect
human lives or cause severe damage to property if the products become faulty.
!
● Complies with standards
● Sink/Source switchable
● Wide voltage range
● The multi-function keypad displays multiple languages (Japanese,
English, German, French, Spanish, Italian, Chinese, Korean).
* This product supports multiple languages such as Japanese, English, German,
French, Spanish and Italian. Another multiple language version is also available,
which supports Japanese, English, Chinese, Korean and simplified Chinese.
(Contact us for the detail separately.)
Page 7
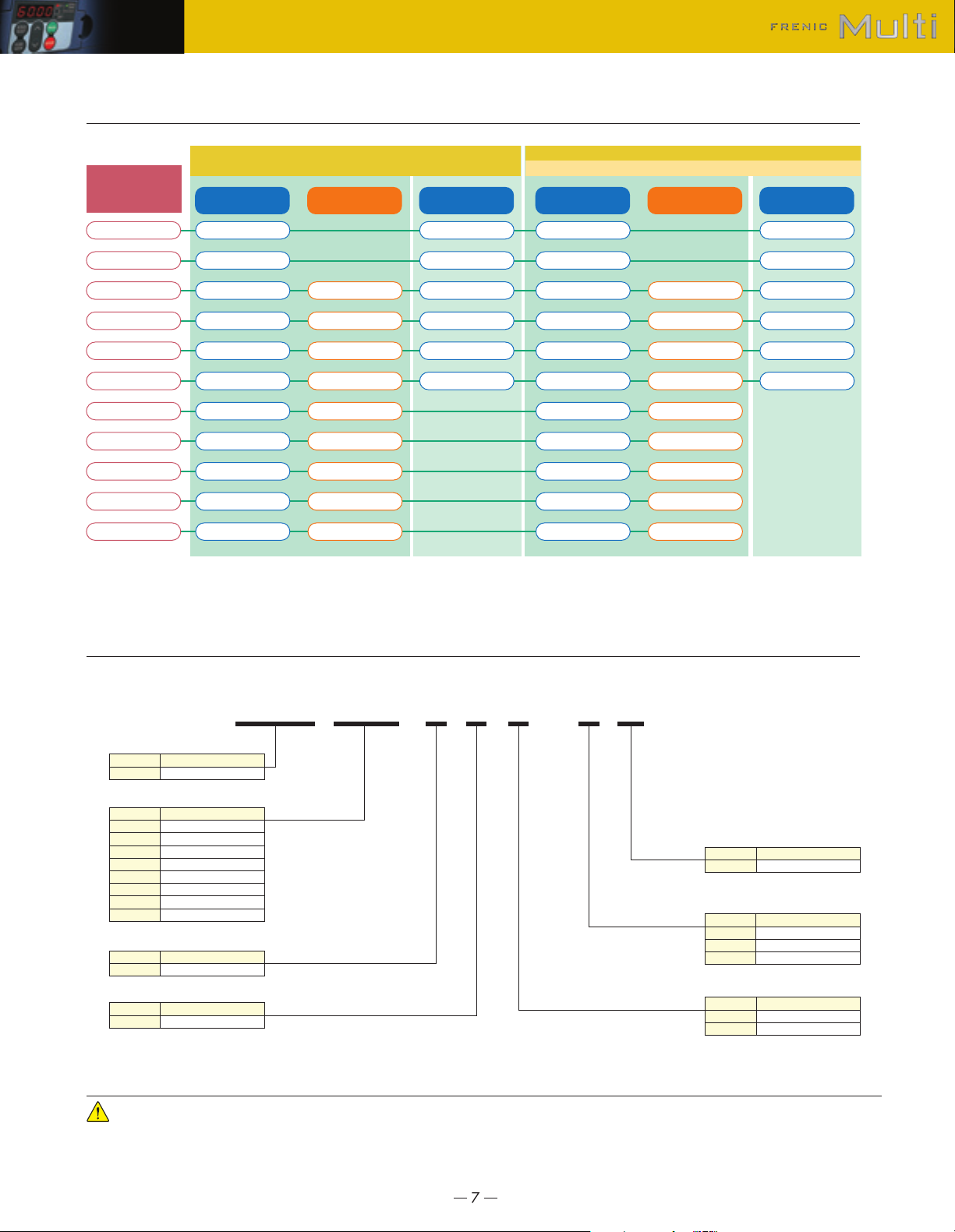
Variation
Model List
Applicable motor
(HP)
rating
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
Three-phase
230V
FRNF12E1S-2U
FRNF25E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-2U
FRN001E1S-2U
FRN002E1S-2U
FRN003E1S-2U
FRN005E1S-2U
FRN007E1S-2U
FRN010E1S-2U
FRN015E1S-2U
FRN020E1S-2U
Standard type
Three-phase
460V
FRNF50E1S-4U
FRN001E1S-4U
FRN002E1S-4U
FRN003E1S-4U
FRN005E1S-4U
FRN007E1S-4U
FRN010E1S-4U
FRN015E1S-4U
FRN020E1S-4U
Single-phase
230V
FRNF12E1S-7U
FRNF25E1S-7U
FRNF50E1S-7U
FRN001E1S-7U
FRN002E1S-7U
FRN003E1S-7U
EMC filter built-in type
Three-phase
230V
FRNF12E1E-2U
FRNF25E1E-2U
FRNF50E1E-2U
FRN001E1E-2U
FRN002E1E-2U
FRN003E1E-2U
FRN005E1E-2U
FRN007E1E-2U
FRN010E1E-2U
FRN015E1E-2U
FRN020E1E-2U
Semi-standard type
Three-phase
460V
FRNF50E1E-4U
FRN001E1E-4U
FRN002E1E-4U
FRN003E1E-4U
FRN005E1E-4U
FRN007E1E-4U
FRN010E1E-4U
FRN015E1E-4U
FRN020E1E-4U
Single-phase
230V
FRNF12E1E-7U
FRNF25E1E-7U
FRNF50E1E-7U
FRN001E1E-7U
FRN002E1E-7U
FRN003E1E-7U
How to read the inverter model
FRN 001 E 1 S - 2 U
Code
FRN
Code Applicable motor rating
F12
F25
F50
001
~
010
015
020
Code
E
Code1Developed inverter series
Series name
FRENIC series
1/8HP
1/4HP
1/2HP
1HP
~
10HP
15HP
20HP
Application range
High performance/Compact
Series
CodeUDestination, Instruction manuals
North America / Canada
2
4
7
S
E
Input power source
Three-phase 230V
Three-phase 460V
Single-phase 230V
Enclosure
Standard type (IP20)
EMC filter built-in type
Code
Code
Caution The contents of this catalog are provided to help you select the product model that is best for you. Before actual use, be sure to read the User's Manual
thoroughly to assure correct operation.
Page 8
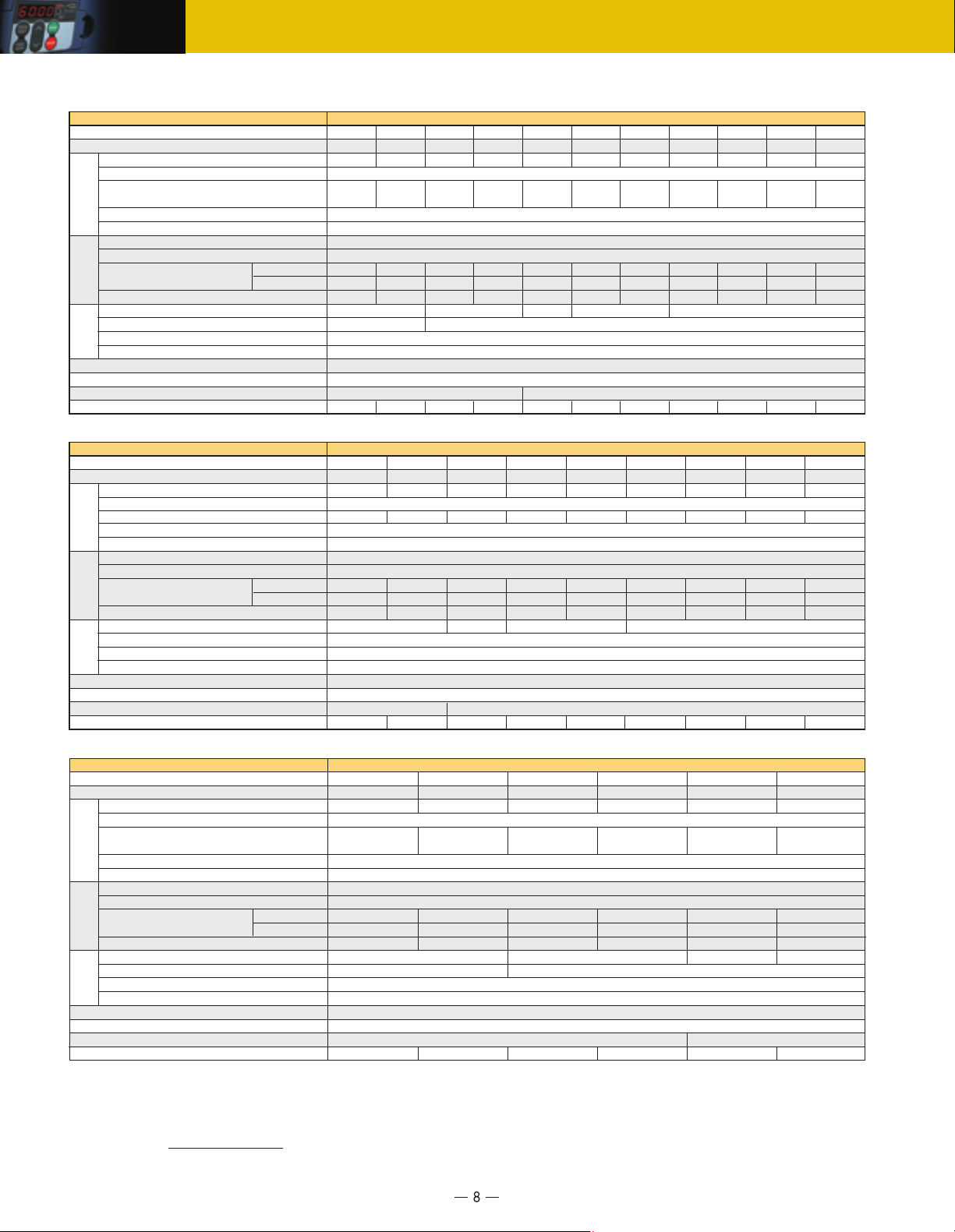
Specifications
●Standard type
■Three-phase 230V (1/8 to 20HP)
Type (FRN
Applicable motor rating [HP] (*1)
Rated capacity [kVA] (*2)
Rated voltage [V] (*3)
Rated current [A] (*4)
Overload capability
Output ratings
Rated frequency [Hz]
Phases, voltage, frequency
Voltage/frequency variations
Rated current [A] (*9)
(without DCR)
Input powerBraking
Required power supply capacity [kVA] (*5)
Torque [%] (*6)
Torque [%] (*7)
DC injection braking
Braking transistor
Applicable safety standards
Enclosure (IEC60529)
Cooling method
Weight / Mass [lbs(kg)]
■Three-phase 460V (1/2 to 20HP)
Type (FRN
Applicable motor rating [HP] (*1)
Output ratings
Input powerBraking
Applicable safety standards
Enclosure (IEC60529)
Cooling method
Weight / Mass [lbs(kg)]
Rated capacity [kVA] (*2)
Rated voltage [V] (*3)
Rated current [A] (*4)
Overload capability
Rated frequency [Hz]
Phases, voltage, frequency
Voltage/frequency variations
Rated current [A] (*9)
(without DCR)
Required power supply capacity [kVA] (*5)
Torque [%] (*6)
Torque [%] (*7)
DC injection braking
Braking transistor
■Single-phase 230V (1/8 to 3HP)
Type (FRN
Applicable motor rating [HP] (*1)
Output ratingsInput powerBraking
Applicable safety standards
Enclosure (IEC60529)
Cooling method
Weight / Mass [lbs(kg)]
(*1) Fuji's 4-pole standard motor
(*2) Rated capacity is calculated by assuming the output rated voltage as 230V for three-phase 230V series and 460V for three-phase 460V series.
(*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
(*4) When setting the carrier frequency (F26) to 3 kHz or less. Use the current ( ) or below when the carrier frequency setting is higher than 4kHz and continuously operating at 100%.
(*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
(*6) Average braking torque obtained when reducing the speed from 60Hz with AVR control OFF (Varies with the efficiency of the motor.)
(*7) Average braking torque obtained by use of external braking resistor (standard type available as option)
(*8) Voltage unbalance [%] =
Three-phase average voltage [V]
If this value is 2 to 3%, use AC REACTOR (ACR: option).
(*9) The value is calculated on assumption that the inverter is connected with a power supply capacity of 500kVA (or 10 times the inverter capacity if the inverter capacity exceeds 50kVA) and %X is 5%.
Rated capacity [kVA] (*2)
Rated voltage [V] (*3)
Rated current [A] (*4)
Overload capability
Rated frequency [Hz]
Phases, voltage, frequency
Voltage/frequency variations
Rated current [A] (*9)
(without DCR)
Required power supply capacity [kVA] (*5)
Torque [%] (*6)
Torque [%] (*7)
DC injection braking
Braking transistor
Item Specifications
E1S-2U)
F12
1/8
0.3
F25
1/4
0.6
F50
1/2
1.2
001
1
2.0
002
2
3.2
003
4.4
Three-phase 200V to 240V (with AVR function)
0.8
1.5
(1.4)(0.7)
3.0
(2.5) (10)(7.0) (23.5)(16.5) (31) (57)(44)
5.0
(4.2)
8.0
11
150% of rated current for 1min, 200% - 0.5s
50, 60Hz
Three-phase, 200 to 240V, 50/60Hz
Voltage: +10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance (*8): 2% or less) Frequency: +5 to -5%
(with DCR)
1.1
0.2
0.93
1.8
0.3
1.6
3.1
0.6
3.0
5.3
1.1
5.7
9.5
2.0
13.2
0.57
150 100 70 2040
Starting frequency: 0.1 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100% of rated current
Built-in
UL508C, C22.2No.14, EN50178:1997
IP20, UL open type
Natural cooling
1.3(0.6)
1.3(0.6) 1.5(0.7) 1.8(0.8) 3.7(1.7) 3.7(1.7) 5.1(2.3) 7.5(3.4) 7.9(3.6) 13(6.1) 16(7.1)
Fan cooling
Item Specifications
E1S-4U)
F50
1/2
1.2
001
2.0
1
2
2.9
002
003
4.4
3
005
7.2
Three-phase 380V to 480V (with AVR function)
1.5 2.5 3.7 5.5 13 18 24 30
9.0
150% of rated current for 1min, 200% - 0.5s
50, 60Hz
Three-phase, 380 to 480V, 50/60Hz
Voltage: +10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance (*8): 2% or less) Frequency: +5 to -5%
(with DCR)
0.85
1.7
0.6
1.6
3.1
1.1
3.0
5.9
2.0
4.4
8.2
2.9
13.0
150
Starting frequency: 0.1 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100% of rated current
Built-in
UL508C, C22.2No.14, EN50178:1997
IP20, UL open type
Natural cooling
Fan cooling
2.4(1.1) 2.6(1.2) 3.7(1.7) 3.7(1.7) 5.1(2.3) 7.5(3.4) 7.9(3.6) 13(6.1) 16(7.1)
Item Specifications
E1S-7U)
F12
1/8
0.3
F25
1/4
0.6
F50
1/2
1.2
Three-phase 200V to 240V (with AVR function)
0.8
(0.7) (1.4) (2.5) (4.2) (7.0) (10)
1.5
150% of rated current for 1min, 200% - 0.5s
50, 60Hz
Single-phase, 200 to 240V, 50/60Hz
Voltage: +10 to -10%, Frequency: +5 to -5%
(with DCR)
1.1
1.8
0.3
2.0
3.3
0.4
3.5
5.4
0.7
150 100
-
Starting frequency: 0.1 to 60.0Hz, Braking level: 0 to 100% of rated current, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s
Built-in
UL508C, C22.2No.14, EN50178:1997
IP20, UL open type
Natural cooling
1.3(0.6) 1.3(0.6) 1.5(0.7) 2.0(0.9) 4.0(1.8) 5.3(2.4)
Max voltage [V] - Min voltage [V]
x 67 (IEC 61800-3)
3
5
7.3
4.9
8.3
2.9
005
5
6.8
17
14.0
22.2
4.9
150
001
1
2.0
6.4
9.7
1.3
007
7.5
10
10.6
17.3
7.4
007
7.5
10
25
21.1
31.5
7.4
150
010
10
13
33
28.8
42.7
10
010
10
14
14.4
23.2
10
204070100
002
2
3.2
8.0 113.0 5.0
11. 6
16.4
2.4
70 40
Fan cooling
015
15
19
21.1
33.0
15
015
15
19
47
42.2
60.7
15
020
20
24
60
57.6
80
20
020
20
24
28.8
43.8
20
003
3
4.4
17.5
24.8
3.5
Page 9
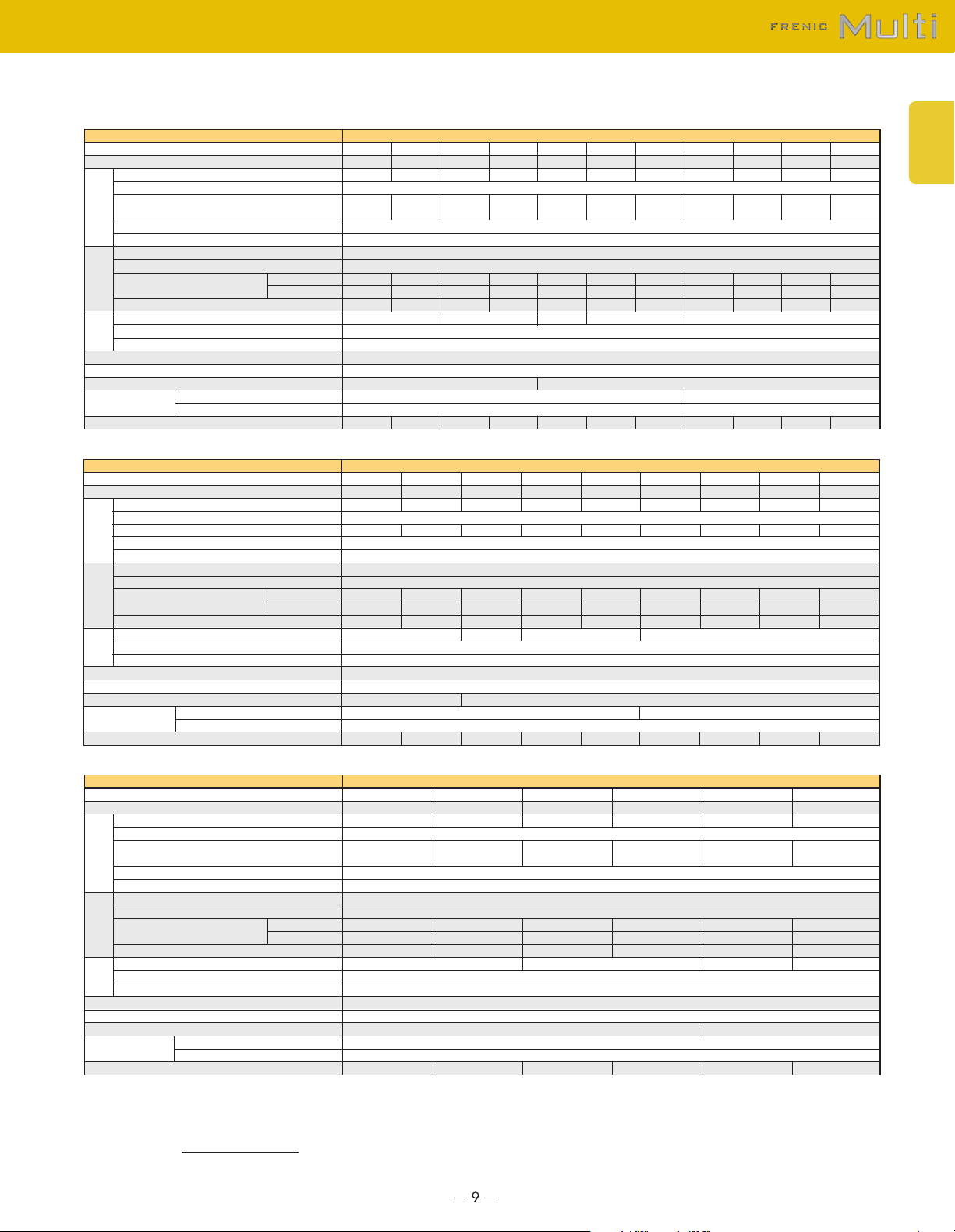
●Semi-standard type
EMC filter built-in type
■Three-phase 230V (1/8 to 20HP)
Type (FRN
Nominal applied motor [HP] (*1)
Rated capacity [kVA] (*2)
Rated voltage [V] (*3)
Rated current [A] (*4)
Overload capability
Output ratingsInput ratings
Rated frequency [Hz]
Phases, voltage, frequency
Voltage/frequency variations
Rated current [A] (*8)
(without DCR)
Required power supply capacity [kVA] (*5)
Torque [%] (*6)
DC injection braking
Braking transistor
Braking
Applicable safety standards
Enclosure
Cooling method
EMC standard
compliance
Weight / Mass [lbs(kg)]
■Three-phase 460V (1/2 to 20HP)
Type (FRN
Nominal applied motor [HP] (*1)
Output ratings
Input ratings
Braking
Applicable safety standards
Enclosure
Cooling method
EMC standard
compliance
Weight / Mass [lbs(kg)]
Rated capacity [kVA] (*2)
Rated voltage [V] (*3)
Rated current [A] (*4)
Overload capability
Rated frequency [Hz]
Phases, voltage, frequency
Voltage/frequency variations
Rated current [A] (*8)
(without DCR)
Required power supply capacity [kVA] (*5)
Torque [%] (*6)
DC injection braking
Braking transistor
■Single-phase 230V (1/8 to 3HP)
Type (FRN
Nominal applied motor [HP] (*1)
Applicable safety standards
Enclosure
Cooling method
EMC standard
compliance
Weight / Mass [lbs(kg)]
*1) Fuji's 4-pole standard motor
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as 230V for three-phase 230V series_lb24.Tdmprfpcc+nf_qc24.Tqcpgcq,
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
*4) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency is set to 4kHz or above.
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates.(Varies with the efficiency of the motor.)
*7) Voltage unbalance [%] =
Three-phase average voltage [V]
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an AC REACTOR.
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 500kVA, %X=5%.
Rated capacity [kVA] (*2)
Rated voltage [V] (*3)
Rated current [A] (*4)
Overload capability
Output ratingsInput ratingsBraking
Rated frequency [Hz]
Phases, voltage, frequency
Voltage/frequency variations
Rated current [A] (*8)
(without DCR)
Required power supply capacity [kVA] (*5)
Torque [%] (*6)
DC injection braking
Braking transistor
Item Specifications
E1E-2U)
F12
1/8
0.30
F25
1/4
0.57
F50
1/2
1.1
001
1
1.9
Three-phase 200 to 240V (with AVR)
0.8
(1.4)(0.7)
1.5
3.0
(2.5) (10)(7.0) (23.5)(16.5) (31) (57)(44)
5.0
(4.2)
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s
50, 60Hz
Three-phase, 200 to 240V, 50/60Hz
(with DCR)
Voltage: +10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance : 2% or less (*7)) Frequency: +5 to -5%
3.0
0.57
1.1
0.2
0.93
1.80
0.30
1.6
3.1
0.6
5.3
1.1
150 100 70 2040
Starting frequency: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Built-in
UL508C, C22.2No.14(pending), EN50178:1997
IP20(IEC60529)/UL open type(UL50)
Natural cooling
Emission
Immunity
Class 1A (EN55011:1998/A1:1999)
2nd Env. (EN61800-3:1996/A11:2000)
1.5(0.7)
1.5(0.7) 1.8(0.8) 2.0(0.9) 5.3(2.4) 5.3(2.4) 6.4(2.9) 11.2(5.1) 11.7(5.3)
Item Specifications
E1E-4U)
F50
1/2
1.1
001
1.9
1
2
2.8
002
Three-phase 380 to 480V (with AVR)
1.5 2.5 3.7 5.5 13 18 24 30
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s
50, 60Hz
Three-phase, 380 to 480V, 50/60Hz
Voltage:+10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance: 2% or less (*7)), Frequency: +5 to -5%
(with DCR)
0.85
1.7
0.6
1.6
3.1
1.1
3.0
5.9
2.0
Starting frequency: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Built-in
UL508C, C22.2No.14 (pending), EN50178:1997
IP20 (IEC60529)/UL open type (UL50)
Emission
Immunity
Natural cooling
Class 1A (EN55011:1998/A1:1999)
2nd Env. (EN61800-3:1996/A11:2000)
Fan cooling
3.3(1.5) 3.5(1.6) 5.5(2.5) 5.5(2.5) 6.6(3.0) 10.6(4.8) 11.0(5.0) 17.9(8.1) 20.0(9.1)
Item Specifications
E1E-7U)
F12
1/8
0.3
Three-phase 200 to 240V (with AVR)
0.8
(0.7) (1.4) (2.5) (4.2) (7.0) (10)
F25
1/4
0.57
1.5
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s
50, 60Hz
Single-phase, 200 to 240V, 50/60Hz
(with DCR)
Voltage: +10 to -10%, Frequency: +5 to -5%
1.1
1.8
0.3
2.0
3.3
0.4
150 100
Starting frequency: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Built-in
UL508C, C22.2No.14 (pending),EN50178:1997
IP20 (IEC60529)/UL open type (UL50)
Emission
Immunity
Natural cooling
Class 1A (EN55011:1998/A1:1999)
2nd Env. (EN61800-3:1996/A11:2000)
1.5(0.7) 1.5(0.7) 1.8(0.8) 2.9(1.3) 5.5(2.5) 6.6(3.0)
Max. voltage [V] - Min. voltage [V]
x 67 (IEC61800-3(5.2.3))
002
2
3.0
8.0
5.7
9.5
2.0
Fan cooling
003
3
4.1
4.4
8.2
2.9
F50
1/2
1.1
3.5
5.4
0.7
003
3
4.1
11
8.3
13.2
2.9
005
5
6.8
9.0
7.3
13.0
4.9
005
6.4
14.0
22.2
007
5
7.5
9.5
17
25
21.1
31.5
4.9
7.4
010
10
12
33
28.8
42.7
10
015
15
17
47
42.2
60.7
15
2nd Env. (EN61800-3:1996+A11:2000)
22.7(10.3) 24.9(11.3)
007
7.5
9.9
10.6
17.3
7.4
010
10
13
14.4
23.2
10
015
15
18
21.1
33.0
15
204070100
2nd Env. (EN61800-3:1996+A11:2000)
001
1
1.9
002
2
3.0
8.0 113.0 5.0
6.4
9.7
1.3
11. 6
16.4
2.4
70 40
Fan cooling
003
4.1
17.5
24.8
3.5
3
020
57.6
80
20
020
20
22
28.8
43.8
20
20
22
Specifications
60
Page 10
Specifications
●Common specifications
Item Explanation
Maximum frequency
Base frequency
Starting frequency
Carrier frequency
Setting range
Accuracy (Stability)
Output frequencyControl
Setting resolution
Control method
Voltage/freq. characteristic
(Non-linear V/f setting)
Torque boost
Starting torque
Start/stop
Frequency setting
Acceleration/deceleration time
Frequency limiter
(Upper limit and lower limit frequencies)
Bias
Gain
Jump frequency
Timer operation
Jogging operation
Auto-restart after momentary
power failure
Torque limit
Current limit
Slip compensation
Droop control
(Load selection)
25 to 400Hz variable setting
25 to 400Hz variable setting
0.1 to 60.0Hz variable setting, Duration: 0.0 to 10.0s
0.75 to 15kHz variable setting
• Analog setting:
• Keypad setting:
• Analog setting: 1/3000 of maximum frequency (ex. 0.02Hz at 60Hz, 0.4Hz at 120Hz)
Keypad setting: 0.01Hz (99.99Hz or less), 0.1Hz (100.0Hz or more)
•
• Link setting: Selectable from 2 types
• 1/2000 of maximum frequency (ex. 0.003Hz at 60Hz, 0.006Hz at 120Hz)
• 0.01Hz (fixed)
• V/f control • Dynamic torque-vector control (magnetic flux estimator) • V/f control (with sensor, when the PG interface card (option) is installed)
Possible to set output voltage at base frequency and at maximum output frequency (common spec).
AVR control can be turned ON or OFF (Factory setting: OFF).
2 points (Desired voltage and frequency can be set.)
Torque boost can be set with the function code F09. Set when 0, 1, 3, or 4 is selected at F37.
Select application load type with the function code F37.
0: Squared variable torque load
1: Constant torque load
2: Auto torque boost
3: Auto energy-save operation (variable torque load in deceleration)
4: Auto energy-save operation (constant torque load)
5: Auto energy-save operation (auto torque boost)
200% or over (Auto torque boost in 0.5Hz operation, slip compensation and auto torque boost)
Keypad
operation
External signals (7digital inputs): FWD (REV), RUN, STOP commands (3 wire operation possible),
coast-to-stop, external alarm, alarm reset, etc.
Linked operation: Operation through RS-485 or field buss (option) communications
Switching operation command: Link switching, switching between communication and inverter (keypad or external signals)
Key operation: Can be set with and keys
External volume: Can be set with external potentiometer (1 to 5kΩ1/2W)
Analog input
Multistep frequency: Selectable from 16 steps (step 0 to 15)
UP/DOWN operation: Frequency can be increased or decreased while the digital input signal is ON.
Linked operation: Frequency can be set through RS-485 or field buss (optional) communications.
Switching frequency setting: Frequency setting can be switched (2 settings) with external signal (digital input).
Switching to frequency setting via communication and multi-frequency setting are available.
Auxiliary frequency setting: Terminal 12 input and terminal C1 input (terminal V2 input) can be added
to main setting as auxiliary frequency.
Inverse operation: Normal/inverse operation can be set or switched with digital input signal and
function code setting.
• +10 to 0V DC /0 to 100% (terminal 12, C1 (V2))
• +20 to +4mA DC/0 to 100% (terminal C1)
Pulse train input: 30kHz (max.)/ Maximum output frequency
0.00 to 3600s
*If 0.00s is set, the time setting is cancelled and acceleration and deceleration is made
according to the pattern given with an external signal.
Acceleration and deceleration time can be independently set with 2 types and selected with digital input signal (1 point).
(Curve)
Acceleration and deceleration pattern can be selected from 4 types:
Linear, S-curve (weak), S-curve (strong), Non-linear
Deceleration with coasting can be stopped with operation stop command.
High and Low limiters can be set. (Setting range: 0 to 400Hz)
Bias of set frequency and PID command can be independently set (setting range: 0 to
Analog input gain can be set between 0 and 200%.
Three operation points and their common jump width (0 to 30.0Hz) can be set.
The inverter operates and stops for the time set with the keypad (1-cycle operation).
• Can be operated using digital input signal or keypad.
• Acceleration and deceleration time (same duration used only for jogging) can be set.
• Jogging frequency: 0.00 to 400.0Hz
• Restarts the inverter without stopping the motor after instantaneous power failure.
• Select "Continuous motor mode" to wait for the power recovering with low output frequency.
Restart at 0Hz, restart from the frequency used before momentary power failure, restart at the set frequency can be selected.
•
• Motor speed at restart can be searched and restarted.
• Controls the output torque lower than the set limit value.
• Can be switched to the second torque limit with digital input signal.
• Soft start (filter function) is available when switching the torque control to 1/2.
Keeps the current under the preset value during operation.
• Compensates for decrease in speed according to the load, enabling stable operation.
• Time constant can be changed. Possible to enable or disable slip compensation during
acceleration/deceleration or in constant output range.
Decrease the speed according to the load torque.
±0.2% of maximum frequency (at 25±10˚C(at 77±50˚F))
±0.01% of maximum frequency (at -10 to +50˚C(at 14 to +122˚F))
Start and stop with and keys
Start and stop with / and keys
Analog input can be set with external voltage/current input
• 0 to
• +4 to +20mA DC/0 to 100% (terminal C1)
±10V DC (0 to ±5V DC)/0 to ±100% (terminal 12, C1 (V2))
±100%).
Remarks
Frequency may drop automatically to protect the
inverter depending on environmental
temperature and output current.This protective
operation can be canceled by function code H98.
Setting with and keys
Three-phase 230V, single-phase 230V: 80 to 240V
Three-phase 460V: 160 to 500V
Three-phase and single-phase 230V: 0 to 240V/0 to 400Hz
Three-phase 400V: 0 to 500V/0 to 400Hz
Keypad (standard)
Multi-function keypad
With data protection
Connected to analog input terminals 13, 12,
and 11. Potentiometer must be provided.
• 0 to +5V DC can be used depending on the
analog input gain (200%). +1 to +5V DC can
be adjusted with bias and analog input gain.
• Voltage can be input (terminal V2) to the
terminal 1.
When the PG interface card (optional) is installed.
If the set frequency is lower than lower limit, continuous
motor running or stop running motor can be selected.
Voltage signal from terminal 12, C1 (V2) and current
signal (from terminal C1) can be set independently.
Related
function code
F03
F04
F23,F24
F26
F27
H98
F03 to F06
H50 to H53
F09, F37
F09, F37
H68, F37
F02
F02
E01 to E05
E98, E99
H30, y98
F01, C30
F18, C50,
C32 to C34,
C37 to C39,
C42 to C44
C05 to C19
F01, C30
H30, y98
F01, C30
E61 to E63
C53
F07, F08
E10,E11
H07
H11
F15, F16
H63
F18, C50 to C52
C32, C34, C37
C39, C42, C44
C01 to C04
C21
H54
C20
F14
H13 to H16
H92, H93
F40, F41
E16, E17
H76
F43, F44
H68
P09 to P12
H28
H28
Page 11
Item Explanation
PID control
Pick-up
Automatic deceleration
Deceleration characteristic
Automatic energy-saving operation
Overload Prevention Control
Auto-tuning
Cooling fan ON/OFF control
Secondary motor setting
Universal DI
Universal AO
Speed control
Positioning control
Rotation direction control
Running/stopping
Life early warning
Cumulative run hours
I/O check
Power monitor
Trip mode
Indication ControlProtection
Running or trip mode
Overcurrent protection
Short circuit protection
Grounding fault protection
Overvoltage protection
Undervoltage
Input phase loss
Output phase loss
Overheating
Overload
Electronic thermal
PTC thermistor
Overload early warning
Motor protectionStorage
Stall prevention
Momentary power failure
protection
Retry function
Command loss detection
Installation location
Ambient temperature
Ambient humidity
Altitude
Environment
Vibration
Ambient temp.
Ambient humidity
Control with PID regulator or dancer controller.
■ Process command
• Key operation ( and keys) : 0 to 100%
• Analog input (terminal 12, C1 (V2)) : 0 to
• Analog input (terminal C1) : 4 to 20mA DC/0 to 100%
• UP/DOWN (digital input) : 0 to 100%
• Communication (RS-485, bus option) : 0 to 20000/0 to 100%
■ Feedback value
• Analog input from terminal 12, C1 (V2) : 0 to
• Analog input (terminal C1) : 4 to 20mA DC/0 to 100%
■ Accessory functions
• Alarm output (absolute value alarm, deviation alarm) • Normal operation/inverse operation
• PID output limiter • Anti-reset wind-up function • Integration reset/hold
Operation begins at a preset pick-up frequency to search for the motor speed to start an idling motor without stopping it.
When the torque calculation value exceeds the limit level set for the inverter during deceleration, the output
frequency is automatically controlled and the deceleration time automatically extends to avoid an trip.
The motor loss increases during deceleration to reduce the load energy regenerating at the inverter
to avoid an trip upon mode selection.
The output voltage is controlled to minimize the total sum of the motor loss and inverter loss at a constant speed.
The output frequency is automatically reduced to suppress the overload protection trip o inverter
caused by an increase in the ambient temperature, operation frequency, motor load or the like.
The motor parameters are automatically tuned.
Detects inverter internal temperature and stops cooling fan when the temperature is low.
One inverter can be used to control two motors by switching (switching is not available while a motor is running). Base
•
frequency, rated current, torque boost, electronic thermal, slip compensation can be set as data for the secondary motor.
• The second motor constants can be set in the inverter. (Auto-tuning possible)
The presence of digital signal in a device externally connected to the set terminal can be sent to the master controller.
The output from the master controller can be output from the terminal FM.
The motor speed can be detected with the pulse encoder and speed can be controlled.
Only one program can be executed by setting the number of pulses to the stop position and deceleration point.
Select either of reverse prevention or forward rotation prevention.
• Speed monitor, output current [A], output voltage [V], torque calculation value, input power [HP],
PID reference value, PID feedback value, PID output, load factor, motor output, period for timer operation [s]
◆Select the speed monitor to be displayed from the following:
Output frequency [Hz], Output frequency 1 [Hz] (before slip compensation),
Output frequency 2 (after slip compensation) [Hz],
Motor speed (set value) [r/min],
Motor speed [r/min], Load shaft speed (set value) [r/min],
Load shaft speed (r/min),
Line speed (set value), Line speed (r/min)
The life early warning of the main circuit capacitors, capacitors on the PC boards and the cooling fan can be displayed.
The cumulative motor running hours, cumulative inverter running hours and cumulative watt-hours can be displayed.
Displays the input signal status of the inverter.
Displays input power (momentary), accumulated power, electricity cost (accumulated power x displayed coefficient).
Displays the cause of trip by codes.
(Overcurrent during acceleration)
•
• (Input phase loss) •
• (Overvoltage during acceleration)
• (Overheating of the heat sink) •
• (Motor protection (PTC thermistor))
• (Inverter overload) •
• (Memory error) •
•
(Optional communication error) •
• (Tuning error) •
• (RS485 communication error (option))
Trip history: Saves and displays the last 4 trip codes and their detailed description.
The inverter is stopped upon an overcurrent caused by an overload.
The inverter is stopped upon an overcurrent caused by a short circuit in the output circuit.
The inverter is stopped upon an overcurrent caused by a grounding fault in the output circuit.
An excessive DC link circuit voltage is detected to stop the inverter.
Stops the inverter by detecting voltage drop in DC link circuit.
Stops or protects the inverter against input phase loss.
Detects breaks in inverter output wiring at the start of running and during running, stopping the inverter output.
The temperature of the heat sink of the inverter or that inside the inverter unit is detected to stop the inverter, upon a failure or overload of the cooling fan.
The inverter is stopped upon the temperature of the heat sink of the inverter or the temperature of the
switching element calculated from the output current.
The inverter is stopped upon an electronic thermal function setting to protect the motor.
A PTC thermistor input stops the inverter to protect the motor.
Warning signal can be output based on the set level before the inverter trips.
The output frequency decreases upon an output current exceeding the limit during acceleration or constant speed operation, to avoid overcurrent trip.
•
A protective function (inverter stoppage) is activated upon a momentary power failure for 15msec or longer.
•
If restart upon momentary power failure is selected, the inverter restarts upon recovery of the voltage within the set time.
When the motor is tripped and stopped, this function automatically resets the tripping state and
restarts operation.
A loss (broken wire, etc.) of the frequency command is detected to output an alarm and continue
operation at the preset frequency (set at a ratio to the frequency before detection).
Shall be free from corrosive gases, flammable gases, oil mist, dusts, and direct sunlight.
(Pollution degree 2 (IEC60664-1)). Indoor use only.
-10 to +50˚C(at +14 to +122˚F)
5 to 95% RH (without condensation)
Altitude [ft(m)]
Lower than 3,300(1,000 )
3,301 to 6,600(1,001 to 2,000)
6,601 to 9,800(2,001 to 3,000)
3mm (vibration width): 2 to less than 9Hz, 9.8m/s
-25 to +65˚C(-13 to +149˚F)
5 to 95%RH (without condensation)
Output decrease
None
Decreases
Decreases*
±10V DC/0 to ±100%
±10V DC/0 to ±100%
•
(Overcurrent during deceleration)
(Undervoltage) •
•
(Overvoltage during deceleration)
(External alarm) •
•
(Motor 1 overload) •
(Overheating of braking resistor)
(Keypad communication error) •
(Option error)
(RS-485 communication error) •
•
(Power LSI error) •
2
: 9 to less than 20Hz, 2m/s2: 20 to less than 55Hz, 1m/s2: 55 to less than 200Hz
•
(Overcurrent at constant speed)
(Output phase loss)
•
(Overvoltage at constant speed)
(Inverter overheat)
(Motor 2 overload)
•
(PG disconnection)
(CPU error)
•
(Operation error)
(Data save error due to undervoltage)
(Simulation error)
Remarks
Trip may occur due to load conditions.
Mode that the motor rotates and mode that the motor does not rotate can be selected.
An external output is issued in a transistor output signal.
When the PG interface card (optional) Is installed.
When the PG interface card (optional) Is installed.
An external output is issued in a transistor output signal.
3-phase 230V / 400V DC, Single-phase 230V/400V DC
3-phase 460V / 800V DC
3-phase 230V / 200V DC, Single-phase 230V/200V DC
3-phase 460V / 400V DC
The protective function can be canceled with function code 99.
The protective function can be canceled with function code 99.
Thermal time constant can be adjusted (0.5 to 75.0min.)
Waiting time before resetting and the number
of retry times can be set.
-10 to 40˚C(+14 to +104˚F)when inverters are installed side by side without clearance.
* If the altitude exceeds 6,600ft(2,000m)
insulate the interface circuit from the
main power supply to conform to the
Low Voltage Directives.
Related
function code
E61 to E63
J01 to J06
J10 to J19
H09, H13, H17
H69, F08
H71
F37, F09
H70
P04
H06
E43
E48
E52
F14
H98
H98
H43
F10 to F12, P99
H26, H27
F10, F12, E34,
E35, P99
H12
H13 to H16
F14
H04, H05
E65
Specifications
Page 12
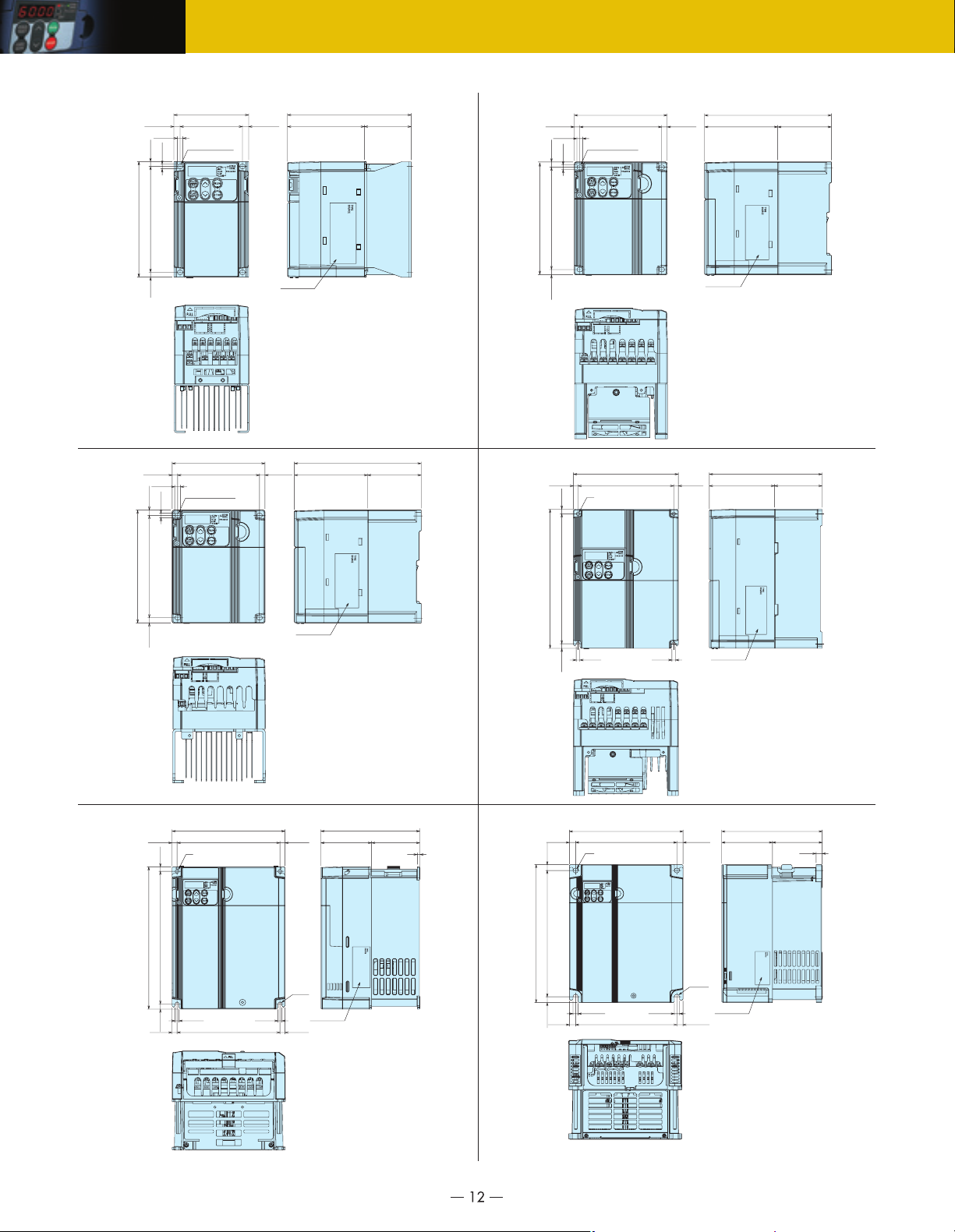
External Dimensions
●Inverter outline (standard type)
Fig. a Fig.b
Fig. c Fig. d
0.26&6.5) 0.26&6.5)
0.24(6)
0.2(5)
0.2(5)
H
H1
0.2(5)
0.26(6.5)
0.28(7)
0.24(6)
0.2(5)
W
W1
C
(elongated hole)
W
W1
C
(elongated hole)
Name plate
0.26(6.5)
D
D1 D2
D
D1 D2
W
C
(elongated hole)
C
W1
W
W1
0.26(6.5)
0.28(7)
0.24(6)
0.2(5)
H
H1
0.24(6)
0.24(6) 0.24(6)
0.26(6.5)
Name plate
D
D1 D2
D
D2D1
H
H1
0.24(6)
Name plate
2-R0.12
(2-R3)
0.31(8)
Name plate
D
D2D1
5
0.24(6)
C
0.24(6)
W
W1
6.46(164)
Fig. e Fig. f
0.31(8) 0.31(8)
H
H1
0.31(8) 0.28(7)
0.31(8)
H
H1
0.47(12)
2-R0.2
(2-R5)
0.47(12)
Name plate
Name plate
D
D2 D1
11.2
0.2(5) 0.2(5)
0.24(6) 0.24(6)
W
C
0.39(10)
W1
7.72(196)
0.39(10)
0.47(12)
0.43(11)
H
H1
0.47(12)
0.43(11)
Page 13

Power supply
voltage
Three-phase
230V
Three-phase
460V
Single-phase
230V
Inverter type Fig.
FRNF12E1S-2U
FRNF25E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-2U
FRN001E1S-2U
FRN002E1S-2U
FRN003E1S-2U
FRN005E1S-2U
FRN007E1S-2U
FRN010E1S-2U
FRN015E1S-2U
FRN020E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-4U
FRN001E1S-4U
FRN002E1S-4U
FRN003E1S-4U
FRN005E1S-4U
FRN007E1S-4U
FRN010E1S-4U
FRN015E1S-4U
FRN020E1S-4U
FRNF12E1S-7U
FRNF25E1S-7U
FRNF50E1S-7U
FRN001E1S-7U
FRN002E1S-7U
FRN003E1S-7U
Dimensions [Unit: inch (mm)]
WW1HH1 DD1D2 C
a
b
d
e
f
c
b
d
e
f
a
b
d
3.15(80)
4.33(110)
5.51(140)
7.09(180)
8.66(220)
4.33(110)
4.33(110)
5.51(140)
7.09(180)
8.66(220)
3.15(80)
4.33(110)
5.51(140)
2.64(67)
3.82(97)
5.04(128)
6.46(164)
7.72(196)
3.82(97)
3.82(97)
5.04(128)
6.46(164)
7.72(196)
2.64(67)
3.82(97)
5.04(128)
4.72(120)
5.12(130)
7.09(180)
8.66(220)
10.24(260)
5.12(130)
5.12(130)
7.09(180)
8.66(220)
10.24(260)
4.72(120)
5.12(130)
7.09(180)
4.33(110)
4.65(118)
6.61(168)
8.07(205)
9.37(238)
4.65(118)
4.65(118)
6.61(168)
8.07(205)
9.37(238)
4.33(110)
4.65(118)
6.61(168)
3.62(92)
4.21(107)
5.20(132)
5.91(150)
5.94(151)
6.22(158)
7.68(195)
4.96(126)
5.91(150)
5.91(150)
5.94(151)
6.22(158)
7.68(195)
3.62(92)
4.21(107)
5.98(152)
5.91(150)
5.94(151)
3.23(82)
3.39(86)
3.43(87)
3.19(81)
3.88(98.5)
3.39(86)
3.39(86)
3.43(87)
3.19(81)
3.88(98.5)
4.02(102)
3.39(86)
3.43(87)
0.39(10)
0.98(25)
1.97(50)
2.52(64)
2.52(64)
3.03(77)
3.80(96.5)
1.57(40)
2.52(64)
2.52(64)
2.52(64)
3.03(77)
3.80(96.5)
0.39(10)
0.98(25)
1.97(50)
2.52(64)
2.52(64)
4-0.20x0.24 (4-5x6)
(elongated hole)
4-0.20x0.28 (4-5x7)
(elongated hole)
φ0.20 (φ5)
φ0.24 (φ6)
φ0.39 (φ10)
4-0.20x0.24 (4-5x6)
(elongated hole)
4-0.20x0.28 (4-5x7)
(elongated hole)
φ0.20 (φ5)
φ.24 (φ6)
φ0.39 (φ10)
4-0.20x0.24 (4-5x6)
(elongated hole)
4-0.20x0.28 (4-5x7)
(elongated hole)
φ0.20 (φ5)
External
Dimensions
●Keypad
0.2
(5.2)
0.19(4.7)
1.65(41.8)
1.28(32.4)
0.19(4.7)
* Dimensions when installing the supplied rear cover
2.03(51.44)
3.12(79.2)
2.71(68.8)
2.01(51.05)
0.53
(13.5)
0.59
(15.08)
0.2
(5.2)
A
0.65
(16.6)
0.39
(10)
0.16
(4.1)
Inside panel
0.17
0.67
(4.25)
(17.1)
0.6
0.88
(22.46)
(15.24)
0.19
(4.7)
0.2(5.2)
1.28(32.4)
[Unit: inch (mm)]
3.12(79.2)
2.71(68.8)
2xM3
Dimensions of panel cutting
(viewed from "A")
cutout
0.67(17)1.77(45)
Panel
0.11
0.08(2)
1.44(36.5)
(2.7)
1.65(41.8)
Page 14

External Dimensions
●Inverter outline (EMC filter built-in type)
Fig. g Fig. h
W
0.26(6.5) 0.26(6.5)
2.64(67)
4-0.2
x0.24(
(elongated hole)
4-5x6)
D
D1 D2
WD
3.82(97)0.26(6.5) 0.26(6.5)
4-0.2Ļ.,06&4-5
(elongated hole)
x
7)
D1 D2
H
4.33(110) 0.2(5)
H1
0.2(5)
2.36(60) D30.39(10)
H1
Fig. i Fig. j
W
5.04(128)0.24(6)
2- 0.2(2- 5)
(6)
0.24
H
6.61(168)
H1
0.2
(5)
0.24(6)
0.36(92)
0.24(6)
7.48(190)
D
D1 D2
D31.06(27)0.41(10.5)
H
H
4.65(118) 0.24(6)0.24(6)
0.28(7)
10.1(256.5)
3.5(89) D30.41(10.5)
WD
5.91(150)
x0.26
(2x6.5)
A
2.17(55)
0.26(6.5)2
1.08(27.5)
(7)
0.28
10.1(256.5)
Detailed drawing A
0.33(8.5)
2.6
( 6.5)
0.47
( 12)
Fig. k Fig. l
0.49
H
12.8(325)
(12.5)
W
7.09(180)
A
2
x0.33
(2x8.4)
D
1.28(32.5)
2.56
(65)
0.33
(8.4)
0.49(12.5)
12.8(325)
0.35(9)
Detailed drawing A
0.33
( 8.4)
0.55
( 14)
H
11.91(302.5) 0.39(10)
W
7.09(180)
x0.33
2
(2x8.3)
D
2.17
(55)
A
1.08
(27.5)
0.33
(8.3)
0.39(10)11.91(302.5)
0.33
( 8.3)
0.35(9)
Detailed drawing A
0.55
( 14)
Page 15

Power supply voltage
Three-phase 230V
Three-phase 460V
Single-phase 230V
Inverter type Fig.
FRNF12E1S-2U
FRNF25E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-2U
FRN001E1S-2U
FRN002E1S-2U
FRN003E1S-2U
FRN005E1S-2U
FRN007E1S-2U
FRN010E1S-2U
FRN015E1S-2U
FRN020E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-4U
FRN001E1S-4U
FRN002E1S-4U
FRN003E1S-4U
FRN005E1S-4U
FRN007E1S-4U
FRN010E1S-4U
FRN015E1S-4U
FRN020E1S-4U
FRNF12E1S-7U
FRNF25E1S-7U
FRNF50E1S-7U
FRN001E1S-7U
FRN002E1S-7U
FRN003E1S-7U
g
i
j
k
h
i
j
l
g
h
i
Dimensions [Unit: inch (mm)]
W H H1 D D1 D2 D3
0.39
(10)
0.98(25)
1.97(50)
2.52
(64)
-
-
1.57(40)
2.52(64)
2.52
(64)
-
-
0.39
(10)
0.98(25)
1.57(40)
2.52
(64)
3.15
(80)
5.51
(140)
7.15
(181.5)
8.66
(220)
4.33
(110)
5.51
(140)
7.15
(181.5)
8.66
(220)
3.15
(80)
4.33(110)
5.51
(140)
4.72
(120)
7.09
(180)
11.22
(285)
13.78
(357)
5.12
(130)
7.09
(180)
11.22
(285)
13.07
(332)
4.72
(120)
5.12(130)
7.09
(180)
6.69
(170)
9.65
(245)
-
-
7.09
(180)
9.65
(245)
-
-
6.69
(170)
7.09(180)
9.65
(245)
4.41
(112)
5.00(127)
5.98(152)
7.64
(194)
8.39
(213)
10.24
(260)
6.65(169)
7.60(193)
7.64
(194)
8.19
(208)
9.98
(250)
4.41
(112)
5.00(127)
5.91(150)
7.64
(194)
4.02
(102)
5.12
(130)
-
-
5.08
(129)
5.12
(130)
-
-
4.02
(102)
4.33(110)
5.12
(130)
0.83
(21.2)
1.43(36.2)
2.41(61.2)
3.37
(85.5)
-
-
2.42(61.5)
3.37(85.5)
3.37
(85.5)
-
-
0.83
(21.2)
1.43(36.2)
2.17(55.2)
3.37
(85.5)
External
Dimensions
Page 16

Keypad Operations
■ Keypad switches and functions
LED monitor
When the motor is running or stopped:
The monitor displays speeds, such as output frequency, set
frequency, motor speed and load shaft speed, output voltage,
output current, and power consumption.
Alarm mode:
The monitor shows the alarm description with a fault code.
Program/Reset key
Used to change the mode.
Programming mode:
Used to shift the digit (cursor movement)
to set data.
Alarm mode:
Resets trip prevention mode.
Function/Data select key
Used to change the LED monitor and to store the
function code and data.
Up/Down keys
During operation: Used to increase or decrease the
frequency or motor speed.
In data setting: Used to indicate the function code number
or to change data set value.
Unit display
The unit of the data displayed at the LED monitor is indicated.
Use the key to switch the displayed data.
Operation mode display
During keypad operation:
When function code is, ,
or (keypad operation), the green KEYPAD
CONTROL LED lights up.
Run key
While the motor is stopped:
Used to start the operation.
This key is invalid if the function code
(operation by external signals) is
set to .
During operation:
The green RUN LED lights up.
Stop key
Used to stop the operation.
During operation:
This key is invalid if the function code (operation by
external signals) is set to .
The inverter stops when the function code is set to
or .
■
Monitor display and key operation
Operation mode
Monitor, keys
Function
Display
Function
Hz
r/min
A
PRG.MODE
m/min
kW
Display
MonitorKeys
KEYPAD
CONTROL
RUN
Function
Display
Indicates absence of operation commands.
Function
Display
Function
Function
Function
Function
Function
This keypad supports the full menu mode that allows you to set or display the following information. Indication and setting change of changed function code,
drive monitor, I/O check, maintenance information, and alarm information. For the actual operation methods, refer to the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual
or User's Manual.
Programming mode Running mode
STOP
Displays the function code and data.
Lighting
Indicates that the program mode is selected.
Hz
r/min
A
PRG.MODE ON
m/min
kW
RUN unlit
Switches to running mode Switches to programming mode
Digit shift (cursor movement) in data setting
Determines the function code, stores and
updates data.
Increases/decreases the function code
and data.
Invalid
Invalid
RUN STOP RUN
Operation selection (keypad operation/terminal operation) is displayed.
Indicates presence of operation commands.
Deceleration stop (switches to
programming mode (STOP)).
The keypad modes are classified into the following 3 modes.
Alarm mode
Displays the output frequency, set frequency, loaded motor
speed, power consumption, output current, and output voltage.
Blinking Lighting Blinking/Lighting
Displays the units of frequency, output current,
power consumption, and rotation speed.
Hz
r/min
Frequency
A
PRG.MODE
PRG.MODE
ON
ON
display
m/min
kW
Hz
r/min
Current
A
display
m/min
kW
Lit in keypad operation mode
Indicates absence of operation commands. Indicates presence of operation commands.
RUN unlit RUN litRUN lit
Switches the LED monitor display. Displays the operation
Increases/decreases the frequency, motor speed
and other settings.
Starts running (switches
to running mode (RUN)).
Invalid
Hz
r/min
Speed
A
m/min
r/min
m/min
kW
Hz
A
kW
PRG.MODE
PRG.MODE
display
Capacity
or
Current
indication
Invalid Invalid
Deceleration stop (switches
to running mode (STOP)).
Displays the alarm description
and alarm history.
None
ON
OFF
blinks
or lit
Indicates that the operation is trip-stopped.
If an alarm occurs during
operation, the lamp is unlit during
keypad operation and lit during
terminal block operation.
Releases the trip and
switches to stop mode
or running mode.
information.
Displays the alarm
history.
Invalid
Page 17

Basic Wiring Diagram
●Wiring diagram
The following diagram is for reference only. For detailed wiring diagrams, refer to the instruction manual.
■ Keypad operation
(Note 2)
MCCB
Power
Three-phase/
single-phase
200 to 240V,
50/60Hz
or three-phase
390 to 480V,
50/60Hz
MCCB: Molded-case circuit breaker
GFCI: Ground-fault circuit interrupter
MC: Magnetic contactor
DCR: DC reactor
DBR: Braking resistor
or
GFCI
Grounding terminal
(Note 3)
MC
(Note 1)
DCR
[13]
[12]
[11]
[C1]
[11]
[FM]
(FWD)
(REV)
(CM)
(X1)
(X2)
(X3)
(X4)
(X5)
(CM)
(PLC)
L1/R
L2/S
L3/T
P1
G
P(
+
)
P1
FMA
FMP
SW6
SOURCE
SW1
PDB
P(+)
SW3
PTC
SW8
C1
30
SINK
RS485 port
(option)
DBR
N(
G
SW7
V2
<Y1>
<Y2>
<CMY>
-)DB
U
V
W
30C
30B
30A
(CM)
(THR)
Main circuit
Motor
Grounding terminal
Control circuit
Alarm output
(for any fault)
Transistor input
■ Run/Stop operation and frequency setting on the keypad
(Note 4)
[Wiring procedure]
(1) Wire the inverter main power circuit.
[Operation method]
(1) Run/Stop: Press or key.
M
(2) Setting frequency: Set the frequency with and keys.
Note1: When connecting a DC REACTOR (DCR option), remove the
jumper bar from across the terminals [P1] and [P (+)].
Note2: Install a recommended molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) or a
ground-fault circuit interrupter (with an overcurrent protection
function) in the primary circuit of the inverter to protect wiring. At
this time, ensure that the circuit breaker capacity is equivalent to
or lower than the recommended capacity.
Note3: Install a magnetic contactor (MC) for each inverter to separate the
inverter from the power supply, apart from the MCCB or GFCI,
when necessary.
Connect a surge killer in parallel when installing a coil such as the
MC or solenoid near the inverter.
Note4: (THR) function can be used by assigning code "9" (external alarm)
to any of the terminals X1 to X5, FWD or REV (function code; E01
to E05, E98, or E99).
Keypad
Operations
Basic
Wiring Diagram
■ Operation by external signal inputs
Power
Three-phase/
single-phase
200 to 240V,
50/60Hz
or three-phase
390 to 480V,
50/60Hz
Potentiometer power supply
Voltage input for setting
DC0 to
Analog
input
MCCB: Molded-case circuit breaker
GFCI: Ground-fault circuit interrupter
MC: Magnetic contactor
DCR: DC reactor
DBR: Braking resistor
±10V
Current/voltage input
for setting
DC +4 to 20 mA/DC0 to 10V
Digital input
(Note 2)
MCCB
or
GFCI
Grounding terminal
(Note 5)
Meter
(Note 1)
DCR
(Note 3)
MC
L1/R
L2/S
L3/T
G
3
2
1
)
(
+
-
)
(
(Note 6)
[13]
[12]
[11]
[C1]
[11]
[FM]
(FWD)
(REV)
(CM)
(X1)
(X2)
(X3)
(X4)
(X5)
(CM)
(PLC)
P1
P(
+
)
P1
FMA
FMP
SW6
SOURCE
SW1
PDB
P(+)
SW3
PTC
SW8
30
SINK
RS-485 port
(option)
DBR
C1
SW7
V2
<CMY>
-)DB
N(
U
V
W
G
30C
30B
30A
<Y1>
<Y2>
(CM)
(Note 4)
(THR)
Main circuit
Motor
Grounding terminal
Control circuit
Alarm output
(for any fault)
Transistor input
M
■ Run/Stop operation and frequency setting through external signals
[Wiring procedure]
(1) Wire both the inverter main power circuit and control circuit.
(2) Set (external signal) at function code . Next, set (voltage input
(terminal 12) (0 to +10V DC)), (current input (terminal C1) (+4 to
20mA DC)), or other value at function code .
[Operation method]
(1) Run/Stop: Operate the inverter across terminals FDW and CM short-
circuited, and stop with open terminals.
(2) Frequency setting: Voltage input (0 to +10V DC), current input (+4 to
20mA DC)
Note1: When connecting a DC REACTOR (DCR option), remove the
jumper bar from across the terminals [P1] and [P (+)].
Note2: Install a recommended molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) or a
ground-fault circuit interrupter (with an overcurrent protection
function) in the primary circuit of the inverter to protect wiring. At
this time, ensure that the circuit breaker capacity is equivalent to
or lower than the recommended capacity.
Note3: Install a magnetic contactor (MC) for each inverter to separate the
inverter from the power supply, apart from the MCCB or GFCI,
when necessary.
Connect a surge killer in parallel when installing a coil such as the
MC or solenoid near the inverter.
Note4: (THR) function can be used by assigning code "9" (external alarm)
to any of the terminals X1 to X5, FWD or REV (function code; E01
to E05, E98, or E99).
Note5: Frequency can be set by connecting a frequency-setting device
(external potentiometer) between the terminals 11, 12 and 13
instead of inputting a voltage signal (0 to +10V DC, 0 to +5V DC
or +1 to +5V DC) between the terminals 12 and 11.
Note 6: For the control signal wires, use shielded or twisted wires.
Ground the shielded wires. To prevent malfunction due to noise,
keep the control circuit wiring away from the main circuit wiring as
far as possible (recommended: 3.94inch(10cm) or more). Never
install them in the same wire duct.
When crossing the control circuit wiring with the main circuit wiring,
set them at right angles.
Page 18

Terminal Functions
■ Terminal Functions
Symbol Terminal name Functions Remark
Division
L1/R,L2/S,L3/T
U,V,W
P1,P (+)
P (+),DB
P (+),N (
Main circuitFrequency settingDigital input
G
13
12
C1
11
X1
X2
X3
X4
X5
FWD
REV
(Hz2/Hz1)
(DCBRK)
(TL2/TL1)
(WE-KP)
(PID-RST)
(PID-HLD)
PLC
CM
Power input
Inverter output
For DC REACTOR
For braking resistor
For DC bus connection
-
)
Grounding
Potentiometer power
supply
Analog setting voltage
input
(Inverse operation)
(Frequency aux. setting)
Analog setting current
input
(Inverse operation)
(Frequency aux. setting)
(V2)
Analog setting voltage
input
(Inverse operation)
(Frequency aux. setting)
(PTC)
(PTC thermistor)
Analog common
Digital input 1
Digital input 2
Digital input 3
Digital input 4
Digital input 5
Forward operation command
Reverse operation command
Forward operation command
(FWD)
Reverse operation command
(REV)
Multistep
(SS1)
freq. selection
(SS2)
(SS4)
(SS8)
Acceleration time
(RT1)
selection command
3-wire operation stop
(HLD)
command
Coast-to-stop command
(BX)
(RST)
Alarm (error) reset
(THR)
Trip command (External fault)
Freq. set 2/Freq. set 1
(M2/M1)
Motor2/Motor1
DC braking command
Torque limit 2/Torque limit 1
(UP)
UP command
(DOWN)
DOWN command
Write enable for KEYPAD
(Changing data is available.)
(Hz/PID)
PID cancel
(IVS)
Inverse mode
changeover
(LE)
Link enable
(U-DI)
Universal DI
(STM)
Starting characteristic selection
Forcible stop
(STOP)
PID differentiation / integration reset
PID integral hold
Jogging operation
(JOG)
PLC terminal
Digital common
(PID control)
(PID control)
(PID control)
Connect a three-phase power supply.
Connect a three-phase motor.
Connect the DC reactor (DCR).
Connect the braking resistor (option).
Used for DC bus connection.
Terminal for inverter chassis (case) and motor grounding
Used for frequency setting device power supply (variable resistance: 1 to 5kΩ)
(10V DC 10mA DC max.)
Used as a frequency setting voltage input.0 to
DC/0 to 100%)
±10V DC/0 to 100% (0 to ±5V
±10 to 0V DC/0 to ±100%
Used for setting signal (PID process command value) or feedback signal.
Used as additional auxiliary setting to various frequency settings.
Used as a frequency setting current input.4 to 20mA DC/0 to 100%
20 to 4mA DC/0 to 100%
Used for setting signal (PID process command value) or feedback signal.
Two terminals are provided.
Connect the potentiometer with
higher than 1/2W.
Input impedance: 22kΩ
Maximum input: +15V DC
However, the current larger than
±20mA DC is handled as ±20mA
DC.
Input impedance: 250Ω
Maximum input: 30mA DC
However, the voltage higher than
±10V DC is handled as ±0V DC.
Used as additional auxiliary setting to various frequency settings.
Used as a frequency setting voltage input.0 to +10V DC/0 to 100% (0 to +5V
DC/0 to 100%)
+10 to 0V DC/0 to 100%
Used for setting signal (PID process command value) or feedback signal.
Input impedance: 22kΩ
Maximum input:+15V DC
However, the voltage higher than
±10V DC is handled as ±10V DC.
Used as additional auxiliary setting to various frequency settings.
Connect the thermistor used to protect the motor.
Common terminal for frequency setting signals (13, 12, C1, FM)
The following functions can be set at terminals X1 to X5, FWD and REV for
signal input.
<Common function>
• Sink and source are changeable using the built-in sliding switch.
• ON timing can be changed between short-circuit of terminals X1 and CM and
open circuits of them. The same setting is possible between CM and any of
the terminals among X2, X3, X4, X5, FWD, and REV.
The motor runs in the forward direction upon ON across (FWD) and CM. The motor decelerates and stops upon OFF.
The motor runs in the reverse direction upon ON across (REV) and CM. The motor decelerates and stops upon OFF.
Two terminals are provided. Isolated
from terminals CM and CMY.
ON state
Source current: 2.5 to 5mA
Voltage level: 2V
Allowable leakage current: Smaller
than 0.5mA
Voltage: 22 to 27V
This function can be set only for the
terminals FWD and REV.
16-step operation can be conducted with ON/OFF signals at (SS1) to (SS8).
2
-
ON
-
3
4
-
ON
-
ON
-
ON
Multistep frequency
5
6
7
-
ON
ON
-
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
8
9
10
11
12
13
-
-
ON
ON
-
-
ON
ON
-
-
-
ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON
14
-
-
ON
-
-
ON
-
ON
ON
ON
15
ON
ON
ON
0
Digital input
(SS1)
(SS2)
(SS4)
(SS8)
ON across (RT1) and CM: The acceleration time 2 setting is available.
OFF across (RT1) and CM: The acceleration time 1 setting is available.
1
-
ON
-
-
-
-
--------
Used for 3-wire operation.
ON across (HLD) and CM: The inverter self-holds FWD or REV signal.
OFF across (HLD) and CM: The inverter releases self-holding.
ON across (BX) and CM: The inverter output is shut off immediately and the motor coasts to a stop.
ON across (RST) and CM: Faults are reset.
OFF across (THR) and CM: The inverter output is shut off immediately and the motor coasts-to-stop.
No alarm signal will be output.
Alarm reset signal width: 0.1(s) or more
Alarm signal will be output.
ON across (Hz2/Hz1) and CM: Freq. set 2 is effective.
ON across (M2/M1) and CM: The motor 2 setting is available.
OFF across (M2/M1) and CM: The motor 1 setting is available.
ON across (DCBRK) and CM: Starts DC braking action.
ON across (TL2/TL1) and CM: The torque limit 2 setting is available.
OFF across (TL2/TL1) and CM: The torque limit 1 setting is available.
The output frequency rises while the circuit across (UP) and CM is connected.
The output frequency drops while the circuit across (DOWN) and CM is connected.
The function code data can be changed from the keypad only when (WE-KP)
is ON.
PID control can be canceled when the circuit across (Hz/PID) and CM is connected. (Operation proceeds
according to the selected frequency setting method such as the multi-step frequency, keypad and analog input.)
The frequency setting or PID control output signal (frequency setting) action mode switches
between normal and inverse actions when the circuit across (IVS) and CM is connected.
Operation proceeds according to commands sent via RS-485 communication
or field bus (option) when the circuit across (LE) and CM are connected.
An arbitrary digital input signal is transmitted to the host controller.
ON across (STM) and CM: Starting at the pick-up frequency becomes valid.
OFF across (STOP) and CM: The inverter is forcibly stopped in the special deceleration time.
ON across (PID-RST) and CM: Resets differentiation and integration values of PID.
ON across (PID-HLD) and CM: Holds integration values of PID.
ON across (JOG) and CM: The operation node enters jogging mode and frequency setting
switches to jogging frequency and acceleration and deceleration time for jogging operation.
Connect to PLC output signal power supply. Common for 24V power.
Common terminal for digital input signal
+24V (22 to 27V) 50mA max.
Isolated from terminals 11 and
CMY. Two terminals are provided.
Related
function
code
F18
C32 to
C35
E61
F18
C37 to
C39
E62
F18
C42 to
C44
E63
H26, H27
E01
E02
E03
E04
E05
E98
E99
C05 to
C19
E10, E11
F07, F08
F01, F30
A01 to A46
P01 to P99
F20 to F22
E16, E17
F40, F41
F01, C30
J02
F00
J01 to J06
J10 to J19
C50, J01
H30, y98
H17, H09
H56
J01 to J06
J10 to J19
C20
H54
Page 19

■ Terminal Functions
Symbol Terminal name Functions Remark
Division
FM
Analog outputPulse outputTransistor output
(PLC)
Y1
Y2
(REF OFF)
(PID-ALM)
CMY
30A,30B,30C
Contact output
-
Communication
Analog monitor
(FMA)
(FMP)
Pulse monitor
Transistor output
power
Transistor output 1
Transistor output 2
Inverter running
(RUN)
Inverter output on
(RUN2)
Speed/freq. arrival
(FAR)
Speed/freq. detection
(FDT)
Undervoltage detection
(LV)
Torque polarity
(B/D)
detection
Inverter output limit (limit on current)
(IOL)
Auto-restarting
(IPF)
Overload early warning (motor)
(OL)
Operation ready output
(RDY)
Motor 2 switching
(SWM2)
Retry in action
(TRY)
Heat sink overheat early warning
(OH)
Frequency arrival 2
(FAR2)
Inverter output limit
(IOL2)
Lifetime alarm
(LIFE)
Command loss detection
Overload preventive control
(OLP)
Current detection
(ID)
Current detection 2
(ID2)
PID alarm output
Brake signal
(BRKS)
Alarm relay output (for any fault)
(ALM)
Transistor output common
Alarm relay output
(for any fault)
RJ-45 connector for
connection of keypad
A monitor signal of analog DC voltage between 0 to +10V DC) can be output
for the item selected from the following:
• Output frequency 1 (before slip compensation) • Output frequency 2 (after slip
compensation) • Output current • Output voltage • Output torque • Load factor. •
Power consumption • PID feedback value (PV) • DC link circuit voltage • Universal
AO. • Motor output • Analog output test. • PID command (SV) • PID output (MV)
One of the following items can be output in a pulse frequency.
•
Output frequency 1 (before slip compensation) • Output frequency 2 (after slip
compensation)
Power consumption
AO
•
Power supply for a transistor output load. (24V DC 50mA DC Max)
The following functions can be set at terminals Y1 or Y2 for signal output.
• The setting of "short circuit upon active signal output" or "open upon active
signal output" is possible.
• Sink/source support (switching unnecessary)
An ON signal is output when the inverter runs at higher than the starting frequency.
A signal is issued when the inverter runs at smaller than the starting frequency or when DC braking is in action.
An active signal is issued when the output frequency reaches the set frequency.
An ON signal is output at output frequencies above a preset detection level.
The signal is deactivated if the output frequency falls below the detection level.
The signal is output when the inverter stops because of undervoltage.
The OFF signal is output when the inverter is running in drive mode and the
ON signal is output in the braking mode or stopped state.
The signal is output when the inverter is limiting the current.
The signal is output during auto restart operation (after momentary power failure and until completion of restart).
The signal is output when the electronic thermal relay value is higher than the preset alarm level.
A signal is issued if preparation for inverter operation is completed.
The motor switching signal (M2/M1) is input and the ON signal is output when the motor 2 is selected.
The signal is output during an active retry.
An early warning signal is issued before the heat sink trips due to overheat.
The signal is output when the time set in E29 elapses after the frequency arrival signal (FAR) is output.
If more than 20ms elapse while one of the following operations is operating:
current limiter for the inverter, automatic deceleration operation or torque limiter.
Outputs alarm signal according to the preset lifetime level.
A loss of the frequency command is detected.
The signal is output when the overload control is activated.
The signal is output when a current larger than the set value has been detected for the timer-set time.
The signal is output when a current larger than the set value 2 has been detected for the timer-set time.
An absolute value alarm or deviation alarm under PID control is issued as a signal.
The signal for enabling or releasing the brake is output.
An alarm relay output (for any fault) signal is issued as a transistor output signal.
Common terminal for transistor output
•
A no-voltage contact signal (1c) is issued when the inverter is stopped due to an alarm.
•
Multi-purpose relay output; signals similar to above-mentioned signals Y1 to Y2 can be selected.
•
An alarm output is issued upon either excitation or no excitation according to selection.
One of the following protocols can be selected.
• Protocol exclusively for keypad (default selection)
• Modbus RTU
• Fuji's special inverter protocol
• SX protocol for PC loader
•
Output current • Output voltage • Output torque • Load factor.o
•
Motor output • Analog output test • PID command (SV) • PID output (MV)
PID feedback value (PV) • DC link circuit voltage • Universal
Connectable impedance (Minimum impedance:
7.5HP(5kW) In the (0 to +10V DC)
In case of voltage output, up to two analog
voltmeters (0 to 10V DC, input impedance:
10kW) can be connected.Gain adjustment
range: 0 to 300%
Up to two analog voltmeters
(0 to10V DC, input impedance:
10kΩ) can be connected.
(Driven at average voltage)
•
Short circuit across terminals CM and CMY to use.
•
Same terminal as digital input PLC terminal
Max. voltage: 27V DC
Max. current: 50mA
Leak current: 0.1mA max.
ON voltage: within 2V (at 50mA)
Detection width: 0 to 10.0 [Hz]
Operation level: 0.0 to 400.0 [Hz]
Hysteresis width: 0.0 to 400.0 [Hz]
The terminal is isolated from terminals 11 and CM.
Contact capacity: 250V AC,0.3A,
Power (+5V) is supplied to the
keypad.
cosφ=0.3, +48V DC, 0.5A
Related
function
code
F29 to
F31
F29,
F31,
F33
E20
E21
E22
E30
E31
E32
F43, F44
F14
F10 to F12
H04, H05
E29
F41 to F44
H69
H42, H43, H98
E65
H70
E34, E35
E37, E38
J11 to J13
J68 to J72
E27
H30
y01 to y20
y98,y99
Terminal
Functions
Page 20

Terminal Functions
■ Terminal Arrangement
●Main circuit terminals
Power
source
Threephase
230V
Threephase
460V
Singlephase
230V
Applied
motor [HP]
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
1/2
1
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
2
3
The code in □ represents followings;
S: standard model, E: EMC filter built-in type
Inverter type Fig.
FRNF12E1□-2U
FRNF25E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-2U
FRN001E1□-2U
FRN002E1□-2U
FRN003E1□-2U
FRN005E1□-2U
FRN007E1□-2U
FRN010E1□-2U
FRN015E1□-2U
FRN020E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-4U
FRN001E1□-4U
FRN002E1□-4U
FRN003E1□-4U
FRN005E1□-4U
FRN007E1□-4U
FRN010E1□-4U
FRN015E1□-4U
FRN020E1□-4U
FRNF12E1□-7U
FRNF25E1□-7U
FRNF50E1□-7U
FRN001E1□-7U
FRN002E1□-7U
FRN003E1□-7U
Fig. A
Fig. B
Fig. C
Fig. B
Fig. C
Fig. D
Fig. E
Fig. A
Fig.
Fig. C
Fig. D
L1/R L2/S L3/T P1 P
G
G
B
G
L1/R L2/SDBL3/T
L2/S
L1/R L3/T P1 P
G
L1/L L2/N P1 P
G
G
DB
(+)N(-)
UDB VW
(+)N(-)
P1 P
U VW
(+)N(-)
UDB VW
U VW
(+)N(-)
G
G
Fig. E
G
L1/L
●Control circuit terminals (common to all the inverter models)
CMY Y1 PLCY2 C1 11 FM CM X1 X2 X3 X4 X5
30A 30B 30C
Terminal size: M3
DB
L2/N
U VW
P1 P
REV11 12 13 CM FWD
(+)N(-)
G
Page 21

●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
▲
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Protective Functions
Protective
Functions
Overcurrent protection
Short circuit protection
Grounding fault
protection
Overvoltage
protection
Undervoltage
protection
Input phase loss
protection
Output phase loss protection
Overheating
protection
Overload protection
External alarm input
Electronic
thermal
PTC thermistor
Motor protection
Overload early
warning
Stall prevention
Alarm relay output
(for any fault)
Memory error
Keypad
communication error
CPU error
Option communication error
Option error
Operation error
Tuning error
RS-485
communication error
Data save error upon Undervoltage
RS-485 communication
error (optional)
Retry
Surge protection
Command loss
detection
PG disconnection
Momentary power
failure protection
Overload avoidance
control
Hardware error
Simulation error
The inverter is stopped for protection against overcurrent.
The inverter is stopped for protection against overcurrent caused by a short circuit in the output circuit.
The inverter is stopped upon start-up for protection against overcurrent caused by a grounding fault in the output circuit.
If the power supply is turned on with the grounding fault, the inverter and the controlled equipment may not be protected.
An excessive voltage (3-phase and Single-phase 230V series: 400V DC, 3-phase 460V series: 800V DC)
in the DC link circuit is detected and the inverter is stopped. If an excessive voltage is applied by mistake,
the protection cannot be guaranteed.
The voltage drop (3-phase 230V series: 200V DC, 3-phase 460V series: 400V DC) in the DC link circuit is detected to stop the inverter.
However, when "F14: 3, 4 or 5" is selected, an alarm is not issued even upon a voltage drop in the DC link circuit.
The input phase loss is detected to shut off the inverter output. This function protects the inverter from being damaged by adding
extreme stress caused by a power phase loss or imbalance between phases. When the load to be connected is small or
DC REACTOR is connected a phase loss is not detected.
Detects breaks in inverter output wiring at the start of operation and during running, to shut off the inverter output.
Stops the inverter output upon detecting excess heat sink temperature in case of cooling fan failure or overload.
Discharging and inverter operation are stopped due to overheating of an external braking resistor.
* Function codes must be set corresponding to the braking resistor.
The temperature inside the IGBT is calculated from the detection of output current and internal temperature, to shut off the inverter output.
With the digital input signal (THR) opened, the inverter is stopped with an alarm.
The inverter is stopped with an electronic thermal function set to protect the motor.
• The standard motor is protected at all the frequencies.
• The inverter motor is protected at all the frequencies.
*The operation level and thermal time constant can be set.
A PTC thermistor input stops the inverter to protect the motor.
• The PTC thermistor is connected between terminals C1 and 11 to set switches and function codes on the control PC board.
Warning signal is output at the predetermined level before stopping the inverter with the electronic thermal function to protect the
motor.
This is protected when the instantaneous overcurrent limit works.
• Instantaneous overcurrent limit: Operates when the inverter output current goes beyond the instantaneous overcurrent limiting level,
and avoids tripping (during acceleration and constant speed operation).
The relay signal is output when the inverter stops upon an alarm.
<Alarm reset>
The key or digital input signal (RST) is used to reset the alarm stop state.
<Storage of alarm history and detailed data>
Up to the last 4 alarms can be stored and displayed.
Data is checked upon power-on and data writing to detect any fault in the memory and to stop the inverter if any.
The keypad (standard) or multi-function keypad (optional) is used to detect a communication fault between the keypad and inverter
main body during operation and to stop the inverter.
Detects a CPU error or LSI error caused by noise.
When each option card is used, a fault of communication with the inverter main body is detected to stop the inverter.
When each option card is used, the option card detects a fault to stop the inverter.
STOP key priority:
Start check:
When tuning failure, interruption, or any fault as a result of turning is detected while tuning for motor constant.
When the connection port of the keypad connected via RS-485 communication port to detect a communication error, the inverter is
stopped and displays an error.
When the undervoltage protection works, an error is displayed if data cannot be stored.
When an optional RS-485 communication card is used to configure the network, a fault of communication with the inverter main body
is detected to stop the inverter.
When the inverter is tripped and stopped, this function automatically resets the tripping state and restarts operation.
(The number of retries and the length of wait before resetting can be set.)
The inverter is protected against surge voltage intruding between the main circuit power line and ground.
A loss (broken wire, etc.) of the frequency command is detected to output an alarm and continue operation at the preset frequency
(set at a ratio to the frequency before detection).
An error displays when the signal line for PG is disconnected while the PG feedback card is installed.
• A protective function (inverter stoppage) is activated upon a momentary power failure for 15msec or longer.
• If restart upon momentary power failure is selected, the inverter restarts upon recovery of the voltage within the set time.
The inverter output frequency is reduced to avoid tripping before heat sink overheating or tripping due to an overload
(alarm indication: or .
The inverter is stopped when poor connection between the control board and power source board or interface board, or short-circuit
between terminals between 13 and 11 is detected.
Simulated alarm is output to check the fault sequence.
Description
During acceleration
During deceleration
During constant
speed operation
During acceleration
During deceleration
During constant speed operation
Pressing the key on the keypad or entering the digital input signal will forcibly decelerate and stop the
motor even if the operation command through signal input or communication is selected.
Start check: If the operation command is entered in the following cases, will be displayed on the
LED monitor to prohibit operation.
• Power-on
• Alarm reset ( key ON or alarm (error) reset [RST] is reset.)
• The link operation selection "LE" is used to switch operation.
LED
indication
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Note: The item indicated with ▲ in the alarm output (30A, B, C) column may not be issued according to some function code settings.
Alarm output
(30A, B, C) Note)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Related
function code
F14
H98
H98
H43, H98
E01 to E05
E98, E99
F10,A06
F11,F12,A07,A08
H26,H27
E34,E35
H12
E20,E21,E27
E01 to E05
E98,E99
F02
H96
P04
H04,H05
E65
F14
H13 to H16
H70
H45
Terminal
Functions
Functions
Protective
Page 22

Function Settings
■ Function Settings
●F codes: Fundamental Functions
Func.
Code
Data Protection
Frequency Command 1
Operation Method
Maximum Frequency 1
Base Frequency 1
Rated Voltage at Base
Frequency 1
Maximum Output Voltage 1
Acceleration Time 1
Deceleration Time 1
Torque Boost 1
Electronic Thermal Overload Protection for Motor 1
Restart Mode
after Momentary
Power Failure
Frequency Limiter
Bias (Frequency command 1)
DC
Braking 1
Starting Frequency 1
Stop Frequency
Motor Sound
Analog Output [FM]
Load Selection/
Auto Torque Boost /
Auto Energy Saving Operation 1
Stop Frequency
Torque
Limiter 1
Control Mode Selection 1
Name Data setting range
0: Disable both data protection and digital reference protection
1: Enable data protection and disable digital reference protection
2: Disable data protection and enable digital reference protection
3: Enable both data protection and digital reference protection
0 : / keys on keypad
1: Voltage input to terminal [12] (-10 to +10 VDC)
2: Current input to terminal [C1] (C1 function) (4 to 20 mA DC)
Sum of voltage and current inputs to terminals [12] and [C1] (C1 function)
3:
5: Voltage input to terminal [C1] (V2 function) (0 to 10 VDC)
7: Terminal command UP /DOWN control
11: Digital input (option)
12: Pulse input (option)
0:
RUN/STOP keys on keypad (Motor rotational direction specified by terminal command FWD/REV )
1: Terminal command FWD or REV
2: RUN/STOP keys on keypad (forward)
3: RUN/STOP keys on keypad (reverse)
25.0 to 400.0
25.0 to 400.0
0: Output a voltage in proportion to input voltage
80 to 240: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 230 V class series)
160 to 500: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 460 V class series)
80 to 240: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 230 V class series)
160 to 500: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 460 V class series)
0.00 to 3600
0.00 to 3600
0.0 to 20.0
Note: This setting takes effect when F37 = 0, 1, 3, or 4.
(Select motor characteristics)
(Overload detection level)
(Thermal time constant)
(Mode selection)
(Braking starting frequency)
(Braking level)
(Braking time)
(Holding time)
(Carrier frequency)
(Mode selection)
(Voltage adjustment)
(Pulse rate)
(Holding Time)
(Limiting Level for driving)
(Limiting Level for braking)
1: For a general-purpose motor with shaft-driven cooling fan
2:
For an inverter-driven motor, non-ventilated motor, or motor with separately powered cooling fan
0.00: Disable1 to 135% of the rated current (allowable continuous drive current) of the motor
0.5 to 75.0
0: Disable restart (Trip immediately)
1: Disable restart (Trip after a recovery from power failure)
4: Enable restart
5: Enable restart (Restart at the starting frequency, for low-inertia load)
(High)
0.0 to 400.0
(Low)
0.0 to 400.0
-100.00 to 100.00
0.0 to 60.0
0 to 100
0.00 : Disable 0.01 to 30.00
0.1 to 60.0
0.01 to 10.00
0.1 to 60.0
0.75 to 15
0 : Level 0 (Inactive)
(Tone)
1 : Level 1
2 : Level 2
3 : Level 3
0 : Output in voltage (0 to 10 VDC) [FMA]
2 : Output in pulse (0 to 6000p/s) [FMP]
0 to 300 [FMA]
Select a function to be monitored from the followings.
(Function)
0: Output frequency 1 (before slip compensation)
1: Output frequency 2 (after slip compensation)
2: Output current
3: Output voltage
4: Output torque
5: Load factor
6: Input power
7: PID feedback amount (PV)
8: PG feedback value
9: DC link bus voltage
10: Universal AO
13: Motor output
14: Calibration
15: PID command (SV)
16: PID output (MV)
25 to 6000 (FMP, Pulse rate at 100% output)
0: Variable torque load
1: Constant torque load
2: Auto-torque boost
3: Auto-energy saving operation (Variable torque load during ACC/DEC)
4: Auto-energy saving operation (Constant torque load during ACC/DEC)
5: Auto-energy saving operation (Auto-torque boost during ACC/DEC)
0.00 to 10.00
20 to 200 999 : Disable
20 to 200 999 : Disable
0: V/f control with slip compensation inactive
1: Dynamic torque vector control
2: V/f control with slip compensation active
3: V/f control with PG
4: Dynamic torque vector control with PG
Min. Unit
-
-
-
0.1
Hz
0.1
Hz
1
1
Note: Entering 0.00 cancels the acceleration time, requiring external soft-start.
Note: Entering 0.00 cancels the deceleration time, requiring external soft-start.
(percentage with respect to "F05: Rated Voltage at Base Frequency 1")
(Restart at the frequency at which the power failure occurred, for general loads)
*1
0.01
0.01
0.1
-
0.01
0.1
-
0.1
0.1
0.01
0.1
1
0.01
0.1
0.01
0.1
1
-
-
1
-
1
-
0.01
1
1
-
min
Hz
Hz
Hz
Hz
Hz
kHz
p/s
copy
-
-
-
V
V
s
s
%
-
A
-
%
%
s
s
-
-
%
-
-
s
%
%
-
setting
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y2
Y2
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y1Y2
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
0
0
2
60.0
60.0
230
460
230
460
6.00
6.00
Depending on the
inverter capacity
1
100% of the motor rated current
5.0
0
70.0
0.0
0.00
0.0
0
0.00
0.5
0.00
0.2
2
0
0
100
0
1440
1
0.00
999
999
0
Default
Data
2
*
Page 23

●F codes: Fundamental Functions
Func.
Code
Current Limiter
Electronic Thermal
Overload Protection
for braking resistor
Name Data setting range
(Mode selection)
0: Disable (No current limiter works.)
1: Enable at constant speed (Disable during ACC/DEC)
2: Enable during ACC/constant speed operation
(Level)
20 to 200
(Discharging capability)
(Allowable average loss)
(The data is interpreted as the rated output current of the inverter for 100%.)
1 to 900 999: Disable
0: Reserved
0.001 to 50.000 0.000: Reserved
●E codes: Extension Terminal Functions
Func.
Code
Terminal X1 function
Terminal X2 function
Terminal X3 function
Terminal X4 function
Terminal X5 function
Acceleration Time 2
Deceleration Time 2
Torque
Limiter 2
Terminal [Y1] Function
Terminal [Y2] Function
Terminal [30A/B/C] Function
*1 When you make settings from the keypad, the incremental unit is restricted by the number of
digits that the LED monitor can display.
(Example) If the setting range is from -200.00 to 200.00, the incremental unit is as follows:
"1" for -200 to -100, "0.1" for -99.9 to -10.0, "0.01" for -9.99 to -0.01, "0.01" for 0.00 to 99.99,
and "0.1" for 100.0 to 200.0
*2 Symbols in the "Data copy" column
Y: Will be copied unconditionally.
Y1: Will not be copied if the rated capacity differs from the source inverter.
Name Data setting range
Selecting function code data assigns the corresponding function to
terminals [X1] to [X5] as listed below.
0 (1000) : Select multi-frequency [SS1]
1 (1001) : Select multi-frequency [SS2]
2 (1002) : Select multi-frequency [SS4]
3 (1003) : Select multi-frequency [SS8]
4 (1004) : Select ACC/DEC time [RT1]
6 (1006) : Enable 3-wire operation [HLD]
7 (1007) : Coast to a stop [BX]
8 (1008) : Reset alarm [RST]
9 (1009) : Enable external alarm trip [THR]
10 (1010) : Ready for jogging [JOG]
11 (1011) : Select frequency command 2/1 [Hz2/Hz1]
12 (1012) : Select motor 2/motor 1 [M2/M1]
13 : Enable DC braking [DCBRK]
14 (1014) : Select torque limiter level [TL2/TL1]
17 (1017) : UP (Increase output frequency) [UP]
18 (1018) : DOWN (Decrease output frequency) [DOWN]
19 (1019) : Enable data change with keypad [WE-KP]
20 (1020) : Cancel PID control [Hz/PID]
21 (1021) : Switch normal/inverse operation [IVS]
24 (1024) : Enable communications link via RS-485 or field bus [LE]
25 (1025) : Universal DI [U-DI]
26 (1026) : Enable auto search for idling motor speed at starting [STM]
27 (1027) : Speed feedback control switch [PG/Hz]
30 (1030) : Force to stop [STOP]
33 (1033) : Reset PID integral and differential components [PID-RST]
34 (1034) : Hold PID integral component [PID-HLD]
42 (1042) : Position control limit switch [LS]
43 (1043) : Position control start/reset command [S/R]
44 (1044) : Serial pulse Receive mode [SPRM]
45 (1045) : Position Control return mode [RTN]
46 (1046) : Overload stopping effective command [OLS]
Setting the value of 1000s in parentheses ( ) shown above assigns a negative logic input to a terminal.
Note: In the case of THR and STOP , data (1009) and (1030) are for normal logic, and "9" and "30" are
for negative logic, respectively.
0.00 to 3600 Note: Entering 0.00 cancels the acceleration time, requiring external soft-start.
0.00 to 3600 Note: Entering 0.00 cancels the acceleration time, requiring external soft-start.
(Limiting Level for driving)
(Limiting Level for braking)
20 to 200 999 : Disable
20 to 200 999 : Disable
Selecting function code data assigns the corresponding function to terminals [Y1], [Y2], and [30A/B/C] as listed below.
0 (1000) : Inverter running [RUN]
1 (1001) : Frequency arrival signal [FAR]
2 (1002) : Frequency detected [FDT]
3 (1003) : Undervoltage detected (Inverter stopped) [LU]
4 (1004) : Torque polarity detected [B/D]
5 (1005) : Inverter output limiting [IOL]
6 (1006) : Auto-restarting after momentary power failure [IPF]
7 (1007) : Motor overload early warning [OL]
10 (1010) : Inverter ready to run [RDY]
21 (1021) : Frequency arrival signal 2 [FAR2]
22 (1022) : Inverter output limiting with delay [IOL2]
26 (1026) : Auto-resetting [TRY]
28 (1028) : Heat sink overheat early warning [OH]
30 (1030) : Service lifetime alarm [LIFE]
33 (1033) : Reference loss detected [REF OFF]
35 (1035) : Inverter output on [RUN2]
36 (1036) : Overload prevention control [OLP]
37 (1037) : Current detected [ID]
38 (1038) : Current detected 2 [ID2]
42 (1042) : PID alarm [PID-ALM]
49 (1049) : Switched to motor 2 [SWM2]
57 (1057) : Brake signal [BRKS]
76 (1076) : PG error signal [PG-ERR]
80 (1080) : Over traveling [OT]
81 (1081) : Time up of the start timer or the end timer [TO]
82 (1082) : Completion of positioning [PSET]
83 (1083) : Current position pulse overflow [POF]
99 (1099) : Alarm output (for any alarm) [ALM]
Setting the value of 1000s in parentheses ( ) shown above assigns a negative logic input to a terminal.
Default
-
%
kWs
kW
-
-
-
-
-
s
s
%
%
-
-
-
Data
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Data
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
2
*
setting
2
180
999
0.000
Default
2
*
setting
0
1
2
7
8
10.0
10.0
999
999
0
7
99
Min. Unit
-
1
1
0.001
Min. Unit
-
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
1
1
-
-
-
Y2: Will not be copied if the rated input voltage differs from the source inverter.
N: Will not be copied.
*3 Reserved for the maker. Do not set any data.
<Changing, validating, and saving function code data when the motor is running>
: Impossible, : Possible (Change data with keys and then
save/validate it with key), : Possible (Change and validate data with
keys and then save it with key)
Settings
Function
Page 24

Functions Settings
■ Functions Settings
●E codes: Extension Terminal Functions
Func.
Code
Frequency Arrival Delay Time
Frequency Arrival
Frequency Detection (FDT)
Overload Early Warning /Current Detection
Current detection 2
Coefficient for Constant Feeding Rate Time
PID Display Coefficient A
B
LED Display filter
LED Monitor
LCD Monitor
LED Monitor
Coefficient for Speed Indication
Display Coefficient for Input Watt-hour Data
Keypad (Menu display mode)
Terminal [C1] Signal Definition
Terminal [12] Extended Function
Terminal [C1]
Terminal [C1]
Reference Loss Detection (Continuous running frequency)
Terminal [FWD] Function
Terminal [REV] Function
Name Data setting range
0.01 to 10.00
(hysteresis width)
(Detection level)
(hysteresis width)
(Item selection)
*4
(Item selection)
(Language selection)
(Contrast control)
(Speed monitor item)
(C1/V2 Function)
Extended Function (C1 function)
Extended Function (V2 function)
0.0 to 10.0
0.0 to 400.0
0.0 to 400.0
0.00 : Disable Current value of 1 to 200% of the inverter rated current
(Level)
0.01 to 600.00
(Timer)
0.00 : Disable Current value of 1 to 200% of the inverter rated current
(Level)
0.01 to 600.00
(Timer)
0.000 to 9.999
-999 to 0.00 to 9990
-999 to 0.00 to 9990
0.0 to 5.0
0: Speed monitor (select by E48)
3: Output current
4: Output voltage
8: Calculated torque
9: Input power
10: PID command
12: PID feedback amount
13: Timer
14: PID output
15: Load factor
16: Motor output
21: Present pulse position
22: Deviation of pulse position
0: Running status, rotational direction and operation guide
1: Bar charts for output frequency, current and calculated torque
0 : Japanese
1 : English
2 : German
3 : French
4 : Spanish
5 : Italian
0 (Low) to 10 (High)
0: Output frequency (Before slip compensation)
1: Output frequency (After slip compensation)
2: Reference frequency
3: Motor speed in r/min
4: Load shaft speed in r/min
5: Line speed in m/min
6: Constant feeding rate time
0.01 to 200.00
0.000 (Cancel/reset) 0.001 to 9999
0: Function code data editing mode (Menus #0 and #1)
1: Function code data check mode (Menu #2)
2: Full-menu mode (Menus #0 through #6)
0: Current input (C1 function), 4 to 20 mADC
1: Voltage input (V2 function), 0 to +10 VDC
Selecting function code data assigns the corresponding function to terminals [12] and [C1] (C1/V2 function) as listed below.
0: None
1: Auxiliary frequency command 1
2: Auxiliary frequency command 2
3: PID command 1
5: PID feedback amount
0: Decelerate to stop 20 to 120 999: Disable
Selecting function code data assigns the corresponding function to terminals [FWD] and [REV] as listed below.
0 (1000) : Select multi-frequency [SS1]
1 (1001) : Select multi-frequency [SS2]
2 (1002) : Select multi-frequency [SS4]
3 (1003) : Select multi-frequency [SS8]
4 (1004) : Select ACC/DEC time [RT1]
6 (1006) : Enable 3-wire operation [HLD]
7 (1007) : Coast to a stop [BX]
8 (1008) : Reset alarm [RST]
9 (1009) : Enable external alarm trip [THR]
10 (1010) : Ready for jogging [JOG]
11 (1011) : Select frequency command 2/1 [Hz2/Hz1]
12 (1012) : Select motor 2/motor 1 [M2/M1]
13 : Enable DC braking [DCBRK]
14 (1014) : Select torque limiter level [TL2/TL1]
17 (1017) : UP (Increase output frequency) [UP]
18 (1018) : DOWN (Decrease output frequency) [DOWN]
19 (1019) : Enable data change with keypad [WE-KP]
20 (1020) : Cancel PID control [Hz/PID]
21 (1021) : Switch normal/inverse operation [IVS]
24 (1024) :
25 (1025) : Universal DI [U-DI]
26 (1026) :
27 (1027) : Speed feedback control switch [PG/Hz]
30 (1030) : Force to stop [STOP]
33 (1033) : Reset PID integral and differential components [PID-RST]
34 (1034) : Hold PID integral component [PID-HLD]
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
Enable communications link via RS-485 or field bus [LE]
Enable auto search for idling motor speed at starting
[STM]
Min. Unit
0.01
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.001
0.01
0.01
0.1
-
-
-
1
-
0.01
0.001
-
-
-
-
-
1
-
-
Hz
Hz
Hz
Data
Default setting
*2
copy
s
Y
Y
Y
Y
A
Y1Y2
s
Y
A
Y1Y2
s
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
s
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
-
Y
%
Y
-
Y
-
Y
0.10
2.5
60.0
1.0
100% of the motor rated current
10.00
100% of the motor rated current
10.00
0.000
100
0.00
0.5
0
0
1
5
0
30.00
0.010
0
0
0
0
0
999
98
99
Page 25

●E codes: Extension Terminal Functions
Func.
Code
Name Data setting range
42 (1042) : Position control limit switch [LS]
43 (1043) : Position control start/reset command [S/R]
44 (1044) : Serial pulse Receive mode [SPRM]
45 (1045) : Position Control return mode [RTN]
46 (1046) : Overload stopping effective command [OLS]
98 : Run forward [FWD]
99 : Run reverse [REV]
Setting the value of 1000s in parentheses ( ) shown above assigns a
negative logic input to a terminal.
Note: In the case of THR and STOP , data (1009) and (1030) are for
normal logic, and "9" and "30" are for negative logic, respectively.
●C codes: Control Functions
Func.
Code
Jump Frequency 1
2
3
Multi-Frequency 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Jogging Frequency
Timer Operation
Frequency Command 2
Analog Input Adjustment
for [12]
Analog Input Adjustment
for [C1] (C1 function)
Analog Input Adjustment
for [C1] (V2 function)
Bias (Frequency command 1)
Bias (PID command 1)
Selection of Normal/Inverse Operation
*1 When you make settings from the keypad, the incremental unit is restricted by the number of
digits that the LED monitor can display.
(Example) If the setting range is from -200.00 to 200.00, the incremental unit is as follows:
"1" for -200 to -100, "0.1" for -99.9 to -10.0, "0.01" for -9.99 to -0.01, "0.01" for 0.00 to 99.99,
and "0.1" for 100.0 to 200.0
*2 Symbols in the "Data copy" column
Y: Will be copied unconditionally.
Y1: Will not be copied if the rated capacity differs from the source inverter.
Y2: Will not be copied if the rated input voltage differs from the source inverter.
N: Will not be copied.
Name Data setting range
0.0 to 400.0
(Hysteresis width)
0.0 to 30.0
0.00 to 400.00
0.00 to 400.00
0 : Disable
1 : Enable
0 : / keys on keypad
1: Voltage input to terminal [12] (-10 to +10 VDC)
2: Current input to terminal [C1] (C1 function) (4 to 20 mA DC)
3:
Sum of voltage and current inputs to terminals [12] and [C1] (C1 function)
5: Voltage input to terminal [C1] (V2 function) (0 to 10 VDC)
7: Terminal command UP / DOWN control
11: Didital input (option)
12: Pulse input (option)
-5.0 to 5.0
(offset)
(Gain)
(Filter time constant)
(Gain base point)
(Polarity)
0.00 to 200.00
0.00 to 5.00
0.00 to 100.00
0 : Bipolar
*1
*1
1 : Unipolar
-5.0 to 5.0
(offset)
(Gain)
(Filter time constant)
(Gain base point)
(offset)
(Gain)
(Filter time constant)
(Gain base point)
(Bias base point)
(Bias value)
(Bias base point)
(Frequency command 1)
0.00 to 200.00
0.00 to 5.00
0.00 to 100.00
-5.0 to 5.0
0.00 to 200.00
0.00 to 5.00
0.00 to 100.00
0.00 to 100.00
-100.00 to 100.00
0.00 to 100.00
0 : Normal operation
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
1 : Inverse operation
Data
Min. Unit
Min. Unit
Hz
0.1
Hz
0.1
Hz
0.01
Hz
0.01
-
-
-
-
%
0.1
%
0.01
s
0.01
%
0.01
-
-
%
0.1
%
0.01
s
0.01
%
0.01
%
0.1
%
0.01
s
0.01
%
0.01
%
0.01
%
0.01
%
0.01
-
-
*3 Reserved for the maker. Do not set any data.
*4 Use these functions by connection with the multi-tasking keypad (optional).
<Changing, validating, and saving function code data when the motor is running>
: Impossible, : Possible (Change data with keys and then
save/validate it with key), : Possible (Change and validate data with
keys and then save it with key)
copy
Data
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
*2
*2
Default setting
Default setting
0.00
0.00
0.00
3.0
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0
2
0.0
100.0
0.05
100.0
1
0.0
100.0
0.05
100.0
0.0
100.0
0.05
100.0
0.00
0.00
0.00
0
Settings
Functions
Page 26

Functions Settings
■ Functions Settings
●P codes: Motor Parameters
Func.
Code
Motor 1
Motor 1 Selection
●H codes: High Performance Functions
Func.
Code
Data Initialization
Auto-reset
Cooling Fan ON/OFF Control
Acceleration/Deceleration Pattern
Limiting the direction of the motor rotation
Starting Mode
Deceleration Mode
Instantaneous Overcurrent Limiting
Restart Mode after Momentary Power Failure
Thermistor
Droop control
Communications Link Function
Capacitance of DC Link Bus Capacitor
Cumulative Run Time of Cooling Fan
Startup Times of Motor 1
Mock Alarm
Initial Capacitance of DC Link Bus Capacitor
Cumulative Run Time of Capacitors on Printed Circuit Boards
Starting Mode
Non-linear V/f Pattern,1
Non-linear V/f Pattern,2
ACC/DEC time
Deceleration Time for Forced Stop
Name Data setting range
(No. of poles)
(Rated capacity)
(Rated current)
(Auto-tuning)
(Online tuning)
(No-load current)
(Slip compensation gain for driving)
(Slip compensation response time)
(Slip compensation gain for braking)
(Rated slip frequency)
2 to 22
0.01 to 30.00 (where, P99 data is 0, 3, or 4.)
0.01 to 30.00 (where, P99 data is 1.)
0.00 to 100.0
0: Disable
1: Enable (Tune %R1 and %X while the motor is stopped.)
2: Enable
0 : Disable
1 : Enable
0.00 to 50.00
(%R1)
0.00 to 50.00
(%X)
0.00 to 50.00
0.0 to 200.0
0.00 to 10.00
0.0 to 200.0
0.00 to 15.00
0: Motor characteristics 0 (Fuji standard motors, 8-series)
1: Motor characteristics 1 (HP rating motors)
3: Motor characteristics 3 (Fuji standard motors, 6-series)
4: Other motors
(Tune %R1, %X and rated slip while the motor is stopped, and no-load current while running.)
Name Data setting range
0: Disable initialization
1: Initialize all function code data to the factory defaults
2: Initialize motor 1 parameters
3: Initialize motor 2 parameters
(Times)
(Reset interval)
(Auto search)
(Mode selection)
(Frequency fall rate)
(Allowable momentary power failure time)
(Mode selection)
(Mode selection)
(Delay time)
(Frequency)
(Voltage)
(Frequency)
(Voltage)
(Jogging operation)
0: Disable 1 to 10
0.5 to 20.0
0: Disable (Always in operation)
1: Enable (ON/OFF controllable)
0: Linear
1: S-curve (Weak)
2: S-curve (Strong)
3: Curvilinear
0: Disable
1: Enable (Reverse rotation inhibited)
2: Enable (Forward rotation inhibited)
0: Disable
1: Enable (At restart after momentary power failure)
2: Enable (At restart after momentary power failure and at normal start)
0: Normal deceleration
1: Coast-to-stop
0 : Disable
1 : Enable
(Restart time)
0.1 to 10.0
0.00 : FSelected deceleration time 0.01 to 100.00
999: Follow the current limit command
0.0 to 30.0 999 : Automatically determined by inverter
0: Disable
Enable (With PTC, the inverter immediately trips with displayed.)0.00 to 5.00V
1:
2:
(Level)
Enable (With PTC, the inverter issues output signal THM and continues to run.
0.00 to 5.00
-60.0 to 0.0
Frequency command Run command
0: F01/C30 F02
1: RS-485 F02
2: F01/C30 RS-485
3: RS-485 RS-485
4: RS-485 (option) F02
5: RS-485 (option) RS-485
6: F01/C30 RS-485 (option)
7: RS-485 RS-485 (option)
8: RS-485 (option) RS-485 (option)
Indication for replacing DC link bus capacitor (0000 to FFFF: Hexadecimal)
Indication of cumulative run time of cooling fan for replacement
Indication of cumulative startup times
0: Disable 1: Enable
Indication for replacing DC link bus capacitor (0000 to FFFF: Hexadecimal)
Indication for replacing capacitors on printed circuit boards (0000 to FFFF: Hexadecimal). Resettable.
0.0 to 10.0
0.0 : Cancel 0.1 to 400.0
0 to 240 : Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 230 V class series)
0 to 500 : Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 460 V class series)
0.0 : Cancel 0.1 to 400.0
0 to 240: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 230 V class series)
0 to 500: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 460 V class series)
0.00 to 3600 *ACC time and DEC time are common.
0.00 to 3600
Min. Unit
2
0.01
0.01
0.01
-
-
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
-
Min. Unit
-
1
0.1
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.1
0.01
0.1
-
0.01
0.1
-
1
-
-
(Once a mock alarm occurs, the data automatically returns to 0.)
-
-
-
0.1
0.1
1
0.1
1
0.01
0.01
Pole
kW
HP
A
-
-
A
%
%
%
s
%
Hz
-
-
Times
s
-
-
-
-
-
-
s
Hz/s
s
-
V
Hz
-
-
-
-
-
-
s
Hz
V
Hz
V
s
s
Data
Default setting
*2
copy
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
N
Y
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
Y
Y1Y2
Y
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
Data
copy
N
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y1Y2
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
N
N
N
N
N
Y
Y
Y2
Y
Y2
Y
Y
4
Rated capacity
of motor
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
0
0
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
100.0
0.50
100.0
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
0
Default setting
*2
0
0
5.0
0
0
0
0
0
1
Depending on the inverter capacity
999
999
0
1.60
0.0
0
-
-
0
Set at factory shipping
-
0.0
0.0
0
0.0
0
6.00
6.00
Page 27

●H codes: High Performance Functions
Func.
Code
UP/DOWN Control
Low Limiter
Slip Compensation 1
Automatic Deceleration
Overload Prevention Control
Deceleration Characteristics
Torque Limiter
(Frequency increment limit for braking)
Output Current Fluctuation Damping Gain for Motor 1
Reserved.
~
C1 Disconnection Detection Time
(PID control feedback line)
Cumulative Motor Run Time 1
DC Braking
STOP Key Priority/
Start Check Function
Clear Alarm Data
Protection/Maintenance Function
Name Data setting range
0 : 0.00
(Initial frequency setting)
(Mode selection)
(Lower limiting frequency)
1 : Last UP /DOWN command value on releasing run command
0 : Limit by F16 (Frequency limiter: Low) and continue to run
If the output frequency lowers less than the one limited by F16 (Frequency limiter: Low), decelerate to stop the motor.
1 :
0.0 (Depends on F16 (Frequency limiter: Low))
0.1 to 60.0
(Operating conditions)
0 : Enable during ACC/DEC and enable at base frequency or above
1 : Disable during ACC/DEC and enable at base frequency or above
2 : Enable during ACC/DEC and disable at base frequency or above
3 : Disable during ACC/DEC and disable at base frequency or above
(Mode selection)
0 : Disable
2 : Enable
4 : Enable
(Canceled if actual deceleration time exceeds three times the one specified by F08/E11.)
(Not canceled if actual deceleration time exceeds three times the one specified by F08/E11.)
0.00 : Follow deceleration time specified by F08/E11 0.01 to 100.0
999: Disable
0 : Disable
1 : Enable
0.0 to 400.0
*3
0.00 to 0.40
0.0: Disable
0.1 to 60.0: Detection time
Change or reset the cumulative data
(Braking response mode)
0 : Slow
1 : Quick
Item
STOP key priority
Start check function
Data
Setting H97 data to "1" clears alarm data and then returns to zero.
0 to 31: Display data on the keypad's LED monitor in decimal format (In each bit, "0" for disabled, "1" for enabled.)
(Mode selection)
Bit 0 : Lower the carrier frequency automatically
Bit 1 : Detect input phase loss
Bit 2 : Detect output phase loss
Bit 3 : Select life judgment threshold of DC link bus capacitor
Bit 4 : Judge the life of DC link bus capacitor
0
Disable
Disable
1
Enable
Disable
2
Disable
Enable
3
Enable
Enable
Min. Unit
-
-
-
-
0.1
Hz
-
-
-
-
0.01
Hz/s
-
-
0.1
Hz
-
0.01
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Data
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
Y
Y
N
Y
*2
Default setting
1
0
1.6
0
0
999
0
5.0
0.20
0.0
1
0
0
19
(bit 4,1,0=1)
●A codes: Motor 2 Parameters
Func.
Code
Maximum Frequency 2
Base Frequency 2
Rated Voltage at Base
Frequency 2
Maximum output Voltage 2
Torque Boost 2
Electronic Thermal Overload Protection for Motor 2
DC
Braking 2
Starting Frequency 2
Load Selection/
Auto Torque Boost /
Auto Energy Saving Operation 2
Control Mode Selection 2
*1 When you make settings from the keypad, the incremental unit is restricted by the number of
digits that the LED monitor can display.
(Example) If the setting range is from -200.00 to 200.00, the incremental unit is as follows:
"1" for -200 to -100, "0.1" for -99.9 to -10.0, "0.01" for -9.99 to -0.01, "0.01" for 0.00 to 99.99,
and "0.1" for 100.0 to 200.0
*2 Symbols in the "Data copy" column
Y: Will be copied unconditionally.
Y1: Will not be copied if the rated capacity differs from the source inverter.
Y2: Will not be copied if the rated input voltage differs from the source inverter.
N: Will not be copied.
Name Data setting range
25.0 to 400.0
25.0 to 400.0
0: Output a voltage in proportion to input voltage
80 to 240: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 230 V class series)
160 to 500: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 460 V class series)
80 to 240V: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 230 V class series)
160 to 500V: Output an AVR-controlled voltage (for 460 V class series)
(Select motor characteristics)
(Overload detection level)
(Thermal time constant)
(Braking starting frequency)
(Braking level)
(Braking time)
0.0 to 20.0
Note: This setting takes effect when A13 = 0, 1, 3, or 4.
1 : For a general-purpose motor with shaft-driven cooling fan
2 :
0.00 :
0.5 to 75.0
0.0 to 60.0 Hz
0 to 100
0.00 : Disable 0.01 to 30.00
0.1 to 60.0
0 : Variable torque load
1 : Constant torque load
2 : Auto-torque boost
3 : Auto-energy saving operation (Variable torque load during ACC/DEC)
4 : Auto-energy saving operation (Constant torque load during ACC/DEC)
5 : Auto-energy saving operation (Auto-torque boost during ACC/DEC)
0 : V/f operation with slip compensation inactive
1 : Dynamic torque vector operation
2 : V/f operation with slip compensation active
3 : V/f operation with PG
4 : Dynamic torque vector operation with PG
(percentage with respect to "A03: Rated Voltage at Base Frequency 2")
For an inverter-driven motor, non-ventilated motor, or motor with separately powered cooling fan
Disable 1 to 135% of the rated current (allowable continuous drive current) of the motor
Data
Min. Unit
0.1
Hz
0.1
Hz
1
V
copy
Y
Y
Y2
*2
Default setting
60.0
60.0
230
460
1
V
Y2
230
460
0.1
%
-
-
0.01
A
0.1
min
0.1
Hz
1
%
0.01
s
0.1
Hz
-
-
-
-
*3 Reserved for the maker. Do not set any data.
<Changing, validating, and saving function code data when the motor is running>
: Impossible, : Possible (Change data with keys and then
save/validate it with key), : Possible (Change and validate data with
keys and then save it with key)
Depending on
Y
the inverter capacity
Y
Y1Y2
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
1
100% of the motor rated current
5.0
0.0
0
0.00
0.5
1
0
Settings
Functions
Page 28

Functions Settings
■ Functions Settings
●A codes: Motor 2 Parameters
Func.
Code
Motor 2
Motor 2 Selection
Slip compensation 2
Output Current Fluctuation Damping Gain for Motor 2
Cumulative Motor Run Time 2
Startup Times of Motor 2
Name Data setting range
(No. of poles)
(Rated capacity)
(Rated current)
(Auto-tuning)
(ON-Line tuning)
(No-load current)
(Slip compensation gain for driving)
(Slip compensation response time)
(Slip compensation gain for braking)
(Rated slip frequency)
(Operating conditions)
2 to 22
0.01 to 30.00 (where, P99 data is 0, 3, or 4.)
0.01 to 30.00 (where, P99 data is 1.)
0.00 to 100.0
0: Disable
1 : Enable (Tune %R1 and %X while the motor is stopped.)
2 : Enable (
0 : Disable
1 : Enable
0.00 to 50.00
(%R1)
0.00 to 50.00
(%X)
0.00 to 50.00
0.0 to 200.0
0.00 to 10.00
0.0 to 10.00
0.00 to 15.00
0 : Motor characteristics 0 (Fuji standard motors, 8-series)
1 : Motor characteristics 1 (HP rating motors)
3 : Motor characteristics 3 (Fuji standard motors, 6-series)
4 : Other motors
0 : Enable during ACC/DEC and enable at base frequency or above
1 : Disable during ACC/DEC and enable at base frequency or above
2 : Enable during ACC/DEC and disable at base frequency or above
3 : Disable during ACC/DEC and disable at base frequency or above
0.00 to 0.40
Change or reset the cumulative data
Indication of cumulative startup times
Data
Min. Unit
2
Pole
0.01
kW
0.01
HP
0.01
A
-
-
Tune %R1, %X and rated slip while the motor is stopped, and no-load current while running.)
-
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
-
-
0.01
-
-
-
A
%
%
%
s
%
Hz
-
-
-
-
-
Default setting
*2
copy
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
Y1Y2
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
N
Y
Y1Y2
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
Y1Y2
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
Y1Y2
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
Y
Y1Y2
Y
Y1Y2
Rated value of Fuji standard motor
Y1Y2
Y
Y
N
N
4
4
0
0
100.0
0.50
100.0
0
0
0.20
-
-
●J codes: Application Functions
Func.
Code
PID Control
PID Control
Overload stop
Braking signal
Name Data setting range
(Mode selection)
(Remote command SV)
P (Gain)
I (Integral time)
D (Differential time)
(Feedback filter)
(Anti reset windup)
(Select alarm output)
(Upper level alarm (AH))
(Lower level alarm (AL))
(Upper limit of PID process output)
(Lower limit of PID process output)
(Speed command filter)
(Dancer reference position)
(Detection width of Dancer position deviation )
P (gain) 2
I (Integration time) 2
D (Derivative time) 2
(Selection PID control block)
(PID control block Selection)
(Detection value)
(Detection level)
(Mode selection )
(Operation condition)
(Released current)
(Brake OFF frequency)
(Brake OFF timer)
(Brake ON frequency)
(Brake ON timer)
0 : Disable
1 : Enable (Process control, normal operation)
2 : Enable (Process control, inverse operation)
3 : Enable (Dancer control)
0 : UP/DOWN keys on keypad
1 : PID command 1
3 : Terminal command UP /DOWN control
4 : Command via communications link
0.000 to 30.000
0.0 to 3600.0
0.0 to 600.00
0.0 to 900.0
0 to 200
0 : Absolute-value alarm
1 : Absolute-value alarm (with Hold)
2 : Absolute-value alarm (with Latch)
3 : Absolute-value alarm (with Hold and Latch)
4 : Deviation alarm
5 : Deviation alarm (with Hold)
6 : Deviation alarm (with Latch)
7 : Deviation alarm (with Hold and Latch)
-100 to 100
-100 to 100
-150 to 150 999 : F Disable
-150 to 150 999 : F Disable
0.00 to 5.00
-100 to 100
0 : Disable switching PID constant
1 to 100
0.000 to 30.00
0.0 to 3600.0
0.00 to 600.00
Bit 0 : PID output pole 0 = addition, 1 = subtraction
Bit 1 : Select compensation of output ratio 0 = speed command, 1 = ratio
0 : Torque
1 : Current
20 to 200
0 : Disable
1 : Decelerate to stop
2 : Coast to a stop
3 : Hit mechanical stop
0 : Enable at constant speed and during deceleration
1 : Enable at constant speed
2 : Enable anytime
0.00 to 600.00
(Timer)
0 to 200
0.0 to 25.0
0.0 to 5.0
0.0 to 25.0
0.0 to 5.0
Data
Min. Unit
-
-
-
-
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
0.001
0.1
0.01
0.1
1
-
1
1
1
1
0.01
1
1
0.001
0.1
0.01
1
-
0.1
-
-
0.01
1
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
Times
s
s
s
%
-
%
%
%
%
s
%
%
times
s
s
-
-
%
-
-
s
%
Hz
s
Hz
s
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
*2
Default setting
0
0
0.100
0.0
0.00
0.5
200
0
100
0
999
999
0.10
0
0
0.100
0.0
0.00
0
0
100
0
0
0
100
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
Page 29

●J codes: Application Functions
Func.
Code
Position control
(Stopping position specifying method)
Overload stopping, torque limit P
Function, torque limit I
Current control level
Name Data setting range
(the start timer)
(Start point: MSD)
(Start point: LSD)
(Position preset: MSD)
(Position preset: LSD)
(Creep speed switch point: MSD)
(Creep speed switch point: LSD)
(Position pre-set condition)
(Position detecting direction)
(Creep speed)
(Stopping position: MSD)
(Stopping position: LSD)
(Completion width)
(Coasting compensation)
(End timer)
(Integral time)
0.0 to 1000.0
-999 to 999
[P], 0 to 9999
-999 to 999
[P], 0 to 9999
0 to 999
0 to 9999
0 to 400
-999 to 999
0 to 9999
0 to 9999
0.0 to 1000.0
0 to 9999
0, 1
0, 1, 2
0, 1
(Gain)
0.000 to 2.000, 999
0.001 to 9.999, 999
50.0 to 150.0
●y codes: Link Functions
Func.
Code
RS-485 Communication (Standard)
(Communications error processing)
(No-response error detection time)
RS-485 Communication (Option)
(Communications error processing)
(No-response error detection time)
Bus Link Function
Loader Link Function
*1 When you make settings from the keypad, the incremental unit is restricted by the number of
digits that the LED monitor can display.
(Example) If the setting range is from -200.00 to 200.00, the incremental unit is as follows:
"1" for -200 to -100, "0.1" for -99.9 to -10.0, "0.01" for -9.99 to -0.01, "0.01" for 0.00 to 99.99,
and "0.1" for 100.0 to 200.0
*2 Symbols in the "Data copy" column
Y: Will be copied unconditionally.
Y1: Will not be copied if the rated capacity differs from the source inverter.
Name Data setting range
(Station address)
(Baud rate)
(Data length)
(Parity check)
(Stop bits)
(Response interval)
(Protocol selection)
(Station address)
(Baud rate)
(Data length)
(Parity check)
(Stop bits)
(Response interval)
(Protocol selection)
(Mode selection)
(Mode selection)
1 to 255
0 : Immediately trip with alarm
1 : Trip with alarm after running for the period specified by timer y03
2 : Retry during the period specified by timer y13.If the retry fails,
trip with alarm . If it succeeds, continue to run.
3 : Continue to run
0.0 to 60.0
(Timer)
0 : 2400 bps
1 : 4800 bps
2 : 9600 bps
3 : 19200 bps
4 : 38400 bps
0 : 8 bits
1 : 7 bits
0 : None (2 stop bits for Modbus RTU)
1 : Even parity (1 stop bit for Modbus RTU)
2 : Odd parity (1 stop bit for Modbus RTU)
3 : None (1 stop bit for Modbus RTU)
0 : 2 bits
1 : 1 bit
0 : No detection
1 to 60
0.00 to 1.00
0 : Modbus RTU protocol
1 : FRENIC Loader protocol (SX protocol)
2: Fuji general-purpose inverter protocol
1 to 255
0 : Immediately trip with alarm
1 : Trip with alarm after running for the period specified by timer y13
2 : Retry during the period specified by timer y13. If the retry fails,
trip with alarm . If it succeeds, continue to run.
3 Continue to run
0.0 to 60.0
(Timer)
0 : 2400 bps
1 : 4800 bps
2 : 9600 bps
3 : 19200 bps
4 : 38400 bps
0 : 8 bits
1 : 7 bits
0 : None (2 stop bits for Modbus RTU)
1 : Even parity (1 stop bit for Modbus RTU)
2 : Odd parity (1 stop bit for Modbus RTU)
3 : None (1 stop bit for Modbus RTU)
0 : 2 bits
1 : 1 bit
0 : No detection
1 to 60
0.00 to 1.00
0 : Modbus RTU protocol
2 : Fuji general-purpose inverter protocol
Frequency command Run command
0 : Follow H30 data Follow H30 data
1 : Via field bus option Follow H30 data
2 : Follow H30 data Via field bus option
3 : Via field bus option Via field bus option
Frequency command Run command
0 : Follow H30 and y98 data Follow H30 and y98 data
1 : Via RS-485 link (Loader) Follow H30 and y98 data
2 : Follow H30 and y98 data Via RS-485 link (Loader)
3 : Via RS-485 link (Loader) Via RS-485 link (Loader)
Data
Min. Unit
s
0.1
p
1
p
1
p
1
p
1
p
1
p
1
Hz
1
p
1
p
1
p
1
s
0.1
p
1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.1
s
%
Min. Unit
1
-
-
-
0.1
s
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1
s
0.01
s
-
-
1
-
-
-
0.1
s
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1
s
0.01
s
-
-
-
-
-
-
Y2: Will not be copied if the rated input voltage differs from the source inverter.
N: Will not be copied.
*3 Reserved for the maker. Do not set any data.
<Changing, validating, and saving function code data when the motor is running>
: Impossible, : Possible (Change data with keys and then
save/validate it with key), : Possible (Change and validate data with
keys and then save it with key)
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Data
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
*2
*2
Default setting
0.0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0.0
0
0
0
0
999
999
100.0
Default setting
1
0
2.0
3
0
0
0
0
0.01
1
1
0
2.0
3
0
0
0
0
0.01
0
0
0
Settings
Functions
Page 30

Functions Settings
■ Functions Settings
●o codes: Link Functions
Func.
Code
Command/feedback input
Speed control
(Pulse line input)
(Pulse compensation coefficient 1)
(Pulse compensation coefficient 2)
Feedback
(Pulse compensation coefficient 1)
(Pulse compensation coefficient 2)
Speed control
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Excessive speed deviation
PG abnormal error selection
DIO option
Transmission error
Bus setting parameter 1
Bus setting parameter 2
Bus setting parameter 3
Bus setting parameter 4
Bus setting parameter 5
Bus setting parameter 6
Bus setting parameter 7
Bus setting parameter 8
Bus setting parameter 9
Bus setting parameter 10
Writing function code allocation 1
Writing function code allocation 2
Writing function code allocation 3
Writing function code allocation 4
Writing function code allocation 5
Writing function code allocation 6
Writing function code allocation 7
Writing function code allocation 8
Read function code allocation 1
Read function code allocation 2
Read function code allocation 3
Read function code allocation 4
Read function code allocation 5
Read function code allocation 6
Read function code allocation 7
Read function code allocation 8
Read function code allocation 9
Read function code allocation 10
Read function code allocation 11
Read function code allocation 12
*1 When you make settings from the keypad, the incremental unit is restricted by the number of
digits that the LED monitor can display.
(Example) If the setting range is from -200.00 to 200.00, the incremental unit is as follows:
"1" for -200 to -100, "0.1" for -99.9 to -10.0, "0.01" for -9.99 to -0.01, "0.01" for 0.00 to 99.99,
and "0.1" for 100.0 to 200.0
*2 Symbols in the "Data copy" column
Y: Will be copied unconditionally.
Y1: Will not be copied if the rated capacity differs from the source inverter.
Name Data setting range
(Input form selection)
(Filter time constant)
(Encode pulse number)
(Filter time constant)
0, 1, 2, 10, 11, 12, 20, 21, 22
0.01 to 200.00
(P item)
0.000 to 5.000
(I item)
0.000 to 5.000
20 to 3600
0.000 to 5.000
1 to 9999
1 to 9999
(Feedback input)
(Encoder pulse number)
(Filter time constant)
20 to 3600
0.000 to 5.000
1 to 9999
1 to 9999
*3
*3
*3
(Output limiter)
(DI mode selection)
0.00 to 100.00
0.1
0.1
0 to 255
0 to 50
(Level)
0.0 to 10.0
(Timer)
0, 1, 2
0: 8 bit binary setting
1: 12 bit binary setting
4: BCD 3-digit setting 0 to 99.9
5: BCD 3-digit setting 0 to 999
(DO mode selection)
0: Output frequency (befor slip compensation)
1: Out put frequency (after slip compensation)
2: Output current
3: Output voltage
4: Output torque
5: Overload rate
6: Power consumption
7: PID feedback amount
9: DC link circuit voltage
13: Motor output
15: PID command (SV)
16: PID command (MV)
99: Individual signal output
(Operation selection)
(Timer selection)
0 to 15
0.0 to 60.0
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
0000H to FFFFH
Data
Min. Unit
-
1
-
0.01
1
1
1
1
1
1
0.01
1
1
1
1
0.1
1
-
-
1
0.1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
s
s
s
-
-
-
s
-
-
%
-
-
-
%
s
-
-
-
s
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.001
0.001
Y2: Will not be copied if the rated input voltage differs from the source inverter.
N: Will not be copied.
*3 Reserved for the maker. Do not set any data.
<Changing, validating, and saving function code data when the motor is running>
: Impossible, : Possible (Change data with keys and then
save/validate it with key), : Possible (Change and validate data with
keys and then save it with key)
copy
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
*2
Default setting
0
10.00
0.100
0.020
1024
0.005
1
1
1024
0.005
1
1
100.00
0
0
0
10
0.5
2
0
0
0
0.0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
Page 31

Peripheral Equipment Connection Diagrams
Remote keypad (Standard equipment)
If the back cover packed with the inverter is mounted
and the extension cable is used, remote operation
can be performed.
Multi-function keypad (to be announced soon)
TP-G1
This multi-function keypad has a large 5-digit 7segment LED with backlit LCD. (It cannot be
mounted on the inverter body.)
Arrestor
CN23
Used to absorb lightning surges that come in from
the power supply to protect all the equipment that is
connected to the power supply.
[Handled by Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
Power
supply
MCCB
or
GFCI
3
STR
V WU
Extension cable for
remote operation
This cable is used if
remote operation is to
be performed.
* Connector type: RJ-45
Radio noise reducing zero phase reactor
ACL-40B, ACL-74B
This is used to reduce noise. For the most part, control effects can be
obtained in frequency band of 1MHz or higher. Since the frequency
band where effects can be obtained is broad, it is effective as a
simple countermeasure against noise. If the wiring distance between
a motor and the inverter is short (65.6ft(20m) is a good guideline), it
is recommended that it be connected to the power supply side, and if
the distance exceeds 65.6ft(20m), connect it to the output side.
EMC compliant filter
EFL-
This is an exclusive filter used to comply with European
regulations in the EMC Directives (emissions). For details,
make connections in accordance with the "Installation Manual."
Power filter
-
RNF
This filter can be used for the same purpose as the
"EMC compliant filter" described above, but it does
not comply with the EMC Directives.
[Handled by Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
[Handled by Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
Output circuit filter
-
OFL-
This filter is connected to the output circuits of low noise type
inverters (carrier frequency 8kHz to 15kHz, 6kHz or greater in
40HP or higher circuits) and is used for the following purposes.
• Suppresses fluctuation of motor terminal voltages.
Prevents damage to motor insulation due to surge
voltage in 460V series inverters.
• Suppresses leak current in output side wiring.
Reduces leak current when multiple motors are run
side by side or when there is long distance wiring.
• Suppresses radiation noise and induction noise
from output side wiring.
If the wiring length in a plant, etc. is long, it is
effective as a countermeasure for noise reduction.
* When this filter is connected, be sure to set the carrier
frequency (F26) at 8kHz or higher (6kHz or higher for 40HP or
larger model).
OFL-
This filter is connected to the inverter output circuit for the
following purposes.
• Suppresses fluctuation of motor terminal voltages.
• Suppresses radiation noise and induction noise
*This filter is not limited by carrier frequency. Also, motor tuning
Surge suppression unit
SSU-
Prevents the motor insulation from being damaged by the
surge current of the inverter.
Surge absorber
S2-A-O: For electromagnetic contactors
S1-B-O: For mini control relays, timers
Absorbs surges and noise generated from other electrical devices to prevent
other equipment from malfunctioning.
[Handled by Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
Surge killer
FLS-323
Absorbs external surges and noise, preventing malfunction of electronic devices used in
control panels, etc.
-4A
Prevents damage to motor insulation due to surge
voltage in 460V serried inverters.
from output side wiring.
If the wiring length in a plant, etc. is long, it is
effective as a noise reduction countermeasure.
can be carried out with this option in the installed state.
-
TA-NS
Magnetic
Contactor
L2 L3L1
L2' L3'L1'
STR
V WU
Y1 Z1X1
Y2 Z2X2
STR G
M
3
Motor
Keypad connector
Interface board
L1/R L2/S L3/T P1DB P
Filter capacitor for radio noise reduction
NFM
Used to reduce noise.
It is effective in the AM radio frequency band.
* Do not use this in the inverter output side.
[Made by NIPPON CHEMI-CON, handled by
Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
Length[ft(m)]
Model
16.4(5)
CB-5S
9.8(3)
CB-3S
3.3(1)
CB-1S
(+)N(-)
UVW
Other
Inverters
Braking Resistor
-
DB
Used to improve the braking capacity
in cases where there is frequent
starting and stopping or when the load
is great from the inertial moment, etc.
M315KPD
Analog frequency meter (45, 60 angle)
TRM-45, FM-60
[Handled by Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
Frequency setting volume
RJ-13, WAR3W-1kΩ
[Handled by Fuji Electric Technica Co., Ltd.]
Inverter loader software for Windows
This software is used to set function codes in the
inverter from a personal computer, to manage data, etc.
USB/RS-485 converter, USB cable
[Handled by System Sacom Sales Corp.].
USB/RS-485
converter
Personal computer
■ Interface card
PG feedback card
OPC-E1-PG
Carries out frequency setting, speed control and position control
through input of pulse strings in accordance with PG feedback.
Applicable PG specifications
• Power supply: 50V, 100mA max
• Output Signal: Open collector or complementary
• Maximum output pulse frequency: 30 kHz or lower
DIO card
OPC-E1-DIO
Used in cases where you desire to add more DI and
DO signals to the FRENIC-Multi unit.
RS-485 communications card
OPC-E1-RS
Connects to a host device (master) such as a personal computer or
PLC for controlling FRENIC-Multi as a subordinate device (slave).
DeviceNet Board
OPC-E1-DEV
Used to set, change and check the function codes
necessary for operation commands, frequency setting,
monitoring and operation from the DeviceNet master.
•
Connection Nodes: Max. 64 units (including the master)
• MAC ID: 0 to 63
• Insulation: 500V DC (photo coupler insulation)
• Communications rates (kbps): 500, 250, 125
• Network power consumption: Max 50mA, 24V DC
CC-Link card
OPC-E1-CCL
GG
Enables the operation command, frequency setting,
function code change and data centralized management
by connecting this card to the CC-Link master unit.
PROFIBUS-DP card (OPC-E1-PDP)
With this interface card, you can do the following operations from
the PROFIBUS-DP master: issuing the operation command,
setting the frequency command, monitoring the operating status,
and changing and checking the settings in all the function codes.
DC Reactor
-
DCR
(For power supply coordination)
1) Used when the power supply's transformer
capacity is 500kVA or higher and is 10 or more
times the rated capacity of the inverter.
2) Used in cases where a thyristors transformer is
connected as a load on the same transformer.
* If a commutating reactor is not used in the thyristors
transformer, it is necessary to connect an AC reactor on the
inverter's input side, and so be sure to verify that this is done.
3) Used to prevent tripping in cases where an
inverter overvoltage trip is caused by opening and
closing of the phase advancing capacitor in the
power supply system
4) Used when there is a phase unbalance of 2% or
greater in the power supply voltage.
(For improving supplied power factor, reducing harmonics)
• Used to reduce the supplied harmonics current (or
improve power factor).
* Concerning reduction effects, please refer to the accompanying guidelines.
Interchangeability attachment (available soon)
MA-E1-
This attachment makes the latest inverters interchangeable
with older inverter models manufactured by Fuji Electric.
External cooling fan attachment (available soon)
PB-E1-
This is an attachment for relocating the inverter's
cooling fan to the outside of the control panel.
Settings
Functions
Connection Diagrams
Peripheral Equipment
Page 32

Options
■ Options
Braking resistor
[Standard type] (DB
[10% ED type] (DB
-2) (DB
-2C) (DB
-4)
-4C)
Fig. A Fig. B Fig. D Fig. EFig. C Fig. F
W
H1
0.28(7)
0.06
H
(1.6)
W
W1
H1
W
W1
H
0.28(7)
D
0.06
(1.6)
D
H1
0.28(7)
0.06(1.6)
W
H
H1
0.20(5)
D
0.05
(1.2)
Type, specifications and external dimensions [Unit: inch(mm)]
W
H
D
H1
0.28(7)
0.06
H
(1.6)
Voltage
230V series 460V series
DB0.75-2
Standard
DB2.2-2
type
DB3.7-2
DB5.5-2
W1
R0.14
W
(R3.5)
φ
0.59
(φ15)
DB7.5-2
H
H1
DB11-2
DB15-2
DB0.75-2C
10%ED
type
0.28(7)
DB2.2-2C
DB3.7-2C
DB5.5-2C
DB7.5-2C
DB11-2C
DB15-2C
0.06
D
(1.6)
D
DB0.75-4
-
-
DB2.2-4
-
-
DB3.7-4
-
-
DB5.5-4
-
-
DB7.5-4
-
-
DB11-4
-
-
DB15-4
DB0.75-4C
DB2.2-4C
DB3.7-4C
DB5.5-4C
DB7.5-4C
DB11-4C
DB15-4C
Dimensions [Unit: inch (mm)]
Fig
W H H1 D
W1
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
C
C
C
C
D
E
E
E
E
F
F
2.52(64)
2.99(76)
2.52(64)
2.99(76)
2.52(64)
3.54(90)
2.91(74)
3.54(90)
2.91(74)
5.59(142)
5.59(142)
5.59(142)
5.59(142)
1.69(43)
2.64(67)
2.64(67)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
12.20(310)
-
13.58(345)
-
18.50(470)
-
13.58(345)
-
18.50(470)
-
17.72(450)
3.54(90)
18.50(470)
2.91(74)
15.35(390)
3.54(90)
20.47(520)
2.91(74)
16.93(430)
2.91(74)
16.93(430)
2.91(74)
16.93(430)
2.91(74)
16.93(430)
2.91(74)
8.70(221)
-
7.40(188)
-
12.91(328)
-
-
14.88(378)
-
-
16.46(418)
-
18.11(460)
1.97(50)
22.83(580)
1.97(50)
11.61(295)
13.07(332)
17.91(455)
13.07(332)
17.91(455)
16.93(430)
17.91(455)
14.57(370)
19.49(495)
16.34(415)
16.34(415)
16.34(415)
16.34(415)
8.46(215)
6.77(172)
12.28(312)
14.25(362)
15.83(402)
17.32(440)
17.32(440)
2.64(67)
3.70(94)
2.64(67)
3.70(94)
2.64(67)
2.66(67.5)
2.64(67)
3.54(90)
2.64(67)
6.30(160)
6.30(160)
6.30(160)
6.30(160)
1.20(30.5)
2.17(55)
2.17(55)
3.07(78)
3.07(78)
5.51(140)
5.51(140)
Mass
[lbs(kg)]
2.9(1.3)
4.4(2.0)
4.4(2.0)
4.4(2.0)
3.7(1.7)
9.9(4.5)
9.9(4.5)
11(5.0)
11(5.0)
15(6.9)
15(6.9)
15(6.9)
15(6.9)
1.1(0.5)
1.8(0.8)
3.5(1.6)
6.4(2.9)
7.3(3.3)
9.5(4.3)
12(5.6)
Standard
type
10%ED
type
[Compact type] (TK80W120Ω)
Braking
resistor
type
(34±1)
1.34±0.04
0.79±0.04
(20±1)
Power
supply
voltage
Threephase
230V
Threephase
460V
Singlephase
230V
Threephase
230V
Threephase
460V
Singlephase
230V
4.92±0.06(125±1.5)
0.18
(4.5)
5.51±0.06(140±1.5)
5.91
(1)
0.04
FRNF50E1□-2U
FRN001E1□-2U
FRN002E1□-2U
FRN003E1□-2U
FRN005E1□-2U
FRN007E1□-2U
FRN010E1□-2U
FRN015E1□-2U
FRN020E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-4U
FRN001E1□-4U
FRN002E1□-4U
FRN003E1□-4U
FRN005E1□-4U
FRN007E1□-4U
FRN010E1□-4U
FRN015E1□-4U
FRN020E1□-4U
FRNF50E1□-7U
FRN001E1□-7U
FRN002E1□-7U
FRN003E1□-7U
FRNF50E1□-2U
FRN001E1□-2U
FRN002E1□-2U
FRN003E1□-2U
FRN005E1□-2U
FRN007E1□-2U
FRN010E1□-2U
FRN015E1□-2U
FRN020E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-4U
FRN001E1□-4U
FRN002E1□
FRN003E1□-4U
FRN005E1□-4U
FRN007E1□-4U
FRN010E1□-4U
FRN015E1□-4U
FRN020E1□-4U
FRNF50E1□-7U
FRN001E1□-7U
FRN002E1□-7U
FRN003E1□-7U
±0.06(
50±1.5)
Inverter type
-4U
19.69(500)
0.18
φ
Type
DB0.75-2 1 100
DB2.2-2 1 40
DB3.7-2
DB5.5-2
DB7.5-2
DB11-2
DB15-2
DB0.75-4 1
DB2.2-4 1 160
DB3.7-4 1 130
DB5.5-4
DB7.5-4
DB11-4
DB15-4
DB0.75-2 1 100
DB2.2-2 1 40
DB0.75-2C 1 100
DB2.2-2C 1 40
DB3.7-2C 1 33
DB5.5-2C
DB7.5-2C
DB11-2C
DB15-2C
DB0.75-4C 1
DB2.2-4C 1 160
DB3.7-4C
DB5.5-4C
DB7.5-4C
DB11-4C
DB15-4C
DB0.75-2C
DB2.2-2C 1
15.75
(400)
4.5)
φ
Protection tube
(
0.05-0.16
(1.25-4)
Qty.
Resistance
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 130
1
1
1
1
1
[Ω]
8.6
200
34.4
8.6
200
34.4
100
33
20
15
10
80
60
40
20
15
10
80
60
40
40
Max braking torque [%]
50 [Hz] 60 [Hz]
[lb-in (N •m)] [lb-in (N •m)]
35.6(4.02)
67.0(7.57)
150
133(15.0)
195(22.0)
328(37.1)
481(54.3)
658(74.4)
150
956(108)
1301(147)
35.6(4.02)
67.0(7.57)
133(15.0)
150
195(22.0)
328(37.1)
481(54.3)
651(73.6)
150
956(108)
1301(147)
35.6(4.02)
67.0(7.57)
150
133(15.0)
195(22.0)
35.6(4.02)
67.0(7.57)
150
133(15.0)
195(22.0)
328(37.1)
481(54.3)
659(74.4)
150
956(108)
1301(147)
35.6(4.02)
67.0(7.57)
133(15.0)
150
195(22.0)
328(37.1)
481(54.3)
651(73.5)
150
956(108)
1301(147)
35.6(4.02)
67.0(7.57)
150
133(15.0)
195(22.0)
29.4(3.32)
55.3(6.25)
110(12.4)
161(18.2)
270(30.5)
358(40.5)
545(61.6)
792(89.5)
1080(122)
29.4(3.32)
55.3(6.25)
110(12.4)
161(18.2)
270(30.5)
398(45.0)
545(61.6)
792(89.5)
1080(122)
29.4(3.32)
55.3(6.25)
110(12.4)
161(18.2)
29.4(3.32)
55.3(6.25)
110(12.4)
161(18.2)
270(30.5)
359(40.5)
545(61.6)
792(89.5)
1080(122)
29.4(3.32)
55.3(6.25)
110(12.4)
161(18.2)
270(30.5)
398(45.0)
545(61.6)
792(89.5)
1080(122)
29.4(3.32)
55.3(6.25)
110(12.4)
161(18.2)
Continuous braking
(100% torque conversion value)
Discharging
17
34
33
37
55
37
55
75
17
34
33
37
55
38
55
75
17
34
33
Braking time
9
9
9
capacity [HPs]
50
55
140
55
37
55
75
50
55
140
55
38
55
75
50
55
[Each cycle is less than 100[s].]
Average allowable
[s]
0.06(0.044)
0.09(0.068)
45
0.10(0.075)
0.10(0.077)
30
0.12(0.093)
20
0.19(0.138)
20
0.25(0.188)
10
0.37(0.275)
0.50(0.375)
0.06(0.044)
45
0.09(0.068)
0.10(0.075)
30
0.10(0.077)
20
0.12(0.093)
20
1.53(1.138)
0.25(0.188)
10
0.37(0.275)
0.50(0.375)
0.06(0.044)
45
0.09(0.068)
0.10(0.075)
30
0.10(0.077)
250
0.1(0.075)
133
73
0.15(0.110)
50
75
0.25(0.185)
20
0.37(0.275)
0.50(0.375)
10
0.74(0.55)
1.01(0.75)
250
133
73
0.15(0.110)
50
75
0.25(0.185)
20
0.37(0.275)
0.50(0.375)
10
0.74(0.55)
1.01(0.75)
250
0.10(0.075)
133
73
0.15(0.110)
50
Repetitive braking
Duty cycle
loss [HP]
6.71(5)
[%ED]
22
18
10
7
5
5
5
5
5
22
18
10
7
5
5
5
5
5
22
18
10
7
37
20
14
10
10
10
10
10
10
37
20
14
10
10
10
10
10
10
37
20
14
10
□: S or E S: standard E: EMC filter built-in type
Power source
voltage
Threephase
230V
Type
Capacity [HP]
Resistance
Resistance [Ω]
Applicable inverter
Applied motor output [HP]
Average braking torque [%]
Allowable duty cycle [%]
Allowable
limits
Continuous allowable braking time
FRNF50
E1□-2U
1/2
150
15
15s
FRN001
E1□-2U
1
130
5
15s
TK80W120Ω
0.11
120
FRN002
E1□-2U
2
100
5
10s
FRN003
E1□-2U
3
65
5
10s
FRN005
E1□-2U
5
45
5
10s
NOTE: This resistor is not applicable to three-phase 460V series and single-phase 230V series.
Page 33

DC REACTOR
Power
W1
W
4xG mounting hole
D1
Applicable
supply
motor rating
voltage
D
H
Threephase
230V
D2
Threephase
460V
Single-
phase
230V
[HP]
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
1/2
1
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
2
3
Inverter type
FRNF12E1□-2U
FRNF25E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-2U
FRN001E1□-2U
FRN002E1□-2U
FRN003E1S-2U
FRN005E1□-2U
FRN007E1□-2U
FRN010E1□-2U
FRN015E1□-2U
FRN020E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-4U
FRN001E1□-4U
FRN002E1□-4U
FRN003E1□-4U
FRN005E1□-4U
FRN007E1□-4U
FRN010E1□-4U
FRN015E1□-4U
FRN020E1□-4U
FRNF12E1□-7U
FRNF25E1□-7U
FRNF50E1□-7U
FRN001E1□-7U
FRN002E1□-7U
FRN003E1□-7U
REACTOR
type
DCR2-0.2
DCR2-0.4
DCR2-0.75
DCR2-1.5
DCR2-2.2
DCR2-3.7
DCR2-5.5
DCR2-7.5
DCR2-11
DCR2-15
DCR4-0.4
DCR4-0.75
DCR4-1.5
DCR4-2.2
DCR4-3.7
DCR4-5.5
DCR4-7.5
DCR4-11
DCR4-15
DCR2-0.2
DCR2-0.4
DCR2-0.75
DCR2-1.5
DCR2-2.2
DCR2-3.7
The code in□represents followings; S: standard model, E: EMC filter built-in type
■ Multi-function keypad (TP-G1) ■ Extension cable for remote operation(CB-□S)
Dimensions Unit: inch (mm)
W1
D
D1
D2
0.59(15)
0.79(20)
0.79(20)
0.39(10)
0.79(20)
0.79(20)
0.91(23)
0.94(24)
0.59(15)
0.59(15)
0.79(20)
0.79(20)
0.59(15)
0.79(20)
0.79(20)
0.94(24)
0.94(24)
0.59(15)
0.20(5)
0.59(15)
0.79(20)
0.79(20)
0.39(10)
0.79(20)
H
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
4.33(110)
4.33(110)
5.12(130)
5.12(130)
5.39(137)
7.09(180)
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
4.33(110)
4.33(110)
4.33(110)
5.12(130)
5.12(130)
6.73(171)
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
3.70(94)
4.33(110)
4.33(110)
W
2.60(66) 2.20(56) 3.54(90) 2.83(72) 0.20(5) 3.70(94)
2.60(66)
2.20(56)
3.54(90)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
3.39(86)
3.39(86)
4.37(111)
4.37(111)
4.37(111)
5.75(146)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
3.39(86)
3.39(86)
4.37(111)
4.37(111)
5.75(146)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
2.60(66)
3.39(86)
3.39(86)
2.20(56)
2.20(56)
2.80(71)
2.80(71)
3.74(95)
3.74(95)
3.74(95)
4.88(124)
2.20(56)
2.20(56)
2.20(56)
2.80(71)
2.80(71)
2.80(71)
3.74(95)
3.74(95)
4.88(124)
2.20(56)
2.20(56)
2.20(56)
2.20(56)
2.80(71)
2.80(71)
3.54(90)
3.54(90)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
4.72(120)
3.54(90)
3.54(90)
3.54(90)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
4.72(120)
3.54(90)
3.54(90)
3.54(90)
3.54(90)
3.94(100)
3.94(100)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.78(96)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
3.78(96)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
2.83(72)
3.15(80)
3.15(80)
Terminal
Mounting hole
0.20x0.31
(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.24x0.43(6x11)
0.24x0.43(6x11)
0.24x0.43(6x11)
0.28x0.43(7x11)
0.28x0.43(7x11)
0.28x0.43(7x11)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.24x0.35(6x9)
0.24x0.35(6x9)
0.24x0.35(6x9)
0.28x0.43(7x11)
0.28x0.43(7x11)
0.28x0.43(7x11)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.20x0.31(5.2x8)
0.24x0.43(6x11)
0.24x0.43(6x11)
Mass
[lbs (kg)]
hole
M4 1.8(0.8)
M4
2.2(1.0)
M4
3.1(1.4)
M4
3.5(1.6)
M4
4.0(1.8)
M4
5.7(2.6)
M5
7.9(3.6)
M5
8.4(3.8)
M6
9.5(4.3)
M6
13(5.9)
M4
2.2(1.0)
M4
3.1(1.4)
M4
3.5(1.6)
M4
4.4(2.0)
M4
5.7(2.6)
M4
5.7(2.6)
M5
9.3(4.2)
M5
9.5(4.3)
M5
13(5.9)
M4
1.8(0.8)
M4
2.2(1.0)
M4
3.1(1.4)
M4
3.5(1.6)
M4
4.0(1.8)
M4
5.7(2.6)
operation (optional) enables remote operation, function code data
setting, monitoring, etc. from the keypad keys and panel.
The keypad is equipped with an LCD panel (with backlight) and the
copy function (for three inverter data).
[Unit: inch(mm)]
5.06(128.5)
3.15(80)
0.72
(18.2)
0.58
0.59
A
Inside
panel
(14.615)
(15.08)
2.40(61) 0.37
2×M3
(9.5)
(13.775)
0.54
0.32
(8.17)
4.12(104.6)
0.41
Backside view
0.67
(16.98)
2.12(53.8)
0.46
(11.68)
0.45
(11.4)
(15.24)
0.06
0.32
(8.1)
(23)
(1)
3.15(80)
2.28(58)
Panel cut part
0.18
(4.5)
0.41
(10.5)
(10.5)
This is used to connect the inverter and the remote keypad.Connection with FRENIC-Multi using an extension cable for remote
0.32(8)
0.04(1)
L
Connector type: RJ-45
Optional type
CB-5S
CB-3S
CB-1S
Length [ft(m)]
16.4(5)
9.8(3)
3.3(1)
Options
5.06(128.5)
24
Dimensions of panel cutting
(viewed from "A")
2.40(61)
4.12(104.6)
0.37
(9.5)
Page 34

Options
■ Interface card
RS-485 communication card (OPC-F1-RS)
Connection with a host (master) device such as PC or PLC allows you
to control FRENIC-Multi as a subordinate (slave) device. (The card is
added to the RS-485 communication devices for FRENIC-Multi.)
NOTE: This option card cannot be connected with the keypad or a
support loader.
●Number of connectable devices: 1 host device and 31 inverters
●Number of ports: 2 ports
●Electric specifications: EIA RS-485
●Synchronization method: Start/stop
●Communication method: Half-duplex
●Transmission speed (bps): 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 and 38400
●Maximum communication distance: 1600ft(500m)
●Terminating resistor: Built-in
PG interface card (OPC-E1-PG) for 5V
When this card is built in the inverter, positioning accuracy will
improve, resulting in reduced positioning time and improved
measuring accuracy by the measuring instrument.
PG interface card (OPC-E1-PG3) for 12V
Incorporating the interface card in the inverter permits accurate
speed control and position control.The interface card can be used
simultaneously with the communication bus for FRENIC-Multi series,
optional DeviceNet card (OPC-E1-DEV), CC-Link card (OPC-E1CCL), and PROFIBUS-DP card (OPC-E1-PDP).
Front installation type External dimensions
■
●OPC-E1-CCL,OPC-E1-DEV ●OPC-E1-DIO
3.13(79.6) 1.87(47.5) 0.43
Built-in type
Built-in type
Built-in type
(11)
DeviceNet card (OPC-E1-DEV)
Connection with the DeviceNet master unit permits application to
the system that requires operation commands and frequency
settings.
DIO card (OPC-E1-DIO)
This card allows frequency setting or status monitoring by
exchanging digital signal data with the host controller.
SY card (synchronized operation)
Using this card allows synchronized operation of the two motors
having a pulse generator (PG).
PROFIBUS-DP card (OPC-E1-PDP)
Connection with the PROFIBUS-DP card permits application to
the system that requires operation commands and frequency
settings.
Note1) An external power supply of 24V is needed to use a separately sold
option card.
Note2) The inverter that can be used with the SY card includes special
specifications. When ordering the SY card, please order together
with the inverter in a set.
Front installation type
Front installation type
NOTE2)
Built-in type
Front installation type
[Unit: inch(mm)]
3.13(79.6) 1.87(47.5) 0.43
(11)
0.16
( 4)
5.0(127)
0.33
(8.4)
0.16
( 4)
5.0(127)
Page 35

■ External cooling attachment
External cooling attachment (PB-E1-7.5/PB-F1-15)
This attachment allows installation of the inverter heat sink outside the panel. With this attachment, it is possible to improve the cooling
effect and to make the panel more compact.
7.56(192) 3.19(81)
0.55(14) 0.55(14)
2x 0.24
(2x 6)
2xM5
6.46(164)
1.24
0.28
(31.5)
3.00(76.3)
(7)
1.87
(47.5)
(1.2)
2x 0.39
(2x 10)
2xM8
(33)
10.31(262)
1.3
7.72(196)
(33)
1.3
(10)
0.39
(37)
2.38
1.46
3.88(98.5)
(60.5)
3.80(96.5)
0.08(2)
9.31(236.5)
7.17(182)
6.46(164)
9.31(236.5)
(5)
5.94(151)
0.20
6.85(174)
Panel machining drawing
1.14
7.64(194)0.41
4×M5
(29)
9.19(233.5)
(10.5)
9.90(251.5)
Panel installation surface
Optional type
PB-E1-7.5
10.83(275)
10.83(275)0.30(7.5)
Applicable inverter type
FRN007E1S-2/4U
FRN010E1S-2/4U
Panel machining drawing
■ Compatible attachment
Compatible attachment (MA-E1-□□)
This attachment allows replacing our previous model with the new one without machining.
MA-E1-0.75 MA-E1-3.7
29.5(75)
5.04(128)
0.44
(11.3)
0.31
(7.8)
6.69(170)
7.09(180)
0.28(7)
11.65(296)
8.74(222)
7.72(196)
6.85(174)
8.43(214)
1.54
(39)
8.39(213)
0.83(21)
4×M8
10.75(273)
Panel installation surface
Optional type
Applicable inverter type
PB-F1-15
Optional type Applicable inverter type Previous inverter type
・MA-E1-0.75
・MA-E1-3.7
*The table below shows the previous and new inverters with are
compatible and do not need attachment for replacement.
FRNF12E1S-2U
FRNF25E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-2U
FRN001E1S-2U
FRNF12E1S-7U
FRNF25E1S-7U
FRNF50E1S-7U
FRN005E1S-2U
FRN005E1S-4U
FRN003E1S-7U
Applicable inverter type Previous inverter type
FRN002E1S-2U
FRN003E1S-2U
FRNF50E1S-4U
FRN001E1S-4U
FRN002E1S-4U
FRN003E1S-4U
FRN002E1S-7U
FRN003E1S-7U
FRN007E1S-2U
FRN007E1S-4U
FRN010E1S-2U
FRN010E1S-4U
FVR1.5E11S-2
FVR2.2E11S-2
FVR0.4E11S-4
FVR0.75E11S-4
FVR1.5E11S-4
FVR2.2E11S-4
FVR1.5E11S-7
FVR2.2E11S-7
FVR5.5E11S-2
FVR5.5E11S-4
FVR7.5E11S-2
FVR7.5E11S-4
FRN015E1S-2/4U
FRN020E1S-2/4U
FVR0.1E11S-2
FVR0.2E11S-2
FVR0.4E11S-2
FVR0.75E11S-2
FVR0.1E11S-7
FVR0.2E11S-7
FVR0.4E11S-7
FVR3.7E11S-2
FVR3.7E11S-4
FVR2.2E11S-7
Options
Page 36

Options
■ Devices requiring wiring
DC Reactor
[P (+), DB
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
B/
*1
For
For connection
control
with Inverter
[ G]
circuit
0.75
2.0
to
1.25
3.5
5.5
8.0
0.75
2.0
to
1.25
3.5
0.75
2.0
to
1.25
and SAR/ models.
Power
Applicable
supply
motor rating
voltage
(HP)
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
Three-
phase
230V
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
1/2
1
2
Three-
phase
460V
3
5
7.5
10
15
20
1/8
1/4
Single-
phase
230V
1/2
1
2
3
The code in□represents followings; S: standard model, E: EMC filter built-in type
Note1) An external power supply of 24V is needed to use a separately sold option card.
Note2) The inverter that can be used with the SY card includes special specifications. When ordering the SY card, please order together with the inverter in a set.
• The frame and series of the MCCB and GFCI models vary according to the transformer capacity and so on of the equipment. Choose the optimum ones according to the catalog and technical data of the
circuit breaker and others.
• Choose the optimum rated sensitive current of the ELCB according to technical data, too. The rated currents of the MCCB and GFCI specified in this table indicate those of SA
• Description in the above table may vary for different ambient temperatures, power supply voltages or other conditions.
*1: Use crimp terminals equipped with insulation sheath or those equipped with an insulation tube or the like.
The cable to be used is 600V-insulated cable with an allowable temperature of 75˚C(167˚F). The ambient temperature is assumed to be 50˚C(122˚F).
Inverter type
FRNF12E1□-2U
FRNF25E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-2U
FRN001E1□-2U
FRN002E1□-2U
FRN003E1□-2U
FRN005E1□-2U
FRN007E1□-2U
FRN010E1□-2U
FRN015E1□-2U
FRN020E1□-2U
FRNF50E1□-4U
FRN001E1□-4U
FRN002E1□-4U
FRN003E1□-4U
FRN005E1□-4U
FRN007E1□-4U
FRN010E1□4U
FRN015E1□-4U
FRN020E1□-4U
FRNF12E1□-7U
FRNF25E1□
-7U
FRNF50E1□-7U
FRN001E1□-7U
FRN002E1□-7U
FRN003E1□-7U
MCCB, GFCI
rated current (A)
With DCR
Without DCR
5
10
10
20
30
40
50
75
15
20
30
50
75
100
125
5
10
15
10
15
20
30
40
20
30
40
50
60
5
10
10
15
20
15
20
30
Magnetic contactor (MC)
Input circuit
With DCR
5
SC-05
SC-4-0
SC-5-1
SC-N1
SC-N2
5
SC-05
SC-4-0
SC-5-1
5
SC-05
Without DCR
SC-05
SC-4-0
SC-5-1
SC-N1
SC-N2S
SC-N3
SC-05
SC-4-0
SC-N1
SC-05
SC-5-1
Output
circuit
SC-05
SC-4-0
SC-5-1
SC-N1
SC-N2
SC-05
SC-4-0
SC-5-1
SC-05
Main power input
(L1/R, L2/S, L3/T)
With DCR
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.5
14.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Recommended cable size (mm2)
Inverter
DC Reactor
output
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
3.5
8.0
14.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
[P1, P (+)]
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.5
8.0
14.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.5
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Without DCR
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.5
14.0
22.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.5
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
[U, V, W]
Page 37

Warranty
When requesting an estimate and placing your orders for the products included in these materials, please be aware that any
items such as specifications which are not specifically mentioned in the contract, catalog, specifications or other materials will
be as mentioned below.
In addition, the products included in these materials are limited in the use they are put to and the place where they can be used,
etc., and may require periodic inspection. Please confirm these points with your sales representative or directly with this
company.
Furthermore, regarding purchased products and delivered products, we request that you take adequate consideration of the
necessity of rapid receiving inspections and of product management and maintenance even before receiving your products.
1. Free of Charge Warranty Period and Warranty Range
1-1 Free of charge warranty period
(1) The product warranty period is ''1 year from the date of purchase'' or 24 months from the manufacturing date imprinted on
(2) However, in cases where the use environment, conditions of use, use frequency and times used, etc., have an effect on
(3) Furthermore, the warranty period for parts restored by Fuji Electric's Service Department is ''6 months from the date that
1-2 Warranty range
(1) In the event that breakdown occurs during the product's warranty period which is the responsibility of Fuji Electric, Fuji
To all our customers who purchase
Fuji Electric FA Components & Systems' products:
Please take the following items into consideration when placing your order.
the name place, whichever date is earlier.
product life, this warranty period may not apply.
repairs are completed.''
Electric will replace or repair the part of the product that has broken down free of charge at the place where the product
was purchased or where it was delivered. However, if the following cases are applicable, the terms of this warranty may
not apply.
1) The breakdown was caused by inappropriate conditions, environment, handling or use methods, etc. which are not
specified in the catalog, operation manual, specifications or other relevant documents.
2) The breakdown was caused by the product other than the purchased or delivered Fuji's product.
3) The breakdown was caused by the product other than Fuji's product, such as the customer's equipment or software
design, etc.
4) Concerning the Fuji's programmable products, the breakdown was caused by a program other than a program
supplied by this company, or the results from using such a program.
5) The breakdown was caused by modifications or repairs affected by a party other than Fuji Electric.
6) The breakdown was caused by improper maintenance or replacement using consumables, etc. specified in the
operation manual or catalog, etc.
7) The breakdown was caused by a chemical or technical problem that was not foreseen when making practical
application of the product at the time it was purchased or delivered.
8) The product was not used in the manner the product was originally intended to be used.
9) The breakdown was caused by a reason which is not this company's responsibility, such as lightning or other disaster.
(2) Furthermore, the warranty specified herein shall be limited to the purchased or delivered product alone.
(3) The upper limit for the warranty range shall be as specified in item (1) above and any damages (damage to or loss of
machinery or equipment, or lost profits from the same, etc.) consequent to or resulting from breakdown of the purchased
or delivered product shall be excluded from coverage by this warranty.
1-3. Trouble diagnosis
As a rule, the customer is requested to carry out a preliminary trouble diagnosis. However, at the customer's request, this
company or its service network can perform the trouble diagnosis on a chargeable basis. In this case, the customer is asked
to assume the burden for charges levied in accordance with this company's fee schedule.
2. Exclusion of Liability for Loss of Opportunity, etc.
Regardless of whether a breakdown occurs during or after the free of charge warranty period, this company shall not be
liable for any loss of opportunity, loss of profits, or damages arising from special circumstances, secondary damages,
accident compensation to another company, or damages to products other than this company's products, whether foreseen
or not by this company, which this company is not be responsible for causing.
3. Repair Period after Production Stop, Spare Parts Supply Period (Holding Period)
Concerning models (products) which have gone out of production, this company will perform repairs for a period of 7 years
after production stop, counting from the month and year when the production stop occurs. In addition, we will continue to
supply the spare parts required for repairs for a period of 7 years, counting from the month and year when the production
stop occurs. However, if it is estimated that the life cycle of certain electronic and other parts is short and it will be difficult to
procure or produce those parts, there may be cases where it is difficult to provide repairs or supply spare parts even within
this 7-year period. For details, please confirm at our company's business office or our service office.
4. Transfer Rights
In the case of standard products which do not include settings or adjustments in an application program, the products shall
be transported to and transferred to the customer and this company shall not be responsible for local adjustments or trial
operation.
5. Service Contents
The cost of purchased and delivered products does not include the cost of dispatching engineers or service costs.
Depending on the request, these can be discussed separately.
Options
Warranty
6. Applicable Scope of Service
Above contents shall be assumed to apply to transactions and use of the country where you purchased the products.
Consult the local supplier or Fuji for the detail separately.
Page 38

MEMO
Page 39

MEMO
Page 40

When running general-purpose motors
• Driving a 460V general-purpose motor
When driving a 400V general-purpose motor with
an inverter using extremely long cables, damage to
the insulation of the motor may occur. Use an
output circuit filter (OFL) if necessary after checking
with the motor manufacturer. Fuji's motors do not
require the use of output circuit filters because of
their reinforced insulation.
•
Torque characteristics and temperature rise
When the inverter is used to run a general-purpose
motor, the temperature of the motor becomes
higher than when it is operated using a commercial
power supply. In the low-speed range, the cooling
effect will be weakened, so decrease the output
torque of the motor. If constant torque is required in
the low-speed range, use a Fuji inverter motor or a
motor equipped with an externally powered
ventilating fan.
• Vibration
When the motor is mounted to a machine,
resonance may be caused by the natural
frequencies, including that of the machine.
Operation of a 2-pole motor at 60Hz or more may
cause abnormal vibration.
* Study use of tier coupling or dampening rubber.
* It is also recommended to use the inverter jump
frequency control to avoid resonance points.
• Noise
When an inverter is used with a general-purpose
motor, the motor noise level is higher than that with
a commercial power supply. To reduce noise, raise
carrier frequency of the inverter. High-speed
operation at 60Hz or more can also result in more
noise.
When running special motors
• High-speed motors
When driving a high-speed motor while setting the
frequency higher than 120Hz, test the combination
with another motor to confirm the safety of highspeed motors.
• Explosion-proof motors
When driving an explosion-proof motor with an
inverter, use a combination of a motor and an
inverter that has been approved in advance.
• Submersible motors and pumps
These motors have a larger rated current than
general-purpose motors. Select an inverter whose
rated output current is greater than that of the
motor.
These motors differ from general-purpose motors in
thermal characteristics. Set a low value in the
thermal time constant of the motor when setting the
electronic thermal facility.
• Brake motors
For motors equipped with parallel-connected
brakes, their braking power must be supplied from
the primary circuit (commercial power supply). If the
brake power is connected to the inverter power
output circuit (secondary circuit) by mistake,
problems may occur.
Do not use inverters for driving motors equipped
with series-connected brakes.
• Geared motors
If the power transmission mechanism uses an oil-
NOTES
lubricated gearbox or speed changer/reducer, then
continuous motor operation at low speed may
cause poor lubrication. Avoid such operation.
• Synchronous motors
It is necessary to use software suitable for this
motor type. Contact Fuji for details.
• Single-phase motors
Single-phase motors are not suitable for inverterdriven variable speed operation. Use three-phase
motors.
* Even if a single-phase power supply is available,
use a three-phase motor as the inverter provides
three-phase output.
Environmental conditions
• Installation location
Use the inverter in a location with an ambient
temperature range of -10 to 50˚C(14 to 122˚F).
The inverter and braking resistor surfaces become
hot under certain operating conditions. Install the
inverter on nonflammable material such as metal.
Ensure that the installation location meets the
environmental conditions specified in "Environment"
in inverter specifications.
Combination with peripheral devices
•
Installing a molded case circuit
breaker (MCCB)
Install a recommended molded case circuit breaker
(MCCB) or a groud-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) in
the primary circuit of each inverter to protect the
wiring. Ensure that the circuit breaker capacity is
equivalent to or lower than the recommended
capacity.
• Installing a magnetic contactor (MC)
in the output (secondary) circuit
If a magnetic contactor (MC) is mounted in the
inverter's secondary circuit for switching the motor
to commercial power or for any other purpose,
ensure that both the inverter and the motor are fully
stopped before you turn the MC on or off. Remove
the surge killer integrated with the MC.
• Installing a magnetic contactor (MC)
in the input (primary) circuit
Do not turn the magnetic contactor (MC) in the
primary circuit on or off more than once an hour as
an inverter fault may result. If frequent starts or
stops are required during motor operation, use
FWD/REV signals.
• Protecting the motor
The electronic thermal facility of the inverter can
protect the motor. The operation level and the motor
type (general-purpose motor, inverter motor) should
be set. For high-speed motors or water-cooled
motors, set a small value for the thermal time
constant to protect the motor.
If you connect the motor thermal relay to the motor
with a long cable, a high-frequency current may
flow into the wiring stray capacitance. This may
cause the relay to trip at a current lower than the
set value for the thermal relay. If this happens,
lower the carrier frequency or use the output circuit
filter (OFL).
•
Discontinuance of power-factor correcting capacitor
Do not mount power factor correcting capacitors in
the inverter (primary) circuit. (Use the DC
REACTOR to improve the inverter power factor.) Do
not use power factor correcting capacitors in the
inverter output circuit (secondary). An overcurrent
trip will occur, disabling motor operation.
• Discontinuance of surge killer
Do not mount surge killers in the inverter output
(secondary) circuit.
• Reducing noise
Use of a filter and shielded wires are typical
measures against noise to ensure that EMC
Directives are met.
• Measures against surge currents
If an overvoltage trip occurs while the inverter is
stopped or operated under a light load, it is
assumed that the surge current is generated by
open/close of the phase-advancing capacitor in the
power system.
We recommend connecting a DC REACTOR to the
inverter.
• Megger test
When checking the insulation resistance of the
inverter, use a 500V megger and follow the
instructions contained in the Instruction Manual.
Wiring
• Wiring distance of control circuit
When performing remote operation, use the twisted
shield wire and limit the distance between the
inverter and the control box to 65.6ft(20m).
• Wiring length between inverter and motor
If long wiring is used between the inverter and the
motor, the inverter will overheat or trip as a result of
overcurrent (high-frequency current flowing into the
stray capacitance) in the wires connected to the
phases. Ensure that the wiring is shorter than
164ft(50m). If this length must be exceeded, lower
the carrier frequency or mount an output circuit filter
(OFL).
• Wiring size
Select cables with a sufficient capacity by referring
to the current value or recommended wire size.
• Wiring type
Do not use multicore cables that are normally used
for connecting several inverters and motors.
• Grounding
Securely ground the inverter using the grounding
terminal.
Selecting inverter capacity
• Driving general-purpose motor
Select an inverter according to the applicable motor
ratings listed in the standard specifications table for
the inverter. When high starting torque is required
or quick acceleration or deceleration is required,
select an inverter with a capacity one size greater
than the standard.
• Driving special motors
Select an inverter that meets the following condition:
Inverter rated current > Motor rated current.
Transportation and storage
When transporting or storing inverters, follow the
procedures and select locations that meet the
environmental conditions that agree with the
inverter specifications.
Fuji Electric Corp. of America
47520 Westinghouse Drive Fremont, CA 94539, U.S.A.
Tel.+1-510-440-1060 Fax.+1-510-440-1063
Information in this catalog is subject to change without notice.
http://www.fujielectric.com
Printed in Japan 2007-7 (G07/G07) CM 30 FIS
Printed on 100% recycled paper
 Loading...
Loading...