Page 1

General Specifications
C2
FECA-TE-2015
Page 2
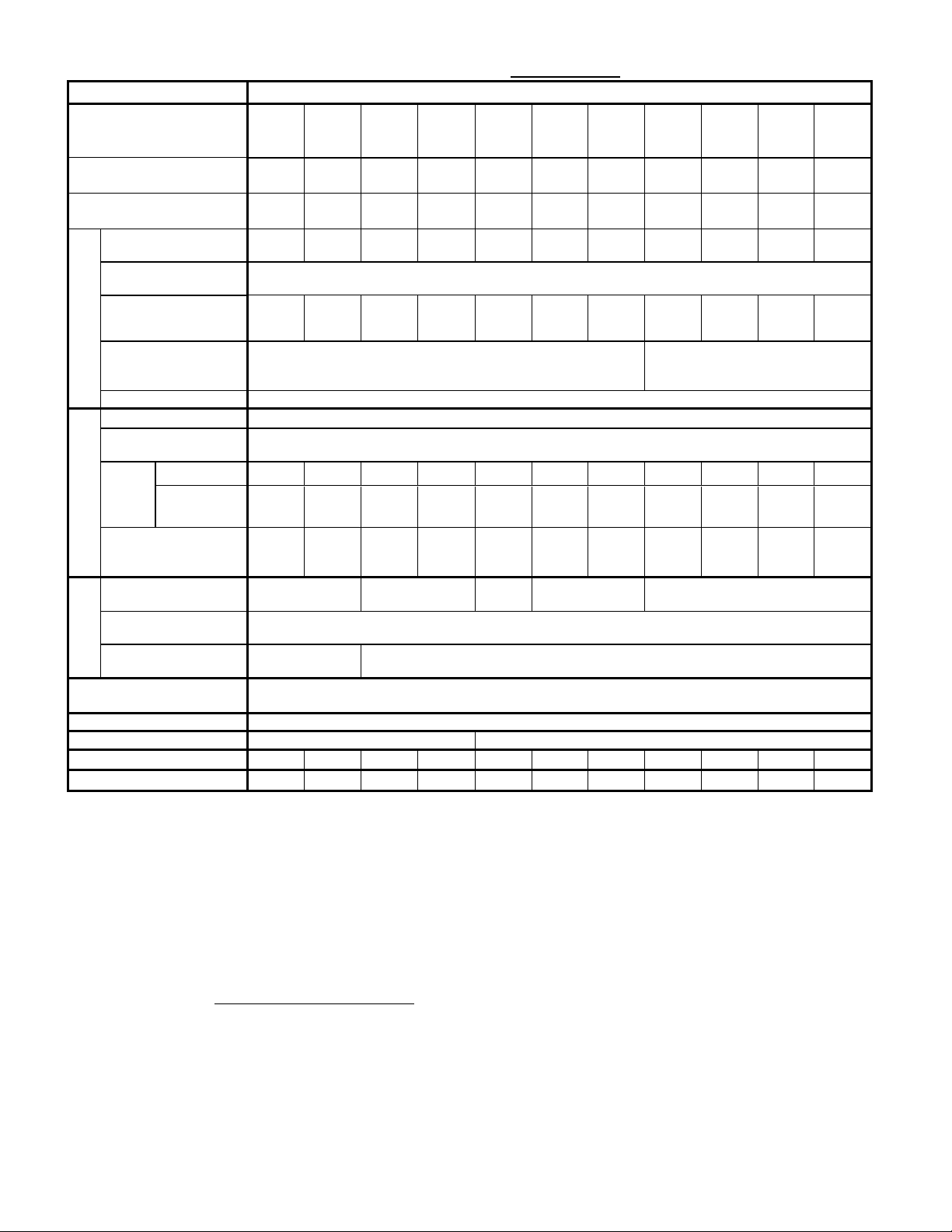
2
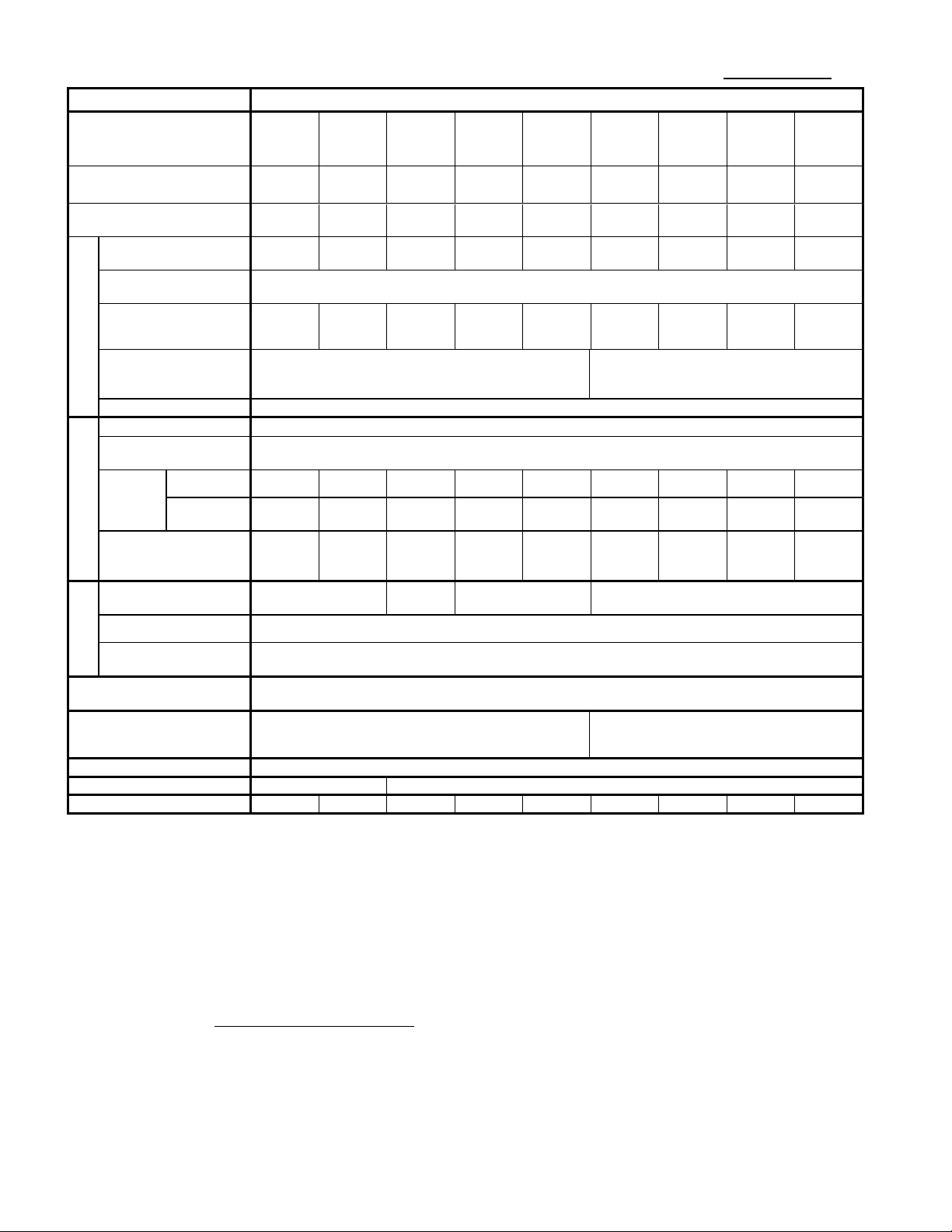
1. Standard Specifications
Items
Specifications
Type
(FRN□□□C2S-2△、
△ = A,U)
0001
0002
0004
0006
0010
0012
0020
0025
0033
0047
0060
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[kW]
(△=A)
0.1
0.2
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
3.7
5.5
7.5
11
15
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[HP]
(△=U)
1/8
1/4
1/2 1 2 3 5
7.5
10
15
20
Output ratings
Rated capacity
*2)
[kVA]
0.30
0.57
1.3
2.0
3.5
4.5
7.2
9.5
12
17
22
Rated voltage
*3)
[V]
Three-phase 200~240V (With AVR)
Rated current [A]
0.8
(0.7)
*4)
1.5
(1.4)
*4)
3.5
(2.5)
*4)
5.5
(4.2)
*4)
9.2
(7.0)
*4)
12.0
(10.0)
*4)
19.1
(16.5)
*4)
25.0
(23.5)
*10)
33.0
(31.0)
*10)
47.0
(44.0)
*10)
60.0
(57.0)
*10)
Overload capability
150% of rated current for 1min
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s (If
the rated current is in parenthesis)
150% of rated current for 1min or
200% of rated current for 0.5s
Rated frequency
50, 60Hz
Input ratings
Main power supply
Three-phase 200~240V,50/60Hz
Voltage/frequency
variations
Voltage: +10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance: 2% or less
*7)
), Frequency: +5 to -5%
Rated
current
*8)
[A]
With DCR
0.57
0.93
1.6
3.0
5.7
8.3
14.0
21.1
28.8
42.2
57.6
Without DCR
1.1
1.8
3.1
5.3
9.5
13.2
22.2
31.5
42.7
60.7
80.0
Required power
supply capacity
*5)
[kVA]
0.2
0.3
0.6
1.1
2.0
2.9
4.9
7.4
10
15
20
Braking
Braking torque
*6)
[%]
150
100
50
30
20
DC braking
Starting frequency
*9)
: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Transistor for
braking resistor
-
Built-in
Applicable safety
standards
UL508C, EN 61800-5-1:2007
Enclosure
IP20 (IEC 60529:1989) / UL open type (UL50)
Cooling method
Natural cooling
Fan cooling
Mass [kg] (△=A)
0.6
0.6
0.7
0.8
1.7
1.7
2.5
3.1
3.1
4.5
4.5
Mass [lbs] (△=U)
1.3
1.3
1.5
1.8
3.7
3.7
5.5
6.8
6.8
9.8
9.8
2004):361800 (IEC 67%
[V] voltageaverage phase-Three
[V] voltageMin.[V] voltageMax.
unbalance Voltage
1) Three-phase 200V series(0.1 to 15kW / 1/8 to 20HP) (△ = A, U only)
*1) Fuji Electric's/US 4-pole standard motor.
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as220V for three-phase 200V series.
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
*4) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency
is set to 3kHz or above or ambient temperature exceeds 40℃(104°F).
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates from 60Hz.(Varies with the efficiency of the motor).
*7)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an AC REACTOR.
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 500kVA (In the case of inverter
capacity is more than 50kVA, it is 10 times of the inverter capacity), %X=5%.
*9) Effective function only in induction motor drive.
*10) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency
is set to 4kHz or above or ambient temperature exceeds 40℃(104°F).
Page 3
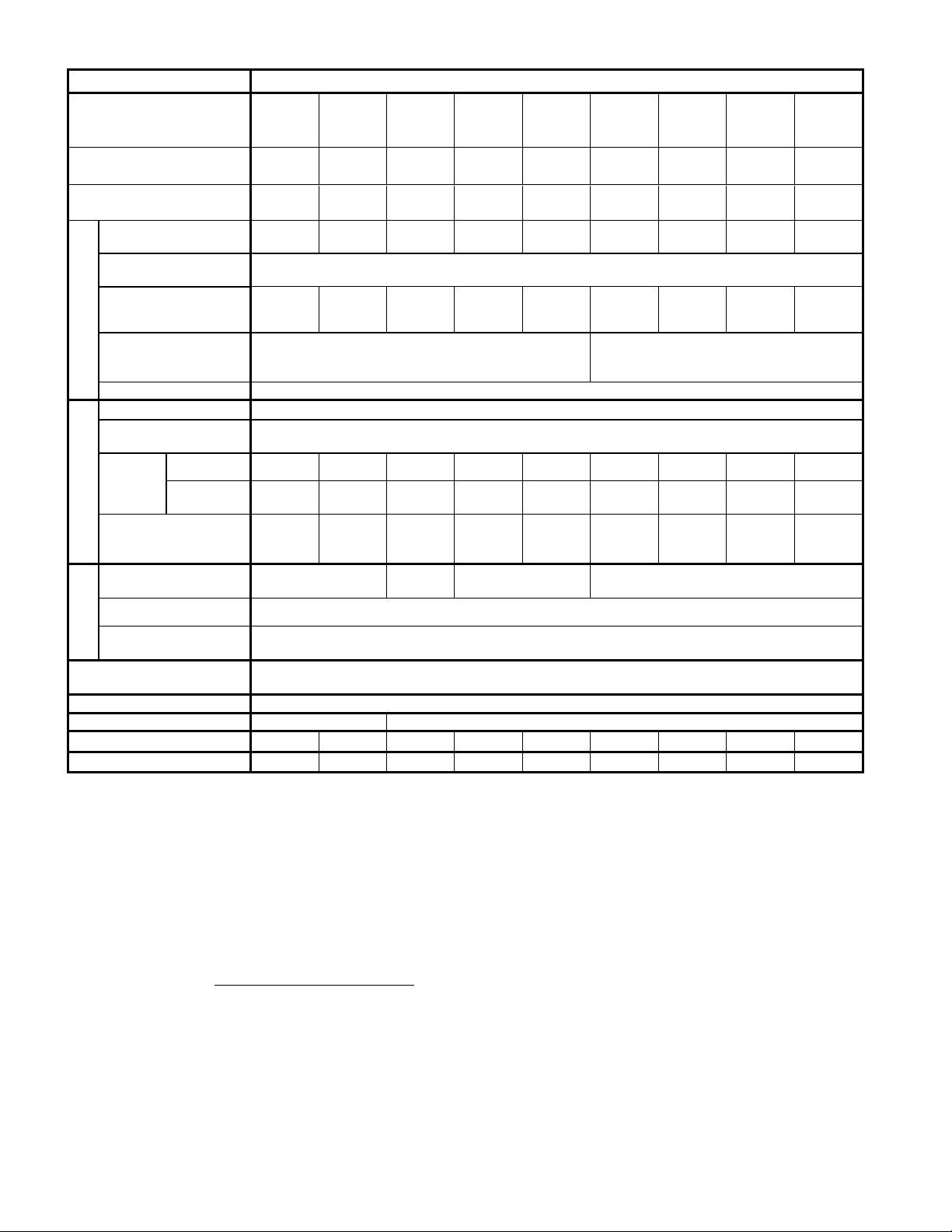
3
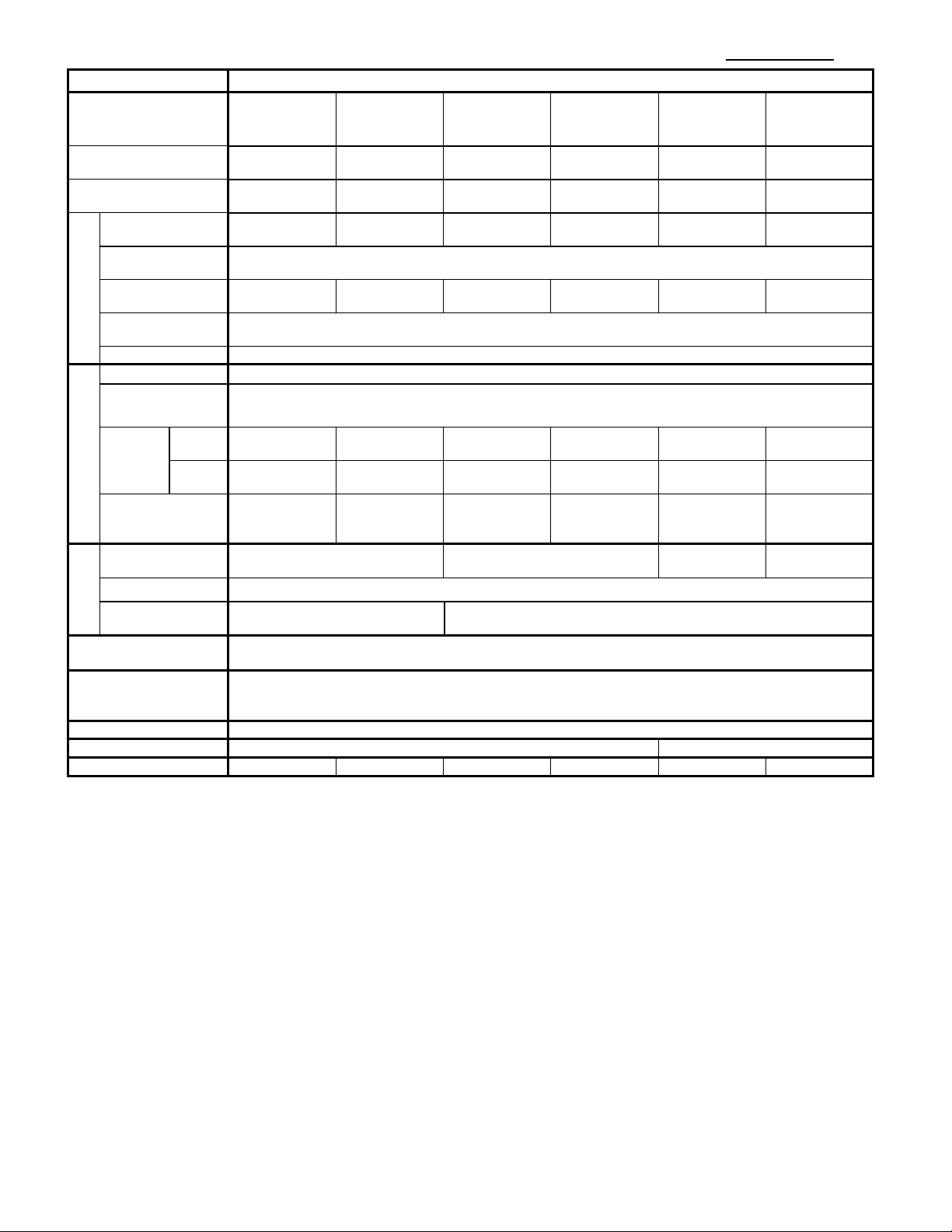
2) Three-Phase 400V Series(0.4 to 15kW / 1/2 to 20HP)
Items
Specifications
Type
(FRN□□□C2S-4△、
△ = A,C,E,U)
0002
0004
0005
0007
0011
0013
0018
0024
0030
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[kW]
(△=A,C,E)
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
3.7(△=A,C)/
4.0(△=E)
5.5
7.5
11
15
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[HP]
(△=U)
1/2 1 2 3 5
7.5
10
15
20
Output ratings
Rated capacity
*2)
[kVA]
1.3
2.3
3.2
4.8
8.0
9.9
13
18
22
Rated voltage
*3)
[V]
Three-phase 380~480V (With AVR)
Rated current [A]
1.8
(1.5)
*4)
3.1
(2.5)
*4)
4.3
(3.7)
*4)
6.3
(5.5)
*4)
10.5
(9.0)
*4)
13.0
18.0
24.0
30.0
Overload capability
150% of rated current for 1min
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for
0.5s (If the rated current is in parenthesis)
150% of rated current for 1min or
200% of rated current for 0.5s
Rated frequency
50, 60Hz
Input ratings
Main power supply
Three-phase 380~480V,50/60Hz
Voltage/frequency
variations
Voltage: +10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance: 2% or less
*7)
), Frequency: +5 to -5%
Rated
current
*8)
[A]
With DCR
0.85
1.6
3.0
4.4
7.3
10.6
14.4
21.1
28.8
Without
DCR
1.7
3.1
5.9
8.2
13.0
17.3
23.2
33.0
43.8
Required power
supply capacity
*5)
[kVA]
0.6
1.1
2.0
2.9
4.9
7.4
10
15
20
Braking
Braking torque
*6)
[%]
100
50
30
20
DC braking
Starting frequency
*9)
: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Transistor for
braking resistor
Built-in
Applicable safety
Standards
UL508C, EN 61800-5-1:2007
Enclosure
IP20 (IEC 60529:1989) / UL open type (UL50)
Cooling method
Natural cooling
Fan cooling
Mass [kg] (△=A,C,E)
1.2
1.3
1.7
1.7
2.5
3.1
3.1
4.5
4.5
Mass [lbs] (△=U)
2.6
2.9
3.7
3.7
5.5
6.8
6.8
9.8
9.8
2004):361800 (IEC 67%
[V] voltageaverage phase-Three
[V] voltageMin.[V] voltageMax.
unbalance Voltage
*1) Fuji Electric's/US 4-pole standard motor.
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as440V for three-phase 400V series.
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
*4) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency
is set to 3kHz or above or ambient temperature exceeds 40℃(104°F).
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates from 60Hz. (Varies with the efficiency of the motor).
*7)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an AC REACTOR.
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 500kVA (In the case of inverter
capacity is more than 50kVA, it is 10 times of the inverter capacity), %X=5%.
*9) Effective function only in induction motor drive.
Page 4
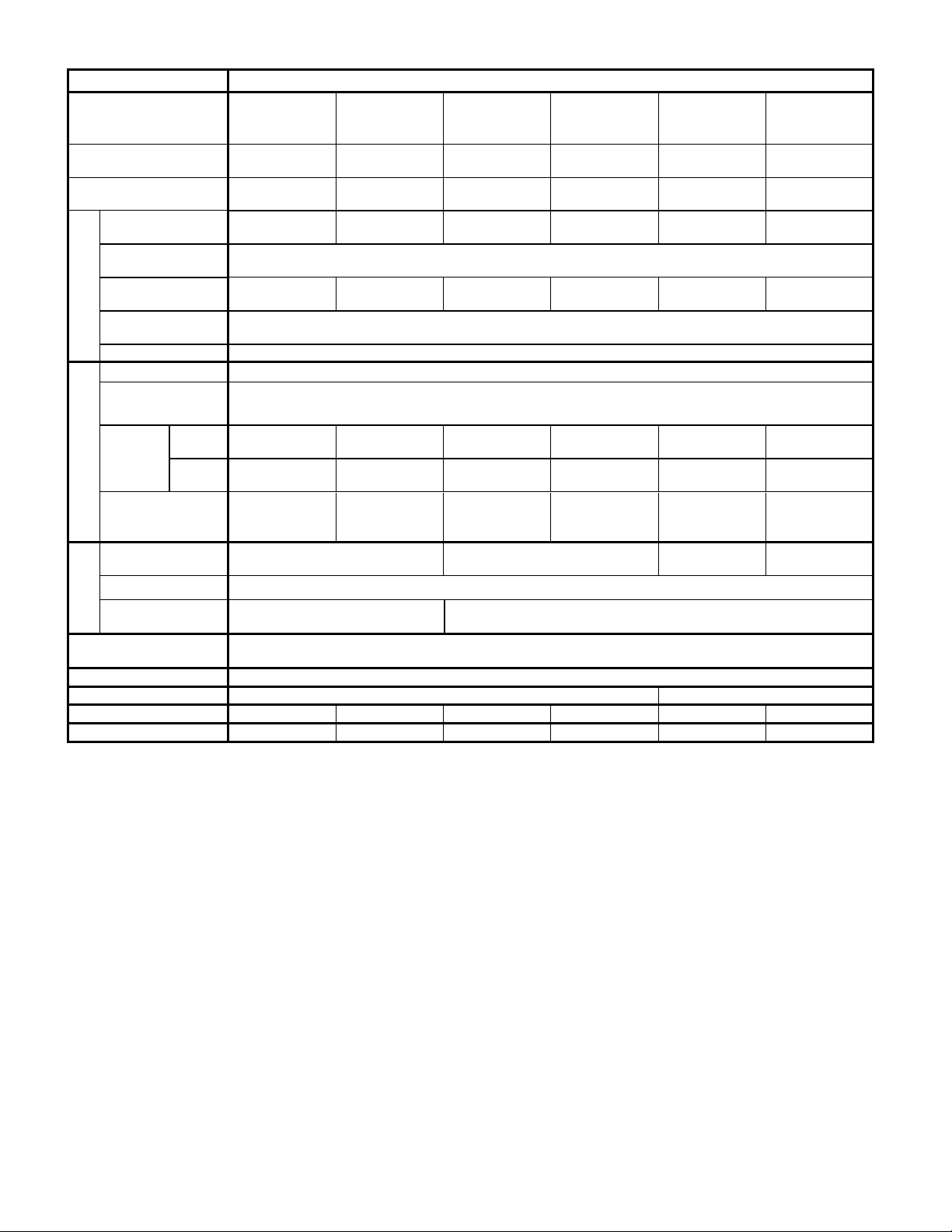
4
3) Single-Phase 200V Series(0.1 to 2.2kW / 1/8 to 3HP)
Items
Specifications
Type
(FRN□□□C2S-7△、
△ = A,C,E,U)
0001
0002
0004 ⓐ
0006
0010
0012
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[kW]
(△=A,C,E)
0.1
0.2
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[HP]
(△=U)
1/8
1/4
1/2 1 2
3
Output ratings
Rated capacity
*2)
[kVA]
0.30
0.57
1.3
2.0
3.5
4.5
Rated voltage
*3)
[V]
Three-phase 200~240V (With AVR)
Rated current [A]
*4)
0.8
(0.7)
1.5
(1.4)
3.5
(2.5)
5.5
(4.2)
9.2
(7.0)
12.0
(10.0)
Overload capability
150% of rated current for 1min
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s (If the rated current is in parenthesis)
Rated frequency
50, 60Hz
Input ratings
Main power supply
Single-phase 200~240V,50/60Hz
Voltage/frequency
variations
Voltage: +10 to -10%, Frequency: +5 to -5%
Rated
current
*7)
[A]
With
DCR
1.1
2.0
3.5
6.4
11.6
17.5
Without
DCR
1.8
3.3
5.4
9.7
16.4
24.0
Required power
supply capacity
*5)
[kVA]
0.3
0.4
0.7
1.3
2.4
3.5
Braking
Braking torque
*6)
[%]
150
100
50
30
DC braking
Starting frequency
*9)
: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Transistor for
braking resistor
-
Built-in
Applicable safety
standards
UL508C, EN 61800-5-1:2007
Enclosure
IP20 (IEC 60529:1989) / UL open type (UL50)
Cooling method
Natural cooling
Fan cooling
Mass [kg] (△=A,C,E)
0.6
0.6
0.7
0.9
1.8
2.5
Mass [lbs] (△=U)
1.3
1.3
1.5
2.0
4.0
5.5
*1) Fuji Electric’s/US 4-pole standard motor.
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as 220V.
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
*4) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency
is set to 3kHz or above or ambient temperature exceeds 40℃(104°F).
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates from 60Hz. (Varies with the efficiency of the motor).
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 500kVA (In the case of inverter
capacity is more than 50kVA, it is 10 times of the inverter capacity), %X=5%.
*9) Effective function only in induction motor drive.
Page 5
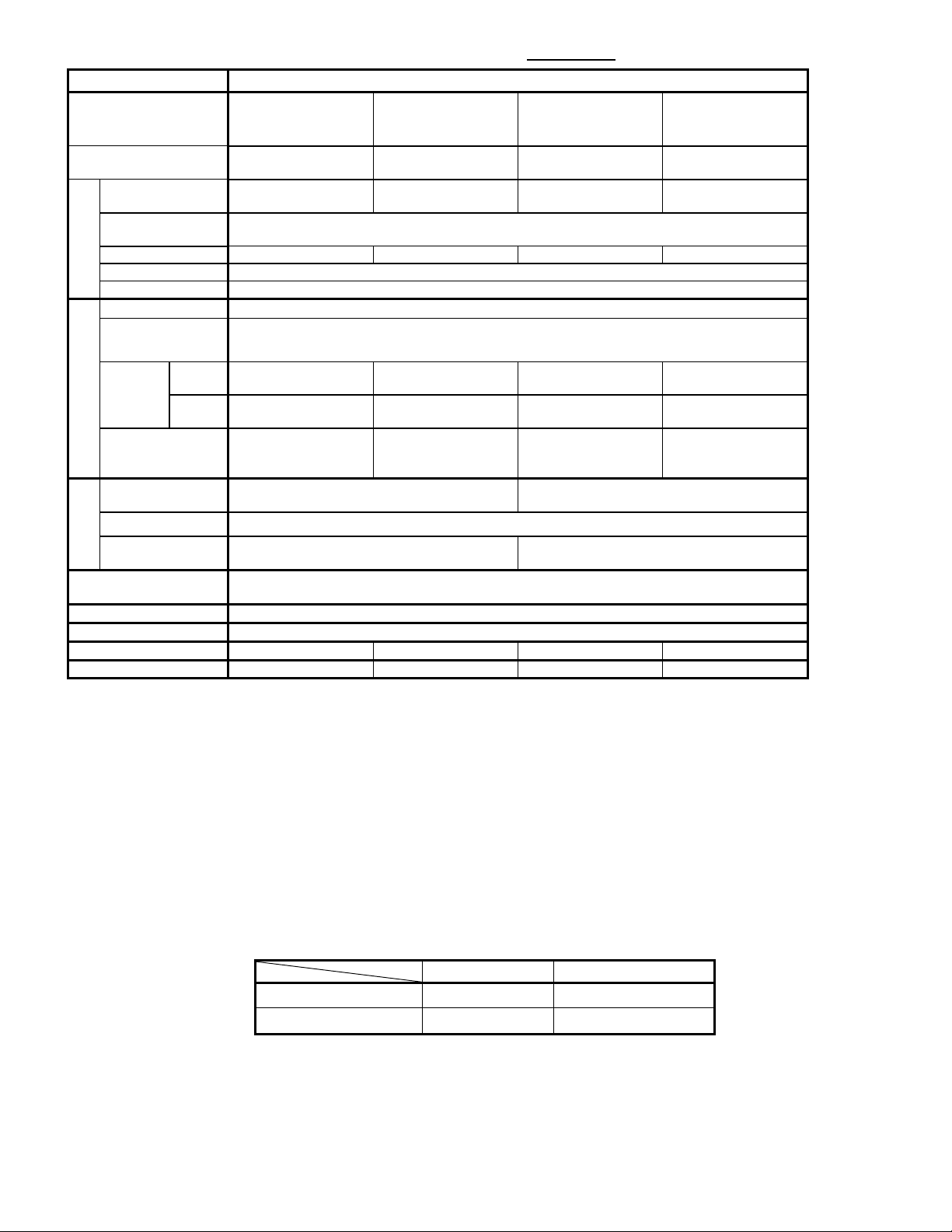
5
4) Single-Phase 100V Series(0.1 to 0.75kW / 1/8 to 1HP) (△ = U only)
Items
Specifications
Type
(FRN□□□C2S-6△、
△ = U)
0001
0002
0003
0005
Nominal applied
motor
*1)
[HP]
1/8
1/4
1/2
1
Output ratings
Rated capacity
*2)
[kVA]
0.26
0.53
0.95
1.6
Rated voltage
*3)
[V]
Three-phase 200~240V (With AVR)
Rated current [A]
0.7
1.4
2.5
4.2
Overload capability
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s
Rated frequency
50, 60Hz
Input ratings
Main power supply
Single-phase 100~120V,50/60Hz
Voltage/frequency
variations
Voltage: +10 to -10%, Frequency: +5 to -5%
Rated
current
*8)
[A]
With
DCR
2.2
3.8
6.4
12.0
Without
DCR
3.6
5.9
9.5
16.0
Required power
supply capacity
*5)
[kVA]
0.3
0.5
0.7
1.3
Braking
Braking torque
*6)
[%]
150
100
DC braking
Starting frequency
*9)
: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Transistor for
braking resistor
-
Built-in
Applicable safety
standards
UL508C
Enclosure
IP20 (IEC 60529:1989) / UL open type (UL50)
Cooling method
Natural cooling
Mass [kg]
0.7
0.7
0.8
1.3
Mass [lbs]
1.5
1.5
1.8
2.9
Shaft output (%)
Maximum torque (%)
w/o DC reactor (DCR)
90
150
w/ DC reactor (DCR)
85
120
*1) Fuji Electric's/US 4-pole standard motor.
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as 220V.
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the twice of power supply voltage.
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates from 60Hz. (Varies with the efficiency of the motor).
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 50kVA, %X=5%.
*9) Effective function only in induction motor drive.
Note
When driven by 100 VAC, the single-phase 100 V series of inverters limit their shaft output and maximum output torque as listed
below. This is to prevent their output voltage from decreasing when load is applied.
Page 6
6
2. Semi-Standard Specifications
Items
Specifications
Type
(FRN□□□C2E-4△、
△ = C,E)
0002
0004
0005
0007
0011
0013
0018
0024
0030
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[kW]
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
3.7(△=C)/
4.0(△=E)
5.5
7.5
11
15
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[HP]
1/2 1 2 3 5
7.5
10
15
20
Output ratings
Rated capacity
*2)
[kVA]
1.3
2.3
3.2
4.8
8.0
9.9
13
18
22
Rated voltage
*3)
[V]
Three-phase 380~480V (With AVR)
Rated current [A]
1.8
(1.5)
*4)
3.1
(2.5)
*4)
4.3
(3.7)
*4)
6.3
(5.5)
*4)
10.5
(9.0)
*4)
13.0
18.0
24.0
30.0
Overload capability
150% of rated current for 1min
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for
0.5s (If the rated current is in parenthesis)
150% of rated current for 1min or
200% of rated current for 0.5s
Rated frequency
50, 60Hz
Input ratings
Main power supply
Three-phase 380~480V,50/60Hz
Voltage/frequency
variations
Voltage: +10 to -15% (Voltage unbalance: 2% or less
*7)
), Frequency: +5 to -5%
Rated
current
*8)
[A]
With DCR
0.85
1.6
3.0
4.4
7.3
10.6
14.4
21.1
28.8
Without
DCR
1.7
3.1
5.9
8.2
13.0
17.3
23.2
33.0
43.8
Required power
supply capacity
*5)
[kVA]
0.6
1.1
2.0
2.9
4.9
7.4
10
15
20
Braking
Braking torque
*6)
[%]
100
50
30
20
DC braking
Starting frequency
*9)
: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Transistor for
braking resistor
Built-in
Applicable safety
Standards
UL508C, EN 61800-5-1:2007
Applicable EMC standards
(EN61800-3:2004 +A1:2012)
(in progress)
Immunity : Second Environment (Industrial)
Emission : Category C2
Immunity : Second Environment (Industrial)
Emission : Category C3
Enclosure
IP20 (IEC 60529:1989) / UL open type (UL50)
Cooling method
Natural cooling
Fan cooling
Mass [kg]
1.5
1.6
3.0
3.1
3.2
(T.B.D.)
(T.B.D.)
(T.B.D.)
(T.B.D.)
2004):361800 (IEC 67%
[V] voltageaverage phase-Three
[V] voltageMin.[V] voltageMax.
unbalance Voltage
1) EMC Filter Built-in Type in Three-Phase 400V Series(0.4 to 15kW / 1/2 to 20HP) (△ = C, E only)
*1) Fuji Electric's/US 4-pole standard motor.
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as440V for three-phase 400V series.
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
*4) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency
is set to 3kHz or above or ambient temperature exceeds 40℃(104°F).
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates from 60Hz. (Varies with the efficiency of the motor).
*7)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an AC REACTOR.
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 500kVA (In the case of inverter
capacity is more than 50kVA, it is 10 times of the inverter capacity), %X=5%.
*9) Effective function only in induction motor drive.
Page 7
7
2) EMC Filter Built-in Type in Single-Phase 200V Series(0.1 to 2.2kW / 1/8 to 3HP) (△ = C, E only)
Items
Specifications
Type
(FRN□□□C2E-7△、
△ = C,E)
0001
0002
0004
0006
0010
0012
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[kW]
0.1
0.2
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
Nominal applied motor
*1)
[HP]
1/8
1/4
1/2 1 2
3
Output ratings
Rated capacity
*2)
[kVA]
0.30
0.57
1.3
2.0
3.5
4.5
Rated voltage
*3)
[V]
Three-phase 200~240V (With AVR)
Rated current [A]
*4)
0.8
(0.7)
1.5
(1.4)
3.5
(2.5)
5.5
(4.2)
9.2
(7.0)
12.0
(10.0)
Overload capability
150% of rated current for 1min
150% of rated current for 1min or 200% of rated current for 0.5s (If the rated current is in parenthesis)
Rated frequency
50, 60Hz
Input ratings
Main power supply
Single-phase 200~240V,50/60Hz
Voltage/frequency
variations
Voltage: +10 to -10%, Frequency: +5 to -5%
Rated
current
*7)
[A]
With
DCR
1.1
2.0
3.5
6.4
11.6
17.5
Without
DCR
1.8
3.3
5.4
9.7
16.4
24.0
Required power
supply capacity
*5)
[kVA]
0.3
0.4
0.7
1.3
2.4
3.5
Braking
Braking torque
*6)
[%]
150
100
50
30
DC braking
Starting frequency
*9)
: 0.0 to 60.0Hz, Braking time: 0.0 to 30.0s, Braking level: 0 to 100%
Transistor for
braking resistor
-
Built-in
Applicable safety
standards
UL508C, EN 61800-5-1:2007
Applicable EMC
standards
EN61800-3:2004 +A1:2012
Immunity : Second Environment (Industrial)
Emission : Category C2
Enclosure
IP20 (IEC 60529:1989) / UL open type (UL50)
Cooling method
Natural cooling
Fan cooling
Mass [kg]
0.7
0.7
0.8
1.2
3.0
3.0
*1) Fuji Electric's/US 4-pole standard motor.
*2) Rated capacity is calculated by regarding the output rated voltage as 220V.
*3) Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
*4) The load shall be reduced so that the continuous operating current is the rated current in parenthesis or less if the carrier frequency
is set to 3kHz or above or ambient temperature exceeds 40℃(104°F).
*5) Obtained when a DC REACTOR is used.
*6) Average braking torque when a motor of no load decelerates from 60Hz. (Varies with the efficiency of the motor).
*8) The currents are calculated on the condition that the inverters are connected to power supply of 500kVA (In the case of inverter
capacity is more than 50kVA, it is 10 times of the inverter capacity), %X=5%.
*9) Effective function only in induction motor drive.
Page 8

8
3. Common Specifications
Items
Specifications
Remark
Output frequency
adjustment
Max. output
frequency
25 to 400Hz adjustable
Base
frequency
25 to 400Hz adjustable
Starting
frequency
0.1 to 60.0Hz
Carrier
frequency
・0.75 to 16kHz adjustable
Note) (*1) In the case of the carrier frequency is 6kHz or above, the carrier frequency may
drop automatically according to the ambient temperature or output current to protect
the inverter. (It has a stop function of automatic reduction.)
・ Carrier frequency modulation: Motor noise may reduced by modulating the carrier
frequency.
Accuracy
Analog setting: ±2% of max freq. (at 25°C), temperature drift: ±0.2% of max freq. (at 25±10°C)
Keypad setting: ±0.01% of max freq. (at 25°C), temperature drift: ±0.01% of max freq. (at 25±10°C)
Setting resolution
・Analog setting :1/1000 of maximum frequency
・Keypad setting :0.01Hz(99.99Hz or below),0.1Hz(100.0 to 400.0Hz)
・Link setting :1/20000 of maximum frequency or 0.01Hz(Fixed)
Control
Control method
Induction Motor
・V/f control, ・Slip compensation, ・Auto-torque boost,
・Dynamic torque vector control, ・Automatic energy saving
Synchronous Motor (*2)
・Synchronous motor drive(without speed/position sensor)
Speed control range : 10% or higher of base frequency
Voltage/freq.
characteristic
200V
series
Possible to set output voltage at base frequency and at maximum respectively
from 80 to 240V. AVR control (*1) can be turned ON or OFF.
2 points (Arbitrary voltage and frequency (*1) can be set.)
Arbitrary voltage (0 to 240V), Arbitrary frequency(0 to 400Hz)
400V
series
Possible to set output voltage at base frequency and at maximum respectively
from 160 to 500V. AVR control (*1) can be turned ON or OFF.
2 points (Arbitrary voltage and frequency (*1) can be set.)
Arbitrary voltage (0 to 500V), Arbitrary frequency(0 to 400Hz)
Torque boost (*1)
・Auto-torque boost(For constant torque load)
・Manual torque boost: Torque boost value can be set 0.0 to 20.0 percent.
・Selectable by load characteristics
(Constant torque load, Variable torque load)
Starting torque (*1)
150% or more at setting frequency 1.0Hz with Slip compensation and auto-torque boost.
Start/Stop
Keypad operation :Start/Stop with RUN, STOP keys (Standard keypad)
Start/Stop with RUN, STOP keys (Remote keypad: Option)
External signals : Forward (Reverse) rotation, stop command (capable of 3-wire operation)
(Digital input) coast-to-stop command, external alarm, alarm reset, etc.
Link operation : RS-485communications(Equipped as standard)
Operation command switch: Link switch
Frequency setting
Key operation: Can be set with , keys(Possible to lock the setting data)
Also can be set with function code (only via communication) and be copied. (*2)
Built-in potentiometer
Analog input : DC0 to +10V/0 to 100%(Terminal 12)
: DC4 to 20mA/0 to 100%, DC0 to 20mA/0 to 100% (Terminal C1)
Multi-frequency: 16 frequencies at maximum are selectable.
UP/DOWN operation: The frequency rises or lowers while the digital input signal is turned
on.
Link operation: Can be set with RS-485 communications.
Frequency setting change: Two types of frequency settings can be switched with an external
signal (Digital input).
Frequency setups through communications or Multi-frequency
are also possible.
Auxiliary frequency setting: Built-in potentiometer, Inputs at terminal 12, C1 can be added to
the main setting as auxiliary frequency settings.
*1 : Effective function only in induction motor drive.
*2 : These functions can be supported by the inverters having a ROM version 0500 or later.
Page 9

9
Items
Specifications
Remark
Control
Frequency setting
Inverse action: The digital input signal and function code setting sets or switches between the
normal and inverse actions
DC0 to +10V/0 to 100% can be switched to DC+10 to 0V/0 to 100%
DC4 to +20mA ”DC0 to +20mA” /0 to 100% can be switched to DC+20 to 0mA
“DC+20 to 0mA” /0 to 100%
Acceleration /
Deceleration time
・0.00 to 3600s
・Two kinds of acceleration and deceleration time can be set and selected individually
(A changeover is possible during operation)
・Acceleration and deceleration pattern can be selected from 4 types: Linear,
・S-curve (weak), S-curve (strong), Curvilinear (constant output max. capacity)
・Shutoff of the operation command coasts the motor to decelerate and stop.
・ACC./DEC time for Jogging operation can be set. (0.00 to 3600s)
S-curve
(free area
setting is
hided
function)
Frequency limiter
(Upper / lower)
・Upper and lower limiters can be set. ( setting range: 0 to 400Hz)
Bias frequency
Bias of set frequency and PID command can be set in the range between 0 and ±100%.
Gain for frequency
setting
The analog input gain can be set in the range from 0 to 200%.
Jump frequency
setting
3 operation points and their common jump hysteresis width (0 to 30Hz) can be set. (ROM version 0499 or earlier)
6 operation points and their common jump hysteresis width (0 to 30Hz) can be set. (ROM version 0500 or later)
Timer operation
Operate and stop by the time set with keypad. (1 cycle operation)
Jogging operation
(*1)
Jogging operation is possible by RUN key(Standard keypad)or digital input.
(ACC./DEC. time for Jogging operation can be set. (ACC. and DEC. time is common.)
Restart after
momentary
power failure (*1)
・Trip at power failure: The inverter trips immediately after power failure.
・Trip at power recovery: Coast-to-stop at power failure and trip at power recovery
・Deceleration stop: Deceleration stop at power failure, and trip after stoppage (*2)
・Start at the frequency selected before momentary stop: Coast-to-stop at power failure and start
after power recovery at thefrequency selected before momentary stop.
・Start at starting frequency: Coast-to-stop at power failure and start at the starting frequency after
power recovery.
Current limit (*1)
(Hardware current
limiting)
Hardware current limiting is used avoiding overcurrent tripping of the inverter, when impact load
change or momentary power failure that can be responded software current limiting. (Hardware
current limiting can be inactive.)
Slip compensation (*1)
・Compensate the lowering the motor speed and get the stabilized operation.
Current limiter
・Control output current so that output current is preset limiting value or less.
PID control
PID control for process control is possible.
・PID command: Keypad, Analog input (Terminal 12,C1), RS-485 communications
・Feed back value: Analog input (Terminal 12,C1)
・Accessory functions
Stop for Slow flowrate function, Normal operation/inverse operation
Integration reset/hold
Automatic
Deceleration
・ If the calculated torque exceeds automatic deceleration level, the inverter avoids
overvoltage trip by automatically controlling the frequency. (*1)
・If the DC link bus voltage exceeds the overvoltage limitation level during deceleration,
the inverter automatically prolongs the deceleration time to three times to avoid
overvoltage trip.
Deceleration
Characteristics
Make the motor loss increase during deceleration so as to reduce the regenerative
energy from motor and avoid Overvoltage trip.
Auto-energy
saving operation (*1)
Control the output voltage so as to minimize the sum of motor loss and inverter loss at
constant speed.
Active drive
The output frequency is automatically reduced to suppress the overload protection trip of the
inverter caused by an increase in the IGBT junction temperature or the ambient temperature,
motor load or the like.
Off-line tuning
(*1)
The motor parameters are automatically tuned. “r1, Xσ, no-load current” (ROM version 0499 or earlier)
The motor parameters are automatically tuned. “r1, Xσ, no-load current, rated slip frequency” (ROM version 0500 or later)
Cooling fan
ON/OFF control
Detects inverter internal temperature and stops cooling fan when the temperature is low.
Second motor
parameters
・One inverter can drive the another motor changing from a motor.
Only induction motor can be set as second motor.
The function data set for second motor are base frequency, rated current, torque boost,Electronic
overload protection for motor, slip compensation, etc…
・Second motor parameters can be preset in the inverter. Auto-tuning is possible.
Limiting the
direction of the
motor rotation
Reverse rotation inhibited,/Forward rotation inhibited selectable
*1: Effective function only in induction motor drive.
*2: These functions can be supported by the inverters having a ROM version 0500 or later.
Page 10

10
Items
Specifications
Remark
Indication
Running
/stopping
・Speed monitor, output current [A], output voltage [V], input power [kW], PID reference value,
PID feedback value, PID output, Time [s] for timer operation, Integrating electric energy
・Select the speed monitor to be displayed among the following.
Output frequency[Hz](Before slip compensation), Output frequency2 [Hz](After slip
compensation), Set frequency, , motor speed [min-1], Line speed [m/min], Constant Feeding
Rate Time [min]
Life early
warning
The life early warning of the main circuit capacitors, capacitors on the PC boards and the
cooling fan can be displayed.
Cumulative run
hours
The cumulative motor running hours, cumulative inverter running hours and cumulative
watt-hours can be displayed.
Page 11

11
Items
Specifications
Remark
Indication
I/O checking
Indicate the status of the Di, Do on the control circuit.
Energy saving
monitor
Input power, Input power×coefficient are indicated.
Trip mode
Displays the cause of trip by codes.
・OC1 (Overcurrent:during acceleration)
・OC2 (Overcurrent:during deceleration)
・OC3 (Overcurrent:at constant speed)
・Lin (Input phase loss)
・LU (Undervoltage)
・OPL(Output phase loss)
・OU1 (Overvoltage:during acceleration)
・OU2 (Overvoltage:during deceleration)
・OU3 (Overvoltage:at constant speed)
・OH1(Overheating of the heat sink)
・OH2(External alarm)
・OH4 (Motor protection (PTC thermistor))
・dbH (Braking resistor overload)
・CoF (PID feedback breaking)
・OL1 (Motor 1 overload)
・OL2 (Motor 2 overload)
・OLU (Inverter overload)
・Er1 (Memory error)
・Er2 (Keypad communications error)
・Er3 (CPU error)
・Er6 (Operation action error)
・Er7 (Tuning error)
・Er8 (RS-485 communications error)
・ErF (Data save error due to undervoltage)
・Erd (Step-out detection(for synchronous
motor drive)) (*2)
・Err (Mock alarm)
Running or trip
mode
Trip history: Saves and displays the last 4 trip codes and their detailed description
Protection
Overcurrent
protection
The inverter is stopped for protection against overcurrent caused by an overload.
LED
indication
OC1
OC2
OC3
Shirt circuit
protection
The inverter is stopped for protection against overcurrent caused by a short circuit in the
output circuit.
Grounding fault
protection
The inverter is stopped only upon start-up for protection against overcurrent caused by a
grounding fault in the output circuit.
Overvoltage
protection
An excessive voltage (3-phase 200V series: 400VDC, 3-phase 400V series: 800VDC) in the
DC link circuit is detected and the inverter is stopped. If a remarkably large voltage is applied
by mistake, the protection cannot be made.
OU1
OU2
OU3
Undervoltage
protection
The voltage drop (3-phase 200V series: 200VDC, 3-phase 400V series: 400VDC) in the DC
link circuit is detected to stop the inverter. However, when "F14: 4 or 5" is selected, an alarm
is not issued even upon a voltage drop in the DC link circuit.
LU
Input phase
loss
The input phase loss is detected to shut off the inverter output. This function protects the
inverter from being broken by adding extreme stress caused by a power phase loss or
unbalance between phases. When the load to be connected is small or DC Reactor is
connected even in the case of an input phase loss, a phase loss is not detected.
Lin
Output phase
loss
Detects breaks in inverter output wiring at the start of operation and during running, to shut off
the inverter output.
OPL
Overheating
The temperature of the heat sink in the event of cooling fan trouble and overload is detected
to stop the inverter.
OH1 Braking resistor is protected from overheat setting Electronic Thermal Overload Protection
for braking resistor appropriately.
dbH
Overload
The temperature inside the IGBT is calculated from the detection of output current and internal
temperature, to shut off the inverter output.
OLU
External alarm
input
With the digital input signal (THR), the inverter is stopped as for an alarm.
OH2
Motor protection
Electronic
thermal
The inverter is stopped upon an electronic thermal function setting to protect the motor.
• The standard motor and inverter motor is protected in the range of all the frequencies.
• Protection for send motor is also possible.
*The operation level and thermal time constant ( 0.5 to 75.0 min) can be set.
OL1
OL2
PTC
thermistor
A PTC thermistor input stops the inverter to protect the motor.
• The PTC thermistor is connected between terminals C1 and 11, a resisitor is connected
between terminals 13 and C1 and setting function codes.
OH4
Overload
early
warning
Warning signal is output at the predetermined level before stopping the inverter with the
electronic thermal function to protect the motor
―
Memory error
Data is checked upon power-on and data writing to detect any fault in the memory and to stop
the inverter.
Er1
*2: These functions can be supported by the inverters having a ROM version 0500 or later.
Page 12

12
Items
Specifications
Remark
Protection
Keypad
communications
error
The remote keypad (optional) is used to detect a communications fault between the keypad
and inverter main body during operation and to stop the inverter.
Er2
CPU error
Detects a CPU error caused by noise and so on and stops the inverter.
Er3
Operation error
STOP key
priority
Pressing the STOP key on the keypad forcibly decelerates and stops
the motor even if the operation command is given through a terminal
block or communications. (Er6 will be displayed after stoppage.)
Er6
Start check
If the operation command is entered in the following cases, Er6 will be
displayed on the LED monitor to prohibit operation.
•Power-on
•Alarm reset (PRG/RESET key ON)
•The link operation selection "LE" is used to switch operation.
Tuning error (*1)
Stop the inverter output when tuning failure, interruption, or any fault as a result of tuning is
detected during tuning for motor constant.
Er7
RS-485
communications
error
When the connection port of the keypad is connected via RS485 communications to the
network to detect a communications error, the inverter is stopped to display the error.
Er8
Data save error
upon
undervoltage
When the undervoltage protection works, an error is displayed if data cannot be stored.
ErF
Step-out
detection (*2)
Stop the inverter when the step-out of the synchronous motor is detected.
Erd
PID feedback
breaking
detection
Stop the inverter output detecting a breaking when the input current is allocated to the PID
control feedback. (Select valid/invalid.)
CoF
Stall
prevention
This is protected when the instantaneous overcurrent limitation works.
Instantaneous overcurrent limitation: operates when the inverter output current goes
beyond the instantaneous overcurrent limiting level, and avoids tripping (during acceleration
and constant speed operation).
Alarm relay
output
(for any fault)
The relay signal is output when the inverter stops upon an alarm. <Alarm reset>
The PRG/RESET key or digital input signal (RST) is used to reset the alarm stoppage state.
Retry function
When the motor is tripped and stopped, this function automatically resets the tripping state
and restarts operation. (The number of retries and the length of wait before resetting can
be set.)
Surge
protection
The inverter is protected against surge voltages intruding across the main circuit power
cable and ground.
Momentary
power failure
protection
A protective function (inverter stoppage) is activated upon a momentary power failure for
15ms or longer.
If restart upon momentary power failure is selected, the inverter restarts upon recovery of
the voltage within the set time.
Mock alarm
Simulated alarm is output by the keypad operation. To check the alarm sequence, simulated
alarm can be output by the keypad operation.
Err
Environment
Installation
location
Shall be free from corrosive gases, flammable gases, oil mist, dusts, and direct sunlight.
(Pollution degree 2 (IEC60664-1:2007)). Indoor use only.
Surrounding air
temperature
-10 to +50°C (14 to 122°F) (IP20)
Ambient
humidity
5 to 95%RH (no condensation)
Altitude
1000m (3300ft) or less (Output derating is not necessary.)
Above 1000m (3300ft) to 3000m (9800ft) or less (Output derating is necessary.)
Above 1000m (3300ft) to 1500m (4900ft) or lower :0.97、
Above 1500m (4900ft) to 2000m (6600ft) or lower:0.95
Above 2000m (6600ft) to 2500m (8200ft) or lower:0.91、
Above 2500m (8200ft) to 3000m (9800ft) lower:0.88
Vibration
3mm(0.12inch) (vibration width) : 2 to less than 9Hz,
9.8m/s2 (32ft/s2) : 9 to less than 20Hz
2m/s2 (6.6ft/s2) : 20 to less than 55Hz
1m/s2 (3.3ft/s2) : 55 to less than 200Hz
Storage
temperature
-25 to +70°C (-13 to 158°F)
Storage
temperature
5 to 95%RH (no condensation)
*1: Effective function only in induction motor drive.
*2: These functions can be supported by the inverters having a ROM version 0500 or later.
Page 13

13
4. Terminal Functions
Symbol
Terminal name
Specification
Remark
Main
circuit
L1/R,L2/S
L3/T
Power input
Connect a three-phase power supply.
(Three-phase 200V, 400V input)
L1/L,L2/N
Connect a single-phase power supply.
(Single-phase 200V input)
U,V,W
Inverter output
Connect a three-phase motor.
P(+),P1
For DC REACTOR
Connect the DC reactor (DCR).
P(+),N(-)
For DC bus
connection
Used for DC bus connection.
P(+),DB
For braking resistor
Connect a external braking resistor
0.4kW(1/2HP) or more
only
(No effection if use at
0.2kW(1/4HP) or less)
G
Grounding
Terminal for inverter grounding
Two terminals are
provided.
Frequency settings
13
Potentiometer power
supply
Used for frequency setting device power supply (variable
resistance: 1 to 5kΩ)
DC10V
12
Voltage input
(Inverse operation)
(PID control)
(Frequency aux.
setting)
・Used as a frequency setting voltage input.
DC 0V to +10V/ 0 to 100%
・DC+10 to 0V // 0 to 100%
・Used for setting signal (PID command value) or feedback
signal.
・Used as additional auxiliary setting to various frequency
settings.
C1
Current input
・Used as a frequency setting current input.
DC4 to 20mA “DC0 to 20mA” / 0 to 100%
(Inverse operation)
(PID control)
(Frequency aux.
setting)
・DC20 to 4mA “DC20 to 0mA” /0 to 100%
・Used for setting signal (PID command value) or feedback
signal
・Used as additional auxiliary setting to various frequency
settings.
For PTC thermistor
connection
・Connect a PTC thermistor for a motor protection.
11
Common for analog
input
Common for Frequency setting input/output signals.
(12,13,C1,FMA)
Two terminals are
provided.
Terminal 11 is isolated
from terminal CM,
Y1E.
Page 14

14
Symbol
Terminal name
Specification
Remark
Digital inputs
X1
Digital input 1
The following functions can be set at terminals X1 to X3, FWD and REV for
signal input.
<Common function>
• Sink and source are changeable using the built-in sliding switch.
• Input logic can be changed between short-circuit of terminals X1 and CM
and open circuits of them. The same setting is possible between CM and
any of the terminals among X2, X3, FWD and REV.
X2
Digital input 2
X3
Digital input 3
FWD
Forward operation
command
REV
Reverse operation
command
(FWD)
Forward operation
command
The motor runs in the forward direction upon ON across (FWD) and CM.
The motor decelerates and stops upon OFF.
This function can be set only
for the terminals FWD and
REV.
Only an active ON signal is
acceptable.
(REV)
Reverse operation
command
The motor runs in the reverse direction upon ON across (REV) and CM.
The motor decelerates and stops upon OFF.
(SS1)
(SS2)
(SS4)
(SS8)
Select Multi-frequency
16 frequencies can be selected with ON/OFF signals at (SS1) to (SS8).
(RT1)
Select ACC/DEC time
ACC1/DEC1 is select when (RT1) is OFF and ACC2/DEC2 is select when
(RT1) is ON.
(HLD)
3-wire operation stop
command
Used for 3-wire operation.
ON across (HLD) and CM: The inverter self-holds FWD or REV signal.
OFF across (HLD) and CM: The inverter releases self-holding.
(BX)
Coast to a stop
The inverter output is shut off immediately and the motor coasts to a stop
when (BX) is ON.
(RST)
Reset alarm
Faults are reset when (RST) is ON.
0.1s or more signal required.
(THR)
External alarm trip
The inverter output is shut off immediately and the motor coasts-to-stop
when (THR) is OFF.
(JOG)
Ready for jogging
Operation mode is changed to Jogging mode and frequency, ACC/DEC
time are changed to those for Jogging operation when (JOG) is ON.
(*1)
(Hz2/Hz1)
Select frequency
command 2/1
Frequency setting 2 is selected when (Hz2/Hz1) is ON.
(M2/M1)
Motor2/Moor1
Motor 1 is effective when (M2/M1) is OFF and Motor 2 is
effective when (M2/M1) is ON.
(DCBRK)
Enable DC braking
DC braking is enable when (DCBRK) is ON.
(WE-KP)
Enable data change with
keypad
Enable data change with keypad when (WE-KP) is ON.
(UP)
UP command
The output frequency increases while (UP) is ON.
(DOWN)
DOWN command
The output frequency decreases while (DOWN) is ON.
(Hz/PID)
Cancel PID control
PID control is canceled when (Hz/PID) is ON/
(Inverter runs with a selected frequency by Multi-frequency, Keypad, analog
input, etc…)
(IVS)
Switch normal/inverse
operation
The frequency setting or PID control output signal (frequency setting) action
mode switches between normal and inverse actions according to (IVS)
ON/OFF status.
(LE)
Enable communication link
via RS-485 or field bus
Enable communication link via RS-485 or field bus when (LE) is ON.
(PID-RST)
Reset PID integral and
differential component
Reset PID integral and differential component when (PID-RST) is ON.
(PID-HLD)
Hold PID integral
component
Hold PID integral component when (PID-HLD) is ON.
PLC
PLC terminal
Connect to PLC output signal power supply. Common for 24V power.
+24V(22 to 27V),
Max.50mA
CM
Common for digital inputs
Common for digital inputs
CM is isolated from 11, Y1E.
Two terminals are provided.
*1: Effective function only in induction motor drive.
Page 15

15
Symbol
Terminal name
Specification
Remark
Transistor outputs
(PLC)
Power supply for transistor
outputs
Power supply for transistor outputs (DC24V DC50mA Max.)
(This terminal is same for PLC terminal for digital input.)
Connect CM with Y1E when
this terminal is used for
transistor outputs.
Y1
Transistor outputs
The following functions can be set at terminals Y1, SO for signal output.
• The setting of "short circuit upon active signal output" or "open upon active
signal output" is possible.
Max. voltage:27Vdc,
max. current:50mA,
leak current:0.1mA
max.
,
ON voltage : within 2V
(at 50mA)
(RUN)
Inverter running (speed
exists)
An active signal is issued when the inverter runs at higher than the stop
frequency.
(FAR)
Frequency arrival
An active signal is issued when the difference between output freq. and set
freq. is equal or less than the value of function code E30 Freq. arrival
(Hysteresis width).
(FDT)
Frequency detected
An active signal is issued when output freq. gets equal or higher than the
value specified by function code E31.
The signal is deactivated if the output frequency falls below the freq. less
than function data E31 minus function data E32.
(LU)
Undervoltage detected
An active signal is issued when inverter dc link voltage is undervoltage
detection level or below.
(IOL)
Inverter output limiting
An active signal is issued when the current limiting, Automatic Deceleration
or torque limiting limits inverter output.
(IPF)
Auto-restarting after
momentary power failure
An active signal is issued until restarting is completed after momentary
power failure.
(OL)
Motor overload early
warning
An active signal is issued when the calculated value of electronic thermal
overload exceeds the preset detection level.
(SWM2)
Select Motor 2
An active signal is issued when motor 2 is selected.
(TRY)
Auto-resetting
An active signal is issued when the auto-resetting is in progress.
(LIFE)
Service lifetime alarm
An active signal is issued when the service lifetime of DC link bus capacitor,
capacitor on the PCBs, cooling fans have expired.
(PID-CTL)
Under PID control
This signal comes ON when the PID control is enabled.
(PID-STP)
Motor stopped due to
slow flowrate under PID
control
This signal is ON when the inverter is in a stopped state by the slow flowrate
stopping function under the PID control. (The inverter is stopped even if a
run command is entered.)
(RUN2)
Inverter output on
An active signal is issued when the inverter runs at higher than stop
frequency or is in DC braking.
(OLP)
Overload prevention
control
An active signal is issued when overload prevention function is in effective.
(ID2)
Current detected 2
An active signal is issued when the output current comes to the current
detection level (for ID) or above and the condition continues for the time
specified current detection timer.
(THM)
Motor overheat detecsted
by thermistor
This signal comes ON when the motor overheat is detected with the
PTC/NTC thermistor.
(BRKS)
Brake signal
This signal is issued to make the mechanical brake ON/OFF.
(*1)
(MNT) ⓑ
Maintenance timer
Alarm signal is generated when time passes or start-up
exceeds over the preset value.
(*2)
(FARFDT)
Logical AND signal of
(FAR) and (FDT)
Logical AND signal of (FAR) and (FDT)
(C1OFF)
Terminal [C1] wire break
When Input current to C1 terminal become less than 2mA, this is interpreted
as wire brake and then ON-singal is generated.
(ID)
Current detected
An active signal is issued when the output current comes to the current
detection level (for ID) or above and the condition continues for
the time specified current detection timer.
(IDL)
Low current detected
This output signal comes ON when the output current drops
below the low current detection level specified by E37 for the
period specified by E38 (Low current detection (Timer)).
(ALM)
Alarm output (for any
alarm)
An active signal is issued when the inverter is in alarm mode.
Y1E
Transistor output
common
Common terminal for transistor output.
Y1E is isolated from 11,CM.
*1: Effective function only in induction motor drive.
*2: These functions can be supported by the inverters having a ROM version 0500 or later.
Page 16

16
Symbol
Terminal name
Specification
Remark
Relay output
30A,30B,
30C
Alarm output (for any
alarm)
A no-voltage contact signal (1c) is issued when the inverter is stopped due
to an alarm.
• Multi-purpose relay output; signals similar to above-mentioned signals Y1
can be selected.
• An alarm output is issued upon either excitation or no excitation according
to selection.
Contact rating: AC250V,
0.3A, cosφ=0.3 DC48V, 0.5A
Analog output
FMA
Analog monitor
Output signal: DC voltage (0 to 10V)
The one of the following signals can be monitored at terminal FMA.
・
Output frequency 1 ( Before slip compensation )
・
Output frequency 1 ( After slip compensation )
・
Output current ・Output voltage
・
Input power ・PID feed back value
・
DC link voltage ・Calibration analog output (+)
・
PID reference ・PID output
Gain: 0 to 300%
Communications
Built-in RJ-45
connector (RS-485)
The one of the following protocol can be selectable.
・
Protocol for keypad (Automatically selected)
・
Modbus RTU
・
FGI bus
・
SX protocol for loader software
With power source for
the keypad and the
switch for changeover
of terminating resistor
ON/OFF.
Communication data
storage can be
selected. (*2)
*2 : These functions can be supported by the inverters having a ROM version 0500 or later.
Page 17

17
5. Basic Wiring Diagram
L1/R
L2/S
L3/T
[13]
G
U
V
W
M
3~
(Note3)
MCCB
or
ELCB
(Note2)
Three-phase
200 to 240V
50/60Hz
or
Three-phase
380 to 480V
50/60Hz
Power supply
P(+)P1 N(-)
G
Main circuit
P(+)
P1
MC
(Note1)
DCR
Motor
Grounding
Grounding
[12]
[11]
[C1]
[11]
[FMA]
(FWD)
(CM)
(REV)
3
2
1
Voltage input
0 to 10Vdc
Power supply for
potentiometer
(Note5)
Control circuit
<Y1E>
<Y1>
(+)
(-)
Current input
4 to 20mAdc
Analog input
(Note6)
Digital input
30A
30B
30C
30
MCCB:Molded case circuit breaker
ELCB:Earth leakage circuit breaker
MC :Magnetic contactor
DCR :DC reactor
DBR :Brake resistor
Transistor
Alarm output
DB
P DB
(Note4)
DBR
(CM)
(THR)
SINK
SOURCE
Meter
L1/L
L2/N
Single-phase
200 to 240V
50/60Hz
or
Single-phase
100 to 120V
50/60Hz
(X1)
(X2)
(X3)
RS‐485 port
(RJ-45)
(CM)
(PLC)
(Factory Setting :
△=E : SOURCE,
OTHER : SINK)
* Switch for termination resistor is built-in.
Page 18

18
Note 1:
When connecting a DC REACTOR (DCR) (option), remove the jumper bar from across the terminals [P1] and [P (+)].
For single-phase 100V input series, DCR shall be connected to the point that is shown below.
Note 2:
Install a recommended molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) or an earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) (with an overcurrent
protection function) in the primary circuit of the inverter to protect wiring. At this time, ensure that the circuit breaker capacity is
equivalent to or lower than the recommended capacity.
Note 3:
Install a magnetic contactor (MC) recommended for each inverter to separate the inverter form the power supply, apart from the
MCCB or ELCB, when necessary. Connect a surge suppressor in parallel when installing a coil such as the MC or solenoid near the
inverter.
Note 4:
(THR) is available when one of terminal functions for X1 to X3, FWD, REV (function code E01 to E03, E98 or E99) is set to the
data “9”.
Note 5:
Frequency can be set by connecting a frequency setting device (external potentiometer) among the terminals 11, 12 and 13 instead
of inputting voltage signal (0 to +10V DC, 0 to +5V DC or +1 to +5V DC) between the terminals 12 and 11.
Note 6:
For the control signal wires, use shielded or twisted wires. Ground shielded wires. To prevent malfunction due to noise, keep the
control circuit wiring away from the main circuit wiring as far as possible (recommended: 10cm(3.94inches) or more), and never set
them in the same wire duct. ⓔ
When crossing the control circuit wiring with the main circuit wiring, set them at right angles.
Note 7:
Three –phase 4wire cable is recommended for motor wiring to reduce the noise emitted. Connect the motor grounding wire to
the inverter grounding terminal G.
Page 19

19
6. Outline: Standard Models
Page 20

20
Page 21

21
Page 22

22
Fuji Electric Corp. of America
47520 Westinghouse Drive, Fremont, CA 94539
Phone: 510-440-1060
www.americas.fujielectric.com
 Loading...
Loading...