Freightliner Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual

®
BUSINESS CLASS M2
STI-455-6
A24-01238-000
Maintenance Manual

BUSINESS CLASS M2 MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Models: M2 100
M2 106
M2 106V
M2 112
M2 112V
STI-455-6 (3/16)
Published by
Daimler Trucks North America LLC
4747 N. Channel Ave.
Portland, OR 97217
Printed in U.S.A.

Foreword
Performing scheduled maintenance operations is important in obtaining safe, reliable operation of your
vehicle. A proper maintenance program will also help to minimize downtime and safeguard warranties.
IMPORTANT: The maintenance operations in this manual are not all-inclusive. Also refer to other
component and body manufacturers’ instructions for specific inspection and maintenance instructions.
Perform the operations in this maintenance manual at scheduled intervals. Perform the pretrip and post-trip
inspections, and daily/weekly/monthly maintenance, as outlined in the vehicle driver’s manual. Major
components, such as engines, transmissions, and rear axles, are covered in their own maintenance and
operation manuals, that are provided with the vehicle. Perform any maintenance operations listed at the
intervals scheduled in those manuals. Your Freightliner Dealership has the qualified technicians and
equipment to perform this maintenance for you. They can also set up a scheduled maintenance program
tailored specifically to your needs. Optionally, they can assist you in learning how to perform these
maintenance procedures.
IMPORTANT: Descriptions and specifications in this manual were in effect at the time of printing.
Freightliner Trucks reserves the right to discontinue models and to change specifications or design
at any time without notice and without incurring obligation. Descriptions and specifications contained
in this publication provide no warranty, expressed or implied, and are subject to revision and editions
without notice.
Refer to www.Daimler-TrucksNorthAmerica.com and www.FreightlinerTrucks.com for more information,
or contact Daimler Trucks North America LLC at the address below.
Environmental Concerns and Recommendations
Whenever you see instructions in this manual to discard materials, you should attempt to reclaim and recycle
them. To preserve our environment, follow appropriate environmental rules and regulations when disposing of
materials.
NOTICE: Parts Replacement Considerations
Do not replace suspension, axle, or steering parts (such as springs, wheels, hubs, and steering gears) with
used parts. Used parts may have been subjected to collisions or improper use and have undetected structural
damage.
© 2001–2016 Daimler Trucks North America LLC
All rights reserved. No part of this publication, in whole or in part, may be translated, reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of Daimler Trucks North America LLC. Daimler Trucks North
America LLC is a Daimler company.
Daimler Trucks North America LLC
Service Systems and Documentation (CVI-SSD)
P.O. Box 3849
Portland, Oregon 97208-3849

Introduction
Descriptions of Service Publications
Daimler Trucks North America LLC distributes the following major service publications in paper and electronic
(via ServicePro®) formats.
Workshop/Service
Manual
Maintenance Manual Maintenance manuals contain routine maintenance procedures and intervals for
Driver’s/Operator’s
Manual
Service Bulletins Service bulletins provide the latest service tips, field repairs, product improve-
Workshop/service manuals contain service and repair information for all vehicle
systems and components, except for major components such as engines, transmissions, and rear axles. Each workshop/service manual section is divided into
subjects that can include general information, principles of operation, removal,
disassembly, assembly, installation, and specifications.
vehicle components and systems. They have information such as lubrication
procedures and tables, fluid replacement procedures, fluid capacities, specifications, and procedures for adjustments and for checking the tightness of fasteners. Maintenance manuals do not contain detailed repair or service information.
Driver’s/operator’s manuals contain information needed to enhance the driver’s
understanding of how to operate and care for the vehicle and its components.
Each manual contains a chapter that covers pretrip and post-trip inspections,
and daily, weekly, and monthly maintenance of vehicle components.
Driver’s/operator’s manuals do not contain detailed repair or service information.
ments, and related information. Some service bulletins are updates to information in the workshop/service manual. These bulletins take precedence over
workshop/service manual information, until the latter is updated; at that time, the
bulletin is usually canceled. The service bulletins manual is available only to
dealers. When doing service work on a vehicle system or part, check for a valid
service bulletin for the latest information on the subject.
IMPORTANT: Before using a particular service bulletin, check the current
service bulletin validity list to be sure the bulletin is valid.
Parts Technical Bulletins Parts technical bulletins provide information on parts. These bulletins contain
lists of parts and BOMs needed to do replacement and upgrade procedures.
Web-based repair, service, and parts documentation can be accessed using the following applications on the
AccessFreightliner.com website.
ServicePro ServicePro® provides Web-based access to the most up-to-date versions of the
publications listed above. In addition, the Service Solutions feature provides diagnostic assistance with Symptoms Search, by connecting to a large knowledge
base gathered from technicians and service personnel. Search results for both
documents and service solutions can be narrowed by initially entering vehicle
identification data.
PartsPro PartsPro® is an electronic parts catalog system, showing the specified vehicle’s
build record.
™
EZWiring EZWiring
Freightliner Custom Chassis Corporation products’ wiring drawings and floating
pin lists available online for viewing and printing. EZWiring can also be accessed from within PartsPro.
makes Freightliner, Sterling, Western Star, Thomas Built Buses, and
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, May 2011 I–1

Introduction
Descriptions of Service Publications
Warranty-related service information available on the AccessFreightliner.com website includes the following
documentation.
Recall Campaigns Recall campaigns cover situations that involve service work or replacement of
parts in connection with a recall notice. These campaigns pertain to matters of
vehicle safety. All recall campaigns are distributed to dealers; customers receive
notices that apply to their vehicles.
Field Service Campaigns Field service campaigns are concerned with non-safety-related service work or
replacement of parts. All field service campaigns are distributed to dealers; customers receive notices that apply to their vehicles.
I–2 Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, May 2011

Page Description
For an example of a Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual page, see Fig. 1.
A
B C
Introduction
Cooling
20−01 Coolant Replacement
20
20−02 Cooling Fan Inspection
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, December 2001
D
12/06/2001
A. Maintenance Operation Number consists of the Group Number followed by the Sequence Number
B. Group Title
C. Group Number
D. Release Date
E. Group Number/Page Number
Fig. 1, Example of a Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual Page
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, May 2011 I–3
E
f020125

Introduction
Group No. Group Title
00...................... General Information
01................................ Engine
09.............................. AirIntake
13 ......................... AirCompressor
15................... Alternators and Starters
20................... Engine Cooling/Radiator
25................................ Clutch
26........................... Transmission
31 ............. Frame and Frame Components
32............................ Suspension
33 ............................. Front Axle
35 ............................. Rear Axle
40........................ Wheels and Tires
41 .............................. Driveline
42................................ Brakes
46............................... Steering
47 ................................. Fuel
49............................... Exhaust
60.................................. Cab
72 ................................ Doors
83................. Heater and Air Conditioner
88.............. Hood, Grille, and Cab Fenders
Maintenance Manual Contents
I–4 Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, May 2011

General Information 00
Index, Alphabetical
Title of Maintenance Operation (MOP) MOP Number
Determining Scheduled Maintenance Intervals.............................................00–01
Initial Maintenance (IM) Operations .....................................................00–06
M1 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check...................................................00–12
M1 Maintenance Operations..........................................................00–07
M2 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check...................................................00–13
M2 Maintenance Operations..........................................................00–08
M3 Maintenance Operations..........................................................00–09
M4 Maintenance Operations..........................................................00–10
M5 Maintenance Operations .......................................................... 00–11
Maintenance Intervals for Schedule I....................................................00–03
Maintenance Intervals for Schedules II and III ............................................. 00–04
Maintenance Schedules .............................................................00–02
Noise Emission Controls.............................................................00–15
Overview of Maintenance Operations ................................................... 00–05
Verification of Inspections Log.........................................................00–16
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016

General Information 00
Determining Scheduled Maintenance Intervals: 00–01
Determining Scheduled
Maintenance Intervals
Performing regular maintenance will help ensure that
your vehicle delivers safe, reliable service and optimum performance. A proper maintenance program
will also help to minimize downtime and safeguard
warranties.
To determine the correct maintenance intervals for
your vehicle, you must first determine the type of service or conditions the vehicle will be operating in.
Most vehicles operate in conditions that fall within
one of the three schedules. Before placing your vehicle in service, determine whether Schedule I, II, or
III applies to your vehicle.
Schedules I-III
Schedule I (severe service) applies to vehicles that
travel up to 6000 miles (10 000 kilometers) annually
or that operate under severe conditions. Examples of
Schedule I usage are:
• operation on extremely poor roads or where
there is heavy dust accumulation
• constant exposure to extreme hot, cold, salt air,
or other extreme climates
• frequent short-distance travel
• construction-site operation
• city operation such as fire truck and garbage
truck.
• farm operation
Schedule II (short-haul transport) applies to vehicles
that travel up to 60,000 miles (100 000 kilometers)
annually and operate under normal conditions. Examples of Schedule II usage are:
• operation primarily in cities and densely populated areas
• local transport with infrequent freeway travel
• high percentage of stop-and-go travel
Schedule III (long-haul transport) is for vehicles that
travel more than 60,000 miles (100 000 kilometers)
annually with minimal city or stop-and-go operation.
Examples of Schedule III usage are:
• regional delivery that is mostly freeway miles
• interstate transport
• any road operation with high annual mileage
Maintenance Schedules
After determining the schedule appropriate to your
vehicle, refer to the Maintenance Schedules to determine when to perform the Initial Maintenance (IM)
and the frequency of performing subsequent maintenance intervals for each schedule.
Maintenance Intervals
Refer to Maintenance Intervals for Schedule I,
Schedule II, and Schedule III to determine which
maintenance interval(s) should be performed when
your vehicle reaches the mileage or hours of operation listed in these tables.
Maintenance Operations
Groups 01 through 83 in this manual have an index
at the beginning of each Group. The index lists the
Title of Maintenance Operations and the maintenance Operation (MOP) Numbers for that Group.
Follow the instructions under the MOP number to
perform the required maintenance.
In addition to the maintenance operations required
for the maintenance interval, perform all the daily
maintenance procedures in Chapter 11, "Pretrip Inspection and Daily Maintenance," in the Business
Class® M2 Driver’s Manual.
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/1
General Information00
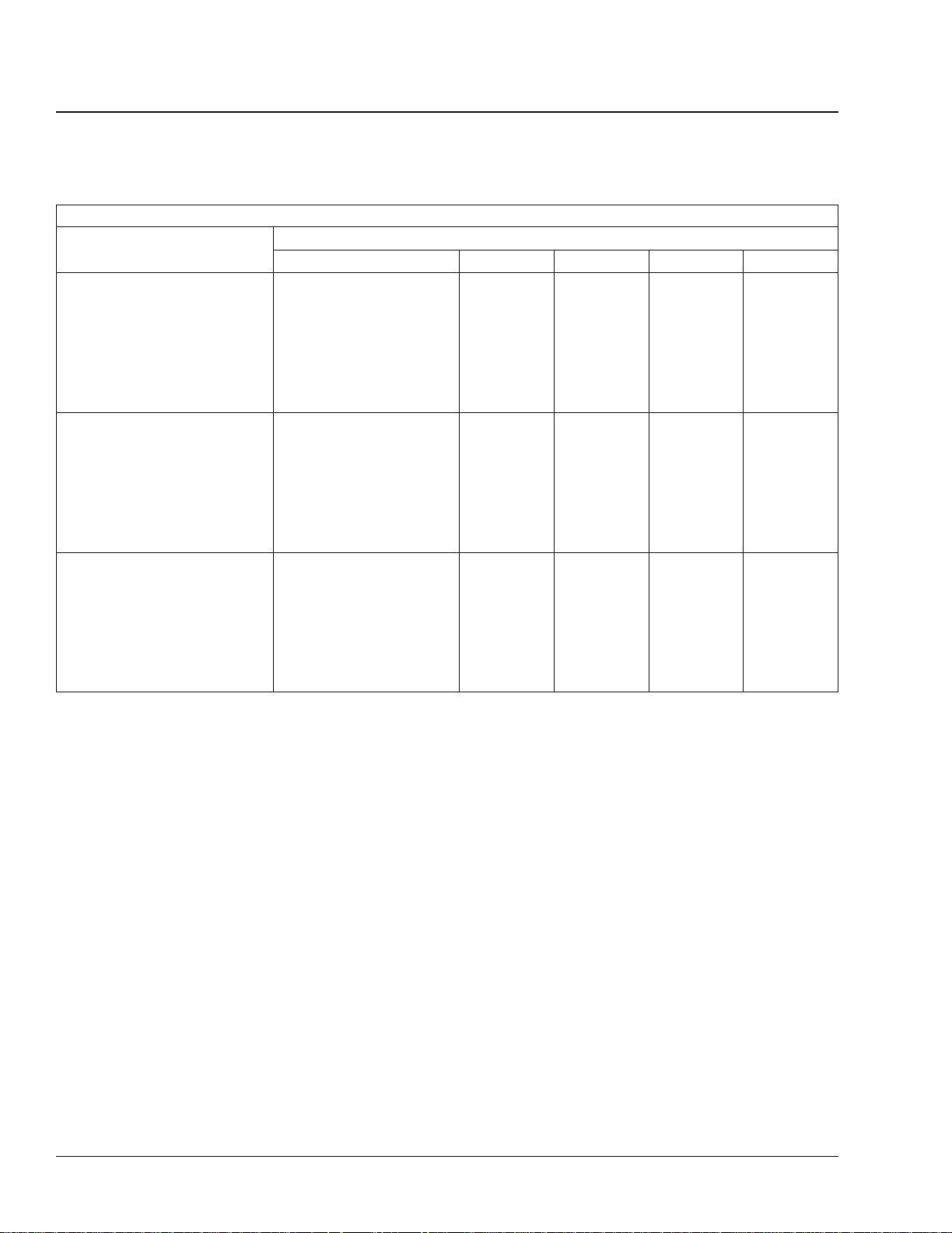
Maintenance Schedules: 00–02
Maintenance Schedules
Schedule
Schedule I
(severe service)
for vehicles that travel up to
6000 miles (10 000 km) annually
Schedule II
(short-haul transport)
for vehicles that travel up to
60,000 miles (100 000 km)
for vehicles that travel over
60,000 miles (100 000 km)
*
For Schedule I vehicles equipped with an hourmeter, use maintenance intervals based on hours of operation rather than mileage.
annually
Schedule III
(long-haul transport)
annually
*
Maintenance Interval Frequency Mileage km Hours
Initial Maintenance (IM) first 1000 1600 100
Maintenance 1 (M1) every 1000 1600 100
Maintenance 2 (M2) every 4000 6400 400
Maintenance 3 (M3) every 8000 12 800 800
Maintenance 4 (M4) every 16,000 25 600 1600
Maintenance 5 (M5) every 32,000 51 200 3200
Initial Maintenance (IM) first 8000 12 000
Maintenance 1 (M1) every 8000 12 000
Maintenance 2 (M2) every 16,000 24 000
Maintenance 3 (M3) every 32,000 48 000
Maintenance 4 (M4) every 64,000 96 000
Maintenance 5 (M5) every 128,000 192 000
Initial Maintenance (IM) first 10,000 16 000
Maintenance 1 (M1) every 10,000 16 000
Maintenance 2 (M2) every 20,000 32 000
Maintenance 3 (M3) every 40,000 64 000
Maintenance 4 (M4) every 80,000 128 000
Maintenance 5 (M5) every 160,000 256 000
Table 1, Maintenance Schedules
Maintenance Intervals
—
—
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/2
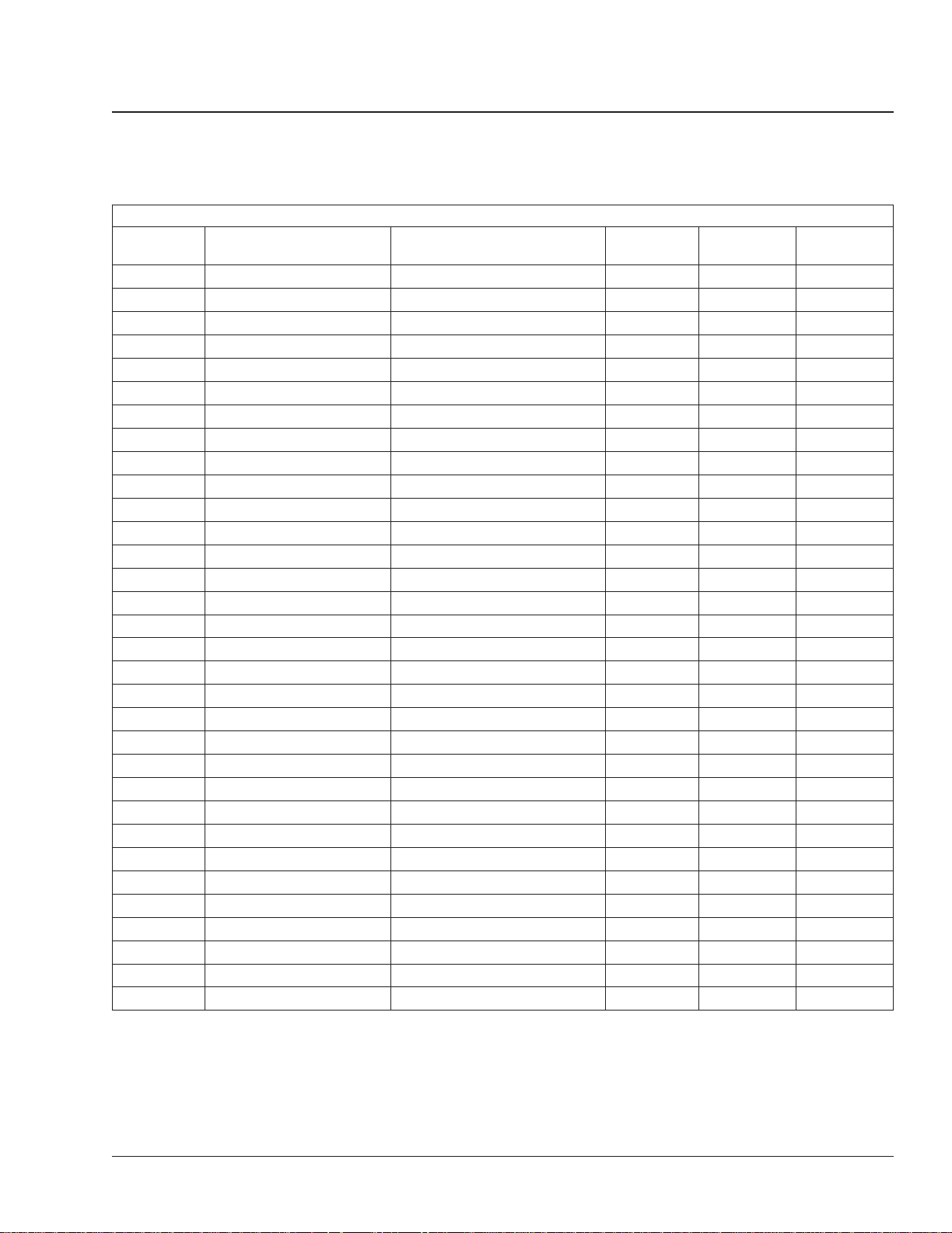
General Information 00
Maintenance Intervals for Schedule I: 00–03
Maintenance Intervals for Schedule I
Maintenance
Sequence
1st IM and M1 1000 1600 100
2nd M1 2000 3200 200
3rd M1 3000 4800 300
4th M1 and M2 4000 6400 400
5th M1 5000 8000 500
6th M1 6000 9600 600
7th M1 7000 11 200 700
8th M1, M2, and M3 8000 12 800 800
9th M1 9000 14 400 900
10th M1 10,000 16 000 1000
11th M1 11,000 17 600 1100
12th M1 and M2 12,000 19 200 1200
13th M1 13,000 20 800 1300
14th M1 14,000 22 400 1400
15th M1 15,000 24 000 1500
16th M1, M2, M3, and M4 16,000 25 600 1600
17th M1 17,000 27 200 1700
18th M1 18,000 28 800 1800
19th M1 19,000 30 400 1900
20th M1 and M2 20,000 32 000 2000
21st M1 21,000 33 600 2100
22nd M1 22,000 35 200 2200
23rd M1 23,000 36 800 2300
24th M1, M2, and M3 24,000 38 400 2400
25th M1 25,000 40 000 2500
26th M1 26,000 41 600 2600
27th M1 27,000 43 200 2700
28th M1 and M2 28,000 44 800 2800
29th M1 29,000 46 400 2900
30th M1 30,000 48 000 3000
31st M1 31,000 49 600 3100
32nd M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 32,000 51 200 3200
Maintenance Interval Service Date Miles km Hours
Table 2, Maintenance Intervals for Schedule I
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/3
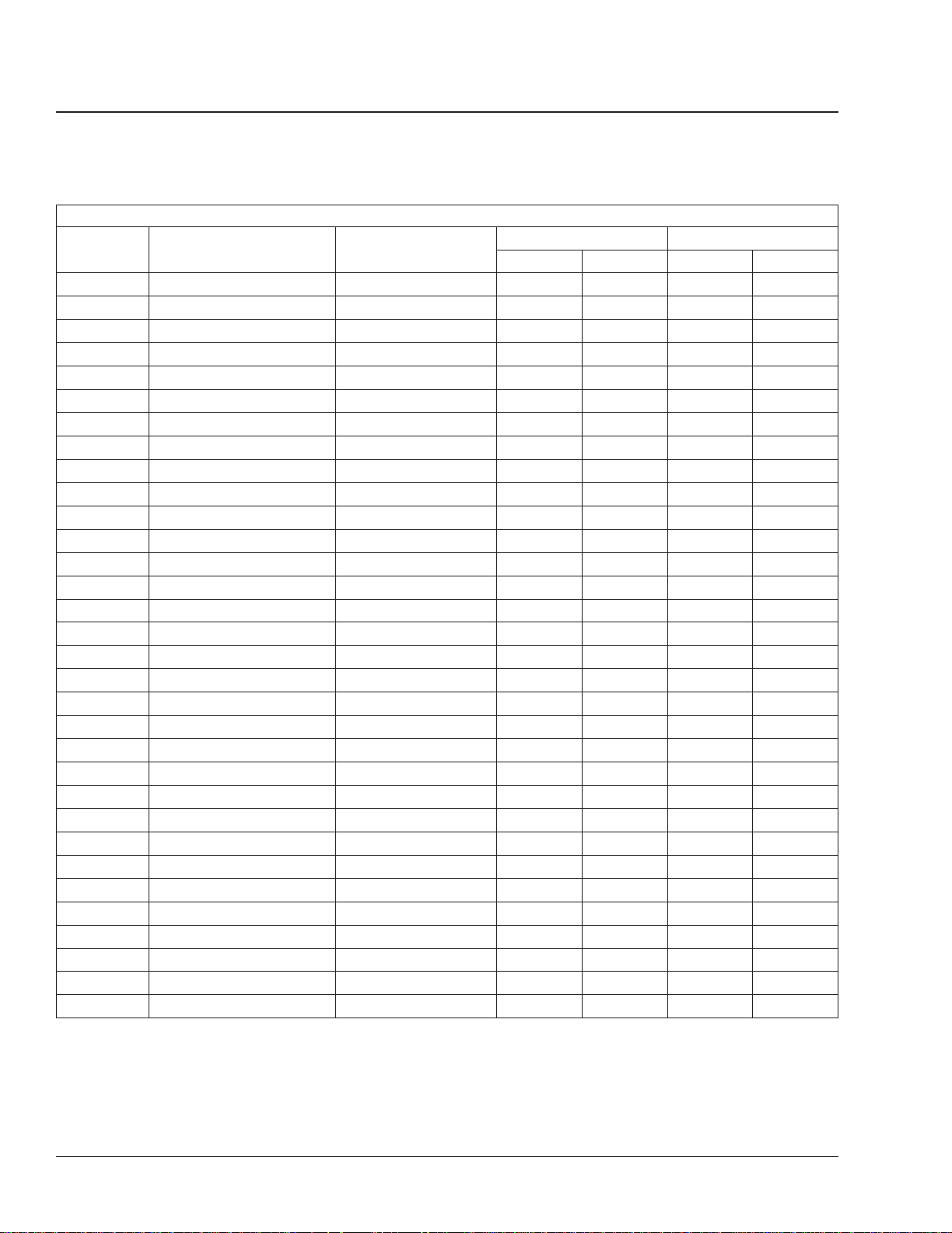
General Information00
Maintenance Intervals for Schedules II and III: 00–04
Maintenance Intervals for Schedules II and III
Maintenance
Sequence
1st IM and M1 8000 12 000 10,000 16 000
2nd M1 and M2 16,000 24 000 20,000 32 000
3rd M1 24,000 36 000 30,000 48 000
4th M1, M2, and M3 32,000 48 000 40,000 64 000
5th M1 40,000 60 000 50,000 80 000
6th M1 and M2 48,000 72 000 60,000 96 000
7th M1 56,000 84 000 70,000 112 000
8th M1, M2, M3, and M4 64,000 96 000 80,000 128 000
9th M1 72,000 108 000 90,000 144 000
10th M1 and M2 80,000 120 000 100,000 160 000
11th M1 88,000 132 000 110,000 176 000
12th M1, M2, and M3 96,000 144 000 120,000 192 000
13th M1 104,000 156 000 130,000 208 000
14th M1, and M2 112,000 168 000 140,000 224 000
15th M1 120,000 180 000 150,000 240 000
16th M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 128,000 192 000 160,000 256 000
17th M1 136,000 204 000 170,000 272 000
18th M1 and M2 144,000 216 000 180,000 288 000
19th M1 152,000 228 000 190,000 304 000
20th M1, M2, and M3 160,000 240 000 200,000 320 000
21st M1 168,000 252 000 210,000 336 000
22nd M1 and M2 176,000 264 000 220,000 352 000
23rd M1 184,000 276 000 230,000 368 000
24th M1, M2, M3, and M4 192,000 288 000 240,000 384 000
25th M1 200,000 300 000 250,000 400 000
26th M1 and M2 208,000 312 000 260,000 416 000
27th M1 216,000 324 000 270,000 432 000
28th M1, M2, and M3 224,000 336,000 280,000 448 000
29th M1 232,000 348 000 290,000 464 000
30th M1 and M2 240,000 360 000 300,000 480 000
31st M1 248,000 372 000 310,000 496 000
32nd M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 256,000 384 000 320,000 512 000
Maintenance Interval Service Date
Table 3, Maintenance Intervals for Schedules II and III
Schedule II Schedule III
Miles km Miles km
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/4
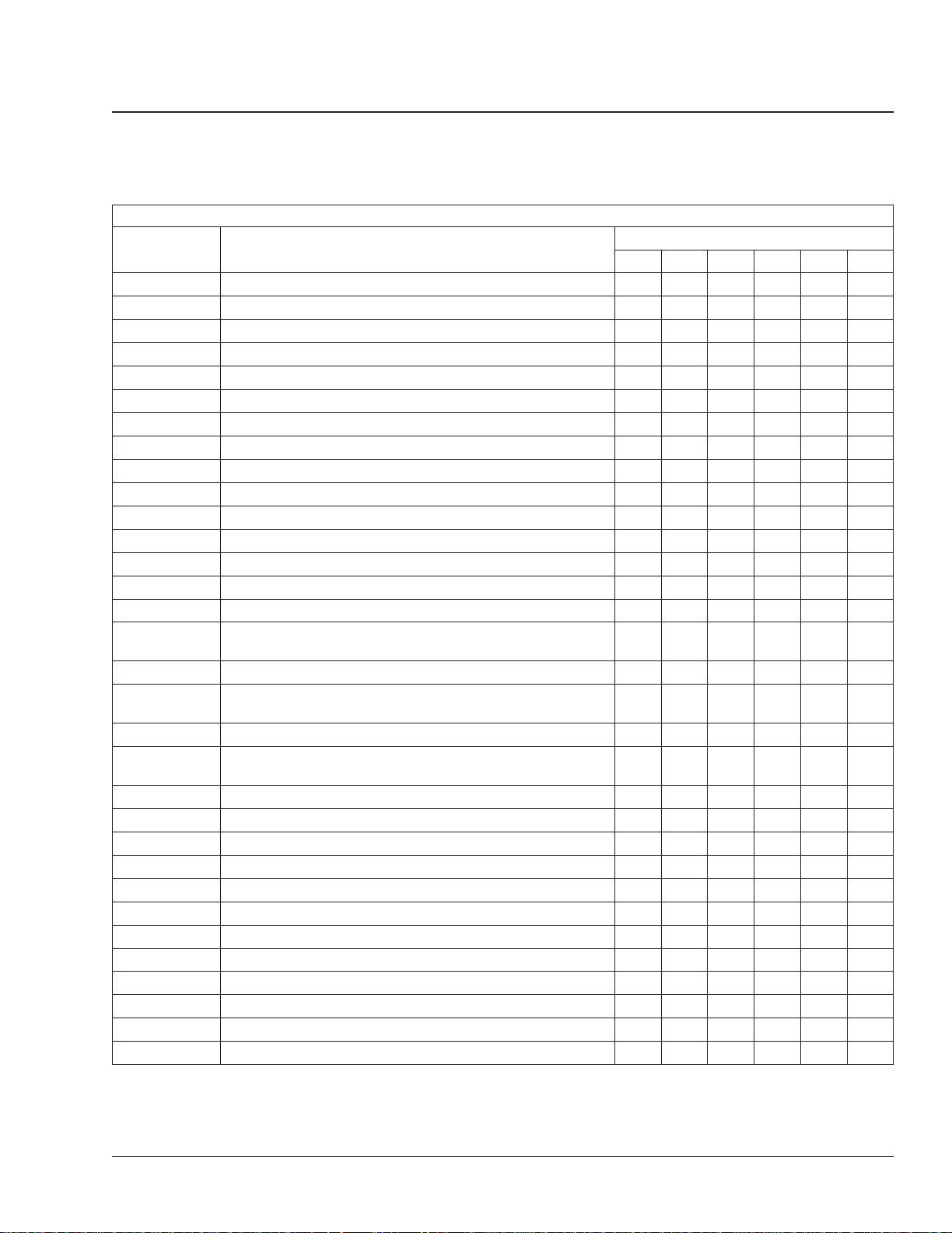
General Information 00
Overview of Maintenance Operations: 00–05
Maintenance Operations for Groups 00 through 88
Maintenance
Operation No.
01-01 Engine Drive Belt Inspecting • • •
01-02 Engine Support Fastener Checking • •
09-01 Air Cleaner Element Inspecting and Replacing • •
13-01 Air Compressor Inspection • • • •
15-01 Alternator, Battery, and Starter Checking • •
20-01 Radiator Cap Inspecting • • • •
20-02 Radiator Pressure Flushing and Coolant Changing • •
20-03 Fan Drive Inspecting (Noise Emission Control) • • • •
20-04 Hybrid Electric System Coolant Changing • •
25-01 Eaton Fuller Clutch Release Bearing Lubricating ••••••
25-02 Eaton Fuller Clutch Release Cross-Shaft Lubricating ••••••
25-03 Clutch Hydraulic Fluid Level Checking •••••
25-04 Clutch Hydraulic Fluid Changing •
25-05 Clutch Adjusting, Manually Adjusted Clutches ••••••
26-01 Transmission Fluid Level Checking •••••
26-02
26-03 Allison and Eaton Fuller Transmission Breather Checking ••••••
26-04
26-05 Allison Transmission Fluid and Filter Changing • • •
26-06
26-07 Mercedes-Benz Transmission Leak Checking •
31-01 Frame Fastener Torque Checking • • •
31-02 Fifth Wheel Inspecting ••••••
31-03 Fifth Wheel Lubricating ••••••
31-04 Trailer Electrical Connector Lubricating ••••••
32-01 Suspension Inspecting ••••••
32-02 Suspension Lubricating ••••••
32-03 Suspension U-Bolt Torque Checking • • • •
33-01 Kingpin Lubricating
33-02 Tie Rod End Lubricating
33-03 Draw Key Nut Torque Checking • • • •
33-04 Tie Rod End Inspecting ••••••
Eaton Fuller Transmission Fluid Changing and Magnetic Plug
Cleaning
Eaton Fuller Transmission Air Filter/Regulator Element
Cleaning
Mercedes-Benz Transmission Fluid Changing and Magnetic
Plug Cleaning
Title of Maintenance Operation
*
†
¶
IM M1 M2 M3 M4 M5
Maintenance Intervals
••••
••••
•
••••••
••••••
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/5
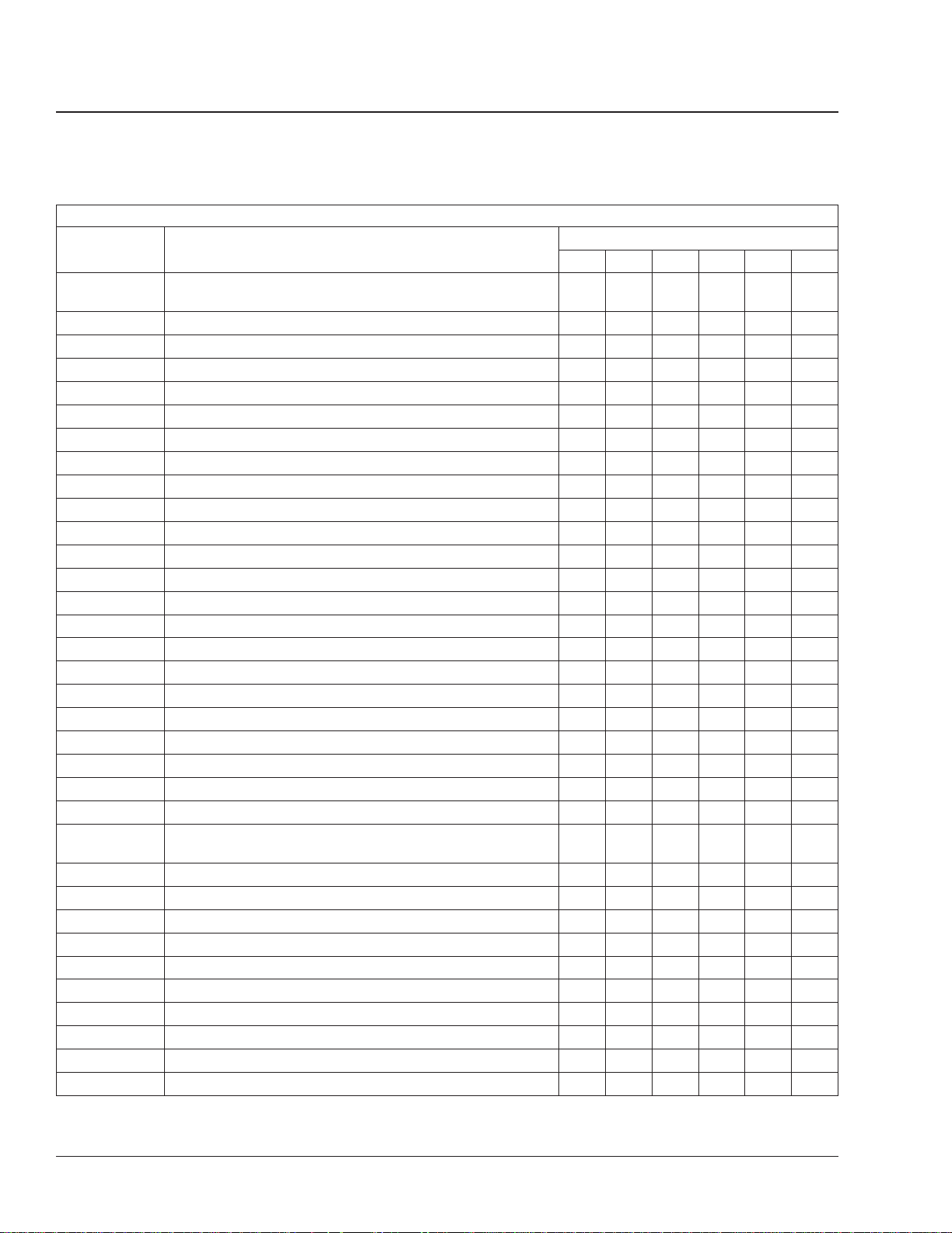
General Information00
Overview of Maintenance Operations: 00–05
Maintenance Operations for Groups 00 through 88
Maintenance
Operation No.
33-05
33-06 All-Axle Alignment Check •
35-01 Axle Lubricant Level Checking ••••
35-02 Axle Breather Checking ••••••
35-03 Axle Lubricant Changing and Magnetic Plug Cleaning • •
40-01 Wheel Nut Checking • • •
40-02 Tire Check ••••••
41-01 Driveline Inspecting ••••••
41-02 Driveline Lubricating ••••••
42-01 Air Brake System Valve Inspection ••••••
42-02 Bendix Air Dryer Desiccant Replacement
42-03 Governor D–2A Check ••
42-04 Bosch Hydraulic Brake System Inspection ••••••
42-05 Dana Spicer, Haldex, and Gunite Slack Adjuster Lubrication ••••••
42-06 Meritor Camshaft Bracket Lubrication • • • •
42-07 Meritor Slack Adjuster Lubrication ••••••
42-08 Air Dryer AD–9, AD–IP, and AD–IS/DRM Check • • • •
42-09 Brake Lines and Fittings Inspection, Hydraulic Brakes ••••••
42-10 Brake Pedal Linkage and Mounting Plate Inspection • • • •
42-11 Air Brake Inspection and Leak Test • • •
42-12 Bendix E-6 Foot Control Valve Inspection and Lubrication •
42-13 Brake Inspection ••••••
42-14 Hydro-Max™Brake System Inspection ••••••
42-15
42-16 Versajust Slack Adjuster Inspection and Lubrication
46-01 Drag Link Inspecting • • •
46-02 Power Steering Fluid Changing • •
46-03 Power Steering Fluid Level Inspecting ••••
46-04 Power Steering Gear Lubricating ••••••
46-05 Drag Link Lubricating ••••••
46-06 Power Steering Filter Changing •
47-01 Fuel Tank Band Nut Tightening •
47-02 Fuel/Water Separator Element Replacing • •
47-03 LNG Fuel System Inspecting •••••
Wheel End Inspection and Maintenance, 6,000-Pound and
8,000-Pound Steer Axles with Oil-Lubricated Hubs
WABCO System Saver Air Dryer Desiccant Cartridge
Replacement
Title of Maintenance Operation
§
§
IM M1 M2 M3 M4 M5
‡
¶
Maintenance Intervals
••••••
•••••
•••••
•••••
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/6
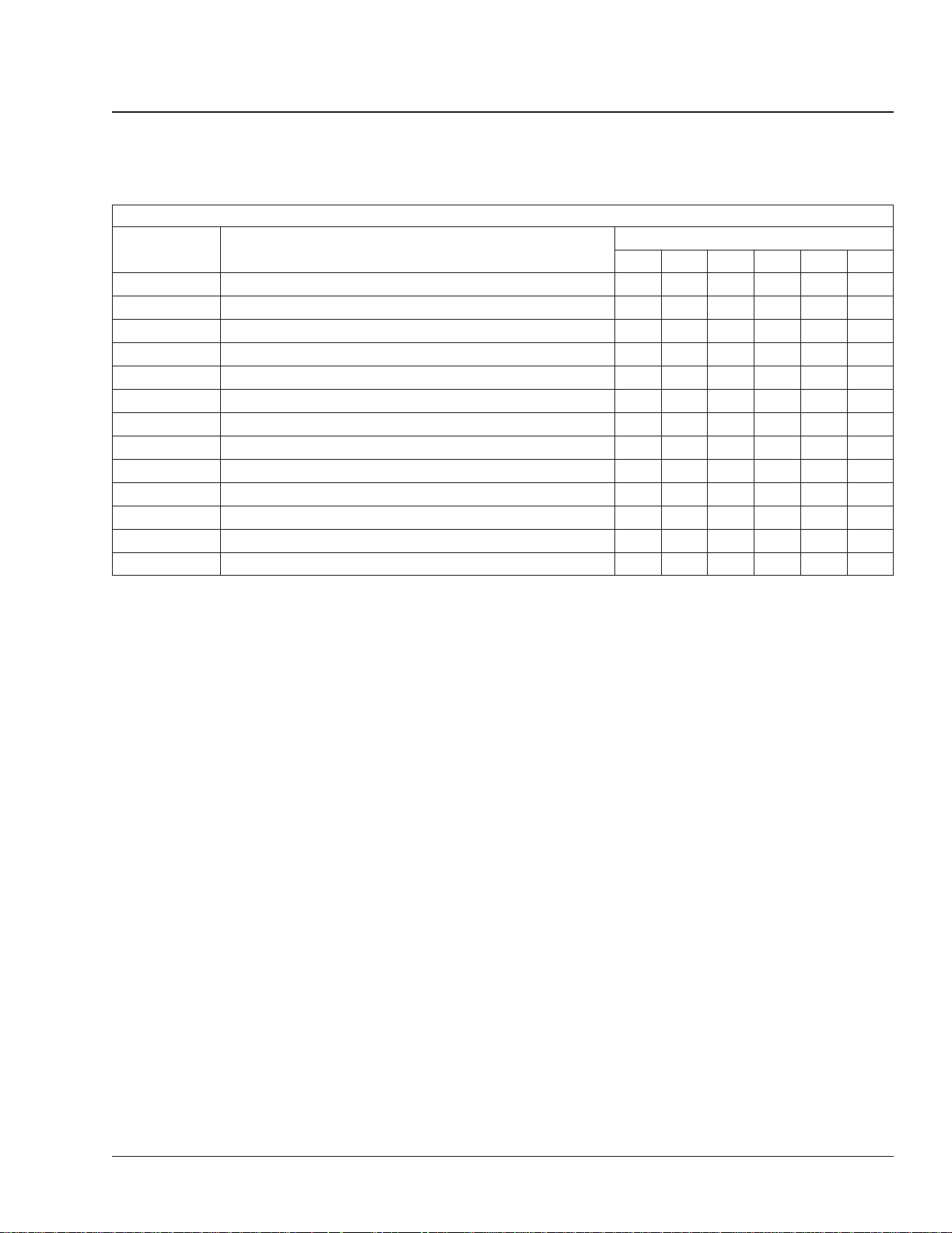
General Information 00
Overview of Maintenance Operations: 00–05
Maintenance Operations for Groups 00 through 88
Maintenance
Operation No.
Title of Maintenance Operation
IM M1 M2 M3 M4 M5
47-04 LNG Vacuum Integrity Testing • • •
47-05 CNG Fuel System Inspecting • • • •
47-06 CNG High-Pressure Fuel Filter Element Replacing •••••
47-07 CNG Fuel Cylinder Inspecting • • •
49-01 Exhaust System Inspecting (Noise Emission Control) • • • •
49-02 CAT CGI Bellows and Piping Inspection •••••
49-03 CAT CGI Bellows Replacement •
60-01 Mirror Folding Check ••
60-02 Aerodynamic Component Inspection •••••
72-01 Door Seals Lubricating ••••••
83-01 Air Conditioner Inspecting ••••••
83-02 HVAC Air Filter Replacing
**
88-01 Hood Rear Support Lubrication •••••
*
Change petroleum-based lubricants at M2 (including M3, M4, and M5). Change synthetic lubricants at M5 only.
†
For Detroit axles, complete this procedure once a year or at the following applicable interval, whichever comes first: every 5000 miles (8000 km) for Schedule
I vehicles; every 25,000 miles (40 000 km) for Schedule II vehicles; or every 100,000 miles (161 000 km) for Schedule III vehicles.
‡
Schedule II and Schedule III vehicles only.
§
If equipped with an oil-coalescing desiccant cartridge, replace the cartridge once a year, regardless of mileage. Otherwise use the M5 maintenance interval.
¶
Complete this procedure every 25,000 miles (40 225 km), 3 months, or 500 operating hours, whichever comes first.
**
Replace the HVAC air filter at the recommended interval or every six months.
Table 4, Maintenance Operations for Groups 00 through 88
Maintenance Intervals
•••
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/7

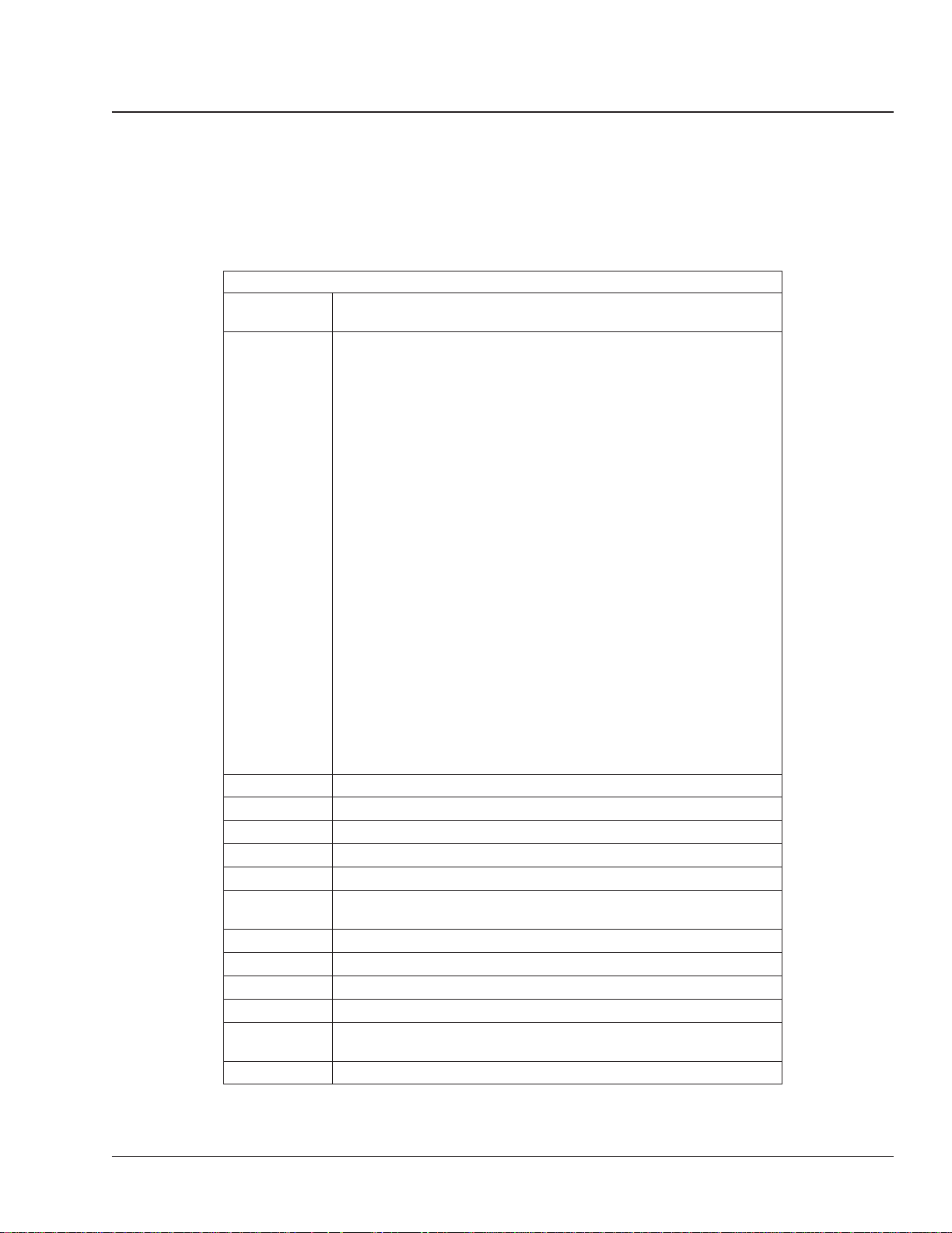
Initial Maintenance (IM) Operations: 00–06
NOTE: The IM Operations include the maintenance
operations in Table 5 and all of the maintenance op-
erations in Table 6, M1 Maintenance Operations.
Initial Maintenance (IM) Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
00-07 Perform All M1 Operations
31-01 Frame Fastener Torque Checking
32-03 Suspension U-Bolt Torque Checking
33-03 Draw Key Nut Torque Checking
33-06 All-Axle Alignment Check
47-01 Fuel Tank Band Nut Tightening
Table 5, Initial Maintenance (IM) Operations
Title of Maintenance Operation
General Information00
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/8
General Information 00
M1 Maintenance Operations: 00–07
IMPORTANT: After performing all operations listed in
this table, perform all daily, weekly, and monthly
maintenance operations listed in the "Pretrip and
M1 Maintenance Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
00-12 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check
• Eaton Fuller Clutch Release Bearing Lubricating
• Eaton Fuller Clutch Release Cross-Shaft Lubricating
• Clutch Hydraulic Fluid Level Checking
• Transmission Fluid Level Checking
• Fifth Wheel Lubricating
• Trailer Electrical Connector Lubricating
• Suspension Lubricating
• Kingpin Lubricating
• Tie Rod End Lubricating
• Axle Lubricant Level Checking
• Driveline Lubricating
• Haldex and Gunite Slack Adjuster Lubricating
• Meritor Slack Adjuster Lubricating
• Power Steering Fluid Level Inspecting
• Power Steering Gear Lubricating
• Drag Link Lubricating
• Door Seals Lubricating
• Hood Rear Support Lubrication
25-05 Clutch Adjusting, Manually Adjusted Clutches
26-03 Allison and Eaton Fuller Transmission Breather Checking
31-02 Fifth Wheel Inspecting
32-01 Suspension Inspecting
33-04 Tie Rod End Inspecting
33-05 Wheel End Inspection and Maintenance, 6,000-Pound and 8,000-
Pound Steer Axles with Oil-Lubricated Hubs
35-02 Axle Breather Checking
40-02 Tire Check
41-01 Driveline Inspecting
42-01 Air Brake System Valve Inspection
42-02 Bendix Air Dryer Desiccant Replacement (with an oil-coalescing des-
iccant cartridge)
42-04 Bosch Hydraulic Brake System Inspection
Title of Maintenance Operation
†
Post-Trip Inspections and Maintenance" chapter of
the Business Class® M2 Driver’s Manual.
*
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/9

M1 Maintenance Operations: 00–07
M1 Maintenance Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
42-09 Brake Lines and Fittings Inspection, Hydraulic Brakes
42-13 Brake Inspection
42-14 Hydro-Max™Brake System Inspection
42-15 WABCO System Saver Air Dryer Desiccant Cartridge Replacement
42-16 Versajust Slack Adjuster Inspection and Lubrication
47-03 LNG Fuel System Inspecting
47-06 CNG High-Pressure Fuel Filter Element
49-02 CAT CGI Bellows and Piping Inspection
60-02 Aerodynamic Component Inspection
83-01 Air Conditioner Inspecting
*
Schedule III vehicles only.
†
If equipped with an oil-coalescing desiccant cartridge, replace the cartridge once a year, regardless of mileage.
Otherwise use the M5 maintenance interval.
‡
Complete this procedure every 25,000 miles (40 225 km), 3 months, or 500 operating hours, whichever comes
first.
§
M1 maintenance interval should be used as a general guideline; the actual frequency of filter element replace-
ment will vary depending on cleanliness of the fuel station system.
Table 6, M1 Maintenance Operations
Title of Maintenance Operation
General Information00
†
‡
§
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/10

General Information 00
M2 Maintenance Operations: 00–08
NOTE: The M2 Maintenance Operations include the
maintenance operations in Table 7 and all of the
M2 Maintenance Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
00-07 Perform All M1 Maintenance Operations
00-13 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check
• Eaton Fuller Transmission Fluid Changing and Magnetic Plug
Cleaning
• Meritor Camshaft Bracket Lubricating
13-01 Air Compressor Inspection
20-01 Radiator Cap Inspecting
20-03 Fan Drive Inspecting (Noise Emission Control)
26-04 Eaton Fuller Transmission Air Filter/Regulator Element Cleaning
33-05
Wheel End Inspection and Maintenance, 6,000-Pound and 8,000Pound Steer Axles with Oil-Lubricated Hubs
42-08 Air Dryer AD–9, AD–IP, and AD–IS/DRM Check
42-10 Brake Pedal Linkage and Mounting Plate Inspection
47-05 CNG Fuel System Inspecting
47-07 CNG Fuel Cylinder Inspecting
49-01 Exhaust System Inspecting (Noise Emission Control)
*
Petroleum-based lubricants only.
†
Schedule II vehicles only.
‡
The fuel cylinder should be inspected every year or 100,000 miles (160 900 km), whichever comes first.
Table 7, M2 Maintenance Operations
Title of Maintenance Operation
*
maintenance operations in Table 6, M1 Maintenance
Operations.
†
‡
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/11

M3 Maintenance Operations: 00–09
NOTE: The M3 Maintenance Operations include the
maintenance operations in Table 8 and all of the
maintenance operations in Table 6, M1 Maintenance
Operations, and
tions.
Table 7, M2 Maintenance Opera-
M3 Maintenance Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
00-07 Perform All M1 Maintenance Operations
00-08 Perform All M2 Maintenance Operations
01-01 Engine Drive Belt Inspecting
26-05 Allison Transmission Fluid and Filter Changing
32-03 Suspension U-Bolt Torque Checking
33-03 Draw Key Nut Torque Checking
40-01 Wheel Nut Checking
42-11 Air Brake Inspection and Leak Test
46-01 Drag Link Inspecting
47-04 LNG Vacuum Integrity Testing
83-02 HVAC Air Filter Replacing
*
Replace the HVAC air filter at the recommended interval or every six months.
Table 8, M3 Maintenance Operations
Title of Maintenance Operation
General Information00
*
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/12

General Information 00
M4 Maintenance Operations: 00–10
NOTE: The M4 Maintenance Operations include the
maintenance operations in Table 9 and all of the
maintenance operations in Table 6, M1 Maintenance
M4 Maintenance Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
00-07 Perform All M1 Maintenance Operations
00-08 Perform All M2 Maintenance Operations
00-09 Perform All M3 Maintenance Operations
01-02 Engine Support Fastener Checking
09-01 Air Cleaner Element Inspecting and Replacing
15-01 Alternator, Battery, and Starter Checking
20-02 Radiator Pressure Flushing and Coolant Changing
20-04 Hybrid Electric System Coolant Changing
31-01 Frame Fastener Torque Checking
35-03 Axle Lubricant Changing and Magnetic Plug Cleaning
42-03 Governor D–2A Check
46-02 Power Steering Fluid Changing
47-02 Fuel/Water Separator Element Replacing
60-01 Mirror Folding Check
Table 9, M4 Maintenance Operations
Title of Maintenance Operation
Operations, Table 7, M2 Maintenance Operations,
and Table 8, M3 Maintenance Operations.
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/13

M5 Maintenance Operations: 00–11
General Information00
NOTE: The M5 Maintenance Operations include the
maintenance operations in Table 10 and all of the
maintenance operations in Table 6, M1 Maintenance
M5 Maintenance Operations
Maintenance
Operation No.
00-07 Perform All M1 Maintenance Operations
00-08 Perform All M2 Maintenance Operations
00-09 Perform All M3 Maintenance Operations
00-10 Perform All M4 Maintenance Operations
25-04 Clutch Hydraulic Fluid Changing
26-06
26-07 Mercedes-Benz Transmission Leak Checking
42-02 Bendix Air Dryer Desiccant Replacement
42-12 Bendix E-6 Foot Control Valve Inspection and Lubrication
42-15 WABCO System Saver Air Dryer Desiccant Cartridge Replacement
46-06 Power Steering Filter Changing
49-03 CAT CGI Bellows Replacement
Mercedes-Benz Transmission Fluid Changing and Magnetic Plug
Cleaning
Table 10, M5 Maintenance Operations
Title of Maintenance Operation
Operations, Table 7, M2 Maintenance Operations,
Table 8, M3 Maintenance Operations, and Table 9,
M4 Maintenance Operations.
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/14

General Information 00
M1 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check: 00–12
Table 11, MOP 00-12, lists the lubrication and fluid
level check maintenance operations that must be
performed at the M1 Maintenance Interval.
MOP 00-12, M1 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check
Maintenance
Operation No.
25-01 Eaton Fuller Clutch Release Bearing Lubricating
25-02 Eaton Fuller Clutch Release Cross-Shaft Lubricating
25-03 Clutch Hydraulic Fluid Level Checking
26-01 Transmission Fluid Level Checking
31-03 Fifth Wheel Lubricating
31-04 Trailer Electrical Connector Lubricating
32-02 Suspension Lubricating
33-01 Kingpin Lubricating
33-02 Tie Rod End Lubricating
35-01 Axle Lubricant Level Checking
41-02 Driveline Lubricating
42-05 Dana Spicer, Haldex, and Gunite Slack Adjuster Lubrication
42-07 Meritor Slack Adjuster Lubrication
42-16 Versajust Slack Adjuster Inspection and Lubrication
46-03 Power Steering Fluid Level Inspecting
46-04 Power Steering Gear Lubricating
46-05 Drag Link Lubricating
72-01 Door Seals Lubricating
88-01 Hood Rear Support Lubrication
*
For Detroit axles, complete this procedure once a year or at the following applicable interval, whichever comes
first: every 5000 miles (8000 km) for Schedule I vehicles; every 25,000 miles (40 000 km) for Schedule II vehicles;
or every 100,000 miles (161 000 km) for Schedule III vehicles.
†
Complete this procedure every 25,000 miles (40 225 km), 3 months, or 500 operating hours, whichever comes
first.
Table 11, MOP 00-12, M1 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check
Title of Maintenance Operation
*
*
†
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/15

M2 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check: 00–13
Table 12, MOP 00-13, lists the lubrication and fluid
level check maintenance operations that must be
performed at the M2 Maintenance Interval.
MOP 00-13, M2 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check
Maintenance
Operation No.
26-02
42-06 Meritor Camshaft Bracket Lubrication
*
Petroleum-based lubricants only.
Eaton Fuller Transmission Fluid Changing and Magnetic Plug
Cleaning
Table 12, MOP 00-13, M2 Lubrication and Fluid Level Check
*
Title of Maintenance Operation
General Information00
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/16

General Information 00
Noise Emission Controls: 00–15
Noise Emission Controls
Federal Law, Part 205:
Transportation Equipment Noise
Emission Controls
Part 205, Transportation Equipment Noise Emission
Controls, requires the vehicle manufacturer to furnish
each new vehicle with written instructions for the
proper maintenance, use, and repair of the vehicle
by the ultimate purchaser to provide reasonable assurance of the elimination or minimization of noise
emission degradation throughout the life of the vehicle. In compliance with the law, the Noise Emission
Control Systems maintenance located in each applicable group within this manual, in conjunction with
the vehicle workshop manual, provides these instructions to owners.
Recommendations for
Replacement Parts
Replacement parts used for maintenance or repair of
noise emission control systems should be genuine
Freightliner parts. If other than genuine Freightliner
parts are used for replacement or repair of components affecting noise emission control, the owner
should be sure that such parts are warranted by their
manufacturer to be equivalent to genuine Freightliner
parts in performance and durability.
2. The use of the vehicle after such device or element of design has been removed or rendered
inoperative by any person.
Among those acts presumed to constitute tampering
are the acts listed below:
1. Removal of engine noise-deadening panels, including cab or hood liners.
2. Removal of or rendering inoperative the engine
speed governor so as to allow engine speed to
exceed the manufacturer’s specifications.
3. Removal of or rendering inoperative the fan
clutch, including bypassing the control on any
thermostatic fan drive to cause it to operate continuously.
4. Removal of the fan shroud.
5. Removal of or rendering inoperative exhaust system components, including exhaust pipe clamping.
6. Removal of air intake system components.
Freightliner Noise Emissions
Warranty
Refer to the vehicle owner’s warranty information
book for warranty information concerning noise emission control systems.
Tampering With the Noise
Control System is Prohibited
Federal law prohibits the following acts or the causing thereof:
1. The removal or rendering inoperative by any person other than for purposes of maintenance, repair, or replacement, of any device or element of
design incorporated into any new vehicle for the
purpose of noise control prior to its sale or delivery to the ultimate purchaser or while it is in use,
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 2016 00/17
General Information00
Verification of Inspections Log: 00–16
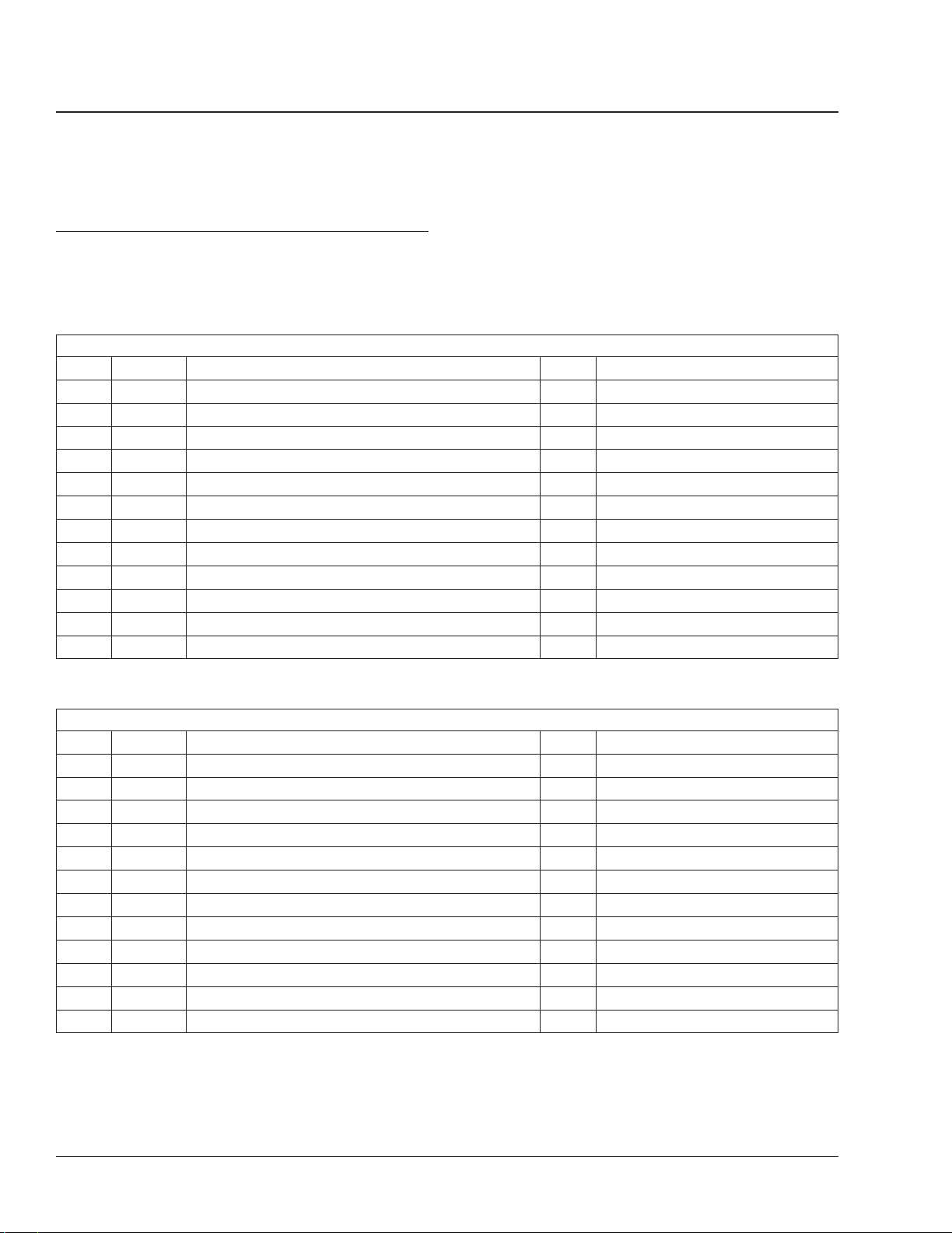
Verification of Inspections Log
The "Verification of Inspections Log" should be filled
out each time the vehicle’s noise emission controls
are maintained or repaired.
Verification of Inspections Log, Group 20
Verification of Inspections Log, Group 20, Engine Cooling/Radiator
Date Mileage Repair Description Cost Repair Facility
Verification of Inspections Log, Group 49
Verification of Inspections Log, Group 49, Exhaust
Date Mileage Repair Description Cost Repair Facility
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, March 201600/18

Engine 01
Index, Alphabetical
Title of Maintenance Operation (MOP) MOP Number
Engine Drive Belt Inspecting ..........................................................01–01
Engine Support Fastener Checking .....................................................01–02
Safety Precautions .................................................................01–00
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, August 2015
Engine 01
01–00 Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions in this section apply to all
procedures within this group.
DANGER
When working on the vehicle, shut down the engine, set the parking brake, and chock the tires.
Before working under the vehicle, always place
jack stands under the frame rails to ensure the
vehicle can not drop. Failure to follow these steps
could result in serious personal injury or death.
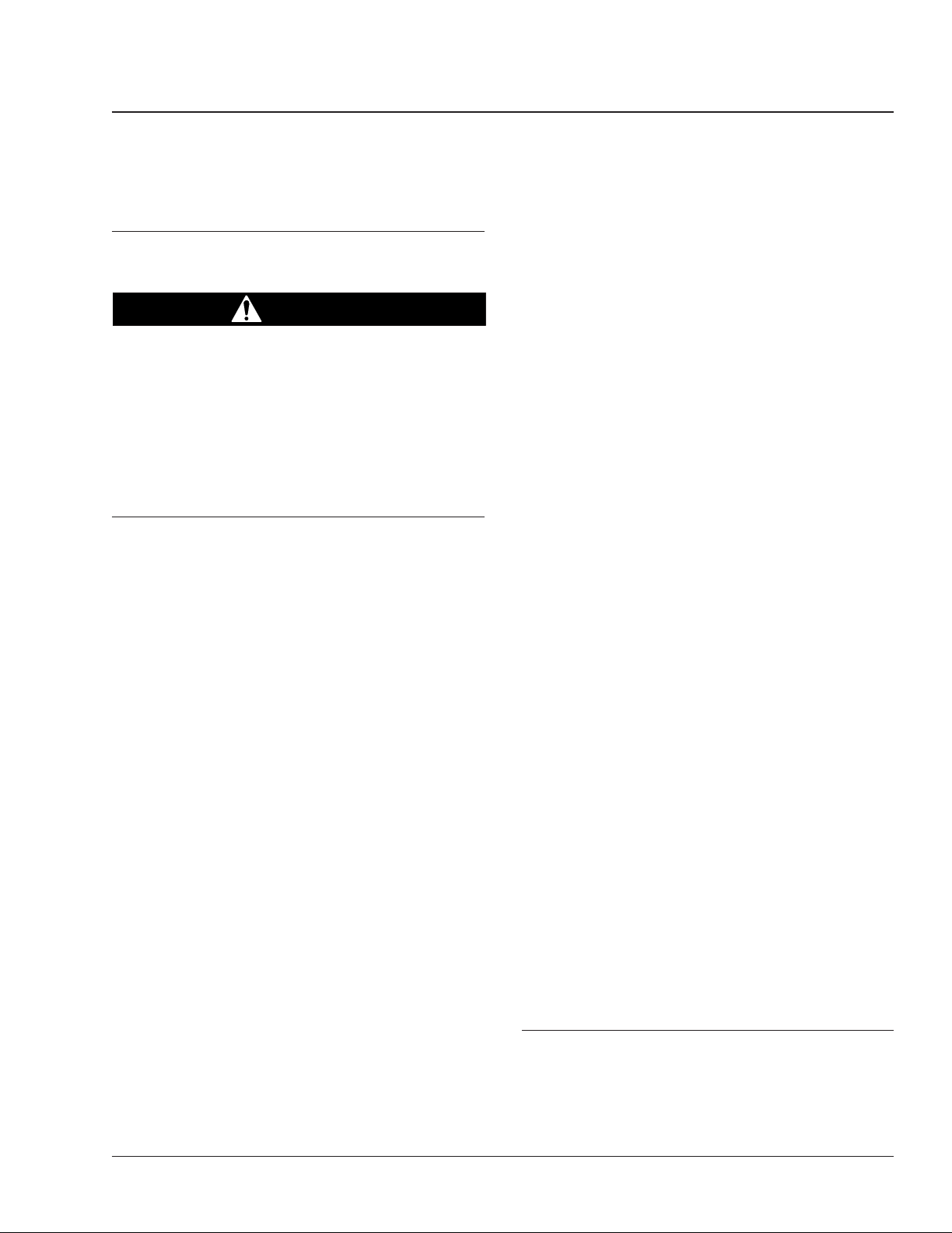
01–01 Engine Drive Belt
Inspecting
Worn or loose drive belts may cause premature pulley bearing failure or engine overheating. Too much
or too little tension on the belt may result in excessive or premature belt wear. Replace the engine
drive belt if any conditions described under Visual
Inspection are found.
Visually inspect all drive belts, then perform the belt
tension inspection. To inspect a belt, gently twist the
belt to view the belt sidewalls and the underside of
the belt. When replacing a matched set of belts, always replace both belts at the same time. Matched
belts must be from the same manufacturer.
Visual Inspection
For examples of drive belt conditions, see Fig. 1.
affecting the belts before replacing the drive
belts. Do not use belt dressing on any belt.
4. Check for uneven ribs on serpentine (poly-V)
belts. Foreign material in the pulley will erode the
undercord ribs causing the belt to lose its gripping power.
5. Check the belt for a jagged or streaked sidewall.
Jagged or streaked sidewalls are the result of
foreign material, such as sand or gravel, in the
pulley, or a rough pulley surface.
6. Check the drive belts for cracks. Small, irregular
cracks are usually indication of an old belt.
7. Visually inspect the pulleys for excessive play or
wobble. Excessive play or wobble indicates a
failure of the pulley bearing. Check for belt
squealing or squeaking. Replace the bearings as
necessary.
NOTE: If it is difficult to distinguish the location
of a supposed bearing noise, obtain a stethoscope and place it on the component being
checked, not the pulley, to isolate the area from
outside interference.
8. Inspect all pulleys for foreign material, oil, or
grease in the grooves.
If the engine drive belt needs to be replaced, see
Group 01 of the Business Class® M2 Workshop
Manual.
Belt Tension Inspection
Engine drive belts on the Mercedes-Benz and Caterpillar engines have belt tensioners that automatically
adjust the tension on the belt. These belts do not
require adjustment.
1. Inspect the belt for glazing. Shiny sidewalls are
evidence of glazing, which is caused by friction
created when a loose belt slips in the pulleys. It
can also be caused by oil or grease contamination on the pulleys.
2. Check for tensile breaks or breaks in the cord
body. Cuts in a belt are usually caused by foreign material in the pulley or by prying or forcing
the belt during removal or installation.
3. Check the belt for ply separation. Oil, grease, or
belt dressing can cause the belt to fall apart in
layers. Repair any oil or coolant leaks that are
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, August 2015 01/1
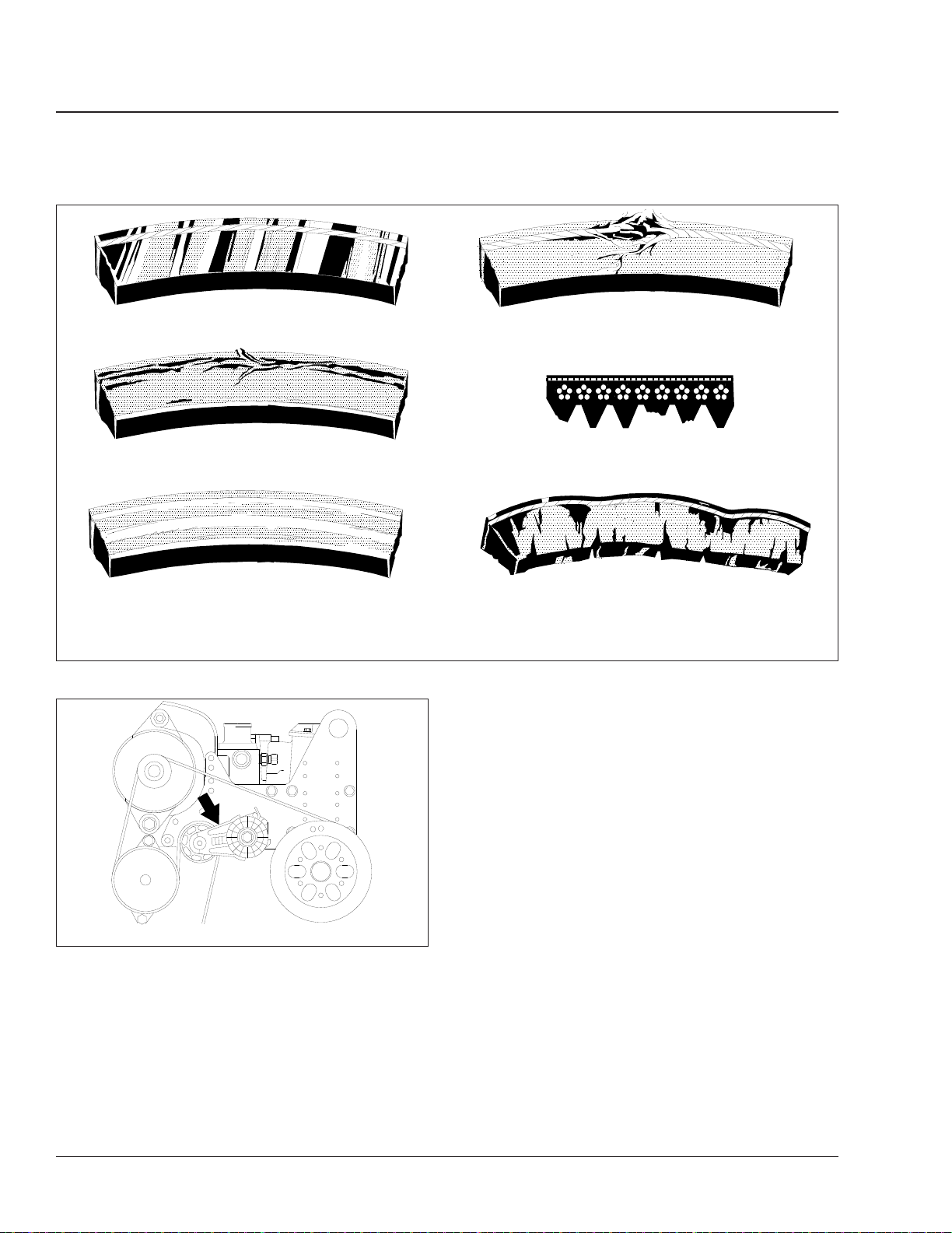
Caterpillar 3126 Engine
Inspect the belt tensioner for unusual noise and excessive looseness or shaking of the pulley bearings.
Fig. 2. If the belt tensioner requires disassem-
See
bly, refer to the engine service manual.
01–02 Engine Support Fastener
Checking
Front and rear engine supports for vehicles built from
January 2007 require no periodic maintenance.
Mounts should be inspected when the engine is re-
Engine01
12
07/12/2001
1. Glazing
2. Tensile Break
3
56
3. Separating Layers
4. Uneven Ribs
Fig. 1, Drive Belt Replacement Conditions
5. Streaked Sidewalls
6. Cracks
4
f150010b
2. Check the tightness of the engine support fasteners at the front of the engine. Tighten the fasteners 136 lbf·ft (327 N·m).
NOTE: When the engine is removed, inspect
the lower and upper isolators for wear. Replace
the isolators if necessary.
07/12/2001
Fig. 2, Belt Tensioner on Caterpillar 3126 Engine
f011990
moved for service. For vehicles manufactured prior to
January 2007, perform the following check.
1. Check the tightness of the engine support fasteners at the rear of the engine. Tighten the fasteners 241 lbf·ft (460 N·m).
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, August 201501/2

Air Intake 09
Index, Alphabetical
Title of Maintenance Operation (MOP) MOP Number
Air Cleaner Element Inspection and Replacement ..........................................09–01
Business Class M2 Maintenance Manual, November 2014
 Loading...
Loading...