Freightliner 122SD, 132SD Driver's Manual

CORONADO
®
Part Number STI 494 3
Publication Number STI-494-6
Driver’s Manual

Foreword
Introduction
This manual provides information needed to operate
and understand the vehicle and its components.
More detailed information is contained in the Owner’s
Warranty Information for North America booklet, and
in the vehicle’s workshop and maintenance manuals.
Custom-built Freightliner vehicles are equipped with
various chassis and cab components. Not all of the
information contained in this manual applies to every
vehicle. For details about components in your vehicle, refer to the chassis specification pages included in all new vehicles and to the vehicle specification decal, located inside the vehicle.
For your reference, keep this manual in the vehicle
at all times.
IMPORTANT: Descriptions and specifications in
this manual were in effect at the time of printing.
Freightliner Trucks reserves the right to discontinue models and to change specifications or
design at any time without notice and without
incurring obligation. Descriptions and specifications contained in this publication provide no
warranty, expressed or implied, and are subject
to revisions and editions without notice.
Environmental Concerns and
Recommendations
Whenever you see instructions in this manual to discard materials, you should first attempt to reclaim
and recycle them. To preserve our environment, follow appropriate environmental rules and regulations
when disposing of materials.
Event Data Recorder
This vehicle is equipped with one or more devices
that record specific vehicle data. The type and
amount of data recorded varies depending on how
the vehicle is equipped (such as the brand of engine,
if an air bag is installed, or if the vehicle features a
collision avoidance system, etc.).
This vehicle is equipped with an event data recorder
(EDR). The main purpose of an EDR is to record
data in certain crash or near-crash situations, such
as air bag deployment or hitting a road obstacle, that
will assist in understanding how a vehicle’s systems
performed. The EDR is designed to record data related to vehicle dynamics and safety systems for approximately 60 seconds. This data can help provide
a better understanding of the circumstances in which
crashes and injuries occur. Data recorded includes
the following items:
•
how various systems in the vehicle were operating
•
engine system information
•
how far (if at all) the driver was depressing the
accelerator
•
if the driver was depressing the brake pedal
•
how fast the vehicle was traveling
NOTE: Data is not recorded by the EDR under
normal driving conditions. Personal data such
as name, gender, age, and crash location are
not recorded. However, other parties such as
law enforcement could combine the EDR data
with the type of personally identifying data routinely acquired during a crash investigation.
To read data recorded by an EDR, special equipment
is required, and access to the vehicle or the EDR is
needed. In addition to the vehicle manufacturer, other
parties that have the special equipment, such as law
enforcement, can read the information if they have
access to the vehicle or the EDR.
Emissions and Fuel Efficiency
Compliance
This vehicle must be regularly inspected and maintained as indicated in the 122SD and Coronado 132
Maintenance Manual, and in the Pre- and Post-Trip
Inspections and Maintenance chapter in this manual,
in order to continue satisfactory performance and
ensure coverage of the vehicle under the manufacturer’s warranty. Many maintenance procedures ensure that the vehicle and engine continue to comply
with applicable emissions standards. Maintenance
procedures, using components engineered to comply
with greenhouse gas emissions and fuel efficiency
regulations, may be performed by an authorized
Daimler Trucks North America dealer, an independent outlet, or the vehicle owner or operator.
The vehicle owner is responsible for determining the
suitability of replacement components to maintain
STI-494-7 (11/14)
Part Number STI 494 3
Printed in U.S.A.

Foreword
compliance with federal and local jurisdictional regulations. Components including, but not limited to,
tires, cab/sleeper side extenders, chassis fairings,
bumper, hood, vehicle speed limiters, and idle reduction timers are specifically designed and manufactured to exacting standards for regulatory fuel efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions compliance. It
is important that these components are always replaced with components that meet or exceed the performance of the originally installed components.
Customer Assistance Center
Having trouble finding service? Call the Customer
Assistance Center at 1-800-385-4357 or 1-800-FTLHELP. Call night or day, weekdays or weekends, for
dealer referral, vehicle information, breakdown coordination, or Fleetpack assistance. Our people are
knowledgeable, professional, and committed to following through to help you keep your truck moving.
Reporting Safety Defects
If you believe that your vehicle has a defect which
could cause a crash or could cause injury or
death, you should immediately inform the National
Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in
addition to notifying Daimler Trucks North America
LLC.
hotline 1-800-333-0510, or contact Transport
Canada by mail at: Transport Canada, ASFAD,
Place de Ville Tower C, 330 Sparks Street, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada K1A 0N5.
For additional road safety information, please visit
the Road Safety website at:
roadsafety
.
www.tc.gc.ca/
If the NHTSA receives similar complaints, it may
open an investigation, and if it finds that a safety
defect exists in a group of vehicles, it may order a
recall and remedy campaign. However, NHTSA
cannot become involved in individual problems
between you, your dealer, or Daimler Trucks North
America LLC.
To contact NHTSA, you may call the Vehicle
Safety Hotline toll-free at 1-888-327-4236 (TTY:
1-800-424-9153); go to
write to: Administrator, NHTSA, 1200 New Jersey
Avenue, SE, Washington, DC 20590. You can also
obtain other information about motor vehicle safety
from
www.safercar.gov.
Canadian customers who wish to report a safetyrelated defect to Transport Canada, Defect Investigations and Recalls, may telephone the toll-free
© 2010–2015 Daimler Trucks North America LLC. All rights reserved. Daimler Trucks North America LLC is a Daimler
company.
No part of this publication, in whole or part, may be translated, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted
in any form by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Daimler Trucks North America LLC. For additional information, please contact Daimler Trucks North
America LLC, Service Systems and Documentation, P.O. Box 3849, Portland OR 97208–3849 U.S.A. or refer to
www.Daimler-TrucksNorthAmerica.comand www.FreightlinerTrucks.com.
www.safercar.gov;or

Contents
Chapter Page
Introduction, Environmental Concerns and Recommendations,
Event Data Recorder, Emissions and Fuel Efficiency Compliance,
Customer Assistance Center, Reporting Safety Defects
1 Vehicle Identification ...................................................... 1.1
2 Vehicle Access .......................................................... 2.1
3 Electrical System ........................................................ 3.1
4 Instruments ............................................................. 4.1
5 Driver Controls .......................................................... 5.1
6 Seats and Restraints ..................................................... 6.1
7 Climate Control .......................................................... 7.1
8 Cab Features ........................................................... 8.1
9 Engine Starting, Operation, and Shutdown .................................... 9.1
10 Optional Engine Systems ................................................. 10.1
11 Emissions and Fuel Efficiency ............................................. 11.1
12 Brake Systems ......................................................... 12.1
13 Manual Transmissions and Clutch .......................................... 13.1
14 Automated and Automatic Transmissions .................................... 14.1
15 Drive Axles ............................................................ 15.1
16 Steering System ........................................................ 16.1
17 Fifth Wheels ........................................................... 17.1
18 Trailer Couplings ........................................................ 18.1
19 Pre- and Post-Trip Checklists ............................................. 19.1
20 Pre- and Post-Trip Inspections and Maintenance .............................. 20.1
21 Cab Appearance ........................................................ 21.1
22 Headlight Aiming ........................................................ 22.1
23 In an Emergency ....................................................... 23.1
Index .................................................................. I.1
.................... Foreword

1
Vehicle Identification
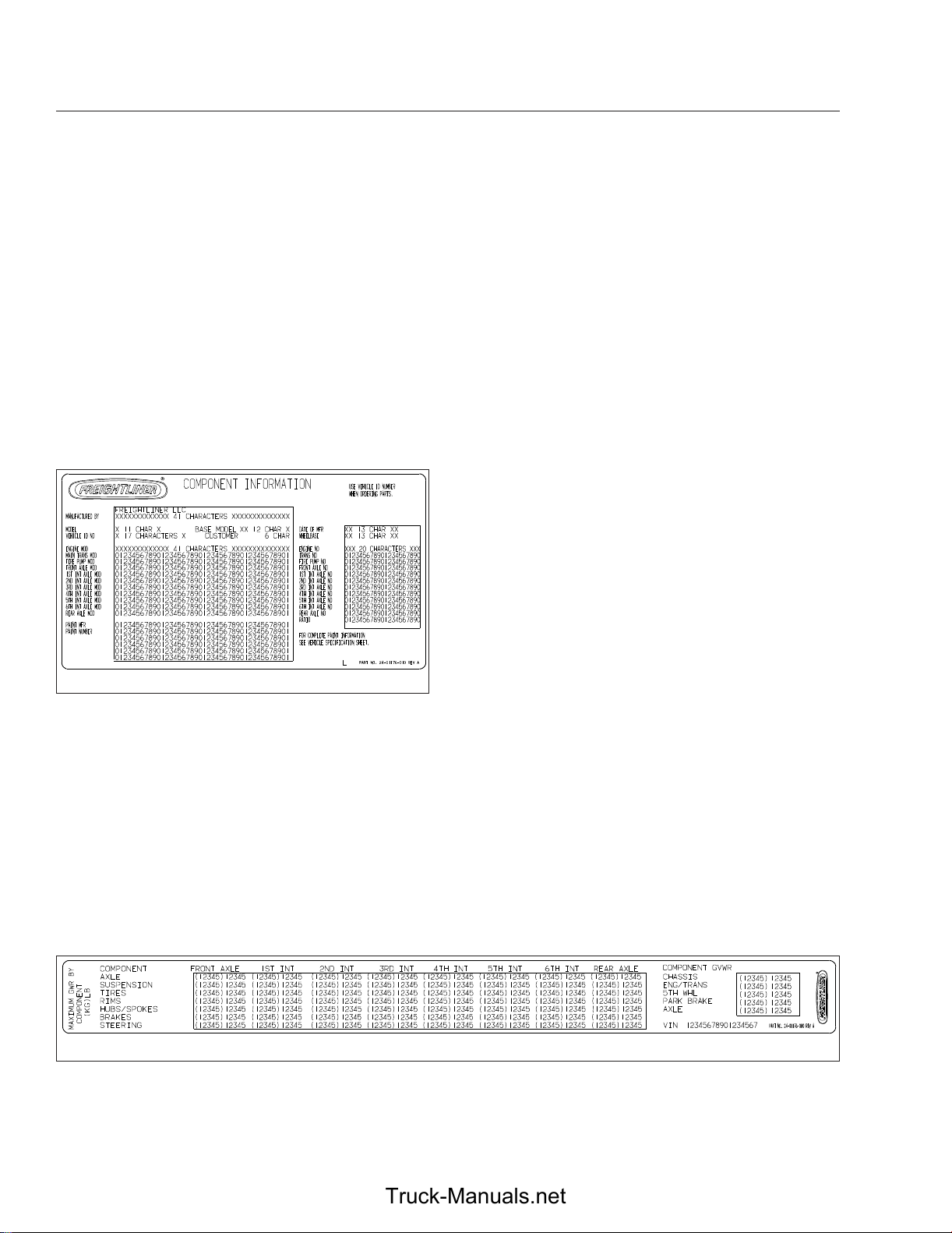
Component Information Label ....................................................... 1.1
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard Labels .......................................... 1.1
Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety Standard Labels ........................................ 1.1
Component GWR Label ............................................................ 1.1
Emissions Labels ................................................................. 1.2
Vehicle Identification
Component Information Label
NOTE: Labels shown in this chapter are examples only. Actual specifications may vary from
vehicle to vehicle.
The component information label lists the vehicle
model, identification number, and major component
models. It also lists the major assemblies and installations shown on the chassis specification sheet.
One copy of the component information label is attached to the inside of the glove box; another copy is
inside the rear cover of the Owner’s Warranty Infor-
mation for North America booklet. An illustration of
the label is shown in
02/20/2012 f080176
Fig. 1.1, Component Information Label
Fig. 1.1.
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standard Labels
NOTE: Due to the variety of Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) certification requirements, not all of the labels shown will apply
to your vehicle.
Tractors with or without fifth wheels purchased in the
U.S. are marked as certified by means of an FMVSS
certification label. See
to the driver-side B-pillar, as shown in
Fig. 1.3. This label is attached
Fig. 1.4.
The tire and rim portion of the FMVSS certification
label certifies suitable tire and rim combinations that
can be installed on the vehicle, for the given gross
axle weight rating. Tires and rims installed on the
vehicle at the time of manufacture may have a higher
load capacity than that certified by the tire and rim
label. If the tires and rims currently on the vehicle
have a lower load capacity than that shown on the
tire and rim label, then the tires and rims determine
the load limitations on each of the axles.
Trucks built without a cargo body that are intended
for service in the U.S. have an incomplete vehicle
certification label attached by the final-stage manufacturer. See
the incomplete vehicle document included with the
vehicle, and certifies that the vehicle conforms to all
applicable FMVSS regulations in effect on the date of
completion.
Fig. 1.5. This label will be attached to
Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety
Standard Labels
In Canada, tractors with fifth wheels are marked as
certified by means of a statement of compliance label
with the Canadian National Safety Mark attached to
the driver-side door frame B-pillar. See
Trucks built without a cargo body and tractors built
without a fifth wheel that are intended for service in
Canada have an incomplete vehicle certification label
attached to the driver-side B-pillar. After completion
of the vehicle, a complete certification label must be
attached by the final-stage manufacturer to certify
that the vehicle conforms to all applicable Canada
Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (CMVSS) regulations
in effect on the date of completion.
Fig. 1.6.
Component GWR Label
The component GWR label is located on the
passenger-side B-pillar. The label provides maximum
GWR ratings for each component.
02/20/2012 f080178
Fig. 1.2, Component GWR Label
1.1
Vehicle Identification
02/20/2012 f080177
Fig. 1.3, Vehicle Certification Label
1
2
02/28/2012 f080182
1. EPA Noise Emission Control Label
2. FMVSS Certification Label
Fig. 1.4, Label Locations
10/10/2006
Fig. 1.6, Canadian National Safety Mark
f080024
Emissions Labels
Aftertreatment System Indicators
Label
Engines and vehicles manufactured after December
31, 2006 and domiciled in the U.S. or Canada are
required to meet all EPA regulations effective as of
the vehicle build date, and are equipped with an
emission aftertreatment system (ATS). Vehicles domiciled outside of the U.S. and Canada may not
have aftertreatment equipment, depending upon local
statutory emissions guidelines. See
A warning label on the driver-side visor contains important warning indicators in the instrument cluster
that pertain to the ATS. See
Fig. 1.7.
It is a violation of U.S. federal law to alter exhaust
plumbing, ATS, or other components in any way that
would bring the engine/vehicle out of compliance with
certification requirements [Ref: 42 U.S.C. S7522(a)
(3)]. It is the owner’s responsibility to maintain the
vehicle so that it conforms to EPA regulations.
Table 1.1.
02/28/2012
Fig. 1.5, Incomplete Vehicle Certification Label
f080180
See Fig. 1.2 for a typical component GWR label.
1.2
Vehicle Identification
Applicable Emissions System Based on Build Date and EPA Regulations
Build Date Regulation: Emissions Components
January 1, 2010–December 31,
2012
From March 5, 2012
Table 1.1, Applicable Emissions System Based on Build Date and EPA Regulations
EPA10 (reduce NOx emissions to 0.2 g/bhp-hr): Aftertreatment device (ATD)
containing a diesel particulate filter that traps soot and ash, with selective catalyst
reduction (SCR) technology that utilizes diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) to convert NOx to
nitrogen and water vapor.
GHG14: Aerodynamic and fuel efficiency components including, but not limited to,
tires, cab/sleeper side extenders, chassis fairings, bumper, hood, vehicle speed
limiters, and idle reduction timers specifically designed to meet regulatory fuel
efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions standards.
IMPORTANT
DPF Regen Needed
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
regeneration is needed.
If flashing, regenerate as soon as
possible. Engine derate possible.
Hot Exhaust
Hot exhaust can cause fire.
Keep flammables and people away
from exhaust.
DEF Refill Needed
DEF
Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) level is
low. Engine derate likely.
Refill tank with certified DEF.
See operator’s manual for complete instructions.
11/30/2010 f080162
Fig. 1.7, ATS Indicators
EPA Noise Emission Control Label
A vehicle noise emission control label (Fig. 1.8)is
located on the driver-side B-pillar as shown in
Fig. 1.4. It is the owner’s responsibility to maintain
the vehicle so that it conforms to EPA regulations.
FREIGHTLINER CORPORATION
THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS TO U.S. EPA REGULATIONS FOR NOISE EMISSION
APPLICABLE TO MEDIUM AND HEAVY TRUCKS.
THE FOLLOWING ACTS OR THE CAUSING THEREOF BY ANY PERSON ARE PROHIBITED BY
THE NOISE CONTROL ACT OF 1972:
A. THE REMOVAL OR RENDERING INOPERATIVE, OTHER THAN FOR PURPOSES OF
MAINTENANCE, REPAIR, OR REPLACEMENT, OF ANY NOISE CONTROL DEVICE OR
ELEMENT OF DESIGN (LISTED IN THE OWNER’S MANUAL) INCORPORATED INTO THIS
VEHICLE IN COMPLIANCE WITH THE NOISE CONTROL ACT.
B. THE USE THIS VEHICLE AFTER SUCH DEVICE OR ELEMENT OF DESIGN HAS
BEEN REMOVED OR RENDERED INOPERATIVE.
10/06/98
VEHICLE NOISE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
24−01656−000
DATE OF MANUFACTURE
01/96
24−00273−020
f080026
1.3
Fig. 1.8, Vehicle Noise Emission Control Label

IMPORTANT: Certain Freightliner incomplete
vehicles may be produced with incomplete noise
control hardware. Such vehicles will not have a
vehicle noise emission control information label.
For such vehicles, it is the final-stage manufacturer’s responsibility to complete the vehicle in
conformity to U.S. EPA regulations (40 CFR Part
205) and label it for compliance.
Vehicle Emission Control Information
Label
Model year 2013 and later vehicles meet additional
requirements as specified by federal greenhouse gas
and fuel efficiency regulations (GHG14). These vehicles are equipped with components that increase
fuel efficiency and reduce GHG emissions. Components may include, but are not limited to, low rolling
resistance tires; aerodynamic devices such as hood,
cab side extenders, and fuel tank fairings; vehicle
speed limiters; and idle shutdown timers.
A Vehicle Emission Control Information Label is located on the driver-side door. See Fig. 1.9.Itisthe
owner’s responsibility to maintain the vehicle so that
it conforms to EPA and NHTSA regulations.
Vehicle Identification
CERTIFIED
CLEAN IDLE
02/20/2012 f080179
Fig. 1.10, CARB Clean Idle Label
MANUFACTURED BY:
VIN:
VEH FAMILY CD:
GVWR−KG
GVWR−LBS
THIS VEHICLE COMPLIES WITH U. S. EPA REGULATIONS FOR XXXX HEAVY DUTY VEHICLES.
SEE OWNER’S MANUAL FOR PROPER MAINTENANCE OF THIS VEHICLE. U PART NO. 24−01177−060 REV A
02/29/2012
Fig. 1.9, Vehicle Emission Control Information Label
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
REGULATORY CLASS:
EMISSION CONTROL IDENTIFIERS:
DATE OF MANUFACTURE:
f080181
Certified Clean Idle Label
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) requires
model year 2008 and newer heavy-duty diesel engines to be equipped with a non-programmable engine shutdown system that automatically shuts down
the engine after five minutes of idling in order to limit
emissions of particulate matter and NOx.
Certified vehicles are equipped with a label placed
near the bottom edge of the driver-side door. See
Fig. 1.10.
1.4

2
Vehicle Access
Cab Door Locks and Handles ....................................................... 2.1
Grab Handles and Access Steps ..................................................... 2.1
Cab-to-Sleeper Access ............................................................. 2.3
Sleeper Exit Door ................................................................. 2.3
Sleeper Luggage Door ............................................................. 2.4
Back-of-Cab Access ............................................................... 2.4
Hood Opening and Closing ......................................................... 2.5
Vehicle Access
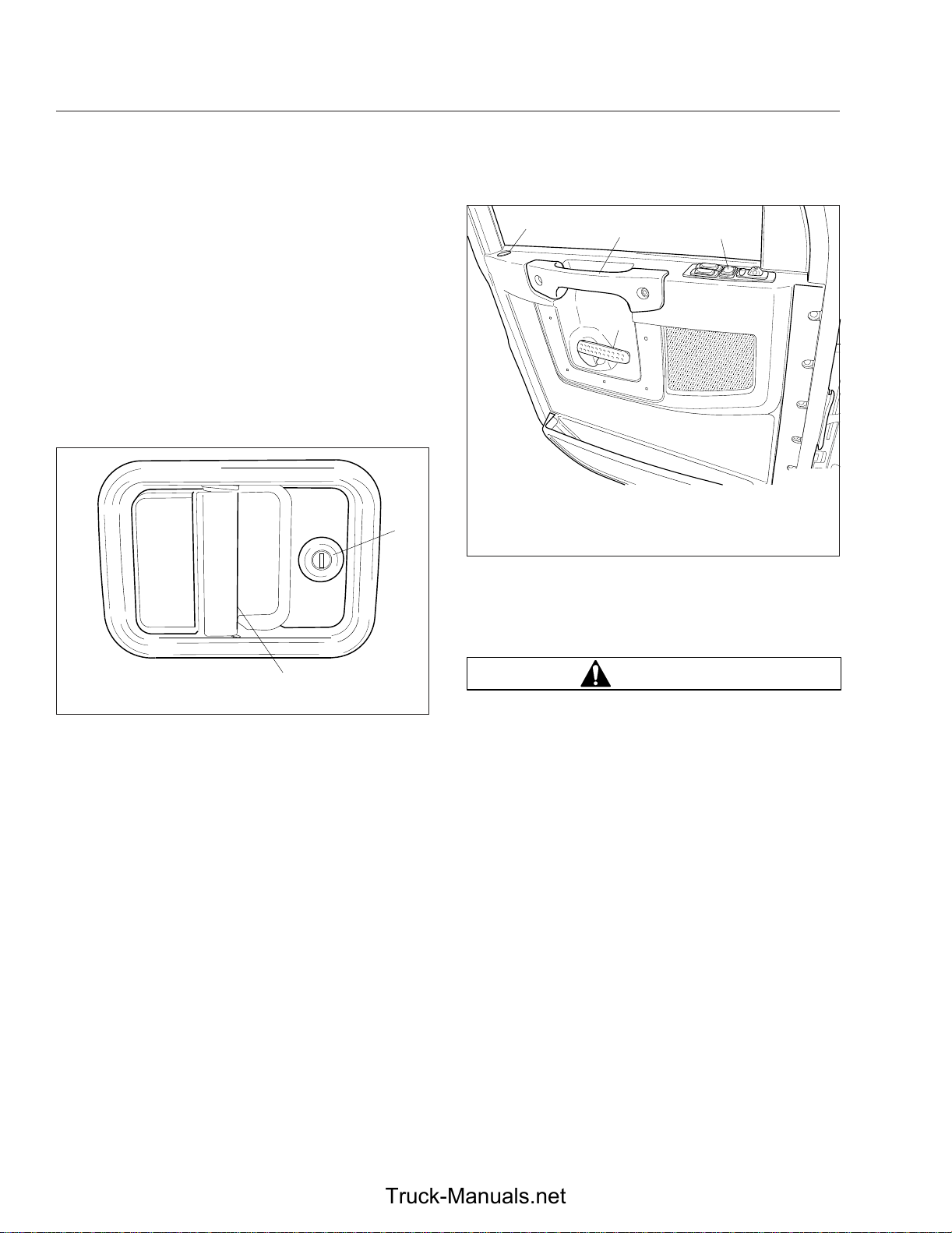
Cab Door Locks and Handles
One common key operates the ignition switch and all
of the door locks.
IMPORTANT: Each key is numbered. Record
the number so a duplicate key can be made, if
needed.
To unlock the driver’s door from outside the cab, insert the key in the lockset and turn it one-quarter turn
clockwise. See
counterclockwise to the original position. Pull out on
the door pull handle to open the door.
Fig. 2.1. To remove the key, turn it
1
1
09/22/2009 f602389
1. Lock Button
2. Integral Door Upper Grab Handle
3. Electric Door Lock
4. Interior Door Handle
2
4
Fig. 2.2, Door Interior
3
Grab Handles and Access
Steps
09/17/2009
1. Lockset 2. Door Pull Handle
Fig. 2.1, Exterior Door Handle
To unlock the passenger’s door from outside the cab,
insert the key in the lockset and turn it one-quarter
turn counterclockwise. Turn the key clockwise to the
original position to remove it.
2
f602388
NOTE: The cab door locks can be operated
when the doors are open.
To lock a door from outside the cab, insert the key in
the lockset and turn it in the direction opposite to the
unlocking direction (counterclockwise for the driver’s
door, clockwise for the passenger’s door). Close the
door if it is open.
To lock either door from inside the cab, push the lock
button downwards. See
To open the door from the inside, lift up on the door
lever. This will unlatch the door whether or not it is
locked.
Fig. 2.2.
WARNING
Wet or dirty shoe soles greatly increase the
chance of slipping or falling. If your soles are wet
or dirty, be especially careful when climbing
onto, or down from, the back-of-cab area.
Always maintain three-point contact with the
back-of-cab access supports while entering and
exiting the back-of-cab area. Three-point contact
means both feet and one hand, or both hands
and one foot, on the grab handles, steps, and
deck plates. Other areas are not meant to support back-of-cab access, and grabbing or stepping in the wrong place could lead to a fall, and
personal injury.
Be careful not to get hands or feet tangled in
hoses or other back-of-cab equipment. Carelessness could cause a person to trip and fall, with
possible injury.
Entering the Driver Side
When entering the cab from the driver side, use the
grab handle and access steps as follows:
2.1

1.
Open the driver side door, and place anything
that you are carrying in the cab.
2.
Using both hands, grasp the grab handle that is
on the B-pillar, or use your left hand on the integral door lower grab handle. See
up as far as is comfortable.
3.
Place your right foot on the bottom step, and pull
yourself up. Move your left hand to the integral
door upper grab handle.
4.
Place your left foot on the top step.
5.
Grasp the steering wheel with your left hand, and
step up.
6.
Step into the cab with your right foot first, and
grasp the steering wheel with your right hand.
Fig. 2.3. Reach
Vehicle Access
Exiting the Driver Side
Exit the cab from the driver side as follows:
IMPORTANT: Do not attempt to exit the cab
while carrying any items in your hands.
1.
Grasp the steering wheel with both hands, place
your left foot on the top step, then stand on the
threshold facing into the cab.
2.
Using your right hand, grasp the grab handle,
located on the B-pillar.
3.
Move your right foot to the bottom step.
4.
Move your left hand to the integral door lower
grab handle.
5.
Step to the ground with your left foot first.
Entering the Passenger Side
2
3
1
09/24/2009
1. Integral Door Lower Grab Handle
2. Integral Door Upper Grab Handle
3. Steering Wheel
4. B-Pillar Grab Handle
Fig. 2.3, Driver-Side Steps and Grab Handle
When entering the cab from the passenger side, use
the grab handles and access steps as follows:
1.
Open the passenger-side door, and place anything that you are carrying in the cab.
2.
Using your left hand, grasp the grab handle
that’s on the rear of the door opening. See
Fig. 2.4.
3.
Using your right hand, grasp the integral door
lower grab handle.
4.
Place your right foot on the bottom step, and
4
step up to the upper step with your left foot.
5.
Place your right foot on the top step, and step
up.
6.
Move your right hand to the upper grab handle
on the windshield post.
7.
Step into the cab with your left foot first.
Exiting the Passenger Side
Exit the cab from the passenger side as follows:
IMPORTANT: Do not attempt to exit the cab
f602390
while carrying any items in your hands.
1.
Using both hands, grasp the grab handle thats
on the windshield post, and place your right foot
on the top step while standing up from the seat
facing inward.
2.
Place your left foot on the bottom step.
2.2
Vehicle Access
To open the sleeper access on vehicles with velour
sleeper curtains, unfasten the snaps at one side,
then push the curtain to the opposite side.
Sleeper Exit Door
3
2
4
1
09/24/2009 f602391
1. Lower Grab Handle
2. Upper Grab Handle
3. Integral Door Upper Grab Handle
4. Integral Door Lower Grab Handle
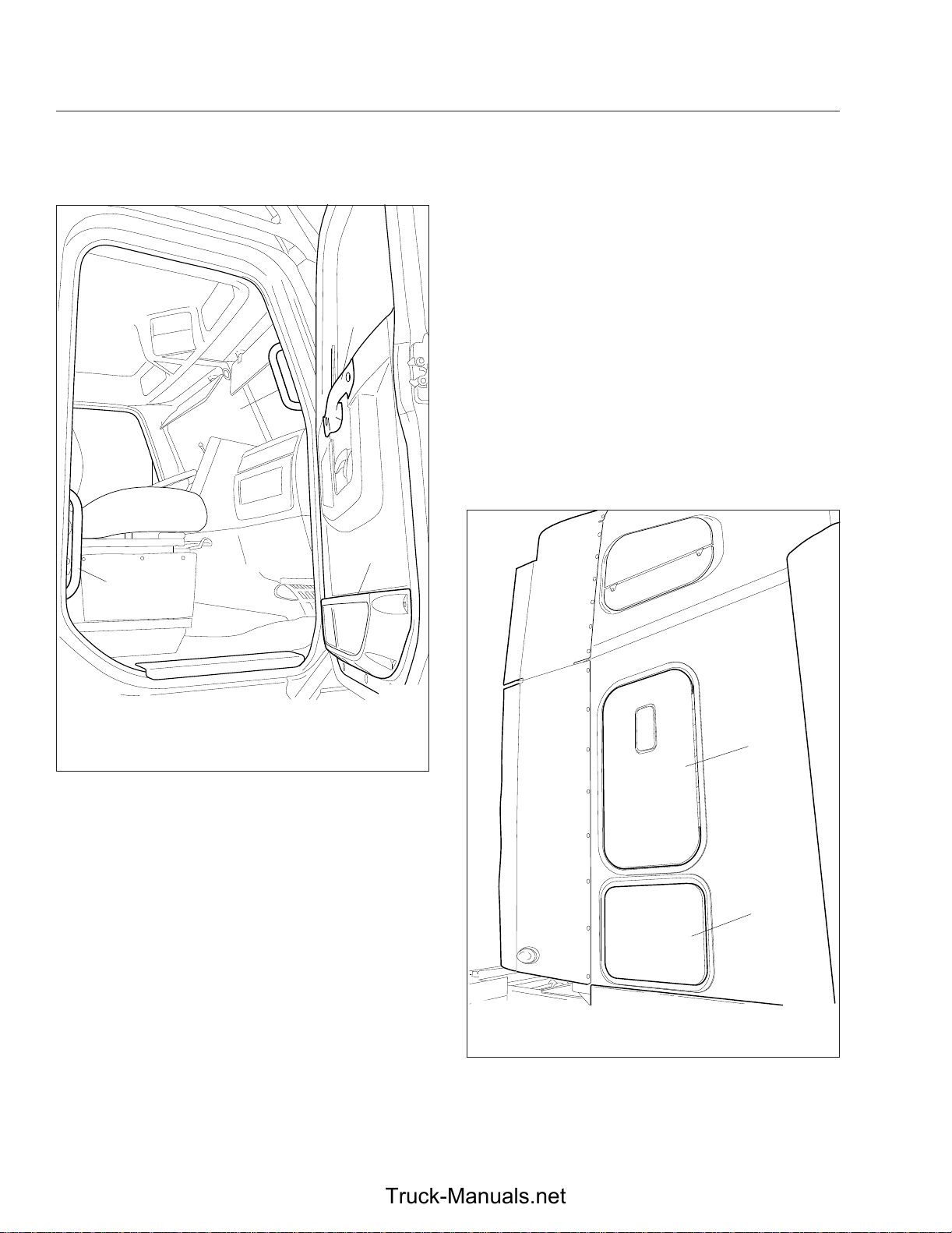
The sleeper door (Fig. 2.5) is not intended for entry
or exit. The door is intended only as a convenient
means to stow or remove personal belongings in and
from the sleeper area. To open the door from inside,
push down on the lever handle located inside the
sleeper compartment to the right of the door. The
door can be opened from the outside by first opening
the baggage door, then pulling the release cable
strap just inside on the left of the baggage door
opening. To close the door, push it closed until it
latches.
1
Fig. 2.4, Passenger-Side Steps and Grab Handles
3.
Move your left hand to the lower grab handle
located at the rear edge of the door opening.
Fig. 2.4.
See
4.
Move your right hand to the integral door lower
grab handle.
5.
Step to the ground with your right foot first.
Cab-to-Sleeper Access
To open the sleeper access on vehicles with vinyl
sleeper curtains, unzip the sleeper curtains. If desired, unsnap the curtains all the way around the
sides and top, and remove the curtains.
2.3
09/21/2009
1. Sleeper Door
2. Luggage Compartment Door
Fig. 2.5, Sleeper Doors
2
f602392
IMPORTANT: The sleeper doors are two-stage
latching. When closing the doors, ensure that
they are completely latched to prevent wind
noise and water intrusion.
Sleeper Luggage Door
To open the sleeper luggage door, pull out on the
lower T-handle lever located inside the driver’s side
or passenger’s side cab door opening. To close the
door, push it closed until it latches.
Back-of-Cab Access
Vehicle Access
4
3
WARNING
External surfaces of the exhaust system remain
hot after the engine has been shut down. When
accessing the back of the cab or sleeper, do not
touch any part of the exhaust system, or severe
burns could occur.
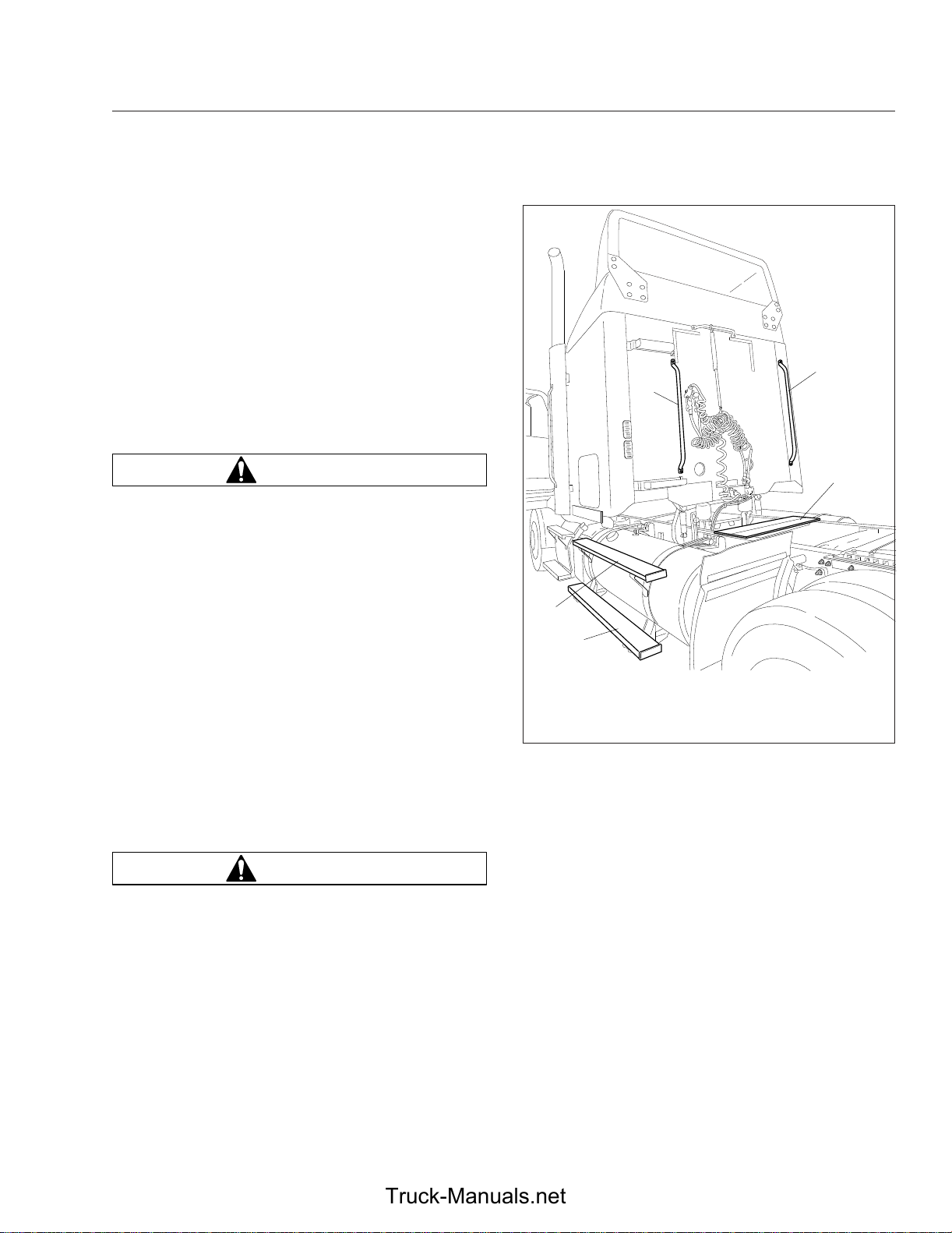
When trailer air and electrical connections cannot be
reached conveniently from the ground, Federal Motor
Carrier Safety Regulations require commercial carriers to provide back-of-cab (BOC) access.
Optional grab handles are mounted either on both
cab sidewalls, or on the left sidewall only. See
. Steps are mounted either on the fuel tank(s) or
2.6
on metal brackets. When a deck plate is necessary,
it is mounted across the top of the frame rails.
Fig.
IMPORTANT: Climb onto, and down from, backof-cab access facing in toward the vehicle, as
you would on a ladder. Do not climb up or down
facing out away from the vehicle.
WARNING
Wet or dirty shoe soles greatly increase the
chance of slipping or falling. If your soles are wet
or dirty, be especially careful when climbing
onto, or leaving, the back-of-cab area.
Always maintain three-point contact with the
back-of-cab access supports while entering and
exiting the back-of-cab area. Three-point contact
means both feet and one hand, or both hands
and one foot, on the grab handles, steps, and
deck plates. Other areas are not meant to support back-of-cab access, and grabbing or step-
5
2
1
11/17/2009 f602401
1. Lower Step
2. Upper Step
3. Left-Hand BOC Grab
Handle
Fig. 2.6, Back-of-Cab (BOC) Access
ping in the wrong place could lead to a fall, and
personal injury.
Be careful not to get hands or feet tangled in
hoses or other back-of-cab equipment. Carelessness could cause a person to trip and fall, with
possible injury.
4. Right-Hand BOC Grab
Handle
5. Deck Plate
Climbing Up to Back-of-Cab
When climbing onto the deck plate, do the following:
1.
Grasp the BOC grab handle with both hands.
Reach up as far as is comfortable.
2.
Place one foot on the bottom step and pull yourself up.
3.
Place your other foot on the top step.
2.4
Vehicle Access
4.
Move your lower hand to a higher position on the
grab handle.
5.
Step onto the deck plate.
Climbing Down from Back-of-Cab
To climb down from the back-of-cab area:
1.
Grasp the BOC grab handle with both hands.
2.
Step one foot at a time onto the top step.
3.
Move your upper hand to a lower position on the
grab handle.
4.
Move one foot to the bottom step.
5.
Move your upper hand to a lower position on the
grab handle.
6.
Step to the ground with your upper foot first.
Hood Opening and Closing
A grab handle at the front of the hood provides a
hand-hold for hood tilting. Two tilt-assist struts help to
tilt the hood open, and to return it to the operating
position. A damper controls the closing rate of the
hood and hood straps prevent the hood from overtravel. In the operating position, the hood is secured
by a hold-down latch on each side of the hood.
10/14/2009
Fig. 2.7, Hood Tilting
2.
Make sure the hood is flush with the cowl, then
secure the hood by engaging both hood holddown latches.
f602393
IMPORTANT: Make sure that both hold-down
latches are fully engaged before operating the
vehicle.
To Tilt the Hood
1.
Apply the parking brakes.
2.
Release both hood hold-down latches by pulling
the ends outward.
NOTICE
Do not let the hood free-fall to the full-open position. To do so could cause damage to the hood
or hood straps.
3.
Using the bumper step and grab handle, slowly
tilt the hood until the straps support it. See
Fig. 2.7.
To Return the Hood
1.
Grasp the grab handle, and lift the hood to the
just-over-center position.
2.5

3
Electrical System
Vehicle Power Supply ............................................................. 3.1
Electrical System
Vehicle Power Supply
WARNING
Do not attempt to modify, add, splice, or remove
electrical wiring on this vehicle. Doing so could
damage the electrical system and result in a fire
that could cause serious personal injury or property damage.
Power Distribution
There are four power distribution modules in the vehicle: the main power distribution module (PDM), the
auxiliary PDM, the powertrain PDM, and the powernet distribution box (PNDB).
The main PDM contains the circuit breakers and
fuses required to protect the vehicle. It is located in
the top of the right-hand dash, and is accessed by
removing the four fasteners in the top of the dash
panel.
The auxiliary PDM is located on the B-pillar access
door, behind the driver’s seat. It controls power to the
HVAC system, the sleeper, and anti-lock braking.
The powertrain PDM is mounted off the driver’s-side
frontwall in the engine compartment. It controls
power to the engine, aftertreatment system, transmission, and other powertrain-related circuits.
The PNDB is mounted on the cab frontwall near the
steering column. It supplies power to the powertrain
PDM, the main PDM and other cab functions, including the clock.
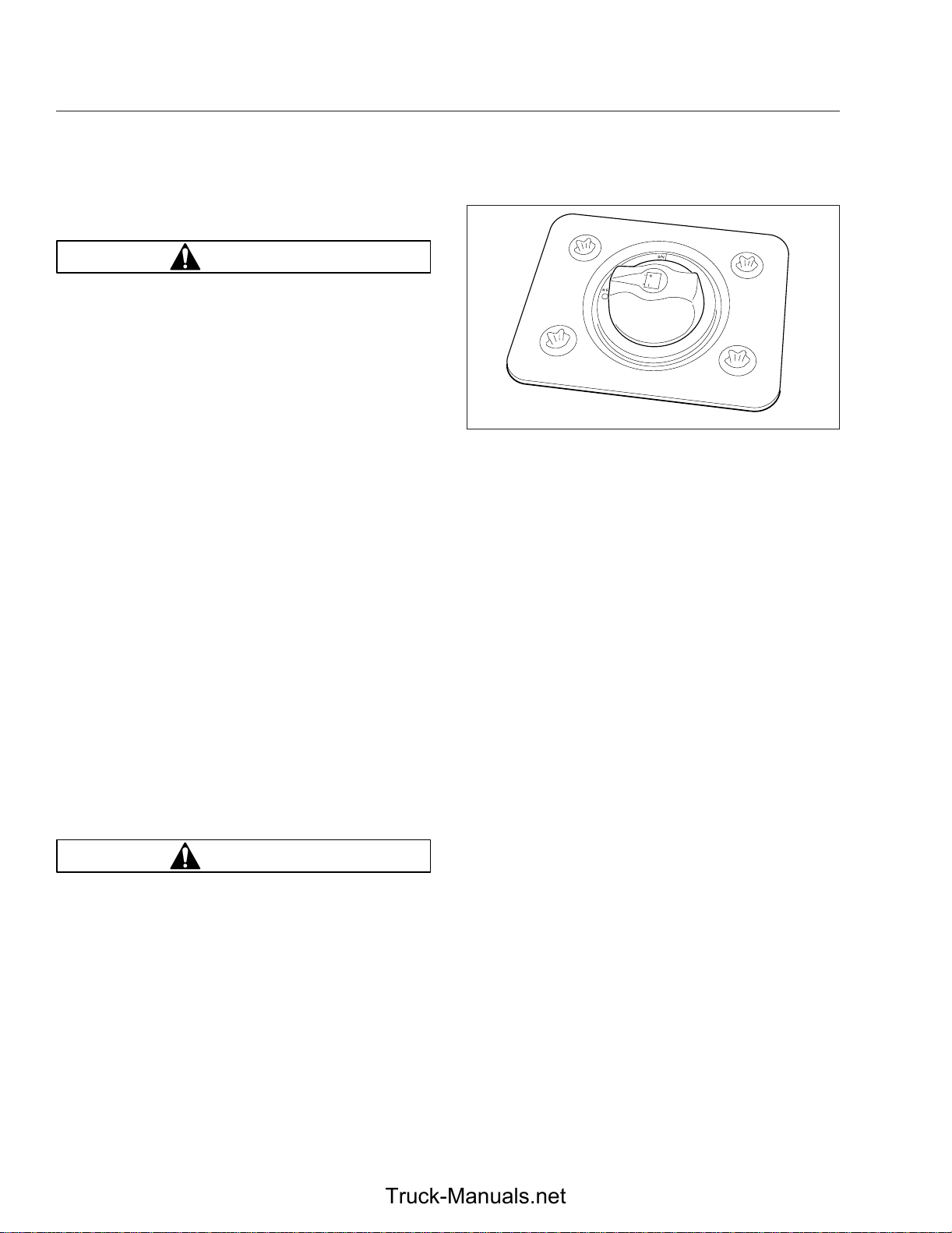
Load Disconnect Switch
WARNING
Turning the load disconnect switch to the OFF
position does not disconnect the connection between the battery and the starter. To work on the
vehicle safely, the negative leads must be disconnected from the battery.
The load disconnect switch is used to avoid excessive draw on the battery when the vehicle is parked
for an extended period of time. See
the load disconnect switch is set to OFF, it signals
the PNDB to disconnect battery power to powertrain
and accessory loads. The power to the
Fig. 3.1. When
05/13/2009 f545527
Fig. 3.1, Load Disconnect Switch
aftertreatment-system control module is disconnected
after the DEF purge function is completed.
The load disconnect switch is mounted in one of two
locations:
•
inside the cab on the left side of the driver’s
seat (left-hand-drive vehicle);
•
on the battery box
IMPORTANT: The ignition should be turned OFF
before turning the load disconnect switch to ON
or OFF.
Low Voltage Disconnect, Optional
The optional Sure Power Low Voltage Disconnect
(LVD) system monitors battery power when accessories are being used while the engine is shut down.
The system automatically turns off cab and sleeper
accessories when voltage drops to 12.3 volts, to ensure that there is enough battery power to start the
vehicle. An alarm sounds for one minute before accessories are turned off. If no action is taken within
that minute, the LVD module will shut off power to
predetermined cab and sleeper circuits. These circuits will remain off until the LVD measures 13.0
volts applied to the system, which can be achieved
by starting the engine. After the engine is started, the
system will reset.
Vehicles are equipped with an LVD label on the
drivers-side sun visor, indicating the presence of the
system.
3.1
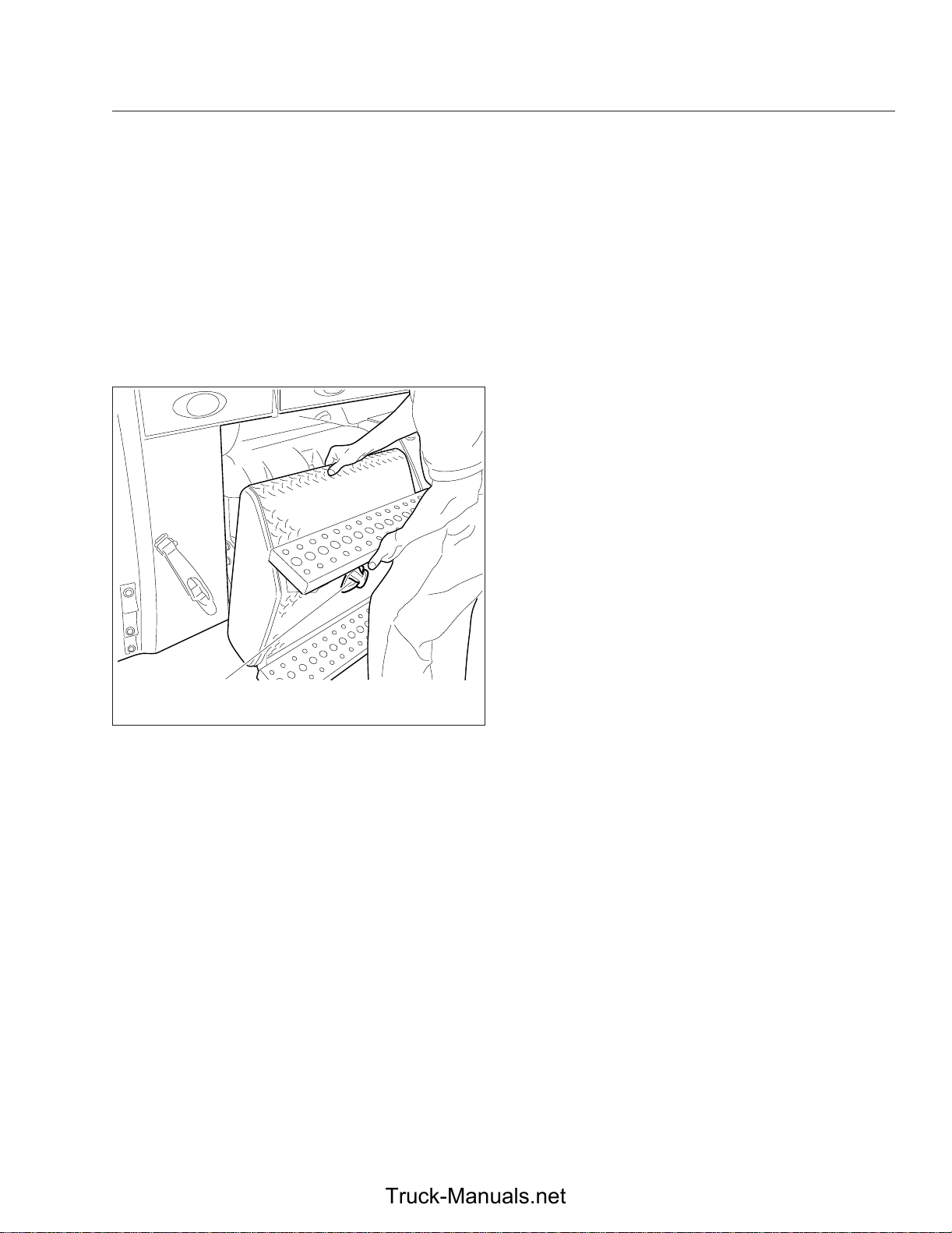
Battery Access
The batteries may be located below the driver’s door,
underneath the steps. To access the batteries located under the steps, turn the latch on the front of
the battery-box cover clockwise to release the catch,
then lift the cover and step assembly upwards and
outwards to expose the plastic battery box. Release
the catch on the plastic cover, then remove it to access the batteries. See
Fig. 3.2.
Electrical System
11/11/2009 f545613
1. Latch
Fig. 3.2, Battery Compartment (under driver’s door)
1
3.2

4
Instruments
Instrumentation Control Units ....................................................... 4.1
Warning and Indicator Lights ........................................................ 4.1
Standard Instruments .............................................................. 4.8
Optional Instruments ............................................................. 4.10
Driver Message Center ........................................................... 4.11
Roll Stability System ............................................................. 4.25
Overhead Instrument Panel ........................................................ 4.27

Instruments
Instrumentation Control Units
The instrument control unit (ICU) provides the driver
with engine and vehicle information. It is comprised
of standard and optional gauges, an audible warning,
a driver message center, and a lightbar containing
warning and indicator lamps (also known as telltales). Warning and indicator lamps illuminate in red
(danger), amber (caution), green (status advisory), or
blue (high-beam headlights active).
122SD and Coronado vehicles are equipped with an
ICU4, ICU4M, or ICU4Me. See Fig. 4.1, Fig. 4.2,
and
Fig. 4.3 for typical ICU layouts.
The following headings in this chapter provide additional information and operating instructions for ICU
components:
•
"Warning and Indicator Lights"
•
"Standard Instruments"
•
"Optional Instruments"
•
"Driver Message Center"
Ignition Sequence
When the ignition is turned on, the ICU runs a selfcheck. Observing the ignition sequence is a good
way to ensure the ICU is functioning properly.
IMPORTANT: Do not crank the engine until the
ICU self-check is complete.
NOTE: Air gauges do not complete a sweep of
their dials during the ignition sequence.
When the ignition is turned on, the following actions
should occur:
•
electronic gauges complete a full sweep of
their dials
•
warning and indicator lamps illuminate, then
are extinguished
•
audible alert sounds for approximately four
seconds or until sufficient air pressure builds
up in the primary and secondary air systems
•
DEF level indicator illuminates all segments
green, then turns them off one at a time before
turning the leftmost segment amber and then
red
•
Freightliner logo displays on the ICU4Me driver
message center for two seconds.
•
software revision level of the ICU is displayed
under the Freightliner logo on the driver message center, followed by any active faults
NOTE: If active faults are present, take the vehicle to an authorized Freightliner service facility
as soon as possible.
If the ICU receives active fault codes, it displays
them one after the other until the parking brake is
released or the ignition is turned off. Once the parking brake is completely released, the ICU displays
the odometer. If there are no active faults, the ICU
displays the odometer after the self-check completes.
When the self-check is complete on an ICU4M, the
fasten seat belt screen displays if the engine is off. If
the engine is running, the idle hours screen displays.
Audible Alerts
An audible alert sounds during the ignition sequence
and whenever one of the following conditions exists:
•
Engine oil pressure falls below the minimum
preset value.
•
Coolant temperature rises above the maximum
preset value.
•
Air pressure falls below approximately 70 psi
(483 kPa).
•
Parking brake is set with the vehicle moving
faster than two miles per hour.
•
System voltage falls below 12 volts.
•
Door is open with the parking brake off.
•
Headlights are on with the door open and the
ignition off.
•
Occupied seat belts are not fastened and the
parking brake is not set (optional).
•
Outside temperature falls below 35°F (1.7°C)
(optional).
Warning and Indicator Lights
The ICU lightbar has three to four rows of warning
and indicator lights with icon symbols (also known as
telltales). The positions of the lights may vary for the
different ICUs, but the symbols are standard for all
applications. See
and commonly used warning and indicator lamps.
Table 4.1 for a listing of standard
4.1
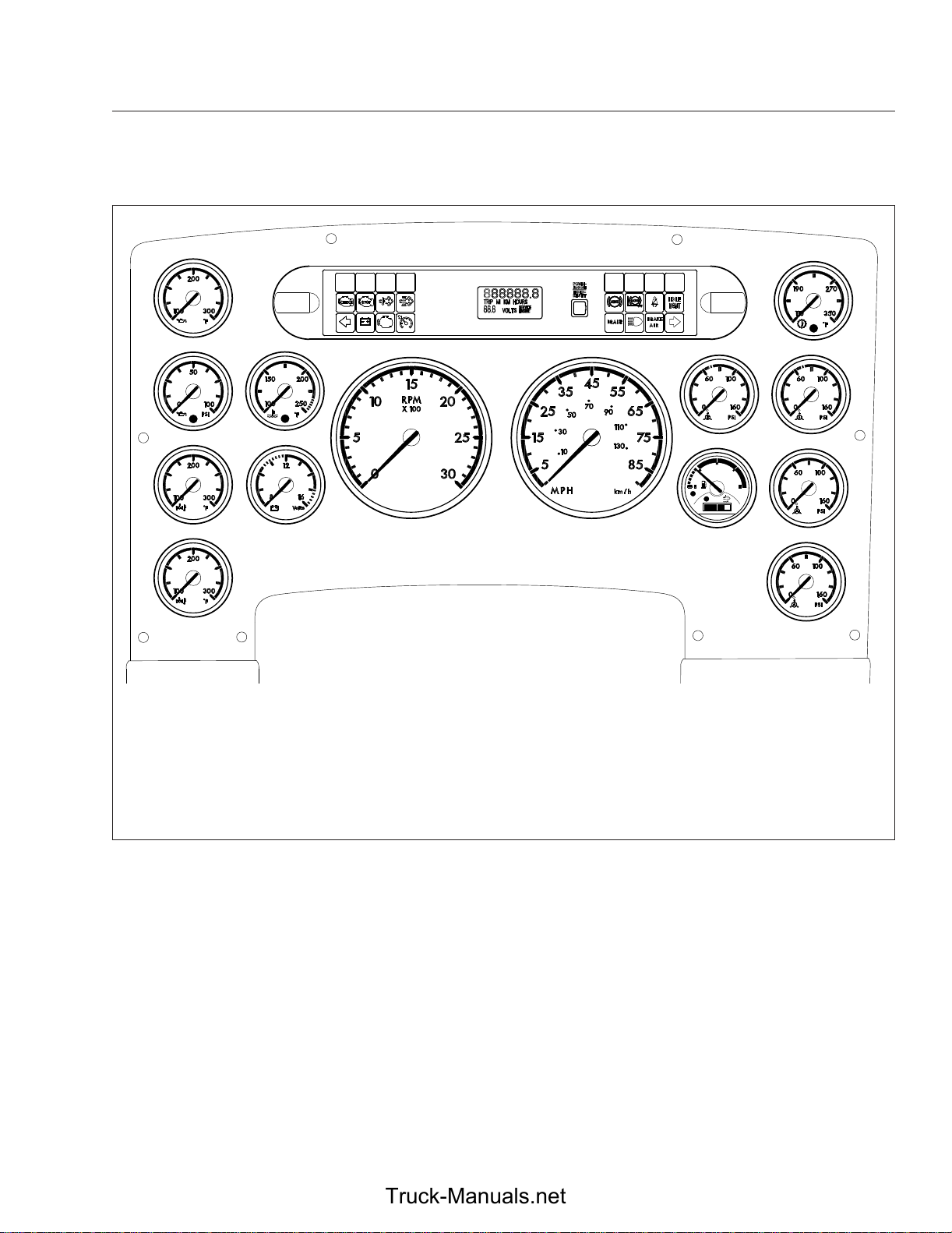
Instruments
1
3
5
7
10/16/2009
1. Engine Oil Temperature Gauge
2. Lightbar
3. Engine Oil Pressure Gauge
4. Coolant Temperature Gauge
5. Forward Drive Axle Oil
Temperature Gauge
6. Battery Voltage Gauge
2
4
6
8
10 11
7. Rear Drive Axle Oil Temperature
Gauge
8. Driver Message Center
9. Mode/Reset Button
10. Tachometer
11. Speedometer
12. Transmission Oil Temperature
Gauge
9
13
1/2
ULTRA LOW SULFUR
DIESEL FUEL ONLY
DEF
EF
15
13. Primary Air Pressure Gauge
14. Secondary Air Pressure Gauge
15. Fuel/DEF Level Gauge
16. Application Air Pressure Gauge
17. Application Air Pressure Gauge
12
14
FE
16
17
f611068
Fig. 4.1, Typical ICU4 Layout
Warning and indicator lamps illuminate in red (danger), amber (caution), green (status advisory), or
blue (high-beam headlights active).
IMPORTANT: Depending upon local jurisdictional emissions guidelines, vehicles and/or engines that are domiciled outside of the U.S. and
Canada may not be compliant with EPA10 or
GHG14 regulations. Noncompliant vehicles may
not be equipped with all of the lamps shown in
Table 4.1.
IMPORTANT: If any red or amber warning and
indicator lamps do not illuminate during the ICU
self-check or do not go out after the self-check
completes, take the action outlined in
Table 4.1,
or take the vehicle to an authorized Freightliner
service facility as soon as possible.
4.2
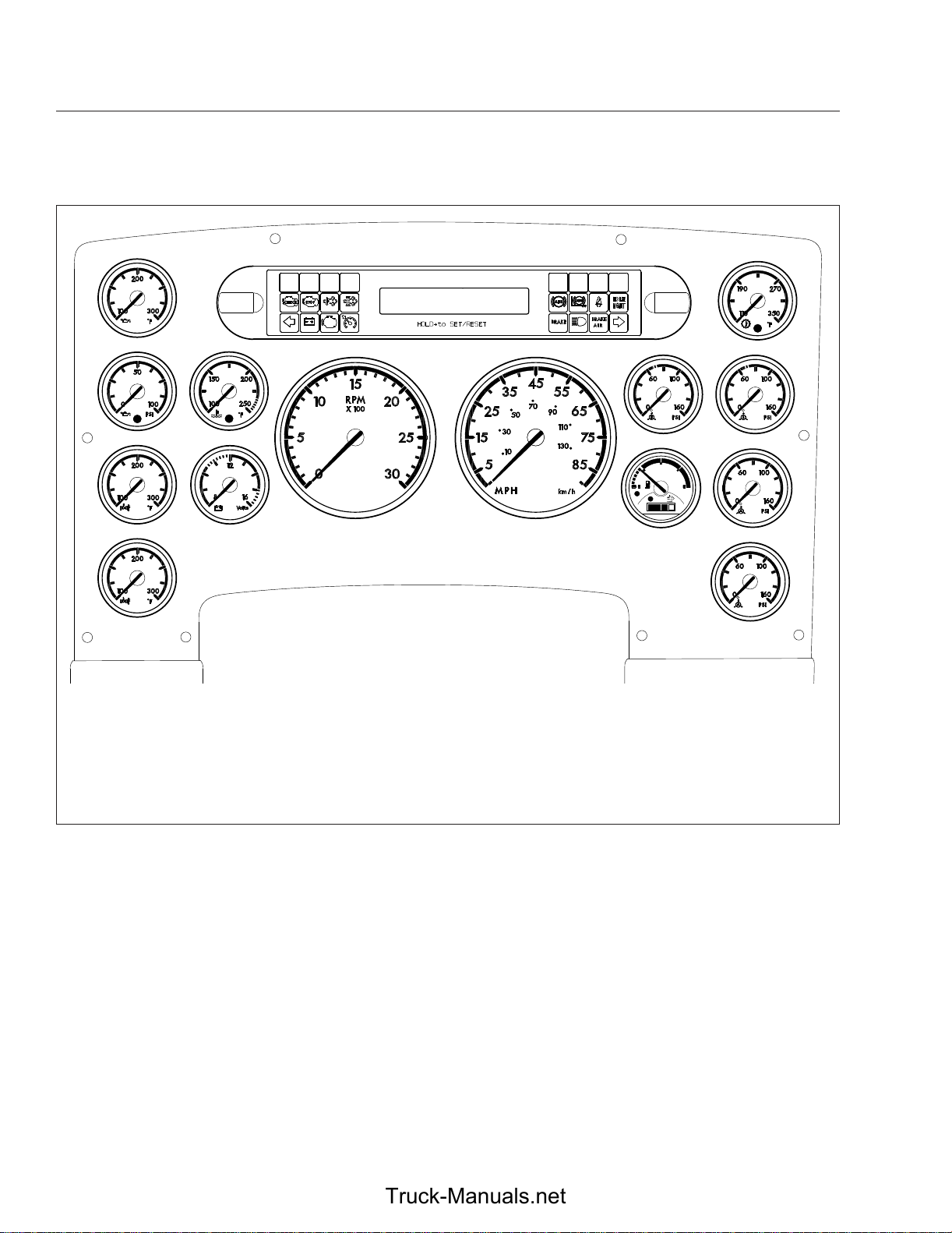
Instruments
1
3
5
2
4
6
7
10/16/2009
1. Engine Oil Temperature Gauge
2. Lightbar
3. Engine Oil Pressure Gauge
4. Coolant Temperature Gauge
5. Forward Drive Axle Oil
Temperature Gauge
6. Battery Voltage Gauge
8
12
910
14
7. Rear Drive Axle Oil Temperature
Gauge
8. Driver Message Center
9. Tachometer
10. Speedometer
12. Primary Air Pressure Gauge
13. Secondary Air Pressure Gauge
14. Fuel/DEF Level Gauge
15. Application Air Pressure Gauge
16. Application Air Pressure Gauge
11. Transmission Oil Temperature
Gauge
1/2
ULTRA LOW SULFUR
DIESEL FUEL ONLY
FE
DEF
EF
11
13
15
16
f611069
4.3
Fig. 4.2, Typical ICU4M Layout

Instruments
5
1
2
7
3
4
02/20/2013 f611204
1. Application Air Pressure Gauge
2. Suspension Air Pressure Gauge
3. Transmission Oil Temperature
Gauge
4. Turbo Pressure Gauge
5. Lightbar
6. Driver Message Center
7. Tachometer and Coolant
Temperature Gauge
8. Fuel/DEF Level Gauge
9. Speedometer and Engine Oil
Pressure Gauge
6
10
11
8
9
12
13
10. Primary Air Pressure Gauge
11. Secondary Air Pressure Gauge
12. Front Axle Temperature Gauge
13. Rear Axle Temperature Gauge
STOP
STOP Engine
Fig. 4.3, ICU4Me Instrument Cluster
Common Warning and Indicator Lamps
Lamp Description Color
Indicates a serious fault that requires engine shutdown
immediately. The engine protection system will reduce the
maximum engine torque and speed, and, if the condition
does not improve, will shut down the engine within 30 to 60
seconds.
*
Safely bring the vehicle to a stop on the side of the road
and shut down the engine as soon as the red light is seen.
If the engine shuts down while the vehicle is in a
hazardous location, turn the key to the OFF position for
a few seconds, then restart the engine and move the
vehicle to a safer location.
Red
4.4

Instruments
Common Warning and Indicator Lamps
Lamp Description Color
CHECK
High Coolant Temperature
Low Air Pressure
Low Engine Oil Pressure
Transmission Overheat Indicates high transmission temperature.
Parking Brake Indicates the parking brake is engaged.
Low Battery Voltage Indicates that battery voltage is 11.9 volts or less.
Unfastened Seat Belt
CHECK Engine
High Exhaust System
Temperature (HEST)
Diesel Particulate Filter
(DPF) Status
*
Indicates the coolant temperature is above the maximum
allowable temperature.
Indicates air pressure in the primary or secondary reservoir
has dropped below approximately 70 psi (483 kPa).
Indicates the engine oil pressure is below the minimum
allowable pressure.
Activates with an audible alert when the system detects that
the parking brake is off and the driver seat belt is not
fastened on some vehicles. On other vehicles, this lamp
illuminates for 15 seconds when the ignition is first turned
on.
Indicates an engine condition (low oil pressure, low coolant
level, high coolant temperature, high DPF soot level, or
uncontrolled DPF regeneration) that requires correction.
Correct the condition as soon as possible. If the condition
worsens, the STOP engine lamp will illuminate.
Slow (10-second) flashing indicates a regeneration (regen)
is in progress.
IMPORTANT: When the HEST lamp is illuminated, do
*
not park the vehicle near flammable material.
Solid illumination indicates high exhaust temperatures at the
outlet of the tail pipe when speed is below 5 mph (8 km/h).
Solid illumination indicates a regen is required. Change to a
more challenging duty cycle (such as highway driving ) to
raise exhaust temperatures for at least twenty minutes, or
perform a parked regen.
Blinking indicates that a parked regen is required
immediately.An engine derate and shutdown will occur.
Red
Amber
4.5
Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL)
Indicates an emissions-related fault. See the engine
operation manual for details.

Vehicle ABS
Trailer ABS
Instruments
Common Warning and Indicator Lamps
Lamp Description Color
Momentary illumination indicates the vehicle ABS is
engaged.
Solid illumination indicates a problem with the vehicle ABS.
Repair the ABS immediately to ensure full braking
capability.
Momentary illumination indicates the trailer ABS is engaged.
Solid illumination indicates a problem with the trailer ABS.
Repair the ABS immediately to ensure full braking
capability.
NO
CHARGE
IDLE
MGMT
WAIT
TO START
START
BLOCKED
WHEEL
SPIN
No Charge
Water in Fuel
Indicates the alternator is not properly powering the
electrical system.
Indicates the fuel may contain water. Drain any water
collected in the fuel/water separators.
Fuel Filter Restriction Indicates the fuel filter is clogged and requires service.
Optimized Idle Indicates optimized idle is enabled.
Check Transmission Indicates an undesirable transmission condition.
Indicates that the system is preventing the starter from
cranking. This can occur when the ignition switch is turned
to START before the gauge sweep has completed, or if the
Wait To Start (EPA10)
starter has overheated.
Turn the ignition switch back to ON, wait for the lamp to go
out, then turn the ignition switch to START again.
Indicates that the system is preventing the starter from
cranking. This can occur when the ignition switch is turned
to START before the gauge sweep has completed, or if the
starter has overheated.
Start Blocked (GHG14)
NOTE: Illumination of the Start Blocked lamp does not
indicate a problem with the starter.
Turn the ignition switch back to ON, wait for the lamp to go
out, then turn the ignition switch to START again.
Flashing indicates the ATC system is active, or the ATC
button has been pressed to allow wheel slip.
Wheel Spin
Solid illumination indicates a problem with the ATC system.
Repair the ATC system immediately to ensure full braking
capability.
Amber
4.6
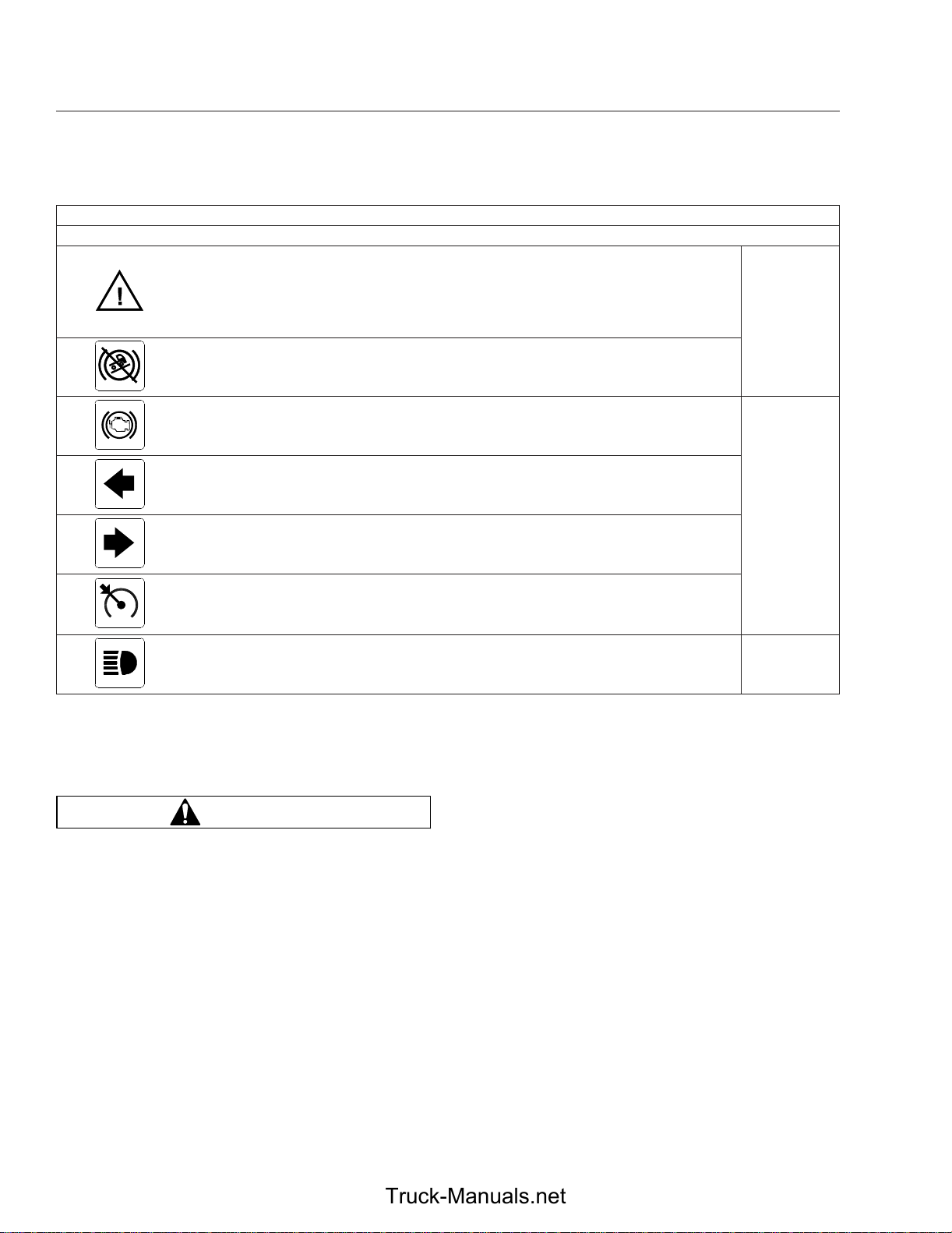
Instruments
Roll Stability
Common Warning and Indicator Lamps
Lamp Description Color
Momentary illumination indicates that a stability event has
occurred.
On vehicles that are also equipped with ATC, flashing
indicates the ATC button has been pressed to allow wheel
slip.
Amber
Hill Start Aid (HSA)
Override
Engine Brake Indicates the engine brake is enabled.
Left-Turn Signal
Right-Turn Signal
Cruise Control
High-Beam Headlights Indicates the high-beam headlights are on. Blue
*
See Fig. 4.4 for an explanation of the aftertreatment system (ATS) warning indicators, and actions required to avoid further engine protection steps.
Table 4.1, Common Warning and Indicator Lamps
Engine Protection System
Indicates the HSA switch has been pressed to override the
hill start assist feature.
Flashing indicates the outside left-turn signal lights are
activated.
Flashing indicates the outside right-turn signal lights are
activated.
Indicates the cruise control is enabled.
NOTE: The ICU4Me does not have a green cruise control
telltale.
ate the engine, allowing it to run at lower rpm and
slower vehicle speed. Drive the vehicle to a safe lo-
WARNING
cation or to a service facility.
IMPORTANT: Safely bring the vehicle to a stop
When the red STOP engine lamp illuminates,
most engines are programmed to shut down automatically within 30 seconds. The driver must
immediately move the vehicle to a safe location
at the side of the road to prevent causing a hazardous situation that could cause bodily injury,
property damage, or severe damage to the engine.
Fig. 4.4 for an explanation of the aftertreatment
See
system (ATS) warning indicators, and actions required to avoid further engine protection steps.
The STOP engine lamp illuminates when the engine
protection system is activated in one of two ways. On
some engines, the engine protection system will der-
on the side of the road and shut down the engine as soon as the red light is seen. If the engine shuts down while the vehicle is in a hazardous location, turn the key to the OFF position
for a few seconds, then restart the engine and
move the vehicle to a safer location.
On other engines, the engine protection system will
shut down the engine. It will first derate the engine,
then shut it down completely 30 to 60 seconds after
the indicator illuminates (depending on the critical
fault type) if the condition does not improve. Bring
the vehicle to a stop on the side of the road before
the engine shuts down.
Green
4.7
Instruments
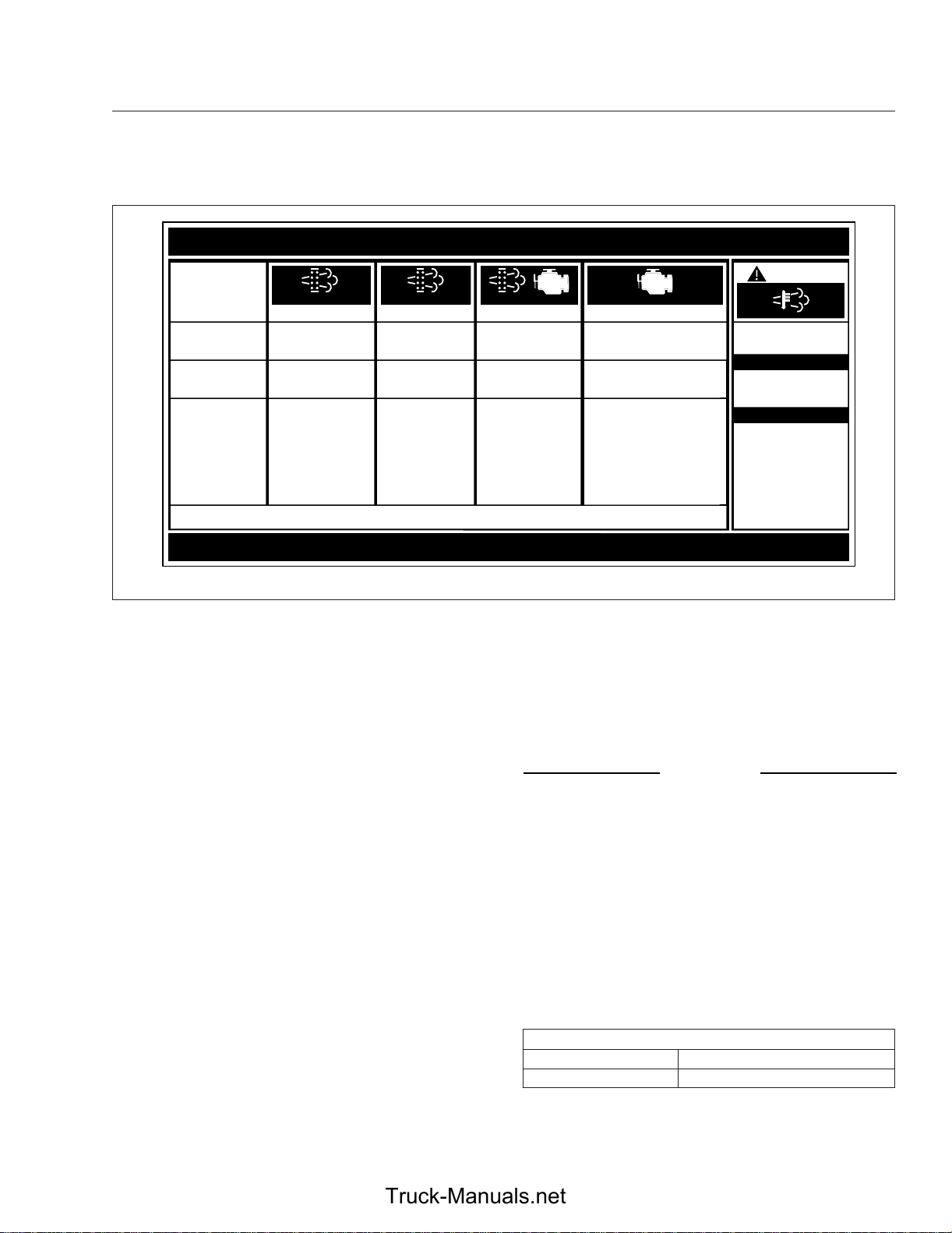
EXHAUST AFTERTREATMENT SYSTEM INFORMATION
INDICATOR
02/20/2009
LAMP(S)
Indicator Lamp
Message(s)
Diesel Particulate
Filter Condition
Required Action
For a driver performed Parked Regeneration, vehicle must be equipped with a dash mounted Regeneration Switch.
(Solid)
Level 1 Level 3Level 2 Level 4
Filter Regeneration
Recommended.
Filter is reaching
capacity
.
Bring vehicle to
highway speeds to
allow for an
Automatic
Regeneration or
perform a Parked
Regeneration.
(Flashing) (Flashing)
Filter
Regeneration
Necessary
Filter is now
reaching maximum
Switch.
capacity
.
To avoid engine
derate, bring vehicle
to highway speeds
to allow for an
Automatic
Regeneration, or
perform a Parked
Regeneration as
soon as possible.
Fig. 4.4, ATS Warning Lamps
Some vehicles may have a shutdown-override
switch, which may be used to momentarily override
the shutdown sequence. See
Chapter 10 for detailed
information regarding the shutdown process.
IMPORTANT: Do not attempt to restart the engine while the vehicle is moving. Bring the vehicle to a safe stop, then restart the engine.
To restart the engine, turn the ignition to OFF, leave
it there a few seconds, then turn the ignition to
START. The engine will run for a short period and
shut down again if the condition does not improve.
Standard Instruments
Standard instruments are present on every vehicle.
They are listed here in alphabetical order, to make
the information easier to find.
Some gauges have an LED warning light that indicates when values have exceeded their preset minimum or maximum values.
Gauges with a warning light include:
•
engine coolant temperature;
•
engine oil pressure;
W
CHECK
Parked Regeneration
Required − Engine
Derate
Filter has reached
maximum capacity
Vehicle must be
parked, and a Parked
Regeneration must
be performed.
Engine will begin
derate.
•
•
•
STOP
Service Regeneration Required.
Engine Derate To Idle Only.
Filter has exceeded maximum
.
capacity.
Vehicle must be parked, and a
Service Regeneration must be
performed. Check engine
operator’s manual for details.
Engine will shut down.
fuel and DEF level;
transmission fluid temperature;
voltmeter.
ARNING
HEST (High Exhaust
System Temperature)
Flashing
A regeneration is in
progress.
Solid
Exhaust components
and exhaust gas are at
high temperature. When
stationary, keep away
from people and
flammable materials or
vapors.
Coolant Temperature Gauge
NOTICE
A sudden increase in coolant temperature may
indicate engine or cooling system failure. Bring
the vehicle to a safe stop and investigate the
cause to prevent further damage. Do not operate
the engine until the cause has been determined
and corrected.
During normal engine operation, the coolant temperature gauge should read between 175 and 195°F
(79 and 91°C). If the temperature remains below
160°F (71°C) or exceeds the maximum temperature
shown in Table 4.2, inspect the cooling system to
determine the cause.
Maximum Coolant Temperature
Engine Make Temperature: °F (°C)
Cummins 225 (107)
f080156
4.8
Instruments
Maximum Coolant Temperature
Engine Make Temperature: °F (°C)
Detroit Diesel 215 (101)
Table 4.2, Maximum Coolant Temperature
1/2
ULTRA LOW SULFUR
DIESEL FUEL ONLY
1
Engine Oil Pressure Gauge
NOTICE
A sudden decrease or absence of oil pressure
may indicate mechanical failure. Bring the vehicle
to a safe stop and investigate the cause to prevent further damage. Do not operate the engine
until the cause has been determined and corrected.
The engine oil pressure gauge displays the current
engine oil pressure. If engine oil pressure falls below
the minimum levels shown in
Table 4.3, the CHECK
engine lamp will illuminate. If the condition does not
improve, the STOP engine lamp will illuminate and
an audible warning will sound. The engine will then
derate or shut down, depending on the type of engine protection system installed.
Minimum Engine Oil Pressure
Engine Model
Cummins 15 (103) 35 (241) min.
Detroit Diesel 14 (97) min. 55 (350) min.
*
Pressures apply with the engine at operating temperature. Oil pressure
may be higher on a cold engine. Observe and record pressures when the
engine is new to create a guide for checking engine condition.
Table 4.3, Minimum Engine Oil Pressure
At Idle Speed:
psi (kPa)
*
At Rated RPM:
psi (kPa)
Fuel/Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF)
Gauge
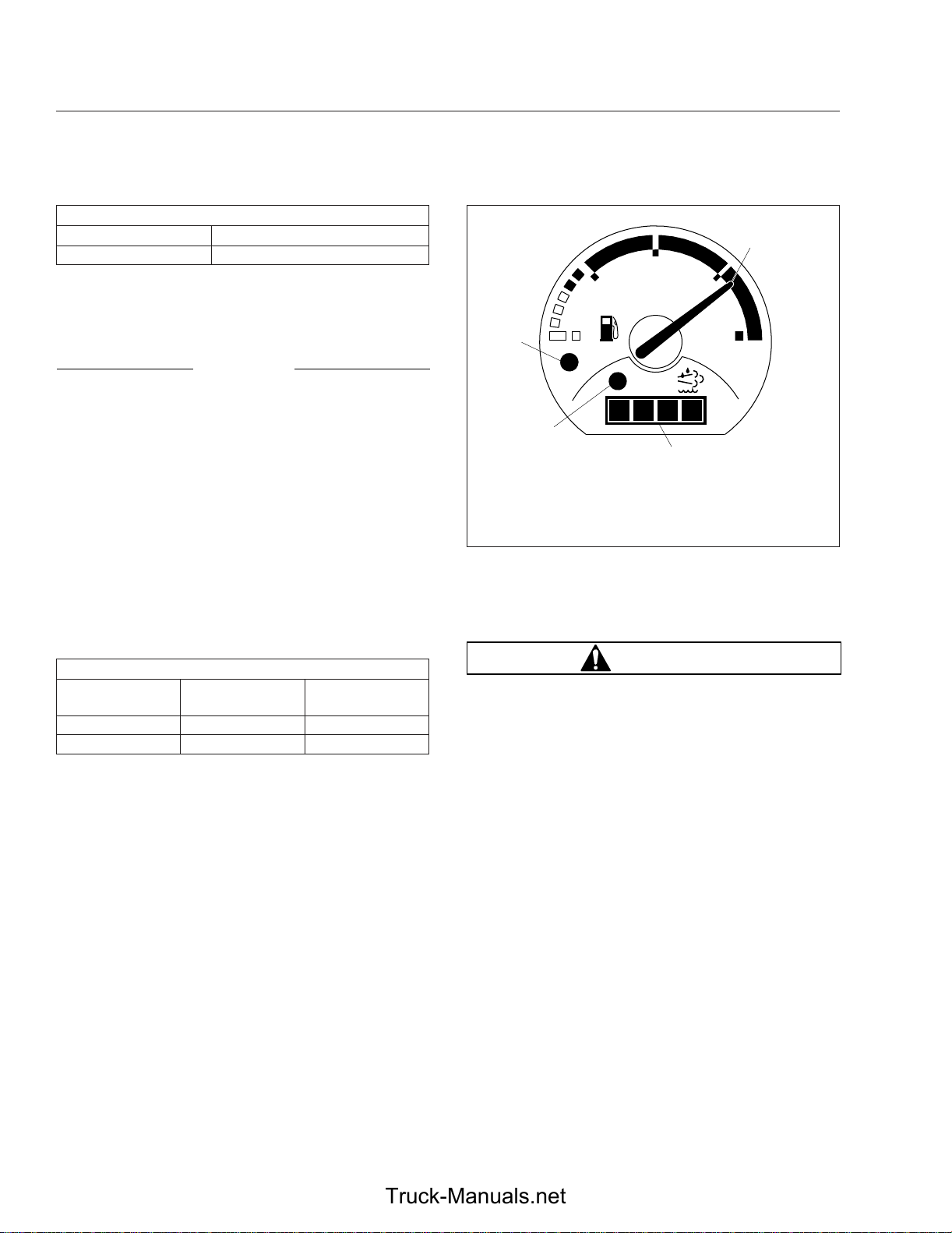
The fuel and DEF levels are measured in a dual purpose fuel/DEF gauge. See
The diesel fuel level is indicated at the top of the
gauge, with a low-fuel warning lamp that illuminates
when the diesel fuel level registers 1/8th of capacity.
The DEF level is indicated in the lightbar on the
lower portion of the gauge. There is a low DEF level
warning lamp that illuminates when the DEF level
reaches 10% of capacity. See
of the exhaust aftertreatment system.
Fig. 4.13.
Chapter 11 for details
4
FE
DEF
EF
3
08/21/2009
1. Diesel Fuel Level Indicator
2. DEF Level Indicator
3. Low DEF Warning Lamp (amber below 10% DEF)
4. Low Fuel Warning Lamp (amber at 1/8 tank of fuel)
Fig. 4.5, Fuel/DEF Gauge
2
f611045
Primary and Secondary Air Pressure
Gauges
WARNING
If air pressure falls below minimum pressure, the
braking ability of the vehicle will be limited. Slow
the vehicle down and bring it to a gradual stop.
Do not attempt to move the vehicle until air pressure has risen above the minimum level. Moving
a vehicle without adequate braking power could
cause an accident resulting in property damage,
personal injury, or death.
Air pressure gauges register the pressure in the primary and secondary air systems. Normal pressure
with the engine running is 100 to 120 psi (689 to 827
kPa) in both systems.
A low air pressure warning lamp and audible warning, connected to both the primary and secondary
systems, activate when air pressure in either system
drops below a minimum pressure of 64 to 76 psi
(441 to 524 kPa).
When the engine is started, the warning light and
buzzer remain on until air pressure in both systems
exceeds minimum pressure.
4.9
Instruments
Speedometer
Two speedometer face options are available. The
U.S. version of the speedometer registers speed in
both miles per hour (mph) and kilometers per hour
(km/h), with mph in larger numbers.
The metric version of the speedometer face reverses
this arrangement, with km/h in larger numbers.
Tachometer
The tachometer indicates engine speed in revolutions
per minute (rpm) and serves as a guide for shifting
the transmission and keeping the engine in the appropriate rpm range. For low idle and rated rpm, see
the engine identification plate.
Voltmeter
The voltmeter indicates the vehicle charging system
voltage when the engine is running and the battery
voltage when the engine is stopped. By monitoring
the voltmeter, the driver can stay aware of potential
battery charging problems and have them fixed before the batteries discharge enough to create starting
difficulties.
The voltmeter will normally show approximately 13.7
to 14.1 volts when the engine is running. The voltage
of a fully charged battery is 12.7 to 12.8 volts when
the engine is stopped. A completely discharged battery will produce only about 12.0 volts. The voltmeter
will indicate lower voltage as the vehicle is being
started or when electrical devices in the vehicle are
being used.
If the voltmeter shows an undercharged or overcharged condition for an extended period, have the
charging system and batteries checked at a repair
facility.
On a vehicle equipped with a battery isolator system,
the voltmeter measures the average voltage of all the
batteries when the engine is running. When the engine is stopped, the voltmeter shows only the gel cell
battery voltage and does not indicate the voltage of
the engine-starting batteries.
the battery becomes fully discharged. If an external charger is needed, disconnect the gel cell
battery and use only an external battery charger
that has been approved for gel cell batteries.
Optional Instruments
Optional instruments are not found on every vehicle.
They are listed here in alphabetical order, to make
the information easier to find.
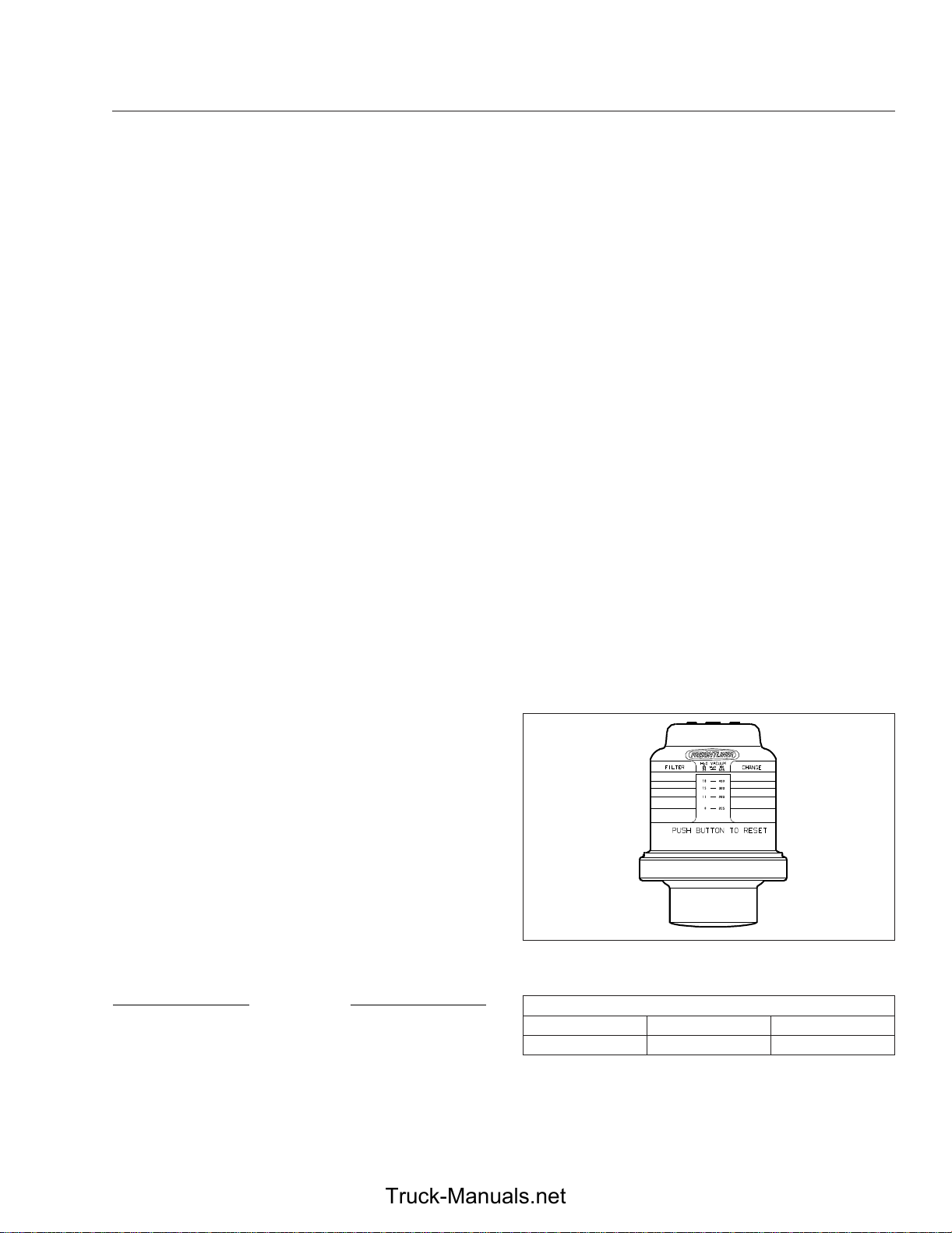
Air Restriction Gauge
The air intake restriction gauge measures the
vacuum on the engine side of the air cleaner. On
standard installations, it is mounted on the air intake
duct in the engine compartment. As an option for
easier viewing, an air intake restriction gauge may be
located in the ICU.
NOTE: Rain or snow can wet the air filter, causing a temporarily higher than normal reading.
Air intake restriction vacuum is measured in inches
of water (inH
graduated indicator (see
gauge on the dash, check the gauge with the engine
off. If the air restriction value equals or exceeds the
value shown in
needs to be replaced.
08/07/2007 f090452
Fig. 4.6, Manual-Reset Air Restriction Indicator with
O). For vehicles equipped with a
2
Table 4.4, the air cleaner element
Fig. 4.6) or a restriction
Graduations
NOTICE
Gel cell batteries can be damaged if the battery
voltage is allowed to drop below 12.0 volts or if
the charging voltage is more than 14.1 volts.
Start the engine to recharge the gel cell before
Maximum Air Intake Restriction Values
Engine Make Initial inH
Cummins 10 25
O
2
Service inH
O
2
4.10
Instruments
Maximum Air Intake Restriction Values
Service inH
Engine Make Initial inH
Detroit Diesel 10 22
Table 4.4, Maximum Air Intake Restriction Value
O
2
O
2
Brake Application Air Pressure Gauge
The application air pressure gauge registers the air
pressure being used to apply the brakes, and should
be used for reference only. The gauge will not register until the foot pedal is depressed or the hand
brake lever is applied.
Drive Axle Oil Temperature Gauges
NOTICE
A sudden increase in oil temperature that is not
caused by a load increase may indicate mechanical failure. Bring the vehicle to a safe stop and
investigate the cause to prevent further damage.
Do not operate the vehicle until the cause has
been determined and corrected.
During normal operation, drive axle oil temperature
gauges should read as follows:
•
160 to 220°F (71 to 104°C) for Detroit™and
Meritor
•
180 to 200°F (82 to 93°C) for Dana Spicer®
drive axles
Under heavy loads, such as when climbing steep
grades, temperatures that exceed the normal oil temperature range for a short period are not unusual. If
the temperature returns to normal when the load decreases, there is no problem.
™
drive axles
Engine Oil Temperature Gauge
Under heavy loads, such as when climbing steep
grades, temperatures that exceed the normal oil temperature range for a short period are not unusual. If
the temperature returns to normal when the load decreases, there is no problem.
Transmission Fluid Temperature
Gauge
The transmission fluid temperature gauge measures
the transmission lubricant operating temperature.
Transmission temperatures vary by application, but
the transmission fluid temperature gauge reading
should not exceed 250°F (121°C).
NOTICE
A sudden increase in transmission fluid temperature that is not caused by a load increase may
indicate mechanical failure. Bring the vehicle to a
safe stop and investigate the cause to prevent
further damage. Do not operate the vehicle until
the cause has been determined and corrected.
Under heavy loads, such as when climbing steep
grades, temperatures that exceed the normal oil temperature range for a short period are not unusual. If
the temperature returns to normal when the load decreases, there is no problem.
Turbocharger Boost Pressure Gauge
The turbocharger boost pressure gauge measures
the pressure in the intake manifold being created by
the turbocharger, in excess of atmospheric pressure.
Driver Message Center
ICU4
Functions
NOTICE
A sudden increase in oil temperature that is not
caused by a load increase may indicate mechanical failure. Bring the vehicle to a safe stop and
investigate the cause to prevent further damage.
Do not operate the engine until the cause has
been determined and corrected.
During normal operation, the engine oil temperature
gauge should read from 200 to 260°F (93 to 126°C).
4.11
The mode/reset button, located on the right side of
the lightbar, controls the driver message center.
Press the mode/reset button to advance one screen;
hold the button down to select a menu choice or
reset the display. When the display is reset, an audible chirp sounds.
Direct Access Screens
When the parking brake is not set, pressing the
mode/reset button will scroll through the direct access screens.
 Loading...
Loading...