Page 1

molbox™ RFM™
(Ver 1.10 and Higher)
Reference Flow Monitor
Operation and Maintenance Manual
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 2

High pressure liquids and gases are potentially hazardous. Energy stored in these liquids and gases
can be released unexpectedly and with extreme force. High pressure systems should be assembled
and operated only by personnel who have been instructed in proper safety practices.
© 1998 - 2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company All rights reserved.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any
form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of DH Instruments, a
Fluke Company 4765 East Beautiful Lane Phoenix AZ 85044-5318 USA.
DH Instruments makes sincere efforts to ensure the accuracy and quality of its’ published materials; however, no warranty,
expressed or implied, is provided. DH Instruments disclaims any responsibility or liability for any direct or indirect damages
resulting from the use of the information in this manual or products described in it. Mention of any product does not constitute an
endorsement by DH Instruments of that product. This manual was originally composed in English and was subsequently translated
into other languages. The fidelity of the translation cannot be guaranteed. In case of conflict between the English version and other
language versions, the English version predominates.
Products described in this manual are manufactured under international patents and one or more of the following U.S. patents:
5,142,483, 5,257,640, 5,331,838, 5,445,035. Other U.S. and international patents pending.
DH Instruments, DH, DHI, molbox, molbox RFM, molbloc, molbloc-L, molbloc-S and CalTool are trademarks, registered and
otherwise, of DH Instruments, a Fluke Company.
LabVIEW is registered trademark of National Instruments Corporation.
Swagelok is a registered trademark of the Swagelok Company.
Document No. 550107f
050512
Printed in the USA.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
T
AABBLLEE
T
O
O
FF
C
OONNTTEENNTTS
C
S
TABLE OF CONTENTS ...............................................................I
TABLES.................................................................................. V
FIGURES................................................................................VI
ABOUT THIS MANUAL............................................................ VII
1. INTRODUCTION ................................................................. 1
1.1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................................................................1
1.1.1 MOLBLOC FLOW ELEMENTS ........................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1.1.1 MOLBLOC-L FLOW ELEMENT....................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1.1.2 MOLBLOC-S FLOW ELEMENT...................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS.........................................................................................................................................................................2
1.2.1 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................................................................................. 2
1.2.2 REFERENCE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (RPT) SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................................. 2
1.2.2.1 UPSTREAM AND DOWNSTREAM RPTS...................................................................................................................................... 2
1.2.2.2 DIFFERENTIAL RPT (MICRORANGE OPTION)............................................................................................................................3
1.2.3 TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SPECIFICATIONS......................................................................................................................3
1.2.4 FLOW MEASUREMENT SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................................................................................3
1.2.4.1 MOLBLOC-L .................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2.4.1.1 MOLBLOC-L FLOW MEASUREMENT SPECIFICATIONS, MICRORANGE OPTION............................................................. 4
1.2.4.1.2 MOLBLOC-L PRESSURE DEPENDENT CALIBRATION TYPES............................................................................................. 4
1.2.4.1.3 MOLBLOC-L RANGES WITH LOW PRESSURE CALIBRATIONS........................................................................................... 6
1.2.4.1.4 MOLBLOC-L RANGES WITH HIGH PRESSURE CALIBRATIONS..........................................................................................7
1.2.4.1.5 MOLBLOC-L DIMENSIONS....................................................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.4.2 MOLBLOC-S.................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2.4.2.1 MOLBLOC-S RANGES............................................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2.4.2.2 MOLBLOC-S PRESSURE DEPENDENT CALIBRATION TYPES.......................................................................................... 11
1.2.4.2.3 MOLBLOC-S DIMENSIONS.....................................................................................................................................................12
1.2.5 FRONT AND REAR PANELS............................................................................................................................................................ 13
1.2.5.1 FRONT PANEL..............................................................................................................................................................................13
1.2.5.2 REAR PANEL................................................................................................................................................................................ 14
2. INSTALLATION ................................................................ 15
2.1 UNPACKING AND INSPECTION ...............................................................................................................................................15
2.1.1 REMOVING FROM PACKAGING...................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.1.2 INSPECTING CONTENTS ................................................................................................................................................................. 15
2.2 SITE REQUIREMENTS............................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.3 INITIAL SETUP............................................................................................................................................................................ 16
2.3.1 PREPARING FOR OPERATION ....................................................................................................................................................... 16
2.3.2 POWER CONNECTION ..................................................................................................................................................................... 16
2.3.3 MOLBOX RFM TO MOLBLOC CONNECTION.................................................................................................................................16
2.3.4 GAS SUPPLY AND FLOWPATH CONNECTIONS........................................................................................................................... 17
2.3.5 VACUUM SUPPLY (MOLBLOC-S ONLY) ........................................................................................................................................ 18
2.3.6 COMMUNICATIONS CONNECTIONS .............................................................................................................................................. 18
2.4 POWER UP AND VERIFICATION.............................................................................................................................................. 18
2.4.1 POWER UP.........................................................................................................................................................................................18
2.4.2 CH E CK P ROPER PRESS URE MEASU REMEN T OP ERATI O N .......................................................................................... 19
2.4.3 CHECK PROPER TEMPERATU R E M EASUR E M ENT OPERATIO N..........................................................................................19
2.4.4 LEAK CHECK.....................................................................................................................................................................................19
2.4.5 CHECK/SET SECURITY LEVEL ....................................................................................................................................................... 20
2.5 ADDITIONAL PRECAUTIONS TO TAKE BEFORE MAKING FLOW MEASUREMENTS .......................................................20
2.6 SHORT TERM STORAGE...........................................................................................................................................................20
Page I © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 4

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3. OPERATION..................................................................... 21
3.1 GENERAL OPERATING PRINCIPLES ......................................................................................................................................21
3.1.1 MOLBLOC-L AND MOLBLOC-S OPERATION................................................................................................................................ 21
3.1.2 MOLBLOC-S BPR LIMITS................................................................................................................................................................. 21
3.1.3 FLOW READY/NOT READY INDICATION ....................................................................................................................................... 22
3.1.3.1 MOLBLOC-L OPERATION............................................................................................................................................................22
3.1.3.2 MOLBLOC-S OPERATION............................................................................................................................................................ 22
3.1.4 SOFT [ON/OFF] KEY ......................................................................................................................................................................... 23
3.1.5 MICRORANGE OPTION (OPTIONAL).............................................................................................................................................. 23
3.1.6 REFERENCE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (RPT) OVERPRESSURE ............................................................................................ 24
3.1.6.1 UPSTREAM AND DOWNSTREAM ABSOLUTE RPTS................................................................................................................ 24
3.1.6.2 DIFFERENTIAL RPT, MICRORANGE OPTION........................................................................................................................... 24
3.2 MAIN RUN SCREEN................................................................................................................................................................... 25
3.2.1 MOLBLOC-L OPERATION................................................................................................................................................................ 25
3.2.2 MOLBLOC-S OPERATION................................................................................................................................................................ 26
3.3 MANUAL OPERATION............................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.3.1 KEYPAD LAYOUT AND PROTOCOL............................................................................................................................................... 27
3.3.2 SOUNDS............................................................................................................................................................................................. 28
3.3.3 SOFT [ON/OFF] KEY ......................................................................................................................................................................... 28
3.3.4 DIRECT FUNCTION KEYS SUMMARY ............................................................................................................................................ 28
3.4 DIRECT FUNCTION KEYS.........................................................................................................................................................29
3.4.1 [K] ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.4.2 [GAS] .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 31
3.4.2.1 MOLBLOC-L OPERATION............................................................................................................................................................32
3.4.2.2 MOLBLOC-S OPERATION............................................................................................................................................................ 33
3.4.3 [UNIT]..................................................................................................................................................................................................34
3.4.3.1 MASS FLOW VS. VOLUME FLOW...............................................................................................................................................35
3.4.3.2 VOLUMETRICALLY BASED MASS FLOW UNITS....................................................................................................................... 36
3.4.3.3 VOLUMETRICALLY BASED MASS FLOW UNITS AT VARIOUS REFERENCE TEMPERATURES (UXXX) ........................... 37
3.4.3.4 VOLUME FLOW UNITS (VLM)......................................................................................................................................................37
3.4.3.5 CUSTOMIZING FLOW UNITS AVAILABLE UNDER THE UNIT FUNCTION.............................................................................. 38
3.4.4 [TARE] ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 39
3.4.4.1 <1TARE> ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
3.4.4.1.1 MOLBLOC-L OPERATION.......................................................................................................................................................40
3.4.4.1.2 MOLBLOC-S OPERATION....................................................................................................................................................... 43
3.4.4.2 <2PURGE>.................................................................................................................................................................................... 44
3.4.4.3 <3LEAK CHECK>.......................................................................................................................................................................... 46
3.4.4.3.1 LEAK CHECK MOLBOX........................................................................................................................................................... 47
3.4.4.3.2 LEAK CHECK SYSTEM........................................................................................................................................................... 49
3.4.4.4 <4AUTOZ>.....................................................................................................................................................................................53
3.4.4.4.1 EDIT AUTOZ.............................................................................................................................................................................55
3.4.4.4.2 RUN AUTOZ............................................................................................................................................................................. 56
3.4.4.5 <5BPR> (MOLBLOC-S OPERATION ONLY) ...............................................................................................................................58
3.4.5 [P&T] (PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE)......................................................................................................................................59
3.4.6 [DISPLAY] .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 61
3.4.6.1 <1RATE> ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 62
3.4.6.2 <2AVG> (AVERAGE) .................................................................................................................................................................... 63
3.4.6.3 <3 HI/LO>....................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
3.4.6.4 <4TOTAL> (TOTALIZER).............................................................................................................................................................. 64
3.4.6.5 <5UNIT>......................................................................................................................................................................................... 66
3.4.6.6 <6DEV>.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 66
3.4.6.7 <7FREEZE>................................................................................................................................................................................... 67
3.4.6.8 <8CLEAN>..................................................................................................................................................................................... 68
3.4.7 [MICRO] (OPTIONAL)........................................................................................................................................................................ 68
3.4.8 [MOLBLOC]........................................................................................................................................................................................70
3.4.8.1 MOLBLOC-L AND MOLBLOC-S SIZE AND RANGE DESIGNATIONS.......................................................................................70
3.4.9 [RES]...................................................................................................................................................................................................71
3.5 [SETUP].......................................................................................................................................................................................72
3.5.1 <1FLOWU>......................................................................................................................................................................................... 72
3.5.2 <2PRESU>..........................................................................................................................................................................................73
3.5.3 <3TEMPU> ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 73
3.5.4 <4MOLBLOC>.................................................................................................................................................................................... 74
3.5.5 <5STAB> ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 74
3.5.6 <6ADJ>............................................................................................................................................................................................... 75
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page II
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
3.6 [SPECIAL]................................................................................................................................................................................... 76
3.6.1 <1RESET>.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 77
3.6.1.1 <1SETS>........................................................................................................................................................................................ 78
3.6.1.2 <2UNITS>...................................................................................................................................................................................... 78
3.6.1.3 <3COM>......................................................................................................................................................................................... 79
3.6.1.4 <4CAL>.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 79
3.6.1.5 <5ALL>........................................................................................................................................................................................... 79
3.6.2 <2LEVEL> .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 80
3.6.2.1 SECURITY LEVELS...................................................................................................................................................................... 80
3.6.3 <3UL> ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 83
3.6.3.1 UPPER LIMIT ALARM AND SEQUENCE.....................................................................................................................................84
3.6.4 <4CAL>............................................................................................................................................................................................... 84
3.6.5 <5PREFS>.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 84
3.6.5.1 <1SCRSVR>..................................................................................................................................................................................85
3.6.5.2 <2SOUND>....................................................................................................................................................................................85
3.6.5.3 <3TIME>......................................................................................................................................................................................... 86
3.6.5.4 <4ID>.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 86
3.6.5.5 <5LOG>.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 87
3.6.6 <6REMOTE>.......................................................................................................................................................................................87
3.6.6.1 COM1 AND COM2......................................................................................................................................................................... 88
3.6.6.2 IEEE-488........................................................................................................................................................................................88
3.6.6.3 RS232 SELF-TEST........................................................................................................................................................................ 88
3.6.7 <7MICRO>.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 89
3.6.8 <8HEAD>............................................................................................................................................................................................ 90
3.6.9 <9BPR>............................................................................................................................................................................................... 91
4. REMOTE OPERATION ....................................................... 95
4.1 OVERVIEW..................................................................................................................................................................................95
4.2 INTERFACING.............................................................................................................................................................................95
4.2.1 RS232 INTERFACE ........................................................................................................................................................................... 96
4.2.1.1 COM1.............................................................................................................................................................................................96
4.2.1.2 COM2.............................................................................................................................................................................................96
4.2.2 IEEE-488 (GPIB).................................................................................................................................................................................97
4.3 COMMANDS................................................................................................................................................................................ 97
4.3.1 COMMAND SYNTAX ......................................................................................................................................................................... 97
4.3.2 COMMAND SUMMARY ..................................................................................................................................................................... 98
4.3.3 ERROR MESSAGES..........................................................................................................................................................................99
4.3.4 COMMAND DESCRIPTIONS...........................................................................................................................................................101
4.3.4.1 IEEE STD. 488.2 COMMON AND STATUS COMMANDS.........................................................................................................101
4.3.4.2 MOLBOX RFM COMMANDS...................................................................................................................................................... 104
4.4 STATUS SYSTEM.....................................................................................................................................................................129
4.4.1 STATUS REPORTING SYSTEM ..................................................................................................................................................... 129
4.4.1.1 STATUS BYTE REGISTER.........................................................................................................................................................129
4.4.1.2 STANDARD EVENT REGISTER................................................................................................................................................. 131
5. MAINTENANCE, ADJUSTMENTS AND CALIBRATION ...........133
5.1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW.............................................................................................................................................................133
5.2 CALIBRATION OF REFERENCE PRESSURE TRANSDUCERS (RPTS)..............................................................................134
5.2.1 PRINCIPLE....................................................................................................................................................................................... 134
5.2.1.1 PA AND PM COEFFICIENTS...................................................................................................................................................... 135
5.2.2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED.................................................................................................................................................................135
5.2.2.1 UPSTREAM AND DOWNSTREAM ABSOLUTE RPTS.............................................................................................................. 135
5.2.2.2 DIFFERENTIAL (MICRORANGE) RPT....................................................................................................................................... 136
5.2.3 SET-UP AND PREPARATION.........................................................................................................................................................136
5.2.3.1 UPSTREAM AND DOWNSTREAM ABSOLUTE RPTS.............................................................................................................. 136
5.2.3.2 MICRORANGE DIFFERENTIAL RPT......................................................................................................................................... 136
5.2.4 VIEWING AND EDITING RPT READINGS AND CALIBRATION INFORMATION........................................................................ 137
5.2.4.1 VIEWING RPT OUTPUTS...........................................................................................................................................................138
5.2.4.2 VIEWING AND EDITING RPT PA, PM AND CALIBRATION DATE...........................................................................................140
5.2.5 RPT CALIBRATION/ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE WITHOUT USING CALTOOL FOR RPTS SOFTWARE ............................ 141
5.3 OHMIC MEASUREMENT SYSTEM VERIFICATION................................................................................................................142
5.4 RELOADING EMBEDDED SOFTWARE INTO MOLBOX RFM FLASH MEMORY.................................................................143
5.5 RELOADING MOLBLOC EEPROM FILE.................................................................................................................................144
Page III © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 6

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
5.6 OVERHAUL...............................................................................................................................................................................144
5.6.1 INTERNAL VIEW..............................................................................................................................................................................145
5.6.1.1 UPSTREAM ABSOLUTE RPT ....................................................................................................................................................146
5.6.1.2 DOWNSTREAM ABSOLUTE RPT..............................................................................................................................................146
5.6.1.3 DIFFERENTIAL MICRORANGE RPT (OPTIONAL)................................................................................................................... 146
5.6.1.4 DISPLAY......................................................................................................................................................................................146
5.6.1.5 POWER SUPPLY........................................................................................................................................................................ 146
5.6.1.6 MICRO BOARD........................................................................................................................................................................... 146
5.6.1.7 VALVING MODULE..................................................................................................................................................................... 146
5.6.1.8 MAIN BOARD ..............................................................................................................................................................................147
5.6.1.9 COOLING FAN ............................................................................................................................................................................147
6. TROUBLESHOOTING .......................................................149
6.1 OVERVIEW................................................................................................................................................................................149
7. APPENDIX ......................................................................155
7.1 CONVERSION OF NUMERICAL VALUES...............................................................................................................................155
7.1.1 PRESSURE ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 155
7.1.2 TEMPERATURE...............................................................................................................................................................................155
7.1.3 FLOW................................................................................................................................................................................................ 156
7.2 WARRANTY STATEMENT....................................................................................................................................................... 159
8. GLOSSARY .....................................................................161
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page IV
Page 7

TABLES & FIGURES
T
AABBLLEES
T
Table 1. molbloc-L Pressure Dependent Calibration Types........................................................................5
Table 2. molbloc-L Ranges with Low Pressure Calibrations.......................................................................6
Table 3. molbloc-L Ranges with High Pressure Calibrations ...................................................................... 7
Table 4. molbloc-S Flow at Various molbloc Upstream Pressures ...........................................................10
Table 5. Minimum molbloc-S Critical Flow (slm) at Various molbloc-S Downstream Pressures ..............10
Table 6. molbloc-S Calibration Types........................................................................................................11
Table 7. molbox RFM Parts List.................................................................................................................15
Table 8. Summary of molbox RFM Direct Function Key Operations.........................................................29
Table 9. Available molbloc-L Gases .......................................................................................................... 32
Table 10. Available molbloc-S Gases........................................................................................................33
Table 11. Available Flow Units...................................................................................................................39
Table 12. Flow Units and Corresponding Total Mass or Volume Units.....................................................65
Table 13. molbloc-L Size and Nominal Range Designations .................................................................... 71
Table 14. molbloc-S Size Designation and Pressure to Flow Conversion Ratio (KF)................................71
Table 15. Pressure Units of Measure Available.........................................................................................73
Table 16. Security Levels - Functions NOT Executed Per Function/Level................................................81
Table 17. Security Levels - Functions NOT Executed Per Function/Level (Continued)............................82
Table 18. COM1 and COM2 Available Settings ........................................................................................88
Table 19. COM1 DB-9F Pin Designation...................................................................................................96
Table 20. COM2 DB-9M Pin Designation..................................................................................................97
Table 21. Command Summary..................................................................................................................98
Table 22. Error Messages........................................................................................................................100
Table 23. Status Byte Register ................................................................................................................129
Table 24. Standard Event Register..........................................................................................................131
Table 25. Troubleshooting Checklist .......................................................................................................149
Table 26. Pressure Unit Conversions......................................................................................................155
Table 27. Temperature Unit Conversion..................................................................................................155
Table 28. Conversions From kg/s To sccm At 0 °C For Various Gases .................................................156
Table 29. Conversions From sccm At 0 °C To Other Volumetrically Based Flow Units .........................156
Table 30. Conversions From Volumetrically Based Flow Units At 0 °C To
Table 31. Conversions From kg/s To mole/s For Various Gases............................................................157
Table 32. Conversion From mole/s To pccm...........................................................................................158
Table 33. Conversion From sccm At 0 °C to Volume Flow Units At Another Pressure
Table 34. Authorized Service Providers ..................................................................................................159
S
Corresponding Units At Another Temperature (uxxx)...........................................................157
And Temperature...................................................................................................................158
Page V © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 8

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
F
IIGGUURREES
F
Figure 1. molbox RFM Front Panel............................................................................................................13
Figure 2. molbox RFM Rear Panel ............................................................................................................ 14
Figure 3. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – MICRORANGE OPTION RPT
Figure 4. Keypad Layout............................................................................................................................27
Figure 5. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – TARING, UPSTREAM
Figure 6. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – TARING molbloc-S OPERATION..................... 44
Figure 7. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – PURGING ......................................................... 45
Figure 8. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – LEAK CHECK molbox.......................................48
Figure 9. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – SYSTEM LEAK CHECK –
Figure 10. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – SYSTEM LEAK CHECK –
Figure 11. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – molbloc-S OPERATION, BPR ON..................92
Figure 12. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – molbloc-S OPERATION, BPR OFF................ 92
Figure 13. Status Byte Register...............................................................................................................130
Figure 14. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – RUN UPSTREAM OR DOWNSTREAM
Figure 15. molbox RFM Internal Pneumatic Schematic – RUN MICRORANGE DIFFERENTIAL
Figure 16. molbox RFM Internal View......................................................................................................145
Figure 17. molbox RFM Valving Assembly Schematic............................................................................147
S
ACTIVE/INACTIVE..................................................................................................................23
molbloc-L OPERATION...........................................................................................................41
CHECKING OFFSET AND STABILITY molbloc-L operation..................................................50
CHECKING OFFSET AND STABILITY molbloc-S operation .................................................52
ABSOLUTE RPT CALIBRATION..........................................................................................139
RPT CALIBRATION ..............................................................................................................139
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page VI
Page 9

ABOUT THIS MANUAL
A
BBOOUUTT
A
This manual provides the user with the information necessary to operate a molbox RFM, Reference Flow
Monitor. It also includes a great deal of additional information provided to help you optimize molbox RFM
use and take full advantage of its many features and functions.
Before using the manual, take a moment to familiarize yourself with the Table of Contents structure: All first
time molbox RFM users should read Section
molbox RFM operating principles. Section 4 is for
provides maintenance and calibration information. Section 6 is a quick troubleshooting guide. Use
troubleshoot unexpected molbox RFM behavior based on the symptoms of that behavior.
Certain words and expressions have specific meaning as they pertain to molbox RFM. Section 8 is useful as
a quick reference for exact definition of specific words and expressions as they are used in this manual.
For those of you who “don’t read manuals”, go directly to section 2.3, initial setup, to set up your
molbox RFM. Then go to section 2.4, power up and verification. This will get you running quickly with
minimal risk of causing damage to yourself or your molbox RFM. THEN… when you have questions or
start to wonder about all the great features you might be missing, get into the manual!
T
T
HHIISS
M
AANNUUAAL
M
L
2. Section 3 provides a comprehensive description of general
remote operation from an external computer. Section 5
Manual Conventions
it to
(CAUTION) is used in throughout the manual to identify user warnings and cautions.
(NOTE) is used throughout the manual to identify operating and applications advice and
additional explanations.
[ ] indicates direct function keys (e.g., [RANGE]).
< > indicates molbox RFM screen displays (e.g., <1yes>).
Page VII © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 10

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
N
N
OOTTEES
S
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page VIII
Page 11

1. INTRODUCTION
.
11.
I
NNTTRROODDUUCCTTIIOON
I
N
1.1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
molbox RFM is a support unit for making low mass flow measurements using molbloc mass
flow elements. molbox RFM reads calibration data off the molbloc EEPROM and measures molbloc
upstream and downstream pressure using built-in high accuracy Reference Pressure
Transducers (RPTs). An ohmic measurement system reads the resistance of the molbloc platinum
resistance thermometers from which molbloc temperature is calculated. Using the molbloc calibration
data, pressures, temperature and gas properties stored in memory, the flow rate of the gas flowing
through the molbloc is calculated. A microrange option is available to increase resolution and accuracy
below 10 % FS of the molbloc-L flow range.
Internal molbox RFM valving supports on-board PRESSURE TRANSDUCER TARING, LEAK TESTING
and SELF PROTECTION functions as well as a gas purge routine.
molbox RFM provides a local user interface via a front panel key pad and display and includes advanced
on-board functions. Remote communication capability is supported with RS232 and IEEE-488 interfaces.
molbox RFM is intended for applications in which a highly compact presentation, high range ability and
lower cost are the primary considerations. A second model, molbox1, is available for applications where
higher accuracy is the most important requirement.
1.1.1 MOLBLOC FLOW ELEMENTS
Two different types of molblocs may be used with molbox RFM; molbloc-L (laminar) and
molbloc-S (sonic).
1.1.1.1 MOLBLOC-L FLOW ELEMENT
molbloc-L is the original molbloc laminar flow element. molbloc-L covers the
lower portion of the molbloc/molbox system flow range. The key molbloc-L
measurement is the differential pressure across the element, which is roughly
proportional to the mass flow rate through it. molbloc-L elements are calibrated
to be used at an absolute pressure that remains nearly constant, while the
differential pressure varies with flow rate. Different operating pressure options
and their effect on molbloc flow range are described in Section 1.2.4.1.2.
1.1.1.2 MOLBLOC-S FLOW ELEMENT
molbloc-S elements use critical (sonic) flow venturi nozzle technology to
measure flows, which overlap with the higher molbloc-L ranges and extend the
high end of the molbloc/molbox RFM system flow range. The mass flow rate
through a molbloc-S element is roughly proportional to the upstream absolute
pressure when the flow is “choked”, so the molbloc-S operating pressure can
vary widely as the mass flow rate is changed throughout the flow range. The
limits of molbloc-S operating pressure and flow ranges are defined by the
molbloc-S calibration type, described in Section 1.2.4.2.2.
Page 1 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 12

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS
1.2.1 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Power Requirements
Fuse
Operating Temperature Range
Storage Temperature Range
Vibration
Weight
Dimensions
Microprocessor
Communication Ports
Reference Pressure Transducers
(RPTs)
Ohmic Measurement System
Gases Supported
Pressure Connections
Pressure Limits
Flow Ranges
CE Conformance
85 to 264 VAC, 47 to 440 Hz, 18 VA max. consumption
1A/250V, slow blow, 5x20mm, NSN: 5920008930491
15 to 35 °C
-20 to 70 °C
Meets MIL-T-28800D
2.55 kg (5.6 lb) max.
8 cm H x 22.5 cm W x 20 cm D
(3.1 in. x 8.9 in. x 7.9 in.) approx.
Motorola 68302, 16 MHz
RS232 (COM1), RS232 (COM2), IEEE-488
Standard: 2 x 600 kPa (87 psia) calibrated range piezoresistive silicon
Microrange option: 12.5 kPa (1.8 psid) piezoresistive silicon
Resolution: 0.004 Ω
Accuracy: ± 0.02 % of reading
Accuracy of 100 and 110 Ω reference resistors: ± 0.01 %
Stability of 100 and 110 Ω reference resistors: ± 0.005 % per three years
With molbloc-L Nitrogen (N2), Air, Argon (Ar), Butane (Butn), Carbon
Monoxide (CO), Helium (He), Oxygen (O2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2),
Carbon Tetrafluoride (CF4), Octofluorocyclobutane (C4F8), Ethane
(C2H6), Ethylene (C2H4), Fluoroform (CHF3), Hexafluoroethane (C2F6),
Hydrogen (H2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous Oxide (N2O), Propane (C3H8),
Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6), Xenon (Xe)
With molbloc-S Nitrogen (N2), Air (dry and humid)
Quick connectors equivalent to Swagelok QM Series (-QM2-B200)
Maximum working pressure 600 kPa absolute (87 psia)
Maximum pressure without damage 800 kPa absolute (115 psia)
NOTE: The microrange option includes a 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi) differential
RPT which may be damaged by differential pressure greater than 100
kPa (15 psi).
See Sections 1.2.4.1.3, 1.2.4.1.4and 1.2.4.2.1
Available. Must be specified.
1.2.2 REFERENCE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (RPT) SPECIFICATIONS
1.2.2.1 UPSTREAM AND DOWNSTREAM RPTS
Type
Range
Resolution
Repeatability
Accuracy
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 2
Piezoresistive silicon
0 to 600 kPa absolute (0 to 87 psia)
6.0 Pa (0.0009 psi)
± 0.01 % FS
Absolute measurements: ± 0.05 % FS for one year
Differential measurements: ± (20 Pa + 0.05 % ΔΡ). Taring sequence eliminates zero
error on measurement of difference between the two RPTs.
Page 13

1. INTRODUCTION
1.2.2.2 DIFFERENTIAL RPT (MICRORANGE OPTION)
Type
Range
Resolution
Repeatability
Accuracy
Piezoresistive silicon
0 to 12.5 kPa differential (0 to 1.8 psid)
0.14 Pa (0.00002 psi)
± 0.01 % FS
± 0.05 % FS for one year. Taring sequence eliminates zero error.
1.2.3 TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications are for molbloc mounted Platinum Resistance Thermometers (PRT) combined
with molbox RFM resistance measurement system and temperature calculation.
Range
Accuracy
Resolution
0 to 40 °C
± 0.05 °C
0.01 °C
The molbox RFM internal resistance measurement system is automatically calibrated using
reference 100 and 110 Ω (± 0.01 %) resistors (see Section
5.3).
1.2.4 FLOW MEASUREMENT SPECIFICATIONS
molbox RFM measures the flow through molbloc flow elements. There are two different
types of molblocs, molbloc-L (laminar) (see Section 1.1.1.1) and molbloc-S (sonic) (see
Section 1.1.1.2). Flow measurement specifications, calibration types, ranges and dimensions
are detailed separately for each molbloc type in Section 1.2.4.1 and 1.2.4.2.
1.2.4.1 molbloc-L
The flow range, useable operating pressure and absolute and differential
pressure associated with molbloc-L operation depend on the molbloc used and
its pressure-dependent calibration options (see Section
Measurement Update Rate
Range
Resolution
Linearity
Repeatability
Precision
Stability
(1 year)
Measurement Uncertainty
(1 year, N2 and any molbox RFM
supported gas for which the molbloc
1 Precision: Combined linearity, hysteresis, repeatability.
2 Stability: aximum change in zero and span over specified time period for typical molbox RFM and
molbloc used under typical conditions. As stability can only be predicted, stability for a specific
molbox RFM should be established from experience.
3 Measurement Uncertainty (Accuracy): Maximum deviation of the molbox RFM flow indication from
the true value of the flow through the molbloc including precision, stability and DHI calibration
standard measurement uncertainty.
in use is calibrated)
1 second
0 to molbloc full scale depending on gas and molbloc
pressure dependent calibration type
(see Section 1.2.4.1.2).
0.01 % FS
± 0.23 % of reading from 10 to 100 % FS,
± 0.023 % FS under 10 % FS
± 0.1 of reading from 10 to 100 % FS,
± 0.01 % FS under 10 % FS
1
± 0.25 % of reading from 10 to 100 % FS,
± 0.025 % FS under 10 % FS
2
± 0.15 % of reading from 10 to 100 % FS,
± 0.015 % FS under 10 % FS
3
± 0.5 % of reading from 10 to 100 % FS,
± 0.05 % FS under 10 % FS
1.2.4.1.2).
Page 3 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 14

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.2.4.1.1 molbloc-L FLOW MEASUREMENT
SPECIFICATIONS, MICRORANGE OPTION
The microrange option (see Section 1.2.2.2) improves molbloc-L flow
measurement specifications below 10 % FS of the molbloc range. With the
microrange option, the affected measurement specifications below 10 % FS
become:
Resolution
Linearity
Repeatability
Precision1
Stability
(1 year)
Measurement Uncertainty
(1 year, N2 and any molbox RFM
supported gas for which the molbloc in
use is calibrated)
1 Precision: Combined linearity, hysteresis, repeatability.
2 Stability: Maximum change in zero and span over specified time period for typical molbox RFM and
molbloc used under typical conditions. As stability can only be predicted, stability for a specific
molbox RFM should be established from experience.
3 Measurement Uncertainty (Accuracy): Maximum deviation of the molbox RFM flow indication from
the true value of the flow through the molbloc including precision, stability and DHI calibration
standard measurement uncertainty.
0.01 % of 10 % FS (0.001 % FS)
± 0.23 % of reading from 1 to 10 % FS
± 0.1 % of reading from 1 to 10 % FS
± 0.25 % of reading from 1 to 10 % FS
2
± 0.15 % of reading from 1 to 10 % FS
3
± 0.5 % of reading from 1 to 10 % FS
1.2.4.1.2 molbloc-L PRESSURE DEPENDENT CALIBRATION
TYPES
See your molbloc’s Calibration Report to determine the calibration type of
the molbloc you are using.
Different pressure dependent calibration options for molbloc-L elements determine
the range of operating pressures over which a molbloc can be used within its
mass flow measurement specifications. The calibration option also affects the
molbloc flow range and the differential pressure associated with the flow range.
Measurement uncertainty (accuracy) specifications for molbloc-L are valid only
for gases with which the molbloc has been calibrated. All molbloc-L elements
are calibrated for N2. Calibrations with other gases are optional. DHI calibration
capability is not maintained at all times for all gases on all molbloc designations.
Check for availability before ordering calibrations.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 4
Page 15
1. INTRODUCTION
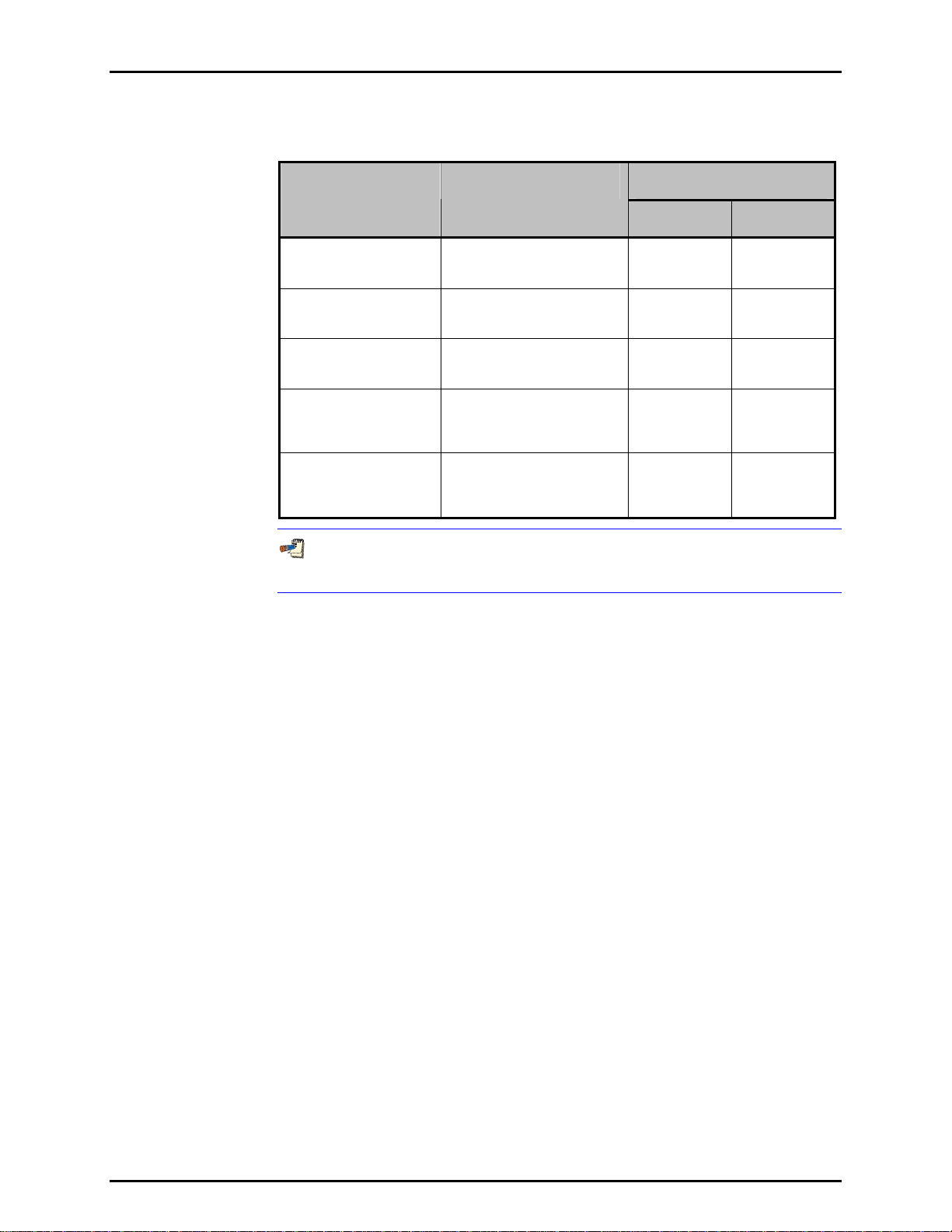
The molbloc-L pressure dependent calibration types are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. molbloc-L Pressure Dependent Calibration Types
CALIBRATION TYPE
Full mod,
low pressure
Full mod,
high pressure
Downstream
Single P,
low pressure
(non-N2 gases only )
Single P,
high pressure
(non-N2 gases only )
OPERATING PRESSURE
200 to 325 kPa absolute
(29 to 48 psia)
upstream of molbloc
325 to 525 kPa absolute
(48 to 76 psia)
upstream of molbloc
Atmospheric pressure (95 to
105 kPa, 13.8 to 15.2 psia)
downstream of molbloc
Any specified single molbloc
upstream pressure between
200 and 325 kPa absolute (29
to 48 psia)
Any specified single molbloc
upstream pressure between
325 and 525 kPa absolute (48
to 76 psia)
NOMINAL DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE AT MAX. FLOW
1E5
MOLBLOC
5 kPa
(.725 psi)
Not available 50 kPa
12.5 kPa
(1.8 psi)
5 kPa
(.725 psi)
Not available 50 kPa
ALL OTHER
MOLBLOCS
50 kPa
(7.5 psi)
(7.5 psi)
80 kPa
(12 psi)
50 kPa
(7.5 psi)
(7.5 psi)
Differential pressure values are nominal and may vary by up to 15 % with the
actual molbloc used.
Page 5 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 16
molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
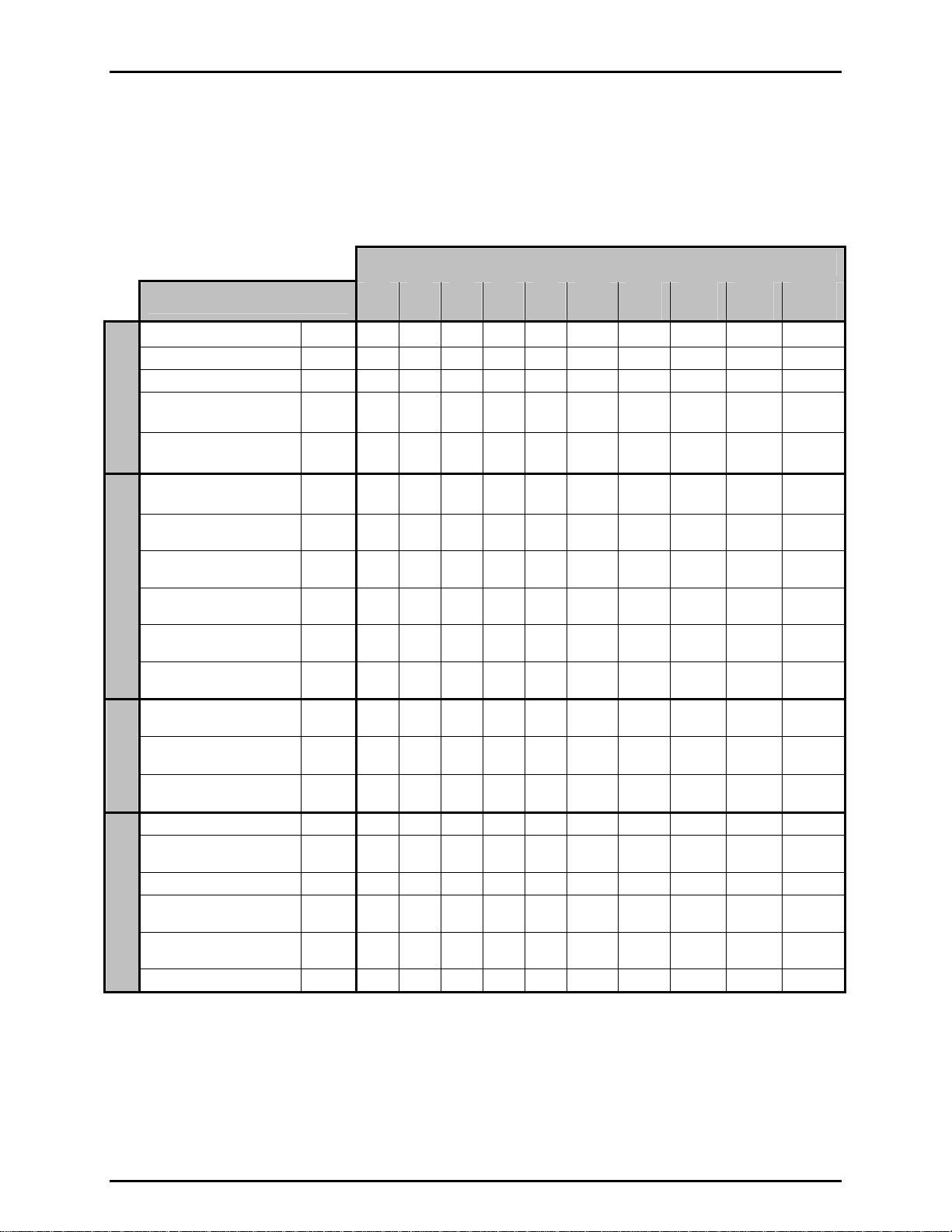
1.2.4.1.3 molbloc-L Ranges with Low Pressure Calibrations
Table 2. molbloc-L Ranges with Low Pressure Calibrations
- full mod, low pressure
- full mod, downstream
- single P, low pressure
SIZE
Nitrogen N2
Argon Ar
Helium He
Sulfur Hexafluoride SF6
INERT
Xenon XE
Butane C4H10
Ethane C2H6
Ethylene C2H4
Hydrogen H2
FLAMMABLE
Methane CH4
Propane C3H8
Carbon
Tetrafluoride
Hexafluorethene C2F6
FLUORO-
CARBONS
Trifluoromethane CHF3
Air Air
Carbon Dioxide CO2
Carbon Monoxide CO
Nitrous Oxide N2O
OTHER
Octafluorocyclobutane
Oxygen O2
A bold value indicates that the maximum flow is limited by the maximum Reynolds number value of 1 200 which is reached
before the normal differential pressure range is reached. In that case, the second value gives the minimum flow for which
relative accuracy is ± 0.5 % of the measured value. With the microrange option, this value is divided by 10 (see Section
1.2.2.2).
Where there is no value in the field (--), this indicates that the maximum Reynolds number is reached before the differential
pressure reaches 5 kPa (1 kPa in the case of the 1E5 molbloc), therefore calibration with that gas is not useful.
[1] Due to low vapor pressure, only downstream calibration type is available.
GASES
[1]
C4F8
CF4
SIZE
1E1
5E1
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000 30 000 100 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000 25 000 80 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000 30 000 100 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000
10 40 80 150 400 800
20 100
20 100 200 400 1
16 80 160 320 800 1 600
20 100 200 400 1
16 80 160 320 800 1 600 8 000 16 000
20 100 200 400 1
10 50 100 200 500 1 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000 30 000 100 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000 30 000 100 000
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000
15
10 50 100 200 500 1 000 5 000 10 000 30 000 80 000
molbloc-L SIZE AND FULL SCALE FLOW (sccm)
SIZE
SIZE
1E2
130
30
609 65
17
SIZE
2E2
270
50
130
34
5E2
670
140
000
000
000
330
85
SIZE
1E3
2 300
2 000
2 000 10
2 000
1 100
175
SIZE
5E3
2 000
500
3 500
500
2 200
1 400
6 000
1 000
7 000
1 000
000
3 000
1 000
4 000
600
2 000
600
4 000
600
1 050
840
SIZE
1E4
6 000
1 000
8 000
7 000
3 000
18 000
2 000
16 000
20 000 60 000 200 000
10 000
2 000
10 000
6 000
1 200
10 000
3 400
1 700
6 000
4 000
11 000
18 000
20 000
40 000
10 000
12 000
12 000
20 000
20 000
SIZE
3E4
3 000
---
---
6 000
5 000
5 000
7 000
3 000
6 000
4 000
4 000
4 000
4 000
--- ---
SIZE
1E5
---
---
30 000
20 000
---
---
60 000
50 000
70 000
40 000
120 000
40 000
---
---
36 000
25 000
---
---
38 000
30 000
60 000
30 000
60 000
30 000
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 6
Page 17
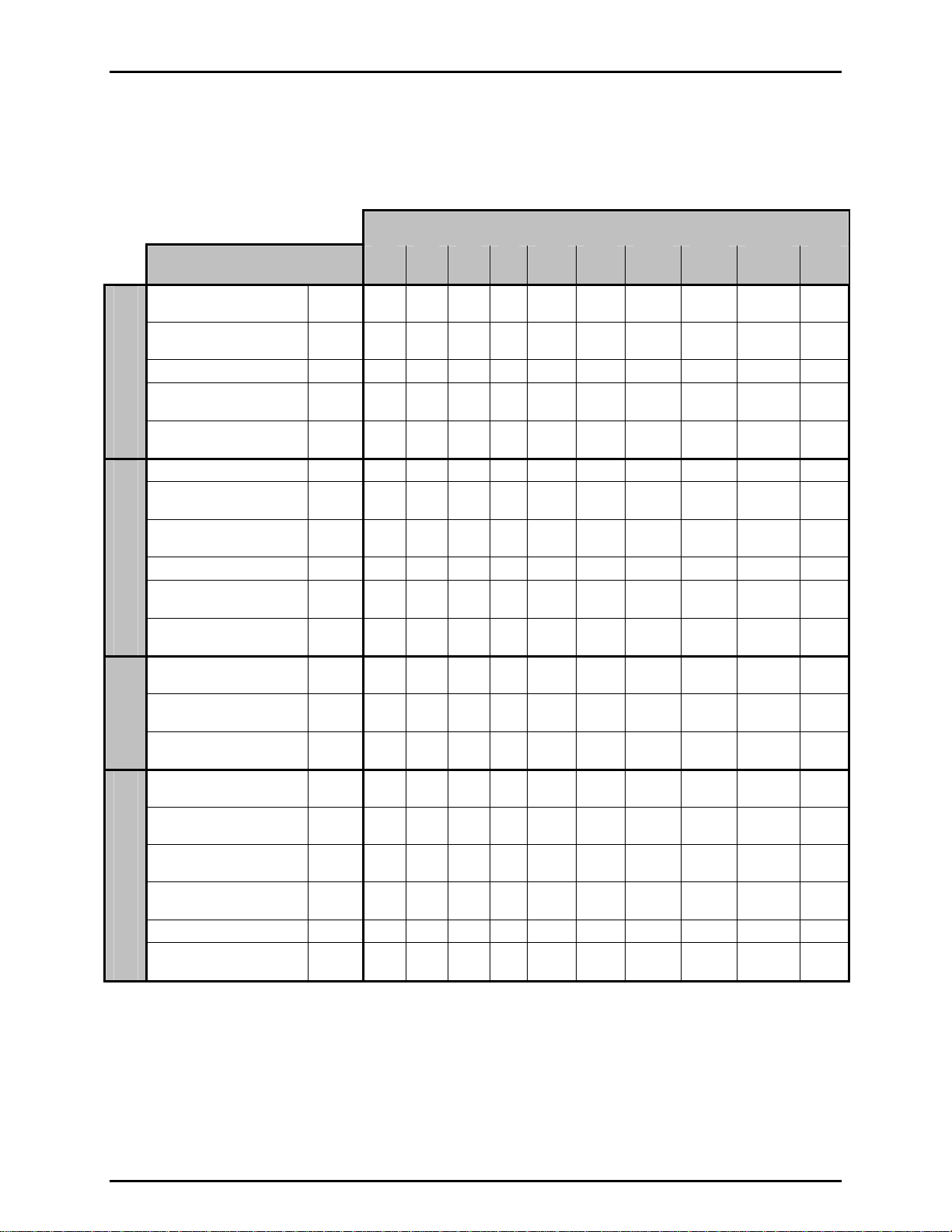
1. INTRODUCTION
1.2.4.1.4 molbloc-L Ranges with High Pressure Calibrations
Table 3. molbloc-L Ranges with High Pressure Calibrations
- full mod, high pressure
- single P, high pressure
SIZE
GASES
Nitrogen N2
SIZE
1E1
5E1
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000 10 000 20 000
molbloc-L SIZE AND FULL SCALE FLOW (sccm)
SIZE
SIZE
1E2
2E2
SIZE
5E2
SIZE
1E3
SIZE
5E3
SIZE
1E4
SIZE
3E4
40 000
SIZE
1E5
N/A
7 500
Argon Ar
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000 10 000 17 000
35 000
N/A
6 000
Helium He
INERT
Sulfur Hexafluoride SF6
Xenon XE
[2]
Butane
C
4H10
Ethane C2H6
Ethylene C2H4
Hydrogen H2
Methane CH4
FLAMMABLE
Propane C3H8
Carbon
CF4
Tetrafluoride
Hexafluorethene C2F6
FLUORO-
CARBONS
Trifluoromethane CHF3
Air Air
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000 10 000 20 000 65 000 N/A
25
100
120
15
30
20 100 150 350 650 1 700
250
* * * * * * * * * N/A
40 200
350
50
700
100
40 200 350 700 2 000 4 000
50
600
150
1 800
200
2 000
300
4 000
2 000
1 400
3 350
950
6 000
2 300
7 000
2 000
6 200
2 800
11 000
1 900
20 000
4 500
22 000
4 000
--
--
11 000
5 700
20 000
13 000
22 000
12 700
40 200 400 900 2 000 4 500 22 000 45 000 130 000 N/A
35 175 350 700 1 700 3 500
13 000
2 000
50 200
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000
25
200
50
400
100
1 000
250
3 500
500
3 500
2 600
3 700
1 200
25
100
120
15
25 125
30
240
30
250
450
50
60
600
150
1 200
150
2 000
300
2 500
1 800
1 500
4 000
1 500
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000 10 000 20 000
33 000 42 000
12 000
11 000
5 400
12 000
2 400
6 000
3 000
12 000
3 000
--
--
12 000
7 300
--
--
12 000
8 800
40 000
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
7 200
Carbon Dioxide CO2
Carbon Monoxide CO
25 125 250 500 1 250 2 500
6 600
1 400
20 000
2 500
20 000
8 800
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000 10 000 20 000 40 000
N/A
N/A
7 500
OTHER
Oxygen O2
20 100 200 400 1 000 2 000 10 000 20 000
40 000
N/A
6 500
Octafluorocyclobutane
[2]
C4F8
Nitrous Oxide N2O
A bold value indicates that the maximum flow is limited by the maximum Reynolds number value of 1 200 which is reached before
the normal differential pressure range is reached. In that case, the second value gives the minimum flow for which relative accuracy
is ± 0.5 % of the measured value. With the microrange option, this value is divided by 10 (see Section 1.2.2.2).
Where there is no value in the field (--), this indicates that the maximum Reynolds number is reached before the differential pressure
reaches 5 kPa (1 kPa in the case of the 1E5 molbloc), therefore calibration with that gas is not useful.
* * * * * * * * * N/A
25 125 250 500 1 250 2 500
11 000
1 500
20 000
3 000
20 000
9 000
N/A
[2] The operating pressure range is greater than the vapor pressure value for the gas.
Page 7 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 18
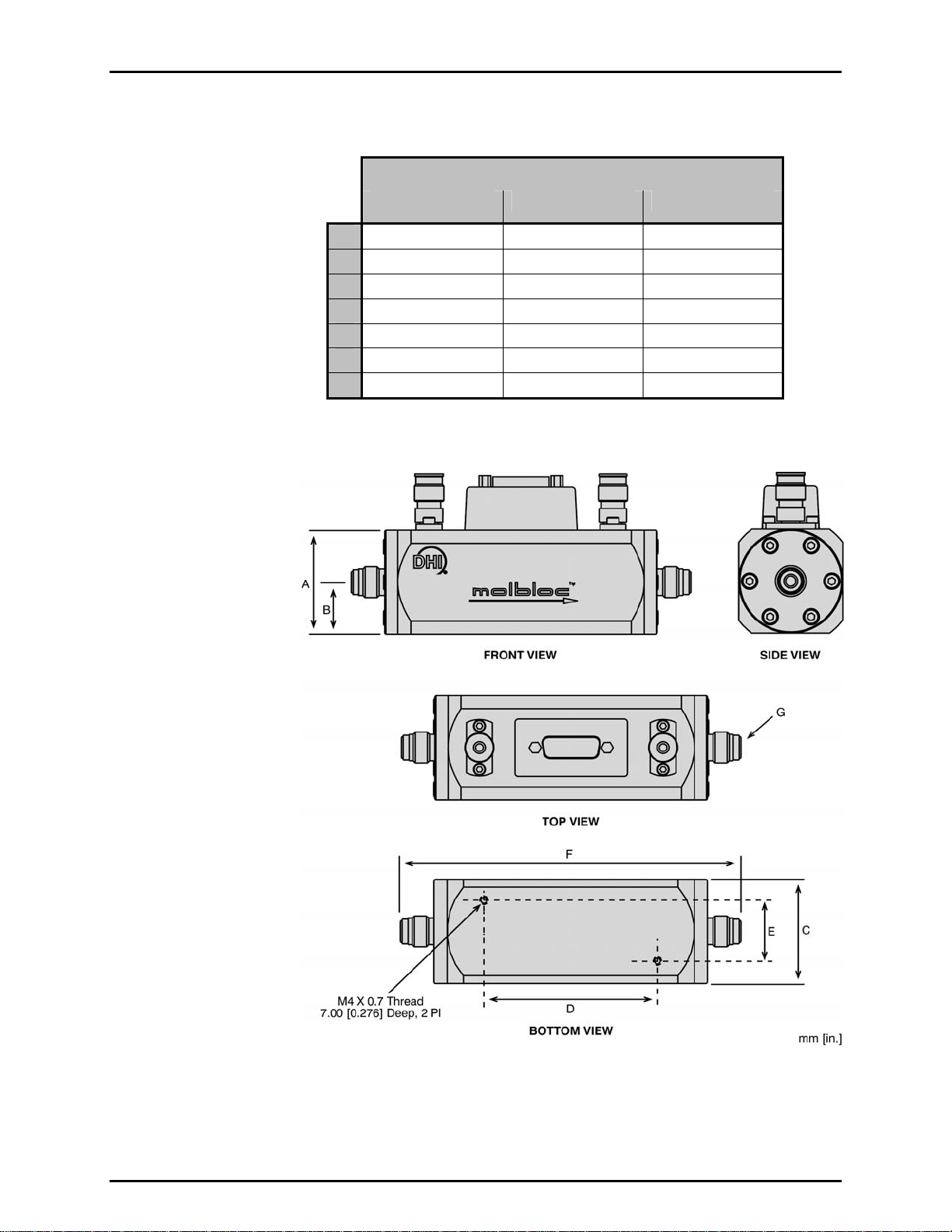
molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.2.4.1.5 molbloc-L DIMENSIONS
5E3 AND LOWER 1E4, 3E4 1E5
58.50 (2.303) 74.50 (2.933) 74.50 (2.933)
A
16.00 (0.630) 24.00 (0.945) 24.00 (0.945)
B
32.00 (1.260) SQ 48.00 (1.890) SQ 48.00 (1.890) SQ
C
68.84 (2.750) 80.00 (3.150) 80.00 (3.150)
D
19.06 (0.750) 28.00 (1.102) 28.00 (1.102)
E
124.00 (4.881) 157.00 (6.181) 164.00 (6.458)
F
1/4 in. VCR M 1/4 in. VCR M 1/2 in. VCR M
G
molbloc-L SIZES [mm(in.)]
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 8
Page 19

1. INTRODUCTION
1.2.4.2 molbloc-S
The flow range and operating pressure associated with molbloc-S operation
depend on the molbloc used and its calibration options (see Section 1.2.4.2.2)
Measurement Update
Range
Resolution
Linearity
Repeatability
Precision
Predicted Stability
(1 year)
Measurement
Uncertainty
With SP molbloc-S
calibration
Measurement
Uncertainty
With LP molbloc-S
calibration
1 Precision: Combined linearity, hysteresis, repeatability.
2. Stability: Maximum change in zero and span over specified time period for typical molbox RFM
and molbloc used under typical conditions. As stability can only be predicted, stability for a
specific molbloc and molbox RFM should be established from experience.
3. Measurement uncertainty (accuracy): Maximum deviation of the molbox RFM flow indication
from the true value of the flow through the molbloc including precision, stability and DHI
calibration standard measurement uncertainty.
1 second
Rate
Depends on molbloc-S pressure dependent calibration type
(see Section 1.2.4.2.2)
0.01 % of FS
± 0.25 % of reading
± 0.10 % of reading
1
± 0.30 % of reading
2
± 0.2 % of reading
± 0.5 % of reading from 50 to 500 kPa
3
± 0.5 % of reading from 50 to 200 kPa
3
± 0.5 % of 50 kPa flow from 20 to 50 kPa
1.2.4.2.1 molbloc-S RANGES
molbloc-S flow ranges are defined by the molbloc’s Pressure to Flow Conversion
Ratio, K
downstream pressure and the acceptable back pressure ratio (see Section
3.1.2). K
between mass flow and the absolute upstream pressure delivered to the
molbloc-S. molbloc-S sizes are defined by the nominal K
nozzle, using scientific notation, for example a 1E3 molbloc-S has a K
sccm/kPa. To differentiate from molbloc-L size designations, this molbloc size is
designated 1E3-S.
The molbox RFM pressure range, the molbloc-S calibration type (see Section
1.2.4.2.2) and the back pressure ratio (BPR) requirements (see Section 3.1.2)
limit the pressures, and flows, over which a molbloc-S can be used within known
measurement uncertainty limits. In practice, the usable range of a molbloc-S in a
given application also may depend on the available gas supply pressure, the presence
and flow capacity of a vacuum pump downstream or the allowable back pressure
on an upstream DUT.
The flow ranges for each molbloc-S size at various typical operating pressures
are summarized in Table 4 and the BPR limits are in Table 5.
, the absolute pressure that can be delivered upstream of molbloc-S, the
F
is expressed in units of sccm/kPa and defines the relationship
F
of the molbloc-S
F
1 000
F
Page 9 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 20
molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
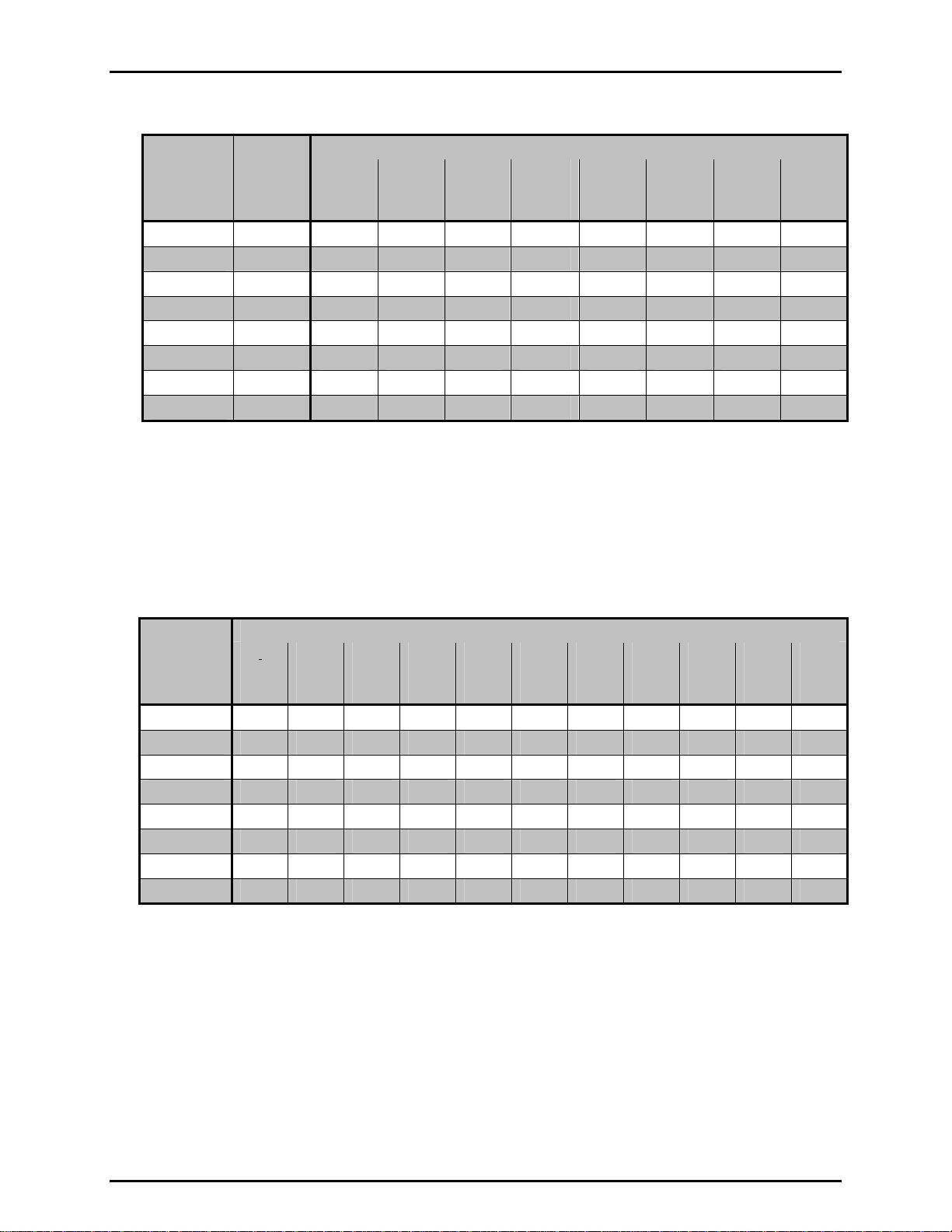
Table 4. molbloc-S Flow at Various molbloc Upstream Pressures
[1][2]
250 kPa
(36 psia)
500 kPa
(70 psia)
molbloc-S
DESIGNATO
R
5E1-S
1E2-S
2E2-S
5E2-S
1E3-S
2E3-S
5E3-S
1E4-S
FLOW [slm @ 0°C] WHEN molbloc-S UPSTREAM PRESSURE IS:
KF
[sccm/kPa]
20 kPa
(3psia)
50 kPa
(7 psia)
100 kPa
(15 psia)
Minimum
without
vacuum
]
[3
150 kPa
(22 psia)
200 kPa
(30 psia)
50 1 2.5 5 7.7 7.5 10 12.5 25
100 2 5 10 15 15 20 25 50
200 4 10 20 28 30 40 50 100
500 10 25 50 67 75 100 125 250
1 000 20 50 100 129 150 200 250 500
2 000 40 100 200 248 300 400 500 1 000
5 000 100 250 500 596 750 1 000 1 250 2500
10 000 200 500 1 000 1 173 1 500 2 000 2 500 5 000
[1] When volumetrically based mass flow units with reference temperatures other than 0°C are used, flow values
will generally be higher; for example, the flow values for a given molbloc and upstream pressure are
approximately 7% higher when expressed in slm @ 20°C. Flow values at a given pressure may vary by up to
2% due to flowpath machining tolerances.
[2] Flow values in table are valid only when critical flow is established.
[3] Minimum upstream pressure to achieve critical flow with atmospheric pressure (approximately 100 kPa)
downstream of molbloc-S (no vacuum).
Table 5. Minimum molbloc-S Critical Flow (slm) at Various molbloc-S Downstream Pressures
molbloc-S
DESIGNATO
R
5E1-S
1E2-S
2E2-S
5E2-S
1E3-S
2E3-S
5E3-S
1E4-S
250
kPa
(36
psia)
[1]
300
kPa
(44
psia)
MINIMUM molbloc-S CRITICAL FLOW [SLM @ 0°C] WITH molbloc DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE OF:
≤ 5
kPa
(0.7
psia)
1
2
4
10
20
40
100
200
10
kPa
(1.5
psia)
[2]
1.7 3.4 4.7 7.7 8.4 9.4 11 14 17 20
[2]
3.4 5.9 8.4 15 16 18 21 27 33 38
[2]
5.9 9.8 16 28 31 34 40 51 63 74
[2]
12 20 37 67 72 80 95 122 149 179
[2]
20
[2]
40
[2]
100
[2]
200
25
kPa
(3.5
psia)
[2]
39 69 129 139 154 184 239 294 349
[2]
73 131 248 268 298 358 468 578 687
[2]
173 317 596 646 746 871 1 145 1 420 1 694
[2]
347 615 1 173 1 273 1 442 1 741 2 240 2 789 3 338
50
kPa
(7
psia)
100
kPa
(15
psia)
110
kPa
(16
psia)
125
kPa
(18
psia)
150
kPa
(22
psia)
200
kPa
(30
psia)
[1] When volumetrically based mass flow units with reference temperatures other than 0 °C are used, flow values
will generally be higher; for example, the flow values for a given molbloc and upstream pressure are
approximately 7 % higher when expressed in slm @ 20 °C. Flow values at a given pressure may vary by up to
2 % due to flowpath machining tolerances.
[2] Limited by 20 kPa minimum calibration pressure rather than back pressure ratio.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 10
Page 21
1. INTRODUCTION
1.2.4.2.2 molbloc-S PRESSURE DEPENDENT CALIBRATION
TYPES
See your molbloc’s Calibration Report to determine the calibration type of
the molbloc you are using.
Measurement uncertainty (accuracy) specifications for molblocs are valid only for
gases with which the molbloc has been calibrated. All molbloc-S elements are
calibrated in one standard gas, either air or N2, and may be calibrated in other
gases. Calibrations with other gases are optional. The set of gases which can
be measured by molbloc-S is separate from the list of molbloc-L gases, and may
be more limited. DHI calibration capability is not maintained at all times for all
gases on all molbloc sizes. Check for availability before ordering calibrations.
molbloc-S calibrations are performed over flow ranges corresponding to one of
two pressure ranges, summarized in Table 6.
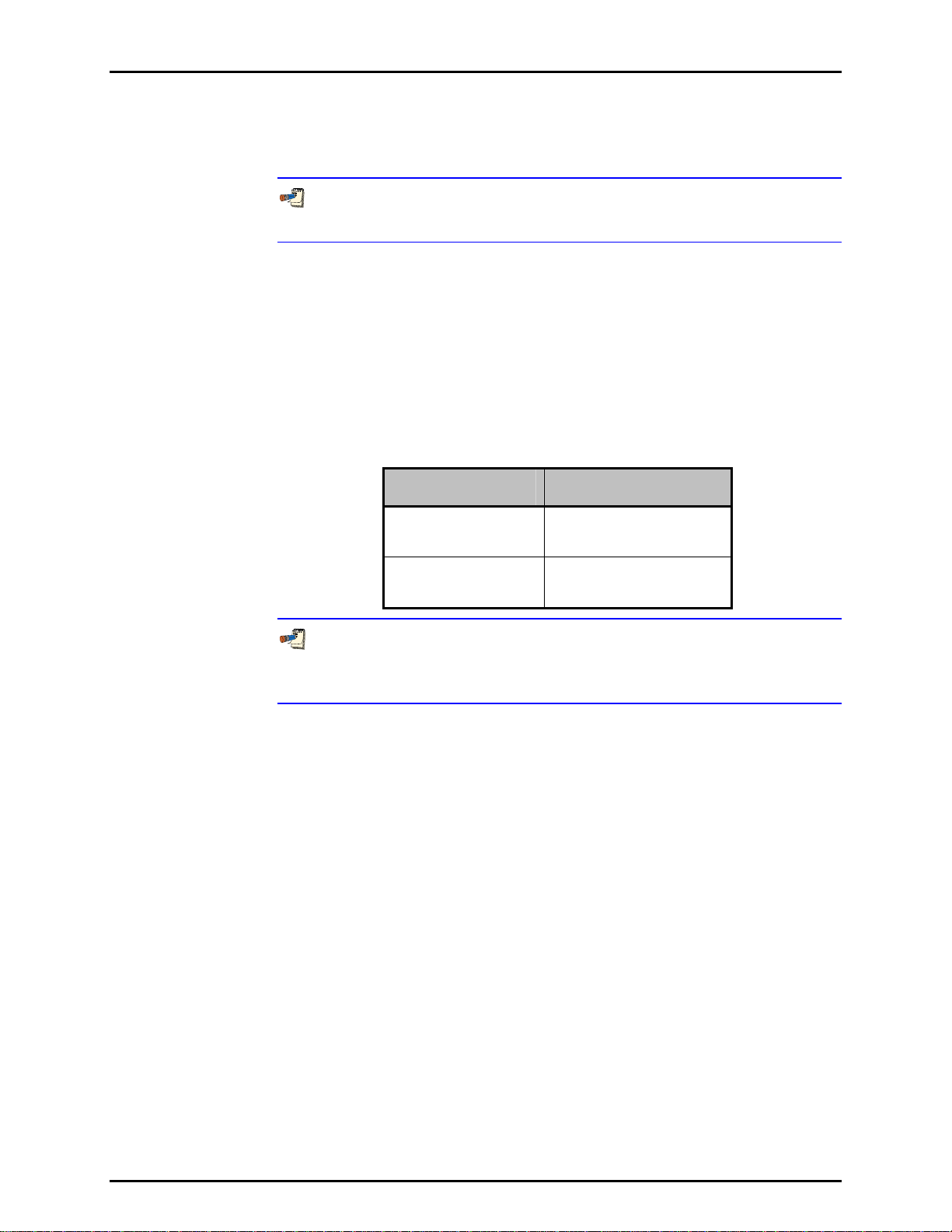
Table 6. molbloc-S Calibration Types
CALIBRATION TYPE
LP
low pressure
SP
standard pressure
OPERATING PRESSURE
20 to 200 kPa absolute (3 to
30 psia
upstream of molbloc
50 to 500 kPa absolute (7 to
70 psia)
upstream of molbloc
molbloc-S flow measurements are valid only when the ratio of pressure
downstream to pressure upstream of the nozzle is high enough to assure a
critical (choked) flow (see Section 3.1.2).
Page 11 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 22
molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
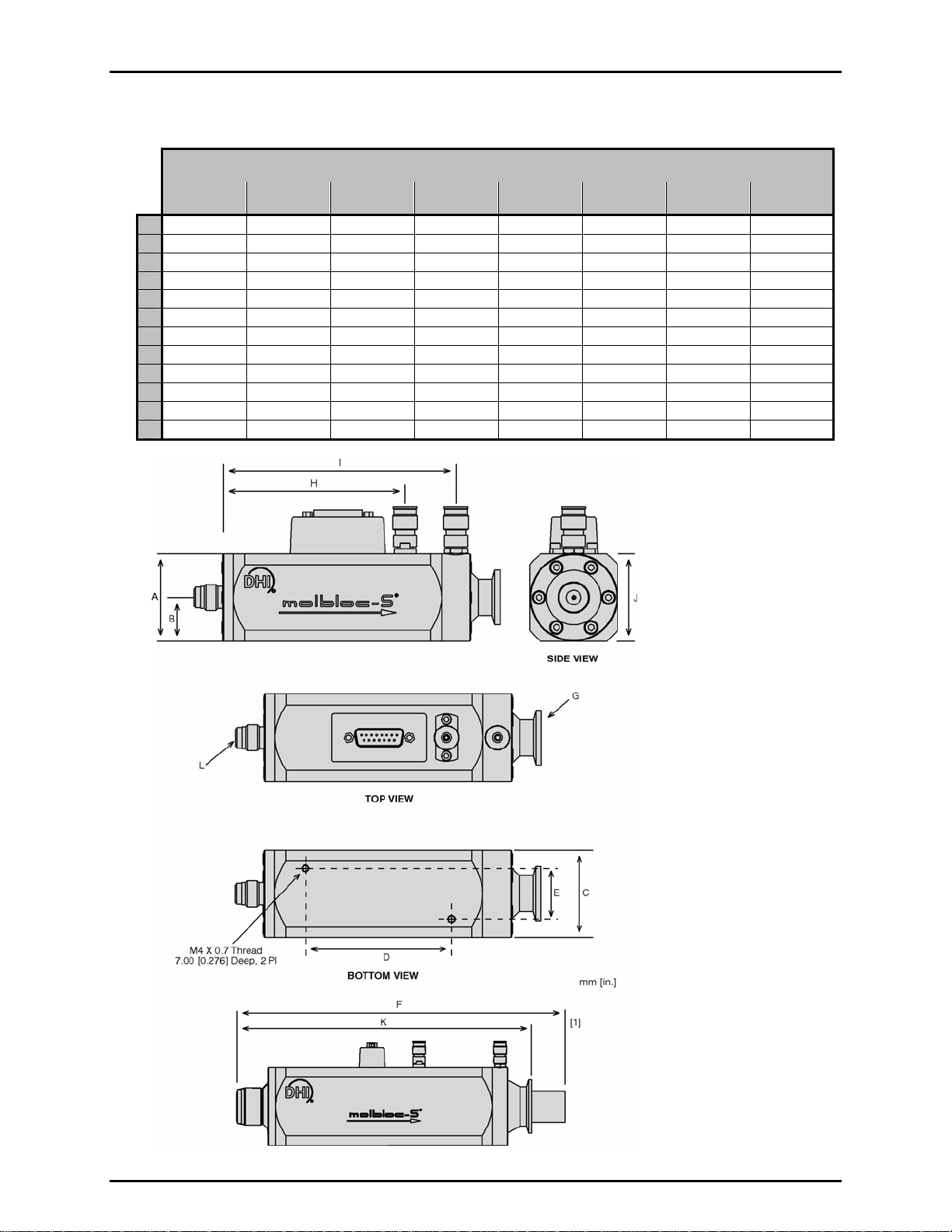
1.2.4.2.3 molbloc-S Dimensions
5E1-S 1E2-S 2E2-S 5E2-S 1E3-S 2E3-S 5E3-S 1E4-S
48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89)SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 80.0 (3.15) SQ 80.0 (3.15) SQ
A
24.0 (0.94) 24.0 (0.94) 24.0 (0.94) 24.0 (0.94) 24.0 (0.94) 24.0 (0.94) 40.0 (1.57) 40.0 (1.57)
B
48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89)SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 48.0 (1.89) SQ 80.0 (3.15) SQ 80.0 (3.15) SQ
C
80.0 (3.15) 80.0 (3.15) 80.0 (3.15) 80.0 (3.15) 80.0 (3.15) 80.0 (3.15) 176.0 (6.93) 176.0 (6.93)
D
28.0 (1.10) 28.0 (1.10) 28.0 (1.10) 28.0 (1.10) 28.0 (1.10) 28.0 (1.10) 44.0 (1.73) 44.0 (1.73)
E
167.5 (6.59) 167.5 (6.59) 171.0 (6.73) 171.0 (6.73) 171.0 (6.73) 175.0 (6.89)
F
KF16 FLANGE KF16 FLANGE KF16 FLANGE KF16 FLANGE KF16 FLANGE KF16 FLANGE KF40 FLANGE KF40 FLANGE
G
100.0 (3.94) 100.0 (3.94) 84.0 (3.31) 84.0 (3.31) 84.0 (3.31) 84.0 (3.31) 154.0 (6.06) 154.0 (6.06)
H
128.0 (5.04) 128.0 (5.04) 128.0 (5.35) 128.0 (5.35) 128.0 (5.35) 128.0 (5.35) 236.0 (9.29) 236.0 (9.29)
I
73.0 (2.87) 73.0 (2.87) 73.0 (2.87) 73.0 (2.87) 73.0 (2.87) 73.0 (2.87) 106.0 (4.17) 106.0 (4.17)
J
167.5 (6.59) 167.5 (6.59) 171.0 (6.73) 171.0 (6.73) 171.0 (6.73) 171.0 (6.73) 290.0 (11.42) 290.0 (11.42)
K
L
¼” VCR M
[2]
¼” VCR M
[2]
½” VCR M
molbloc-S SIZE [mm(in.)]
[2]
½” VCR M
[2]
½” VCR M
[2]
½” VCR M
[1]
299.7 (11.80)
[2]
1” NPT M
[1]
331.0 (13.03)
[2]
1” NPT M
[1] On some molbloc-S elements,
the venturi nozzle extends
beyond the molbloc
downstream flange, making
the overall length dimension,
F, longer than the fitting to
fitting length dimension, K.The
nozzle overhang may interfere
with some molbloc-S
downstream connections or
the connection of a blank off
cap for leak testing, so a 40
mm diameter ISO-KF nipple is
supplied with 5E3-S and 1E4S molblocs.
[2] Default connector type is
listed. Additional upstream
connector options may be
available. Contact your DHI
Sales Representative for
details.
[1]
[2]
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 12
Page 23
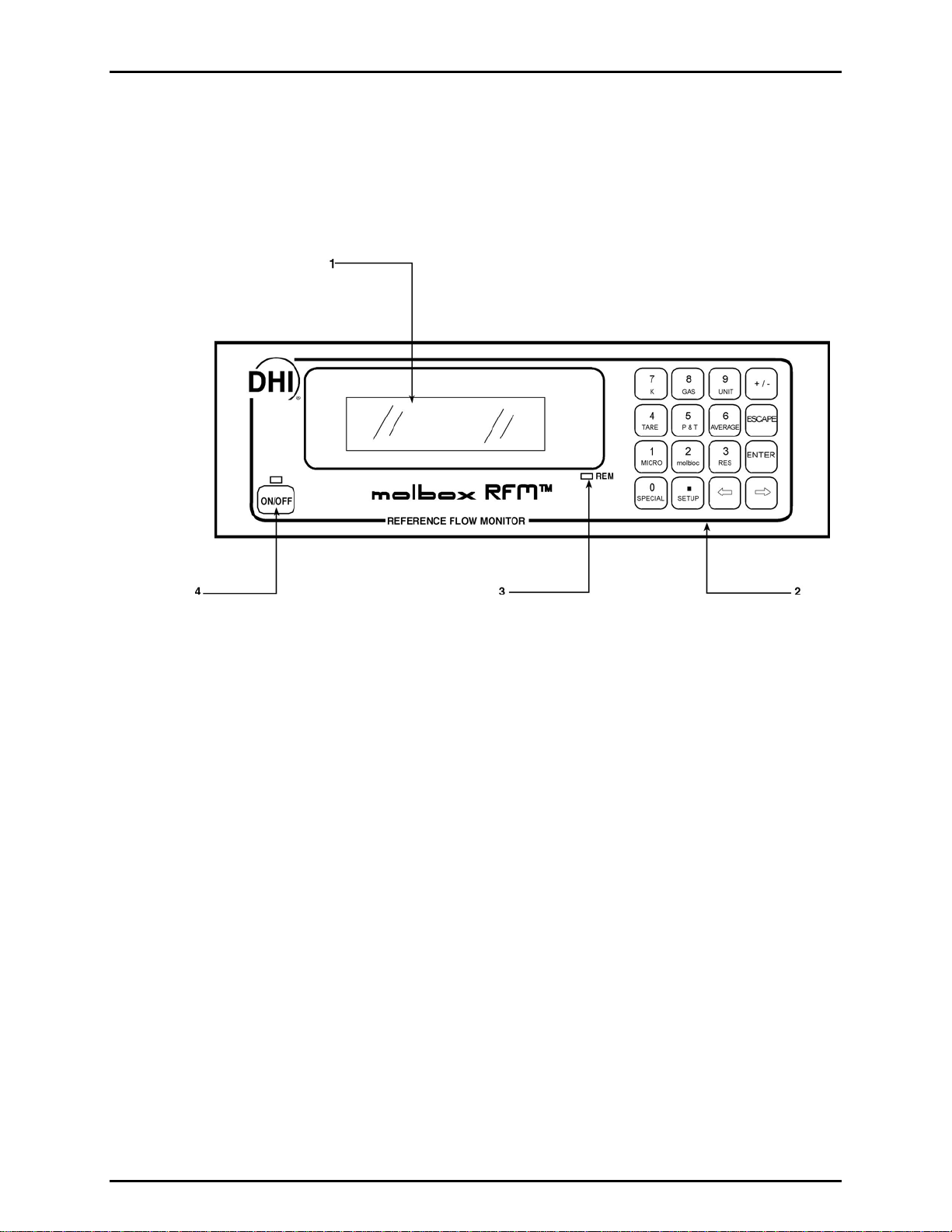
1. INTRODUCTION
1.2.5 FRONT AND REAR PANELS
1.2.5.1 FRONT PANEL
The front panel assembly provides a 2 x 20 vacuum fluorescent display, a
membrane keypad for local user interface and a SOFT ON/OFF key.
1. Display
2. Multi-function Keypad P
3. Remote Communication Indicator
4. SOFT ON/OFF Key and Indicator
Figure 1. molbox RFM Front Panel
Page 13 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 24
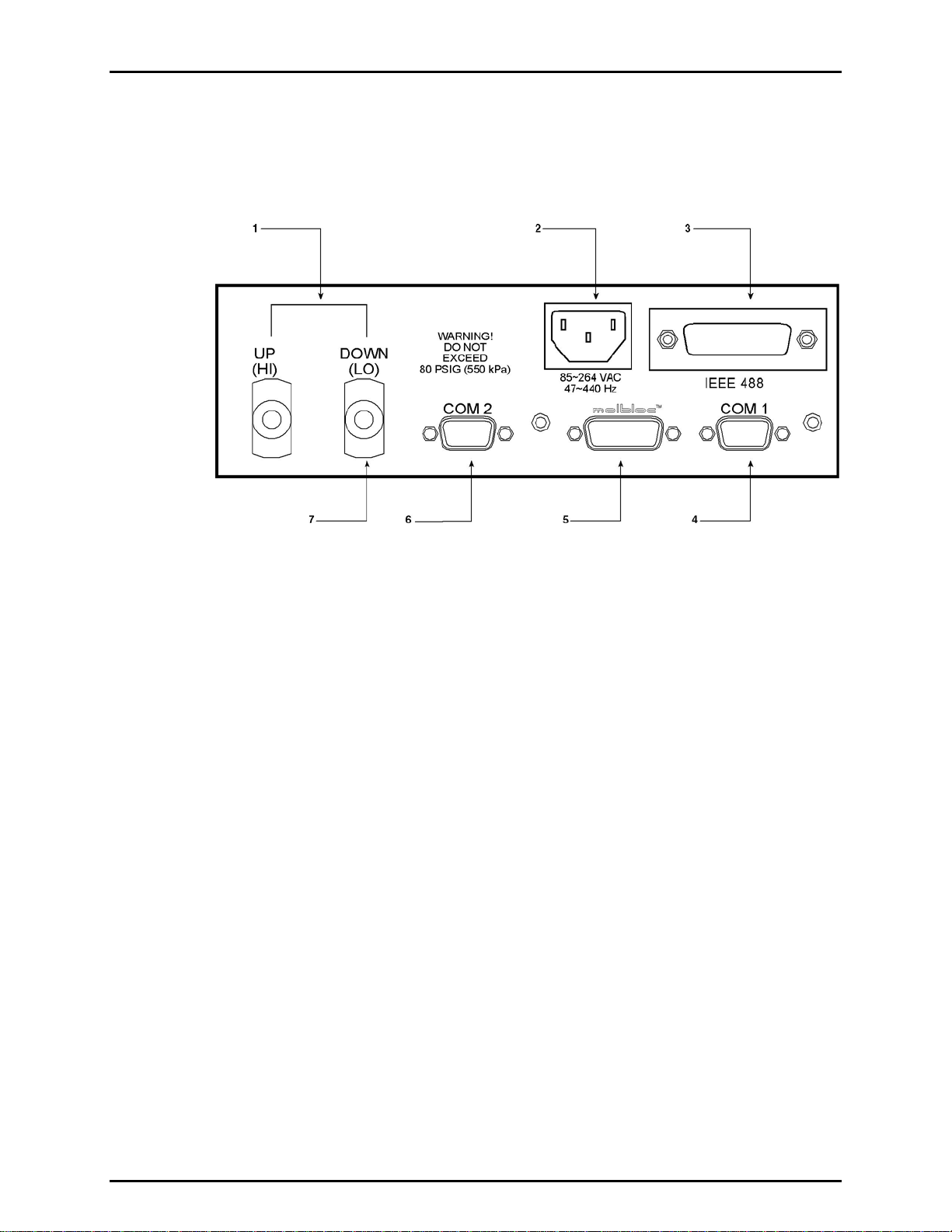
molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.2.5.2 REAR PANEL
The rear panel assembly provides pressure and electrical connections to a
molbloc mass flow element, communications interfaces and the power
connection module.
1. Quick connectors to molbloc pressure connections (color coded)
2. Electrical power connector (IEC320-313)
3. IEEE-488 (GPIB) connector for host communications
4. COM1 (RS232) connector for host communications
5. Electrical connection to molbloc
6. COM2 (RS232) connector for communications with an external device
7. Product label (on bottom of case)
Figure 2. molbox RFM Rear Panel
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 14
Page 25
.
22.
I
NNSSTTAALLLLAATTIIOON
I
N
2.1 UNPACKING AND INSPECTION
2.1.1 REMOVING FROM PACKAGING
molbox RFM is delivered, along with its standard accessories, in a corrugated container with
polyurethane inserts to hold it in place.
Remove the molbox RFM and its accessories from the shipping container and remove each
element from its protective plastic bag.
2.1.2 INSPECTING CONTENTS
Check that all items are present and have NO visible damage.
A molbox RFM includes:
2. INSTALLATION
Table 7. molbox RFM Parts List
DESCRIPTION PART #
molbox RFM Reference Flow Monitor FAM0005
Report of Calibration 550100
ACCESSORIES, INCLUDING:
1 Operation and Maintenance Manual 550107
1 Power Cord (7.5 ft.) 100770
1 Set of (2) molbox to molbloc pressure connecting
tubes
1 molbox to molbloc electrical/data connection
cable
2 straight through quick connector stem 101889*
1 General Accessories CD (white)
(Important: Includes system support software
and documentation.)
* Equivalent to Swagelok P/N SS-QM2-S-200
2.2 SITE REQUIREMENTS
Install molbox RFM on any stable surface at a convenient height. The front feet are
extendible so that the unit can be inclined for easier viewing.
The molbox RFM can also be mounted in a standard 19-in. rack mount using the optional
rack mount kit (P/N 401465). For additional information, contact your DHI Sales
Representative.
401125
102096
102987
When installing molbox RFM, consideration should be given to where the molbloc flow
measuring element and associated hardware will be located. molbox RFM may be placed on
a shelf or cart at a different height than the molbloc, but the distance between the molbloc
and molbox is limited by the length of the cable and pneumatic lines connecting them. If you
will locate the molbox at a different height than the molbloc, the small errors that would be
associated with the difference in pressure can be removed using the molbox RFM head
correction (see Section 3.6.8).
Page 15 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 26
molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
If the molbloc/molbox system is being used to calibrate other devices (DUTs), the molbloc
may need to be connected upstream or downstream of the DUT to operate within the
pressure limits of the molbloc’s calibration type (see Sections 1.2.4.1.2, 2.2.4.2.2) and to
accommodate the pressure requirements of the DUT. Se e th e mo lb lo c’ s Ca l ib ra ti on R eport to
determine the calibration type of the molbloc you are using.
If the molbloc is connected upstream of the DUT, it is important to supply the molbloc with a
stable regulated gas source. The volume present between the molbloc and the device to be
calibrated should be minimized for low flows.
In some cases, molbloc-S is used with a vacuum source downstream to reduce the pressure
at w h i c h critical flow is reached. Consider the placement of the vacuum pump and connections.
Generally, a large vacu u m p u m p i s needed that should be isolated from the work area due to
noise and oil vapor considerations. If the vacuum pump and/or vacuum kit was purchased
from DHI, see the instruction sheets and/or manuals that are included with the hardware.
Optional molstics are offered for mounting molblocs. They provide a convenient means of
addressing supply regulation, filtering and interconnection issues with high quality, configured
hardware. For additional information, contact your DHI Representative.
If a DUT is located upstream of the molbloc and is contaminated, contaminates may flow
from the DUT to the molbloc and alter the molbloc calibration. If the DUT must be connected
upstream of the molbloc, be sure it is clean before flowing and consider installing a filter
between the DUT and the molbloc.
2.3 INITIAL SETUP
2.3.1 PREPARING FOR OPERATION
To prepare molbox RFM for check out and operation:
n Remove the plastic caps from the molbox RFM rear panel pressure connections.
o Remove the protective plastic sheet from the front panel display.
p Familiarize yourself briefly with the front and rear panels (see Section 1.2.5).
Follow the steps described in Sections 2.3.1 to 2.3.6
2.3.2 POWER CONNECTION
Connect the power cable supplied to molbox RFM and to a power source. Power
requirements are 85 to 264 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz, 22 VA max. consumption.
molbox RFM is always powered and active when power is supplied through the rear panel
power connector. The front panel ON/OFF key controls a SOFT ON/OFF (see Section 3.3.3).
2.3.3 MOLBOX RFM TO MOLBLOC CONNECTION
There are two pressure connections (upstream and downstream) and one electrical/data
connection between molbox RFM and a molbloc.
For the pressure connections, use the molbox RFM to molbloc pressure tubes (P/N 401125)
supplied with the molbox RFM. Following the color coding on the pressure lines, connect the
upstream (HI) molbox RFM rear panel quick connector to the upstream port of the molbloc
and the downstream (LO) quick connector to the downstream port. Push firmly on the quick
connectors until they click into place to assure that the connection is properly completed.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 16
Page 27

2. INSTALLATION
For the electrical/data connection, use the molbox to molbloc electrical/data connection cable
(P/N 102096). Connect the cable to the molbloc and then to molbox RFM rear panel
connector labeled “molbloc”.
Avoid making molbloc electrical connections to molblocs while molbox RFM is plugged in.
Damage to the molbloc EEPROM may result (see Section 5.5.5)
2.3.4 GAS SUPPLY AND FLOWPATH CONNECTIONS
Connect a gas supply to the molbloc. Gas supply requirements are:
• The gas supply must be clean and dry (especially free from oil and particulates) to avoid
contaminating the molbloc.
• For correct measurements, the gas must be of the same species as that selected by the
molbox RFM GAS function (see Section 3.4.2). Gas purity affects the measurement
uncertainty of flow measurements as molbox RFM uses the thermodynamic properties
of the flowing gas in its flow calculations. Generally, gases with purity of 99.9 % or
better are used for molbloc measurements. Except when using ambient air with
molbloc-S, the test gas should be free of any humidity (dew point less than – 40 °C).
• If the molbloc is connected upstream of the DUT, the supply pressure must be regulated
and stable within the limits of the molbloc-L pressure dependent calibration type (see
Section
connected downstream of the DUT, use regulators and
1.2.4.1.2) or molbloc-S calibration type (see section 1.2.4.2.2). If the molbloc is
valves to make sure that the
pressure that is delivered to the molbloc will be within the limits of the molbloc calibration type.
• Care should also be taken to make sure that the pressure and flow supplied to the
molbloc are always low enough to avoid over pressuring the molbox RFM RPTs (see
Sections 1.2.2, 3.1.6). If a DUT upstream of the molbloc is operated at high pressure, a
pressure reducing regulator should be connected between the DUT and the molbloc to
ensure that even momentary high pressure spikes do not reach the molbox RPTs.
The gas supplied to the molbloc should be clean and dry. Contamination of the molbloc
flow passage with liquids, particulates or any other matter will alter the molbloc
calibration and can lead to out of tolerance flow measurements.
NEVER connect a pressure source to the molbloc that is greater than the overpressure
limit of your molbox RFM. molbox RFM overpressure limit is 660 kPa absolute/560 kPa
gauge (95 psia/80 psig). Overpressure can damage the molbox RFM internal RPTs (see
Section 1.2.2, 3.1.6).
If you are using a DHI molstic: Install the molbloc into the molstic and connect a gas
supply following the molstic instruction sheet or manual. The flow through the molbloc must
be in the direction of the arrow engraved on the molbloc.
If you are NOT using a DHI molstic: Connect a gas supply to the molbloc according to the
molbloc instruction sheet and the pressure limits of the molbloc calibration type. A valve
should be installed between the pressure supply and the molbloc to allow flow to the molbloc
to be interrupted. The flow through the molbloc must be in the direction of the arrow
engraved on the molbloc.
Adaptor kits are available from DHI to make connections from the molbloc or molstic fittings
to other common connector types. Ask you DHI Sales Representative about your specific
adaptor requirements.
Page 17 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 28

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Operating at pressures other than those of the molbloc-L pressure dependent calibration type
(see Section 1.2.4.1.2) or molbloc-S calibration type (see Section 1.2.4.2.2) may result in
out of tolerance flow measurements. Refer to the molbloc Calibration Report to
determine its calibration type.
2.3.5 VACUUM SUPPLY (molbloc-S ONLY)
In some cases molbloc-S is operated with a vacuum downstream of the molbloc to reduce the back
pressure so that critical flow can be reached at a lower upstream pressure (see Section 3.1.2).
There is no lower limit to the pressure that may safely be applied to molbox RFM RPTs.
If you are using DHI supplied downstream vacuum connect kit and vacuum pump:
Install the kit and pump following the supplied instruction sheet or manual. Carefully follow
the pump manufacturer’s recommendations for pump operation.
If you are NOT using DHI supplied downstream vacuum connect kit and vacuum
pump: Carefully evaluate vacuum pump specifications to be sure that the vacuum source
available has the pumping speed necessary to safely handle the planned flows and to
maintain low enough pressure at planned flow rates.
Be sure to provide facilities to avoid flowing into the pump when the pump is not ON as this
will cause pressure to build up on the pump and may damage it. Normally, a shut-off valve
should be included between the pump and the molbloc-S.
It is preferable to install a check valve with very low cracking pressure between the molbloc
and the vacuum shut-off valve.
Adaptor kits are available from DHI to make connections from the molbloc or molstic fittings
to other common connector types. Ask you DHI Sales Representative about your specific
adaptor requirements.
Operating at pressures other than those of the molbloc-S calibration type may result in
out of tolerance flow measurements (see Section 1.2.4.2.2). Refer to the molbloc
Calibration Report to determine its calibration type.
2.3.6 COMMUNICATIONS CONNECTIONS
If molbox RFM is being interfaced to a computer, connect an RS232 cable to molbox RFM
COM1 or an IEEE-488 cable (cables not supplied) to the molbox RFM IEEE-488 interface.
Configure the interface (see Section
3.6.6).
2.4 POWER UP AND VERIFICATION
2.4.1 POWER UP
Connect the molbox RFM power cable to an electric supply of 85 to 264 VAC (47 to 440 Hz).
Observe the front panel display as molbox RFM initializes, error checks, calibrates its internal
ohmic measurement system and goes to the main run screen (see Section 3.2). The top left
side of the main run screen should display a flow value near zero or <BPR HI>. If <NO
BLOC> is displayed, molbox RFM has not been able to identify a molbloc connection and
load molbloc information. Verify that a valid molbloc is properly connected (see Section
2.3.3) and press [SETUP], <4molbloc> to load the molbloc data. If molbox RFM is still
unable to identify a molbloc, the molbloc may require reloading of EEPROM information or
molbox RFM may require repair.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 18
Page 29

2. INSTALLATION
If the molbox RFM fails to reach the main run screen: Service may be required. Record
the sequence of operations and displays observed and contact a DHI Authorized Service
Provider (see Section 7.2).
molbox RFM is always powered and active when power is supplied through the rear panel
power connector. The front panel ON/OFF key controls a SOFT ON/OFF only (see Section
3.1.4).
2.4.2 CHECK PROPER PRESSURE MEASUREMENT OPERATION
Check that the molbox RFM pressure measurements are operating properly. Proceed as
follows:
n Connect the molbloc to the molbox RFM (see Section
o Shut off the gas supply to the molbloc and open one or
2.3.3).
both molbloc ends to atmospheric
(ambient) pressure.
p Press [P&T] and observe the display of the pressure measured by the upstream and
downstream absolute RPTs. Observe the upstream and downstream pressures
(see Section 3.4.5). These should indicate current atmospheric pressure and be in
agreement within ± 0.5 kPa (0.1 psi). If the two readings disagree by more than ± 0.5
kPa (0.1 psi), one or both RPTs may be out of calibration and service may be required.
A difference in the RPT readings could also indicate that there is some flow through the
molbloc. Check the flowpath valve or disconnect the molbloc to ensure that there is
actually no flow.
q If the molbox RFM is equipped with the microrange option, and the option is currently
active, the bottom line left side of the display is <mDP>. Observe the differential
pressure value following this indication (see Section 3.4.5). It should be 0, ± 50 Pa
(0.004 psi). If the indication is different from zero by more than ± 50 Pa (0.004 psi), the
microrange differential RPT may be out of calibration and service may be required.
Again, a non-zero differential pressure could indicate an unexpected flow through the
molbloc.
r Press [ESCAPE] to return to the main run screen.
2.4.3 CHECK PROPER TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT OPERATION
Check that the molbox RFM temperature measurement is operating properly.
Proceed as follows:
n Connect a molbloc to the molbox RFM (see Section
o From the molbox RFM main run
screen, press [P&T] twice to arrive at the temperature
2.3.3).
display screen. Observe the temperature readings of the two molbloc PRTs
(see Section 3.4.5). If the molbloc has been in a stable temperature environment for 30
to 60 minutes, the temperature indications should be roughly ambient temperature and
the two indications should agree within ± 0.2 °C. If the two readings disagree more than
± 0.2 °C, there may be a problem with the molbloc or the molbox RFM TEMPERATURE
MEASUREMENT function and service may be required.
2.4.4 LEAK CHECK
It is recommended that a new molbox RFM be leak checked at start-up to assure that no
internal leaks developed during shipping and handling. Run the molbox RFM on-board
INTERNAL LEAK CHECKING function (see Section 3.4.5).
Page 19 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 30

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.4.5 CHECK/SET SECURITY LEVEL
molbox RFM has a security system based on user levels. By default, the security system is
set to “low”, which includes certain access restrictions, and there is no password required to
change the security level (see Sections 3.6.2). As part of the molbox RFM startup, set your
desired security level and a password.
molbox RFM is delivered with the security level set at low to avoid inadvertent altering of
critical internal settings but with access to changing security levels unrestricted. It is
recommended that the low security level be maintained at all times and password
protection be implemented if control over setting of security levels is desired.
2.5 ADDITIONAL PRECAUTIONS TO TAKE BEFORE MAKING FLOW MEASUREMENTS
Before using molbox RFM to make meaningful flow measurements, consider the following:
• Be sure that the gas pressure connected to the molbloc is not great enough to overpressure the
molbox RFM internal RPTs.
• For molbloc-L operation, the pressure measuring RPTs should be tared at the operating line pressure
(see Section 3.4.4.1).
• Operating pressure should be within the limits of the molbloc calibration type (see Sections 1.2.4.1.2.
and 1.2.4.2.2).
• The gas type selected should be the gas flowing through the molbloc (see Section 3.4.2).
• For best accuracy, the gas type should be a gas with which molbloc has been calibrated. See the
molbloc Calibration Report or press [SETUP], <4molbloc>, [ENTER] to see if the gas is included in
the molbloc calibration gas list (see Section 3.5.4).
• Do not supply a gas or connect a device under test upstream of the molbloc that may contaminate
the molbloc.
• Be sure the flow unit of measure you are using is correct. Many different types of flow units of
measure are commonly used. Before selecting a unit of measure, familiarize yourself with Section
3.4.3 thoroughly.
• Troubleshooting: For information on typically encountered start-up and operational issues, see
Section 6.
2.6 SHORT TERM STORAGE
The following is recommended for short term storage of molbox RFM:
• Vent the molbox RFM pressure ports.
• Disconnect the power supply.
When molbox RFM will NOT be used for some time, it may be left powered. Use the SOFT ON/OFF key
to turn OFF the display.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 20
Page 31

.
33.
O
PPEERRAATTIIOON
O
N
3.1 GENERAL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
3.1.1 molbloc-L AND molbloc-S OPERATION
molbox RFM operates somewhat differently depending on whether a molbloc-L or molbloc-S is
connected to it. mobloc-L and molbloc-S operation use different displays and flow calculations and
some menu items are present for only one type of molbloc.
Most molbox R FM settings, such as gas, units, K factor, etc. , are com mon to bo th molbloc-L and
molbloc-S operation. Changes made to these settings while operating one type of molbloc
will still be in effect when the other type of molbloc is connected. The only setting that is
used for both molbloc types but is stored independently for each type is tare. See section
3.4.4.1 for details on the tare function.
Several of the molbox RFM screen displays and functions described in this section are
different for molbloc-L and molbloc-S operation. Where the differences are major, the
description of these functions is divided into two parts.
3. OPERATION
3.1.2 molbloc-S BPR LIMITS
To make flow measurements within predictable measurement uncertainty limits with a molbloc-S
flow element, critical (sonic) flow conditions must be present. Critical flow exists when the
gas velocity reaches the local speed of sound at the throat of the molbloc-S venturi nozzle.
molbox RFM uses the back pressure ratio, or BPR (the ratio of the molbloc-S downstream
absolute pressure to the upstream absolute pressure) to determine whether the flow is critical.
For venturi nozzles in general, the BPR must remain below a certain value for critical flow to
exist. Commonly accepted practice for typical venturi nozzle use suggests that this limiting
BPR value, or “choking ratio”, is approximately 0.5. That is, the absolute pressure downstream
of the nozzle must be less than one half of the absolute pressure upstream of the nozzle.
Empirical study of the venturi nozzles used in molbloc-S shows that the actual choking ratio,
or maximum BPR for critical flow, varies between about 0.4 and 0.9 as a function of the
Reynolds number (Re) over which the molblocs are used. molbox RFM continually
calculates Re during flow measurement and can monitor the BPR to ensure that it does not
exceed the choking ratio at the current Re conditions. molbox RFM uses a conservative BPR
limit t o indicate to the user when the BPR approaches the choking ratio, to ensure that flow
measurements are only made under “safe” critical flow conditions. molbox RFM includes
features to measure BPR, automatically alert the operator when the BPR is too high and
prevent measurements when flow is not critical (see Sections 3.1.3.2, 3.4.4.5, 3.6.9).
Maintaining a sufficiently low BPR must be considered by molbloc-S users when selecting
molbloc-S sizes and hardware setups to use for flow measurements. For example, if a
molbloc-S will be used with atmospheric pressure downstream, then the molbloc can only be
used over a range of upstream pressures starting at the maximum pressure for its calibration
type down to a minimum pressure value at which the BPR becomes equal to the BPR limit
calculated by molbox RFM. Since mass flow through molbloc-S is proportional to the
upstream absolute pressure, the flow range for the molbloc in this application is defined by
this BPR limit. To maximize the range of a molbloc-S element, a vacuum pump can be
connected downstream to reduce the downstream pressure while flowing. When the
downstream pressure is kept sufficiently low, the upstream pressure, and thus the mass flow
rate, can be adjusted all the way down to the minimum value for the molbloc’s pressure
dependent calibration type without being limited by the BPR value.
Page 21 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 32

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Depending on the placement of the molbloc-S in relation to the DUT and other hardware, and
the availability and capacity of a vacuum pump that may be used, the molbloc-S downstream
pressure will vary in different applications. Calculating Re for different molbloc-S sizes and
flow rates, and estimating the choking ratio (maximum BPR limit) as a function of Re is
somewhat complex, so Table 5 is offered to give the minimum flow that can be achieved with
each molbloc-S size, without exceeding molbox BPR limits, when the molbloc-S downstream
pressure is known: In actual operation, molbox RFM calculates the Re and BPR ratio and
provides an indication of whether the BPR is adequate for measurements to be made.
3.1.3 FLOW READY/NOT READY INDICATION
The character to the left of the measured flow on the MAIN run screen provides a flow
Ready/Not Ready indication. This indication is intended to provide the user with a clear and
objective indication of when a stable flow has been achieved.
Ready <*> is indicated when the current stability (rate of change) of flow is less than the
stability limit. The user can set the stability limit (see Section 3.5.5). The Ready/Not Ready
indication is often used when comparing molbox RFM and a test device to help determine
when steady state flow conditions are present so that a valid comparison reading can be made.
3.1.3.1 molbloc-L OPERATION
In molbloc-L operation, the Ready/Not Ready indication also helps guard against
using molblocs above their valid range by monitoring the Reynolds number of the
flow. If the Reynolds number of the current flow exceeds 1 300, the Ready (<*>)
indicator flashes. The current Reynolds number value can be viewed using
[P&T] (see Section
range limits for the flowing gas and the pressure dependent calibration type (see
Section 1.2.4.1.2), a Reynolds number of 1 200 will never be exceeded
used as the warning limit to allow for individual molbloc differences).
Ready/Not Ready character indications are:
<*> Flow Ready (stable).
<*> (Flashing): Reynolds number > 1 300.
<↓> Flow Not Ready (unstable and decreasing).
<↑> Flow Not Ready (unstable increasing).
3.4.5). If molblocs are used within the pressure and flow
(1 300 is
3.1.3.2 molbloc-S OPERATION
In molbloc-S operation, the Ready/Not Ready indication is also used to warn the
user when the BPR (back pressure ratio) is too high to ensure critical flow (see
Sections 3.1.2). When the BPR is beyond the choking limit, molbloc-S flow
measurements may not be valid and the Ready indicator becomes <P>. The
Ready/Not Ready indicators based on flow stability are also used in molbloc-S
operation, but the <P> indicator takes priority over other indicators.
Ready/Not Ready character indications are:
<*> Flow Ready (stable).
<↓> Flow Not Ready (unstable and decreasing).
<↑> Flow Not Ready (unstable increasing).
<P> Flow Not Ready (BPR high / sub-critical flow)
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 22
Page 33

3. OPERATION
3.1.4 SOFT [ON/OFF] KEY
molbox RFM is equipped with a SOFT [ON/OFF] key and indicator LED on the bottom left hand
corner of the front panel. The purpose of the SOFT ON/OFF key is to put molbox RFM into a
dormant mode in which the display is turned OFF but power is still supplied and OVERPRESSURE
functions are still active. When molbox RFM is ON, the ON/OFF indicator is ON continuously.
When molbox RFM is SOFT OFF, the ON/OFF indicator blinks every 5 seconds.
When molbox RFM is SOFT OFF, receiving a remote command turns it ON.
When molbox RFM is SOFT OFF, an overpressure conditions turns it ON.
3.1.5 MICRORANGE OPTION (OPTIONAL)
The molbox RFM offers a microrange option to improve molbloc-L flow measurement specifications
below 10 % of full scale of the molbloc being used (see Section 1.2.4.1.1). The microrange option is
only active during molbloc-L operation and has no effect on molbloc-S operation or specifications.
The microrange option includes a low differential pressure RPT to improve the measurement of
differential pressure across the molbloc below 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi). A three-way valve and on-board
logic automatically put the low differential RPT into and out of service. This allows it to be used as
the source of differential pressure values whenever differential pressure is under 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi)
and bypassed for protection from overpressure when differential pressure exceeds 13.5 kPa (2 psi)
(see Figure 3).
With automatic microrange operation ON, the microrange option (if present) is used transparently to
the operator to optimize flow measurement resolution and accuracy (see Section 3.4.7). With
automatic microrange operation OFF, the microrange option is not used and all measurements are
made using the upstream and downstream absolute RPTs only.
When the type of molbloc connected to molbox RFM is changed from molbloc-L to molbloc-S, or
molbox RFM power is cycled, the last state of the microrange option (ON or OFF) is retained for
molbloc-L operation.
The microrange option can also be controlled manually by pressing [SPECIAL] and selecting
<7micro> (see Section 3.6.7).
The microrange indicator on the main run screen (see Section 3.4.7) indicates the status of the
microrange option.
1. High Isolation: Open
2. Low Isolation: Open
3. Bypass: Closed
4. Mirorange Bypass: Closed (microrange active)
Open (microrange inactive)
Figure 3. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic – MICRORANGE OPTION RPT ACTIVE/INACTIVE
Page 23 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 34

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
To determine if a molbox RFM is equipped with the microrange option, check the model
number on the product label on the bottom of the molbox RFM case. If the model number
includes a “-M”, the microrange option is installed.
The microrange option is only active during molbloc-L operation. Mirorange has no effect
on molbloc-S operation or measurement specifications.
3.1.6 REFERENCE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (RPT) OVERPRESSURE
3.1.6.1 UPSTREAM AND DOWNSTREAM ABSOLUTE RPTS
Every molbox RFM has two absolute RPTs, one measures molbloc upstream
pressure, the other usually measures molbloc downstream pressure and may
provide a second measurement of molbloc upstream pressure in molbloc-S
operation. In normal operation, they are not used at pressures greater than 600
kPa absolute (87 psia).
Exposing the molbox RFM RPTs to pressures greater than the maximum
operating pressure may damage them. molbox RFM has a system of warnings
and alarms to protect itself from overpressure (see Section
3.6.3.1).
3.1.6.2 DIFFERENTIAL RPT, MICRORANGE OPTION
The microrange option low differential RPT has no overpressure warnings or
alarms in normal operation. It is, to the extent possible, protected from
overpressure automatically and transparently as it is put into and out of service
using the molbox RFM on-board valving.
In run calibration operation (see Section 5.2.4.1), the microrange RPT has an
OVERPRESSURE function whose operation is similar to the absolute RPT
overpressure function (see
kPa (2 psi) differential.
When an overpressure condition occurs
during run calibration of the microrange
transducer, the display of microrange
pressure indicates:
Be sure the pressure conditions that caused the overpressure to occur have
been cleared. Then press [ENTER] to reactivate the microrange RPT.
When using molbox RFM equipped with the microrange option, avoid very rapid
pressurization of one molbloc port. Attempt to open flow isolation valves
slowly. The microrange option low differential RPT is protected from
overpressure automatically by internal valving. However, dumping pressure very
rapidly on one port of the molbloc while the differential RPT is active could
cause a very sudden surge in differential pressure that can overpressure it.
Section 3.6.3). Overpressure occurs at about 13.7
Microrange RPT:
OVERP! kPa [ENTER]
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 24
Page 35

3.2 MAIN RUN SCREEN
The molbox RFM MAIN run screen is its home display that is reached upon power up and
from which other functions and menus are accessed. It is the top level of all menu structures.
It indicates the current measured flow as well as a variety of additional information, if desired.
The appearance of the MAIN run screen differs depending on whether the active molbloc is a
molbloc-L or a molbloc-S.
3.2.1 molbloc-L OPERATION
Some items in the molbloc-L MAIN run screen may change or flash at times, to indicate that
certain limits are exceeded, as described in the text accompanying the following screen display:
1. <*> Ready/Not Ready indication: <*> when Ready (flashes if
Reynolds number of the flow exceeds 1 300 or if flow was not
ready for a full averaging period in AVERAGE display), <↑>
(increasing) or <↓> (decreasing) indicating direction of flow
rate evolution when Not Ready (see Section
2. <FL
3. <UNIT>: Current flow unit of measure (see Section 3.4.3).
4. <k>: Indicates whether a gas correction factor (K factor) is currently being applied to the measured flow (see
5. <m>: Microrange option indicator (see Sections 3.4.7 and 3.6.7). Possible indications include:
6. <GGGG>: Indicates the current molbox gas selection (see Section 3.4.2). This should be the gas that is
7. <D>: Indication of what is being displayed on the bottom line of the display as set by the DEVIATION function
<R>: Current DISPLAY mode is RATE (see Section
<
<H> Current DISPLAY mode is HI/LO (see Section 3.4.6.3).
<∑> Current DISPLAY
<=> Current DISPLAY
<D> Current DISPLAY
<F> Current DISPLAY
Blank, No character Current DISPLAY mode is CLEAN (see Section
8. <DISPLAY
OWWW>: Numerical value and sign of the flow
measured by molbox RFM. Result of last flow averaging
cycle if in AVERAGE display (see Section 3.4.6.2). Flashes if
Reynolds number of the flow
Section 3.4.1). <k> if a factor is being applied, blank if no factor is being applied.
Blank, NO character: The microrange option is currently OFF or the molbox RFM is not equipped with
the microrange option.
<m>: Automatic microrange is ON (see Section 3.4.7).
<d>: Manual microrange is ON and the differential pressure reading being used to calculate flow is
coming from the microrange differential RPT (see Section 3.6.7).
<a> (flashing): Manual microrange is ON and the differential pressure reading being used to calculate
flow is NOT coming from the microrange low differential RPT. It is the difference between the upstream
and downstream absolute RPTs (see Section 3.6.7).
flowing through the molbloc.
(see Section 3.4.6.6). Possible indications include:
corner of the display, current DISPLAY
AVERAGE screen (see Section
exceeds 1 300.
σ> Current DISPLAY mode is AVERAGE (see Section 3.4.6.2).
mode is TOTAL (see Section 3.4.6.4).
mode is UNIT (see Section 3.4.6.5).
mode is DEVIATION (see Section 3.4.6.6).
mode is FREEZE (see Section 3.4.6.7).
MODE DATA>: Information displayed depends on current display mode (see Section 3.4.6).
3.4.6.2).
3. OPERATION
3.1.3).
*FLOWWW unitkm GGGG
D DISPLAY MODE DATA
mode is “average” and this is the instantaneous reading
3.4.6.1); or if <n avg> is in the bottom right hand
3.4.6.8).
When a number is too large to show in the allocated display space, molbox RFM
displays <********>.
Page 25 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 36

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
molbox RFM has a SCREEN SAVER function that causes the display to dim if NO key is
pressed for 10 minutes. Pressing a key restores full power to the display. The screen
saver activation time can be changed or screen saving can be completely suppressed (see
Section 3.6.5.1).
3.2.2 molbloc-S OPERATION
As with molbloc-L there are limits on some of the conditions that may exist if the user expects
to make accurate flow measurements with molbloc-S. The key condition that can be monitored is
the back pressure ratio, or BPR, which determines whether critical flow through the molbloc
is achieved (see Section 3.1.2).
When the BPR is in a “safe” region for critical flow measurements, the appearance of the
MAIN run screen is identical to the MAIN run screen for molbloc-L operation (see Section
3.2.1). When the molbox RFM BPR limit is exceeded, there are two possible MAIN run
screen indicators. A flashing flow value and unit indicate that the BPR limit has been
exceeded. In this condition, the flow may not be critical and flow measurements should not
be relied on to meet specifications. When the BPR limit is exceeded by a large margin, the
flow is almost certainly not critical and the calculated value may be nonsensical,
so the flow value is not shown and is replaced by <BPR HI>.
When molbloc-S is in the BPR OFF mode (see Section 3.6.9), BPR is not monitored and
invalid flow values may be displayed in the molbloc-S MAIN run screen with no indication
that a the BPR value is high.
1. <*> Ready/Not Ready indication; <*> when Ready <↑>
(increasing) or <↓> (decreasing) indicating direction of flow
rate evolution when Not Ready; <P> when BPR is higher
than choking limit. (see Section 3.1.2).
2. <FLOWWW>: Numerical value and sign of the flow
measured by molbox RFM. Result of last flow averaging
cycle if in AVERAGE display (see Section
if BPR
is higher than the choking limit. If BPR exceeds the
choking limit by a large margin, <BPR HI> replaces the flow
value.
3. <UNIT> Current flow unit of measure (see Section 3.4.3). Flashes if BPR is higher than the choking limit.
4. <k>: Same as molbloc-L (see Section 3.4.1).
5. <GGGG>: Indicates the current molbox gas selection (see Section 3.4.2). This should be the gas that is
flowing through the molbloc. <AirW> indicates that air is selected and a humidity correction is being applied
(see Section 3.4.2.2).
6. <D>: Same as molbloc-L (see Section 3.4.6).
3.4.6.2). Flashes
*FLOWWW unitk GGGG
D DISPLAY MODE DATA
7. <DISPLAY MODE DATA>: Information displayed depends on current display mode (see Section 3.4.6).
When a number is too large to show in the allocated display space, molbox RFM
displays <********>.
molbox RFM has a SCREEN SAVER function that causes the display to dim if NO key is
pressed for 10 minutes. Pressing a key restores full power to the display. The screen
saver activation time can be changed or screen saving can be completely suppressed (see
Section 3.6.5.1).
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 26
Page 37

3.3 MANUAL OPERATION
molbox RFM is designed to offer the optimum balance between simple, intuitive operation
and the availability of a wide variety of functions with a high level of operator discretion. The
local operator interface is through the front panel’s 2 x 20 character alpha-numeric display
and a 4 x 4 multi-function keypad. Remote operation by RS232 or IEEE-488 interface is also
available (see Section 4).
3.3.1 KEYPAD LAYOUT AND PROTOCOL
Molbox RFM has a 4 x 4 keypad for local operator access to direct functions, function menus
and for data entry.
3. OPERATION
1. The Function/Data keys allow very commonly
used functions to be accessed directly from the
MAIN run screen by a single keystroke. The name of
the function is on the bottom half of the key (see
Section 3.4). These keys enter numerical values
when editing.
2. The Editing and Execution keys are for
execution, suspending execution, backing up in
menus and editing entries
3. The Menu/Data keys provide access to function
menus from the MAIN run screen. The menu
name is on the bottom half of the key. The SETUP
menu is for more frequently used functions. The
SPECIAL menu is for less frequently used and
internal functions. These keys enter numerical
values when editing.
Figure 4. Keypad Layout
Pressing the [ENTER] key generally causes execution or forward movement in the menu tree.
Pressing the [ESCAPE] key generally allows movement back in the menu tree and/or causes
execution to cease or suspend without changes being implemented. Pressing [ESCAPE]
repeatedly eventually returns to the MAIN run screen. From the MAIN run screen, pressing
[ESCAPE] allows momentary viewing of the molbox RFM identification screen.
Pressing the [+/-] key changes a numerical sign when editing. It also toggles through
multiple screens when available.
Pressing the [←] and [→] keys allows reverse and forward cursor movement when editing
data entry. These keys are also used to scroll through menu choices.
Menu selections can be made by pressing the number of the selection directly or by pressing
[←] and [→] to place the cursor on the number of the desired selection and pressing
[ENTER].
Some screens go beyond the two lines provided by the display. This is indicated by a
flashing arrow in the second line of the display. Press [←] and [→] to move the cursor
to access the lines that are NOT visible or directly enter the number of the hidden menu
choice if you know it.
Page 27 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 38

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.3.2 SOUNDS
molbox RFM is equipped with a variable frequency tone device to provide
audible feedback and alarms. Sounds are used for the following indications:
Valid key press
Brief beep. Choice between three frequencies or
NO sound is available (see Section 3.6.5.2).
Invalid key press
Descending two tone “blurp”. Choice of NO sound
is available (see Section 3.6.5.2).
Totalizing time complete
Purge time complete
Near overpressure limit
Three, 2 second beeps (see Section 3.4.6.4).
Three, 2 second beeps (see Section 3.4.4.2).
Intermittent 1 second beeps (see Section 3.6.3).
exceeded
Overpressure limit
5 second high frequency beep (see Section 3.6.3).
exceeded
3.3.3 SOFT [ON/OFF] KEY
molbox RFM is equipped with a SOFT [ON/OFF] key and indicator LED on the bottom left hand
corner of the front panel. The purpose of the SOFT ON/OFF key is to put molbox RFM into a
dormant mode in which the display is turned OFF but power is still supplied and
OVERPRESSURE functions are still active. When molbox RFM is ON, the ON/OFF indicator is
ON continuously.
When molbox RFM is SOFT OFF, the ON/OFF indicator blinks every 5 seconds.
When molbox RFM is SOFT OFF, receiving a remote command turns it ON.
When molbox RFM is SOFT OFF, an overpressure conditions turns it ON.
3.3.4 DIRECT FUNCTION KEYS SUMMARY
Local operation of molbox RFM is through the front panel 4 x 4 pressure sensitive keypad. To
minimize the u se of mult i-lay ered menu structures, the keypad numerical keys also provide
direct access to the most commonly used functions. The function accessed is labeled on the
bottom half of the each key. Direct function keys are active whenever molbox RFM is in its
MAIN run screen.
corresponding manual sections for full detail on each direct function.
It may be useful to keep a copy of Table 8, Summary of molbox RFM Direct Function Key
Operations, near the molbox RFM, especially when first becoming acquainted with its
operation.
Table 8 summarizes the operation of the direct function keys. See
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 28
Page 39

3. OPERATION
Table 8. Summary of molbox RFM Direct Function Key Operations
DIRECT FUNCTION KEYS ARE ACTIVE FROM THE MAIN RUN SCREEN
SEE CORRESPONDING MANUAL SECTIONS FOR FULL DETAIL
Menu of commonly used setup features including unit changes and stability setting.
Menu of less frequently used internal functions and settings including preferences, resets,
molbox calibration, remote interfaces, BPR (back pressure ratio) when using molbloc-S.
Turn automatic microrange ON/OFF.
Load the molbloc that is currently connected to molbox RFM. Use this to activate a new
molbloc after a molbloc change or to view details on the molbloc that is currently in use.
Set the resolution with which the measured flow and other values are displayed.
Run the TARE, LEAK CHECK, PURGE, AutoZ and BPR functions.
Display the current pressure measurements (first press).
Display the current molbloc temperature measurements (second press).
Define the DISPLAY function for the second line of the molbox RFM display. Choices include
rate, average, hi/lo, totalize, 2
Set/change a DUT gas correction factor (K factor).
nd
unit, deviation, freeze, clean.
Set flow measurement gas.
Set flow measurement unit. Choice of units can be customized.
3.4 DIRECT FUNCTION KEYS
3.4.1 [K]
PURPOSE
To cause the flow value calculated by molbox RFM to be multiplied by a factor, K. Generally
used to apply a test device’s gas correction factor used when a test device is calibrated with
a gas other than its normal process gas.
PRINCIPLE
Frequently, when testing or calibrating a flow-measuring device, it is not possible to flow the gas
with which that device will normally be operated (the process gas). This may be because the
Page 29 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 40

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
process gas is toxic or corrosive or simply because it is not available or convenient to use.
When the process gas cannot be used for calibration, it is common to use a different gas for
testing or calibrating (the calibration gas). In this case, a factor representing the relationship
between the calibration gas and the process gas for the test device may be applied so that
the calibration gas simulates the process gas. The calibration gas that simulates the
process gas is often called a surrogate gas for the process gas.
The relationship between a test device’s process gas and calibration gas is frequently
called a K factor or gas conversion factor. The factor’s value depends on specific properties
of the test device and determining the value is the responsibility of the device manufacturer.
For example, Silane (SiH4) is a frequently used gas in semiconductor processing. SiH4 is
highly toxic and requires extensive handling precautions so it is not practical for use in
calibration and testing. A major manufacturer of Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) recommends
that MFCs that are to be used with Silane be tested with Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6), a nontoxic, non-flammable gas, using a conversion factor of 0.970. In other words:
SF6 flow x 0.970 = equivalent SiH4 flow for the MFC
The K function in molbox RFM allows a gas conversion factor to be entered by which flow
values measured by molbox RFM will be multiplied. In this example, 0.970 would be entered
as K so that the values indicated by molbox RFM when SF6 is flowing through the molbloc
simulate the flow of SiH4 for that manufacturer's MFC.
When the K function is active, molbox RFM performs all of its flow calculations normally but
multiplies the current flow value by the value of the K factor prior to displaying it.
The gas selected on molbox RFM which is displayed in the upper right corner of the molbox
RFM display should always be the gas that is actually flowing through the molbloc.
K factors or gas conversion factors are based on the properties of the device
being tested. Their availability and validity are the responsibility of that
device's manufacturer. molbloc/molbox does not use factors or conversion coefficients
between gases. Flow is calculated from molbloc characteristics and specific gas
properties for each gas supported by molbox. The gas selected on molbox RFM
(see Section 3.4.2) which is displayed in the upper right corner of the molbox RFM display
should always be the gas that is actually flowing through the molbloc.
If the K function and the ADJ function are both active, the ADJ adder and multiplier are
first applied to the measured molbloc flow, then the result is multiplied by the K factor.
This order of operations reflects the fact that the ADJ values are intended to represent
an adjustment to be applied to the molbloc flow while measuring the calibration gas that
is flowing, and the K factor is a correction related to gas effects on the device under test
measurement (See Section 3.4.6).
OPERATION
To enable a gas conversion factor press [K] from any
run screen. The display is:
If <2off> is selected, no conversion factor will
be applied. If <1on> is selected, the next screen is:
K Factor?
1on 2off
K Factor:
1.00000
The value of the gas conversion factor can be edited as desired. Pressing [ENTER] returns
to the MAIN run screen with the entered K factor active. The letter <K> is always
appended to the flow unit indication in the run screens when the K function is ON
(e.g., sccmK). A K factor value of 1 is handled as if the K function were OFF.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 30
Page 41

3. OPERATION
When the K function is ON, as indicated by a <K> following the current flow unit in the
first line of the MAIN run screen, the current molbox RFM flow indication equals:
(flow as calculated by molbox RFM for the selected gas) x (the current K factor)
So the indicated flow is actually in error (biased) relative to the true flow through the
molbloc by the value of the K factor. Care should be taken to ensure that the correct
molbloc range is selected for tests when a K factor is used, since the actual flow rate
through the molbloc is different from the device under test range in the process gas.
3.4.2 [GAS]
PURPOSE
To specify the gas that is currently flowing through the molbloc so that molbox RFM uses the
correct gas property values in its flow calculations.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM calculates the flow through a molbloc from:
• molbloc geometric characteristics
• gas pressures
• gas temperature
• specific characteristics of the flowing gas
The gas characteristics include:
• gas density under standard conditions
• change in gas density with pressure and temperature
• gas viscosity under standard conditions (when needed)
• changes in gas viscosity with pressure and temperature
Proprietary algorithms are used to calculate gas density and viscosity (when needed) under
the actual flowing pressure and temperature conditions from density and viscosity under
standard conditions.
The characteristics of molbox RFM supported gases and corresponding algorithms are
stored in molbox RFM memory. To correctly calculate the flow of a gas, the correct
information for that gas must be used. The molbox RFM GAS function allows the user to
specify the flowing gas so that molbox RFM will use the correct gas information in calculating
the flow through the molbloc.
The set of available calibration gases that can be used is not the same with molbloc-L and
molbloc-S, and the operation of the GAS function is different. They are described separately below.
Page 31 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 42

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.4.2.1 molbloc-L OPERATION
The molbox RFM gases available for use with molbloc-L at the time of this
manual printing are listed in Table 9.
Table 9. Available molbloc-L Gases
<1inert> <2flammable> <3toxic> <4other>
<1N2> Nitrogen
<2He> Helium
<3Ar> Argon
<Butn> is used to identify Butane in molbox RFM because the chemical symbol for
Butane (C4H10) has more than the 4 characters used by molbox RFM to abbreviate
gas identifications.
<1H2> Hydrogen
<2O2> Oxygen
<3CH4> Methane
<4C2H4> Ethylene
<5C3H8> Propane
<6C2H6> Ethane
<7Butn> Butane
<1CO> Carbon Monoxide <1Air> Air
<2C2F6> Hexafluoroethane
<3N2O> Nitrous Oxide
<4CF4> Carbon Tetrafluoride
<5SF6> Sulfur Hexafluoride
<6CHF3> Fluoroform
<7C02> Carbon Dioxide
<8Xe> Xenon
<9C4F8> Octafluorocyclobutane
Mixtures of known gases in known concentrations can be measured by calculation
and use of the ADJ function (see Section 3.5.6).
OPERATION (molbloc-L OPERATION)
To specify the gas flowing through molbloc-L,
press [GAS]. The display is:
1inert 2flammable
3toxic 4other
The gases available are grouped in categories to
facilitate finding a specific gas and as a reminder to the
user when selecting a gas that may require special
precautions in use. There is a list of gases under each
1N2 2He 3Ar
category. For example, the <1inert> selection displays:
Select the desired gas. Pressing [ENTER] returns to the last run screen with the newly
selected gas active. The selected gas is always displayed in the upper right hand corner of
the MAIN run screen.
The gas selected on molbox RFM should always be the gas that is flowing through
the molbloc. molbloc/molbox does not use K factors or gas conversion factors
between gases. When calibrating or testing a device with a surrogate gas, molbox RFM
should be set to the surrogate gas. The K factor or gas conversion factor, if used,
defines the relationship between the surrogate gas and the process gas for the device
being tested, not for molbloc/molbox (see Section 3.4.1, PRINCIPLE). The K factor is
supplied by the manufacturer of the device being tested.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 32
Page 43

3. OPERATION
3.4.2.2 molbloc-S OPERATION
The molbox RFM gases available for use with molbloc-S at the time of this
manual printing are listed in Table 10.
Table 10. Available molbloc-S Gases
GAS
<1N2> Nitrogen
In addition to dry air, molbox RFM supports measurement of ambient (humid) air
flow with molbloc-S. When Air is selected as the molbloc-S test gas, the user is
prompted to enter a value of the humidity ratio (also known as the absolute
humidity or water ratio) of the ambient air. The humidity ratio, W, is defined as
the ratio of water mass to gas mass in the flowing air. It is different from the
relative humidity value, which is usually expressed as a percentage. Typical values
of W are between zero and 0.06. molbox RFM does not accept an entry for W
greater than 0.1.
Typically, humidity measuring instruments report relative humidity, which is
dependent on the ambient pressure and temperature. Users who do not have
the W value available can use DHI’s free Unit of Measure Converter software
utility or COMPASS for molbox calibration software to calculate W from
measured pressure, temperature, and relative humidity. Visit
www.dhinstruments.com, or se e your DHI sales representative for a copy of the
Unit of Measure Converter software utility. Air relative humidity, pressure and
temperature are converted to the humidity ratio, W, following Dalton’s
thermodynamic principals using water saturation properties:
<2Air> Air (dry and humid)
Rule and
RH
⎛
PP
⎜
⎝
gamb
100
⎛
⋅−
⎜
⎝
⎞
⎟
⎠
RH
100
ambambambg
⎞
⎟
⎠
CTCTCTCP
+++=
32
P
⋅
g
W
62188.
P is the water saturation pressure, which can be calculated as:
g
0
If dry air will be measured, then the user should enter a W value of zero when
prompted. Zero is the default W value.
When a non-zero W value is entered, molbox applies a correction to its air flow
measurement for the change in air density due to humidity. If a correction for W
is being applied to air flow measurements, a <W> is placed to the right of the
<Air> gas indication in the MAIN run screen.
3
where
=
C
0
C
1
=
C
2
C
3
⋅=
1
:
0649289.0
0528.53
−=
1327760
−=
2
9.14509
Page 33 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 44

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The humid air correction applied to the molbloc measured flow is (from ASME
FEDSM98-5309):
)( dWcWbWaratioqm +++=
where
a
b
c
d
If an incorrect value of W is entered (for example, using any non-zero W value
while flowing dry air), an error will be introduced into the air flow
measurement. W, humidity ratio, is different from relative humidity.
OPERATION (molbloc-S operation)
To specify the gas flowing through molbloc-S, press [GAS]. The display is:
The display is:
Select the desired gas. Pressing [ENTER] returns to the last run screen with the
newly selected gas active. The selected gas is always displayed in the upper
right hand corner of the MAIN run screen.
:
0000.1
=
336872.0
−=
158514.0
=
131924.0
=
1N2 2Air
32
If <2Air> is selected,
The display is:
Leave the value at zero when dry air is being flowed. Enter the appropriate nonzero value (see section immediately above) if humid air is being flowed.
The gas selected on molbox RFM should always be the gas that is flowing
through the molbloc. molbloc/molbox does not use K factors or gas
conversion factors between gases. When calibrating or testing a device with
a surrogate gas, molbox RFM should be set to the surrogate gas. The K
factor or gas conversion factor, if used, defines the relationship between the
surrogate gas and the process gas for the device being tested, not for
molbloc/molbox (see Section 3.4.1 and 3.4.2 PRINCIPLE). The K factor is
supplied by the manufacturer of the device being tested.
Humidity ratio:
0:1
3.4.3 [UNIT]
PURPOSE
To specify the flow unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays measured flow values.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM calculates the mass flow of various gases in kilograms/second [kg/s]. molbox
RFM also supports conversions to a variety of other flow units of measure. The UNIT function
allo w s the user to select the flow unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays measured flow.
These include units o f mass flow , inc ludin g vol umetr ical ly bas ed ma ss fl ow uni ts (i .e., sccm)
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 34
Page 45

3. OPERATION
as well as units of volume flow (i.e., ccm). See Table 11 for a complete listing of the unit
conversions available. molbox RFM can also display the measured flow in two different units
of measure simultaneously (see Section
3.4.6.5).
OPERATION
The UNIT function is used to set the unit of measure of the molbox RFM flow display. To
change the flow unit of measure press [UNIT].
The display is:
1sccm 2slm 3uccm
4pccm 5mg/s 6vlm
Select the desired unit. For all units except <uxxx> or <vlm>, operation then returns to the
run screen with the flow unit of measure changed to the selected unit. When user units (i.e.,
uxxx) are selected, the reference temperature must be specified before the unit is activated
(see Section 3.4.3.3). When “vlm” (volume) units are selected, a menu of volum
e units is
accessed. The desired volume unit must be selected and then the temperature and pressure
of the flowing gas must be specified (see Section
3.4.3.4).
See Section 7.1.3 for specific molbox RFM flow unit conversion calculations.
molbox RFM supports many more flow units of measure than the six default units of the
UNIT function. The six units available under the UNIT function can be customized to
include any molbox RFM supported units in any order (see Section 3.4.3.5).
Many different types of flow units are commonly used including a wide variety of mass
flow units as well as volume flow units. Please read Sections 3.4.3.1 through 3.4.3.5 for
additional information on the various unit definitions and how they are handled by molbox
RFM before making unit of measure selections.
3.4.3.1 MASS FLOW VS. VOLUME FLOW
COMPASS for molbox software users: conversions to volume (sometimes
called actual) flow units are handled in COMPASS. When using COMPASS,
the molbox always operates in mass flow units.
molbox RFM measures mass flow (quantity of material per quantity of time).
molbox RFM always calculates flow in terms of kg/second [kg/s]. It also supports
conversions of kg/second to a variety of other flow units. These include other
mass flow units such as g/s and mole/s as well as volumetrically based mass
flow units (i.e., sccm and slm) (see Section 3.4.3). In steady state flow, mass
flow is the same at different points in the flow system independent of gas
pressure and temperature. Therefore, the measurement of mass flow made by
the molbloc/molbox represents the mass flow at the same time at other points in
a steady state flow system.
molbox RFM can also make conversions to volume fl ow under specific pressure
and temperature conditions by dividing the mass flow by the density of the gas
under the specific pressure and temperature conditions (see Section
Volume flow is sometimes referred to as actual flow.
3.4.3.4).
Page 35 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 46

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Volume flow is dependent on the actual temperature and pressure of the
flowing gas at the point where volume flow is to be measured. Generally, this
point is not at the molbloc, it is at another point in the flow system (e.g., at the
device under test). At another point in the flow system, it is quite likely that the gas
pressure and temperature are different from the gas pressure and temperature at
the molbloc. Then, even in steady state flow conditions, the volume flow at the
molbloc and the volume flow at another point in the system are likely to be different.
Therefore, to accurately predict volume flow at another point in the system,
molbox RFM must calculate volume flow based on the mass flow through the
molbloc and the gas pressure and temperature at that other point, not at the
molbloc. For this reason, molbox RFM requires that gas pressure and temperature
conditions at the DUT be specified for volume flow measurements.
Estimating the flowing gas pressure and temperature at the point at which
volume flow is to be measured may be difficult.
The relevant gas pressure when measuring volume flow is the gas’s absolute pressure.
In cases in which the volume flow measurement is open to atmospheric
(ambient) pressure, the volume flow pressure is atmospheric pressure. In other
cases, there may be ways to estimate the pressure at the volume flow
measurement point but it probably should be measured.
For temperature, if the volume flow measurement point is very near the molbloc,
one possibility is to use the molbloc temperature measurement. By design, the
molbloc causes the temperature of the gas that flows through the molbloc to take
on the molbloc temperature. Therefore, the temperature of the gas as it exits the
molbloc is the same as the molbloc temperature. If the volume flow measurement
point is not immediately downstream of the molbloc, the best estimate of gas
temperature may be ambient temperature or the temperature of the device or
bath used to stabilize gas temperature if one is present.
Because volume flow (sometimes called actual flow) is dependent on gas
pressure and temperature at the flow measurement point, gas pressure and
temperature must be specified by the user when selecting volume flow units
on molbox RFM. The measurement uncertainty (accuracy) in the volume flow
measurement is highly dependent on the measurement uncertainty in the
pressure and temperature specified. Typically, temperature errors have an
effect on flow of about 0.35 %/°C and pressure errors have an effect on flow
of about 1%/kPa (6.8%/psi) if the DUT is used near atmospheric pressure.
3.4.3.2 VOLUMETRICALLY BASED MASS FLOW UNITS
molbox RFM supports a number of volumetrically based mass flow units of
measure. Volumetrically based mass flow units should not be confused with
volume or actual flow units (see Section 3.4.3.4). Volumetrically based mass
flow units define mass in terms of the quantity of gas that occupies a volume
under standard conditions of pressure and temperature. Since there is no
universally accepted definition of standard conditions, molbox RFM supports the
three most common variances.
• Standard units (sxxx): The “s” prefix indicates standard. Volumetrically
based mass flow units preceded with the letter “s” (i.e., sccm, slm, scfh)
define standard conditions as pressure of 101.325 kPa absolute (14.6959
psia) and temperature of 0 °C (32 °F) and take into account the true
compressibility of the flowed gas.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 36
Page 47

3. OPERATION
• User units (uxxx): The u prefix indicates user. This option is designed to
provide support for volumetrically based mass flow units with a reference
temperature other than 0 °C (see Section
mass flow units preceded with the letter “u” (i.e., uccm, ulm) define
3.4.3.3). Volumetrically based
standard
conditions as pressure of 101.325 kPa (14.6959 psia) with the user
specifying the reference temperature. User units take into account the true
compressibility of the flowed gas.
• Perfect units (pxxx): The “p” prefix indicates perfect. This option is
designed to provide support for volumetrically based mass flow units that
assume ideal gas compressibility for all gases. Volumetrically based mass
flow units preceded with the letter “p” (i.e., pccm, plm) assume a gas
compressibility factor of 1 for all gases and define standard conditions as
pressure of 101.325 kPa (14.6959 psia) and temperature of 0 °C (32 °F).
Volumetrically based mass flow units at reference temperatures other than
0 °C (32 °F) can be defined using user units (see Section 3.4.3.3).
In early 1996, SEMI (a semiconductor industry interest group) adopted
standard E12-96, which specifies that perfect units be used for
volumetrically based mass flow units. To comply with the SEMI standard,
pccm should be used rather than sccm. To purchase a copy of the relevant
SEMI standard, contact SEMI at telephone 415.964.5111 or email
semihq@semi.org.
3.4.3.3 VOLUMETRICALLY BASED MASS FLOW UNITS AT
VARIOUS REFERENCE TEMPERATURES (UXXX)
Units starting with the letter “u” (user units) are volumetrically based mass flow units
(see Section 3.4.3.3) for which a reference temperature other than 0 °C is desired.
When a user unit is selected, the reference
temperature desired must be specified.
After a user unit is selected, the display is:
Temperature ref?
0ºC
Enter the reference temperature desired for the volumetrically based mass flow
unit selected. The temperature unit can be changed between °C and °F by pressing
[SETUP] and selecting <3tempU> (see Section
3.5.3). The temperature sel ecte d
applies to all the user units.
Volumetrically based mass flow units, including user units (uxxx) and perfect
units (pxxx), are discussed further in Section 3.4.3.2.
3.4.3.4 VOLUME FLOW UNITS (VLM)
See Section 3.4.3.1 before using volume flow units. Volume flow is
sometimes referred to as actual flow.
Page 37 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 48

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
To measure flow in volume flow units (sometimes referred to as actual flow
units), press [UNIT], <vlm> under the UNIT function. If <vlm> is not available,
see Section
3.4.3.5. This selection accesses the menu of volume units available.
Select the desired volume flow unit:
1. Current volume flow pressure.
2. Current volume flow temperature. Indicates
<bloc> if the current setting is to use the
molbloc temperature.
To retain the current volume flow pressure and temperature, select <1no> and
operation returns to the MAIN run screen with the selected volume flow unit
active. To change the volume flow pressure and/or temperature select <2yes>.
The next screen gives the choice of
having the volume flow gas temperature
be either the molbloc temperature or a
user specified temperature. If <2user>
is selected, a screen to enter the temperature
is presented before continuing. If
<1molbloc> is selected, the volume flow
temperature will automatically be taken
as the molbloc temperature.
P101.325kPa T21.1ºC
Edit P&T? 1no 2yes
Gas temperature:
1molbloc 2user
The next screen is to edit the volume
flow pressure in the current pressure unit
of measure. Pressing [ENTER] accepts
the edited value as the volume flow
pressure and returns to the MAIN run
screen with the selected volume flow unit
Volume unit gas pres
101.325 kPa
and gas temperature and pressure active.
The temperature and pressure units of measure used to specify volume flow
conditions can be changed using [SETUP], <2presU> for pressure (see
Section 3.5.2) and [SETUP], <3tempU> for temperature (see Section 3.5.3).
Because volume flow is dependent on gas pressure and temperature at the
flow measurement point, gas pressure and temperature must be specified by
the user when selecting volume flow units. The measurement uncertainty in
the volume flow measurement is highly dependent on the measurement
uncertainty in the pressure and temperature specified (see Section
3.4.3.1).
3.4.3.5 CUSTOMIZING FLOW UNITS AVAILABLE UNDER THE UNIT FUNCTION
The UNIT function provides a choice of six different flow units of measure. The units
that are available by default are the six indicated in Section 3.4.3. However,
molbox RFM supports many other units. These other units can
available for selection by customizing the UNIT function.
be made
To customize the UNIT function,
press [SETUP] and select <1flowU>.
The display is:
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 38
Set up user unit #1
Page 49

3. OPERATION
<#1> corresponds to the first of the six
available selections under the UNIT
function. Enter the number of the
selection that you would like to change.
Flow unit type: 1std
2user 3perfect 4vlm
The display becomes:
Select the flow unit type of the desired flow unit (see Table 11). Then select the
desired unit.
Table 11. Available Flow Units
<1std> <2user> <3perfect> <4vlm>
<1mol/s>
<2kg/s>
<3mg/s>
<4slm>
<5sccm>
<6scfm>
<7scfh>
<8slh>
<9sm3h>
<1ulm>
<2uccm>
<3ucfm>
<4ucfh>
<5um3h>
<1plm>
<2pccm>
<3pcfm>
<4pcfh>
<5plh>
<6pm3h>
<1ccm>
<2lm>
<3lh>
<4m3h>
<6cfm>
<7cfh>
The <4vlm> unit selection embeds the selection “vlm” into the UNIT function
rather than a specific volume unit. The “vlm” selection provides access to all
of the volume flow units. In summary the unit types are:
<1std> (standard): mass flow units for which “standard” conditions are
temperature of 0 °C, standard atmosphere and using
the true compressibility factor of the gas.
<2user>: mass flow units for which “standard” conditions are a
user settable temperature, standard atmosphere and
using the true compressibility factor of the gas.
<3perfect>: mass flow units for which “standard” conditions are
temperature of 0 °C, standard atmosphere and
assuming a compressibility factor of 1 for all gases.
<4vlm>: volume flow
units.
See Sections 3.4.3.1 to 3.4.3.4 for additional information on flow unit types.
3.4.4 [TARE]
PURPOSE
[TARE] accesses five functions.
• TARE function: To zero the molbox RFM differential pressure readings during
molbloc-L operation or verify the two RPTs by comparing them against each other during
molbloc-S operation (see Section 3.4.4.1).
• PURGE function: To purge the molbloc connecting lines and molbox RFM internal volume
of a first gas with a second gas by flowing the second gas through the molbox RFM (see Section
3.4.4.2).
• LEAK CHECK function: To check the molbox RFM internal pneumatic circuit and/or the
external test circuit to which molbox RFM is connected, for leaks (see Section 3.4.4.3).
Page 39 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 50

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
• AUTOZ function: To periodically offset the molbox RFM RPTs relative to a reference
pressure value in order to compensate for possible changes in the RPT zero between full
recalibrations (see Section 3.4.4.4).
• BPR function (present only in molbloc-S operation): To measure and display the
molbloc-S back pressure ratio (BPR) while operating in a BPR mode, which does not
continuously read and display BPR (see Section 3.4.4.5).
OPERATION
Pressing [TARE] accesses a display with the choice
of four functions (five functions with molbloc-S).
Select the desired function. See the following for
principles and operation:
1tare 2purge
3leak check 4AutoZ ↓
5BPR
Some screens (e.g., the Tare menu) may go beyond the two lines provided by the display.
This is indicated by a flashing arrow in the second line of the display. Press the [←] and
[→] keys to move the cursor to access the lines that are NOT visible or directly enter the
number of the hidden menu choice if you know it.
3.4.4.1 <1TARE>
The purpose and operation of the tare function is different for molbloc-L and
molbloc-S operation. Tare values are generated and stored independently for
the two molbloc types. For example, a tare value generated during molbloc-L
operation is not used during molbloc-S operation, but is saved and used again
when a molbloc-L is connected to the molbox.
Tare is described separately for the two molbloc types below.
3.4.4.1.1 molbloc-L OPERATION
PURPOSE
To zero the molbox RFM differential pressure reading at the molbloc
operating pressure. Zeros the differential between the two high pressure
absolute transducers as well as the microrange transducer if present.
PRINCIPLE
The molbox RFM TARE function can be considered the equivalent of the
ZEROING function performed on many instruments prior to
making measurements. molbox RFM calculates the flow through the molbloc
from the differential pressure across the molbloc. The differential pressure
across the molbloc is measured by taking the difference in the absolute pressure
measured by the molbox RFM’s two internal RPTs. One RPT is connected to
the upstream molbloc pressure port and the other to the downstream molbloc
pressure port. If the molbox RFM has the microrange option (see Section 3.1.5),
when the differential pressure is under 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi), the microrange
option’s low differential RPT is used as the source of the differential pressure
measurement.
If a common pressure is applied to both absolute transducers (and both legs of
the microrange option differential RPT if present) the differential pressure
indicated should be zero. If a differential pressure is observed, the value
indicated represents an offset in the differential measurement, which will appear
as an offset or “zero error” on the flow through the molbloc calculated by the
molbox RFM. The TARE function allows the differential indication between the
two RPTs to be zeroed at the molbloc operating pressure to eliminate the zero
error in differential pressure measurement.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 40
Page 51

3. OPERATION
When the TARE function is activated, molbox RFM’s internal valves operate to
pneumatically connect together the two absolute transducers, and both legs of
the microrange option differential transducer if present, at the molbloc operating
pressure. The user can select whether this pressure is the upstream or
downstream molbloc pressure so that the tare can be made at the pressure that
will be held stable during operation (generally by a regulator or because it is
open to atmosphere). Activating the tare causes molbox RFM to record the
current differential as the tare value. The tare value will be used to correct all
subsequent RPT readings. For the absolute transducers the tare value is the
difference between the two transducer readings (hi - lo). The upstream RPT will
be corrected by (- tare value/2) and the downstream RPT will be corrected by (+
tare value/2). For the microrange differential RPT, the tare value is the differential
value read. The differential transducer will be corrected by subtracting the tare
value from the current reading.
1. High Isolation: Open
2. Low Isolation: Closed
3. Bypass: Open
4. Mirorange Bypass: Open
Figure 5. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic – TARING, UPSTREAM molbloc-L OPERATION
OPERATION
At a minimum, the TARE function should be executed whenever the operating
pressure of the molbloc is changed significantly, at the beginning of each
test or any time a significant zero error is observed. For best results, it is
possible to tare before every reading since taring can be executed while
flowing. Best results will be obtained if the TARE function is executed with a
stable flow through the molbloc.
To access the TARE function press [TARE], <1tare>.
The display is:
Select tare pressure:
1upstream 2dnstream
Selecting <1upstream> will tare the molbox RFM RPTs at the molbloc’s
upstream pressure (see Figure 5). Selecting <2dnstream> will tare the RPTs at
the molbloc’s downstream pressure (Low isolation valve open, High isolation
valve closed). Select the position where the pressure will remain the most stable
during molbloc operation.
Page 41 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 52

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The next display is:
1. The current pressure read by the upstream
(left) and downstream (right) RPTs without
taking into account the current tare value.
These are untared readings in the current
pressure units.
2. <T>, flashing, to indicate that this is a TARE
display showing the tare between the two
absolute RPTs.
3. The difference between the untared upstream
and downstream absolute pressure readings
(upstream – downstream). This differential
value is always in Pascal [Pa].
4. The flow corresponding to the current untared
differential pressure in the current flow units.
This display allows the current untared absolute pressures and the resulting untared
differential pressure from the difference of the two absolute RPTs to be observed.
The flow value represents the current untared zero error in terms of flow. It does
not necessarily represent the current zero error on flow measurements as a tare
value other than zero is probably already active.
Press [ENTER] when ready. Molbox RFM makes measurements to determine a
new tare value. The next display is:
202.347 kPaa 202.311
T 36 Pa 0.06 sccm
1. The tare value currently in use [Pa].
2. The new tare value, resulting from this
execution of the TARE function [Pa].
3. Microrange tare value currently in use [Pa}
4. New microrange tare value [Pa].
OldT: 44Pa m 20
NewT: 36Pa m 20
Press [ENTER] to activate the new tare and return to the MAIN run screen.
Press [ESCAPE] to return to the [TARE] display without activating the new tare,
leaving the old tare active.
The tare screen shows the upstream and downstream RPT readings
WITHOUT the current tare applied. The [P&T] screen shows the RPT readings
WITH the tare applied (see Section 3.4.5).
Limits and Errors
Excessively large tare values can diagnose molbox RFM transducer malfunction,
the need to recalibrate or possible poor execution of the TARE function. To
protect against improper taring and to alert to possible RPT malfunction, molbox
RFM checks the tare values before they are activated and displays warnings
when appropriate. In the most extreme case, molbox RFM will not allow the tare
value to be activated. The limits checked and their consequences are as follows:
Upstream and downstream absolute pressure RPTs coherence test:
When attempting to activate a new tare, molbox RFM checks the coherence
between the two transducers and alerts the operator to excessive
disagreements. The test has two levels.
If the new tare is 700 Pa < tare > 10 000 Pa, a caution message is displayed.
Pressing [ENTER] overrides the caution and activates the new tare.
Pressing [ESCAPE] returns to the TARE screen.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 42
Page 53

3. OPERATION
If the new tare is > 10 000 Pa, the new tare cannot be activated.
Pressing [ENTER] or [ESCAPE] returns to the tare screen. It is likely that
molbox RFM needs service or a grossly incorrect adjustment has been made to
one or both of the RPTs.
Microrange differential pressure RPT zero drift test (if microrange
option present): When attempting to activate a new tare, molbox RFM checks
the zero offset value of the microrange RPT. If the new tare is > 999 Pa, the new
tare cannot be activated. Press [ENTER] or [ESCAPE] to go back to the tare
screen. It is likely that molbox RFM needs service or a grossly incorrect
adjustment has been made to the differential RPT.
If a caution message appears or a tare cannot be activated during the taring
process, repeat the taring process. If the caution persists, the calibration
of the RPT(s) should be verified. If the tare still cannot be activated, the
RPT(s) should be recalibrated and molbox RFM may require other service.
3.4.4.1.2 molbloc-S Operation
PURPOSE
To check the molbox RFM RPT absolute pressure readings by comparing them
at a common molbloc-S upstream absolute pressure.
PRINCIPAL
When measuring the flow through molbloc-S, the critical pressure measured by
molbox RFM is the molbloc upstream pressure. The downstream pressure is
only monitored to be sure that critical flow conditions exist (see Section 3.1.2). To
reduce the uncertainty on the upstream pressure measurement, molbox RFM
employs internal valving to direct the upstream pressure to both RPTs, and the
average of the two readings is used as the measured molbloc upstream
pressure. To take advantage of this RPT averaging, the molbox RFM must be in
either BPR OFF or Auto BPR mode (see Section 3.6.9).
molbox RFM dynamically tares the two RPT readings when they are connected
together, so the user can view the “live” average pressure that is calculated
and to allow smooth pressure and flow measurements during valve transitions
in the Auto BPR mode (see Section 3.6.9). RPT taring in molbloc-S operation
occurs automatically when needed and does not need to be initiated or
performed by the user.
The molbloc-S TARE function is available to allow the user to conveniently verify
that the two RPT measurements agree within an acceptable tolerance when a
common pressure is applied to them. When the TARE function is selected, the
molbox RFM internal valves operate to connect both Q-RPTs the active channel
UPSTREAM pressure port (see Figure 6). The RPT readings and the difference
between the two RPT readings (tare value) is displayed for evaluation by the user.
A message is also displayed to indicate to the user whether the tare value is
acceptable, or indicates a need for pressure verification or calibration of the RPTs.
There is no need for the customer to save a new tare value during molbloc-S operation.
As during molbloc-L operation, the molbloc-S tare value is the difference
between the two transducer readings (hi - lo). In BPR modes where the tare
value is dynamically calculated and applied, the upstream RPT is corrected by
(- tare value/2) and the downstream RPT is corrected by (+ tare value/2).
Page 43 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 54

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Figure 6. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic – TARING molbloc-S OPERATION
1. High Isolation: Open
2. Low Isolation: Closed
3. Bypass: Open
4. Mirorange Bypass: Open
OPERATION
To access the TARE function press [TARE], <1tare>. The display is:
1. The current pressure read by the upstream
(left) and downstream (right) RPTs without
taking into account the current tare value.
These are untared readings in the current
pressure units.
2. <T>, to indicate that this is a TARE display
showing the tare between the two absolute
RPTs.
3. The difference between the untared upstream
and downstream absolute pressure readings
(upstream – downstream). This differential
value is always in Pascal [Pa].
4. Tare message
<OK> If tare is less than 300 Pa,
<CHECK> if tare is between 300 and 1250 Pa
<NEED CAL> if tare is greater than 1250 kPa
201.032 kPa ^201.013
T 19.3 Pa OK
The tare screen shows the upstream and downstream RPT readings
WITHOUT the current tare applied. The [P&T] screen shows the RPT readings
WITH the tare applied (see Section
3.4.5).
3.4.4.2 <2Purge>
PURPOSE
To purge the lines between the molbloc and the molbox RFM and the internal
molbox RFM volumes of one gas with another gas by setting up an internal
valving configuration in which gas flows through the molbox RFM.
PRINCIPAL
molbox RFM supports the measurement of flow of a variety of gases. To
calculate the flow, the thermodynamic characteristics of the gas must be known.
These are stored in molbox RFM memory. For the flow to be calculated
correctly, the gas flowing through the molbloc must be the gas that is selected on
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 44
Page 55

3. OPERATION
the molbox RFM (see Section 3.4.2). When switching from the measurement of
one gas to another, the old gas remaining in the circuit and the new gas being
flowed may mix for some time so that the gas flowing through the molbloc is not
purely the new gas. Erroneous measurements may result. For this reason, it is
important to purge the lines upstream and downstream of the molbloc when
changing gases. It is also important to purge the molbox RFM itself which, since
there is normally no flow through it, may trap and hold the old gas.
The PURGE function is designed to facilitate purging the molbox RFM. It sets up
the molbox internal valving so that flow can pass through the molbox RFM (see
Figure 7). In this configuration, the lines between the molbloc and molbox RFM
and the molbox RFM internal volume can be purged by simply flowing the new
gas in the normal flowing configuration. The flow resistance through the molbloc
creates a differential pressure, which causes flow through the molbox RFM to
occur, purging it with the new gas.
1. High Isolation: Open
2. Low Isolation: Open
3. Bypass: Open
4. Mirorange Bypass: Open
Figure 7. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic – PURGING
OPERATION
For best results, the PURGE function should be executed whenever the
species of the gas flowing through the molbloc is changed. Prior to
activating the PURGE function, set flow through the molbloc to the highest
rate that is practical. Then, with the gas flowing, activate the PURGE
function. Very small volumes of gas remain trapped (dead ended) in the
molbox RFM in the PURGE configuration. Therefore, it may be desirable to
execute the PURGE function more than once to clear these volumes by the
pressure changes caused by PURGE execution.
To access the PURGE function press
[TARE], <2purge>. The display is:
Page 45 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Set purge time:
15 sec
Page 56

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The purge time can be edited. Pressing [ENTER] causes molbox RFM to set
its internal valving to the purge configuration (see Figure 14) and go to the
PURGE display:
1. The current pressure read by the upstream
(left) and downstream (right) RPTs in the
current pressure unit of measure.
2. <PURGING> to indicate that this is a PURGE
display.
3. Countdown of purge time remaining in
seconds.
molbox RFM remains in the purge condition until the purge time countdown
elapses. It then automatically returns to normal operation. When the countdown
elapses operation returns to the run screen from which PURGE was accessed.
202.347 kPaa 202.311
PURGING 15 sec
The appropriate purge time setting is dependent on the flow rate and the
volumes upstream and downstream of the molbloc. Typically, 15 to 30
seconds is adequate. The time needed increases as flow rates go down and
volumes go up.
To interrupt the PURGE function, press [ESCAPE].
When using the PURGE function, remember that the molbox RFM absolute
RPTs are exposed to the pressure. Do not apply pressure greater than 600
kPa absolute (87 psia).
3.4.4.3 <3Leak Check>
PURPOSE
To access the molbox LEAK CHECK and SYSTEM LEAK CHECK functions
which use molbox RFM’s pressure and flow measurement capabilities to check
molbox RFM and/or the system to which it is connected for leaks.
PRINCIPAL
molbox RFM is used both as a tool to accurately measure unknown flow values
and as a calibration standard to calibrate other devices by comparison. Leaks
with in the molbox RFM pneumatic circuit can cause erroneous flow measurements.
Leaks in the external flow circuit can cause the flow through the molbloc to be
different from the flow at another point in the system so that, even with an
accurate measurement and steady state flow, the molbox RFM indication is not
an accurate indication of flow at the other point in the system.
To obtain valid measurement results, it is important that leaks in molbox RFM
and/or the external flow system be identified and eliminated to the extent
possible. molbox RFM uses its precision on-board pressure and flow
measurement capabilities to help identify leaks with INTERNAL and EXTERNAL
LEAK TESTING functions.
OPERATION
Press [TARE] and select <3leak check> to access the LEAK CHECK functions.
Then select <1molbox> or <2system>.
<1molbox> is designed to leak check the internal molbox RFM pneumatic circuit.
<2system> is designed to leak check the system to which the molbloc/molbox
is connected.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 46
Page 57

3. OPERATION
3.4.4.3.1 Leak Check molbox
PURPOSE
To check the internal molbox RFM pneumatic circuit for leaks.
PRINCIPAL
It is normally not necessary to run the MOLBOX LEAK CHECK procedure
frequently. It i s int ended for troubleshooting purposes when there appears to be
a leak or other molbox RFM measurement problem whose source cannot be
identified by the SYSTEM LEAK CHECK or other troubleshooting means. It is
recommended to run the MOLBOX LEAK CHECK after it has been shipped or if it
is suspected that the molbox has been exposed to a large shock or liquid or
particulate contamination.
OPERATION
Press [TARE] and select <3leak check>, <1molbox>. If the molbox RFM has a
microrange option, microrange RPT <1active> or <2bypassed> must be
selected to proceed (see Section 3.1.5). The next display is:
1. The pressure read by the upstream transducer
(left), the downstream transducer (right) and
the pressure unit of measure (middle).
2. Indicator that the figure that follows is
differential pressure.
3. Differential pressure across the molbloc in
current pressure unit of measure.
4. Prompt for the action to take when ready.
The molbox RFM internal valving is in its normal measuring configuration (see
Figure 3). This display is intended to assist the operator in setting the leak
check pressure.
Apply the maximum differential pressure across the molbloc that is normally
encountered during flow measurement while working at your typical absolute
working pressure. Neither pressure should be less than atmosphere. Use the
<DP> indication on the molbox RFM display to set the absolute and differential
pressure.
347.458 kPaa 307.455
DP 40.003 <ENTER>
Once the pressure setting is correct,
press [ENTER]. The molbox RFM
actuates its internal valves to isolate itself
from the molbloc and trap the upstream
and downstream pressures on its RPTs
Vent molbloc ports
<ENTER>
(see Figure 8). The display is:
Assure that both molbox RFM rear panel pressure connections are vented.
Since the pressure quick connections on the molbox RFM and the quickconnectors on the molbloc pressure connection tubes seal when disconnected,
they cannot be vented by simply disconnecting them. The easiest way to assure
that the connections are vented is to maintain the normal connections to the
molbloc, shut off the molbloc gas source and open one or both ends of the
molb loc so it can vent to atmospheric pressure. Another alternative is to install the
non-sealing quick connectors (P/N 101889) provided in the molbox accessories (see
Section 2. 1.2) into the molbox quick connectors.
Page 47 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 58

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Figure 8. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic – LEAK CHECK molbox
1. High Isolation: Closed
2. Low Isolation: Closed
3. Bypass: Closed
4. Mirorange Bypass: Closed if Active
Open if Bypassed
Once the molbox RFM pressure connections are vented, press [ENTER].
1. The pressure read by the upstream RPT (left),
the downstream RPT (right) and the pressure
unit of measure (middle).
2. The ratio of the upstream RPT reading to the
downstream RPT reading.
3. Leak check count down in seconds.
347.466 kPaa 35.459
1.03579:1 WAIT: 60
molbox RFM counts down for 60 seconds while monitoring the ratio of the two
pressures and then determines whether an internal leak was present.
A significant leak in a pressure isolation valve or a bypass valve between the two
channels will cause the ratio between the two pressures to vary.
The molbox RFM LEAK CHECK function
should end with the prompt:
molbox passed the
leak check
If any other prompt is present, repeat the process. If the molbox RFM is
equipped with the microrange option, run the leak test with the microrange in the
opposite condition (active or bypassed). If the leak check fails consistently, note
the failure message and contact a DHI Authorized Service Provider.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 48
Page 59

3. OPERATION
3.4.4.3.2 Leak Check System
PURPOSE
To leak check the external system that is connected to the molbox RFM.
PRINCIPAL
It is recommended to run the SYSTEM LEAK CHECK whenever critical physical
connections in the system attached to the molbloc are broken and reconnected.
Critical connections are ones that are between the molbloc and the DUT, which,
if they were to leak, would cause the flow through the molbloc and the DUT to
differ. Whenever a new DUT is connected to the system, it is a good idea to run
the SYSTEM LEAK CHECK.
The SYSTEM LEAK CHECK monitors changes in pressure in a closed system
defined by the user to help determine whether a leak exists in the system. One of
the ways a leak is detected is by monitoring pressure decay in the pressurized
closed system. When the test volume is large, significant leaks may exist without
being detected because the pressure decay caused by the leak is reduced.
Therefore, the SYSTEM LEAK CHECK is most effective when the volume of the
closed system is minimized.
For molbloc-L operation, the SYSTEM LEAK CHECK also measures flow through
the molbloc to help determine whether a leak is present upstream or downstream of
the molbloc. Since molbloc-S is not capable of calculating meaningful flow values
with the very small differential pressure present during this test, the SYSTEM LEAK
CHECK operates differently for molbloc-L and molbloc-S operation, as described in
the OPERATION sections immediately below.
The SYSTEM LEAK CHECK function uses molbox RFM’s high precision
pressure and flow measurement capabilities to help determine whether a
leak exists in the system to which the molbloc is connected. This feature is
to assist the operator in flow measurement and calibration. The system to
which the molbloc is connected is the responsibility of the user. Failures in
the system leak check do not normally indicate defects in the molbox RFM or
molbloc itself. The molbox leak check is used to identify molbox RFM failures.
OPERATION – molbloc-L Operation
To access the system leak check press [TARE] and select <3leak check>,
<2system>. The display is:
1. The pressure read by the upstream RPT
(left), the downstream RPT (right) and
the pressure unit of measure (middle).
347.589 kPaa 347.580
This display is intended to assist the operator in setting the leak check pressure.
molbox RFM has actuated internal valves to connect the upstream and
dow ns tr eam RPTs together, so they are both measuring an equal system pressure.
(see Figure 9).
Page 49 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 60

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Figure 9. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic
– SYSTEM LEAK CHECK – CHECKING OFFSET AND STABILITY
molbloc-L operation
1. Channel A High Isolation: Open
2. Channel A Low Isolation: Open
3. Bypass: Open
4. Microrange Bypass: Open
Close an isolation valve downstream or plug the exhaust of the flow system that
is being tested (downstream of the molbloc and the DUT if the molbloc/molbox is
being used to test another device).
Using the molbox RFM display to read the pressure set the pressure to the
normal operating pressure.
FOR SYSTEMS WITH MASS FLOW CONTROLLERS (MFCs):
Keep in mind that the valves in most MFCs are not intended to provide a
complete gas shutoff and so they may not be suitable to close off the test
system. If an MFC is downstream of the molbloc and its downstream port
is open to atmosphere, it is best to close the system by connecting a cap to
the MFC outlet fitting or by connecting a shutoff valve downstream. If the
MFC valve is closed (most MFCs have normally closed valves) when the
operating pressure is applied from the upstream side, most of the gas will
be stopped by the MFC valve and will not immediately fill the volume between
the MFC valve and the downstream cap or valve. If this happens, the gas
may leak by the MFC valve to fill this volume during the test and cause a
pressure decay and an apparent system leak. The solution is to send a
setpoint signal to the MFC to open the MFC valve while pressurizing the system.
Then close the MFC valve (remove the setpoint signal) after the system is
pressurized to avoid heating of the test gas by the energized valve.
Next, close an isolation valve upstream of
the molbloc so the gas supply is no longer
open to the system being checked. Once
the pressure has stabilized, press
[ENTER]. The display is:
The molbox RFM is checking:
• For pressure and temperature stability before running the system leak test
• That the disagreement between the two RPTs is not excessive
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 50
347.587 kPaa 347.583
WAIT: 30
Page 61

3. OPERATION
After 30 seconds, if the stability check is not passed, molbox RFM displays:
• If the pressure was not stable:
• If the molbloc temperature change
was too great:
• If the offset between the RPTs was
too great:
Leak is too large to
continue
Temp change was too
great to find leaks
Offset excessive
check tare
If any of the above three prompts occurs, check the external system for leaks
and/or run the molbox RFM leak check before proceeding. If the tare was
excessive, tare the molbox RPTs before running the leak check again (see Section
3.4.4.1).
Once the 30 second pressure stability/offset
check has been successfully completed,
molbox RFM displays:
347.592 kPaa 347.583
0.101 sccm [ENT]
When [ENTER] is pressed, molbox RFM’s valves actuate to set up the system
leak check configuration which is identical to the normal operating configuration
(see Figure 3). The display becomes:
1. Pressure read by the upstream RPT (left), the
downstream RPT (right) and the pressure unit
of measure (middle).
2. Current measured flow.
3. Time remaining in the leak check in seconds.
347.592 kPaa 347.583
0.101 sccm 30
possible system
upstream leak
molbox RFM measures pressure and flow for a 40 second countdown. After the
countdown has elapsed, molbox RFM displays its conclusion from the
measurements. The display will be either:
possible system
or
downstream leak
System passed system
or
leak check
Upstream and downstream refer to the possible location of the leak relative to
the position of the molbloc and the normal flow direction in the system. If you are
unable to locate a leak in the flow path components, check or replace the
upstream and downstream molbloc to molbox pressure tubes and their connectors
and retry the test. They are a critical part of the pneumatic system and if a
significant leak is present in these tubes, it will cause an error in flow
measurement.
OPERATION – molbloc-S Operation
In molbloc-S operation, SYSTEM LEAK CHECK is a one-part test which tests for
pressure decay in the closed system.
To access the system leak check press [TARE] and select <3leak check>,
<2system>.
The display is:
Leak check:
1run 2view
If <2view> is selected the test results screen (see below) is displayed with the
results from the most recent leak test.
Page 51 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 62

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
To run the leak test, select <1run>.
molbox RFM actuates internal valves to connect the upstream and downstream
RPTs together, so they are both measuring an equal system pressure. (see
Figure 10).
1. High Isolation: Open
2. Low Isolation: Open
3. Bypass: Open
4. Mirorange Bypass: Open
Figure 10. molbox RFM
Internal Pneumatic Schematic
– SYSTEM LEAK CHECK – CHECKING OFFSET AND STABILITY
molbloc-S operation
Close an isolation valve downstream or plug the exhaust of the flow system that
is being tested (downstream of the molbloc and the DUT if the molbloc/molbox is
being used to test another device).
Open an isolation valve upstream of the molbloc to allow the working pressure to
pressurize the system.
FOR SYSTEMS WITH MASS FLOW CONTROLLERS (MFCS)
Keep in mind that the valves in most MFCs are not intended to provide a
complete gas shutoff and so they may not be suitable to close off the test
system. If an MFC is downstream of the molbloc and its downstream port
is open to atmosphere, it is best to close the system by connecting a cap to
the MFC outlet fitting or by connecting a shutoff valve downstream. If the
MFC valve is closed (most MFCs have normally closed valves) when the
operating pressure is applied from the upstream side, most of the gas will
be stopped by the MFC valve and will not immediately fill the volume between
the MFC valve and the downstream cap or valve. If this happens, the gas
may leak by the MFC valve to fill this volume during the test and cause a
pressure decay and an apparent system leak. The solution is to send a
setpoint signal to the MFC to open the MFC valve while pressurizing the
system. Then close the MFC valve (remove the setpoint signal) after the
system is pressurized to avoid heating of the test gas by the energized valve.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 52
Page 63

3. OPERATION
Next, close the isolation valve upstream of the molbloc so the gas supply is no
longer open to the system being checked. Once the pressure has had time to
stabilize, press [ENTER].
The next display is:
ENTER to start
60 s leak check
Press [ENTER] to begin the test
The next display is:
1. The average pressure from the two molbox
RFM absolute RPTs.
2. Current absolute pressure measurement in
active pressure unit of measure.
3. SYSTEM LEAK CHECK count down in
seconds.
199.16 kPa a
leak testing 60s
Press [ESCAPE] to abort the leak test.
Pressing [ENTER] while the test is in progress restarts the test and reset the leak
test timer.
When the test is complete, a test results screen is displayed:
1. The total change in average pressure over the
test interval.
2. The currently selected pressure unit of measure.
3. Average rate of pressure change, per second,
during the test.
ΔP –0.0720 kPa
Rate –0.0012 kPa/s
Since flow systems using molbloc-S will may use widely varying flow rates and
tubing sizes, and test volumes may be quite large, it is difficult to predict what
size pressure rate of change is acceptable to avoid significant flow errors. Your
best guide may be to run the SYSTEM LEAK CHECK often with your hardware,
find a typical rate of change which represents a sound setup, and attempt to
match that rate each time. In any case, you should be able to achieve a rate of
change smaller than 0.01 % / second of the absolute line pressure.
If you observe a relatively large leak rate and are unable to locate a leak in the
flowpath components, check or replace the upstream and downstream molbloc
to molbox pressure tubes and their connectors and retry the test. They are a
critical part of the pneumatic system and if a significant leak is present in these
tubes, it will cause an error in flow measurement.
3.4.4.4 <4AutoZ>
PURPOSE
To offset the molbox RFM absolute reference pressure transducers (RPTs)
relative to a reference value in order to compensate for possible changes in RPT
zero between full recalibrations.
Improper use of the AutoZ function can cause out of tolerance pressure
measurements. AutoZ should be used only by qualified personnel for the
purpose of rezeroing the molbox RFM reference pressure transducer
absolute pressure measurement function.
Page 53 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 64

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The AutoZ function has no effect on the microrange (differential) RPT
measurement (if present).
PRINCIPAL
AutoZ Purpose and Principle
The main component of the change over time of the molbox RFM RPTs is
change in zero or offset, independent of span. Offsetting or “rezeroing” molbox
RFM RPTs relative to a reference between recalibrations allows measurement
uncertainty specifications to be maintained with less frequent full calibrations.
The molbox RFM AutoZero function (AutoZ) provides full on-board support for
the rezeroing process to simplify its application by the user.
The AutoZero function uses three values:
1. P
: The absolute pressure value indicated by the AutoZ reference, the
std,0
device that is acting as the reference relative to which to offset the RPT.
The pressure at which AutoZ is performed is normally atmospheric pressure
and the P
value can be supplied a) by manual entry, or b) automatically
std,0
from a DHI RPMx Reference Pressure Monitor.
2. P
: The absolute pressure reading of the RPT, with no AutoZ offset, at the
u,0
time AutoZ is performed.
3. P
P
offset
(P
std,0
The AutoZ function manages the determination, storage and application of P
: The difference between the absolute pressure reading of the RPT
offset
with no AutoZ offset (P
) and the indication of the AutoZ reference (P
u,0
P
offset
= P
u,0
- P
std,0
std,0
represents the change in zero of the RPT relative to the AutoZ standard
).
offset
):
for both molbox RFM RPTs in absolute mode. The AutoZ handles both molbox
RFM RPTs simultaneously as they are of the same range and always used
together.
The source of P
must be an absolute pressure, nominally atmospheric
std,0
pressure, with uncertainty significantly better than that of the RPT that is being
AutoZeroed (see Section 1.2.2). This can be accomplished with a variety of
digital barometers or with a piston gauge able to set absolute pressure.
When the RPTs are used with AutoZ ON, absolute pressure is calculated as:
P
= P
u,0
offset
- P
abs
When RPTs are used with AutoZ OFF, P
When the RPT is calibrated, P
is set to zero. P
offset
regular intervals using the AutoZ function. The most recent value of P
offset
is ignored.
offset
is then redetermined at
is
offset
applied to the RPT reading to correct for change in zero over time.
Recommendations for the Use of the AutoZ Function
The AutoZ function provides a powerful and easy to use tool for improving the
stability over time of molbox RFM RPTs and maximizing the recalibration interval
by compensating for change in zero between full recalibrations. The following
simple recommendations will help assure that you use this feature to best
advantage.
• Always leave AutoZ ON when operating if the AutoZ routine has been run
regularly using a valid atmospheric reference.
• Run AutoZ to update P
only when a reference whose measurement
offset
uncertainty is known to be significantly better than that of the molbox RFM
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 54
Page 65

3. OPERATION
RPTs is available. Though it may not be practical and generally is not
necessary, the best possible reference with which to run AutoZ in absolute
measurement mode is a gas operated piston gauge (such as a DHI PG7601)
applying an absolute pressure near atmospheric pressure to the molbox
RFM test port. The best day to day reference is a properly calibrated DHI
RPM4 with a BA100K RPT interfaced directly as an external device to the
molbox RFM COM2 port.
• Allow the molbox RFM to stabilize at atmospheric pressure and ambient
temperature for 10 to 15 minutes before running AutoZ.
If AutoZ is on, the AutoZ value will be applied while running the calibration of
molbox RPTs and an AutoZ indication is included in the run calibration screen
(See Section 5.2.4.1).
OPERATION
To access the molbox RFM AutoZ function press [TARE], <4AutoZ>. The
display is:
1. Active RPT designator.
2. Indication of whether AutoZ is currently ON or
OFF for this RPT and measurement mode.
1off 2view
3edit 4run ON
• Select <1off> (or <1on>) to change the AutoZ status.
• Select <2view> to view the current values of P
P
should be zero when the molbox RFM is new or has just been calibrated.
offset
for the two RPTs.
offset
• Select <3edit> to edit the values of Poffset.
The value of P
• Select <4run> to run the AutoZ routine which determines and activates P
values by measurement of P
is always displayed and entered in Pascal (Pa).
offset
(see Section 3.4.4.4.2).
std,0
offset
3.4.4.4.1 Edit AutoZ
The edit AutoZ function should be used with great caution as entering
inappropriate values and turning ON AutoZ may result in out of tolerance
measurements. In normal operation, the value of the AutoZ offset, P
offset
should be changed using the run AutoZ function (see Section 3.4.4.4.2).
Before editing P
, (see Section 3.4.4.4, PRINCIPLE).
offset
Page 55 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
,
Page 66

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
To edit the current P
1. Edit field for the value of P
(1, Hi) RPT.
2. Edit field for the value of P
(1, Hi) RPT.
values, press [TARE], <4AutoZ>, <3edit>. The display is:
offset
of the upstream
offset
Poffset:18.7 Pa UP1
of the upstream
offset
Poffset:-3.5 Pa DN2
Edit the P
value(s) as desired and press [ENT] to activate the new value(s).
offset
Press [ESC] to abandon changes.
The value of P
is always displayed and entered in Pascal (Pa).
offset
3.4.4.4.2 Run AutoZ
Run AutoZ is the function by which the current RPT reading is compared to a
reference, P
The value of P
, at atmospheric pressure to determine a new value of P
std,0
is then used by AutoZ to automatically correct the RPT for
offset
possible change in zero over time (see Section 3.4.4.4, PRINCIPLE).
To access run AutoZ, press [TARE], <4AutoZ>, <4run>. The display is:
offset
.
AutoZ by:
1. Selection of source of P
to AutoZ.
Selecting <1Entry> allows the value of P
reference to which
std,0
std,0
Selecting <2COM> allows the value of P
to be entered from the front panel keypad.
std,0
1Entry 2COM2
to be read automatically from a DHI
RPMx connected to molbox RFM’s COM2 communications port.
When AutoZ is run, the molbox RFM internal valves are actuated to connect both
molbox RPTs to the Hi port on the molbox RFM rear panel (see Figure 21 in
Section 5.2.4.1). Be sure the Hi port is fully open to atmosphere when running
AutoZ. Note that the molbox RFM quick connectors and molbox to molbloc
pressure lines are self sealing and therefore DO NOT open to atmosphere
unle ss a quick connector stem is inserted. Use a quick connector stem (DHI P/N
101889, equivalent to Swagelok SS-QM2-S-200) supplied with the molbox RFM
accessories to open the port to atmosphere.
Allow the molbox RFM to stabilize at atmospheric pressure and ambient
temperature for 10 to 15 minutes before running AutoZ.
If running AutoZ results in a value of P
that is greater than ± 0.025 % FS of
offset
the span of the RPT that is being AutoZeroed, the RPT and/or the reference
used as the source of Pstd,0 may be out of tolerance or the AutoZ process may
have been faulty. Before activating a new P
greater than ± 0.025 % FS of
offset
the active RPT, check to be sure that both the RPT and the reference were in
good working order, properly vented to stable atmospheric pressure, at the
same height, and reading in the same pressure units when AutoZ was run.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 56
Page 67

3. OPERATION
When the run AutoZ selection is made, if a HEAD correction is currently active
(see Section 3.6.8) the head correction is momentarily disabled while
running AutoZ to avoid “zeroing out” the head value.
The value of P
is always displayed and entered in Pascal (Pa).
offset
Run AutoZ by Entry
AutoZ by entry allows the value of P
(see Section 3.4.4.4, PRINCIPLE) to be
std,0
entered directly from the molbox RFM front panel. This provides a simple way of
AutoZeroing relative to an independent reference device such as a house
barometer that does not interface directly with molbox RFM.
To access run AutoZ by entry press [TARE], <4AutoZ>, <4run>, <1Entry>.
The display is:
1. Real time reading (without head correction) of
upstream (1, Hi) RPT in unit of measure on
line 2.
2. Real time reading (without head correction) of
downstream (2, Lo) RPT in unit of measure on
line 2.
3. Entry field for the value of P
pressure unit of measure.
. in the current
std,0
Enter the value of the AutoZ reference (P
96.772 kPaa 96.778
Pstd,0:96.7752
) in the same unit of measure as the
std,0
display and press [ENT]. molbox RFM logs the readings and calculates a new
AutoZ offset value. The next display is:
1. Current/previous value of P
upstream (1, Hi) RPT.
2. Current/previous value of P
downstream (2, Lo) RPT.
3. New value of P
RPT for the AutoZ that was just run.
4. New value of P
RPT for the AutoZ that was just run.
for the upstream (1, Hi)
offset
for the downstream (2, Lo)
offset
Press [ENT] to activate the new values of P
of a new AutoZ reference (P
offset
offset
std,0
for the
for the
) value.
Old: 0.0 Pa 0.0
New: 3.7 Pa 2.6
or [ESC] to start over with entry
offset
The value of P
is always in Pascal (Pa). The value of P
offset
is entered in
std,0
the current pressure unit of measure.
Run AutoZ by COM2
AutoZ by COM2 allows a DHI RPMx Reference Pressure monitor connected to the
molbox RFM COM2 to act as the AutoZ reference (source of Pstd,0) (see Section
3.4.4.4, PRINCIPLE). The RPMx is read and the new P
is calculated automatically.
offset
To access run AutoZ by COM2 press [TARE], <4AutoZ>, <4run>, <2COM2>.
For molbox RFM to communicate with an RPMx connected to its COM2 port,
the molbox RFM and the RPMx RS-232 interfaces must be set up properly
(see Section 3.6.6.1). If, the molbox RFM is unable to locate an RPM ON COM2
when running AutoZ by COM2, it times out after 6 seconds and displays an
error message.
Page 57 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 68

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
If molbox RFM is able to communicate with an RPMx on its COM2 port, the display is:
1. Real time reading (without head correction) of
upstream (1, Hi) RPT in unit of measure on
line 2.
2. Real time reading (without head correction) of
downstream (2, Lo) RPT in unit of measure on
line 2.
3. Real time reading of the RPMx connected to
molbox RFM COM2 to provide the value of
AutoZ P
offset
.
Observe the pressure outputs verify that they are stable. A 10 to 15 minute wait,
after venting, is recommended before running AutoZ. When ready, press [ENT]
to cause AutoZ to run. molbox RFM logs both RPT readings and calculates a
new AutoZ offset value. The display is:
1. Current/previous value of P
upstream (1, Hi) RPT.
2. Current/previous value of P
downstream (2, Lo) RPT.
3. New value of P
for the AutoZ that was just run.
4. New value of P
RPT for the AutoZ that was just run.
for the upstream (1, Hi) RPT
offset
for the downstream (2, Lo)
offset
offset
offset
Press [ENT] to activate the new values of P
for the
for the
96.772 kPaa 96.778
Pstd,0:96.7752
Old: 0.0 Pa 0.0
New: 3.7 Pa 2.6
or [ESC] to start over.
offset
The value of P
is always displayed and entered in Pascal (Pa).
offset
3.4.4.5 <5BPR> (molbloc-S OPERATION ONLY)
PURPOSE
To quickly measure the molbloc-S upstream and downstream pressure and
calculate and display the BPR (back pressure ratio) when molbox RFM is in a
molbloc-S BPR mode which would not otherwise measure the BPR.
The <5BPR> menu selection is only present during molbloc-S operation.
PRINCIPAL
molbox RFM uses the back pressure ratio, or BPR (the ratio of the molbloc-S
downstream absolute pressure to the upstream absolute pressure) to determine
whether the flow through the throat of the molbloc-S venturi nozzle is critical and
flow measurements within predictable uncertainty limits can be made with
molbloc-S (see Section 3.1.2). When operating molbox RFM with molbloc-S, the
user may select different BPR monitoring modes (see Section 3.6.9). The BPR
function allows the user to measure and display BPR directly at any time
regardless of the current BPR mode.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 58
Page 69

OPERATION
Select [TARE], <5BPR>. The display is:
3. OPERATION
1. The current pressure read by the upstream
(left) and downstream (right) RPTs without
taking into account the current tare value.
These are untared readings in the current
pressure unit of measure.
2. The current BPR (ratio of downstream to
upstream absolute pressure).
259.312 kPa ↓99.5769
BPR 0.38
Press [ENTER] or [ESCAPE] to exit the BPR function and return to the previous
RUN screen and BPR mode.
3.4.5 [P&T] (PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE)
PURPOSE
To provide continuous display of the pressures measured by molbox RFM, the Reynolds
number of the flow through the molbloc, the temperature of the molbloc and other pressure
measurement information depending on whether a molbloc-L or molbloc-S is connected to
molbox RFM.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM continuously measures pressures and molbloc temperature and uses these
measurements to calculate flow.
The pressure at the molbloc upstream and downstream ports is read by two absolute
Reference Pressure Transducers (RPTs). In molbloc-L operation, the flow is calculated from
the differential pressure across the molbloc. The differential pressure is calculated as the
difference between the two absolute RPT measurements (upstream - downstream) and is
displayed in the pressure screen. If the molbox RFM is equipped with the microrange option,
differential pressure below 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi) is measured by the microrange option’s low
differential pressure RPT.
In molbloc-S operation, the flow is calculated from the molbloc-S upstream pressure. The
upstream pressure may be read by either one or both of the RPTs, depending on which BPR
mode is used (see Section 3.6.9). When molbox RFM is in a valve state called BPR OFF,
the molbloc-S downstream pressure is not measured and both RPTs are used to measure
the molbloc-S upstream pressure. Their readings are averaged to reduce the uncertainty of
the molbloc-S upstream pressure measurement. An indicator is used next to the “downstream”
RPT value to show whether the RPT is currently measuring the molbloc downstream or
upstream pressure. Whenever the molbloc-S downstream pressure is measured, the BPR is
calculated and shown in the P&T pressure screen. When both RPTs measure the upstream
pressure (BPR OFF mode), the indicated pressure for both RPTs is adjusted to equal the
average of the two using the dynamic tare and BPR is no longer displayed.
Since the displays and operation of the P&T pressure screen are different for molbloc-L and
molbloc-S operation, they are described separately in the OPERATION sections below.
For temperature measurement, two Platinum Resistance Thermometers (PRTs) are embedded
in each molbloc. These are connected to the molbox RFM by the molbox to molbloc cable.
The molbox RFM ohmic measurement system reads the resistance of the PRTs and
calculates molbloc temperature.
molbox RFM continuously calculates the Reynolds number of the flow through the molbloc.
molbox RFM’s current pressure and temperature readings as well as the Reynolds number of
the current flow can be displayed using the P&T function.
Page 59 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 70

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
OPERATION – molbloc-L Operation
Press [P&T] from any run screen. The display is:
1. Pressure read by the upstream RPT (left), the downstream
RPT (right) and the pressure unit of measure (middle).
2. The current differential pressure in the current pressure unit
of measure. <DP> indicates the value is differential pressure.
<mDP> indicates the measurement is from the microrange
differential RPT (if present).
3. Current Reynolds number of the flow through the molbloc.
Pressing [P&T] again or the [+/-] key toggles between the pressure screen and the
temperature screen:
97.788 kPa 97.783
mDP 0.005 Re 0.02
1. The average molbloc temperature in the current unit of
measure (upstream + downstream/2).
2. The temperature measured by the upstream molbloc platinum
resistance thermometer in the current unit of measure.
3. The temperature measured by the downstream molbloc platinum
resistance thermometer in the current unit of measure.
21.80ºC
21.82ºC 21.78ºC
To leave the P&T function and return to the MAIN run screen, press [ESCAPE].
To change the pressure and/or temperature unit of measure, see Sections 3.5.2 and 3.5.3.
OPERATION – molbloc-S operation
1. The current pressure read by the upstream (left) and
downstream (right) RPTs and the current pressure unit of
measure (middle). In BPR OFF or Auto modes, tare is
automatically applied to these readings. In BPR ON mode,
tare is never applied.
2. Arrow to indicate which pressure is being read by the
“downstream” RPT. Down arrow indicates downstream
pressure, Up arrow indicates upstream pressure.
3. The current BPR (ratio of downstream to upstream absolute
pressure).
4. Current Reynolds number.
259.31 kPa ↓ 99.577
BPR 0.38 Re 11039
Pressing [P&T] again or the [+/-] key toggles between the pressure screen and the
temperature screen:
1. The average molbloc temperature in the current unit of
measure (upstream + downstream/2).
2. The temperature measured by the upstream molbloc platinum
resistance thermometer in the current unit of measure.
3. The temperature measured by the downstream molbloc platinum
resistance thermometer in the current unit of measure.
To leave the P&T function and return to the MAIN run screen, press [ESCAPE].
To change the pressure and/or temperature unit of measure, see Sections 3.5.2 and 3.5.3.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 60
21.80ºC
21.82ºC 21.78ºC
Page 71

3. OPERATION
3.4.6 [DISPLAY]
PURPOSE
To select, from a variety of choices, the information that is displayed in the molbox RFM main
run display.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM supports a variety of ADVANCED FLOW MEASUREMENT functions that are
generally displayed on the second (bottom) line of the molbox RFM display. In summary, the
available DISPLAY functions included are:
RATE: Calculates and displays the current rate of change of flow in current flow
units/second (see Section
3.4.6.1). This function is a useful indication of
stability of the flow being measured. It is often used as a “go/no go” criterion
for when to take data when comparing molbox RFM and a DUT (e.g., in a
calibration).
AVERAGE: Calculates the average flow measurement over a user specified period of time
and displays the average, the standard deviation about the mean and a
countdown in seconds to the next average (see Section
3.4.6.2). This function
is often used to filter out flow noise in an unstable system or to gather a
corresponding sample when comparing molbloc/molbox
measurements to
another device with a long integration time (e.g., a volumetric flow standard).
The magnitude of the noise is quantified by the standard deviation about the
mean. A second screen allows the instantaneous flow values to be viewed
during an averaging cycle.
the
HI/LO: Records and displays the maximum and minimum flows measured since HI/LO
reset (see Section
and maximum
3.4.6.3). This function is used to keep track of the minimum
flow observed over a period of time or to monitor whether a flow
min/max limit has been exceeded.
TOTAL: Totalizes the mass or volume flowed over a period of time (see Section
3.4.6.4). Used to measure total mass or volume over
a period of time. Can be
useful in calibrating or verifying a totalizing flow device, when comparing
molbloc/molbox to a gravimetric standard or to add or remove a specific
quantity of mass or volume to/from a system.
UNIT: Displays the measurement of flow through the molbloc simultaneously in a
second flow unit (see Section
working with an unfamiliar flow unit of measure
3.4.6.5). This function is convenient when
to simultaneously display a
familiar unit or any time a real time flow unit conversion is desired.
DEVIATION: Continuously calculates and displays the deviation, in % of reading, between
the current flow measured by molbox RFM and a target flow defined by the
user (see Section
3.4.6.6). This function is useful in quickly calculating
the
error of a DUT’s measurement or control, or the evolution of flow around and/or
away from a desired set point.
FREEZE: Captures and displays the instantaneous flow value measured by molbox RFM
when the [ENTER] key is pressed (see Section 3.4.6.7). This function is useful
to record the flow present at the time of an operator observed trigger event.
CLEAN: Blanks out the second line of the display (see Section 3.4.6.8). This function is
used when a simple display of
flow measured by the molbox RFM, without
additional information, is desired.
Page 61 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 72

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
OPERATION
To select a DISPLAY function, press [DISPLAY] from the MAIN run screen.
The display is:
The cursor is on the active DISPLAY function. Selecting a DISPLAY function returns to the
MAIN run screen with the selected function active.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE for a summary of DISPLAY functions and Sections 3.4.6.1
through 3.4.6.8 for detailed information on each DISPLAY function.
In molbloc-S operation, at times, the back pressure ratio, BPR, will be too high for molbox
RFM to calculate a meaningful flow value. When this occurs, the top line of the run screen
display always reads <BPR HI> and the bottom line shows the label <BPR> and the
current measured BPR value. This display has priority over the appearance of the display
functions described in this section, but the display will return to normal when the BPR
returns to a usable level for molbloc-S measurements (see Section 3.1.2).
1avg 2rate 3hi/lo
4total 5unit 6dev ↓
7freeze 8clean
The default DISPLAY function is RATE which causes the second line of the display to
show <R> followed by the current rate of change of flow in current flow unit of measure
per second (see Section 3.4.6.1).
3.4.6.1 <1RATE>
PURPOSE
To activate the RATE DISPLAY.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
OPERATION
To activate the RATE DISPLAY press [DISPLAY] and select <1rate>. Selecting <1rate>
returns to the MAIN run screen with the RATE DISPLAY active.
With the RATE DISPLAY active, the MAIN run screen is:
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. Current rate of change of flow in current flow
unit of measure per second.
* 101.27 sccm N20
R 0.03/sec
The RATE DISPLAY is different and separate from the stability setting that
is used to set the stability criterion on which the Ready/Not Ready
indication is based (see Sections
rate
current
of change to be displayed and has NO affect on the stability
setting or the Ready/Not Ready condition.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 62
3.1.3). The RATE DISPLAY only causes the
Page 73

3. OPERATION
To go to a DISPLAY other than RATE, press [DISPLAY] and make a new
DISPLAY choice.
3.4.6.2 <2AVG> (AVERAGE)
PURPOSE
To activate the AVERAGE DISPLAY and/or adjust the period of time over which
averaging occurs.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
OPERATION
To access the AVERAGE DISPLAY, press [DISPLAY] and select <2avg>.
The display is:
Averaging Period:
1. Edit field for averaging period in seconds.
Default is 20. Minimum 3, maximum 999.
20 s
Edit the averaging time period if desired. Pressing [ENTER] returns to the MAIN
run screen with the AVERAGE DISPLAY active.
With the AVERAGE DISPLAY active the MAIN run screen is:
1. Average flow measured over last completed
averaging period.
2. Standard deviation of last completed
averaging period.
3. Countdown in seconds until completion of ongoing averaging period.
* 101.99 sccm N20
δ 0.06 18 sec
The AVERAGE DISPLAY has a second screen that allows the instantaneous
flow readings to be viewed while an averaging cycle is running. Pressing [+/-]
toggles between the MAIN run AVERAGE screen and the instantaneous values
AVERAGE screen. The instantaneous AVERAGE screen is:
1. Instantaneous flow value at molbox RFM’s
normal integration rate.
2. Countdown in seconds until completion of ongoing averaging period.
3. Current rate of change of flow in flow unit of
measure/second..
* 101.59 sccm N20
R 0.0025 18 sec
Page 63 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 74

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.4.6.3 <3 HI/LO>
PURPOSE
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
OPERATION
To activate the HI/LO DISPLAY press [DISPLAY] and select <3hi/lo>. Selecting
<3hi/lo> resets the HI/LO values and returns to the MAIN run screen with the
HI/LO DISPLAY active. With the HI/LO DISPLAY active, the MAIN run screen is:
To activate the HI/LO DISPLAY.
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. Highest flow observed since HI/LO reset.
3. Lowest flow observed since HI/LO reset.
* 101.22 sccm N20
H 101.44 L99.113
The HI/LO values change each time a new HI or LO flow value occurs.
The HI/LO record can be reset at any time by pressing [ENTER] allowing a
HI/LO reset without going back through the DISPLAY menu.
Changing the flow unit of measure, the gas, the K factor or running a TARE
function while in HI/LO resets the HI/LO record.
To go to a DISPLAY other than HI/LO, press [DISPLAY] and make a new
DISPLAY choice.
3.4.6.4 <4TOTAL> (TOTALIZER)
PURPOSE
To activate the TOTALIZER DISPLAY.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
OPERATION
To activate the TOTALIZER DISPLAY, press [DISPLAY] and select <4total>.
The display is:
Totalizing period:
1. Edit field for time over which to totalize
(hh:mm:ss). Default period is 00:10:00;
maximum 99:59:59.
00:10:00
Edit the totalizing period as desired. Pressing [ENTER] returns to the MAIN run
screen with the TOTALIZER DISPLAY active. With the TOTALIZER DISPLAY
active the MAIN run screen is:
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 64
Page 75

3. OPERATION
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. Total mass or volume accumulated over
elapsed totalizing run time.
3. Units of measure of mass or volume (derived
from the current flow unit) of the totalized
value (see Table 12). The units of measure
are not shown if the screen space is needed
to show a large totalized value.
4. Elapsed totalizing time (hh:mm:ss). Always
starts from zero and counts up until totalizing
period elapses.
* 101.45 sccm N20
Σ0.00 scc 00:00:00
Press [ENTER] to start totalizing. The elapsed time counter starts and the total
mass or volume begins to accumulate. Totalizing continues until the set totalize
period is complete. When the totalizing period is complete, molbox RFM sounds
three beeps and displays the totalizing complete screen in which the total flow or
volume and elapsed totalizing time are frozen with totalizing time NOT flashing.
To start a new totalizing run from the totalizing complete screen, press [ENTER].
This clears the previous total, resets to the totalizing timer and starts totalizing.
Certain functions cannot be executed while totalizing. These functions
include change K, change gas, change flow unit of measure, tare. If <Access
restricted while totalizing> is displayed when a function key is pressed
during totalizing, the function is one that cannot be executed while
totalizing. To execute the function, abort the totalizing run or wait until
after the run has completed. This feature is to avoid accidentally aborting
or corrupting a totalizing run.
To set a new totalizing time without going back through the [DISPLAY]
menu, press [ENTER] and select <2new> from the TOTALIZER screen. To
freeze a split total without stopping the totalizing run, press [ENTER] or
[ESCAPE] while totalizing.
Table 12. Flow Units and Corresponding Total Mass or Volume Units
FLOW UNIT
mol/s mol
kg/s kg
mg/s mg
slh or slm sl
sccm scc
scfh or scfm scf
Ulm ul
Uccm ucc
ucfm or ucfh ucf
plm or plh pl
pccm pcc
pcfm or pcfh pcf
lm or lh l
ccm cc
m3m or m3h m3
cfm or cfh cf
TOTAL MASS OR
VOLUME UNIT
Page 65 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 76

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.4.6.5 <5UNIT>
PURPOSE
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
To activate the UNIT DISPLAY.
OPERATION
To activate the UNIT DISPLAY, press [DISPLAY] and select <5unit>. The unit
of measure that will be used for the second line of the MAIN run screen display
must then be selected. The unit selection process is identical to that of the
[UNIT] function key (see Section 3.4.3). Once the unit has been selected
operation returns to the MAIN run screen with the UNIT DISPLAY active.
With the UNIT DISPLAY active the MAIN run screen is:
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. Flow equivalent of the current measured flow
in the alternate flow unit of measure.
3. Alternate flow unit of measure selected in
UNIT DISPLAY.
* 101.27 sccm N20
= 0.1013 slm
The reference temperature setting for the user units (i.e., uccm and ulm)
(see Section 3.4.3.3) and the temperature and pressure settings for volume
units (see Section 3.4.3.4) apply to the units in the main UNIT selections as
well as the UNIT DISPLAY selection. Therefore, it
is not possible to
simultaneously display user units or volume units with different reference
temperatures and/or pressures. When you change the temperature or
pressure setting for one type of unit, you change it for that type of unit
wherever it is used. It is possible to show the difference between volumetrically
based mass flow units at 0 °C and another temperature by choosing the “s”
version (e.g., sccm) for 0 °C as the main unit and a user unit with a different
reference temperature as the UNIT DISPLAY, or vice-versa.
To go to a DISPLAY other than UNIT, press [DISPLAY] and make a new
DISPLAY choice.
3.4.6.6 <6DEV>
PURPOSE
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 66
To activate the DEVIATION DISPLAY and/or edit the deviation target.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
Page 77

3. OPERATION
OPERATION
To activate the DEVIATION DISPLAY, press [DISPLAY] and select <6dev>.
The display is:
Target:
1. Edit field to edit the target value from which
the deviations is to be measured.
100.00 sccm
Edit the desired target value. Pressing [ENTER] returns to the MAIN run screen
with DEVIATION DISPLAY active using the entered target value.
With the DEVIATION DISPLAY active the MAIN run screen is:
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. Target value in current flow unit of measure.
3. Deviation of current flow from target value in
% of reading.
* 100.53 sccm N20
D 0.53 % T 100.00
Pressing [ENTER] from the MAIN run screen when the DEVIATION DISPLAY is
active goes directly to the target editing screen. This allows the target value
to be changed without going through the DISPLAY menu.
The DEVIATION DISPLAY target value is the value from which % deviations (D)
are measured by the DEVIATION DISPLAY following:
D = (current flow – target)
target
x 100
To go to a DISPLAY other than DEVIATION, press [DISPLAY] and make a new
DISPLAY choice.
3.4.6.7 <7FREEZE>
PURPOSE
Page 67 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
To activate the FREEZE DISPLAY.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
OPERATION
To activate the FREEZE DISPLAY press [DISPLAY] and select <7freeze>.
Selecting <7freeze> returns to the MAIN run screen with the FREEZE DISPLAY active.
Page 78

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
With the FREEZE DISPLAY active, the MAIN run screen is:
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. Flow measured in the current flow units when
[ENTER] was pressed (displays 0.00 by
default when FREEZE DISPLAY is first
activated).
* 101.75 sccm N20
F 99.24
Pressing [ENTER] causes the current flow measured by molbox RFM to be
captured and displayed.
If the flow measurement unit is changed while the FREEZE DISPLAY is active,
the FREEZE value defaults back to zero.
To go to a DISPLAY other than FREEZE, press [DISPLAY] and make a new
DISPLAY choice.
3.4.6.8 <8CLEAN>
PURPOSE
To activate the CLEAN DISPLAY.
See Section 3.4.6, PRINCIPLE.
OPERATION
To activate the CLEAN DISPLAY press [DISPLAY] and select <8clean>.
Selecting <8clean> returns to the MAIN run screen with the CLEAN DISPLAY active.
With the CLEAN DISPLAY active, the MAIN run screen is:
1. Standard MAIN run screen top line.
2. “Clean” second line.
* 101.45 sccm N2O
To go to a DISPLAY other than CLEAN, press [DISPLAY] and make a new
DISPLAY choice.
3.4.7 [MICRO] (OPTIONAL)
PURPOSE
To turn ON and OFF automatic operation of the optional MICRORANGE FLOW
MEASUREMENT function.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 68
Page 79

3. OPERATION
PRINCIPLE
Use of the microrange feature improves molbox RFM flow measurements while using
molbloc-L only. Microrange has no effect and is disabled during molbloc-S operation.
The molbox RFM microrange option (if present) improves molbox RFM flow measurements
when using a molbloc-L element below 10 % FS of its measurement range. Flow measurement
resolution and accuracy are enhanced by implementing a low differential pressure RPT which
improves the resolution and accuracy of differential pressure measurement when differential
pressure is below 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi). See Section 3.1.5 for microrange operational principles
and Section 1.2.4.1.1 for microrange specifications.
In automatic microrange mode, use of the microrange option to improve flow measurement is
optimized in a manner that is transparent to the user. In particular, the transition between the two
different types of differential pressure measurement is smoothed out by weighted averaging of
the differential values in a transition zone between 10 and 12.5 kPa differentials (1.5 to 1.8 psi).
The MICRO function turns ON and OFF the microrange option’s automatic mode.
With automatic microrange OFF, the microrange option differential pressure RPT
measurements are not used at all (unless manual microrange is ON, see Section 3.6.7). With
automatic microrange option ON, the differential pressure value used to calculate mass flow
can come from the difference between the upstream and downstream RPTs, the microrange
differential RPT or a combination of the two during the transition from one method to the other.
The microrange option can also be operated in a manual mode (see Section 3.6.7).
OPERATION
The MICRO function can be operated at any time from the main run screen.
Pressing [MICRO] causes automatic microrange to turn ON if it is OFF and to turn OFF if it is
ON. When [MICRO] is pressed, the molbox RFM displays a 3 second message indicating
whether it is turning automatic microrange ON or OFF and then returns to the main run
screen in the new condition. Automatic microrange ON is indicated by an <m> in the
microrange status character of the main run screen. If molbox RFM is not equipped with the
microrange option, a 5 second message indicates that the microrange option is not installed.
Don’t confuse this message with <Access denied> which displays when the security level
setting restricts [MICRO] key access (see Section 3.6.2).
Turning microrange OFF may reduce the accuracy of flow measurements below 10 % of the
molbloc flow measurement range and lead to unexpected results.
Automatic microrange option ON is indicated by an “m” in the microrange option
designator character of the main run screen (top line, 6th character from the right).
Microrange option OFF is indicated by a blank designator (see Section3.2).
Use of the MICRO function overrides the current setting of manual microrange option made
by pressing [SPECIAL] and selecting <7micro> (see Section 3.6.7). If manual microrange is
ON, pressing [MICRO] turns OFF manual microrange and turns ON automatic microrange.
Page 69 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 80

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.4.8 [MOLBLOC]
PURPOSE
To initialize and/or rapidly identify a molbloc that is connected to molbox RFM.
PRINCIPLE
molblocs carry an EEPROM on which are stored the molbloc identification header, molbloc
specific flow calibration coefficients and the zero offset of the molbloc platinum resistance
thermometers. molbox RFM must have this information to accurately identify the molbloc to
which it is connected and to correctly calculate flow through the molbloc. molbox RFM does
not continuously read the information off the molbloc EEPROM. It reads and loads the
information on the molbloc EEPROM each time it powers up. However, if the molbloc
connected to the molbox is changed without turning the molbox RFM OFF and back ON, the
new molbloc and the previous molbloc’s calibration information will continue to be used.
The [molbloc] function key provides a rapid and simple way of causing the molbox RFM to load the molbloc to which it is connected and display a summary of its characteristics. This is useful when changing molblocs or to identify the molbloc that is currently in service.
More complete molbloc information, including a list of gases for which the molbloc has
specific calibration coefficients, can be accessed by pressing [SETUP] and selecting
<4molbloc> (see Section 3.5.4).
OPERATION
Press the [molbloc] function key at any time from the main run screen. molbox RFM will
take a moment to read the molbox EEPROM and then display a summary of the molbloc
identification header including range designation, serial number and calibration date. This
screen is displayed for 5 seconds before operation returns to the main run screen.
If molbox RFM is unable to establish communications
with a molbloc, the display is:
molbloc not detected
ENTER searches again
Pressing [ESCAPE] returns to the run screen. Pressing [ENTER] repeats the molbloc search
just as if [molbloc] had been pressed again.
There is a risk of corrupting the molbloc EEPROM information when molbloc to molbox
RFM electrical connections are made with the molbox RFM power ON. The recommended
procedure is to power OFF the molbox RFM when making and breaking molbloc
electrical connections. The SOFT POWER OFF does not remove power from the
molbloc cable, so the power cord must be disconnected to power OFF the molbox RFM.
3.4.8.1 molbloc-L AND molbloc-S SIZE AND RANGE DESIGNATIONS
Until mid-1999, molbloc-L elements (molbloc-S was not available at the time) were
always identified by “Range”. The molbloc-L “Range” is the molbloc’s nominal full
scale flow in Nitrogen (N2) at an operating pressure of 250 kPa absolute. Actual
molbloc ranges change with the molbloc pressure dependent calibration type and
gas (see Section
elements have been designated by size with a sizing code (see Table 13).
1.2.4.1.2). Since mid-1999, in addition to nominal range, molbloc-L
On molbloc-L EEPROMs, the molbloc is still identified by its nominal
than by its size. The identification of the molbloc displayed by [SETUP],
<4molbloc> identifies molbloc-L by both its nominal range and sizing code.
molbloc-L size and range designation correspondence are given in Table 13.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 70
range
rather
Page 81

3. OPERATION
Table 13. molbloc-L Size and Nominal Range Designations
molbloc
“NOMINAL
RANGE”
DESIGNATION
10 sccm
50 sccm
100 sccm
200 sccm
500 sccm
1 slm
5 slm
10 slm
30 slm
100 slm
molbloc-L SIZE
DESIGNATION
1E1
5E1
1E2
2E2
5E2
1E3
5E3
1E4
3E4
1E5
molbloc-S elements are also identified by size designations, each of which relate
to a specific molbloc-S K
value. molbloc-S flow ranges depend on calibration
F
type and the pressure limitations of the application and molbox used. For
information on the possible molbloc-S flow ranges with various operating
pre s s u re s , se e Section 1.2.4.2.2). molbloc-S size and K
value correspondence are
F
given in Table 14.
Table 14. molbloc-S Size Designation and Pressure to Flow Conversion Ratio (KF)
K
F
(sccm/kPa)
50
100
200
500
1 000
2 000
5 000
10 000
molbloc-S SIZE
DESIGNATION
5E1-S
1E2-S
2E2-S
5E2-S
1E3-S
2E3-S
5E3-S
1E4-S
3.4.9 [RES]
PURPOSE
To set the resolution of molbox RFM’s display of the flow through the molbloc and other flow
display and entry values.
PRINCIPLE
The resolution with which the flow measured by molbox RFM is displayed can be adjusted. This
feature can be used to reduce the resolution when lower precision measurements are being
made and additional digits might confuse or distract the operator.
The resolution setting determines the number of digits with which flow is displayed. The desired
resolution is calculated based on the nominal nitrogen gas full scale of the molbloc range in
the current flow unit of measure and then rounded to the furthest digit to the right (i.e., resolution
of 0.01 % on a 100 sccm molbloc is 0.01 sccm).
Page 71 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 82

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The default (and maximum) resolution setting is 0.01 % of the molbloc full scale. The RES
setting does not affect the resolution of flow information transmitted remotely.
Remote information is always sent using flow resolution of 0.001% of molbloc full scale
(0.0001% when microrange is active).
OPERATION
To access the resolution function press [RES].
Press the [←] to decrease the resolution and [→] to increase the resolution. Each press
changes the resolution by a factor of 10. Once the desired resolution is displayed, press
[ENTER] to set the selected resolution and return to the main run screen.
The resolution setting affects the display of the measured flow as well as other
indications and settings (e.g., quantities shown by the [DISPLAY] functions).
3.5 [SETUP]
PURPOSE
The [SETUP] key accesses a menu of commonly used molbox RFM functions and features that do NOT
have direct function keys. These functions include:
<1flowU> To customize the flow unit choices available under [UNIT] (see Sections 3.5.1 and 3.4.3).
<2presU> To
select/change the unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays pressure values
(see Section 3.5.2).
<3temp
U> To select/change the unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays temperature values
(see Section 3.5.3).
molbloc> To initialize a molbloc when it is connected to molbox RFM and/or to identify the molbloc
<4
currently connected to molbox RFM (see Section 3.5.14).
<5stab> To
change the stability limit that serves as the criterion for the flow Ready/Not Ready
indication (see Sections 3.5.5 and 3.1.3).
<6adj> To s
et an adder and multiplier to adjust molbox RFM flow readings (see Section 3.5.6).
OPERATION
To access the SETUP menu, press [SETUP] from the MAIN
screen. The display is:
run
1flowU 2presU 3tempU
4molbloc 5stab 6adj
See Sections 3.5.1 to 3.5.6 for detailed information on each SETUP function.
3.5.1 <1flowU>
PURPOSE
To customize the selection of flow units of measure that are available for selection from the
[UNIT] function key (see Section 3.4.3).
PRINCIPLE/OPERATION
See Section
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 72
3.4.3.5.
Page 83

3. OPERATION
3.5.2 <2presU>
PURPOSE
To select/change the unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays pressure values.
OPERATION
To set the unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays pressure values, press [SETUP]
and select <2presU>.
The display is:
Pressure unit type:
1SI 2other 3user
Select the unit type desired, then select the unit desired. After the unit selection, operation
returns to the previous run screen with the selected pressure unit of measure active.
The pressure units of measure available are listed in Table 15.
Table 15. Pressure Units of Measure Available
<1SI> <2Other> <3User>*
<1Pa>
<2kPa>
<3mPa>
<4mbar>
<5bar>
<6mmHg>
<7mmWa>
*3User: User defined unit.
<1psi>
<2psf>
<3inHg>
<4inWa>
<5kcm2>
<1user>
The “user” unit is defined in terms of user units/Pa when the user unit is selected.
See Section 7.1.1 for definition of the pressure unit conversions used by molbox RFM.
3.5.3 <3tempU>
PURPOSE
To select the unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays temperature values.
OPERATION
To set the unit of measure in which molbox RFM displays temperature values, press
[SETUP] and select <3tempU>.
The display is:
Select the desired unit. After the unit selection, operation returns to the run screen with the
selected temperature unit active.
See Section 7.1.2 for definition of the temperature unit conversions used by molbox RFM.
Page 73 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Temperature unit:
1celcius 2fahrenheit
Page 84

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.5.4 <4MOLBLOC>
PURPOSE
To initialize a molbloc when it is connected to molbox RFM and/or to identify the molbloc
currently connected to molbox RFM. To determine the gases with which the molbloc has
been calibrated.
PRINCIPLE
molbox uses molbloc specific calibration information contained in the molbloc's EEPROM to
determine whether it should operate in molbloc-L or molbloc-S mode and in its calculation of
flow through the molbloc. For the molbox RFM to correctly calculate the flow through the
molb l o c , i t must use the specific information for the molbloc that is currently connected. molbloc
EEPROM information is r ead and stored by molbox RFM in the molbox power up sequence
when it is turned on, or by selecting [SETUP], <4molbloc>.
The <4molbloc> function may be used any time there is a change in the molbloc connected
to a channel to assure that molbox RFM uses the correct molbloc information on subsequent
measurements. The <4molbloc> function can also be used to display identifying information
on the molbloc currently connected to the molbox RFM and to determine the gases with
which the molbloc has been calibrated.
OPERATION
To access the molbloc function, press [SETUP], and <4molbloc>.
Operation is similar to operation of the [molbloc] direct function key (see Section 3.4.8).
However, when in the molbloc identification screen, pressing [ENTER] causes a list of the
gases for which the molbloc has specific calibration coefficients to be displayed. The gases
are listed using their chemical abbreviationsError! Reference source not found.. After
viewing, press [ESCAPE] to return to the current run screen.
3.5.5 <5STAB>
PURPOSE
To change the stability limit that serves as the criterion for the flow Ready/Not Ready
indication (see Section 3.1.3).
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM continuously monitors the rate of change of
connected and compares this rate to the stability limit to make a Ready/Not Ready determination
(see Section 3.1.3). The STABILITY function allows the stability limit to be adjusted by the user to
increase or decrease the stability required for a Ready (<*>) condition to occur.
The default stability limit is ± 0.5 sccm/second (or its equivalent in another flow unit).
The stability limit value is automatically converted when the flow unit of measure
is changed.
flow through the molbloc to which it is
The stability limit is separate and different from the RATE DISPLAY function
(see Section 3.4.6.1) which allows the current rate of change of pressure to be displayed.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 74
Page 85

3. OPERATION
OPERATION
To adjust the stability limit press [SETUP] and select <5stab>. The display is:
Flow stability test:
1. Entry field for setting the desired stability limit in the current
flow unit of measure. Recalls the default stability limit or the
last stability limit set.
0.5 sccm/s
Edit the stability limit setting as desired. Pressing [ENTER] activates the new stability limit
and returns to the current run screen.
The stability limit value is automatically converted when flow units of measure
are changed.
The [RES] setting affects the resolution of the stability limit value. If the stability limit
display does not have enough resolution to set the desired value, use [RES] to adjust the
resolution (see Section 3.4.9).
3.5.6 <6ADJ>
PURPOSE
To apply adder (FA) and multiplier (FM) coefficients to the flow measured by molbox RFM.
PRINCIPLE
The ADJ function gives the user the capability to adjust mass flow readings made by molbox
RFM. This is accomplished by setting an adder and a multiplier.
The adder (FA) and multiplier (FM) adjust the displayed value of the flow through the molbloc
as calculated by the molbox RFM following:
corrected flow = (calculated flow * FM) + FA
If a K factor is active (see Section 3.4.1), the adder and multiplier are applied to the
calculated flow before the K factor is applied.
Using the Flow ADJ Function with molbloc-L to Handle a Gas Mixture
Use of ADJ to handle gas mixtures as described below is NOT valid with molbloc-S.
The flow ADJ function can be used to adjust flow readings to measure a gas mixture if the
molecular weight and relative content of each component gas is known. Note that this
method does not take into account the actual viscosity or compressibility factor of the gas
mixture. The thermodynamic properties of the highest concentration gas are used. Therefore,
the uncertainty in the measured flow is increased and the method is best when the highest
concentration gas is greater than 90% of the mixture.
To use this feature, set the molbox RFM [GAS] (see Section 3.4.2) to the highest
concentration gas, then adjust the flow multiplier by:
molecular weight of the mix
molecular weight of the gas selected on the molbox
Page 75 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 86

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
For example, to adjust a gas mix that is 95 % Nitrogen (N2) and 5 % Oxygen (O2):
n Calculate the molecular weight of the mix.
N
molecular weight = 28.016
2
O
molecular weight = 31.999
2
Mix molecular weight = (28.016 x 0.95) + (31.999 x 0.05) = 28.215
o Select N
p Calculate:
, the highest concentration gas, as the molbox RFM gas.
2
molecular weight of the mix
molecular weight of the gas selecton on the molbox
=
28.215
28.016
=
1.0071
q Set flow multiplier in ADJ function to 1.0071.
OPERATION
To access the ADJ function press [SETUP] and select
<6adj>. The display is:
Adder: 0 sccm
Mult: 1.00000
Edit the values as desired. Pressing [ENTER] returns you to the MAIN run screen with the
edited adder and multiplier values applied.
When the <6adj> function is active (an adder or multiplier other than 0 and 1 is entered), there is
an indicator on the top line of the main run screen. The indicator is an “A” in the character to the
right of the molbox flow units. The indicator uses the same position as the “K” indicator (see
section 3.2). If there is an ADJ and K active at the same time, the indicators will alternate,
appearing every other update of the flow value (about once each second).
The flow adder and multiplier of the ADJ function, if different from 0 and 1, alter the flow
readings made by the molbox. The ADJ function is always "ON". When using adders and
multipliers, great caution should be taken to ensure that they are entered and changed
correctly and that they are 0 and 1 if no adder or multiplier effect is desired. The ADJ
function is restricted in all User Security Levels except “none” to protect against
unintentional flow adjustment (See section 3.6.2).
3.6 [SPECIAL]
PURPOSE
The [SPECIAL] key accesses a menu of molbox RFM functions and settings that are less commonly or
not normally used in regular operation. These functions include:
<1reset> Access and execute various reset options (see Section 3.6.1).
<2
level> Set user protection levels that restrict access to certain functions and to edit the user
password (see Section 3.6.2).
<3ul>
<4cal> View and adjust the molbox RFM pressure transducers and reference resistors (see Section 3.6.4).
<5prefs> Set display screen saver time, unit ID number and date and time (see Section 3.6.5).
<6remote> View and edit molbox RFM COM port (RS232) and IEEE-488 interface settings (see Section 3.6.6).
<7log> View and/or clear the molbox RFM event log (see Section 3.6.7).
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 76
Set upper pressure limit alarm (see Section 3.6.3).
Page 87

3. OPERATION
<8head> Set the height for the pressure fluid head correction (see Section 3.6.8).
<9BPR> Set the back pressure ratio (BPR) mode (for molbloc-S operation only) (see Section 3.6.9).
OPERATION
To access the SPECIAL menu, press [SPECIAL] from the MAIN run screen.
1reset 2level 3ul
The display is:
4cal 5prefs 6remote ↓
7log 8head 9BPR
Select the desired function.
See Sections 3.6.1 to 3.6.9 for detailed SPECIAL function descriptions.
Some screens (e.g., the SPECIAL menu) go beyond the two lines provided by the display. This is
indicated by a flashing down arrow in the second line of the display. Press the [←] and [→] keys to
move the cursor to access the lines that are NOT visible or directly enter the number of the hidden
menu choice if you know it.
3.6.1 <1RESET>
PURPOSE
To reset various molbox RFM settings to default or factory values.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM stores its user definable settings in non-volatile memory. The reset menu allows
the user to selectively or completely reset these settings to factory defaults. Reset clears
settings that the user may have made, and should be used only to restore the molbox RFM to a
known state. molbox RFM will go through its reboot routine after any type of reset is executed.
OPERATION
To access the reset choices press [SPECIAL] and
select <1reset>. The display is:
Select the desired reset. After confirmation, the reset occurs. A reset always puts the molbox
RFM through its start up routine as if power had been turned OFF and back ON.
See Sections 3.6.1.1 through 3.6.1.5 for detailed information on the specific reset choices.
RESET functions change user settings that affect flow measurement. If not used
properly, resetting can cause out of tolerance measurements. RESET functions should
only be used by qualified personnel with reference to this manual for information on the
RESET functions.
1sets 2units 3com
4cal 5all
Page 77 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 88

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.6.1.1 <1SETS>
PURPOSE/OPERATION
To access Reset - Sets, press [SPECIAL] and select <1reset>, <1sets>.
Reset - Sets clears and sets to default the user settings for various measurements.
These include:
• Flow unit of measure to sccm (see Section
• Pressure unit of measure to kPa (see Section
3.4.3).
3.5.2).
• Temperature unit of measure to °C (see Section 3.5.3).
• Gas type to N2 (see Section 3.4.2).
Stability criterion to 0.5 sccm (see Section 3.5.5).
•
• K factor to 1 (see Section 3.4.1).
• DISPLAY function to Rate (see Section
3.4.6.1).
• RPT Tare value to 0 (see Section 3.4.4.1).
• Tare preference to upstream pressure (see Section 3.4.4.1.1).
• Flow adder to 0 and flow mu
ltiplier to 1 (see Section 3.5.6).
• Resolution to 0. 01 % (see Section 3.4.9).
BPR mode to Auto (see Section 3.6.9)
•
3.6.1.2 <2UNITS>
PURPOSE/OPERATION
To access Reset - Units, press [SPECIAL] and select <1reset>, <2units>.
Reset - Units clears and sets to default all UNIT OF MEASURE functions. These include:
• Six flow units of measure selectable from [UNIT] to defaults (see Section
• Flow unit
eference temperature for uxxx units of measure to 0 °C (see Section 3.4.3.3).
• R
• Volume flow unit of measure conditions
of measure to sccm (see Section 3.4.3).
to molbloc for temperature and
standard atmospheric pressure for pressure (see Section 3.4.3.4).
• Pressure unit of measure to kPa (see Section 3.5.2).
• User pressure unit coefficient to 1.00/Pa (see Section 3.5.2).
• Temperature unit of measure to °C (see Section 3.5.3).
3.4.3).
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 78
Page 89

3. OPERATION
3.6.1.3 <3COM>
OPERATION/PURPOSE
To access Reset - Com, press [SPECIAL] and select <1reset>, <3com>.
Reset - Com clears and sets to default the molbox RFM communications ports
(see Section 3.6.6). This includes:
• COM1 and COM2
Baud rate: 2 400
Parity: Even
Data bits: 7
Stop bits: 1
Terminating characters: <CR>, <LF>
• IEEE-488 (GPIB)
Address: 10
Terminating characters: <CR>, <LF>
3.6.1.4 <4CAL>
Use special caution with this reset as critical calibration data may be altered.
To access Reset - Cal, press [SPECIAL] and select <1reset>, <4cal>.
Reset - Cal clears and sets to default the user calibration coefficients for molbox
RFM Reference Pressure Transducers (RPTs) (see Section 5.2). If the molbox
RFM has been recalibrated at any time since its original factory calibration, the
recalibration adjustment was done using these user calibration coefficients. The
RPT cal coefficient defaults are:
• Upstream and downstream absolute RPTs:
Adder 0
Multiplier: 1
Calibration Date: 19980101
• Microrange differential RPT:
Adder: 0
Multiplier: 1
PURPOSE/OPERATION
Calibration Date: 19980101
Reset - Cal has NO effect on the reference resistance values used to calibrate
the molbox RFM internal ohmic measurement system (see Section 5.3).
3.6.1.5 <5ALL>
PURPOSE/OPERATION
To return molbox RFM to the original, as delivered factory condition. Performs the
RESET - SETS, UNITS, COM and CAL functions and resets all other settable
values to defaults.
Page 79 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
To access Reset - All, press [SPECIAL] and select <1reset>, <5all>.
Use special caution with this reset as critical calibration data may be altered.
Page 90

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.6.2 <2level>
PURPOSE
To set user protection levels that restrict access to certain functions and to edit the
password required for changing user levels.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM’s front panel user interface provides the means to access all molbox RFM
user defined data, settings and functions including calibration data.
Inadvertent, uninformed or unauthorized altering or deleting of data, settings and
functions could require extensive reconfiguration by the user and might cause invalid
readings. For these reasons, depending upon the application in which molbox RFM is
being used, it may be desirable to restrict access to certain functions. The USER LEVEL
function makes this possible. Four different levels of security are available: none, low,
medium and high.
Access to changing security levels can be left open, or be protected by a password so
that security levels can be used as a convenient way to avoid accidental changing of data
or as a secured means of preventing tampering with molbox RFM settings.
3.6.2.1 SECURITY LEVELS
The security levels are structured to support typical operating environments
as follows:
None This level is intended for use only by the system manager and/or
calibration facility. It allows access and editing in all areas including
critical metrological information and other settings that affect
measurement integrity.
Low Low security is designed to protect the specific metrological information
and SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC AND MAINTENANCE functions of the
system against accidental alteration. It is intended for an advanced
operator performing many different tasks. Low security is the default
user level setting.
Medium Medium security is designed to protect specific metrological information
in the system and to assure that the molbox RFM is operated using
consistent operational parameters.
High High security protects all operating parameters. It is intended to
minimize operator choices (e.g., to perform repeated identical tests
under consistent conditions).
molbox RFM is delivered with the security level set to low to avoid
inadvertent altering of critical internal settings but with unrestricted access
to changing security level setting. It is recommended that the low security
level be maintained at all times and password protection be implemented if
control over setting of security levels is desired.
If there is a risk of unauthorized changing of the security level, changing
authority should be password protected (see OPERATION of this section).
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 80
Page 91

3. OPERATION
The High security level disables remote communications and returns an error
message (“ERROR”) to all remote commands. All other security levels have
NO effect on remote communications.
The security levels are structured to support typical levels of operation.
Specifically, the security levels prevent execution of the functions accessed by
the key strokes marked by “•”.
Table 16. Security Levels - Functions NOT Executed Per Function/Level
KEYS LOW MEDIUM HIGH
[K]
[GAS]
[UNIT]
[UNIT] (change temperature/pressure conditions)
[TARE] (access menu)
[TARE], <1tare>, <select tare pressure>
[TARE], <2purge>, (change purge time)
[TARE], <4AutoZ>, <1on/off>
[TARE], <4AutoZ>, <3edit>
[TARE], <4AutoZ>, <4run>
[P&T]
[DISPLAY]
[DISPLAY], (change times/target)
[MICRO]
[molbloc]
[RES]
[SETUP], <1flowU>
[SETUP], <2presU>
[SETUP], <3tempU>
[SETUP], <4molbloc>
[SETUP], <5stab>
[SETUP], <6adj>
[SPECIAL], <1reset>
[SPECIAL], <1reset>, <3com>
[SPECIAL], <1reset>, <4cal>
[SPECIAL], <1reset>, <5all>
[SPECIAL], <4cal>
[SPECIAL], <4cal>, <any 3edit>
[SPECIAL], <5prefs>
[SPECIAL], <5prefs>, <1ScrSvr>
[SPECIAL], <5prefs>, <2sound>
• •
• •
• •
• • •
• • •
• •
• •
• • •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• • •
• •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• •
• • •
• •
• •
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Page 81 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 92

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Table 17. Security Levels - Functions NOT Executed Per Function/Level
KEYS LOW MEDIUM HIGH
[SPECIAL], <5prefs>, <3time> (make changes)
[SPECIAL], <5prefs>, <4ID>, <2edit>
[SPECIAL], <5prefs>, <5log> (clear log)
[SPECIAL], <6remote>
[SPECIAL], <6remote> (changes settings)
[SPECIAL], <7micro>
[SPECIAL], <8head>
[SPECIAL], <9BPR> (change mode)
Remote communications disabled
OPERATION
molbox RFM is delivered with NO active password so access to the User
Level menu is open. The user level is set to <1Low>. User levels can be
changed freely until a password has been created. RESET functions (see
Section
3.6.1) do not affect the password setting.
(Continued)
• • •
• • •
• • •
• •
• •
• •
• •
•
•
To access the USER LEVEL function, press [SPECIAL], <2level>.
If NO password yet exists or if the
correct password has been entered,
the display is:
Selecting <1change user level> brings
up the restriction menu:
1change user level
3edit password
Restriction: 1none
2low 3medium 4high
Select the desired restriction level, or press [ESCAPE] to return to the current
run screen.
Selecting <2edit passw ord> displays the
user password and allows it to be edited.
Passwords can be up to six numbers in
length and cannot start with a zero.
Password: pppppp
0 disables password
If 0 is entered as the password value, then the password is made inactive and a
password will NOT be required to access the user level menu. This is the factory
default with a security level of <2low>.
Once a password has been entered, the user level cannot be changed without
reentering the password.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 82
Page 93

If there is an active password, the molbox RFM password entry screen
appears.
The user must enter the user defined
password or the factory secondary
password to proceed. When a password
is entered correctly, operation proceeds
to the <1change user level 2edit
password> screen.
The first field, <nnnn>, is the serial number of the molbox RFM, followed by a
second field, <xx>, that counts the number of times that a secondary password
has been used. The second field increments each time a secondary password
is used. The third field, <pppppp>, is for normal password entry.
The factory secondary password is available in case the user password has
been misplaced or forgotten. A factory secondary password can be obtained by
contacting a DHI Authorized Service Provider (see Section 7.2). The factory secondary
password is different for each molbox RFM and changes each time it is used.
3.6.3 <3UL>
PURPOSE
3. OPERATION
RFM SN nnn-xx
Password: pppppp
To set an upper pressure limit above which molbox RFM will produce a warning, interrupt
operation and isolate its internal pressure transducers.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM contains two, high precision reference pressure transducers (RPTs). These
can be fatally damaged by large overpressures. The UL function uses molbox RFM's internal
capabilities to attempt to protect the RPTs against overpressure. molbox RFM continuously
monitors the pressure read by the RPTs. When the pressure passes the level set by the UL
function, molbox RFM warns the operator by sounding an audible alarm. Beyond the UL limit
there is an overpressure limit, which is not user selectable. If the pressure reaches the
overpressure limit, molbox RFM uses its internal valves to isolate the RPTs.
OPERATION
To access the Upper Limit (UL) function, press [SPECIAL], <3ul>. The display is:
The indication is of the current upper limit setting in
the current pressure unit of measure. To specify a
different pressure unit of measure, use [SETUP],
<2presU> (see Section
3.5.2).
Transducer Max Pres:
630.000 kPaa
To change the upper limit, enter the value desired (see max UL limits below) and press
[ENTER]. The display returns to the MAIN run screen with the new upper limit in effect.
The maximum upper limit settings, which are also the default values, are 5 % above the molbox
maximum operating pressure ranges. For molbox RFM, the max UL value is 630 kPa absolute
(91 psia). The overpressure limit, which cannot be edited, is 660 kPa absolute (96 psia)
If the overpressure limit is exceeded, all molbox RFM isolation valves close and normal
operation is interrupted. Normal operation can be reestablished by turning molbox RFM's power
OFF and back ON or pressing [ENTER]. Be sure to correct the situation that led to the
overpressure condition prior to rebooting molbox RFM or pressing [ENTER]. See Sections
3.6.3.1, 3.1.6 for additional details.
Page 83 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 94

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.6.3.1 UPPER LIMIT ALARM AND SEQUENCE
When the pressure reaches the upper limit, molbox RFM continues normal
operation but sounds an audible alarm. The alarm ceases if the pressure is
decreased below the upper limit.
When pressure reaches the overpressure
limit, molbox RFM valves close, normal
operation ceases and the display
indicates:
670.250 kPa 651.780
OVERP! CHK & PWR DWN
The top line indicates the current pressure measurement of the upstream (left)
and downstream (right) RPTs. The bottom line is the over pressure warning.
Pressure indications that are grossly out of scale generally indicate that the
RPT(s) have been fatally overpressured.
Other menus can be observed but the MAIN run screen can not be accessed
and no molbox RFM internal valves can be operated. To return the molbox RFM
to normal operation, it must be turned OFF and back ON or press [ENTER] from
the overpressure screen. When molbox normal operation is reestablished, its
isolation valves will open. Be sure the situation that led to the overpressure
condition is corrected before attempting to reestablish normal operation.
The upper limit and overpressure functions are intended to use molbox RFM's
features to the extent possible to protect the molbox RFM reference pressure
transducers (RPTs) against overpressure. The system is not failsafe and an
overpressure causing fatal damage to the RPTs can still occur. Ultimately,
protection of the RPTs is the responsibility of the user. RPTs damaged by
overpressure are not covered under the product warranty.
molbox RFM continuously monitors for maximum pressure. Whenever the
overpressure limit is exceeded, the pressure value reached, time and date are
logged to a privileged location. This information can be of use in determining
the events that led to an overpressure situation.
3.6.4 <4CAL>
To calibrate and adjust the molbox RFM reference pressure transducers and ohmic
measurement system.
The CALIBRATION functions are considered part of molbox RFM maintenance and are
therefore covered in the maintenance section of this manual (see Section 5).
3.6.5 <5PREFS>
PURPOSE
To access a menu of molbox RFM internal operational preferences and functions.
These include:
• <scrSvr>: View and change the SCREEN SAVER function (see Section 3.6.5.1).
• <sounds>: View and change valid and invalid keypad entry sound settings
(see Section 3.6.5.2).
• <time>: View and edit the internal time and date settings (see Section 3.6.5.3).
• <ID>: View and edit the molbox RFM user ID (see Section 3.6.5.4).
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 84
Page 95

OPERATION
3. OPERATION
To access the PREFS menu press [SPECIAL],
and select <5prefs>. The display is:
1ScrSvr 2sound 3time
4ID
See Sections 3.6.5.1 to 3.6.5.4 for detailed information on each PREFS function.
3.6.5.1 <1SCRSVR>
PURPOSE
To adjust the time setting of molbox RFM’s SCREEN SAVER function.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM has a SCREEN SAVER function which causes the display to dim
after a front panel key is NOT pressed for a certain amount of time. The default
time activates the screen saver after 10 minutes. The time can be adjusted by
the user or screen saving can be completely eliminated.
OPERATION
To access the SCREEN SAVER function, press [SPECIAL] and select
<5prefs>, <1ScrSav>. Edit the time, in minutes, after which the screen saver
will activate to dim the screen. Set zero to eliminate the SCREEN SAVER
function.
Setting screen saver time to zero eliminates the SCREEN SAVER function so
that the display remains permanently at full brightness. The display may also
be completed suppressed using the SOFT [ON/OFF] key (see Section 3.3.3).
3.6.5.2 <2SOUND>
PURPOSE
To adjust or suppress the molbox RFM keypad valid and invalid key
press sounds.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM provides audible feedback by a brief “beep” when a valid key press
is made. Invalid key presses are indicated by a descending two tone “blurp”.
The frequency of this valid key press beep may be selected from three choices
or all keypress sounds may be suppressed.
OPERATION
To access the key press SOUND function, press [SPECIAL] and select <5prefs>,
<2sound>.
Select <1none> to suppress the valid and invalid key press sounds completely.
Select between <2lo>, <3mid> or <4hi> to adjust the valid key press
tone frequency.
The SOUND function only affects the valid key press tone.
Page 85 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 96

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.6.5.3 <3TIME>
PURPOSE
To view and edit the molbox RFM internal time and date settings.
OPERATION
To access the TIME function press
[SPECIAL] and select <5prefs>,
<3time>. The display is:
Select <1time> to edit the time. Edit hours, then minutes, then am/pm by
pressing [ENTER] at each entry. Seconds go to zero when minutes are entered.
Select <2date> to edit the date. The date must be specified in
YYYYMMDD format.
The molbox RFM date and time are set to United States Mountain Standard
Time in the final test and inspection process at the factory. If desired, use
the DATE function to set your local time and date.
Edit: 1time 2 date
08:32:11 am 19980101
3.6.5.4 <4ID>
PURPOSE
To view or edit the molbox RFM user ID and to view the molbox RFM
serial number.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM has a factory programmed serial number that is included on the
product label on the bottom of the case and can be viewed in the
introductory screen.
molbox RFM also allows the user to store a unique, twelve character,
alpha numeric ID number. This feature is frequently used to assign an
organizational control ID (e.g., an asset number, tool number, standard
number, etc.). The ID function allows the ID number to be viewed and edited.
It also displays the molbox RFM factory serial number.
OPERATION
To access the ID function press [SPECIAL] and select <5prefs>, <4ID>.
Select <1view>, to view the current ID.
Select <2edit>, to edit the ID.
The ID has twelve characters. When the edit screen is opened, the cursor is on
the first character. Numerical values can be entered directly from the keypad.
In addition, the [←] and [→] keys can be used to toggle through a list of available
alpha numeric characters. Holding the key slews through the characters.
Character order going up ([→]) is: blank space, symbols, lower case letters,
upper case letters, numbers. Press [ENTER] to select a character and move to
the next character.
When a character is selected the cursor moves to the next character. To leave a
blank character, press [ENTER] with the field for that character blank. Use this
for the trailing characters if the ID being entered is less than twelve characters.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 86
Page 97

3. OPERATION
After the last of the twelve characters has been entered, the <Save ID?> option
is offered. Select <1no> to return to the ID edit screen. Select <2yes> to save
the edited ID.
The ID can also be set remotely from a computer which is quite a bit more
convenient than entering characters from the keyboard (see Section 4.3.4).
The ID cannot be cleared or reset by any RESET functions (see Section 3.6.1).
3.6.5.5 <5LOG>
PURPOSE
To view and/or clear the molbox RFM event log.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM records to a log each time one of the following events occurs:
• An over-pressure occurs (see Sections 3.1.6, 3.6.3)
• A memory fault occurs
OPERATION
To view the event log press [SPECIAL] and select <5prefs>, and then <5log>.
The oldest logged event appears. Pressing [ENTER] steps through the logged
events from the oldest to the most recent and ending with the option to clear the
log <Yes> or <No>.
If NO events have been logged: <End of log> displays.
3.6.6 <6REMOTE>
PURPOSE
To configure the molbox RFM COM1, COM2 and IEEE-488 communication ports. To test
COM1 and COM2 communications.
PRINCIPLE
The molbox RFM has two RS232 communications ports referred to as COM1 and COM2 and
a single IEEE-488 port. COM1 and the IEEE-488 port are for communicating with a host
computer (see Section
(e.g., a multimeter, second molbox, MFC controller, etc.). These ports can be set up from the
molbox RFM front panel.
molbox
RFM provides a self-test for its RS232 communication ports. The self-test allows
verification that the molbox RFM RS232 ports (COM1 and COM2) are operating properly and
that a valid interface cable is being used.
The RS232 test has two steps:
n COM1 sends a message to COM2.
4.1). COM2 is reserved for communicating with an external device
o COM2 sends a message to COM1.
In each step, molbox RFM checks the message received at the receiving COM port. If the
receiving COM port times out or receives an incorrect message, that step of the test fails.
OPERATION
To access the port configurations, press [SPECIAL] and select <6remote>.
Select <1COM1>, <2COM2>, or <3IEEE-488> to view and/or edit that port’s settings.
Press [SPECIAL] and select <6remote>, <4RS232test> to access the RS232 self-test.
Page 87 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 98

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.6.6.1 COM1 AND COM2
The COMx ports can be set for the specific settings required by the user.
The settings are baud rate, parity, data bits and stop bits. The available options are:
Table 18. COM1 and COM2 Available Settings
BAUD RATE
PARITY
DATA BITS
STOP BITS
300, 600, 1 200, 2 400, 4 800, 9 600, 19 200
NONE, ODD or EVEN
7 or 8
1 or 2
The default COMx settings are 2400, E, 7,1 for both COM ports.
The molbox RFM appends a carriage return (<CR>) and a line feed (<LF>) to all
messages that are sent out of the COM1 port to the host. It looks for a carriage
return to terminate incoming messages and ignores line feeds. The user MUST
wait for a reply to each message sent to the molbox RFM before sending another
message to it (see Section
4.2.1).
3.6.6.2 IEEE-488
The IEEE-488 port address can be defined from 1 to 31. The default address is 10.
The molbox RFM sends a line feed (<LF>) and asserts the EOI line at the end of
all transmitted messages. It looks for a line feed and/or assertion of the EOI line
to terminate incoming messages (see Section 4.2.2).
3.6.6.3 RS232 SELF-TEST
The RS232 self-test is provided to check the molbox RFM COM ports and the
interface cable independently of an external device or computer.
If you are having difficulty communicating with molbox RFM from a host
computer using RS232, the RS232 self test can help establish that the molbox
RFM COM1 port you are trying to communicate with and the interface cable you
are using are good.
To run a self test of the RS232 ports (COM1 and COM2), press [SPECIAL] and
select <6remote>, <4RS232test>.
The display prompts you to connect COM1 to COM2 using a standard pin-to-pin
DB-9F to DB-9M RS232 cable (see Section
4.2.1.1).
Once the cable has been installed, press [ENTER] to run the self-test. The test
is first executed in the COM1→COM2 direction and then in the COM2→COM1
direction.
If the COM1→COM2 test
passes: <PASSED> displays briefly and the test
proceeds to COM2→COM1.
If COM2→COM1 passes: <PASSED> is displayed briefly followed by the
conclusion, <molbox RFM RS232 test has PASSED>.
If a test fails: Execution is suspended until [ENTER] is pressed.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 88
Page 99

3. OPERATION
The molbox RFM RS232 test can fail for three reasons:
1. The RS232 cable being used is incorrect (see Section 4.2.1.1 for
information on the correct cable).
2. COM1 and COM2 do NOT have the same serial communications settings
and therefore cannot communicate together (see Section 3.6.6.1 to set
the COM ports).
3. COM1 or COM2 is defective.
The reason for failed communications is almost always a cable or incorrect
RS232 interface settings. Be sure that these are correct before concluding
that a COM port is defective.
3.6.7 <7MICRO>
PURPOSE
To turn ON and OFF manual operation of the OPTIONAL MICRORANGE FLOW
MEASUREMENT function.
See also Sections 3.1.5 and 3.4.7 for additional information on the optional microrange
measurement option.
Manual microrange is intended for special uses of the microrange option as explained in
PRINCIPLE of this section. Normal use of the microrange is in automatic operation using
the MICRO function (see Section 3.4.7).
PRINCIPLE
The molbox RFM microrange option (if present) improves molbox RFM flow measurements
below 10 % FS of the measurement range. See Section 1.2.4.1.1 for a complete description of
microrange principles. The differences between automatic microrange and manual microrange
are that in manual microrange:
The differential pressure value used to calculate flow is either 100 % difference between the
upstream and downstream absolute RPTs (P1 - P2) or 100 % readings from the microrange
differential RPT. No special transitioning from one method to the other is applied.
The current source of the differential pressure measurement used to calculate flow is indicated
by the microrange option designator character in the main run screen (<d> when the source is
the microrange differential RPT; <a> flashing when the source is the difference between the
upstream and downstream absolute RPTs).
Pressing [SPECIAL] and selecting <7micro> allows manual microrange to be turned ON and
OFF. With manual microrange OFF, the microrange option differential pressure RPT
measurements are not used at all (unless automatic microrange is ON, see Section 3.4.7).
With manual microrange option ON, the differential pressure value used to calculate mass
flow is either the difference between the upstream and downstream RPTs if differential
pressure is > 12.5 kPa (1.8 psi) or the microrange differential RPT if differential pressure is <
12.5 kPa (1.8 psi).
The microrange option can also be operated in automatic mode (see Section 3.4.7).
Page 89 © 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
Page 100

molbox™ RFM™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
OPERATION
To access the MANUAL MICRORANGE function, press [SPECIAL] and select <7micro>.
The display is:
Manual microrange:
1off 2on
If the manual microrange option is not installed, this menu will not appear. An <Option
not installed> message appears in its place.
Select <1off> or <2on>. Operation returns to the run screen with the manual microrange in
the condition specified.
Turning the microrange option OFF may reduce the accuracy of flow measurements under
10 % of the flow measurement range and may lead to unexpected results.
Manual microrange option ON is indicated by <d> (option ON, using microrange
differential RPT) or <a> flashing (option ON, not currently using microrange differential
RPT) in the microrange option designator character of the main run screen (top line,
th
6
character from the right). Manual microrange option OFF is indicated by a blank
designator or the <m> that indicates automatic microrange ON.
Turning ON or OFF manual microrange by pressing [SPECIAL] and selecting <7micro>
overrides the current setting of automatic microrange (see Section 3.4.7).
3.6.8 <8HEAD>
PURPOSE
To cause a pressure fluid head correction to be added or subtracted to the pressure
measured by the molbox RFM reference pressure transducers in order to predict the
pressure at height the height of the molbloc when the molbloc is at a level other than the
molbox RFM’s reference level.
PRINCIPLE
molbox RFM measures absolute and differential pressure in molbloc flow elements. The
molbox RFM reference pressure transducers (RPTs) are calibrated with the height of the rear
panel pressure quick connectors as the pressure reference level. Sometimes, when
performing a calibration or test, the molbloc is at a different height than the molbox RFM’s
pressure reference level. This difference in height, frequently called head, can cause a
significant difference between the pressure measured by the molbox RFM at its reference
level and the pressure actually present at the molbloc at a different height. In this case, it is
useful to make a head correction to the pressure measured by the molbox RFM in order to
predict the pressure actually applied at a different height.
molbox RFM can calculate head pressures for all the gases it supports (see Section 3.4.2),
over its working pressure range. The HEAD function allows the difference in height between
the molbox RFM and the molbloc to be specified and causes the resulting head pressure to
be added to the pressure measured at the molbox RFM rear panel quick connectors.
[SPECIAL], <8head>, is used to specify the height difference between the molbox RFM rear
panel quick connectors and another height. Entering a height of zero turns the function off.
© 1998-2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company Page 90
 Loading...
Loading...