Fluke 863, 867B Service Manual

867B,863
®
Graphical Multimeters
Service Manual
PN 689312
December 1997
© 1997 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
All product names are trademarks of their respective companies.

Table of Contents
Chapter Title Page
1 Introduction and Specifications .......................................................................................... 1-1
1-1.. Introduction ............................................................................................................. 1-3
1-2. Description .............................................................................................................. 1-3
1-3. Power Requirements ............................................................................................... 1-3
1-4. Options, Accessories and Related Equipment ....................................................... 1-4
1-5. Operating Instructions ............................................................................................ 1-4
1-6. Obtaining Service ................................................................................................... 1-4
1-7. Conventions Used in This Manual ......................................................................... 1-5
1-8. Chapter Contents .................................................................................................... 1-5
1-9. Specifications .......................................................................................................... 1-6
2 Theory of Operation............................................................................................................. 2-1
2-1. Introduction ............................................................................................................. 2-3
2-2. Start-Up Sequence .................................................................................................. 2-3
2-3. Function Selection .................................................................................................. 2-3
2-4. Power Supply .......................................................................................................... 2-4
2-5. Power Supply Input Voltages ................................................................................. 2-4
2-6. Power Supply Output Voltages and Currents ........................................................ 2-6
2-7. Power Supply Signals ............................................................................................ 2-7
2-8. Power ON/OFF Requirements ............................................................................... 2-8
2-9. NiCd Charging Requirements ................................................................................ 2-8
2-10. Battery and Line Level Detection .......................................................................... 2-8
2-11. Power Supply Functional Blocks ........................................................................... 2-9
2-12. Input Power Selector (A) ........................................................................................ 2-9
2-13. Boost Preregulator (B) ............................................................................................ 2-10
2-14. Battery Charger (C) ................................................................................................ 2-10
2-15. DC-DC Converter (D) ............................................................................................ 2-12
2-16. Backlight Current Sink (E) ..................................................................................... 2-12
2-17. Power Switch Circuitry (F) .................................................................................... 2-12
2-18. LCD Contrast Control (G) ...................................................................................... 2-12
2-19. Power-On Reset Circuit (H) ................................................................................... 2-12
2-20. Linear Post Regulators (I) ....................................................................................... 2-13
2-21. Input Overload Protection ...................................................................................... 2-13
i

Contents (continued)
2-22. Volt/Ohms Input Protection ................................................................................... 2-13
2-23. External Trigger and Logic Activity Input Protection ........................................... 2-14
2-24. Amps / mA / µA Input Protection .......................................................................... 2-14
2-25. Input Signal Conditioning ...................................................................................... 2-14
2-26. AC Volts ................................................................................................................. 2-14
2-27. DC Volts ................................................................................................................. 2-16
2-28. mV DC .................................................................................................................... 2-16
2-29. Ohms ....................................................................................................................... 2-17
2-30. Diode Test ............................................................................................................... 2-17
2-31. Capacitance ............................................................................................................. 2-17
2-32. mA/µA .................................................................................................................... 2-18
2-33. Amps ....................................................................................................................... 2-18
2-34. Waveform Processing ............................................................................................. 2-19
2-35. Overview ................................................................................................................. 2-19
2-36. Detailed Description ............................................................................................... 2-19
2-37. Waveform Triggering ............................................................................................. 2-20
2-38. Overview ................................................................................................................. 2-20
2-39. Dual Trigger ............................................................................................................ 2-20
2-40. Single Trigger ......................................................................................................... 2-21
2-41. External Trigger ...................................................................................................... 2-21
2-42. Glitch Capture ......................................................................................................... 2-22
2-43. Single Shot .............................................................................................................. 2-22
2-44. Frequency Trigger .................................................................................................. 2-22
2-45. Logic Activity Trigger ............................................................................................ 2-22
2-46. Peak Hold ................................................................................................................ 2-22
2-47. Auto Diode .............................................................................................................. 2-22
2-48. Component Test ...................................................................................................... 2-23
2-49. Digital Circuitry ...................................................................................................... 2-24
2-50. RS-232 Serial Port .................................................................................................. 2-24
3 Maintenance .......................................................................................................................... 3-1
3-1. Introduction ............................................................................................................. 3-3
3-2. Warranty Repairs and Shipping Information ......................................................... 3-3
3-3. Static-Safe Handling ............................................................................................... 3-3
3-4. Cleaning .................................................................................................................. 3-4
3-5. Disassembly ............................................................................................................ 3-4
3-6. Reasssembly ............................................................................................................ 3-7
3-7. Replacing the 440 mA Fuse ................................................................................... 3-9
3-8. Replacing the 11A (High Energy) Fuse ................................................................. 3-9
4 Perfomance Testing and Calibration ................................................................................. 4-1
4-1. Introduction ............................................................................................................. 4-3
4-2. Required Test Equipment ....................................................................................... 4-3
4-3. Alternative Test Equipment (Fluke 5500A) ........................................................... 4-3
4-4. Performance Tests .................................................................................................. 4-4
4-5. mV DC Test ............................................................................................................ 4-4
4-6. DC Volts Test ......................................................................................................... 4-6
4-7. Diode Test ............................................................................................................... 4-7
4-8. AC Volts Test ......................................................................................................... 4-8
4-9. Ohms and Conductance Tests ................................................................................ 4-10
4-10. Capacitance Test ..................................................................................................... 4-11
4-11. Frequency Test ........................................................................................................ 4-12
4-12. Duty Cycle Test ...................................................................................................... 4-14
4-13. Logic Test (867B Only) .......................................................................................... 4-15
ii

Contents (continued)
4-14. Amps Tests ............................................................................................................. 4-16
4-15. Peak Hold Test ........................................................................................................ 4-19
4-16. Component Test (867B Only) ................................................................................ 4-19
4-17. Rel Test/Touch Hold Test ...................................................................................... 4-20
4-18. Glitch Capture Test ................................................................................................. 4-21
4-19. External Trigger Test .............................................................................................. 4-21
4-20. Calibration ...............................................................................................................4-22
4-21. Measuring the System Resistance .......................................................................... 4-22
4-22. Starting Calibration Mode on the GMM ................................................................ 4-22
4-23. mV DC Calibration ................................................................................................. 4-23
4-24. DC Volts Calibration .............................................................................................. 4-24
4-25. DC mAuA Calibration ............................................................................................ 4-24
4-26. DC Amps Calibration ............................................................................................. 4-24
4-27. Ohms/nS Calibration .............................................................................................. 4-25
4-28. Modifying the Displayed Value ............................................................................. 4-25
4-29. Ohms Calibration .................................................................................................... 4-26
4-30. AC Volts Calibration .............................................................................................. 4-27
4-31. AC mA(A Calibration ............................................................................................ 4-27
4-32. AC Amps Calibration ............................................................................................. 4-27
4-33. Internal Constants Calibration ................................................................................ 4-28
4-34. Setting LCD Voltage .............................................................................................. 4-28
5 List of Replaceable Parts ..................................................................................................... 5-1
5-1. Introduction ............................................................................................................. 5-3
5-2. How To Obtain Parts .............................................................................................. 5-3
5-3. Manual Status Information ..................................................................................... 5-3
5-4. Newer Instruments .................................................................................................. 5-3
5-5. Service Centers ....................................................................................................... 5-4
5-6. Parts ......................................................................................................................... 5-4
6 Schematic Diagrams.............................................................................................................6-1
iii

List of Tables
Table Title Page
1-1. Power Sources ......................................................................................................... 1-4
1-2. Accessories Included with Each GMM ................................................................... 1-4
2-1. Power Supply Inputs................................................................................................ 2-4
2-3. Power Supply Signals.............................................................................................. 2-7
2-4. Power Source Detection .......................................................................................... 2-9
2-5. Average Converter................................................................................................... 2-15
2-6. RMS Converter (U3) ............................................................................................... 2-16
2-7. Test Point Voltages.................................................................................................. 2-16
2-8. Ohms Ratiometric Measurements ........................................................................... 2-17
2-9. Amps Measurement Paths....................................................................................... 2-18
4-1. Recommended Test Equipment............................................................................... 4-4
4-2. mV DC Performance Test ....................................................................................... 4-4
4-3. DC Volts Performance Test..................................................................................... 4-6
4-4. Diode Test Performance Test .................................................................................. 4-7
4-5. AC Volts RMS Performance Test ........................................................................... 4-8
4-6. AC Volts Average Performance Test...................................................................... 4-8
4-7. Ohms Performance Test .......................................................................................... 4-10
4-8. Conductance Performance Test............................................................................... 4-10
4-9. Capacitance Performance Test ................................................................................ 4-11
4-10. Frequency (AC Volts) Performance Test ................................................................ 4-12
4-11. Frequency (mAuA) Performance Test .................................................................... 4-12
4-12. Duty Cycle Performance Test.................................................................................. 4-14
4-13. Logic Performance Test .......................................................................................... 4-15
4-14. DC Amps Performance Test.................................................................................... 4-16
4-15. AC Amps RMS Performance Test .......................................................................... 4-16
4-16. AC Amps Average Performance Test ..................................................................... 4-17
4-17. Peak Hold Performance Test................................................................................... 4-19
4-18. Component Test Performance Test ......................................................................... 4-19
4-19. Rel Performance Test .............................................................................................. 4-20
4-20. Touch Hold Performance Test................................................................................. 4-20
4-21. Glitch Capture Performance Test ............................................................................ 4-21
4-22. External Trigger Performance Test ......................................................................... 4-21
5-1. 860 Series Final Assembly ...................................................................................... 5-5
5-2. A1 Main PCA.......................................................................................................... 5-8
iv

List of Figures
Figure Title Page
1-1. Temperature and Humidity...................................................................................... 1-7
2-1. Block Diagram......................................................................................................... 2-5
2-2. Power Supply Blocks .............................................................................................. 2-11
2-3. Keypad Connections................................................................................................ 2-25
3-1. Disassembly............................................................................................................. 3-5
3-2. Reassembly.............................................................................................................. 3-8
3-3. Replacing the 400 mA Fuse..................................................................................... 3-9
4-1. Configuration 1 (mV DC) ....................................................................................... 4-5
4-2. Configuration 2 (DC Volts)..................................................................................... 4-6
4-3. Configuration 6 (AC Volts)..................................................................................... 4-9
4-4. Configuration 5 (Ohms) .......................................................................................... 4-11
4-5. Configuration 7 (PM5139) ...................................................................................... 4-13
4-6. Configuration 7 (PM5139) ...................................................................................... 4-14
4-7. Configuration 9 (PM5139) ...................................................................................... 4-16
4-8. Configuration 3 (mAuA, DC and AC) .................................................................... 4-17
4-9. Configuration 4 (Amps, DC and AC)...................................................................... 4-18
4-10. Configuration 8 (Component Test).......................................................................... 4-19
4-11. Initiating Calibration ............................................................................................... 4-22
4-12. Entering Calibration Mode...................................................................................... 4-23
4-13. Modifying the Displayed Value .............................................................................. 4-25
4-14. Ohms Calibration..................................................................................................... 4-26
5-1. 860 Series Final Assembly ..................................................................................... 5-7
5-2. A1 Main PCA.......................................................................................................... 5-16
v

Chapter 1
Introduction and Specifications
Title Page
1-1. Introduction............................................................................................. 1-3
1-2. Description.............................................................................................. 1-3
1-3. Power Requirements ............................................................................... 1-3
1-4. Options, Accessories and Related Equipment......................................... 1-4
1-5. Operating Instructions............................................................................. 1-4
1-6. Obtaining Service.................................................................................... 1-4
1-7. Conventions Used in This Manual.......................................................... 1-5
1-8. Chapter Contents..................................................................................... 1-5
1-9. Specifications.......................................................................................... 1-6
1-1

Introduction and Specifications
Introduction
Introduction 1-1.
This manual includes the following information:
• Specifications (Chapter 1):
• Theory of Operation (Chapter 2):
• General Maintenance (Chapter 3):
• Performance Testing and Calibration procedures (Chapter 4):
• List of Replaceable Parts (Chapter 5):
• Schematic Diagrams and component locators (Chapter 6):
The information in this manual is applicable to both the 867B and 863 models unless
otherwise indicated.
Description 1-2.
The Fluke 867B and 863 Graphical Multimeters (GMMs) provide full digital multimeter
(DMM) capabilities along with graphical waveform displays and trend plotting. Model
867B also provides component testing and logic activity testing.
1
Power Requirements 1-3.
The GMM can be powered with the Battery Eliminator or with 6 “AA” (ANSI/NEDAL40) alkaline cells. New alkaline batteries provide a minimum of 6 hours of continuous
operation. You can also use the NiCd battery pack. Depending on battery condition, a
fully charged NiCd battery pack provides 8 hours (typical) or less of continuous
operation. Internal charging is available on Model 867B.
1-3
867B,863
Service Manual
Battery Eliminator Operation
Alkaline Battery Operation (6 AA,
ANSI/NEDA-L40)
Table 1-1. Power Sources
Model 867B Model 863
••
••
NiCd Battery Pack Operation (with
internal charging)
NiCd Battery Pack Operation (with
external charging)
•
•
Options, Accessories and Related Equipment 1-4.
Accessories supplied with Fluke 867B and 863 GMMs are listed in Table 1-2.
Table 1-2. Accessories Included with Each GMM
Model 867B Model 863
TL70A Test Leads (2)
Battery Eliminator
NiCd Battery Pack
••
•
•
Operating Instructions 1-5.
Operating instructions for the Fluke 867B and 863 Graphical Multimeters can be found in
the Users Manual. For ordering information, see “How to Obtain Parts” in Chapter 5.
Obtaining Service 1-6.
A GMM under warranty will be promptly repaired or replaced (at Fluke’s option) and
returned at no charge. See the registration card for warranty terms. If the warranty has
expired, the GMM will be repaired and returned for a fixed fee. Contact the nearest
Service Center for information and prices. A list of U.S. and International Service
Centers is available on the World Wide Web at www.fluke.com. Refer to Chapter 3 for a
list of Fluke telephone numbers.
1-4

Introduction and Specifications
Conventions Used in This Manual
Conventions Used in This Manual 1-7.
The following conventions are used in this manual:
• “GMM” refers to all Graphical Multimeter models in the 860 Series.
• “863” and “867B” are specifically mentioned where a description does not apply to
all models in the 860 Series.
• A “pca” is a printed circuit board and its attached parts.
• A pin or connection on a component is specified by the component reference
designator, a dash (-), and a pin number. For example, component U30, pin 92 would
be U30-92.
Chapter Contents 1-8.
The chapters in this manual document service for the GMM as follows:
• Chapter 1. Introduction and Specifications describes the Service Manual, explains
special terminology and conventions, and provides complete GMM specifications.
• Chapter 2. Theory of Operation describes the GMM’s circuitry in terms of functional
blocks, with a description of each block’s role in overall operation. A detailed circuit
description is then given for each block.
1
• Chapter 3. General Maintenance provides information on general maintenance,
handling precautions and disassembly instructions. Instructions covering warranty
repairs and shipping the instrument to a service center are also contained in this
chapter.
• Chapter 4. Performance Testing and Calibration contains information on required test
equipment, performance test procedures and calibration of the GMM.
• Chapter 5. List of Replaceable Parts describes parts used in the GMM along with
ordering information.
• Chapter 6. Schematic Diagrams contains a full set of schematic diagrams and
component locators.
1-5

867B,863
Service Manual
Specifications 1-9.
General
Display: LCD - Dot Matrix, 240 X 200 pixels
Fluke 867B: Transmissive, Backlit
Fluke 863: Reflective
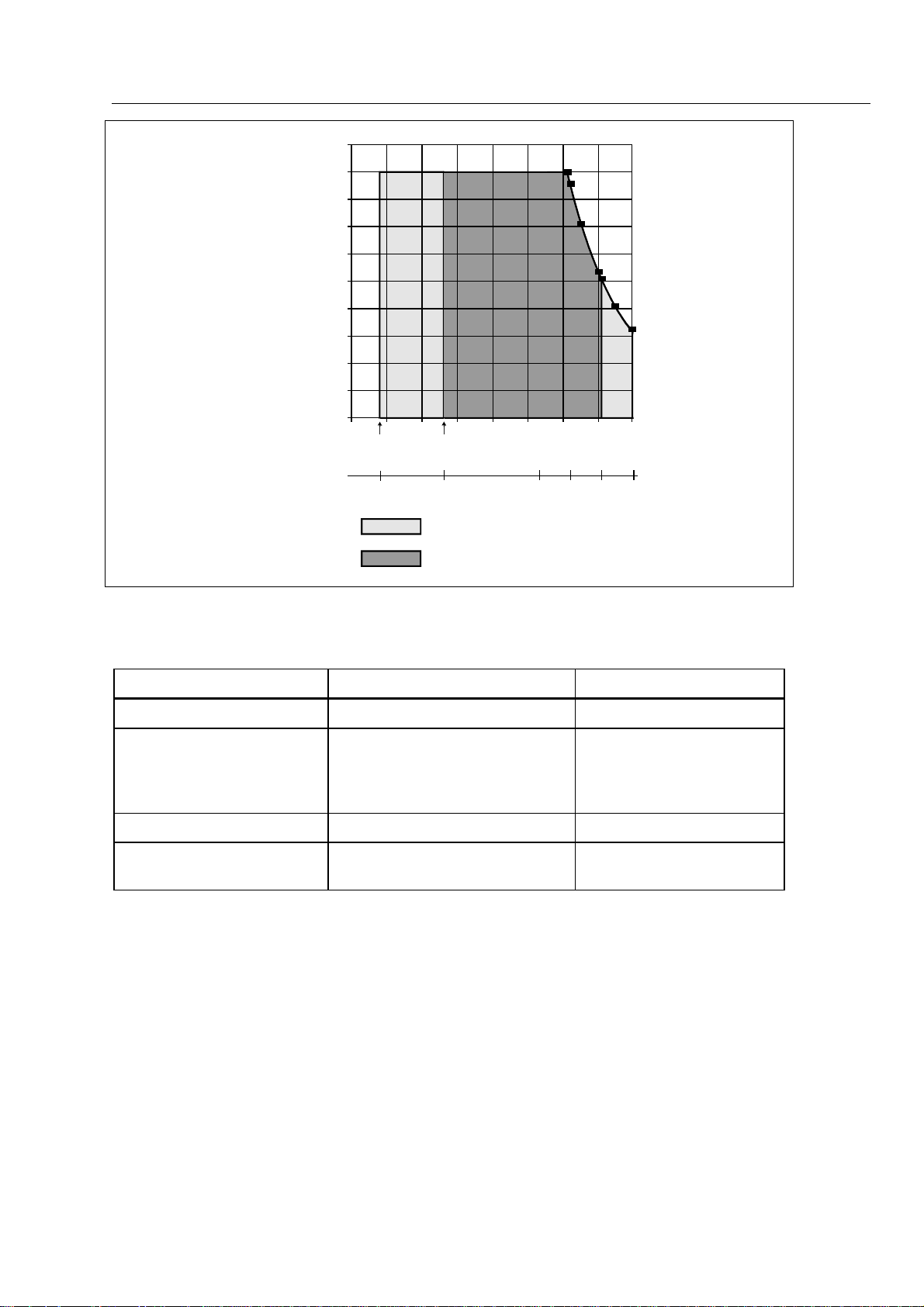
Temperature Operating: 0°C to 50°C (See Figure 1-1.)
Storage: -20°C to 60°C (Batteries Removed)
Charging: 0 to 45°C
Temperature Coefficient: (0.1 X % Accuracy) per °C (0°C to 18°C and 28°C to 59°C)
Relative Humidity: 0% to 90% non-condensing
Altitude Operating/Non-operating: 6,562 ft. (2,000 meters)/ 40,000 ft. (12,200 meters)
Input Impedance: 10 MΩ
Shock and Vibration: per MIL-T-28800, class 3, sinusoidal, non-operating
Dimensions: 5.4 x 9.7 x 2.7 in. (137 x 246 x 68 mm)
Weight: 3 lbs (1.35 kg)
Battery Operating Time (backlight off or low)
Alkaline: 8 hours typical
NiCd:
863: 10 hours typical
867B: 8 hours typical
Battery Recharge Time: 16 hours minimum from full discharge
Drip Proof Case: per IEC 529; IP 52, Drip Proof
Safety: Designed to meet IEC 1010-1 Category III, UL3111, CSA-C22.2. 1010-1-92, CE and TUV
requirements
Certification:
Electromagnetic Interference
RF Emissions EN-50081-1 Commercial Limits
VFG 243-1991
FCC Part 15 Class B,
RF Susceptibility: EN 50082-1 Industrial Limits
1-6
%RH
Introduction and Specifications
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
-4
32
Temperature ( F)
°
Specifications
1
-20
Figure 1-1. Temperature and Humidity
0
Temperature ( C)
= Storage (-20 C —° 60 C)
= Normal Operation (0 C —
30 40 50 60
°
°
°
50 C)
°
Power
Fluke 867B Fluke 863
Battery Eliminator/Charger Yes Optional Eliminator only
NiCd Battery Pack Yes
Alkaline Batteries 6 AA Cells Optional Customer Supplied Yes
Battery Life: NiCad
Alkaline
≥8 hrs (supplied)
≥8 hrs (optional)
Optional BP7217 Battery
Pack
Optional BC7210 Ext.
Charger
≥10 hrs (optional)
≥8 hrs (supplied)
os1f.eps
1-7
867B,863
3
Service Manual
Resolution and Accuracy
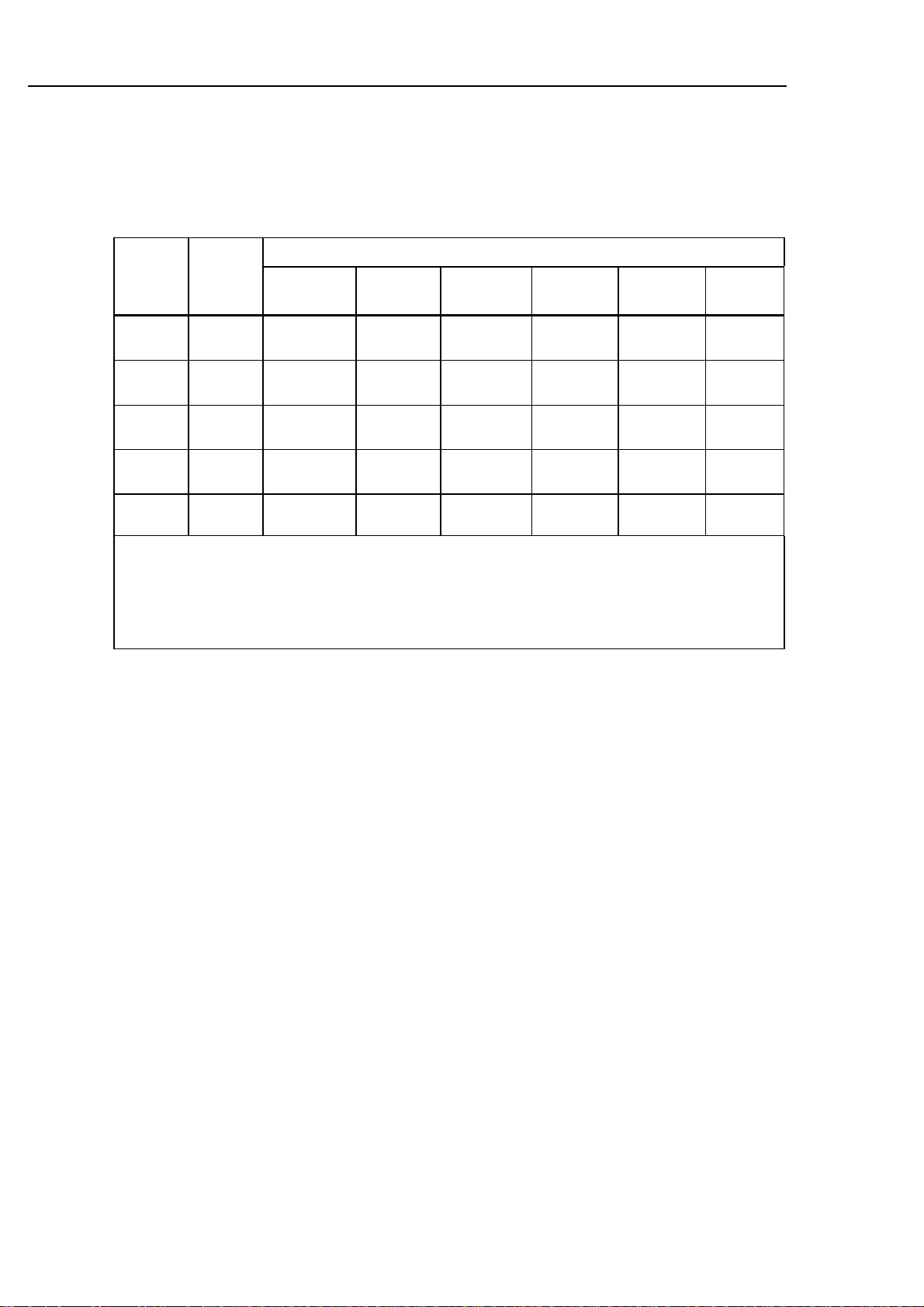
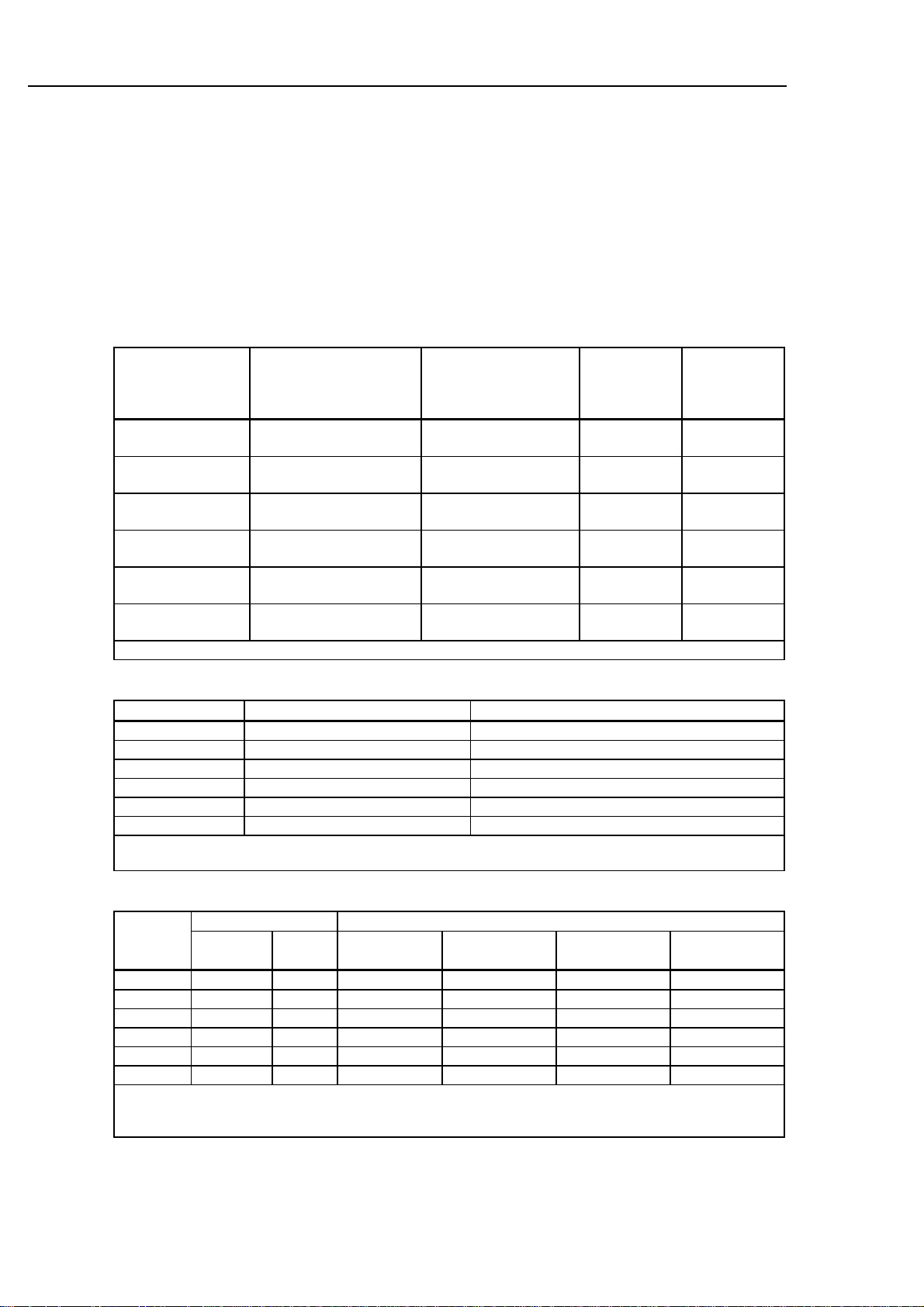
AC Volts (True RMS, AC-Coupled) [±(percent of reading + counts)]
The following specifications apply within 1 year of calibration when operating in a temperature range of
18°C (64°F) to 28°C (82°F).
Frequency
Range Res.
20 -
50 Hz
50 -
1 kHz
1 kHz 30 kHz
30 kHz-
100 kHz
100kHz-
200kHz
200 kHz-
300 kHz
00.00 mV 0.01 mV 1.5% + 10
0.19 dB
3.0000V 0.1 mV
30.000V 1 mV 1.5% + 10
300.00V 10 mV 1.5% + 10
1000.0V 100 mV
300 mV - 300V ranges ≥3:1, 1000V range ≥3:1 decreasing to ≥1.41:1 as input voltage increases to 1000V (peak
voltage not to exceed 1414V).
Measurement Range: 300 mV range from 10% to 100% of range.
1.5% + 10
0.19 dB
0.19 dB
0.19 dB
1.5% + 10
0.19 dB
3V - 1000V ranges from 5% to 100% of range.
For frequencies > 100 kHz 30% to 100% of range (all ranges).
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
1.5% + 10
0.19 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
0.5% + 10
0.10 dB
NA NA NA NA
4% + 200
1.39 dB
4% + 200
1.39 dB
4% + 200
1.39 dB
4% + 200
1.39 dB
8% + 200
1.68 dB
8% + 200
1.68 dB
8% + 200
1.68 dB
8% + 200
1.68 dB
10%+ 200
1.82 dB
10%+ 200
1.82 dB
10%+ 200
1.82 dB
10%+ 200
1.82 dB
1-8
Introduction and Specifications
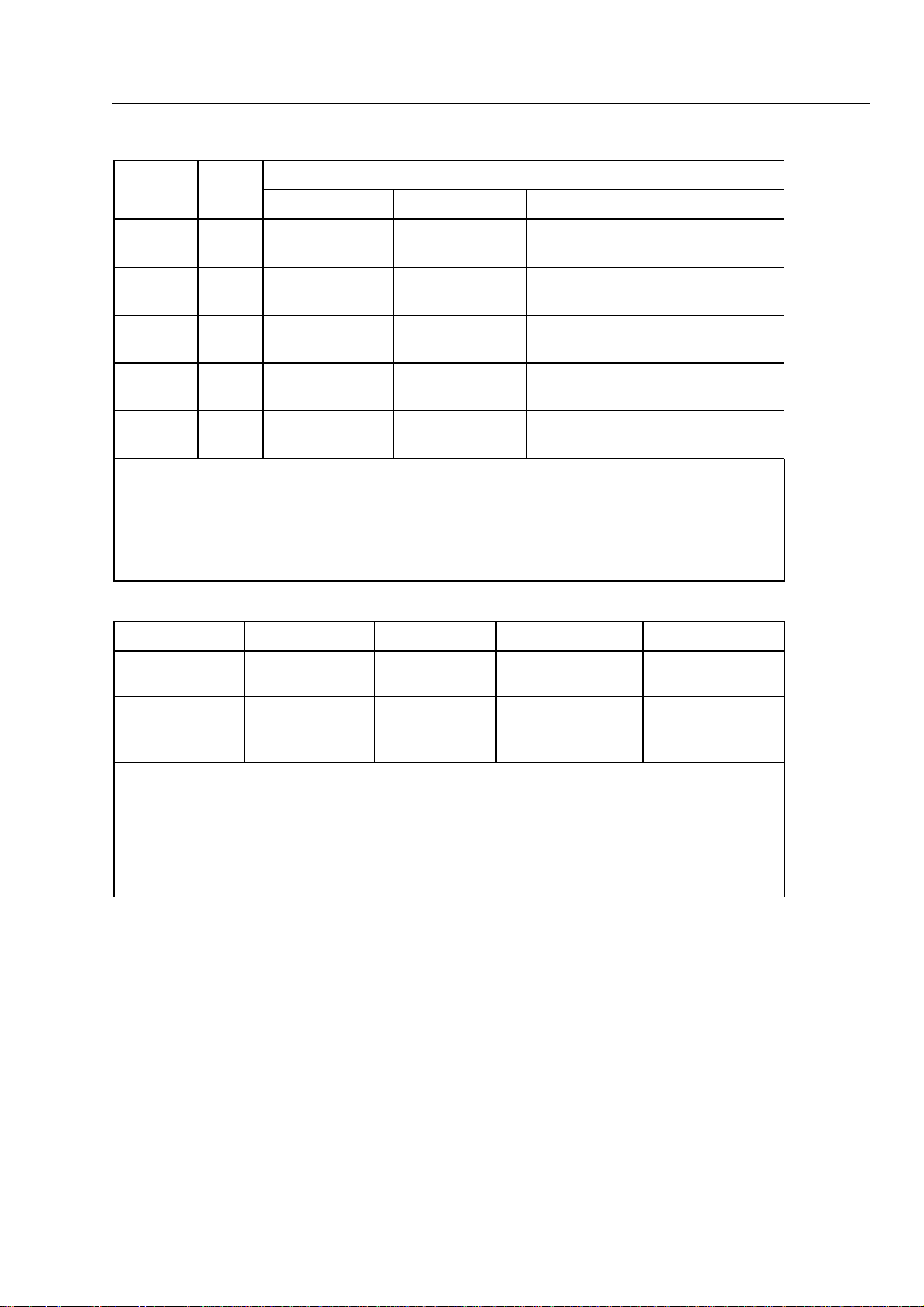
AC Volts - Average Responding AC Coupled [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Frequency
Range Res.
20 - 50 Hz 50 - 1 kHz 1 kHz - 30 kHz 30 kH - 50 kHz
Specifications
1
300.0 mV 0.1 mV 1.5% + 4
0.25 dB
3.000V 1 mV 1.5% + 4
0.25 dB
30.00V 10 mV 1.5% + 4
0.25 dB
300.0V 100 mV 1.5% + 4
0.25 dB
1000V 1 V 1.5% + 4
0.25 dB
Input Impedance: 1.11 MΩ ±1% in series with 0.1 µF
Volts-Hertz Product: 2 x 10
Common Mode Rejection: >60 dB at 50 Hz and 60 Hz (1 kΩ unbalance)
Common Mode Volts-Hertz Product: 1 x 10
dBm Reference: 2, 4, 8, 16, 50, 75, 93, 110, 125, 135, 150, 300, 600, 900, 1000, and 1200Ω
Overload Protection: 1000V rms
7
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
1.5% + 4
0.25 dB
7
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
0.5% + 4
0.16 dB
NA NA
DC Volts [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Function Range Res. Fluke 867B Fluke 863
mV DC
V DC 300.00V 0.01 V 0.025% + 2 0.04% + 2
Input Impedance: V DC-10 MΩ, mV DC-10 MΩ, mV DC Hi-Z ->1000 MΩ
Normal Mode Rejection: >60 dB at 50 Hz or 60 Hz
Common Mode Rejection: >120 dB a dc, >90 dB at 50 Hz and 60 Hz (1 kΩ unbalance)
Overload Protection: 1000 V rms
Maximum Allowable Peak AC + DC Voltage (without causing a reading error)
300 mV, 3000 mV ranges: 15V
30V range: 1000V; 300V, 1000V ranges: 1414V
300.00 mV 0.01 mV 0.025% + 2 0.04% + 2
3000.0 mV 0.1 mV 0.025% + 2 0.04% + 2
30.000V 0.001 V 0.025% + 2 0.04% + 2
1000.0V 0.1 V 0.025% + 2 0.04% + 2
2% + 4
0.25 dB
2% + 4
0.25 dB
2% + 4
0.25 dB
2% + 4
0.25 dB
1-9
867B,863
Service Manual
Diode Test (Manual)
Diode Test (Auto)
Current Ranges
Range: 3V
Resolution: 0.0001V
Accuracy: ±0.05% of reading + 2 digits
Open Circuit Voltage: 3.1V
Accuracy: 20%
Ranges for True
RMS AC Current
and DC Current
300.00 µA
3000.0 µA
1
1
True RMS
Measurement Range
(% Range to % Full
Scale)
Ranges for Average
Responding AC
Current
Maximum
Burden
Voltage
5% - 100% 300.0 µA 0.03V 440 mA @
5% - 100% 3000 µA 0.3V 440 mA @
Fuse
Protection
1000V
1000V
30.000 mA 5% - 100% 30.00 mA 0.03V 440 mA @
1000V
300.00 mA 5% - 100% 300.0 mA 0.3V 440 mA @
1000V
3.0000A 5% - 100% 3.000A 0.1V 11A @
1000V
10.000A 5% - 100% 10.00A 0.3V 11A @
1000V
1. DC ranges available on the Fluke 867B only.
DC Current Accuracy [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Range Resolution Accuracy
1
300 µA
3000 µA
30 mA
1
2
0.01 µA0.1% + 15
0.1 µA0.1% + 2
1 µA 0.05% + 15
300 mA 10 µA0.1% + 2
3A 100 µA0.2% + 15
10A 1 mA 0.2% + 2
1. Ranges available on the Fluke 867B only.
2. Fluke 863 30 mA DC range accuracy 0.1% + 15.
AC Current Accuracy [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Range Resolution True RMS AC Current Accuracy (Average AC counts)
True RMS Avg. 20 Hz to
50 Hz
50 Hz to
3 kHz
3 kHz to
10 kHz
300 µA10.01 µA0.1 µA1% + 10 (4) 0.75% + 10 (4) 2% + 20 (4) 2% + 40 (4)
3000 µA10.1 µA1 µA1% + 10 (4) 0.75% + 10 (4) 2% + 20 (4) 2% + 40 (4)
30 mA 1 µA 10 µA1% + 10 (4) 0.75% + 10 (4) 2% + 20 (4) 2% + 40 (4)
300 mA 10 µA 100 µA1% + 10 (4) 0.75% + 10 (4) 2% + 20 (4) NA
3A 100 µA1 mA1% + 10 (4) 0.75% + 10 (4) NA NA
10A 1 mA 10 mA 1% + 10 (4) 0.75% + 10 (4) NA NA
1. Ranges available on the Fluke 867B only.
2. Replace counts with Average AC counts for Average Responding AC measurements. In 300 µA
range, floor count increases to 20 with battery eliminator.
2
10 kHz to
30 kHz
1-10
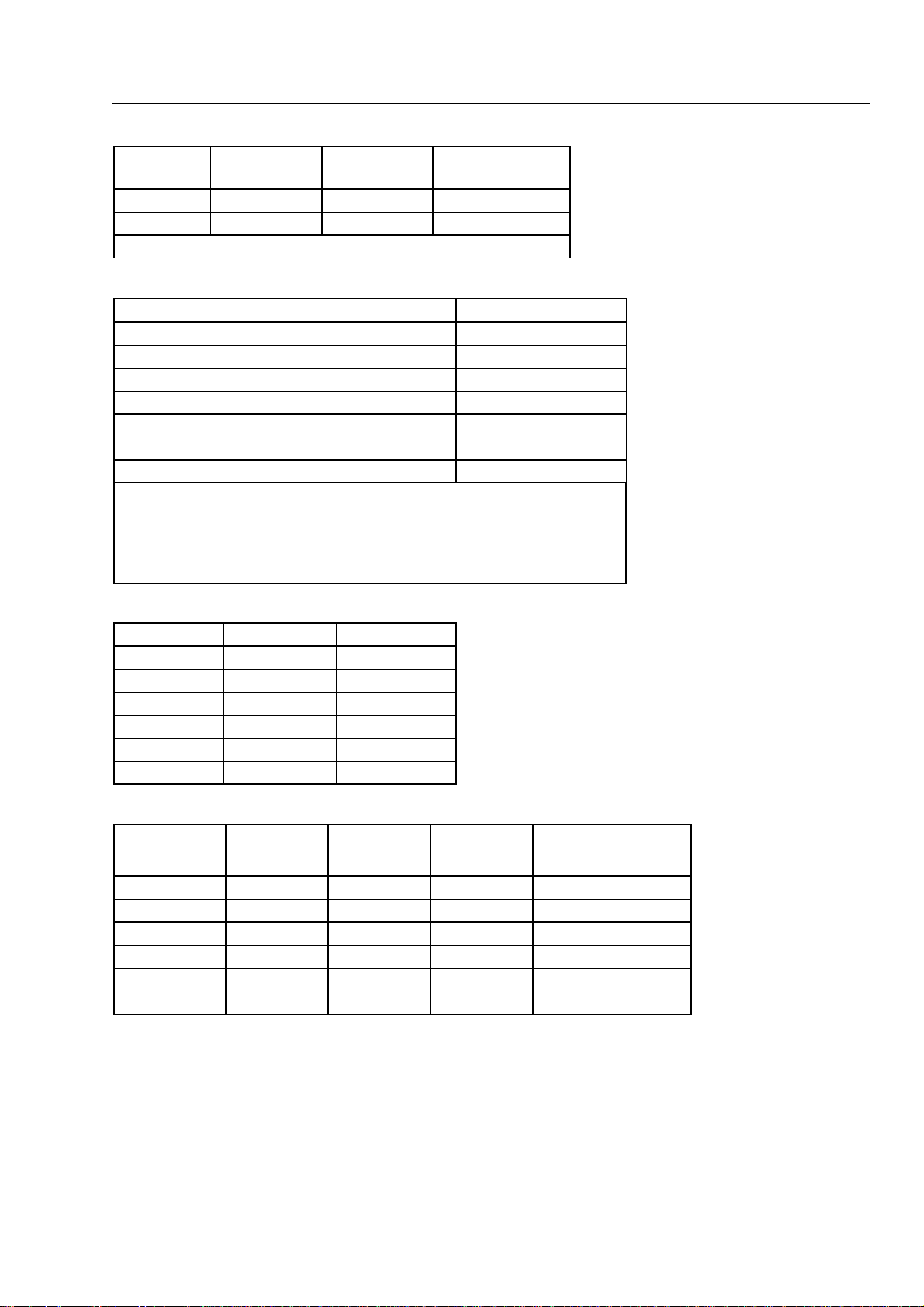
Conductance [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Range Resolution Accuracy
300.00 nS 0.01 nS 0.5% + 20 3.2V
3000.0 nS 0.1 nS 0.5% + 20 3.2V
Overload Protection: 1000V rms
Open Circuit
Capacitance [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Range Resolution Accuracy
10000 pF
.1000 µF 100 pF 1.9% + 2
1.000 µF 1 nF 1.9% + 2
10.00 µF 0.01 µF1.9% + 2
100.0 µF0.1 µF1.9% + 2
1000 µF1 µF1.9% + 2
10000 µF
Overload Protection: 1000V rms
1. 10,000 pF range last digit reads zero.
2. 10,000 µF range last two digits read zero.
3. Using REL to zero internal offset.
1
2, 3
10 pF 1.9% + 20
100 µF 10% + 900
Voltage
Introduction and Specifications
Specifications
1
Continuity Beeper Values
Range Beeper On Beeper Off
300Ω 32Ω 136Ω
3 kΩ 212Ω 725Ω
30 kΩ 1586Ω 4799Ω
300 k Ω 15.3 kΩ 45.5 kΩ
3 MΩ 152.7 kΩ 459.1 kΩ
30 MΩ 66 kΩ 194 kΩ
Resistance [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Range Resolution Accuracy Maximum
Current
300.00Ω 0.01 Ω 0.07% + 10 1 mA 3.2V
3.0000 kΩ 0.1 Ω 0.07% + 2 120 µA1.5V
30.000 kΩ 1 Ω 0.07% + 2 14 µA1.5V
300.00 kΩ 10 Ω 0.07% + 2 1.5 µA1.5V
3.0000 MΩ 100 Ω 0.15% + 2 150 nA 1.5V
30.000 MΩ 1 kΩ 0.2% + 3 320 nA 3.2V
Open Circuit
Voltage
1-11
867B,863
Service Manual
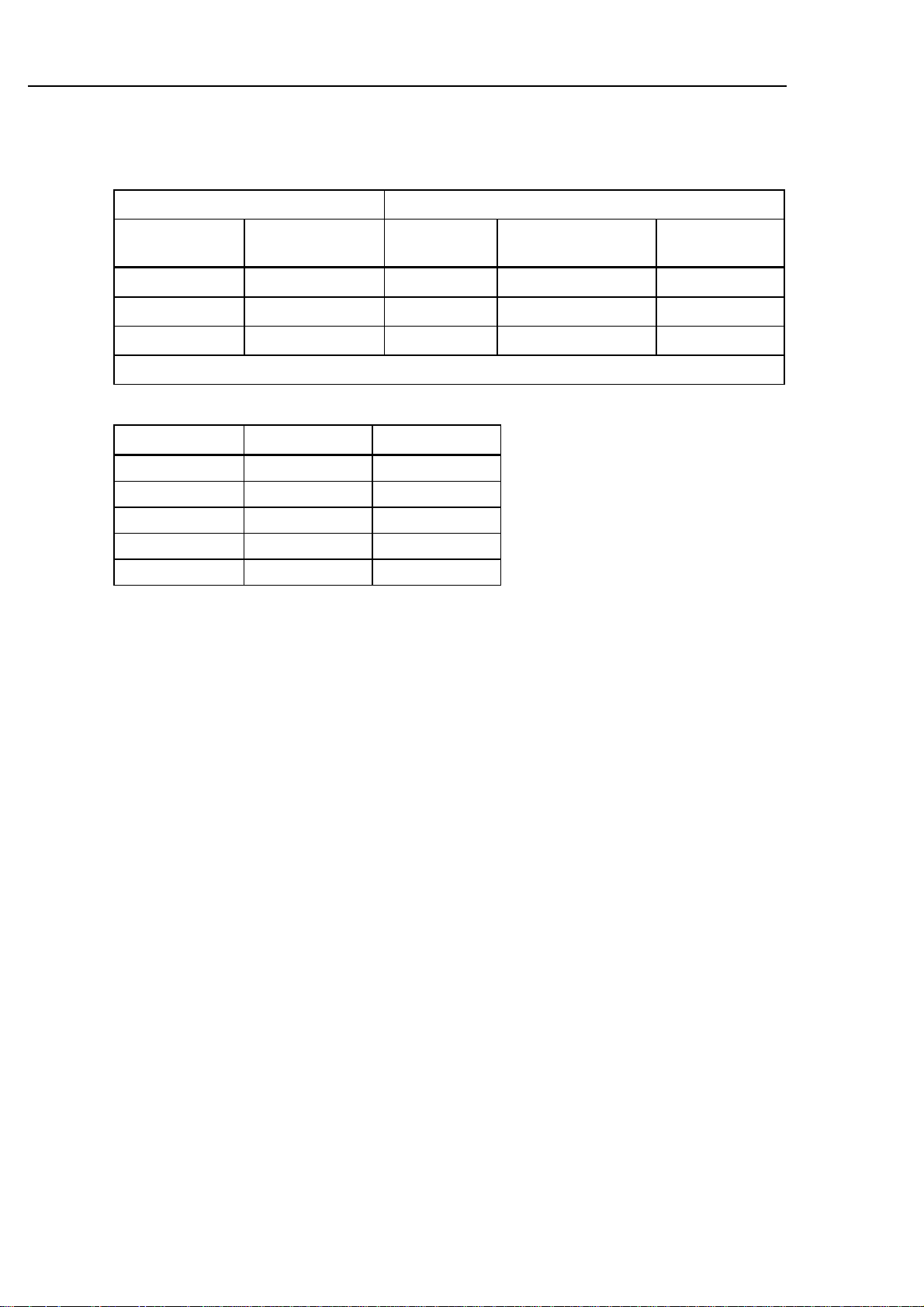
Frequency
AC Sensitivity
AC Volts AC Current
Frequency Sine Wave
Level
2 Hz - 500 kHz 60 mV rms 5 Hz - 30 kHz 300 µA - 300 mA 20% of range
500 kHz - 1 MHz 100 mV rms 5 Hz - 2 kHz 3A 300 mA
1 MHz - 2 MHz* 1V rms 5 Hz - 2 kHz 10A 3A
* Use single trigger mode for inputs above 1 MHz.
Frequency Ranges Sine Wave
Level
Accuracy [±(percent of reading + counts)]
Range Resolution Accuracy
1000.00 Hz 0.01 Hz 0.05% + 2
10.0000 kHz 0.1 Hz 0.05% + 1
100.000 kHz 1 Hz 0.05% + 1
1.00000 MHz 10 Hz 0.05% + 1
2.0000 MHz 100 Hz 0.05% + 1
Duty Cycle
Range: 0.1% to 99.9%
Accuracy: ±(5.2% divided by the pulse width in microseconds + 2 counts) (1 ms = 1000 microseconds).
Period
Ranges: 999.99 µs, 9.999 ms, 99.99 ms, and 999 ms
Accuracy: ±(0.05% of reading + 2 counts)
Pulse Width
Ranges: 999.99 µs, 9.999 ms, 99.99 ms, and 999 ms
Accuracy: ±(5.2% divided by the pulse width in microseconds + 2 counts) (1 ms = 1000 microseconds).
1-12
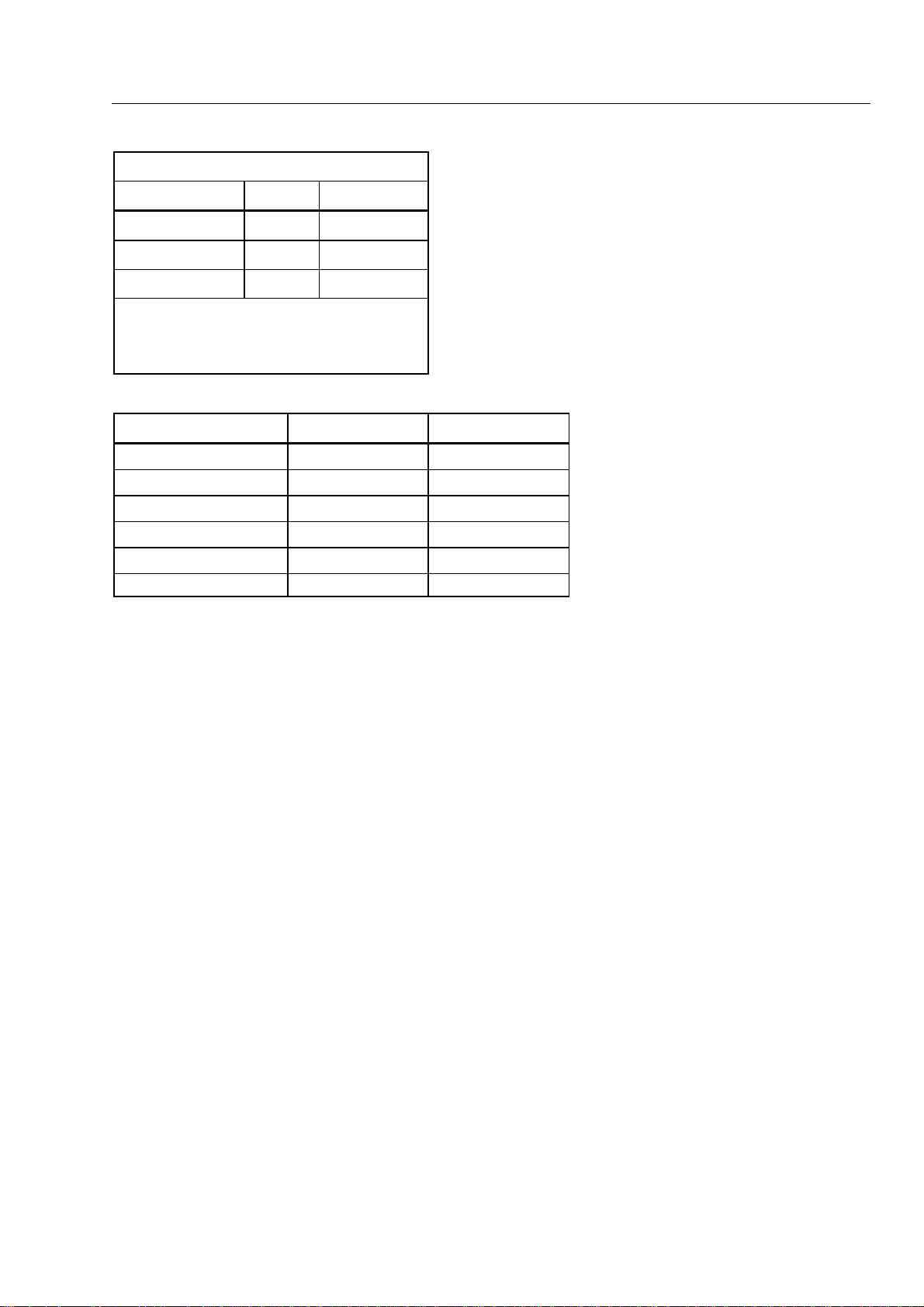
Logic (Fluke 867B Only)
Trigger Levels
Logic Family Low High
3V CMOS 1.4V 1.7V
5V CMOS 2.6V 2.8V
TTL 1.7V 1.9V
1. Frequency measurements will trigger on the
logic family high levels. All measurements are
made using the Logic/Ext. Trig. input jack.
2. For frequency > 1 MHz use full logic level.
Frequency Measurements
Frequency Resolution Accuracy
1
Introduction and Specifications
Specifications
1
1000.00 Hz
10.0000 kHz
100.000 kHz
1.00000 MHz
2.0000 MHz
10.0000 MHz 100 Hz 0.05% + 1
0.01 Hz
0.1 Hz
1 Hz
10 Hz
100 Hz
0.05% + 2
0.05% + 1
0.05% + 1
0.05% + 1
0.05% + 1
1-13
867B,863
Service Manual
Component Test
Peak Hold
MIN/MAX/AVG
View Mode Specifications
Frequency Capacitance
2 Hz 0.72 µF to 72 µF
20 Hz 0.072 µF to 7.2 µF
200 Hz 7200 pF to 0.72 µF
2 kHz 720 pF to 0.072 µF
18.75 kHz 77 pF to 7700 pF
Captures peak minimums and maximums of signals ≥10 µs.
Accuracy: ±(5% of reading + 30 counts)
Accuracy: add 8 counts to the number of counts in the accuracy table of the selected function.
Horizontal Specifications
Sample Rate: 4.8 Megasamples per second
Sample per Division: 20 per horizontal division
Samples Captured: 512 in Single Shot and Glitch Capture; 256 all other modes
Update Rate: 4 times per second
Time Base
Modes: Single Shot and Recurrent
Ranges: From 4.2 µs per division to 5 seconds per division
Trigger
Types: Internal and External
Coupling: AC, DC and Glitch Capture
External Trigger Impedance: 1 MΩ in parallel with ≤75 pF
External Trigger Input: Logic/External Trigger Terminal
External Trigger Level: ±5V adjustable in ±10 steps
Amplitude Specifications
Amplitude Resolution: 8 bits
Frequency Response (-3 dB)
Volts DC Coupled: DC to 1 MHz
Volts AC Coupled: 3 Hz to 1 MHz
1-14
Input Impedance
Refer to the meter mode specifications
Glitch Capture
Glitch Trigger Level: 20% of range 300 mV - 300V
6% of range 1000V
Minimum Glitch Time: 1 µs

Chapter 2
Theory of Operation
Title Page
2-1. Introduction............................................................................................. 2-3
2-2. Start-Up Sequence .............................................................................. 2-3
2-3. Function Selection .............................................................................. 2-3
2-4. Power Supply .......................................................................................... 2-4
2-5. Power Supply Input Voltages ............................................................. 2-4
2-6. Power Supply Output Voltages and Currents..................................... 2-6
2-7. Power Supply Signals ......................................................................... 2-7
2-8. Power ON/OFF Requirements............................................................ 2-8
2-9. NiCd Charging Requirements............................................................. 2-8
2-10. Battery and Line Level Detection....................................................... 2-8
2-11. Power Supply Functional Blocks............................................................ 2-9
2-12. Input Power Selector (A) .................................................................... 2-9
2-13. Boost Preregulator (B)........................................................................ 2-10
2-14. Battery Charger (C) ............................................................................ 2-10
2-15. DC-DC Converter (D) ........................................................................ 2-12
2-16. Backlight Current Sink (E) ................................................................. 2-12
2-17. Power Switch Circuitry (F)................................................................. 2-12
2-18. LCD Contrast Control (G) .................................................................. 2-12
2-19. Power-On Reset Circuit (H) ............................................................... 2-12
2-20. Linear Post Regulators (I)................................................................... 2-13
2-21. Input Overload Protection....................................................................... 2-13
2-22. Volt/Ohms Input Protection................................................................ 2-13
2-23. External Trigger and Logic Activity Input Protection........................ 2-14
2-24. Amps / mA / µA Input Protection....................................................... 2-14
2-25. Input Signal Conditioning....................................................................... 2-14
2-26. AC Volts ............................................................................................. 2-14
2-27. DC Volts ............................................................................................. 2-16
2-28. mV DC................................................................................................ 2-16
2-29. Ohms................................................................................................... 2-17
2-30. Diode Test........................................................................................... 2-17
2-31. Capacitance......................................................................................... 2-17
2-32. mA/µA ................................................................................................ 2-18
2-33. Amps................................................................................................... 2-18
2-34. Waveform Processing ............................................................................. 2-19
2-35. Overview............................................................................................. 2-19
2-36. Detailed Description ........................................................................... 2-19
2-1

867B,863
Service Manual
2-37. Waveform Triggering.............................................................................. 2-20
2-38. Overview............................................................................................. 2-20
2-39. Dual Trigger........................................................................................ 2-20
2-40. Single Trigger ..................................................................................... 2-21
2-41. External Trigger.................................................................................. 2-21
2-42. Glitch Capture..................................................................................... 2-22
2-43. Single Shot.......................................................................................... 2-22
2-44. Frequency Trigger .............................................................................. 2-22
2-45. Logic Activity Trigger........................................................................ 2-22
2-46. Peak Hold................................................................................................ 2-22
2-47. Auto Diode.............................................................................................. 2-22
2-48. Component Test ...................................................................................... 2-23
2-49. Digital Circuitry...................................................................................... 2-24
2-50. RS-232 Serial Port .................................................................................. 2-24
2-2

Theory of Operation
Introduction
Introduction 2-1.
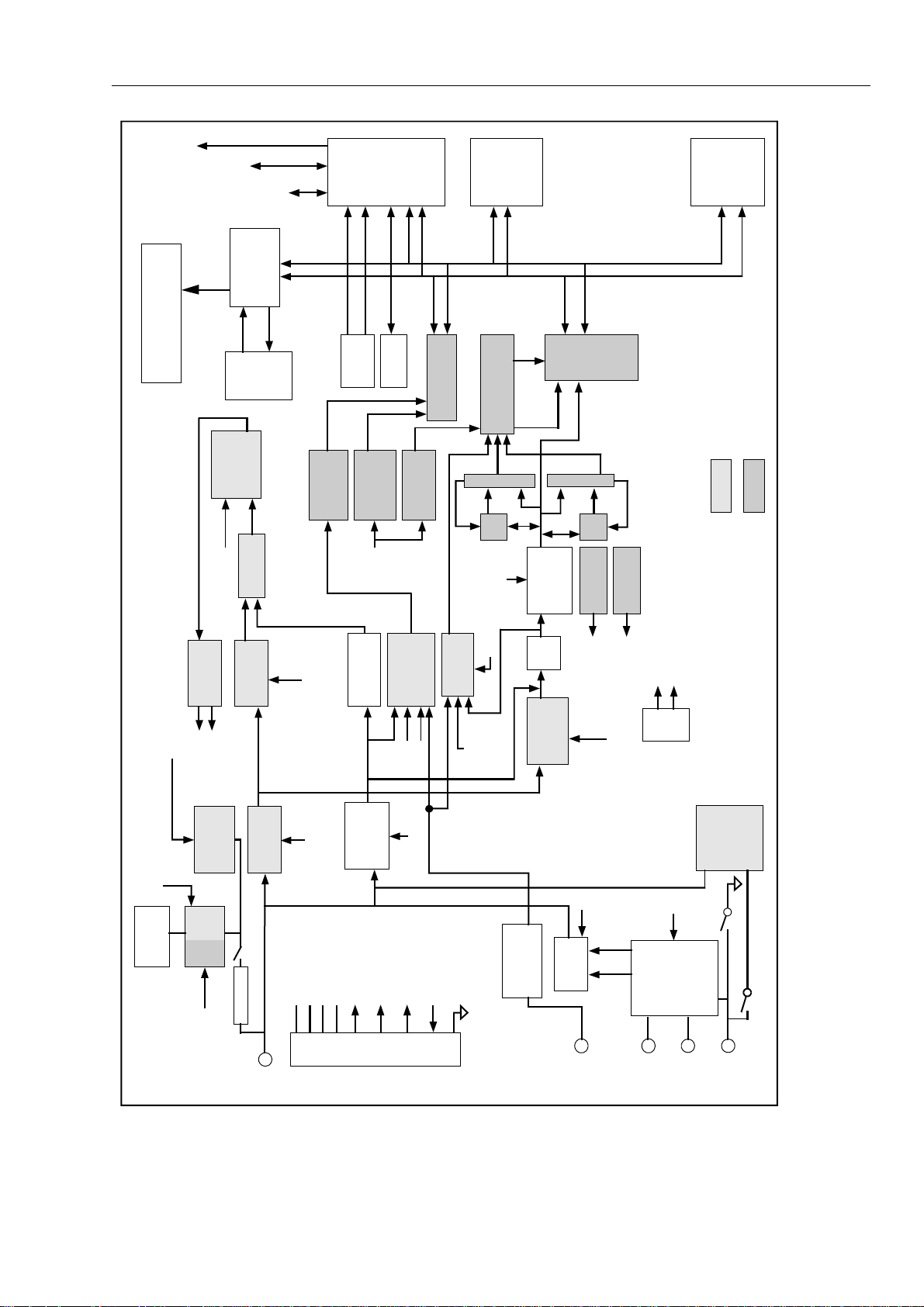
This chapter describes the functional blocks shown in Figure 2-1. Overall descriptions
are broken down into Power Supply, Analog Circuitry, and Digital Circuitry.
For all measurements, inputs (e.g., Ë and â) are applied through overvoltage
(and overcurrent) protection circuits, switched to an appropriate range, and branched into
two signal paths. One path leads first to a Fast A/D Converter (8-bit, 4.8-MHz sample
rate) that digitizes the data, then to a digital gate array that stores and processes the data.
The other path leads to a Slow A/D Converter (high accuracy, dual slope) in the U30
custom IC. The microprocessor takes data from both the Slow A/D Converter (U30) and
the custom digital IC (U24) storage to simultaneously display a waveform and a 4-1/2
digit meter reading. Power supplies include 5.2V dc and -5.2V dc for analog circuitry,
3.3V dc for digital circuits, and VEE (nominally -23V dc) for the LCD module.
Start-Up Sequence 2-2.
The GMM sequences through the following steps when power is applied:
• The 3.3V power supply comes up.
• The reset pin on the microprocessor (U25-1) goes high.
2
• The microprocessor (U25) begins executing the program stored in EEPROMs U11
and U19.
• LCD controller (U13) data is initialized.
• VEE is turned on (-20V dc), and the display comes on.
Function Selection 2-3.
When the selector is turned to a new function, a rotary switch wiper sets up a resistor
divider by grounding the selected resistor in series with R170. The resulting voltage is
read by the microprocessor (U25-83).
2-3
867B,863
Service Manual
Power Supply 2-4.
The GMM can be powered with a Fluke BP7217 rechargeable battery pack (6 - 4/3A
NiCd cells), 6 AA alkaline batteries, or a battery eliminator. The GMM automatically
detects power by source (NiCd battery pack, AA alkaline batteries, or battery
eliminator.) Diodes provide reverse polarity protection for the batteries.
The NiCd battery pack recharges in a minimum of 16 hours when the GMM is not
operating or at a trickle rate while the GMM is operating. Only cells in the Fluke BP7217
battery pack can be charged internally. Internal charging is not available with Model 863.
Caution
Do not attempt to place other batteries in the BP7217 battery
pack; damage to the batteries could result.
A low battery indicator ( ) comes on when battery voltage drops below a preset
++++
voltage level. This level is the same for all types of batteries: remaining battery life can
vary from minutes to hours, depending on battery type, ambient temperature, and battery
history. A low-battery power down can also occur. (No automatic power down occurs
when the GMM is powered by the battery eliminator.)
Refer to Chapter 1 for battery and battery eliminator specifications.
Power Supply Input Voltages 2-5.
Refer to Table 2-1.
Table 2-1. Power Supply Inputs
Input Source Voltage Lifetime (w/o Backlight)
Line 12 ±5% volts --
NiCd Battery Pack (Fluke BP7217) 6-10 volts 867B : ≥ 8 hrs typical
863: ≥ 10 hrs typical
Alkaline (6-AA) 5.5-10 volts ≥ 8 hrs typical
2-4
Theory of Operation
Power Supply
2
Adjust
LCD
Contrast
RS-232
To /F ro m
240 x200, Backlight
LCD Module - Drivers,
4 1/2 Digit
To/From uProcessor
ADControl
U21
U13
RIC
To /F r o m
LCD Controller
1335
I/O
Dsiplay
SRAM
32 x 8
A/D
(25 bits)
2 Frequency
Counters
Multiplexer
H8
I/O
INT1
Module
Keyboard
(25 bits)
Reference
Counter
CLK
MICROPROCESSOR
U25
Data
Addr
EEPROM
Status and
Control R egs
Circuitry
Divide by
U11, U19
Acquisition Cnt.
Min
ROM
(Trigger) Circuit
4.8 MHz
2 128 x 8
Addr
CompareCompare
U10
Flash A/D
U20
SRAM
32k x 8
System
Acq.
Ram
512 x 8
Data
RIC Function Blocks - U30
DIC Function Blocks - U24
Max
DAC1
8 bit/10 Mhz
DAC2
SWCrtl13
Circuitry
UART
SWCtrl3
SWControl
Ohms/
SWCrtl10
U11
10Bit DAC
Component
DACData
DC Filter
ADControl
DC Input
Capacitance
Source
Test Source
Protection
Volts/ohms
SWCrtl1
SWCrtl0
Attenuation
-5.2 volts
5.2 volts
AC Input
BATTELIM
Voltage VEE
LCD
3.27 volts
Dual
U3 RMS
Converter
Attenuation
& x10 gain
BATTLVL
BATTTYPE
To uProcessor A/D
To u P r o ce s s o r A/ D
Power Supply
Trigger
Comparators
Te st
DC Level
DAC)
DACL1
DACL2
ACR1-4
To uProcessor A/D
POWER_DOWN*
(Comp.
From uProcessor
Filter
Circuit
x1/10,x1,x10
Combination/
Multiplexer
Attenuation
Logic Activity/
External Trigger
Trigger
External
Logic Activity/
DACL2
DACL1
IR1
mA/A
uA
Wakeup* to Power Supply
To uProcessor A/D
Rotary
Switch
SWCtrl6
Voltage
Tes t
Component
Current to
SHUNTS
Switching
Current
AMPS
mA/uA
Volts/Ohms/Current
Component Test
COM
Figure 2-1. Block Diagram
os2f..eps
2-5
867B,863
Service Manual
Power Supply Output Voltages and Currents 2-6.
Refer to Table 2-2.
Table 2-2. Power Supply Outputs
Name Voltage
VDD 5.2V 0.26 5.0% 50 mV rms** 43 mA 224 mW 0.2V p-p maximum noise
VAD 3.27V 0.07 2.0% 50 mV rms** 12 mA 40 mW ±0.02%/C max
VCC 3.27V 0.07 2.0% 50 mV rms** 82 mA 271 mW VAD and VCC are tied
VSS -5.2V 0.26 5.0% 50 mV rms** 32 mA 166 mW 0.2V p-p maximum noise
VEE -20V na 5 mA 115 mW TC = -38 mV/°C, center
IBL+ * 4V ±15% na 80 mA 264 mW current for backlight
IBL- na Current Return for IBL+,
* IBL is controlled by a linear current source taken from unregulated DC.
** Measured with an 8842A in AC rms mode.
Tol ±±±± V Tol ±±±±%
Ripple
(peak to
peak)
mA Power Notes
to 1 MHz BW
together, unregulated
DC used for IBL+
to 1 MHz BW
value adjusted and
stored at test
LED, ±15%
max 1.5V burden voltage
2-6
Theory of Operation
Power Supply
Power Supply Signals 2-7.
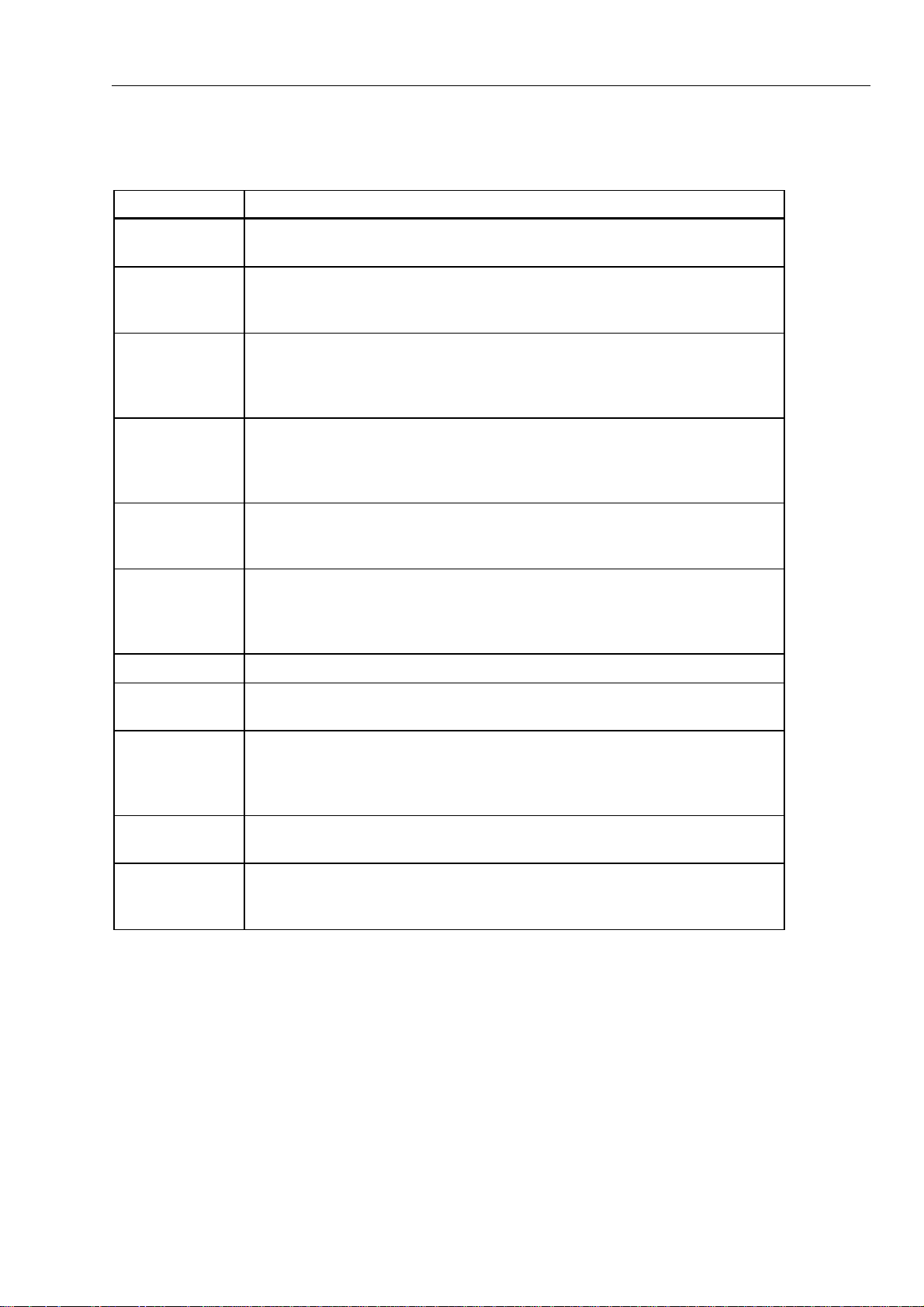
Table 2-3. Power Supply Signals
Signal Name Description
BACKLIGHT_ON* Control signal generated by U25. In Model 867B, this signal toggles the backlight
power levels.
BATT_LVL Monitors an attenuated (0 to 5V) version of the raw battery voltage. This signal is
monitored by the U25 microprocessor A/D Converter. The attenuation factor is
0.0909:1 with an output impedance of approximately 91 kΩ.
BATT_TYPE Monitors an attenuation level of the battery charging voltage. The attenuation ratio is
0.0901:1 with an output impedance of approximately 91 kΩ.=If the measured voltage
is greater than 11 volts, the battery is assumed to be an alkaline cell. Voltages 10.5
volts and below indicate that a Fluke BP7217 battery pack has been installed.
BATT_ELIM This is a contact on the battery eliminator input receptacle. It is pulled to LINE with 5
kΩ and tied to GND4 through=475Ω,=forming a 10.51:1 divider. If open (voltage
>1.0V), a line-powered battery eliminator has been installed. If closed (shorted to
ground), the battery eliminator is not plugged-in or is not powered.
2
CONTRAST PWM signal from U25. The frequency is set at U25_SYSCLK/(CLOCK_DIVIDER x
COUNTER_LIMIT), yielding 4.8 MHz/(4 x 4096), equaling 293 Hz. The PWM signal
has 12-bit resolution, which can vary the duty cycle from 0 to 100%.
IBL+ Current source generated by power supply used to run the LCD backlight. Current
source is controlled by the BACKLIGHT_ON* control signal. Typical current level is
80 mA. This is the sourcing node derived from unregulated DC, typically +6.0V
(5.8V minimum.)
IBL- Current return for IBL+, with approximately 1V burden.
POWER_DOWN Powers down the GMM. Signal is generated by U25. This signal shuts the GMM off
completely. Pulled-down to GND with 20 kΩ.
PWR_RESET* Signal generated by the power supply when the VCC power supply drops below 3.0
volts. The reset lasts 100 milliseconds minimum. If the selector is left in the OFF
position or the GMM is powered down, the PWR-RESET* signal restarts the 100 ms
time-out period. This signal is pulled up to VCC by 10 kΩ .
VEE_ON Control signal generated by U25. Turns the VEE power supply on and off. Pulled
down to ground by 100 kΩ .
WAKEUP* This signal is generated by both the rotary selector switch and the WAKEUP button.
Upon going LOW, followed by a return to HIGH, the GMM powers up. In the OFF
position, this feature is overridden by the OFF switch.
2-7

867B,863
Service Manual
Power ON/OFF Requirements 2-8.
NiCd Charging Requirements 2-9.
The GMM is turned off when the selector is rotated to OFF. If the selector is
immediately rotated beyond OFF, the GMM does not turn off. If the selector remains in
OFF for 125 ms, GMM software recognizes a valid OFF signal. If the selector remains in
the OFF position for more than 250 ms and an OFF signal is not generated, a hardware
timeout occurs and the GMM powers off.
The signal PWR_RESET* goes true (LOW) immediately when a software OFF signal or
hardware timeout is generated. This action forces a complete restart sequence, with
PWR_RESET* remaining low for at least 100 ms.
After a software OFF signal has occurred, turn the GMM on by rotating the selector to
any function or by pressing (the WAKEUP button.). If a hardware timeout has
occurred, pressing does not turn the GMM on; the selector must be rotated to a new
function.
Models 867B use an internal two-state charger. The initial charge state is at
approximately 170 mA (±30 mA) to allow for full overnight charging (16 hours
minimum). The second charge state is at approximately 40 mA (±15 mA) to allow for
battery charge maintenance without full charging from a discharged condition.
A timer (reset each time the battery eliminator is plugged in) controls the charge state.
The rate shifts to 40 mA after approximately 16 hours of accumulated charge time.
The 40-mA rate is used with batteries below approximately 6 volts to limit the amount of
power dissipated when a completely dead battery pack is used. After this 6-volt cutoff
point has been reached, the GMM starts charging at 170 mA.
Battery and Line Level Detection 2-10.
The BATT_LVL signal is an attenuated version of the battery and charging voltages.
Table 2-4 summarizes the values to be used by the software to control LOW BATTERY
detection and SOFT SHUTDOWN. After LOW BATTERY is detected, the backlight is
turned off and backlight control is disabled.
2-8
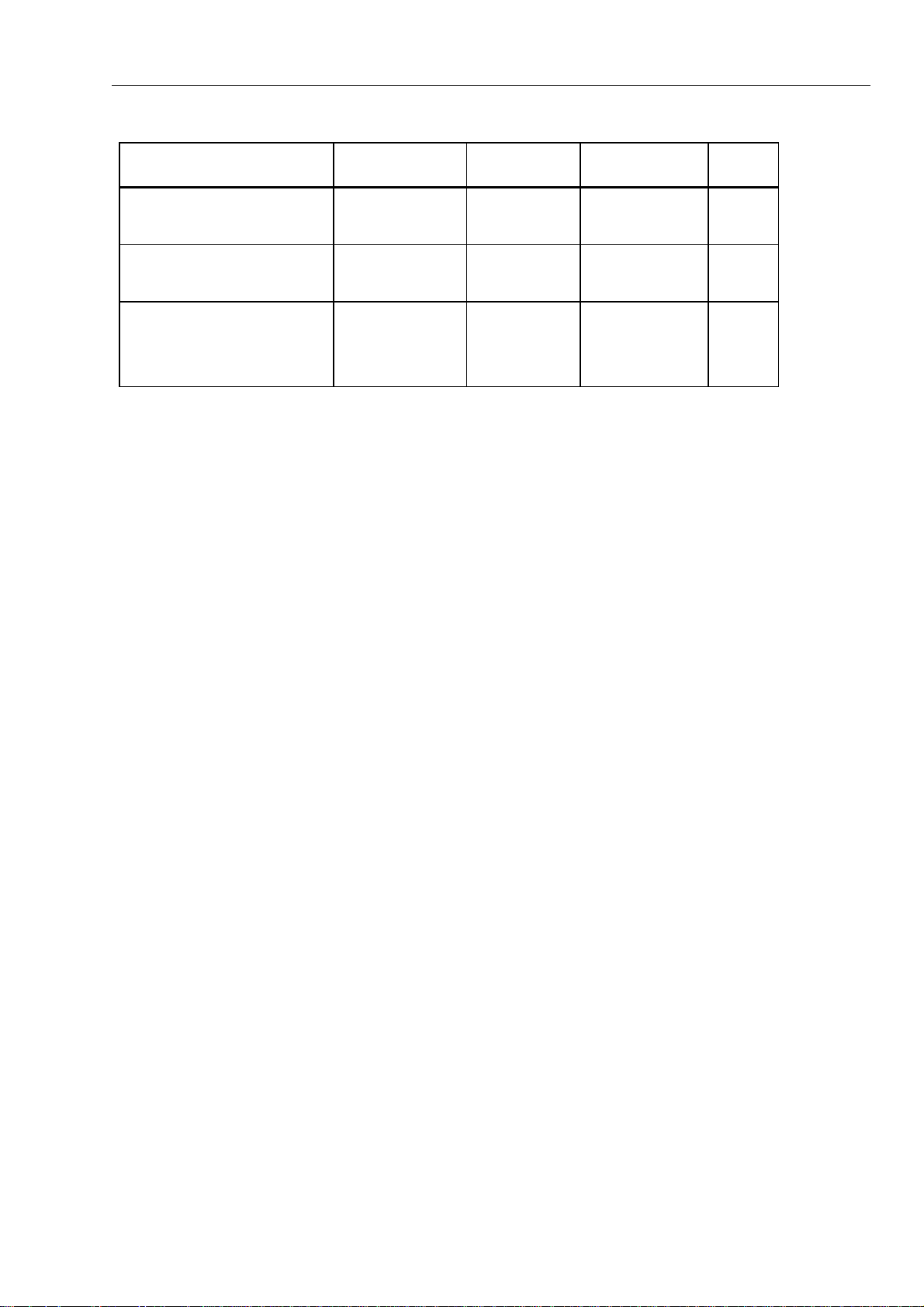
Table 2-4. Power Source Detection
Theory of Operation
Power Supply Functional Blocks
2
POWER TYPE DETECTION
Battery Eliminator connected BATT_ELIM
≥ 1.0 Volts
NiCd Battery Pack installed BATT_TYPE
5 ≤ V ≤10.5 Volts
Alkaline (AA) Batteries installed BATT_TYPE
V ≤ 4.5 or
V ≥ 11 Volts
LOW BATTERY SOFT POWER-
OFF
na na 0.0951
6.2V 5.7V 0.0909
6.2V 4.8V 0.0909
SCALE
FACTOR
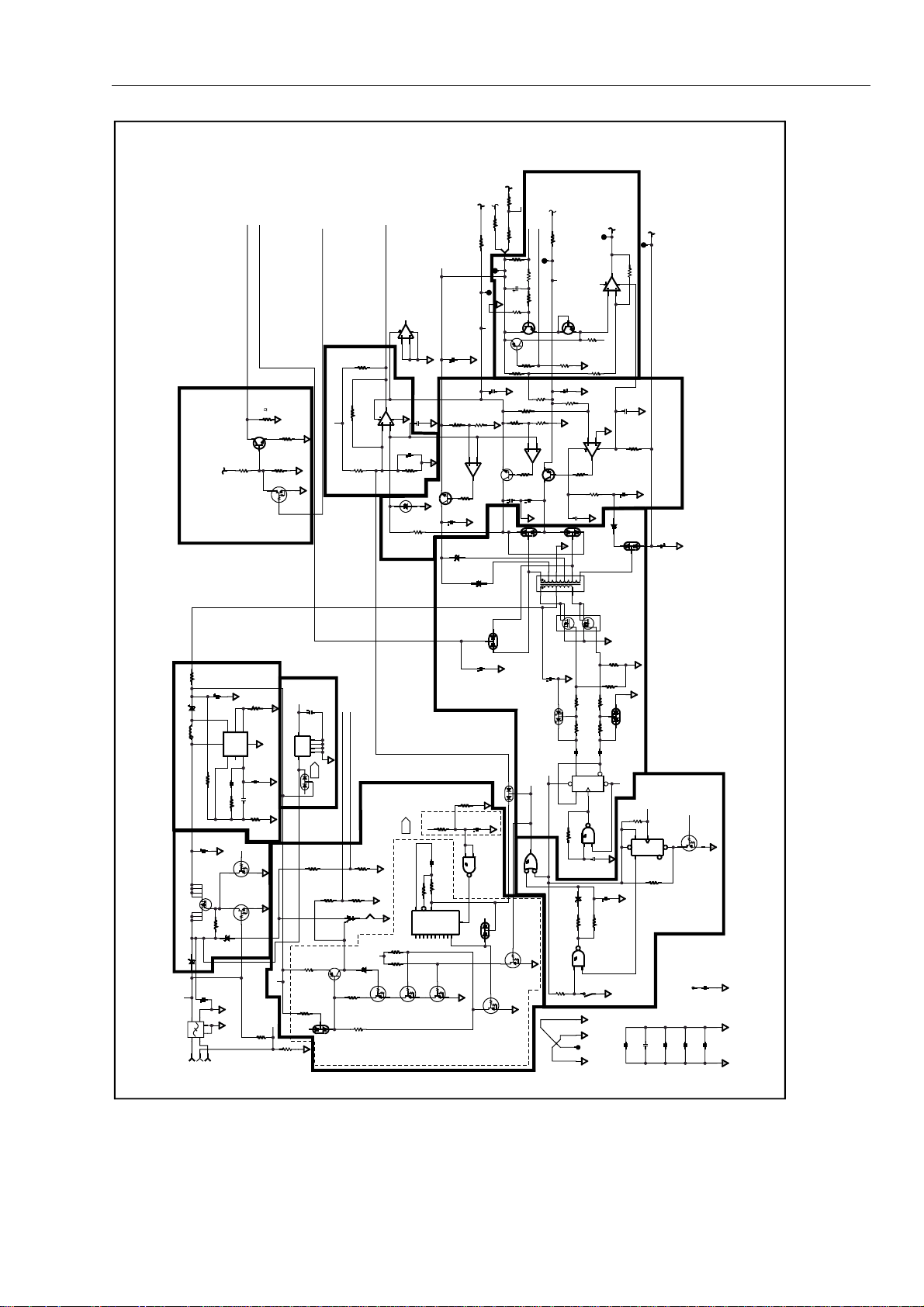
Power Supply Functional Blocks 2-11.
Refer to the Schematic Diagram in Chapter 7 during the following discussion. The power
supply consists of the circuit blocks listed below. Each block is identified with a letter
(A-J) keyed to Figure 2-2.
• Input power selector (A)
• Boost Preregulator (B)
• NiCd battery charger and timeout (C)
• DC-DC Converter (D)
• Backlight current sink (E)
• Power switch, wake-up and power down circuitry (F)
• LCD contrast control and temperature compensator (G)
• Power on reset (H)
• Linear post-regulators (I)
• +5 volt bias supply (J)
Input Power Selector (A) 2-12.
The input power selector automatically selects either battery eliminator power (line) or
battery. If a battery eliminator is connected to the GMM, +12 volts (±5%) is applied
through line filter FL1 to the anode of CR21. This 12 volts turns on Q13, which pulls
down the gate of Q14, turning it on. Current can then flow from the battery eliminator to
the boost circuit (B). Note that CR22 is back-biased.
If an eliminator is not connected, Q13 is off. Current is not allowed to flow through Q14
until Q12 is turned on. Q12 is turned on when enough voltage remains on the battery to
supply the bias regulator (J) and the power wake-up circuitry is enabled. When the GMM
is off (with no eliminator connected), Q14 is off and only the bias supply draws current.
The maximum off-state current draw is 100 µA.
CR21 and CR22 perform the power selection process.
2-9

867B,863
Service Manual
Boost Preregulator (B) 2-13.
Battery Charger (C) 2-14.
The boost preregulator outputs +15 volts from an input of +12 volts from the battery
eliminator or 5.5 to 10 volts from the battery.
U27 provides this boost in conjunction with L1, CR20, and C3. If U27 is not functioning,
the voltage at the positive of C3 is approximately 0.4 volts below the voltage on C90.
R114 provides peak current limiting to prevent rapid burnout of the boost circuit in the
event of an overload. Since R114 requires a functional U27, it does not provide complete
protection. R12 and R73 set the output voltage, while the other discrete components
provide timing and compensation for the regulator.
The output of this stage is delivered to the NiCd battery charger (C) and to the DC-DC
converter (D). R125 allows the charger and boost circuit to be tested independently of
the rest of the GMM. R125 is especially useful if a large load causes <15 volts at the
cathode of CR20.
The battery charger consists of the following two sections:
• Q22 and its associated components provide a linear current source of either 170 mA
or 40 mA to charge the NiCd battery. Transistors Q1, Q2, Q3, Q6, and Q11 provide
logic control of the charger state.
• The other part of the circuit is U32 and its associated components, which provide a
timeout of at least 16 hours to prevent continuous overcharging of the battery. This
circuit is reset each time a battery eliminator is plugged in (via U34, R141, R140
and C91).
A full charge of approximately 170 mA can only be provided to the battery if Q1, Q2,
and Q6 are turned on, Q3 is off, and Q11 is off. These states correspond to the GMM
being connected to line but turned off and U32 not being timed out. U32 is inhibited
from advancing by CR5 when power is on.
VR1 prevents Q2 from turning on until the battery voltage rises above about 5.8 volts.
This prevents excessive power dissipation in Q22 with a dead battery or shorted cells.
Note
The Fluke battery pack (BP7217) uses an extra wire to allow charging
current to flow. If individual batteries are installed, no connection is made,
and no charging current can flow.
2-10
Theory of Operation
Power Supply Functional Blocks
VCC
+3.3
0
VDD
VAD
RIC_VCC
R60
+5.2
IBL-
IBL+
BACKLIGHT_ON*
PWR_RESET*
INT_VCC
0
R87
0
R52
TP5
TP4
7
U22
LM393DT
RES
8
4
6
5
10.0K
R115
U22
R158
47
(867B only)
D
0
R16
Q21
4401
1
80 MA
BACKLIGHT
CURRENT SINK
3.24K
R106
VDD
E
0.2 (867B only)
D
3.24K
R11
D
D
10K
MUN2211
Q5
LM393DT
R124
3.32M
INT_VCC
8
3
6.34K
R69
H
D
1
RES
0.1UF
C58
25V
CER
D
4
D
2
10UF
C19
20%
16V
D
R81
31.6K
4401
+2.5V
U31
Q23
D
C9
LM4040-2.5
R119
10.0K
D
INT_VDD
1UF
C2
20V
D
1UF
C88
20V
3.24K
R128
R132
10.0K
D
6
5
4401
Q18
VCCDRIVE
7
MC33172
U2
475
R72
10UF
20%
16V
D
CR19
1N5817
CR18
1N5817
VSS
VEE_ON
CONTRAST
0
R62
R48
M2
TP1
10.0K
R35
R8
10.0K
10UF
C62
6V
R43
221K
221K
R41
6429
Q17
100K
R143
Q10
5087
R123
R116
1.82K
D
5.62K
10.0K
R19
10.0K
10.7K
R39
R89
3
2
U4
MC33172
VDDDRIVE
1
475
R133
1UF
C65
1UF
C61
20V
20V
D
CR16
MMBD7000
1
7
G
-5.2
VEE
-20
-24V
0
INT_VSS
Q19
4403
8
TP2
TP3
1
CONTRAST
CONTROL
LCD
Q20
6429
R142
100K
1UF
C12
20V
10.0K
R13
D
+REG
R46
0.22UF
C63
D
65432
9
8
7
5
R50
316K
MC33172
U2
VCCDRIVE
8
4
INT_VDD
3
2
R120
59.0K
INT_VSS
D
18.7K
R9
D
D
6
5
8
4
U4
7
475
MC33172
VDDDRIVE
475
R94
CER
D
VR2
CR17
MMBD7000
T1
RITA-6303
6
TPS ARE 40MIL PADS
0.22UF
C34
CER
-REG
D
I
475
R117
1UF
C1
35V
D
5240B
CR6
MMBD7000
1UF
C71
35V
D
2
1
3
2
4
Q16
CR12
BAV74
1UF
C21
20V
0
R125
D
R114
0.2
C3
25V
CR20
20%
220UF
1N5817
21
L1
330UH
8
VS
INM COL
1
140.0K
R12
2200PF
C59
BA
R122
D
C90
25V
20%
220UF
8765
SI9430DY
Q14
4
321
R137
100K
CR22
CR21
1N5817
10UF
C60
35V
LINE
CBB
D D
CBB
GND
FL1
PSG CG1
312
P3P3P3
D
765
LM3578AN
EMIT
CLIMOSC
4
D
GND
INP
3
2
680PF
C56
CER
CER
22PF
C23
CER
221K
D D
R73 U27
10.0K
POK-1
Q12
MUN2211
10K
D
Q13
MUN2211
D
10K
1N5817
+15
BATT_ELIM
4.99K
R7
J
+5B
16V
C85
10UF
20%
1
7632
BATT_LVL
BATT_TY PE
OUTIN
GND
U15
LM2936M
D
8
4
CR8
MMBD7000
C
100K
R141
LINE
5
1.00MEG
R14
12.1
R113
1/2W
1.82K
R74
D
R6
475
100K
R27
D
100K
R29
1.00MEG
R56
D
M4
D
BT1
6-4/3A
VR1
LINE
5231B
Q22
MJD32
10%
R15
6.49K
R55
10K
Q2
MUN2211
24.9K
R100
CR9
MMBD7000
10UF
16VAL20%
C84
R68
R44
1.00MEG
464K
111097
CKI
CKO
CKO*
+5B
U32
74HC4060DT
Q5Q6Q7Q8Q9
Q10
Q12
Q13
Q14
Q4
1
6
5
3
2
4
151413
100K
R28
100K
10K
10K
Q1
Q6
MUN2211
MUN2211
D
CR5
66.5K
R140
MMBD7000
D
1UF
C91
20V
D
5
4
+5B
U34
HC132
6
12
RESET
MMBD7000
CR15
D
10K
Q3
MUN2211
SI9955DY
1UF
C94
35V
D
CR14
BAT54S
+5B
POK-1
3
+5B
U34
HC132
1
2
10K
D
Q11
MUN2211
R126
D
M1
D
10.0K
R127
D
R23
22.1
R36
475
C57
CER
0.01UF
9
Q
U33
10
PR
HC74
D
11
12
11
U34
R10
10.0K
HC132
13
12
C22
CR25
BAT54
R138
100K
8
+5B
HC132
U34
9
10
S1
1.00MEG
3
5
1
TP6
D
D
10.0K
R131
D
R26
22.1
CR10
BAT54S
R17
475
CER
C24
0.01UF
8
Q
13
CL
+5B
POK-1
WAKEUP*
R57
100K
2
+5B
D
4
PR
HC74
Q
D
U33
5
CER
1%
470PF
1UF
C10
20V
D
R139
1.00MEG
D
OFF
C103
C104
CER
1000PF
MECCA CLIP TP
POWER_DOWN
3
10K
1
CL
+5B
Q
6
100K
R130
D
Q30
MUN2211
F
47PF
C117
5%
CER
D
WP1
PUT CAP AT
SHIELD SCREW
3
C105
C106
C107
CER
1000PF
CER
CER
CER
1000PF
1000PF
1000PF
D
Figure 2-2. Power Supply Blocks
os3f.eps
2-11
 Loading...
Loading...