Page 1

43
®
Power Quality A nal yzer
Service Manual
4822 872 05377
September 1998, Rev. 3, 07/ 00
© 1998, 2000 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserv ed. Printed in the Netherlands
All product names are trademarks of their respective companies.
Page 2

SERVICE CENTERS
To locate an authorized service center, visit us on the World Wide Web:
http://www.fluke.com
or call Fluke using any of the phone num bers li ste d bel ow:
+1-888-993-5853 in U.S.A. and Canada
+31-402-678-200 in Europe
+1-425-356-5500 from other countries
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter Title Page
1 Safety Instructions............................................................................. 1-1
1.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 1-3
1.2 Safet y Precautions ................................................................................... 1-3
1.3 Caution and Warning Statements............................................................. 1-3
1.4 Symbols.................................................................................................. 1-3
1.5 Impaired Safety....................................................................................... 1-4
1.6 General Safety Information...................................................................... 1-4
2 Characteristics................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 2-3
2.2 Safety Specifications............................................................................... 2-3
2.3 Function Specifications........................................................................... 2-4
2.3.1 Electrical functions........................................................................... 2-4
2.3.2 Scope............................................................................................... 2-5
2.3.3 Meter................................................................................................ 2-7
2.3.4 Record.............................................................................................. 2-7
2.4 Miscellaneous.......................................................................................... 2-8
2.5 Current Probe.......................................................................................... 2-8
2.6 Environmental Conditions....................................................................... 2-9
2.7 Electromagnetic Immunity....................................................................... 2-10
3 Circuit Descriptions........................................................................... 3-1
3.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 3-3
3.2 Block Diagram........................................................................................ 3-3
3.2.1 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits ............................................ 3-3
3.2.2 Trigger Circuit.................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.3 Digital Circuit.................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.4 Power Circuit................................................................................... 3-6
3.2.5 Start-up Sequence, Operating Modes................................................ 3-7
3.3 Detailed Circuit Descriptions................................................................... 3-9
3.3.1 Power Circuit................................................................................... 3-9
3.3.2 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits ............................................ 3-14
3.3.3 Trigger Circuit.................................................................................. 3-20
i
Page 4

43
Service Manual
3.3.4 Digital Circuit.................................................................................. 3-24
4 Performance Verification.................................................................. 4-1
4.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 4-3
4.2 Equipment Required For Verification...................................................... 4-3
4.3 How To Verify........................................................................................ 4-3
4.4 Display and Backlight Test...................................................................... 4-4
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in the SCOPE MODE. ..................................... 4-5
4.5.1 Input 1 Trigger Sensitivity Test........................................................ 4-6
4.5.2 Input 1 Frequency Response Upper Transition Point Test................. 4-7
4.5.3 Input 1 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test................................ 4-7
4.5.4 Input 2 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test................................ 4-9
4.5.5 Input 2 Trigger Level and Trigger Slope Test ................................... 4-10
4.5.6 Input 2 Trigger sensitivity Test......................................................... 4-12
4.5.7 Input 1 Trigger Level and Trigger Slope Test ................................... 4-13
4.5.8 Input 1 and 2 DC Voltage Accuracy Test.......................................... 4-15
4.5.9 Input 1 and 2 AC Voltage Accuracy Test.......................................... 4-17
4.5.10 Input 1 and 2 AC Input Coupling Test............................................ 4-19
4.5.11 Input 1 and 2 Volts Peak Measurements Test.................................. 4-20
4.5.12 Input 1 and 2 Phase Measurements Test.......................................... 4-21
4.5.13 Input 1 and 2 High Voltage AC & DC Accuracy Test..................... 4-22
4.6 Ohms/Continuity/Capacitance................................................................. 4-25
4.6.1 Resistance Measurements Test. ........................................................ 4-25
4.6.2 Diode Test Function Test ................................................................. 4-26
4.6.3 Continuity Function Test.................................................................. 4-26
4.6.4 Capacitance Measurements Test....................................................... 4-27
4.7 Inrush Current......................................................................................... 4-28
4.8 Sags & Swells......................................................................................... 4-29
4.9 Harmonics............................................................................................... 4-30
4.10 VOLT/AMPS/HERTZ........................................................................... 4-30
4.11 POWER. ............................................................................................... 4-31
4.12 Transients. ............................................................................................. 4-32
5 Calibration Adjustment...................................................................... 5-1
5.1 General.................................................................................................... 5-3
5.1.1 Introduction...................................................................................... 5-3
5.1.2 Calibration number and date............................................................. 5-3
5.1.3 General Instructions.......................................................................... 5-4
5.2 Equipment Required For Calibration....................................................... 5-4
5.3 Starting Calibration Adjustment.............................................................. 5-4
5.4 Contrast Calibration Adjustment.............................................................. 5-6
5.5 Warming Up & Pre-Calibration............................................................... 5-7
5.6 Final Calibration...................................................................................... 5-7
5.6.1 HF Gain Input 1. .............................................................................. 5-8
5.6.2 Delta T Gain, Trigger Delay Time & Pulse Adjust Input 1 ............... 5-9
5.6.3 Gain DMM (Gain Volt).................................................................... 5-10
5.6.4 Volt Zero.......................................................................................... 5-12
5.6.5 Gain Ohm......................................................................................... 5-12
5.6.6 Capacitance Gain Low and High ...................................................... 5-13
5.6.7 Capacitance Clamp & Zero............................................................... 5-14
5.6.8 Capacitance Gain.............................................................................. 5-14
5.7 Save Calibration Data and Exit................................................................ 5-15
6 Disassembling ................................................................................... 6-1
ii
Page 5

Contents (continued)
6.1. Introduction............................................................................................ 6-3
6.2. Disassembling Procedures...................................................................... 6-3
6.1.1 Required Tools................................................................................. 6-3
6.2.2 Removing the Battery Pack.............................................................. 6-3
6.2.3 Removing the Bail............................................................................ 6-3
6.2.4 Opening the Test Tool...................................................................... 6-3
6.2.5 Removing the Main PCA Unit.......................................................... 6-5
6.2.6 Removing the Display Assembly...................................................... 6-6
6.2.7 Removing the Keypad and Keypad Foil............................................ 6-6
6.3 Disassembling the Main PCA Unit.......................................................... 6-6
6.4 Reassembling the Main PCA Unit........................................................... 6-8
6.5 Reassembling the Test Tool..................................................................... 6-8
7 Corrective Maintenance .................................................................... 7-1
7.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 7-3
7.2 Starting Fault Finding.............................................................................. 7-4
7.3 Charger Circuit........................................................................................ 7-4
7.4 Starting with a Dead Test Tool................................................................ 7-6
7.4.1 Test Tool Completely Dead .............................................................. 7-6
7.4.2 Test Tool Software Does not Run..................................................... 7-7
7.4.3 Software Runs, Test Tool not Operative........................................... 7-7
7.5 Miscellaneous Functions ......................................................................... 7-7
7.5.1 Display and Back Light.................................................................... 7-7
7.5.2 Fly Back Converter .......................................................................... 7-8
7.5.3 Slow ADC........................................................................................ 7-9
7.5.4 Keyboard.......................................................................................... 7-10
7.5.5 Optical P o rt (S eri al R S232 Interface)................................................ 7-11
7.5.6 Input Channel 1 and 2 Voltage Measurements.................................. 7-11
7.5.7 Ohms and Capacitance Measurements.............................................. 7-12
7.5.8 Trigger Functions............................................................................. 7-13
7.5.9 Reference Voltages........................................................................... 7-14
7.5.1 0 Buzzer Circuit ................................................................................ 7-14
7.5.11 Reset ROM Line (ROMRST)......................................................... 7-14
7.5.12 RAM Test...................................................................................... 7-14
7.5.13 Power ON/OFF.............................................................................. 7-15
7.5.14 PWM Circuit.................................................................................. 7-15
7.5.15 Randomize Circuit.......................................................................... 7-15
8 List of Replaceable Parts.................................................................. 8-1
8.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 8-3
8.2 How to Obtain Parts................................................................................ 8-3
8.3 Final Assembly Parts............................................................................... 8-4
8.4 Main PCA Unit Parts............................................................................... 8-6
8.5 Main PCA Parts ...................................................................................... 8-7
8.6 Accesso ry Replacement Parts .................................................................. 8-23
9 Circuit Diagrams................................................................................ 9-1
9.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 9-3
9.2 Schematic Diagrams ................................................................................ 9-3
10 Modifications...................................................................................... 10-1
10.1 Software modifications.......................................................................... 10-3
10.2 Hardware modifications......................................................................... 10-3
iii
Page 6

Page 7

List of Tables
Table Title Page
1-1. Symbols............................................................................................................ 1-3
2-1. No Visible Disturbance...................................................................................... 2-10
2-2. Disturbance < 1 %............................................................................................. 2-10
2-3. Disturbance < 10 %........................................................................................... 2-10
3-1. Fluke 43 Main Blocks....................................................................................... 3-3
3-2. Fluke 43 Operating Modes ................................................................................ 3-8
3-3. Input 1 Volt age Ranges And Trace S ensitivity................................................... 3-17
3-4. Ohms Ranges , Trace Sensitivity, and Current.................................................... 3-18
3-5. Capacitance Ranges, Current, and Pulse Width.................................................. 3-19
3-6. D-ASIC PWM Signals ...................................................................................... 3-27
4-1. Input 1 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test................................................. 4-8
4-2. Volts DC Measurement Verification Points....................................................... 4-17
4-3. Volts AC Measurement Verification Points....................................................... 4-19
4-4. Input 1 and 2 AC Input Coupling Verification Points ........................................ 4-20
4-5. Volts Peak Measurement Verification Points..................................................... 4-21
4-6. Phase Measurement Verification Points............................................................. 4-22
4-7. V DC and V AC High Voltage Verification Tests.............................................. 4-25
4-8. Resistance Measurement Verification Points...................................................... 4-26
4-9. Capacitance Measurement Verification Points................................................... 4-27
4-10. Volts/AMPS/HERZ verification points.............................................................. 4-31
4-11. Power Measurement Verification points............................................................ 4-31
5-1. HF Gain Calibration Points Fast ........................................................................ 5-9
5-2. HF Gain Calibration Points Slow....................................................................... 5-9
5-3. Volt Gain Calibration Points <300V .................................................................. 5-11
5-4. Ohm Gain Calibration Points............................................................................. 5-13
7-1. Starting Fault Finding........................................................................................ 7-4
8-1. Final Assembly Parts......................................................................................... 8-4
8-2. Main PCA Unit................................................................................................. 8-6
8-3. Main PCA......................................................................................................... 8-7
9-1. Parts Location Main PCA Side 1....................................................................... 9-4
9-2. Parts Location Main PCA Side 2....................................................................... 9-5
v
Page 8

Page 9

List of Figures
Figure Title Page
2-1. Max. Input Voltage vs. Frequency..................................................................... 2-4
3-1. Fluke 43 Block Diagram.................................................................................... 3-2
3-2. Fluke 43 Start-up Sequence, Operating Modes................................................... 3-8
3-3. Power Supply Block Diagram............................................................................ 3-9
3-4. C HAGATE Cont rol Volt age.............................................................................. 3-11
3-5. Fly-Back Converter Current and Control Voltage.............................................. 3-12
3-6. Fly-Back Converter Block Diagram................................................................... 3-13
3-7. Back Light Converter Voltages.......................................................................... 3-14
3-8. C-ASIC Block Diagram..................................................................................... 3-15
3-9. Capacitance Measurement................................................................................. 3-19
3-10. T-ASIC Trigger Section Block Diagram............................................................ 3-20
3-11. Random Repetitive Sampling Mode .................................................................. 3-22
3-12. Reference Voltage Section................................................................................. 3-23
3-13. LCD Control..................................................................................................... 3-26
4-1. Display Pixel Test Pattern ................................................................................. 4-4
4-2. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Scope Output 50Ω.................................................. 4-6
4-3. Test Tool Input 2 to 5500A NORMAL output................................................... 4-9
4-4. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Normal Output....................................................... 4-13
4-5. Test Tool Input 1-2 to 5500A Normal Output.................................................... 4-15
4-6. Test Tool Input 1-2 to 5500A Normal Output for >300V................................... 4-22
4-7. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Normal Output 4-Wire ........................................... 4-25
4-8. Test Tool Input 2 to 5500A NORMAL output................................................... 4-28
4-9. Test Tool Input 1 & 2 5500A Normal Output .................................................... 4-29
4-10. Bargraph Harmonics Volt.................................................................................. 4-30
4-11. Bargraph Harmonics Ampere............................................................................. 4-30
4-12. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Normal Output ....................................................... 4-32
5-1. Version & Calibration Screen ............................................................................ 5-3
5-2. Display Test Pattern .......................................................................................... 5-7
5-3. HF Gain Calibration Input Connections............................................................. 5-8
5-4. 5500A Scope Output to Input 1 ......................................................................... 5-10
5-5. Volt Gain Calibration Input Connections <300V............................................... 5-11
5-6. Volt Gain Calibration Input Connections 500V ................................................. 5-12
5-7. Four-wire Ohms calibration connections............................................................ 5-13
5-8. Capacitance Gain Calibration Input Connections............................................... 5-14
6-1. Fluke 43 Main Assembly................................................................................... 6-4
vii
Page 10

43
Service Manual
6-2. Flex Cable Connectors....................................................................................... 6-5
6-3. Main PCA Unit Assembly................................................................................. 6-7
6-4. Mounting the display shielding bracket.............................................................. 6-9
6-5. Battery pack installation.................................................................................... 6-9
7-1. Operative Test Tool without Case...................................................................... 7-3
8-1. Fluke 43 Final Assembly................................................................................... 8-5
8-2. Main PCA Unit................................................................................................. 8-7
9-1. Circuit Diagram 1, Channel 1 Circuit ................................................................ 9-7
9-2. Circuit Diagram 2, Channel 2 Circuit ................................................................ 9-8
9-3. Circuit Diagram 3, Trigger Circuit..................................................................... 9-9
9-4. Circuit Diagram 4, Digital Circuit ..................................................................... 9-10
9-5. Circuit Diagram 4 (cont), Digital Circuit Keyboard ........................................... 9-11
9-6. Circuit Diagram 5, Power Circuit...................................................................... 9-12
9-7. Main PCA side 1, PCB Version <3.................................................................... 9-13
9-8. Main PCA side 2, PCB Version <3.................................................................... 9-14
9-9. Main PCA side 1, PCB version 3....................................................................... 9-15
9-10. Main PCA side 2, PCB version 3....................................................................... 9-16
viii
Page 11

Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
Title Page
1.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 1-3
1.2 Safet y Precautions ................................................................................... 1-3
1.3 Caution and Warning Statements............................................................. 1-3
1.4 Symbols.................................................................................................. 1-3
1.5 Impaired Safety....................................................................................... 1-4
1.6 General Safety Information...................................................................... 1-4
1-1
Page 12

Page 13
1.1 Introduction
Read these pages carefully before beginning to install and use the instrument.
The following paragraphs contain information, cautions and warnings which must be
followed to ensure safe operation and to keep the instrument in a safe condition.
Servicing described in this manual is to be done only by
qualified ser vice personnel. To avoid electrical shock, do not
service the instrument unless you are qualified to do so.
1.2 Safety Precautions
For the correct and safe use of this instrument it is essential that both operating and
service personnel follow general l y accept ed safet y procedures i n addition to the safety
precautions s p eci fied in this manual. S pecific warning and cau t i o n s tatements, where
they apply, will be found throughout the manual. Where necessary, the warning an d
caution s t at em en t s an d / o r s y m b o l s are m ark ed o n t h e i n s t ru m en t .
Warning
Safety Instructions
1.1 Introduction
1
1.3 Caution and Warning Statements
Caution
Used to indicate correct operating or mainte nance procedures
to prevent damage to or destruction of the equipment or other
property.
Warning
Calls attention to a potential danger that requires correct
procedures or practices to prevent personal injury.
1.4 Symbols
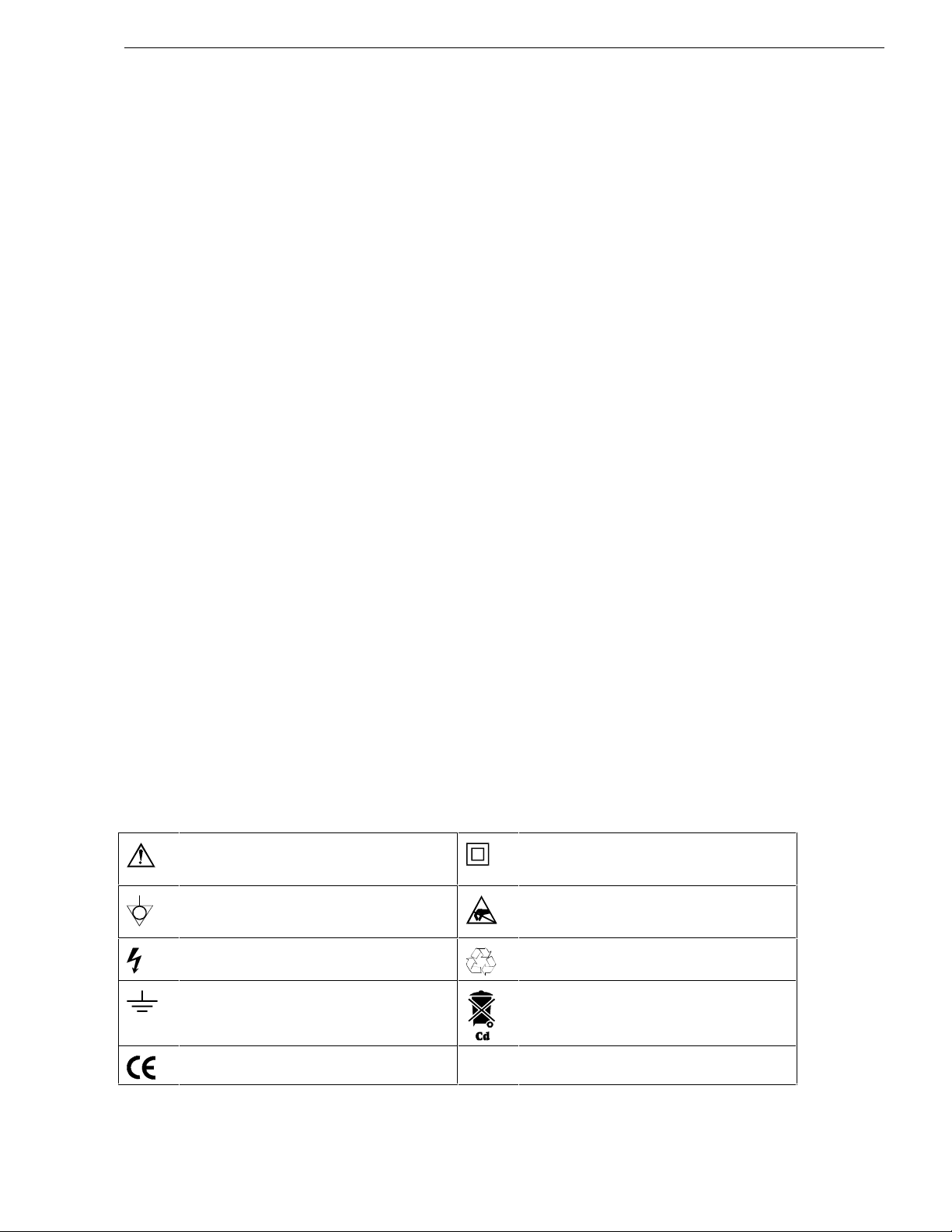
Table 1-1 shows the symbols used on the test tool or in this manual.
Table 1-1. Symbols
Read the safety information in the Users
Manual
Equal potential inputs, connected
internally
DOUBLE INSULATION (Protection
Class)
Static sensitive components
(black/yellow).
Live voltage Recycling information
Earth Disposal information
Conformité Européenne
1-3
Page 14

43
Service Manual
1.5 Impaired Safety
1.6 General Safety Information
Whenever it is likely that safety has been impaired, the instrument must be turned off
and disconnected from line power. The matter should then be referred to qualified
technicians. Safety is likely to be impaired if, for example, the instrument fails to
perform the intended measurements or shows visible damage.
Warning
Removing the instrument covers or removing parts, except
those to which access can be gained by hand, is likely to
expose live parts and accessible terminals which can be
dangerous to life.
The instrument shall be disconnected from all voltage sources before it is opened.
Capacitors i n s i d e t h e i n s t ru m en t can h o l d t h ei r ch arge ev en i f t h e i n s t ru m en t h as been
separated from all voltage sources.
Components which are import ant for t he s afety of t h e in st rum ent m ay only be repl aced
by components obtained through your local FLUKE organization. These parts are
indicated wi t h an as t eri s k (* ) i n t h e L i s t o f R ep l aceab l e P art s , Chapter 8.
1-4
Page 15

Chapter 2
Characteristics
Title Page
2.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 2-3
2.2 Safety Specifications............................................................................... 2-3
2.3 Function Specifications........................................................................... 2-4
2.3.1 Electrical functions........................................................................... 2-4
2.3.2 Scope............................................................................................... 2-5
2.3.3 Meter................................................................................................ 2-7
2.3.4 Record.............................................................................................. 2-7
2.4 Miscellaneous.......................................................................................... 2-8
2.5 Current Probe.......................................................................................... 2-8
2.6 Environmental Conditions....................................................................... 2-9
2.7 Electromagnetic Immunity....................................................................... 2-10
2-1
Page 16

Page 17

2.1 Introduction
Safety Characteri s ti cs
The Fluke 4 3 h as b een d esigned and tested in accordance wi t h S t an d ard s ANSI/ISA
S82.01-1994, EN 61010.1 (1993) (IEC 1010-1), CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 1010. 1-92
(including approval), UL3111-1 (including approval) Safety Requirements for
Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Use.
This manual contains information and warnings that must be followed by the user to
ensure safe operation and to keep the instrument in a safe condition. Use of this
equipment in a manner not specified by the manufacturer may impair protection
provided by the equipment.
Performance Cha racteri s tics
FLUKE guarantees the properties expressed in numerical values with the stated
tolerance. Specified non-tolerance numerical values indicate those that could be
nominally expected from the mean of a range of identical ScopeMeter test tools.
Environmental Data
The environmental data mentioned in this manual are based on the results of the
manufacturer’s verification procedures.
Characteristics
2.1 Introduction
2
2.2 Safety Specifications
Safety Characteri s ti cs
Designed and tested for measurements on 600 Vrms Category III, Pollut i on Degree 2
in accordance wit h :
• EN 61010.1 (1993) (IEC 1010-1)
• ANSI/ISA S82.01-1994
• CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.1010.1-92 (including approval)
• UL3111-1 (including approval)
Installat i o n Category III refers to distributi o n l ev el and fi x ed i n s t al l at i o n ci rcu i t s
inside a building.
Maximum input voltage Input 1 and 2
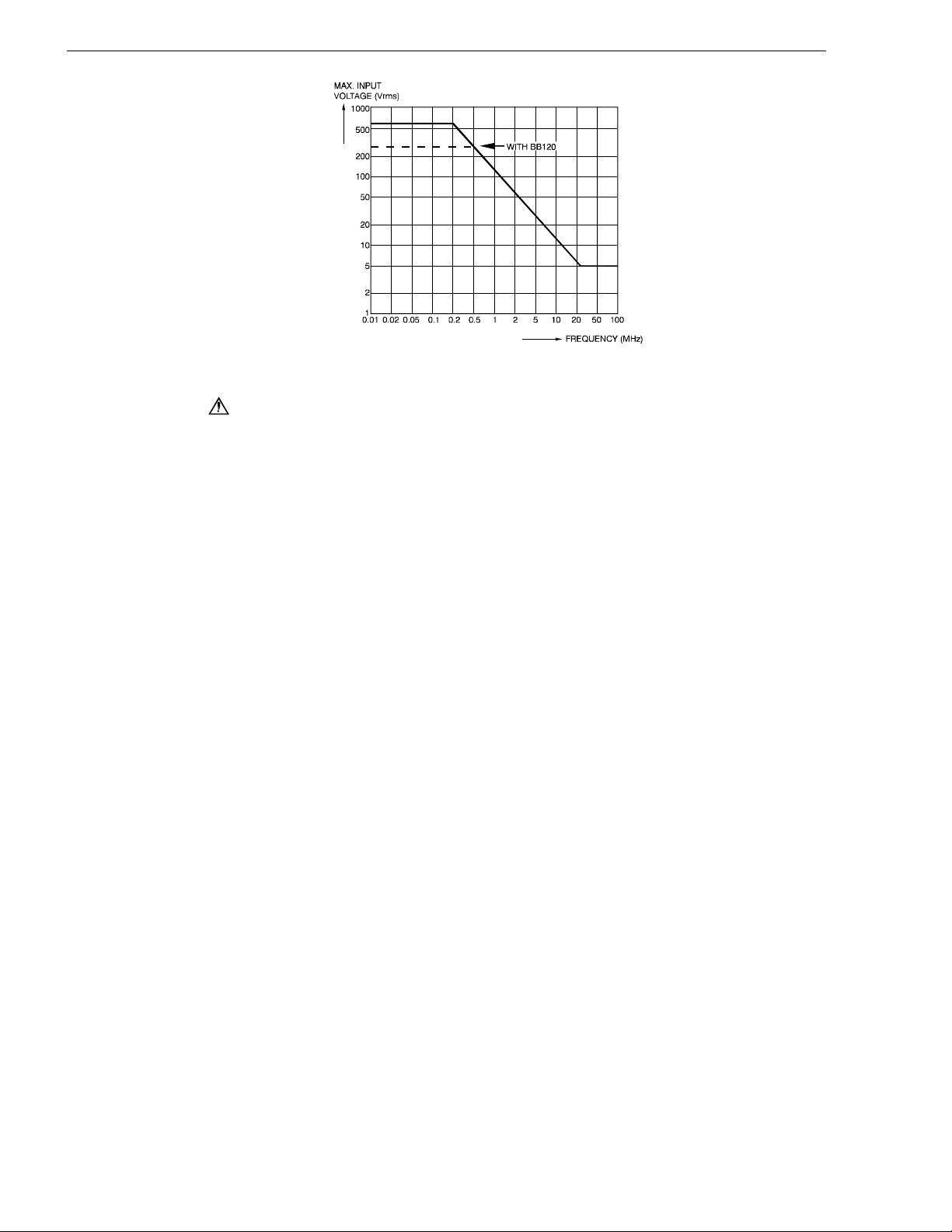
Direct on inputs or with test leads TL24............................................. (see Figure 2-1)
0 to 66 kHz..............................................................................................600 Vrms
> 66 kHz....................................................................................derating to 5 Vrms
With Shielded Banana-to-BNC Adapter Plug BB120 ......................... (see Figure 2-1)
0 to 400 kHz............................................................................................300 Vrms
> 400 kHz..................................................................................derating to 5 Vrms
2-3
Page 18
43
Service Manual
ST8571
Figure 2-1. Max. Input Voltage vs. Fr equency
Maximum floating voltage
From any terminal to ground
0 to 400 Hz ............................................................................................. 600 Vrms
2.3 Function Specifications
The accuracy of all measurements i s wi thin ± (% of reading + number of counts) from
18 °C to 28 °C. For all specifications, probe specifications must be added.
2.3.1 Electrical functions
Specifications are valid for signals with a fundamental between 40 and 70 Hz.
Minimum input voltage ............................................................................. 4 V peak-peak
Minimum input current ............................................................ 10 A peak-peak (1 mV/A)
Input bandwidth.............................................. DC to 15 kHz (unless specified otherwise)
Volts / Amps / Hertz
Readings...................................................................Vrms (ac+dc), Arms (ac+dc), Hz
Voltage ranges (auto)..................................................... 5 V; 50 V; 500 V; 1250 V
minimum step...........................................................1 mV; 10 mV; 100 mV; 1 V
Current ranges (auto)............................................... 50.00 A to 500.0 kA, 1250 kA
minimum step.................................................... 10 mA; 0.1 A; 1 A; 100 A, 1 kA
Frequency range...................................................................... 10.0 Hz to 15.0 kHz
40.0 to 70.0 Hz...................................................................... ±(0.5 % + 2 counts)
resolution.................................................................0.1 Hz; 1 Hz; 10 Hz; 100 Hz
Power
Readings.......................................................................Watt, VA, VAR, PF, DPF, Hz
Watt, VA, VAR ranges (auto) ....................250 W to 250 MW, 625 MW, 1. 56 GW
when selected: t o t al ( %r): ......................................................±(2 % + 6 counts)
when selected: fundamental ( %f):..........................................±(4 % + 4 counts)
DPF.....................................................................................................0.00 to 1.00
0.00 to 0.25....................................................................................not specified
0.25 to 0.90..............................................................................................± 0.04
0.90 to 1.00..............................................................................................± 0.03
±(1 % + 10 counts)
±(1 % + 10 counts)
2-4
Page 19

Characteristics
2.3 Function Spec ifications
PF ........................................................................................................ 0.00 to 1.00
Frequency range.......................................................................10.0 Hz to 15.0 kHz
40.0 to 70.0 Hz...................................................................±(0.5 % + 2 counts)
Harmonics
Number of harmonics ............................................................ DC..21, DC..33, DC..51
Readings / Cursor readings
Vrms... fund. ±(3 % + 2 counts).... 31
Irms.... fund. ±(3 % + 2 counts)....31
Watt.... fund. ±(5 % + 10 counts). . 31
st
±(5 % + 3 counts)... 51st ±(15 % + 5 counts)
st
±(5 % + 3 counts)... 51st ±(15 % + 5 counts)
st
±(10 % + 10 counts)51st ±(30 % + 5 counts)
Frequency of fundamental....................................................................... ± 0.25 Hz
Phase.................................................................................... fund. ±3° ... 51
K-factor (in Amp and Watt).........................................................................± 10 %
Sags & Swells
Recording times (selectable)............................. 4 minutes to 8 days, endless (16 days)
Readings / Cursor Readings
Vrms actual, Arms actual (cycle by cycle calculation)............... ±(2 % + 10 counts)
Vrms max, Arms max (idem at cursor)......................................±(2 % + 12 counts)
Vrms average, Arms average (only at cursor)............................ ±(2 % + 10 counts)
Vrms min, Arms min (idem at cursor).......................................±(2 % + 12 counts)
± 0.04
st
± 15°
2
Transients
Detection of voltage transients......................................................................... > 40 ns
Useful input bandwidth input 1 (with test leads TL24)............................DC to 1 MHz
Reference signal............................................................................................Vrms, Hz
Detection wh en transients ex ceed s p eci fi ed v o l t ag e l evel (selectable)
Number of transient memories (temporary)..............................................................40
Cursor readi ng
Inrush
Graphic display
Cursor readings
2.3.2 Scope
Input Impedance
Input 1.....................................................................................1 MΩ // 12 pF (± 2 pF)
Input 2.....................................................................................1 MΩ // 10 pF (± 2 pF)
After START, the Vrms and frequency of the signal are measured.
From th es e d at a a p u re s i n e wav e i s cal cu l at ed .
Voltage levels.................................. 20 %, 50 %, 100 %, 200 % of reference signal
Vpeak min, Vpeak max at cursor............................................... ± 5 % of full scale
Current ranges (selectable).................1 A, 5 A, 10 A, 50 A, 100 A, 500 A, 1000 A
Inrush times (selectable).........................................1 s, 5 s, 10 s, 50 s, 100 s, 5 min
A peak max at cursor 1 ...............................................................± 5 % of full scale
A peak max at cursor 2 ...............................................................± 5 % of full scale
Time between cursors...............................................................±(0.2 % + 2 pixels)
Horizontal
Time base modes (selectable).......................................................Normal, Single, Roll
Ranges (selectable within modes)
In Normal.......................................................................................5 s to 20 ns/div
In Single shot....................................................................................5 s to 1 µs/div
In Roll mode.....................................................................................60 s to 1 s/div
Time base error............................................................................ < ±(0.4 % + 1 pixel)
2-5
Page 20

43
Service Manual
Maximum sampling rate
10 ms to 60 s................................................................................................5 MS/s
20 ns to 10 ms............................................................................................25 MS/s
Trigger source (auto)........................................................................ Input 1 or Input 2
Trigger
Mode....................................................................................................auto triggering
Sources......................................Input 1, Input 2, Automatic (not manually selectable)
Error for frequencies < 1 MH z
Voltage Level............................................................................................± 0.5 div
at positive slope the top of the trigger symbol and at negative trigger the bottom of
the trigger symbol is the trigger point.
Time Delay Real Time sampling............................................................ ± 1 sample
Time Delay Quasi Random sampling.......................................................... ± 10 ns
Sensitivity input 1
@ 40 MHz...................................................................................................≥ 4 div
@ 25 MHz................................................................................................≥ 1.5 div
@ DC - 5 MHz............................................................................≥ 0.5 div or 5 mV
Sensitivity input 2
@ DC – 20 kHz ........................................................................................≥ 0.5 div
Slope Selection................................................................................Positive, negative
Level Control
Range Manual control...........................................> ± 4 div, within dynamic range
Delay ( horizontal move )......... -10 div - 0 div, used for horizontal move functionality
Vertical
Voltage ranges.....................................................................50.0 mV/div to 500 V/div
Trace accuracy .............................................................................±(1 % + 2 pixels)
Bandwidth input 1 (voltage)
excluding test leads or probes.............................................. DC to 20 MHz (-3 dB)
with test leads TL24.............................................................. DC to 1 MHz (-3 dB)
with 10:1 probe PM8918 (optional)..................................... DC to 20 MHz (-3 dB)
with shielded test leads STL120 (optional)........................DC to 12.5 MHz (-3 dB)
DC to 20 MHz (-6 dB)
Lower transition point (ac coupling)..................................................10 Hz (-3 dB)
Bandwidth input 2 (current)
with Banana-to-BNC adapter.............................................................DC to 15 kHz
Lower transition point (ac coupling)..................................................10 Hz (-3 dB)
Scope readings
The accuracy of all s co p e read i n g s i s v al i d fro m 1 8 °C to 28 °C with relative humidity
up to 90 % for a period of one year after calibration. Add 0.1 x (the specified
accuracy) for each °C below 18 °C or above 28 °C. More than one waveform period
must be visible on the screen.
V dc, A dc.....................................................................................±(0.5 % + 5 counts)
V ac and V ac+dc (True RMS) input 1
DC to 60 Hz..............................................................................±(1 % + 10 counts)
60 Hz to 20 kHz.....................................................................±(2.5 % + 15 counts)
20 kHz to 1 MHz......................................................................±(5 % + 20 counts)
1 MHz to 5 MHz.....................................................................±(10 % + 25 counts)
5 MHz to 20 MHz...................................................................±(30 % + 25 counts)
A ac and A ac+dc (True RMS) input 2
DC to 60 Hz..............................................................................±(1 % + 10 counts)
60 Hz to 15 kHz......................................................................±(30 % + 25 counts)
2-6
Page 21

Frequency (Hz), Pulse width, Duty cycle (2.0 % to 98.0 %)
Phase (Input 1 to Input 2)
Peak voltage
Crest
2.3.3 Meter
Ohm
Ranges..................................................................... 500.0 Ω to 5.000 MΩ, 30.00 MΩ
Max. Measurement Current.............................................................................. 0.5 mA
Measurement Voltage at open circuit..................................................................< 4 V
Characteristics
2.3 Function Spec ifications
1 Hz to 1 MHz.........................................................................±(0.5 % + 2 counts)
1 MHz to 10 MHz.......................................................................±(1 % + 2 counts)
10 MHz to 30 MHz.................................................................. ±(2.5 % + 2 counts)
Up to 60 Hz...................................................................................................... ±2°
60 Hz to 400 Hz................................................................................................ ±5°
Peak max, Peak min....................................................................± 5 % of full scale
Peak-peak.................................................................................± 10 % of full scale
Range.................................................................................................... 1.0 to 10.0
±(5 % + 1 count)
±(0.6 % + 5 counts)
2
Diode
Accuracy...........................................................................................±(2 % +5 counts)
Max. Measurement Current.............................................................................. 0.5 mA
Measurement Voltage at open circuit..................................................................< 4 V
Continuity
Beep.................................................................................................... < 30 Ω (± 5 Ω)
Measurement Current.......................................................................................0.5 mA
Detection of shorts............................................................................................ > 1 ms
Capacitance
Ranges........................................................................................ 50.00 nF to 500.0 µF
Max. Measurement Current.............................................................................. 0.5 mA
Temperature
Ranges (°C or °F)..................................... -100.0 to +400.0 °C or -200.0 to +800.0 °F
2.3.4 Record
Record times (selectable)............................................. 4 min to 8 days, endless (16 days)
Number of readings.........................................................................1 or 2 simultaneously
Record is av ai l ab l e fo r t h e fun ct i o n s :
• volts / amps / hertz
• power
• harmonics
• ohms / continuity / capacitance
• temperature
• scope
±(2 % +10 counts)
±(0.5 % + 5 counts)
2-7
Page 22

43
Service Manual
2.4 Miscellaneous
Display
Useful screen area............................................................ 72 x 72 mm (2.83 x 2.83 in)
Resolution..........................................................................................240 x 240 pixels
Backlight ............................................................... Cold Cathode Fluorescent (CCFL)
Power
External
Power Adapter .......................................................................................... PM8907
Input Voltage.....................................................................................10 to 21 V dc
Power....................................................................................................5 W typical
Internal
Rechargeable Ni-Cd battery pack.................................................................BP120
Voltage range........................................................................................ 4 to 6 V dc
Operating Time........................................................................................... 4 hours
Charging Time ................................................................ 4 hours with Fluke 43 off
12 hours with Fluke 43 on
Refresh cycle......................................................................................8 to 14 hours
Memory
Number of screen memories.....................................................................................10
Number of transient memories (temporary).............................................................. 40
Mechanical
Height x width x depth........................................232 x 115 x 50 mm (9.1 x 4.5 x 2 in)
Weight (including battery pack)............................................................1.1 kg (2.5 lb.)
Interface ...................................................................................RS232, optically isolated
Supported Printers........................ HP Deskjet
Serial via PM9080 (optically isolated RS232 Adapter/Cable).
Parallel via PAC91 (optically isolated Print Adapter Cable, optional).
To PC....................................................................... Dump and load settings and data
Serial via PM9080 (optically isolated RS232 adapter/cable),
using SW43W (FlukeView
2.5 Current Probe
Safety Characteri s ti cs
Designed for measurements on 600 Vrms Category III. Protection class II, doubl e or
reinforced ins u l at i o n req uirements in accord an ce wi t h :
• IEC 1010-1
• ANSI/ISA S82
• CSA-C22.2 No.1010.1-92
• UL1244
®
, Laserjet®, PostScript and Epson FX80
®
Power Quality Analyzer software).
2-8
Electrical S pecifications
Current range.....................................................................................1 A to 500 Arms
AC current over range limit.......................................................................... 700 Arms
Maximum 10 minutes, followed by removal from current carrying conductor
for 30 minutes.
Output Signal......................................................................................... 1 mV ac/A ac
Page 23

Characteristics
2.6 Environmental Conditions
Accuracy
5 to 10 Hz
1 to 500 A........................................................................................-3 dB typically
10 to 20 Hz
1 to 300 A......................................................................................................± 5 %
300 to 400 A................................................................................................ ± 15 %
400 to 500 A................................................................................................ ± 25 %
20 to 45 Hz
1 to 500 A......................................................................................................± 5 %
45 to 65 Hz
1 to 20 A...........................................................................±5 % of reading + 0.3 A
20 to 100 A .................................................................................... ±5 % of reading
± 3 ° phase shift
100 to 500 A..................................................................................±2 % of reading
± 5 ° phase shift
65 Hz to 3 kHz
1 to 50 A......................................................................................... ±(5 % + 0.4 A)
50 to 500 A ....................................................................................................± 5 %
Influence of tem p erat u re o n accu racy ..................................<0.15 % per 10 °C (18 °F)
Altitude
During operation............................................................................. 2.0 km (6560 feet)
While stored ................................................................................. 12 km (40 000 feet)
2
2.6 Environmental Conditions
Environmental...................................................MIL 28800E, Type 3, Class III, S t yle B
Temperature
During operation................................................................... 0 to 50 °C (32 to 122 °F)
While stored .......................................................................-20 to 60 °C (-4 to 140 °F)
Humidity
During operation:
0 to 10 °C (32 to 50 °F) ............................................................... non-condensing
10 to 30 °C (50 to 86 °F)......................................................................95 % ± 5 %
30 to 40 °C (86 to 104 °F).....................................................................75 % ± 5 %
40 to 50 °C (104 to 122 °F)...................................................................45 % ± 5 %
While st or ed:
-20 to 60 °C (-4 to 140 °F)............................................................. non-condensing
Altitude
During operation.......................................................................... 4.5 km (15 000 feet)
The maximum input and floating voltage is 600 Vrms up to 2 km.
Linearly derating from 600 down to 400 Vrms between 2 km to 4.5 km.
While stored ................................................................................. 12 km (40 000 feet)
Vibration........................................................................................................... max. 3 g
Shock................................................................................................................max. 30 g
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Emission..............................................EN 50081-1 (1992): EN55022 and EN60555-2
Immunity.................................................EN 50082-2 (1992): IEC1000-4-2, -3, -4, -5
(See also Tables 2-1 to 2-3)
Enclos ure Protection ......................................................................... IP51, ref.: IEC529
2-9
Page 24
43
Service Manual
2.7 Electromagnetic Immunity
The Fluk e 43 , includi ng s t an d ard acces s o ri es , conforms wi t h t h e E EC directive 89 / 3 3 6
for EMC immunity, as defined by IEC1000-4-3, with the addition of the following
tables.
Disturbance wi th tes t lead s T L 24 or Cu rren t Cl amp 80i -500s
• Volts / amps / hertz
• Resi s t an ce, Capacitan ce
• Power
• Harmonics
Table 2-1. No Visibl e Di st ur bance
No visible distur bance E = 3 V/m E = 10 V/m
Frequency: 10 kHz - 27 MHz
Frequency: 27 MHz - 1 GHz
(-)
(-)
(-): no visi b l e d i s t u rb ance
Disturbance with test leads TL24 in scope mode
• V ac+dc (True R M S )
Table 2-2. Distur bance < 1 %
Disturbance less than 1 %
of full scale
Frequency: 10 kHz - 27 MHz
Frequency: 27 MHz - 200 MHz
Frequency: 200 MHz - 1 GHz
E = 3 V/m E = 1 0 V/m
2 V/div - 500 V/div
500 mV/div -
500V/div
(-)
(-): no visi b l e d i s t u rb ance
Table 2-3. Distur bance < 10 %
Disturbance less than 10 %
of full scale
Frequency: 10 kHz - 27 MHz
E = 3 V/m E = 10 V/m
1 V/div
(-)
(-)
10 V/div - 500 V/div
2 V/div - 500 V/div
5 mV/div - 500 V/div
5 V/div
2-10
Frequency: 27 MHz - 200 MHz
Frequency: 200 MHz - 1 GHz
200 mV/div
(-)
1 V/div
(-)
(-): no visi b l e d i s t u rb ance
Ranges not specified in Tables 2 and 3 may have a disturbance of more than 10 % of full
scale.
Page 25

Chapter 3
Circuit Descript ions
Title Page
3.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 3-3
3.2 Block Diagram........................................................................................ 3-3
3.2.1 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits ............................................ 3-3
3.2.2 Trigger Circuit.................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.3 Digital Circuit.................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.4 Power Circuit................................................................................... 3-6
3.2.5 Start-up Sequence, Operating Modes................................................ 3-7
3.3 Detailed Circuit Descriptions................................................................... 3-9
3.3.1 Power Circuit................................................................................... 3-9
3.3.2 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits ............................................ 3-15
3.3.3 Trigger Circuit.................................................................................. 3-20
3.3.4 Digital Circuit.................................................................................. 3-24
3-1
Page 26
43
Service Manual
3-2
ST7965.EPS
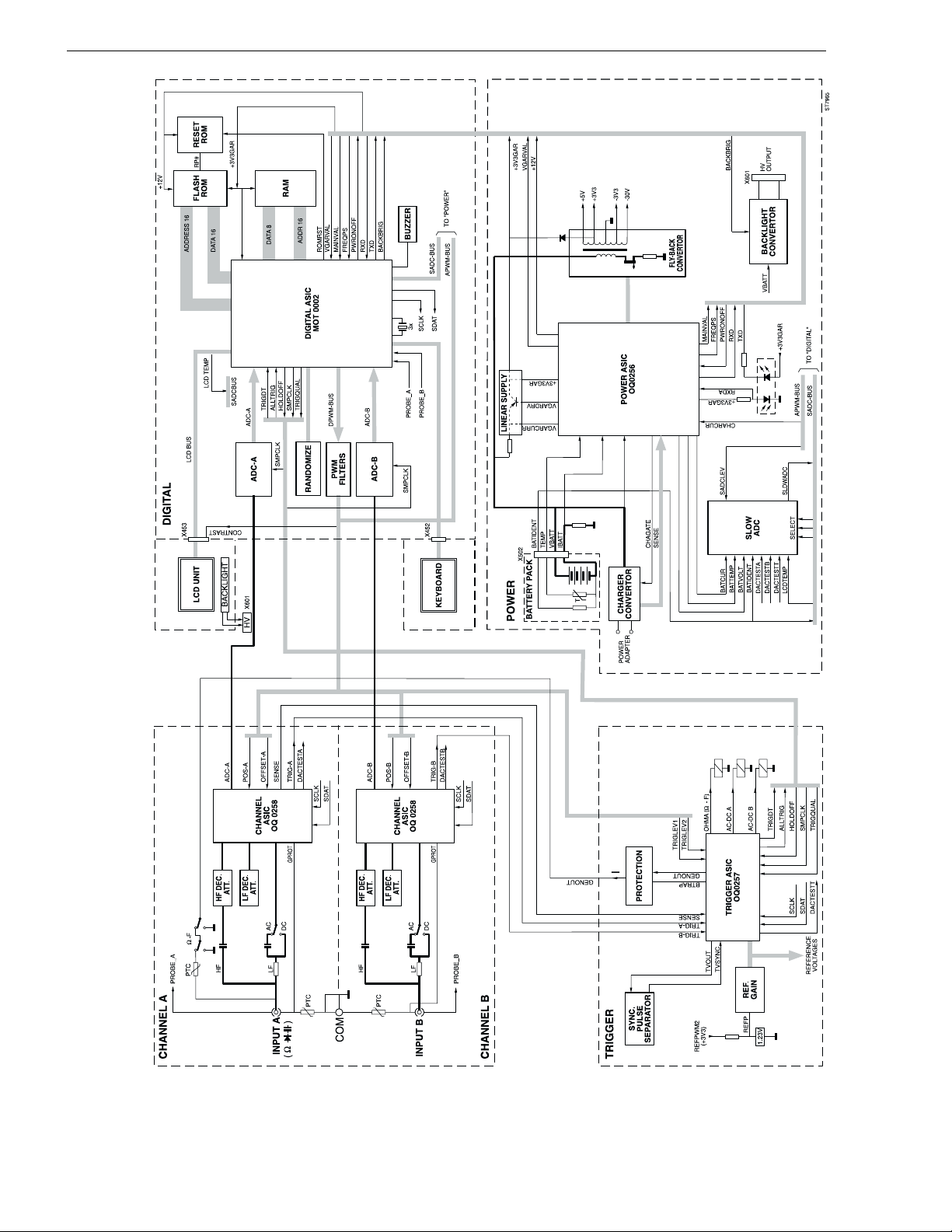
Figure 3-1. Fluke 43 Bl ock Di agr am
Page 27
3.1 Introduction
Section 3.2 describes the functional block diagram shown in Figure 3-1. It provides a
quick way to get familiar with the test tool basic build-up.
Section 3.3 describes the principle of operation of the test tool functions in detail, on the
basis of the circuit diagrams shown in Figures 9-1 to 9-5.
For all measurements, input signals are applied to the shielded input banana jackets.
Traces and readings are derived from the s ame input s i gnal sam pl es.
3.2 Block Diagram
In the block diagram Figure 3-1, the test tool is divided in five main blocks. Each block
represents a functional part, build up around an Application Specific Integrated Circuit
(ASIC). A d et ai l ed ci rcu i t d i ag ram of each b l o ck i s s ho wn i n Section 9.
Table 3-1 provides an overview of the blocks in which the test tool is broken down, the
main block function, the ASIC name, and the applicable circuit diagram.
Circuit Descri ptions
3.1 Introduction
3
Table 3-1. Fluke 43 Main Blocks
Block Main Functions ASIC Circuit
Diagram
INPUT 1 Input 1 signal conditioning C(hannel)-ASIC OQ0258 Figure 9-1
INPUT 2 Input 2 signal conditioning C(hannel)-ASIC OQ0258 Figure 9-2
TRIGGER Tr igger select ion and conditioning
Current source for resist ance, capacitance,
continuity, and diode measurements
AC/DC input coupling and
Voltage reference source
DIGITAL Analog to Digital Conversion
Acquisition of ADC samples
Micro controller (
Keyboard- and LCD control
POWER Power supply, bat t er y char ger
LCD back light voltage converter
Optical interface input
µP-ROM-RAM)
Ω/F relay control
T(rigger)-ASIC OQ 0257 Figure 9-3
D(igital)-ASIC MOT0002 Figure 9-4
P(ower)-ASIC OQ0256 Figure 9-5
All circuit s , except the LC D un i t an d the KEYBOARD, are l o cat ed on on e P r i nt ed
Circuit Board (PCB), called the MAIN PCB.
The ASIC’s are referred t o as C -ASIC (Channel AS IC ), T-ASIC (Trigger AS IC),
P-ASIC (Po wer AS IC ), and D-ASIC (Digi t al ASIC).
3.2.1 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits
The basic input signal for the Input 1 and Input 2 circuits (hardware) is voltage. The
reading of Input 1 is in (milli)Volts. The reading of Input 2 is in Amperes. So the
voltage on Input 2 is assumed to be supplied by a current clamp. From the measured
voltage sam p l es the readings are cal cu l at ed by t h e i n s t ru m en t fi rm ware. For exampl e:
power readings are calculated from the Input 1 and Input 2 voltage samples.
3-3
Page 28

43
Service Manual
The Input 1 and Input 2 measurement circuits are partially identical. The differences are:
• Only Input 1 provides facilities for Ohms, Continuity, Diode, and Capacitance
measurements.
• The bandwidth of the Input 1 circuit is 20 MHz, the bandwidth of Input 2 is 15 kHz.
• Input 2 has an additional hum rejection circuit.
The circuit description below applies to the Input 1 and Input 2 circuit.
Input 1 and Input 2 measurement principle
An input voltage applied to Input 1 or Input 2 is supplied to the C-ASIC via the HF path
(Input 1 only) and the LF path. Depending on the actual measurement function the
Input-1 HF path in the C-ASIC is enabled or disabled. The HF DECade ATTenuator and
LF DECade ATTenuator are external components for the HF and LF path. The C-ASIC
converts (attenuates, amplifies) the input signal to a normalized output voltage
ADC-A/ADC-B, which is supplied to the Analog to Digital Converters (ADC-A and
ADC-B) on the DIGITAL part. The D-ASIC acquires the digital samples to build the
traces, and t o cal cu l ate readings.
For the electrical functions the current Input 2 circuit is operating in low voltage ranges.
For example a current of 10A measured with a 1 mV/A current clamp generates 10 mV
(voltage range 10 mV/div). To minimize the influence of interference voltages, Input 2
has no HF path, and has an additional hum reject circuit.
The lowest Input 1 voltage range for electrical measurements is 4V/div, which is high in
comparison with the Input 2 range.
Ohms, Continuity, and Diode measurement function (Input 1 only)
The T-ASIC s up p l i es a cu rren t v i a t h e Ω/F relays to the unknown resistance Rx or diode
connected to the Input 1 and the COM input jacket. The voltage drop across Rx or the
diode is measured according to t he Input 1 m easurem ent pri nci pl e.
Capacitance measurement function (Input 1 only)
The T-ASIC s up p l i es a cu rren t v i a t h e Ω/F relays to the unknown capacitance Cx,
connected to the Input 1 and the COM input jacket. Cx is charged and discharged by this
current. The C-ASIC converts the charging time and the discharging time into a pulse
width signal. This signal is supplied to the T-ASIC via the C-ASIC trigger output
TRIG-A. The T-ASIC shapes and levels the signal, and supplies the resulting pulse
width signal ALLTRIG to the D-ASIC. The D-ASIC counts the pulse width and
calculates t h e cap aci t an ce read i n g .
Scope measurement functi o n
In the Scop e m eas u rem en t s fu n ct i o n t h e t es t t o o l s h o ws the traces and readings derived
from the input signals. The Input 1 HF path is enabled, which results in a 20 MHz
bandwidth. The Input 2 bandwidth is 15 kHz.
Other measu rement function s
Volts/Amperes/Hertz (LF), Power (LF), Harmonics (LF), Sags & Swells (LF),
Transient s , In ru s h C u rrent (LF), and T em p erat u re m eas u rem en t res u l t s are cal cu l at ed
from acquired input voltage samples. For functions with (LF), the HF path of Input 1 is
disabled, which results in a 15 kHz bandwidth for both Input channels.
3-4
Miscellaneous
Control of the C-ASIC, e.g. selecting the attenuation factor, is done by the D-ASIC via
the SDAT and SCLK serial communicati o n lines.
Page 29

An offset com pen s at i o n v ol tage and a trace pos ition control voltage are provided by the
D-ASIC via the AP WM bus.
The C-ASIC’s also provide conditioned input voltages on the TRIG-A/TRIG-B line. One
of these voltages will automatically be selected as trigger source by the T-ASIC.
3.2.2 Trigger Circuit
The T ASIC selects one of the possible trigger sources TRIG-A (Input 1) or TRIG-B
(Input 2). For triggering on transients the selected trigger source signal is processed via
the high pass Trigger Filter (TVOUT-TVSYNC lines). Two adjustable trigger levels are
supplied by the D-ASIC via the PWM FILTERS (TRIGLEV1 and TRIGLEV2 l in e).
Depending on the selected trigger conditions (- source, - level, - edge, - mode), the
T-ASIC generates the final trigger signal TRIGDT, which is supplied to the D-ASIC.
The TRIG-A input is also used for capacitance measurements (see Section 3.2.1).
The T-ASIC i n cl u d es a co n s t an t cu rrent source for resis t an ce an d capacitance
measurements. The current i s s uppli ed vi a t he GENOUT out put and th e Ω/F relays to
the unknown resistance Rx or capacitance Cx connected to Input 1. The SENSE signal
senses the v o l t ag e acros s Cx and controls a CLAMP ci rcu i t in the T-ASIC . This circui t
limits the voltage on Input 1 at capacitance measurements. The protection circuit
prevents the T-ASIC from being damaged by voltages supplied to the input during
resistance o r cap aci tance measuremen t s .
Circuit Descri ptions
3.2 Block Diagram
3
The T-ASIC contains opamps to derive reference voltages from a 1.23 V reference
source. The g ai n fact o rs fo r t h es e op am p s are d et erm i n ed b y res i s t o rs i n t h e R E F GAIN
circuit. The reference voltages are supplied to various circuits.
The T-ASIC also controls the Input 1/2 AC/DC input coupling relays, and the Ω/F relay.
Control data for the T-ASIC are provided by the D-ASIC via the SDAT and SCLK serial
communication lines.
3.2.3 Digital Circuit
The D-ASIC includes a micro processor, ADC sample acquisition logic, trigger logic,
display and keyboard control logic, I/O ports, and various other logic circuits.
The instrument software is stored in the 8M FlashROM; the 4M RAM is used for
temporary data storage.
For Voltage and Resistance measurements, the conditioned Input 1/2 voltages are
supplied to the ADC-A and ADC-B ADC. The voltages are sampled, and digitized by
the ADC’s. The output data of the ADC’s are acquired and processed by the D-ASIC.
For capacitance measurements the pulse width of the T-ASIC output signal ALLTRIG,
which is proportional to the unknown capacitance, is counted by the D-ASIC.
The DPWM-BUS (Digital Pulse Width Modulation) supplies square wave signals with a
variable duty cycle to the PWM FILTERS circuit (RC filters). The outgoing
APWM-BUS (Analog PWM) provides analog signals of which the amplitude is
controll ed b y t h e D-AS IC. These vol tages are used to con t ro l e.g. the t race p ositions
(C-ASIC), t he trigger levels (T-ASIC), and th e b at t ery ch arge cu rren t (P -ASIC).
In random sampling mode (Scope mode time base faster than 1 µs/d), a trace is bu ilt-up
from several acqu i s i tion cycles. During each acqu i s i t i o n , a number of trace s am p l es are
placed as pix els i n t h e LC D. The RANDOMIZE circuit takes care that t h e st arting
moment o f each acq u i s ition cycle (trigger release signal HOLDOFF goes low) is random.
3-5
Page 30

43
Service Manual
This prev ents that at each n ex t acq u i s ition th e t race is sampled at the same time
positi o n s , and that t h e d i s p l ay ed t r ace m i s s es s am p l es at s o m e p l aces o n t h e LCD.
The D-ASIC supplies control data and display data to the LCD module. The LCD
module is connected to the main board via connector X453. It consists of the LCD, LCD
drivers, and a fluorescent back light lamp. As the module is not repairable, no detailed
description and diagrams are provided. The back light supply voltage is generated by the
back light converter on the POWER part.
The keys of the keyboard are arranged in a matrix. The D-ASIC drives the rows and
scans the matrix. The contact pads on the keyboard foil are connected to the main board
via connector X452. The ON-OFF key is not included in the matrix, but is sensed by a
logic circuit in the D-ASIC, that is active even when the test tool is turned off.
Via the PROBE-A and PROBE-B lines, connected to the Input 1 and Input 2 banana
shieldi n g, the D-ASIC can d et ect i f a p ro be is connected.
The D-ASIC sends commands to the C-ASICs and T-ASIC via the SCLK and SDAT
serial control lines, e.g. to select the required trigger source.
Various I/O lines are provided, e.g. to control the B UZZER and the S low-ADC (vi a the
SADC bus).
3.2.4 Power Circuit
The test t o ol can be powered vi a t h e p o wer ad ap t er, or by the b at t ery pack .
If the power adapt er i s co n n ect ed , it powers th e t es t t o o l an d ch arg es t h e bat tery via the
CHARGER-CONVERTER ci rcuit . The battery charge current is sensed by sense
resistor Rs (signal IBAT). It is controlled by changing the output current of the
CHARGER-CONVERTER (cont rol si gnal C HAGATE).
If no power adapter is connected, the battery pack supplies the VBAT voltage. The
VBAT voltage powers the P-ASIC, and is also supplied to the FLY BACK
CONVERTER (switched mode power supply).
If the test tool is turned on, the FLY BACK C ONVER TER generates supply voltages for
various test tool circuits.
The +3V3GAR supply voltage powers the D-ASIC, RAM and ROM. If the test tool is
turned off, the battery supplies the +3V3GAR voltage via transistor V569. This
transistor is controlled by the P-ASIC. So when the test tool is turned off, the D-ASIC
can still control the battery charging process (CHARCURR signal), the real time clock,
the on/off key, and the seri al R S232 interface (to turn the tes t t ool on).
To monitor and control the battery charging process, the P-ASIC senses and buffers
battery signals as temperature (TEMP), voltage (BATVOLT), current (IBAT).
Via the SLOW ADC various analog signals can be measured by the D-ASIC. Involved
signals are: battery voltage (BATVOLT), battery type (IDENT), battery temperature
(TEMP), battery curren t (B ATC UR ) LC D t em perat u re (LC DTEMP, from LCD uni t ),
and 3 test output pins of the C-ASIC’s, and the T-ASIC (DACTEST). The signals are
used for control and test purposes.
3-6
The BACK LIGHT CONVERTER generat es t he 400V ! supply voltage for the LCD
fluorescent back light lamp. If the lamp is defective a 1.5 kV voltage can be present for
0.2 second maximum. The brightness is controlled by the BACKBRIG signal supplied
by the D-ASIC.
Serial communication with a PC or printer is possible via the RS232 optically isolated
interface. The P-AS IC buffers t h e recei ved data l i ne (RXDA) and supplies the buffered
data (RXD) to the D-ASIC. The transmit data line TXD is directly connected to the
D-ASIC.
Page 31

3.2.5 Start-up Sequence, Operating Modes
The test tool sequences through the next steps when power is applied (see Figure 3-2):
1. The P-ASIC is directly powered by the battery or power adapter voltage VBAT.
Initially the Fly Back Converter is off, and the D-ASIC is powered by VBAT via
transistor V569 (+3V3GAR).
If the voltage +3V3GAR is below 3.05 V, the P-ASIC keeps its output signal
VGARVAL (supplied to the D-ASIC) low, and the D-ASIC will not start up. The
test tool is not working, and is in the Idle mode.
2. If the voltage +3V3GAR is above 3.05 V, t he P -ASIC m akes the line VGARVAL
high, and the D-ASIC will start up. The test tool is operative now. If it is powered
by batteries only, and not tu rned on, it is in the Off mod e. In this mode the
D-ASIC is active: the real time clock runs, and the ON/OFF key is monitored to see
if the test tool will be turned on.
3. If the p ower a dapter is co n nected (P-ASIC output MAINVAL hi gh), and / or the
test tool is tu rned on, the embedded D-ASIC program, called mask software, starts
up. The mask software checks if valid instrument software is present in the Flash
ROM. If not, the test tool does not start up and the mask software continues running
until the test tool is turned off, or the power is removed. This is called the Mask
active mode. The mask active mode can also be entered by pressing the ^ and > key
when turning on the test tool.
Circuit Descri ptions
3.2 Block Diagram
3
If valid instrument software is present, one of the following modes becomes active:
Charge mode
The Charge mode is entered when the test tool is powered by the power adapter,
and is turned off. The F LY-B AC K C ONVER TER i s off. The CHARGER-
CONVERTER charges th e bat t eries (i f i ns t al l ed).
Operational & Charge mode
The Operational & Charge mode is entered when the test tool is powered by th e
power adapter, and i s turned on . The F LY-B AC K C ONVER TER is on, t he
CHARGER-CONVERTER suppl ies th e primary current. If batteries are install ed,
they will be charged. In this mode a battery refresh (see below) can be done.
Operational mode
The Operational mode is entered when the test tool is powered by ba tteri es o n ly,
and is turned on. The FLY-BACK CONVERTER is on, th e batteries supply the
primary current. If the battery voltage (VBAT) drops below 4V when starting up the
fly back converter, the Off mode is entered.
Battery Refresh
Each 3 mont h s t h e b at t eri es n eed a d eep discharge-full ch arg e cy cl e, called a
“refresh”. This prevents battery capacity loss due to the memory effect. A refresh
cycle takes 16 hours maximum, depending on the battery status.
A refresh can be started via the keyboard (
SETUP
power adapter is co n n ect ed . Du ri n g a refres h, first the b at t eries are complet el y
discharged, and then t h ey are co m p l et el y ch arg ed again.
=> START BATTERY REFRESH ) if the test tool is on, and the
=>
=>
I=> INSTRUMENT
3-7
Page 32

43
& TURN ON
Service Manual
VGARVAL=L
VGARVAL=H
Idle mode
Off mode
TURN ON or
MAINVAL=H
Flash ROM
Mask StartUp
Flash ROM OK
Extern StartUp
NOT OK
OR
&
MAINVAL=L & (TUR N OFF or BATTVOLT <4V)
Software
TURN ON & BATTVOLT > 4 & MAINVAL=L TURN OFF&MAINVAL=H
TURN ON & MAINVAL=H
Operational
Mode
MAINVAL=H
Operational &
Charge Mode
MAINVAL=L TURN ON
TURN OFF
Mask Active
mode
Charge Mode
TURN OFF
BATTVOLT < 4V
or
AutoShutDown
or
TURN OFF
Battery refresh
MAINVAL=L
Figure 3-2. Fluke 43 St ar t - up Sequence, Operating Modes
Table 3-2 shows an overview of the test tool operating modes.
Table 3-2. Fluke 43 O per at i ng M odes
Mode Conditions Remark
Idle mode No power adapter and no batt er y no activity
Off mode No power adapter connected, batt er y
installed, test tool off
Mask active mode No valid instrument soft ware, or ^ and > key
pressed when turning on
Charge mode Power adapter connected and test t ool off Batteries will be charged
Operational &
Power adapter connected and test t ool on Test tool operational, and
Charge mode
Operational mode No power adapter connected, batt er y
installed, and test tool on
P-ASIC & D-ASI C p owe r e d
(VBAT & +3V3GAR).
Mask software runs
batteries will be charged
Test tool operational, powered
by batteries
3-8
Page 33

3.3 Detailed Circuit Descriptions
60
CHASENSN
TEMP
TEMPHI
IBATP
CHASENSP
VCHDRIVE
VADALOW
VADAPTER
BATTEMP
VGARVAL
VBATSUP
5
4
69
66
VBATHIGH
7
COSC
3.3.1 Power Circuit
The description below refers to circuit diagram Figure 9-5.
Power Sources , Operating Modes
Figure 3-3 shows a simplified diagram of the power supply and battery charger circuit.
VBAT
FROM PO WE R
ADAPTER
R501
R502
C502
CHARGER/CONVERTER
V506
V503
L501
C503
R504
R506
R507
R503
R513
R512
R514
R516
VGARDRIVE
VBATT
CHAGATE
IIMAXCHA
3
9
16
14
15
6
19
8
20
V569
Vref
CONTROL
linear regulator
linear regulator
Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
BATVOLT
BATCUR
CHARCURR
43
V565
V566
P7VCHA
SUPPLY
+3V3GAR
C553
MAINVAL
C507
CONVERTER
Amplify
Level shift
100kHz
FLY BACK
64
78
79
77
80
12
18
18
3
POWER ASIC
Figure 3-3. Powe r Suppl y Bl ock Diagr a m
As described in Section 3.2.5, the test tool operating mode depends on the connected
power source.
The voltage VBAT is supplied either by the power adapter via V506/L501, or by the
battery pack. It powers a part of the P-ASIC via R503 to pin 60 (VBATSUP). If the test
tool is off, the Fly Back Converter is off, and VBAT powers the D-ASIC via transistor
V569 (+3V3GAR). This +3V3GAR voltage is controlled and sensed by the P-ASIC. If
it is NOT OK (<3.05V), t he out put VGAR VAL (pi n 64) i s lo w. The VGAR VAL l i ne i s
connected to the D-ASIC, and if the line is low, the D-ASIC is inactive: the test tool is in
the Idle mode. A low VGARVAL line operates as a res et for t he D-ASIC.
If VGARVAL is high (+3V3GAR > 3.05V), the D-ASIC becom es act i ve, and t h e Off
mode is entered. The D-AS IC moni t ors th e P -AS IC out put pi n 12 M AINVAL, and th e
test tool ON/OFF status. By pressing the ON/OFF key, a bit in the D-ASIC indicating
the test tool ON/OFF status is toggled. If no correct power adapter voltage is supplied
(MAINVAL is low), and the t est t ool i s not t urned on, the Off mode will be maintained.
If a correct power adapter voltage is suppli ed (MAINVAL hi gh), or i f t he t est t ool i s
turned on, the mask software starts up. The mask software checks if valid instrument
software is pr esen t . If not, e. g . no instru m en t fi rm ware i s l o aded , the mask so ft ware wi l l
3-9
Page 34

43
Service Manual
keep running, and the test tool is not operative: the test tool is in the Mask active state.
For test purposes the mask active mode can also be entered by pressing the ^ and > key
when the test tool is turned on.
If valid software is present, one of the three modes Operational, Operational &
Charge or Charge will become active. The Charger/Converter circuit is active in the
Operational & Charge and in the Charge mode. The Fly back converter is active in the
Operational and in the Operational & Charge mode.
Charger/Converter (See also Figure 3-3.)
The power adapt er po wers the Charge Con t ro l ci rcu i t in the P-ASIC via an in t ern al l i n ear
regulator. The power adapter voltage is applied to R501. The Charger/Converter circuit
controls t h e b at t ery charg e cu rrent. If a charged batt ery p ack i s i ns t al led VBAT is
approximately +4.8V. If no battery pack is installed VBAT is approximately +15V. The
voltage VBAT is supplied to the battery pack, to the P-ASIC, to the Fly Back Converter,
and to transistor V569. The FET control signal CHAGATE is a 100 kHz square wave
voltage with a variable duty cycle, supplied by the P-ASIC Control circuit. The duty
cycle determines the amount of energy loaded into L501/C503. By controlling the
voltage VBAT, the battery charge current can be controlled. The various test tool
circuits are supplied by the Fly Back Converter and/or V569.
Required power adapter voltage
The P-ASIC supplies a current to reference resistor R516 (VADALOW pin 8). It
compares the voltage on R516 to the power adapter voltage VADAPTER on pin 20
(supplied via R502, and attenuated in the P-ASIC). If the power adapter voltage is below
10V, the P-ASIC out put pi n 12, and t h e li ne M AINVAL, are l ow. Thi s s ignal on pi n 12
is also suppli ed to t h e P -AS IC i nt ernal control ci rcui t , whi ch th en m akes t he C HAGATE
signal high. As a result FET V506 becomes non-conductive, and the Charger/Converter
is off.
Battery cha rge current control
The actual charge current is sensed via resistors R504-R506-507, and filter R509-C509,
on pin 9 of the P-ASIC (IBATP). The sense voltage is supplied to the control circuit.
The required charge current information is supplied by the D-ASIC via the CHARCUR
line and filter R534-C534 to pin 80. A control loop in the control circuit adjusts the
actual charge current to the required value.
The filtered CHARCUR voltage range on pin 80 is 0... 2.7V for a charge current from
0.5A to zero. A voltage of 0V complies to 0.5A (fast charge), 1.5V to 0.2A (top off
charge), 2.3V to 0.06A (trickle charge), and 2.7V to 0A (no charge). If the voltage is > 3
Volt, the charger converter is off (V506 permanently non-conductive).
The D-ASIC derives the required charge current value from the battery voltage VBAT.
The P-ASIC converts this voltage to an appropriate level and supplies it to output pin 78
(BATVOLT). The D-ASIC measures t his voltage vi a t h e S l o w ADC. The momen t ary
value, and the voltage change as a function of time (-dV/dt), are used as control
parameters.
3-10
Charging process
If the battery voltage drops below 5.2V, and the battery temperature is between 10 and
45°C, the charge current is set to 0.5A (fast charge). From the battery voltage change dV/dt th e D-AS IC can see when the b at t ery i s fu l l y ch arged , and stop fas t ch arge.
Additionally a timer in the D-ASIC limits the fast charge time to 6 hours. After fast
charge, a 0.2A top off charge current is supplied for 2 hours. Then a 0.06A trickle
Page 35

Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
charge current is applied for 48 hours maximum. If the battery temperature becomes
higher than 50°C, the charge current i s s et t o zero .
Battery temperature monitoring
The P-ASIC supplies a current to a NTC resistor in the battery pack (TEMP pin 5). It
conditions the voltage on pin 5 and supplies it to output pin 79 BATTEMP. The DASIC measures this voltage via the slow ADC. It uses the BATTEMP vol tage to decide
if fast charge is allowed (10-45°C), or no charge is allowed at all (<10°C, >50°C).
Additionally the temperature is monitored by the P-ASIC. The P-ASIC supplies a
current to reference resistor R512 (TEMPHI pin 4), and compares the resulting TEMPHI
voltage to the voltage on pin 5 (TEMP). If the battery temperature is too high, the
P-ASIC C o nt ro l ci rcu i t s et s t h e ch arg e curren t t o zero , i n cas e t h e D-AS IC fails to d o
this.
If the battery temperature monitoring system fails, a bimetal switch in the battery pack
interrupts the battery current if the temperature becomes higher then 70 °C.
Maximum VBAT
The P-ASIC supplies a current to reference resistor R513 (VBATHIGH pin 7). It
compares the voltage on R513 to the battery voltage VBAT on pin 3 (after being
attenuated in the P-ASIC). The P-ASIC limits the voltage VBAT to 7.4V via its internal
Control circuit. This happens if no battery or a defective battery (open) is present.
3
Charger/Converter input current
This input current is sensed by R501. The P-ASIC supplies a reference current to R514.
The P-ASIC compares the voltage drop on R501 (P-ASIC pin 14 and 15) to the voltage
on R514 (IMAXCHA pin 6). It limits the input current (e.g. when loading C503/C555
just after connecting the power adapter) via its internal Control circuit.
CHAGATE control si gn al
To make the FET conductive its Vgs (gate-source voltage) must be negative. For that
purpose, the CHAGATE volt age mu s t be negat i v e wit h resp ect to VC HDR IVE. The
P-ASIC voltage VCHDRIVE also limits the swing of the CHAGATE signal to 13V.
VCHDRIVE
VCHDRIVE -13V
10 µs
Figure 3-4. CHAGATE Cont rol Volta ge
V506 “OFF”
V506 “ON”
+3V3GAR Voltage
When the test tool is not turned on, the Fly Back Converter does not run. In this
situation, the +3V3GAR voltage for the D-ASIC, the FlashROM, and the RAM is
supplied via transistor V569. The voltage is controlled by the VGARDRV signal
supplied by the P-ASIC (pin 69). The current sense voltage across R580 is supplied to
pin 70 (VGARCURR). The voltage +3V3GAR is sensed on pin 66 for regulation. The
internal regulator in the P-ASIC regulates the +3V3GAR voltage, and limits the current.
3-11
Page 36

43
Service Manual
Fly Back Co n v erter
When the test tool is turned on, the D-ASIC makes the PWRONOFF line (P-ASIC pin
62) high. Then the self oscillating Fly Back Converter becomes active. It is started up
by the internal 100 kHz oscillator that is also used for the Charger/Converter circuit.
First the FLYGATE signal turns FET V554 on (see Figure 3-5), and an increasing
current flows in the primary transformer winding to ground, via sense resistor R551. If
the volt age FLYSENSP acro s s t h i s res i s t o r exceed s a cert ai n v al u e, the P-ASIC t u rn s
FET V554 off. Then a decreasing current flows in the secondary windings to ground. If
the windings are “empty” (all energy transferred), the voltage VCOIL sensed by the
P-ASIC (pin 52) is zero, and the FLYGATE signal will turn FET V554 on again.
Primary current
Secondary current
V554 “ON”
FLYGATE SIGNAL
Figure 3-5. Fly-Back Converter Current and Control Vol t age
V554 “OFF”
The output voltage is regulated by feeding back a part of the +3V3A output voltage via
R552-R553-R554 to pin 54 (VSENS). This voltage is referred to a 1.23 V reference
voltage. Any deviation of the +3V3A voltage from the required 3.3V changes the
current level at which current FET V554 will be switched off. If the output voltage
increases, the current level at which V554 is switched off will become lower, and less
energy is transferred to the secondary winding. As a result the output voltage will
become lower.
An internal current source supplies a current to R559. The resulting voltage is a
reference for the maxi m um allowable prim ary curren t (IM AXF LY). The voltage acros s
the sense resi s t o r (FLYSENSP ) i s co m pared t o t h e IM AXF L Y v oltage. If the cu rrent
exceeds the s et limit, FET V554 will be turned off.
Another internal current source supplies a current to R558. This resulting voltage is a
reference for the maximum all owabl e out put vol t age (VOUTHI). The -3V3A out put
voltage (M3V3A) is attenuated and level shifted in the P-ASIC, and then compared to
the VOUTHI voltag e. If t h e -3 V3A v oltage exceeds the s et limit, F ET V554 will be
turned off.
The FREQPS control signal is converted to appropriate voltage levels for the FET switch
V554 by the BOOST circuit. The voltage VBAT supplies the BOOST circuit power via
V553 and R561. The FREQPS signal is also supplied to the D-ASIC, in order to detect
if the Fly Back converter is running well.
V551 and C552 limit the voltage on the primary winding of T552 when the FET V554 is
turned of. Th e s i g n al S NUB increases the FLYGATE high l ev el t o d ecreas es
ON-resistance of V554 (less power dissipation in V554).
3-12
Page 37

Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
3
VBAT
C553
V553
R561
C551
COSC
FLYBOOST
43
SNUB
48 47
BOOST
CONTROL
C552
49
63
55
57
44
52
58
51
54
62
72
FLYGATE
FREQPS
FLYSENSP
IMAXFLY
VCOIL
-3V3A
VOUTHI
VSENS
PWRONOFF
REFP (1.23V)
T552
V551
V554
R551
R559
R558
POWER ASIC
Figure 3-6. Fly- Back Convert er Bl ock Di agr am
V561
V562
V563
V564
R570
+5VA
+3V3A
-3V3A
-30VD
R552
R554
R553
Slow ADC
The Slow ADC en abl es t h e D-AS IC to measure th e fo l l o wi ng s i g nal s :
BATCUR, BATVOLT, B ATTEMP , B ATIDENT (B att ery current, - volt age, temperature, - type ), DACTEST-A, DAC TES T-B , and DACTEST-T (test output of the
C-ASIC’s and the T-ASIC).
De-multiplexer D531 supplies one of these signals to its output, and to the input of
comparator N531 TP536). The D-ASIC supplies the selection control signals
SELMUX0-2. T he Slow ADC works acco rd i ng t o t h e s ucces s i v e app rox i m at i o n
principle. The D-ASIC changes the SADCLEV signal level, and thus the voltage level
on pin 3 of the comparator step wise, by changing the duty cycle of the PWM signal
SADCLEVD. The comparat or output S L OWADC is m oni to red by t he D-AS IC , who
knows now if the previous input voltage step caused the comparator output to switch.
By increasing the voltage steps, the voltage level can be approximated within the
smallest possible step of the SADCLEV voltage. From its set SADCLEVD duty cycle,
the D-ASIC knows voltage level of the selected input.
RS232
The optical interface enables s erial com m uni cat ion (R S232) between the test tool and a
PC or printer.
The received data line RXDA (P-ASIC pin 75) is connected to ground vi a a 20 kΩ
resistor in the P-ASIC.
If no light is received by t h e l i g h t s ensitive diode H522, the RXDA line is +200 mV,
which corresponds to a “1” (+3V) on the RXD (P-ASIC output pin 76) line.
If light i s recei v ed , the light sensitive diode will conduct, and the RXDA line goes low
(0...-0.6V), which corresponds to a “0” on the RXD line.
The level on the RXDA line is compared by a comparator in the P-ASIC to a 100 mV
3-13
Page 38

43
Service Manual
level. The comparator output is the RXD line, which is supplied to the D-ASIC for
communication, and for external triggering.
The D-ASIC controls the transmit data line TXD. If the line is low, diode H521 will
emit light.
The supply voltage for the opti cal i n t erface receive ci rcui t (R XDA), i s t he + 3 V3S ADC
voltage. The +3V3SADC voltage is present if the test tool is turned on, or if the Power
Adapter is con n ect ed (o r b o t h ). So if the Po wer Ad ap t er i s pres en t , serial comm u n i cat i o n
is always p os s i b l e, even when the t es t tool is off.
Backli g h t Co nverter
The LCD back light is provided by a ∅2.4 mm fluorescent lamp in LCD unit. The back
light converter generates the 300-400 Vpp ! supply voltage. The circuit consist of:
• A pulse width modulated (PWM) buck regulator to generate a variable, regulated
voltage (V600, V602, L600, C602).
• A zero voltage switched (ZVS) resonant push-pull converter to transform the
variable, regulated voltage into a high voltage AC output (V601, T600).
The PWM buck regulator consists of FET V600, V602, L600, C602, and a control
circuit in N600. FET V600 is turned on and off by a square wave voltage on the COUT
output of N600 pin 14). By changing the duty cycle of this signal, the output on C602
provides a variable, regulated voltage. The turn on edge of the COUT signal is
synchroni zed wi th each zero detect.
Outputs AOUT and BOUT of N600 provide complementary drive signals for the pushpull FETs V601a/b (dual FET). If V601a conducts, the circuit consisting of the primary
winding of transformer T600 and C608, will start oscillating at its resonance frequency.
After half a cycle, a zero voltage is detected on pin 9 (ZD) of N600, V601a will be
turned off, and V601b is turned on. This process goes on each time a zero is detected.
The secondary current is sensed by R600/R604, and fed back to N600 pin 7 and pin 4 for
regulation of the PWM buck regulator output voltage. The BACKBRIG signal supplied
by the D-ASIC provides a pulse width modulated (variable duty cycle) square wave. By
changing the duty cycle of this signal, the average on-resistance of V604 can be changed.
This will change the secondary current, and thus the back light intensity. The voltage on
the “cold” side of the lamp is limited by V605 and V603. This limits the emission of
electrical i n t erferen ce.
R605 and R606 provide a more reliable start-up of the backlight (PCB version 3 up
only).
Voltage at T600 pin 4
Voltage AOUT
Voltage BOUT
Voltage COUT
3-14
zero
detect
zero
detect
Figure 3-7. Back Light Convert er Vol t ages
Page 39

3.3.2 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits
The description below refers to circuit diagrams Figure 9-1 and Figure 9-2.
The Input 1 and Input 2 circuits are partly identical. Both circuits condition input
voltages. See section 3.2.1 for a description of the differences between Input 1 and 2.
The Input 1/2 circuitry is built-up around a C-ASIC OQ0258. The C-ASIC is placed
directly behind the input connector and transforms the input signal to levels that are
suitable for the ADC and trigger circuits.
The C-ASIC
Figure 3-8 shows the simplified C-ASIC block diagram. The C-ASIC consists of
separate paths for HF and LF signals, an output stage that delivers signals to the trigger
and ADC circuits and a control block that allows software control of all modes and
adjustments. The transition frequency from the LF-path to the HF-path is approximately
20 kHz, bu t t h ere i s a l arg e o verl ap .
CHANNEL ASIC OQ 0258
Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
3
INPUT
C
AC
R
DC
HF IN
LF IN
GROUND
PROTECT
Figure 3-8. C-ASIC Block Di agr am
HF-PATH
LF-PATH
CAL POS BUS SUPPLY
OUTPUT
STAGE
CONTROL SUPPLY
ADC
TRIGGER
LF input
The LF-input (pin 42) is connect ed t o a LF decade attenuator in voltage mode, or to a
high im p ed ance b u ffer fo r res i s t an ce an d cap aci t an ce m eas u rem en t s . The LF decade
attenuator consists of an amplifier with switchable external feedback resistors R131 to
R136. Depending on the selected range the LF attenuation factor which will be set to 110-100-1000-10,000. The C-ASIC includes a LF pre-amplifier with switchable gain
factors for the 1-2-5 steps.
HF input (not used for Input 2)
The HF component of the input signal is supplied to four external HF capacitive
attenuators via C104. Depending on the required range, the C-ASIC selects and buffers
one of the attenuator outputs :1 (HF0), :10 (HF1), :100 (HF2), or :1000 (HF3). By
attenuating the HF3 input internally by a factor 10, the C-ASIC can also create a :10000
attenuation factor. Inputs of not selected input buffers are internally shorted. To control
the DC bias of the buffers inputs, their output voltage is fed back via an internal feed
back resistor and external resistors R115, R111/R120, R112, R113, and-R114. The
internal feed back resistor and filter R110/C105 will eliminate HF feed back, to obtain a
3-15
Page 40

43
Service Manual
large HF gain. The C-ASIC includes a HF pre-amplifier with switchable gain factors for
the 1-2-5 steps. The C-ASIC also includes circuitry to adjust the gain, and pulse
response.
ADC output pin 27
The combined conditioned HF/LF signal is supplied to the ADC output (pin 27) via an
internal ADC buffer. The output voltage is 150 mV/d. The MIDADC si gnal (pi n 28),
supplied by the ADC, matches the middle of the C-ASIC output voltage swing to the
middle of the ADC input voltage swing.
TRIGGER output pin 29
The combined conditioned HF/LF signal is also supplied to the trigger output (pin 29)
via an internal trigger buffer. The output voltage is 100 mV/d. This signal (TRIG-A) is
supplied t o t h e TR IGGE R ASIC for trigg eri ng , and for capacitan ce m eas ur em ents.
For capacitance measurements the ADC output is not used, but the TRIG-A output pulse
length i n d i cates the measu red cap aci t an ce, see “Capacitan ce m eas u rements” below.
GPROT input pin 2
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) resistors (R106-R206) are provided between the
Input 1 and Input 2 shield ground, and the COM input (instrument ground). This
prevents damage to the test tool if the various ground inputs are connected to different
voltage levels. The voltage across the PTC resistor is supplied via the GPROT input pin
2 to an input buffer. If thi s vol tage exceeds ±200 mV, the ground protect circuit in the
C-ASIC makes the DACTEST output (pin 24) high. The DACTEST line output level is
read by the D-ASIC via the slow ADC (See 3.3.2 “Power”). The test tool will give a
ground error warning.
Because of ground loops, a LF i n terference vol t age can aris e across P TC res i st or R 106
(mainly mains interference when the power adapter is connected). To eliminate this LF
interference voltage, it is buffered (also via input GPROT, pin 2), and subtracted from
the input signal. Pin 43 (P R OTGND) is th e ground reference of the input buffer.
CALSIG input pin 36
The reference circuit o n t h e T R IGGE R p art s up p l i es an accurat e + 1 .23 V DC volt ag e t o
the CALSIG input pin 36 via R141. This voltage is used for internal calibration of the
gain, and t h e cap aci t an ce m eas u rem en t threshold levels. A reference cu rren t Ical i s
supplied by the T-ASIC via R144 for calibration of the resistance and capacitance
measurement function. For ICAL see also Section 3.3.3.
POS input pin 1
The PWM circuit on the Digital part provides an adjustable voltage (0 to 3.3 V) to the
POS input via R151. The vol t age level i s us ed t o m ove th e input s ignal t race on the
LCD. The REFN line provides a negative bias voltage via R152, to create the correct
voltage swing level on the C-ASIC POS input.
OFFSET input pin 44
The PWM circuit on the Digital part supplies an adjustable voltage (0 to +3.3 V) to the
OFFSET input via R153. The voltage level is used to compensate the offset in the LF
path of the C-ASIC. The REFN line provides a negative bias voltage via R152, to create
the correct voltage swing level on the C-ASIC POS input.
3-16
Page 41

Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
DACTEST output pin 24
As described above, the DACTEST output is used for signaling a ground protect error. It
can also be used for testing purposes. Furthermore the DACTEST output provides a CASIC reset output signal (+1.75V) after a power on.
ADDRESS outpu t p i n 23
The output provides a replica of the input voltage to the SENSE line via R165. In
capacitance mo de, the sense s i gn al co n t ro l s t h e C L AM P fu n ct i o n in the T-ASIC (S ee
Section 3.3.3).
TRACEROT input pin 31
The TRACEROT signal is supplied by the T-ASIC. It is a triangle sawtooth voltage.
SDAT, SCL K
Control information for the C-ASIC, e.g. selection of the attenuation factor, is sent by
the D-ASIC via the SDA data line. The SCL line provides the synchronization clock
signal.
Input 1 Voltage Measurements
The input voltage is applied to the HF attenuator inputs of the C-ASIC via C104, and to
the LF input of the C-ASIC via R101/R102, AC/DC input coupling relay K171, and
R104. The C-ASIC conditions the input voltage to an output voltage of 50 mV/d. This
voltage is supplied to the ADC on the Digital part. The ADC output data is read and
processed by t h e D-AS IC, and represen t ed as a nu m eri cal reading, an d as a g rap h i cal
trace.
3
Table 3-3. shows the relation between the Input 1 reading range (V) and the trace
sensitivity (V/d.) in the Scope mode. The selected trace sensitivity determines the
C-ASIC attenuation/gain factor. The reading range is only a readout function, it does not
change the hardware range or the wave form display.
Table 3-3. Input 1 Vol t age Ranges And Trace Sensi tivity
range 50 mV 50 mV 50 mV 500
mV
trace ../div 5 mV 10 mV 20 mV 50 mV 100
range 5V 50V 50V 50V 500V 500V 500V 1250V
trace ../div 2V 5V 10V 20V 50V 100V 200V 500V
500
mV
mV
500
mV
200
mV
5V 5V
500
mV
1V
During measuring, input voltage measurements, gain measurements, and zero
measurements are done. As a result, the voltage supplied to the ADC is a multiplexed
(zero, + reference, -reference, input voltage) signal. In ROLL mode however, no gain
and zero measurements are done. Now the ADC input voltage includes only the
conditioned input voltage.
The input voltage is connected to Input 1. The shield of the input is connected to system
ground (⊥) via a PTC ground protection resistor. If a voltage is applied between the
Input 1 and Input 2 ground shield, or between one of these ground shields and the black
COM input, the PTC resistor will limit the resulting current. The voltage across the PTC
resistor is supplied to the C-ASIC GPROT input, and causes a ground error warning
(high voltage level) on output pin 24 (DACTEST).
3-17
Page 42

43
Service Manual
Input 2 Voltage Measurements
The Input 2 circuit has no HF path. The principle of operation is the same as for the
Input 1 LF path. The input ground is connected via PTC resistor R201 to the
measurement ground. Any voltage across the PTC resistor will be added to the input
signal, and cause a mis-reading. This influences Input 2 in particular as this input
operates mostly in the lowest voltage ranges (see section 3.2.1). For this reason a hum
rejection circuit is added for Input 2. The voltage across the PTC is supplied to the
inverting X1 amplifier N202. Then the AC part of the N202 output signal is subtracted
from the input sigal on the C-ASIC LF input (pin 42).
Resistan ce Meas urements (Input 1 only)
The unknown resistance Rx is connected to Input 1, and the black COM input. The
T-ASIC supplies a constant current to Rx via relay contacts K173, and the PTC resistor
R172. The voltage across Rx is supplied to a high impedance input buffer in the C-ASIC
via the LF input pin 42. The C-ASIC conditions the voltage across Rx to an output
voltage of 50 mV/d. This voltage is supplied to the ADC on the Digital part. The ADC
data is read and processed by the D-ASIC, and represented as a numerical reading, and a
bar graph.
Table 3-4 shows the relation between the reading range (Ω), the trace sensitivity (Ω/d.),
and the current in Rx,
Table 3-4. Ohms Ranges, Tr ace Sensi t ivity, and Current
Range 50
Sensitivity ../div 20Ω 200Ω 2 kΩ 20 kΩ 200 k Ω 2 MΩ 10 MΩ
Current in Rx 500 µA 500 µA 50 µA5 µA 500 nA 50 nA 50 nA
Ω 500Ω 5kΩ 50 kΩ 500 kΩ 5 MΩ 30 M Ω
To protect the current source from being damaged by a voltage applied to the input, a
PTC resistor R172 and a protection circuit are provided (See Section 3.3.3 “Current
Source”).
During measuring, input voltage measurements, gain measurements, and zero
measurements are done. As a result, the voltage supplied to the ADC is a multiplexed
(zero, + reference, -reference, input voltage) signal.
Capacitan ce Mea s urements (Input 1 only)
The capacitance measurement is based on the equation: C x dV = I x dt. The unknown
capacitor Cx is charged with a constant known current. The voltage across Cx increases,
and the time lapse between two different known threshold crossings is measured. Thus
dV, I and dt are known and the capacitance can be calculated.
The unknown capacitance Cx is connected to the red Input 1 safety banana socket, and
the black COM input. The T-ASIC supplies a constant current to Cx via relay contacts
K173, and protection PTC resistor R172. The voltage on Cx is supplied to two
comparators in the C-ASIC via the LF input. The threshold levels th
and th2of the
1
comparators are fixed (see Figure 3-9). The time lapse between the first and the second
threshold crossing depends on the value of Cx. The resulting pulse is supplied to the
TRIGGER output pin 29, which is connected to the analog trigger input of the T-ASIC
(TRIG-A signal). The T-ASIC adjusts the pulse to an appropriate level, and supplies it
to the D-ASIC via its ALLTRIG output. The pulse widt h is measured and processed by
the D-ASIC, and represented on the LCD as numerical reading. There will be no trace
displayed.
3-18
Page 43

+Iref
-Iref
ref clamp
th2
Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
0
pos. clamp active
I-Cx
3
th1
0
neg. clamp active neg. clamp active
U-Cx
TRIG-A
Figure 3-9. Capacit ance M easur em ent
The T-ASIC supplies a positive (charge) and a negative (discharge) current. A
measurement cy cl e s t arts from a dis charg ed s i t u at i o n (U
After reaching th e fi rs t t h res h ol d l ev el (t h
) the pulse width measurement is started. The
1
=0) with a charg e cu rrent.
CX
dead zone between start of charge and start of pulse width measurement avoids
measurement erro rs d ue to a series resi s t an ce of C x .
The pulse width measurement is stopped after crossing the second threshold level (th
),
2
the completes the first part of the cycle.
Unlimited increase of the capacitor voltage is avoided by the positive clamp in the
T-ASIC. The output of the high impedance buffer in the C-ASIC supplies a replica of
the voltage across Cx to output pin 23 (ADDRESS). Via R165, this vol tage is supplied
to a clamp circuit in the T-ASIC (SENSE, pin 59). This clamp circuit limits the positive
voltage on Cx to 0.45V.
Now the second part of the measurement is started by reversing the charge current. The
capacitor will be discharged in the same way as the charge cycle. The time between
passing both threshold levels is measured again. A clamp limits the minimum voltage
on Cx to 0V.
Averaging t he res u lts of bot h m eas u rem en t s can cel s t h e effect o f a p o s s i b l e p aral l el
resistance, and suppresses the influence of mains interference voltages.
Table 3-5 sh o ws the relation b et ween t h e cap aci t an ce ran g es , the charge current an d t h e
pulse width at full scale.
Table 3-5. Capacitance Ranges, Curr ent , and Pulse Width
Range 50 nF 500 nF 5000 nF 50 µF 500 µF
Current µA0.5 µA5 µA 50 µA 500 µA 500 µA
Pulse width at Full Scale 25 ms 25 ms 25 ms 25 ms 250 ms
To protect the current source if a voltage is applied to the input, a PTC resistor R172,
and a protection circuit on the TRIGGER part, are provided (see Section 3.3.3).
Probe Detection
The Input 1 and Input 2 safety banana jacks are provided with a ground shield, consisting
of two separated half round parts. One half is connected to ground via the protection
PTC resistor R106/R206. Via a 220K resistor installed on the input block, the other half
is connected to the probe input of the D-ASIC (pin 54, 55). If the shielded STL120 test
3-19
Page 44

43
Service Manual
3.3.3 Trigger Circuit
lead, or a BB120 shielded banana-to-BNC adapter, is inserted in Input 1 or Input 2, it
will short the two ground shield halves This can be detected by the D-ASIC.
Supply Voltages
The +5VA, +3V3A, and -3V3A supply voltages are supplied by the Fly Back Converter
on the POWER part. The voltages are present only if the test tool is turned on.
The description refers to circuit diagram Figure 9-3. The trigger section is built up
around the T-ASIC OQ0257. It provides the following functions:
• Triggering: trigger source selection, trigger signal conditioning, and generation of
trigger information to be supplied to the D-ASIC.
• Current s o u rce fo r res i s t an ce an d cap aci t an ce m eas u rem en t s .
• Voltage reference source: buffering and generation of reference voltages.
• AC/DC rel ay an d R es i s t an ce/ Capacitance (Ω/F ) rel ay co n t ro l .
Triggering
Figure 3-10 shows the block diagram of the T-ASIC trigger section.
trigger se ct io n
select
logic
freq.
detect
synchronize
delta-t
35
ALLTRIG
42
TRIGQUAL
34
TRIGDT
39
HOLDOFF
38
SMPCLK
29
DACTEST
TRIGLEV1
TRIGLEV2
TRIG A
TRIG B
10
11
13
15
Figure 3-10. T-ASI C Tri gger Sect ion Block Diagram
TRIGGER ASIC OQ0257
analog
trigger
path
16
TVSYNC
High pass
filter
ALLTRIG
DUALTRIG
12
TVOUT
The analog trigger path uses the Input 1 (TRIG A) or Input 2 (TRIG B) signal for
triggering.
In the Transients mode the TRIG A or TRIG B signal is routed via a high pass filter
(TVOUT - TVSYNC). The High Pass Filter consists of C395 and R399.
The TRIG-A, TRIG-B, or TVSYNC signal, and two trigger level voltages TRIGLEV1
and TRIGLEV2, are supplied to the analog trigger part. The trigger level voltages are,
supplied by the PWM section on the Digital part (See Section 3.3.4). The TRIGLEV1
voltage is used for triggering on a negative slope of the Input 1/2 voltage. The
TRIGLEV2 voltage is used for triggering on a positive slope of the Input 1/2 voltage.
As the C-ASIC inverts the Input 1/2 voltage, the TRIGA, TRIGB slopes on the T-ASIC
input are inverted! From the selected trigger source signal and the used trigger level
voltages, the ALLTRIG and the DUALTRIG trigger signal are derived. The select logic
selects which one will be used by the synchronization/delta-T circuit to generate the final
trigger. There are three possibilities:
3-20
Page 45

Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
1. Single shot triggering.
The DUALTRIG signal is supplied to the synchronization/delta-T circuit. The
trigger levels TRIGLEV1 and TRIGLEV2 are set just above and below the DC level
of the input signal. A trigger is generated when the signal crosses the trigger levels.
A trigger will occur on both a positive or a negative glitch. This mode ensures
triggering, when the polarity of an expected glitch is not known.
2. Qualified triggering .
The ALLTRIG signal is supplied to T-ASIC output pin 35, which is connected to the
D-ASIC input pin 21. The D-ASIC derives a qualified trigger signal TR IGQUAL
from ALLTRIG, e.g . o n each 10 t h ALLTR IG p ul s e a TRIGQUAL p ul s e is g i ven.
The TRIGQUAL is supplied to the synchronize/delta-T circuit via the select logic.
3. Normal triggering.
The ALLTRIG signal is supplied to the synchronization/delta-T circuit.
The ALLTRIG signal includes all triggers. It is used by the D-ASIC for signal analysis
during AUTOSET.
Traditio nal ly a small t rigger gap is app l i ed fo r each t he trigger level. In noisy s i g n al s ,
this small-gap-triggering would lead to unstable displaying of the wave form, if the noise
is larger than the gap. The result is that the system will trigger randomly. This problem
is solved by increasing the trigger gap (TRIGLEV1 - TRIGLEV2) automatically to 80%
(10 to 90%) of the input signal peak-to-peak value. This 80% gap is used in AUTOSET.
3
Note
The ALLTRIG signal is also used for capacitance measurements (S. 3.3.2).
The Synchronize/Delta-t part provides an output pulse TRIGDT. The front edge of this
pulse is the real trigger moment. The pulse width is a measure for the time between the
trigger moment, and the moment of the first sample after the trigger. This pulse width
information is required in random repetitive sampling mode (see below). The
HOLDOFF signal, supplied by the D-ASIC, releases the trigger system. The sample
clock SMPCLK, also provided by the D-ASIC, is used for synchronization.
Real time sampling TRIGDT signal
For time base settings of 1 µs/d and slower, the pixel distance on the LCD is ≥40 ns (1
divisi o n is 25 pixel s ). As the maxi m u m s am ple rate is 25 MH z, a s am p l e i s taken each
40 ns. So the first sample after a trigger can be assigned to the first pixel, and successive
samples t o each nex t p i x el . A trace can be built-up from a single period of the input
signal.
Random rep eti ti v e (eq uivalent) s a mp l i ng TRIGDT s i gnal
For time base settings below 1 µs/d, the time between two successive pixels on the
screen is smaller than the time between two successive samples. For example at 2 0 n s / d ,
the time between two pixels is 20:25=0.8 ns, and the sample distance is 40 ns (sample
rate 25 MHz). A number of sweeps must be taken to reconstruct the original signal, see
Figure 3-11. As the samples are taken randomly with respect to the trigger moment, the
time dt must be known to position the samples on the correct LCD pixel. The TRIGDT
signal is a measure for the time between the trigger and the sample moment dt. The
pulse duration of the TRIGDT signal is approximately 4 µs...20 µs.
3-21
Page 46

43
Service Manual
TRIGGER
SAMPL ES SWEEP 1
SAMPL ES SWEEP 2
PIX EL
Figure 3-11. Random Repetitive Sampling M ode
3
dt1
4
dt2
21346591078 11
13
14
1512 13 16
14
DACTEST output
A frequency detector in the T-ASIC monitors the ALLTRIG signal frequency. If the
frequency is too high to obtain a reliable transmission to the D-ASIC, the DACTEST
output pin 29 will become high. The DACTEST signal is read by the D-ASIC via the
slow ADC on the Power part. It and indicates that the D-ASIC cannot use the ALLTRIG
signal (e.g. for qualified triggering).
Current Source
A current source in the T-ASIC suppl i es a DC current to th e GENOUT output pi n 1. The
current is u s ed for resistance and capacitance measurem en t s . It is adj us table in decades
between 50 nA and 500 µA depending on the measurement range, and is derived from an
external reference curren t . This reference current i s s u p plied by the R E FP reference
voltage via R323 and R324 to input REFOHMIN (pin 6).
The SENSE input signal is the buffered voltage on Input 1. For capacitance
measurement s i t is suppl ied to a clamp circuit in t h e T-ASIC (pin 59 ). The clamp circu i t
limits the positive voltage on the unknown capacitance to 0.45V.
The protection circuit prevents the T-ASIC from being damaged by a voltage applied to
Input 1 during resistance or capacitance measurements. If a voltage is applied, a current
will flow via PTC resistor R172 (on the Input 1 part), V358/V359, V353, V354 to
ground. The resulting voltage across the diodes is approximately -2V or +15V.
R354/R356, and V356/V357 limit the voltage on the T-ASIC GENOUT output (pin 1).
The BOOTSTRAP output si gnal on pi n 3 i s t he buffered GENOUT s ignal on pin 1, or
the buffered SENSE signal on pin 59. It is supplied to the protection diodes via R352,
R353, and to protection transistor V356, to minimize leakage currents.
On the ICAL-output of the T-ASIC (pin 5) a copy of the output current on GENOUT is
available. The current is supplied to the Input 1 C-ASIC via R144. As ICAL shows the
same time/temperature drift as the GENOUT measurement current, it can be used for
internal cal ibration of t h e res i s t an ce an d capacitance measurem en t fu n ct i o n .
Capacitor C356 is used for hum/noise suppression.
3-22
Page 47

Circuit Descri ptions
62
56
636454
52518
REFP
GAINPWM
GAINREFN
GAINADCB
GAINADCT
REFATT
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
Reference Voltage Ci rcu i t
This circui t deri v es s ev eral reference v o l t ag es fro m t h e 1 .23 V main reference s ou rce.
3
+3.3V
+3.3V
-1.23V
+0.1V
+1.23V
R309
R311
R312
R308
R306
R310
R303
R307
V301
1.23V
REFPWM2
REFP
REFPWM1
GNDREF
REFN
REFADCB
73
P-ASIC
OQ0256
72
71
+
-
T-ASIC
+
1
-
55
57
53
+
2
-
+
3
-
OQ0257
+
4
-
+1.6V
R302
R301
R305
REFADCT
Figure 3-12. Reference Vol t age Sect i on
The output of an amplifier in the P-ASIC supplies a current to the +1.23 V reference
source V301 via R307. The +3.3 V REFPWM2 voltage is used as reference for the
PWMB outputs of the D-ASIC on the Digital part.
The +1.23 V R E FP voltag e i s u s ed as main reference source fo r t he referen ce ci rcu i t.
This circuit consists of four amplifiers in the T-ASIC, external gain resistors, and filter
capacitors.
Amplifier 1 and connected resistors supply the REFPWM1 reference voltage. This
voltage is a reference for the PWMA outputs of the D-ASIC on the Digital section. It is
also used as reference voltage for the LCD supply on the LCD unit.
Amplifier 2 and connected resistors supply the -1.23 V REFN reference voltage, used for
the trigger level voltages TRIGLEV1&2, the C-ASIC POS-A and POS-B voltages, and
the C-ASIC OFFSET-A and OFFSET-B voltages. REFN is also the input reference for
amplifiers 3 and 4.
3-23
Page 48

43
Service Manual
3.3.4 Digital Circuit
Amplifier 3 and 4 and connected resistors supply the REFADCT and REFADCB
reference voltages fo r t h e ADC ’s . Both vol t ag es directly infl u en ce t h e g ai n accu racy o f
the ADC’s.
The T-ASIC can select some of the reference voltages to be output to pin 8 (REFATT).
The REFATT voltage is used for internal calibration of the Input 1 and B overall gain.
Tracerot Si gnal
The T-ASIC generates the TRACEROT signal, used by the C-ASIC’s. Control signals
TROTRST and TROTCLK are provided by the D-ASIC.
AC/DC Relay and Ω/ F Rel ay Con trol
The Input 1/2 AC/DC relays K171/K271, and the Input 1 Ω/F relay K173 are controlled
by the T-ASIC output signals ACDCA (pin 22), ACDCB (pin 23) and OHMA (pin 24).
SCLK, SDAT Signals
T-ASIC control data, e.g. for trigger source/mode/edge selection and relay control, are
provided by the D-ASIC via the SCLK and SDAT serial control lines..
See the Fluke 43 block diagram Figure 3-1, and circuit diagram Figure 9-4.
The Digital part is built up around the D-ASIC MOT0002. It provides the following
functions:
• Analog to Digital Conversion of the conditioned Input 1 and Input 2 signals
• ADC data acq u i s i t i o n for traces and numeri cal read i n g s
• Trigger processing
• Pul s e wi d t h m eas u rem en t s , e.g. for cap aci t an ce m eas u rement functi on
• Microprocessor, Flash EPROM and RAM control
• Display control
• Keyboard control, ON/OFF control
• Miscellaneous functions, as PWM signal generation, SDA-SCL serial data control,
Slow ADC control, serial RS232 in t erface control , buzzer cont rol , etcetera.
The D-ASIC is p erman en t l y po wered by t h e + 3V3 GAR v o l t age. The P-ASIC i n d i cat es
the status of the +3V3GAR voltage via the VGARVAL line connected to D-ASIC pin
89. If +3V3GAR is correct VGARVAL is high, the D-ASIC will start-up, and the
D-ASIC functions are operative regardless of the test tool is ON/OFF status.
Analog to Digital Conversion
For voltage and resistance measurements, the Input 1/2 (2 for voltage only) signal is
conditioned by the C-ASIC to 150 mV/d. Zero and gain measurements are done to
eliminate offset and gain errors. The C-ASIC output voltage is supplied to the Input 1/2
ADC (D401/D451 pin 5). The ADC samples the analog voltage, and converts it into an
8-bit data byte (D0-D7). The data are read and processed by the D-ASIC, see below
“ADC data Acquisition”.
3-24
The sample rate depends on the sample clock supplied to pin 24. The sample rate is 5
MHz or 25 MHz, depending on the instrument mode. The ADC input signal is sampled
Page 49

Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
on the rising edge of the sample clock. The digital equivalent of this sample is available
on the outputs D0-D7 with a delay of 6 sample clock cycles.
The reference voltages REFADCT and REFADCB determine the input voltage swing
that corresponds to an output data swing of 00000000 to 11111111 (D0-D7). The
reference voltages are supplied by the reference circuit on the Trigger part. The ADC
output voltages MIDADC-A/B are supplied to the C-ASIC’s (input pin 28), and are
added to the conditioned input signal. The MIDADC voltage matches the middle of the
C-ASIC output swing to the middle of the ADC input swing.
Current IREF is supplied to pin 7 of the ADC’s via R403/R453 for biasing internal ADC
circuits.
ADC data acqui si ti on for traces and nu meri cal read i n g s
During an acqu i s i t i o n cycle, ADC samp l es are acqu i red fo r (S co p e) t races an d n u m eri cal
readings.
The test t oo l s o ft ware s t art s an acq u i s i t i o n cycle. The D-ASIC acq ui res d at a fro m t h e
ADC, and stores them internally in a cyclic Fast Acquisition Memory (FAM). The
D-ASIC also makes the HOLDOFF line low, to enable the T-ASIC to generate the
trigger signal TRIGDT. The acquisition cycle is stopped if the required number of
samples is acquired. From the FAM the ADC data are moved to the RAM D475. The
ADC data sto red i n t h e R A M are pro ces s ed an d rep res en t ed as t races an d readings.
3
Triggering (HO L DO FF, TRIGDT, Ran domize)
To start a new trace, the D-ASIC mak es t h e HOLDOFF signal l o w. No w t h e T-AS IC
can generate the trigger signal TRIGDT. For signal frequencies higher than the system
clock frequency, and in the random repetitive sampling mode, no fixed time relation
between the HOLDOFF si gnal and t h e sy st em cl ock i s al l owed. The RANDOMIZE
circuit desynchronizes the HOLDOFF from the clock, by phase modulation with a LF
ramp signal.
Trigger qualifying (ALLTRIG, TRIGQUAL)
The ALLTRIG signal supplied by the T-ASIC contains all possible triggers. For normal
triggering the T-ASIC uses ALLTRIG to generate the final tri gger TRIGDT. F o r
qualified t ri g g eri n g t h e D-ASIC returns a qu al i fi ed , e.g. each n
T-ASIC (TRIGQUAL). Now t he T-AS IC deri ves t he fi nal t ri gger TR IGDT from t he
qualified trigger signal TRIGQUAL.
Capacitance measurements (ALLTRIG)
As described in Section 3.3.2, capacitance measurements are based on measuring the
capacitor charging time using a known current. The ALLTRIG pulse signal represents
the charging time. The time is counted by the D-ASIC.
Microprocess o r, RO M a nd RAM control , ma s k ROM
The D-ASIC includes a microprocessor with a 16 bit data bus. The instrument software
is loaded in Flash ROM D472.
th
, trigger pulse to the
Measurement data and instrument settings are stored in RAM D475. All RAM data will
be lost if all power sources (battery and power adapter) are removed.
The D-ASIC has on-chip mask ROM. If no valid Flash ROM software is present when
the test tool is turned on, the mask ROM software will become activate. The test tool
can be forced to stay in the mask ROM software by pressing the ^ and > key, and then
turning the test tool on. When active, the mask ROM software generates a 100 kHz
square wave on pin 59 of the D-ASIC.
3-25
Page 50

43
Service Manual
The circuit D480 and related parts create a delay for the ROMWRITE enable signal.
This prevents the ROM write proces being disabled before all data have been written
(PCB version 3 up only).
Display Control
The LCD uni t i n cl u d es the LCD, th e L C D d ri v ers , an d t h e fl u o res cent b ack l i g h t l am p .
It is connected to the main board via connector X453. The LCD is built up of 240
columns of 240 pixels each (240x240 mat rix). The D-ASIC supplies the dat a and
control signals for the LCD drivers on the LCD unit (Figure 3-13).
FRAME
Column
Driver
Din
DCl
LnCl
M
Carry
Column
Driver
Din
DCl
LnCl
M
Carry
Column
LCDAT0-3
DATACLK0
LINECLK
MM
Driver
Din
DCl
LnCl
Common Driver Common Driver Common Driver
LnCl
MMM
X1..80 X81..160 X161..240
Y1..80
LEFT
Y81..160
Y161..240
Figure 3-13. LCD Control
Do Di Do Di
LnCl LnCl
TOP
FRONTVIEW
LCD
PIXEL (0,0)
3-26
Each 14 ms the LCD picture is refreshed during a frame. The frame pulse (FRAME)
indicates that the concurrent LINECLK pulse is for the first column. The column drivers
must have been filled with data for the first column. Data nibbles (4 bit) are supplied via
lines LCDAT0-LCDAT3. During 20 data clock pulses (DATACLK0) the driver for
Y161..240 is filled. When it is full, it generates a carry to enable the driver above it,
which is filled now. When a column is full, the LINECLK signal transfers the data to
the colum n d ri v er o u t p uts. Via the co m mon drivers t h e LINE C L K al s o s el ect s t h e n ext
column to be filled. So after 240 column clocks a full screen image is built up.
The LCD unit generates various voltage levels for the LCD drivers outputs to drive the
LCD. The various levels are supplied to the driver outputs, depending on the supplied
data and the M(ultiplex) signal. The M signal (back plane modulation) is used by the
LCD drivers to supply the various DC voltages in such an order, that the average voltage
does not contain a DC component. A DC component in the LCD drive voltage may
cause memory effect s in the LCD.
The LCD contrast is controlled by the CONTRAST voltage. This voltage is controlled
by the D-ASIC, which supplies a PWM signal (pin 37 CONTR-D) to PWM filter
R436/C436. The voltage REFPWM1 is used as bias voltage for the contrast adjustment
circuit on the LCD unit. To compensate for contrast variations due to temperature
Page 51

Circuit Descri ptions
3.3 Detailed Circuit Des c r iptions
variations, a temperature dependent resistor is mounted in the LCD unit. It is connected
to the LC DTE M P 1 l ine. The resi s t an ce chan g e, wh i ch rep res en t s t h e LCD temperature,
is measured by t h e D-AS IC via the S-ADC on the POWER part.
The back light lamp is located at the left side of the LCD, so this side becomes warmer
than the right side. As a result the contrast changes from left to right. To eliminate this
unwanted effect, the CONTRAST control voltage is increased during building up a
screen image. A FRAME puls e s t art s t h e new s creen i m age. The FRAME p ulse is also
used to discharge C404. After the FRAME pulse, the voltage on C404 increases during
building up a screen image.
Keyboard Control, ON/OFF Control
The keys are arranged in a 6 rows x 6 columns matrix. If a key is pressed, the D-ASIC
drives the rows, and senses the columns. The ON/OFF key is not included in the matrix.
This key toggles a flip-flop in the D-AS IC via th e ONKEY lin e (D-ASIC pin 72). As
the D-ASIC is permanently powered, the flip-flop can signal the test tool on/off status.
PWM Signals
The D-ASIC generates various pulse signals, by switching a reference voltage
(REFPWM1 or REFPWM2), with software controllable duty cycle (PWMA, PWMB
pins 26-40). By filtering the pulses in low pass filters (RC), software controlled DC
voltages are generated. The voltages are used for various control purposes, as shown in
Table 3-6.
3
Table 3-6. D-ASIC PWM Signals
PWM signal Function Destination Reference
HO-RNDM HOLDOFF randomize cont r ol R487 of RANDOMIZE c ir c uit REFPWM1
TRGLEV1D,
TRIGLEV2D
POS-AD, POS-BD Input 1,B position contr ol C-ASIC REFPWM1
OFFSETAD,
OFFSETBD
BACKBRIG Back light brightness control Back light convert er ( PO WER part ) REFPWM1
CONTR-D Display contrast control LCD unit REFPWM1
SADCLEVD S ADC compar a tor voltag e SLOW ADC (POWER part) REFPWM2
CHARCURD Battery charge c u rrent con t rol P-ASIC REFPWM2
Trigger level control T-ASIC REFPWM1
Input 1,B offset cont r ol C-ASIC REFPWM1
SDA-SCL Serial Bus
The unidirectional SDA-SCL serial bus (pin 56, 57) is used to send control data to the CASIC’s (e.g. change attenuation factor), and the T-ASIC (e.g. select other trigger source).
The SDA line transmits the data bursts, the SCL line transmits the synchronization clock
(1.25 MHz).
Probe Detection
Via the probe detection inputs PROBE-A and PROBE-B (pin 54, 55), the D-ASIC
detects if the Input 1 and 2 probes have been connected/disconnected. The SUPPRDET
signal (pin 99) can suppress the probe detection. If this signal is low, The PROBE-A
and PROBE-B lines are permanently low (via R471, R472), regardless of a probe is
connected or not connected. This function is used in all appropriate modes except the
SCOPE mode.
TXD, RXD Serial Interface (Optical Port)
3-27
Page 52

43
Service Manual
The optical interface out put i s di rect l y connect ed t o th e TXD l i ne (pi n 86). The opt i cal
input line is buffered by the P-ASIC on the power part. The buffered line is supplied to
the RXD input (pin 87). The serial data communication (RS232) is controlled by the
D-ASIC.
Slow ADC Control, S ADC B u s
The SELMUX0-2 (pins 96-98) and SLOWADC (pin 100) lines are used for
measurements of various analog signals, as described in Section 3.3.1. “SLOW ADC”.
BATIDENT
The BATTIDENT line (pin 90) is connected to R508 on the Power part, and to a resistor
in the battery pack. If the battery is removed, this is signaled to the D-ASIC
(BATTIDENT line goes high).
MAINVAL, FREQPS
The MAINVAL signal (pin91) is supplied by the P-ASIC, and indicates the presence of
the power adapter voltage (high = present).
The FREQPS signal (pin 93) is also supplied by the P-ASIC. It is the same signal that
controls the Fly Back Converter control voltage FLYGATE. The D-AS IC measures the
frequency in order to detect if the Fly Back Converter is running within specified
frequency limits.
D-ASIC Clocks
A 25 MHz crystal (B403) controls the D-ASIC system clock. For the real time clock,
counting the time and date, an additional 32.768 kHz crystal (B401) is provided. When
the test tool is turned on, a 16MHz microprocessor clock (derived from B402) becomes
active.
Buzzer
The Buzzer is directly dri ven by a 4 kHz s quare wave from t he D-AS IC (pi n 101) via
FET V522. If the test tool is on, the -30VD supply from the Fly Back converter is
present, and the buzzer sounds l oudly. If the -30VD is not present, th e buzzer sounds
weak, e.g. when the Mask Act i v e m o de is entered.
3-28
Page 53

Chapter 4
Performance Verification
Title Page
4.1 Introduction............................................................................................. 4-3
4.2 Equipment Required For Verification....................................................... 4-3
4.3 How To Verify........................................................................................ 4-3
4.4 Display and Backlight Test...................................................................... 4-4
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in the SCOPE MODE....................................... 4-5
4.5.1 Input 1 Trigger Sensitivity Test ......................................................... 4-6
4.5.2 Input 1 Frequency Response Upper Transition Point Test.................. 4-7
4.5.3 Input 1 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test................................ 4-7
4.5.4 Input 2 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test................................ 4-9
4.5.5 Input 2 Trigger Level and Trigger Slope Test.................................... 4-10
4.5.6 Input 2 Trigger sensitivity Test. ........................................................ 4-12
4.5.7 Input 1 Trigger Level and Trigger Slope Test.................................... 4-13
4.5.8 Input 1 and 2 DC Voltage Accuracy Test. ......................................... 4-15
4.5.9 Input 1 and 2 AC Voltage Accuracy Test .......................................... 4-17
4.5.10 Input 1 and 2 AC Input Coupling Test............................................. 4-19
4.5.11 Input 1 and 2 Volts Peak Measurements Test .................................. 4-20
4.5.12 Input 1 and 2 Phase Measurements Test.......................................... 4-21
4.5.13 Input 1 and 2 High Voltage AC & DC Accuracy Test...................... 4-22
4.6 Ohms/Continuity/Capacitance. ................................................................. 4-25
4.6.1 Resistance Measurements Test. ......................................................... 4-25
4.6.2 Diode Test Function Test.................................................................. 4-26
4.6.3 Continuity Function Test................................................................... 4-27
4.6.4 Capacitance Measurements Test........................................................ 4-27
4.7 Inrush Current.......................................................................................... 4-28
4.8 Sags & Swells.......................................................................................... 4-29
4.9 Harmonics............................................................................................... 4-30
4.10 VOLT/AMPS/HERTZ........................................................................... 4-30
4.11 POW E R................................................................................................. 4-31
4.12 Transients.............................................................................................. 4-32
4-1
Page 54

Page 55

4.1 Introducti on
Procedures in this chapter should be performed by qualified
service personnel only. To avoid electrical shock, do not
perform any servicing unless you are qualified to do so.
The test tool should be calibrated and in operating condition when you receive it.
The followi n g perform an ce t es t s are p ro vided to ensure that t h e t es t to ol is in a pro p er
operating condition. If the test tool fails any of the performance tests, calibration
adjustm en t (s ee Chap t er 5 ) and / o r rep ai r (s ee C h ap t er 7 ) is necess ary.
The Performance Verification Procedure is bas ed on the s p eci fi cat ions, listed in Chap t er
2 of this Servi ce M anu al . T he v al u es giv en h ere are val id for ambient t emperat u res
between 18 °C and 28 °C.
The Performance Verification P ro ced u re i s a q uick way to check most of th e test tool’s
specificat i o n s . Becau s e o f t h e hig h l y in t eg rat ed d es i g n of the t es t t o ol, i t i s not al way s
necessary to check al l features separat el y . For example: t he dut y cycl e, pulse width, an d
frequency measurement are based on the same measurement principles; so only one of
these functions needs to be verified.
Warning
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.1 Introduction
4
4.2 Equipment Requir e d For Verification
The primary source instrument used in the verification procedures is the Fluke 5500A. If
a 5500A is not available, you can substitute another calibrator as long as it meets the
minimum test require me nts.
• Fluke 5500A Multi Product Calibrator, including 5500A-SC Oscilloscope Calibration
Option.
• Stackable Test Leads (4x), supplied with the 5500A.
• 50Ω Coax Cables (2x), Fluke PM9091 (1.5m) or PM9092 (0.5m).
• 50Ω feed through termination’s (2x), Fluke PM9585.
• Fluke BB120 Shielded Banana to Female BNC adapters (2x), supplied with the Fluke
43.
• Dual Banana Plug to Female BNC Adapter (1x), Fluke PM9081/001.
• Dual Banana Jack to Male BNC Adapter (1x), Fluke PM9082/001.
4.3 How To Verify
Verification p ro cedu res fo r t h e d i s play function and measu re fu n ct i o ns foll o w. For each
procedure the test requirements are listed. If the result of the test does not meet the
requirements, the test tool should be recalibrated or repai red if neces sary.
Follow these general instructions for all tests:
• For all tests, power the test tool with the PM8907 power adapter. The battery pack
must be installed.
• Allow the 5500A to satisfy its specified warm-up period.
• For each test point , wait for the 5500A to settle.
• Allow the test tool a minimum of 20 minutes to warm up.
4-3
Page 56

43
Service Manual
4.4 Display and Backlight Test
Before doing the tests, you must reset the test tool to put it in a defined state.
Proceed as fol l o ws to res et the t es t to ol:
• Press
• Press and hold
• Press an d release
Wait until the test tool has beeped twice, and th en rel eas e
to turn the test tool off.
.
to turn the test tool on.
When the test too l has
beeped twice, the RESET was su cces s fu l .
Proceed as fol lows to test the dis play an d th e back l ight:
1. Press
to turn the test tool on.
2. Remove the adapter power, and verify that the backlight is dimmed.
3. Apply the adapter power and verify that the backlight brightness is set to maximum.
4. Press
5. Press and hold
6. Press an d rel eas e
to leave the S T ARTU P screen.
.
.
7. Release
The test tool shows the calibration menu in the bottom of the display.
Do not press now! If you did, press
twice to turn the test tool off and on,
and start at 4.
8. Press (PREV) three times.
The test tool shows
Contrast (CL 0100):MANUAL
9. Press (CAL) .
The test tool shows a dark display; the test pattern as shown in Figure 4-1 may not be
visible or hardly visible.
Observe the display closely, and verify that no light pixels are shown.
Figure 4-1. Display Pixel Test Pattern
4-4
Page 57

Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
11. Press .
The test pattern is removed; the test tool shows
12. Press (CAL) .
The test tool shows the display test pattern shown in Figure 4-1, at default contrast.
Observe the test pattern closely, and verify that the no pixels with abnormal contrast
are present in the display pattern squares. Also verify that the contrast of the upper
left and upper right square of the test pattern are equal.
Contrast (CL 0110):MANUAL
4
13. Press
The test pattern is removed; the test tool shows
14. Press (CAL) .
The test tool shows a light display; the test pattern as shown in Figure 4-1 may not be
visible or hardly visible.
Observe the display closely, and verify that no dark pixels are shown.
15. Press
return to the normal operating mode.
.
Contrast (CL 0120):MANUAL
twice to turn the test tool OFF and ON to exit the calibration menu and to
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in the SCOPE MODE.
Before performing the Input 1 and Input 2 tests, the test tool must be set in a defined
state, by performing a RESET.
Proceed as fol l o ws to res et the t es t to ol:
• Press
• Press and hold
• Press an d release
Wait until the test tool has beeped twice, and th en rel eas e
beeped twice, the RESET was su cces s fu l .
to turn the test tool off.
.
to turn the test tool on.
When the test too l has
Now you must select the SCOPE MODE.
• Press
• Press
• Press up-down
• Press
to leave the S T ARTU P s creen .
.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode.
4-5
Page 58

43
Service Manual
4.5.1 Input 1 Trigger Sensitivity Test
Proceed as follows to test the Input 1 trigger sensitivity:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4-2.
ST8004.CGM
Figure 4-2. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Scope Output 50Ω
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode.
3. Select timebase of 100 ns/d.
• Press
• Press
to select RANGE.
to select 100 ns/d.
4. Select sensitivity of 200 mV/d.
• Press
to select 200 mV/d.
5. Set the 5500A to source a 5 MHz leveled sine wave of 100 mV peak-to-peak
(SCOPE output, MODE levsine).
6. Verify that the signal is well triggered , if necessary adjust the trigger level (see 7).
7. Adjusting trigger level.
• Press
to highlight TRIGGER, then press to adjust the trigger level.
8. Set the 5500A to source a 25 MHz leveled sine wave of 400 mV peak-to-peak.
9. Select timebase of 20 ns/d.
• Press
to select RANGE.
4-6
• Press
to select 20 ns/d.
10. Verify that the signal is well triggered , if necessary adjust the trigger level (see 7).
11. Set the 5500A to source a 40 MHz leveled sine wave of 1.8V peak-to-peak.
12. Verify that the signal is well triggered, if necessary adjust the trigger level (see 7).
13. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Page 59

4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
4.5.2 Input 1 Frequency Response Upper Transition Point Test
Proceed as follows to test the Input 1 frequency response upper transition point:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-2).
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Select the following test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Input 1 Reading
to go to Input 1 READING.
to highlight AC + DCrms.
to confirm; mark changes to ■
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Set the 5500A to source a leveled sine wave of 1.2V peak-to-peak, 50 kHz (SCOPE
output, MODE levsine).
5. Adjust the amplitude of the sine wave to a reading of 424 mV ± 8 mV.
6. Set the 5500A to 20 MHz, without changing the amplitude.
7. Observe the Input 1 trace and check the readi ng is ≥ 297 mV.
8. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Note
The lower transition point is tested in Section 4.5.9.
4.5.3 Input 1 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test
Proceed as follows to test the Input 1 frequency measurement accuracy:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-2).
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted
to select SCOPE mode.
4-7
Page 60

43
Service Manual
3. Select the following test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Input 1 coupling.
to select the Input 1 coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■
to highlight Input 1 Reading
to go to Input 1 READING.
to highlight Hz.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Set the 5500A to source a leveled sine wave of 600 mV peak-to-peak (SCOPE
output, MODE levsine).
5. Set the 5500A frequency according to the first test point in Table 4-1.
6. Observe the Input 1 Reading on the test tool and check to see if it is within the range
shown under the appropriate column.
7. Continue through the test points.
8. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-1. Input 1 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test
5500A output, 600 mVpp I nput 1 Reading
1 MHz 0.98 to 1.03 MHz
10 MHz 09.7 to 10.3 MHz
40 MHz 38.8 to 41.2 MHz
Note
Duty Cycle and Pulse Width measurements are based on the same
princip l es as Fr eq u en cy mea s u r ements. Therefore t h e Duty Cycle and
Pulse Width measurement function will not be verified separately.
4-8
Page 61

4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
4.5.4 Input 2 Frequency Measurement Accuracy Test
Proceed as follows to test the Input 2 frequency measurement accuracy:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4-3.
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4
Figure 4-3. Test Tool Input 2 to 5500A NORMAL output
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Select the following test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Input 2 Reading
to go to Input 2 READING.
to highlight Hz.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 Coupling menu.
ST8588.wmf
• Press
• Press
• Press
4. Set the 5500A to source a sine wave of 600 mV, 15 kHz (NORMAL output, MODE
WAVE sine).
5. Observe the Input 2 main reading on the test tool and check the reading between 14.8
and 15.2 kHz.
6. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■
to return to SCOPE.
4-9
Page 62

43
Service Manual
4.5.5 Input 2 Trigger Level and Trigger Slope Test
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test shown in Figure 4-3.
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
3. Make Input 2 active:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight the Input 2 READING.
to select Input 2 READING.
to highlight AC+DCrms.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 Coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Select trigger on channel 2.
• Short-circuit Input 1 with a BB120 and a 50Ω feed through terminator.
• Set the 5500A to source 1V, 50 Hz sine wave (NORMAL output, MODE WAVE
sine).
5. Select the following test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select RANGE, then press t o select RANGE 2.
to select 1 kA/d.
to select a timebase of 10 ms/d.
.
• Press to select TRIGGER.
• Using
set the trigger level to +2 divisions from the screen center. For
positive slope triggering, the trigger level is the top of the trigger icon (
6. Set the 5500A to source 0.4V DC.
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Time base.
).
4-10
Page 63

4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
• Press .to select the TI M E BASE menu.
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
7. Verify that no trace is s hown on the test tool display, and that at the upper right
corner of the display HOLD is not shown. If the display shows HOLD then press
. Hold should disappear and the test tool is re-armed for a trigger.
8. Increase the 5500A voltage slowly in 0.1V steps, using the 5500A EDIT FIELD
function , unt il the test tool is trig g ered , an d th e t r aces are s ho w n.
9. Verify that the 5500A voltage is between +1.5V and +2.5V when the test tool is
triggered.
To repeat the test set the 5500A to 0.4V and start at step 5.
10. Set the 5500A to Standby.
11. Press
to select SINGLE.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Trigger slope.
to select the TRIGGER SLOPE menu.
to highlight positive trigger ( ).
to confirm; changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
to clear the dis p l ay .
12. Select n egat i v e TRIGGER SLOPE.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
13. Set the trigger level to +2 divisions from the screen center. For negative slope
triggering, the trigger level is the bottom of the trigger icon (
• Press
• Using
14. Set the 5500A to source +3V DC.
15. Verify that no trace is shown on the test tool display, and that at the upper right
corner of the display HOLD is not shown. If the display shows HOLD then press
. Hold should disappear and the test tool is re-armed for a trigger.
16. Decrease the 5500A voltage slowly in 0.1V steps, using the 5500A EDIT FIELD
function , unt il the test tool is trig g ered , an d th e t r aces are s ho w n.
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Trigger slope.
to select the TRIGGER SLOPE menu.
to highlight negative trigger ( ).
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
).
to select TRIGGER.
set the trigger level to +2 divisions from the screen center.
4-11
Page 64

43
Service Manual
4.5.6 Input 2 Trigger sensitivity Test.
17. Verify that the 5500A voltage is between +1.5V and +2.5V when the test tool is
triggered.
To repeat the test, start at step 1 2.
18. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Proceed as follows to test the Input 2 trigger sensitivity:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test shown in Figure 4-3.
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode.
3. Make Input 2 active:
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 2 READING.
• Press to highlight AC+DCrms.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 Coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Select trigger on channel 2.
• Short-circuit Input 1 with a BB120 and a 50Ω feed through piece.
4-12
• Set the 5500A to source a 5 kHz leveled sine wave of 50 mV (NORMAL output,
MODE wave sine).
5. Select the following test tool setup:
• Press
to select RANGE 2.
• Press to select 200A/d.
• Press
to select a timebase of 50 µs/d.
6. Verify that the signal is well triggered , if necessary adjust the trigger level (see 7).
7. Adjusting trigger level.
• Press
• Press
.
to highlight TRIGGER.
• Press to adjust.
Page 65

8. Select timebase of 10 µs/d.
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
4
• Press
• Press
9. Set the 5500A to source a 20 kHz leveled sine wave of 62.5 mV peak-to-peak (half a
divisions on the display).
10. Verify that the signal is well triggered , if necessary adjust the trigger level (see 7).
11. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
4.5.7 Input 1 Trigger Level and Trigger Slope Test
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4-4.
to select RANGE.
to select 10 µs/d.
Figure 4-4. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Normal Output
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Select the following test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
to highlight AC+DCrms.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
ST8586.WMF
• Press
to return to SCOPE.
4-13
Page 66

43
Service Manual
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Using
to select Input 1 RANGE.
to select 1V/d.
to select a timebase of 10 ms/d.
to leave RANGE 1.
to select TRIGGER.
set the trigger level to +2 divisions from the screen center. For
positive slope triggering, the trigger level is the top of the trigger icon (
4. Set the 5500A to source 0.4V DC.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Time base.
.to sel ect the TIME BASE menu.
to select SINGLE.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Trigger slope.
to select the TRIGGER SLOPE menu.
).
• Press
• Press
• Press
to highlight positive trigger ( ).
to confirm; changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
5. Verify that no trace is s hown on the test tool display, and that at the upper right
corner of the display HOLD is not shown. If the display shows HOLD then press
. Hold should disappear and the test tool is re-armed for a trigger.
6. Increase the 5500A voltage slowly in 0.1V steps, using the 5500A EDIT FIELD
function , unt il the test tool is trig g ered , an d th e t r aces are s ho w n.
7. Verify that the 5500A voltage is between +1.5V and +2.5V when the test tool is
triggered.
To repeat the test set the 5500A to .4V and start at step 5.
8. Set the 5500A to Standby.
9. Press
to clear the dis p l ay .
10. Select n egat i v e TRIGGER SLOPE.
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Trigger slope.
to select the TRIGGER SLOPE menu.
4-14
• Press
• Press
to highlight negative trigger ( ).
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
Page 67

Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
• Press to return to SCOPE.
11. Set the 5500A to source +3V DC.
12. Set the trigger level to +2 divisions from the screen center. For negative slope
triggering, the trigger level is the bottom of the trigger icon (
).
4
• Press
• Using
13. Verify that no trace is shown on the test tool display, and that at the upper right
corner of the display HOLD is not shown. If the display shows HOLD then press
. Hold should disappear and the test tool is re-armed for a trigger.
14. Decrease the 5500A voltage slowly in 0.1V steps, using the 5500A EDIT FIELD
function , unt il the test tool is trig g ered , an d th e t r aces are s ho w n.
15. Verify that the 5500A voltage is between +1.5V and +2.5V when the test tool is
triggered.
To repeat the test, start at step 1 2.
16. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
4.5.8 Input 1 and 2 DC Voltage Accuracy Test.
to select TRIGGER.
set the trigger level to +2 divisions from the screen center.
WARNING
Dangerous voltages will be present on the calibration source
and connecting cables during the following steps. Ensure that
the calibrator is in standby mode before making any connection
between the calibrator a nd the test tool .
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A in Figure 4-5.
Figure 4-5. Test Tool Input 1-2 to 5500A Normal Output
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode.
ST8001.CGM
4-15
Page 68

43
Service Manual
3. Select DC coupling & reading for Input 1 and 2.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
to highlight DC.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING
to highlight DC.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
• Press
• Press
• Press
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Set the 5500A to source the appropriate DC voltage from table 4-2.
5. Observe the main reading and check to see if it is within the range shown under the
appropriate column.
6. Select the appropriate sensitivity for the test tool:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select RANGE 1 or RANGE 2.
to select RANGE 1 or press to select RANGE 2.
to select the ranges mentioned in the table.
7. Continue through the test points.
8. When you are finished, set the 5500A to 0 (zero) Volt, and to Standby.
4-16
Page 69

4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
Table 4-2. Volts DC Measurement Verification Points
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4
Sensitivity
Input 1 Input 2 Input 1
5 mV/div 5 A/div 15 mV 14.4 to 15.6
10 mV/div 10 A/div 30 mV 29.3 to 30.7
20 mV/div 20 A/div 60 mV 59. 2 to 60.8 59.65 to 60.35
50 mV/div 50 mV/div 150 mV 148.7 to 151.3 148.7 to 151.3
100 mV/div 100 A/div 300 mV 298.0 to 302.0 298. 0 to 302.0
200 mV/div 200 A/div 500 mV 497.0 to 503.0 497. 0 to 503.0
500 mV/div 500 A/div 1.5V 1.487 to 1.513 1. 487 to 1.513
1 V/div 1 kA/div 3V 2.980 to 3.020 2.980 to 3.020
2 V/div 2 kA/div 5V 4.970 to 5.030 4.970 to 5.030
5500A output,
V DC
[mV or V/div]
-500 mV -497.0 to -503.0 -497.0 to -503.0
0 mV -0.5 to + 0.5 -0.5 to + 0.5
-5V -4.970 to -5.030 -4.970 to -5.030
0V -0.005 to +0.005 -0.005 to +0.005
DC Reading
2)
2)
Input 2
[A or kA/div]
14.88 to 15.13
29.80 to 30.20
2)
2)
5 V/div 5 kA/div 15V 14.87 to 15.13 14.87 to 15.13
10 V/div 10 kA/div 30V 29.80 to 30.20 29.80 to 30.20
20 V/div 20 kA/div 50V 49.70 to 50.30 49.70 to 50.30
-50V -49.70 to -50.30 -49.70 to -50.30
0V -0.05 to + 0.05 -0.05 to +0.05
50 V/div 50 kA/div 150V 148.7 to 151.3 148.7 to 151.3
100 V/div 100 kA/div 300V 298.0 to 302.0 298.0 to 302.0
1)
The 500V and 1250V range will be tested in Section 4.5.13
2)
Due to calibrator noise, occasionally OL (overload) can be shown.
4.5.9 Input 1 and 2 AC Voltage Accuracy Test
Warning
Dangerous voltages will be present on the calibration source
and connecting cables during the following steps. Ensure that
the calibrator is in standby mode before making any connection
between the calibrator a nd the test tool .
Proceed as follows to test the Input 1 and 2 AC Voltage accuracy:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-5).
4-17
Page 70

43
Service Manual
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
3. Select DC coupling & reading for Input 1 and 2.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
to highlight ACrms.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
to highlight AC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING
to highlight ACrms.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
to highlight AC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Select the appropriate sensitivity for the test tool:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select RANGE 1 or RANGE 2.
to select RANGE 1 or press to select RANGE 2.
to select the ranges mentioned in the table.
5. Select the appropriate timebase setting for the test tool
• Press
• Press
when RANGE, RANGE 1, or RANGE 2 is not highlighted.
to select
6. Set the 5500A to source the appropriate AC voltage.
7. Observe the Input 1 and Input 2 main reading and check to see if it is within the
range shown under the appropriate column.
4-18
8. Continue through the test points.
Page 71

4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
9. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-3. Volts AC Measurement Verification Points
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4
Sensitivity
Input 1 Input 2 Input 1 Input 2
200 mV/div 200A/ div 10 ms/d 500 mV 60 Hz 494.0 to 506.0 494.0 to 506.0
2V/div 2kA/div 20 µ/d 5V 20 kHz 4.860 to 5.140
20V/div 20kA/div 10 ms/d 50V 60 Hz 49.40 to 50.60 49.40 to 50.60
1)
The 500V and 1250V range will be tested in Section 4.5.14
Time
base
20 µ/d 500 mV 20 kHz 486.0 to 514.0
10 ms/d 5V 60 Hz 4.940 to 5.060 4.940 to 5.060
20 µ/d 50V 20 kHz 48.60 to 51.40
5500A output
Volts rms
5500A
Frequency
Reading 1 & 2
4.5.10 Input 1 and 2 AC Input Coupling Test
Proceed as follows to test the Input 1 and 2 AC coupled input lower transition point:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-5).
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
to select the MENU.
• Press
• Press
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
3. Select AC coupling & reading for Input 1 and 2.
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
• Press to highlight ACrms.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
to highlight AC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING
to highlight ACrms.
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
4-19
Page 72

43
Service Manual
• Press to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
to highlight AC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Set the 5500A to source an AC voltage, to the first test point in Table 4-4 (NORMAL
output, WAVE sine).
5. Observe the Input 1 and Input 2 main reading and check to see if it is within the
range shown under the appropriate column.
6. Continue through the test points.
7. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-4. Input 1 and 2 AC Input Coupling Verification Points
5500A output, V rms 5500A Frequency Readi ng 1 Reading 2
500.0 mV 10 Hz > 344.0 > 344.0
500.0 mV 33 Hz > 469.0 > 469.0
500.0 mV 60 Hz > 486.5 > 486.0
4.5.11 Input 1 and 2 Volts Peak Measurements Test
WARNING
Dangerous voltages will be present on the calibration source
and connecting cables during the following steps. Ensure that
the calibrator is in standby mode before making any connection
between the calibrator a nd the test tool .
Proceed as fol l o ws to test the Vo l t s P eak measu rem en t fu nction:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-5).
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Select DC coupling & Peak m/m reading for Input 1 and 2.
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
to highlight Peak m/m.
4-20
• Press
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
Page 73

4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
• Press to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
4. Set the 5500A to source a sine wave, to the first test point in Table 4-5 (NORMAL
output, WAVE sine).
5. Observe the Input 1 and Input 2 main reading and check to see if it is within the
range shown under the appropriate column.
6. Continue through the test points of table 4-5.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING.
to highlight Peak m/m.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
7. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-5. Volts Peak Measurement Verification Points
5500A output, Vrms (sine) 5500A Frequency Reading 1 Reading 2
1.768 (5V peak) 1 kHz 4.50 to 5.50 4. 50 to 5.50
4.5.12 Input 1 and 2 Phase Measurements Test
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-5).
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Select DC coupling for Input 1 and 2; Reading Phase for Input 2:
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
• Press
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
4-21
Page 74

43
Service Manual
• Press to highlight DC Coupling.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING.
to highlight Phase.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Set the 5500A to source a sine wave, to the first test point in Table 4-6 (NORMAL
output, WAVE sine).
5. Observe the Input 1 and Input 2 main reading and check to see if it is within the
range shown under the appropriate column.
6. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-6. Phase Measurement Verification Points
5500A output, Vrms (sine) 5500A Frequency Reading 1 & 2
1.5V 400 Hz -2 to +2 Deg
4.5.13 Input 1 and 2 High Voltage AC & DC Accuracy Test
Warning
Dangerous voltages will be present on the calibration source
and connecting cables during the following steps. Ensure that
the calibrator is in standby mode before making any connection
between the calibrator a nd the test tool .
Proceed as follows to test the Input 1 & 2 High Voltage DC Accuracy:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4-6.
4-22
Page 75

Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.5 Input 1 and Input 2 Tests in t he SCOPE MODE.
4
Figure 4-6. Test Tool Input 1-B to 5500A Normal Output for >300V
2. Select the AUTO test tool setup:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the MENU.
till SCOPE is highlighted.
to select SCOPE mode
3. Select DC coupling & reading for Input 1 and 2.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
to highlight DC.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
ST8129.CGM
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING
to highlight DC.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
4. Select the appropriate sensitivity for the test tool:
4-23
Page 76

43
Service Manual
• Press to select RANGE 1 or RANGE 2.
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select RANGE 1 or
to select RANGE 2.
to select the ranges mentioned in the table.
5. Set the 5500A to source the appropriate DC voltage (NORMAL output, WAVE
sine).
6. Observe the Input 1 and 2 main reading (V DC) and check to see if it is within the
range shown under the appropriate column.
7. Continue through the test points of table 4-7.
8. Select DC coupling and ACrms reading for Input 1 and 2.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select menu SCOPE SETUP.
to select Input 1 READING.
to highlight ACrms.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
• Press to highlight Input 1 Coupling.
• Press
to select the Input 1 Coupling menu.
• Press to highlight DC Coupling.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to select Input 2 READING.
to select the Input 2 READING
to highlight ACrms.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to highlight Input 2 Coupling.
to select the Input 2 COUPLING.
to highlight DC Coupling.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to return to SCOPE.
9. Select the appropriate sensitivity for the test tool:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select RANGE 1 or RANGE 2.
to select RANGE 1 or
to select RANGE 2.
to select the ranges mentioned in the second part of table 4-7.
4-24
10. Set the 5500A to source the appropriate AC voltage (NORMAL output, WAVE
sine).
Page 77
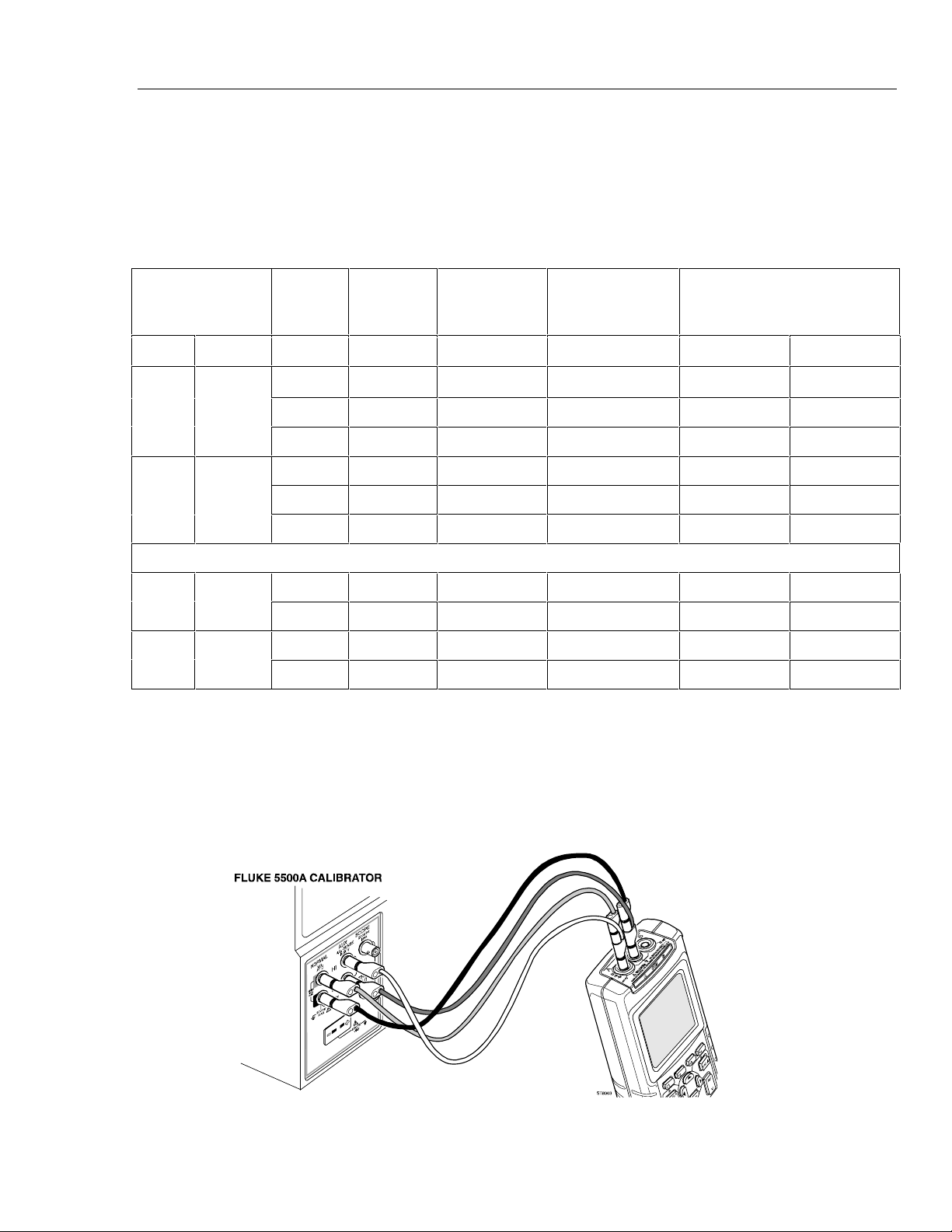
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.6 Ohms/Continuity/Capacitance.
11. Observe the Input 1 and 2 main reading (AC) and check to see if it is within the range
shown under the appropriate column.
12. Continue through the test points of table 4-7.
13. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby
Table 4-7. V DC and V AC High Voltage Verification Tests
4
Sensitivity
Input 1 Input 2 Input 1 & 2 Input 1 Input 2
200V/d 200kA/d 10 ms/d 0V DC -0.5 to +0.5
500V/d 500kA/d 10 ms/d +600V DC +0. 592 to +0.608
500V/d 500kA/d 50 µs/d 600V 10 kHz 0.570 to 0.630
200V/d 200kA/d 10 ms/d 500V 60Hz 494.0 to 506.0 494.0 to 506.0
Time/
div.
10 ms/d +500V DC +497.0 to +503.0
10 ms/d -500V D C -497.0 to -503.0
10 ms/d -600V D C -0.592 to -0.608
10 ms/d 0V DC -0.005 to +0.005
10 ms/d 600V 60Hz 0.584 to 0.616 0.584 to 0.616
50 µs/d 500V 10 kHz 486.0 to 514.0
5500A
output
Vrms
5500A
Frequency
Continue at test point 8
Reading (DC) Reading (AC)
4.6 Ohms/Continuity/Capacitance.
4.6.1 Resistance Measurements Test.
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4-7.
Figure 4-7. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Normal Output 4-Wire
ST8003.CGM
4-25
Page 78

43
Service Manual
2. Select OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANCE:
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the main MENU.
to highlight OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANC E.
to select the item.
3. Set the 5500A to the first test point in Table 4-8.
Use the 5500A “COMP 2 wire” mode for the verifications up to and including 50 kΩ.
For the higher values, the 5500A will turn off the “COMP 2 wire” mode.
4. Observe the Input 1 main reading and check to see if it is within the range shown
under the appropriate column.
5. Continue through the test points.
6. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-8. Resistance Measurement Verification Points
5500A output Reading
0Ω 000.0 to 000.5
400Ω 397.1 to 402.9
4 kΩ 3.971 to 4.029
40 kΩ 39.71 to 40.29
400 kΩ 397.1 to 402.9
4 MΩ 3.971 to 4.029
30 MΩ 29.77 to 30.23
4.6.2 Diode Test Function Test
Proceed as fol l o ws to test the Di o d e Tes t fun ct i o n :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-7).
2. Select OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANCE:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
to select the main MENU.
to highlight OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANC E.
to select the item.
to select DIODE.
3. Set the 5500A to 1 kΩ. Use the 5500A “COMP 2 wire” mode.
4. Observe the main reading and check to see if it is within 0.425 and 0.575V.
5. Set the 5500A to 1V DC.
6. Observe the main reading and check to see if it is within 0.975 and 1.025V.
4-26
7. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Page 79

4.6.3 Continuity Function Test
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-7).
2. Select OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANCE:
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.6 Ohms/Continuity/Capacitance.
4
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Set the 5500A to 25Ω. Use the 5500A “COMP 2 wire” mode.
4. Listen to hear that the beeper sounds continuously.
5. Set the 5500A to 35Ω.
6. Listen to hear that the beeper does not sound.
7. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
4.6.4 Capacitance Measurements Test
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test (see Figure 4-7).
Ensure that the 5500A is in Standby.
2. Select OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANCE:
• Press
to select the main MENU.
to highlight OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANC E.
to select the item.
to select CONTINUITY.
to select the main MENU.
• Press
• Press
• Press
3. Set the 5500A to the first test point in Table 4-9. Use the 5500A “COMP OFF”
mode.
4. Observe the Input 1 main reading and check to see if it is within the range shown
under the appropriate column.
5. Continue through the test points.
6. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
7. Remo ve all test leads from the test tool to check th e zero po i nt.
8. Observe the Input 1 reading and check to see if it is between 00.00 and 00.10 nF.
9. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
to highlight OHMS/CONTINUITY/CAPACITANC E.
to select the item.
to select CAPACITANCE
4-27
Page 80

43
Service Manual
Tab le 4- 9. Capacit ance M easurement Veri ficatio n P oints
5500A output Reading
40 nF 39.10 to 40.90
300 nF 293.0 to 307.0
3 µF 2.930 to 3.070
30 µF 29.30 to 30.70
300 µF 293.0 to 307.0
0
(remove test tool input connections )
4.7 Inrush Current.
Proceed as fol l o ws to test the INR USH CURRENT.
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4.8.
Figure 4-8. Test Tool Input 2 to 5500A NORMAL output
0.00 to 0.10
(see steps 7...10)
ST8588.wmf
4-28
2. Press .
3. Press
4. Press
to highlight INRUSH CURRENT.
to enter mode.
Now the MAXIMUM CURRENT is highlighted. If the CURRENT IS NOT 1000A then:
1. Press
2. Press to highlight 1000A.
3. Press
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
4. Set the 5500A to 0V (NORMAL output).
5. Press
6. Press
7. Press
to highlight INRUSH TIME.
to select.
to highlight 10 seconds.
Page 81

8. Press to confirm; mark changes to ■.
Performance Veri fi cat ion
4.8 Sags & Swells
4
9. Press
10. Press
11. Set the 5500A to 1.5V.
Now the measurement should start and continue for 10s. The trigger point is after 2
divisions. With
cursors.
Checking t h e res u lt:
1. Press
2. Press
3. Press
4. Observe t he read i n g s an d v eri fy that t h ey are betw een 1.38 and 1.62 kA.
5. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby
to highlight START.
to start th e measu rem en t.
to move the left cursor to the fourth division.
to toggle to the right cursor.
to move the right cursor to the fifth division.
4.8 Sags & Swells
Proceed as fol lows to test the sags & sw el ls mod e.
you can move a cursor and with you can toggle between the
Figure 4-9. Test Tool Input 1 & 2 5500A Normal Output
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 4.9.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Press
Now the RECORD TIME is highlighted. If the time is not 4 minutes then:
1. Press
2. Press to hig hlight 4 minutes.
3. Press
.
to highlight SAGS & SWELLS.
to enter mode.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
ST8001.CGM
4-29
Page 82

43
Service Manual
4. Set the 5500A to source a sine wave of 5V, 60Hz (NORMAL output, MODE wave
sine).
5. Press
6. Press
7. After approximately 30 seconds press .
8. Press
9. Check t h e read i n gs MAX, V
10. Check the readings MAX, A
11. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby
to highlight START.
and move the cursor into the measured region.
4.9 Harmonics.
Proceed as foll o ws to test HARMONICS:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test shown in Figure 4-9.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Press
5. Set the 5500A to source a square wave 2.5V, 60Hz (NORMAL output, WAVE
square).
to highlight HARMONICS.
to select HARMONIC S.
,MIN. of Input 1 is between 4.80 and 5.20.
,MIN. of Input 2 is 4.80 and 5.20.
.
6. Check the bargraphs of VOLTS look like the ones in Figure 4-10.
7. Press
8. Check the bar graph look like the one in Figure 4-11.
9. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby
Figure 4-10. Bargraph Harmonics Volt Figure 4-11. Bargraph Harmonics Ampere
to enter the AMPS mode.
4.10 VOLT/AMPS/ HE RTZ.
Proceed as follows to test VOLT/AMPS/HE R T Z:
4-30
Page 83

Performance Veri fi cat ion
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test shown in Figure 4-9.
2. Press
3. Press to highlight VOLT/AMPS/HERTZ.
4.11 POWER.
4
4. Press
to select VOLT/AMPS/HERTZ.
5. Set the 5500A to source the AC voltages in the table (NORMAL output, Wave sine)
and check the read i n g s .
6. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-10. Volts/AMPS/HERTZ verification points
5500A output 5500A Freq. Reading1 Reading 2
Volt Hertz Amperes
0 ± 10 counts ± 10 counts
5.5V 70Hz 5.34 - 5.66 69.4 - 70.6 5. 34 - 5.66
4.5V 70Hz 69.4 - 70.6 4.445 - 4.555
4.11 POWER.
Proceed as follows to test POWER:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as for the previous test shown in Figure 4-9.
2. Press
3. Press to highlight POWER.
4. Press
to select POWE R.
5. Set the 5500A to source the AC voltages in the table (NORMAL output, Wave sine)
and check the read i n g s .
6. When you are finished set the 5500A to Standby.
Table 4-11. Power Measurement Verification points
5500A output Reading
Input 1 Input 2 W VA VAR PF DPF Hz
00± 4 counts ± 4 counts ± 4 counts
4.472V/60Hz 4.472/60Hz 19.4-20.6 19.4-20.6 ± 4 counts 0.96-1.00 0. 97-1.00 59.5-60.5
5.916V/60Hz 5.916V/60Hz 34.3-35.7 34.3-35.7 ± 4 counts 0. 96-1.00 0.97-1.00 59.5-60.5
4-31
Page 84

43
Service Manual
4.12 Transients.
Proceed as follows to test the TRANSIENTS fu n ct i on:
1. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as show in Figure 4-12.
Figure 4-12. Test Tool Input 1 to 5500A Normal Output
ST8586.WMF
2. Press .
3. Press
4. Press
to highlight TRANSIENTS.
to select the TRANSIENTS mode.
VOLTAGE CHANGE will be highlighted, continue with:
1. Press
2. Press
3. Press
4. Press
.
to select 20%.
to confirm; mark changes to ■.
to select START.
5. Set the 5500A to 20V, 60Hz (NORMAL output, WAVE sine).
6. Press
to start the test. No transients should be captured.
7. Set the 5500A to 22.5V.
8. Now transients should be captured. After 40 transients (maximum) the 40th transient
will be visible.
9. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
4-32
Page 85

Chapter 5
Calibration Adjustment
Title Page
5.1 General.................................................................................................... 5-3
5.1.1 Introduction...................................................................................... 5-3
5.1.2 Calibration number and date............................................................. 5-3
5.1.3 General Instructions.......................................................................... 5-4
5.2 Equipment Required For Calibration....................................................... 5-4
5.3 Starting Calibration Adjustment.............................................................. 5-4
5.4 Contrast Calibration Adjustment.............................................................. 5-6
5.5 Warming Up & Pre-Calibration............................................................... 5-7
5.6 Final Calibration...................................................................................... 5-7
5.6.1 HF Gain Input 1. .............................................................................. 5-8
5.6.2 Delta T Gain, Trigger Delay Time & Pulse Adjust Input 1 ............... 5-9
5.6.3 Gain DMM (Gain Volt).................................................................... 5-10
5.6.4 Volt Zero.......................................................................................... 5-12
5.6.5 Gain Ohm......................................................................................... 5-12
5.6.6 Capacitance Gain Low and High ...................................................... 5-13
5.6.7 Capacitance Clamp & Zero............................................................... 5-14
5.6.8 Capacitance Gain.............................................................................. 5-14
5.7 Save Calibration Data and Exit................................................................ 5-15
5-1
Page 86

Page 87

5.1 General
5.1.1 Introduction
The following information, provides the complete Calibration Adjustment procedure for
the Fluke 43 test tool. The test tool allows closed-case calibration using known reference
sources. It m eas u res t h e referen ce s i g n al s , calculates the correction factors, and s t o res
the correction factors in RAM. After completing the calibration, the correction factors
can be stored i n F lashROM.
The test tool should be calibrated after repair, or if it fails the performance test. The test
tool has a normal calibration cycle of one year.
5.1.2 Calibration number and date
When storing valid calibration data in FlashROM after performing the calibration
adjustment procedure, the calibration date is set to the actual test tool date, and
calibration number is raised by one. To display the calibration date and - number:
Calibration Adjustment
5.1 General
5
1. Press
2. Press
3. Press
4. Press
5. Press
6. Press
7. Press
8. Press
to switch on the Fluke 43.
to leave th e s t art u p s creen .
to go to the MENU screen.
to highlight INSTRUMENT SETUP item.
to open the INSTRUMENT SETUP menu.
to highlight VERSION & CALIBRATION
to open the VERSION & C ALIB R ATION m enu.
to return to the INSTRUMENT SETUP menu.
Figure 5-1. Version & Calibration Screen
VERSION.BMP
5-3
Page 88

43
Service Manual
5.1.3 General Instructions
5.2 Equipment Required For Calibration
Follow these general instructions for all calibration steps:
• Allow the 5500A t o s ati s fy i t s s peci fi ed warm -up period. For each calibration poi nt ,
wait for the 5500A to settle.
• The required warm up period for the test tool is included in the WarmingUp &
PreCal cal i b rat ion step.
• Ensure that the test tool battery is charged sufficiently.
The primary source instrument used in the calibration procedures is the Fluke 5500A. If
a 5500A is not available, you can substitute another calibrator as long as it meets the
minimum test requirements.
• Fluke 5500A Multi Product Calibrator, including 5500A-SC Oscilloscope
Calibration Option.
• Stackable Test Leads (4x), supplied with the 5500A.
• 50Ω Coax Cables (2x), Fluke PM9091 or PM9092.
• 50Ω feed through termination (2x), Fluke PM9585.
• Fluke BB120 Shielded Banana to Female BNC adapters (2x), supplied with the
Fluke 43.
• Dual Banana Plug to Female BNC Adapter (1x), Fluke PM9081/001.
• Male BNC to Dual Female BNC Adapter (1x), Fluke PM9093/001.
5.3 Starting Calibration Adjustment
Follow the steps below to start calibration adjustments.
1. Power the test tool via the power adapter input, using the PM8907 power adapter.
2. Check the actual test tool date, and adjust the date if necessary:
• Press
If the date on the startup s creen is correct then con t inue at step 3.
• Press to leave th e S T AR T UP screen.
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Adjust the date with
• When ready, press
to switch on the Fluke 43.
to go to MENU.
to highlight INSTRUMENT SETUP item.
to open the INSTRUMENT SETUP menu.
to highlight DATE
to open the DATE menu.
and if neces s ary .
.
5-4
• Press
3. Select the Mainten an ce m o d e.
to exit the INSTRUMENT SETUP menu.
Page 89

Calibration Adjustment
5.3 Starting Calibration Adjustment
The Calibration Adjustment Procedure uses built-in calibration setups, that can be
accessed in t h e M ai n t en an ce m o d e.
To enter the M ai n t en ance m o d e p roceed as fo l l o ws :
5
• Press and hold
.
• Press an d release .
• Release
.
• The display shows the Calibration Adjustment Screen.
The display shows the first calibration step
calibration status
:IDLE (valid) or :IDLE (invalid).
Warming Up (CL 0200) , and the
4. Continue with either a. or b. below:
a. To calibrate the display contrast adjustment range and the default contrast, go to
Section 5.4 Contrast Calibration Adjustment.
This calibration step is only required if the display cannot made dark or light
enough, or if the display after a test tool reset is too light or too dark
b. To calibrate the test tool without calibrating the contrast, go to Section 5.5
Warming Up & Pre-calibration
Expla n a ti o n o f s creen messages and key functions.
When the test tool is in the Maintenance Mode, only the F1, F2, F3, and ENTER soft
keys, the ON/OFF key, and the backlight key can be operated, unless otherwise stated.
The calibrat i o n adjustment s creen s ho w s t h e act u al cal i b rat i o n s t ep (n am e an d n umber)
and its status :
Cal Name (CL nnnn) :Sta t us Calibration step nnnn
Status can be:
IDLE (valid) After (re)entering this step, the calibration process is not started.
The calibration data of this step are valid. This means that the
last time this step was done, the calibration process was
successful . It does no t n eces s ari l y m ean t h at t h e u n i t m eet s the
specifications related to this step!
IDLE (invalid) After (re)entering this step, the calibration process is not started.
The calibration data are invalid. This means that the unit will not
meet the sp eci fications i f t h e cal ibration data are saved.
BUSY aaa% bbb% Calibration adjustment step in progress; progress % for Input 1
and Input 2.
READY Calibration adjustment step finished.
Error :xxxx Calibration adjustment failed, due to wrong input signal(s) or
because the test tool is defect i ve. The error codes xxxx are
shown for production purposes only.
5-5
Page 90

43
Service Manual
5.4 Contrast Calibration Adjustment
Functions of the keys F1-ENTER are:
PREV select the previous s tep
NEXT select the nex t s tep
CAL start the calibration adjustment of the actual step
EXIT l eav e t h e M ai n t en an ce m o d e
Readings and traces
After complet i n g a cal i b rat ion step, read i n g s an d t races are s h o wn u s i n g the new
calibration data.
After entering the Maintenance mode, the test tool display shows
Warming Up (CL 0200):IDLE (valid).
Do not press
now! If you did, turn the test tool off and on, and enter the
Maintenance mode again.
Proceed as follows to adj u st t he m axim u m di s pl ay darkness (C L0100), t h e default
contrast (CL0110) , and the maximum display brightness (CL0120).
1. Press a three times to select the first calibration step. The display shows:
Contrast (CL 0100) :MANUAL
2. Press CAL. The display will show a dark test pattern, see Figure 5-2
3. Using
adjust the display to the maximum darkness, at which the test pattern is
only just visible.
4. Press to select the default contrast calibration. The display shows:
Contrast (CL 0110) :MANUAL
5. Press CAL. The display shows the test pattern at default contrast.
6. Using
7. Press to select maximum brightness calibration. The display shows:
Contrast (CL 0120) :MANUAL
set the display to optimal (becomes default) contrast.
8. Press CAL. The display shows a bright test pattern.
9. Using
adjust the display to the maximum brightness, at which the test pattern is
only just visible.
10. You can now :
• Exit, if only the Contrast had to be adjusted. Continue at Section 5.7.
OR
5-6
• Do the complete calibration. Press
and continue at Section 5.5.
to select t h e n ext step (Warmin g Up ),
Page 91

Figure 5-2. Displ ay Test Pat t er n
5.5 Warming Up & Pre-Calibration
After entering the Warming-Up & Pre-Calibration state, the display shows:
WarmingUp (CL 0200):IDLE (valid) or (invalid).
Calibration Adjustment
5.5 Warming Up & P r e- Calibr ation
5
You must always start the Warming Up & Pre Calibration at
Starting at another step will make the calibration invalid!
Proceed as fol l o ws :
1. Remove all input connections from the test tool.
2. Press
The display shows the calibration step in progress, and its status.
The first step i s
counted down from 00:29:59 to 00:00:00. Then the other pre-calibration steps are
performed automatically. The procedure takes about 60 minutes.
3. Wait until the display shows
4. Continue at Section 5.6.
to start the Warming-Up & Pre-Calibration.
5.6 Final Calibration
You must always start the Final Calibration at the first step of Section 5.6.1. Starting at
another step will make the calibration invalid!
If you proceeded to step N (for example st ep C L 0615), t h en retu rn t o a previ ous s t ep
(for example step CL 0613), and then calibrate this step, the complete final calibration
becomes invalid. You must do the final calibration from the beginning (step CL 0600)
again.
Warming Up (CL0200) .
WarmingUp (CL0200) :BUSY 00:29:59 . The warming-up period is
End Precal :READY
You can repeat a step that sh o ws t h e s t at u s
:READY by pressing again.
5-7
Page 92

43
Service Manual
5.6.1 HF Gain Input 1.
Proceed as follows to do t he HF Gain Input 1&2 calibrati on:
1. Press
to select the first calibration step in Table 5-1 ( HFG & FI AB (CL 0600): )
2. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-3. Do NOT use a 50Ω
termination!
Figure 5-3. HF Gai n Cal ibration Input Connect i ons
3. Set the 5500A to source a 1 kHz fast rising edge square wave (Output SCOPE,
MODE edge) to the first calibration point in Table 5-1.
4. Set the 5500A in operate (OPR).
5. Press
to start the calibration.
ST8097.CGM
6. Wait until the display shows calibration status
7. Press
to select the next calibration step, set the 5500A to the next calibration
READY .
point, and start the calibration. Continue through all calibration points in Table 5-1.
8. Set the 5500A to source a 1 kHz square wave (Output SCOPE, MODE wavegen,
WAVE square), to the first calibration point in Table 5-2.
9. Press
10. Press
11. Wait until the display shows calibration status
12. Press
to select the first step in Table 5-2.
to start the calibration.
READY.
to select the next calibration step, set the 5500A to the next calibration
point, and start the calibration. Continue through all calibration points Table 5-2.
13. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
14. Continue at Section 5.6.2.
5-8
Page 93

Calibration Adjustment
Table 5-1. HF Gain Calibration Points Fast
Cal step 5500A Setting
(1 kHz, no 50 Ω!)
HFG & FI AB (CL 0600) 10 mV 20 mV
HFG & FI AB (CL 0601) 25 mV 50 mV
HFG & FI AB (CL 0602) 50 mV 100 mV
HFG & FI AB (CL 0603) 100 mV 200 mV
HFG & FI AB (CL 0604) 250 mV 500 mV
HFG & FI AB (CL 0605) 500 mV 1 V
HFG & FI AB (CL 0606) 1 V 2 V
1)
Test Tool Input Si gnal Requirements
(1 kHz, t
<100 ns, flatness after r ising
rise
edge: <0.5% after 200 ns)
5.6 Final Calibration
1)
5
HFG & FI AB (CL 0607)
[HFG & FI A (CL 0608)]
1)
As the 5500A output is not terminat ed with 50Ω, its output voltage is two times its set volt age
2)
After starting t he f irs t st ep in this t able cell, these st eps ar e done automatically.
2)
2.5 V 5 V
Table 5-2. HF Gain Calibration Points Slow
Cal step 5500A Setting
(1 kHz, MODE wavegen,
WAVE square)
Test Tool Input Si gnal Requirements
(1 kHz square, t
<2 µs,
rise
flatness after rising edge: <0. 5% af t er 4
µs)
HF-Gain AB (CL 0609) 25 V 25 V
HF-Gain A (CL 0612),
[HF-Gain A (CL 0615)
1)
After starting t he f irs t st ep in this t able cell, these st eps ar e done automatically.
1)
50 V 50 V
5.6.2 Delta T Gain, Trigger Delay Time & Pulse Adjust Input 1
Proceed as fol l o ws t o do t h e cal i b rat ions:
1. Press
2. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-4.
to select calibration step Delta T (CL 0700):IDLE
5-9
Page 94

43
Service Manual
ST8004.CGM
Figure 5-4. 5500A Scope Out put t o Input 1
3. Set the 5500A to source a 1V, 1 MHz fast rising (rise time ≤ 1 ns) square wave
(SCOPE output, MODE edge).
4. Set the 5500A to operate (OPR).
5. Press
to start the calibration.
The Delta T gain, Trigger Delay (CL0720), and Pulse Adjust Input 1 (CL0640) will
be calibrated.
6. Wait until the display shows
7. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
8. Continue at Section 5.6.3.
5.6.3 Gain DMM (Gain Volt)
Dangerous voltages will be present on the calibration source
and connection cables during the following steps. Ensure that
the calibrator i s in standby mode before making any
connection between the calibrator and the test tool.
Proceed as fol l o ws t o d o t h e Gai n DMM cal ibration.
1. Press
2. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-5.
to select the first calibration step in Table 5-3.
Pulse Adj A (CL 0640):READY.
Warning
5-10
Page 95

Calibration Adjustment
5.6 Final Calibration
Figure 5-5. Volt Gain Calibrat i on Input Connections <300V
3. Set the 5500A to supply a DC voltage, to the first calibration point in Table 5-3.
4. Set the 5500A to operate (OPR).
5
ST8001.CGM
5. Press
6. Wait until the display shows calibration status
7. Press
to start the calibration.
:READY.
to select the next calibration step, set the 5500A to the next calibration
point, and start the calibration. Continue through all calibration points of Table 5-3
8. Set the 5500A to Standby, and continue with step 9.
Table 5-3. Volt G ain Calibration Point s <300V
Cal step I nput value
Gain DMM (CL0800) 12.5 mV
Gain DMM (CL0801) 25 mV
Gain DMM (CL0802) 50 mV
Gain DMM (CL0803) 125 mV
Gain DMM (CL0804) 250 mV
Gain DMM (CL0805) 500 mV
Gain DMM (CL0806) 1.25V
Gain DMM (CL0807) 2.5V
Gain DMM (CL0808) 5V
Gain DMM (CL0809) 12.5V
Gain DMM (CL0810) 25V
Gain DMM (CL0811) 50V (set 5500A to O PR!)
Gain DMM (CL0812) 125V
Gain DMM (CL0813) 250V
9. Press to select calibration step Gain DMM (CL0814) :IDLE
5-11
Page 96

43
Service Manual
10. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-6.
ST8129.CGM
Figure 5-6. Volt Gain Calibrat i on Input Connections 500V
11. Set the 5500A to supply a DC voltage of 500V.
12. Set the 5500A to operate (OPR).
13. Press
Gain DMM (CL0814) and Gain DMM (CL0815) will be calibrated now.
14. Wait until the display shows calibration status
15. Set the 5500A to 0V (zero) and to Standby.
16. Continue at Section 5.6.4.
5.6.4 Volt Zero
Proceed as fol l o ws t o d o t h e Volt Zero calibrat i o n:
1. Press
2. Terminate Input 1 and Input 2 with the BB120 and a 50Ω or lower termination.
3. Press to start the zero calibration of all mV/d settings (CL0820...CL0835)
4. Wait until the display shows
5. Remove the 50Ω termination from the inputs.
6. Continue at Section 5.6.5.
5.6.5 Gain Ohm
Proceed as fol l o ws t o d o t h e Gai n Ohm cal ibration:
to start the calibration.
Gain DMM (CL0815): READY.
to select calibration adjustment step Volt Zero (CL 0820): I DLE.
Volt Zero (CL 0835):READY.
5-12
1. Press
to select calibration adjustment step Gain Ohm (CL 0860):IDLE
2. Connect the UUT to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-7.
Notice that the sense leads must be conn ect ed d i rect l y t o t h e t es t tool.
Page 97

Calibration Adjustment
5.6 Final Calibration
ST8003.CGM
Figure 5-7. Four- w ire Ohms calibr at i on connections
3. Set the 5500A to the first test point in Table 5-4. Use the 5500A “COMP 2 wire”
mode for the calibration adjustments up to and including 100 kΩ. For the higher
values, the 5500A will turn off the “COMP 2 wire” mode.
4. Set the 5500A to operate (OPR).
5
5. Press
6. Wait until the display shows the calibration status
7. Press
to start the calibration.
:READY.
to select the next calibration step, set the 5500A to the next calibration
point, and start the calibration. Continue through all calibration points.
8. When you are finished, set the 5500A to Standby.
9. Continue at Section 5.6.6.
Table 5-4. Ohm Gain Calibration Points
Cal Step Input Value
Gain Ohm (CL 0860) [Cap. Pos. (CL 0920), Cap. Neg. ( CL 0921)]
Gain Ohm (CL 0861) [Cap. Pos. (CL 0922), Cap. Neg. ( CL 0923)]
Gain Ohm (CL 0862) [Cap. Pos. (CL 0924), Cap. Neg. ( CL 0925)]
Gain Ohm (CL 0863) [Cap. Pos. (CL 0926), Cap. Neg. ( CL 0927)]
Gain Ohm (CL 0864) 1 MΩ
Gain Ohm (CL 0865) [Gain Ohm (CL 0866) ]
1)
The capacitance measurement curr ent calibrat ions (Cap. Pos. and Cap. Neg) ar e done aut om atically
after the Gain O hm calibrat ion.
2)
The Gain Ohm (CL0866) calibration step is done automatically aft er t he G ain O hm ( CL0865) calibrat ion.
2)
1)
1)
1)
1)
100 Ω
1 kΩ
10 kΩ
100 kΩ
10 MΩ
5.6.6 Capacitance Gain Low and High
Proceed as fol l o ws t o d o the Capacitance Gain calibrati o n :
1. Press
2. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-8.
to select calibration adjustment step Cap. Low (CL 0900):IDLE
5-13
Page 98

43
Service Manual
ST8002.CGM
Figure 5-8. Capacit ance Gain Calibrati on I nput Connect i ons
3. Set the 5500A to supply 250 mV DC.
4. Set the 5500A to operate (OPR).
5. Press to start the calibration.
6. Wait until the display shows
7. Press
to select calibration adjustment step Cap. High (CL 0910):I DLE
8. Set the 5500A to supply 50 mV DC.
9. Press
to start the calibration.
10. Wait until the display shows
11. Set the 5500A to Standby.
12. Continue at Section 5.6.7.
5.6.7 Capacitance Clamp & Zero
Proceed as fol l o ws t o do t h e C ap aci t an ce Clamp Volt ag e & Zero cal i b rat i o n :
1. Press
2. Remove any input connection from the test tool (open inputs).
3. Press
The capacitan ce m eas u rem en t clamp volt ag e
the capacitan ce ran g es
now.
4. Wait until the display shows
to select calibration adjustment step Cap. Clamp (CL 0940): I DLE
to start the calibration.
Cap. Zero (CL 0950)... Cap. Zero (CL 0953) will be calibrated
Cap. Low (CL 0900):READY.
Cap High (CL 910):READY.
Cap. Clamp (CL 0940), and the zero of
Cap. Zero (CL 0953): READY.
5-14
5. Continue at Section 5.6.8.
5.6.8 Capacitance Gain
Proceed as fol l o ws t o d o the Capacitance Gain calibrati o n :
1. Press
2. Connect the test tool to the 5500A as shown in Figure 5-8.
3. Set the 5500A to 500 nF.
to select calibration adjustment step Cap. Gain (CL 0960) : I DLE
Page 99

4. Set the 5500A to operate (OPR).
Calibration Adjustment
5.7 Save Calibration Dat a and E x it
5
5. Press
6. Wait until the display shows
7. Continue at Section 5.7 to save the calibration data.
to start the calibration.
Cap. Gain (CL 0960): READY.
5.7 Save Calibration Data and Exit
Proceed as fol l o ws t o s av e t h e cal i b rat i o n dat a, and to exit the Maint enan ce m o d e:
1. Remove all test leads from the test tool inputs.
2. Press (EXIT). The test tool will display:
Calibration data are valid
Save data and EXIT maintenance?
Note
Calibration data valid indicates that the calibration adjustment procedure
is performed correctly. It does not indicate that the test tool meets the
characteristics listed in Chapter 2.
3. Press
The calibration number and date will be updated only if the calibration
data have been changed and the data are valid.
The calibration data will change when a calibration adjustment has been
done. The data will not change when just entering and then leaving the
maintenance mode without doing a calibration adjustment.
The calibration number and date will NOT be updated if only the display
contrast has been adjusted.
Possib le error messages.
Invalid calibration data:
WARNING.Calibration data NOT valid.
Save data and EXIT?
Proceed as fol l o ws :
• To return to the Maintenance mode:
⇒ Press NO.
(YES) to save and exit.
Notes
Now press
test tool, starting at Section 5.5.
until the display shows WarmingUp (CL 0200):IDLE, and calibrate the
5-15
Page 100

43
Service Manual
• To exit and save the INVALID cal i brat i on dat a:
⇒ Press
The test tool will show the message
your service center
YES.
The test tool needs calibration. Please cont act
at power on. The calibration date and number will not be
updated. A complete recalibrat i on mu st be done.
• To exit and maintain the old calibration data:
⇒ Turn the test tool off.
No power adapter voltage
WARNING.No adapter present.
Calibration data will not be saved.
Exit maintenance mode?
• To save the calibration data:
⇒ Press
NO
The test t o ol returns to t h e m ai n t en an ce m o de. Connect a co rrect p o wer ad ap t er, and
press
to exit and save.
• To exit without saving the calibration data:
⇒ Press YES
5-16
 Loading...
Loading...