Page 1
790 ACTIVE SMART
REFRIGERATOR FREEZER
517800
Page 2

2
Page 3

3
MANUAL 517800 - DATE OF ISSUE MAY 2004
The specifications and servicing procedures outlined in this manual are subject to change without notice.
The latest version is indicated by the reprint date and replaces any earlier editions.
Fisher & Paykel Appliances Inc
27 Hubble, Irvine
California, CA92618
USA
Telephone: 949 790 8900
Facsimile: 949 790 8911
Fisher & Paykel Appliances Ltd
Technical Publications
PO Box 58-732, Greenmount, Auckland
78 Springs Road, East Tamaki
New Zealand
Telephone: 09 273 0600
Facsimile: 09 273 0656
COPYRIGHT FISHER & PAYKEL LTD 2004
Page 4

4
C O N T E N T S
1 TERMINOLOGY ..........................................................................................................6
2 SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................................................7
2.1 Cabinet Specifications.........................................................................................................................7
2.2 Model Number Identification................................................................................................................8
2.3 Serial Number Identification ................................................................................................................8
3 SERVICING REQUIREMENTS ...................................................................................9
3.1 Interface Pen Mk 2 ..............................................................................................................................9
3.2 Health & Safety....................................................................................................................................9
3.2.1 Good Work Practices ...........................................................................................................9
3.2.2 Environmental Health And Safety........................................................................................9
3.2.3 Good Practice And Safety....................................................................................................9
4 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS .............................................................................10
4.1 Levelling ........................................................................................................................................... 10
4.2 Air Space Requirements .................................................................................................................. 11
4.3 Temperature Adjustment.................................................................................................................. 11
5 THEORY OF OPERATION........................................................................................12
5.1 Internal Air Flow ............................................................................................................................... 12
5.2 Defrost Cycle .................................................................................................................................... 13
5.3 The Refrigeration Circuit .................................................................................................................. 14
5.4 Servicing Features ........................................................................................................................... 15
5.4.1 Condensate Disposal........................................................................................................15
5.4.2 Internal Condenser ........................................................................................................... 16
5.4.3 Cross Rail.......................................................................................................................... 19
5.4.4 Divider Partition................................................................................................................. 19
6 ELECTRONICS SECTION ........................................................................................20
6.1 Overview Function Description......................................................................................................... 20
6.1.1 Control & Peripheral Functions ......................................................................................... 20
6.1.2 Power/Control Module ...................................................................................................... 20
6.1.3 Display Module ................................................................................................................. 21
6.1.4 Door Switches................................................................................................................... 21
6.1.5 Compressor....................................................................................................................... 22
6.1.5.1 Variable Capacity Compressor Control Overview ....................................................... 22
6.1.5.2 Built-in Electronic Protections (Within the Module/Inverter) ........................................ 23
6.1.5.2.1 Compressor Start-up............................................................................................ 23
6.1.5.2.2 Overload Detection and Protection ...................................................................... 23
6.1.5.2.3 Power Limitation (Temperature Protection) ......................................................... 23
6.1.5.2.4 Short Circuit Protection ........................................................................................ 23
6.1.5.3 VCC Module/Inverter Identification.............................................................................. 23
6.1.5.4 Fault Finding ................................................................................................................ 23
6.1.5.4.1 High Voltage Power Supply Circuit ...................................................................... 23
6.1.5.4.2 Signal Circuit ........................................................................................................ 23
6.1.6 Defrost Heater................................................................................................................... 24
6.1.7 Thermal Fuses .................................................................................................................. 25
6.1.8 Low Ambient Heater .........................................................................................................25
6.1.9 PC / FC Fans .................................................................................................................... 26
6.1.10 Light .................................................................................................................................. 26
6.1.11 Thermistor Temperature Sensors ..................................................................................... 27
Page 5

5
6.2 Fault Finding Procedure....................................................................................................................28
6.2.1 Fault Code Display Status .................................................................................................28
6.2.2 Diagnostic Mode ................................................................................................................ 31
6.2.3 Sensor Temperature Conversion ......................................................................................31
6.2.4 Input/Output Status............................................................................................................ 32
6.2.5 Data Download ..................................................................................................................33
6.2.6 Manual Defrost ..................................................................................................................33
6.2.7 Show Room Mode .............................................................................................................33
6.2.8 Special Option Mode (Israel) .............................................................................................34
6.3 Door Gasket - (Integral) ....................................................................................................................34
7 REMOVING AND REFITTING OF COMPONENTS.................................................. 35
7.1 Removal Of Power/Control Module ..................................................................................................35
7.2 PC Sensor Replacement...................................................................................................................35
7.3 FC Sensor Replacement................................................................................................................... 35
7.4 PC Fan Motor - “T” Model .................................................................................................................36
7.5 PC Fan Motor - “B” Models ...............................................................................................................36
7.6 Cross / Base Rail Door Reed Switches ............................................................................................36
7.7 Defrost Heating Element...................................................................................................................36
7.8 Removal Of Display Module .............................................................................................................37
7.9 Thermal Fuse ....................................................................................................................................37
7.10 Replacement Of Interior Lamp..........................................................................................................37
7.11 Replacement Of Low Ambient Heater - “T” Model..........................................................................37
7.12 Replacement Of Low Ambient Heater - “B” Model .........................................................................38
7.13 Replacement Of Low Ambient Heater - “B” Model (In Return Air Grill) ..........................................38
7.14 Evaporator Replacement ..................................................................................................................38
7.15 Removal Of The FC Evaporator Cover.............................................................................................39
7.16 Pressure Testing Of The Refrigeration System ................................................................................40
7.17 Transporting Of Refrigerators ...........................................................................................................41
8 WIRING DIAGRAM ................................................................................................... 42
9 SERVICE REFERENCE ........................................................................................... 43
9.1 “B” Models.........................................................................................................................................43
9.2 “T” Models .........................................................................................................................................46
10 FLOW DIAGRAMS.................................................................................................... 48
10.1 Refrigerator Not Operating................................................................................................................48
10.2 No Power To Power/Control Module And/Or Display Module ..........................................................49
10.3 PC/FC Warm.....................................................................................................................................50
10.4 FC Too Cold – PC Too Warm...........................................................................................................51
10.5 PC Too Cold......................................................................................................................................52
10.6 Ice/Condensation Forming................................................................................................................53
10.7 No Light.............................................................................................................................................54
10.8 Door Switch Not Operating ...............................................................................................................55
10.9 Defrost Heater Faults ........................................................................................................................56
10.10 Compressor Faults.......................................................................................................................57
10.11 Compressor Runs Continuously ..................................................................................................57
10.12 Compressor Will Not Run And Is Hot To Touch ..........................................................................58
10.13 Compressor Electrical Tests ........................................................................................................ 58
10.14 Refrigeration System Faults.........................................................................................................59
Page 6

6
1 TERMINOLOGY
The following are terms used in this manual:
“B” MODELS
Dual temperature refrigerator/freezers in which the freezer compartment is below the refrigerator
compartment.
“T” MODELS
Dual temperature refrigerator/freezers in which the freezer compartment is above the refrigerator
compartment.
FC COMPARTMENT
Freezer compartment. The compartment in a dual temperature refrigerator used for keeping frozen food,
where the temperature is maintained at approximately –16
o
C (3oF).
PC COMPARTMENT
Provision compartment. The compartment in a dual temperature refrigerator used for keeping fresh food,
where the temperature is maintained at approximately 4
o
C (39oF).
CABINET WRAPPER
Pre-painted steel.
LINER
A one-piece vacuum formed ABS liner with a plug-in divider.
DIVIDER PARTITION
Injected moulding of HIPS, with two outer injected moulded housings, and an insulated ducted moulded
polystyrene inner core.
FAN MOTORS
DC 12 volt brushless variable speed fan motors for air circulation in both the FC and PC compartments.
EVAPORATOR
Aluminium corrugated type mounted vertically on the back wall of the FC.
SUCTION & CAPILLARY LINE
Foamed into the back of the cabinet with all joints of the evaporator in the FC.
POWER/CONTROL MODULE
Contains the microprocessor that controls all functions of the refrigerator and gathers data from the sensors.
This module also contains support circuitry to switch the various outputs.
DISPLAY MODULE
Using signals from the Power Module, this module generates the L.E.D. display. The lamp is also switched
via this module.
REED SENSORS
A reed switch encapsulated within a plastic housing, mounted on the cross and base rails behind a plastic
cover. A magnet housed just under the lower end cap of each door activates this sensor when the door is
closed.
LOW AMBIENT HEATER
Two types are used. A PCB type is used in the air duct of “T” models. A blanket wire type is used in the
divider of “B” models.
Page 7
7
2 SPECIFICATIONS
2.1 Cabinet Specifications
DIMENSIONS E521T E522B
Height 1695mm (67.8 inches) 1695mm (67.8 inches)
Depth 703mm (28.7 inches) 703mm (28.7 inches)
Width 790mm (31.1 inches) 790mm (31.1 inches)
CAPACITY GROSS VOLUME IN LITRES (AS 1430)
Provision Compartment 400 litres (14.1 cu.ft.) 360 litres (12.7 cu.ft.)
Freezer Compartment 117 litres (4.13 cu.ft.) 160 litres (5.65 cu.ft.)
TOTAL 517 litres (18.25 cu.ft.) 520 litres (18.36 cu.ft.)
ELECTRONICS 110 volt
Display Module Part No. 881218 Part No. 881218
Power/Control Module Part No. 884252 Part No. 884252
Module/Inverter Part No. 884260 Part No. 884260
SUCTION LINE ASSEMBLY
Part Number 875113 874810
DEFROST ELEMENT
Part Number 881414 881414
COMPRESSOR SPECIFICATIONS
Make Embraco Embraco
Model VEG Y6H VEG Y6H
Part Number 884259 884259
Volts 110 110
Hertz 53 - 150 53 - 150
Phase 3 3
Input Watts 55.7 - 205 55.7 - 205
Output Watts 97 - 468 97 - 468
Nominal BTU 330 - 1596 330 - 1596
Start Resistance (Ohms) 6.40 6.40
Run Resistance (Ohms) 6.40 6.40
Starting Device Type Inverter Inverter
Oil Charge (cm3) 430 430
Refrigerant Type R134a R134a
Gas Charge 140 Grams of R134a 135 Grams of R134a
Page 8
8
2.2 Model Number Identification
The following is an example of the model number identification for Fisher & Paykel Appliances:
E 522 B R E D FP SM
Cabinet/Door Colour (1)
Brand (Fisher & Paykel)
Series (2)
Style (3)
Door Hinging Side (4)
Freezer Location (5)
Approximate Capacity in Litres (6)
Type of System (7)
(1) Colour of Cabinet/Door WW = White Cabinet/White Doors
SM = Silver Wrapper/Matt Stainless Steel Doors
SX = Silver Wrapper/Brushed Stainless Steel Doors
(2) Series The series of the cabinet is located on the serial plate as Series A, B, etc.
(3) Style E = Elegence
I = Inox
M = Iridium
(4) Door Hinging L = Left Hand
R = Right Hand
(5) Freezer Location B = Bottom
T=Top
(6) Litreage of Cabinet Approximate total capacity.
(7) Type of System E = Electronic
N=No Frost
C=Cyclic
2.3 Serial Number Identification
The serial number consists of three letters and six digits and contains the following information:
Example:
B I Q 123456
Sequential Serial Number
Manufacturing Plant Code
FISHERPAYKUL Code indicates month of manufacture
CUMBERLAND Code indicates year of manufacture
Cumberland Code
Letter C U M B E R L A N D
Year 1234567890
Fisherpaykul Code
Letter F I S H E R P A Y K U L
Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Manufacturing Plant Code
A Laundry – Australia
F Refrigeration – New Zealand
M Range & Dishwasher
N Laundry – New Zealand
Q Refrigeration - Australia
In the example above, the appliance was manufactured in the second month of the fourth year (2004) at the
New Zealand Refrigeration plant.
Page 9

9
3 SERVICING REQUIREMENTS
3.1 Interface Pen Mk 2
Used to retrieve and download data from the electronic control module when used in conjunction with the
Fisher & Paykel Smart Tool diagnostic program on a laptop computer. The part number of the interface pen
is 425930.
3.2 Health & Safety
3.2.1 Good Work Practices
1. Take care while removing all plastic components especially when cold.
2. Leave the product clean and tidy when service work is completed.
3. Extreme heat in cabinets will cause plastic deterioration or distortion and thermal fuses in the defrost
heater to go open circuit (be careful with heat guns).
3.2.2 Environmental Health And Safety
When servicing products, consider safety and health issues and requirements which must be adhered to at
all times. Specific safety issues are:
1. Electrical safety.
2. Electrostatic discharge.
3. Mixing of foam insulation.
4. Vapours while brazing.
5. Reclaiming of refrigerant.
3.2.3 Good Practice And Safety
1. Take care when removing or servicing any electrical components to avoid electrical shock or short circuit
conditions.
2. Take care when removing plastic components at low temperatures as breakages can occur with these
components.
3. Extreme heating of plastic components can cause distortion of those parts being heated.
4. Avoid overheating temperature sensitive devices such as the element thermal fuses and cabinet sensors.
5. Avoid using solvents, citrus-based cleaners on all plastic parts. We advise only warm soapy water be
used.
Page 10
10
4 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
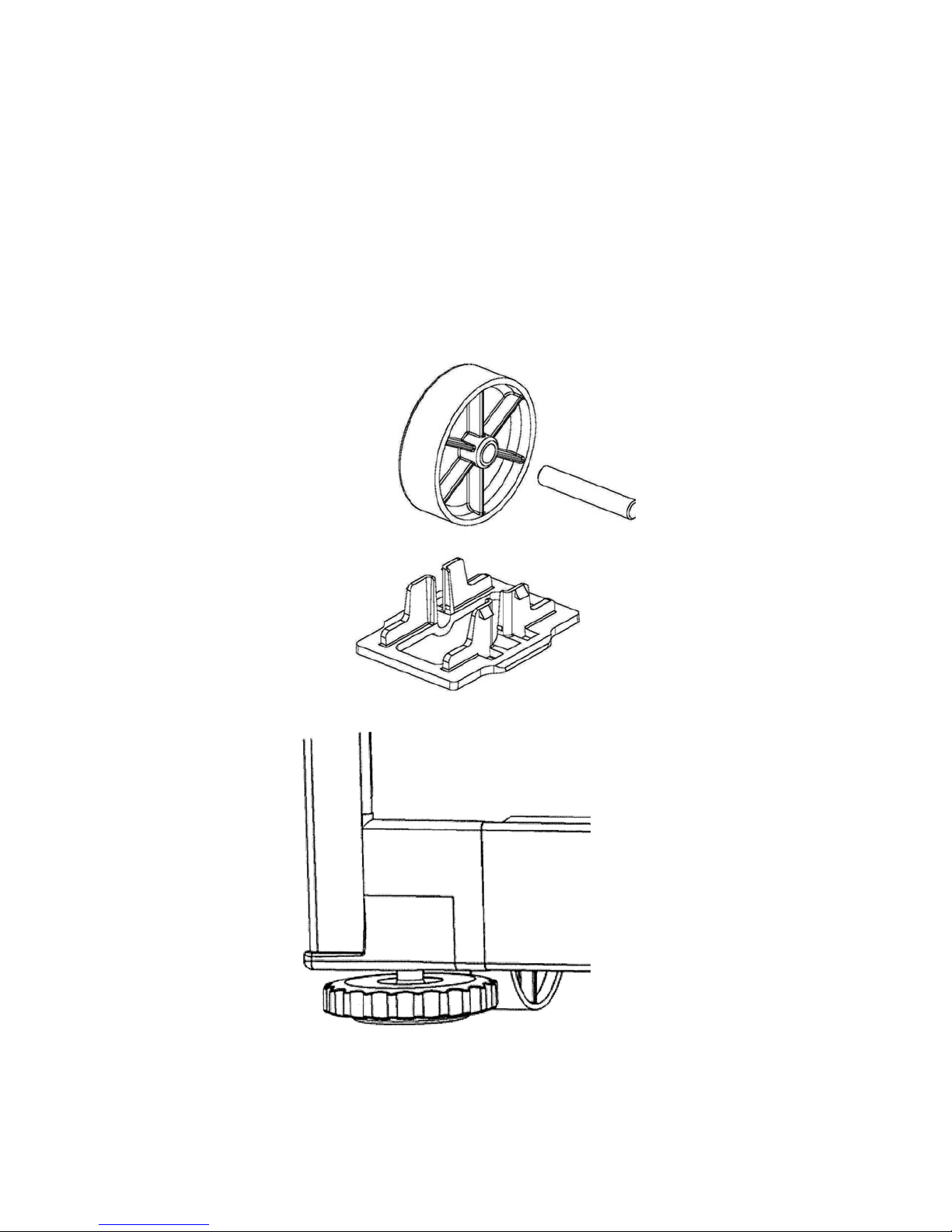
4.1 Levelling
The word 'level' is somewhat of a misnomer as a 'spirit level' need not be used to set the appliance level. It
is preferable to have the appliance level in appearance where both doors will close with the aid of the door
closing components. It is also important that the appliance sits solidly on the floor.
• Front and rear rollers are fitted ex factory.
• Cabinet levelling can be done by adjustment of the front roller levelling wheel fitted ex factory. See
diagram 4.1B.
• Weight should be lifted off the cabinet for ease of adjustment.
• The product should be levelled with the majority of the weight on the hinge side front foot. The opposite
side front foot should then be adjusted to stabilise the product.
REAR ROLLERS
Diagram 4.1A
FRONT ROLLER/LEVELLING WHEEL
Diagram 4.1B
Page 11

11
4.2 Air Space Requirements
On all refrigerators and freezers it is important that an air gap is left around the product:
• 2 inches clearance at top
• 1 inch clearance each side
4.3 Temperature Adjustment
Refer DISPLAY MODULE in Section 6.1.3.
Page 12
12
5 THEORY OF OPERATION
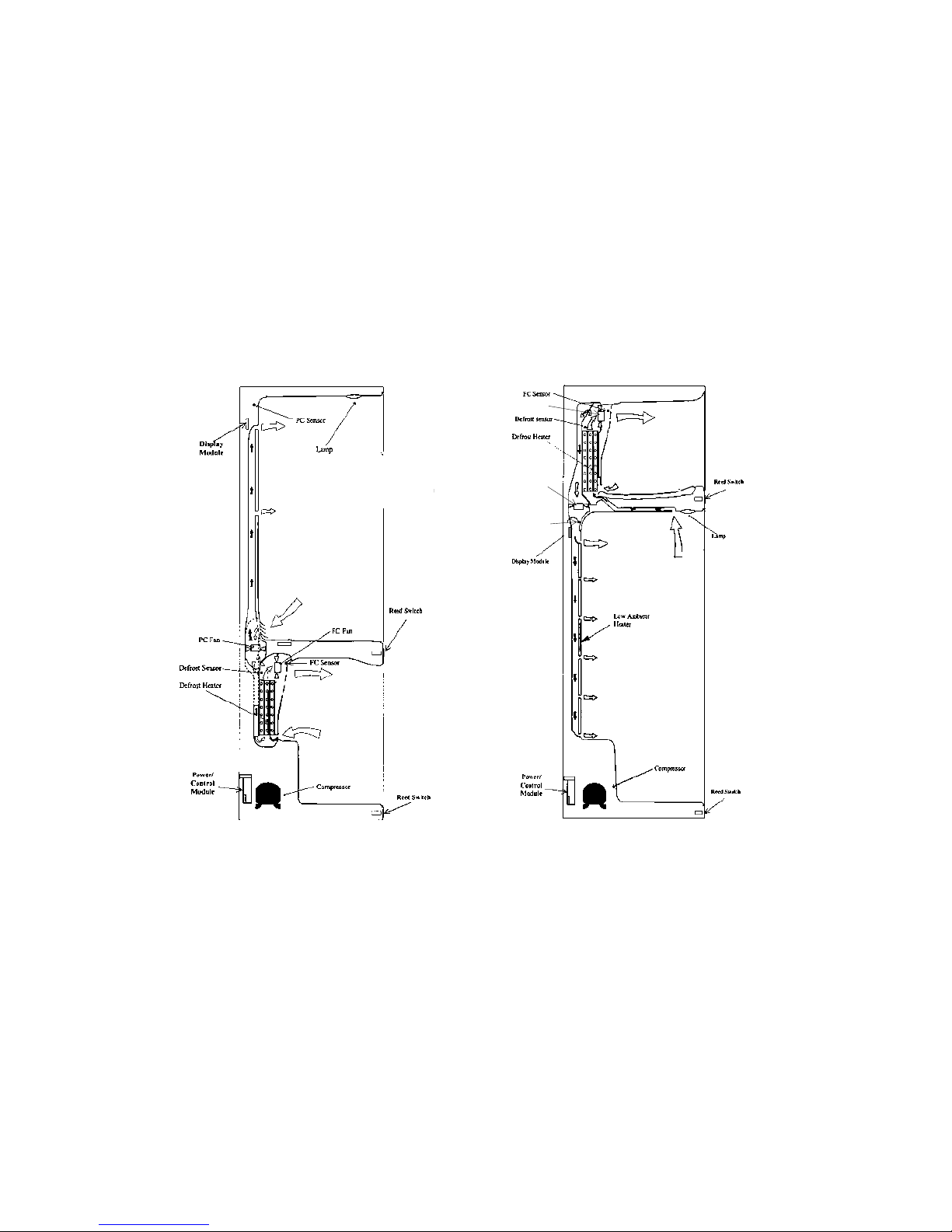
5.1 Internal Air Flow
The freezer fan draws air through the evaporator and into a duct in the rear wall of the freezer compartment.
This air exits through the fan grill at the top of the freezer compartment. The air behind the freezer coil cover
is also diverted through the divider partition to another fan which supplies the cold air into the provision
compartment. The amount of air is controlled electronically by two sensors which in turn regulate the speed
of both PC and FC fans to maintain selected temperatures in each compartment.
Air from the PC returns to the FC evaporator by way of the return air duct which is built into the divider
partition. This air is drawn across the evaporator by the evaporator FC fan motor to be recirculated again
throughout the PC / FC compartments.
“B” Model
Active Smart
Diagram 5.1A
“T” Model
Active Smart
PC Fan
PC Sensor
FC Fan
Diagram 5.1B
Page 13
13
5.2 Defrost Cycle
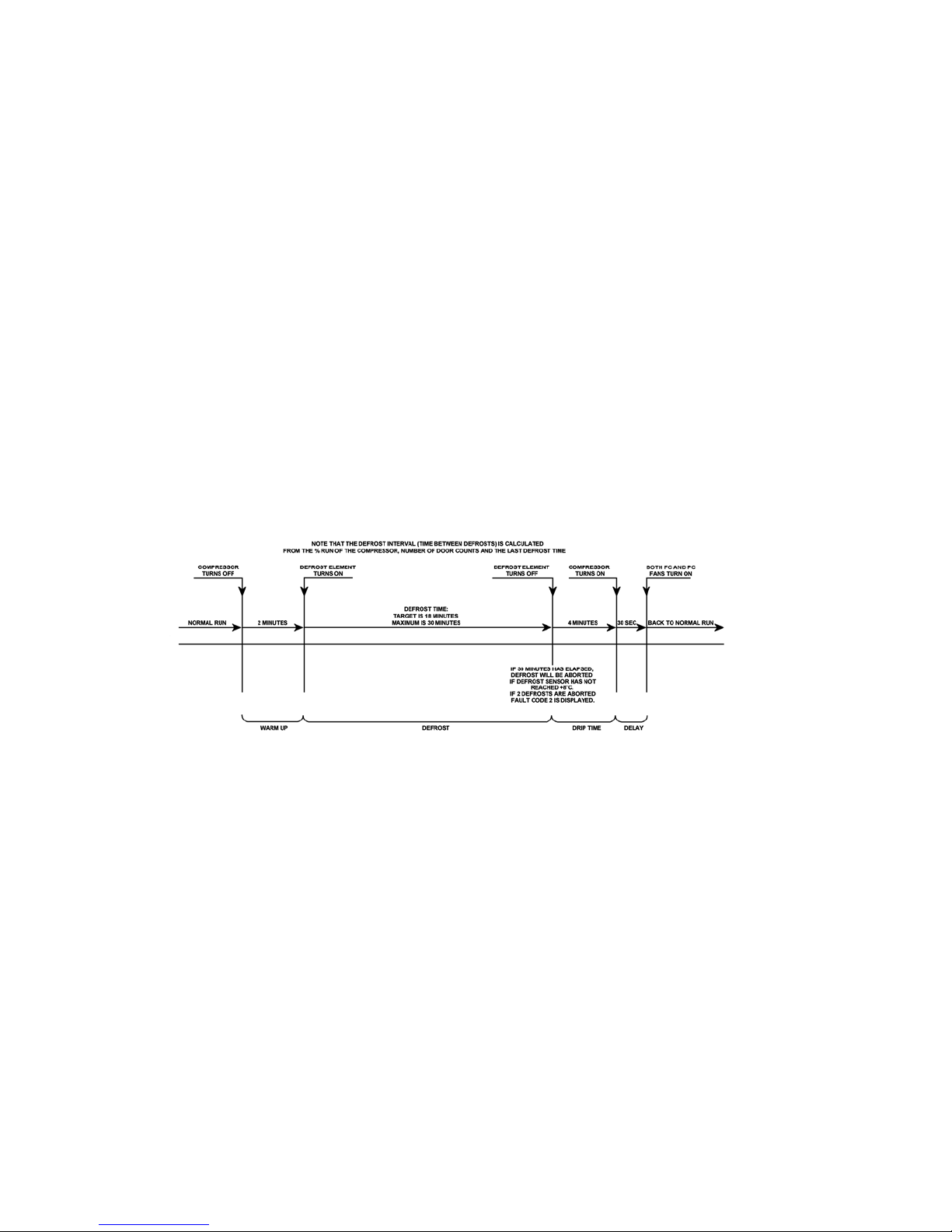
A heating element is used to defrost the ice accumulated on the evaporator. The defrosts are adaptive to
the usage and environment and are controlled by the power/control module. During a defrost, the
temperature above the evaporator is sensed by the defrost sensor located on the evaporator chassis. This
sensor must register +8
o
C (46oF) before terminating the defrost heater element. If the sensor does not
register a temperature of +8
o
C (46oF) within 30 minutes of the commencement of the defrost cycle, the
defrost will be terminated. If two successive defrost attempts fail to reach this temperature, a fault code is
displayed (refer Section 6.2.1). Previous defrost history, the number of door openings, and the compressor
run time are used to determine the interval between defrosting. The typical time interval for defrosts is
between 12 and 24 hours. However, it can be as short as 5 hours or as long as 96 hours depending on the
usage and environment.
NOTE: The defrost cycle will not start if the defrost sensor is above +8°C (46
o
F).
The defrost cycle follows a predefined sequence:
There is a delay of 2 minutes before the element starts to heat (commonly known as evaporator
warm up time).
The defrost element will remain on until the defrost sensor has reached +8
o
C (46oF).
The compressor will remain off for a further 4 minutes (commonly known as drip time).
The compressor will restart, and a further 30 seconds later both fans will restart.
The following table outlines the defrost cycle of an Active Smart refrigerator.
Diagram 5.2
Page 14
14
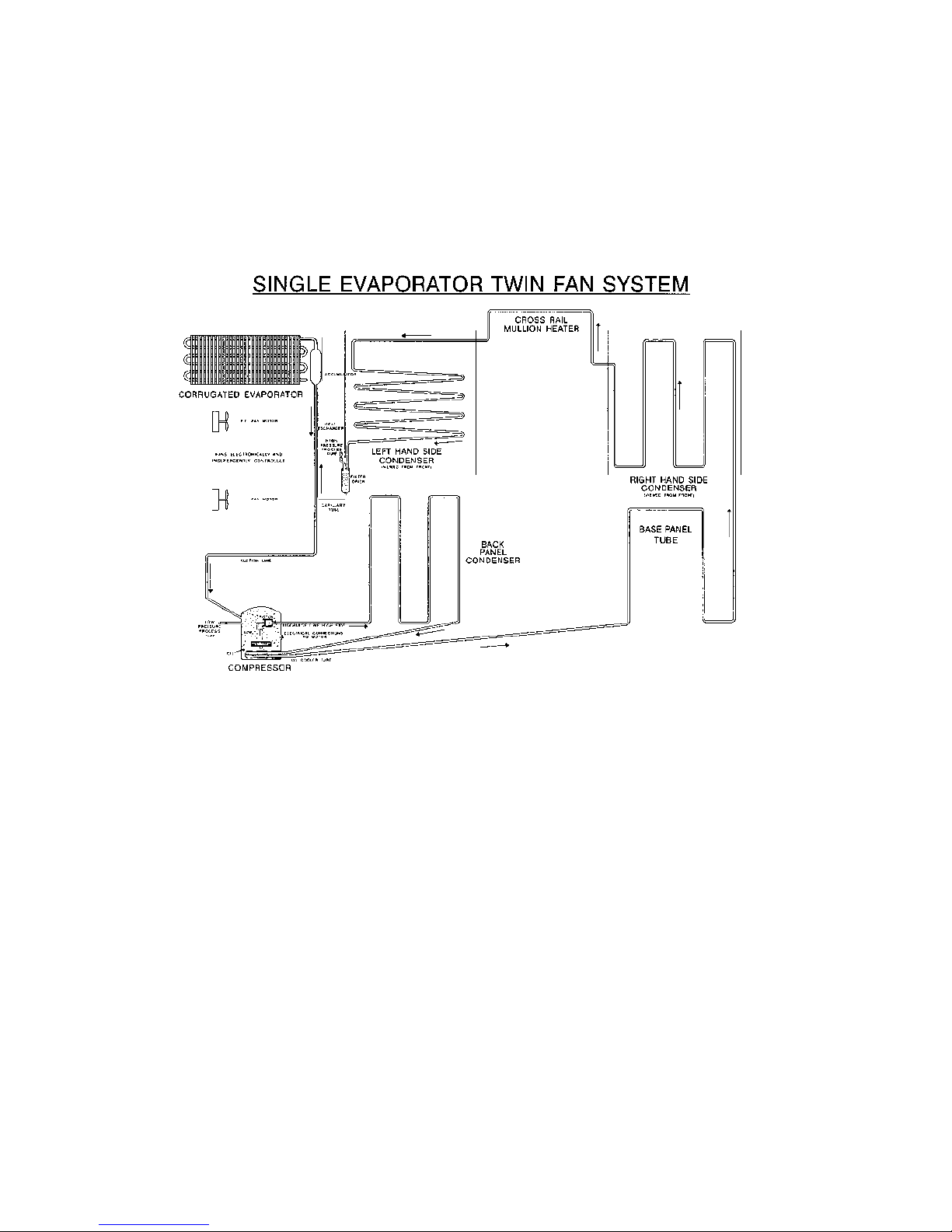
5.3 The Refrigeration Circuit
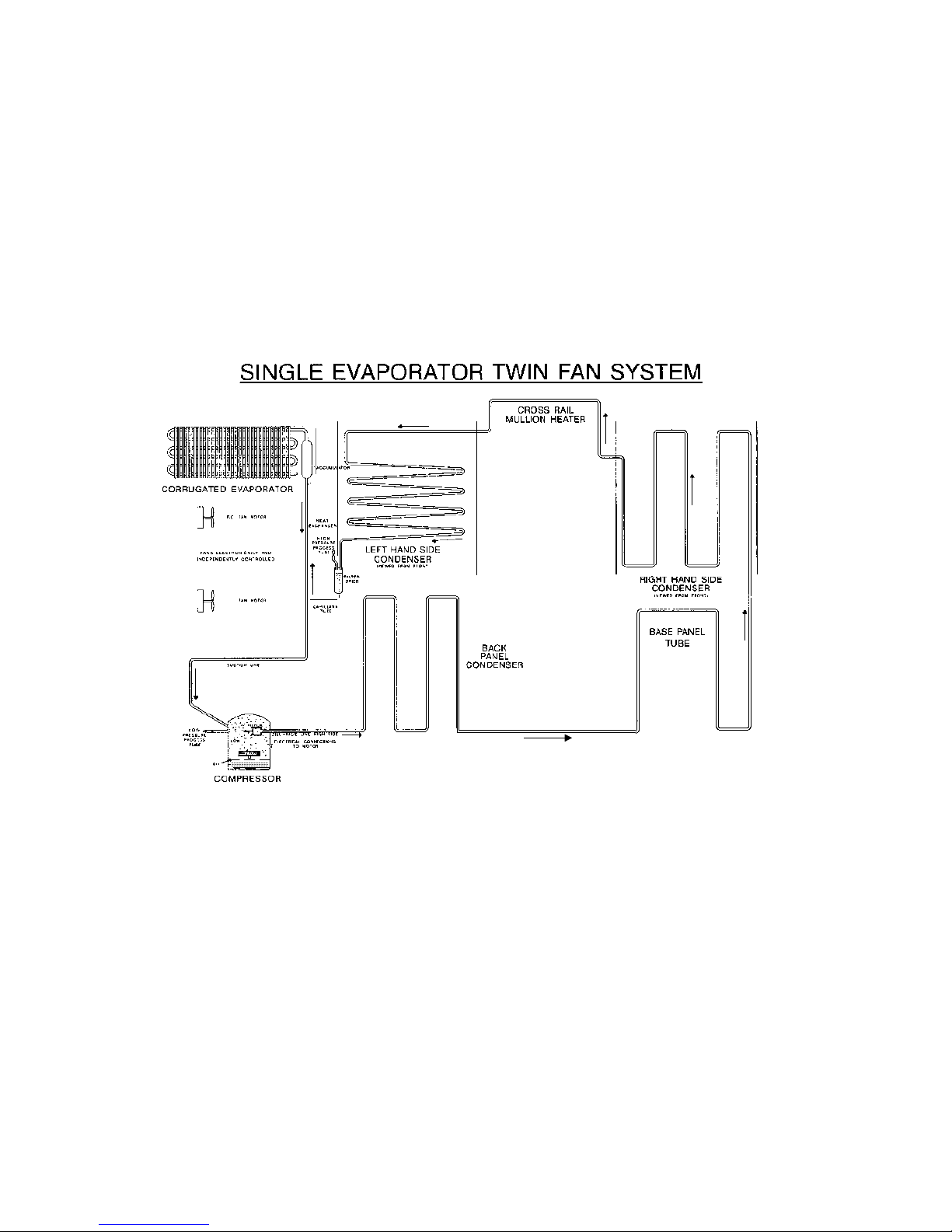
The compressor discharges high pressure, high temperature gas into the back panel condenser circuit first,
and then into the right hand side condenser in the cabinet by way of the base tube. This tube runs from the
compressor compartment forward to the front bottom edge of the cabinet, returning down the left hand side
to be connected to the left hand side condenser coil.
A loop from this condenser coil forms the cross rail mullion on dual temperature cabinets. The condenser
then continues across the top front edge of the cabinet to form the right hand side condenser before entering
the filter drier which is mounted vertically in the unit compartment.
Now the high pressure gas has been condensed, the liquid refrigerant flows through the capillary tube,
entering the evaporator mounted in the freezer compartment. The liquid refrigerant then boils off due to the
low suction pressure applied to within the evaporator from the compressor. The heat laden vapour is drawn
back to the compressor by way of the suction line to start the cycle all over again.
The above information relates to the cabinet, not the drawing below.
F.F.C.
Diagram 5.3
Page 15
15
5.4 Servicing Features
5.4.1 Condensate Disposal
During the defrost cycle, which is electronically timed and controlled, live frost is melted off the evaporator by
means of heat from the defrost element. Condensate from the evaporator defrosting drops into a collection
trough, which has an outlet hole in the centre of the liner. A tube then allows the condensate to flow into a
water evaporation tray above the compressor.
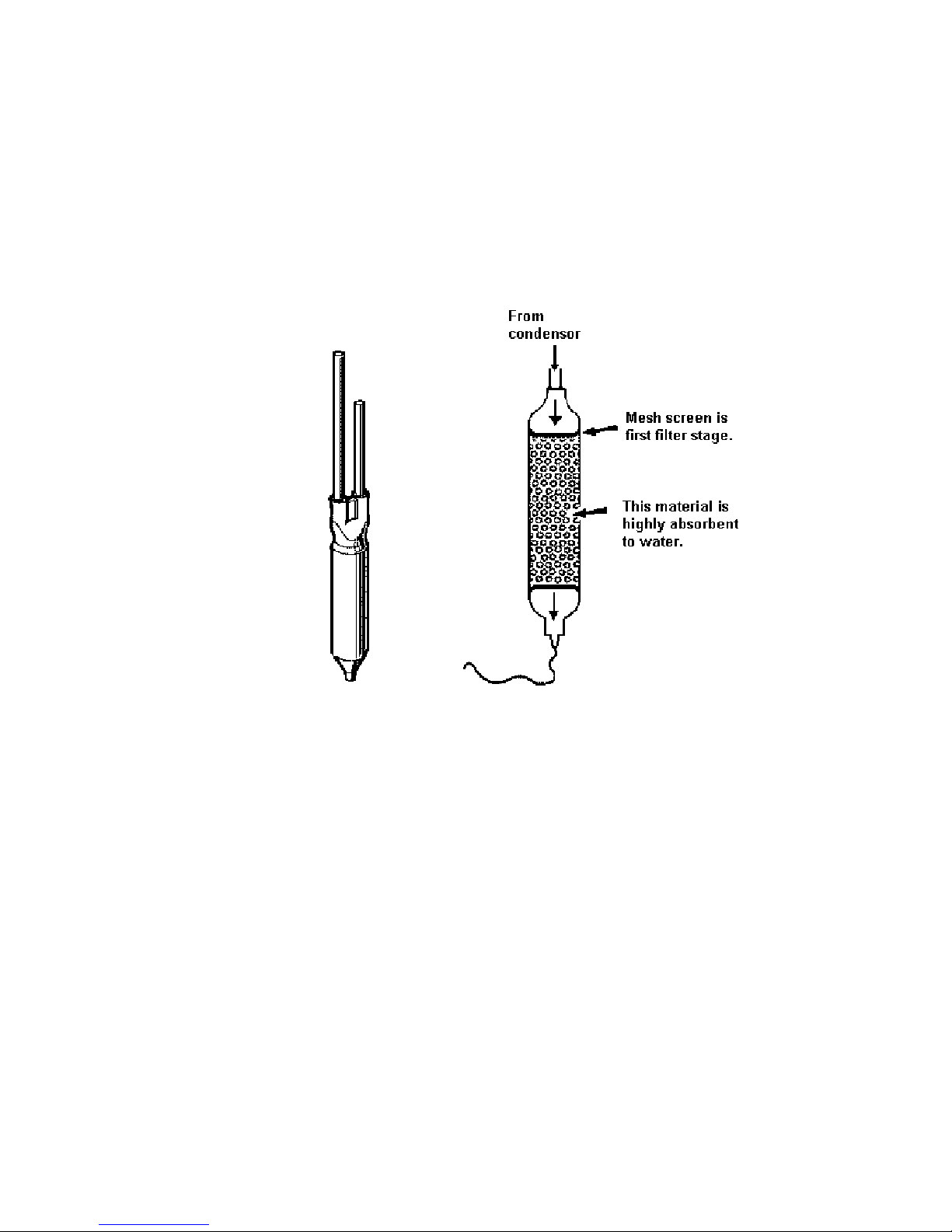
FILTER DRIER
Diagram 5.4.1
The filter drier or molecular sieve, as the name suggests, is both a filter and a drier. Whenever a system is
opened, it is essential that the filter drier is replaced. ALWAYS ensure that replacement filter driers are kept
well sealed and airtight prior to being fitted to a system.
PLEASE NOTE: When filter driers are replaced on systems being serviced, it is important that the filter
drier is either cut from the system or the desiccant is removed before heat is applied to the old filter
drier. Failure to do so will drive any moisture held in the desiccant back into the system.
ALWAYS mount vertically or as near to vertical as possible and use the correct desiccant to suit the
refrigerant being used.
XH7 or XH9 suits R134a.
Page 16
16
5.4.2 Internal Condenser
The internal condenser is made in three sections (see circuit diagram below). One third of the condenser is
attached to the back panel, and the other parts are attached to the inside of the right and left sides of the
cabinet wrapper (as viewed from the back) all being foamed into place. It is very important, if pressure
testing the high side circuit, to split the condenser into its 3 sections to locate which section is at fault.
Always ease the back panel away from the cabinet slightly before pressure testing the internal pipework.
This will prevent a pressure build-up within the cabinet should any leak be found internally in the foam
insulation. Such a leak could pressurise and damage the cabinet liner.
The back panel condenser comes as part of the back panel and should always be replaced as a complete
assembly if the back panel is ever removed.
F.F.C.
Diagram 5.4.2A
Page 17
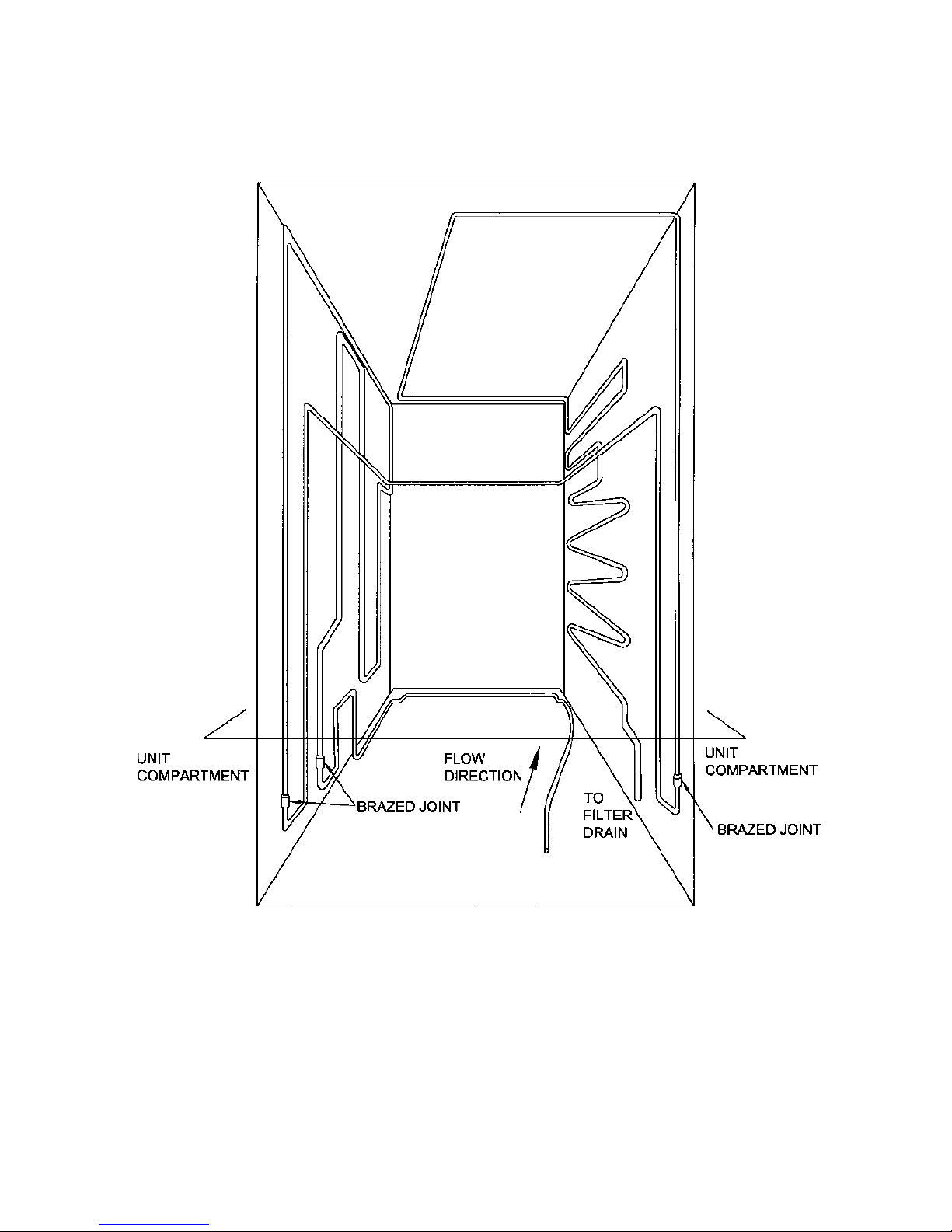
17
CONDENSER LAY OUT 680 / 790
"T" MODELS
CONDENSER WITH TUBE CROSS RAIL
FROM BACK PANEL
CONDENSER
BACK PANEL CIRCUIT REMOVED FOR CLARITY
ALL BRAZED CONDENSER JOINTS ARE EXTERNAL IN UNIT COMPARTMENT
Diagram 5.4.2B
Page 18
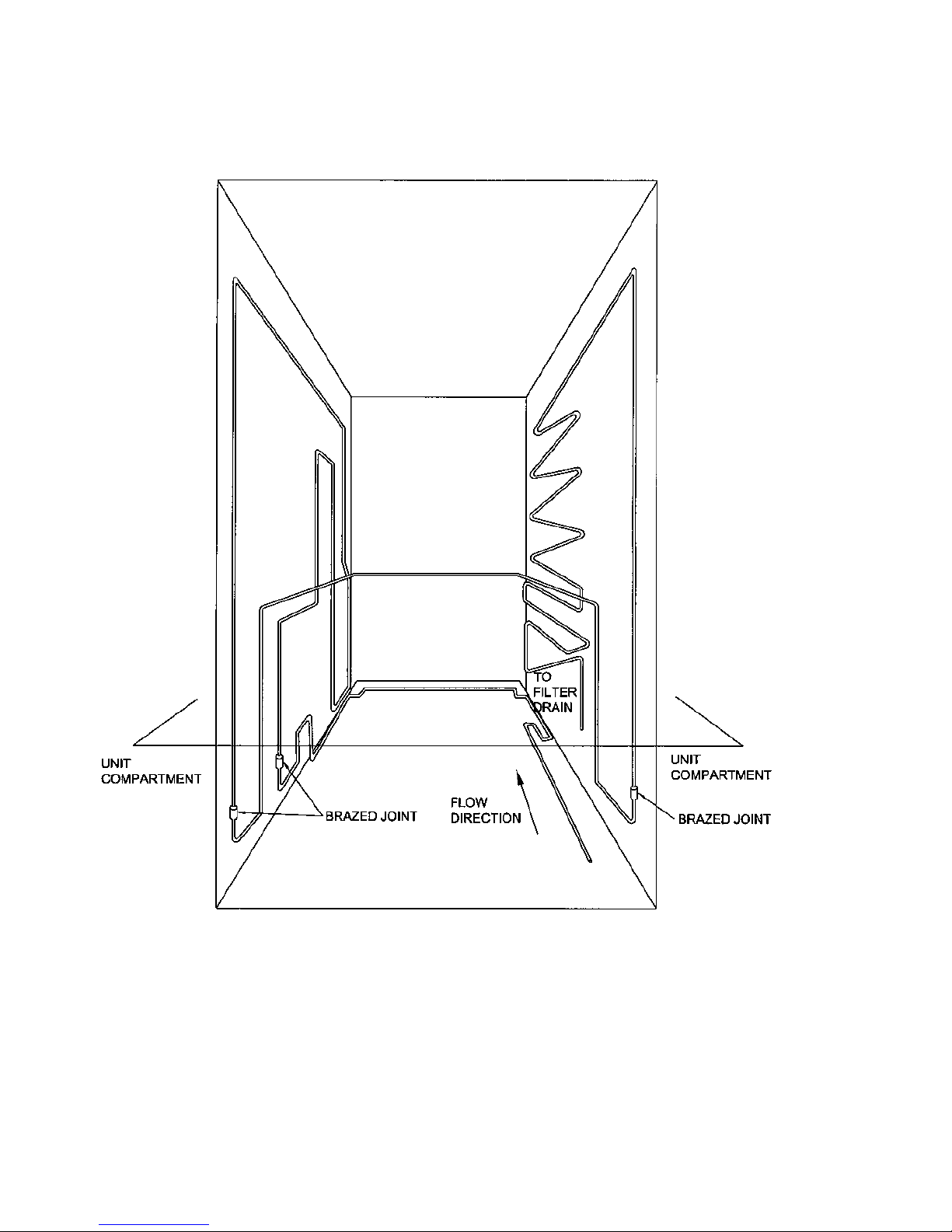
18
CONDENSER LAY OUT 680 / 790
"B" MODELS
CONDENSER WITH TUBE CROSS RAIL
FROM BACK PANEL
CONDENSER
ALL BRAZED CONDENSER JOINTS ARE EXTERNAL IN UNIT COMPARTMENT
Diagram 5.4.2C
Page 19

19
5.4.3 Cross Rail
The cross rail contains part of the condenser copper tubing (mullion heater) providing heat to the gasket area
between the PC and FC compartments, preventing sweating of the gasket. Also mounted on the cross rail is
the Reed Sensor, under the plastic cover in the centre.
5.4.4 Divider Partition
This is moulded in two outer pieces and has an inner polystyrene moulded duct assembly that is wax coated.
This provides a barrier between the FC and PC compartments, also allowing return air from the PC to move
back to the FC evaporator in ‘T’ models. In both models it houses the PC fan motor. The divider is fitted into
the cabinet as an assembly and cannot be replaced.
“B” DIVIDER PARTITION
Diagram 5.4.4
Page 20

20
6 ELECTRONICS SECTION
6.1 Overview Function Description
The electronic system consists of several parts:
Power/control module, display module, compressor, defrost heater, ambient heater, provision compartment
fan, freezer compartment fan, light, temperature sensors and door sensors.
The purpose of the power/control module is to turn on the compressor, which cools the evaporator, then to
use the fans to efficiently cool the compartments. Both fans turn on with the compressor. The freezer
compartment (FC) fan is kept at a constant speed while the provision compartment (PC) fan is regulated to
provide the balanced cooling for both compartments. The function of the microprocessor in the
power/control module is to provide independence of both compartments to their set temperatures, although
the environment of one compartment effects the other as they are linked by the ducts as can seen by the
diagrams showing internal air flow of the cabinet (diagrams 5.1A and 5.1B).
6.1.1 Control & Peripheral Functions
The control system consists of the power/control module located in the unit compartment of the refrigerator,
the slave display module located in the back of the refrigerator compartment and various sensors and
actuators controlled by the power module. The function and brief description of each of these units is
defined below.
6.1.2 Power/Control Module
This module is the electronic brain and control centre of the refrigerator. It contains a microprocessor,
support circuitry and switching devices. The power/control module controls the Provision Compartment (PC)
and Freezer Compartment (FC) temperatures by sensing the temperature and door state and operating the
compressor and fans accordingly. This module also houses the alarm beeper.
The power/control module collects information on the refrigerator operation. Faults and diagnostic
information is stored in its memory. They include the temperature setting, the history of FC and PC
temperatures (approx 18 hours), defrost history (the last 12 defrosts) and fault history. This will help the
service technician find and remedy the cause of failure. All this memory will be retained even when the
fridge is disconnected from mains power supply.
The beeper is used to signal prolonged door opening and other fault conditions:
1. If the door is left open longer than 90 seconds, the alarm will sound. This will repeat every 30 seconds
until the door is closed.
2. If the doors are left open longer than 5 minutes, the alarm will sound continuously and the PC light will
turn off. The alarm will stop with the closing of the door.
3. All electronic faults, when detected, will sound the alarm and the L.E.D.’s on the display module will flash
indicating the fault code. The pressing of any button will cancel the alarm but the fault code will remain
until the cabinet has been serviced.
Page 21

21
STAGE 4.2 POWER/CONTROL MODULE
Diagram 6.1.2
6.1.3 Display Module
This module contains the user interface, and also the circuitry to drive the lamp. It is controlled via a 5-wire
communications interface from the power/control module.
The user interface of push button switches and Light Emitting Diode (L.E.D.) display on the display module
printed circuit board is used to input and display the required set temperatures for the refrigerator
compartments.
The user interface is positioned at the rear of the provision compartment (PC). The interface automatically
displays the current temperature setting for the PC compartment. This is shown as a series of L.E.D. lights
on a thermometer symbol. To adjust the temperature of the PC, simply press the temperature up or down
buttons to the appropriate setting.
Press the mode button on the left-hand side of the interface to select the FC compartment. The indicator
light will flash for 8 seconds to show a new compartment has been selected. Press the up or down buttons
to adjust the temperature as necessary.
Further presses of the mode button will toggle between the PC and FC compartments.
DISPLAY MODULE (Stage 4.2)
Diagram 6.1.3
6.1.4 Door Switches
“Reed” switches are used to detect the opening and closing of the doors. Two small magnets that are built
into the PC and FC doors activate them. The reed switches are encapsulated within a plastic housing, which
is clipped under the plastic covers on the base and cross rails.
Page 22

22
6.1.5 Compressor
The compressor is turned on when cooling is required. It is switched by the power/control module sending a
low voltage frequency signal to the inverter.
The refrigerator is fitted with a variable capacity compressor (VCC). This improves energy efficiency and
maintains a more stable temperature in both the provision compartment and the freezer compartment. The
compressor windings are wired in a 3 phase star formation with the resistance between any two pins being
the same (6.4 ohms).
6.1.5.1 Variable Capacity Compressor Control Overview
The V4.2 power/control module on VCC product is identical to that on non-VCC product. The stage 4.2
power/control module senses if it is connected to a VCC compressor and uses the appropriate algorithm.
The compressor can operate at speeds between 1590 and 4500 rpm inclusive. On the Fisher & Paykel
product we operate the compressor at a select number of different speeds between 1590 and 4500 rpm to
reduce the variation in sound produced by the compressor. An electronic module/inverter connected
between the power/control module and the compressor controls the speed. (Refer Photo 6.1.5.1) This it
does by supplying a modulated DC 3 phase supply to the compressor. Warning: Permanent damage will
occur if the compressor is directly connected to the AC supply line.
The power/control module monitors, amongst other things, the refrigerator compartment temperatures (via
thermistors) and the defrost cycle, and from this information sends signals to the electronic module/inverter
to determine compressor speeds.
Whenever the compressor starts, it is run at 2200 rpm for 2.5 seconds to establish lubrication, and is then
run at 1590 rpm for a further 27 seconds before changing to any other higher speed as requested by the
power/control module. This is to provide a softer start before the compressor potentially ramps up to some
higher speed.
Whenever the fridge is plugged in/turned on, and/or after a defrost, in the first cooling cycle the control will
run the compressor, after its initial start procedure, at its maximum speed, which is 4500 rpm. The
compressor will stay at its maximum speed until both compartments have reached their cut-out temperature,
at which point the compressor will switch off and the refrigerator goes into the warm-up cycle.
In the subsequent cooling cycles the algorithm will vary the compressor speed according to the amount of
cooling required to achieve an average temperature in each compartment (as measured by the thermistors),
equal to the compartment set temperatures with a 1 hour run-time.
In low ambients where the heat load and/or cabinet usage is low, the compressor will be likely to run at its
minimum speed (1590rpm), and switch off more frequently than once every hour, similar to most non-VCC
product.
When the compressor is running at slow speeds, the evaporator may not be fully flooded, but this is normal.
Photo 6.1.5.1
Power/control
module
Module/inverter
Variable Capacity
Compressor
Page 23

23
6.1.5.2 Built-in Electronic Protections (Within the Module/Inverter)
6.1.5.2.1 Compressor Start-up
In case any anomaly occurs during compressor starting, the control will wait 6 seconds before repeating the
start-up. If the compressor doesn’t start after 12 trials, the control will wait 8 minutes before repeating the
start-up procedure (this condition may be when pressures are not equalised between suction and discharge
sides in the refrigeration system, eg; after an interruption in the mains supply).
6.1.5.2.2 Overload Detection and Protection
The control can detect an overload condition by monitoring the current consumed by the compressor. If
overload is detected the control reduces the current by reducing the speed of the compressor until the
overload disappears, when the speed will return to the required value.
If the overload increases, the control will continue to decrease the current until the minimum speed of 1590
rpm may be reached, at which point the compressor may “stall”, and the control will return to the start-up
procedure.
6.1.5.2.3 Power Limitation (Temperature Protection)
The control limits the power supplied to the compressor to 200 watts to keep all electrical components below
a safe operating limit. The power is limited in the same way as the current in the overload protection.
6.1.5.2.4 Short Circuit Protection
In a case where a short circuit occurs, (eg; motor winding damage, connection faults etc), the same current
limiting control is actuated to reduce further damage. In the case of a major failure, a fuse within the inverter
will break the current supplied to the control. This fuse cannot be replaced in servicing.
6.1.5.3 VCC Module/Inverter Identification
The module/inverter has an identification label giving the following information:
6.1.5.4 Fault Finding
6.1.5.4.1 High Voltage Power Supply Circuit
Whenever power is supplied to the refrigerator, there should always be 110V mains voltage in the high
voltage harness between the power/control module and the VCC module/inverter. This can be checked by
removing the rear cover of the VCC module/inverter and testing with a multimeter. There should be 110V
across the spade terminals above the edge connector at the top of the module (refer Photo 6.1.5.4). If this is
not present, check the continuity of the harness from the power/control module. If there is continuity through
the harness, replace the power/control module.
6.1.5.4.2 Signal Circuit
With a multimeter that can measure frequency, the signal circuit between the power/control module and the
VCC module/inverter can be checked. Remove the rear cover of the VCC module/inverter and connect the
multimeter across the two pins beside the signal harness edge connector. When the compressor is meant to
be running, the frequency should be between 53Hz and 150Hz. At start up the frequency will be 75Hz for
2.5 seconds, then 53Hz for 27 seconds before changing to 150Hz. Multiplying the frequency of the signal
circuit by 30 will give the compressor speed, so if the frequency is 53Hz the compressor speed will be
1590rpm, and if it is 150Hz the compressor speed will be 4500rpm.
VCC3
11
56
XX
A
XX
Inverter Version
Voltage:
11 = 115-127V
24 = 220-240V
Frequency:
50 – 60 Hz
Electronic board version
A = Stand alone version box
F = Attached version box
Cable configeration
Page 24

24
Photo 6.1.5.4
6.1.6 Defrost Heater
A heating element is used to defrost the ice accumulated on the evaporator. The defrosts are adaptive to
the usage and environment and are controlled by the power/control module. During a defrost, the
temperature above the evaporator is sensed by the defrost sensor located on the evaporator chassis. This
sensor must register +8
o
C (46oF) before terminating the defrost heater element. Previous defrost history, the
number of door openings, and the compressor percentage run time are used to determine the interval
between defrosting. The typical time interval for defrosts is between 12 and 24 hours. However, it can be as
short as 5 hours or as long as 96 hours depending on the usage and environment.
DEFROST ELEMENT
Diagram 6.1.6
High voltage
test point
Signal circuit
test point
Page 25

25
6.1.7 Thermal Fuses
There are two thermal fuses mounted in the wiring harness of the defrost element, having a tripping
temperature of 72
0
C (1610F). Once open circuit they can not be reset. Replacement is part of the element
heater assembly.
These fuses in both leads of the element protect the refrigerator from any over heating through failure of the
element itself or a triac failure in the power/control module. Both sides are protected in case phase and
neutral are reversed.
NOTE: Care should be taken if manually defrosting the evaporator (i.e.. using heat guns), to ensure that the
thermal fuses are not over heated.
6.1.8 Low Ambient Heater
In low ambient temperatures a 12 Volt, 7 Watt low power heater is used to keep the temperature in the
provision compartment above freezing. The ambient heater is controlled by the power/control module which
runs the heater at 58% duty cycle to give 4.1 watts of heat. This is achieved by the use of pulse width
modulation (PWM). The heater is situated in the air duct of the “T” models and in the divider partition on “B”
models. The purpose of the element is to warm the area if the ambient becomes too low. The element is on
when the cabinet cycles off. The low ambient heater operates during both the compressor on and off cycles
when the percentage of compressor run time averaged over the previous four cycles drops below 65%. It
switches off when the percentage run time increases to above 70%. The heater will always be switched off
during the defrost cycle and whenever the PC door is open. There may be less than 4 cycles in the
calculation if a defrost has occurred or there were long cycle times.
“T” MODEL
Diagram 6.1.8
Page 26

26
6.1.9 PC / FC Fans
There are two 12 Volt DC electrically commutated motor (ECM) fans. They provide the required cooling
power to both compartments. The motors are provided with from 18% to 100% voltage by using a pulse
width modulating (PWM) technique. The power/control module controls the switching on and off of the
compressor and the fans. The speed of the FC fan is set and the speed of the PC fan is regulated by
altering the voltage supplied to it.
The FC fan will always runs at a constant speed.
The PC fan speed can be adjusted to meet the requirement of that compartment. Therefore the PC fan
speed will be set at the average speed used from the previous cycles under normal door openings and
loading conditions. During the off cycle of the compressor the PC fan will run at a very low speed to prevent
air transfer in the ducts between the two compartments.
When the compressor is turned on, the fans will also be switched on, except immediately following a defrost
cycle where there is a delay of 30 seconds after the compressor has started before the fans switch on.
Diagram 6.1.9
6.1.10 Light
A 12 volt, 10 watt halogen lamp is used in the PC. To prevent overheating, the lamp is turned off after 5
minutes of the door being left open. The power/control module controls this.
LIGHT FITTING, LAMP AND COVER
Diagram 6.1.10
NOTE: It is important that the lamp pins are tight in the lamp socket.
FC FAN (Viewed from front
)
PC FAN (Viewed from FC side)
Page 27

27
6.1.11 Thermistor Temperature Sensors
These sensors are used to monitor temperatures within the refrigerator. There are 3 of them:
1. Defrost sensor mounted on the evaporator chassis above the evaporator, used to measure the
temperature when in defrost. (Colour Black)
2. FC sensor mounted on the FC fan cover, used to measure the temperature in the FC. (Colour White)
3. PC sensor mounted in the PC on the duct cover and used to sense the PC temperature. (Colour White)
Thermistor sensors are used for temperature measurement, therefore once the temperature of the
refrigerator has reached its set temperature, the power/control module will turn the compressor off.
Their electrical resistance changes as the temperature changes. The table below lists some typical
resistance values. The temperature can be read using Diagnostic Mode as described in the next section.
Diagram 6.1.11
THERMISTOR SENSOR RESISTANCE TABLE
TEMPERATURE
(°C/°F)
RESISTANCE
(K Ohms ±5%)
-30 / -22 25.17
-25 / -13 19.43
-20 / -4 15.13
-15 / 5 11.88
-10 / 14 9.392
-5 / 23 7.481
0 / 32 6.000
5 / 41 4.844
10 / 50 3.935
15 / 59 3.217
20 / 68 2.644
25 / 77 2.186
30 / 86 1.817
35 / 95 1.518
40 / 104 1.274
45 / 113 1.075
50 / 122 0.9106
Page 28

28
6.2 Fault Finding Procedure
6.2.1 Fault Code Display Status
If a fault should develop in the temperature measurement system, defrost system, fans or low ambient
heater, a fault code will be shown automatically on the display and the fault audio alarm will sound. At the
same time, the bottom L.E.D. will flash red alternately with the fault L.E.D.(s) When any control button is
pressed, the audio alarm is turned off although the display will continue to be “flashed” instead of the normal
“back-lit” display.
The refrigerator goes through a sequence of tests whenever it is turned on at the power supply or whenever
the door is closed while it is on. It takes 20 seconds to complete the test sequence, and opening a door will
interrupt it. If, for example, there is a fault with the fans/low ambient heater connector at the power module
(it may be unplugged) and a door is opened as soon as the fault audio alarm sounds, the fault code shown
will be code 13 (low ambient heater drawing less current than expected). This is because the low ambient
heater is the first item tested and so the refrigerator will fault for this but carry on with more tests. If the doors
are left closed until the tests are completed, the fault code shown will be code 11 (the current measured for
the ambient heater, PC fan and FC fan is lower than expected). It is therefore recommended that if the fault
audio alarm sounds as soon as the refrigerator is turned on, or as soon as the doors are closed, the service
technician should wait for 20 seconds before opening the door to check the fault code. This will allow the
refrigerator to complete the sequence of tests and will ensure that the fault code displayed is the correct one.
To reset the audio alarm, disconnect the refrigerator from the power supply for a few seconds. If this is not
done, the audio alarm will automatically reset after 72 hours.
Fault codes will be in a binary code and the L.E.D.s that flash will have the following binary values:
To determine the value of the displayed fault code, add up the values of the L.E.D.s that are flashing (ignore
the flashing red L.E.D.). The faults and their respective fault code that can be checked and serviced in the
field are as follows:
Display Code: 1
Reason: On the last power up, the power/control module failed its self-test.
Primary Action: Replace power/control module.
Display Code: 2
Reason: The previous 2 defrosts were aborted after 30 minutes.
Primary Action: Check defrost heater assembly in the FC. If faulty, replace.
Secondary Action: Check power module is supplying 230V to heater during defrost. If not, replace
power module.
Display Code: 3
Reason: The resistance of all the temperature sensors is outside the normal range. (> 45K
Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the 6 way RAST connector at the power module.
Secondary Action: Re-terminate the 6 way RAST connector.
Tertiary Action: Replace the power module.
Mode
Temperature Down
Temperature Up
1
2
4
8
16
32
64
128
Page 29

29
Display Code: 4
Reason: The resistance of all the temperature sensors is outside the normal range. (< 660
Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the 6 way RAST connector at the power module.
Secondary Action: Re-terminate the 6 way RAST connector.
Tertiary Action: Replace the power module.
Display Code: 5
Reason: The resistance of the FC sensor is outside the normal range. (> 45K Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the sensor connection at the power module.
Secondary Action: Replace the sensor.
Display Code: 6
Reason: The resistance of the FC sensor is outside the normal range. (< 660 Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the sensor connection at the power module.
Secondary Action: Replace the sensor.
Display Code: 7
Reason: The resistance of the evaporator sensor is outside the normal range. (> 45K
Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the sensor connection at the power module.
Secondary Action: Replace the sensor.
Display Code: 8
Reason: The resistance of the evaporator sensor is outside the normal range. (< 660
Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the sensor connection at the power module.
Secondary Action: Replace the sensor.
Display Code: 9
Reason: The resistance of the PC sensor is outside the normal range. (> 45K Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the sensor connection at the power module.
Secondary Action: Replace the sensor.
Display Code: 10
Reason: The resistance of the PC sensor is outside the normal range. (< 660 Ohms).
Primary Action: Check the sensor connection at the power module.
Secondary Action: Replace the sensor.
Display Code: 11
Reason: The current measured for the ambient heater, PC fan and FC fan is lower than
expected.
Primary Action: Check the 6 way fan/LAH RAST connector at the power module.
Secondary Action: Reterminate the 6 way fan/LAH RAST connector.
Tertiary Action: Replace the power module.
Display Code: 12
Reason: The current measured for the ambient heater, PC fan and FC fan is higher than
expected.
Primary Action: Check the 6 way fan/LAH RAST connector at the power module.
Secondary Action: Reterminate the 6 way fan/LAH RAST connector.
Tertiary Action: Replace the power module.
Display Code: 13
Reason: Low ambient heater is drawing less current than expected. Either the heater or
wiring is open circuit or the heater is faulty.
Primary Action: Check wiring and connections at both heater and power module.
Secondary Action: Check ambient heater resistance. If not within limits, replace.
Page 30

30
Display Code: 14
Reason: Low ambient heater is drawing more current than expected. Either there is a short
in the heater or wiring, or the heater is faulty.
Primary Action: Check wiring and connections at both heater and power module.
Secondary Action: Check ambient heater resistance. If not within limits, replace.
Display Code: 15
Reason: The PC fan is drawing less current than expected. Either the wiring is open circuit
or the fan is faulty.
Primary Action: Check PC fan wiring and connections at both fan and power module.
Secondary Action: Check fan. If faulty, replace.
Display Code: 16
Reason: The PC fan is drawing more current than expected. Either the wiring is shorted or
the fan is faulty.
Primary Action: Check PC fan wiring and connections at both fan and power module.
Secondary Action: Check fan. If faulty, replace.
Display Code: 17
Reason: The FC fan is drawing less current than expected. Either the wiring is open circuit
or the fan is faulty.
Primary Action: Check FC fan wiring and connections at both fan and power module.
Secondary Action: Check fan. If faulty, replace.
Display Code: 18
Reason: The FC fan is drawing more current than expected. Either the wiring is shorted or
the fan is faulty.
Primary Action: Check FC fan wiring and connections at both fan and power module.
Secondary Action: Check fan. If faulty, replace.
Example Fault Code: 8 + 4 + 1 = 13
13 = Low Ambient Heater Open Circuit
Page 31

31
6.2.2 Diagnostic Mode
To enter the diagnostic mode, Press and hold the MODE button, then press the TEMPERATURE UP button.
The L.E.D.s indicate the PC sensor temperature. The current PC sensor temperature is displayed in a code
form (refer Section 6.2.3 Sensor Temperature Conversion).
Return to normal operation by pressing the MODE button.
CAUTION: In reading temperatures there is a need to enter the required mode when the door is first opened
as all temperature readings are only sensor temperature/air temperatures and these will change rapidly with
the increase in air temperature as soon as the door is opened.
Press the up button.
1 time = FC sensor temperature. The current FC sensor temperature is displayed in a code form
(refer Section 6.2.3 Sensor Temperature Conversion).
2 times = Defrost sensor temperature. The current defrost sensor temperature is displayed in a code
form (refer Section 6.2.3 Sensor Temperature Conversion).
3 times = Inputs/outputs status (refer Section 6.2.4 Input/Output Status).
To exit the diagnostic mode, press the MODE button. If not terminated manually, diagnostic mode will time
out and go back to default display after 5 minutes.
Note: The door alarms do not operate when the appliance is in diagnostic mode.
6.2.3 Sensor Temperature Conversion
To obtain the temperature of either compartment sensor or defrost sensor:
1. Enter the diagnostic mode (refer Section 6.2.2 – Diagnostic Mode) and scroll to the appropriate sensor
temperature.
2. Add up the binary number indicated by the L.E.D. light pattern (refer figure below).
3. Subtract 40 from the result to get the temperature.
0.5
1
2
4
8
16
32
Page 32

32
Example:
Add up the number corresponding to each L.E.D. that is on:
0.5 + 4 + 8 + 32 = 44.5
Subtract 40 from the result
44.5 - 40 = 4.5
o
C
Hence the temperature is 4.5
o
C
6.2.4 Input/Output Status
The Input/Output Status menu displays what devices (e.g. light, PC door, FC door, compressor, etc) are
currently running or turned on.
To enter the menu, the steps are:
1a. Press and hold the MODE button (a short beep will sound).
1b. Whilst still holding the MODE button, briefly press the TEMPERATURE UP button (a short beep will
sound); this enters diagnostic mode.
Steps 1a and 1b need to be completed within 8 seconds.
2. Press the TEMPERATURE UP button 3 times.
The respective L.E.D. turns on when a device is running, as shown below.
3. Return to normal operation by pressing the MODE button.
Upper door open
Lower door open
PC fan on
Low ambient heater on
Light on
FC fan on
Defrost heater on
Compressor on
Page 33

33
6.2.5 Data Download
To retrieve information from the control module, one of the following is required:
• A Light Pen (part number 425930) and a Cassiopeia Smart Tool.
• A Light Pen (part number 425930) and a laptop computer with the Fisher & Paykel Smart Tool
diagnostic program loaded.
The steps to download data are:
1a. Press and hold the MODE button (a short beep will sound).
1b. Whilst still holding the MODE button, briefly press the TEMPERATURE UP button (a short beep will
sound); this enters diagnostic mode.
Steps 1a and 1b need to be completed within 8 seconds.
2. Press the TEMPERATURE DOWN button once; this enters data download mode.
A red L.E.D. turns on and should be visible on the display.
3. Place the Light Pen over the top of the red L.E.D. until downloading is complete.
4. Return to normal operation by pressing the MODE button.
If additional help or information is required, please refer to the instructions provided with the Smart Tool, or
ask your Technical Representative.
6.2.6 Manual Defrost
To manually force a defrost, the steps are:
1a. Press and hold the MODE button (a short beep will sound).
1b. Whilst still holding the MODE button, briefly press the TEMPERATURE DOWN button (a long beep
will sound).
Steps 1a and 1b need to be completed within 8 seconds.
2. To check if the fridge is in defrost mode, repeat step 1a & 1b.
If a long beep sounds, then the defrost cycle has started.
3. To exit manual defrost mode, turn the refrigerator off at the power supply, and then while pressing the
MODE button, switch the refrigerator on again at the power supply. If this is not done, the refrigerator
will automatically exit from the manual defrost mode when the defrost is completed.
NOTE: The defrost cycle will not start if the defrost sensor is above +8°C (46°F).
The defrost cycle follows a predefined sequence:
There is a delay of 2 minutes before the element starts to heat (commonly known as evaporator warm
up time).
The defrost element will remain on until the defrost sensor has reached +8
o
C (46°F), or until 30
minutes has elapsed if the defrost sensor does not reach +8°C (46°F).
The compressor will remain off for a further 4 minutes (commonly known as drip time).
The compressor will restart and a further 30 seconds later both fans will restart.
6.2.7 Show Room Mode
Go into diagnostic mode (press MODE and TEMPERATURE UP buttons together) then hold the
TEMPERATURE UP button only for 3 seconds. The Show Room Mode will be entered, which turns off the
normal system control leaving only the PC light operating with no door alarms. There will be a “long” beep
and while the doors are opened the L.E.D. display will go through an attention grabbing sequence unless
buttons are pressed, at which time the display will respond as normal. 8 seconds after the last button press
the display sequence will continue. The mode may be exited by switching off the appliance at the power
supply.
Page 34

34
6.2.8 Special Option Mode (Israel)
The Active Smart refrigerator is fitted with a special option mode, should the customer wish to disconnect the
operation of the interior lights and the alarm.
To enter this mode the customer is required to push and hold the compartment select MODE button on the
display board for 10 seconds.
When the cabinet is in this special option mode the following will not operate:
The interior light will not turn on when the PC door is opened.
There will be no set temperature lights (L.E.D.s) displayed on the display module.
The door alarm will be disconnected and will not sound even if the doors were to be left open.
The customer may exit this mode at anytime by pushing and holding the compartment select MODE button
for 10 seconds.
Note: When in the special option mode the Active Smart will operate as normal without the above being
used. In normal operation, the set temperature L.E.D.s and interior light will be seen when the PC door is
opened.
6.3 Door Gasket - (Integral)
The door gasket is able to be replaced as a separate part.
All replacement doors are supplied minus the door gasket. The door gasket is a replaceable part of the
door. It is held in place against the door liner by means of a moulding which locks the gasket in place once
pushed into it. There are no screws or retainers to remove or fit.
To Remove the Gasket
Pull on any section of the gasket to pull it away from the moulding.
To Replace the Gasket
Having removed the old gasket, lay the new gasket around the door gasket moulding. First fit all corners,
then push the remaining gasket into place around the door.
Diagram 6.3
Page 35

35
7 REMOVING AND REFITTING OF
COMPONENTS
7.1 Removal Of Power/Control Module
Located in the unit compartment on the right hand side and held in place by 2 self-tapping screws.
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove both mounting screws and earth screw (on the green / yellow earth wire) on the compressor
mounting tray.
3. Pull the power/control module outwards to disengage the mounting lugs at the back of the module.
4. Remove all connectors along the top edge of the power/control module.
5. Remove the defrost connector (brown wires) and the VCC high voltage supply connector which is
connected to the terminals marked “H Rail” on the side of the power/control module.
6. Refit in reverse order.
Note: It is important that the power/control module is clipped securely to the side of the unit compartment
and the copper earth spring clip is not damaged as this maintains good earthing and provides a low
inductance path to the chassis for RF voltage. Check that the flat pins at the back of the module are properly
engaged with the lugs on the unit compartment when refitting.
Initialisation Of The Power/Control Module After Installation
The power/control module needs to know whether it is fitted into a “B” or “T” model upon installation because
it performs different functions when either the PC or FC doors are opened. To do this, we need to “initialise”
the power/control module.
To initialise the power/control module, the service technician must have the FC door closed and the PC door
open, then press any of the buttons on the user interface in the PC. The power/control module then knows
that the reed switch that is open circuit is controlled by the PC door, and the one that is closed circuit is
controlled by the FC door.
If the power/control module is not initialised, as may be the situation for a new service module, the lights will
not turn on and the fans will run with the door open. If the operator presses a button with both doors opened,
the illegal raspberry audible feedback will sound, indicating that the module is unable to be initialised.
7.2 PC Sensor Replacement
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove all PC shelving.
3. Remove bottom PC air duct cover.
4. Remove polystyrene duct cover insulation.
5. Disconnect low ambient heater - “T” model only.
6. Remove 1 screw from top duct cover and unclip - “T” model only.
7. Remove PC sensor from its location.
8. Replacement of the new sensor is done by cutting the wiring back from the sensor end, and soldering
in a new sensor, making sure both connecting wires are not shorting but are insulated with heat shrink
sleeving.
9. Refit in reverse order.
7.3 FC Sensor Replacement
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Prise out the fan shroud using a flat blade screwdriver at the bottom of the grill cover.
3. Remove the FC fan motor plug connection.
4. Unclip the FC sensor and remove the evaporator coil cover.
5. Replacement of the new sensor is done by cutting the wiring back from the sensor end and soldering
in a new sensor, making sure both connecting wires are not shorting but are insulated with heat shrink
sleeving.
6. Refit in reverse order.
Page 36

36
7.4 PC Fan Motor - “T” Model
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove all PC shelving.
3. Remove bottom PC air duct cover.
4. Remove polystyrene duct cover insulation.
5. Disconnect low ambient heater.
6. Remove 1 screw from top duct cover and unclip.
7. Unplug PC fan motor plug.
8. Withdraw downwards.
9. Refit in reverse order.
Note: When refitting the PC fan motor, the back of the fan motor faces downwards. Ensure there is a loop
in the wiring harness between the fan motor and its housing.
7.5 PC Fan Motor - “B” Models
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove all PC shelving.
3. Remove the duct grill in the PC.
4. Remove the PC duct cover and polystyrene insulation.
5. Using 2 fingers, withdraw the fan motor upwards. It is mounted horizontally in the divider partition.
6. With the motor out, this will expose a small multi plug and socket connection to the fan motor and
wiring harness. Unplug.
7. To refit back together, fit the wiring harness multi plug first into the pocket of the divider partition.
8. Using your 2 fingers, slip the motor back into the divider partition to fit horizontally. Note: The back of
the fan motor faces upwards.
9. Refit duct covers and test.
The PC fan is supported by a rubber band type suspension. It is important that the fan sits central to the
housing and that there is a loop in the fan motor wiring harness between the motor and the housing. This
loop should be on a horizontal plane to the fan motor. This also applies to the FC suspended fan.
7.6 Cross / Base Rail Door Reed Switches
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove the door switch cover (located in the center of the cross and base rails).
3. Unclip the encapsulated reed switch from the housing.
4. Replacement of the new switch is done by cutting the wiring back from the switch end and soldering in
a new switch, making sure both connecting wires are not shorting but are insulated with heat shrink
sleeving. Take care not to leave too much excess wire as the reed switch must be able to be fitted
back in to the housing.
5. Refit in reverse order.
7.7 Defrost Heating Element
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove the fan grill cover. This unclips with the aid of a small screwdriver.
3. Unplug the fan motor and unclip the evaporator sensor.
4. Remove the evaporator cover.
5. Lift the evaporator upwards to clear the bottom of the divider partition and pull the bottom edge of the
evaporator forward.
6. Remove the cable ties from the thermal fuses.
7. Bend the first half of the evaporator clips and side deflectors away from the front bank of the
evaporator on both sides.
8. Drop the element down and out of the evaporator bank.
9. Refit in reverse order.
Page 37

37
7.8 Removal Of Display Module
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove all PC shelving.
3. Remove bottom PC air duct cover.
4. Remove polystyrene duct cover insulation.
5. Disconnect low ambient heater – “T” model only.
6. Remove 1 screw from top duct cover and unclip – “T” model only.
7. Compress clips on display module and release it from the top duct cover.
8. Unplug the 5 and 3 way edge connectors from the display module.
9. Refit in reverse order.
7.9 Thermal Fuse
This is part of the element assembly and is to be replaced as part of the defrost heater element assembly.
Having a tripping temperature of 72
o
C (162oF), they are not resettable.
7.10 Replacement Of Interior Lamp
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove the lens cover with the aid of a small flat bladed screwdriver.
3. Remove the faulty lamp.
4. With the protective wrapper still covering the new lamp, fit it into the holder.
5. Cut the wrapper from the lamp. Avoid handling of the new lamp as this will shorten the life of the
new lamp.
6. Refit the lens cover and test.
NB: Only a 12 volt 10 watt halogen lamp should be fitted. It is important that the lamp terminal is tight in the
lamp socket.
Diagram 7.10
7.11 Replacement Of Low Ambient Heater - “T”
Model
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove all PC shelving.
3. Remove bottom PC air duct cover.
4. Remove polystyrene duct cover insulation.
5. Disconnect low ambient heater.
6. Refit in reverse order.
Page 38

38
7.12 Replacement Of Low Ambient Heater - “B”
Model
This element is mounted in the floor of the divider and is not replaceable. If it should be found to be open
circuit, a replacement low ambient heater can be fitted to the return air grill.
7.13 Replacement Of Low Ambient Heater - “B”
Model (In Return Air Grill)
This element is mounted in the return grill of the divider. It is of the blanket wire type on an aluminium tape
stuck to the grill itself.
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Remove all the PC shelving and crisper bins.
3. Remove the PC duct cover.
4. Remove the PC air return grill and unplug the element from the harness.
5. Peel off the old element and replace with the new.
6. Refit in reverse order.
7.14 Evaporator Replacement
The evaporator is located in the FC compartment mounted on the back wall on its own carrier, with a grill
covering a fan motor which is housed in the front cover.
Having determined that the evaporator needs replacing:
1. Unplug the refrigerator from the power supply.
2. Recover the refrigerant.
3. Remove the FC door.
4. Remove the evaporator coil cover.
5. Clean both suction and capillary pipes with emery cloth.
6. With the tube cutter, cut the suction pipe as close as possible to the induction brazed joint (cutting the
suction capillary side of the joint).
7. With a file or knife cut the capillary where it enters the transition joint on the evaporator.
8. With the element wiring disconnected, the evaporator can be removed.
9. Take the replacement evaporator and fit it to the carrier, fitting the defrost element assembly and the 2
heat shrink sleeving onto the pipes.
10.Align the evaporator and joints ready to be soldered into position.
11.Lay the product on its back.
12.Place a protective covering over the back of the liner to protect it should solder drop onto it while the
joint connections are being made.
13.Having fitted the suction and capillary lines together with a protective heat shrink sleeving placed on
the pipe first away from the heated area, heat the “J” type soldering iron to temperature with the oxyacetylene or LPG. This should be cleaned and tinned prior to the soldering operation.
14.Hook the iron over the joint area and allow the pipework to heat while applying the solder. Once the
joint appears to have a full puddle of solder around the joint area, remove the iron and allow the joint
to cool.
15.The same applies for the capillary, applying more heat to the transition joint as it is heavier in material
than the capillary.
16.Pressure test both joints.
17.Fit heat shrink sleeving over the joint and heat, having placed damp rags around the area of the ABS
liner as heating the heat shrink can cause the liner to be overheated. It is also important to keep the
thermal fuse in the element circuit away from the heat gun, as heat from the heat gun can cause the
thermal fuse to go open circuit.
Note: The solder used to solder these FC joints is a special solder containing 5% antimony and 95% tin and
is supplied with the evaporator kit. Also, the solder contains a special flux as a resin core in itself. No other
type of solder should ever be used.
Page 39

39
7.15 Removal Of The FC Evaporator Cover
Fan cover Removal Tool (T models only)
The following illustration shows a tool that can be made in your workshop. This tool can be used to release
and remove the freezer compartment fan cover in the Active Smart “T” model refrigerators. If preferred, the
tool can be made from a screwdriver with a shaft length of approximately 200mm (7 to 8 inches) long and 4.5
mm (¼ inch) diameter.
B models are removed by grasping the bottom of the evaporator cover and pulling up and forward.
Diagram 7.15
Page 40

40
7.16 Pressure Testing Of The Refrigeration System
The use of the in-line pressure gauge can speed up and eliminate the incorrect diagnosis of a leak within a
refrigeration system. In some cases it has been found to be the service manifold that was being used that
was leaking and not the system. There are very few parts on the in-line pressure gauge that can leak.
Rule one:
In pressure testing any cabinet, before disconnecting any joint please be 100% sure that it is not the joint
that is at fault, otherwise a lot of time can be lost looking for a joint/leak that doesn't exist.
Rule two:
Only use dry nitrogen to pressure test a system, NOT REFRIGERANT OR COMPRESSED AIR.
NEVER
OXYGEN
Rule three:
Don’t over pressurise the system. It could be dangerous.
How to use the In-line Pressure Gauge
Step 1:
Cut and connect the pipe circuit to be tested to the in-line pressure gauge and braze this joint.
Step 2:
At the other end of the pipe circuit being tested, crimp off the pipe with crimp off pliers and braze this end off
to totally seal the circuit.
Step 3:
Connect a nitrogen bottle to the in-line pressure gauge by means of a hose with a Schrader valvedepressing key in the hose coupling.
Step 4:
Open the nitrogen bottle fully with the regulator backed off.
Step 5:
Increase the regulator pressure in the circuit being tested to 150 psi.
Step 6:
Close nitrogen bottle valve, back off pressure regulator.
Step 7:
Disconnect the hose coupling to the Schrader valve fitting.
Step 8:
Seal the Schrader valve with its sealing cap.
Step 9:
Use a bit of masking tape to mark the face of the pressure gauge at the set pressure. Record date and time
also.
Step 10:
Check all exposed brazed joints with soap bubbles including the joints on the in-line pressure gauge.
Step 11:
Allow pipe circuit under test to sit on drop off test. This could take a number of days for a result.
NOTE: In some cases a leak may not be found by pressurising the circuit whereas a vacuum pulled on the
same circuit will find it. Keep this in mind as oil within the circuit can block a hole.
In some cases, if the brazed joint is warmed while under pressure, this can thin the oil and help to expose
the leak. A heat gun or hair drier is useful.
Page 41

41
7.17 Transporting Of Refrigerators
It is preferable to transport the refrigerator in an upright position.
It is recommended that:
If a cabinet is to be transported lying down, then the cabinet should be placed on the right-hand side when
standing facing the front of the refrigerator. If looking at the back of the refrigerator when it is laid down in
this manner, you will see the power cord entering the cabinet at the bottom and the discharge and suction
pipes on the compressor uppermost. (Refer diagram).
Diagram 7.17A
Note: We mark all our refrigerator and freezer cartons with a number of stars on one side of the carton. If
the product is to be laid on its side for transporting at any time, the side of the carton with stars on should
face upwards (see diagram). If transporting a cabinet that has been used, be sure to empty the water
evaporator tray prior to laying the cabinet down as water from the water evaporator tray can enter the
electronic power module which is attached to the side of the unit compartment.
Ideally, the product should be transported standing upright.
Diagram 7.17B
Page 42

42
8 WIRING DIAGRAM
??
??
??
?
Page 43

43
9 SERVICE REFERENCE
9.1 “B” Models
PC TOO COLD
Cold Crispers * Ambient heater open circuit
(alarm will sound and fault
code will be displayed)
- Check continuity of element using multimeter.
Ice In Crispers * PC fan fitted upside down - Fan hub to be facing PC
* PC fan not going - Check voltage to plug, check wiring polarity
* Air leakage base duct cover - Seal with foam tape on duct divider spigot
* PC sensor location - Ensure tip of sensor not against duct
Bottom of Compartment Cold –
Top Warm
* PC fan not going (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Check for mechanical obstruction
- Check power to plug
- Check polarity
- Check for broken wires
- Replace fan
Total Compartment Too Cold * FC fan not going (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Check power to plug
- Check for broken wires
- Check polarity
- Replace fan
* Short of gas - Check run percentage, if high check evaporator
- Check fully flooded evaporator, check for leak
* PC sensor inaccurate - Check calibration of sensor ice point using interface binary
or refer to thermistor resistance table in service manual
PC TOO WARM
Top of Compartment Warm –
Bottom Cold
* PC fan not going (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Check power to plug
- Check polarity
- Check for broken wires
- Check fan is not jammed with ice or anything else
- Replace fan
* PC fan upside down - Fan hub to be facing FC – refit
* Return duct iced up - De-ice duct area behind chassis
- Check PC duct insulation for good seal in return duct
- Check doors are sealing
Total Compartment Warm * PC duct blocked - Defrost evaporator chassis
- Check for door seal
* Evaporator iced up - Check defrost element, check continuity
- Check door seal / door left open
* No refrigeration - Does cabinet run? If not check power supplies. If yes
check refrigeration system
If running, check for live frost/fully flooded evaporator. If
not check for leak
* Fans not working (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Is there a 12Volt supply, PC light working
- If yes check fan connection(s) at fan end, also at power
module end of the harness
- If no check for power/control module failure.
* Power/control module
failure
- Are lamp / interface L.E.D.’s working?
- If not check display module connection
- If OK is compressor running
- If not replace power module
FC TOO COLD
Total Compartment Too Cold * FC sensor location - Check set temperature
Sensor clipped and located in correct position
* Faulty sensor - Check calibration of sensor ice point using interface binary
or refer to thermistor resistance table in service manual
* PC faulty fan (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Check PC cooling, fan running
Page 44

44
FC TOO WARM
Total Compartment Warm * Iced up evaporator - Check defrost element is working (alarm will sound and
fault code will be displayed if faulty), replace if faulty.
- Check doors are sealing or have they been left open,
adjust and advise customer.
- FC fan jammed, clear restriction, replace fan if necessary.
- Check defrost sensor position, reposition onto chassis if
not already there.
* No refrigeration - Does cabinet run? If no check power supplies. If yes
check refrigeration system. If running check for live frost
/ fully flooded evaporator, if not check for leak.
TOTAL CABINET TOO WARM * No refrigeration - Does cabinet run? If no check power supplies. If yes
check refrigeration system. If running, check for live
frost/fully flooded evaporator. If not, check for leak.
- Compressor is not running, check power/control module
voltage outputs. Check compressor and ancillaries.
- Check reed switches are working OK by entering the
Input/Output mode (refer to Section 6.2.4) and placing a
magnet over the reed switch
FC COOLING - PC WARMING * Iced up evaporator - Check defrost circuit continuity
- Doors sealing, adjust
- PC fan is running, if not refer PC too warm
* Iced up return duct - De-ice duct area
- Check PC duct insulation for good seal in return duct
- Check doors are sealing
ALARM ON * Defrost heater - Check display for any fault code
- Check defrost element continuity
- Put cabinet into manual defrost, wait for defrost relay to
“click” on (2 ½ minutes after pressing buttons)
- If no “click”, check power/control module
- If “click” heard, check the defrost heater 110v output at the
power/control module
* Sensors (alarm will sound
and fault code will be
displayed)
- Check console for fault codes 0-5
- Sensors above or below limit, refer thermistor service
table in service manual
* Door switch fault - Check that no fault code is shown on the display
- Check that PC/FC doors activate reed switches
- Check also reed switches with magnet
- Check wiring harness to power/control module
FAULT DISPLAYED, NO ALARM * Display flashing fault code,
but no alarm sounding
- Alarm has been switched off by user
- Piezo alarm faulty, replace power/control module
LIGHT NOT FUNCTIONING
* Blown bulb - Check power supply to socket 7Volts, if nil check plug at
display module
- Check continuity of bulb, if nil replace
* Cabinet type - Power / console module not initialised, close FC door and
press compartment select button
* Poor connection - Spread halogen bulb legs
- Check lamp holder, replace where possible
- Check connector on display module
CONSOLE NO L.E.D. LIGHTS * Power/control module no
power
- Check harness and plugs on 5 way display module
harness at both ends
- Initiate cabinet
* Power/control module not
initialized
- Initialize power/control module, close FC door and push
any button on display module
- If raspberry noise still made, check door switches
Page 45

45
NOISY FAN FC * Ice on cover - Clear ice off cover and check doors are sealing
* Ice on grill - Clear ice off grill and check doors are sealing
* Fan off mountings - Refit
* Wires touching - Tuck wires away from fan blade
* Capillary touching - Shift capillary from fan area, make sure it is not touching
any part of the cabinet
* Fan motor noisy - Fit replacement
* Wires pulled tight - Re route wiring
ICE BUILD UP IN
COMPARTMENT
* Doors sealing - Check gaskets are sealing, adjust gaskets
- Check fans are operating
REFRIGERATION NOISE * Popping, farting - Evacuate and recharge with ISCEON 49
* Gurgling, whistling - Check alignment of capillary and apply sound dampening
tape
Page 46

46
9.2 “T” Models
PC TOO COLD * FC fan not going (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Check power to plug
- Check polarity
- Replace fan
* Short of gas - Check run percentage, if high check evaporator
- Check fully flooded evaporator, check for leak
* PC sensor inaccurate - Check calibration of sensor ice point using interface binary
or refer to thermistor resistance table in service manual
PC TOO WARM * Evaporator iced up - Check defrost element, check continuity
- Check door seal/door left open
* No refrigeration - Does cabinet run? If no, check power supplies. If yes,
check refrigeration system
- If running, check for live frost/fully flooded evaporator. If
not, check for leak
* Fans not working (alarm will
sound and fault code will be
displayed)
- Is there a 12Volt supply, PC light working
- If yes, check fan connection(s) at fan end, also at
power/control module end of the harness
- If no, check for power/control module failure
* Power/control module
failure
- Are lamp / interface L.E.D.’s working
- If not check display module connection
- If OK is compressor running ?
- If not replace power/control module
* PC delivery duct blocked - De-ice area behind chassis
-
FC TOO COLD * FC sensor location - Check set temperature
- Sensor clipped and located in correct position
* Faulty sensor - Check calibration of sensor ice point using interface binary
or refer to thermistor resistance table in service manual
* PC faulty fanr - Check PC cooling, fan running
FC TOO WARM * No refrigeration - Does cabinet run? If no check power supplies. If yes
check refrigeration system
- If running, check for live frost/fully flooded evaporator. If
not, check for leak
TOTAL CABINET TOO WARM * No refrigeration - Does cabinet run? If no check power supplies. If yes
check refrigeration system
- If running, check for live frost/fully flooded evaporator
- If not, check for leak
- Compressor is not running, check power/control module
voltage outputs
- Check compressor and ancillaries
FC COOLING - PC WARMING * Iced up evaporator - Check defrost circuit continuity
- Doors sealing, adjust
- Is PC fan is running? (alarm will sound and fault code will
be displayed if faulty). If not, refer PC too warm
Page 47

47
ALARM ON * Defrost heater - Check display for any fault code
- Check defrost element continuity
- Put cabinet into manual defrost, wait for defrost relay to
“click” on (2 ½ minutes after pressing buttons)
- If no “click”, check power/control module
- If “click” heard, check the defrost heater 110v output at the
power/control module
* Sensors - Check display for fault codes 0-5
- Sensors above or below limit, refer thermistor service
table in service manual
* Door switch fault - Check that no fault code is shown on the display
- Check that PC / FC doors activate reed switches
- Check also reed switches with magnet
- Check wiring harness to power/control module
- Check wiring harness to console board
FAULT DISPLAYED, NO ALARM * Display flashing fault code,
but no alarm sounding
- Alarm has been switched off by user
- Piezo alarm faulty on board, replace board
LIGHT NOT FUNCTIONING * Blown bulb - Check power supply to socket 7Volts, if nil check plug at
display module
- Check continuity of bulb, nil replace
* Cabinet type - Power/control module not initialised, close FC door and
press compartment select button
* Poor connection - Spread halogen bulb legs
- Check lamp holder, replace where possible
- Check connector on display module
CONSOLE - NO L.E.D. LIGHTS * Power/control module no
power
- Check harness and plugs on 5 way display module
harness at both ends
- Initialize cabinet
RASPBERRY NOISE * Power/control module not
initialized
- Initialise power/control module, close FC door and push
any button on display module
- If raspberry noise still made, check door switches
NOISY FAN PC * Wires touching - Tuck wires away from fan blade
* Faulty fan - Fit replacement
NOISY FAN FC * Ice on cover - Clear ice off cover and check doors are sealing
* Ice on grill - Clear ice off grill and check doors are sealing
* Fan off mountings - Refit
* Wires touching - Tuck wires away from fan blade
* Capillary touching - Shift capillary from fan area make sure it is not touching
any part of the cabinet
* Fan motor noisy - Fit replacement
* Wires too tight - Re route wiring
ICE BUILD UP IN
COMPARTMENT
* Doors sealing - Check gaskets sealing, adjust gaskets
- Check fans are operating
REFRIGERATION NOISE * Popping, farting - Evacuate recharge with ISCEON 49, check alignment of
capillary
* Gurgling, whistling - Check alignment of capillary and apply sound dampening
tape
Page 48

48
Does the
display
module
indicate a
fault code?
Refer to Section
6.2.1
Repair or replace
faulty components
Replace
power/control
module
Refer to Section
10.12
Replace display
module
Is there
power to the
refrigerator?
Check house
outlet socket
No
Yes
Has product
been
initialised?
Is there 12V
DC between the
power/control module
and the display
module?
No
Is there
power to the
power/control
module?
Are any
L.E.D.s on at
the display
module?
Is the
compressor
warm?
Yes
Yes
Is there 12V
DC at the
display
module?
Repair or replace
faulty components
No
With FC door
closed and PC
door open, press
Mode button
No
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Refer to Section
10.13
10 FLOW DIAGRAMS
10.1 Refrigerator Not Operating
Page 49

49
Is continuity
of power cable and
all harness
connections
OK?
Compressor
circuitry
/wiring OK?
Repair or replace
faulty components
Replace
power/control
module
Is there
power to the
refrigerator?
(PC light &
L.E.D.s on)
Repair fault in
house wiring
No
Is there
power to the
house outlet
socket?
Yes
Yes
No
Repair or replace
faulty components
No
No
Yes
Yes
10.2 No Power To Power/Control Module And/Or
Display Module
Page 50

50
10.3 PC/FC Warm
Is there
excessive ice
on FC cover
or
evaporator?
Is defrost
heater installed
correctly or drain
iced/blocked?
Does the
compressor
run?
Adjust temperature
settings.
Advise customer
product OK
Does the
display
module
indicate a
fault code?
Is the defrost
sensor
located
correctly?
Is Smart Tool
download
available?
Refer to Section
10.10
Refer to Section
6.2.1
Repair or replace
faulty components
Are
temperature
settings
correct?
Are
temperatures
of contents of
PC & FC
OK?
Advise customer
temperatures OK
Advise customer
refrigerator working
OK
Refer to Section
10.6
Repair/relocate
Repair/clear
blockage etc
Are there
any signs that FC
& PC temperatures,
fan speeds or
defrosts are
not OK?
Using an
external sensor,
are the temperatures
of contents of PC
& FC OK?
No
No
No
No
NoNo
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Page 51

51
Air ducts
blocked with
ice?
Adjust temperature
settings.
Advise customer
product OK
Does the
display
module
indicate a
fault code?
Are sensors
and covers
installed
correctly?
Is Smart Tool
download
available?
Refer to Section
6.2.1
Repair or replace
faulty components
Are
temperature
settings
correct?
Check door gasket
sealing is OK
Install components
correctly, sealing
any air leaks
No
YesYes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Do download
temperatures and
actual contents
temperatures
match?
No
No
Clear ice & check
for causes
Yes
Yes
No
10.4 FC Too Cold – PC Too Warm
Page 52

52
Are actual
temperatures
correct?
Adjust temperature
settings.
Advise customer
product OK
Does the
display
module
indicate a
fault code?
Are contents
of PC frozen?
Is Smart Tool
download
available?
Refer to Section
6.2.1
Repair or replace
faulty components
Are
temperature
settings
correct?
Check assembly of
all ducts & covers
Check for
blockages in air
duct, ice etc
YesYes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Are recorded
temperatures
correct?
No
Advise customer
temperatures are
OK
Yes
No No
No
Yes
10.5 PC Too Cold
Page 53

53
Does frost
pattern on
evaporator indicate
heavy usage?
Is Smart Tool
data
available?
Repair or replace
faulty components
Check that drain is
not blocked
Are the door
gaskets
sealing
correctly?
Explain to customer that
some ice/condensation is
normal in heavy usage
situations
Is the product
getting heavy
usage?
No
No
No
No
Yes
Yes Yes
Yes
10.6 Ice/Condensation Forming
Page 54

54
Are all
connections
OK?
Has product
been
initialised?
Check is light
bulb OK?
With FC door
closed and PC
door open, press
Mode button
Replace faulty
component
Repair
Replace
power/control
module
Repair/replace
faulty component
Refer to
Section 9.8
OK?
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
No
No
10.7 No Light
Page 55

55
Is door
magnet in
place?
Switch product off and
then on at power outlet
to remove from any
special modes
Place diagnostics
into input/output
mode. Refer
Section 6.2.4
If available, a Smart Tool data
download will verify door switch
failures by very high door open
counts V actual openings
Replace reed
switch
Repair
Yes
No
Yes
No
Does FC door
L.E.D. switch on &
off as FC door is
opened and closed?
Does PC light
switch on & off as
PC door is opened
and closed?
Are reed switch
harness connections
at power/control
module OK?
Refit door magnet
No
Yes
No
10.8 Door Switch Not Operating
Page 56

56
Does
download
confirm
defrost
failures?
Does the
display
module
indicate a
fault code?
Is Smart Tool
download
available?
Refer to Section
6.2.1
Repair or replace
faulty components
Advise customer
no fault found
Check correct operation of
defrost heater. Check location
of defrost sensor. Check if door
has been left ajar
Yes
No
Repair/replace
faulty components
Are defrost heater
resistance and
connections OK?
Is there excessive
solid ice build-up
on or around
evaporator?
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
10.9 Defrost Heater Faults
Page 57

57
Refer to Section
10.1
Compressor will
not run and is cold
to touch
Refer to Section
10.12
Compressor will
not run and is hot
to touch
Refer to Section
10.11
Compressor runs
continuously
Are the
L.E.D.s on
the display
module
illuminated?
Is
refrigeration
taking place?
With FC door
closed and PC
door open, press
Mode button
Check for loss of
gas (leak) or
blockage
Check for correct fitting of
sensors. Check sensor
resistances (refer Section
6.1.11)
Refer to Section
10.3
Check for loss of
gas (leak) or
blockage
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Are the FC/PC
reaching set
temperatures?
Yes
No
10.10 Compressor Faults
10.11 Compressor Runs Continuously
Page 58

58
When defrost sensor
reaches +8 degrees C (46
degrees F) the compressor
will start
Has the
system gone
into defrost
mode?
Is current
being drawn
by defrost
element?
Yes
Check compressor
and system for
leaks/blockages and
repair as required
Yes
No
Remove FC cover.
Is there a full frost
pattern on the
evaporator?
Yes
10.12 Compressor Will Not Run And Is Hot To Touch
10.13 Compressor Electrical Tests
OK?
Refit original
electronic
module/inverter
Are
compressor
winding
resistances
OK?
OK?
Substitute
power/control
module
Yes
No
Replace
compressor
No
Are electrical
connections
to
compressor
OK?
Substiute electronic
module/inverter
Repair connections
OK?
Refit replacement
electronic
module/inverter
No
Yes
Yes
No
Problem solved
Yes
Yes
Page 59

59
Are the
compartment
temperatures
set correctly?
Wait until
refrigerator
completes defrost
cycle
Adjust settings.
Advise customer
product OK
Check
temperatures
Check compressor
and system for
leaks/blockage and
repair as required
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Remove FC cover.
Is there a full frost
pattern on the
eva
p
orator?
Yes
Should the
compressor be
running? (Check
defrost and cycle
temperatures)
Is there power to
the compressor?
Refer Section
6.1.5.4
Repair as required
No
Yes
10.14 Refrigeration System Faults
 Loading...
Loading...