Fairchild Semiconductor MM74HC423ASJ, MM74HC423ASJX, MM74HC423AMTCX, MM74HC423AM, MM74HC423AMX Datasheet
...
September 1983
Revised February 1999
MM74HC423A Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator
© 1999 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation DS005338.prf www.fairchildsemi.com
MM74HC423A
Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator
General Description
The 74HC423A high speed monostable multivibrators (one
shots) utilize advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology.
They feature speeds comp arable to low power Schottky
TTL circuitry while r etaining the low power and high noise
immunity characteristic of CMOS circuits.
Each multivibrator fea tures b oth a n egative , A, a nd a po sitive, B, transition trigg ered input, either of which can be
used as an inhibit input. Also includ ed is a clear input that
when taken LOW resets the one shot . The MM74HC423A
cannot be triggered from clear.
The MM74HC423A is retriggerable. That is, it may be triggered repeatedly while i ts outputs are generating a p ulse
and the pulse will be extended.
Pulse width stability over a wide range of temperature and
supply is achieved using linear CMOS techniques. The output pulse equation is sim ply: PW = (R
EXT
) (C
EXT
); where
PW
is in seconds, R is in ohms, and C is in farads. All inputs
are protected from damage due to static discharge by
diodes to V
CC
and ground.
Features
■ Typical propagation delay: 40 ns
■ Wide power supply range: 2V–6V
■ Low quiescent current: 80 µA maximum (74HC Series)
■ Low input current: 1 µA maximum
■ Fanout of 10 LS-TTL loads
■ Simple pulse width formula T = RC
■ Wide pulse range: 400 ns to ∞ (typ)
■ Part to part variation: ±5% (typ)
■ Schmitt Trigger A & B in puts allow infinite ri se and fall
times on these inputs
Ordering Code:
Devices also availab le in Tape and Reel. Specify by appending th e s uffix let t er “X” to the ordering cod e.
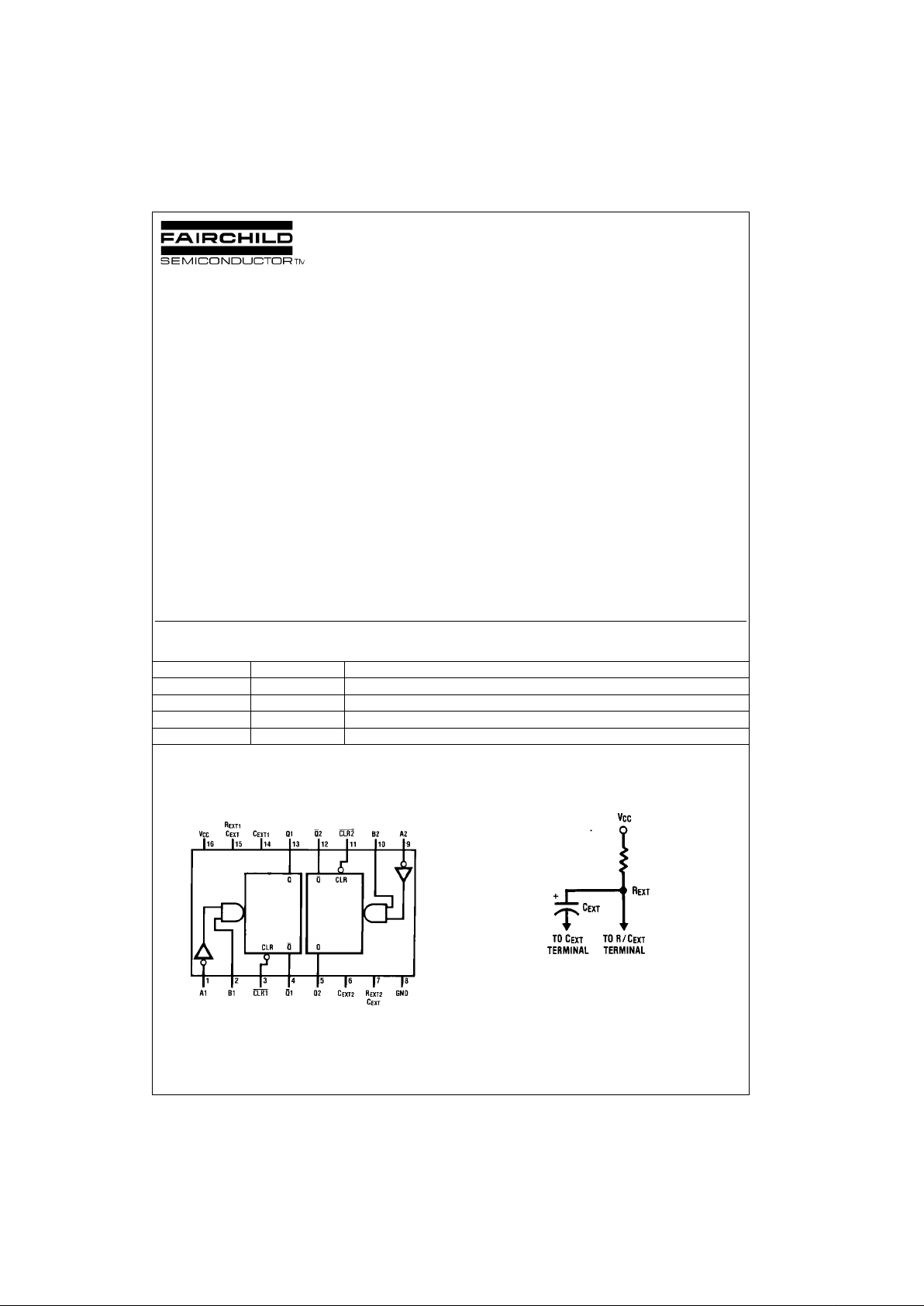
Connection Diagrams
Pin Assignments f or DIP, SOIC, SOP and TSSOP
Top View
Timing Component
Note: Pin 6 and Pin 14 must be ha rd-wired to GND.
Order Number Package Number Package Description
MM74HC423AM M16A 16-Lead Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC), JEDEC MS-012, 0.150” Narrow
MM74HC423ASJ M16D 16-Lead Small Outline Package (SOP), EIAJ TYPE II, 5.3mm Wide
MM74HC423AMTC MTC16 16-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP), JEDEC MO-153, 4.4mm Wide
MM74HC423AN N16E 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300” Wide
www.fairchildsemi.com 2
MM74HC423A
Truth Table
H = HIGH Level
L = LOW Level
↑=Transition from LOW-to-High
↓=Transition from HIGH-to-LOW
= One HIGH Level Pulse
= One LOW Level Pulse
X = Irrelevant
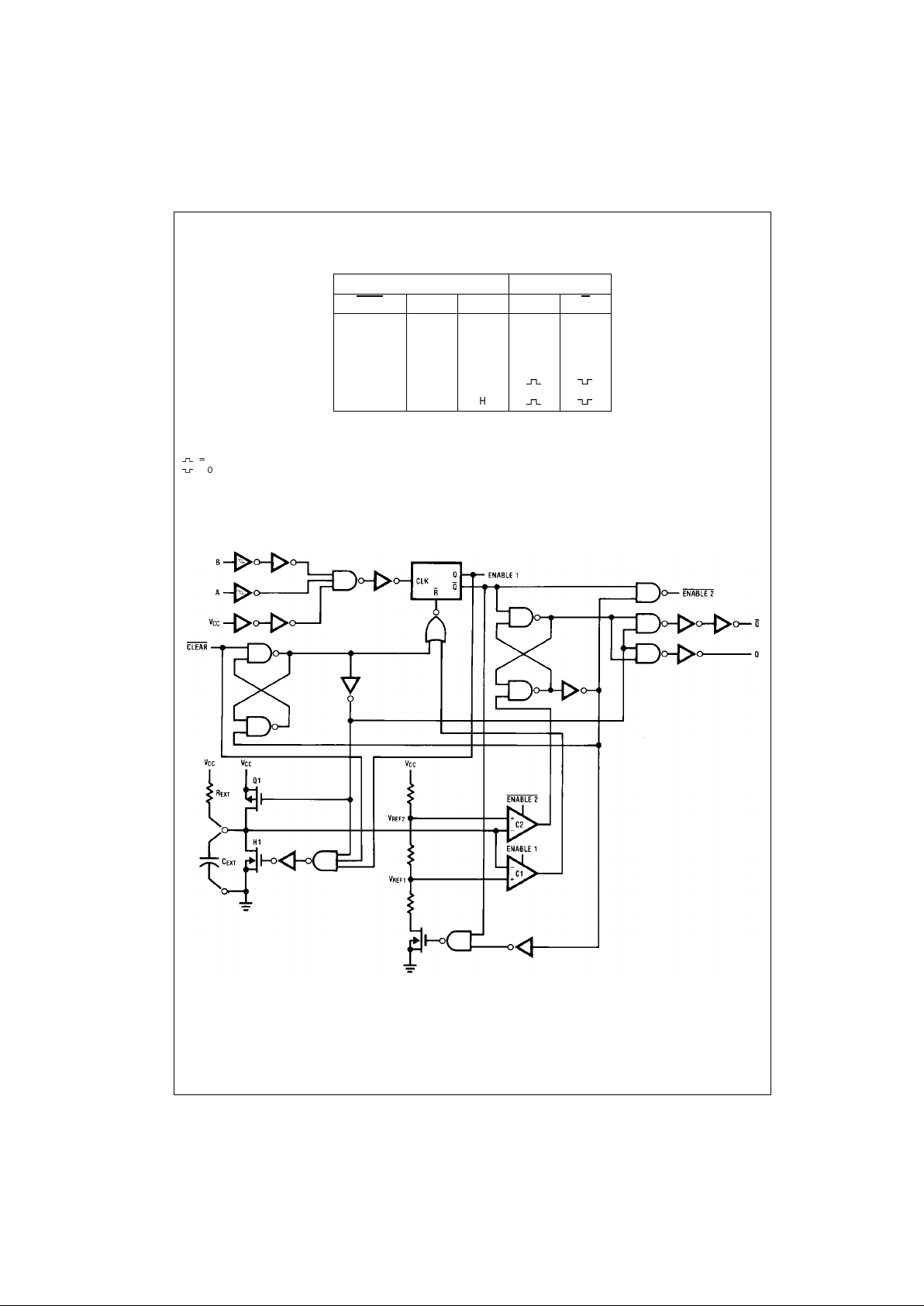
Logic Diagram
Inputs Outputs
Clear
ABQQ
LXXLH
XHXLH
XXLLH
HL↑
H ↓ H

3 www.fairchildsemi.com
MM74HC423A
Theory of Operation
FIGURE 1.
TRIGGER OPERATION
As shown in Figure 1 an d the Logic Diagram before an
input trigger occurs, the one-shot is in the quiescent state
with the Q output LOW, and the timing capacitor C
EXT
com-
pletely charged to V
CC
. When the trigger input A goes from
V
CC
to GND (while inputs B and clear are held to VCC) a
valid trigger is recognized, which turns on comparator C1
and N-Channel transistor N11. At the same time the output
latch is set. With transistor N1 on, the ca pacitor C
EXT
rap-
idly discharges toward GND until V
REF1
is reached. At this
point the output o f c ompar ator C 1 c hanges state an d tra nsistor N1 turns OFF. Comparator C1 then turns OFF while
at the same time comp arator C2 turns on. Wi th transistor
N1 OFF, the capacitor C
EXT
begins to charge through the
timing resistor, R
EXT
, toward VCC. When the voltage across
C
EXT
equals V
REF2
, comparator C2 chan ges state causing
the output latch to reset (Q go es LOW) whi le at the sam e
time disabling comparator C2. This ends the timing cycle
with the one-shot in the quiescent state, waiting for the next
trigger.
A valid trigger is also recognized when trigger input B goes
from GND to V
CC
(while input A is at GND and input clear
is at V
CC
2.)
It should be noted that in the quiescent sta te C
EXT
is fully
charged to V
CC
causing the current thro ugh resistor R
EXT
to be zero. Both comparators are “OFF” with the total
device current due only to r everse junction leakages. An
added feature of the M M7 4H C42 3A i s th at the ou tput latch
is set via the input trig ger without regard to the capacitor
voltage. Thus, propa gation delay from trigger to Q is i ndependent of the value of C
EXT
, R
EXT
, or the duty cycle of the
input waveform.
RETRIGGER OPERATION
The MM74HC423A is re trig gered if a valid tr igge r occurs 3
followed by another trigger 4 before the Q output has
returned to the qu iescent (zero) state. Any retrigger, after
the timing node voltage at pin or has begun to rise from
V
REF1
, but has not yet reached V
REF2
, will cause an
increase in output pulse width T. When a valid retrigger is
initiated 4, the voltage at the R/C
EXT
pin will again drop to
V
REF1
before progressing along the RC charging curve
toward V
CC
. The Q output will remain high until time T, after
the last valid retrigger.
Because the trigger-control circuit flip-flop resets shortly
after C
X
has discharged to the reference voltage of the
lower reference c ircuit, th e minimum retrigger time, t
rr
is a
function of internal prop agation delays and the discharge
time of C
X
:
Another removal/ret rigger time occurs when a short clear
pulse is used. Upon receipt of a clear, the one shot must
charge the capacitor up to the upper tr ip point before the
one shot is ready to r eceive the next trigger. This time is
dependent on the capacitor used and is approximately:
 Loading...
Loading...