Fairchild Semiconductor FDN306P Datasheet
December 2001
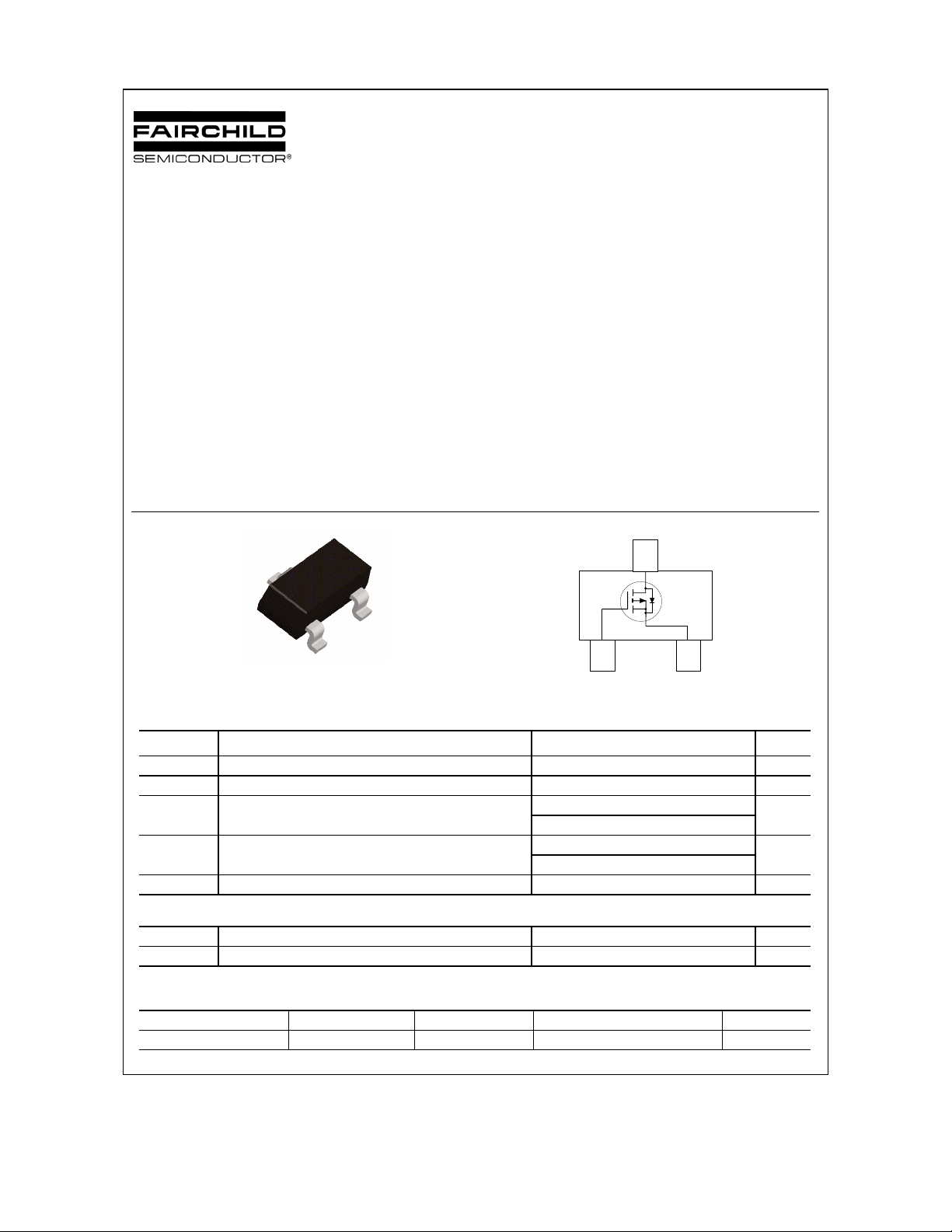
FDN306P
P-Channel 1.8V Specified PowerTrench
MOSFET
FDN306P
General Description
This P-Channel 1.8V specified MOSFET uses
Fairchild’s advanced low voltage PowerTrench process.
It has been optimized for battery power management
applications.
Applications
• Battery management
• Load switch
• Battery protection
D
Features
• –2.6 A, –12 V. R
R
R
• Fast switching speed
• High performance trench technology for extremely
low R
• SuperSOT
power handling capability than SOT23 in the same
footprint
DS(ON)
TM
-3 provides low R
= 40 mΩ @ VGS = –4.5 V
DS(ON)
= 50 mΩ @ VGS = –2.5 V
DS(ON)
= 80 mΩ @ VGS = –1.8 V
DS(ON)
and 30% higher
DS(ON)
D
S
G
SuperSOT -3
TM
Absolute Maximum Ratings T
G
o
=25
C unless otherwise noted
A
Symbol Parameter Ratings Units
V
Drain-Source Voltage –12 V
DSS
V
Gate-Source Voltage
GSS
ID Drain Current – Continuous (Note 1a)
– Pulsed
Maximum Power Dissipation (Note 1a) 0.5 PD
TJ, T
Operating and Storage Junction Temperature Range –55 to +150
STG
(Note 1b)
±8
–2.6
–10
0.46
S
V
A
W
°C
Thermal Characteristics
R
θJA
R
θJC
Thermal Resistance, Junction-to-Ambient
Thermal Resistance, Junction-to-Case
(Note 1a) 250
(Note 1) 75
Package Marking and Ordering Information
Device Marking Device Reel Size Tape width Quantity
306 FDN306P 7’’ 8mm 3000 units
2001 Fairchild Sem iconductor Corporation
°C/W
°C/W
FDN306P Rev D (W )
FDN306P
Electrical Characteristics T
= 25°C unless otherwise noted
A
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Off Characteristics
BV
Drain–Source Breakdown Voltage
DSS
∆BVDSS
∆T
I
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current VDS = –10 V, VGS = 0 V –1
DSS
I
GSSF
I
GSSR
Breakdown Voltage Temperature
Coefficient
J
Gate–Body Leakage, Forward VGS = 8 V, VDS = 0 V 100 nA
Gate–Body Leakage, Reverse VGS = –8 V, VDS = 0 V –100 nA
V
= 0 V, ID = –250 µA
GS
= –250 µA,Referenced to 25°C
I
D
–12 V
–3
mV/°C
µA
On Characteristics (Note 2)
V
Gate Threshold Voltage
GS(th)
∆VGS(th)
∆TJ
R
DS(on)
Gate Threshold Voltage
Temperature Coefficient
Static Drain–Source
On–Resistance
I
On–State Drain Current VGS = –4.5 V, VDS = –5 V –10 A
D(on)
V
= VGS, ID = –250 µA
DS
= –250 µA,Referenced to 25°C
I
D
VGS = –4.5 V, ID = –2.6 A
V
= –2.5 V, ID = –2.3 A
GS
= –1.8V, ID = –1.8 A
V
GS
= –4.5 V, ID = –2.6A , TJ=125°C
V
GS
–0.4 –0.6 –1.5 V
2.5
30
39
54
40
40
50
80
54
mV/°C
mΩ
gFS Forward Transconductance VDS = –5 V, ID = –2.6 A 10 S
Dynamic Characteristics
C
Input Capacitance 1138 pF
iss
C
Output Capacitance 454 pF
oss
C
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
rss
= –6 V, V
V
DS
f = 1.0 MHz
= 0 V,
GS
302 pF
Switching Characteristics (Note 2)
t
Turn–On Delay Time 11 20 ns
d(on)
tr Turn–On Rise Time 10 20 ns
t
Turn–Off Delay Time 38 61 ns
d(off)
tf Turn–Off Fall Time
Qg Total Gate Charge 12 17 nC
Qgs Gate–Source Charge 2 nC
Qgd Gate–Drain Charge
= –6 V, ID = –1 A,
V
DD
= –4.5 V, R
V
GS
= –6 V, ID = –2.6 A,
V
DS
V
= –4.5 V
GS
GEN
= 6 Ω
35 56 ns
3 nC
Drain–Source Diode Characteristics and Maximum Ratings
IS Maximum Continuous Drain–Source Diode Forward Current –0.42 A
VSD Drain–Source Diode Forward
Voltage
Notes:
1. R
is the sum of the junction-to-case and case-to-ambient thermal resistance where the case thermal reference is defined as the sol der mounting surface of
θJA
the drain pins. R
is guaranteed by design while R
θJC
a) 250°C/W when mounted on a
2
pad of 2 oz. copper.
0.02 in
Scale 1 : 1 on letter size paper
2. Pulse Test: Pulse Width ≤ 300 µs, Duty Cycle ≤ 2.0%
VGS = 0 V, IS = –0.42 (Note 2) –0.6 –1.2 V
is determined by the user's board design.
θCA
b) 270°C/W when mounted on a
minimum pad.
FDN306P Rev D W )
 Loading...
Loading...