Page 1
®
SERVICE MANUAL
Stylus PHOTO 890
Color ink jet printer
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290
Stylus PHOTO 1290/1280
Page 2

Notice
All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION.
All effort have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual. However, should any errors be detected, SEIKO EPSON would
greatly appreciate being informed of them.
The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
All effort have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual. However, should any errors be detected, SEIKO EPSON would
greatly appreciate being informed of them.
The above not withstanding SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION can assume no responsibility for any errors in this manual or the consequences
thereof.
EPSON is a registered trademark of SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION.
General Notice: Other product names used herein are for identification purpose only and may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective owners. EPSON disclaims any and all rights in those marks.
Copyright © 2000 SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION.
Imaging & Information Product Division
TPCS Quality Assurance Center
Page 3
PRECAUTIONS
Precautionary notations throughout the text are categorized relative to 1)Personal injury and 2) damage to equipment.
DANGER Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in serious or fatal personal injury. Great caution should be exercised in performing
procedures preceded by DANGER Headings.
WARNING Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in damage to equipment.
The precautionary measures itemized below should always be observed when performing repair/maintenance procedures.
DANGER
1. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM THE POWER SOURCE AND PERIPHERAL DEVICES PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR PROCEDURES.
2. NO WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS UNFAMILIAR WITH BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL ELECTRONICS
TECHNICIANS IN THEIR LINE OF WORK.
3. WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DICTATED WITHIN THIS MANUAL, DO NOT CONNECT THE UNIT TO A POWER SOURCE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. WHEN
THE POWER SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CONNECTED, USE EXTREME CAUTION IN WORKING ON POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
4. WHEN DISASSEMBLING OR ASSEMBLING A PRODUCT, MAKE SURE TO WEAR GLOVES TO AVOID INJURIER FROM METAL PARTS WITH SHARP EDGES.
WARNING
1. REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY BY AN EPSON CERTIFIED REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
2. MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE SOURCE VOLTAGES IS THE SAME AS THE RATED VOLTAGE, LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATING PLATE. IF THE EPSON
PRODUCT HAS A PRIMARY AC RATING DIFFERENT FROM AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO NOT CONNECT IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3. ALWAYS VERIFY THAT THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED FROM THE POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING PRINTED CIRCUIT
BOARDS AND/OR INDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4. IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE MICROPROCESSORS AND CIRCUITRY, USE STATIC DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAPS, WHEN
ACCESSING INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5. DO NOT REPLACE IMPERFECTLY FUNCTIONING COMPONENTS WITH COMPONENTS WHICH ARE NOT MANUFACTURED BY EPSON. IF SECOND SOURCE IC OR
OTHER COMPONENTS WHICH HAVE NOT BEEN APPROVED ARE USED, THEY COULD CAUSE DAMAGE TO THE EPSON PRODUCT, OR COULD VOID THE
WARRANTY OFFERED BY EPSON.
Page 4

PREFACE
This manual describes basic functions, theory of electrical and mechanical operations, maintenance and repair procedures of EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/
1290. The instructions and procedures included herein are intend ed for the experienced repair technicians, and attention should be given to the precautions on the
preceding page. The chapters are organized as follows:
CHAPTER 1. PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS
Provides a general overview and specifications of the product.
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Describes the theory of electrical and mechanical operations of the product.
CHAPTER 3. TROUBLESHOOTING
Provides the step-by-step procedures for troubleshooting.
CHAPTER 4. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
Describes the step-by-step procedures for disassembling and assembling the
product.
CHAPTER 5. ADJUSTMENTS
Provides Epson-approved methods for adjustment.
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
Provides preventive maintenance procedures and the lists of Epson-approved
lubricants and adhesives required for servicing the product.
APPENDIX
Provides the following additional information for reference:
• EEPROM Address Map
• Connector Pin Assignments
• Component Layout
• Exploded Diagrams
• Electrical Board Circuit Diagrams
Page 5

Symbols Used in this Manual
Various symbols are used throughout this manual either to provide additional information on a specific topic or to warn of possible danger present
during a procedure or an action. Be aware of all symbols when they are used, and always read NOTE, CAUTION, or WARNING messages.
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
C A U T I O N
C H E C K
P O I N T
W A R N I N G
Indicates an operating or maintenance procedure, practice or condition that is necessary to keep the product’s quality.
Indicates an operating or maintenance procedure, practice, or condition that, if not strictly observed, could result in damage to, or
destruction of, equipment.
May indicate an operating or maintenance procedure, practice or condition that is necessary to accomplish a task efficiently. It may also
provide additional information that is related to a specific subject, or comment on the results achieved through a previous action.
Indicates an operating or maintenance procedure, practice or condition that, if not strictly observed, could result in injury or loss of life.
Page 6

Revision Status
Revision Issued Date Description
A November 16, 2000 First Release
Revision:
• page-78: A warning message for static electricity added.
B December 27, 2000
C February 8, 2001
• page -79: Caution messages for torque and ink tube position added
• page -90& page -92: Caution messages for ink tube installation added.
• page -121: PG adjustment tool added.
Revision:
• All chapters: Stylus PHOTO 1280(for EAI) added.
• page -68: Misdescription for Maintenance Request Error corrected.
• page -128: Stylus PHOTO 1280(for EAI) added to Destination in the adjustment program.
• page -182: C393 MAIN-C Board circuit diagram added.
D June 4,2002
Revision:
• “Lubrication” on page -156: The lubrication of Oil O-12 for the Stylus Photo 1280/129 0 added.
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS
1.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 11
1.1.1 Features ...................................................................................................... 11
1.1.2 Accessories, Consumable Products, and Options ...................................... 12
1.2 Basic Specifications .......................................................................................... 14
1.2.1 Printing Specification ................................................................................ 14
1.2.2 Control Code ........................................................... ................................... 14
1.2.3 Paper Feeding ............................................................................................ 14
1.2.4 Input Data Buffer ....................................................................................... 14
1.2.5 Paper Specifications ................................................................................... 15
1.2.5.1 EPSON Special Media ............................................................... ....... 15
1.2.6 Printing Area .............................................................................................. 17
1.2.6.1 Cut Sheet ........................................................................................... 17
1.2.6.2 Envelopes .......................................................................................... 18
1.2.7 Adjust Lever .............................................................................................. 18
1.2.8 Ink Cartridge ................................................... ........................................... 19
1.2.9 Electric Specification ...................................... ... .................................... ... . 20
1.2.10 Reliability ................................................................................................ 20
1.2.11 Environmental Condition ......................................................................... 21
1.3 Interface ............................................................................................................. 22
1.3.1 Parallel Interface (Forward Channel) ........................................................ 22
1.3.2 Parallel Interface (Reserve Channel) ......................................................... 25
1.3.3 USB Interface ............................................................................................ 26
1.3.4 Prevention of Data Transfer Time-out ....................................................... 27
1.3.5 Interface Selection ..................................................................................... 27
1.3.6 IEEE1284.4 Protocol .......... .................................... ................................... 27
1.4 Operations ......................................................................................................... 28
1.4.1 Buttons ....................................................................................................... 28
1.4.2 Indicators ................................................................................................... 28
1.4.3 Panel Functions ....................................................... ................................... 28
1.4.4 Special Setting Mode ................................................................................. 29
1.4.5 Printer Initialization ................................................................................... 30
1.4.6 Initialization Value .................................................................................... 30
1.5 Dimension .......................................................................................................... 31
Chapter 2 OPERATING PRINCIPLES
2.1 Overview .......................................................................... .................................. 34
2.1.1 Printhead Mechanism ................................................................................ 35
2.1.2 Carriage Mechanism .................................................................................. 36
2.1.2.1 Carriage Motor (CR Motor) .............................................................. 36
2.1.2.2 Platen Gap (PG) /Parallelism Adjustment Mechanism ..................... 37
2.1.2.3 Carriage Home Position (HP) Detection ........................................... 37
2.1.3 Paper Feeding Mechanism .................................................. ....................... 37
2.1.3.1 CR Lock Mechanism ..................................................... .................... 39
2.1.4 Paper Loading Mechanism ........................................................................ 40
2.1.4.1 Drive Transmission to the ASF Unit ................................................. 40
2.1.4.2 Paper Loading Operation .................................................................. 41
2.1.4.3 Pump Mechanism .............................................................................. 42
2.1.4.4 Capping Mechanism .......................................................................... 43
2.2 Electrical Circuit Operating Principles .......................................................... 44
2.2.1 C378PSB/PSE Board ....................................................... .......................... 44
2.2.1.1 Electrical Circuit ................................................ ............................... 44
2.2.1.2 Protection Circuits ............................................................................. 46
2.2.1.3 Power Supply Control Function ............................................... ......... 46
2.2.1.4 Energy Save Mode ............................................................................ 46
2.2.2 C393MAIN Board Circuit Operation Principles ....................................... 47
2.2.2.1 Printhead Driver Circuit .................................................................... 50
2.2.2.2 RTC (Real Time Clock)/ Reset/ EEPROM Circuit ........................... 51
2.2.2.3 Motor Driver Circuit ......................................................................... 52
2.2.2.4 ASF/Pump Motor Driver Circuit ....................................................... 57
2.2.2.5 Sensor Circuit .................................................................................... 58
Chapter 3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.1 Overview .......................................................................... .................................. 61
3.1.1 Self-Diagnostic Function ........................................................................... 62
3.1.1.1 Troubleshooting with LED Error Indicators ..................................... 62
3.1.1.2 Error Conditions ................................................................................ 62
3.1.1.3 Remedies for Paper Out Error ........................................................... 65
Page 8

3.1.1.4 Remedies for the Paper Jam Error ..................................................... 67
3.1.1.5 Remedies for No Ink Cartridge Error/Ink Cartridge Problem ........... 67
3.1.1.6 Remedies for Maintenance Request Error ......................................... 68
3.1.1.7 Remedies for Fatal Error ................................................................... 69
3.1.2 Isolating the Faulty Part on the Power Supply Board ................................ 72
3.1.3 Isolating the Faulty Part according to the Phenomenon ............................ 72
Chapter 4 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
4.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 78
4.1.1 Precaution for Disassembling the Printer .................................................. 78
4.1.2 Tools .......................................................................................................... 79
4.1.3 Specifications for Screws .......................................................................... 80
4.1.4 Service Checks After Repair ..................................................................... 81
4.2 Disassembly Procedures ................................................................................... 82
4.2.1 HOUSING Removal .................................................................................. 83
4.2.2 Circuit Board Assembly Removal ............................................................. 84
4.2.3 Panel Unit Removal ................................................... ................................ 86
4.2.4 Printhead Unit Removal ............................................................................ 88
4.2.5 TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY Removal ........................................... . 89
4.2.6 Ink Unit Removal ...................................................................................... 91
4.2.7 MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR Removal ........................................................ 94
4.2.8 MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF Removal ...................................................... 95
4.2.9 DE Unit Removal ...................................................................................... 96
4.2.10 ASF Unit Removal .................................................................................. 99
4.2.10.1 SHAFT, ROLLER, LD Removal .................................................. 101
4.2.10.2 ROLLER ASSEMBLY, LD, RIGHT/LEFT Removal ................. 106
4.2.11 Carriage Unit Removal .......................................................................... 107
4.2.12 BOARD ASSEMBLY, ENCODER Removal ....................................... 109
4.2.13 ROLLER, PF Removal .......................................................................... 110
4.2.13.1 SCALE, PF Installation ................................................................. 113
4.2.14 MOTOR ASSEMBLY, PF Removal ..................................................... 116
4.2.15 PE Sensor Unit Removal ....................................................................... 117
Chapter 5 ADJUSTMENT
5.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 119
5.1.1 Adjustment Items ..................................................................................... 119
5.1.2 Adjustment Tools ..................................................................................... 120
5.2 Adjustment ...................................................................................................... 121
5.2.1 Parallelism Adjustment ............................................................................ 121
5.2.1.1 Using PG Adjustment Tool ............................................................. 121
5.2.1.2 Using Thickness Gauge ................................................................... 124
5.2.2 Backlash Adjsutment ............................................................................ 125
5.2.3 Adjustment Program Feature ................................................................... 127
5.2.3.1 How to Install the Program ............................................................. 128
5.2.3.2 How to Uninstall the Program ......................................................... 128
5.2.4 Starting the Service Program ................................................................... 128
5.2.4.1 Adjusting Program Initial Setting ................................................... 128
5.3 Individual Adjustment Program ................................................................... 130
5.3.1 Head ID ............................................. ..................................... .................. 130
5.3.1.1 Head ID Input ............................................................................... 130
5.3.1.2 Head ID Check ................................................................................ 132
5.3.2 Bi-Directional Adjustment .................................................................... 133
5.3.2.1 Input Bi-D Adjustment Value ...................................................... 135
5.3.2.2 Check Present Adjustment Data ...................................................... 136
5.3.3 Input/Check USB ID ............................................................................... 137
5.3.3.1 Input USB ID ..................................................... ............................. 138
5.3.3.2 Check USB ID ...................................................... ........................... 138
5.3.4 Maintenance ......................................... .................................................... 139
5.3.4.1 Head Cleaning Operation ................................................................ 139
5.3.5 Ink Charge Operation ............................................................................. 140
5.3.6 Refurbishment for DOA .......................................................................... 141
5.3.7 Protection Counter .................................................................................. . 143
5.3.7.1 Check the Present Counter Value ............................... ..................... 143
5.3.7.2 Clear the Protection Counter Value ................................................ 143
5.3.8 Appendix Items .......................................... .................................... .......... 145
5.3.8.1 CSIC Information ......................................................................... 145
5.3.8.2 EEPROM Data Check ................................................................... 146
5.3.8.3 Changing EEPROM Data .............................................................. 146
5.3.9 A4 Check Pattern Printing ..................................................... .................. 147
5.4 Sequential Repair Adjustment Program ...................................................... 149
5.4.1 Function ............................................................................................... .... 149
5.4.1.1 How to start the program ................................................................. 149
5.4.1.2 Printhead Removal .......................................................................... 150
5.4.1.3 Printhead Replacement .................................................................... 151
5.4.1.4 Main Board Replacement ................................................................ 152
5.4.1.5 Carriage Unit Replacement/ Removal ............................................. 152
5.4.1.6 CR Motor Replacement ................................................................... 152
5.4.1.7 Printer Mechanism Replacement .................................................... 152
Page 9

5.4.1.8 Waste Ink Pad Replacement ............................................................ 152
5.4.1.9 Clogged Nozzle Recovery ............................................................... 152
Chapter 6 MAINTENANCE
6.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 155
6.1.1 Cleaning ................................................................................................... 155
6.1.2 Service Maintenance ................................................................................ 155
6.1.2.1 Head Cleaning ...... ........................................................................... 155
6.1.2.2 Maintenance Request Error Clear ................................................... 155
6.1.3 Lubrication ............................................................................................... 156
Chapter 7 APPENDIX
7.1 Connector Summary ...................................................................................... 166
7.1.1 Connector Alignment ............................................................................... 166
7.1.2 Connector Pin Assignment ...................................................................... 166
7.1.3 EEPROM Address Map ........................................................................... 169
7.2 Circuit Board Component Layout ................................................................ 174
7.3 Electrical Circuit Board Diagrams ............................................................... 179
7.4 Exploded Diagrams ........................................................................................ 186
7.4.1 Exploded Diagrams for Stylus PHOTO 890 ........................................... 186
7.4.2 Exploded Diagrams for Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290 ................................ 191
7.5 Parts List ......................................................................................................... 196
7.5.1 Parts List for Stylus PHOTO 890 .................................................. ... ....... 196
7.5.2 Parts List for Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290 ................................................. 201
Page 10
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS
CHAPTER
1
Page 11
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.1 Overview
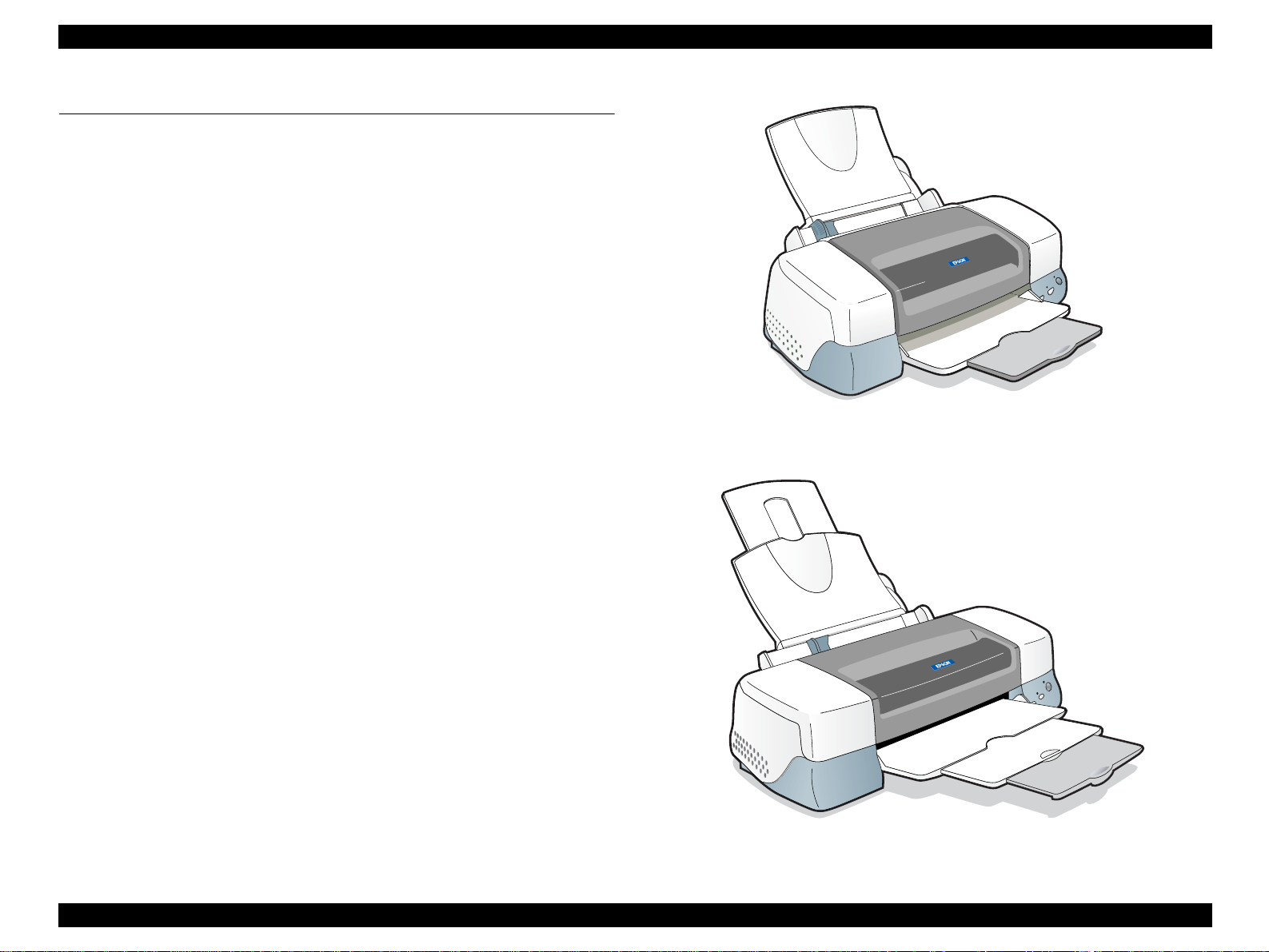
The EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890 and EPSON Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290 are designed
for both home use and office use. Stylus PHOTO 1280 is for EAI use only.
1.1.1 Features
The main features of the products are:
High-quality color print (6 colors)
High-speed & image quality bidirectional printing
Photo quality print enabled by photo mach technology
Supports microweave and super microweave
Prints at high resolution (2880x 720 dpi)
Two built-in interfaces
Bi-directional parallel interface (IEEE-1284 level 1 device)
USB I/F
Small size requiring less space.
Figure 1-1. Stylus PHOTO 890
Used only in Windows or Macintosh environment.
Built-in ASF (auto sheet feeder) supports multiple sizes of paper.
Stylus PHOTO 890: From postcard size up to A4
Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290: From postcard size up to A3 (W)
CSIC keeps track of ink life information on the ink cartridge side.
Figure 1-2. Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Overview 11
Page 12
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.1.2 Accessories, Consumable Products, and Options
ACCESSORIES
Users Guide
Ink cartridge (Black and color)
CD-ROM (Printer driver and utilities)
CONSUMABLE PRODUCTS
NOTE: The product codes of the ink cartridges may vary by location.
NOTE: The availability of special media varies by location.
NOTE: The products with an asterisk (*)are only available for Stylus PHOTO
1280/1290.
Table 1-1. Consumable Products
Product Name Code
Black ink cartridge T007
Color ink cartridge (Stylus PHOTO 890) T008
Color ink cartridge (Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290) T009
EPSON Premium Ink Jet Plain Paper (A4) S041214
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper (A4)
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper (Letter)
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper (A3)*
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper (Super A3/B)*
EPSON Iron-On Cool Peel Transfer Paper (A4)
EPSON Iron-On Cool Peel Transfer Paper (Letter)
EPSON Iron-On Cool Peel Transfer Paper (A3)*
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper (A4)
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper (Letter)
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper (Legal)
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper (A3)*
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper (Super A3/B)*
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper (B)*
S041059/S041025
S041060/S041028
S041065/S041046
S041066/S041047
S041154
S041153/S041155
S041238
S041061/S041026
S041062/S041029
S041067/S041048
S041068/S041045
S041069/S041043
S041070/S041044
Table 1-1. Consumable Products (continued)
Product Name Code
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Cards (A6)
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Cards(5x8”)
EPSON Photo Quality Ink Jet Cards(8x10”)
EPSON Photo Quality Self Adhesive Sheet (A4) S041106
EPSON Ink Jet Note Cards A6 (with envelops) S041147
EPSON Ink Jet Greeting Cards 5x8” (with envelopes)
EPSON Ink Jet Greeting Cards 8x10” (with envelopes)
EPSON Matte Paper-Heavyweight (A4)
EPSON Matte Paper-Heavyweight (Letter)
EPSON Matte Paper-Heavyweight (A3)*
EPSON Matte Paper-Heavyweight (Super A3/Super B)*
EPSON Photo Paper (A4)
EPSON Photo Paper (Letter)
EPSON Photo Paper (A3)*
EPSON Photo Paper (Super A3/Super B)*
EPSON Photo Paper (B)*
EPSON Photo Paper (4x6”)
EPSON Photo Paper (100 x 150 mm)
EPSON Photo Paper (200 x 300 mm)
EPSON Photo Paper (89 mmx 7M)
EPSON Photo Paper (100 mm x 8M)
EPSON Photo Paper (210 mm x 10M)
EPSON Photo Paper (329 mm x 10M)*
EPSON Panoramic Photo Paper (210 x 594 mm) S041145
EPSON Photo Paper Cards (A4) S041177
S041054
S041121
S041122
S041148
S041149
S041256/S041258/
S041259
S041257
S041260/S041261/
S041262
S041263/S041264/
S041265
S041140
S041141
S041142
S041143
S041156
S041134
S041255
S041254
S041281
S041279
S041280
S041233
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Overview 12
Page 13
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 1-1. Consumable Products (continued)
Product Name Code
Photo Quality Glossy Film (A4)
Photo Quality Glossy Film (Letter)
Photo Quality Glossy Film (A3)*
Photo Quality Glossy Film (Super A3/B)*
Photo Quality Glossy Film (B)*
Photo Quality Glossy Film (A6)
S041071
S041072
S041073
S041074
S041075
S041107
EPSON Photo Stickers 16 (A6)
EPSON Photo Stickers 4 (A6)
EPSON Ink Jet Transparencies (A4)
EPSON Ink Jet Transparencies (Letter)
EPSON Premium Glossy Photo Paper (A4)
EPSON Premium Glossy Photo Paper (Letter)
EPSON Premium Glossy Photo Paper (A3)*
EPSON Premium Glossy Photo Paper (B)*
EPSON Premium Glossy Photo Paper (Super A3/ SuperB)*
EPSON Ink Jet Back Light Film (A3)* S041131
S041144
S041176
S041063
S041064
S041287/S041297
S041286
S041288
S041290
S041289
OPTIONS
Table 1-2. Options
Product Name Code
Parallel Interface cable (shielded) C83602*
USB I/F Interface cable (shielded) C83623*
Roll Paper Holder C81106*
* The asterisks are substitutions for the last digits of the product name, which may vary by
country.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Overview 13
Page 14
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.2 Basic Specifications
1.2.1 Printing Specification
Print Method: On demand ink jet
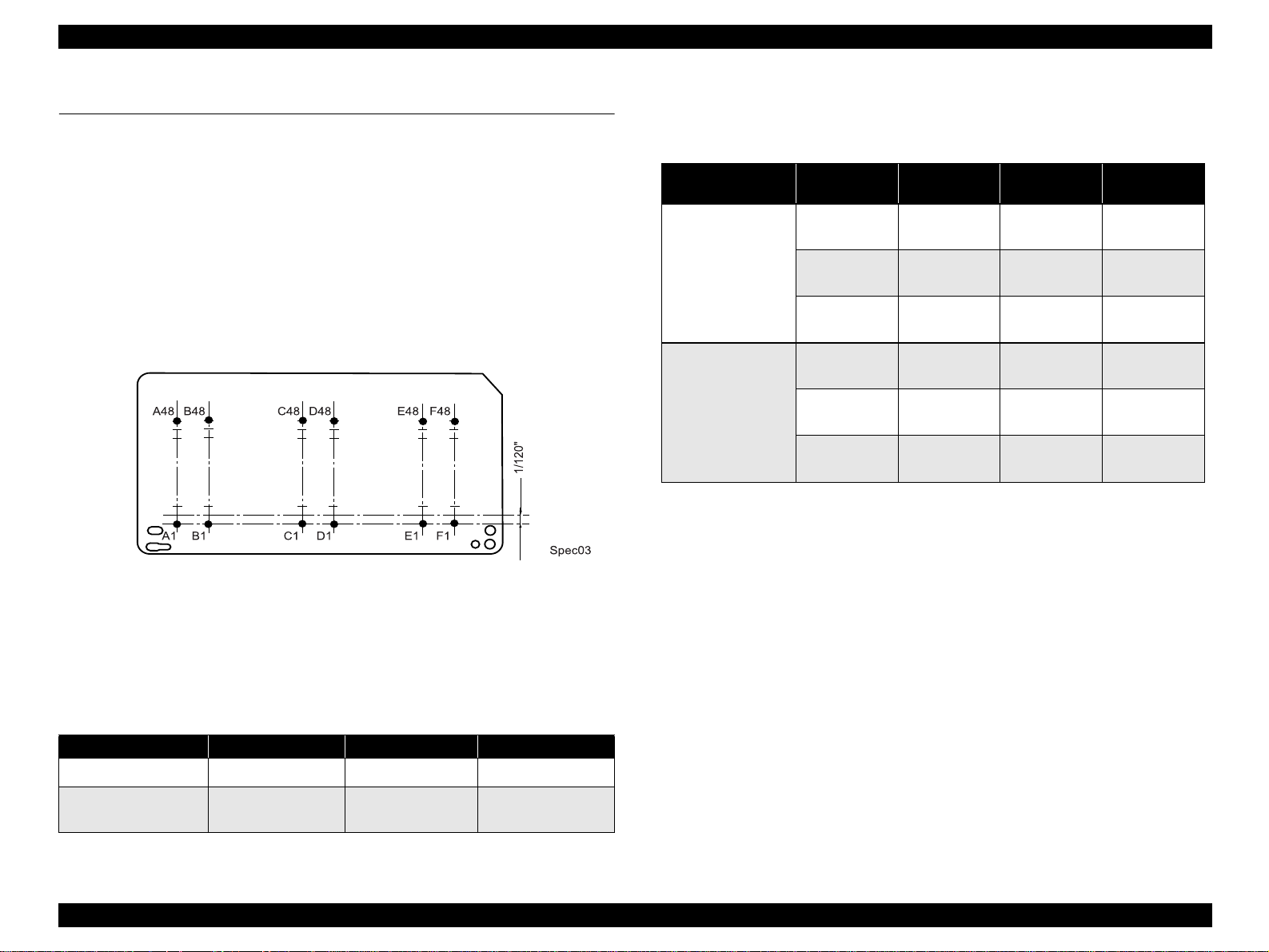
Nozzle Configuration
Monochrome: 48 nozzles (120 dpi)
Color: 48 nozzles x 5 (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Light cyan,
Light magenta) (120 dpi)
The following figure shows nozzle configuration viewed from the back of the
printhead:
* The value is the speed of normal-dot printing.
Raster Graphic Mode
Table 1-4. Raster Graphics Mode
Model
Stylus PHOTO 890
Stylus PHOTO
1280/1290
Horizontal
Resolution
180 dpi
360 dpi
720 dpi
180 dpi
360 dpi
720 dpi
Printable
Area
209.8mm/
8.26”
209.8mm/
8.26”
209.8mm/
8.26”
322.986mm/
12.716”
322.986mm/
12.716”
322.986mm/
12.716”
1.2.2 Control Code
ESC/P Raster command
Available Dot CR Speed
1488 23.8/19 IPS
2976 23.8/19 IPS
5952 19 IPS
2289 23.8/19 IPS
4578 23.8/19 IPS
9156 19 IPS
Figure 1-3. Nozzle Configuration
Print Direction Bi-direction with logic seeking
Print Speed & Printable Columns
Character Mode
Table 1-3. Character Mode
Model Character Pitch Printable Columns LQ Speed
Stylus PHOTO 890 10 CPI (Pica) 80 238CPS*
Stylus PHOTO 1280/
1290
10 CPI (Pica) 127 238CPS*
EPSON Remote command
1.2.3 Paper Feeding
Feeding method: Friction feed with ASF
Paper Path: Cut-sheet ASF (top entry, front out)
Feed Speed: 110mm/sec (10.16mm feed)
152.4mm(6.0inch)/sec (Fast, continues feed)
1.2.4 Input Data Buffer
256 KB
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 14
Page 15
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.2.5 Paper Specifications
The asterisk(*) indicates Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290 use only.
CUT SHEET
Size: See the table below:
Table 1-5. Paper Specifications - Cut Sheet
Size Specifications (Width x Length)
*
A3
A4 210 mm (8.3”) x 297 mm (11.7”)
A5 148 mm x 210 mm
A6 148mm x 105 mm
*
B
Letter 216 mm (8.5”) x 279 mm (11.0”)
Half Letter 139.7 mm x 215.9 mm
Legal 216 mm (8.5”) x 356 mm (14.0”)
Executive 184.2 mm (7.25”) x 266.7 mm (10.5”)
2L 178 mm x 127 mm
L 127 mm x 127 mm
5” x 8” 127 mm x 203 mm
8” x 10” 203 mm x 254 mm
Double Side A4 210 mm x 297 mm
297mm (11.7”) x 420mm (16.5”)
279 mm x 432
ENVELOPE
Size (Width x Length):
#10 241.3mm (9 1/2”) x 104.8mm(4 1/8”)
DL 220mm (8.7”) x 110mm (4.3”)
C6 162mm (6.4”) x 114mm (4.5”)
220 x 132 220mm x 132 mm
Thickness: 0.16mm (0.006”) - 0.52mm (0.02”)
Weight: 45g/m2 (12Ib.) - 75g/m2 (20Ib.)
Quality: Bond paper, PPC, Air mail
Note1: Envelope printing is only available at normal temperature.
Note 2: Keep the longer side of the envelope horizontally at setting.
1.2.5.1 EPSON Special Media
EPSON offers specifically- designed media for ink jet printers.
PHOTO QUALITY INK JET PAPER
Size (Width x Length):
*
A3+
A3
*
329mm x 483mm
297mm x 420mm
A4 210mm x 297mm
A6 105mm x 148mm
*
B
210mm x 297mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
Legal 216mm x 356mm
5” x 8” 127mm x 203mm
8” x 10” 203mm x 254mm
User Defined 89 to 241.3 mm x 89 to 1117.6 mm
Quality: Plain paper, Bond paper
Thickness: 0.08mm- 0.11mm (0.003”- 0.004”)
(Normal paper)
Weight: 64g/m2 - 90g/m2 (55kg-78kg, 17lb.- 24Ib.)
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 15
Page 16

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
360 DPI INK JET PAPER
Size (Width x Length):
A3+
A3
*
*
A4 210mm x 297mm
A6 105mm x 148mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
INK JET TRANSPARENCIES
Size (Width x Length):
A4 210mm x 297mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
PHOTO QUALITY GLOSSY FILM
Size (Width x Length):
*
A3+
*
A3
A4 210mm x 297mm
A6 105mm x 148mm
*
B
Letter 216mm x 279mm
329mm x 483mm
297mm x 420mm
329mm x 483mm
297mm x 420mm
210mm x 297mm
200 x 300mm 216mm x 338mm(cut-line)
Roll Paper (89mm x 7m, 100mm x 8m,
210mm x 10m, 329mm x 10m
PHOTO QUALITY ADHESIVE SHEET
Size (Width x Length):
A4 210mm x 297mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
IRON-ON COOL PEEL TRANSFER PAPER
Size (Width x Length):
A3
*
297mm x 420mm
A4 210mm x 297mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
PHOTO STICKERS
Size (Width x Length):
A6 105mm x 148mm /16
A6 105mm x 148mm /4
MATTE PAPER-HEAVYWEIGHT
*
)
PHOTO PAPER
Size (width x length):
*
+A3
*
A3
A4 210mm x 297mm
*
A6
*
B
Letter 216mm x 279mm
329mm x 483mm
297mm x 420mm
105mm x 148mm
210mm x 297mm
Size (Width x Length):
*
A3+
A3
*
329mm x 483mm
297mm x 420mm
A4 210mm x 297mm
*
B
210mm x 297mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
100mm x 150mm
Roll Paper (89mm x 7m, 100mm x 8m,
210mm x 10m, 329mm x 10m
*
)
Photo Paper Card 2 175.4mm x 113.6mm (cut-line)
Panoramic Photo Paper 210mm x 594mm
152.4mm (6“) x 101.6mm (4“)(no cut-line)
100mm x 150mm
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 16
Page 17
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
PREMIUM GLOSSY PHOTO PAPER
Size (Width x Length):
+A3
A3
*
*
329mm x 483mm
297mm x 420mm
A4 210mm x 297mm
*
B
210mm x 297mm
Letter 216mm x 279mm
Roll Paper (89mm x 7m, 100mm x 8m,
127mm x 8m*,210mm x 10m,
329mm x 10m
INK JET BACK LIGHT FILM
Size (Width x Length):
A3
*
297mm x 420mm
1.2.6 Printing Area
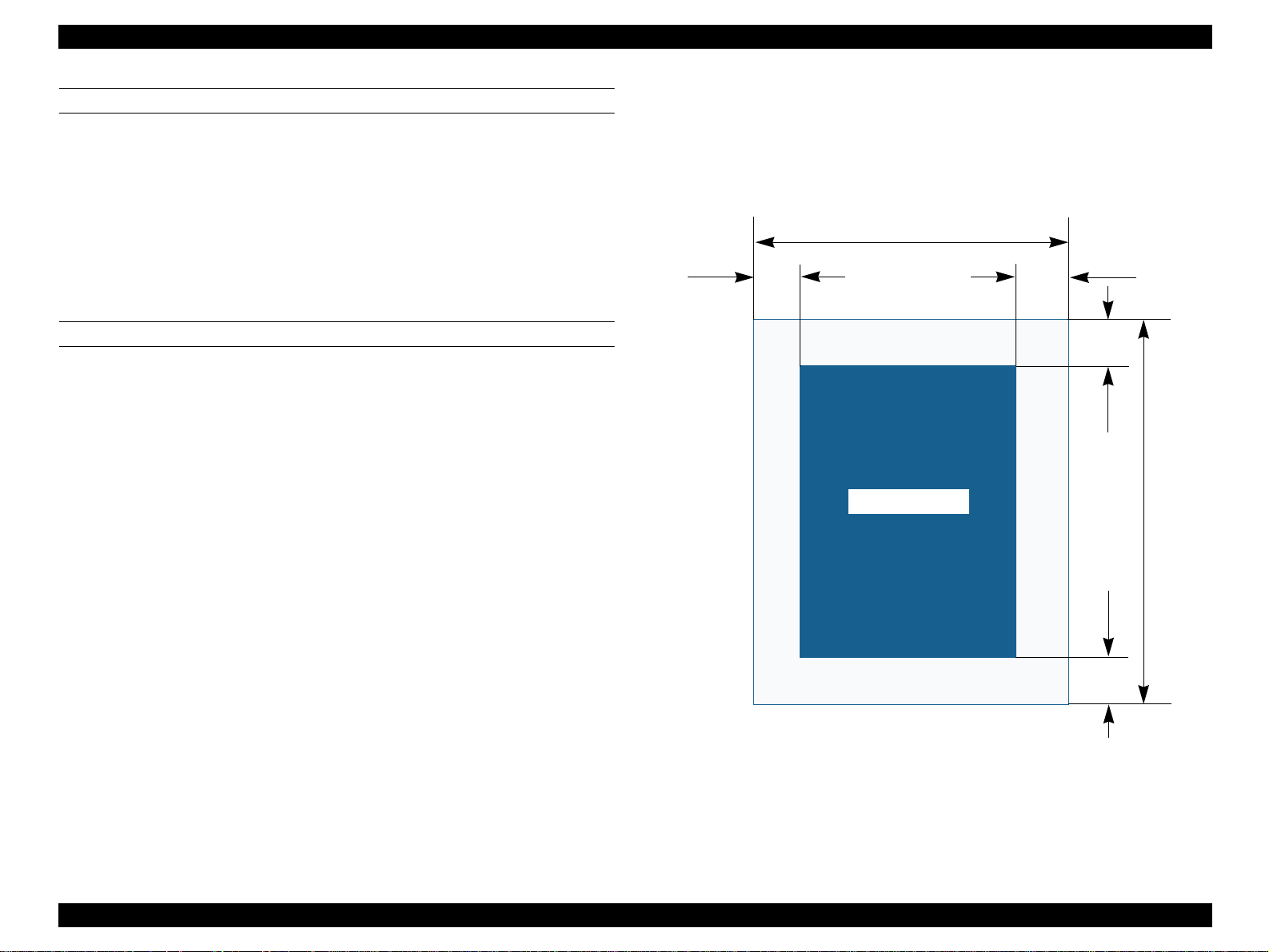
1.2.6.1 Cut Sheet
See the figure below and the following tables for the printing area for Stylus PHOTO
890/Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290.
PW
LM
*
)
Printable Area
RM
TM
PL
BM
Figure 1-4. Printable Area for Cut Sheet
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 17
Page 18

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 1-6. Printing Area
Left Margin
Paper Size
A3*
A3+*
A4
Letter
B5
Legal
Statement
Exclusive
*
: Stylus PHOTO 1290 only.
*1
:Bottom margin can be reduced to 3mm when paper dimension is
(min.)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
3 mm
(0.12”)
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
defined by using command, otherwise it remains 14mm.
As for an area between 3mm and 14mm margin, print quality may
decline.
*2
: Zero mm can be set by special command.
Right Margin
(min.)
Top Margin
(min.)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
3 mm (0.12”)*23 mm (0.12”)
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
Bottom Margin
(min.)
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
14 mm (0.54”) /
3mm (0.12”)
*1*2
1.2.6.2 Envelopes
LM
Printable Area
Figure 1-5. Printable Area for Envelopes
Table 1-7. Envelope Margin
Left Margin
Size
(min.)
#10 3 mm (0.12”) 28 mm (1.10”) 3 mm (0.12”) 14 mm (0.55”)
DL 3 mm (0.12”) 7 mm (0.28”) 3 mm (0.12”) 14 mm (0.55”)
Right Margin
(min.)
Top Margin
(min.)
Bottom Margin
RM
TM
BM
(min.)
C6 3 mm (0.12”) 3 mm (0.12”) 3 mm (0.12”) 14 mm (0.55”)
1.2.7 Adjust Lever
Set the adjust lever according to the type of paper as shown in the following table.
Table 1-8. Adjust Lever Setting Position
Paper Setting Position Gap
Cut sheet, OHP Sheet, Label,
Postcard
Envelope Rear (+) +0.9 mm
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 18
Front (0) 0 mm
Page 19

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.2.8 Ink Cartridge
BLACK INK CARTRIDGE
The black ink cartridge specifications for Stylus PHOTO 890 and Stylus PHOTO
1280/1290 are common.
Type: Exclusive Cartridge
Color: Black
Print Capacity: 540 pages/A4
(ISO/IEC 10561 Letter Pattern at 360 dpi)
Ink Life: 2 years from the indicated date of production
Storage Temperature
Packed (in transit): -30 to 60 oC (within a month at 40 oC, within 120
hours at 60
Packed (storage): -30 to 40 oC (within a month at 40 oC)
Installed: -20 oC to 40 oC (within a month at 40 oC)
Dimension: 20.1 mm (W) x 66.85 mm (D) x 38.5 m m (H)
o
C)
COLOR INK CARTRIDGE
Note some of the color ink specifications for the Stylus PHOTO 890 and Stylus
PHOTO 1280/1290 are different as indicated.
Type: Exclusive Cartridge
Color: Magenta, Cyan, Yellow, Light Cyan,
Light Magenta
Print Capacity:
Stylus PHOTO 890 220 pages / A4 (360 dpi, 5% duty each color)
Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290330 pages / A4 (360 dpi, 5% duty each color)
Ink Life: 2 years from the indicated date of production
Storage Temperature
Packed (in transit): -30 to 60 oC (within a month at 40 oC, within 120 hours
Packed (storage): -30 to 40 oC (within a month at 40 oC)
Installed: -20 oC to 40 oC (within a month at 40 oC)
Dimension:
Stylus PHOTO 890 49.1 mm (W) x 66.85 mm (D) x 38.5 mm (H)
Stylus PHOTO 1280/129049.1 mm (W) x 84.05 mm (D) x 41.8mm (H)
at 60
o
C)
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 19
Page 20

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.2.9 Electric Specification
120V VERSION
Rated Voltage: AC120V
Input Voltage Range: AC99∼132V
Rated Frequency Range: 50∼ 60Hz
Input Frequency Range: 49.5∼ 60.5Hz
Rated Current: 0.4A(Max0.7A)
Power Consumption: Approx. 15W (ISO10561 Letter Pattern)
Approx. 3W in standby mode
Energy Star compliant
Insulation Resistance: 10M ohms min.
(between AC line and chassis, DC 500V)
Dielectric Strength: AC 1000V rms. 1 minute or
AC 1200V rms. 1 second
(between AC line and chassis)
220 ∼ 240V VERSION
Rated Voltage: AC220V∼240V
1.2.10 Reliability
Total Print Volume Black: 25,000 pages (A4, Letter)
Color: 10,000 pages (A4, Letter)
Printhead Life: 3000 million dots/nozzl e
Input Voltage Range: AC198∼264V
Rated Frequency Range: 50∼60Hz
Input Frequency Range: 49.5∼60.5Hz
Rated Current: 0.2 A(Max0.35A)
Power Consumption: Approx. 15W (ISO10561 Letter Pattern)
Approx. 3W in standby mode
Energy Star compliant
Insulation Resistance: 10M ohms min.
(between AC line and chassis, DC 500V)
Dielectric Strength: AC 1500V rms. 1 minute
(between AC line and chassis)
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 20
Page 21
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.2.11 Environmental Condition
TEMPERATURE
Operating: 10 to 35°C
Non-Operating: -20 to 60°C
Within 1 month at 40°C /120 hours at 60°C
*1
: In a shipment container.
*2
: Refer to Figure 1-6 "Temperature/Humidity Range" for condition.
HUMIDITY
Operating: 20 to 80% RH (without condensation)
Not-Operating: 5 to 85% RH (without condensation)
90
80
70
60
Humidity (%)
50
40
30
20
*2
*1
RESISTANCE TO SHOCK
Operating: 1G, within 1 ms, X, Y, Z directions
Non-operating: 2G, within 2 ms, X, Y, Z di recti ons
*1
: In a shipment container.
*1
RESISTANCE TO VIBRATION
Operating: 0.15G
Non-operating: 0.5 0G
*1
: In a shipment container.
*2
*1
C A U T I O N
When storing the printer, make sure the printhead is capped.
When transporting the printer, ensure the ink cartridges are
installed in the printer and the printhead is capped.
If the printer power is off with the printhead left uncapped, turn
the printer on with the ink cartridges installed, cap the
printhead, and turn the printer off.
Ink freezes at below -4°C. It will be usable again after keeping it
for about three hours at 25
*1
°
C.
10
20
27
30
35
40
Temperature (°C)
Figure 1-6. Temperature/Humidity Range
*1
: In a shipment container.
*2
: Refer to Figure 1-6 "Temperature/Humidity Range" for condition.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Basic Specifications 21
Page 22
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.3 Interface
The EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 provides USB and parallel interfaces as
standard.
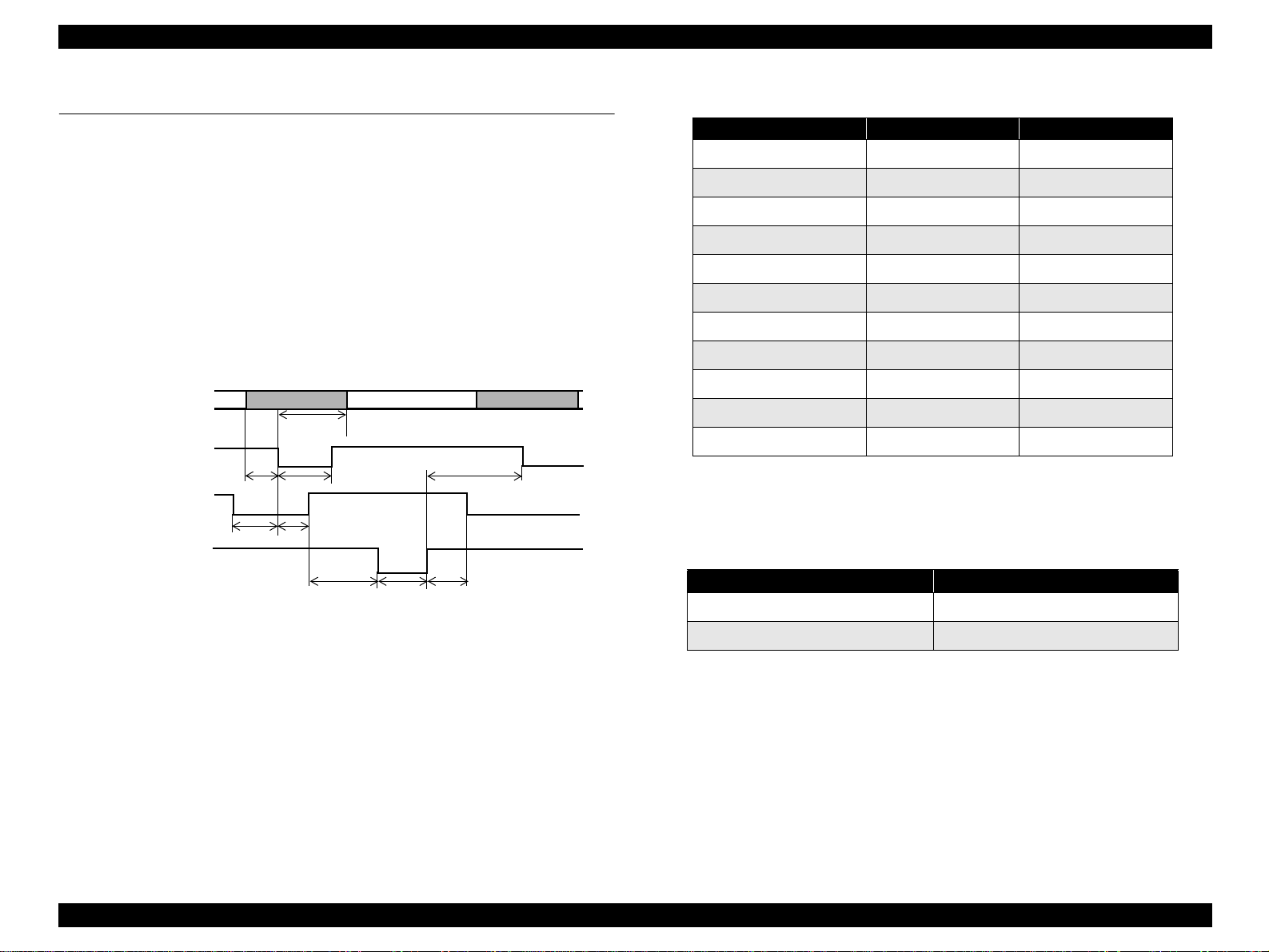
1.3.1 Parallel Interface (Forward Channel)
Transmission Mode: 8 bit parallel, IEEE-1284 compatibility mode
Synchronization: By STROBE pulse
Handshaking: By BUSY and ACKNLG signal
Signal Level: TTL compatible level
Adaptable Connector: 57-30360 (amphenol) or equivalent
DATA
-STROBE
BUSY
-ACKNLG
data byte n
hold
t
stb
ready
t
setup
t
t
busy
t
t
reply
ack
t
t
Figure 1-7. Data Transmission Timing
t
nbusy
data byte n+1
next
Table 1-9. Parameters
Parameter Minimum Maximum
tsetup 500ns -
thold 500ns -
tstb 500ns -
tready 0 -
tbusy - 500ns
tt-out* - 120ns
tt-in** - 200ns
treply 0 -
tack 500ns 10us
tnbusy 0 -
tnext 0 -
* Rise and fall time of every output signal.
** Rise and fall time of every input signal.
*** Typical timing for tack is shown on the following page.
Table 1-10. Typical Time of Tack
Parallel I/F Mode Typical Time of tack
High Speed 0.5us
Normal Speed 2us
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Interface 22
Page 23
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 1-11.
Signal Level: TTL Compatible (IEEE-1284 level 1 device)
Parameter Minimum Maximum Condition
VOH* - 5.5V
VOL* -0.5V -
IOH* - 0.32mA VOH = 2.4V
IOL* - 12mA VOL = 0.4V
CO - 50pF
VIH - 2.0V
VIL 0.8V -
IIH - 0.32mA VIH = 2.0V
IIL - 12mA VIL = 0.8V
CI - 50pF
* A low logic level on the Logic H signal is 2.0V or less when the printer is turned off,
and this signal is equal to or exceeding 3.0V when the printer is turned on. The
receiver shall provide an impedance equivalent to 7.5K ohm to ground.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Interface 23
Page 24
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 1-12. Connector Pin Assignment and Signals
Pin No. Signal Name
1 -STROBE 19 In The strobe pulse. Read-in of data is performed at the falling edge of this pulse.
2-9 DATA0-DATA7 20-27 In
10 -ACKNLG 28 Out This signal is a negative pulse indicating that the printer can accept data again.
11 BUSY 29 Out A high signal indicates that the printer cannot receive data.
12 PE 28 Out A high signal indicates paper-out error.
13 SLCT 28 Out Always at high level when the printer is turned on.
14 -AFXT 30 In Not used.
17 Chassis GND - - Chassis GND
18 Logic H - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.9K ohm resister.
31 -INIT 30 In
32 -ERROR 29 Out A low signal indicates printer error condition.
Return
GND Pin
In/Out Functional Description
The DATA0 through DATA7 signals represent data bits 0 to 7, respectively.
Each signal is at high level when data is logical 1 and low level when data is logical 0.
The falling edge of a negative pulse or a low signal on this line causes the printer to initialize. Minimum
50us pulse is necessary.
35 +5 - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.3K ohm resister.
36 -SLIN 30 In Not used.
16,33
19-30
15,34 NC - - Not connected.
GND - - Signal GND
NOTE: In/Out refers to the direction of signal flow seen from the printer side.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Interface 24
Page 25
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.3.2 Parallel Interface (Reserve Channel)
Transmission Mode: IEEE-1284 nibble mode
Adaptable Connector See forward channel.
Synchronization: Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
Pin No. Signal Name
1 HostClk 19 In Host clock signal.
2-9 DATA0-DATA7 20-27 In
10 PtrClk 28 Out Printer clock signal.
11 PtrBusy / DataBit-3,7 29 Out Printer busy signal and reverse channel transfer data bit 3 or 7.
12 AckDataReq / DataBit-2,6 28 Out Acknowledge data request signal and reverse channel transfer data bit 2 or 6.
13 Xflag / DataBit-1,5 28 Out X-flag signal and reverse channel transfer data bit 1 or 5.
14 HostBusy 30 In Host busy signal.
31 -INIT 30 In Not used.
32 -DataAvail / DataBit-0,4 29 Out Data available signal and reverse channel transfer data bit 0 or 4.
36 1284-Active 30 In 1284 active signal.
Handshaking: Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
Data Trans. Timing: Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
Signal Level: IEEE-1284 level 1 device (See forward channel.)
Table 1-13. Connector Pin Assignment and Signals
Return
GND Pin
In/Out Functional Description
The DATA0 through DATA7 signals represent data bits 0 to 7, respectively. Each signal is
at high level when data is logical 1 and low level when data is logical 0. These signals are
used to transfer the 1284 extensibility request values to the printer.
18 Logic-H - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.9K ohm resistor.
35 +5V - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.3K ohm resistor.
17 Chassis GND - - Chassis GND
16,33, 19-30 GND - - Signal GND
15,34 NC - - Not connected
NOTE: In/Out refers to the direction of signal flow from the printer’s point of view.
Extensibility Request:
The printer responds affirmatively when the extensibility request values are 00H
or 04H, which means:
00H: Request Nibble Mode Reverse Channel Transfer.
04H: Request Device ID;
Return Data Using Nibble Mode Rev Channel Transfer.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Interface 25
Page 26
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Device ID:
The printer sends the following device ID string when requested.
When IEEE1284.4 is enabled,
<00H><5AH>
*1
/ <00H><5CH>
*2
MFG: EPSON
CMD: ESCPL2,BDC,D4
MDL: Stylus[SP]Photo[SP]890
/Stylus[SP]Photo[SP]1290
CLS: PRINTER
DES: EPSONStylus[SP]Photo[SP]890
/EPSONStylus[SP]Photo[SP]1290
When IEEE1284.4 is enabled,
<00H><57H>
*1
/ <00H> <59H>
*2
MFG: EPSON
CMD: ESCPL2,BDC,D4
MDL: Stylus[SP]Photo[SP]890
/Stylus[SP]Photo[SP]1290
CLS: PRINTER
DES: EPSONStylus[SP]Photo[SP]890
/EPSONStylus[SP]Photo[SP]1290
*1
: Stylus PHOTO 890 only
*2
: Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290 only
1.3.3 USB Interface
Standard: Based on:
“Universal Serial Bus Specifications Rev. 1.1”
“Universal Serial Bus Device Class Definition for
Printing Devices Version 1.1”
Bit rate: 12Mbps (Full Speed Device)
Data encoding: NRZI
Adaptable connector: USB Series B
Recommended cable length:2 meters
Table 1-14. Connector Pin Assignment and Signals
Pin No. Signal Name I/O Function Description
1VCC -
2 -Data Bi-D Data
3+DataBi-D
4 Ground - Cable ground
Pin #2
Cable power. Max. power
consumption is 2mA.
Data, pull up to +3.3 V via 1.5K
ohm resistor.
Pin #1
NOTE 1:[00H] denotes a hexadecimal value of zero.
NOTE 2:MDL value depends on the EEPROM setting.
NOTE 3:CMD value depends on the IEEE1284.4 setting.
Pin #3
Pin #4
Figure 1-8. USB Pin Assignment
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Interface 26
Page 27

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.3.4 Prevention of Data Transfer Time-out
Generally, hosts abandon data transfer to peripherals when the peripheral is in the busy
state for dozens of seconds continuously. To prevent this kind of time-out, the printer
receives data very slowly, several bytes per minute, even if the printer is in the busy
state. The slowdown starts when the remaining input buffer becomes several hundreds
of bytes, and the printer finally gets into the busy state continuously when the input
buffer is full.
USB and IEEE1284.4 on the parallel interface do not require such function.
On
An initial state is IEEE1284.4 communication and data that received it by the time
it is able to take synchronization by magic string (1284.4 synchronous commands)
is discarded.
Off
An initial state is compatible interface and never starts IEEE1284.4
communication even if magic strings (1284.4 synchronous commands) are
received.
1.3.5 Interface Selection
The printer has two built-in interfaces: the USB and parallel interface.
These interfaces are selected automatically.
Automatic Selection
In this automatic interface selection mode, the printer is initialized to the idle state
while scanning which interface receives data when it is powered on. Then the
interface which received data first is selected. When the host stops data transfer
and the printer is in the stand-by state for seconds, the printer is returned to the idle
state. As long as the host sends data or the printer interface is in the busy state, the
selected interface is let as it is.
Interface State and Interface Selection
When the parallel interface is not selected, the interface gets into the busy state.
When the printer is initialized or returned to the idle state, the parallel interface
gets into the ready state. Note that the interrupt signal such as the -INIT signal on
the parallel interface is not effective while that interface is not selected.
1.3.6 IEEE1284.4 Protocol
The packet protocol described by IEEE1284.4 standard allows a device to carry on
multiple exchanges or conversations which contain data and/or control information
with another device at the same time across a single point-to-point link. The protocol is
not, however, a device control language. It does provide basic transport-level flow
control and multiplexing services. The multiplexed logical channels are independent of
each other and blocking of one has no effect on the others. The protocol operates over
IEEE1284.
Automatic Selection
An initial state is compatible interface and starts IEEE1284.4 communication
when magic strings (1284.4 synchronous commands) are received.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Interface 27
Page 28
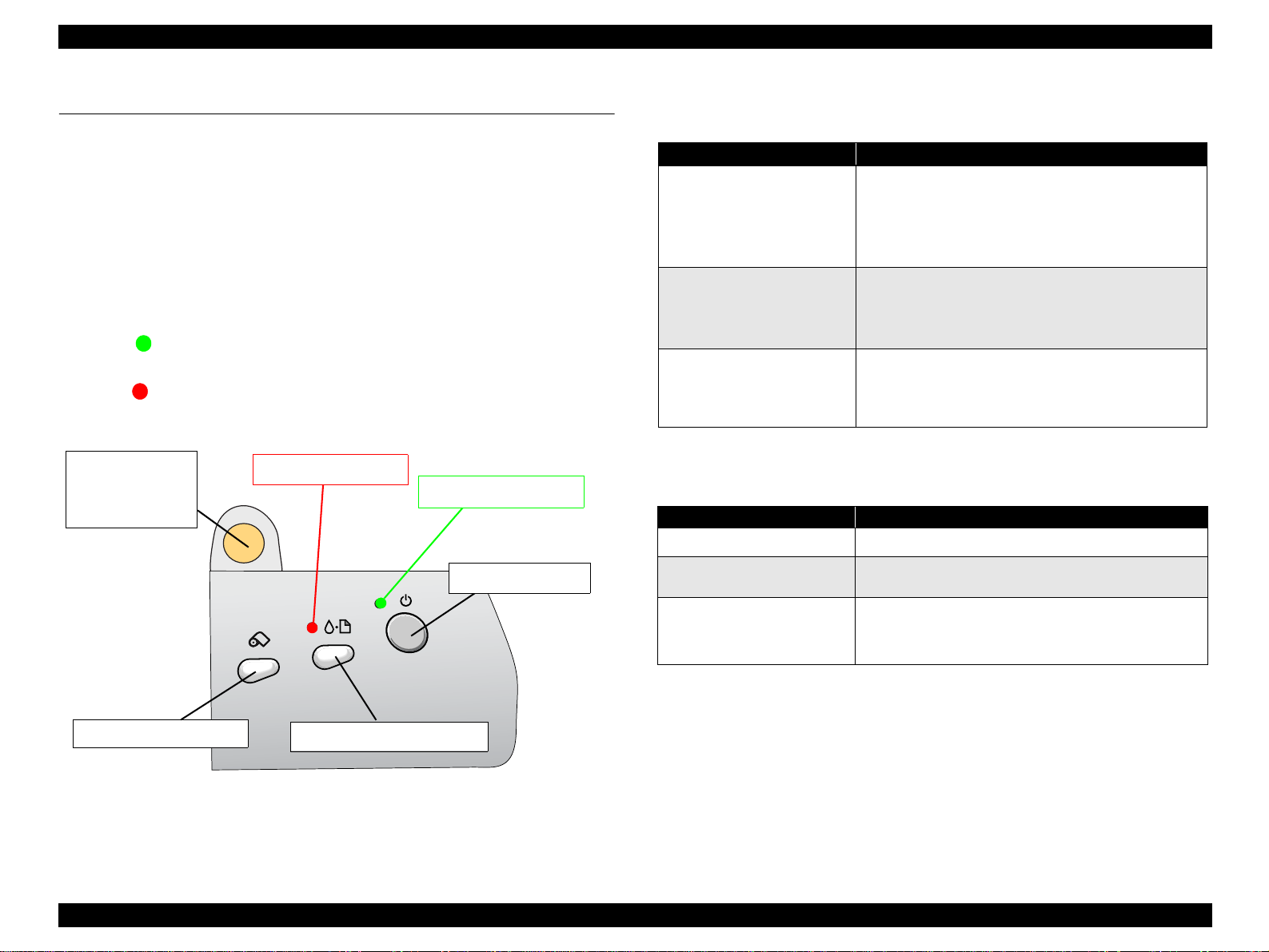
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.4 Operations
1.4.1 Buttons
Roll Paper button
Maintenance button
Ink Cartridge replacement button
Power button
1.4.2 Indicators
Power
Lights when the operating switch is “ON” and AC power is supplied.
Error
Lights during the error condition, and blinks during the ink low condition.
Ink Cartridge
replacement
button
Error indicator
Power indicator
Power button
1.4.3 Panel Functions
Table 1-15. Panel Functions
Buttons Function
Maintenance
Roll Paper
Ink Cartridge Replacement
*1
: Press the button for 3 seconds.
Table 1-16. Power On Panel Functions
Buttons Pressing with Power On Function
Maintenance • Starts status printing
Roll Paper
Maintenance
+
Roll Paper
• Loads or ejects paper.
• Returns a carriage to the home position when the
carriage is at the ink cartridge replacement position.
*1
• Starts the head cleaning
• Returns from an error condition.
• Loads or ejects Roll Paper. (Back Out feed*1)
• Feeds and returns from the Tear-Off operation.
• Returns a carriage to the home position when the
carriage is at the ink cartridge replacement position.
• Starts the Ink Cartridge change sequence.
Moves the carriage to the carriage change position.
• Returns a carriage to the home position when the
carriage is at the ink cartridge replacement position.
• Changes code pages /select IEEE1284.4 mode for
parallel I/F*3.
• Enters the special settings mode. (Factory use only).
.
*2
.
*2
: According to the content of 1BH of the EEPROM, one of the following
actions needs to be carried out. (See Table 1-17 on page 29)
Roll Paper button
Maintenance button
*3
: Do not mention the information to the users.
Figure 1-9. Control Panel
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Operations 28
Page 29
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
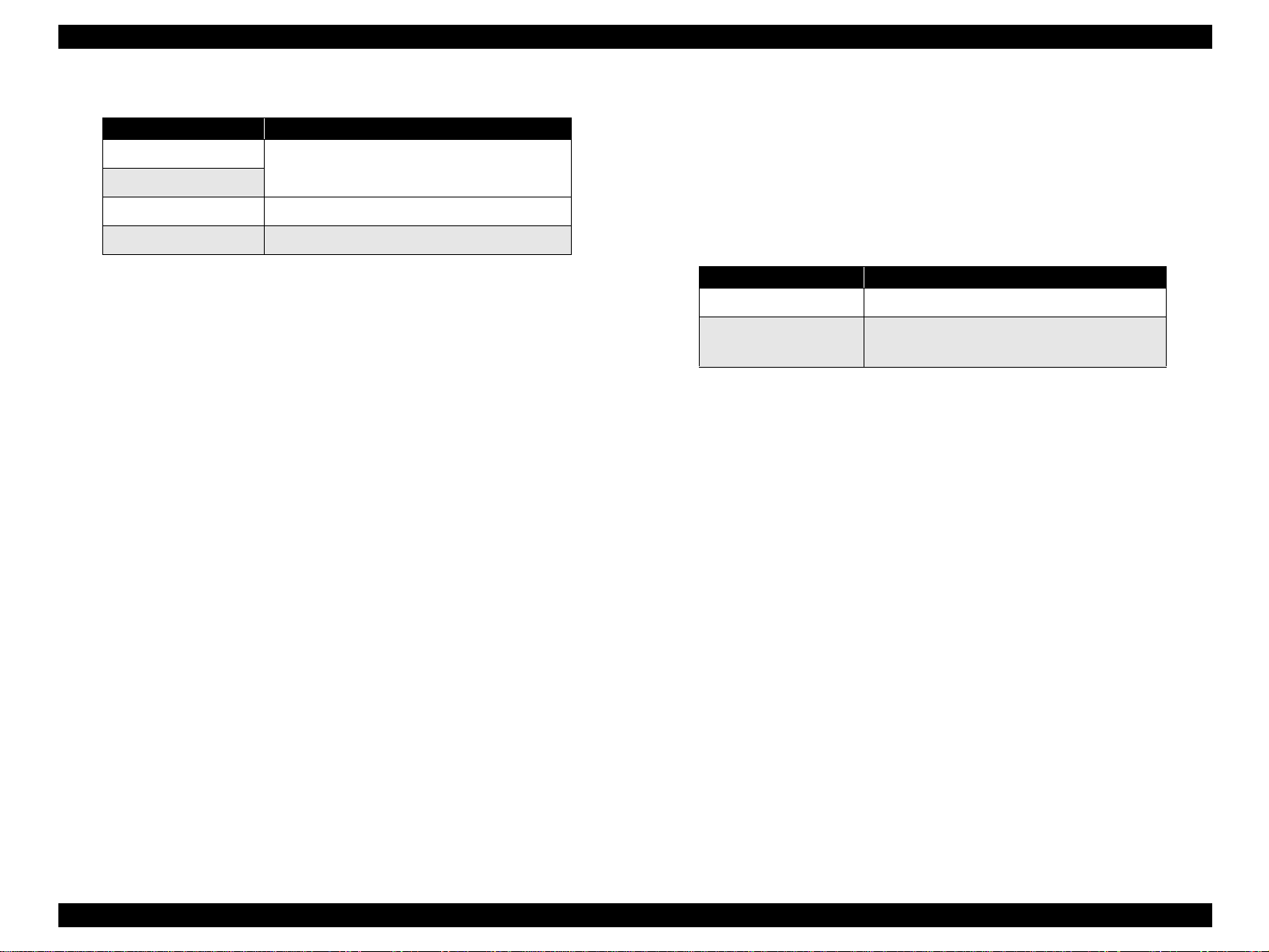
Table 1-17. Content of 1BH of EEPROM
[bit7] [bit6] Actions
00
11
01 Starts the hex-dump mode.
10 Starts the self test mode.
*4: Factory default setting.
Prints firmware version, ink counter, selected code
page and nozzle check pattern.
1.4.4 Special Setting Mode
To enter the special setting mode, press the Maintenance button and the Roll Paper
button while turning on the printer until the Power indicator blinks. While it is blinking
(for 3 seconds), press the specified button to activate the desirable setting mode.
NOTE: The special setting mode is not described in the user’s manual.
Table 1-18. Special Setting Mode
Buttons Functions
Maintenance • Initializes the EEPROM and Timer IC.
Roll Paper
*1
: Pressing the button for 10 seconds.
EEPROM/Timer IC Reset
The following will be reset when this operation is executed.
Interface selection (04H)
CL Time (68H, 69H)
Power Off timer (6AH, 6BH)
Waste Ink Counter Reset
The following will be reset when this operation is executed.
*1
• Resets the ink overflow counter (Protection
Counter) in the EEPROM.
Ink counter A0 (6CH, 6DH)
Ink counter A80 (6EH, 6FH)
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Operations 29
Page 30

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.4.5 Printer Initialization
EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 executes initialization by using 3 methods
mentioned below.
1. Hard Initialization
The Hard Unitization will be performed when the printer is turned on or
recognizes the cold reset command. (remote RS command)
The following will be performed during initialization.
Initializes printer mechanism.
Clears input data buffer.
Clears print buffer.
Sets default values.
2. Software Initialization
The ESC@ command also initializes the printer.
The following will be performed during initialization.
Clears print buffer.
Sets default values.
3. Panel Initialization
The Panel Initialization will be performed if the printer is turned off and back on
within 10 seconds, or *INIT signal (negative pulse) is input.
The following will be performed during initialization.
1.4.6 Initialization Value
When the printer is initialized, it clears the following settings to their initialization
values. However, panel setting values, default setting values, and values set by the
remote command remain as they are.
Top of page Current TOP
Line feed 4.23mm(1/6 inch)
Right margin 80 columns (Stylus PHOTO 890)
127 columns (Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290)
Left margin 1st column
Character pitch 10 cpi
Print mode Text mode (Non graphics mode)
Caps the printer head.
Ejects paper.
Clears input data buffer.
Clears print buffer.
Sets default values.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Operations 30
Page 31

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1.5 Dimension
EXTERNAL DIMENSION
Stylus PHOTO 890
When stored(mm): 471 (W) x 290 (D) x 175 (H)
For use(mm): 471 (W) x 613 (D) x 302(H)
Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290
When stored(mm): 609(W) x 311(D) x 175 mm (H)
For use(mm): 609(W) x 766(D) x 414mm (H)
WEIGHT
Stylus PHOTO 890
Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290
: 6.0 kg
:8.4 kg
Figure 1-10. Stylus PHOTO 890 in Use
Figure 1-11. Stylus PHOTO 1280/1290 in Use
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Dimension 31
Page 32

EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1280/1290 Revision C
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS Dimension 32
Page 33

OPERATING PRINCIPLES
CHAPTER
2
Page 34

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1 Overview
This section describes the operating principles of the printer mechanism and electrical
circuit boards. The major components of the EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 are:
Printer mechanism: Stylus Photo 890: M4T12
Stylus Photo 1290: M4S61
Main board:
Stylus Photo 890 : C393MAIN-C/C393MAIN-B
Stylus Photo 1290: C393MAIN/C393MAIN-B
Power supply board: C378PSB/PSE Board
PRINTER MECHANISM
Unlike other EPSON ink jet printers, the
motor as power source. The DC motor enables the printer to lower noise during
printing. Table 2-1 shows various motor types used in the printer and their applications.
Table 2-1. Motor Types and Corresponding Applications
Motor Name Type Application / Feature
CR motor
DC motor with
brush
EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290
uses a DC
Table 2-2.
Drives the carriage making little noise. Works with
a linear scale to monitor motor’s operating
condition.
The basic structure of the printer mechanism is mostly common to the Stylus COLOR
400, except that the Stylus Photo 890/1290 uses a Pump/ASF motor. With this motor
equipped, the paper loading mechanism and the pumping mechanisms are
independently driven, which allows the printer to offer higher throughput.
Figure 2-1 shows the printer mechanism block diagram for the Stylus Photo 890/1290.
Rotary Encoder
Intermittent Gear
PF Motor Pinion
PF Motor
Flashing Window
(at 80th or 136th column)
Photo Interrupter (Encoder)
Notched Roller
Carriage Unit
Printhead
Timing Belt
Cap Unit
(without a valve)
PF Drive Gear (high precision)
Photo Interrupter (Encoder)
Detector Wheel
ASF Sensor
LD Roller Shaft
Loading Rollers
PE Sensor
Pump/ASF Motor
Supplies power to drive paper feeding rollers used to
PF motor
Pump/ASF
motor
DC motor with
brush
4-Phase / 48-pole
stepping motor
send paper at specified speeds and load/eject paper.
To monitor paper feeding pitch, a loop scale is
attached beside the high-precision gear.
Sends drive for pump operation and paper feeding
from ASF. Since this is a stepping motor, it has no
scales or photo sensors that are used to monitor
motor’s operating condition.
Pump Unit
CR Guide Shaft
PF Roller
Liner Scale
CR Motor
PG Lever
ASF/Pump Disengage
Gear Train
Figure 2-1. Printer Mechanism Block Diagram
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 34
Page 35

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.1 Printhead Mechanism
The printhead mechanism operating principles of the Stylus Photo 890/1290 are
basically the same as for the previous EPSON ink jet printers. This printer, however,
employs a newly developed ink and improved printhead driving method to provide a
higher print quality and faster printing speed than ever. Also, an IC called CSIC that
stores ink-life data is attached to each ink cartridge. With this IC, ink life of each
cartridge can be individually monitored. Note, like for other models, a head voltage
must be written with a PC.
The printhead mechanism consists of ink cartridges and printheads. Each printhead is
composed of PZT (Piezo Electric Element), nozzle surface, ink supply needle, nozzle
selection circuit board, cartridge sensor, CSIC, and CSIC connection circuit. Figure 2-2
shows its component layout.
CSIC
Ink Cartridge
Nozzle Selector
Circuit Board
CSIC Connection
Circuit
Ink Supply Needle
Ink Cartridge
An ink cartridge stores ink to be supplied to the printhead.
CSIC:
CSIC is a non-volatile memory EEPROM attached to each black and color ink
cartridge. It keeps the following information:
1) Ink remaining level
2) Number of cleanings performed
3) Number of installation of the ink cartridge
4) Accumulated installation time of the cartr idge
5) Model name of the printer in use
6) Ink cartridge production information
Printhead
PZT
Driven by the print signal from the control circuit board, it ejects ink from the
nozzle plate.
Nozzle plate
Ink pressured by the PZT is ejected from this plate.
Ink supply needle
Connects the ink cartridge and printhead to run ink to the printhead.
CSIC connection circuit
Connects the control circuit board and CSIC attached on the ink cartridge.
One end of the harness is connected to the control board together with the
printhead cable.
Nozzle selection circuit board
This circuit, controlled by ASIC on the control circuit board, selects nozzles
Nozzle Plate
PZT
to be driven for printing. On the other hand, head drive voltage is produced on
the controller circuit side.
Figure 2-2. Printhead Mechanism
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 35
Page 36

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.2 Carriage Mechanism
The carriage mechanism of the Stylus Photo 890/1290 is composed of the carriage
motor (CR motor), carriage guide shaft, platen gap adjustment/parallelism adjust ment
mechanism, carriage lock mechanism, and so on.
2.1.2.1 Carriage Motor (CR Motor)
The carriage mechanism of this printer is mostly the same as for other ink jet printers’
except it uses a DC motor as power source. See the table below for the carriage motor
specifications.
Table 2-3. Carriage Motor Specifications
Table 2-4.
Items Specifications
Type DC Motor with brush
Drive Voltage +42 V +/- 5% (Applied to the driver)
Coil resistance 29.2 ohms +/- 25%
Inductance 30.0 mH +/- 25%
Photo Coupler
Carriage Unit
Linear Encoder
Adjust Lever
Platen Surface
Eccentric Shaft
CR Motor
Parallelism Adjustment
Bushing
Carriage Guide
Shaft
Drive Method Constant Current Chopping
Driver IC LB1947
Op03
Figure 2-3. Carriage Mechanism (Top view)
In previous ink jet printers, since a stepping motor is used as a CR motor, the CR motor
controls the carriage position under the open loop system. This printer, however,
controls carriage speed and position with the closed loop system enabled by a DC
motor and encoder. This system, also used in the Stylus COLOR 900, is applied to
maintain a constant print quality. The CR motor also produces the print timing signal
(PTS signal) used for an accurate ink ejection timing. (Refer to Section 2.2.2.3 for
further information on the CR motor control circuit.)
For printing, the CR motor moves the carriage unit in the printing area along the CR
guide shaft.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 36
Page 37

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.2.2 Platen Gap (PG) /Parallelism Adjustment Mechanism
The PG adjust lever is attached to the left end of the carriage guide shaft. When the
carriage guide shaft, which has an eccentricity, rotates as the adjustment lever moves, it
narrows or widens the distance (=PG: from 1.2 mm to 2.1 mm). This mechanism
enables the user to print with a correct PG according to print result or other conditions
such as paper curl.
Also, the parallelism adjustment bushings are attached to the right and left ends of the
carriage guide shaft. They are used to set the carriage guide shaft parallel with a platen.
Table 2-5. Platen Gap Adjust Lever Setting
Table 2-6.
Lever Position PG adjustment value
Front (0) 0 mm (=PG is 1.2 mm)
Rear (+) + 0.9 mm (=PG is 2.1 mm)
2.1.2.3 Carriage Home Position (HP) Detection
Unlike previous Epson ink jet printers, the carriage home position is detected with the
drive current from the CR motor and speed/position signal from the linear encoder.
2.1.3 Paper Feeding Mechanism
The paper feeding mechanism transports paper loaded from ASF using the PF rollers
and paper eject rollers. A new type of DC motor is used as the PF motor. See the table
below for the PF motor specifications.
Table 2-7. PF Motor Specifications
Table 2-8.
Item Description
Motor type DC Motor with Brush
Drive voltage +42V +/- 5% (Applied to the driver)
Coil Resistance 29.2ohm +/- 25%
Inductance 30.0mH +/- 25%
Control method Constant current chopping drive
Stepping motor that is used in other printers as the PF motor controls paper feed by the
open loop system. On the other hand, this printer controls paper feeding mechanism
with the closed loop system by employing the DC motor and rotary encoder for more
accurate paper feeding. Therefore, a rotary encoder attached to the left end of the PR
roller shaft controls paper feed amount. For detailed information, see Section "PF
motor driver circuit".
Drive from the PF motor is sent to the PF rollers and paper eject rollers as described
below.
Drive transmission to the PF rollers:
PF motor pinion gear
Drive transmission to the eject rollers:
PF motor pinion gear
gear (28)
→
Paper eject rollers
→
Spur gear (76) → PF rollers
→
Spur gear (76) → Combination gear (13.5, 308) → Spur
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 37
Page 38

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Figure 2-4 gives the paper feeding mechanism block diagram, showing the parts along
the PF motor drive transmission paths.
Combination Gear
(13.5, 308)
Spur Gear (76)
PF Motor Pinion Gear
Paper Eject Roller
PF Roller
PF Motor
Front Paper Guide
Paper Eject Roller
Figure 2-4. Paper Feeding Mechanism
The printer loads paper at the ASF, which is detected by the PE sensor attached to the
right side of the top frame, and advances it to send the paper’s leading edge to the
halfway of the front paper guide. Then, to correct paper deflection, the printer feeds the
paper back specified steps toward ASF, and advances the paper again toward the front
paper guide and stops it at the specified TOF (Top Of Form) position. Once printing
starts, the paper is fed by the PF rollers and sub rollers. For printing or transporting the
tailing edge area (14 mm), a notched roller and drive from the paper eject roller are
used. Like the Stylus Photo 870/1270, this printer also provides this extra printable
range of 14 mm from the bottom edge, excluding the bottom margin of 3mm, by
changing the position of the star wheel gear; it has been shifted by 5
the eject roller toward the front paper guide. Due to this change, the tailing edge of
paper is suppressed, and the printer can advance paper steadily. See Figure 2-5 next
page that shows how paper is transported and parts involved.
°
from the top of
[Previous Models]
Platen Surface
Notched Roller
Paper
Paper Eject Roller
[Stylus Photo 890/1290]
Figure 2-5. Paper Transportation
Printhead
Bottom Margin (3 mm)
5
°
Steady Feeding
Support Roller
PF Roller
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 38
Page 39

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.3.1 CR Lock Mechanism
The carriage lock mechanism prevents the carriage from being left uncapped for a long
time, which is usually caused by vibration during printer transportation, user’s
mishandling of the printer, and so on. If the carriage unit is left uncapped for a long
time, ink on the printhead surface dries gradually and, eventually, ink can not flow to
nozzles. In addition to that, there is a possibility that the nozzles clogged with dried ink
can not be recovered by a head cleaning. To avoid this problem, the printer locks the
carriage unit under the circumstances below:
After Power-Off
If the printer power is turned off in the middle of printing or other operations, the
printer completes the initialization sequence and then performs a carriage lock.
After Power-On
When the printer is turned on, the printer automatically begins a power-on cleaning
and then performs a carriage lock.
[Power-on cleaning]
The printer runs a power-on cleaning automatically when its power is turned on. Since
the timer IC on the main control circuit board is powered by a lithium battery that is
also mounted on the board, it keeps counting the printer’s power off time. According to
the power of time counted, the printer selects the cleaning level to perform.
After paper ejection
If the printer does not receive any print data after Load/Eject button is pressed, it
performs a carriage lock and enters a standby status. But if paper is fed into the printer,
the printer does not perform it.
Top View
Bushing
Paper Eject Roller
CR Lock Lever
Middle Frame
Figure 2-6. CR Lock Mechanism
Right Side View
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 39
Page 40

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.4 Paper Loading Mechanism
The paper loading mechanism loads paper at the ASF unit and feeds paper to the PF
rollers. The ASF unit is the same as in previous models. A 4-phase 48-pole PM type
stepping motor is used as the ASF/Pump motor to drive ASF. Drive sent from this
motor is transmitted to the ASF side and Pump side via the disengage mechanism (DE
mechanism). See Figure for the ASF/Pump motor specifications.
Table 2-9. ASF/Pump Motor Specifications
Items Description
Motor type 4 Phase/ 48-pole /PM type pulse motor
Drive method Bipolar constant current drive
Drive voltage
Coil Resistance 10.4 ohm +/- 10%
Inductance 15.0 ohm +/- 10%
The rotation directions in order to drive ASF unit/ Pump mechanism are as shown
below.
Table 2-10. Directions of ASF Unit/Pump Mechanism Rotation
Rotation Direction
*2
CW
*3
CCW
ASF Paper Loading Roller
Rotation Direction
+42V +/- 5% (applied to the driver)
Pump Rotation Direction
Reverse Rotation Normal Rotation
Normal Rotation Reverse Rotation
*1
2.1.4.1 Drive Transmission to the ASF Unit
1) The CR unit moves to the right end of the CR shaft, which then pushes the DE
lock lever to the right end.
2) The ASF/Pump motor rotates counterclockwise specified steps (viewed from the
motor pinion gear side).
3) With the ASF-Pump motor’s rotation of step 2), the planetary gear set in the DE
unit shifts toward the combination gear (12, 22.4).
4) The carriage unit moves from the right end of the CR shaft specified steps, which
causes the DE lock lever to fix the planetary gear unit.
5) Torque from the ASF/Pump motor is transmitted as described below.
Motor pinion gear
Combination gear (14, 28)
Figure 2-7 shows the disengage mechanism and its parts.
Combination Gear
14, 28
→
Planetary gear (15.2) → Combination gear (12, 22.4) →
→
Spur gear (32) in ASF
Combination Gear 12, 22.4
Planetary Gear 15.2 Unit
DE Lock Lever
A
*1
: Refer to “Drive Transmission to the ASF Unit” on page -40
*2
: CW refers to clockwise from ASF/Pump Motor Pinion side
*3
: CCW refers to counterclockwise from ASF/Pump Motor Pinion side
Drive from the ASF/Pump motor is sent to the ASF unit by the switching operation of
ASF-Pump Motor Pinion Gear
Figure 2-7. Disengage Mechanism
Combination Gear 17.19, 25.6
the carriage unit and the DE mechanism described in the following section.
The ASF unit loads paper by the torque sent from the ASF/Pump motor via the DE
mechanism as described in the following section.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 40
Page 41

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.4.2 Paper Loading Operation
Multiple paper loading prevention mechanism is included in the ASF unit to ensure
steady paper loading. To prevent any paper from falling from the paper set position
into the paper path, the paper return lever pushes paper that may have fallen off back
onto the hopper. After this motion is completed, the LD roller starts loading paper. The
paper loading mechanism, including the multiple paper loading prevention mechanism,
is described in the following steps.
1) When the printer power is turned on, the ASF/Pump motor rotates
counterclockwise to detect ASF home position. Then it rotates clockwise specified
steps to set the LD roller and paper return lever in their standby status. (See
“Standby State” in Figure 2-1.)
2) When the paper loading signal is sent from the PC and the Load/Eject button is
pressed, the ASF/Pump motor turns counterclockwise to let the LD roller start
loading paper. (See “Paper Pick Up State” in Figure 2-1.)
3) When the paper is transported to the PF roller, the LD roller stops where it loses
friction. (See “PF Roller Paper Feed State” in Figure 2-1.)
4) When the next print signal is sent and Load/Eject button is pressed*, the ASF/
Pump motor rotates clockwise specified steps to set the LD roller and the paper
return lever in standby status. (See “Standby State” in Figure 2-1.)
* If the printer does not receive any print signal for TBD seconds in step 4, the LD
roller and the paper return lever automatically return to the standby state.
LD Roller
Paper Return
Lever
Standby State
Flowchart 2-1. Multiple Paper Loading Prevention Mechanism
Hopper
Cam
Hopper Spring
Pad Spring
Pad
2
Paper Load State
Pinch Roller
3
PF Roller Paper
Feeding State
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 41
Page 42

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Torque transmission to the pump unit
2.1.4.3 Pump Mechanism
The pump mechanism absorbs ink from the printhead and the cap assembly. The wiper
for head cleaning is included in the cap assembly.
The pump mechanism is driven by the ASF/Pump motor, a 4phase 48-pole PM type
stepping motor. See Table for the ASF/Pump motor specifications. When the torque
from the ASF/Pump motor is switched to the pump unit side, the pump mechanism acts
differently according to the directions of the ASF/Pump motor rotation, as shown in the
table below.
Table 2-11. ASF/Pump Motor Functions
Directions Corresponding Functions
Counterclockwise
Clockwise
• Absorbs ink.
•Sets the wiper.
• Releases tube.
• Resets the wiper.
The torque from the ASF/Pump motor is transmitted to the pump mechanism as
described below:
1) The CR unit moves to the right end of the CR shaft, which then pushes the DE
lock lever to the right end.
2) The ASF-Pump moto r rotates clockwise (viewed from the motor pinion gear
side) specified steps.
3) With the rotation of step 2), the planetary gear set in the DE unit moves toward
the combination gear (17.19, 25.6).
4) The CR unit moves specified steps from the right end of the CR shaft to the
left. With this motion, the DE lock lever fixes the planetary gear set.
5) Torque from the ASF/Pump motor is transmitted as described below.
Motor pinion gear
Tension belt → Pump unit gear → Pump unit
→
DE pump mechanism and operating principle are as shown in the figure below.
Planetary gear (15.2) → Combination gear (17.19, 25.6)
→
Combination Gear 14, 28
Combination Gear 12, 22.4
Planetary Gear 15.2
A
DE Lock Lever
Tension Belt
Figure 2-9. Pump Operating Principle
ASF/Pump Motor Pinion Gear
Figure 2-8. Torque to the Pump Mechanism
Combination Gear 17.19, 25.6
Pump Unit Gear
1. When the pump unit rotates CCW from ASP/Pump motor side, rollers rotates
compressing a tube, and the ink in the tube is pressed from the capping unit down
to waste ink pads.
2) When the pump unit rotates CW, the rollers stop compressing the tube, and the ink
is not pressed to the waste in pack.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 42
Page 43

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.1.4.4 Capping Mechanism
The capping mechanism, which is driven by the pump unit, caps the printhead closely
to maintain air tightness inside the cap. This operation is required to vacuum ink from
the ink cartridges, printhead, and cap. Also, to moisten the inside of the cap while the
printer power is off, this mechanism works to keep the cap and the printhead surface in
a tight contact. This function prevents ink from clogging while the printer is not in use.
Previous Models
Negative
pressure is
released here.
Closed state
Ink Ejection
Hole
Valve
Released state
The capping mechanism of this printer is a newly designed valveless capping
mechanism. So, unlike previous printers, it does not integrates an air valve. The air
valve is usually equipped to remove bubbles created inside the cap by releasing the
negative pressure. However, due to change in the ink sequence, the new valveless
capping mechanism enables the printer to maintain the initial ink charge and cleaning
effects at the same level as before. Figure 2-10 outlines the valveless capping
mechanism.
Stylus Photo 890/1290
Ink Ejection
Hole
There is no air valve
assembled.
Figure 2-10. Valveless Capping Mechanism
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 43
Page 44

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2 Electrical Circuit Operating Principles
The electric circuit of the Stylus Photo 890/1290 consists of the following:
Control circuit board:
Power supply board: C378PSB/PSE
Panel board: C393PNL
C393MAIN/C393MAIN-B/C393MAIN-C
Refer to Figure 2-11 for the major connection of the boards and their roles.
C393PNL Panel Board
C393PNL Panel Board
Printer Mechanism
Printer Mechanism
CR Motor
C393MAIN / C393MAIN-B/
C393MAIN / C393MAIN-B/
C393MAIN-C Control Board
C393MAIN-C Control Board
PF Motor
ASF/Pump Motor
3.3V Regulator
3.3V Regulator
Head Driver Circuit
Sensors
Power OFF
+5VDC
+42VDC
2.2.1 C378PSB/PSE Board
The power supply board for the Stylus Photo 890 and Stylus Photo 1290 is C378PSB/
PSE. It uses a RCC switching regulator system, and supplies +42VDC and +5VDC to
the printer mechanism and control board.
2.2.1.1 Electrical Circuit
The table below shows the voltages produced in this circuit and their applications.
Table 2-12. Application of the DC Voltages
Table 2-13.
Voltage Application
• CR Motor
+42VDC ± 2VDC
+5VDC ± 0.25VDC
NOTE: The 5VDC is only applied to the parts and locations shown in the table above.
The C393MAIN uses 3.3V drive chips for most of the logic-line chips (CPU,
ASIC, ROM, DRAM). For this reason, those chips are not driven by the +5VDC
produced by the but power supply board but the 3.3VDC that is reduced by the
3.3VDC regulator on the C378PSB/PSE.
• ASF/Pump Motor
• PF Motor
• Head driving power supply
• Logic sensor circuit
•Panel LED
• Nozzle selection circuit (on the printhead)
• I/F control circuit
C378PSB/PSE Power
C378PSB/PSE Power
Supply Board
Supply Board
Figure 2-11. Electric Circuit of Stylus COLOR 890/1290
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 44
Page 45

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Figure 2-12 shows the block diagram for the C378PSB/PSE bo ard.
The C378PSB/PSE Board produces the +42VDC and +5VDC using AC power as
described below:
1. Regardless of the power switch’s on/off condition, voltage is always applied to the
primary side of the power supply board from the moment or at the state that ACplug is plugged in. F1, a fuse, prevents AC100V from flowing into the circuit. A
power thermistor TH1 also protects the circuit from rush current after power-on.
The filter circuit composed of L1, C1, and C2 prevents high harmonic wave noise
generated in the switching circuit from going out, and eliminates the noise from
outside.
2) The AC voltage is full-wave rectified by the diode bridge DB1 and smoothed by
C11.
3) Switching FET Q1 turns on via starting resistors R18 and R28 that are located on
the AC side to begin switching operation. By arranging the starting resistors on the
AC side, half waves of the AC voltage are only applied, and power used for this
operation is reduced compared with usual serial layout.
4) When the primary side is on, because the diode (D51) on the secondary side is
installed in the reverse direction, energy (current) led by the electromagnetic
induction through the trans (T1) does not flow to the secondary side.
5) When the energy charged in the transformer reaches a saturated state, the voltage
which keeps Q1 on becomes weak gradually. At the point this voltage drops to a
certain level, C13 absorbs the reverse current and Q1 quickly shuts off.
6) When the primary side is turned off, the energy charged in T1 is opened according
to the diode(D51) direction on the secondary side. +42 V DC is output by these
circuit operations and the number of T1 spiral coil.
7) +5VDC is generated out of this +42VDC. Forming reference sawteeth waveform s
with an external RC integrating circuit, IC51 produces stable +5VDC with a
chopping circuit.
Figure 2-12. C378PSB/PSE Board Block Diagram
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 45
Page 46

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.1.2 Protection Circuits
The C378PSB/PSE board has the various protection circuits to stop voltage outputs if
an abnormal condition relating to the control circuit or the printer mechanism’s duty
occurs.
+42VDC Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit:
The output level of the +42V line is monitored by a detection circuit composed of
numbers of Zener diodes, and the information is fed back to the primary side via
photo coupler PC1. Along with the fed back signal, the switching FET on the
primary side varies the level of the voltage output to the secondary side by
changing its frequency to keep the voltage up.
+42VDC line over current protection circuit:
If the +42 VDC line is over currented, the output voltage level drops drastically.
When the voltage level is 36V or lower, zener diode ZD90 detects that condition
and sends information to the primary side via photo coupler PC1. In the primary
circuit, then, switching operation stops to protect the electrical circuits and printer
mechanism. To reset the circuit, turn the printer off and back on.
+42VDC line over voltage protection circuit:
If the voltage level of the +42VDC line exceeds 59V, zener diodes D52 and ZD87
detect it and feed back the information to the primary side via photo coupler PC1 .
The switching operation in the primary side then stops to protect the electrical
circuits and printer mechanism.
+5V line constant voltage/constant current control circuit:
Both +5V line output voltage and +5V line output current are monitored by
chopper IC (IC51). Detected information is input to the IC’s internal comparator
and stabilizing circuit. When the IC detects abnormally high current level, it stops
outputting voltage. The circuit recovers automatically.
2.2.1.3 Power Supply Control Function
Since this printer has the power switch in the secondary circuit, even if its power is
turned off through the operation panel, it can continue to supply voltage to the +5VDC
line and +42VDC line for about 30 seconds. This extra time allows the printer to
complete the following operations:
If the printer is in a printing motion and the CR unit is out of its home position, the
printer stops printing, returns the CR unit to the home position, and performs CR
lock operation. Then the printer power shuts down.
If the printer is not printing but paper loaded at ASF remains in the printer, the
printer ejects the paper before the printer power shuts down.
2.2.1.4 Energy Save Mode
The power supply circuit enters the energy save mode by the signal ESAVE sent from
the control circuit. One the circuit is in this mode, it maintains the +42V line level in a
range from +20V to +23V.
+5V line over voltage protection circuit:
If the +5VDC output level exceeds 12V, zener diode ZD53 detects that condition
and feeds back the information to the primary side via photo coupler PC1. The
switching operation in the primary side then stops to protect the electrical circuits
and printer mechanism.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 46
Page 47

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.2 C393MAIN Board Circuit Operation Principles
The C393MAIN board includes the following:
Logic circuit (CPU, ASIC, DRAM, EEPROM, and so on)
Various motor control/driver circuits (CR motor, PF motor, and ASF/Pump
motor)
Head control/driver circuits
Interface circuit (parallel I/F, USB I/F)
Sensor circuit
Timer circuit
Reset circuit
The C393MAIN/C393MAIN-B/C393MAIN-C board is mainly different from other
main boards in the following points.
Use of 3.3V drive logic chips
IC21, the 3.3 V regulator IC on the C393MAIN, produ ces 3.3 V by pressuring
down the 5.5 VDC generated on the C378PSB/PSE board to drive several chips.
These chips are used to reduce power used to drive the logic circuit. See the table
below that separately shows the chips driven by the +5V and +3V.
Table 2-14. 3.3V Drive Chips & 5.5V Drive Chips
Table 2-15.
There are three kinds of main board installed on EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290.
Stylus Photo 890 is equipped with either C393MAIN-B or C393MAIN-C while Stylus
Photo 1290 is equipped with either C393MAIN or C393MAIN-B. Block diagram of
each main board are shown in the following figures below.
CR Encoder senser
Head
CR1
Timer &
Reset IC
(IC4)
IC4
E0BA13KA
IC7
+5V 3.3V
CPU
Sensors
USB I/F Circuit
(Except high speed)
PNL Board
ASIC
P-ROM
D-RAM
RTC/Reset/EEPROM
USB I/F Circuit
(During high speed)
Figure 2-13. Block Diagram for the C393MAIN Board
(For Stylus Photo 1290 only)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 47
Page 48

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
CR Encoder senser
Head
CR1
Timer &
Reset IC
(IC4)
IC4
IC7
E0BA13KA
Figure 2-14. Block Diagram for the C393MAIN-B Board
(For Stylus Photo 890/1290)
CR Encoder senser
Head
CR1
Timer &
Reset IC
(IC4)
IC4
E0BA13KA
IC7
Figure 2-15. Block Diagram for the C393MAIN-C Board
(For Stylus Photo 890 only)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 48
Page 49

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 2-16 shows the major ICs on the C393MAIN Board and their functions.
Table 2-16. Major Element on C393MAIN
IC Location Functions
A 144-pin QFP package. Operates at 24.0MHz. Power supply voltage is
CPU (HD6412670)
(C393MAIN/
C393MAIN-C)
ASIC (E05B87**)
(C393MAIN/
C393MAIN-C)
ASIC
(E01A20CA**)
IC18
IC19
IC19
3.3V.
• Sets the current value for the ASF/Pump motor.
• Measures the printhead temperature.
• Several interrupting functions
• Outputs the system clock signal.
A 240-pin QFP package. Operates at 48.0MHz/24.0MHz/28.0MHz. Power
supply voltage is 3.3V.
• Controls interfaces.
• Controls specified motors.
• Controls the printhead drive waveform circuit.
• Transfers serial data to the printhead.
• Controls the ASF/ Pump mot o r
• Receives panel control signals and sensor signals
•EEPROM
• Controls detection of the signals output from the encoder.
• CPU and ASIC are built in in the IC.
PROM IC2
DRAM IC5
RTC IC
RTC9822**
IC4
8/16Mbit
• Stores the firmware or firmware +CG
A 16Mbit DRAM. Power supply voltage is 3.3V.
• Serves as specified buffers and work area
• Resets the +5V/+24 VDC line circuits.
• Serves as the timer powered by a lithium battery.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 49
Page 50

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.2.1 Printhead Driver Circuit
The printhead driver circuit includes:
Common driver IC10 (E09A14RA)/IC11 (E09A15KA) directly attached to
the C393MAIN board.
Nozzle selector IC (IR2C95F or SED6125T0A) on the head board.
The common driver generates reference drive waveforms according to the output
signals from ASIC on the C393MAIN board. The reference drive waveforms are
amplified by the transistors Q2 and Q3 and then transferred to the nozzle selector IC on
the head board. Print data is converted to serial data by the ASIC and then also sent to
the nozzle selector IC on the head board. Based on the serial data, the nozzle selector
IC determines the nozzles to be actuated. The selected nozzles (PZT) are driven
according to the drive waveforms produced by the common driver. See Figure 2-16 for
the printhead driver circuit block diagram.
Head common driver circuit
The head common driver IC10 (E09A14RA)/IC11 (E09A15KA) generates
reference head drive waveforms according to the output of the following 9 signal
lines: A0-A4, CLK1, CLK2, RST, FLOOR, and DATA.
By the DATA signal output from the IC19 ASIC (E01A20CA**), the original data
for the head drive waveform is written in the memory in the IC10/IC11. Addresses
for the written data are determined by the A0 - A4 signals, and, of among, data
used to determine the waveform angles is selected. Then, setting the selected data,
producing trapezoid waveform value, and canceling the data are performed by the
rising edges of the CLK1 and CLK2 signals.
Head nozzle selector circuit
Print data is converted into serial data by the ASIC (E01A20CA**). Then the
converted data is allocated to the six rows, the number of the head nozzle rows, to
be transferred to the nozzle selector IR2C95F (Sharp) or SED6125T0A (EPSON)
through the six signal lines (HS01 to HS06). Data transmission from IC19 ASIC
(E01A20CA**) to the nozzle selector synchronizes with the LAT signal and SCK
clock signal. Referring to the transferred data, The nozzle selector IC selects the
nozzles to be activated, and the PZTs of the activated nozzles are driven by the
drive waveforms output from the head common driver.
Figure 2-16. Printhead Driver Circuit
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 50
Page 51

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.2.2 RTC (Real Time Clock)/ Reset/ EEPROM Circuit
RTC9822**includes built-in RTC and EEPROM and functions as a reset. The RTC
part has an electric two-layer condenser for backup. The RTC/Reset/EEPROM circuits
are attached on the C393MAIN board to monitor two voltages: +5V for the logic line
and +42V for the drive line. When each circuit detects abnormality on the
corresponding line, it resets CPU and ASIC to prevent the printer from operating
abnormally.
IC4 RTC9822** is attached on the main board as a RTC/Reset/ EEPROM circuit IC.
EEPROM part backups default setting value and each parameter. IC4
RTC9822**monitors +3.3, +5V, and +45 lines but can reset them independently. See
Figure 2-17 for the block diagram for the reset circuits.
+42V line reset circuit
The VIN port of the IC5 reset IC monitors the +45V line. When the IC detects an
abnormal voltage level (36V or lower), it outputs a reset signal from the VDT port
to CPU and ASIC.
Figure 2-17. RTC/Reset/EEPROM Circuit Block Diagram
+3.3V Line Reset Circuit
The VDD port of IC4 reset IC monitors the +5V line. When the IC detects an
abnormal voltage level (2.5 V or lower), it outputs a reset signal from the RST port
to CPU and ASIC.
+5V Line Reset Circuit
The VDD port of IC4 reset IC monitors the +5V line. When the IC detects an
abnormal voltage level (4.2 V or lower), it outputs a reset signal from the RST port
to CPU and ASIC.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 51
Page 52

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.2.3 Motor Driver Circuit
Stylus Photo 890/1290 is equipped with 3 kinds of motors, the CR motor and PF motor
that are a DC motor and an ASF/Pump motor, and a stepping motor. The DC motor on
the C393MAIN board is used for DC motor control.
CR motor driver circuit
IC9 (A39374SLB) on the C393MAIN/C393MAIN-B board controls the CR and PFDC
motor while IC9(A3958SLB) on the C393MAIN-C board controls the CR motor.
ASIC sends signals of IC9 through IC8 and determines current of the CR motor. By
setting RST_DCMCU of ASIC “LOW “ level, the motor turns into a
“SLEEP”condition for energy saving.
The block diagram of the CR motor driver IC (IC9) is as shown below.
op13b
Figure 2-19. CR Motor Driver Block Diagram (C393MAIN-B)
Figure 2-18. CR Motor Driver Circuit Block Diagram (C393MAIN)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 52
Page 53

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
+
-
+
-
1/180”
1/720”
Phase A
Phase B
1/360”
Backward Rotation
(Counterclockwise)
Figure 2-20. CR Motor Driver Circuit Block Diagram (C393MAIN-C)
NOTE: When C393MAIN-C is installed, ASIC sends signals of IC9 and IC1 through IC8
and determines current of the CR motor.
ASIC (IC19) controls the CR position by referring to the pulses sent from the linear
encoder. Based on the data sent from ASIC, the CPU sets an appropriate drive current
value used to determine the CR position and the direction in which the CR moves.
ASIC outputs specified control signals to the motor driver. The motor driver IC9 then
outputs CR motor drive current to the CR motor.
Unlike stepping motors, the DC motor that drives the carriage
carriage position by referring to the pulses given. For this reason, a linear scale is
attached along the carriage operation range to detect the carriage position. The linear
encoder sensor outputs two kinds of TTL level pulses: Phase A and Phase B.
can not detect the current
Phase A
Phase B
LED
Lens
Photo
Photo
Diodes
Diodes
Forward Rotation
(Clockwise)
Comparators
Comparators
A
A
Phase A
B
B
Phase B
Figure 2-21. CR Linear Scale Encoder Pulse
Direction for the CR’s current movement is detected based on the pulse waveforms of
the shifted Phases A and B. Carriage position is, on the other hand, controlled based on
a cycle of Phase A output waveform (1 cycle=1/180 inches). Also, all rising and falling
edges of the waveforms in the both phases (1 cycle=720) are used to control the
position of the CR that is in its home position for ink system.
Home position detection
Home position is detected based on the pulses output from the linear scale sensor
and DC motor control current value. The basic home position detection sequence
is as described below:
1) The linear encoder pulse counter in the ASIC (IC19) is reset by an
initialization sequence at power-on.
2) The CR motor turns forward (clockwise) to move the carriage to the right.
ASIC(IC19)assumes that the CR is in contact with the right frame when the
following conditions are satisfied:
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 53
Page 54

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
ASIC(IC19) detects the motor control current value is 720mA.
P1 (= number of pulses output during the above carriage movement) is
30* or less.
1/180”
* Specified val ue that indicates CR is in the home position. (All edges in the
waveform are used in this condition.)
3) The CR motor rotates backward (counterclockwise) to move the carriage back
to the left, and ASIC(IC19) assumes that the carriage enters the CR lock lever
position when the following conditions are satisfied:
ASIC(IC19) detects the motor control current value is 500 mA.
Difference between P1 and P2 (= number of pulses output while the CR
moves from the right frame) is 30 or less.
4) The CR motor rotates backward to move the carriage to the right again, and if
ASIC (IC19) detects the motor control current value is 720 mA, it assumes
that the CR comes in back in contact with the right frame.
5) Difference between P1 and P3 (= number of pulses output for the CR’s
movement from the CR lock lever position to the right frame) is 4 or less.
When all the conditions in the sequence are satisfied, the printer detects the CR is in
the home position.
PTS (Print Timing Signal) production
The circuit produces PTS signal (cycle: 1/360 inches) by dividing waveform
cycles of Phase A. The print timing signal is used to eject ink at a correct timing.
Phase A
Phase A
Phase B
Phase B
1/360”
Figure 2-22. Print Timing Signal and Linear Encoder Phase A
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 54
Page 55

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
PF motor driver circuit
DC motor is used as the PF motor in this printer. IC9 (A39374SLB) on the
C393MAIN/C393MAIN-B board controls the CR and PFDC motor while
IC9(A3958SLB) on the C393MAIN-C board controls the CR motor.
The block diagram of the PF motor driver circuit is as shown below:
op13b
Figure 2-24. PF Motor Driver Circuit Block Diagram (C393MAIN-B)
Figure 2-23. PF Motor Driver Circuit Block Diagram (C393MAIN)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 55
Page 56

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
1/1440”
1/5760“
Phase A
Phase B
Forward Rotation
(Clockwise)
Figure 2-25. PF Motor Driver Circuit Block Diagram (C393MAIN-C)
ASIC(IC19)controls paper feeding amount by referring to the encoder pulses. ASIC
sends a proper drive current value to the motor driver. Based on the control signal from
ASIC, the motor driver (IC9or IC1) outputs drive current to the PF motor.
Unlike a stepping motor, this DC motor can not detect paper feeding amount by
referring to the pulses given. For this reason, a loop scale is attached on the Gear 76 to
detect paper feed amount.
The loop scale encoder sensor outputs two kinds of TTL level pulses Phase A and
Phase B to ASIC (IC19). Direction of the PF motor rotation is determined by the phase
between the output waveforms from Phase A and the waveforms form Phase B
Phase A
Phase B
LED
Backward Rotation
(Counterclockwise)
Lens
Photo
Photo
Diodes
Diodes
Comparators
Comparators
A
+
A
-
B
+
B
-
Figure 2-26. Loop Scale Encoder Pulse
Phase A
Phase B
op25
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 56
Page 57

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.2.4 ASF/Pump Motor Driver Circuit
ASF/Pump motor is a PM type stepping motor. The block diagram for the ASF/Pump
motor is as shown below:
Figure 2-27. ASF/Pump Motor Circuit Block Diagram
(C393MAIN/C393MAIN-C)
Figure 2-28. ASF/Pump Motor Circuit Block Diagram
(C393MAIN-B)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 57
Page 58

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
2.2.2.5 Sensor Circuit
Stylus Photo 890/1290 has the following five sensors to detect printer’s status.
PE sensor
ASF sensor
Ink cartridge sensor (CSIC connector on the head board)
Head thermistor sensor
PF motor encoder
CR motor encoder
The block diagram for the sensor circuit is as shown below:
Figure 2-30. Sensor Circuit Block Diagram (C393MAIN-B)
Figure 2-29. Sensor Circuit Block Diagram
(C393MAIN/C393MAIN-C)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 58
Page 59

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Each sensor’s functions and operating principles are as described below:
PE sensor
The PE sensor is located at the bottom right edge of the top frame in the printer
mechanism. It detects paper on the rear paper guide using a photo sensor and PE
sensor lever that are included in the sensor. When paper is present, the PE sensor
lever does not cut in between the photo sensor terminals. So it outputs a LOW
signal to the ASIC. If there is no paper, on the other hand, the lever cuts in between
the photo sensor terminals. So it outputs a HIGH signal to the ASIC.
ASF sensor
The ASF sensor, located at the left edge of the ASF, detects ASF home position.
This sensor consists of the ASF HP detector wheel and a transmission photo
sensor. A small portion of the ASF HP sensor has a cutout, and when the cutout
comes into position between the photo diode terminals, that condition is detected
as ASF home position. In this status, since the photo diode terminals are not
blocked by the wheel, a LOW signal is output to ASIC. Otherwise, a HIGH signal
is output. Referring to the ASF home position detected by this sensor, the printer
drives the ASF/Pump motor to set the LD roller and paper return lever ready to the
paper loading position.
Ink cartridge sensor (CSIC connector on the head board)
Ink cartridge sensor detects whether a black or color ink cartridge is installed.
Installation condition is determined depending on the CSIC’s connection. When a
cartridge is installed, a LOW signal to ASIC is output. On the other hand, a HIGH
signal is output when a cartridge is out.
resolution of the sensor is 1/180 inch. It outputs HIGH signals for the black bands
and LOW signals for the transparent parts of the linear scale to the ASIC. The
printer controls the CR motor based on the signals output from this sensor. CR
home position is also detected based on the signals from this sensor.
Head thermistor
The head thermistor is directly attached on the head driver board. It monitors the
temperature around the printhead and feeds back the temperature to the CPU
analog port. The printer refers to this information to control head driver voltage
based on the ink viscosity.
PF motor encoder
The PF motor encoder includes the loop scale attached to the left end of the PF
roller shaft and the transmission photo sensor. The minimum resolution of the
sensor is 1/180 inches. The sensor outputs HIGH signals for the black lines and
LOW signals for the transparent parts to the ASIC. The printer controls the PF
motor based on the signals output from this sensor.
CR motor encoder
CR motor encoder consists of the transmission photo sensor assembled in the CR
unit and the linear scale attached along the CR scanning line. The minimum
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuit Operating Principles 59
Page 60

TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER
3
Page 61

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
3.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to troubleshoot problems. It consists of the sections shown
in the flowchart below. When identifying and troubleshooting problems, be sure to
proceed to the correct section specified in the flowchart.
STARTSTART
Troubleshooting with
LED error indicators
Isolating the defective
parts on the power supply
board
Figure 3-1. Troubleshooting Flowchart
Isolating the problem
with exhibited
phenomenon
Table 3-1. Motor Resistance and Measurement Procedure
Motor
CR Motor CN14 Pin 1 & 2 29.2
PF Motor CN13 Pin 1 & 2 29.2 Ω +/- 25%
ASF/Pump Motor CN15
Connector
to check
Check pins Coil resistance
Ω
+/- 25%
Pin 1 & 3 or Pin
2 & 4
10.4
Ω
+/-10%
Table 3-2. Sensor Check and Measurement Procedure
Sensor Checkpoints Signal level
LOW Paper present
PE Sensor CN5, Pin 1 &2
HIGH Paper out
LOW In the ASF home
ASF Sensor CN6, Pin 1 &2
HIGH Out of the ASF home
Corresponding
condition
position
position
Following sections give detailed information on each step in the flowchart. Be sure to
perform troubleshooting by following the specified steps without omitting any
necessary operations.
Following tables show the checkpoints for each motor and sensor.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 61
Page 62

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
3.1.1 Self-Diagnostic Function
The EPSON Stylus PHOTO 890/1290 is equipped with the self-diagnostic function.
With this function, the printer can check its operations after power-on, and shows its
various conditions using LED indicators.
3.1.1.1 Troubleshooting with LED Error Indicators
l
Table 3-3. Error Indication of Operation Panel
Printer Status
Power On condition On - 11
Ink sequence Blink - 7
Ink Cartridge replacement mode Blink - 6
Data Processing Blink - 10
Paper Out
Paper Jam
Double Feed Error
Ink End (Black)
*1
*1
*1
*1
Indicators
Priority
Power Error
-On5
- On 5
On 4
- On->Blink 9
Table 3-3. Error Indication of Operation Panel
Printer Status
Maintenance Request (Ink
Overflow Counter error)
Fatal Error Off On 1
Special setting Blink2 Blink2 -
Alt Blink Alt Blink 2
Indicators
Priority
Power Error
3.1.1.2 Error Conditions
This printer indicates an error when detecting the following conditions, and sets the
interface signal “/ERROR” to LOW and “BUSY” to HIGH to stop data input. In this
condition, the printer automatically enters non-printable status. Note if the printer is
establishing communication by IEEE1284.4 protocol, however, it remains in printable
status.
Each error condition is described below:
Ink Out
When the printer runs out of the most of the ink of any color, it warns Ink Low and
keeps printing.
Ink Level Low (Black) - Blink->Blink 9
Ink End (Color)
Ink Level Low (Color) - Blink->Blink2 9
Ink End (Black & Color)
Ink Level Low (Black & Color) - Blink->On 9
No Ink Cartridge (Black or Color) - On 8
Reset, Timer IC reset, EEPROM
clear
Ink Overflow Counter Reset On On
*1
*1
- On->Blink2 9
- Blink->Blink 9
On On -
Ink End
Ink in black/color cartridge ends.
Remaining level of ink is low. In this case, the printer warns of the condition with
LED indicators. If ink runs out, on the other hand, the printer shows an ink end
condition and stops its operation. Note the error occurs if ink of any color in the
color ink cartridge runs out.
Paper Out
The printer attempts to load paper but fails.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 62
Page 63

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Paper Jam
The printer fails to eject remaining paper with the specified number of paper
feeding steps at power-on.
The printer can not eject paper despite the FF command is sent or Maintenance
Switch is pressed.
No Ink Cartridge
Ink cartridge is not installed or installed incorrectly.
Information in CSIC of the ink cartridge is not read or written properly.
Maintenance Request
Total wasted ink amount reaches its capacity by cleaning and flashing. The printer
indicates the error and stops operations.
C A U T I O N
Maintenance request error is not cleared until the waste ink pad is
replaced with a new one, and the waste ink counter in EEPROM is
reset by the service operation.
Fatal Error
A fatal error is indicated when a carriage control error or CG access error occurs.
Double Feed Error
If the printer fails to load paper during duplex printing, the error occurs. Refer to
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 63
Page 64

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-4. Error Condition and Possible Causes
No. Error Possible Causes Refer to:
1 Paper Out 1. Failure in paper loading
2. PE sensor connector is disconnected.
3. Sensor actuator is not acting properly or sensor bracket is not installed correctly.
4. PE sensor is defective.
5. ASF operates abnormally.
2 Paper Jam 1. Paper length is beyond the specifications.
2. The sensor is left on because paper dust or other foreign matter is lodged.
3. Sensor actuator is not acting properly or sensor bracket is not installed correctly.
4. PE sensor is defective.
5. Hopper release lever is not attached properly.
3 Ink End / No Ink Cartridge 1. CSIC is not connected properly.
2. CSIC is defective.
3. Head FPC is defective.
4. Control board is defective.
4 Maintenance Request Protect counter is showing limit. Table
5 Fatal Error 1. Linear encoder FFC is disconnected from the sensor or liner encoder is not attached
to the carriage.
2. Linear encoder is dislocated.
3. ASF sensor is dislocated or ASF sensor connector is disconnected.
4. ASF sensor is defective or it fails to detect ASF home position.
5. PF encoder FFC is disconnected from the encoder sensor or the encoder fails to read
the slit pattern on the loop scale.
6. CR motor coil is discontinued or burned.
7. PF motor coil is discontinued or /burned.
8. ASF/Pump motor coil is discontinued or burned.
Improper engagement of ASF gear (32) and the combination gear (14, 28) in the DE
unit.
9. Torsion spring (0.618) has come off the DE lock lever or hook in the DE unit.
Table 3-5
Table 3-6
Table 3-7
Table 3-9
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 64
Page 65

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
3.1.1.3 Remedies for Paper Out Error
This section provides checkpoints and corresponding actions to take when a Paper Out
error occurs for either of the following reasons:
Paper is set in the ASF hopper but not fed.
Paper is loaded but not detected by the PE sensor actuator.
Be sure to follow the steps in the order listed in the table.
NOTE: If the exhibited problem is similar to a problem listed under “Problem”, take the
actions in the right column. If not, proceed to the next step.
Table 3-5. Remedies for Paper Out Error
Step Problem Check & Actions
1 Maintenance Switch is
pressed but paper is not
loaded even when the
ASF LD rollers turn,
and a Paper Out error is
displayed.
2 The Maintenance
Switch is pressed and
the ASF LD rollers
turn. But they turn
again to send paper
beyond TOP position.
Then a Paper Out error
is displayed.
1. Set a cleaning sheet in the ASF up side down.
2. Holding the top edge, press the Maintenance Switch to
remove micro pearl from the paper load roller.
To remove severe soiling, staple a cloth moistened with
alcohol to a postcard and clean the roller in the same
manner.
CL Sheet
Non-adhesive Area
Non-adhesive Area
Adhesive Area
This side down
Check if the connector (yellow, 3-pin) for the PE sensor is
connected to PE sensor or CN5 on the Main Board.
PE Sensor
Connector
Base Sheet
Base Sheet
(Postcard)
(Postcard)
Staples
Cloth moistened
with alcohol
Torsion Spring
<Printer Bottom>
Ditto Ditto
• Using your hand, move the actuator as if it were being
pushed by incoming paper. Then release the actuator
and check if it automatically returns to its original
position with the tension of the torsion spring.
• Referring to the illustration above, check that the sensor
base is securely installed to the frame. If the sensor base
is loose or installed insecurely, instal it securely.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 65
Page 66

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-5. Remedies for Paper Out Error (continued)
Step Problem Check & Actions
3 Ditto Check if the PE sensor is defective. Manually toggling the
actuator, measure the voltage at CN5/Pin 3. The correct
voltage levels are as follows:
4 The Maintenance
SwitchMaintenance
SwitchMaintenance
Switch is pressed and
the hopper appears to
be working OK. But
paper is not loaded.
Then a Paper Out error
is displayed.
Hand-rotate the shaft in the ASF in the paper feed direction
and check if the hopper springs back every time you rotate
the shaft.
NOTE:Even though the ASF HP sensor is working
properly, the hopper does not load paper if it is not
operating at the correct timing. To solve that problem,
disassemble and reassemble the ASF or replace it. In case
the ASF HP sensor detects the ASF home position during
paper feed sequence, the printer enters a fatal error
condition.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 66
Page 67

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
3.1.1.4 Remedies for the Paper Jam Error
This section includes the checkpoints and actions to take to troubleshoot the Paper Jam
error when it occurs during paper feeding or after the printer is turned on.
The printer detects the Paper Jam Error in the following condition.
When the printer is turned on, the PE sensor detects paper and attempts to
eject it using the PF roller. But the paper detection signal does no change to
HIGH.
Be sure to follow the steps in the order described in the tables.
NOTE: If the exhibited problem is similar to a problem listed under “Problem”, take the
actions in the right column. If not, proceed to the next step.
Table 3-6. Remedies for Paper Jam Error
Step Problem Check & Actions
1 The PF roller turn to eject
paper but can not eject it
completely. Then a Paper
Jam error is displayed.
Explain to the user that a Paper Jam error occurs if the
paper whose length is beyond the specifications is
used.
Table 3-6. Remedies for Paper Jam Error
Step Problem Check & Actions
2 The printer is turned on,
the PF roller turns
continuously for ten
seconds, and then a Paper
Jam error is displayed.
3 ditto Referring to Table 3-5 / Step 3, check if the sensor is
4 Paper is loaded at the ASF
and fed by the PF roller,
but its leading edge dose
not reach the front paper
guide.
The ASF repeats paper
feeding motion and the
Fatal Error is displayed.
Check if there is any paper debris or dust lodged on the
PE sensor. Also, viewing the PE sensor from the front,
check its lever is set in the correct position.
PE Sensor Lever
Paper Guide Assy.
operating properly.
Check if the ASF hopper release lever is properly
installed to the LD roller shaft.
Right ASF Hopper
PF Roller
Left ASF Hopper
3.1.1.5 Remedies for No Ink Cartridge Error/Ink Cartridge Problem
This section includes the checkpoints and corresponding actions to take to troubleshoot
the No Ink Cartridge Error / Ink Cartridge Problem.
Be sure to follow the steps in the order listed in the table.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 67
Page 68

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
NOTE: If the exhibited problem is similar to a problem listed under “Problem”, take the
actions in the right column. If not, proceed to the next step.
Table 3-7. Remedies for No Ink Cartridge Error/Ink Cartridge Problem
Step Problem Check & Actions
1 The printer is turned on
and then displays a No
Ink Cartridge error.
2 Ditto Check the level of the ink remaining using the printer
3 Ditto Replace the ink cartridges with new ones.
4 Ditto
• Check if any ink cartridges are installed improperly.
If so, reinstall them.
• Try removing the ink cartridges and reinstalling them.
driver or progress meter.
• CSIC is defective.
• Check if the head FFC is correctly connected to the
head.
• Check if the head FFC is properly connected to the
connector on the main board.
• Check if the main board is defective.
3.1.1.6 Remedies for Maintenance Request Error
If the printer is in this error condition (ink overflow counter error), it stops all
operations including data transfer, except for Special Setting Mode.
Table 3-8. Remedies for Maintenance Request Error
Step Problem Check & Actions
1 The Power(green) and Error (red)
LEDs blink alternately.
2 Ditto
3 Ditto
• Remove Absorber Tray (Refer to
“TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY
Removal” on page -89).
• Replace Waste Ink Pad with a new one.
• Switch to Sepecial Setting Mode
Turn the power on while pressing the
Maintenance and Roll Paper Switches
simultaniously to switch to Special
Setting Mode.
• While the Power and Error LEDs are
blinking (3 seconds), press the Roll
Paper Switch for 10 seconds.
• Then, the ink overflow counter in
EEPROM is reset.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 68
Page 69

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
3.1.1.7 Remedies for Fatal Error
A fatal error is basically caused by any of the following conditions:
The printer fails to detect the CR home position.
The printer fails to detect signals from the linear scale.
The ASF sensor fails to detect the ASF home position.
The following table shows various causes of the fatal error and corresponding
solutions. Be sure to follow the steps correctly to troubleshoot the fatal error.
NOTE: If the exhibited problem is similar to a problem listed under “Problem”, take the
actions in the right column. If not, proceed to the next step.
Table 3-9. Remedies for Fatal Error
Step Problem Check & Actions
1 The printer is powered
on and the CR unit
leaves its home
position and then
collides with the right/
left frame. After that, a
fatal error is displayed.
2 Ditto
3 When the Printer is
turned on, the CR
moves a little and you
hear the ASF Hopper
moving.
After that, a fatal error
is displayed.
Check the linear encoder board visually for the following:
• Is the linear encoder board properly installed to the
carriage? If not, install it properly.
• Is the encoder FFC connected to the connector? If not,
connect it properly.
• Check that the linear encoder belt passes through the
slot in the sensor.
• Check that the sensor is free from dust and paper
debris.
• Referring to the figure below, check that the ASF
sensor is attached to the correct position.
• Check that both connectors 1 and 2 are securely
connected.
ASF Frame (Left)
Linear Encoder Board
ASF Sensor
Control
Board
Connector 1
Connector 2
(CN6)
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 69
Page 70

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-9. Remedies for Fatal Error (continued)
Step Problem Check & Actions
4 Ditto Turn the printer on and check for the correct voltages at
the pins shown in the figure below:
CN6
To Pin 3
(ASFV)
To Pin 2
(GND)
• When the ASF HP detector wheel is in home
position, the voltage is 0.7 V or less.
• When the ASF HP detector wheel is out of home
position, the voltage is 2.4 V or more.
Table 3-9. Remedies for Fatal Error (continued)
Step Problem Check & Actions
5 The printer is turned on
and the carriage and the
PF motor move a little.
After that, a fatal error
is displayed.
6 The printer is turned on
but the CR motor does
not operate at all. After
that, a fatal error is
displayed.
Check for the signal output from the PF encoder at either
pair of the following pins on the main control board:
• Pin 1 an Pin 4 of CN12
• Pin 1 and Pin 2 of CN12
Check for the signal output from the linear encoder at
either pair of the following pins on the main control board:
• Pin 1 an Pin 4 of CN12
• Pin 1 and Pin 2 of CN12
Encoder Output Waveform
Measure the coil resistance of the CR motor using a meter
as shown below:
Resistance: 29.2Ω ± 25%
CR MotorCR Motor
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 70
Page 71

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-9. Remedies for Fatal Error (continued)
Step Problem Check & Actions
7 The printer is turned on
but the PF motor does
not operate at all. After
that, a fatal error is
displayed.
8 The printer is turned on
but the ASF hopper
does not make noises.
After that, a fatal error
is displayed.
Measure the coil resistance of the PF motor using a meter
as shown below:
Resistance: 29.2Ω ± 25%
PF Motor PF Motor
Measure the coil resistance of the ASF/Pump motor.
Resistance: 10.4 Ω ± 10%
Step 1
To Pin 3
To Pin 1
To Pin 2
Table 3-9. Remedies for Fatal Error (continued)
Step Problem Check & Actions
9 The Printer is turned on
but:
• ASF makes no
noises.
• ASF does not move
but its gear is
making noises.
After that, a fatal error
is displayed.
10 The printer is turned on
but the ASF dose not
move at all. After that,
a fatal error is
displayed.
Check that the ASF unit is properly installed by the correct
points as shown below:
Check that the torsion spring is securely attached to the
DE lock lever and DE unit.
Tension Spring (0.618)
Stylus Photo 890
Stylus Photo 1290
Step 2
CR Motor
CR Motor
To Pin 4
DE Lock Lever
NOTE: Be sure to measure the resistance at each pair of
points shown above.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 71
Page 72

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
3.1.2 Isolating the Faulty Part on the Power Supply Board
This section explains how to troubleshoot the following problems:
The printer is turned on but it does not perform initialization and no LED
indicators come on.
Problems occurs after the printer is turned on.
Be sure to troubleshoot in the order specified since the steps are listed in the
disassembly order to facilitate the job.
NOTE: If you answer “Yes” to a question listed under “Checkpoint”, take the action
described to the right under “Action”. If “No”, proceed to the next step.
Table 3-10. Isolating the Faulty Part on the Power Supply Board
Step Checkpoint Action
1 Is the Panel FFC
disconnected from the
connector on the panel
board?
2 Is the Panel FFC
disconnected from CN11
(black, 12-pin) on the
Main Board?
The power switch for this printer is in the secondary
side. Therefore, if the FFC does not transmit signals, the
power supply board is not active despite the main board
operates properly.
The power switch for this printer is in the secondary
side. Therefore, if the FFC does not transmit signals, the
power supply board is not active despite the main board
operates properly.
3.1.3 Isolating the Faulty Part according to the Phenomenon
Refer to this section if you could not solve the problem in Section 3.1.1.1 or Section
3.1.2 or need more information to isolate the cause according to the exhibited
phenomenon. This section mostly covers the problems relating to the main control
circuit and other parts.
Table 3-11. Phenomenons Exhibited
No. Phenomenon Exhibited Table to refer to
1 CR motor does not rotate. Table 3-12
2 PF motor does not rotate. Table 3-13
3 Pump/ASF motor does not rotate. Table 3-14
4 Cleaning does not solve the print problem. Table 3-15
3 Has the Pin 3 of the panel
FFC broken?
4 Has the fuse (F1) on the
power supply board
blown out?
5 Is CN1 on the power
supply board
disconnected?
6 Is CN10 on the main
board disconnected?
7 - Replace the Power Supply Board with a new one.
Check for the Pin 3 using a circuit tester.
Check if the F1 located beside CN1 on the power supply
board has blown out.
Check if CN1 is properly connected. CN1 supplies AC
power to the primary side of the power supply board.
Check if CN10 on the main board is properly connected.
CN10 supplies DC voltage to the control circuit.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 72
Page 73

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-12. CR Motor does not Work
Step Checkpoint Action
1 Getting ready for
checking
waveforms.
2 Checking the
waveforms to
solve the
problem.
Using an oscilloscope, check the outputwaveform at CN14
(CR motor connector) on the main board. For checking, press
the Maintenance Switch to drive the CR motor.
NOTE: Be sure to disconnect the CR motor cable.
Drive the CR motor and check that the waveform shown below
is output from each pin of CN14.
Table 3-13. PF Motor does not Work
Step Checkpoint Action
1 Getting ready for
checking
waveforms.
2 Checking the
waveform to
solve the
problem.
Using an oscilloscope, check the outputwaveform at CN13 (PF
motor connector) on the main board. For checking, press the
Maintenance Switch to drive the PF motor.
NOTE: Be sure to disconnect the PF motor cable.
Drive the PF motor and check that the waveform shown below
is output from each pin of CN13.
• If the waveform appears as shown, replace the CR motor.
• If not, replace the main control board.
• If the waveform appears as shown, replace the PF motor.
• If not, replace the main control board.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 73
Page 74

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-14. ASF/Pump Motor does not Work
Step Checkpoint Action
1 Getting ready for
checking
waveforms.
2 Checking the
waveforms to
solve the
problem.
Using an oscilloscope, check the outputwaveform at CN115
(ASF motor connector) on the main board. For checking,
press the Maintenance Switch to drive the CR motor.
NOTE: Be sure to disconnect the ASF/Pump motor cable.
Drive the ASF/Pump motor and check that the waveform
shown below is output from each pin of CN15.
Table 3-15. Cleaning Does not Solve the Problem
Step Checkpoint Action
1 Run the head cleaning
7 or 8 times repeatedly.
2 Perform the initial ink
charge operation.
3 Printhead FFC is
disconnected.
Run the head cleaning by pressing the Cleaning button.
You can perform the initial ink charge operation in the
manner described below:
1. Using the adjustment program, perform the initial
ink charge operation (= resets the initial ink charge
flag in the EEPROM).
2. Turn the printer off and back on.
Take out the main board and check if the head FFCs are
connected to CN8 and CN9. If they are connected aslant
as shown below, reconnect them, and then run a print
check.
Check that the connectors are not
connected aslant.
4 Check the cap for any
foreign matter, dirt, or
damage.
• If the waveform appears as shown, replace the ASF/Pump
motor.
• If not, replace the main control board.
Remove the printer
mechanism and
release the carriage
lock to move the
carriage unit away
from home position.
Then, examine the cap
rubber closely for any
problem in the figure
at right.
Dust
Damage
Rubber part
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 74
Page 75

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-15. Cleaning Does not Solve the Problem (continued)
Step Checkpoint Action
5 Check if the
compression spring has
come off the cap unit.
6 Check if any ink tubes
are disconnected from
the cap unit.
Check if the compression spring is correctly assembled
in the cap unit as shown below.
Compression Spring
Note if the compression spring has come off the cap
unit, the cap can not cover the head closely with enough
air tightness, and ink will not be absorbed as a result.
Referring to the figure below, check the following:
• Are all ink tubes securely connected to the cap unit?
• Are any ink tubes damaged?
Cap Unit Ink Tube
Cap Unit
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 75
Page 76

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Table 3-15. Cleaning Does not Solve the Problem (continued)
Step Checkpoint Action
7 Check if the head FFCs
have come off the
printhead.
8 Check if the head
driver is defective.
Remove the head FFC holder from the CR unit, and
check that both FFCs are properly connected. Even if
they appear to be properly connected (not slant), try
disconnecting and then connecting them.
Head Board
The common driver transistors Q2 and Q3 are attached
the heat sink on the main board. To check their
conditions, check the sawtooth waveform at the emitter
terminals the transistors using an oscilloscope.
Head FFCs
Table 3-15. Cleaning Does not Solve the Problem (continued)
Step Checkpoint Action
9 Check if the pre-driver
IC (IC10 or IC11) is
defective.
If the waveform is not output in the previous step, check
for the waveform at the base of Q2 and Q3. Check for
the sawtooth waveform output from the pre-driver IC.
• If the correct waveform is output, transistor Q2/Q3 is
defective.
• If the correct waveform is not output, the pre-driver
IC is defective.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 76
Page 77

DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER
4
Page 78

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.1 Overview
This chapter describes procedures for disassembling the main components of the
EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290. Unless otherwise specified, disassembly units or
components can be reassembled by reversing the disassembly procedure. Therefore, no
assembly procedures are included in this chapter. Precautions for any disassembly or
assembly procedure are described under the heading “CAUTION” and “CHECK
POINT”. Any adjustments required after disassembling the units are described under
the heading “REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT”.
4.1.1 Precaution for Disassembling the Printer
See the precautions given under the heading “WARNING” and.“CAUTION” in this
section when disassembling or assembling EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290.
W A R N I N G
Disconnect the power cable before disassembling or
assembling the printer.
If you need to work on the printer with power applied,
strictly follow the instructions in this manual.
Wear protective goggles to protect your eyes from ink. If
ink gets in your eye, flush the eye with fresh water and
see a doctor immediately.
Always wear gloves for disassembly and reassembly to
avoid injury from sharp metal edges.
To protect sensitive microprocessors and circuitry, use
static discharge equipment, such as anti-static wrist
straps, when accessing internal components.
Never touch the ink or wasted ink with bare hands. If ink
comes into contact with your skin, wash it off with soap
and water immediately. If irritation occurs, contact a
physician.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Overvi ew 78
Page 79

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.1.2 Tools
C A U T I O N
Never remove the ink cartridge from the carriage unless
this manual specifies to do so.
When transporting the printer after installing the ink
cartridge, be sure to pack the printer for transportation
without removing the ink cartridge.
Use only recommended tools for disassembling,
assembling or adjusting the printer.
Observe the specified torque when tightening screws.
Apply lubricants and adhesives as specified. (See
Chapter 6 for details.)
Make the specified adjustments when you disassemble
the printer.
(See Chapter 5 for details.)
When assembling, if an ink cartridge is removed and
needs to be installed again, be sure to install a new ink
cartridge because of the following reasons;
1.Once the ink cartridge mounted on the printer is removed,
air comes in and creates bubbles in the cartridge. These
bubbles clog ink path and cause printing malfunction.
2.If an ink cartridge in use is removed and is reinstalled, ink
quantity will not be detected correctly since the counter to
check ink consumption is cleared.
Because of the reasons above, make sure to return the
printer to the user with a new ink cartridge installed.
Make sure the tip of the waste ink tube is located at
correct position when reassembling the waste ink tube.
Otherwise it will cause ink leakage.
Table 4-1 lists the tools recommended for disassembling, assembling, or adjusting the
printer. Use only tools that meet these specifications.
Table 4-1. Tool List
Tools
(+) Driver No.2 O.K. B743800200
(+) Driver No.1 O.K. B743800400
Tweezers O.K. B741000100
Hexagon Box Driver
(Paired side: 5.5mm)
Scale PF unit Assembling tool EPSON exclusive 1050767
Mounting Plate Scale Attachment
tool
ROM Extractor No.F749 EPSON exclusive 2035659
Black Empty Cartridge
(Stylus Photo 890/1290)
Color Empty Cartridge
(Stylus Photo 890 only)
Color Empty Cartridge
(Stylus Photo 1290 only)
*1
*2
*3
Commercially
Available
O.K. B741700100
EPSON exclusive 1051765
EPSON exclusive
EPSON exclusive 1049786 (#F741)
EPSON exclusive 1049787 (#F742)
1049785 (#F738)
Code
*1
NOTE:
: Common cartridge with Stylus Photo 870/1270.
*2
: Common cartridge with Stylus Photo 870.
*3
: Common cartridge with Stylus Photo 1270.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Overvi ew 79
Page 80

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.1.3 Specifications for Screws
Table 4-2 shows screw specifications. During assembly and disassembly, make sure
that the specified types of screws are used at proper locations, referring to the table
below.
Table 4-2. Screw Specifications
Body Name Size
+Bind S-tite (CBS) M3x6
+Bind P-tite (CBP) M3x6
+Bind P-tite (CBP) M3x8
+Bind P-tite (CBP) M2.5x5
+Pan head (C.P.) M3x6
--- +Pan head B-tite Sems M3X8
+Bind S-tight Sems (CBS Sems) M3x6
+Bind S-tight (CBS) M3x10
--- +Pan head B-tite Sems 1.7 x 5
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Overvi ew 80
Page 81

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.1.4 Service Checks After Repair
Before returning the printer after servicing, use the check list below, which enables you
to keep record of servicing and shipping more efficiently.
Table 4-3. Inspection Checklist for Repaired Printer
Category Component Item to check Is Check Req uired?
Self-test Is the operation normal? Checked / Not necessary
On-line test Was the on-line test successful? Checked / Not necessary
Printhead Is ink ejected normally from all nozzles? Checked / N ot necessary
Does the carriage move smoothly? Checked / Not necessary
Any abnormal noise during movement? Checked / Not necessary
Carriage mechanism
Printer units
Paper feeding mechanism
Adjustment Specified adjustment items Are adjusted conditions all right? Checked / Not necessary
Lubricant Specified lubricated item
Function ROM version Newest version: Checked / Not necessary
Ink cartridges are the ink cartridges installed correctly? Checked / Not necessary
Shipment package
Others Attached items Are all attached items from users included? Checked / Not necessary
Protection conditions during
transport
Any dirt or obstacles around the shaft of carriage
guide?
Is the CR motor at the correct temperature
(not over heating)?
Is paper fed smoothly? Checked / Not necessary
Does paper get jammed? Checked / Not necessary
Does paper get skew during paper feeding? Checked / Not necessary
Are papers multi fed? Checked / Not necessary
Does the PF motor get overheated? Checked / Not necessary
Abnormal noise during paper feeding? Checked / Not necessary
Is the paper path clear of all obstructions? Checked / Not necessary
Is lubrication applied to the specified locations? Checked / Not necessary
Is the quantity of lubrication adequate? Checked / Not necess ary
Is all the pointed parts firmly fixed? Checked / Not necessary
Checked / Not necessary
Checked / Not necessary
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Overvi ew 81
Page 82

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2 Disassembly Procedures
The flowchart below shows procedures for disassembly.
START
START
HOUSING Removal
Circuit Board
Assembly Removal
MOTOR ASSEMBLY,
CR Removal
DE Unit Removal
PE Sensor Unit
Removal
Printhead Unit
Removal
Panel Unit Removal
TRAY, ABSORBER
ASSEMBLY Removal
Ink Unit Removal
MOTOR ASSEMBLY,
ASF Removal
BOARD ASSEMBLY,
ENCODER Removal
ASF Unit Removal
SHAFT, ROLLER,
LD Removal
ROLLER ASSEMBLY,
LD, RIGHT/LEFT
Figure 4-1. Flowchart of Disassembly
Carriage Unit
Removal
ROLLER, PF Removal
MOTOR ASSEMBLY,
PF Removal
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 82
Page 83

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.1 HOUSING Removal
Since the printer mechanism itself structures the bottom part, it appears just by
removing HOUSING.
1. Open the printer cover and set the PG adjustment lever to (+).
2. Remove the four screws (CBS, 3x10) securing HOUSING, and remove it.
CBS (3x10)
C A U T I O N
C H E C K
P O I N T
When removing HOUSING, push it to the rear a little first, and
then lift it up.
When installing HOUSING, make sure the PG
adjustment lever is set to (+).
After assembling HOUSING, ensure the head FFC is
not caught in the back of HOUSING.
CBS (3x10)
Figure 4-2. HOUSING Removal
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 83
Page 84

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.2 Circuit Board Assembly Removal
Since BOARD ASSEMBLY, MAIN and BOARD ASSEMBLY, POWER SUPPLY
are built in a bracket separated from the Printer Mechanism, they can be removed as
one unit.
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Remove the screws (CBS, 3x6) securing the M/B Unit to the printer mechanism.
Refer to Figure 4-3.
Stylus Photo 890: 7 screws
Stylus Photo 1290: 8 screws
COVER, CABLE
CBS (3x6)
COVER,
CBS (3x6)
4. Disconnect all cables from the connectors on the main board and power supply
board.
CN1(AC Source connector on the power supply board)
CN5 (PE sensor)
CN6 (ASF sensor)
CN15 (ASF/Pump motor)
CN8 (Head FFC)
CN9 (Head FFC)
CN19 (from the secondary side of the PS board)
CN11 (Panel Unit)
CN12 (PF Encoder Sensor)
5. After removing BOARD ASSY, MAIN without cables, remove SHIELD PLATE,
M/B Unit from the printer mechanism.
CBS (3x6)
CBS (3x6)
Figure 4-3. Removing the M/B Shield Plate
3. Lifting up SHIELD PLATE, M/B Unit a little, remove COVER, CABLE and
COVER, CABLE; B together with the cables.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 84
Page 85

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
C378PSB/PSE
Board
SHIELD PLATE, M/
Earth Plate
CP (3x6)
CBS (3x6)
Earth Plate
C393MAIN Board
C A U T I O N
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
Since the CN10 is a locking connector, be sure to unlock it
before disconnecting the cables.
Since the head FFCs have the same number of pins, be sure to
connect them to the right connectors.
When connecting the cables, connect them to the correct
connectors paying attention to the number of the pins.
Be sure to perform the following adjustments when you replace
the Main Board:
1. Head ID input (Refer to Chapter 5.)
2. Bi-D adjustment (Refer to Chapter 5.)
3. USB ID input (Refer to Chapter 5.)
Be sure to replace the following parts when replacing the Main
Board:
1. Waste ink absorbers
2. Ink cartridge (BK & Color)
Note this part replacement is required since several counters stored
in the EEPROM are lost with a Main board replacement.
Figure 4-4. Circuit Board Removal
6. For removing each circuit board assembly from the M/B Shield Plate, remove the
screws securing each unit and shield plate.
C393MAIN Board: Total 10 screws
7 screws: CBS (3x6)
3 screws: CP (3x6)
C378PSB/PSE Board: Total 4 screws (CBS, 3x6)
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 85
Page 86

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.3 Panel Unit Removal
C H E C K
P O I N T
When installing SHIELD PLATE, M/B to the printer
mechanism, set the cables, COVER CABLE, and COVER,
CABLE; B as shown in the figure below:
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Remove the harness for the Panel Unit from the frame in the printer mechanism.
COVER,
Opening
COVER, CABLE; B
Opening
Figure 4-5. Setting the Cables to the Cable Covers
C H E C K
P O I N T
When installing the harness to the printer mechanism, be sure to
stick it along the marking line on the frame.
Marking Line
Harness
3. Remove 4 screws (CBS, 3x6) securing the Panel Unit together with HOUSING,
REINFORCING, RIGHT to the printer mechanism.
4. Release the hook for the for HOUSING, REINFORCING, RIGHT from the square
cutout in the printer mechanism.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 86
Page 87

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
5. Remove 1 screw (CBP, 3x8) securing Panel Unit to the printer mechanism and
release the pins fit in the printer mechanism.
Then remove the Panel Unit along with HOUSING, REINFORCING, RIGHT.
CBS (3x6)
Pins
Panel Unit
CBS (3x6)
6. Remove 2 screws (CBP, 3x8) securing SHIELD PLAT, PANEL to the Panel Unit,
and then remove SHIELD PLATE, PANEL.
SHIELD PLATE, PANEL
CBP (3x8)
CBP (3x8)
BOARD ASSEMBLY, PANEL
Cup P-Tite (3x6)
Harness
CBP (3x8)
Figure 4-7. BOARD ASSEMBLY, PANEL Removal
7. Remove screws (CBP, 3x8 & Cup P-Tite, 3x6) securing BOARD ASSEMBLY
PANEL to the Panel Unit.
8. Disconnect the harness from BOARD ASSEMBLY, PANEL.
When removing the Panel Unit, watch out for the stacker
assembly. Since the stacker assembly is attached to the Panel
Unit and HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT, if you remove the Panel
Unit, the stacker assembly will also come off.
HOUSING,
REINFORCING, RIGHT
C A U T I O N
Cutout
Figure 4-6. Panel Unit Removal
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 87
Page 88

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.4 Printhead Unit Removal
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Set the PG lever to the rear.
3. Using tweezers, put the CR lock lever down to unlock the carriage.
4. Release the three hooks (A, B, C) fixing HOLDER, CABLE to the carriage, and
remove HOLDER, CABLE.
Head FFC
HOLDER, CABLE
C
B
A
Figure 4-8. Printhead Removal
5. Disconnect the head FFC from the connector on the printhead.
6. Remove the FFC from the BOARD ASSEMBLY, ENCODER.
BOARD ASSEMBLY,
ENCODER
FFC
HEAD
CBP (3x6)
CBB (W2)
M2.5x6
Figure 4-10. HEAD Removal
7. Move the carriage to the left end of the printer manually.
8. Remove 2 screw (CBP, 3x6 & CCB Sems W2, 2.5x6) securing the printhead to the
carriage, and remove the printhead.
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
When you replace the Printhead Unit, perform the following
adjustments:
1. Initial ink charge (Refer to Chapter 5)
2. Head ID Input (Refer to Chapter 5)
3. Bi-D Adjustment (Chapter 5)
Figure 4-9. Encoder FFC Removal
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 88
Page 89

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.5 TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY Removal
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Remove the Panel Unit. (Refer to Section 4.2.3.)
3. Remove 2 screws (CBS, 3x6) securing HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT to the front left
part of the printer mechanism.
Pin
CBP (3x8)
HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT
Figure 4-11. HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT Removal
4. Remove 1 screw (CBP, 3x8) securing HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT to the
HOUSING, SUB, LEFT.
5. Release the pin fixing HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT to the printer mechanism, and
then remove HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT toward the front.
CBS (3x6)
6. Remove 2 screws (CBS, 3x6) securing HOUSING, SUB, LEFT to the printer
mechanism.
7. Release 3 hooks (2 at the bottom and 1 in the front) fixing HOUSING, SUB, LEFT
to the printer mechanism, and remove HOUSING, SUB, LEFT.
8. Remove 1 or 2 screws (CBP, 3x6: Stylus Photo 890 1 screw, Stylus Photo 1290 2
screws) securing PAPER GUIDE, LOWER to TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY
at the middle of the printer mechanism, and then remove PAPER GUIDE,
LOWER.
ABSORBER,
WASTE INK,
LARGE/SMALL
Hook in TRAY,
ABSORBER
CBP (3x8)
TRAY, ABSORBER
FRAME,
C A U T I O N
When removing HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT, watch out for the
CBP (3x8)
Stacker Assembly. Since the Stacker Assembly is fixed by the
Panel Unit and HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT, it will come off as
HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT is removed.
SPACER, TRAY
PAPER GUIDE,
LOWER
Figure 4-12. TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY Removal
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 89
Page 90

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
9. Removing 1 screw (CBP, 3x8) securing TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY to the
right part of the printer mechanism.
10. Remove SPACER, TRAY securing TRAY, ABSORBER to the left side of the
printer mechanism, and then remove TRAY, ABSORBER by moving it
downward.
11. Remove ABSORBER, WASTE INK, LARGE/ SMALL from TRAY,
ABSORBER.
C A U T I O N
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
When installing TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY to the
printer mechanism, make sure they are securely jointed with
SPACER, TRAY. Refer to Figure 4-12.
Be careful not to damage SCALE, PF, (loop scale) when
installing SPACER, TRAY.
When installing ABSORBER ASSEMBLY, make sure the Ink
Tube is correctly placed in the ABSORBER ASSEMBLY. If
not, it may cause an ink leakage.
If you replace TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY, be sure to
perform the Waste ink counter reset operation. (Refer to
Chapter.)
When installing TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY to the
printer mechanism, make sure it securely joins to FRAME,
RIGHT by its hook in the right.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 90
Page 91

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.6 Ink Unit Removal
NOTE: Ink Unit consists of the Pump Unit, Cleaner Head, and Cap Assembly.
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Remove the Panel Unit. (Refer to Section 4.2.3.)
3. Remove SHEET, INK STOPPER.
SHEET, INK STOPPER
Figure 4-13. SHEET, INK STOPPER Removal
FRAME, MIDDLE CBS (3x6)
CBS (3x6)
Ink Unit
FRAME, TOP
CBS (3x6)
4. Remove TRAY, ABSORBER ASSEMBLY. (Refer to Section 4.2.5.)
5. Remove the three screws (CBS, 3x6) securing the Ink Unit to the FRAME,
MIDDLE.
Hook in the Cap Assembly
6. Remove 3 screws (CBS, 3x6) securing the Ink Unit to FRAME, TOP. Then
remove the Ink System Assembly.
Figure 4-14. Ink Unit Removal
7. Release the hook fixing the Cap Assembly to the Ink Unit, and then remove the
Cap Assembly.
8. Disconnect the tube from the Cap Assembly.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 91
Page 92

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
C A U T I O N
C H E C K
P O I N T
1. When handling CLEANER, HEAD, note the points below:
Do not touch CLEANER, HEAD with your bare hands.
Ware gloves or use tweezers.
Do not smear CLEANER, HEAD with oil or grease.
When installing CLEANER, HEAD, set the rubber side
(black side) facing to the right.
2. When replacing the Cap Assembly, do not touch its sealing
rubber part.
When assembling, make sure the Ink Tube is correctly placed
at the correct position. If not, it may cause an ink leakage.
1. When assembling the Cap Assembly to the Ink System
Assembly, make sure ABSORBER, SLIDER, CAP is assembled
in the cap assembly. ABSORBER, SLIDER, CAP should be set
as shown in Figure 4-15 in advance.
2. Check that the ink tube is securely connected to the connection
part of the Cap Assembly. (See Figure 4-16.) Also, make sure
the tube is not bent or crushed by the connection area. (See
Figure 4-17.)
3. Check that the ink tube is placed correctly in the Ink System.
(See to Figure 4-16.) Pay special attention in connecting the tube
to the Pump Unit. Connect the tube by strictly following the
instruction given in Figure 4-18.
4. When assembling, be careful not to crush or leave any stress on
the ink tube that connects the Pump Unit and Cap Assembly.
Also,
5. After installing the Pump Unit, ensure that CLEANER, HEAD
moves back and forth with rotation of the gear.
°
ABSORBER,
SLIDER, CAP
About 60-90
About 45
°
Figure 4-15. Setting the ABSORBER, SLIDER, CAP
Cap Assembly
Pump Unit
Ink Tube
Figure 4-16. Ink Tube Installation (1)
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 92
Page 93

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
Tube is not stretched out.
Figure 4-17. Ink Tube Installation (2)
Tube is not bent.
Marking line on the tube
2 mm
Pump Unit
Figure 4-18. Connecting the Tube to the Pump Unit
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 93
Page 94

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.7 MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR Removal
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1)
2. Using tweezers or a small screw driver, put the carriage lock lever down to the
front, and then slide the carriage to the middle of the printer mechanism.
3. Push the HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN to loosen the CR Timing Belt, and then
disengage the timing belt from the pulley on the CR motor.
SCALE,
HOLDER, PULLEY,
DRIVEN
Timing Belt
Pulley in MOTOR
ASSEMBLY, CR
Figure 4-19. Timing Belt Removal
4. Disconnect the connector for MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR from the connector on
the main board. (Refer to Section 4.2.2.)
5. Remove 2 screws (CP, 3x6) securing MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR to FRAME,
TOP, and then remove MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR.
C A U T I O N
FRAME, TOP
CP (3x6)
MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR
Figure 4-20. MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR Removal
When pushing HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN, be careful not
to damage SCALE, PF (loop scale).
When releasing the timing belt, be careful not to damage
SCALE, CR (linear encoder).
When removing MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR, be sure not to hit
the edge of the installation hole with the motor’s pulley.
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
When removing MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR, execute Bi-D
adjustment. See “Bi-Directional Adjustment“on page 133.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 94
Page 95

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.8 MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF Removal
1. Remove HOUSING (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Remove the harness for MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF from the main board. (Refer
to Section 4.2.2.)
3. Lower LEVER, PLANETARY UNIT.
LEVER, PLANETARY
[Lever is held up.] [Lever is lowered.]
Figure 4-21. Setting LEVER, PLANETARY UNIT
4. Remove 2 screws (CBP, 3x8) securing MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF to
BRACKET, MOTOR, ASF. Then push the motor assembly to the rear and then to
the right to remove it.
C H E C K
P O I N T
BRACKET, MOTOR, ASF
MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF
CBP (3x8)
Figure 4-22. MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF Removal
When installing MOTOR, ASSEMBLY, ASF5, make sure the
DE unit and LEVER, PLANETARY UNIT are set as shown
below:
DE Unit (BRACKET,
MOTOR, ASF)
LEVER,
PLANETARY UNIT
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 95
Page 96

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.9 DE Unit Removal
1. Remove HOUSING (Refer to Section 4.2.2.)
2. Remove MOTOR ASSEMBLY, CR. (See Section 4.2.7.)
3. Remove the Ink Unit. (Refer to Section 4.2.6.)
4. Remove 2 screws (CBS, 3x6) securing SHEET, PROTECTION INK to FRAME,
BOTTOM, and then remove the sheet.
FRAME, TOP
SHEET, PROTECTION, INK
FRAME, BOTTOM
CBS (3x6)
5. Remove MOTOR, CR. (Refer to Section 4.2.7.)
6. Loosen 1 (CBS, 3x6) securing the LEVER ASSEMBLY, COMBINATION
GEAR to FRAME, MIDDLE.
7. Remove the tension sprig (7.37) hung to FRAME MIDDLE and LEVER
ASSEMBLY, COMBINATION GEAR, and then remove TENSION BELT,
PUMP, TRANSMISSION from the combination gear (12, 22.92).
TENSION SPRING, 7.37
LEVER ASSEMBLY,
COMBINATION GEAR
FRAME, MIDDLE
CBS (3x6)
COMBINATION
GEAR, 12, 22.92
TENSION BELT, PUMP,
TRANSMISSION
Figure 4-23. SHEET, PROTECTION, INK Removal
Figure 4-24. TENSION BELT, PUMP, TRANSMISSION Removal
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 96
Page 97

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
8. Remove the tension spring (0.618) attached to the LEVER, DE, LOCK and DE
Unit.
LEVER, DE,
TENSION SPRING, 0.618
Figure 4-25. TENSION SPRING, 0.618 Removal
9. Release the hook in the DE Unit (BRACKET, MOTOR, ASF) securing LEVER,
DE, LOCK. Then push the lever out to the right to release it from the installation
hole in the DE Unit and remove it.
LEVER, DE, LOCK
Locking position
LEVER, DE, LOCK
Figure 4-26. LEVER, DE, LOCK Removal
C A U T I O N
When removing LEVER, DE, LOCK, be careful not to break the
hook in the DE Unit.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 97
Page 98

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
10. Remove the CBS screw (3x6) and CBP (3x8) screw securing the DE unit to
FRAME, MIDDLE and FRAME, TOP, respectively. Then remove DE unit.
SCALE, CR
CBP (3x8)
C H E C K
P O I N T
Check that all gears are assembled in the DE unit correctly as
shown in the figure below:
Combination Gear,
12, 22.4
Combination Gear,
17.19, 25.6
LEVER, PLANETARY UNIT
Retaining Ring, D8.8
Felt, D3.6
Combination
Gear, 14, 28
BRACKET,
MOTOR, ASF
Figure 4-28. Parts Layout in DE Unit
Before assembling MOTOR ASSEMBLY, ASF to the DE Unit,
set LEVER, PLANETARY UNIT to the pump side. (See Figure
CBP (3x6)
4-28.)
Set TENSION BELT, PUMP, TRANSMISSION to the 17.19
gear of the Combination Gear (17.19, 25.6) before securing the
Figure 4-27. DE Unit Removal
11. Remove the harnesses from the harness clamp in the DE Unit.
C A U T I O N
Be sure to remove the screw (CBP, 3x8) carefully so you do not
DE unit to FRAME, MIDDLE.
DE Unit
Combination Gear,
17.19, 25.6
TENSION BELT, PUMP,
TRANSMISSION
damage the linear encoder (SCALE, CR).
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 98
Page 99

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
4.2.10 ASF Unit Removal
1. Remove HOUSING. (Refer to Section 4.2.1.)
2. Remove the following cables from the cable clamp in the left side of the ASF
Assembly.
ASF HP sensor cable
MOTOR ASSEMBLY, PF cable
3. Disconnect the ASF HP sensor cable from the connector on the sensor.
4. Remove the head FFC from the ASF Unit.
5. Remove 1 screw (CBS Sems, 3x6) and SHAFT, MOUNT, CR that are securing
the ASF Unit to FRAME, BOTTOM at the rear right and rear left, respectively.
Paper Support Sub Unit
ASF viewed from the right
CBS Sems (3x6)
ASF viewed from the left
SHAFT, MOUNT, CR
Figure 4-29. ASF Unit Removal (1)
6. Tilting the paper support sub unit, release the hook fixing the ASF Unit to
FRAME, BOTTOM, and remove the ASF Unit toward the rear.
Figure 4-30. ASF Unit Removal (2)
Hook in the ASF Unit
Figure 4-31. ASF Unit Removal (3)
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 99
Page 100

EPSON Stylus Photo 890/1280/1290 Revision C
C H E C K
P O I N T
When installing the ASF assembly to FRAME, BOTTOM, make
sure the protrusion on the ASF fits in the installation hole in
FRAME, MIDDLE. (See Figure 4-32.)
When installing the ASF Unit, ensure the spur gear 32 in the
ASF Unit and the inner gear of the combination gear (14, 28) in
the DE Unit are meshed. (See Figure 4-32.)
When installing the ASF Unit, make sure the Hopper Assembly
is raised.
Stylus Photo 890
Stylus Photo 1290
Combination Gear
14, 28
Installation Hole
Protrusion
Gear 32
C H E C K
P O I N T
When connecting the cables for ASF HP sensor and MOTOR
ASSEMBLY, PF, set them in the cable clamp in the rear left part
of the ASF Unit as shown in the figure below:
Cable Clamp
Combination Gear
14, 28
Installation Hole
Gear 32
Protrusion
Figure 4-32. Check Points in ASF Assembly
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Disassembly Procedures 100
 Loading...
Loading...