Page 1
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
November 2014
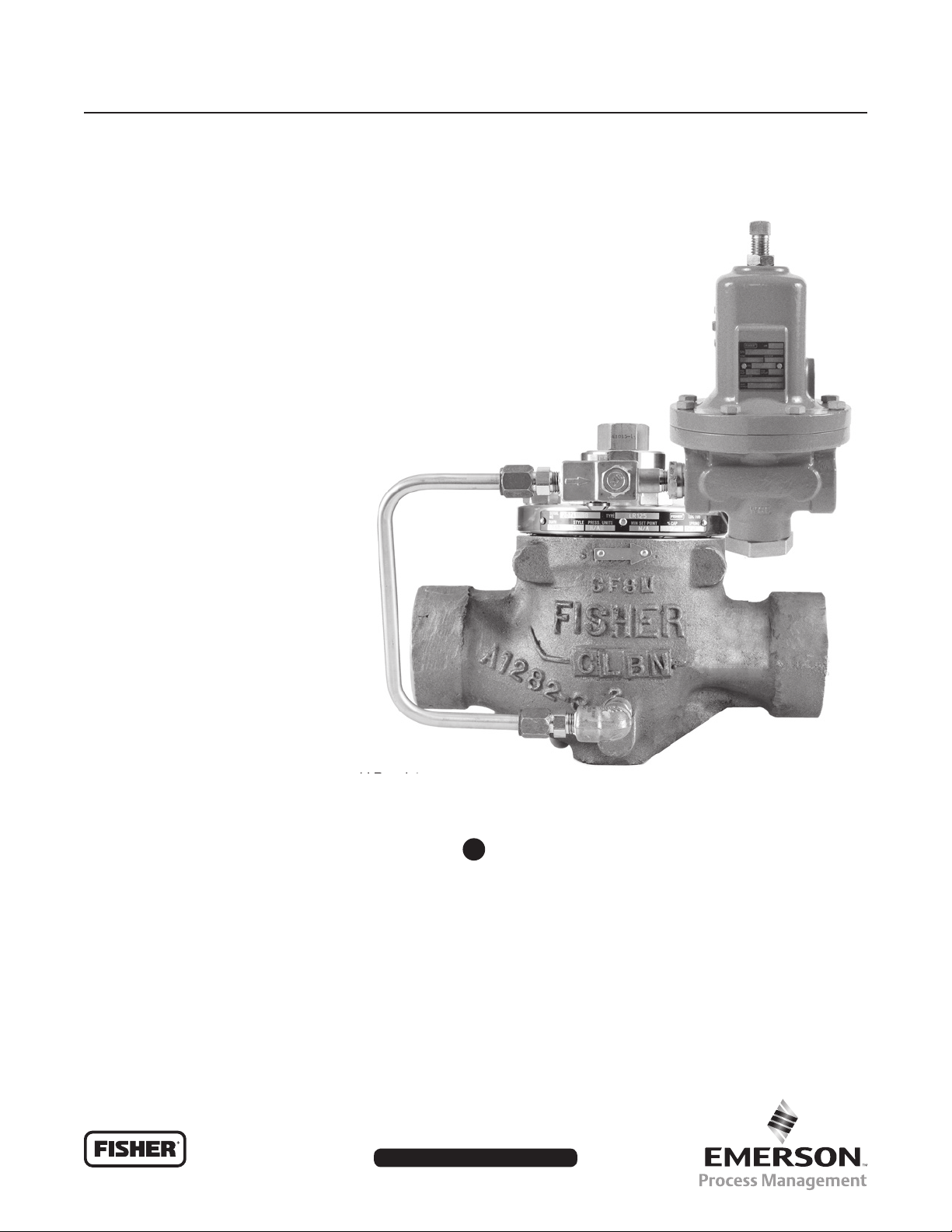
Type LR125 Pressure Reducing Liquid Regulator
• Rugged design
• Reliable
• Thoroughly tested
• Internally actuated
• Compact
• 1, 2, 3, 4 in. body sizes
• Recommended for water
and oil applications
• Full SST construction
available for harsh
environments
• API 614 Compliant
Figure 1. Type LR125 Pressure Reducing Liquid Regulator
Introduction
The Type LR125 pilot-operated, pressure reducing
regulator is designed for liquid industrial/commercial
applications. The Type LR125 provides smooth
operation, tight shutoff and long life. Its internally
actuated metal plug eliminates disadvantages
associated with exible element style regulators, and
the specially engineered ow path de ects debris,
protecting the seat from damage and erosion. The
Type LR125 is used in conjunction with a Type MR95H
pilot and Type 112 restrictor. An internal inlet strainer
prevents large particles from entering the main valve,
limiting damage to internal parts.
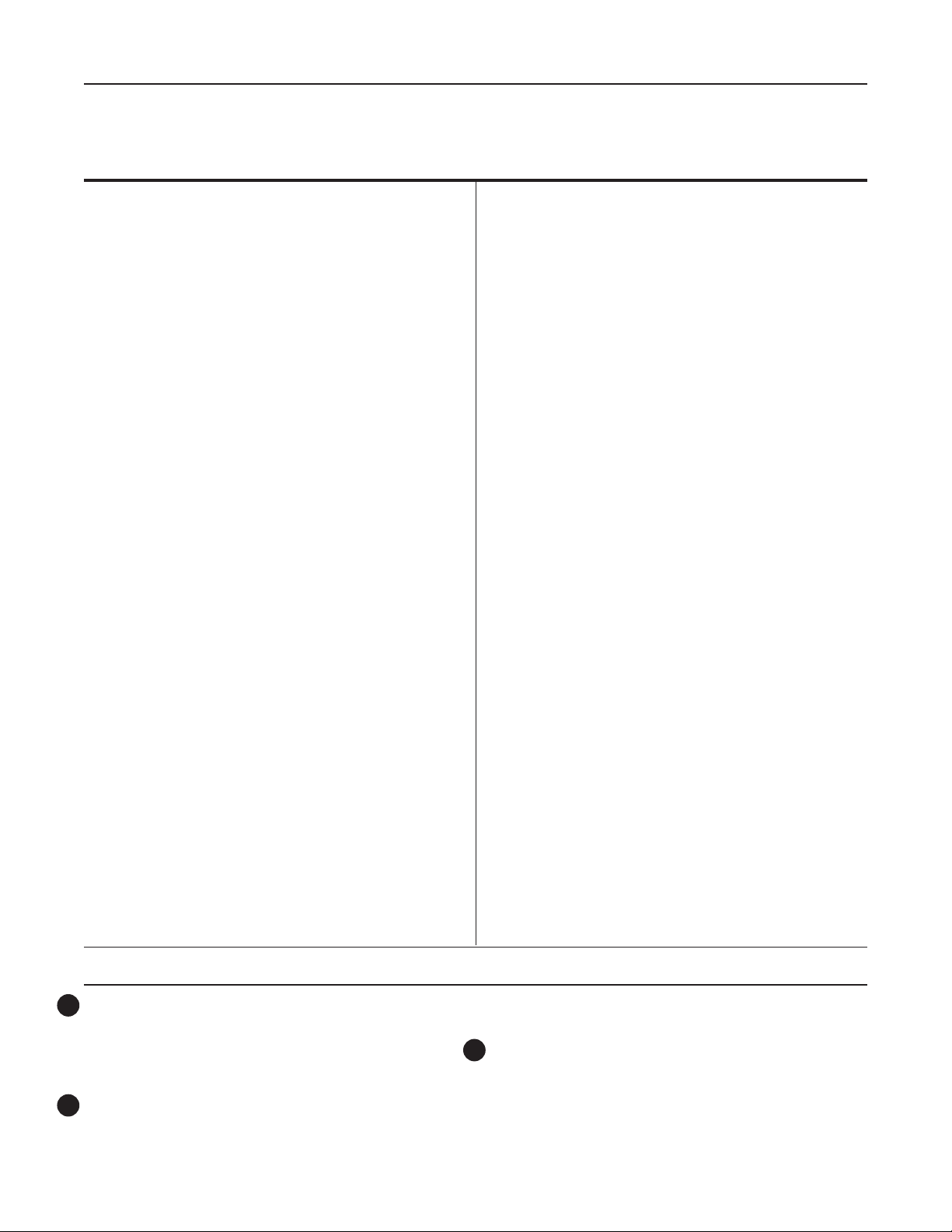
Features and Bene ts
1
Tight Shutoff—The Type LR125 uses a diaphragm
and metal plug, eliminating the disadvantages of
exible element style regulators. When open, the
metal plug de ects particles and debris away from
the diaphragm. The result is enhanced resistance to
particle erosion, which provides excellent shutoff over
an extended life. When closed, loading pressure and
the main spring push the diaphragm onto the taperededged seat on the cage.
www.fisherregulators.com
D103575X012
Page 2
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Specications
The Specications section lists the specications for the Type LR125 regulator. Factory specication is stamped
on the nameplate fastened on the regulator at the factory.
Main Valve Body Sizes, End Connection Styles and
Structural Design Ratings
(1)(2)
See Table 1
Maximum Inlet Pressures
(1)
Type LR125 Main Valve: See Table 1
Type MR95H Pilot: See Table 2
Type 112 Restrictor: 1500 psig / 103 bar
Maximum Outlet Pressure
Type LR125 Main Valve: See Table 1
Type MR95H Pilot: See Table 2
Outlet (Control) Pressure Ranges
See Table 3
Main Valve Plug Travel
1 in. / DN 25: 0.37 in. / 9.4 mm
2 in. / DN 50: 0.68 in. / 17 mm
3 in. / DN 80: 0.98 in. / 25 mm
4 in. / DN 100: 1.19 in. / 30 mm
Main Valve Minimum Differential Pressures
(1)
See Table 5
Temperature Capabilities
(1)
See Table 4
Main Valve Flow Direction
Up through the center of the cage and down
through the cage slots
Main Valve Internal Inlet Strainer Sizes
1 in. / DN 25: 12 Mesh (0.0661 in. / 1.68 mm)
(3)
2, 3 and 4 in. / DN 50, 80 and 100:
10 Mesh (0.0787 in. / 2 mm)
(3)
Regulating Capacities
See Table 11
Flow and IEC Sizing Coefcients
Type LR125 Main Valve: See Table 6
Type MR95H Pilot: See Table 7
Type 112 Restrictor: See Table 8
Pressure Registration
External: 1/2 NPT
Spring Case Vent
Type Y602-12
Approximate Weights
Options
• Pre-piped Pilot Supply
• Travel Indicator
Construction Materials
Type LR125 Main Valve
Body: WCC Steel, CF8M or CF3M Stainless Steel
Bonnet: Steel or Stainless Steel
Bonnet Bushing: Steel or Stainless Steel
Cage: Stainless steel
Spring: Stainless steel
Top Plug: Stainless steel
Bottom Plug: Stainless steel
Internal Inlet Strainer: Stainless steel
Diaphragm: Nitrile (NBR) or Fluorocarbon (FKM)
O-rings: Nitrile (NBR) or Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Flanged Locknut: Stainless Steel
Backup Rings: Polytetrauoroethylene (PTFE)
Upper Spring Seat: Stainless steel
Indicator Protector and Cover: Plastic
Indicator Stem: Stainless steel
Indicator Fitting: Stainless steel
Travel Indicator Plug: Stainless steel
Type MR95H Pilot
Body: WCC Steel or CF8M Stainless Steel
Spring Case: WCC Steel or CF8M Stainless Steel
Orice: Stainless Steel
Diaphragm: Neoprene (CR) or Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Disk: Nitrile (NBR) or Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Mounting Parts
Pilot Mounting Pipe Nipple: Plated steel or
Stainless steel
Pipe Fittings: Plated steel or Stainless steel
Tubing: Stainless Steel
Type 112 Restrictor
Body: 15-5 Stainless Steel
Groove Valve: Stainless steel
Retainer: Stainless steel
Pipe Plug: Stainless steel
O-rings: Nitrile (NBR) or Fluorocarbon (FKM)
See Table 9
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Bulletin and any applicable standard or code limitation should not be exceeded.
2. Ratings and end connections other than ASME standards can usually be provided; contact your local Sales Ofce.
3. Nominal sieve opening
2
Debris Protection—The specially engineered ow
path, along with the metal plug, allows ow through the
regulator without seat impingement. The addition of an
internal inlet strainer prevents large particles from entering
the regulator, minimizing damage to internal parts.
3
High Accuracy—Multiple control pressure ranges
offered by Type MR95H pilot and lower accuracy class
2
inherent to pilot operated pressure regulator design
provide the Type LR125 with tight and accurate control.
Long Life—The robust design of the Type LR125 with
4
its metal plug and specially engineered ow path allows
ow through the regulator without seat impingement.
The diaphragm design eliminates the possibility of
taking a “set”, a common problem with exible element
Page 3
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
TYPE LR125 PRESSURE REDUCING REGULATOR
3
W5092
TYPE MR95H PILOT
10
7
7
W7398
TRIM PACKAGE
11
9
1
TYPE MR95H PILOT
5
6
8
4
12
2
W7344
TYPE LR125 PRESSURE REDUCING REGULATOR
Figure 2. Type LR125 Features and Bene ts
style regulators. To prevent damage, the diaphragm is
fully supported in both the open and closed positions.
These features enable the Type LR125 components to
work longer with less wear and tear.
5
Full Usable Capacity—Fisher® branded regulators
are laboratory tested. One hundred percent of the
published ow capacity can be used with con dence.
Thorough Laboratory Testing—Emerson Process
6
Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. (Emerson™)
state-of-the-art ow laboratory allows thorough testing of
all new designs. Tests are conducted on Fisher branded
regulators for performance features such as ow,
strength, shutoff and material compatibility.
7
Easy In-Line Maintenance—Top-entry design
reduces maintenance time. Trim parts can be
inspected, cleaned and replaced without removing
the body from the pipeline. No special alignment is
required when replacing the diaphragm.
W7345
8
O-ring Design—The Type LR125 uses elastomer
O-rings instead of gaskets, reducing maintenance and
assembly time.
9
In-Service Travel Indicator—The optional travel
indicator responds to the precise movement of the
diaphragm and plug assembly and shows the actual
valve position. The travel indicator makes in-service
inspection and troubleshooting easy. Also, it can be used
for remote alarming and monitoring stem position.
Versatility—The Type LR125 uses the E-body, making
10
available the standard construction materials and end
connections (ASME and EN) used by other E-body
regulators and control valves. Type MR95H can handle
inlet pressures up to 300 psig / 20.7 bar and outlet
pressures from 15 to 150 psig / 1.0 to 10.3 bar.
11
Easy-to-Maintain—The pilot is designed to allow quick
and simple in-line trim inspection and parts replacement.
3
Page 4
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
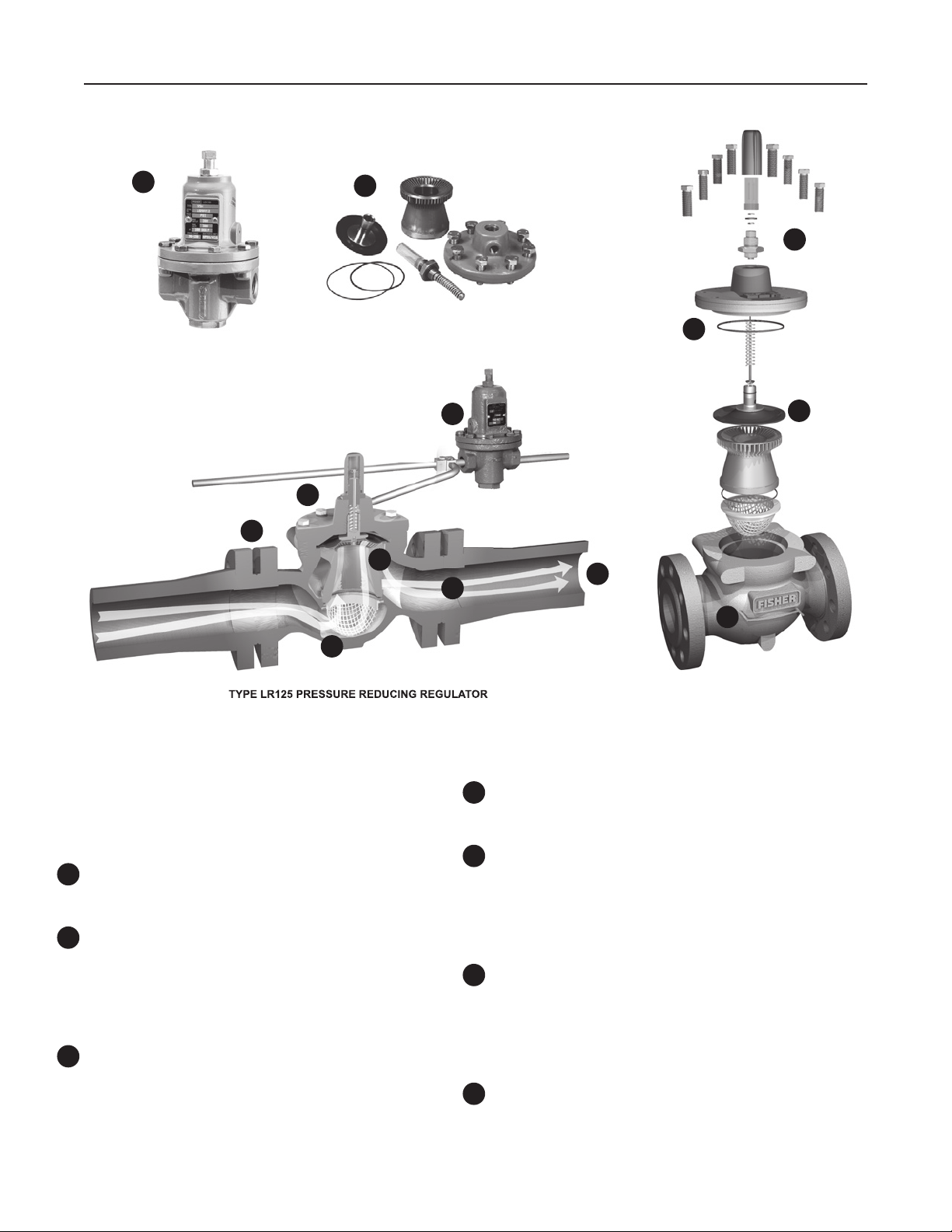
TYPE MR95H PILOT
SUPPLY LINE
M1215
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
TYPE 112 RESTRICTOR
CONTROL SPRING
VALVE PLUG
MAIN SPRING
DIAPHRAGM AND
PLUG ASSEMBLY
INTERNAL STRAINER
DIAPHRAGM
TYPE LR125 WITH TYPE MR95H PILOT AND TYPE 112 RESTRICTOR
Figure 3. Type LR125 Operational Schematic
Powder Paint Coating—Carbon steel body is powder
12
paint coated providing superior impact, abrasion and
corrosion resistance.
Pilot Type Description
Type MR95H—High-pressure pressure reducing pilot
for 15 to 150 psig / 1.0 to 10.3 bar outlet pressures.
Designed to handle inlet pressures up to 300 psig /
20.7 bar.
Principle of Operation
As long as the outlet (control) pressure is above the
outlet pressure setting, the pilot valve plug or disk
remains closed (Figure 3). Force from the main spring, in
addition to inlet pressure bleeding through the restrictor,
provide downward loading pressure to keep the main
valve diaphragm and plug assembly tightly shutoff.
When the outlet pressure decreases below the pilot
outlet pressure setting, the pilot plug or disk assembly
opens. Loading pressure bleeds downstream through
the pilot faster than it can be replaced through the
supply line. This reduces loading pressure on top of
the main valve diaphragm and plug assembly and
lets the unbalanced force between inlet and loading
pressure overcome the main spring force to open the
Type LR125 diaphragm and plug assembly.
As the outlet pressure rises toward the outlet pressure
setting, it compresses the pilot diaphragm against
the pilot control spring and lets the pilot valve plug
or disk close. Loading pressure begins to build up
on the Type LR125 diaphragm and plug assembly.
The loading pressure, along with force from the main
spring, pushes the diaphragm and plug assembly onto
the tapered-edge seat, producing tight shutoff.
4
Page 5

Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Table 1. Type LR125 Main Valve Body Sizes, End Connection Styles, Structural Design Ratings and Maximum Operating
Inlet Pressures
MAIN VALVE BODY SIZE
In. DN psig bar psig bar
1, 2, 3 and 4 25, 50, 80 and 100
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Bulletin and any applicable standard or code limitation should not be exceeded.
2. Ratings and end connections for other than ASME standard can usually be provided. Contact your local Sales Ofce for assistance.
3. Maximum cold working pressure (CWP) per ASME B16.34 or product Bulletin limit, whichever is lowest. Temperature may decrease these maximum pressures.
4. Not available for 4 in. / DN 100 body size.
Table 2. Type MR95H Pilot Maximum Cold Working Pressure
BODY SIZE BODY AND SPRING CASE MATERIAL MAXIMUM INLET PRESSURE MAXIMUM OUTLET PRESSURE
1/2 NPT
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Bulletin, and any applicable standard or code limitation should not be exceeded.
2. Temperature and/or the body end connection may decrease these maximum pressures.
(1)
MAIN VALVE
BODY MATERIAL
WCC Steel
CF8M Stainless steel
Steel
Stainless steel
END CONNECTION STYLE
NPT or SWE
(1 and 2 in. only)
CL150 RF 290 20.0 290 20.0
CL300 RF 750 51.7
CL600 RF 1500 103
PN 16/25/40 RF
(1 and 2 in. only)
CL150 RF 275 19.0 275 19.0
CL300 RF 720 49.6
PN 16/25/40 RF
(1)(2)
(4)
NPT
(4)
300 psig / 20.7 bar
300 psig / 20.7 bar
STRUCTURAL DESIGN
(2)
RATING
1500 103 300 20.7
580 40.0
1440 99.2 300 20.7
580 40.0
(3)
MAXIMUM OPERATING
INLET PRESSURE
300 20.7
300 20.7CL600 RF 1440 99.2
300 psig / 20.7 bar
300 psig / 20.7 bar
(3)
Table 3. Outlet (Control) Pressure Ranges
PILOT
Type MR95H
OUTLET PRESSURE RANGE SPRING WIRE DIAMETER SPRING FREE LENGTH
psig bar In. mm In. mm
15 to 30
25 to 75
70 to 150
1.0 to 2.1
1.7 to 5.2
4.8 to 10.3
0.207
0.234
0.283
5.26
5.94
7.19
2.50
2.60
2.44
63.5
65.9
62.0
SPRING PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
ERCA04288A0 Yellow
ERAA01910A0 Green
ERAA01911A0 Red
Table 4. Diaphragm Material Selection Information
17E68 NITRILE (NBR) 17E97 NITRILE (NBR) 17E88 FLUOROCARBON (FKM)
Liquid Temperature -20 to 150°F / -29 to 66°C 0 to 150°F / -18 to 66°C 0 to 250°F / -18 to 121°C
General Applications
Heavy Particle Erosion Fair Excellent Good
1. Fluorocarbon (FKM) is limited to 200°F / 93°C in hot water.
Best for low pressure
differential and cold temperature
service applications.
Installation
The robust design of the Type LR125 allows this regulator
to be installed indoors or outdoors. This regulator
is designed to withstand the elements. The powder
paint coating protects regulator against minor impacts,
abrasions and corrosion. When installed outdoors,
the Type LR125 does not require protective housing.
However, the Type MR95H pilot should be oriented so
that the pilot spring case vent is pointed down. Otherwise,
make sure the vent is protected so that rain, moisture,
insects or any debris will not accumulate inside or block
the vent assembly.
venting of the pilot spring case as required by applicable
codes and regulations.
When installed indoors, install remote
Best for abrasive or
erosive service applications.
Best for high temperature
applications.
Overpressure Protection
Overpressuring any portion of a regulator or associated
equipment may cause personal injury, leakage
or property damage due to bursting of pressurecontaining parts. Provide appropriate pressure relieving
or pressure limiting devices to ensure that the limits in
the Specications section are not exceeded. Common
methods of external overpressure protection include
relief valves, monitoring regulators, shutoff devices
and series regulation. Regulator operation within
ratings does not prevent the possibility of damage from
external sources or from debris in the pipeline. Install
additional strainer or lter upstream of the regulator for
applications with high levels of debris.
(1)
5
Page 6

Bulletin 71.2:LR125
150 /
10.3
135 /
9.3
120 /
8.3
105 /
7.2
90 /
6.2
75 /
5.2
psig / bar
60 /
4.1
OUTLET PRESSURE (P2)
45 /
3.1
30 /
2.1
CAVITATION PREDICTION
15 /
1.0
0
CONTINUOUS SERVICE REGION
INTERMITTENT SERVICE REGION
FULL CAVITATION REGION
30 /
2.1
60 /
4.1
90 /
6.2
psig / bar
150 /
10.3
120 /
8.3
INLET PRESSURE (P1)
180 /
12.4
210 /
14.5
240 /
16.5
270 /
18.6
Figure 4. Cavitation Sizing for Water
Table 5. Main Valve Minimum Differential Pressures
MAIN VALVE
BODY SIZE
In. DN Diaphragm Code Diaphragm Material psid bar d psid bar d
17E68 (standard) Nitrile (NBR), Low Minimum Differential 30 2.1 30 2.1
1 25
2 50
3 80
4 100
1. See Table 1 for structural design ratings and Table 2 for Type MR95H pilot rating.
17E97 Nitrile (NBR), High Erosion Resistance 35 2.5 35 2.5
17E88 Fluorocarbon (FKM), High Temperature Capability 30 2.1 30 2.1
17E68 (standard) Nitrile (NBR), Low Minimum Differential 18 1.2 19 1.3
17E97 Nitrile (NBR), High Erosion Resistance 24 1.7 24 1.7
17E88 Fluorocarbon (FKM), High Temperature Capability 18 1.2 19 1.3
17E68 (standard) Nitrile (NBR), Low Minimum Differential 21 1.5 28 1.9
17E97 Nitrile (NBR), High Erosion Resistance 23 1.6 23 1.6
17E88 Fluorocarbon (FKM), High Temperature Capability 21 1.5 28 1.9
17E68 (standard) Nitrile (NBR), Low Minimum Differential 16 1.1 30 2.1
17E97 Nitrile (NBR), High Erosion Resistance 16 1.1 34 2.3
17E88 Fluorocarbon (FKM), High Temperature Capability 16 1.1 30 2.1
DIAPHRAGM
(1)
MINIMUM DIFFERENTIAL, PERCENT OF CAPACITY
For 90% Capacity For 100% Capacity
300 /
20.7
Table 6. Flow and Sizing Coef cients for Type LR125 Main Valve at 100% Capacity
MAIN VALVE BODY SIZE REGULATING COEFFICIENTS WIDE-OPEN COEFFICIENTS
In. DN C
1 25 14.8 33.4 15.2 33.5 0.88 0.706 0.06 0.94
2 50 50.8 37.2 52.4 37.2 0.92 0.875 0.09 0.96
3 80 91.4 38.8 94.1 38.8 0.94 0.952 0.09 0.97
4 100 147 38.7 151 38.7 0.85 0.947 0.09 0.92
6
V
C
1
C
V
C
1
K
m
IEC SIZING COEFFICIENTS
X
T
F
D
F
L
Page 7

Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Table 7. Flow and Sizing Coefcients for Type MR95H Pilot
BODY SIZE,
IN. / DN
1/2 / 15 2.9 35.5 0.79 0.797 0.70 0.89
2
Km = F
L
Table 8. Type 112 Restrictor Flow Coefcients
RESTRICTOR SETTING C
Table 9. Approximate Weights Including Type MR95H Pilot and Restrictor
WIDE-OPEN COEFFICIENT
C
v
Setting 2 0.03
Setting 4 0.07
Setting 6 0.14
Setting 8 0.17
C
1
K
m
v
X
IEC SIZING COEFFICIENTS
T
F
D
C
35
F
L
1
BODY SIZE
In. DN NPT or SWE CL150 RF CL300 RF CL600 RF
1 25 22 / 10 24 / 11 28 / 13 32 / 15
2 50 51 / 23 54 / 24 58 / 26 65 /29
3 80 103 / 47 107 / 49 110 / 50 123 / 56
4 100 139 / 63 145 / 66 159 / 72 192 / 87
Cavitation Sizing
MAIN VALVE BODY,
LBS / kg
Cavitation Region—Cavitation may occur. Damage
to regulator components and piping is possible. The
Note
The cavitation sizing graph in Figure 4
applies to water only. For cavitation
sizing for other liquids, contact your
local Sales Ofce.
Use Figure 4 to determine cavitation sizing of
Type LR125. The Cavitation Prediction Curve depicts
P1 and P2 combinations where cavitation is likely
to occur. The curve shape was determined through
analysis and lab conrmation on water. Determine the
desired inlet pressure and outlet pressure of the system
and nd the intersection of those values on the graph.
No Cavitation Region—Cavitation is not expected
in this region. Damage to regulator components and
piping is highly unlikely as a result of cavitation.
Note
Emerson™ denies responsibility for
damage and voids the warranty if the
product is used within the Cavitation
Region (see Figure 4).
risk of damage increases as P1 and P2 move down
and to the right on the table. Cavitation damage can
be avoided by dividing the total pressure drop into
stages so that the P1 and P2 combination falls into the
“No Cavitation Region” at every stage.
Capacity Information
Note
Flow capacities are laboratory veried;
therefore, regulators may be sized for
100% ow published capacities. It is not
necessary to reduce published capacities.
The capacity information on the following pages is based
on four % droop, 10%, 20%, 30% and 40%. Droop is
the negative control deviation or pressure offset below
the setpoint of the regulator.
Table 10 shows Cv values at different % droop and
selected inlet pressures and outlet pressure settings.
Table 11 shows the liquid regulating capacities of the
Type LR125 regulator at selected inlet pressures and outlet
pressure settings. Flows are in gallons per minute (GPM)
and liters per minute (L/min) of water.
7
Page 8
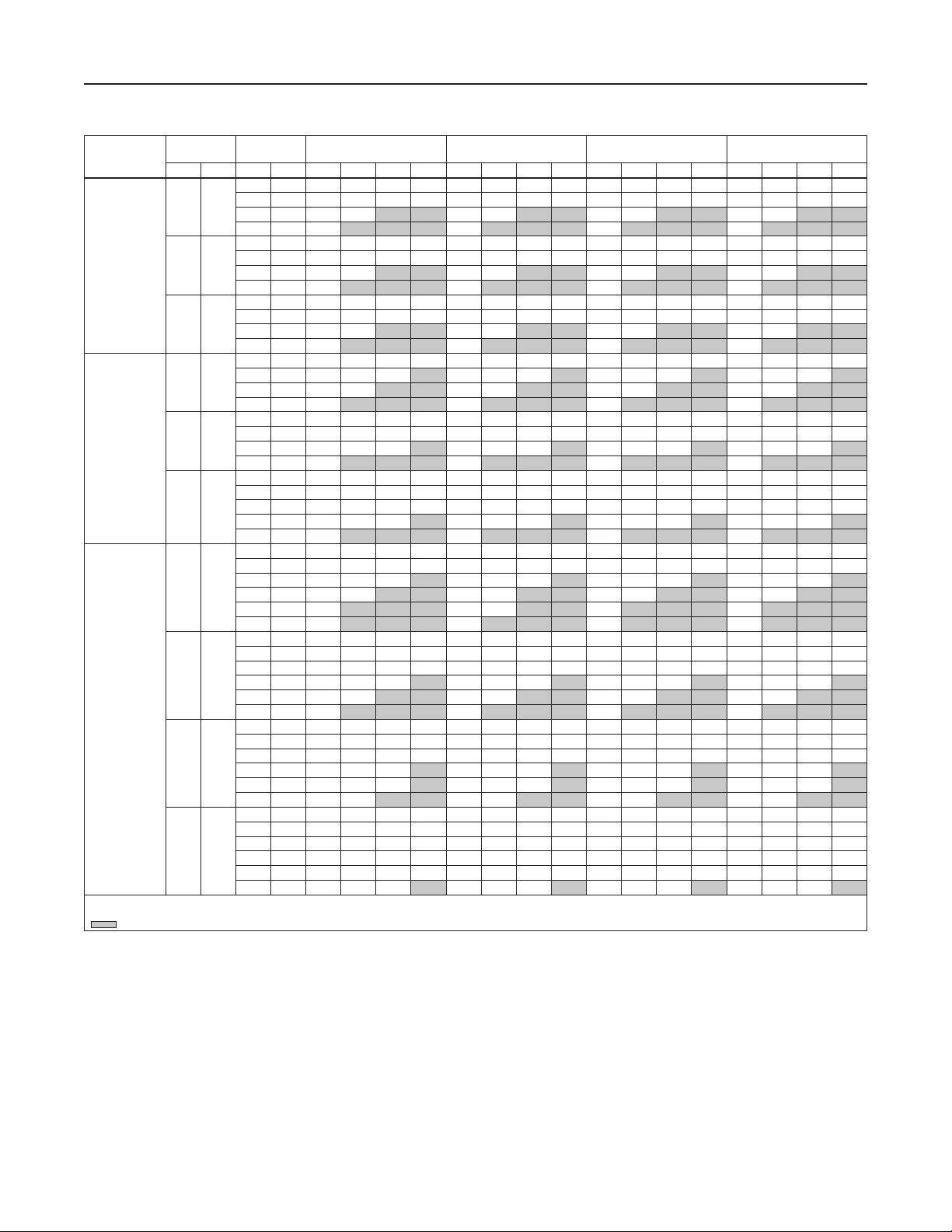
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Table 10. C
SPRING
RANGE AND
COLOR
15 to 30 psig /
1.0 to 2.1 bar
Yellow
25 to 75 psig /
1.7 to 5.2 bar
Green
70 to 150 psig /
4.8 to 10.3 bar
1. Type LR125 on liquid service with 1/2 NPT Type MR95H Pilot, 100% Cage Capacity with internal inlet strainer and Type 112 Restrictor Setting of “4”.
2. Values published in this table are laboratory tested and are presented based on % droop (negative control deviation only) or pressure offset below setpoint.
(1)
at % Droop (Pressure Offset Below Setpoint)
v
OUTLET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 30% 40% 10% 20% 30% 40% 10% 20% 30% 40% 10% 20% 30% 40%
15 1.0
20 1.4
30 2.1
25 1.7
50 3.4
75 5.2
70 4.8
100 6.9
Red
125 8.6
150 10.3
Exceeds recommended maximum pressure drop ratio of 0.65.
INLET 1 IN. / DN 25 2 IN. / DN 50 3 IN. / DN 80 4 IN. / DN 100
45 3.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 39.7 44.2 48.3 50.8 83.0 89.2 91.4 91.4 133.4 143.4 147.0 147.0
50 3.4 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 39.2 44.5 48.4 50.6 83.3 89.6 91.4 91.4 134.0 144.1 147.0 147.0
60 4.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 38.3 44.9 48.5 50.0 84.1 90.4 91.4 91.4 135.2 145.4 147.0 147.0
65 4.4 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 37.8 45.2 48.6 49.8 84.5 90.8 91.4 91.3 135.9 146.0 147.0 146.8
50 3.4 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
60 4.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 48.5 50.7 50.7 50.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
70 4.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 46.1 50.0 50.5 49.9 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
75 5.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 44.9 49.7 50.3 49.7 91.2 91.4 91.4 91.4 146.7 147.0 147.0 146.1
60 4.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
75 5.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.7 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
90 6.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.2 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
100 6.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 47.6 50.8 50.6 49.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
55 3.7 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
75 5.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.6 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
80 5.4 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.5 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
90 6.1 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.3 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
80 5.4 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 49.0 50.1 49.9 49.7 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
100 6.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 49.1 50.1 50.0 49.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
125 8.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 49.2 50.0 50.1 50.1 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
150 10.2 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 49.3 50.0 50.2 50.3 91.4 91.4 91.4 90.9 147.0 147.0 147.0 146.2
110 7.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
125 8.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
150 10.2 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 49.8 49.8 49.5 49.9 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
175 11.9 14.7 14.8 14.8 14.8 45.3 46.5 46.4 47.1 86.1 87.9 88.0 88.7 138.5 141.3 141.6 142.6
200 13.6 14.2 14.5 14.6 14.5 40.7 43.1 43.3 44.2 80.6 83.4 84.0 84.6 129.6 134.2 135.1 136.0
100 6.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.5 49.4 49.3 49.9 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
125 8.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 46.1 46.0 46.6 47.5 87.7 88.6 89.5 91.4 141.1 142.5 144.0 147.0
150 10.2 14.7 14.8 14.7 14.8 41.6 42.7 43.8 45.0 82.8 84.0 84.9 86.6 133.1 135.0 136.5 139.2
175 11.9 14.6 14.8 14.8 14.8 44.6 46.0 46.0 46.7 85.2 87.0 87.2 87.9 137.1 139.9 140.2 141.4
190 12.9 14.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 46.4 47.9 47.3 47.7 86.7 88.8 88.5 88.8 139.4 142.8 142.4 142.8
200 13.6 14.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 47.7 49.2 48.2 48.4 87.7 90.0 89.5 89.3 141.0 144.7 143.9 143.7
130 8.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.0 49.6 49.7 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
150 10.2 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.1 49.5 49.2 49.3 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
175 11.9 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 48.4 48.9 48.7 48.8 90.7 91.4 91.4 91.4 145.9 147.0 147.0 147.0
200 13.6 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 46.7 48.3 48.2 48.4 88.1 90.3 90.4 90.4 141.6 145.2 145.4 145.3
250 17.0 14.2 14.2 14.2 14.2 43.2 47.1 47.3 47.4 82.8 86.2 86.5 86.5 133.2 138.6 139.1 139.2
275 18.7 13.9 13.7 13.7 13.7 41.5 46.5 46.8 46.9 80.2 84.1 84.5 84.6 129.0 135.3 135.9 136.1
155 10.5 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
175 11.9 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 50.8 50.8 50.8 50.6 91.4 91.4 91.4 91.4 147.0 147.0 147.0 147.0
200 13.6 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 45.9 47.5 48.3 48.4 88.4 90.5 91.2 91.2 142.2 145.5 146.6 146.7
250 17.0 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 43.6 46.4 46.9 47.0 85.2 87.7 88.2 88.1 137.0 141.1 141.9 141.8
275 18.7 14.7 14.6 14.6 14.6 42.5 45.8 46.3 46.3 83.6 86.3 86.7 86.6 134.4 138.9 139.5 139.3
300 20.4 14.5 14.3 14.3 14.3 41.4 45.3 45.6 45.6 82.0 85.0 85.2 85.1 131.8 136.6 137.1 136.8
180 12.2 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 45.4 47.2 49.0 49.0 89.3 91.3 91.4 91.4 143.5 146.8 147.0 147.0
200 13.6 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 45.0 46.7 48.3 48.3 88.8 90.7 91.4 91.4 142.8 145.9 147.0 147.0
225 15.3 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 44.5 46.2 47.5 47.5 88.2 90.0 90.9 90.9 141.8 144.7 146.3 146.2
250 17.0 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 44.0 45.7 46.6 46.6 87.5 89.3 89.9 89.8 140.8 143.6 144.7 144.4
275 18.7 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 43.5 45.2 45.8 45.7 86.9 88.5 88.9 88.6 139.8 142.4 143.0 142.5
300 20.4 14.8 14.8 14.8 14.8 43.1 44.7 44.9 44.9 86.3 87.8 87.9 87.4 138.8 141.2 141.4 140.6
(2)
8
Page 9

Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Table 11. Capacity
SPRING
RANGE AND
COLOR
15 to 30 psig /
1.0 to 2.1 bar
Yellow
25 to 75 psig /
1.7 to 5.2 bar
Green
70 to 150 psig /
4.8 to 10.3 bar
Red
1. Type LR125 on liquid service with 1/2 NPT Type MR95H Pilot, 100% Cage Capacity with internal inlet strainer and Type 112 Restrictor Setting of “4”.
2. Values published in this table are laboratory tested and are presented based on % droop (negative control deviation only) or pressure offset below setpoint.
Exceeds recommended maximum pressure drop ratio of 0.65.
(1)
, Water (GPM / L/min) for 1 and 2 in. / DN 25 and 50 Bodies at % Droop (Pressure Offset Below Setpoint)
OUTLET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min
15 1.0
20 1.4
30 2.1
25 1.7
50 3.4
75 5.2
70 4.8
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
INLET
45 3.1 83 314 85 322 87 329 89 336 223 843 254 961 284 1074 305 1154
50 3.4 89 338 91 345 93 352 95 359 237 897 274 1037 304 1151 324 1226
60 4.1 101 382 103 388 104 394 106 400 261 989 311 1178 341 1292 357 1353
65 4.4 106 402 108 408 109 414 111 419 272 1028 329 1245 359 1358 372 1409
50 3.4 84 317 86 327 89 336 91 345 287 1088 296 1121 305 1154 313 1185
60 4.1 96 363 98 372 100 380 103 388 314 1190 336 1272 344 1302 349 1323
70 4.8 107 404 109 412 111 419 113 427 333 1259 368 1392 378 1429 380 1440
75 5.1 112 423 114 430 116 438 117 445 339 1284 382 1446 393 1487 394 1493
60 4.1 85 322 89 336 92 350 96 363 292 1105 305 1154 317 1201 329 1246
75 5.1 103 388 106 400 109 412 112 423 352 1332 363 1373 373 1413 383 1449
90 6.1 117 445 120 455 123 465 126 475 403 1526 413 1562 422 1597 426 1611
100 6.8 126 479 129 488 132 498 134 507 407 1541 443 1676 450 1703 451 1707
55 3.7 84 319 88 331 91 343 94 354 290 1096 301 1138 311 1178 321 1216
75 5.1 107 406 110 415 112 425 115 434 368 1393 377 1426 385 1458 392 1484
80 5.4 112 425 115 434 117 443 119 452 385 1458 394 1490 402 1520 407 1541
90 6.1 122 460 124 469 126 477 128 485 417 1580 425 1609 433 1637 435 1648
80 5.4 88 331 94 354 99 376 105 396 290 1097 317 1200 335 1267 351 1329
100 6.8 110 415 115 434 119 452 124 469 364 1378 388 1469 403 1526 417 1579
125 8.5 132 501 136 517 140 532 144 546 440 1665 461 1746 475 1798 488 1847
150 10.2 152 574 155 588 159 601 162 613 505 1912 524 1984 538 2037 551 2086
110 7.5 96 365 105 396 112 425 119 452 331 1254 359 1360 385 1458 410 1550
125 8.5 112 425 119 452 126 477 132 501 385 1458 410 1550 433 1637 454 1720
150 10.2 134 509 140 532 146 553 152 574 452 1711 472 1787 489 1851 511 1934
175 11.9 153 577 159 601 164 620 169 639 469 1776 498 1885 514 1945 537 2031
200 13.6 164 620 171 647 177 670 180 683 469 1775 510 1932 526 1992 551 2085
100 6.8 90 341 98 372 106 400 113 427 307 1163 327 1240 352 1334 380 1438
125 8.5 117 441 123 465 129 488 135 510 363 1373 382 1447 406 1537 432 1637
150 10.2 137 519 143 541 148 560 154 582 388 1469 414 1567 440 1666 468 1772
175 11.9 154 585 161 610 166 629 171 646 472 1788 501 1898 516 1953 539 2039
190 12.9 164 620 171 648 176 665 180 682 523 1981 555 2100 562 2126 580 2196
200 13.6 170 643 178 672 182 688 186 704 558 2111 591 2236 592 2240 608 2301
130 8.8 94 354 105 396 115 434 124 469 321 1216 353 1337 384 1454 416 1575
150 10.2 115 434 124 469 132 501 140 532 388 1469 414 1567 440 1666 468 1772
175 11.9 136 517 144 546 152 574 159 601 446 1688 476 1804 499 1889 524 1983
200 13.6 155 588 162 614 169 639 175 663 489 1853 529 2002 550 2081 572 2166
250 17.0 180 681 185 700 191 723 196 742 547 2071 614 2324 634 2400 653 2472
275 18.7 189 715 191 724 197 745 202 763 565 2138 649 2458 670 2535 687 2602
155 10.5 96 365 110 415 122 460 132 501 331 1254 377 1426 417 1580 454 1720
175 11.9 117 443 128 485 138 524 148 560 402 1520 440 1665 475 1799 506 1917
200 13.6 138 524 148 560 157 594 165 626 429 1623 475 1798 512 1938 541 2046
250 17.0 174 657 181 686 189 714 196 741 512 1937 568 2151 598 2265 622 2353
275 18.7 187 708 193 731 200 757 206 779 542 2053 606 2295 633 2398 655 2479
300 20.4 198 750 203 767 209 790 214 810 567 2148 640 2424 665 2516 684 2591
180 12.2 99 376 115 434 128 485 140 532 305 1153 365 1383 424 1607 465 1761
200 13.6 119 452 132 501 144 546 155 588 363 1374 418 1582 471 1783 507 1919
225 15.3 140 532 152 574 162 614 172 651 422 1599 474 1793 520 1968 552 2088
250 17.0 159 601 169 639 178 675 187 709 472 1788 521 1972 561 2125 589 2231
275 18.7 175 663 184 697 193 730 201 762 515 1950 562 2129 597 2258 622 2354
300 20.4 190 720 199 752 207 782 214 812 553 2093 599 2267 627 2373 650 2461
10% 20% 30% 40% 10% 20% 30% 40%
1 IN. / DN 25 2 IN. / DN 50
(2)
- continued -
9
Page 10

Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Table 11. Capacity
Setpoint)
SPRING
RANGE AND
COLOR
15 to 30 psig /
1.0 to 2.1 bar
Yellow
25 to 75 psig /
1.7 to 5.2 bar
Green
70 to 150 psig /
4.8 to 10.3 bar
Red
1. Type LR125 on liquid service with 1/2 NPT Type MR95H Pilot, 100% Cage Capacity with internal inlet strainer and Type 112 Restrictor Setting of “4”.
2. Values published in this table are laboratory tested and are presented based on % droop (negative control deviation only) or pressure offset below setpoint.
Exceeds recommended maximum pressure drop ratio of 0.65.
(1)
, Water (GPM / L/min) for 3 and 4 in. / DN 80 and 100 Bodies at % Droop (Pressure Offset Below
(2)
(continued)
OUTLET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min GPM L/min
15 1.0
20 1.4
30 2.1
25 1.7
50 3.4
75 5.2
70 4.8
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
INLET
45 3.1 466 1762 512 1939 537 2032 548 2076 749 2835 824 3119 863 3268 882 3339
50 3.4 503 1906 552 2090 574 2174 585 2215 810 3065 888 3362 924 3497 941 3563
60 4.1 573 2171 626 2370 643 2434 653 2471 922 3491 1007 3812 1034 3915 1050 3974
65 4.4 606 2295 661 2502 675 2554 683 2586 975 3690 1063 4024 1085 4108 1099 4159
50 3.4 517 1957 533 2017 548 2076 563 2133 832 3148 857 3245 882 3339 906 3430
60 4.1 592 2242 606 2295 620 2347 633 2397 953 3606 975 3691 997 3774 1018 3855
70 4.8 659 2495 672 2542 684 2589 696 2635 1060 4013 1080 4089 1100 4164 1120 4238
75 5.1 689 2606 702 2658 714 2702 725 2746 1107 4192 1129 4274 1148 4346 1160 4390
60 4.1 525 1988 548 2076 571 2161 592 2242 844 3197 882 3339 918 3475 953 3606
75 5.1 633 2397 653 2471 672 2542 690 2612 1018 3855 1050 3974 1080 4089 1110 4201
90 6.1 725 2746 743 2811 759 2874 776 2936 1167 4417 1194 4521 1221 4622 1247 4722
100 6.8 781 2956 797 3016 812 3075 828 3133 1256 4754 1282 4851 1307 4946 1331 5039
55 3.7 521 1972 541 2047 560 2119 578 2188 838 3172 870 3292 900 3408 930 3519
75 5.1 662 2507 678 2566 693 2624 708 2680 1065 4032 1090 4127 1115 4220 1139 4310
80 5.4 693 2624 708 2680 723 2735 737 2789 1115 4220 1139 4310 1162 4399 1185 4486
90 6.1 751 2843 765 2895 778 2946 792 2996 1208 4572 1230 4656 1252 4738 1273 4819
80 5.4 541 2047 578 2188 613 2321 646 2447 870 3292 930 3519 986 3733 1039 3935
100 6.8 678 2566 708 2680 737 2789 765 2895 1090 4127 1139 4310 1185 4486 1230 4656
125 8.5 818 3095 843 3190 867 3282 891 3372 1315 4977 1355 5130 1395 5279 1433 5424
150 10.2 937 3545 959 3629 980 3710 996 3770 1506 5702 1542 5836 1576 5967 1602 6063
110 7.5 596 2256 646 2447 693 2624 737 2789 958 3628 1039 3935 1115 4220 1185 4486
125 8.5 693 2624 737 2789 778 2946 818 3095 1115 4220 1185 4486 1252 4738 1315 4977
150 10.2 830 3143 867 3282 903 3416 937 3545 1335 5054 1395 5279 1452 5495 1506 5702
175 11.9 893 3380 942 3566 974 3688 1011 3827 1436 5437 1515 5736 1567 5931 1626 6155
200 13.6 927 3511 987 3737 1020 3860 1053 3985 1492 5646 1588 6010 1640 6209 1693 6409
100 6.8 556 2105 606 2295 653 2471 696 2635 894 3385 975 3691 1050 3974 1120 4238
125 8.5 691 2614 736 2786 780 2954 833 3152 1111 4205 1184 4481 1255 4750 1339 5070
150 10.2 772 2923 814 3081 853 3228 900 3405 1242 4701 1309 4956 1372 5192 1447 5477
175 11.9 902 3414 949 3591 978 3704 1014 3839 1450 5490 1526 5776 1574 5956 1631 6175
190 12.9 977 3698 1028 3890 1051 3980 1080 4088 1571 5947 1653 6257 1691 6401 1737 6575
200 13.6 1026 3884 1080 4087 1099 4161 1123 4250 1650 6246 1737 6574 1768 6693 1806 6836
130 8.8 578 2188 646 2447 708 2680 765 2895 930 3519 1039 3935 1139 4310 1230 4656
150 10.2 708 2680 765 2895 818 3095 867 3282 1139 4310 1230 4656 1315 4977 1395 5279
175 11.9 836 3165 891 3372 937 3545 980 3710 1345 5090 1433 5424 1506 5702 1576 5967
200 13.6 924 3497 989 3743 1031 3901 1069 4047 1486 5624 1590 6019 1658 6275 1719 6509
250 17.0 1048 3967 1124 4253 1160 4392 1193 4515 1685 6380 1807 6841 1866 7063 1918 7261
275 18.7 1091 4131 1175 4447 1210 4580 1241 4696 1755 6644 1890 7153 1946 7367 1995 7553
155 10.5 596 2256 678 2566 751 2843 818 3095 958 3628 1090 4127 1208 4572 1315 4977
175 11.9 723 2735 792 2996 855 3236 914 3460 1162 4399 1273 4819 1375 5205 1470 5565
200 13.6 827 3131 905 3425 967 3660 1020 3860 1330 5035 1455 5509 1555 5887 1640 6208
250 17.0 999 3782 1074 4067 1124 4256 1166 4414 1607 6082 1728 6541 1808 6845 1875 7099
275 18.7 1065 4033 1142 4323 1188 4495 1225 4636 1714 6487 1837 6953 1910 7230 1970 7457
300 20.4 1122 4249 1201 4548 1243 4704 1276 4830 1805 6834 1932 7314 1999 7565 2052 7769
180 12.2 599 2266 707 2677 792 2996 867 3282 963 3645 1137 4306 1273 4819 1395 5279
200 13.6 716 2709 811 3072 891 3372 959 3629 1151 4357 1305 4940 1433 5424 1542 5836
225 15.3 836 3166 922 3491 996 3771 1056 3998 1345 5091 1483 5614 1602 6065 1699 6431
250 17.0 939 3554 1018 3853 1083 4100 1135 4298 1510 5716 1637 6196 1742 6593 1826 6912
275 18.7 1029 3894 1102 4172 1160 4390 1205 4562 1654 6262 1773 6711 1865 7060 1938 7337
300 20.4 1109 4198 1178 4459 1228 4648 1267 4797 1783 6751 1895 7172 1975 7476 2038 7715
10% 20% 30% 40% 10% 20% 30% 40%
3 IN. / DN 80 4 IN. / DN 100
10
Page 11

TYPE MR95H PILOT
OPTIONAL
1/4 NPT PILOT
SUPPLY CONNECTION
ERAA00985_B
INDICATOR COVER
TYPE 112
RESTRICTOR
A
B
1/4 NPT
VENT
1/2 NPT
CONTROL
LINE
CONNECTION
E
G
TYPE LR125 WITH TYPE MR95H PILOT
Figure 5. Type LR125 Dimensions
Table 12. Type LR125 Dimensions
BODY SIZE
In. DN CL150 RF CL300 RF CL600 RF CL150 RF CL300 RF CL600 RF
1 25
2 50
3 80
4 100
3.62 /
91.9
5.0 /
127.0
5.9 /
149.3
6.9 /
176.3
A B
3.88 /
98.6
5.3 /
133.4
6.3 /
158.8
7.3 /
184.2
4.13 / 104.9 7.25 / 184.2 7.75 / 196.9 8.25 / 209.6
5.6 /
143.0
168.3
196.9
10.00 / 254.0 10.50 / 266.7 11.25 / 286.0
6.6 /
11.75 / 298.5 12.50 / 317.5 13.25 / 336.6
7.8 /
13.88 / 352.6 14.50 / 368.3 15.50 / 393.7
DIMENSIONS, IN. / mm
M
D D
7.40 /
189.0
9.00 /
229.0
13.30 /
338.0
14.70 /
373.0
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
TRAVEL INDICATOR
COVER REMOVAL
CLEARANCE
T
D
1
5.40 /
137.0
6.89 /
175.0
9.33 /
236.9
10.47 /
265.9
E G
11.39 /
289.3
11.65 /
295.9
13.68 /
347.5
15.24 /
387.1
2.40 /
60.0
3.10 /
79.0
3.80 /
97.0
5.10 /
130.0
D
1
WCC
Steel
8.10 /
205.8
8.18 /
207.8
8.66 /
220.0
9.52 /
241.8
VALVE TRIM
REMOVAL
V
CLEARANCE
M
CF8M
SST
8.10 /
205.8
9.18 /
233.2
9.66 /
245.4
9.52 /
241.8
T V
2.97 /
75.4
2.00 /
51.0
3.80 /
97.0
3.80 /
97.0
9.40 /
238.8
11.00 /
279.4
15.00 /
381.0
17.00 /
431.8
Ordering Information
Carefully review each specication, then complete
the Ordering Guide on this page. If a pilot setpoint
is not requested, the regulator will be factory set at
the approximate midrange. Please complete the
specications worksheet at the bottom of the ordering
guide on page 12.
Ordering Guide
Body Size (Select One)
1 in. / DN 25***
2 in. / DN 50***
3 in. / DN 80***
4 in. / DN 100***
Body Material and End Connection Style (Select One)
WCC Steel Body
NPT (Available in 1 and 2 in. bodies only)***
SWE (Available in 1 and 2 in. bodies only)***
CL150 RF***
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
PN 16/25/40 RF* (Not available in 4 in. body)
_____________ specify rating
CF8M Stainless Steel Body
NPT (Available in 1 and 2 in. bodies only)***
CL150 RF***
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
PN 16/25/40 RF* (Not available in 4 in. body)
_____________ specify rating
Main Valve Diaphragm Material (Select One)
17E68 Nitrile (NBR) (low minimum differential
capability) (standard)***
17E97 Nitrile (NBR) (high erosion resistant)***
17E88 Fluorocarbon (FKM)
(high temperature capability)**
Main Valve O-ring Material (Select One)
Nitrile (NBR) (standard)***
Fluorocarbon (FKM)**
Travel Indicator (Select One)
No (standard)***
Yes***
Inlet Body Tap (Select One)
Inlet body tap only (standard)***
Inlet body tap with pre-piped pilot supply***
Inlet/outlet body taps only***
Inlet/outlet body taps with pre-piped pilot supply and
pilot bleed***
11
Page 12
Bulletin 71.2:LR125
Ordering Guide (continued)
Pilot Diaphragm Material (Select One)
Neoprene (CR) (standard)***
Fluorocarbon (FKM)**
Pilot Valve Plug Material (Select One)
Nitrile (NBR) (standard)***
Fluorocarbon (FKM)***
Type MR95H Pilot Outlet Pressure Range (Select One)
15 to 30 psig / 1.0 to 2.1 bar, Yellow***
25 to 75 psig / 1.7 to 5.2 bar, Green***
70 to 150 psig / 4.8 to 10.3 bar, Red***
Main Valve Replacement Parts Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one diaphragm cartridge and O-rings kit to
match this order.
Pilot Replacement Parts Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one replacement kit to match this order.
Regulators Quick Order Guide
* * * Readily Available for Shipment
* * Allow Additional Time for Shipment
Special Order, Constructed from Non-Stocked Parts.
*
Consult your local Sales Ofce for Availability.
Availability of the product being ordered is determined by the component with the
longest shipping time for the requested construction.
Specication Worksheet
Application:
Specic Use ___________________________________
Line Size _____________________________________
Fluid Type ____________________________________
Specic Gravity ________________________________
Temperature __________________________________
Does the Application Require Overpressure Protection?
Yes No
Pressure:
Maximum Inlet Pressure _________________________
Minimum Inlet Pressure __________________________
Differential Pressure ____________________________
Set Pressure __________________________________
Maximum Flow ________________________________
Accuracy Requirements:
Less Than or Equal To:
5% 10% 20% 40%
Construction Material Requirements (if known):
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
Industrial Regulators
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
Tel: +1 800 558 5853
Outside U.S. +1 972 548 3574
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai 201206, China
Tel: +86 21 2892 9000
Europe
Bologna 40013, Italy
Tel: +39 051 419 0611
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
For further information visit www.fisherregulators.com
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners. Fisher is a mark owned by Fisher Controls International LLC,
a business of Emerson Process Management.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be construed as warranties or
guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to modify or improve the designs or specications of such
products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and
maintenance of any Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. product remains solely with the purchaser.
Natural Gas Technologies
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
Tel: +1 800 558 5853
Outside U.S. +1 972 548 3574
Asia-Pacic
Singapore 128461, Singapore
Tel: +65 6770 8337
Europe
Bologna 40013, Italy
Tel: +39 051 419 0611
Chartres 28008, France
Tel: +33 2 37 33 47 00
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
TESCOM
Emerson Process Management
Tescom Corporation
USA - Headquarters
Elk River, Minnesota 55330-2445, USA
Tels: +1 763 241 3238
+1 800 447 1250
Europe
Selmsdorf 23923, Germany
Tel: +49 38823 31 287
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai 201206, China
Tel: +86 21 2892 9499
©Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc., 2012, 2014; All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...