Page 1

AC Power
For Business-Critical Continuity™
Liebert FPC
User Manual - 15 kVA - 300kVA, 3 Phase, 50 & 60 Hz
™
Page 2

Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.0 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
1.1 Unpacking and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.1.1 Unpacking and Preliminary Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.1.2 Handling Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.1.3 Unit Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1.4 Location Considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1.5 Floor Pedestal Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.2 Additional Distribution Mounting & Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2.1 Liebert FDC Distribution Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2.2 Distribution Cabinet Electrical Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.3 Power and Control Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.3.1 Input Power Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.3.2 Junction Box Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.3.3 System Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1.3.4 Grounding Electrode Conductor for FPCs With Transformer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
1.3.5 Output Power Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.3.6 Control Wiring Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.0 EQUIPMENT INSPECTION AND STARTUP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.1 Internal Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.2 Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.0 INSPECTION AND STARTUP CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.1 Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.2 Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.3 Monitoring System Check-Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.4 Equipment Connection Check-Out of Units With Distribution Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.0 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
4.1 Startup Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.1 Emergency Shutdown—If Emergency Power Off switch is supplied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.2 Normal System Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.3 Normal System Turn ON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.4 Manual Restart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.2 Basic Monitor Panel (Units Without Monitoring) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.3 Power Monitor Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.0 MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
5.1 Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.2 Inspection and Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.2.1 Inspection Schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
i
Page 4

FIGURES
Figure 1 Typical cabinet and floor planning dimension data, 23" (584mm) cabinet, 15-125 kVA . . . . . . . . 3
Figure 2 Typical cabinet and floor planning dimension data, 47" (1194mm) cabinet 50-300kVA . . . . . . . . 4
Figure 3 Recommended minimum service and ventilation clearances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4 Floor pedestal details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 5 Electrical connection location for 23" (584mm) cabinet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 6 Electrical connection location for 47" (1194mm) cabinet—Front view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 7 Electrical connection location for 47" (1194mm) cabinet—Rear view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 8 Electrical connection location for 47" cabinet with SqD I-Line panelboard—Front view. . . . . . . 11
Figure 9 Electrical connection location for 47" cabinet with SqD I-Line panelboard—Rear view . . . . . . . 11
Figure 10 Low voltage control junction box connections, typical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 11 Main input junction box connections, typical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 12 Typical grounding arrangements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 13 Typical Liebert FPC equipment arrangement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 14 Simplified shutdown circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 15 Typical control wiring for units without monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 16 Typical control wiring for units with monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 17 Basic monitoring panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 18 Power monitor panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
TABLES
Table 1 23-inch cabinet weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Table 2 47-inch cabinet weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Table 3 Liebert FPC heat output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 4 Suggested minimum input wire size data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 5 Main input circuit breaker interrupting rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 6 Main input junction box electrical connections (4 wire) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 7 Main input junction box without transformer electrical connections (5 wire) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 8 Low-voltage (control) junction box dimensions, typical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 9 Main input (power) junction box dimensions, typical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 10 Minimum grounding electrode conductor size (AWG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 11 Panelboard main circuit breaker torque specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 12 Branch circuit breaker torque specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 13 Terminal block compression lug torque specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 14 Torque specifications, general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 15 ASCII interface default parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 16 RS-232 ASCII port customer commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 17 Monitored parameters data definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
ii
Page 5

IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
NOTE
Read the entire manual before installing or operating the system.
WARNING
!
The shipping bands may be under tension. Use appropriate eye, face, and hand protection to
safeguard against injury from band backlash.
WARNING
!
Verify that all incoming line voltage (power) and low-voltage (control) circuits are
de-energized and locked out before installing cables or making connections, whether in the
junction box or in the unit.
Equipment inspection and start-up should be performed only by trained personnel. Lethal
voltages are present during start-up procedures. Electrical safety precautions must be
followed throughout inspection and startup.
Only qualified service personnel should perform maintenance on the Liebert FPC system. All
voltage sources to the unit must be disconnected before inspecting or cleaning within the
cabinet.
Lethal voltages exist within the equipment during operation. Observe all warnings and
cautions in this manual. Failure to comply may result in serious injury or death. Obtain
qualified service for this equipment as instructed.
The monitoring system contains a lithium battery for memory backup. There is a danger of
explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with same or equivalent type.
Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
NOTE
The unit should not be loosened from the shipping pallet until all handling by fork lift or pallet
jack is completed.
All power and control wiring should be installed by licensed electricians and must comply with
the NEC and applicable codes.
1
Page 6

1.0 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
1.1 Unpacking and Installation
NOTE
Read the entire manual before installing and operating the system. Upon receipt of a Liebert
FPC™, the installer should perform the following steps to ensure a quality installation.
1.1.1 Unpacking and Preliminary Inspection
A quality installation begins on the receiving dock.
1. Inspect the shipping crate(s) for damage or signs of mishandling before unpacking the unit(s).
Check the Shock-Watch™ indicator.
2. Remove the packing and inspect the equipment for any obvious shipping damages.
3. If the FPC was shipped in an export crate, open the shipping crate carefully.
Use care to avoid puncturing the container with sharp objects that would damage the contents.
4. Remove the packing and vapor barriers and inspect the equipment for any obvious shipping
damages.
NOTE
The units should not be loosened from the shipping pallet until all handling by fork lift or
pallet jack is completed. Complete internal inspection should be accomplished only after
equipment positioning and prior to electrical hookup.
Installation Instructions
5. If any damage is observed, immediately file a damage claim with the shipping agency and forward
a copy to:
Liebert Corporation
1050 Dearborn Drive
P.O. Box 29186
Columbus, Ohio 43229 USA
1.1.2 Handling Considerations
The Liebert FPC™ (and cables, if furnished) is bolted to a wooden pallet to allow handling by forklift
equipment.
The Liebert FPC and cable reels are furnished with casters to allow the unit to be rolled into place
after it has been unbolted from the pallet. The FPC should be kept on the shipping pallet until it has
been moved by forklift as close as practical to its installation location.
Refer to the cabinet drawings furnished with the FPC for the unit’s size and weight. Typical cabinet
dimensions and weights are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
The route to the FPC’s installation area should be planned to ensure that all passages, including doorways, elevators, ramps and hallways, are large enough to accommodate the unit and that the floors
are strong enough to support the weight. Determine whether any corners or offsets would cause problems in maneuvering the unit.
Liebert recommends removing the exterior side panels, if supplied, before the unit is moved. This will
prevent scratches, dents and other damage to the panels.
2
Page 7
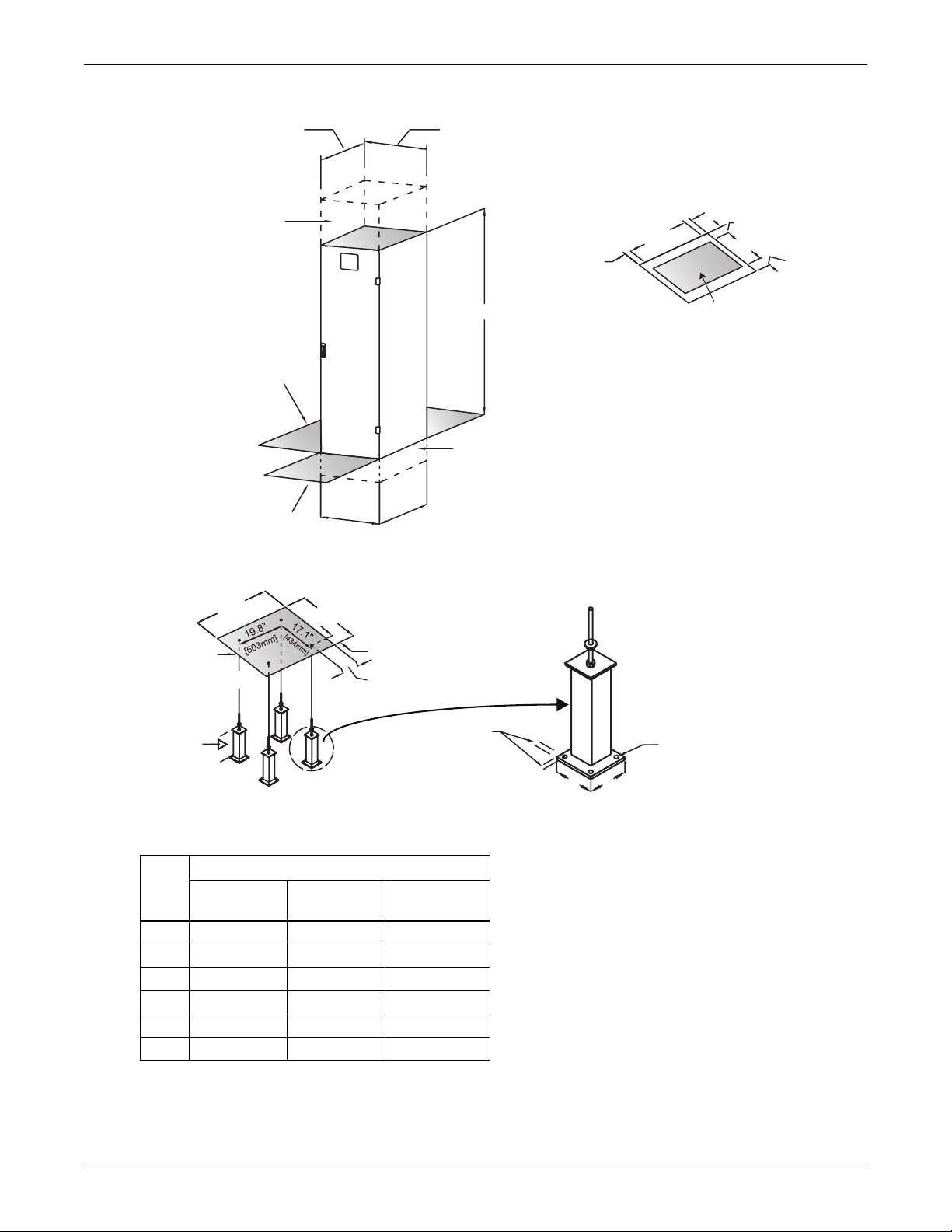
Installation Instructions
Figure 1 Typical cabinet and floor planning dimension data, 23" (584mm) cabinet, 15-125 kVA
Overall Dim.
39-1/2" (1003mm)
Including hinge
and bezel
projection
Overhead clearance
of 18" (457mm)
recommended
for cooling airflow
Minimum side
clearance of 42" (1067mm)
recommended for service access
if unit is equipped with
distribution monitoring option
Shaded areas indicate
recommended clearance
of 42" (1067mm) at front and
rear for service access
Cabinet Dimensional Data
23-1/2"
(597mm)
Unit Base Outline
36.4"
(925mm)
Overall Dimension
25.2" (640mm)
including side
panels
78-1/2" (1995mm)
For units with bottom
cable access, clearance
of 6" (152mm) below
unit is recommended
for cooling airflow
and cable entry/exit
34" (864mm)
1.2"
(30mm)
Front
Footprint and Floor
Cutout Dimensions
1.2"
(30mm)
6"
(152mm)
11-1/2" (292mm)
Shaded area indicates
cable access and
cooling airflow
6" (152mm)
36.4" (925mm)
Unit Base Outline
Floor Pedestals
available from
6" (152mm) to 18"
(457mm)
Table 1 23-inch cabinet weight
Unit
kVa
15 1010 (458) 1060 (480) 750 (340)
30 1090 (494) 1140 (517) 750 (340)
50 1160 (526) 1235 (560) 750 (340)
75 1350 (612) 1450 (658) 800 (363)
100 1540 (699) 1665 (755) 800 (363)
125 1650 (748) 1775 (805) 800 (363)
23-1/2" (597mm)
Front
Weight, lb (kg)
60Hz 50Hz
Optional Floor Pedestals
3.2" (81mm)
8.3"
(211mm)
Dia. location
3/4" (19mm)
typical
6" (152mm) 6" (152mm)
Without
Transformer
.56" (14mm)
diameter; 4 holes
typical
3
Page 8
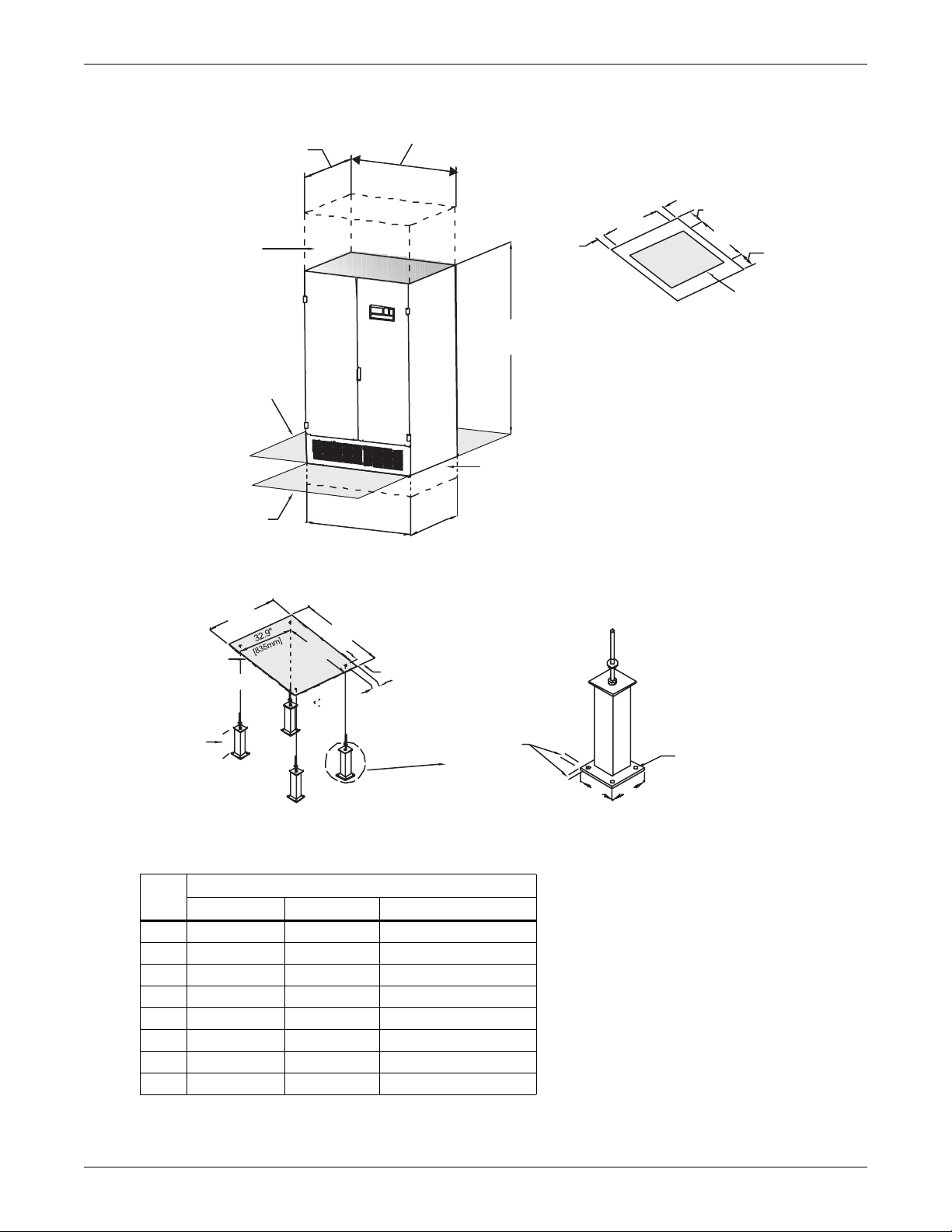
Installation Instructions
Figure 2 Typical cabinet and floor planning dimension data, 47" (1194mm) cabinet 50-300kVA
Overall Dimension
Overall Dim.
39-1/2" (1003mm)
Including hinge
and bezel
projection
48.6" (1235mm)
including side panels
1.3"
(33mm)
6" (152mm)
33.8" (859mm)
Overhead clearance
of 18" (457mm)
recommended
for cooling airflow
Minimum side clearance
78-1/2"
(1995mm)
1.3"
(33mm)
Front
Footprint and Floor
Cutout Dimensions
35" (889mm)
6" (152mm)
Shaded area indicates
cable access and
cooling airflow
of 42" (1067mm) recommended
for service access if unit is
equipped with distribution
monitoring option
For units with bottom
cable access, clearance
Shaded areas indicate
recommended clearance
of 42" (1067mm) at front and
rear for service access
47"
(1194mm)
Unit Base Outline
36.4"
(925mm)
of 6" (152mm) below
unit is recommended
for cooling airflow
and cable entry/exit
Cabinet Dimensional Data
36.4" (925mm)
Unit Base Outline
Front
Floor Pedestals
available from
6" (152mm) to
18" (457mm)
Optional Floor Pedestals
Table 2 47-inch cabinet weight
Unit
kVA
50 1891 (858) 1966 (892) 1335 (606)
75 1995 (905) 2095 (950) 1335 (606)
100 2191 (994) 2316 (1051) 1335 (606)
125 2298 (1042) 2423 (1099) 1360 (617)
150 2490 (1129) 2640 (1198) 1360 (617)
200 2610 (1184) 2810 (1275) 1360 (617)
225 2800 (1270) 3000 (1361) 1390 (631)
300 2845(1290) 3045 (1381) 1390 (631)
60 Hz 50 Hz Without Transformer
47" (1194mm)
43.8"
(1112mm)
Weight, lb (kg)
1.5" (38mm)
2.3" (58mm)
Dia. location
3/4" (19mm)
typical
9/16" (14mm)
diameter; 4 holes
typical
6" (152mm)
6" (152mm)
4
Page 9

1.1.3 Unit Preparation
The Liebert FPC may be easily removed from the shipping pallet and installed by customer personnel. A typical procedure is as follows:
1. Set the palletized assembly in a level area where there is enough room to roll the Liebert FPC and
entire cable assembly off the pallet onto the floor.
2. Cut the shipping bands.
WARNING
!
The shipping bands may be under tension and may snap violently when cut. Use eye, face and
hand protection to guard against injury when the bands are cut.
3. Remove the factory-provided ramp from its shipping position.
One ramp is provided for every five units. Ramps are packed either in front of or on top of a set of
cable reel(s).
4. Place the ramp adjacent to the pallet to provide a smooth path from pallet to floor.
5. Remove side panels from the Liebert FPC, if supplied. An Allen wrench for the side panels is
furnished in the installation packet.
6. Remove the bolts and two mounting brackets holding the unit to the shipping pallet.
Mounting brackets are located on either side of the unit.
7. If cables are on wheeled cable reel(s), remove the bolts holding the reel(s) to the pallet and remove
the nailed-on shipping blocks.
8. Roll the unit off the pallet onto the floor, carefully guiding the cable reel(s) after it.
9. Roll the FPC and the cable reel(s) to the installation area. For units to be placed on a raised floor,
use care when positioning unit over the floor cutout to prevent the casters from falling through
the cutout.
Installation Instructions
CAUTION
!
Before maneuvering the unit into its final position, read and follow all advisories in 1.1.4 Location Considerations.
1.1.4 Location Considerations
The Liebert FPC should be placed near the load(s) it will supply, preferably within the data center.
Equipment location should employ the shortest output distribution cable runs consistent with logical
equipment arrangement and allowance for expansion.
The FPC is intended for indoor installation in an area with ambient temperatures of 32°F to 104°F
(0°C to 40°C) with a relative humidity of 0% to 95% (non-condensing).
Bottom clearance is required for units with bottom entry/exit of cables. This clearance may be provided by a raised floor at least 6" (150mm) high. Figures 1 and 2 show the typical raised-floor cutout
dimensions for cables and cooling airflow.
When units are not installed on a raised floor, or if the raised floor will not support the unit, optional
floor pedestals may be used. (CSA regulations require FPC arrangements employing a raised floor.
Non-raised floor applications are not CSA approved.) Units with top cable exit provisions do not
require bottom clearance.
Recommended minimum service clearances are shown in Figure 3. The National Electrical Code
(NEC) requires the indicated front and rear clearances for service access. Clearance above the unit is
required for cooling airflow (exhaust). Units with optional distribution monitoring also require service
access clearance on the left side.
As do all electrical devices, the Liebert FPC produces heat under normal operation. (See Table 3.)
This heat must be accounted for when calculating the environmental conditions of the room.
5
Page 10
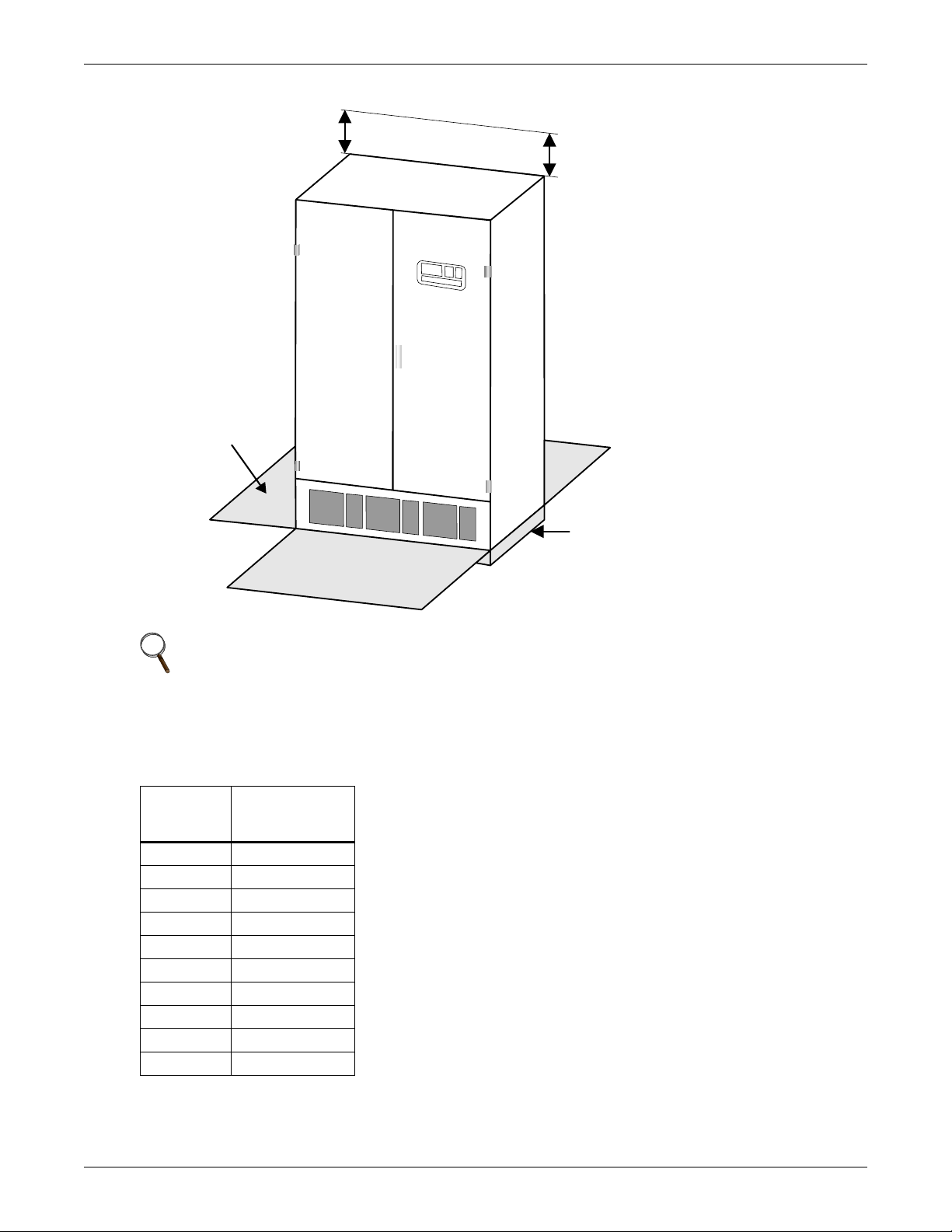
Figure 3 Recommended minimum service and ventilation clearances
Minimum clearance
of 18" (457mm)
above unit is
recommended for
cooling airflow
See Notes 2
and 3.
Installation Instructions
Front and rear access
is required. See
Notes 1 and 2.
NOTE
1. Service access is required at the front and rear.
2. Service access clearance dimensions: 36" (914mm) for units up to 150V to ground. 42"
(1067mm) for units over 150V to ground.
3. Service access is required on the left side, if unit is equipped with Liebert Distribution
Monitoring Option.
Table 3 Liebert FPC heat output
Full Load
Unit kVA
15 2,500 (0.73)
30 4,600 (1.35)
50 6,200 (1.82)
75 8,150 (2.39)
100 9,900 (2.90)
125 11,500 (3.37)
150 12,500 (3.66)
200 15,500 (4.54)
225 15,800 (4.63)
300 18,450 (5.40)
Heat Output
BTU/Hr (kW)
Minimum clearance
of 6" (152mm) below
unit is recommended
for cable entry and exit
6
Page 11
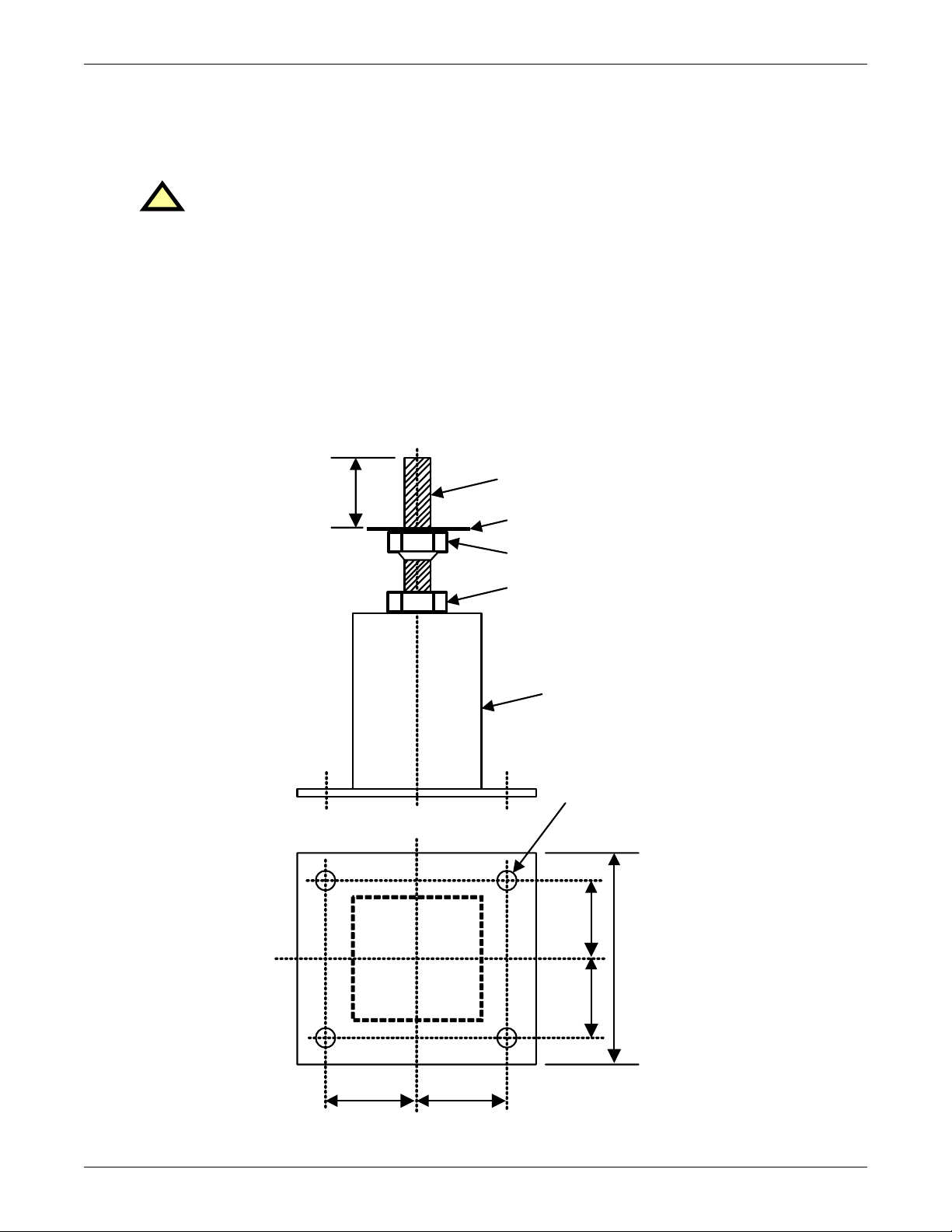
1.1.5 Floor Pedestal Installation
Floor pedestals are optional equipment that provide clearance for bottom cable entry or exit for FPC
units not installed on raised flooring. The pedestals are adjustable over a limited range (approximately 3-1/2" [89mm]) to allow leveling the FPC and minor adjustments in the unit’s installed height.
CAUTION
!
Floor pedestals may be reverse-assembled for shipping. Before installation, the pedestals
should be reassembled as shown in Figure 4. When the pedestal is properly assembled, the
washer on top of the welded nut provides a bearing surface for the unit’s weight.
1. Insert the pedestal threaded shaft into the pedestal holes in the cabinet base as shown in
Figures 1 and 2.
2. Adjust the pedestal height by turning the welded nut/shaft assembly into or out of the pedestal
base as required.
3. Lock the height by tightening the jam nut against the pedestal base.
The pedestal may be anchored to the floor by means of the four holes in the base. Locations of
floor pedestals are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure 4 Floor pedestal details
Installation Instructions
3"
(76m m)
Threaded
Shaft
Washer
Welded Nut
Jam Nut
Pedestal
Base
.56" ( 14 mm)
diam eter
mounting holes
2-1/4"
(57mm)
6"
(152mm)
square
2-1/4"
(57mm)
2-1/ 4"
(57mm)
2-1/4"
(57mm)
7
Page 12

1.2 Additional Distribution Mounting & Wiring
For Liebert FPCs with more than four panelboards, the additional panelboards are furnished in Liebert FDC enclosures, which are shipped separately from the Liebert FPC.
1.2.1 Liebert FDC Distribution Mounting
The Liebert FDC distribution cabinet has the same base dimensions as a 23" (584mm) cabinet FPC
(23-1/2" wide x 38" deep [597 x 965mm]) and may be mounted on either the left or right side of the FPC.
1. Provide a floor cutout for exit of output cables, as shown in Figure 1.
2. Remove the side panel, internal panel and the lower panel bracket from the FPC.
3. Remove the FDC side panel and internal panel, if supplied, and align the FDC with the FPC and
bolt the units’ frames together (hardware provided by others).
If floor pedestals are used for the FPC, two additional floor pedestals are required for the outside
corners of the FDC. See Figure 1.
4. Install the lower panel bracket on the opposite side of the FDC cabinet.
5. Make electrical connections. For details, see “Electrical Field Connections” drawings supplied
with the unit.
6. Install the FPC side panel on the FDC cabinet.
1.2.2 Distribution Cabinet Electrical Connections
Five field-supplied conductors (3-phase conductors, neutral and ground) are needed to connect the
FDC cabinet to the FPC cabinet in the field.
For Liebert FPCs with transformers, the distribution cabinet phase conductors are connected directly
to the transformer terminals:
Phase A to X1
Phase B to X2
Phase C to X3
The FDC’s neutral and ground conductors are connected to the FPC’s neutral busbar and main
ground busbar (see unit wiring diagram for location).
For Liebert FPCs without transformers, the distribution cabinet phase and neutral conductors are
connected to the corresponding output power distribution terminal blocks inside the FPC. The distribution cabinet ground conductor is connected to the main ground busbar.
For all Liebert FPCs with current monitoring, route each distribution cabinet conductor through the
appropriate current transformer (CT) in the FPC.
Installation Instructions
NOTE
Distribution cabinet conductors must pass through the current transformers in the same
direction as the FPC panelboard conductors. Use the existing FPC panelboard wiring for
reference.
1.3 Power and Control Wiring
Power and control wiring should be installed by licensed electricians. All power and control wiring
must comply with the NEC and applicable local codes.
1.3.1 Input Power Connections
If the FPC is furnished with a main input junction box, input power connections are made as detailed
in 1.3.2 - Junction Box Installation.
If a junction box is not furnished, the input power feeder is connected to the main input circuit
breaker located inside the FPC. (See Figures 5 through 8.)
WARNING
!
Verify that all incoming line voltage (power) and low-voltage (control) circuits are
de-energized and locked out before installing cables or making connections, whether in the
junction box or in the FPC.
8
Page 13

To minimize disturbances from other loads in the building, the 3-phase power input to the FPC
should be supplied directly from the service entrance or other power source (a dedicated power
feeder).
The input feeder circuit should be sized in accordance with the NEC and any local building codes to
ensure the feeder’s ability to safely carry the system’s full load current, including losses.
Input feeder conductors should be sized for no more than 2% voltage drop. If operation at undervoltage conditions for extended periods of time is desired, the input feeders must be oversized.
Typical conductor size data is shown in Table 4. All connections must comply with the NEC and all
other applicable codes.
For units with a transformer, the main input feeder should consist of 3-phase conductors and one
(safety) ground conductor (3W + G).
For units without a transformer, the main input feeder must consist of 3-phase conductors, one neutral and one (safety) ground conductor (4W + G).
Figure 5 Electrical connection location for 23" (584mm) cabinet
Installation Instructions
15006 - Rev. 0
9
Page 14

Figure 6 Electrical connection location for 47" (1194mm) cabinet—Front view
Installation Instructions
FPC15000 Rev. 0
Figure 7 Electrical connection location for 47" (1194mm) cabinet—Rear view
10
FPC15000 Rev. 0
Page 15

Installation Instructions
Figure 8 Electrical connection location for 47" cabinet with SqD I-Line panelboard—Front view
FPC15002 Rev. 0
Figure 9 Electrical connection location for 47" cabinet with SqD I-Line panelboard—Rear view
Square “D”
I-Line Panelboard
1.75"
(44.4mm)
(22mm)
1.75"
(44.4mm)
.88"
(22mm)
.88"
3.28" (83mm)
3.28" (83mm)
Detail B
Output Ground Busbar
Approx. 1/4" Thick
FPC15002 Rev. 0
11
Page 16

Table 4 Suggested minimum input wire size data
Units with Transformers Transformerless Units
Installation Instructions
kVA
15
30
50
75
100
125
Input
Voltage
Input
FLA
Input
OPD
Suggested Feeder
Wire Size (AWG)
Full Load
Amps
MIB Trip
Amps
Suggested Feeder
Wire Size (AWG)
208 43 60 #6 AWG 42 60 #6 AWG
240 38 50 #8 AWG - - -
380 24 30 #10 AWG 23 30 #10 AWG
400 23 30 #10 AWG 22 30 #10 AWG
415 22 30 #10 AWG 21 30 #10 AWG
480 19 25 #10 AWG - - -
600 15 20 #12 AWG - - -
208 87 110 #2 AWG 83 110 #2 AWG
240 75 100 #2 AWG - - -
380 48 60 #6 AWG 46 60 #6 AWG
400 45 60 #6 AWG 43 60 #6 AWG
415 44 60 #6 AWG 42 60 #6 AWG
480 38 50 #8 AWG - - -
600 30 40 #8 AWG - - -
208 145 200 #3/0 AWG 139 175 #2/0 AWG
240 125 175 #2/0 AWG - - -
380 79 100 #2 AWG 76 100 #2 AWG
400 75 100 #2 AWG 72 90 #2 AWG
415 72 90 #2 AWG 70 90 #2 AWG
480 63 80 #4 AWG - - -
600 50 70 #4 AWG - - -
208 215 300 350 kcmil 208 300 350 kcmil
240 186 250 250 kcmil - - -
380 118 150 #1/0 AWG 114 150 #1/0 AWG
400 112 150 #1/0 AWG 108 150 #1/0 AWG
415 108 150 #1/0 AWG 104 150 #1/0 AWG
480 93 125 #1 AWG - - -
600 74 100 #2 AWG - - -
208 286 400 (2) #3/0 AWG * 278 350 (2) #2/0 AWG *
240 248 350 (2) #2/0 AWG * - - -
380 157 200 #3/0 AWG 152 200 #3/0 AWG
400 149 200 #3/0 AWG 144 200 #3/0 AWG
415 143 200 #3/0 AWG 139 175 #2/0 AWG
480 124 175 #2/0 AWG - - -
600 99 125 #1 AWG - - -
208 358 450 (2) #4/0 AWG * 347 450 (2) #4/0 AWG *
240 310 400 (2) #3/0 AWG * - - -
380 196 250 250 kcmil 190 250 250 kcmil
400 186 250 250 kcmil 180 225 #4/0 AWG
415 179 225 #4/0 AWG 174 225 #4/0 AWG
480 155 200 #3/0 AWG - - -
600 124 175 #2/0 AWG - - -
12
Page 17

Table 4 Suggested minimum input wire size data (continued)
Units with Transformers Transformerless Units
Installation Instructions
kVA
Input
Voltage
Input
FLA
Input
OPD
Suggested Feeder
Wire Size (AWG)
Full Load
Amps
MIB Trip
Amps
Suggested Feeder
Wire Size (AWG)
208 427 600 (2) 350 kcmil * 416 600 (2) 350 kcmil *
240 370 500 (2) 250 kcmil * - - -
380 234 300 350 kcmil 228 300 350 kcmil
150
400 223 300 350 kcmil 217 300 350 kcmil
415 215 300 350 kcmil 209 300 350 kcmil
480 185 250 250 kcmil - - -
600 148 200 #3/0 AWG - - -
380 312 400 (2) #3/0 AWG * 304 400 (2) #3/0 AWG *
400 297 400 (2) #3/0 AWG * 289 400 (2) #3/0 AWG *
200
415 286 400 (2) #3/0 AWG * 278 350 (2) #2/0 AWG *
480 247 350 (2) #2/0 AWG * - - -
600 197 250 250 kcmil - - -
380 352 450 (2) #4/0 AWG * 342 450 (2) #4/0 AWG *
400 334 450 (2) #4/0 AWG * 325 450 (2) #4/0 AWG *
225
415 322 450 (2) #4/0 AWG * 313 400 (2) #3/0 AWG *
480 278 350 (2) #2/0 AWG * - - -
600 222 300 350 kcmil - - -
380 469 600 (2) 350 kcmil * 456 600 (2) 350 kcmil *
400 446 600 (2) 350 kcmil * 433 600 (2) 350 kcmil *
300
415 430 600 (2) 350 kcmil * 417 600 (2) 350 kcmil *
480 372 500 (2) 250 kcmil * - - -
600 297 400 (2) #3/0 AWG * - - -
* Parallel feeders per NEC 300-20 and 310-4
FLA = Full Load Amps of Power Center
OPD = Overcurrent Protection Device inside FPC
Wire sizes based on NEC 2005, Table 310-16, using 75°C copper conductor
1. Main input power feeder should be a dedicated feeder direct from service entrance or other power source possible
2. Ground conductors recommended to be insulated conductors run with power conductors for increased system performance. Ground
conductor minimum size per NEC Table 250-66. Input power feeder conduit may be used as the safety ground conductor. When conduit
is used, adequate electrical continuity must be maintained at conduit connections to enclosures and throughout conduit run.
3. Input feeder wire size listed in this table is the minimum feeder size recommended. Larger wire size may be required because of voltage
drop or supply overcurrent protection device.
4. For transformerless units with 3-phase 4W + G input feeder larger wire size may be required because of excessive neutral current (see
NEC Table 310-15 note 4: For best performance, the unit should be located as close to load as practical.
Table 5 Main input circuit breaker interrupting rating
Standard interrupting rating*
208V 480V 380-415V 600V
65 kA 35 kA 35 kA 18 kA
* Refer to unit specification sheet for units equipped
with non-standard main input breakers.
13
Page 18

1.3.2 Junction Box Installation
Main input (power) and low-voltage (control) junction boxes are available for the Liebert FPC to simplify customer connections.
The junction boxes, if used, can either be shipped with the system or can be advance-shipped for
installation during the roughing-in stage of new construction.
Liebert supplies flexible, 10-foot-long (3m) conduit with cables for connecting the junction boxes to the
unit. The junction boxes should be installed a maximum of 8 ft. (2.4m) from the feeder entrance of the
unit.
Liebert recommends centering the junction boxes under a floor tile that is easily removed.
Junction box connections must be installed in compliance with the NEC and all other applicable
codes.
WARNING
!
Verify that incoming line voltage (power) and low-voltage (control) circuits are de-energized
and locked out before installing cables or making any connections in the junction box.
Typical junction box connections are shown in Figure 16 and described in 1.3 - Power and Control
Wiring.
Table 6 Main input junction box electrical connections (4 wire)
Junction Box Size
Inches (mm) Electrical Connections
27 x 14 x 6
(686 x 356 x 152)
35 x 22 x 6
(889 x 559 x 152)
400A 3 pole power block with 1/2 -13 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
750A ground busbar with two sets of 3/8 - 16 studs on 1.75” centers
750A phase busbars with 1/2 -13 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
750A ground busbar with two sets of 3/8 -16 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
Installation Instructions
Table 7 Main input junction box without transformer electrical connections (5 wire)
Junction Box Size
Inches (mm) Electrical Connections
27 x 14 x 6
(686 x 356 x 152)
35 x 22 x 6
(889 x 559 x 152)
400A 3 pole power block with 1/2 -13 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
750A neutral busbar with two sets of 1/2 -13 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
750A ground busbar with two sets of 3/8–16 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
750A phase busbars with 1/2 -13 studs on 1.75” centers
1500A neutral busbar with two sets of 1/2 -13 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
750A ground busbar with two sets of 3/8 - 16 studs on 1-3/4" (44mm) centers
Dimensions are given on the drawings furnished with the unit. Typical dimensions of the junction
boxes are as follows:
Table 8 Low-voltage (control) junction box dimensions, typical
Width, inches (mm)
Length, inches (mm)
Height, inches (mm)
8 (203)
10 (254)
4 (102)
Table 9 Main input (power) junction box dimensions, typical
Input Voltage
Unit kVa
15-100 kVA, L x W x H, inches (mm) 27 x 14 x 6 (686 x 356 x (152)
125-150 kVA, L x W x H, inches (mm)
200 kVA, L x W x H, inches (mm)
225 kVA, L x W x H, inches (mm)
300 kVA, L x W x H, inches (mm)
208-240V 380-415V 480-600V
35 x 22 x 6
(889 x 559 x 152)
N/A
N/A
N/A
27 x 14 x 6 (686 x 356 x (152)
27 x 14 x 6 (686 x 356 x (152)
35 x 22 x 6
(889 x 559 x 152)
35 x 22 x 6 (889 x 559 x 152)
(686 x 356 x (152)
27 x 14 x 6
14
Page 19

Figure 10 Low voltage control junction box connections, typical
1 2 3 4 5 6 10 11 127 8 9 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
Build ing
Interface
Relay
Factory-supplied
low-voltage control cable
Installation Instructions
Figure 11 Main input junction box connections, typical
A
B
C
Customer input
power connection
3-phase, 3-wir e + GND
for units with transformer
3-phase, 4-wir e + GND
for units without tr ansform er
N
G
1.3.3 System Grounding
The performance and safety of any power conditioning system depend on proper grounding.
Figure 12 shows the typical grounding arrangements for the Liebert FPC.
Equipment Grounding
Equipment grounding is primarily for safety. Correct implementation of grounding also enhances
equipment performance. All power feeders must include equipment grounding means as required by
the NEC and local codes.
An insulated ground conductor is recommended to be run in each feeder conduit. Ground conductors
must be at least the minimum size per NEC Table 250-66. Larger wire sizes may be used for
increased system performance.
Factory-supplie d
input power c able
assemby
NOTE : Parallel cables
are used on units with
higher -ampacity
Neutral bus bar a nd wire
furnished on units
without transformer
If the input power feeder conduit is used as a grounding conductor, adequate electrical continuity
must be maintained at all conduit connections.
CAUTION
!
Using isolating bushings in a metal conduit run can be a safety hazard and is not
recommended.
15
Page 20

Signal Reference Grid
If the unit is used to supply power to a computer room or area that is equipped with a signal reference
grid or a grounded raised-floor stringer system, a grounding conductor should be connected from the
system ground bus to the grid or floor system. This conductor should be stranded or braided #8 AWG
or larger, and as short as practical. Less than 3 ft. (1m) is recommended.
1.3.4 Grounding Electrode Conductor for FPCs With Transformer
Required by code - The Liebert FPC with transformer must be grounded according to the safety
practices of NEC 250-26. A local grounding electrode conductor is recommended in addition to the
equipment safety ground which is normally run with the input power conductors. (See Figures 5
through 8.)
As shown in Figure 12, the grounding electrode conductor is run from the unit to the nearest effectively grounded location (listed in order of preference):
• Building steel
• Metal water pipe
• Other made grounding electrode
The grounding electrode conductor’s size is based on the secondary circuit conductors. Table 10
shows the minimum recommended grounding electrode conductor according to the NEC
(Table 250-66).
Table 10 Minimum grounding electrode conductor size (AWG)
Output Voltage
kVA
100 0 4 4
125 0 2 2
150 00 2 2
200 00 0 0
225 00 0 0
300 00 0 0
AWG wire size based on 75°C copper conductors
208V 380V 415V
15 8 8 8
30 8 8 8
50 4 8 8
75 2 6 6
Installation Instructions
Recommended methods for running the grounding electrode conductor (arranged by preference for
system performance; as acceptable by local and other applicable codes):
• Outside of conduit (where not subject to damage)
• Inside non-metallic conduit
• Inside non-ferrous conduit
• Inside ferrous conduit, bonded to the ferrous conduit at both ends, as acceptable by local and other
applicable codes
16
Page 21

Figure 12 Typical grounding arrangements
Installation Instructions
Service
Entrance
N
G G G
Service entrance
grounding electrode
system
Input
J-box
(if used )
Liebert FPC
(w ith transformer)
Local grounding
electrode
conduc tor per
NEC 250-28
Typical Liebert FPC
with transformer grounding arrangement
N
Signal reference grid
(if used)
Output
Service
Entrance
N
G
Servic e entrance
grounding electrode
system
Input
J-box
(if used)
N
G
Typical Liebert FPC
without transformer grounding
Liebert FPC
(without transformer )
Signal reference grid
N
G
(if used)
Output
17
Page 22

1.3.5 Output Power Connections
Output circuit breaker(s) and/or panelboards with ground and neutral provisions are provided inside
the unit for connecting load(s) as required. (See Figures 5 through 8.)
Flexible output distribution cables for use in data processing areas under a raised floor are optional
and may be factory-supplied. Cable lengths and layout should be well-planned:
• Cable access—Cable routes should follow aisles between equipment. This will facilitate access to
cables for installation, routine inspection and alterations.
• Cable length—Measure the distance to the load equipment following right-angle paths, rather
than diagonally or directly. Always measure to the extreme far side of the equipment with respect
to the unit to ensure adequate cable length.
• Air circulation—Prevent restriction of airflow under the raised floor by running the flexible conduits flat on the subfloor, in parallel paths.
For best performance, the Liebert FPC should be installed as close as practical to the load.
Initial system output loading should be between 50% and 75% of rated capacity. This allows the addition of loads without immediately investing in another power conditioner. The high partial-load efficiency of the FPC permits such sizing without imposing an energy-use penalty during initial
operation.
Balancing of loads is good design practice on any 3-phase system. Accordingly, each distribution panel
is load-balanced at the factory, based on output branch circuit breaker sizes. All additions to the system should be arranged so as to preserve this balance.
Installation Instructions
For phase-shifted, multi-output units, to ensure proper harmonic current cancellation, the loads
should be balanced across the multiple outputs as well. For example, with a dual-output unit, the
loads should be balanced across the six output phases. For a quadruple output unit, the loads should
be balanced across the 12 output phases.
WARNING
!
Verify that all incoming line voltage (power) and low-voltage (control) circuits are
de-energized and locked out before installing cables or output breakers or making
connections, whether in the junction box or in the unit.
Verify that incoming line voltage circuits are de-energized and locked out before installing
output breakers and cables.
Code Compliance—All output cables and connections must comply with the NEC and all other
applicable codes.
Padlock-Off Provisions—All output cables without receptacles that are hard-wired to the load
equipment must be equipped with a padlock-off accessory for the output circuit breaker. The
padlock-off accessory is to be used to lock-out and tag the circuit breaker when service is performed on
the hard-wired load equipment in accordance with OSHA safety rules.
18
Page 23

Figure 13 Typical Liebert FPC equipment arrangement
Installation Instructions
Liebert FPC
Ground electrode conductor
(not by Liebert) required per
NEC for units with transformer
Remote Emergency
Power Off Switch (REPO)
Main input power to unit
(not by Liebert)
3-phase, 3-wire plus ground
for units with transformer
3-phase, 4-wire plus ground
for units without transformer
*Transient suppression plate
Main input junction box and cable
Low voltage junction
box and cable
* Flexible distribution cables
per customer specifications
* Optional devices : Refer to the
specification sheet for options
supplied
Building i nterface and
alarm connections
(not by Liebert)
19
Page 24

1.3.6 Control Wiring Connections
NEC Article 645 requires that emergency power off (EPO) switches be located at the principal room
exits. All standard Liebert power conditioning systems have provisions for external shutdown control
from Remote Emergency Power Off (REPO) stations. Figure 14 is a simplified diagram of the shutdown circuitry of the Liebert FPC.
Low-Voltage Control Circuit
Control wiring connections must comply with the NEC and all other applicable codes.
WARNING
!
Verify that all incoming high-voltage (power) and low-voltage (control) circuits are
de-energized and locked out before installing cables or making connections, whether in the
junction box or in the unit.
As shown in Figure 14, the control circuit operates on 24VDC. The shutdown device (represented by
the REPO switch) activates a low-current, 24VDC relay that in turn operates the shunt-trip mechanism. The shunt-trip solenoid opens the Main Input Breaker, which de-energizes the power center.
Multiple-Unit Shutdown
When more than one power center is installed by the user, a typical requirement is that actuation of a
single device (REPO for example) must shut down all power centers. The low-voltage control circuits
of all standard Liebert FPC systems are designed to meet this requirement.
Installation Instructions
External Control Wiring Connections
External control wiring connections for remote shutdown, alarm, and/or monitoring are made to the
low-voltage junction box (if used) or to the low-voltage control terminal strip located inside the unit.
Control wiring connections vary with the type of monitoring system furnished with the unit. Two typical control wiring configurations are shown in Figures 15 and 16.
Figure 14 Simplified shutdown circuit
Liebert FPC
K5
K6
+
24VDC
Source
Main
Input
Breaker
-
Shunt
Trip
+24VDC
Unit EPO
K6 6
Overtemp
Switch
K5
Remote
Shutdown
Devices
1
4
N.O. REPO
N.C. REPO
2
20
7 4
3
R1
B
9 6
1A
Building
Interface
Relay
3
Page 25

Figure 15 Typical control wiring for units without monitoring
Installation Instructions
Low Voltage
Terminal Strip
Overtemp Alarm N.O. W208
Overtemp Alarm N.C. W207
N.C. REPO W202
Factory-Supplied Wiring
Building
Interface
Relay
Alarm Com. W206
N.O. REPO W205
24VDC W204
REPO Com. W203
24VDC W201
A
R
B
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
96
4
1
3
BLK
WHT
GRN
Remove jumper
when Normally
Closed (N.C.)
REPO is used
Overtemp
S
Alarm Output
N.O. REPO
N.C. REPO
NOTES
1. All switching devices are to be suitable for switching low current 24VDC. Minimum
recommended wire size is 18AWG stranded copper with 300V insulation.
All wiring and devices are field supplied except where noted. See installation manual for
detailed installation procedures.
2. Low voltages terminal strip may be located in unit or low voltage control junction box.
3. The total load on the 24VDC supply (both N.O. and N.C. REPO circuits) must be limited to
1A.
4. Multiple normally open (N.O.) REPO switches may be paralleled.
Multiple normally closed (N.C.) REPO switches may be connected in series. all lamps (if used)
are connected in parallel.
5. The summary alarm contacts are rated for 0 to 30VAC or VDC, 0.5A, 10W maximum.
21
Page 26

Figure 16 Typical control wiring for units with monitoring
Low Voltage
Terminal Strip
21
Comm Cable+(RED)
Comm Cable-(BLK)
RS-232 RXD (WHT)
RS-232 TXD (RED)
RS-232 COM (BLK)
5th Customer Alarm W214
4th Customer Alarm W213
3nd Customer Alarm W212
2nd Customer Alarm W211
1st Customer Alarm W210
Summary Alarm N.O. W208
Summary Alarm N.O. W208
Summary Alarm N.C. W207
Summary Alarm Com. W206
Factory-Supplied Wiring
N.O. REPO W205
REPO Com. W203
N.C. REPO W202
24VDC W204
24VDC W201
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
To
SiteScan
System
Remove jumper
when fifth customer
alarm is used
Optional
customer
alarm
inputs
Summary
S
Alarm Output
BLK
WHT
GRN
N.O. REPO
N.C. REPO
Installation Instructions
NOTES
Remove jumper
when Normally
Closed (N.C.)
REPO is used
Building
Interface
Relay
A
7
R
96
B
4
1
3
1. All switching devices are to be suitable for switching low current 24VDC. Minimum
recommended wire size is 18AWG stranded copper with 300V insulation.
All wiring and devices are field-supplied except where noted.
See installation manual for detailed installation procedures.
2. Low voltages terminal strip may be located in unit or low voltage control junction box.
3. The total load on the 24VDC supply (both N.O. and N.C. REPO circuits) must be limited to 1A.
4. Multiple normally open (N.O.) REPO switches may be paralleled.
Multiple normally closed (N.C.) REPO switches may be connected in series. All lamps (if used)
are connected in parallel.
5. The summary alarm contacts are rated for 0 to 30VAC or VDC, 0.5A, 10W maximum.
6. Customer alarms 1 through 4 are normally open (indicates alarm on contact closure). Customer
alarm 5 is normally closed (indicates alarm on contact opening).
7. RS-232 communication port is connected to the low voltage terminal strip inside unit only.
Connect using suitable 300V communication cable.
22
Page 27

2.0 EQUIPMENT INSPECTION AND STARTUP
2.1 Internal Inspection
A detailed internal inspection should be performed after the unit is in place and before it is energized, to ensure trouble free startup. The same internal inspection should be carried out when performing preventive maintenance.
WARNING
!
Verify that all incoming line voltage (power) and low-voltage (control) circuits are
de-energized and locked out before performing the internal inspection.
Open the unit - Gain access to the internal components of the Liebert FPC unit by removing the
exterior panels and internal accent panels.
Visually inspect - Be sure wiring and components are not damaged.
Check power connections - Check all power connections for tightness. Refer to Tables 11
through 14 for torque requirements of all electrical connections.
Perform formal detailed inspection - Follow the procedures described in 3.0 - Inspection and
Start-Up Checklist when performing detailed inspection.
2.2 Startup
Equipment Inspection and Startup
Checklists
Follow the detailed step-by-step checklist (3.0 - Inspection and Startup Checklist) when installing
and starting up the Liebert FPC.
Initial System Startup
A qualified electrician must be employed to perform the equipment inspection and startup. Liebert
system startup may be arranged by calling your local Liebert sales representative or Liebert Global
Services. In the United States, call 1-800-LIEBERT.
Warranty
A copy of the appropriate checklist (furnished with the equipment) must be completed, signed, dated
and returned to Liebert Corporation. Warranty coverage of the equipment is not effective unless the
checklist has been received by the factory.
WARNING
!
Equipment inspection and startup should be performed only by trained personnel. Hazardous
voltages are present during startup procedures.
Electrical safety precautions must be followed throughout inspection and startup.
23
Page 28

Table 11 Torque specifications, general
Electrical connections
with 1 Belleville washer
Torque Torque
lb-in N-m lb-in N-m
Bolt shaft size, in./mm
1/4 / M6 40 4.5 80 9.0
5/16 / M8 80 9.0 180 18.0
3/8 / M10 120 13.6 240 27.1
1/2 / M12 480 54.3 — —
Input and output breakers
Up to 150 amp 80 9.0 160 18.0
175 - 500A 120 13.6 240 27.1
Electrical connections
with 2 Belleville washers
Table 12 Panelboard main circuit breaker torque specifications
Torque
lb-in N-m
Busbar-to-breaker 240 27.1
Equipment Inspection and Startup
Table 13 Branch circuit breaker torque specifications
Breaker size lb-in N-m
Up to 30 amp 20 4.0
40 to 100 amp 20 5.1
Table 14 Terminal block compression lug torque specifications
AWG wire size
or range
#14 - #10 35 4.0
#8 40 4.5
Torque
lb-in N-m
24
Page 29

3.0 INSPECTION AND STARTUP CHECKLIST
Unit Serial Number
Unit Model Number
Date
3.1 Inspection
WARNING
!
All equipment inspection procedures are to be performed with power to the unit turned off
and locked out.
___ 1. Confirm that the exterior of unit is undamaged (including cables and receptacles, if
furnished).
___ 2. Confirm that service and ventilation clearances are adequate. (See Figures 1 through 3.)
___ 3. Remove accessible exterior and internal panels.
___ 4. Inspect all wire and conductor insulation for damage.
___ 5. Check all transformer terminal connections for tightness. Retorque if necessary.
___ 6. Check all breaker connections for tightness. Retorque if necessary.
___ 7. Check all terminal block connections for tightness. Retorque if necessary.
___ 8. Check transformer mounting bolts for tightness. Retorque if necessary.
___ 9. Remove any foreign objects from the components or the interior area of the unit.
Make sure air passages on transformers are clear and free of debris.
___ 10. Check that the intake and exhaust air screens are clean and free of obstructions.
___ 11. Replace internal and exterior side panels, leaving access to circuit breakers for the following
start-up procedure.
Inspection and Startup Checklist
25
Page 30

3.2 Startup
!
1. Make certain that all circuit breakers are in the OFF position and that power to the unit is locked
out.
___ 2. Remove the cover of the Main Input Junction Box. Verify proper input power connections to
___ 3. Turn ON the building power to the junction box. Check the phase rotation at the junction box.
___ 4. Check and record the input voltages at the junction box:
___ 5. Turn OFF and lock out the building power to the input junction box.
___ 6. Replace the junction box cover.
___ 7. Verify proper input power connections to unit, including equipment grounding conductor and
___ 8. Turn ON the building input power to the unit.
___ 9. Check the phase rotation at the main input breaker. Phase rotation should be A, B, C, left-to-
___ 10. Check and record the input voltage at the main input breaker. Measured voltages should
___ 11. Turn ON the main input breaker; wait one minute. (If breaker trips OFF, check for wiring
___ 12. Check the phase rotation at the line side terminals (top) of the panelboard main breaker(s)
___ 13. Check and record the voltages at the line-side terminals of the output circuit breaker.
If output voltage is incorrect, check for wiring errors, incorrect input voltage, or improper transformer tap. Contact Liebert Global Services at 1-800-LIEBERT in the United States or your local
Liebert representative for assistance.
Inspection and Startup Checklist
WARNING
Startup procedures should be performed only by qualified personnel. Hazardous voltages are
present in the equipment throughout the majority of the start-up procedure. Use proper
safety equipment. proceed with caution.
When opening the main input circuit breaker wait a minimum of one minute before reclosing.
NOTE
Steps 2 through 6 apply to the Main Input Junction Box. If this installation is not provided
with a Main Input Junction Box, proceed to Step 7.
unit, including equipment grounding conductor.
Phase rotation should be A, B, C, as indicated.
Volts, Phase A to Phase B = ______________
Volts, Phase B to Phase C = ______________
Volts, Phase C to Phase A = ______________
local grounding electrode conductor.
right.
correspond to the unit’s nameplate input voltage.
Volts, Phase A to Phase B = ______________
Volts, Phase B to Phase C = ______________
Volts, Phase C to Phase A = ______________
errors including control connections. Contact Liebert Global Services or the location factory
representative for assistance.)
and any subfeed output circuit breaker(s). The rotation should be A, B, C, left-to-right.
Measured voltages should correspond to the unit’s nameplate output voltage (within +4%,0%).
Volts, Phase A to Phase B = _______________
Volts, Phase B to Phase C = _______________
Volts, Phase C to Phase A = _______________
Volts, Phase A to Neutral = _______________
Volts, Phase B to Neutral = _______________
Volts, Phase C to Neutral = _______________
26
Page 31

NOTE
The Liebert FPC transformer has input voltage taps for each input phase. The taps are
arranged in 2-1/2% or 5% intervals ranging from -10% to nominal to +5%. This permits the
transformer to provide the proper output voltage for a range of input voltages. Should it be
necessary, the tap arrangement may be changed to match the input voltage:
• Open main input circuit breaker.
• Select tap arrangement to match input voltage. (Refer to transformer nameplate for tap
information.)
• Secure each line to its proper tap.
• Repeat Steps 11 to 13.
___ 14. Press the local EMERGENCY POWER OFF switch, if supplied, and verify system shutdown.
Turn the unit back on.
___ 15. Repeat Step 14 for each remote EMERGENCY POWER OFF switch with which the system is
equipped.
CAUTION
!
The Remote Emergency Power Off switch may shut down more equipment or systems than
just the Liebert FPC.
3.3 Monitoring System Check-Out
Inspection and Startup Checklist
Basic Indicators
___ 1. Turn ON the building power to the unit, then turn the main input breaker ON.
___ 2. Check that the local EMERGENCY POWER OFF button, if supplied, is illuminated and that
the ALARM PRESENT / SILENCE indicator is off.
Manual Restart Check
If the Liebert FPC is equipped with Manual Restart:
___ 1. Turn on building power to the FPC. Turn Main Input Breaker ON.
___ 2. Turn off all building power to FPC.
___ 3. Observe that Main Input Breaker automatically trips open upon power loss.
___ 4. Restore building power to the FPC and return Main Input Breaker to ON.
Power Monitor Panel
If the Liebert FPC is equipped with a Power Monitor Panel:
___ 1. Turn ON the FPC.
___ 2. Ensure that the voltage values indicated by the Monitor Panel correspond to the voltage
values measured at the input and output circuit breaker (Steps 10 and 13 in 3.2 - Startup).
Centralized Monitor
If the Liebert FPC is connected to a Centralized Monitoring System:
___ 1. Turn ON the FPC and the Centralized Monitoring System.
___ 2. Verify proper communication to the monitor system operation.
Control Voltage
___ 1. Obtain access to the low voltage terminals in the Low-Voltage Junction Box (if used), or in the
low-voltage control section inside unit.
___ 2. With the FPC ON, measure and record the DC control voltage on terminals 1 (+) and 3 (com).
___ 3. Control Voltage = ____________________ (Voltage should be between 16 and 23VDC).
27
Page 32

Inspection and Startup Checklist
Customer Alarms
If customer alarms are provided:
___ 1. With the FPC ON, simulate alarm operation by jumpering the appropriate low-voltage control
terminals. (Refer to the control wiring installation drawing furnished with the unit.)
___ 2. Verify correct alarm annunciation by the Power Monitor Panel and/or by the Centralized
Monitoring System.
3.4 Equipment Connection Check-Out of Units With Distribution Cables
CAUTION
!
All loads should be disconnected or turned off before proceeding with the following steps.
For units with output distribution cables, be sure that NO output receptacles are connected to
load equipment plugs and that the receptacles are not in contact with foreign objects.
Pay special attention to those output cables intended for direct wiring connection; the exposed
conductor ends of these cables must not be in contact with each other or with any foreign
objects.
___ 1. Turn on main input power to the unit, then turn on the panelboard main output breaker(s).
___ 2. Individually turn on each branch circuit breaker and check the output voltage (also phase
rotation, if a 3-phase circuit) at the receptacle or cable end.
___ 3. Turn OFF all branch circuit breakers and the panelboard main output circuit breaker(s).
___ 4. Connect the load equipment per equipment manufacturer’s specifications and
recommendations.
___ 5. Turn on the panelboard main output breaker(s).
___ 6. Turn on branch circuit breakers to the load equipment.
CAUTION
!
Observe the power-up sequence recommended by the equipment manufacturer.
___ 7. Verify that all load equipment operates properly.
___ 8. Replace all unit panels. After performing the inspection and start-up procedure described in
3.0 - Inspection and Startup Checklist in this manual, complete the Start-Up and
Inspection form furnished with the unit, sign the completed form and return it to:
Liebert Corporation
1050 Dearborn Drive
P.O. Box 29186
Columbus, Ohio 43229 USA
NOTE
Warranty is not in effect until the inspection and startup form is received by the
factory.
28
Page 33

4.0 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
4.1 Startup Procedures
Before the unit is placed into service after initial installation, after equipment relocation, or after
equipment has been de-energized for an extended period of time, perform equipment inspection and
start-up procedures as detailed in 2.0 - Equipment Inspection and Startup and 3.0 - Inspection
and Startup Checklist.
After initial system startup, the following guidelines can be used for standard equipment operation.
These guidelines should be reviewed for any special equipment modifications, special site considerations or company policies that may require changes to the standard equipment operation.
4.1.1 Emergency Shutdown—If Emergency Power Off switch is supplied
To perform an immediate system shutdown during emergency conditions, lift the clear protective
cover and push the Emergency Power Off (EPO) switch on the FPC’s monitoring panel.
NOTE
Depending on the particular control circuit wiring, operation of the unit EPO switch may cause
other equipment to also shutdown.
If the site is equipped with a Remote Emergency Power Off (REPO) switch to perform an immediate
room shutdown, actuate one of the REPO switches. NEC Article 645 requires a REPO switch at the
principal exit doors.
Operating Instructions
4.1.2 Normal System Shutdown
To perform a normal system shutdown, perform an orderly load equipment shutdown according to the
load equipment manufacturer’s recommended shutdown sequence. The load equipment can be turned
OFF at each piece of load equipment or at the FPC’s output distribution (circuit breaker) panels
located behind the FPC’s front door. Turn OFF all unit output breakers, then turn OFF the unit’s
main input circuit breaker. To remove all power from the FPC, turn OFF the building power to the
FPC’s input breaker or junction box.
4.1.3 Normal System Turn ON
Make certain all of the FPC’s circuit breakers are in the OFF position. All unit circuit breakers are
located behind the front doors. Turn ON building power to the FPC. Turn ON the FPC’s main input
circuit breaker. If the circuit breaker has been tripped OFF (instead of being turned OFF), the circuit
breaker handle must be moved to the OFF position before being turned ON. If the FPC has a voltage
monitoring panel, verify proper output voltages before turning ON output circuit breakers. Turn ON
the panelboard main breakers. Individually turn ON each output circuit breaker following the load
equipment manufacturer’s startup sequence.
4.1.4 Manual Restart
If the FPC’s manual restart feature has been selected, the unit’s main input circuit breaker will be
tripped upon a power failure, preventing repetitive application of unstable voltage and allowing for an
orderly system restart. If the main input circuit breaker is tripped upon a power failure, wait until
power is restored, then follow the instructions in 4.1.3 - Normal System Turn ON.
29
Page 34

4.2 Basic Monitor Panel (Units Without Monitoring)
Alarm Present/Silence
Upon occurrence of a transformer overtemperature condition, the “Alarm Present/Silence” switch will
become illuminated and the audible alarm will be activated. Pushing the “Alarm Present/Silence”
switch will silence the audible alarm. The cause of the overtemperature condition should be investigated and corrected. Possible causes include transformer overload, excessive non-linear loading, inadequate ventilation, high or low input voltage, or monitoring malfunction. Failure to correct the
overtemperature condition may result in an automatic system shutdown due to the second stage of
overtemperature sensing. After correction of the alarm condition, the alarm will automatically reset.
Figure 17 Basic monitoring panel
Operating Instructions
EMERGENCY
POWER
OFF
ALARM
PRESENT
SILENCE
4.3 Power Monitor Panel
Monitored Parameters - A 4 x 20 character LCD is provided to indicate the input voltages (line-toline), output voltages (line-to-line and line-to-neutral), output currents (each phase, neutral and
ground), output voltage THD, output current THD, crest factor, K-factor, output kVA, kW, kWH,
power factor, percent load and output frequency. Pressing the Scan switch will activate the
“Autoscan” mode where all monitored parameters are sequentially displayed automatically. Momentarily pressing the “Hold/Sequence” switch interrupts the “Autoscan” mode. Pressing the “Hold/
Sequence” switch allows manual selection of the sequentially displayed parameters.
Figure 18 Power monitor panel
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
X – Y = 208
Y – Z = 208
Z – X = 208
Liebert FPC
X – N = 120
Y – N = 120
Z – N = 120
SCAN
HOLD
SEQUENC E
FPC16000
EMERGENCY
POWER
OFF
ALARM
PRESENT
SILENCE
Liebert FPC
30
FPC16001
Page 35

Operating Instructions
Alarms - Upon occurrence of any of the following alarms, the alarm message appears on the LCD display, the Alarm Present/Silence switch is illuminated, and the audible alarm is activated. Pressing
the “Alarm Present/Silence” switch silences the audible alarm. After the alarm condition is corrected,
the alarm can be reset by pressing the “Alarm Present/Silence” switch when prompted by the LCD
display or by way of any Central Monitoring System.
• Output Overvoltage - Indicates one or more of the output phase voltages has exceeded the preset limit (normally +6% of nominal). The high output voltage should be verified and corrective
action taken. In the absence of other procedures, a normal (orderly) system shutdown should be
performed to prevent load equipment damage.
• Output Undervoltage - Indicates one or more of the output phase voltages has exceeded the
preset limit (normally -13% of nominal). The low output voltage should be verified and corrective
action taken. In the absence of other procedures, a normal (orderly) system shutdown should be
performed to prevent load equipment damage.
• Output Voltage THD - Indicates that the voltage distortion on one or more of the output phases
has exceeded the preset limit (normally 10% THD). The cause of the high output voltage distortion should be investigated and corrective action (if any) taken.
••Transformer Overtemp - Indicates a unit transformer overtemperature condition. The cause
of the overtemperature condition should be investigated and corrected. Possible causes include
unit overload, excessive non-linear loading, inadequate ventilation, high or low input voltage, or
monitoring malfunction. Failure to correct the overtemperature condition may result in an automatic system shutdown due to the second stage of overtemperature sensing.
• Output Overcurrent - Indicates one or more of the output phase currents has exceeded the preset limit (normally 95% of the unit’s full load amp rating). The overcurrent condition should be
verified and corrective action taken. In the absence of other procedures, some of the output loads
should be turned off to reduce unit loading. If unbalanced phase currents exist, some of the loads
should be shifted from the higher loaded phase(s) to the lower loaded phase(s).
• Neutral Overcurrent - Indicates that the neutral current has exceeded the preset limit (normally 95% of the unit’s full load amp rating). The overcurrent condition should be verified and
investigated to see if corrective action is required. In some cases, high neutral current indicates
phase current unbalance which should be corrected. Where high neutral currents are the result of
harmonic load currents, all affected components (including output wiring) should be verified to be
suitable for the current.
• Frequency Deviation - Indicates that the output frequency has exceeded preset limits (normally Ø0.5 Hz). The frequency deviation should be verified and the cause investigated and corrected.
• Phase Sequence Error - Indicates that the output phase sequence is not A, B, C. The phase
sequence should be verified and corrective action taken. Three-phase loads sensitive to phase
sequence should not be operated without proper phase sequence.
• Phase Loss - Indicates that one or more of the phase voltages is low or missing. The low voltage
condition should be verified and corrective action taken. In the absence of other procedures, a normal (orderly) shutdown should be performed to prevent equipment damage.
• Ground Overcurrent - Indicates the system ground current has exceeded the preset limit (nor-
mally 5 amps). The overcurrent condition should be verified and corrective action taken. Possible
causes are wiring errors, ground faults, or excessive leakage current.
• Customer Alarms (5) - Indicates customer-designated alarms. The cause and corrective action
depend on the nature of the alarm. See 1.3.6 - Control Wiring Connections for contact closure
connection information.
31
Page 36

Operating Instructions
To Set Unit Clock - To set the clock from the unit front panel, simultaneously press the Scan and
Hold membrane switches while the time and date screen is displayed on the LCD. A cursor should
appear on the selected time and date field. Use the Scan switch to increment the highlighted field and
the Hold switch to decrement the highlighted field. Use the Silence push button to select the next
time and date field. The time can be displayed in AM/PM or 24-hour format. Simultaneously press the
Scan and Hold switches to exit the clock set screen.
RS-232 ASCII Communications Port - Units with power monitoring are equipped with an isolated
RS-232 ASCII Communications Port, which allows access to unit monitored parameters and alarm
information. The RS-232 port connections are located on the low voltage control terminal strip inside
the unit. See typical control wiring in Figure 16.
The ASCII interface default parameters are shown in Table 15.
Table 15 ASCII interface default parameters
Parameter Default
Interface RS-232 using EIA voltage levels
Baud rate 9600
Parity None
Data bits 8
Stop bits 1
Terminator <CR>
Hand shaking Not supported
Structure Half-duplex
Echo OFF
Change to receive after transmit 1.28 msec
Minimum delay to transmit after receive 120 µsec
Maximum response time turn around 300 msec
Maximum response completion time 500 msec
Minimum delay between commands 500 msec
Maximum intercharacter delay 12.5 msec
The ASCII port uses a Query-Response Format.
Table 17 shows the list of available customer commands. Only one command is serviced at a time.
Valid commands are terminated with a carriage return [0Dh]. Commands are accepted in upper or
lower case. Responses are in upper case, terminated with a line feed [0Ah] and carriage return [0Dh].
Table 16 RS-232 ASCII port customer commands
Command Description Typical Response
Time? <CR>
Date? <CR>
UID? <CR>
kVA? <CR>
V? <CR>
SS1? <CR> System Information
SA? <CR> Number of Active Alarms
UPMD?
<CR>
Unit: Time
Unit: Date
Unit ID
Nominal kVA
Nominal L-L Voltage
(20-character fields
with comma separators)
(20-character alarms
with time stamp)
Monitored Parameters
(32 comma-separated
data fields—see
Table 17 for descriptions
of field positions)
03:40:37A<LF><CR>
05-15-97<LF><CR>
Unit_No._PDU_21B____<LF><CR>
0150<LF><CR>
0208<LF><CR>
UNIT_MODEL_NUMBER___SERIAL NUMBER_______
SITE_ID_NUMBER______TAG_NUMBER__________<LF><CR>
02, OUTPUT_OVERVOLTAGE__05-15-97,01:25:30A
OUTPUT_OVERCURRENT__05-15-97,01:27:46A<LF><CR>
0484,0485,0483,0210,0212,0211,0121,0122,0121,0068,
0085,0120,0131,0018,0030,0092,0033,0600,0038,0041,
0043,0549,0632,0599,0000,1528,0018,0019,0020,0045,
0047,0049,0044<LF><CR>
32
Page 37

Table 17 Monitored parameters data definitions
Field # Data item Units
1 Input Voltage A-B Volts
2 Input Voltage B-C Volts
3 Input Voltage C-A Volts
4 Output Voltage X-Y Volts
5 Output Voltage Y-Z Volts
6 Output Voltage Z-A Volts
7 Output Voltage X-N Volts
8 Output Voltage Y-N Volts
9 Output Voltage Z-N Volts
10 Output Current X Amps
11 Output Current Y Amps
12 Output Current Z Amps
13 Neutral Current Amps
14 Ground Current 0.1 Amps
15 Output Power kW
16 Power Factor 0.01 Power Factor
17 Output Power kVA
18 Output Frequency 0.1 Hz
19 Output Vx THD 0.1%
20 Output Vy THD 0.1%
21 Output Vz THD 0.1%
22 Output Ix THD 0.1%
23 Output ly THD 0.1%
24 Output Iz THD 0.1%
25 Output kW-Hrs kW-Hrs
26 Output Ix Crest Factor 0.1
27 Output ly Crest Factor 0.1
28 Output Iz Crest Factor 0.1
29 Output Ix K-Factor 0.1
30 Output ly K-Factor 0.1
31 Output Iz K-Factor 0.1
32 Output Loading % of Full Load
Operating Instructions
33
Page 38

5.0 MAINTENANCE
5.1 Repair
Even the most reliable equipment may fail. Liebert Global Services is at your service to assure fast
repair of your unit and minimum downtime of your installation.
WARNING
!
Only qualified service personnel should perform maintenance on the Liebert FPC system.
Standard electrical troubleshooting procedures should be used to isolate problems in the unit. If there
are questions, don’t hesitate to contact Liebert Global Services.
Repair or replacement of standard items, such as circuit breakers, fuses, transformers, capacitors and
indicator lights can either be handled by qualified electricians or referred to Liebert Global Services.
Repairs related to the monitoring system should be referred to Liebert Global Services. To contact
LGS for information or repair service in the United States, call 1-800-LIEBERT.
5.2 Inspection and Cleaning
Air circulation through the cabinet may cause dust to accumulate on internal components. Cleaning
should be done as necessary during electrical inspections.
Maintenance
Annual general system inspections, cleaning, and operation checks are recommended to ensure system performance and long service life.
WARNING
!
Only qualified service personnel should perform maintenance on the Liebert FPC system. All
voltage sources to the unit must be disconnected before inspecting or cleaning within the
cabinet.
5.2.1 Inspection Schedule
• It is difficult to establish a schedule for periodic cleanings because conditions vary from site to
site. Inspections after the first 24 hours, 30 days and 6 months of operation should help determine
a pattern for the inspection schedule.
• Electrical connections and component mountings should be inspected after the first 24 hours,
30 days, and 6 months of operation. Inspections should be conducted annually thereafter.
• Ventilation openings and grilles should be inspected and cleaned every 6 months to one year.
• A complete inspection and operational checkout should be performed annually. This is best done
by performing the inspection and start-up procedure as detailed in 3.0 - Inspection and Star-
tup Checklist.
• LGS offers a complete range of preventive maintenance services. These include thorough equipment performance checks and calibration of electronics. Contact Liebert Global Services in the
United States by calling 1-800-LIEBERT for details.
34
Page 39

Page 40

Ensuring The High Availability
0f Mission-Critical Data And Applications.
Emerson Network Power, the global leader in enabling business-critical
continuity, ensures network resiliency and adaptability through
a family of technologies—including Liebert power and cooling
technologies—that protect and support business-critical systems.
Liebert solutions employ an adaptive architecture that responds
to changes in criticality, density and capacity. Enterprises benefit
from greater IT system availability, operational flexibility and
reduced capital equipment and operating costs.
While every precaution has been taken to ensure the accuracy
and completeness of this literature, Liebert Corporation assumes no
responsibility and disclaims all liability for damages resulting from use of
this information or for any errors or omissions.
© 2007 Liebert Corporation
All rights reserved throughout the world. Specifications subject to change
without notice.
® Liebert and the Liebert logo are registered trademarks of Liebert
Corporation. All names referred to are trademarks
or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Technical Support / Service
Web Site
www.liebert.com
Monitoring
800-222-5877
monitoring@emersonnetworkpower.com
Outside the US: 614-841-6755
Single-Phase UPS
800-222-5877
upstech@emersonnetworkpower.com
Outside the US: 614-841-6755
Three-Phase UPS
800-543-2378
powertech@emersonnetworkpower.com
Environmental Systems
800-543-2778
Outside the United States
614-888-0246
Locations
United States
1050 Dearborn Drive
P.O. Box 29186
Columbus, OH 43229
Europe
Via Leonardo Da Vinci 8
Zona Industriale Tognana
35028 Piove Di Sacco (PD) Italy
+39 049 9719 111
Fax: +39 049 5841 257
Asia
7/F, Dah Sing Financial Centre
108 Gloucester Road, Wanchai
Hong Kong
852 2572220
Fax: 852 28029250
SL-20412_REV04_09-07
Emerson Network Power.
The global leader in enabling Business-Critical Continuity.
AC Power
Connectivity
DC Power
Business-Critical Continuity, Emerson Network Power and the Emerson Network Power logo are trademarks and service marks of Emerson Electric Co.
©2007 Emerson Electric Co.
Embedded Computing
Embedded Power Power Switching & Controls
Monitoring
Outside Plant
Precision Cooling
EmersonNetworkPower.com
Racks & Integrated Cabinets
Services
Surge Protection
 Loading...
Loading...