Page 1

Application Guidelines
Copeland Stream™ Semi-Hermetic Compressors
4MF-13X to 4MK-35X & 6MM-30X to 6MK-50X
Page 2

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
1 Safety instructions ............................................................................................ 1
1.1 Icon explanation ................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Safety statements .............................................................................................................. 1
1.3 General instructions ........................................................................................................... 1
2 Product description .......................................................................................... 3
2.1 Common information about Copeland Stream™ semi-hermetic compressors ................. 3
2.2 About these guidelines ....................................................................................................... 3
2.3 Nomenclature ..................................................................................................................... 3
2.4 Nameplate information ....................................................................................................... 4
2.5 Application range ............................................................................................................... 4
2.5.1 Qualified refrigerants and oils ................................................................................ 4
2.5.2 Application limits ..................................................................................................... 5
2.6 Design features .................................................................................................................. 5
2.6.1 Compressor construction ....................................................................................... 5
2.6.2 Compressor cooling ............................................................................................... 5
2.6.3 Demand cooling ..................................................................................................... 5
2.6.4 Unloaded start ........................................................................................................ 5
2.6.5 Capacity control ...................................................................................................... 5
2.6.6 Oil pumps ............................................................................................................... 6
2.6.7 Oil pressure ............................................................................................................ 6
2.6.8 Oil circulation .......................................................................................................... 6
2.6.9 Oil level ................................................................................................................... 6
3 Installation ......................................................................................................... 7
3.1 Compressor handling ......................................................................................................... 7
3.1.1 Delivery................................................................................................................... 7
3.1.2 Transport and storage ............................................................................................ 7
3.1.3 Positioning and securing ........................................................................................ 7
3.1.4 Installation location ................................................................................................. 8
3.1.5 Mounting parts ........................................................................................................ 8
3.2 Pressure safety controls .................................................................................................... 8
3.2.1 High-pressure control ............................................................................................. 8
3.2.2 Low-pressure control .............................................................................................. 8
3.2.3 Maximum allowable pressures ............................................................................... 8
3.3 Brazing procedure .............................................................................................................. 9
3.4 Screens .............................................................................................................................. 9
4 Electrical connection ...................................................................................... 10
4.1 General recommendations............................................................................................... 10
4.2 Electrical installation ........................................................................................................ 10
4.2.1 Part-winding motors (YY/Y) – Code A .................................................................. 10
4.2.2 Star / Delta motors (Y/∆) – Code E ...................................................................... 10
Page 3

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
4.3 Wiring diagrams ............................................................................................................... 10
4.3.1 Wiring diagram for part-winding motors (AW…) .................................................. 11
4.3.2 Wiring diagram for Star / Delta motors (EW…) .................................................... 13
4.4 Protection devices ............................................................................................................ 15
4.5 CoreSense™ Diagnostics ................................................................................................ 15
4.6 CoreSense™ Protection .................................................................................................. 16
4.6.1 Motor protection ................................................................................................... 16
4.6.2 Oil pressure control .............................................................................................. 17
4.7 Crankcase heaters ........................................................................................................... 18
5 Starting up & operation................................................................................... 19
5.1 Leak test........................................................................................................................... 19
5.2 System evacuation ........................................................................................................... 19
5.3 Preliminary checks – Pre-starting .................................................................................... 19
5.4 Charging procedure ......................................................................................................... 19
5.5 Initial start-up ................................................................................................................... 20
5.6 Minimum run time ............................................................................................................ 20
5.7 Recommended inverter range ......................................................................................... 20
6 Maintenance & repair ...................................................................................... 21
6.1 Exchanging the refrigerant ............................................................................................... 21
6.2 Replacing a compressor .................................................................................................. 21
6.3 Lubrication and oil removal .............................................................................................. 21
6.4 Oil additives ..................................................................................................................... 22
6.5 Unbrazing system components ....................................................................................... 22
7 Dismantling & disposal ................................................................................... 22
Appendix 1: Stream compressor connections ......................................................... 23
Appendix 2: Tightening torques in Nm ..................................................................... 24
Disclaimer ................................................................................................................... 24
Page 4

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 1
1 Safety instructions
Copeland™ brand products semi-hermetic compressors are manufactured according to the
latest European safety standards. Particular emphasis has been placed on the user’s safety.
These compressors are intended for installation in systems according to the Machinery Directive
MD 2006/42/EC. They may be put to service only if they have been installed in these systems
according to instructions and conform to the corresponding provisions of legislation. For relevant
standards please refer to the Manufacturer’s Declaration, available on request.
These instructions should be retained throughout the lifetime of the compressor.
You are strongly advised to follow these safety instructions.
1.1 Icon explanation
WARNING
This icon indicates instructions to
avoid personal injury and material
damage.
CAUTION
This icon indicates instructions to
avoid property damage and possible
personal injury.
High voltage
This icon indicates operations with a
danger of electric shock.
IMPORTANT
This icon indicates instructions to
avoid malfunction of the compressor.
Danger of burning or frostbite
This icon indicates operations with a
danger of burning or frostbite.
NOTE
This word indicates a
recommendation for easier operation.
Explosion hazard
This icon indicates operations with a
danger of explosion.
1.2 Safety statements
Refrigerant compressors must be employed only for their intended use.
Only qualified and authorized HVAC or refrigeration personnel are permitted to install,
commission and maintain this equipment.
Electrical connections must be made by qualified electrical personnel.
All valid standards for connecting electrical and refrigeration equipment must be
observed.
The national legislation and regulations regarding personnel protection must be
observed.
Use personal safety equipment. Safety goggles, gloves,
protective clothing, safety boots and hard hats should be worn
where necessary.
1.3 General instructions
WARNING
System breakdown! Personal injuries! Never install a system in the field
and leave it unattended when it has no charge, a holding charge, or with the
service valves closed without electrically locking out the system.
System breakdown! Personal injuries! Only approved refrigerants and
refrigeration oils must be used.
WARNING
High shell temperature! Burning! Do not touch the compressor until it has
cooled down. Ensure that other materials in the area of the compressor do
not get in touch with it. Lock and mark accessible sections.
CAUTION
Overheating! Bearing damage! Do not operate compressors without
refrigerant charge or without being connected to the system.
Safety
instruction
s
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 5

2 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
CAUTION
Contact with POE! Material damage! POE lubricant must be handled
carefully and the proper protective equipment (gloves, eye protection, etc.)
must be used at all times. POE must not come into contact with any surface
or material that might be harmed by POE, including without limitation, certain
polymers, eg,. PVC/CPVC and polycarbonate.
IMPORTANT
Transit damage! Compressor malfunction! Use original packaging. Avoid
collisions and tilting.
Page 6

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 3
2 Product description
2.1 Common information about Copeland Stream™ semi-hermetic compressors
These guidelines cover Copeland Stream™ semi-hermetic compressors. The semi-hermetic
reciprocating compressor family consists of different ranges. The Stream™ series of 4M* and
6M* models ranges from 13 hp to 50 hp.
Cooling
capacity
(kW)
COP
-
Cooling
capacity
(kW)
COP
-
Cooling
capacity
(kW)
COP
-
4MF-13X 13 33.20 3.28 31.60 2.29 10.65 1.43 177
4MA-22X 22 34.60 3.41 32.70 2.39 10.45 1.44 178
4ML-15X 15 39.70 3.30 38.40 2.31 13.30 1.48 180
4MH-25X 25 39.90 3.30 38.50 2.37 12.40 1.44 187
4MM-20X 17 43.50 3.28 42.00 2.31 15.10 1.49 182
4MI-30X 27 43.70 3.30 42.80 2.37 14.40 1.47 188
4MT-22X 22 49.30 3.26 47.60 2.31 16.95 1.48 183
4MJ-33X 30 48.60 3.30 47.60 2.38 16.15 1.49 190
4MU-25X 25 55.10 3.20 53.10 2.27 18.60 1.45 186
4MK-35X 32 54.50 3.17 53.50 2.31 18.25 1.45 202
6MM-30X 27 65.80 3.21 64.20 2.30 22.70 1.45 215
6MI-40X 35 64.70 3.16 64.60 2.34 21.90 1.44 219
6MT-35X 32 73.60 3.17 72.40 2.30 25.60 1.47 221
6MJ-45X 40 72.60 3.16 72.40 2.32 24.30 1.45 223
6MU-40X 40 81.10 3.07 81.40 2.29 28.40 1.44 225
6MK-50X 50 80.70 3.05 80.90 2.29 27.30 1.41 230
Footprint
(mm)
Medium temperature
2)
High temperature
1)
Low temperature
3)
Displacement
(m3/h)
Nominal
horsepower
hp
Model
62
381 x 305
717888
99
120
135
153
R404A
R134a
R404A
Net
weight
(kg)
1)
R134a Evaporating 5°C, condensing 50°C, suction superheat 10K, subcooling 0K
2)
R404A Evaporating -10°C, condensing 45°C, suction gas temperature 20°C, subcooling 0K
3)
R404A Evaporating -35°C, condensing 40°C, suction gas temperature 20°C, subcooling 0K
Table 1: Stream compressors range and performance
Stream semi-hermetic compressors are suitable for a wide range of applications in the form of
either single compressors, condensing units or as multi-compressor equipment.
The compressor is only one component which must be combined with many others to build a
functional and efficient refrigeration system.
Therefore the information in this manual relates to Copeland Stream semi-hermetic
compressors with standard equipment and accessories only.
2.2 About these guidelines
These guidelines are intended to enable users to ensure the safe installation, starting, operation
and maintenance of semi-hermetic compressors. They are not intended to replace the system
expertise available from system manufacturers.
2.3 Nomenclature
The model designation contains the following technical information about Stream compressors:
Safety
instruction
s
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 7

4 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
2.4 Nameplate information
All important information for identification of the compressor is printed on the nameplate located
below the compressor oil pump. The type of refrigerant used should be stamped on the
nameplate by the installer.
Figure 1
The year and month of production are shown as part of the serial number (Jan = A, Feb = B, …
Dec = L).
2.5 Application range
2.5.1 Qualified refrigerants and oils
WARNING
Use of R450A and R513A refrigerants! Risk of compressor damage!
Refrigerant migration of R450A or R513A into the compressor crankcase
could cause low oil viscosity, which could lead to compressor damage. When
using R450A or R513A it is critical to meet the following requirements:
maintain adequate superheat settings with a minimum superheat of 8-10K;
no liquid refrigerant migration into the compressor at any time, especially
during standstill, during or after defrost, or after reverse mode for example
in heat pumps;
pumpdown is recommended;
the use of a crankcase heater is mandatory;
retrofit to R450A and R513A is only allowed for compressors which are
approved for these refrigerants.
Contact Application Engineering for any further information.
IMPORTANT
It is essential that the glide of refrigerant blends (primarily R407C) is carefully
considered when adjusting pressure and superheat controls.
Oil recharge values can be taken from Copeland™ brand products Select software available at
www.emersonclimate.eu.
Qualified refrigerants
R134a, R22, R404A, R407A,
R407C, R407F, R448A, R449A,
R450A, R507, R513A
R22
Copeland brand products
standard oils
Emkarate RL 32 3MAF
Suniso 3 GS
Servicing oils
Emkarate RL 32 3MAF
Mobil EAL Arctic 22 CC
Shell 22-12, Suniso 3 GS
Fuchs Reniso KM 32, Capella WF32
Table 2: Qualified refrigerants and oils for recharging and topping up
To recharge:
When the compressor is completely empty of oil, the amount of oil to be "recharged" is
typically 0.12 litre less than the original oil charge (oil will already be present in the system).
To top up:
During commissioning, planned maintenance or servicing, add oil so that the compressor oil
level is between min ¼ and max ¾ of sight glass.
Page 8

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 5
2.5.2 Application limits
For application envelopes please refer to Copeland brand products Select software at
www.emersonclimate.eu.
2.6 Design features
2.6.1 Compressor construction
All compressors are fitted with Stream valve plates which cannot be dismantled. To maintain the
high capacity of these compressors in case of exchange, the correct valve-plate-to-body gasket
must always be selected.
Each cylinder head has 2 plugged 1/8" - 27
NPTF tapped holes for connecting highpressure switches.
These high-pressure switches must be
calibrated and tested before putting the
compressor into service. They must stop the
compressor if the allowable pressure is
exceeded.
The complete cylinder head is under
discharge pressure.
Figure 2
2.6.2 Compressor cooling
Compressor motors must always be cooled, and cylinder head cooling may also be needed at
certain operating conditions.
All Stream compressors are suction gas-cooled. With suction gas-cooled compressors, the
motor is cooled by refrigerant gas that is led over the motor. An additional fan may be required
depending upon the operating conditions (see Copeland brand products Select software at
www.emersonclimate.eu).
2.6.3 Demand cooling
"Demand Cooling" as the term implies means liquid refrigerant injection on demand.
For low temperature applications with R407F, R407A, R448A, R449A and R22, Demand Cooling
can be required on the following compressors:
4MF-13X 4ML-15X 4MM-20X 4MT-22X 4MU-25X
6MM-30X 6MT-35X 6MU-40X
NOTE: R22 is no longer allowed for new refrigeration systems in Europe.
2.6.4 Unloaded start
With direct starting the motor of a compressor is switched directly into the mains by means of a
switch. The resulting breakaway starting current amounts to multiple times the rated motor
current operating maximum, without consideration being given to transient phenomena.
In the case of high-powered motors the breakaway starting currents become so large that they
lead to disruptive voltage dips in the mains. The compressors that are subject to current
limitation must therefore by all means be equipped with starting load reduction to guarantee
perfect starting even when the voltages amount to less than approximately 85% of the voltage
on the nameplate.
2.6.5 Capacity control
For 4M* and 6M* compressors a mechanical capacity control is available. The system used is
blocked suction. Be aware that unloaded operation changes the application range of the
compressor.
NOTE: For the application range of the compressors with capacity control, refer to
Technical Information D7.21.2 "Stream semi-hermetic compressor capacity control".
Safety
instruction
s
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 9

6 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
2.6.6 Oil pumps
The oil pumps used for Stream compressors are independent of their rotating direction.
On compressors delivered with CoreSense™ Diagnostics (-D), the oil pump integrates the
electronic switch for integrating oil pressure safety functionality.
Compressors with CoreSense™ Protection (-P) are designed to accommodate fittings for an
OPS2, FD-113ZU, or Sentronic oil safety system or a standard oil pressure switch (OPS2 oil
sensor included in the oil pump).
2.6.7 Oil pressure
Normal oil pressure is between 1.05 and 4.2 bar higher than crankcase pressure. Net oil
pressure can be read by connecting two pressure gauges to the compressor and comparing the
readings. One gauge should be connected to the oil pump. The second gauge should be
connected to the crankcase (T-fitting instead of plug on the compressor crankcase) or the
suction service valve.
During irregular operating conditions, eg, a blockage of the suction filter, the pressure measured
at the suction shut-off valve of the compressor may differ widely from that measured at the
crankcase. Therefore pressure drops have to be avoided.
2.6.8 Oil circulation
Oil returns with the suction gases through a suction strainer and separates in the motor chamber
reaching the crankcase by way of oil return relief valve in the partition between motor housing
and crankcase. This relief valve closes on compressor start-up due to the pressure difference
arising between motor side and crankcase, thus slowing down pressure decrease in the
crankcase over a certain period of time. It reduces the foaming of the oil/refrigerant mixture that
would occur if the pressure decreased rapidly. The valve does not reopen until the pressure has
been equalized by means of a crankcase ventilating valve. This second valve connects the
crankcase and suction side cylinder head. It reduces the pressure difference by means of a very
small bore in the plate of the valve so slowly that oil foams less and only limited oil/refrigerant
foam is transferred to the oil pump.
Four-cylinder compressors have one crankcase ventilating valve on the left cylinder bank
whereas six-cylinder compressors have two ventilating valves on the left and right cylinder
banks.
2.6.9 Oil level
All compressors are delivered with sufficient oil for normal operation (see Table 2). The optimum
oil level should be checked by operating the compressor until the system is stable and then
comparing the sight glass reading with the appropriate diagram below. The oil level should be
min ¼ and max ¾ of the sight glass.
For service compressors when an oil regulator is used the oil level should be min ¼ and max ¾
of the sight glass. The level can also be checked within 10 seconds of compressor shutdown.
For 4M* and 6M* compressors a higher oil level may be accepted when an oil regulator is in use
because the oil separator will reduce excessive oil circulation.
Figure 3: Sight glass reading on 4M* and 6M* compressors
Page 10

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 7
3 Installation
WARNING
High pressure! Injury to skin and eyes possible! Be careful when
opening connections on a pressurized item.
3.1 Compressor handling
3.1.1 Delivery
Please check whether the delivery is correct and complete. Any deficiency should be reported
immediately in writing.
Standard delivery:
Suction and discharge shut-off valves
Oil charge, oil sight glass
Mounting kit
CoreSense™ Diagnostics or CoreSense™ Protection module
Holding charge up to 2.5 bar(g) (dry air)
3.1.2 Transport and storage
WARNING
Risk of collapse! Personal injuries! Move compressors only with
appropriate mechanical or handling equipment according to weight. Keep in
the upright position. Do not stack pallets on top of each other. Keep the
packaging dry at all times.
Figure 4
Compressors are delivered on pallets. Cooling fans are delivered in separate boxes.
Accessories may be mounted or delivered loose. Solenoid valves are never mounted.
3.1.3 Positioning and securing
IMPORTANT
Handling damage! Compressor malfunction! Only use the lifting eyes
whenever the compressor requires positioning. Using discharge or suction
connections for lifting may cause damage or leaks.
If possible, the compressor should be kept horizontal during handling.
For safety reasons two lifting eyes should be fitted before moving a compressor (½" - 13 UNC).
Otherwise refer to drawings on Figure 5 to see how to apply other lifting methods.
4M* 6M*
max. 220 kg max. 260 kg
Figure 5
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 11

8 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
In order to avoid refrigerant leaks or other damage the compressors should not be lifted by the
service valves or other accessories.
3.1.4 Installation location
Ensure the compressors are installed on a solid level base.
3.1.5 Mounting parts
To minimize vibration and start/stop impulses flexible mounting should be used. For this purpose
one set of spring mounting parts for each of the Stream models is delivered with each 4M* and
6M* compressor.
Due to differences in weight (cylinder / motor side) different springs have to be used on both
sides. Springs have different colours for easier identification: violet on motor side and orange on
cylinder side.
Operational position Transport position
Figure 6: Position of vibration dampers during transport and operation
When Stream compressors are mounted in racks rubber mounting parts should be used.
A compressor may be rigidly mounted, ie, without springs. In this case more shock and vibration
loading will be transmitted to the frame.
Unevenness in the mounting surface will have to be compensated by the rack and/or the
compressor bottom plate/feet. Excessive unevenness can result in too high mechanical stress to
the system and could damage the compressor or rack. Therefore, the flatness of the mounting
location is essential. In addition, both vibration/shock and mechanical stress to compressor can
be avoided by using rubber mounting parts.
If the installation requires a very high level of vibration absorption, additional vibration absorbers
– available on the market – can be fitted between the rails and the foundation.
3.2 Pressure safety controls
3.2.1 High-pressure control
A high-pressure control with a maximum cut-out setting of 28.8 bar(g) is required.
The high-pressure cut-out should have a manual reset feature for the highest level of system
protection.
3.2.2 Low-pressure control
The normal minimum cut-out setting is 0.1 bar(g) for R404A.
The low-pressure cut-out should have a manual reset feature for the highest level of system
protection.
3.2.3 Maximum allowable pressures
The maximum allowable pressures according to EN 12693 shown on the compressor nameplate
are obligatory and must not be exceeded.
High-pressure side (HP): 28.0 bar (g) (up to S/N 14K46143M)
32.5 bar (g) (from S/N 14K46144M onwards)
Low-pressure side (LP): 22.5 bar
Transport clamp
Page 12

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 9
Figure 7: Suction tube brazing areas
NOTE: The compressor operating range may be restricted for various reasons. Check the
application range limitations in Copeland brand products Select software at
www.emersonclimate.eu.
3.3 Brazing procedure
IMPORTANT
Blockage! Compressor breakdown! Maintain a flow of oxygen-free
nitrogen through the system at very low pressure during brazing. Nitrogen
displaces the air and prevents the formation of copper oxides in the system.
If allowed to form, the copper oxide material can later be swept through the
system and block screens such as those protecting capillary tubes, thermal
expansion valves, and accumulator oil return holes.
Contamination or moisture! Bearing failure! Do not remove the plugs until
the compressor is set into the unit. This minimises any entry of contaminants
and moisture.
Refer to Figure 7 and procedure below for the brazing of the suction and discharge lines:
The copper-coated steel tubes on Stream
compressors can be brazed in approximately the same
manner as any copper tube.
Recommended brazing material: any silfos
material is recommended, preferably with a minimum
of 5% silver. However, 0% silver is acceptable.
Be sure tube fitting inner diameter and tube outer
diameter are clean prior to assembly.
Using a double-tipped torch, apply heat in area 1.
As the tube approaches brazing temperature,
move the torch flame to area 2.
Heat area 2 until braze temperature is attained, moving the torch up and down and rotating
around the tube as necessary to heat the tube evenly. Add braze material to the joint while
moving the torch around the joint to flow braze material around the circumference.
After the braze material flows around the joint, move the torch to heat area 3. This will draw
the braze material down into the joint. The time spent heating area 3 should be minimal.
As with any brazed joint, overheating may be detrimental to the final result.
To disconnect:
Heat joint areas 2 and 3 slowly and uniformly until the braze material softens and the tube
can be pulled out of the fitting.
To reconnect:
Recommended brazing materials: Silfos with minimum 5% silver or silver braze used on
other compressors.
3.4 Screens
CAUTION
Screen blocking! Compressor breakdown! Use screens with at least
0.6 mm openings.
The use of screens finer than 30 x 30 meshes (0.6 mm openings) anywhere in the system
should be avoided with these compressors. Field experience has shown that finer mesh screens
used to protect thermal expansion valves, capillary tubes or accumulators can become
temporarily or permanently plugged with normal system debris and block the flow of either oil or
refrigerant to the compressor. Such blockage can result in compressor failure.
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 13

10 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
4 Electrical connection
4.1 General recommendations
The compressor terminal box has a wiring diagram on the inside of its cover. Before connecting
the compressor, ensure that the supply voltage, the phases and the frequency match the
nameplate data.
The knockouts have to be removed before the electrical glands can be installed. First make sure
that the terminal box is closed with the terminal box cover. We recommend to use a subland
twist driller to avoid any damage to the box while removing the knockouts.
Figure 8
4.2 Electrical installation
All compressors can be started Direct-On-Line.
The position of bridges required for Direct-On-Line start (depending on type of motor and/or
mains voltage) is shown in Chapter 4.3 "Wiring diagrams".
4.2.1 Part-winding motors (YY/Y) – Code A
Part-winding motors contain two separate windings (2/3 + 1/3) which are internally connected in
star and operated in parallel. You cannot change the voltage by changing the electrical
connections as the motor is only suitable for one voltage.
The first part-winding, ie, the 2/3 winding on terminals 1-2-3, can be used for part-winding start
(remove the bridges!). After a time delay of 1 ± 0.1 seconds the second part-winding, ie, the 1/3
winding on terminals 7-8-9, must be brought on line.
4.2.2 Star / Delta motors (Y/∆) – Code E
This motor is interchangeable for star (Y) or delta (∆) operation by means of bridges. It is
suitable for two voltages, eg, 230V in delta, 400V in star connection. If the supply voltage and
the nominal voltage of the motor in ∆-connection are identical, the star connection motor can
also be used for starting (remove the bridges!).
4.3 Wiring diagrams
The position of the jumpers in the terminal box and the recommended wiring diagrams are
shown in Figures 9 to 12.
Twist driller
Page 14
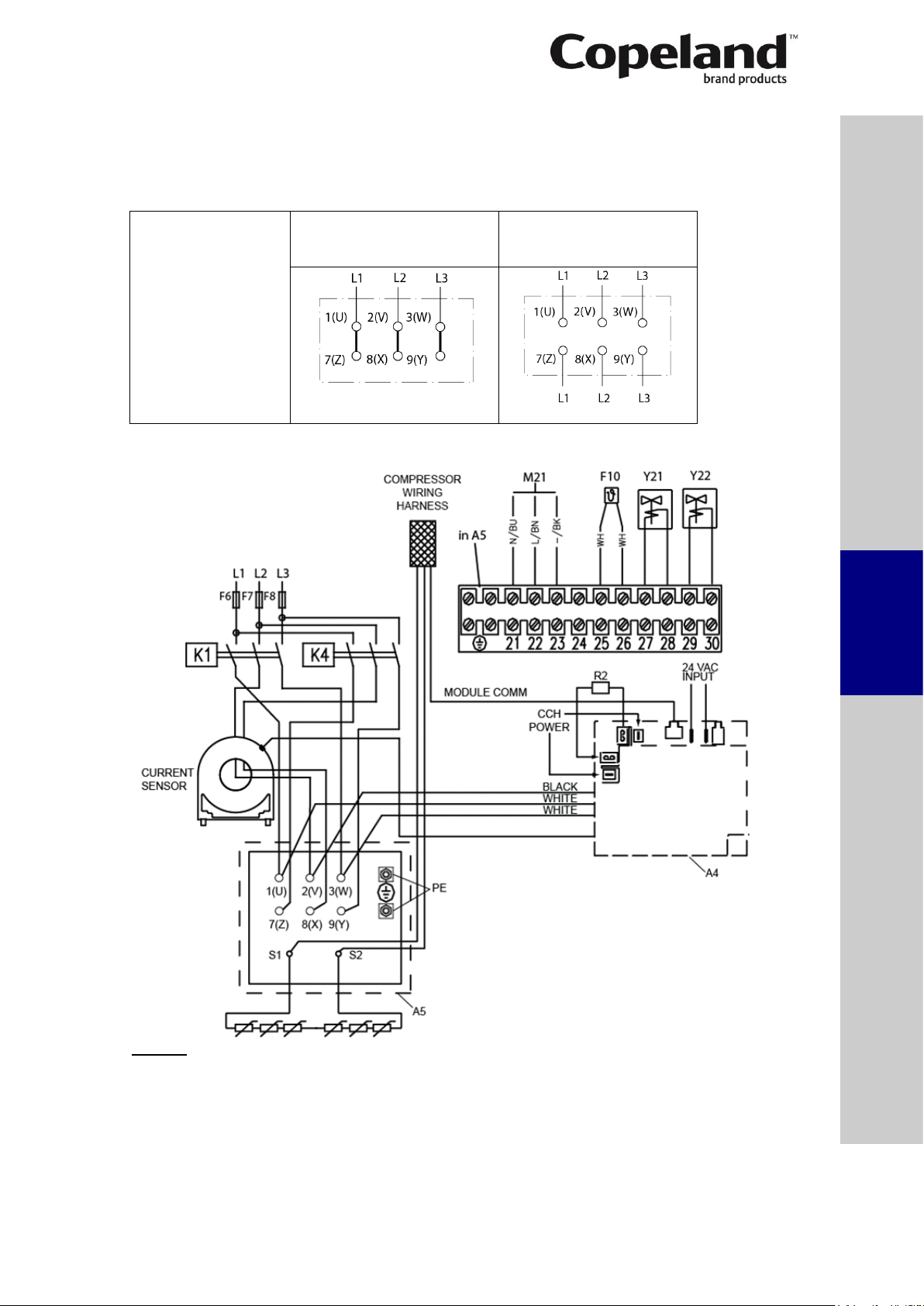
C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 11
4.3.1 Wiring diagram for part-winding motors (AW…)
Part winding motors can be connected direct-on-line or part-winding start.
NOTE: The sensor module inside the terminal box requires a separate 24V AC power
supply.
Part-winding motor:
Y – Y
Code A
Direct-on-line start
Y - Y
Part-winding start
First start step 1–2-3
Y - Y
4.3.1.1 Compressors with CoreSense Diagnostics module
Legend
A4 ....... Sensor module K1 ........ Contactor M1
A5 ....... Compressor terminal box K4 ........ Contactor M1 for second part-winding
CCH .... Crankcase heater M21 ..... Fan motor / condenser
F6 ....... Fuse for control circuit R2 ........ Crankcase heater
F7 ....... Fuse for control circuit Y21 ...... Solenoid valve capacity control 1
F8 ....... Fuse for control circuit Y22 ...... Solenoid valve capacity control 2
F10 ..... Thermal protection switch M21
Figure 9
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 15

12 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
4.3.1.2 Compressors with CoreSense Protection module
Legend
A1 ....... CoreSense Protection module K1 ........ Contactor M1
A2 ....... OPS2 Oil pressure switch K4 ........ Contactor M1 for second part-winding
A5 ....... Compressor terminal box M21 ..... Fan motor / condenser
F6 ....... Fuse for control circuit R2 ........ Crankcase heater
F7 ....... Fuse for control circuit Y21 ...... Solenoid valve capacity control 1
F8 ....... Fuse for control circuit Y22 ...... Solenoid valve capacity control 2
F10 ..... Thermal protection switch M21 Y3 ........ Solenoid valve unloaded start
Figure 10
Page 16

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 13
4.3.2 Wiring diagram for Star / Delta motors (EW…)
Star / Delta motors can be connected direct-on-line or Star / Delta start.
NOTE: The sensor module inside the terminal box requires a separate 24V AC power
supply.
Star / Delta motor
Y - ∆
Code E
Direct-on-line start
∆
Direct-on-line start
Y
Star / Delta start
∆
4.3.2.1 Compressors with CoreSense Diagnostics module
Legend
A4 ....... Sensor module K1 ........ Contactor M1
A5 ....... Compressor terminal box K2 ........ Contactor M1 Y-connection
CCH .... Crankcase heater K3 ........ Contactor M1 Δ-connection
F6 ....... Fuse for control circuit M21 ..... Fan motor / condenser
F7 ....... Fuse for control circuit R2 ........ Crankcase heater
F8 ....... Fuse for control circuit Y21 ...... Solenoid valve capacity control 1
F10 ..... Thermal protection switch M21 Y22 ...... Solenoid valve capacity control 2
Figure 11
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 17

14 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
4.3.2.2 Compressors with CoreSense Protection module
Legend
A1 ....... CoreSense Protection module K1 ........ Contactor M1
A2 ....... OPS2 Oil pressure switch K2 ........ Contactor M1 Y-connection
A5 ....... Compressor terminal box K3 ........ Contactor M1 Δ-connection
F6 ....... Fuse for control circuit M21 ..... Fan motor / condenser
F7 ....... Fuse for control circuit R2 ........ Crankcase heater
F8 ....... Fuse for control circuit Y21/22 . Solenoid valve capacity controls
F10 ..... Thermal protection switch M21 Y3 ........ Solenoid valve unloaded start
Figure 12
Page 18

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 15
4.4 Protection devices
Independently from the internal motor protection, fuses must be installed before compressor
start-up. The selection of fuses has to be carried out according to VDE 0635, DIN 57635,
IEC 269-1 or EN 60-269-1.
4.5 CoreSense™ Diagnostics
CoreSense™ Diagnostics is used for all 4M* and 6M* Stream semi-hermetic compressors. It
combines oil and motor protection in one module, replacing OPS1/2 and the electronic module
INT69TM. In addition it provides advanced protection against faults such as high discharge
temperature, locked rotor, single/missing phase, voltage imbalance and low voltage protection.
The module is capable of communication via Modbus® protocol. An external overload protection
is not necessary.
Figure 13: CoreSense Diagnostics module
Discharge temperature
Sensor
Oil Pressure Sensor Motor Temperature Sensor (PTC)
CoreSense
Control Module
Current Sensor
Sensor Module
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 19

16 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
For the electrical connection of the CoreSense Diagnostics module, refer to the wiring diagram
below:
Figure 14: CoreSense module wiring diagram
NOTE: For more information please refer to Technical Information D7.8.4 "CoreSense™
Diagnostics for Stream refrigeration compressors".
4.6 CoreSense™ Protection
4.6.1 Motor protection
Stream compressors with "-P" at the end of the description are equipped with a CoreSense
Protection device. The temperature-dependent resistance of the thermistor (also PTCresistance) is used to sense the winding temperature. Two chains of three thermistors each
connected in series are embedded in the motor windings in such a manner that the temperature
of the thermistors can follow with little inertia.
The CoreSense Protection module switches a control relay depending on the thermistor
resistance. It is installed in the terminal box to which the thermistors are connected.
Caution: The maximum test voltage for thermistors is 3V.
The total resistance of the thermistor chains on a cold compressor should be ≤ 1800Ω.
Protection class of the module: IP20.
IMPORTANT
Different sources for power supply and contact 11-14! Module
malfunction! Use the same potential for the power supply (L) and the switch
contact of the control loop (11-14).
Control circuit wiring:
Figure 15: Control circuit wiring diagram
Page 20

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 17
4.6.2 Oil pressure control
The oil pressure switch breaks the control circuit when the pressure difference between the oil
pump outlet and the crankcase is too low. The switch must be properly adjusted and tamperproof. If the oil differential pressure drops below the minimum acceptable value the compressor
will be stopped after a 120-second delay. After having solved the problem the control has to be
reset manually.
NOTE: Proper oil pressure safety control with an approved switch is a condition of
warranty!
The following oil pressure switches can be delivered as accessories:
Electronic oil pressure switch OPS2
Mechanical oil pressure switch ALCO FD-113ZU
4.6.2.1 Electronic oil pressure switch – OPS2
The specifications for the OPS2 oil pressure switch are as follows:
Differential pressure: 0.95 ± 0.15 bar
Time delay: 120 ± 15 sec.
Where there is a 5-wire cable connection between the electrical control panel and the
compressor terminal box to the OPS module, the same wires can be applied to the OPS2 which
will give the functions of an OPS1 module.
To obtain use of all of the features of the OPS2 a 7-wire cable between the electrical control
cabinet and the compressor terminal box should be used. Wiring diagrams for OPS2 are shown
in Technical Information D7.8.3 "DWM Copeland™ Semi-hermetic Compressor Oil Pressure
Differential Switch OPS2" available at www.emersonclimate.eu. The wiring diagram relates to an
option using a 7-wire cable.
Wiring:
Brown (BN) = Power supply input
Violet (VIO) = Running signal from the compressor
Grey (GR) = Input changeover contact from the
daisy chain
Orange (OG) = Output changeover contact linked to
the compressor contactor
Pink (PK) = Output changeover contact linked to the
alarm
Blue (BU) = Power supply output
Figure 16
NOTE: Where a 5- or 7-wire cable is stated a 4- or 6-wire cable is required. In some
countries only a 5- or 7-wire cable is available. See more information about OPS2 in
Technical Information D7.8.3 "DWM Copeland™ Semi-hermetic Compressor Oil Pressure
Differential Switch OPS2".
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 21

18 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
4.6.2.2 Mechanical oil pressure switch – ALCO FD-113ZU (A22 - 057)
Specifications for electro-mechanical oil pressure switches are as follows:
Cut-out pressure: 0.63 ± 0.14 bar
Cut-in pressure: 0.9 ± 0.1 bar
Time delay: 120 ± 15 sec.
The Alco Control FD-113ZU mechanical oil pressure switch operates with the above set points.
Legend:
11 ..... Voltage connection
21 ..... Control voltage connection
22 ..... Control circuit
24 ..... Alarm connection
A2..... Oil pressure switch
A5..... Compressor terminal box
R ....... Relay
N ....... Neutral connection
t ........ Time delay
Figure 17
Protection class: IP30.
4.7 Crankcase heaters
IMPORTANT
Oil dilution! Bearing malfunction! Turn the crankcase heater on 12 hours
before starting the compressor.
A crankcase heater is used to prevent refrigerant from migrating into the shell during standstill
periods. Heaters for 4M* and 6M* compressors are screwed into a sleeve (see Figure 18).
The crankcase heater is available in 120V, 230V and 480V.
The operation of 120V and 230V crankcase heaters is controlled by the CoreSense Diagnostics
module; this is not possible with 480V heaters.
Figure 18: 100 Watt crankcase heater element
Page 22

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 19
5 Starting up & operation
WARNING
Diesel effect! Compressor destruction! The mixture of air and oil at high
temperature can lead to an explosion. Avoid operating with air.
5.1 Leak test
The suction shut-off valve and discharge shut-off valve on the compressor must remain closed
during pressure testing to prevent air and moisture from entering the compressor. The test
pressure (dried nitrogen) must not exceed 20.5 bar provided no other system component’s
pressure is lower. In this case the lower pressure is the test pressure.
5.2 System evacuation
Before commissioning, remove the holding charge then evacuate with a vacuum pump. Proper
evacuation reduces residual moisture to 50 ppm. The installation of adequately sized access
valves at the furthest point from the compressor in the suction and liquid lines is advisable. To
achieve undisturbed operation the compressor valves are closed and the system is evacuated
down to 0.3 mbar / 0.225 Torr. Pressure must be measured using a vacuum pressure (Torr)
gauge on the access valves and not on the vacuum pump; this serves to avoid incorrect
measurements resulting from the pressure gradient along the connecting lines to the pump.
Then the compressor must be evacuated.
Due to the factory holding charge of dry air the compressor is under pressure (about 1 to
2.5 bar), this is to indicate that the compressor does not leak.
When removing plugs from the compressor in order to connect a pressure gauge or to fill in oil,
the plug may pop out under pressure and oil can spurt out.
5.3 Preliminary checks – Pre-starting
Discuss details of the installation with the installer. If possible, obtain drawings, wiring diagrams,
etc. It is ideal to use a check-list but always check the following:
Visual check of the electrics, wiring, fuses etc.
Visual check of the plant for leaks, loose fittings such as TXV bulbs etc.
Compressor oil level
Calibration of HP & LP switches and any pressure actuated valves
Check setting and operation of all safety features and protection devices
All valves in the correct running position
Pressure and compound gauges fitted
Correctly charged with refrigerant
Compressor electrical isolator location & position
5.4 Charging procedure
CAUTION
Low suction pressure operation! Compressor Damage! Do not operate
with a restricted suction. Do not operate with the low-pressure cut-out
bridged.
The system should be liquid-charged through the liquid-receiver shut-off valve or through a valve
in the liquid line. The use of a filter drier in the charging line is highly recommended. The majority
of the charge should be placed in the high side of the system to prevent bearing washout during
first-time start.
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance
&
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 23

20 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
5.5 Initial start-up
CAUTION
Oil dilution! Bearing malfunction! It is important to ensure that new
compressors are not subjected to liquid abuse. Turn the crankcase heater on
12 hours before starting the compressor.
CAUTION
High discharge pressure operation! Compressor damage! Do not use
the compressor to test opening set point of high-pressure cut-out.
The compressor must be equipped according to our technical documentation considering the
application intended. Make sure this requirement is met before start-up.
For brazing connections where dissimilar or ferric metals are joined a silver alloy rod with a
minimum content of 30% silver shall be used being either flux-coated or with a separate flux.
Bolt torque settings are listed in Appendix 2.
With the exception of rubber-coated metallic gaskets (Wolverine) all gaskets should be oiled
before fitting. O-rings should also be oiled.
NOTE: A compressor should never be operated beyond its approved application range!
Check by consulting the appropriate data sheet. To avoid motor damage the compressor
MUST NOT be started, nor may high-potential testing be carried out under vacuum.
5.6 Minimum run time
Emerson Climate Technologies recommends a maximum of 10 starts per hour. The most critical
consideration is the minimum run time required to return oil to the compressor after start-up.
5.7 Recommended inverter range
Stream compressors are released for inverter applications from Control Techniques or other
brands available on the market.
Over a frequency range the compressor system combination can have frequency bands with
higher vibration. The degree of vibration and frequency bands are highly dependent on the
system. To help reduce these vibration levels rubber mounting should be used on all inverter
driven compressors.
Active oil management should be used for all inverter driven compressors.
Page 24

C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 21
6 Maintenance & repair
6.1 Exchanging the refrigerant
Qualified refrigerants and oils are given in Chapter 2.5.1.
It is not necessary to replace the refrigerant with new unless contamination due to an error such
as topping up the system with an incorrect refrigerant is suspected. To verify correct refrigerant
composition, a sample can be taken for chemical analysis. A check can be made during shut
down by comparing the refrigerant temperature and pressure using precision measurements at a
location in the system where liquid and vapour phases are present and when the temperatures
have stabilised.
In the event that the refrigerant needs replacing, the charge should be recovered using a
suitable recovery unit.
In the event that R22 in a system with mineral oil is to be replaced with an HFC refrigerant, the
oil must also be changed.
NOTE: Please refer to Technical Information CC7.26.1 "Refrigerant Changeover from
HCFC to HFC Refrigerants" and CC7.26.3 "Refrigerant Changeover from R404A/R507 to
HFC R407A, R407F, R448A, R449A".
6.2 Replacing a compressor
CAUTION
Inadequate lubrication! Bearing destruction! Exchange the accumulator
after replacing a compressor with a burned out motor. The accumulator oil
return orifice or screen may be plugged with debris or may become plugged.
This will result in starvation of oil to the new compressor and a second
failure.
In the case of a motor burnout, the majority of contaminated oil will be removed with the
compressor. The rest of the oil is cleaned through the use of suction and liquid line filter driers. A
100% activated alumina suction line filter drier is recommended but must be removed after
72 hours. It is highly recommended that the suction accumulator be replaced if the system
contains one. This is because the accumulator oil-return orifice or screen may be plugged with
debris or may become plugged shortly after a compressor failure. This will result in starvation of
oil to the replacement compressor and a second failure. When a single compressor or tandem is
exchanged in the field, it is possible that a major portion of the oil may still be in the system.
While this may not affect the reliability of the replacement compressor, the extra oil will add to
rotor drag and increase power usage.
6.3 Lubrication and oil removal
CAUTION
Chemical reaction! Compressor destruction! Do not mix up ester oils with
mineral oil and/or alkyl benzene when used with chlorine-free (HFC)
refrigerants.
The compressor is supplied with an initial oil charge. The standard oil charge for use with
refrigerants R404A, R407A, R407C, R407F, R448A, R449A, R450A, R507, R513A and R134a is
a polyolester (POE) lubricant Emkarate RL 32 3MAF. In the field the oil level could be topped up
with Mobil EAL Arctic 22 CC if 3MAF is not available. The standard mineral oil for R22 is Suniso
3GS.
One disadvantage of POE is that it is far more hygroscopic than mineral oil (see Figure 19).
Only brief exposure to ambient air is needed for POE to absorb sufficient moisture to make it
unacceptable for use in a refrigeration system. Since POE holds moisture more readily than
mineral oil it is more difficult to remove it through the use of vacuum. Compressors supplied by
Emerson Climate Technologies contain oil with low moisture content, and it may rise during the
system assembling process. Therefore it is recommended that a properly sized filter-drier is
installed in all POE systems. This will maintain the moisture level in the oil to less than 50 ppm. If
oil is charged into a system, it is recommended to use POE with moisture content no higher than
50 ppm.
Safety
instructions
Product
description
Installation
Electrical
connection
Starting up &
operation
Maintenance &
repair
Dismantling &
disposal
Page 25

22 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
The diagram below compares the hygroscopic characteristics of POE oil with mineral oil
(moisture absorption in PPM at 25°C and 50% relative humidity).
Figure 19: Absorption of moisture in ester oil in comparison to mineral oil in ppm by weight at 25°C and 50%
relative humidity (h=hours)
If the moisture content of the oil in a refrigeration system reaches unacceptably high levels,
corrosion and copper plating may occur. The system should be evacuated down to 0.3 mbar or
lower. If there is uncertainty as to the moisture content in the system, an oil sample should be
taken and tested for moisture. Sight glass/moisture indicators currently available can be used
with the HFC refrigerants and lubricants; however, the moisture indicator will just show the
moisture content of the refrigerant. The actual moisture level of POE would be higher than the
sight glass indicates. This is due to the high hygroscopicity of the POE oil. To determine the
actual moisture content of the lubricant, samples have to be taken from the system and
analysed.
6.4 Oil additives
Although Emerson Climate Technologies cannot comment on any specific product, from our own
testing and past experience, we do not recommend the use of any additive to reduce
compressor bearing losses or for any other purpose. Furthermore, the long-term chemical
stability of any additive in the presence of refrigerant, low and high temperatures, and materials
commonly found in refrigeration systems is complex and difficult to evaluate without rigorously
controlled chemical laboratory testing. The use of additives without adequate testing may result
in malfunction or premature failure of components in the system and, in specific cases, in voiding
the warranty on the component.
6.5 Unbrazing system components
WARNING
Explosive flame! Burning! Oil-refrigerant mixtures are highly flammable.
Remove all refrigerant before opening the system. Avoid working with an
unshielded flame in a refrigerant charged system.
Before opening up a system it is important to remove all refrigerant from both the high and low
sides of the system. If a brazing torch is then applied to the low side while the low side shell and
suction line contain pressure, the pressurized refrigerant and oil mixture could ignite when it
escapes and contacts the brazing flame. To prevent this occurrence, it is important to check both
the high and low sides with manifold gauges before unbrazing. Instructions should be provided in
appropriate product literature and assembly (line repair) areas. If compressor removal is
required, the compressor should be cut out of system rather than unbrazed.
7 Dismantling & disposal
Removing oil and refrigerant:
Do not disperse in the environment.
Use the correct equipment and method of removal.
Dispose of oil and refrigerant properly.
Dispose of compressor properly.
Page 26
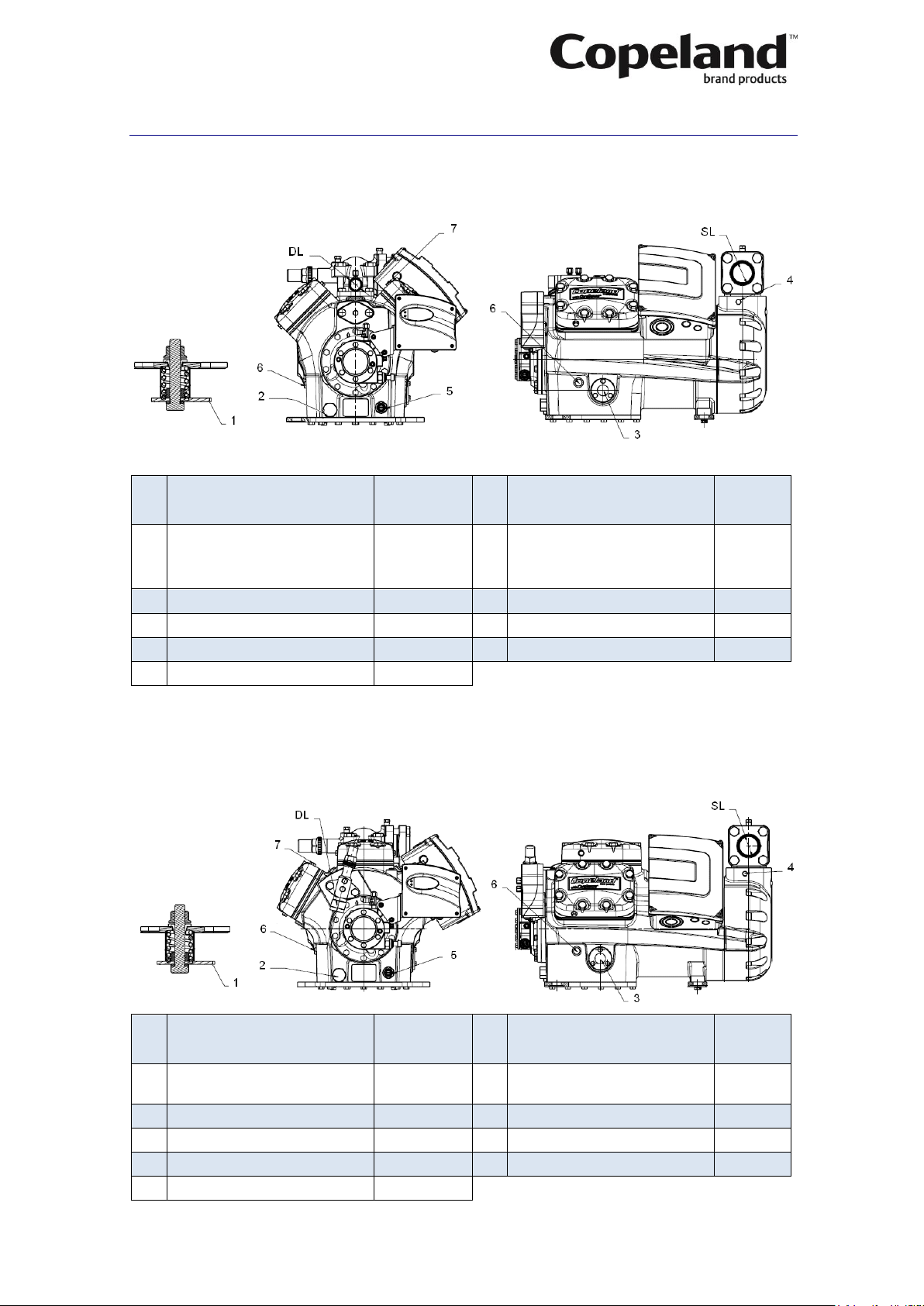
C6.3.1/0116-0716/E 23
Appendix 1: Stream compressor connections
4M*
4MF-13X 4ML-15X 4MM-20X 4MT-22X 4MU-25X
4MA-22X 4MH-25X 4MI-30X 4MJ-30X 4MK-32X
SL
Suction line size (sweat)
4MF13X, 4ML15X, 4MA22X
Ø 1 5/8"
DL
Discharge line size (sweat)
4MF13X, 4ML15X, 4MA22X,
4MM20X, 4MH25X, 4MI30X
Ø 1 1/8"
SL
Suction line size (sweat)
4MM20X, 4MH25X, 4MI30X,
4MT22X,4MJ33X, 4MU25X,
4MK35X
Ø 2 1/8"
DL
Discharge line size (sweat)
4MT22X,4MJ33X, 4MU25X,
4MK35X
Ø 1 3/8"
1
Base mountings
Ø 25.5 mm
5
Crankcase heater
2 Magnetic plug
1" - 16 UN
6
Plug oil charge
1/4" 3 Oil sight glass
1/4"-20 UNC
7
Plug high pressure connection
1/8" 4 Plug low pressure connection
1/8"
6M*
6MM-30X, 6MT-35X, 6MU-40X
6MI-40X, 6MJ-45X, 6MK-50X
SL
Suction line size (sweat)
6MM30X, 6MT35X,
6MI40X, 6MJ45X
Ø 2 1/8"
DL
Discharge line size (sweat)
6MT35X, 6MU-40X,
6MJ45X, 6MK-50X
Ø 1 5/8"
SL
Suction line size (sweat)
6MK50X, 6MU40X
Ø 2 5/8"
DL
Discharge line size (sweat)
6MI40X, 6MM30X
Ø 1 3/8"
1
Base mountings
Ø 25.5 mm
5
Crankcase heater
2
Magnetic plug
1" - 16 UN
6
Plug oil charge
1/4"
3
Oil sight glass
1/4"-20 UNC
7
Plug high pressure connection
1/8"
4
Plug low pressure connection
1/8"
Page 27

24 C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
Appendix 2: Tightening torques in Nm
Suction
shut-off valve
1/2"-13 UNC
Discharge
shut-off valve
1/2"-13 UNC
53 - 84 Nm
53 - 84 Nm
SW 19
SW 19
5/8"-11 UNC
Rotalock nut
1 3/4"-12 UNF
104 - 164 Nm
41 - 54 Nm
SW 23.8
SW 50
Bottom plate
3/8"-16 UNC
Mounting foot
3/8"-16 UNC
57 - 68 Nm
57 - 68 Nm
SW 14.2
SW 14.2
Stator cover
1/2"-13 UNC
Housing cover
3/8"-16 UNC
68-79 Nm
57 - 68 Nm
SW 18
SW 14.2
Oil pump
5/16"-18 UNC
Oil sight glass
1/4"-20 UNC
31 - 37 Nm
4.5 - 6 Nm
SW 12.7
SW 11
Oil
pressure switch –
OPS2
60 - 75 Nm
Magnetic plug
1"-16 UN
102 - 136 Nm
SW 25.4
Terminal stud
10-32 UNF
Terminal stud
thermistors
10 - 32 UNF
3-4 Nm
3.4 - 4 Nm
SW 9
SW 9
1/4"-28 UNF
Mounting plate
for terminals
3/8"-16 UNC
5-6.5 Nm
57 - 68 Nm
SW 10
SW 14.2
Cylinder head
1/2"-13 UNC
Bolt for
connecting rod
1/4"-28 UNF
129-149 Nm
15 - 18 Nm
SW 18
Torx screws*
Plug 4
1/4"-18 NPTF
27 - 50 Nm
SW 17.5
* In case of replacement of the piston con-rod assemblies, clean the Torx screws and apply
Loctite 2701.
The ranges of torque values given in this specification are
assembly torques. Torque after joint relaxation must be within
15% of the minimum assembly torque unless re-torque is called
for and must not be above 10% of the maximum assembly
torque.
Disclaimer
1. The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only and are not to
be construed as warranties or guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or
services described herein or their use or applicability.
2. Emerson Climate Technologies GmbH and/or its affiliates (collectively "Emerson"), as
applicable, reserve the right to modify the design or specifications of such products at any
time without notice.
3. Emerson does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any
product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any Emerson product
remains solely with the purchaser or end user.
4. Emerson does not assume responsibility for possible typographic errors contained in this
publication.
Page 28

BENELUX
Josephinastraat 19
NL-6462 EL Kerkrade
Tel. +31 77 324 02 34
Fax +31 77 324 02 35
benelux.sales@emerson.com
UK & IRELAND
Unit 17, Theale Lakes Business Park
Reading, Berkshire RG7 4GB
Tel: +44 1189 83 80 00
Fax: +44 1189 83 80 01
uk.sales@emerson.com
BALKAN
Selska cesta 93
HR-10 000 Zagreb
Tel. +385 1 560 38 75
Fax +385 1 560 38 79
balkan.sales@emerson.com
GERMANY, AUSTRIA & SWITZERLAND
Senefelder Str.
3
DE-63477 Maintal
Tel. +49 6109 605 90
Fax +49 6109 60 59 40
ECTGermany.sales@emerson.com
FRANCE, GREECE & MAGHREB
8, Allée du Moulin Berger
FR-69134 Ecully Cédex
Tel. +33 4 78 66 85 70
Fax +33 4 78 66 85 71
mediterranean.sales@emerson.com
ITALY
Via Ramazzotti, 26
IT-21047 Saronno (VA)
Tel. +39 02 96 17 81
Fax +39 02 96 17 88 88
italy.sales@emerson.com
SPAIN & PORTUGAL
C/ Pujades, 51-55 Box 53
ES-08005 Barcelona
Tel. +34 93 412 37 52
Fax +34 93 412 42 15
iberica.sales@emerson.com
SWEDEN, DENMARK, NORWAY & FINLAND
Norra Koxåsvägen 7
SW-443 38 Lerum
Tel. +46 725 386486
nordic.sales@emerson.com
EASTERN EUROPE & TURKEY
Pascalstr. 65
DE-52076 Aachen
l. +49 2408 929 0
Te
Fax +49 2408 929 525
easterneurope.sales@emerson.com
POLAND
Szturmowa 2
PL-02678 Warsaw
Tel. +48 22 458 92 05
Fax +48 22 458 92 55
poland.sales@emerson.com
RUSSIA & CIS
Emerson LLC
Dubininskaya str. 53, build. 5, 4th floor
115054 Moscow, Russia
Phone: +7 (495) 995 95 59
Fax: +7 (495) 424 88 50
ROMANIA
el. +40 374 13 23 50
T
Fax +40 374 13 28 11
Ancuta.Ionescu@Emerson.com
ASIA PACIFIC
Suite 2503-8, 25/F, Exchange Tower
33 Wang Chiu Road, Kowloon Bay
Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel.
Fax
+852 2866 3108
+852 2520 6227
MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
PO Box 26382
Jebel Ali Free Zone - South, Dubai - UAE
Tel. +971 4 811 81 00
Fax +971 4 886 54 65
mea.sales@emerson.com
For more details, see www.emersonclimate.eu
Connect with us: facebook.com/EmersonClimateEurope
C6.3.1/0116-0716/E
Emerson Climate Technologies - European Headquarters - Pascalstrasse 65 - 52076 Aachen, Germany
Tel. +49 (0) 2408 929 0 - Fax: +49 (0) 2408 929 570 - Internet: www.emersonclimate.eu
The Emerson Climate Technologies logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. Emerson Climate Technologies Inc. is a subsidiary of Emerson Electric Co.
Copeland is a registered trademark and Copeland Scroll is a trademark of Emerson Climate Technologies Inc.. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Emerson Climate Technologies GmbH shall not be liable for errors in the stated capacities, dimensions, etc., as well as typographic errors. Produc ts, specifications, designs
and technical data contained in this document are subject to modification by us without prior notice. Illustrations are not binding.
© 2015 Emerson Climate Technologies, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...