Page 1

Hawk
Digital Servo Drive
Installation Guide
July 2014 (Ver. 1.401)
www.elmomc.com
Page 2

Notice
This guide is delivered subject to the following conditions and restrictions:
• This guide contains proprietary information belonging to Elmo Motion Control Ltd. Such
information is supplied solely for the purpose of assisting users of the Hawk servo drive
in its installation.
• The text and graphics included in this manual are for the purpose of illustration and
reference only. The specifications on which they are based are subject to change without
notice.
• Elmo Motion Control and the Elmo Motion Control logo are trademarks of Elmo Motion
Control Ltd.
• Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Document no. MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Copyright 2014
Elmo Motion Control Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Catalog Number
Related Products
Evaluation Board
Evaluation Board User Manual
Catalog Number: EVA-WHI/GUI/BEL
MAN-EVLBRD-WHI-BEL-GUI.pdf (available on our web site)
Page 3
Revision History
Version Date Details
1.0 May 2008 Initial release
1.1 June 2009 MTCR 05-009-53: Updated Section 3.8.3; added Sections
3.15 and 3.16
1.2 July 2010 MTCR 03-010-02: Updated Section 3.4, Figure 22 and Section
4.1.8
1.3 September 2012 Formatted according to the new template
“Metronome” was replaced by the “Composer” software.
1.301 February 2013 Added a caution and recommendation on the type of
cleaning solution to use for the Elmo unit.
1.400 June 2013 Addition of 50/100, 20/200, R75/60, and R75/48 models
Page 4

Elmo Worldwide
Head Office
Elmo Motion Control Ltd.
60 Amal St., P.O. Box 3078, Petach Tikva 49516
Israel
Tel: +972 (3) 929-2300 • Fax: +972 (3) 929-2322 • info-il@elmomc.com
North America
Elmo Motion Control Inc.
42 Technology Way, Nashua, NH 03060
USA
Tel: +1 (603) 821-9979 • Fax: +1 (603) 821-9943 • info-us@elmomc.com
Europe
Elmo Motion Control GmbH
Hermann-Schwer-Strasse 3, 78048 VS-Villingen
Germany
Tel: +49 (0) 7721-944 7120 • Fax: +49 (0) 7721-944 7130 • info-de@elmomc.com
China
Elmo Motion Control Technology (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
Room 1414, Huawen Plaza, No. 999 Zhongshan West Road, Shanghai (200051)
China
Tel: +86-21-32516651 • Fax: +86-21-32516652 • info-asia@elmomc.com
Asia Pacific
Elmo Motion Control APAC Ltd.
B-601 Pangyo Innovalley, 621 Sampyeong-dong, Bundang-gu, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do,
South Korea (463-400)
Tel: +82-31-698-2010 • Fax: +82-31-801-8078 • info-asia@elmomc.com
Page 5

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Table of Contents
Hawk Installation Guide
Chapter 1: Safety Information .......................................................................................... 8
1.1. Warnings ......................................................................................................................... 9
1.2. Cautions .......................................................................................................................... 9
1.3. Directives and Standards .............................................................................................. 10
1.4. CE Marking Conformance ............................................................................................. 11
1.5. Warranty Information .................................................................................................. 11
Chapter 2: Introduction ................................................................................................. 12
2.1. ExtrIQ Product Family ................................................................................................... 12
2.1.1. Drive Description ........................................................................................... 13
2.2. Product Features .......................................................................................................... 14
2.2.1. Current Control .............................................................................................. 14
2.2.2. Velocity Control ............................................................................................. 14
2.2.3. Position Control ............................................................................................. 14
2.2.4. Communication Options ................................................................................ 14
2.2.5. Feedback Options .......................................................................................... 15
2.2.6. Fault Protection ............................................................................................. 15
2.3. System Architecture ..................................................................................................... 16
2.4. How to Use this Guide .................................................................................................. 16
5
Chapter 3: Installation ................................................................................................... 18
3.1. Site Requirements ........................................................................................................ 18
3.2. Unpacking the Drive Components ................................................................................ 18
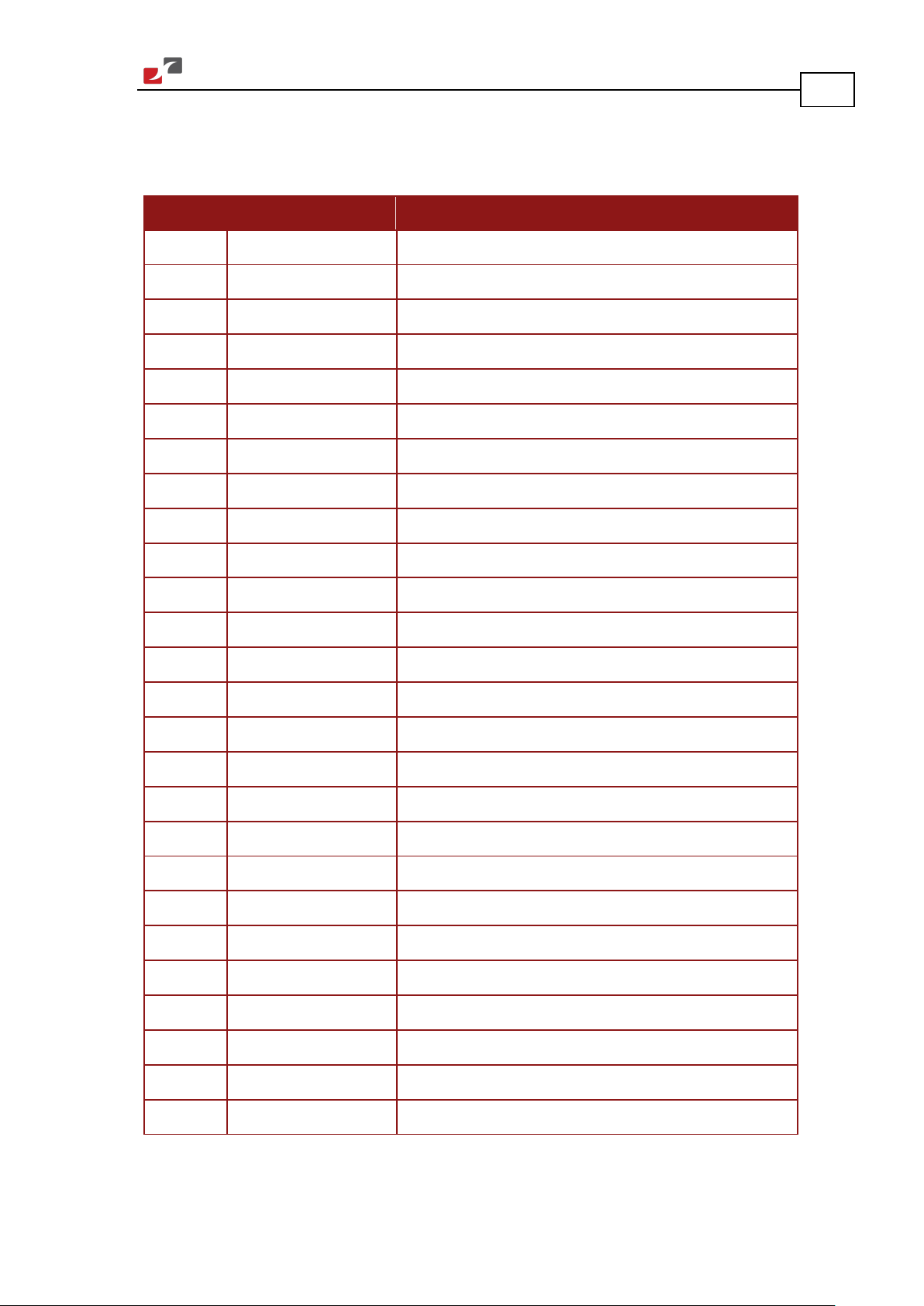
3.3. Pinouts .......................................................................................................................... 19
3.3.1. Connector Types ............................................................................................ 19
3.3.2. Connector J1 .................................................................................................. 20
3.3.3. Connector J2 .................................................................................................. 21
3.4. Mounting the Hawk ...................................................................................................... 22
3.5. Integrating the Hawk on a PCB ..................................................................................... 23
3.5.1. Traces ............................................................................................................. 23
3.5.2. Grounds and Returns ..................................................................................... 23
3.6. The Hawk Connection Diagram .................................................................................... 25
3.7. Main Power and Motor Power ..................................................................................... 26
3.7.1. Connecting Motor Power .............................................................................. 26
3.7.2. Connecting Main Power ................................................................................ 27
3.8. Auxiliary Supply (for drive logic) ................................................................................... 27
3.8.1. Single Supply .................................................................................................. 28
3.8.2. Separate Auxiliary Supply .............................................................................. 28
3.8.3. Shared Supply ................................................................................................ 29
3.9. Main Feedback .............................................................................................................
30
3.10. Auxiliary Feedback ........................................................................................................ 39
Page 6

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Table of Contents
3.10.1. Main and Auxiliary Feedback Combinations ................................................. 40
3.10.2. Auxiliary Feedback: Emulated Encoder Output Option (YA[4]=4) ................. 41
3.10.3. Auxiliary Feedback: Single-Ended Encoder Input Option (YA[4]=2) .............. 43
3.10.4. Auxiliary Feedback: Pulse-and-Direction Input Option (YA[4]=0) ................. 45
3.11. I/Os ............................................................................................................................... 47
3.11.1. Digital Input ................................................................................................... 48
3.11.2. Digital Output ................................................................................................ 50
3.11.3. Analog Input .................................................................................................. 52
3.12. Communications ........................................................................................................... 53
3.12.1. RS-232 Communication ................................................................................. 53
3.12.2. CAN Communication ..................................................................................... 54
3.13. Powering Up ................................................................................................................. 56
3.14. Initializing the System ................................................................................................... 56
3.15. Heat Dissipation............................................................................................................ 56
3.15.1. Hawk Thermal Data ....................................................................................... 56
3.15.2. Heat Dissipation Data .................................................................................... 57
3.15.3. How to Use the Charts ................................................................................... 59
3.16. Evaluation Board and Cable Kit .................................................................................... 60
6
Chapter 4: Technical Specifications ................................................................................ 61
4.1. Features ........................................................................................................................ 61
4.1.1. Motion Control Modes .................................................................................. 61
4.1.2. Advanced Positioning Control Modes ........................................................... 61
4.1.3. Advanced Filters and Gain Scheduling........................................................... 61
4.1.4. Fully Programmable ....................................................................................... 61
4.1.5. Feedback Options .......................................................................................... 62
4.1.6. Input/Output ................................................................................................. 62
4.1.7. Built-In Protection ......................................................................................... 63
4.1.8. Accessories .................................................................................................... 63
4.1.9. Status Indication ............................................................................................ 63
4.1.10. Automatic Procedures ................................................................................... 63
4.2. Hawk Dimensions ......................................................................................................... 64
4.3. Power Ratings for up to 100 V models ......................................................................... 65
4.4. Power Ratings for 200 V models .................................................................................. 66
4.5. Auxiliary Supply ............................................................................................................ 66
4.6. Environmental Conditions ............................................................................................ 67
4.7. Control Specifications ................................................................................................... 68
4.7.1. Current Loop .................................................................................................. 68
4.7.2. Velocity Loop ................................................................................................. 69
4.7.3. Position Loop
................................................................................................. 69
4.8. Feedbacks ..................................................................................................................... 70
4.8.1. Feedback Supply Voltage ............................................................................... 70
4.8.2. Main Feedback Options ................................................................................. 70
4.8.2.1. Incremental Encoder Input ........................................................... 70
4.8.2.2. Digital Halls ................................................................................... 71
Page 7

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Table of Contents
4.8.2.3. Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder ................................. 71
4.8.2.4. Resolver ........................................................................................ 72
4.8.2.5. Tachometer ................................................................................... 72
4.8.2.6. Potentiometer .............................................................................. 73
4.8.3. Auxiliary Feedback Port (output mode YA[4]= 4) .......................................... 74
4.8.4. Auxiliary Feedback Port (input mode YA[4]= 2, 0)......................................... 75
4.9. I/Os ............................................................................................................................... 76
4.9.1. Digital Input Interfaces .................................................................................. 76
4.9.2. Digital Output Interface ................................................................................. 77
4.9.3. Analog Input .................................................................................................. 77
4.10. Communications ........................................................................................................... 78
4.11. Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) .................................................................................. 78
4.12. Compliance with Standards .......................................................................................... 79
7
Page 8

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Chapter 1: Safety Information
Warning:
Caution:
Hawk Installation Guide
In order to operate the Hawk servo drive safely, it is imperative that you implement the safety
procedures included in this installation guide. This information is provided to protect you and
to keep your work area safe when operating the Hawk and accompanying equipment.
Please read this chapter carefully before you begin the installation process.
Before you start, ensure that all system components are connected to earth ground. Electrical
safety is provided through a low-resistance earth connection.
Only qualified personnel may install, adjust, maintain and repair the servo drive. A qualified
person has the knowledge and authorization to perform tasks such as transporting, assembling,
installing, commissioning and operating motors.
The Hawk servo drive contains electrostatic-sensitive components that can be damaged if
handled incorrectly. To prevent any electrostatic damage, avoid contact with highly insulating
materials, such as plastic film and synthetic fabrics. Place the product on a conductive surface
and ground yourself in order to discharge any possible static electricity build-up.
8
To avoid any potential hazards that may cause severe personal injury or damage to the product
during operation, keep all covers and cabinet doors shut.
The following safety symbols are used in this manual:
This information is needed to avoid a safety hazard, which might cause bodily
injury.
This information is necessary for preventing damage to the product or to
other equipment.
www.elmomc.com
Page 9

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Safety Information
1.1. Warnings
• To avoid electric arcing and hazards to personnel and electrical contacts, never
connect/disconnect the servo drive while the power source is on.
• Power cables can carry a high voltage, even when the motor is not in motion. Disconnect
the Hawk from all voltage sources before it is opened for servicing.
• The Hawk servo drive contains grounding conduits for electric current protection. Any
disruption to these conduits may cause the instrument to become hot (live) and dangerous.
• After shutting off the power and removing the power source from your equipment, wait at
least 1 minute before touching or disconnecting parts of the equipment that are normally
loaded with electrical charges (such as capacitors or contacts). Measuring the electrical
contact points with a meter, before touching the equipment, is recommended.
1.2. Cautions
• The Hawk servo drive contains hot surfaces and electrically-charged components during
operation.
9
• The maximum DC power supply connected to the instrument must comply with the
parameters outlined in this guide.
• When connecting the Hawk to an approved 12 to 195 VDC auxiliary power supply, connect
it through a line that is separated from hazardous live voltages using reinforced or double
insulation in accordance with approved safety standards.
• Before switching on the Hawk, verify that all safety precautions have been observed and
that the installation procedures in this manual have been followed.
• Do not clean any of the Hawk drive's soldering with solvent cleaning fluids of pH greater
than 7 (8 to 14). The solvent corrodes the plastic cover causing cracks and eventual damage
to the drive's PCBs.
Elmo recommends using the cleaning fluid Vigon-EFM which is pH Neutral (7).
For further technical information on this recommended cleaning fluid, select the link:
http://www.zestron.com/fileadmin/zestron.com-usa/daten/electronics/Product_TI1s/TI1VIGON_EFM-US.pdf
www.elmomc.com
Page 10

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Safety Information
1.3. Directives and Standards
The Hawk conforms to the following industry safety standards:
Safety Standard Item
Approved IEC/EN 61800-5-1, Safety Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems
Recognized UL 508C Power Conversion Equipment
In compliance with UL 840 Insulation Coordination Including Clearances and
Creepage Distances for Electrical Equipment
10
In compliance with UL 60950-1
(formerly UL 1950)
Safety of Information Technology Equipment
Including Electrical Business Equipment
In compliance with EN 60204-1 Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
The Hawk also conforms to the following military qualitative standards:
Military Qualitative Standard Item
In compliance with MIL-STD-704 Aircraft, Electric Power Characteristics
In compliance with MIL-STD-810 Environmental Engineering Considerations and
Laboratory Tests
In compliance with MIL-STD-1275 Characteristics of 28 Volt DC Electrical Systems in
Military Vehicles
In compliance with MIL-STD-461 Requirements for the Control of Electromagnetic
Interference Characteristics of Subsystems and
Equipment
In compliance with MIL-HDBK-217 Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment
In compliance with ISO-9001:2008 Quality Management
The Hawk servo drive has been developed, produced, tested and documented in accordance
with the relevant standards. Elmo Motion Control is not responsible for any deviation from the
configuration and installation described in this documentation. Furthermore, Elmo is not
responsible for the performance of new measurements or ensuring that regulatory
requirements are met.
www.elmomc.com
Page 11

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Safety Information
1.4. CE Marking Conformance
The Hawk servo drive is intended for incorporation in a machine or end product. The actual end
product must comply with all safety aspects of the relevant requirements of the European
Safety of Machinery Directive 98/37/EC as amended, and with those of the most recent
versions of standards EN 60204-1 and EN 292-2 at the least.
According to Annex III of Article 13 of Council Directive 93/68/EEC, amending Council Directive
73/23/EEC concerning electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits, the
Hawk meets the provisions outlined in Council Directive 73/23/EEC. The party responsible for
ensuring that the equipment meets the limits required by EMC regulations is the manufacturer
of the end product.
1.5. Warranty Information
The products covered in this manual are warranted to be free of defects in material and
workmanship and conform to the specifications stated either within this document or in the
product catalog description. All Elmo drives are warranted for a period of 12 months from the
time of installation, or 18 months from time of shipment, whichever comes first. No other
warranties, expressed or implied — and including a warranty of merchantability and fitness for
a particular purpose — extend beyond this warranty.
11
www.elmomc.com
Page 12
MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Chapter 2: Introduction
ExtrIQ
Hawk Installation Guide
This installation guide describes the Hawk servo drive and the steps for its wiring, installation
and power-up. Following these guidelines ensures maximum functionality of the drive and the
system to which it is connected.
12
2.1.
Elmo Motion Control’s ExtrIQ product family is a set of durable motion control products for
applications operating under extreme environmental conditions. The products are capable of
withstanding the following extreme conditions:
Feature Operation Conditions Range
Ambient
Temperature
Range
Temperature
Shock
Altitude
Maximum
Humidity
Product Family
Non-operating Conditions -50 °C to +100 °C (-58 °F to 212 °F)
Operating conditions -40 °C to +70 °C (-40 °F to 160 °F)
Non-operating conditions -40 °C to +70 °C (-40 °F to 160 °F) within 3
min
Non-operating conditions Unlimited
Operating conditions -400 m to 12,000 m (-1312 to 39370 feet)
Non-operating conditions Up to 95% non-condensing humidity at
35 °C (95 °F)
Operating conditions Up to 95% non-condensing humidity at
25 °C (77 °F), up to 90% non-condensing
humidity at 42 °C (108 °F)
Vibration
Mechanical
Shock
ExtrIQ products have a high power density in the range of 50 W to 65,000 W and current
carrying capacity of up to 140 A (280 A peak). ExtrIQ has been tested using methods and
procedures specified in a variety of extended environmental conditions (EEC) standards
including:
• MIL-STD-704- Aircraft, Electric Power Characteristics
• MIL-STD-810- Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests
• MIL-STD-1275- Characteristics of 28 Volt DC Electrical Systems in Military Vehicles
• MIL-STD-461- Requirements for the Control of Electromagnetic Interference Characteristics
of Subsystems and Equipment
• MIL-HDBK-217- Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment
• ISO-9001:2008
Operating conditions 20 Hz to 2000 Hz, 14.6g
Non-operating conditions ±40g; Half sine, 11 msec
Operating conditions ±20g; Half sine, 11 msec
www.elmomc.com
Page 13

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Introduction
Based on Elmo Motion Control’s innovative ExtrIQ core technology, they support a wide range
of motor feedback options, programming capabilities and communication protocols.
2.1.1. Drive Description
The Hawk series of digital servo drives is designed to deliver “the highest density of power and
intelligence”. The Hawk delivers up to 4.8 kW of continuous power or 8.0 kW of peak power in
a 119. 6 cc (6.95 in³) package (80 x 24.5 x 61 mm or 3.15" x 0.965" x 2.4").
The Hawk is designed for OEMs. It operates from a DC power source in current, velocity,
position and advanced position modes, in conjunction with a permanent-magnet synchronous
brushless motor, DC brush motor, linear motor or voice coil. It is designed for use with any
type of sinusoidal and trapezoidal commutation, with vector control. The Hawk can operate as
a stand-alone device or as part of a multi-axis system in a distributed configuration on a realtime network.
The Hawk drive is easily set up and tuned using Elmo’s Composer software tools. This Windowsbased application enables users to quickly and simply configure the servo drive for optimal use
with their motor. The Hawk, as part of the
Elmo Composer motion control language.
ExtrIQ product line, is fully programmable with
13
Power to the Hawk is provided by a 12 to 195 VDC isolated DC power source (not included with
the Hawk). A “smart” control-supply algorithm enables the Hawk to operate with only one
power supply with no need for an auxiliary power supply for the logic.
If backup functionality is required for storing control parameters in case of power-loss, an
external 12 to 195 VDC isolated supply should be connected (via the +VL terminal on the Hawk)
providing maximum flexibility and backup functionality when needed.
Note: This backup power supply can operate from any voltage source within the 12 to 195
VDC range. This is much more flexible than a standard 24 VDC power supply requirement.
If backup power is not needed, two terminals (VP and VL) are shorted so that the main power
supply will also power the control/logic supply. In this way there is no need for a separate
control/logic supply.
The Hawk is a PCB mounted device which enables efficient and economic implementation.
The Hawk is available in two models:
• The Standard Hawk is a basic servo drive which operates in current, velocity and position
modes including Follower and PT & PVT. It operates simultaneously via RS-232 and CAN DS
301, DS 305, DS 402 communications and features a third-generation programming
environment.
• The Advanced Hawk includes all the motion capabilities and communication options
included in the Standard model, as well as advanced positioning capabilities: ECAM, Dual
Loop and increased program size.
Both versions operate with RS-232 and CAN communication.
www.elmomc.com
Page 14

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Introduction
2.2. Product Features
2.2.1. Current Control
• Fully digital
• Sinusoidal commutation with vector control or trapezoidal commutation with encoder
and/or digital Hall sensors
• 12-bit current loop resolution
• Automatic gain scheduling, to compensate for variations in the DC bus power supply
2.2.2. Velocity Control
• Fully digital
• Programmable PI and FFW (feed forward) control filters
• Sample rate two times current loop sample time
• “On-the-fly” gain scheduling
14
• Automatic, manual and advanced manual tuning and determination of optimal gain and
phase margins
2.2.3. Position Control
• Programmable PIP control filter
• Programmable notch and low-pass filters
• Position follower mode for monitoring the motion of the slave axis relative to a master axis,
via an auxiliary encoder input
• Pulse-and-direction inputs
• Sample time: four times that of the current loop
• Fast event capturing inputs
• PT and PVT motion modes
• Fast output compare (OC)
• Position-based and time-based ECAM mode that supports a non-linear follower mode, in
which the motor tracks the master motion using an ECAM table stored in flash memory
• Dual (position/velocity) loop
2.2.4. Communication Options
Depending on the application, Hawk users can select from two communication options:
• RS-232 serial communication
• CAN for fast communication in a multi-axis distributed environment
www.elmomc.com
Page 15

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Introduction
2.2.5. Feedback Options
• Incremental Encoder – up to 20 Mega-Counts (5 Mega-Pulse) per second
• Digital Halls – up to 2 kHz
• Incremental Encoder with Digital Halls for commutation – up to 20 Mega-Counts per
second for encoder
• Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder – up to 250 kHz (analog signal)
Internal interpolation - up to x4096
Automatic correction of amplitude mismatch, phase mismatch, signals offset
Auxiliary emulated, unbuffered, single-ended, encoder output
• Resolver
Programmable 10 to 15 bit resolution
Up to 512 revolutions per second (RPS)
Auxiliary emulated, unbuffered, single-ended, encoder output
• Tachometer, Potentiometer
15
• Elmo drives provide supply voltage for all the feedback options
2.2.6. Fault Protection
The Hawk includes built-in protection against possible fault conditions, including:
• Software error handling
• Status reporting for a large number of possible fault conditions
• Protection against conditions such as excessive temperature, under/over voltage, loss of
commutation signal, short circuits between the motor power outputs and between each
output and power input/return
• Recovery from loss of commutation signals and from communication errors
www.elmomc.com
Page 16
MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Introduction
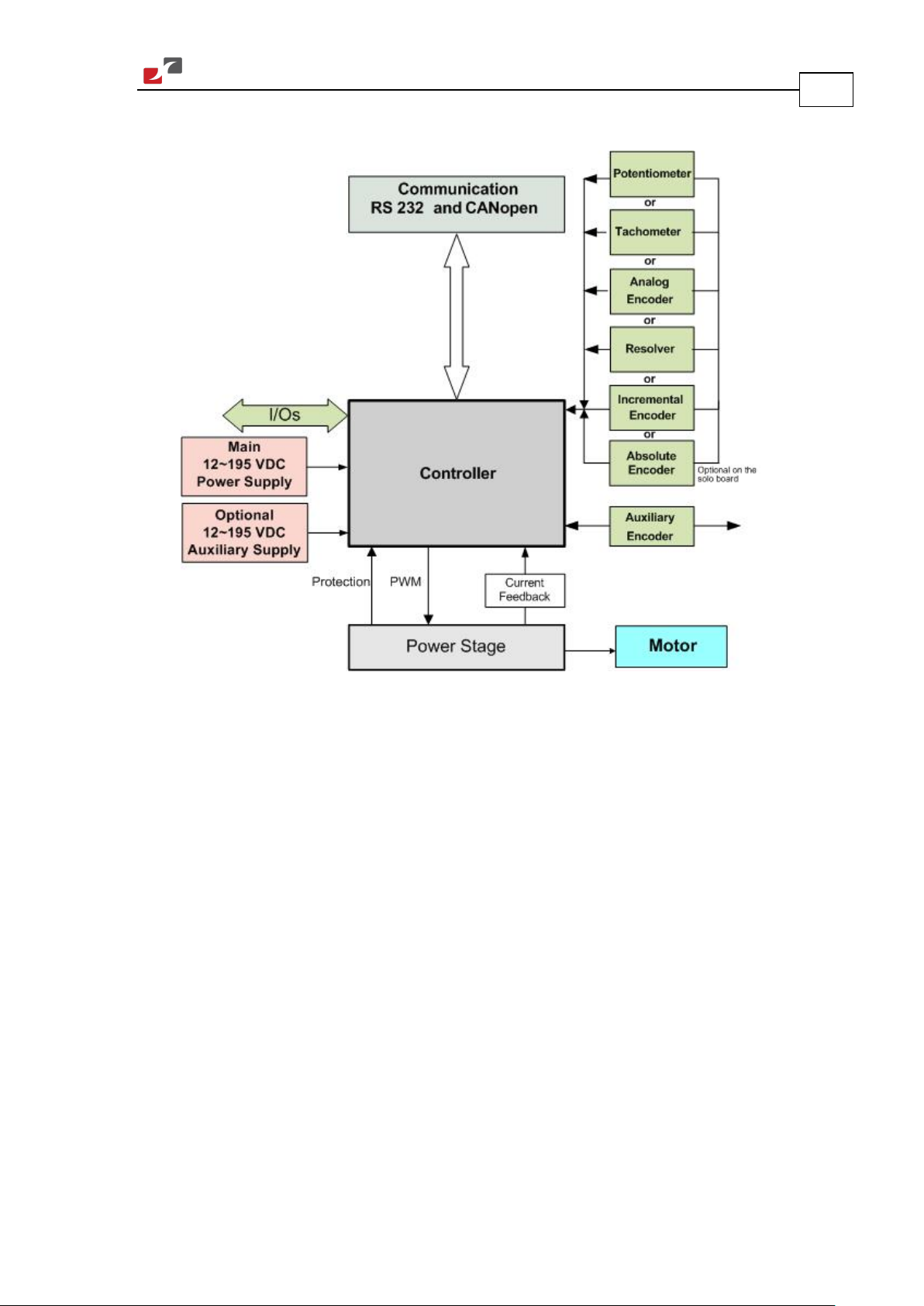
2.3. System Architecture
16
Figure 1: Hawk System Block Diagram
2.4. How to Use this Guide
In order to install and operate your Elmo Hawk servo drive, you will use this manual in
conjunction with a set of Elmo documentation. Installation is your first step; after carefully
reading the safety instructions in the first chapter, the following chapters provide you with
installation instructions as follows:
• Chapter 3, Installation, provides step-by-step instructions for unpacking, mounting,
connecting and powering up the Hawk.
• Chapter 4, Technical Specifications, lists all the drive ratings and specifications.
Upon completing the instructions in this guide, your Hawk servo drive should be successfully
mounted and installed. From this stage, you need to consult higher-level Elmo documentation
in order to set up and fine-tune the system for optimal operation. The following figure
describes the accompanying documentation that you will require.
www.elmomc.com
Page 17

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Introduction
17
Figure 2: Elmo Digital Servo Drive Documentation Hierarchy
As depicted in the previous figure, this installation guide is an integral part of the Hawk
documentation set, comprising:
• The SimplIQ Software Manual, which describes the comprehensive software used with the
Hawk
• The SimplIQ Command Reference Manual, which describes, in detail, each software
command used to manipulate the Hawk motion controller
• The Composer Software Manual, which includes explanations of all the software tools that
are part of Elmo’s Composer software environment
• The Whistle, Bell & Guitar Evaluation Board User Guide contains information about how to
use the Evaluation Board and Cable Kit
www.elmomc.com
Page 18

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Chapter 3: Installation
Hawk Installation Guide
The Hawk must be installed in a suitable environment and properly connected to its voltage
supplies and the motor.
3.1. Site Requirements
You can guarantee the safe operation of the Hawk by ensuring that it is installed in an
appropriate environment.
Feature Value
Ambient operating temperature -40 °C to +70 °C (-40 °F to 160 °F)
Maximum operating altitude 12,000 m (39370 feet)
Maximum non-condensing humidity 95%
Operating area atmosphere No flammable gases or vapors permitted in area
18
Models for extended environmental conditions are available.
Caution:
The Hawk dissipates its heat by convection. The maximum operating ambient
temperature of 0 °C to 40 °C (32 °F to 104 °F) must not be exceeded.
3.2. Unpacking the Drive Components
Before you begin working with the Hawk, verify that you have all of its components, as follows:
• The Hawk servo drive
• The Composer software and software manual
The Hawk is shipped in a cardboard box with Styrofoam protection.
To unpack the Hawk:
1. Carefully remove the servo drive from the box and the Styrofoam.
2. Check the drive to ensure that there is no visible damage to the instrument. If any damage
has occurred, report it immediately to the carrier that delivered your drive.
www.elmomc.com
Page 19
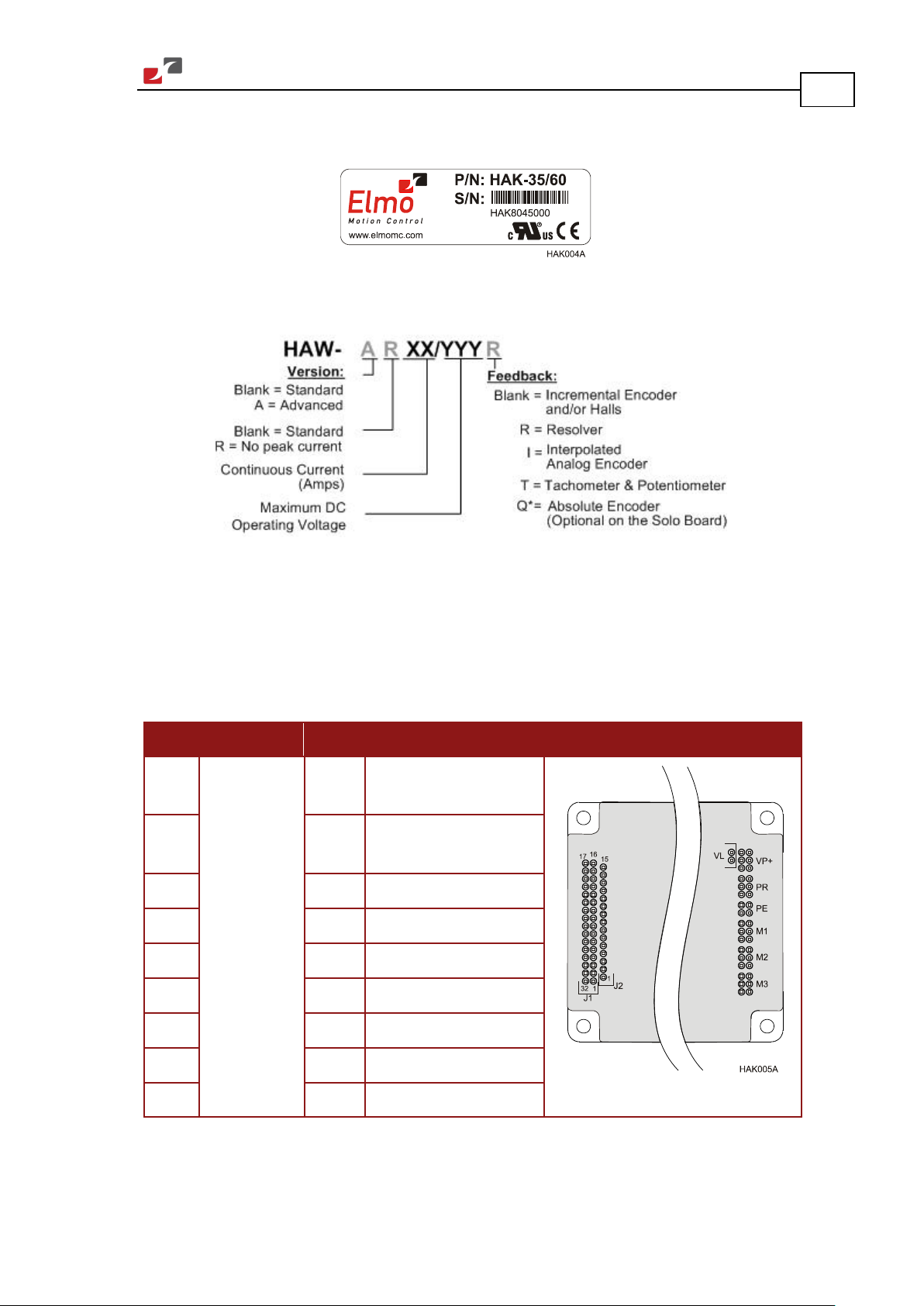
MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3. To ensure that the Hawk you have unpacked is the appropriate type for your requirements,
locate the part number sticker on the side of the Hawk. It looks like this:
The part number at the top gives the type designation as follows:
19
4. Verify that the Hawk type is the one that you ordered, and ensure that the voltage meets
your specific requirements.
3.3. Pinouts
The Hawk has nine connectors.
3.3.1. Connector Types
Pins Type Port Function Connector Location
2x16
15 J2 Main Feedback, Analog
6 VL Auxiliary power input
6 VP+ Positive power input
6 PR Power input return
2 mm pitch
0.51 mm sq
J1 I/O, COMM,
Auxiliary Feedback
Input, LED
4 PE Protective earth
6 M1 Motor power output 1
6 M2 Motor power output 2
2 M3 Motor power output 3
www.elmomc.com
Page 20
MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.3.2. Connector J1
Connector J1: Main Feedback and Analog Input functions
Pin (J1) Signal Function
1 RS232_RX RS232 receive
2 RS232_TX RS232 Transmit
3 RS232_COMRET Communication return
4 AUX PORT CHA Auxiliary port CHA (bidirectional)
5 AUX PORT CHB Auxiliary port CHB (bidirectional)
6 SUPRET Supply return
7 OUT1 Programmable digital output 1
8 OUT2 Programmable digital output 2
9 OUT3 Programmable digital output 3
20
10 OUT4 Programmable digital output 4
11 IN1 Programmable digital input 1
12 IN2 Programmable digital input 2
13 IN3 Programmable digital input 3
14 IN4 Programmable digital input 4
15 IN5 Programmable digital input 5
16 IN6 Programmable digital input 6
17 INRET6 Programmable digital input 6 return
18 INRET5 Programmable digital input 5 return
19 INRET4 Programmable digital input 4 return
20 INRET3 Programmable digital input 3 return
21 INRET2 Programmable digital input 2 return
22 INRET1 Programmable digital input 1 return
23 OUTRET4 Programmable digital output 4 return
24 OUTRET3 Programmable digital output 3 return
25 OUTRET2 Programmable digital output 2 return
26 OUTRET1 Programmable digital output 1 return
www.elmomc.com
Page 21

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
Pin (J1) Signal Function
27 +5 V Encoder +5 V supply voltage.
Maximum output current: 200 mA.
28 COMRET Common return
29 AUX PORT INDEX Auxiliary port index (bidirectional)
30 CAN_COMRET CAN communication return
31 CAN_L CAN_L busline (dominant low)
32 CAN_H CAN_H busline (dominant high)
3.3.3. Connector J2
Connector J2: Communications, Auxiliary Feedback and I/O functions
Pin (J2) Signal Function
21
1 +5V Encoder/Hall +5V supply voltage
Maximum output current: 200 mA
2 SUPRET Supply return
3 ANALIN1+ Analog input 1+
4 ANALIN1- Analog input 1-
5 CHA Channel A input
6 CHA- Channel A input complement
7 CHB Channel B input
8 CHB- Channel B input complement
9 INDEX+ Index input
10 INDEX- Index input complement
11 HA Hall sensor A input
12 HB Hall sensor B input
13 HC Hall sensor C input
14 LED_2_OUT Bi-color indication output 2 (Cathode)
15 LED_1_OUT Bi-color indication output 1 (Anode)
www.elmomc.com
Page 22
MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
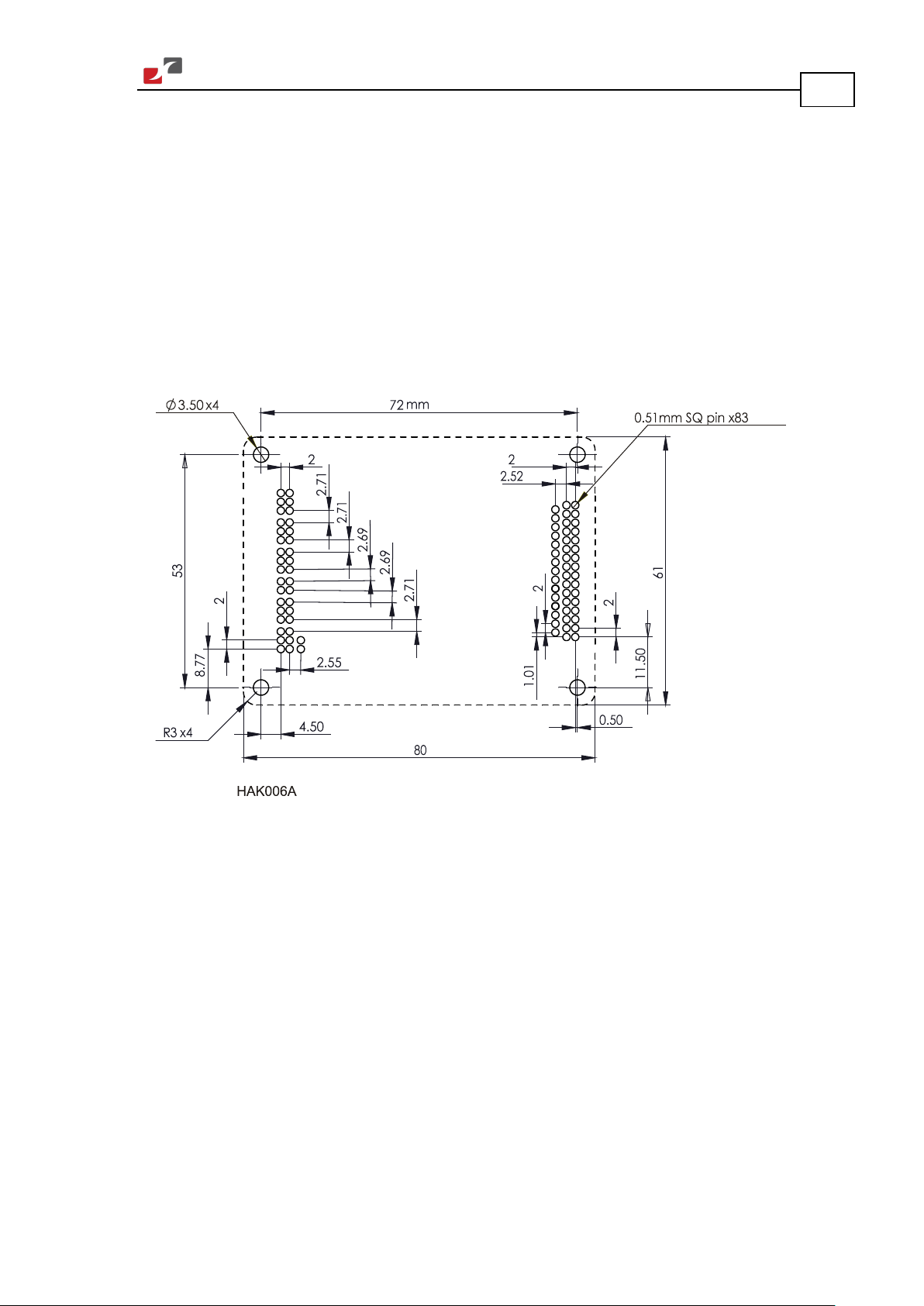
3.4. Mounting the Hawk
The Hawk was designed for mounting on a printed circuit board (PCB) via 2 mm pitch 0.51 mm
square pins. When integrating the Hawk into a device, be sure to leave about 1 cm (0.4")
outward from the heatsink to enable free air convection around the drive. We recommend that
the Hawk be soldered directly to the board. Alternatively, though this is not recommended, the
Hawk can be attached to socket connectors mounted on the PCB. If the PCB is enclosed in a
metal chassis, we recommend that the Hawk be screw-mounted to it as well to help with heat
dissipation. The Hawk has screw-mount holes on each corner of the heatsink for this purpose –
see below.
22
Figure 3: The Hawk Footprint
When the Hawk is not connected to a metal chassis, the application’s thermal profile may
require a solution for heat dissipation due to insufficient air convection. In this case, we
recommend that you connect an external heatsink.
www.elmomc.com
Page 23

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.5. Integrating the Hawk on a PCB
The Hawk is designed to be mounted on a PCB, either by soldering its pins directly to the PCB
or by using suitable socket connectors. In both cases the rules in the following sub-sections
apply.
3.5.1. Traces
1. The size of the traces on the PCB (thickness and width) is determined by the current
carrying capacity required by the application.
The rated continuous current limit (Ic) of the Hawk is the current used for sizing the
motor traces (M1, M2, M3 and PE) and power traces (VP+, PR and PE).
For control, feedbacks and Inputs/outputs conductors the actual current is very small
but “generous” thickness and width of the conductors will contribute to a better
performance and lower interferences.
2. The traces should be as short as possible to minimize EMI and to minimize the heat
generated by the conductors.
3. The spacing between the high voltage conductors (VP+, PR, M1, M2, M3, VL) must be at
least:
23
Surface layer: 1.5 mm
Internal layer: 0.5 mm
Complying with the rules above will help satisfy UL safety standards, MIL-STD-275 and the IPCD-275 standard for non-coated conductors, operating at voltages lower than 200 VDC.
3.5.2. Grounds and Returns
The “Returns” of the Hawk are structured internally in a star configuration. The returns in each
functional block are listed below:
Functional Block Return Pin
Power PR (Power Return)
Internal Switch Mode P.S. PR (Power Return)
RS232 Communications RS232_COMRET (J1/3)
CAN Communications CAN_COMRET (J1/30)
Control section COMRET (J1/28)
Main Feedback SUPRET (J2/2)
Aux. Feedback SUPRET (J1/6)
Analog input ANLRET (J2/2)
The returns above are all shorted within the Hawk in a topology that results in optimum
performance.
1. When wiring the traces of the above functions, on the Integration Board, the Returns of
each function must be wired separately to its designated terminal on the Hawk. DO NOT
www.elmomc.com
Page 24
MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
USE A COMMON GROUND PLANE. Shorting the commons on the Integration Board may
cause performance degradation (ground loops, etc.).
2. Inputs: The 6 inputs are optically isolated from the other parts of the Hawk. Each input has
a separate floating return (INRET1 for input 1 and INRET2 for input 2, etc.). To retain
isolation, the Input Return pins, as well as other conductors on the input circuit, must be
laid out separately.
3. Outputs: The 4 outputs are optically isolated from the other parts of the Hawk. Each
output has a separate floating return (OUTRET1 for output 1 and OUTRET2 for output 2,
etc.) To retain isolation, the Output Return pins, as well as other conductors on the output
circuit, must be laid out separately.
4. Return Traces: The return traces should be as large as possible, but without shorting each
other, and with minimal cross-overs.
5. Main Power Supply and Motor Traces: The power traces must be kept as far away as
possible from the feedback, control and communication traces.
6. PE Terminal: The PE terminal is connected directly to the Hawk’s heat-sink. The heat-sink
serves as an EMI common plane. The PE terminal should be connected to the system's
Protective Earth. Any other metallic parts (such as the chassis) of the assembly should be
connected to the Protective Earth as well.
24
7. Under normal operating conditions, the PE trace carries no current. The only time these
traces carry current is under abnormal conditions (such as when the device has become a
potential shock or fire hazard while conducting external EMI interferences directly to
ground). When connected properly the PE trace prevents these hazards from affecting the
drive.
Caution:
Follow these instructions to ensure safe and proper implementation. Failure to
meet any of the above-mentioned requirements can result in
drive/controller/host failure.
www.elmomc.com
Page 25

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.6. The Hawk Connection Diagram
25
Figure 4: The Hawk Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 26

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.7. Main Power and Motor Power
The Hawk receives power from main supply and delivers power to the motor. The table below
describes the pinout connections to the main power and motor power cables.
Pin Function Cable Pin Positions
VP+ Pos. Power input Power
PR Power return Power
PE Protective earth Power
AC Motor DC Motor
PE Protective earth Motor Motor
M1 Motor phase Motor N/C
M2 Motor phase Motor Motor
26
M3 Motor phase Motor Motor
Note: When connecting several drives to several motors, all should be wired in an identical
manner. This will enable the same ExtrIQ program to run on all drives.
Table 1: Connector for Main Power and Motor
3.7.1. Connecting Motor Power
Connect the M1, M2, M3 and PE pins on the Hawk in the manner described in Section 3.5
(Integrating the Hawk on a PCB). The phase connection is arbitrary as the Composer will
establish the proper commutation automatically during setup. However, if you plan to copy the
setup to other drives, then the phase order on all copy drives must be the same.
Figure 5: AC Motor Power Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 27

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Caution:
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.7.2. Connecting Main Power
Connect the VP+, PR and PE pins on the Hawk in the manner described in Section 3.5
(Integrating the Hawk on a PCB).
Note: The source of the 12 to 195 VDC Main Power Supply must be isolated.
Figure 6: Main Power Supply Connection Diagram (no Auxiliary Supply)
27
3.8. Auxiliary Supply (for drive logic)
Notes for 12 to 195 VDC auxiliary supply connections:
• The source of the 12 to 195 VDC Auxiliary Supply must be isolated.
Connect the VL and PR pins on the Hawk in the manner described in Section 3.5 (Integrating
the Hawk on a PCB).
Pin Function Pin Positions
VL Auxiliary Supply Input
PR Supply Input Return
Power from the Hawk to the motor
must come from the Main Supply
and NOT from the Auxiliary Supply.
Table 2: Auxiliary Supply Pins
www.elmomc.com
Page 28

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.8.1. Single Supply
A single isolated DC power supply can provide power for both the main power and the Auxiliary
(Drive Logic) Supply. The drawing below shows how a single supply is connected.
Figure 7: Single Supply for both the Main Power Supply and the Auxiliary Supply
28
3.8.2. Separate Auxiliary Supply
Power to the Auxiliary Supply can be provided by a separate Auxiliary Supply.
Figure 8: Separate Auxiliary Supply Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 29

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.8.3. Shared Supply
A “Main” DC Power Supply can be designed to supply power to the drive's logic as well as to
the Main Power (see Figure 7 and the upper portion of Figure 9). If backup functionality is
required for continuous operation of the drive’s logic in the event of a main power-out, a
backup supply can be connected by implementing “diode coupling” (see the Aux. Backup
Supply in Figure 9).
Note: Elmo’s Evaluation Board (Catalog number: EVA-WHI/GUI/BEL) implements diode
coupling on the board. When you create your own PCB, you need to implement diode coupling.
29
Figure 9: Shared Supply Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 30

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.9. Main Feedback
The Main Feedback port is used to transfer feedback data from the motor to the drive.
The Hawk can accept any one the following devices as a main feedback mechanism:
• Incremental encoder only
• Incremental encoder with digital Hall sensors
• Digital Hall sensors only
• Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) encoder (option)
• Resolver (option)
• Tachometer (option)
• Potentiometer (option)
• Absolute Encoder (optional on the solo board)
30
www.elmomc.com
Page 31

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Incremental
Interpolated
Resolver
Tachometer and
(J2)
mA
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
31
Encoder
Analog Encoder
Potentiometer
HAW-XX/YYY_ HAW-XX/YYYI HAW-XX/YYYR HAW-XX/YYYT
Signal Function Signal Function Signal Function Signal Function
1 +5V Encoder/Hall
+5V supply
2 SUPRET Supply return SUPRET Supply return SUPRET Supply return SUPRET Supply return
3 ANALIN+ is used for Analog Input
4 ANALIN- is used for Analog Input
5 CHA Channel A A+ Sine A S1 Sine A Tac 1+ Tacho Input 1
6 CHA- Channel A
complement
7 CHB Channel B B+ Cosine B S2 Cosine B Tac 2+ Tacho Input 2
8 CHB- Channel B
complement
9 INDEX Index R+ Reference R1 Vref f=1/TS,
10 INDEX- Index
complement
+5V Encoder/Hall
+5V supply
A- Sine A
complement
B- Cosine B
complement
R- Reference
complement
+5V Encoder/Hall
+5V supply
S3 Sine A
complement
S4 Cosine B
complement
50 mA Max
R2 Vref
complement
f = 1/TS, 50
Max
+5V Encoder/Hall +5V
supply
Pos. (20 V max)
Tac 1- Tacho Input 1
Neg. (20 V max)
Pos. (50 V max)
Tac 2- Tacho Input 2
Neg. (50 V max)
POT Potentiometer
Input (5 V Max)
NC -
11 HA Hall sensor A
input
12 HB Hall sensor B
input
13 HC Hall sensor C
input
14 LED_2_OUT (AOKLED cathode) is used for LED indication
15 LED_1_OUT (AOKLED anode) is used for LED indication
HA - NC - HA Hall sensor A
HB - NC - HB Hall sensor B
HC - NC - HC Hall sensor C
Table 3: Main Feedback Pin Assignments
input
input
input
www.elmomc.com
Page 32

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
32
Figure 10: Main Feedback- Incremental Encoder with Digital Hall Sensors Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 33

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
33
Figure 11: Main Feedback – Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 34

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
34
Figure 12: Main Feedback – Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder with Digital Hall
Sensors Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 35

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
35
Figure 13: Main Feedback – Resolver Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 36

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
36
Figure 14: Main Feedback – Resolver and Digital Hall Sensors Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 37

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
37
Figure 15: Main Feedback – Tachometer Feedback with Digital Hall Sensors
Connection Diagram for Brushless Motors
Figure 16: Main Feedback – Tachometer Feedback Connection Diagram for Brush Motors
www.elmomc.com
Page 38

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
38
Figure 17: Main Feedback – Potentiometer Feedback with Digital Hall Sensors
Connection Diagram for Brushless Motors
Figure 18: Main Feedback –
Potentiometer Feedback Connection Diagram for Brush Motors and Voice Coils
www.elmomc.com
Page 39

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.10. Auxiliary Feedback
For auxiliary feedback, select one of the following options:
a. Single-ended emulated encoder outputs, used to provide emulated encoder signals to
another controller or drive. The Emulated Encoder Output Option is only available when
using a Resolver, Analog Encoder, Tachometer, Potentiometer or Absolute Encoder as the
main feedback device. The absolute model provides differential emulated encoder output.
This option can be used when:
The Hawk is used as a current amplifier to provide position data to the position
controller.
The Hawk is used in velocity mode, to provide position data to the position controller.
The Hawk is used as a master in follower or ECAM mode.
b. Single-ended auxiliary encoder input, for the input of position data of the master encoder
in follower or ECAM mode.
c. Pulse-and-direction input, for single-ended input of pulse-and-direction position
commands.
39
When using one of the auxiliary feedback options, the relevant functionality is software
selected for that option. Refer to the SimplIQ Command Reference Manual for detailed setup
information.
www.elmomc.com
Page 40

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.10.1. Main and Auxiliary Feedback Combinations
The Main Feedback is always used in motion control devices whereas Auxiliary Feedback is
often, but not always used. The Auxiliary Feedback connector on the Hawk has three bidirectional pins (CHA, CHB and INDEX). When used in combination with Main Feedback, the
Auxiliary Feedback can be set, by software, as follows:
40
Main
Feedback
Software
Setting
Incremental
Encoder Input
Interpolated
Analog
(Sin/Cos)
Encoder Input
Resolver
Input
YA[4] = 4
(Aux. Feedback: output)
Auxiliary Feedback
(Aux. Feedback: input)
YA[4] = 2
YA[4] = 0
(Aux. Feedback: input)
Potentiometer
or
Tachometer
Input
Typical
Applications
Analog Encoder applications where
position data is required in the
Encoder’s quadrature format.
Resolver applications where position
data is required in the Encoder’s
quadrature format.
Tachometer or potentiometer
applications where position data is
required in the Encoder’s quadrature
format.
Any application where two
feedbacks are used by the
drive.
The Auxiliary Feedback port
serves as an input for the
auxiliary incremental
encoder.
For applications such as
Follower, ECAM, or Dual
Loop.
Any application where two
feedbacks are used by the
drive.
The Auxiliary Feedback port
serves as an input for Pulse
& Direction Commands.
www.elmomc.com
Page 41

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.10.2. Auxiliary Feedback: Emulated Encoder Output Option
(YA[4]=4)
Pin (J1) Signal Function Pin Positions
28 COMRET Common return
29 INDEX Auxiliary index output
5 CHBO Auxiliary Channel B output
4 CHAO Auxiliary Channel A output
Notes:
• The Emulated Encoder Output Option is only available
when using a Resolver, Analog Encoder, Tachometer
or Potentiometer as the main feedback device.
• The Hawk’s Auxiliary Feedback is single-ended. When
mounted on an integration board, circuitry can be
added to make it differential (Figure 21 (highly
recommended)).
41
Table 4: Emulated Single-Ended Encoder Output Pin Assignments
Figure 19: Emulated Encoder Direct Output – Acceptable Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 42

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
42
Figure 20: Emulated Encoder Buffered Output – Recommended Connection Diagram
Figure 21: Emulated Encoder Differential Output – Highly Recommended Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 43

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.10.3. Auxiliary Feedback: Single-Ended Encoder Input Option (YA[4]=2)
Pin (J1) Signal Function Pin Positions
27 +5 V Encoder supply voltage
6 SUPRET Supply return
29 INDEX Auxiliary index input
5 CHB Auxiliary channel B input
4 CHA Auxiliary channel A input
Note: The Hawk’s Auxiliary Feedback is single-ended.
When mounted on an integration board, circuitry can be
added to make it differential (Figure 24 (highly
recommended)).
43
Table 5: Single-Ended Auxiliary Encoder Pin Assignment
Figure 22: Single-Ended Auxiliary Encoder Input - Acceptable Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 44

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
44
Figure 23: Single-ended Auxiliary Encoder Input - Recommended Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 45

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
45
Figure 24: Differential Auxiliary Encoder Input – Highly Recommended Connection Diagram
3.10.4. Auxiliary Feedback: Pulse-and-Direction Input Option (YA[4]=0)
Pin (J1) Signal Function Pin Positions
28 COMRET Common return
5 DIR/CHB Direction input (push/pull 5 V or
open collector)
4 PULS/CHA Pulse input (push/pull 5 V or open
collector)
Note: The Hawk’s Auxiliary Feedback is single-ended. When
mounted on an integration board, circuitry can be added to
make it differential (Figure 27 (highly recommended)).
Table 6: Pulse-and-Direction Pin Assignments
www.elmomc.com
Page 46

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
Figure 25: Pulse-and-Direction Auxiliary Encoder Input – Direct Connection Diagram
46
Figure 26: Pulse-and-Direction Auxiliary Encoder Input – Buffered Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 47

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
Figure 27: Pulse-and-Direction Auxiliary Encoder Input – Differential Connection Diagram,
Highly Recommended
47
3.11. I/Os
The Hawk has:
• 6 Digital Inputs
• 4 Digital Outputs
• 1 Analog Input
I/O J1 J2 Total
Digital Input 6 - 6
Digital Output 4 - 2
Analog Input - 1 1
www.elmomc.com
Page 48

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.11.1. Digital Input
Each of the pins below can function as an independent input.
Pin (J1) Signal Function Pin Positions
11 IN1 Programmable input 1
(general purpose, RLS, FLS, INH)
12 IN2 Programmable input 2
(general purpose, RLS, FLS, INH)
13 IN3 Programmable input 3
(general purpose, RLS, FLS, INH)
14 IN4 Programmable input 4
(general purpose, RLS, FLS, INH)
15 IN5 Hi-Speed Programmable input 5
(event capture, Main Home,
general purpose, RLS, FLS, INH)
48
16 IN6 Hi-Speed Programmable input 6
(event capture, Auxiliary Home,
general purpose, RLS, FLS, INH)
17 INRET6 Programmable input 6 return
18 INRET5 Programmable input 5 return
19 INRET4 Programmable input 4 return
20 INRET3 Programmable input 3 return
21 INRET2 Programmable input 2 return
22 INRET1 Programmable input 1 return
Table 7: Digital Input Pin Assignments
www.elmomc.com
Page 49

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
49
Figure 28: Digital Input Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 50

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.11.2. Digital Output
Pin (J1) Signal Function Pin Positions
7 OUT1 High-Speed Programmable digital
output 1
8 OUT2 Programmable digital output 2
9 OUT3 Programmable digital output 3
10 OUT4 Programmable digital output 4
26 OUTRET1 Programmable digital output 1 return
25 OUTRET2 Programmable digital output 2 return
24 OUTRET3 Programmable digital output 3 return
23 OUTRET4 Programmable digital output 4 return
50
Table 8: Digital Output Pin Assignment
www.elmomc.com
Page 51

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
51
Figure 29: Digital Output Connection Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 52

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.11.3. Analog Input
Pin (J2) Signal Function Pin Positions
3 ANLIN1+ Analog input 1+
4 ANLIN1- Analog input 1-
2 ANLRET Analog ground
52
Table 9: Analog Input Pin Assignments
Figure 30: Analog Input with Single-Ended Source
www.elmomc.com
Page 53

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.12. Communications
The communication interface may differ according to the user’s hardware. The Hawk can
communicate using the following options:
a. RS-232, full duplex
b. CAN
RS-232 communication requires a standard, commercial 3-core null-modem cable connected
from the Hawk to a serial interface on the PC. The interface is selected and set up in the
Composer software.
In order to benefit from CAN communication, the user must have an understanding of the basic
programming and timing issues of a CAN network.
For ease of setup and diagnostics of CAN communication, RS-232 and CAN can be used
simultaneously.
3.12.1. RS-232 Communication
53
Notes for connecting the RS-232 communication cable:
• Connect the shield to the ground of the host (PC). Usually, this connection is soldered
internally inside the connector at the PC end. You can use the drain wire to facilitate
connection.
• The RS-232 communication port is non-isolated.
• Ensure that the shield of the cable is connected to the shield of the connector used for RS-
232 communications. The drain wire can be used to facilitate the connection.
Pin (J1) Signal Function Pin Location
1 RS232_Rx RS-232 receive
2 RS232_Tx RS-232 transmit
3 RS232_COMRET Communication return
Table 10: RS-232 Pin Assignments
www.elmomc.com
Page 54

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
Figure 31: RS-232 Connection Diagram
3.12.2. CAN Communication
54
Notes for connecting the CAN communication cable:
• Connect the shield to the ground of the host (PC). Usually, this connection is soldered
internally inside the connector at the PC end. You can use the drain wire to facilitate
connection.
• Ensure that the shield of the cable is connected to the shield of the connector used for
communications. The drain wire can be used to facilitate the connection.
• Make sure to have a 120-Ω resistor termination at each of the two ends of the network
cable.
• The Hawk’s CAN port is non-isolated.
Pin (J1) Signal Function
Pin Positions
30 CAN_GND CAN ground
31 CAN_L CAN_L busline (dominant low)
32 CAN_H CAN_H busline (dominant high)
Table 11: CAN - Pin Assignments
www.elmomc.com
Page 55

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
55
Figure 32: CAN Network Diagram
Caution:
When installing CAN communication, ensure that each servo drive is allocated a
unique ID. Otherwise, the CAN network may hang.
www.elmomc.com
Page 56

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.13. Powering Up
After the Hawk is connected to its device, it is ready to be powered up.
Caution:
Before applying power, ensure that the DC supply is within the specified range
and that the proper plus-minus connections are in order.
3.14. Initializing the System
After the Hawk has been connected and mounted, the system must be set up and initialized.
This is accomplished using the Composer, Elmo’s Windows-based software application. Install
the application and then perform setup and initialization according to the directions in the
Composer Software Manual.
3.15. Heat Dissipation
The best way to dissipate heat from the Hawk is to mount it so that its heatsink faces up. For
best results leave approximately 10 mm of space between the Hawk's heatsink and any other
assembly.
56
3.15.1. Hawk Thermal Data
• Heat dissipation capability (θ): Approximately 8 °C/W.
• Thermal time constant: Approximately 360 seconds (thermal time constant means that the
Hawk will reach 2/3 of its final temperature after 6 minutes).
• Shut-off temperature: 86 °C to 88 °C (measured on the heatsink)
www.elmomc.com
Page 57

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk 48V Power Dissipation
Hawk 60V Power Dissipation
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.15.2. Heat Dissipation Data
Heat Dissipation is shown in graphically below:
57
www.elmomc.com
Page 58

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk 100V Power Dissipation
Hawk 200V Power Dissipation
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
58
www.elmomc.com
Page 59

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.15.3. How to Use the Charts
The charts above are based upon theoretical worst-case conditions. Actual test results show
30% to 50% better power dissipation.
To determine if your application needs a heatsink:
1. Allow maximum heatsink temperature to be 80 °C or less.
2. Determine the ambient operating temperature of the Hawk.
3. Calculate the allowable temperature increase as follows:
for an ambient temperature of 40 °C , ΔT= 80 °C – 40 °C = 40 °C
4. Use the chart to find the actual dissipation power of the drive. Follow the voltage curve to
the desired output current and then find the dissipated power.
5. If the dissipated power is below 5 W the Hawk will need no additional cooling.
Note: The chart above shows that no heatsink is needed when the heatsink temperature is
80 °C, ambient temperature is 40 °C and heat dissipated is 5 Watts.
59
www.elmomc.com
Page 60

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Installation
3.16. Evaluation Board and Cable Kit
A circuit board is available for evaluating the Hawk. It comes with standard terminal blocks for
power connections and D-sub plugs/sockets for signal connections. The Evaluation Board is
provided with a cable kit.
60
Figure 33: The Evaluation Board (available upon request)
Evaluation Board
Evaluation Board User Manual
Catalog Number: EVA-WHI/GUI/BEL
MAN-EVLBRD-WHI-BEL-GUI.pdf (available on our web site)
www.elmomc.com
Page 61

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Chapter 4: Technical Specifications
Hawk Installation Guide
This chapter provides detailed technical information regarding the Hawk. This includes its
dimensions, power ratings, the environmental conditions under which it can be used, the
standards to which it complies and other specifications.
4.1. Features
The Hawk's features determine how it controls motion, as well as how it processes host
commands, feedback and other input.
4.1.1. Motion Control Modes
• Current/Torque - up to 14 kHz sampling rate
• Velocity - up to 7 kHz sampling rate
• Position - up to 3.5 kHz sampling rate
61
4.1.2. Advanced Positioning Control Modes
• PTP, PT, PVT, ECAM, Follower, Dual Loop, Current Follower
• Fast event capturing inputs
• Fast output compare (OC)
• Motion Commands: Analog current and velocity, PWM current and velocity, digital (SW)
and Pulse and Direction
4.1.3. Advanced Filters and Gain Scheduling
• “On-the-Fly” gain scheduling of current and velocity
• Velocity and position with “1-2-4” PIP controllers
• Automatic commutation alignment
• Automatic motor phase sequencing
4.1.4. Fully Programmable
• Third generation programming structure with motion commands – “Composer”
• Event capturing interrupts
• Event triggered programming
www.elmomc.com
Page 62

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.1.5. Feedback Options
• Incremental Encoder – up to 20 Mega-Counts (5 Mega-Pulse) per second
• Digital Halls – up to 2 kHz
• Incremental Encoder with Digital Halls for commutation – up to 20 Mega-Counts per
second for encoder
• Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder – up to 250 kHz (analog signal)
Internal Interpolation - up to x4096
Automatic Correction of amplitude mismatch, phase mismatch, signal offset
Emulated encoder outputs, single-ended, unbuffered of the Analog encoder
• Analog Hall Sensor
• Resolver
Programmable 10 to 15 bit resolution
Up to 512 revolutions per second (RPS)
Emulated encoder outputs, single-ended, unbuffered of the Resolver.
62
• Auxiliary Encoder inputs (ECAM, follower, etc.) single-ended, unbuffered.
• Tachometer & Potentiometer
• The Hawk can provide power (5 V, 2x200 mA max) for Encoders, Resolver or Halls.
4.1.6. Input/Output
• One Analog Input – up to 14-bit resolution
• Six separate programmable Digital Inputs, optically isolated (two of which are fast event
capture inputs).
Inhibit/Enable motion
Software and analog reference stop
Motion limit switches
Begin on input
Abort motion
Homing
General-purpose
• Four separate programmable Digital Outputs, optically isolated (open collector) one with
fast output compare (OC):
Brake Control
Amplifier fault indication
General-purpose
Servo enable indication
• Pulse and Direction inputs (single-ended)
• PWM current command output for torque and velocity
www.elmomc.com
Page 63

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.1.7. Built-In Protection
• Software error handling
• Abort (hard stops and soft stops)
• Status reporting
• Protection against:
Shorts between motor power outputs
Shorts between motor power outputs and power input/return
Failure of internal power supplies
Over-heating
• Continuous temperature measurement. Temperature can be read on the fly; a
warning can be initiated x degrees before temperature disable is activated.
Over/Under voltage
Loss of feedback
Following error
Current limits
63
4.1.8. Accessories
• External heatsink (TBD)
• Evaluation Board, see Section 3.16 for a picture and more details.
Catalog number: EVA-WHI/GUI/BEL
• Cable Kit, see Section 3.16 for more details.
Catalog number: CBL-EVAUNIKIT01
4.1.9. Status Indication
• Output for a bi-color LED
4.1.10. Automatic Procedures
• Commutation alignment
• Phase sequencing
• Current loop offset adjustment
• Current loop gain tuning
• Current gain scheduling
• Velocity loop offset adjustment
• Velocity gain tuning
• Velocity gain scheduling
• Position gain tuning
www.elmomc.com
Page 64

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.2. Hawk Dimensions
64
www.elmomc.com
Page 65

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.3. Power Ratings for up to 100 V models
Feature Units
35/48
20/60
25/60
35/60
20/100
25/100
50/100
R45/48
R75/48
R45/60
R75/60
Minimum supply voltage VDC 11 14 23 11
Nominal supply voltage VDC 42 50 85 42 50 85
Maximum supply voltage VDC 48 59 95 48 59 95
14 23
65
R35/100
Maximum auxiliary supply
voltage
Maximum continuous
power output
Efficiency at rated power
(at nominal conditions)
Maximum output voltage 97% of DC bus voltage at f=22 kHz
Amplitude sinusoidal/DC
continuous current (Ic)
Sinusoidal continuous
RMS current limit (Ic)
Peak current limit A 2 x Ic No peak
Weight g (oz) 165 g (5.8 oz)
Dimensions mm (in)
Digital in/Digital out/ Analog in 6/4/1
Mounting method PCB mount
VDC 48 59 95 48 59 95
W 1300 960 1200 1700 1600 2000 4000 1700 3000 2200 3700 2800
% > 97
A 35 20 25 35 20 25 50 45 75 45 75 35
A 25 14.1 17.7 24.8 14.1 17.7 35.3 31.8 53 31.8 53 24.8
80 x 61 x 24.5 (3.15" x 2.4" x 0.965")
www.elmomc.com
Page 66

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.4. Power Ratings for 200 V models
Feature Units
66
10/200
Minimum supply voltage VDC 46
Nominal supply voltage VDC 170
Maximum supply voltage VDC 195
Maximum auxiliary supply voltage VDC 195
Maximum continuous power output W 1600 2700 3200 4800
Efficiency at rated power (at nominal
conditions)
Maximum output voltage 97% of DC bus voltage at f=22 kHz
Amplitude sinusoidal/DC continuous
current (Ic)
Sinusoidal continuous RMS current limit
(Ic)
Peak current limit A 2 x Ic No peak
Weight g (oz) 165 g (5.8 oz)
Dimensions mm (in) 80 x 61 x 24.5 (3.15" x 2.4" x 0.965")
Digital in/Digital out/ Analog in 6/4/1
% > 97
A 10 17 20 30
A 7 12 14.1 21.2
17/200
20/200
R30/200
Mounting method PCB mount
The following notes apply to all the above Power Rating models up to 100 V and 200 V.
Note on current ratings: The current ratings of the Hawk are given in units of DC amperes
(ratings that are used for trapezoidal commutation or DC motors). The RMS (sinusoidal
commutation) value is the DC value divided by 1.41.
4.5. Auxiliary Supply
Feature Details
Auxiliary power supply Isolated DC source only
Auxiliary supply input voltage 12 VDC to 195 VDC
Auxiliary supply input power 7 VA
www.elmomc.com
Page 67

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.6. Environmental Conditions
Feature Operation Conditions Range
67
Ambient
Temperature
Range
Temperature
Shock
Altitude
Maximum
Humidity
Vibration
Mechanical
Shock
Non-operating conditions -50 °C to +100 °C (-58 °F to 212 °F)
Operating conditions -40 °C to +70 °C (-40 °F to 160 °F)
Non-operating conditions -40 °C to +70 °C (-40 °F to 160 °F) within 3
min
Non-operating conditions Unlimited
Operating conditions -400 m to 12,000 m (-1312 to 39370 feet)
Non-operating conditions Up to 95% non-condensing humidity at 35 °C
(95 °F)
Operating conditions Up to 95% non-condensing humidity at 25 °C
(77 °F), up to 90% non-condensing humidity
at 42 °C (108 °F)
Operating conditions 20 Hz to 2000 Hz, 14.6g
Non-operating conditions ±40g; Half sine, 11 msec
Operating conditions ±20g; Half sine, 11 msec
www.elmomc.com
Page 68

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.7. Control Specifications
4.7.1. Current Loop
Feature Details
Controller type Vector, digital
68
Compensation for bus voltage
“On-the-fly” automatic gain scheduling
variations
Motor types
• AC brushless (sinusoidal)
• DC brushless (trapezoidal)
• DC brush
• Linear motors
• “Voice” coils
Current control
• Fully digital
• Sinusoidal with vector control
• Programmable PI control filter based on a pair of
PI controls of AC current signals and constant
power at high speed
Current loop bandwidth < 2.5 kHz
Current sampling time
Programmable 70 to 100 µsec
Current sampling rate Up to 16 kHz; default 11 kHz
www.elmomc.com
Page 69

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.7.2. Velocity Loop
Feature Details
Controller type PI
69
Velocity control
• Fully digital
• Programmable PI and FFW control filters
• “On-the-fly” gain scheduling
• Automatic, manual and advanced manual tuning
Velocity and position feedback
options
• Incremental Encoder
• Digital Halls
• Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder (optional)
• Resolver (optional)
• Tachometer and Potentiometer (optional)
Note: With all feedback options, 1/T with automatic
mode switching is activated (gap, frequency and
derivative).
Velocity loop bandwidth <350 Hz
Velocity sampling time
140 to 200 µsec (2x current loop sample time)
Velocity sampling rate Up to 8 kHz; default 5.5 kHz
Velocity command options
• Analog
• Internally calculated by either jogging or step
Note: All software-calculated profiles support on-the-fly
changes.
4.7.3. Position Loop
Feature Details
Controller type “1-2-4” PIP
Position command options
Position loop bandwidth <80 Hz
Position sampling time
Position sampling rate Up to 4 kHz; default 2.75 kHz
• Software
• Pulse and Direction
• Analog Potentiometer
280 to 400 µsec (4x current loop sample time)
www.elmomc.com
Page 70

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.8. Feedbacks
The Hawk can receive and process feedback input from diverse types of devices.
4.8.1. Feedback Supply Voltage
The Hawk has two feedback ports (Main and Auxiliary). The Hawk supplies voltage only to the
main feedback device and to the auxiliary feedback device if needed.
Feature Details
Main encoder supply voltage 5 V +5% @ 200 mA maximum
Auxiliary encoder supply voltage 5 V +5% @ 200 mA maximum
4.8.2. Main Feedback Options
4.8.2.1. Incremental Encoder Input
Feature Details
70
Encoder format
• A, B and Index
• Differential
• Quadrature
Interface RS-422
Input resistance
Differential: 120 Ω
Maximum incremental encoder frequency Maximum absolute: 5 MHz pulses
Minimum quadrature input period (PIN) 112 nsec
Minimum quadrature input high/low period (PHL) 56 nsec
Minimum quadrature phase period (PPH) 28 nsec
Maximum encoder input voltage range
Common mode: ±7 V
Differential mode: ±7 V
Figure 34: Main Feedback - Encoder Phase Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 71

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Signal offsets
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.8.2.2. Digital Halls
Feature Details
71
Halls inputs
• H
, HB, HC.
A
• Single ended inputs
• Built in hysteresis of 1 V for noise immunity
Input voltage Nominal operating range: 0 V < V
Maximum absolute: -1 V < V
High level input voltage: V
Low level input voltage: V
In_Hall
InHigh
InLow
> 2.5 V
< 1 V
< 5 V
In_Hall
< 15 V
Input current Sink current (when input pulled to the common): 5
mA
Maximum frequency f
MAX
: 2 kHz
4.8.2.3. Interpolated Analog (Sine/Cosine) Encoder
Feature Details
Analog encoder format
Analog input signal level
• Sine and Cosine signals
• Offset voltage: 2.2 V to 2.8 V
• Differential, 1 V peak to peak
Input resistance
Maximum analog signal frequency f
Differential 120 Ω
: 250 kHz
MAX
Interpolation multipliers Programmable: x4 to x4096
Maximum “counts” frequency 80 mega-counts/sec “internally”
Automatic errors correction
Signal amplitudes mismatch
Signal phase shift
Encoder outputs
See Auxiliary Encoder Outputs specifications (
4.8.3)
www.elmomc.com
Page 72

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.8.2.4. Resolver
Feature Details
72
Resolver format
• Sine/Cosine
• Differential
Input resistance
Differential 2.49 kΩ
Resolution Programmable: 10 to 15 bits
Maximum electrical frequency (RPS) 512 revolutions/sec
Resolver transfer ratio 0.5
Reference frequency 1/Ts (Ts = sample time in seconds)
Reference voltage Supplied by the Hawk
Reference current up to ±50 mA
Encoder outputs
See Auxiliary Encoder Output specifications (
4.8.2.5. Tachometer*
Feature Details
Tachometer format Differential
4.8.3)
Maximum operating differential voltage for TAC1+, TAC1- ±20 V
Maximum absolute differential input voltage for TAC1+, TAC1- ±25 V
Maximum operating differential voltage for TAC2+, TAC2- ±50 V
Maximum absolute differential input voltage for TAC2+, TAC2- ±60 V
Input resistance for TAC1+, TAC1- 46 kΩ
Input resistance for TAC2+, TAC2- 100 kΩ
Resolution 14 bit
* Only one Tachometer port can be used at a time (either TAC1+/TAC1- or TAC2+/TAC2-).
TAC1+/TAC1- is used in applications with having a Tachometer of less than 20 V.
TAC2+/TAC2- is used in applications with having a Tachometer of between 20 V and 50 V.
www.elmomc.com
Page 73

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.8.2.6. Potentiometer
Feature Details
Potentiometer Format Single-ended
Operating Voltage Range 0 to 5 V supplied by the Hawk
Potentiometer Resistance 100 Ω to 1 kΩ … above this range, linearity is affected
detrimentally
Input Resistance 100 kΩ
Resolution 14 bit
73
www.elmomc.com
Page 74

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.8.3. Auxiliary Feedback Port (output mode YA[4]= 4)
Feature Details
74
Emulated output
• A, B, Index
• Single ended
Output current capability Maximum output current: IOH (max) = 2 mA
Available as options
High level output voltage: V
Minimum output current: I
Low level output voltage: V
• Emulated encoder outputs of analog encoder
> 3.0 V
OH
= 2 mA
OL
< 0.4 V
OL
• Emulated encoder outputs of the resolver
• Emulated encoder outputs of the tachometer
• Emulated encoder outputs of the potentiometer
Maximum frequency f
Edge separation between A & B
: 5 MHz pulses/output
MAX
Programmable number of clocks to allow adequate
noise filtering at remote receiver of emulated encoder
signals
Index (marker): Length of pulse is one quadrature (one quarter of an
encoder cycle) and synchronized to A&B
Figure 35: Auxiliary Feedback - Encoder Phase Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 75

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.8.4. Auxiliary Feedback Port (input mode YA[4]= 2, 0)
Feature Details
75
Encoder input,
pulse and direction input
• A, B, Index
• Single ended
Input voltage VIn Low: 0 V < VIL < 0.8 V
V
High: 2 V < VIH < 5 V
In
Maximum absolute voltage: 0 < V
< 5.5 V
In
Input current: ±1 µA
Available as options
• Single-ended Encoder inputs
• Pulse and Direction inputs
Edge separation between A & B Programmable number of clocks to allow adequate
noise filtering at remote receiver of emulated encoder
signals
Index (marker) Length of pulse is one quadrature (one quarter of an
encoder cycle) and synchronized to A&B
Figure 36: Auxiliary Feedback - Encoder Phase Diagram
www.elmomc.com
Page 76

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Rin = 1.43K
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.9. I/Os
The Hawk has:
• 6 Digital Inputs
• 4 Digital Outputs
• 1 Analog Input
4.9.1. Digital Input Interfaces
Feature Details
76
Type of input
• Optically isolated
• Each input has its own return
Input current
Iin = 2.4 mA @ Vin = 5 V
for all inputs
High-level input voltage 2.5 V < Vin < 10 V, 5 V typical
Low-level input voltage 0 V < Vin < 1 V
Minimum pulse width > 4 x TS, where TS is sampling time
Execution time (all inputs):
the time from application of voltage on
input until execution is complete
If input is set to one of the built-in functions —
Home, Inhibit, Hard Stop, Soft Stop, Hard and Soft
Stop, Forward Limit, Reverse Limit or Begin —
execution is immediate upon detection: 0<T<4xTS
If input is set to General input, execution depends
on program. Typical execution time: ≅ 0.5 msec.
High-speed inputs – 5 & 6 minimum pulse
width, in high-speed mode
T < 5 µsec
Notes:
• Home mode is high-speed mode and can be
used for fast capture and precise homing.
• High speed input has a digital filter set to
same value as digital filter (EF) of main
encoder.
• Highest speed is achieved when turning on
optocouplers.
Figure 37: Digital Input Schematic
www.elmomc.com
Page 77

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
must be selected to limit the
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.9.2. Digital Output Interface
Feature Details
77
Type of output
• Optically isolated
• Open collector and open emitter
Maximum supply output (VCC) 30 V
Max. output current
I
(max) (V
out
= Low)
out
VOL at maximum output voltage (low
(max) ≤ 15 mA
I
out
V
(on) ≤ 0.3 V
out
level)
RL The external resistor RL
output current to no more than 15 mA.
Executable time If output is set to one of the built-in functions —
Home flag, Brake or AOK — execution is immediate
upon detection:
0 < T < 4 x TS
If output is set to General output and is executed
from a program, the typical time is approximately
0.5 msec.
Figure 38: Digital Output Schematic
4.9.3. Analog Input
Feature Details
Maximum operating differential voltage ± 10 V
Maximum absolute differential input voltage ± 16 V
Differential input resistance 3.74 kΩ
Analog input command resolution 14-bit
www.elmomc.com
Page 78

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.10. Communications
Specification Details
RS-232 Signals:
• RxD , TxD , Gnd
• Full duplex, serial communication for setup and control.
• Baud Rate of 9,600 to 57,600 bit/sec.
CAN CAN bus Signals:
• CAN_H, CAN_L, CAN_GND
• Maximum Baud Rate of 1 Mbit/sec.
Version:
• DS 301 V4.01
Layer Setting Service and Protocol Support:
• DSP 305
Device Profile (drive and motion control):
78
• DSP 402
4.11. Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM)
Feature Details
PWM resolution 12-bit
PWM switching frequency on the load 2/Ts (factory default 22 kHz on the motor)
www.elmomc.com
Page 79

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
4.12. Compliance with Standards
Specification Details
Quality Assurance
ISO 9001:2008 Quality Management
Design
Approved IEC/EN 61800-5-1, Safety Printed wiring for electronic equipment
(clearance, creepage, spacing, conductors
sizing, etc.)
MIL-HDBK- 217F Reliability prediction of electronic equipment
(rating, de-rating, stress, etc.)
79
• UL 60950
• IPC-D-275
• IPC-SM-782
Printed wiring for electronic equipment
(clearance, creepage, spacing, conductors
sizing, etc.)
• IPC-CM-770
• UL 508C
• UL 840
In compliance with VDE0160-7 (IEC 68) Type testing
Safety
Recognized UL 508C Power Conversion Equipment
In compliance with UL 840 Insulation Coordination Including Clearances
and Creepage Distances for Electrical
Equipment
In compliance with UL 60950 Safety of Information Technology Equipment
Including Electrical Business Equipment
Approved IEC/EN 61800-5-1, Safety Adjustable speed electrical power drive
systems
In compliance with EN 60204-1 Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
www.elmomc.com
Page 80

MAN-HAWIG (Ver. 1.401)
Hawk Installation Guide Technical Specifications
EMC
Approved IEC/EN 61800-3, EMC Adjustable speed electrical power drive
systems
80
In compliance with EN 55011 Class A with
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
EN 61000-6-2: Immunity for industrial
environment, according to:
IEC 61000-4-2 / criteria B
IEC 61000-4-3 / criteria A
IEC 61000-4-4 / criteria B
IEC 61000-4-5 / criteria B
IEC 61000-4-6 / criteria A
IEC 61000-4-8 / criteria A
IEC 61000-4-11 / criteria B/C
Workmanship
In compliance with IPC-A-610, level 3 Acceptability of electronic assemblies
PCB
In compliance with IPC-A-600, level 2 Acceptability of printed circuit boards
Packing
In compliance with EN 100015 Protection of electrostatic sensitive devices
Environmental
In compliance with 2002/96/EC Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
regulations (WEEE)
Note: Out-of-service Elmo drives should be
sent to the nearest Elmo sales office.
In compliance with 2002/95/EC
(effective July 2006)
Restrictions on Application of Hazardous
Substances in Electric and Electronic
Equipment (RoHS)
www.elmomc.com
 Loading...
Loading...