Page 1

D-Link AirPro DWL-A520
5 GHz Wireless PCI Adapter
Manual
Rev. 031802
Building Networks for People
Page 2

Contents
Package Contents .................................................... 3
Introduction............................................................... 4
Wireless Basics ........................................................ 6
Getting Started ....................................................... 10
Using the Configuration Utility ................................ 17
Troubleshooting...................................................... 24
Networking Basics .................................................. 29
Technical Specifications ......................................... 59
Contacting Technical Support................................. 61
Limited Warranty and Registration ......................... 62
2
Page 3

Package Contents
Contents of Package:
• D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 5GHz Wireless PCI Adapter
• Manual and Drivers on CD
• Quick Installation Guide (printed)
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
• A desktop computer with an available 32-bit PCI Card slot
• Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows ME, or Windows 98 SE
• At least 32 MB of memory and a 300 MHz processor or higher
• An 802.11a Access Point (e.g., DWL-5000AP for Infrastructure
Mode) or another 802.11a wireless adapter (e.g., DWL-A650 for
laptops or another DWL-A520 for Ad-Hoc mode.)
System Requirements:
Page 4

Introduction
The D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter is an advanced IEEE
802.11a compatible, high performance, wireless adapter that supports data
transfer speeds of up to 72 Mbps in Turbo Mode.
It is an ideal way to connect your desktop computer to a Wireless Local Area
Network (WLAN.) After completing the steps outlined in the Quick Install
Guide (included in your package) you will have the ability to share
information and resources, such as files and printers, and take full
advantage of a “connected” environment for work or play! Please take a
look at our Getting Started section in this manual. You will see several
options for setting up a network using the DWL-A520.
The DWL-A520 comes with software drivers for the most popular Microsoft
Windows operating systems and can be integrated into a larger network,
running Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows ME, Windows 98SE, in
either Ad Hoc mode (without an Access Point) or Infrastructure mode (with
an Access Point.)
This manual provides a quick introduction to wireless technology and its
application as it relates to networking. Take a moment to read through this
manual and get acquainted with wireless technology.
4
Page 5
Product Features
• Adheres to 802.11a standard in providing high data wireless transfer
rates of up to 54 Mbps. Capable of providing data rates of up to 72
Mbps in Turbo Mode.
• Operation in the 5.2GHz Unlicensed National Information
Infrastructure (U-NII) frequency band
• Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) – a new
technique for transmitting high-speed data over a radio wave.
• Dynamic data rate scaling from 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 and
72Mbps depending upon reception quality.
• Maximum reliability, throughput and connectivity with automatic data
rate switching.
• Supports Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) data encryption at
64/128/152-bit encryption with dynamic key exchange for security.
• Supports infrastructure networks via Access Point and Ad-Hoc
networks via peer-to-peer communication.
• Built-in dual diversity antenna for reduced interference in a multi-path
environment.
• Requires an available 32-bit PCI Card slot that is PCI 2.2 compliant.
• User-friendly configuration and diagnostic utilities.
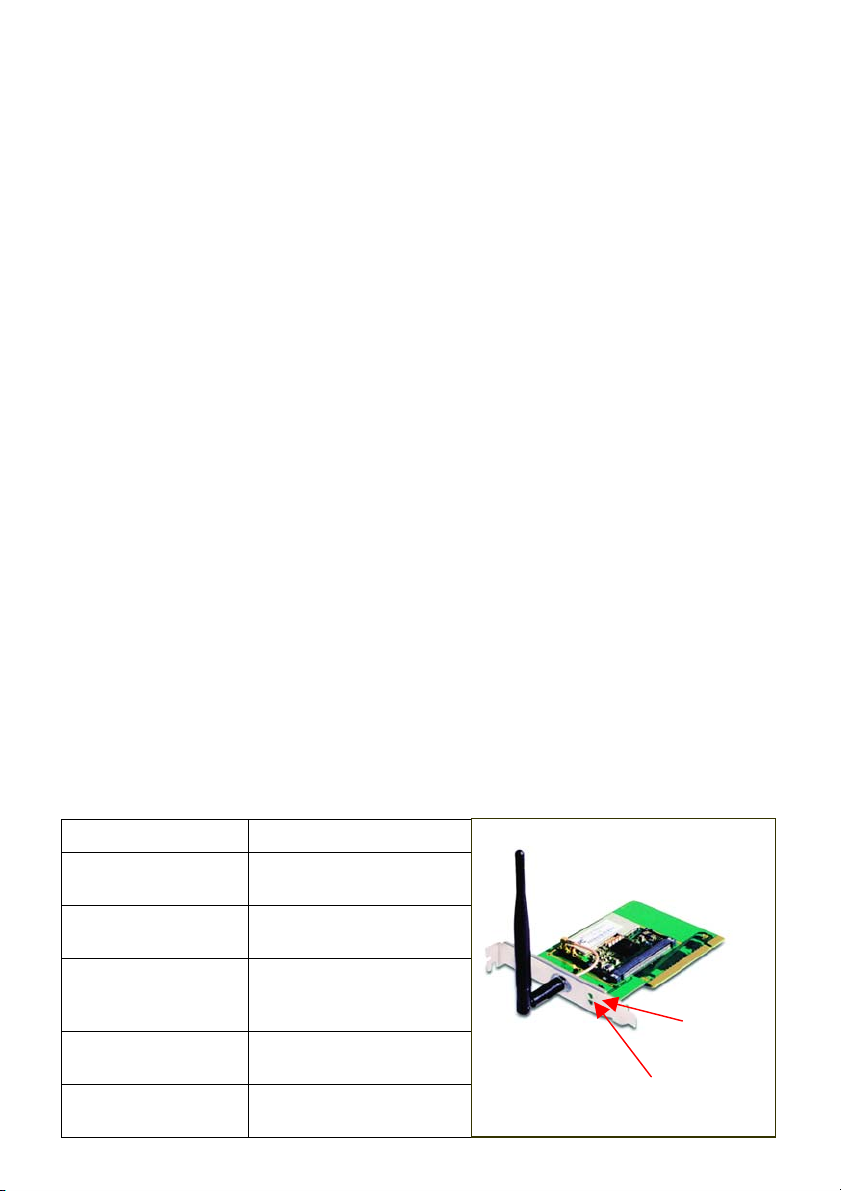
LED
LED stands for light-emitting diode. The DWL-A520 Wireless PCI
Adapter has two LEDs: POWER and ACTIVITY.
Network Mode LED Activity
Network Activity Both LEDs flash in
unison
Searching for a
Network Connection
Associated with the
Network, but No
Activity
Power Save Mode
(Power-up or Reset)
Adapter is disabled Only the POWER LED
Both LEDs flash
alternately
Both LEDs flicker dimly
POWER LED – slow rate
blink
flashes
ACTIVITY
POWER
Page 6

Wireless Basics
D-Link AirPro wireless products are based on industry standards to provide
easy-to-use and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your
home or business. Strictly adhering to IEEE 802.11a, the D-Link AirPro
wireless family of products will allow you to access the data you want, when
and where you want it. No longer will you be limited to one location or forced
to run new wiring through your home or office. You will be able to enjoy the
freedom that wireless networking delivers.
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a cellular computer network that transmits and
receives data with radio signals instead of wires. Wireless LANs are used
increasingly in both home and office environments. Innovative ways to utilize
WLAN technology are helping people to work and communicate more
efficiently. Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other fixed
infrastructure has proven to be beneficial for many users.
Wireless users can use the same network applications they use on an
Ethernet LAN. Wireless adapter cards used on laptop and desktop systems,
support the same protocols as Ethernet adapter cards. For most users, there
is no noticeable functional difference between a wired Ethernet desktop
computer and a wireless computer equipped with a wireless adapter other
than the added benefit of the ability to roam within the wireless-cell. Under
many circumstances, it may be desirable for mobile network devices to link
to a conventional Ethernet LAN in order to use servers, printers or an
Internet connection supplied through the wired LAN. A Wireless Access
Point (AP) is a device used to provide this link.
People use wireless LAN technology for many different purposes.
Mobility - Productivity increases when people have access to data in any
location within the operating range of the WLAN. Ad-hoc management
decisions based on real-time information can significantly improve worker
efficiency.
Low Implementation Costs - WLANs are easy to set up, manage, change
and relocate. Networks that frequently change, both physically and logically,
can benefit from WLANs ease of implementation. WLANs can operate in
locations where installation of wiring may be impractical. Furthermore, IEEE
standardization mandates interoperability of all WLAN devices that conform
to the 802.11a set of standards.
Installation Speed and Simplicity - Installing a wireless LAN system can
be fast and easy and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls and
ceilings.
6
Page 7

Wireless Basics (continued)
Installation Flexibility - Wireless technology allows the network to go where
wires cannot go.
Reduced Cost-of-Ownership - While the initial investment required for
wireless LAN hardware might be higher than the cost of wired LAN hardware,
overall installation expenses and life-cycle costs will be significantly lower.
Long-term cost benefits are greatest in dynamic environments requiring
frequent moves, adds, and changes.
Scalability - Wireless LAN systems can be configured in a variety of
topologies to meet the needs of specific applications and installations.
Configurations are easily changed and range from peer-to-peer networks
suitable for a small number of users to full infrastructure networks of
thousands of users that allow roaming over a broad area.
D-Link AirPro Wireless LAN products include:
802.11a 5GHz Wireless Cardbus Adapters used with laptop
computers (DWL-A650)
802.11a 5GHz Wireless PCI cards used with desktop computers
(DWL-A520)
802.11a 5GHz Wireless Access Points (DWL-5000AP)
Standards - Based Technology
The IEEE 802.11a standard designates that devices operate at an optimal
data rate of 54 Megabits per second. This means you will be able to transfer
large files quickly or even watch a movie in MPEG format over your network
without noticeable delays. This technology works by transmitting high-speed
digital data over a radio wave utilizing OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplexing) technology. OFDM works by splitting the radio signal
into multiple smaller sub-signals that are then transmitted simultaneously at
different frequencies to the receiver. OFDM reduces the amount of
crosstalk (interference) in signal transmissions. D-Link AirPro products will
automatically sense the best possible connection speed to ensure the
greatest speed and range possible with the technology.
Page 8

Wireless Basics (continued)
Installation Considerations
Designed to go up to 900 feet (~300 meters), D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 lets
you access your network with your computer from virtually anywhere you
want. Keep in mind, however, that the number and thickness of walls,
ceilings or other objects that the wireless signals must pass thru may limit
range. Typical ranges vary depending on the types of materials and
background RF noise in your home or business. The key to maximizing
range is to follow these basic principles:
Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the Access Point and
1.
your receiving device to a minimum - Each wall or ceiling can reduce
your D-Link AirPro Wireless product’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.)
For some businesses or for a large residential home deployment, it may
be beneficial to have more than one access point with overlapping
coverage.
2. Be aware of the direct line between Access Points and computers with
wireless adapters - A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at a 45degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree
angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick! Try to make sure that the
Access Points and Adapters are positioned so that the signal will travel
straight through a wall or ceiling for better reception.
3. Building Materials make a difference - A solid metal door or aluminum
studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position Access Points,
and computers with wireless adapters so that the signal passes through
drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
4. Make sure that the antenna is positioned for best reception by using the
software signal strength tools included with your product.
5. Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical
devices or appliances that generate extreme RF noise.
8
Page 9

Wireless Basics (continued)
For the average residence, range should not be a problem. If you
experience low or no signal strength in areas of your home that you wish to
access, consider positioning the Access Point in a location directly between
the computers with wireless adapters that will be connected. Additional
Access Points can be connected to provide better coverage in rooms where
the signal does not appear as strong as desired.
Using radio frequency (RF) technology, WLANs (Wireless Local Area
Networks) transmit and receive data over the air, minimizing the need for
wired connections. Thus, WLANs combine data connectivity with user
mobility, and, through simplified configuration, enable movable LANs.
Page 10
Getting Started
To begin, select the type of wireless network you will be building.
We will discuss the following types of networks in this section:
1. A Home Internet Network
with A Residential Gateway/Router
2. A Home Internet Network with Multiple IP Addresses
3. An Ad Hoc Network
4. An Ad Hoc Network with Internet Sharing
Please select, from the four types of networks described above, the type of
network that is appropriate for your needs. Please follow the instructions in
the corresponding section that follows.
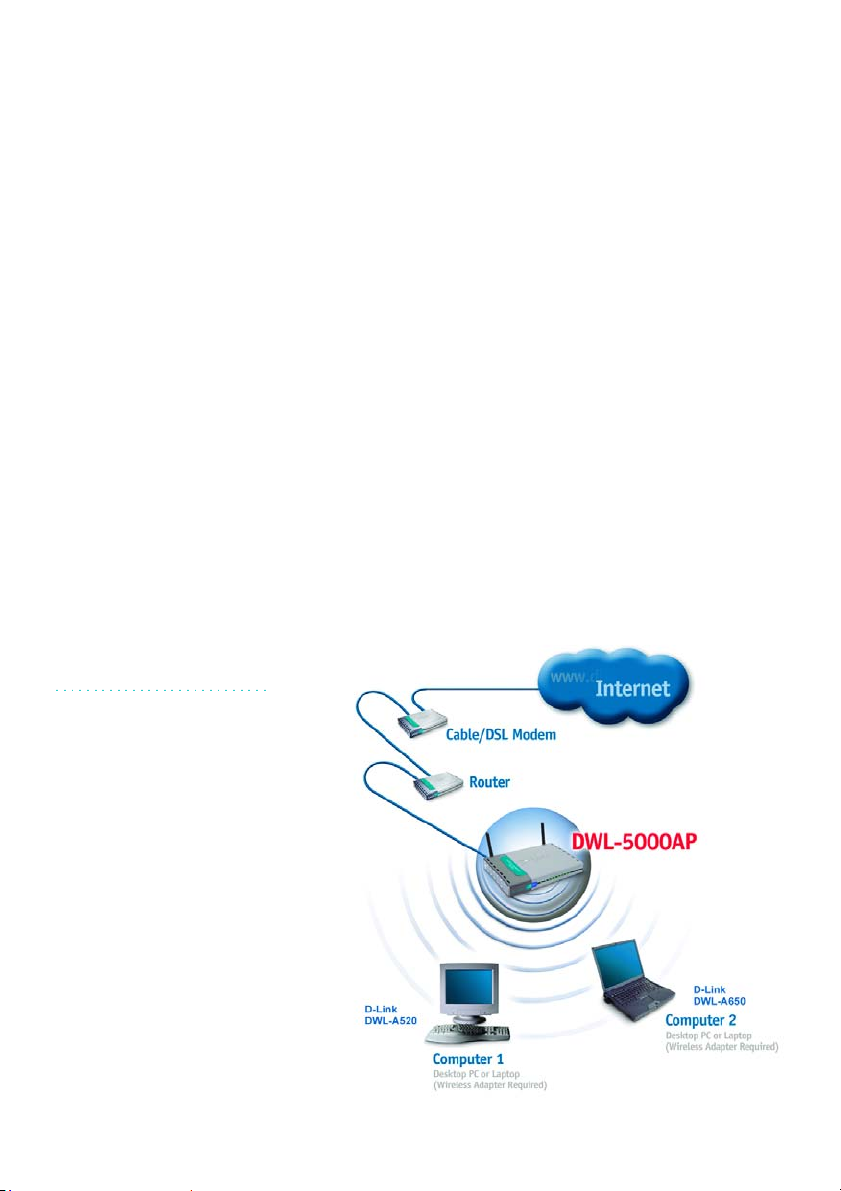
1. A Home Internet Network with A Residential Gateway/Router
(Network administrators with Dynamic IPs can also follow these instructions.)
If you have two or more computers (laptops or desktops) and want to share
files, printers, and Internet access using a DHCP-capable Residential
Gateway/Router – or - if you want to connect to an Ethernet network that
uses Dynamic (DHCP) IP addresses, then follow the instructions on the next
page. When it is complete, your network may look similar to this:
DHCP stands for
Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol.
It is a protocol for
assigning dynamic IP
addresses
“automatically.” With a
DHCP-capable
gateway, there is no
need to manually
assign an IP address.
10
Page 11

1. A Home Internet Network with A Residential Gateway/Router
(continued)
(Requirements: A Residential Gateway/Router connected with an Ethernet
(CAT5) cable to an 802.11a Access Point such as the DWL-5000AP.)
This type of installation requires that you provide a dynamic IP address for
each computer on your network. You will need a DHCP-capable Residential
Gateway/Router for your network.
To complete the installation, please follow these steps:
1. Connect the Router/Gateway (for example, the D-Link DI-704P) to
a Broadband connection, (e.g., a Cable modem such as the D-Link
DCM-200 cable modem or a DSL modem such as the D-Link DSL-
300.)
2. Connect the 802.11a Access Point (DWL-5000AP) to the router.
3. Install the D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter into a
desktop computer on your wireless network. (You can also install the
D-Link AirPro DWL-A650 Wireless Cardbus Adapter into a laptop
computer. Please refer to the Quick Install Guide included with each
product.)
4. Check the Device Manager to confirm that the wireless adapter is
installed correctly. Please refer to the Networking Basics section in
this manual entitled: Checking the Installation of the Drivers for
the Wireless Adapter.
5. By default, the wireless adapter is set to obtain a Dynamic IP
Address. If you are having difficulty connecting, check to make sure
that the IP Address of the wireless adapter is within the IP address
range of your network. Please refer to the Networking Basics
section in this manual entitled: Checking The IP Address.
6. Learn to share printers and files. Please refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual entitled: Adding and Sharing Printers
in Windows XP.
Page 12
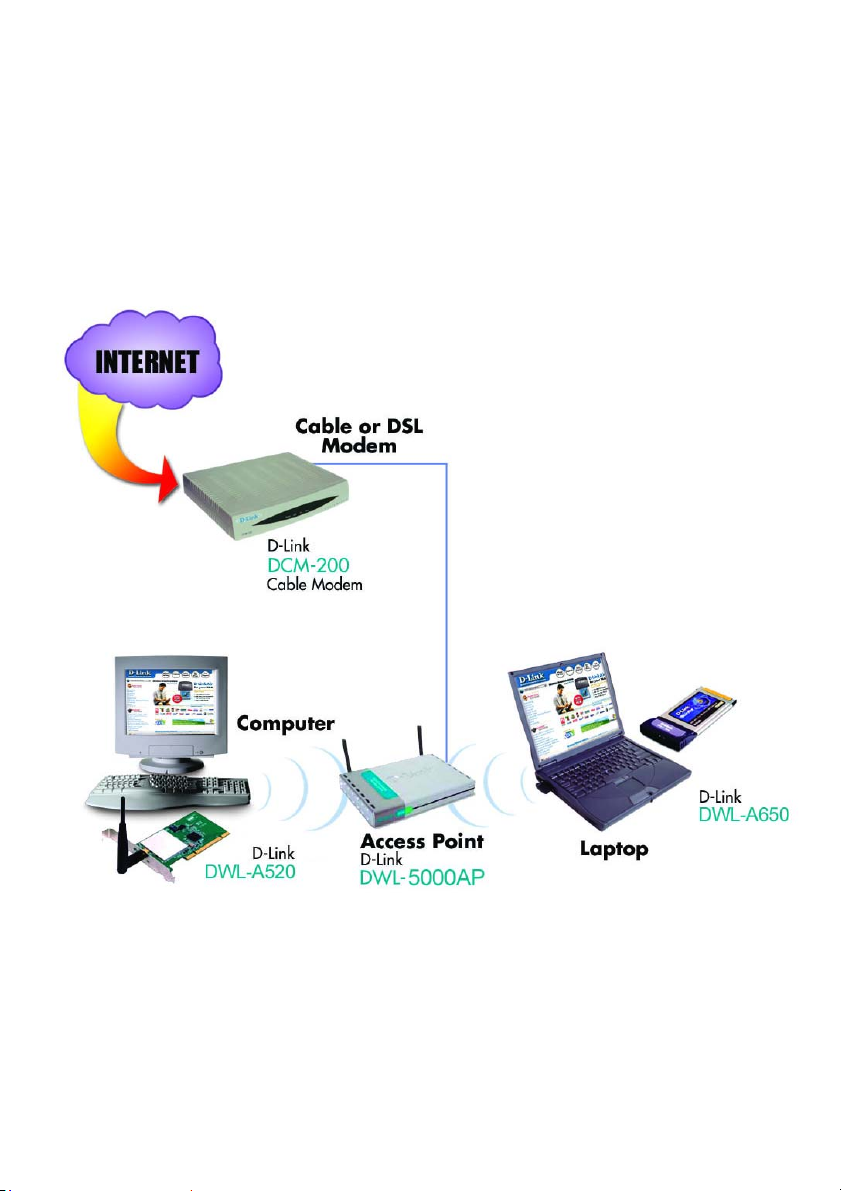
2. A Home Internet Network with Multiple IP Addresses
(Network administrators with Static IPs can also follow these instructions.)
If you have two or more computers (laptops or desktops) and want to share
files, printers, and Internet access using multiple IP addresses that you have
purchased from your Internet Service Provider -or- you want to connect to
an Ethernet network that uses Static IP Addresses, then follow the
instructions on the next page. When you have completed your network, it
should look similar to this:
Please note that this type of installation requires that your ISP (Internet
Service Provider) provides you a static IP address for each computer and
the Access Point on your network. Please refer to the manual that came
with your Access Point to determine its configuration.
12
Page 13

2. A Home Internet Network with Multiple IP Addresses (continued)
Please follow these steps to complete the installation:
1. Connect the Wireless Access Point (the D-Link AirPro DWL-
5000AP is shown in the example) to a Broadband connection (i.e., a
Cable modem such as the D-Link DCM-200 cable modem.)
2. Install the D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter into a
desktop computer on your wireless network. (You can also install the
D-Link AirPro DWL-A650 Wireless Cardbus Adapter into a laptop
computer. Please refer to the Quick Install Guide included with each
product.)
3. Check the Device Manager to confirm that the wireless adapter is
installed correctly. Please refer to the Networking Basics section in
this manual entitled: Checking the Installation of the Drivers for
the Wireless Adapter.
4. Set the Static IP Address of the wireless adapters. Please refer to
the Networking Basics section in this manual entitled: Assigning
an IP Address.
Note: The IP Address for all computers must be in the same IP Address
range, and the Subnet Mask must be the same for all the computers on the
network. For example: If the first computer is assigned an IP Address of
192.168.0.2 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, then the second
computer can be assigned an IP Address of 192.168.0.3 with a Subnet Mask
of 255.255.255.0, etc.
If you are using a PPPoE client (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet)
please contact your ISP (Internet Service Provider) for further instructions
regarding connecting to the Internet.
5. Learn to share printers and files. Please refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual entitled: Adding and Sharing Printers
in Windows XP.
Page 14
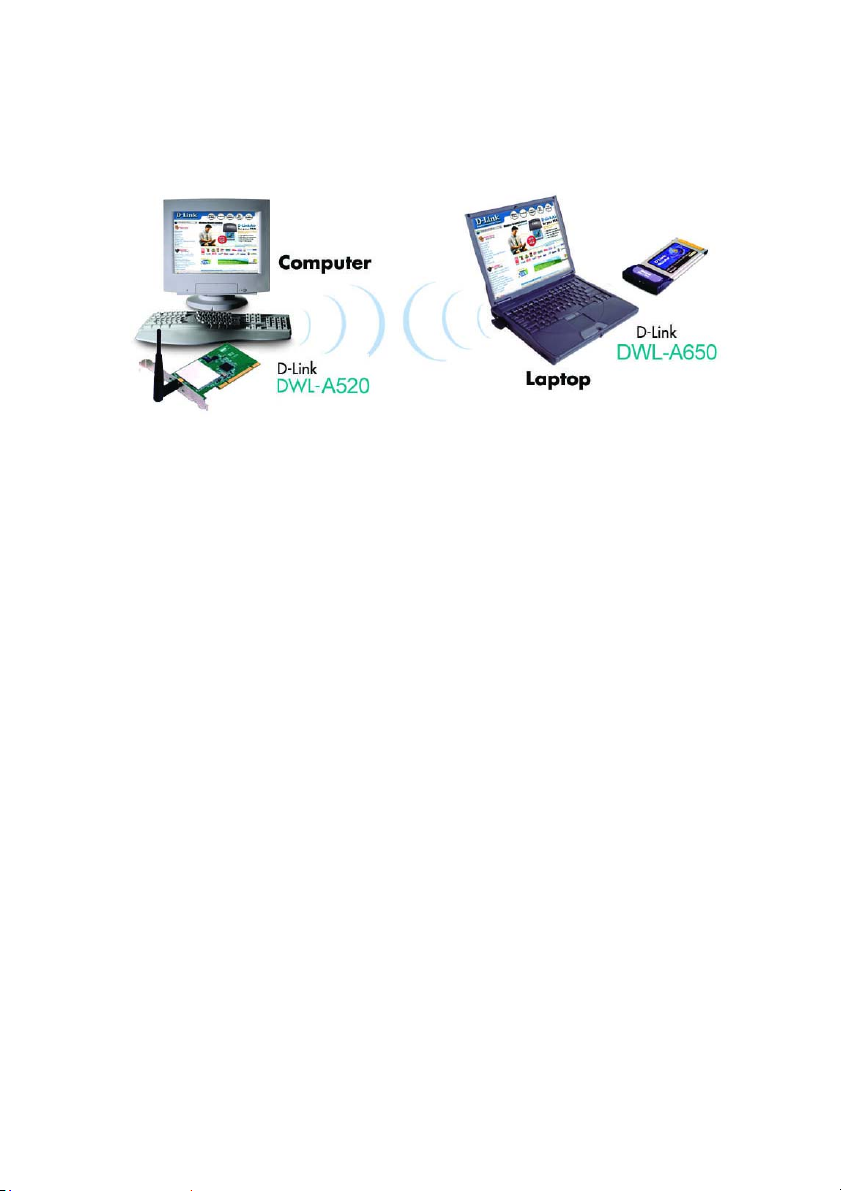
3. An Ad Hoc Network
If you have two or more computers (desktops or laptops) and want to share
files and printers, but no Internet connection, please complete the following
instructions. When your Ad Hoc network is complete it may look similar to
this:
(Requirements: Wireless network adapters -for example, the D-Link AirPro DWL-
A650 and the DWL-A520.)
To complete this installation, please follow these steps:
1. Install the D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter into a
desktop computer on your wireless network. (You can also install the
D-Link AirPro DWL-A650 Wireless Cardbus Adapter into a laptop
computer. Please refer to the Quick Install Guide included with each
product.)
2. Set the Static IP Address of the wireless adapters. Please refer to
the Networking Basics section in this manual entitled: Assigning
an IP Address.
Note: The IP Address for all computers must be in the same IP Address range, and
the Subnet Mask must be the same for all computers on your network. For example:
If the first computer is assigned an IP Address of 192.168.0.2 with a Subnet Mask of
255.255.255.0, then the second computer can be assigned an IP Address of
192.168.0.3 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, etc.
3. Check the Device Manager to confirm that the wireless adapter is
installed correctly. Please refer to the Networking Basics section in
this manual entitled: Checking the Installation of the Drivers for
the Wireless Adapter.
4. Check the Wireless Configuration for each wireless adapter.
Please refer to the Networking Basics section in this manual
entitled: Checking the Wireless Configuration.
5. Learn to share printers and files. Please refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual entitled: Adding and Sharing Printers
in Windows XP.
14
Page 15
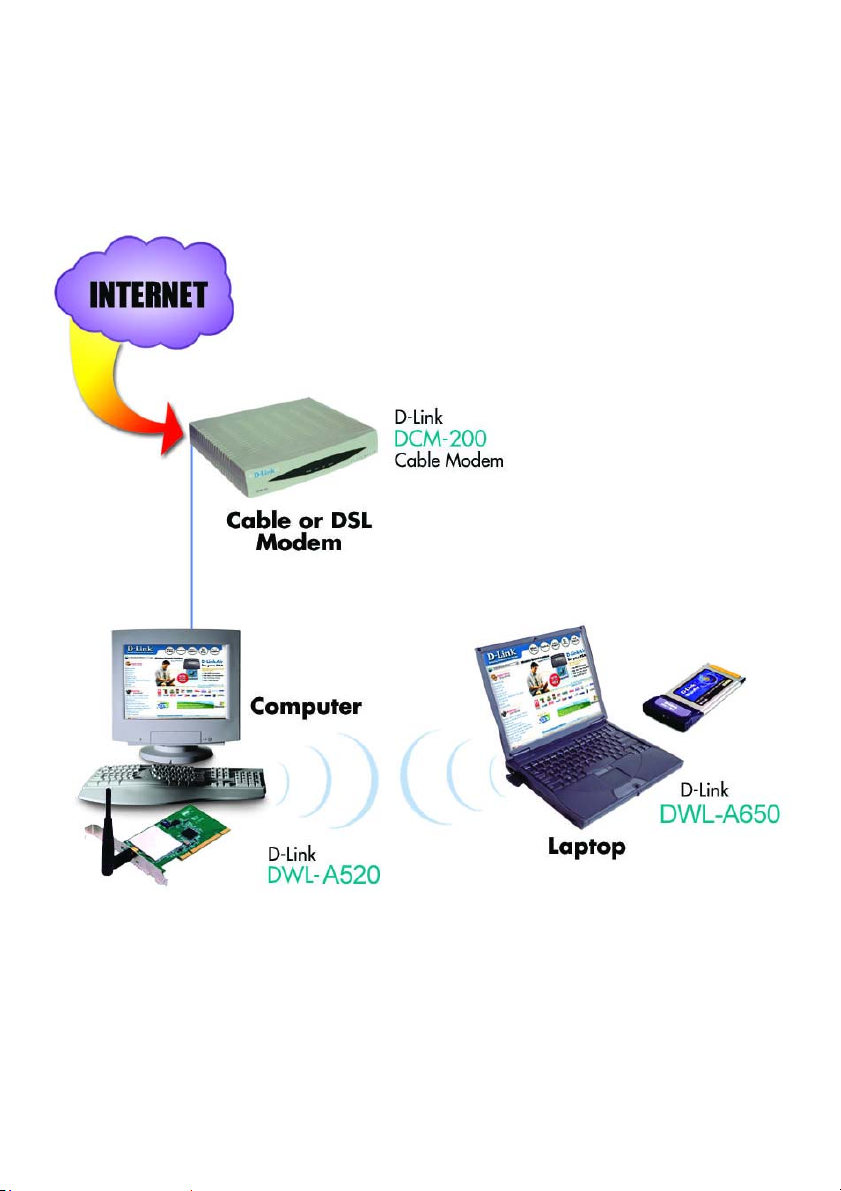
4. An Ad Hoc Network with Internet Sharing
If you have two or more computers (desktops or laptops) and want to share
files, printers, and Internet access using one computer or laptop as an
Internet Server, then follow the instructions below. When you have
completed your network, it should look similar to this:
DFE-530TX
To share an Internet connection with Internet Sharing software you will need
to purchase Internet Sharing software or use the Internet Connection
Sharing (ICS) utility provided with Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows
ME or Windows 98SE.
Please follow your software documentation to properly configure the Internet
sharing software after you install your wireless networking adapters. To
install your wireless network adapter follow the instructions on the next page.
Page 16

4. An Ad Hoc Network with Internet Sharing (continued)
If the Internet Sharing Software will be installed on the same computer into
which you are installing this wireless network adapter, then follow these
steps:
1. Install the D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter (please
refer to the Quick Install Guide.)
2. Check the Device Manager to confirm that your adapter is installed
correctly. Please refer to the Networking Basics section in this
manual entitled: Checking the Installation of the Drivers for the
Wireless Adapter.
3. Install your Internet Sharing Software
4. If required by the ICS software, set the static IP Address for the
wireless adapter. Please refer to the Networking Basics section in
this manual entitled: Assigning an IP Address.
Note: The IP Address for all the computers on the network must be in the same IP
Address range, and the Subnet Mask must be the same for all the computers on the
network. For example: If the first computer is assigned an IP Address of
192.168.0.2 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, then the second computer can
be assigned an IP address of 192.168.0.3 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, etc.
5. Learn to share printers and files. Please refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual entitled: Adding and Sharing Printers.
If the Internet Sharing Software will be installed on a computer other than
the one in which you are installing the D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless
PCI Adapter, then follow these steps:
1. Install the D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter into the
computer (please refer to the Quick Install Guide.)
2. Check the IP Address for the wireless adapter. Please make
certain that all the computers on your network are in the same IP
Address range. Please refer to the Networking Basics section in
this manual entitled: Checking your IP Address.
Note: By default, the wireless adapter is set to obtain a Dynamic IP
Address, automatically.
3. Learn to share printers and files. Please refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual entitled: Adding and Sharing
Printers in Windows XP.
16
Page 17
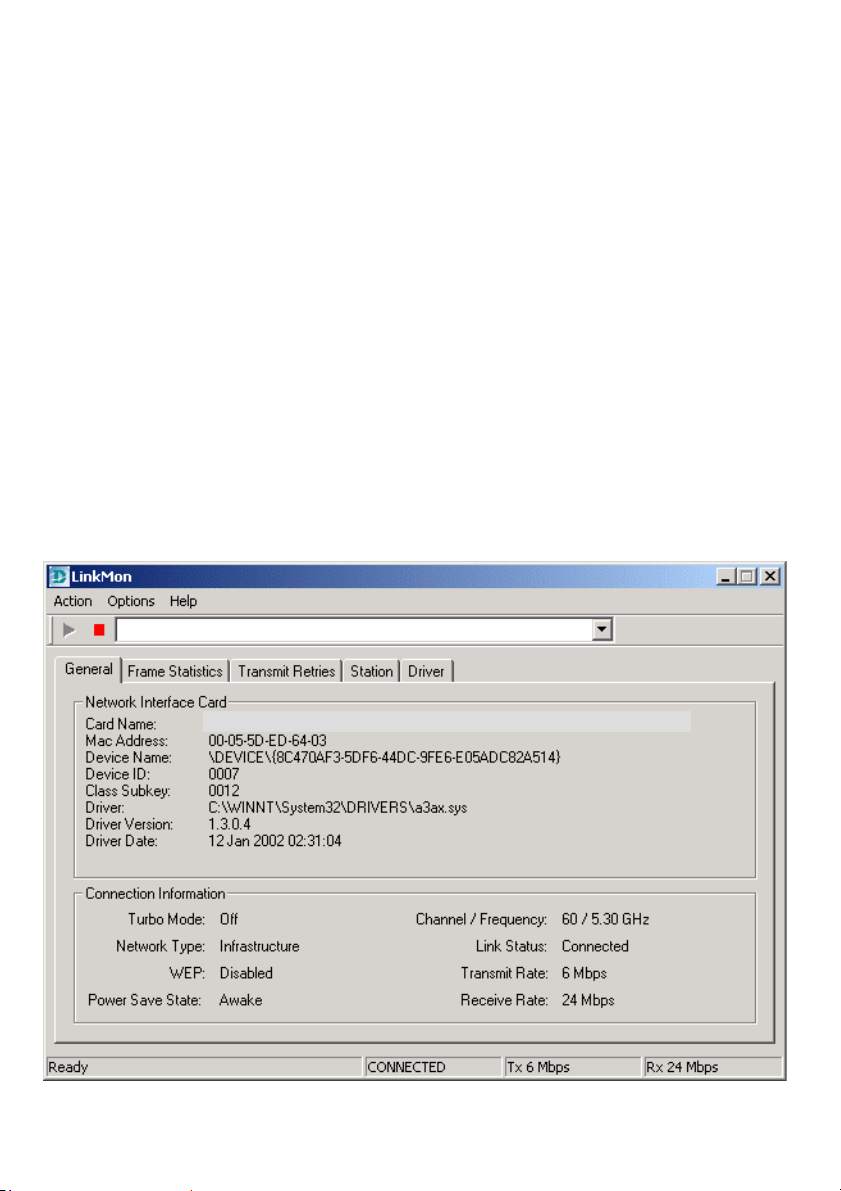
Using the Configuration Utility
The Configuration Utility program for the DWL-A520 is called LinkMon.
Please refer to the Quick Install Guide that came with the DWL-A520 for
instructions on how to install LinkMon on your computer. Once you have
installed LinkMon (the configuration utility), you can read this section of the
manual to find out how to monitor and configure your DWL-A520 adapter
using LinkMon. There are five tabs in the LinkMon Configuration Utility
program. In this section we will describe the uses for each tab in the
Configuration Utility window.
To access LinkMon once it has been installed, just double-click on the
LinkMon icon in the taskbar.
Under the General Tab you will find general information about the program
and its operations.
General Tab
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
Page 18

Using the Configuration Utility (continued)
Under the Frame Statistics Tab you will find statistical information showing
the number of frames being sent and received, retry count on frames sent,
frame checksum error counts for received frames, and receive signal
strength indicator (RSSI) information.
Frame Statistics Tab
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
18
Page 19
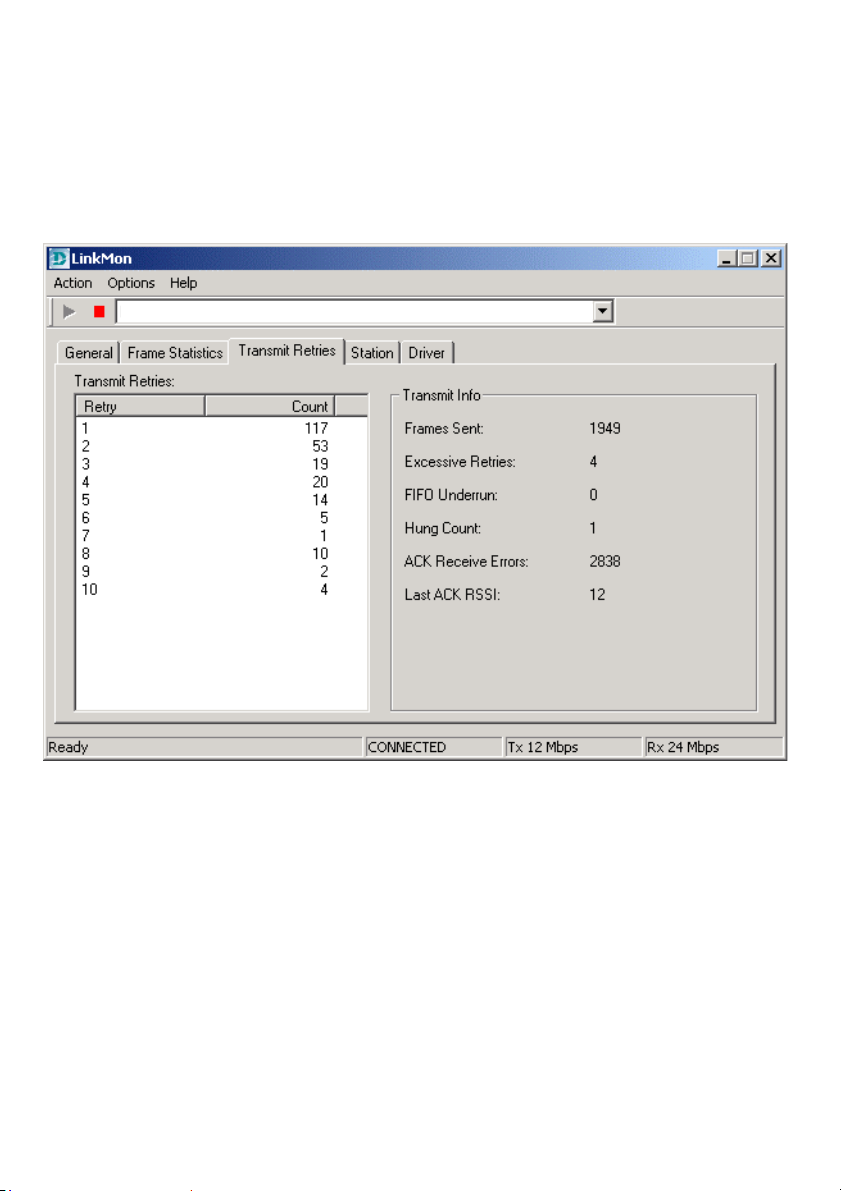
Using the Configuration Utility (continued)
Under the Transmit Retries Tab you will find detailed transmit retry
statistical information for transmitted frames.
Transmit Retries Tab
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
Page 20

Using the Configuration Utility (continued)
Under the Station Tab you will find detailed BSS information including SSID,
BSSID, association status, operating channel frequency, and information
about scanned APs.
Station Tab
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
Default
BSS – (Basic Service Set) when one AP is connected to a wired network
and a set of wireless stations, it is a BSS.
SSID – (Service Set Identifier) it is essentially a network name; a name that
identifies a wireless network. All Access Points and all devices attempting to
connect to a specific WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) must use the
same SSID.
20
Page 21

Using the Configuration Utility (continued)
Under the Driver Tab you will find statistical data pertaining to NDIS
(Network Driver Interface Specification) driver operations.
Driver Tab
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
Page 22

Using the Configuration Utility (continued)
The Action menu allows the unloading of the NDIS driver, and the resetting
of the network interface card (NIC.) Note that unloading the driver and
resetting the NIC are options that are available only in Windows XP and
Windows 2000.
L-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
On the Options menu, choose Settings:
0 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter
22
Page 23

Using the Configuration Utility (continued)
Under the Display Tab, you can select the data display modes of
Cumulative, or Relative. Cumulative mode displays statistical data
collected when LinkMon is started. Relative mode displays differences in
the statistical data since the last update of collected data.
Under the Log File Tab, the logging function can be enabled to log to a file
the statistical information collected by the LinkMon utility, for later reference
or post processing by an application such as Microsoft Excel.
x
C:\Temp\Logfile
Click the Enable Logging click-box to enable LinkMon to write a log file.
You must also specify the full DOS path to the log file, such as
C:\Temp\Logfile.
Page 24

Troubleshooting
This chapter provides solutions to problems that can occur during the
installation and operation of the DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter. Read the
following descriptions if you are having problems.
1. Checking the Installation of the Drivers for the Wireless Adapter
• Go to Start
• Right-click on
My Computer
• Click Properties
• Select the Hardware Tab
• Click Device Manager
24
Page 25

Troubleshooting (continued)
• Double-click on Network
Adapters
• Right-click on D-Link Air
Pro DWL-A520 Wireless
PCI Adapter
• Select Properties to check
that the drivers are
installed properly.
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
• Look under Device
Status
to check that the
device is working
properly.
• Click OK
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
Page 26

Troubleshooting (continued)
2. The computer does not recognize the DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless
PCI Adapter.
• Make sure that the DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter is properly
seated in the computer’s PCI slot.
• Check that the DWL-A520 is installed in a 32-bit PCI 2.2 slot.
• If Windows does not detect the hardware upon insertion of the
adapter, make sure to completely remove drivers that were
previously loaded. To remove the drivers, do the following:
A. Under Tools> select Folder Options…> select View >
under Hidden files and folders > select Show hidden
files and folders
B. Uncheck Hide extension for known file types > click on
Apply
C. Search for the files NetA3x.inf and A3ax.sys. Remove
these files from the INF and SYSTEM32 (DRIVERS) folders
in the Windows directory. Note: Windows XP and Windows
2000 will rename .inf files that have not received
certification into oem.inf files (e.g., oem1.inf.)
3. The DWL-A520 802.11a Wireless PCI Adapter does not work properly
after the driver is installed.
• Restart the computer. (In some cases, it will be necessary to restart
the computer after installing the drivers.)
• In Windows XP, go to Start>Control Panel>System>Hardware
Tab> click on the Device Manager Tab> click on Network
Adapters> double click on D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI
Adapter> make sure that “This device is working properly” is
displayed under Device Status under the General Tab. (Please refer
to Checking the Installation of the Drivers for the Wireless
Adapter in the Troubleshooting section on the previous page of this
manual for more information.)
• If the device is not working properly and a yellow exclamation mark is
displayed, then there is probably a resource conflict. First, try
inserting the card into a different PCI slot. If there is still a problem,
make sure the computer system has a free IRQ and if necessary,
26
Page 27

Troubleshooting (continued)
uninstall the drivers, restart the system, and repeat the driver
installation procedure.
4. The computer with the wireless adapter installed is unable to
connect to the wireless network.
• In Infrastructure mode, make sure the same Service Set Identifier
(SSID) is specified on the settings for the wireless clients and access
points. The SSID factory default setting for the D-Link AirPro
products is Default. (Please refer to Checking the Wireless
Configuration in the Networking Basics section of this manual for
more information.)
• In Ad-Hoc mode, both wireless clients will need to have the same
SSID. Please note that it might be necessary to set up one client to
establish a BSS (Basic Service Set) and wait briefly before setting
up other clients. This prevents several clients from trying to establish
a BSS at the same time, which can result in multiple singular BSSs
being established, rather than a single BSS with multiple clients
associated to it. (Please see the Status Tab in Linkmon in the
Configuration Utilities section or see Checking the Wireless
Configuration in the Networking Basics section of this manual to
learn more about BSS-Basic Service Set.)
• Check that the Network Connection for the wireless client is
configured properly. Select AP (Infrastructure) when connecting to
an access point and select Ad-Hoc mode when connecting without
an access point. Double-click on the network connection icon in
the taskbar > click on Properties > click on Configure > select the
Settings Tab > click on Modify to change the settings for the
wireless adapter. (Please refer to Checking the Wireless
Configuration in the Networking Basics section of this manual for
more information.)
• Verify that the Turbo Mode setting is exactly the same for wireless
clients and the access point. Please note that the wireless
connection will not be established in Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc mode
if Turbo Mode is enabled on one end of the wireless connection and
not the other. (Please refer to Checking the Wireless
Configuration in the Networking Basics section of this manual for
more information.)
• If Enable Security is selected, make sure that the correct encryption
keys are entered on both the wireless clients and the access points.
Page 28

Troubleshooting (continued)
(Please see Checking the Wireless Configuration in the
Networking Basics section of this manual for more information.)
5. The wireless client cannot access the Internet in the Infrastructure
mode.
• Make sure the wireless client is associated and joined with the
correct Access Point. To check this connection: Right-click on the
Networking Icon in the taskbar> select View Available Wireless
Networks. The Connect to Wireless Network screen will appear.
Please make sure you have selected the correct available network,
as shown in the illustrations below.
• Check that the IP Address assigned to the wireless adapter is within
the same IP Address range as the access point and gateway. (For
example: if one computer has an IP Address of 192.168.0.2, the
other computers should have IP Addresses that are sequential, like
192.168.0.3 and 192.168.0.4. The subnet mask must be the same
for all the computers on the network.) To check the IP Address
assigned to the wireless adapter, double-click on the Network
Connection Icon in the taskbar > select the Support tab and the IP
Address will be displayed. (Please refer to Checking the IP
Address in the Networking Basics section of this manual.)
• If it is necessary to assign a Static IP Address to the wireless
adapter, please refer to the appropriate section in Networking
Basics. If you are entering a DNS Server Address, you must also
enter the Default Gateway Address. (Remember that if you have a
DHCP-capable router, you will not need to assign a Static IP Address.
See Networking Basics: Assigning a Static IP Address.)
28
Page 29

Networking Basics
Using the Network Setup Wizard in Windows XP
In this section you will learn how to establish a network at home or work,
using Microsoft Windows XP.
Note: Please refer to websites such as http://www.homenethelp.com
and http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000
networking computers using Windows 2000, ME or 98.
Go to START>CONTROL PANEL>NETWORK CONNECTIONS
Select Set up a home or small office network
for information about
When this screen appears, click Next.
Page 30

Networking Basics
Please follow all the instructions in this window:
Click Next
In the following window, select the best description of your computer. If your
computer connects to the internet through a gateway/router, select the
second option as shown.
Click Next
30
Page 31

Networking Basics
Enter a Computer description and a Computer name (optional.)
Click Next
Enter a Workgroup name. All computers on your network should have the
same Workgroup name.
Click Next
Page 32

Networking Basics
Please wait while the wizard applies the changes.
When the changes are complete, click Next.
Please wait while the wizard configures the computer.
This may take a few minutes.
32
Page 33

Networking Basics
In the window below, select the best option. In this example, Create a
Network Setup Disk has been selected. You will run this disk on each of
the computers on your network. Click Next.
Insert a disk into the Floppy Disk Drive, in this case drive A:
Format the disk if you wish, and click Next.
Page 34

Networking Basics
Please wait while the wizard copies the files.
Please read the information under Here’s how in the screen below. After
you complete the Network Setup Wizard you will use the Network Setup
Disk to run the Network Setup Wizard once on each of the computers on
your network. To continue, click Next.
34
Page 35

Networking Basics
Please read the information on this screen, then click Finish to complete the
Network Setup Wizard.
The new settings will take effect when you restart the computer. Click Yes
to restart the computer.
You have completed configuring this computer. Next, you will need to run
the Network Setup Disk on all the other computers on your network. After
running the Network Setup Disk on all your computers, your new wireless
network will be ready to use.
Page 36

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
To name your computer, please follow these directions:
In Windows XP:
• Click Start (in the
lower left corner of
the screen)
• Right-click on My
Computer
• Select Properties
and Click
• Select the
Computer Name
Tab in the System
Properties window.
You may enter a
Computer description if
you wish, this field is
optional.
To rename the computer
and join a domain,
• Click Change
36
Page 37

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer (continued)
• In this window, enter
the Computer
name.
• Select Workgroup
and enter the name
of the Workgroup.
• All computers on
your network must
have the same
Workgroup name.
• Click OK
Checking the Installation of the Drivers for the Wireless Adapter
• Go to Start
• Right-click on
My Computer
• Click Properties
Page 38

Networking Basics
Checking the Installation of the Drivers for the Wireless Adapter
• Select the Hardware Tab
• Click Device Manager
• Click on Network
Adapters
• Right-click on D-Link Air
Pro DWL-A520 Wireless
PCI Adapter
• Select Properties to check
that the drivers are
installed properly.
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
38
Page 39

Networking Basics
p
Checking the Installation of the Drivers for the Wireless Adapter
• Look under Device
Status
to check that the
device is working
properly.
• Click OK
Checking the Wireless Configuration
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
• Double-click on the Local Area
Connection Icon in the taskbar.
In this window you will see
the Signal Strength and the
Status of the DWL-A520.
In this case the Status and
the Signal Strength are fine.
For more information:
• Click Pro
erties
Page 40

Networking Basics
Checking the Wireless Configuration
• Click Configure to
access more
information.
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
• Select Settings
This screen shows the
wireless configuration.
• Click Modify to
check on the
configuration.
40
Page 41

Networking Basics
t
Checking the Wireless Configuration
• The Network
Name (SSID)
should be set to
Default.
• The Network
Connection
should be set to
the correct mode
(Infrastructure
or Ad Hoc.)
• The Turbo Mode
setting (Disabled
in the example
here) must be
the same on all
the stations in
your network.
• Click on the
Security Tab
If Enable
•
Security is
selected on one
station on your
network, it must
be selected on
all stations.
Likewise, if
Enable Security
is deselected on
one station, it
must be
deselected on all
stations
• Check to see that your IP Address and your Subnet Mask are in the correc
range. See the Networking Basics sections: Checking the IP Address and
Assigning a Static IP Address.
.
Page 42

Networking Basics
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP
• Right-click on the
Networking Icon in
the task bar
• Click on Status
The following window will display
• Click the Support tab.
• Click Close
42
Page 43

Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address
Note: Residential Gateways/Broadband Routers will automatically assign IP
Addresses to the computers on the network, using DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol) technology. If you are using a DHCP-capable
Gateway/Router you will not need to assign Static IP Addresses.
If you are not using a DHCP capable Gateway/Router, or you need to assign a
Static IP Address, please follow these instructions:
• Go to Start
• Double-click on
Control Panel
• Double-click on
Network Connections
Page 44

Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address
• Right-click on Local
Area Connections.
• Double-click
Properties
• Highlight Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP)
• Click Properties
D-Link AirPro DWL-A520 Wireless PCI Adapter
44
Page 45

Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address
• Select Use the following IP address
in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window,
• Input your IP address and subnet mask. (The IP Addresses on your
network must be within the same range. For example, if one computer
has an IP Address of 192.168.0.2, the other computers should have IP
Addresses that are sequential, like 192.168.0.3 and 192.168.0.4. The
subnet mask must be the same for all the computers on the network.)
• Input your DNS server addresses. (Note: If you are entering a DNS
server address, you must enter the IP Address of the Default
Gateway.)
The DNS server information will be provided by your ISP (Internet Service
Provider.)
• Click OK
You have completed the assignment of a Static IP Address. (You do not need to
assign a Static IP Address if you have a DHCP-capable Gateway/Router.)
Page 46

Networking Basics
Adding and Sharing Printers in Windows XP
After you have run the Network Setup Wizard on all the computers in your
network (please see the Network Setup Wizard section at the beginning of
Networking Basics,) you can use the Add Printer Wizard to add or share a
printer on your network.
Whether you want to add a local printer (a printer connected directly to one
computer,) share an LPR printer (a printer connected to a print server) or
share a network printer (a printer connected to your network through a
Gateway/Router,) use the Add Printer Wizard. Please follow the directions
below:
First, make sure that you have run the Network Setup Wizard
the computers on your network.
We will show you 3 ways to use the Add Printer Wizard
1. Adding a local printer
2. Sharing an network printer
3. Sharing an LPR printer
on all of
Adding a local printer
(A printer connected directly to a computer)
A printer that is not shared on the network and is connected directly to one
computer is called a local printer. If you do not need to share your printer
on a network, follow these directions to add the printer to one computer.
• Go to Start>
Printers and
Faxes
46
Page 47

Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
• Click on Add a printer
• Click Next
Page 48

Networking Basics
t
r
r
Adding a local printer
• Select Local printer
attached to this computer
• (Deselect Automatically detect
and install my Plug and Play
printer if it has been selected.)
• Click Next
• Select Use the
following port:
• From the pull-down
menu select the
correct port for your
printer
(Most computers use the
LPT1: port, as shown in
the illustration.)
• Click Next
• Select and highlight the
correct driver for your
printer.
• Click Next
(If the correct driver is no
displayed, insert the CD o
floppy disk that came with you
printer and click Have Disk.)
48
Page 49

Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
• At this screen, you can
change the name of the
printer (optional.)
• Click Next
• Select Yes, to print a
test page. A
successful printing will
confirm that you have
chosen the correct
driver.
• Click Next
This screen gives you
information about your
printer.
• Click Finish
Page 50

Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
When the test page has
printed,
• Click OK
• Go to Start> Printers and
Faxes
A successful installation will
display the printer icon as
shown at right.
You have successfully added a
local printer.
50
Page 51

Networking Basics
Sharing a network printer
After you have run the Network Setup Wizard on all the computers on your
network, you can run the Add Printer Wizard on all the computers on your
network. Please follow these directions to use the Add Printer Wizard to
share a printer on your network:
• Go to Start>
Printers and Faxes
• Click on Add a Printer
• Click Next
• Select Network Printer
• Click Next
Page 52

Networking Basics
Sharing a network printer
• Select Browse for a printer
• Click Next
• Select the printer you
would like to share.
• Click Next
• Click Finish
52
Page 53

Networking Basics
Sharing a network printer
To check for proper installation:
• Go to Start>
Printers and Faxes
The printer icon will appear
at right, indicating proper
installation.
You have completed
adding the printer.
To share this printer on
your network:
• Remember the
printer name
• Run the Add Printer
Wizard on all the
computers on your
network.
• Make sure you have
already run the
Network Setup
Wizard on all the
network computers.
After you run the Add
Printer Wizard on all the
computers in the
network, you can share
the printer.
Page 54

Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
To share an LPR printer (using a print server,) you will need a Print Server such as
the DP-101P+. Please make sure that you have run the Network Setup Wizard on
all the computers on your network. To share an LPR printer, please follow these
directions:
• Go to Start>
Printers
and Faxes
• Click on
Add a Printer
The screen to the
right will display.
• Click Next
• Select
Local
printer…
• Click Next
54
Page 55

Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
• Select Create a new port
• From the pull-down menu,
select Standard TCP/IP
Port, as shown.
• Click Next
• Please read the instructions
on this screen.
• Click Next
• Enter the Printer IP
Address and the Port
Name, as shown.
• Click Next
Page 56

Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
• In this screen,
select Custom.
• Click Settings
• Enter the Port
Name and the
Printer Name or
IP Address.
• Select LPR
• Enter a Queue
Name. If there
is more than
one port on the
print server, you
must name the
Queue.
• Click OK
56
Page 57

Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
• This screen will show
you information
about your printer.
• Click Finish
• Select the printer you
are adding from the
list of Printers.
• Insert the printer
driver disk that came
with your printer.
• Click Have Disk
If the printer driver is already
installed,
• Select Keep existing
driver
• Click Next
Page 58

Networking Basics
r
Sharing an LPR printer
• You can rename your
printer if you choose. It
is optional.
Please remember the name of
your printer. You will need this
information when you use the
Add Printer Wizard on the
other computers on you
network.
• Click Next
• Select Yes, to print a
test page.
• Click Next
This screen will display
information about your
printer.
• Click Finish to
complete the
addition of the
printer.
Please run the
•
Add Printer
Wizard on all the
computers on your
network in order to
share the printer.
Note: You must run the Network Setup Wizard
on all the computers on your network before you
58
run the Add Printer Wizard.
Page 59

Networking Basics
Other Tasks
For help with other tasks in home or small office networking, see Using the
Shared Documents folder and Sharing files and folders in the Help and
Support Center in Microsoft Windows XP.
Technical Specifications
Standards
• IEEE 802.11a (Wi-Fi5)
Adapter Type
• PCI 2.2 compliant
• PCI 32-bit interface
Supported OS
• Windows XP
• Windows 2000
• Windows ME
• Windows 98SE
Frequency Range
• 5.150-5.350 GHz
Data Rates
• 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54, 72 Mbps
Modulation Technology
• Orthogonal Division Frequency Multiplexing (OFDM)
Modulation Techniques
• BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying)
• QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying)
• 16 QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)
• 64 QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)
Data Security
• 64, 128, 154-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Encryption
Media Access Control
• CSMA/CA
Diagnostic LED
• Power
• Link
Page 60

Current Consumption
• Sleep mode - <40mW
• Transmit mode - 1650mW
• Receive mode – 1250mW
Operating Voltage
• 3.3V± -10%
Network Architecture
• Ad-Hoc Mode (Peer-to-Peer without Access Point)
• Infrastructure Mode (Communications to wired networks via
Access Points with Roaming)
Antenna Type
• Integrated dual diversity antennas with 1.5dBi gain
Available Channels:
• Eight non-overlapping channels for North America
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure)
• 30,000 hours
Physical Dimensions
• L ~ 5.24 inches (133 mm)
• W ~ 4.76 inches (121 mm)
• H ~ 0.71 inches (18mm
Temperature
• Operating: 0ºC to 60ºC (32ºF to 140ºF)
• Storing: -20ºC to 85ºC (-4ºF to 185ºF)
Humidity:
• 5%-95%, non-condensing
Emissions:
• FCC part 15b
• UL1950-3
Warranty
• Three Years
60
Page 61

Contacting Technical Support
You can find the most recent software and user documentation on the D-Link
website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States
for the duration of the warranty period on this product.
U.S. customers can contact D-Link technical support through our web site,
or by phone.
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(800) 758-5489
24 hours a day, seven days a week.
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
When contacting technical support, please provide the following information:
• Serial number of the unit
• Model number or product name
• Software type and version number
Page 62

Limited Warranty and Registration
D-Link Systems, Inc. (“D-Link”) provides this 3-Year warranty for its product only to the person or entity
who originally purchased the product from:
•
D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor.
•
Products purchased and delivered with the fifty United States, the District of Columbia, US
3-Year Limited Hardware Warranty: D-Link warrants that the hardware portion of the D-Link products
described below (“Hardware”) will be free from material defects in workmanship and materials from the
date of original retail purchase of the Hardware, for the period set forth below applicable to the product
type (“Warranty Period”).
3-Year Limited Warranty for the Product(s) is defined as follows
D-Link’s sole obligation shall be to repair or replace the defective Hardware at no charge to the original
owner. Such repair or replacement will be rendered by D-Link at an Authorized D-Link Service Office. The
replacement Hardware need not be new or of an identical make, model or part; D-Link may in its
discretion replace the defective Hardware (or any part thereof) with any reconditioned product that D-Link
reasonably determines is substantially equivalent (or superior) in all material respects to the defective
Hardware. The Warranty Period shall extend for an additional ninety (90) days after any repaired or
replaced Hardware is delivered. If a material defect is incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines in
its sole discretion that it is not practical to repair or replace the defective Hardware, the price paid by the
original purchaser for the defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to D-Link of the
defective Hardware. All Hardware (or part thereof) that is replaced by D-Link, or for which the purchase
price is refunded, shall become the property of D-Link upon replacement or refund.
Limited Software Warranty:
substantially conform to D-Link’s then current functional specifications for the Software, as set forth in the
applicable documentation, from the date of original delivery of the Software for a period of ninety (90)
days (“Warranty Period”), if the Software is properly installed on approved hardware and operated as
contemplated in its documentation. D-Link further warrants that, during the Warranty Period, the magnetic
media on which D-Link delivers the Software will be free of physical defects. D-Link’s sole obligation shall
be to replace the non-conforming Software (or defective media) with software that substantially conforms
to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in writing, the
replacement Software is provided only to the original licensee, and is subject to the terms and conditions
of the license granted by D-Link for the Software. The Warranty Period shall extend for an additional
ninety (90) days after any replacement Software is delivered. If a material non-conformance is incapable
of correction, or if D-Link determines in its sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the nonconforming Software, the price paid by the original licensee for the non-conforming Software will be
refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming Software (and all copies thereof) is first returned to
D-Link. The license granted respecting any Software for which a refund is given automatically terminates.
What You Must Do For Warranty Service:
Registration is conducted via a link on our Web Site (http://www.dlink.com/
must be individually registered for warranty service within ninety (90) days after it is purchased and/or
licensed.
FAILURE TO PROPERLY TO REGISTER MAY AFFECT THE WARRANTY FOR THIS PRODUCT.
Submitting A Claim
the Warranty Period to an Authorized D-Link Service Office.
•
•
•
•
D-Link may reject or return any product that is not packaged and shipped in strict compliance with the
foregoing requirements, or for which an RMA number is not visible from the outside of the package. The
product owner agrees to pay D-Link’s reasonable handling and return shipping charges for any product
Possessions or Protectorates, US Military Installations, addresses with an APO or FPO.
•
Hardware (excluding power supplies and fans)
•
Spare parts and spare kits Ninety (90) days.
D-Link warrants that the software portion of the product (“Software”) will
). Each product purchased
. Any claim under this limited warranty must be submitted in writing before the end of
The customer must submit as part of the claim a written description of the Hardware defect or
Software nonconformance in sufficient detail to allow D-Link to confirm the same.
The original product owner must obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number from the
Authorized D-Link Service Office and, if requested, provide written proof of purchase of the product
(such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) before the warranty service is provided.
After an RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged securely in the
original or other suitable shipping package to ensure that it will not be damaged in transit, and the
RMA number must be prominently marked on the outside of the package.
The customer is responsible for all shipping charges to and from D-Link (No CODs allowed).
Products sent COD will become the property of D-Link Systems, Inc. Products should be fully insured
by the customer and shipped to D-Link Systems Inc., 53 Discovery Drive, Irvine CA 92618.
62
Page 63

that is not packaged and shipped in accordance with the foregoing requirements, or that is determined by
D-Link not to be defective or non-conforming.
What Is Not Covered:
This limited warranty provided by D-Link does not cover: Products that have been subjected to abuse,
accident, alteration, modification, tampering, negligence, misuse, faulty installation, lack of reasonable
care, repair or service in any way that is not contemplated in the documentation for the product, or if the
model or serial number has been altered, tampered with, defaced or removed; Initial installation,
installation and removal of the product for repair, and shipping costs; Operational adjustments covered in
the operating manual for the product, and normal maintenance; Damage that occurs in shipment, due to
act of God, failures due to power surge, and cosmetic damage; and Any hardware, software, firmware or
other products or services provided by anyone other than D-Link.
Disclaimer of Other Warranties:
PROVIDED “AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY CANNOT BE
DISCLAIMED IN ANY TERRITORY WHERE A PRODUCT IS SOLD, THE DURATION OF SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTY SHALL BE
LIMITED TO NINETY (90) DAYS. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY COVERED UNDER THE LIMITED WARRANTY PROVIDED HEREIN, THE
ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY, SELECTION AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT IS WITH THE PURCHASER OF THE
PRODUCT.
Limitation of Liability:
NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY OR OTHER LEGAL OR EQUITABLE THEORY FOR ANY LOSS OF USE OF THE PRODUCT,
INCONVENIENCE OR DAMAGES OF ANY CHARACTER, WHETHER DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF GOODWILL, WORK STOPPAGE, COMPUTER FAILURE OR
MALFUNCTION, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA CONTAINED IN, STORED ON, OR INTEGRATED WITH ANY PRODUCT
RETURNED TO D-LINK FOR WARRANTY SERVICE) RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, RELATING TO WARRANTY
SERVICE, OR ARISING OUT OF ANY BREACH OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY, EVEN IF D-LINK HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE SOLE REMEDY FOR A BREACH OF THE FOREGOING LIMITED WARRANTY IS REPAIR,
REPLACEMENT OR REFUND OF THE DEFECTIVE OR NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT.
GOVERNING LAW
states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, or limitations on how
long an implied warranty lasts, so the foregoing limitations and exclusions may not apply. This limited
warranty provides specific legal rights and the product owner may also have other rights which vary from
state to state.
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW , D-LINK IS NOT LIABLE UNDER ANY CONTRACT,
: This 3-Year Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of California. Some
EXCEPT FOR THE 3-YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY SPECIFIED HEREIN, THE PRODUCT IS
Trademarks
Copyright® 2002 D-Link Corporation. Contents subject to change without prior notice. D-Link is a
registered trademark of D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All other trademarks belong to their
respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any
derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission from D-Link
Corporation/D-Link Systems Inc., as stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976.
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communication. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
•
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
•
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
•
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
•
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Modifications to this device are not authorized, may violate FCC regulation Part 15.407, and will void the
warranty for this product. This device is intended to operate in the frequency band of 5.15 to 5.25 GHz
under all conditions of normal operation. According to FCC 15.407 (e), normal operation of this device is
restricted to indoor use only to reduce any potential harmful interference to co-channel Mobile Satellite
Systems, or radar systems that use 5.25 to 5.35 GHz and 5.65 to 5.85 GHz frequency bands. This
interference could also damage this device.
Registration: Register your D-Link
AirPro
DWL-A520 online at http://www.dlink.com/sales/reg
 Loading...
Loading...