Page 1

UNIFIED ACCESS POINT
ADMINISTRATOR’S GUIDE
PRODUCT MODEL: DWL-2600AP, DWL-3600AP, DWL-3610AP, DWL-6600AP,
DWL-6610AP, DWL-6610APE, DWL-6700AP, DWL-8600AP, DWL-8610AP,
DWL-8710AP,DWL-6620APS, DWL-7620AP
UNIFIED WIRED & WIRELESS ACCESS SYSTEM
RELEASE 6.61
OPYRIGHT 2017. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
© C
Page 2

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Table of Contents
Section 1 - About This Document ............................................................................................9
Document Organization ......................................................................................................................................... 9
Additional Documentation ..................................................................................................................................... 9
Document Conventions ......................................................................................................................................... 9
Online Help, Supported Browsers, and Limitations ............................................................................................. 10
Section 2 - Getting Started ......................................................................................................11
Administrator’s Computer Requirements ............................................................................................................ 11
Wireless Client Requirements ............................................................................................................................. 12
Dynamic and Static IP Addressing on the AP ...................................................................................................... 13
Recovering an IP Address ............................................................................................................................. 13
Discovering a Dynamically Assigned IP Address .......................................................................................... 13
Installing the UAP ................................................................................................................................................ 13
Basic Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 16
Connecting to the AP Web Interface by Using the IPv6 Address .................................................................. 17
Using the CLI to View the IP Address.................................................................................................................. 17
Conguring the Ethernet Settings ....................................................................................................................... 18
Using the CLI to Congure Ethernet Settings ............................................................................................... 18
Conguring IEEE 802.1X Authentication ............................................................................................................. 19
Using the CLI to Congure 802.1X Authentication Information ..................................................................... 20
Verifying the Installation ......................................................................................................................................20
Conguring Security on the Wireless Access Point .............................................................................................21
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status ...............................................................................22
Viewing Interface Status ...................................................................................................................................... 22
Wired Settings (Internal Interface) ................................................................................................................ 22
Wireless Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 22
Viewing Events .................................................................................................................................................... 23
Conguring Persistent Logging Options ........................................................................................................ 23
Conguring the Log Relay Host for Kernel Messages .................................................................................. 24
Enabling or Disabling the Log Relay Host on the Events Page .................................................................... 24
Viewing Transmit and Receive Statistics ............................................................................................................. 25
Viewing Wireless Multicast Forwarding Statistics ............................................................................................... 26
Viewing Associated Wireless Client Information ................................................................................................. 27
Viewing TSPEC Client Associations .................................................................................................................... 27
Link Integrity Monitoring ................................................................................................................................ 29
Viewing Rogue AP Detection............................................................................................................................... 29
Saving and Importing the Known AP List ...................................................................................................... 31
Viewing Managed AP DHCP Information ............................................................................................................ 32
Viewing TSPEC Status and Statistics Information .............................................................................................. 32
Viewing TSPEC AP Statistics Information ........................................................................................................... 33
Viewing Radio Statistics Information ................................................................................................................... 34
Viewing Email Alert Operational Status ............................................................................................................... 35
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point .................................................................................36
Ethernet Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 36
IPv6 Tunnel .........................................................................................................................................................38
Wireless Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 38
Using the 802.11h Wireless Mode ................................................................................................................. 41
Enabling AeroScout™ Engine Support .........................................................................................................41
Modifying Radio Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 42
Conguring Radio and VAP Scheduler................................................................................................................ 47
Scheduler Association Settings ........................................................................................................................... 49
Virtual Access Point Settings ............................................................................................................................... 50
None (Plain-text) ........................................................................................................................................... 53
Static WEP .................................................................................................................................................... 53
IEEE 802.1X .................................................................................................................................................. 55
WPA Personal ............................................................................................................................................... 57
WPA Enterprise ............................................................................................................................................. 58
Conguring Wireless Multicast Forwarding ......................................................................................................... 59
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 2
Page 3

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Conguring the Wireless Distribution System (WDS) ......................................................................................... 60
WEP on WDS Links ...................................................................................................................................... 62
WPA/PSK on WDS Links .............................................................................................................................. 62
Controlling Access by MAC Authentication ......................................................................................................... 63
Conguring a MAC Filter and Station List on the AP..................................................................................... 63
Conguring MAC Authentication on the RADIUS Server .............................................................................. 64
Conguring Load Balancing ................................................................................................................................ 64
Managed Access Point Overview ........................................................................................................................ 65
Transition Between Modes ............................................................................................................................ 65
Conguring Managed Access Point Settings ................................................................................................66
Conguring 802.1X Authentication ...................................................................................................................... 67
Creating a Management Access Control List (ACL) ............................................................................................ 68
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services ....................................................................69
Web Server Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 69
Conguring SNMP on the Access Point .............................................................................................................. 70
Setting the SSH Status ........................................................................................................................................ 72
Setting the Telnet Status ..................................................................................................................................... 73
Conguring DDP ................................................................................................................................................. 73
Conguring Quality of Service ............................................................................................................................. 73
Conguring Email Alert ........................................................................................................................................ 76
Enabling the Time Settings (NTP) ....................................................................................................................... 78
Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3 ............................................................................................80
Conguring SNMPv3 Views ................................................................................................................................ 80
Conguring SNMPv3 Groups .............................................................................................................................. 81
Conguring SNMPv3 Users ................................................................................................................................ 82
Conguring SNMPv3 Targets .............................................................................................................................. 83
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point ..............................................................................84
Saving the Current Conguration to a Backup File ............................................................................................. 84
Restoring the Conguration from a Previously Saved File .................................................................................. 85
Rebooting the Access Point ................................................................................................................................86
Resetting the Factory Default Conguration ................................................................................................. 86
Rebooting the Access Point ..........................................................................................................................86
Upgrading the Firmware ...................................................................................................................................... 86
Packet Capture Conguration and Settings ........................................................................................................ 88
Packet Capture Status .................................................................................................................................. 89
Packet Capture Parameter Conguration ..................................................................................................... 89
Packet File Capture ....................................................................................................................................... 90
Remote Packet Capture ................................................................................................................................ 90
Packet Capture File Download ...................................................................................................................... 92
Support Information Conguration and Settings ................................................................................................. 92
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS) ......................................................93
Conguring VAP QoS Parameters ...................................................................................................................... 93
Managing Client QoS ACLs .................................................................................................................................94
IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs ......................................................................................................................................94
MAC ACLs ..................................................................................................................................................... 95
ACL Conguration Process ........................................................................................................................... 95
Creating a DiffServ Class Map .......................................................................................................................... 100
Dening DiffServ ......................................................................................................................................... 101
Creating a DiffServ Policy Map ......................................................................................................................... 105
Client QoS Status .............................................................................................................................................. 106
Conguring RADIUS-Assigned Client QoS Parameters ................................................................................... 107
Section 9 - Clustering Multiple APs .....................................................................................109
Managing Cluster Access Points in the Cluster .................................................................................................109
Clustering APs ............................................................................................................................................. 109
Viewing and Conguring Cluster Members ................................................................................................. 109
Removing an Access Point from the Cluster ............................................................................................... 112
Adding an Access Point to a Cluster ........................................................................................................... 112
Navigating to Conguration Information for a Specic AP........................................................................... 112
Navigating to an AP by Using its IP Address in a URL ................................................................................ 112
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 3
Page 4

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Managing Cluster Sessions ............................................................................................................................... 113
Sorting Session Information ........................................................................................................................ 114
Conguring and Viewing Channel Management Settings ................................................................................. 114
Stopping/Starting Automatic Channel Assignment ...................................................................................... 115
Viewing Current Channel Assignments and Setting Locks ......................................................................... 11 5
Viewing the Last Proposed Set of Changes ................................................................................................ 11 5
Conguring Advanced Settings ................................................................................................................... 116
Viewing Wireless Neighbourhood Information .................................................................................................. 116
Viewing Details for a Cluster Member ......................................................................................................... 11 8
Cluster Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................................................ 11 9
Appendix A - Default AP Settings .........................................................................................120
Appendix B - Conguration Examples ................................................................................122
Conguring a VAP ............................................................................................................................................. 122
VAP Conguration from the Web Interface ................................................................................................. 122
VAP Conguration from the CLI .................................................................................................................. 123
VAP Conguration Using SNMP ................................................................................................................. 123
Conguring Radio Settings ................................................................................................................................ 124
Radio Conguration from the Web Interface ............................................................................................... 124
Radio Conguration from the CLI ................................................................................................................ 124
Radio Conguration Using SNMP ............................................................................................................... 125
Conguring the Wireless Distribution System ................................................................................................... 125
WDS Conguration from the Web Interface ................................................................................................ 125
WDS Conguration from the CLI ................................................................................................................. 126
WDS Conguration Using SNMP ................................................................................................................ 126
Clustering Access Points ................................................................................................................................... 126
Clustering APs by Using the Web Interface ................................................................................................ 126
Clustering APs by Using the CLI ................................................................................................................. 127
Clustering APs by Using SNMP .................................................................................................................. 128
Conguring Client QoS ..................................................................................................................................... 128
Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface ............................................................................................. 128
Conguring QoS by Using the CLI .............................................................................................................. 132
Appendix C - DWL-6700AP Prole and Conguration Table .............................................135
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 4
Page 5

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
List of Figures
Figure 1 - Administrator UI Online Help ................................................................................................................... 10
Figure 2 - Web UI Login Prompt .............................................................................................................................. 15
Figure 3 - Provide Basic Settings ............................................................................................................................ 15
Figure 4 - Command Line Interface (CLI) Connection ............................................................................................ 18
Figure 5 - Viewing Interface Status ......................................................................................................................... 22
Figure 6 - Viewing Events ........................................................................................................................................ 23
Figure 7 - Viewing Trafc Statistics ......................................................................................................................... 25
Figure 8 - Viewing WMF Transmit and Receive Statistics ....................................................................................... 26
Figure 9 - Viewing Client Association Information ................................................................................................... 27
Figure 10 - Viewing TSPEC Client Associations ..................................................................................................... 28
Figure 11 - Viewing Rogue and Known Access Points ............................................................................................ 29
Figure 12 - Managed AP DHCP Information ........................................................................................................... 32
Figure 13 - Viewing TSPEC Status and Statistics ................................................................................................... 32
Figure 14 - View TSPEC Status and Statistics ........................................................................................................ 33
Figure 15 - View Radio Statistics ............................................................................................................................. 34
Figure 16 - Email Alert Operational Status .............................................................................................................. 35
Figure 17 - Modify Ethernet (Wired) settings ........................................................................................................... 36
Figure 18 - Modify IPv6 Tunnel Settings ................................................................................................................. 38
Figure 19 - Modify Wireless Settings ....................................................................................................................... 39
Figure 20 - Modify Radio Settings ........................................................................................................................... 42
Figure 21 - Scheduler Conguration ....................................................................................................................... 48
Figure 22 - Scheduler Conguration (Modify Rule) ................................................................................................. 49
Figure 23 - Scheduler Association Settings ............................................................................................................. 50
Figure 24 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings ..................................................................................................... 51
Figure 25 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (Static WEP) ............................................................................... 54
Figure 26 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (IEEE802.1X) .............................................................................. 56
Figure 27 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (WPA Personal) .......................................................................... 57
Figure 28 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (WPA Enterprise) ........................................................................ 58
Figure 29 - Wireless Multicast Forwarding .............................................................................................................. 60
Figure 30 - Congure WDS Bridges ........................................................................................................................ 61
Figure 31 - Congure MAC Authentication .............................................................................................................. 63
Figure 32 - Modify Load Balancing Settings ............................................................................................................ 64
Figure 33 - Congure Managed AP Wireless Switch Parameters ........................................................................... 66
Figure 34 - Modify 802.1X Supplicant Authentication Settings ................................................................................67
Figure 35 - Congure Management Access Control Parameters ............................................................................ 68
Figure 36 - Congure Web Server Settings ............................................................................................................. 69
Figure 37 - SNMP Conguration ............................................................................................................................. 71
Figure 38 - Set SSH Status ..................................................................................................................................... 72
Figure 39 - Set Telnet Status ................................................................................................................................... 73
Figure 40 - DDP Status Conguration ..................................................................................................................... 73
Figure 41 - Modify QoS Queue Parameters ............................................................................................................ 74
Figure 42 - Email Alerts Conguration ..................................................................................................................... 77
Figure 43 - Time Settings (NTP) .............................................................................................................................. 78
Figure 44 - SNMPv3 Views Conguration ............................................................................................................... 80
Figure 45 - SNMPv3 Groups Conguration ............................................................................................................. 81
Figure 46 - SNMPv3 User Conguration ................................................................................................................. 82
Figure 47 - SNMPv3 Targets Conguration ............................................................................................................. 83
Figure 48 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Save (TFTP) .................................................................... 84
Figure 49 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Save (HTTP) .................................................................... 84
Figure 50 - Conrmation Prompt ............................................................................................................................. 85
Figure 51 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Restore (TFTP) ................................................................ 85
Figure 52 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Restore (HTTP) ............................................................... 85
Figure 53 - Rebooting the Access Point .................................................................................................................. 86
Figure 54 - Performing AP Maintenance ................................................................................................................. 86
Figure 55 - Manage Firmware (TFTP) ..................................................................................................................... 87
Figure 56 - Manage Firmware (HTTP) .................................................................................................................... 87
Figure 57 - Packet Capture Conguration & Settings ............................................................................................. 88
Figure 58 - Packet Capture Status .......................................................................................................................... 89
Figure 59 - Packet Capture Conguration ............................................................................................................... 89
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 5
Page 6

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Figure 60 - Packet File Capture .............................................................................................................................. 90
Figure 61 - Remote Packet Capture ........................................................................................................................ 91
Figure 62 - Packet Capture File Download ............................................................................................................. 92
Figure 63 - Support Information .............................................................................................................................. 92
Figure 64 - Congure Client QoS VAP Settings ...................................................................................................... 93
Figure 65 - Congure Client QoS ACL Settings ...................................................................................................... 95
Figure 66 - Congure Client QoS DiffServ Class Map Settings ............................................................................ 101
Figure 67 - Congure Client QoS DiffServ Policy Map Settings ............................................................................ 105
Figure 68 - QoS Conguration Status For Associated Clients ..............................................................................106
Figure 69 - Manage Access Points In The Cluster (Passive) ................................................................................ 110
Figure 70 - Manage Access Points In The Cluster (Active) ................................................................................... 110
Figure 71 - Manage Sessions Associated With The Cluster ................................................................................. 11 3
Figure 72 - Automatically Manage Channel Assignments ..................................................................................... 114
Figure 73 - View Neighboring Access Points ......................................................................................................... 117
Figure 74 - Viewing Details For A Cluster Member ................................................................................................ 11 8
Figure 75 - VAP Conguration from the Web Interface ......................................................................................... 122
Figure 76 - Radio Conguration from the Web Interface ....................................................................................... 124
Figure 77 - WDS Conguration from the Web Interface ........................................................................................ 125
Figure 78 - Clustering APs by Using the Web Interface (Passive) ........................................................................ 126
Figure 79 - Clustering APs by Using the Web Interface (Active) ........................................................................... 127
Figure 80 - Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface (ACL Name) ................................................................128
Figure 81 - Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface (Rule1) ........................................................................ 128
Figure 82 - Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface (Rule2) ........................................................................ 129
Figure 83 - Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface (VAP QoS Parameters) ............................................... 129
Figure 84 - Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface (Class Map Name) ...................................................... 130
Figure 85 - Conguring QoS by Using the Web Interface (Rule) .......................................................................... 130
Figure 86 - Congure Client QoS DiffServ Policy Map Settings (Policy Map Name) ............................................ 130
Figure 87 - Congure Client QoS DiffServ Policy Map Settings (Rule) ................................................................. 131
Figure 88 - Congure Client QoS VAP Settings .................................................................................................... 131
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 6
Page 7

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
List of Tables
Table 1 - Typographical Conventions ...................................................................................................................... 10
Table 2 - Requirements for the Administrator’s Computer ....................................................................................... 12
Table 3 - Requirements for Wireless Clients ........................................................................................................... 13
Table 4 - Basic Settings Page ................................................................................................................................. 17
Table 5 - CLI Commands for Ethernet Setting ........................................................................................................ 19
Table 6 - CLI Commands for the 802.1X Supplicant ............................................................................................... 20
Table 7 - Logging Options ....................................................................................................................................... 24
Table 8 - Log Relay Host ......................................................................................................................................... 24
Table 9 - Transmit/Receive ...................................................................................................................................... 26
Table 10 - WMF Transmit and Receive Statistics Table .......................................................................................... 27
Table 11 - Associated Clients ................................................................................................................................... 27
Table 12 - TSPEC Client Associations ..................................................................................................................... 29
Table 13 - Rogue AP Detection ............................................................................................................................... 31
Table 14 - TSPEC Status and Statistics .................................................................................................................. 33
Table 15 - TSPEC AP Statistics ............................................................................................................................... 34
Table 16 - Radio Statistics Information .................................................................................................................... 35
Table 17 - Email Alert Status ................................................................................................................................... 35
Table 18 - Ethernet Settings .................................................................................................................................... 37
Table 19 - IPv6 Tunnel Settings ............................................................................................................................... 38
Table 20 - Wireless Settings .................................................................................................................................... 41
Table 21 - Radio Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 47
Table 22 - Scheduler Conguration ......................................................................................................................... 48
Table 23 - Scheduler Association Settings .............................................................................................................. 50
Table 24 - Virtual Access Point Settings .................................................................................................................. 53
Table 25 - Static WEP .............................................................................................................................................. 55
Table 26 - IEEE 802.1X ........................................................................................................................................... 57
Table 27 - WPA Personal ......................................................................................................................................... 57
Table 28 - WPA Enterprise ....................................................................................................................................... 59
Table 29 - Wireless Multicast Forwarding ................................................................................................................ 60
Table 30 - WDS Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 61
Table 31 - WEP on WDS Links ................................................................................................................................ 62
Table 32 - WPA/PSK on WDS Links ........................................................................................................................ 62
Table 33 - MAC Authentication ................................................................................................................................ 64
Table 34 - RADIUS Server Attributes for MAC Authentication ................................................................................. 64
Table 35 - Load Balancing ....................................................................................................................................... 65
Table 36 - Managed Access Point ........................................................................................................................... 66
Table 37 - IEEE 802.1X Supplicant Authentication .................................................................................................. 67
Table 38 - Management ACL ................................................................................................................................... 68
Table 39 - Web Server Settings ............................................................................................................................... 70
Table 40 - SNMP Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 72
Table 41 - SSH Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 73
Table 42 - Telnet Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 73
Table 43 - DDP Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 73
Table 44 - QoS Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 76
Table 45 - Email Alert Conguration ........................................................................................................................ 78
Table 46 - NTP Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 79
Table 47 - SNMPv3 Views ....................................................................................................................................... 80
Table 48 - SNMPv3 Groups ..................................................................................................................................... 82
Table 49 - SNMPv3 Users ....................................................................................................................................... 82
Table 50 - SNMPv3 Targets ..................................................................................................................................... 83
Table 51 - Packet Capture Status ............................................................................................................................ 89
Table 52 - Packet Capture Conguration ................................................................................................................ 89
Table 53 - Packet File Capture ................................................................................................................................ 90
Table 54 - Remote Packet Capture ......................................................................................................................... 92
Table 55 - Packet Capture File Download ............................................................................................................... 92
Table 56 - Support Information ................................................................................................................................ 92
Table 57 - VAP QoS Parameters ............................................................................................................................. 94
Table 58 - ACL Conguration ................................................................................................................................. 100
Table 59 - DiffServ Class Map ............................................................................................................................... 104
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 7
Page 8

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Table 60 - DiffServ Policy Map .............................................................................................................................. 106
Table 61 - Client QoS Status ................................................................................................................................. 107
Table 62 - Client QoS RADIUS Attributes .............................................................................................................. 108
Table 63 - Access Points in the Cluster ..................................................................................................................111
Table 64 - Cluster Options ......................................................................................................................................111
Table 65 - Single IP Management Options .............................................................................................................111
Table 66 - Secure Join Clustering ......................................................................................................................... 112
Table 67 - Session Management ........................................................................................................................... 113
Table 68 - Channel Assignments ........................................................................................................................... 115
Table 69 - Last Proposed Changes ....................................................................................................................... 115
Table 70 - Advanced Channel Management Settings ........................................................................................... 116
Table 71 - Wireless Neighborhood Information ..................................................................................................... 118
Table 72 - Cluster Member Details ........................................................................................................................ 119
Table 73 - Cluster Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................................... 119
Table 74 - UAP Default Settings ............................................................................................................................ 121
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 8
Page 9

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 1 - About This Document
Section 1 - About This Document
This guide describes setup, conguration, administration and maintenance for the D-Link DWL-x600AP Unied Access
Point (UAP) on a wireless network.
Document Organization
The Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide contains the following sections:
•) “Section 1 - About This Document” on page 9
•) “Section 2 - Getting Started” on page 11
•) “Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status” on page 22
•) “Section 4 - Managing the Access Point” on page 36
•) “Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services” on page 69
•) “Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3” on page 80
•) “Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point” on page 84
•) “Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)” on page 93
•) “Section 9 - Clustering Multiple APs” on page 109
•) “Appendix A - Default AP Settings” on page 120
•) “Appendix B - Conguration Examples” on page 122
Additional Documentation
The following documentation provides additional information about Unied Access Point software:
•) The Unied Access Point CLI Command Reference describes the commands available from the command-line
interface (CLI) for managing, monitoring, and conguring the switch.
•) The User Manual for the D-Link Unied Wired and Wireless System provides information about setting up and
managing the Unied Wireless Switch (UWS), including information about how to use the switch to manage
multiple UAPs.
•) Release notes for the D-Link Unied Wired and Wireless System detail the platform-specic functionality of the
software packages, including issues and workarounds.
Document Conventions
This section describes the conventions this document uses.
Note: A note provides more information about a feature or technology and cross-references to
related topics.
Caution! A caution provides information about critical aspects of AP conguration, combinations of
settings, events, or procedures that can adversely affect network connectivity, security, and so on.
The following table describes the typographical conventions used in this guide.
Symbol Example Description
Bold Click Apply to save your settings. Menu titles, page names, and button names.
Blue Text See “Document Conventions” on
page 9
Courier Font WLAN-AP# show network
Courier Font
Italics
Square Brackets [ ] [Value] Indicates an optional xed parameter.
October 2017
Value
Hyperlink text.
Screen text, le names, commands, user-typed
command-line entries.
Command parameter, which might be a variable or
xed value.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 9
Page 10
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Symbol Example Description
Curly Braces {} {Choice1 | Choice2} Indicates that you must select a parameter from the
list of choices.
Vertical Bars | Choice1 | Choice2 Separates the mutually exclusive choices.
Braces within square
brackets [{}]
[{Choice1 | Choice2}] Indicate a choice within an optional element.
Table 1 - Typographical Conventions
Section 1 - About This Document
Online Help, Supported Browsers, and Limitations
Online help for the UAP Administration Web pages provides information about all elds and features available from
the user interface (UI). The information in the online help is a subset of the information available in the Unied Access
Point Administrator’s Guide.
Online help information corresponds to each page on the UAP Administration UI.
For information about the settings on the current page, click the Help link on the upper right side of a page.
The following gure shows an example of the online help available from the links on the user interface.
October 2017
Figure 1 - Administrator UI Online Help
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 10
Page 11

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 2 - Getting Started
Section 2 - Getting Started
The D-Link DWL-x600AP unied access point (UAP) provides continuous, high-speed access between wireless
devices and Ethernet devices. It is an advanced, standards-based solution for wireless networking in businesses of
any size. The UAP enables wireless local area network (WLAN) deployment while providing state-of-the-art wireless
networking features.
The UAP can operate in two modes: Standalone Mode or Managed Mode. In Standalone Mode, the UAP acts
as an individual access point in the network, and you manage it by using the Administrator Web User Interface
(UI), command-line interface (CLI), or SNMP. In Managed Mode, the UAP is part of the D-Link Unied Wired and
Wireless System, and you manage it by using the D-Link Unied Wireless Switch. If an AP is in Managed Mode, the
Administrator Web UI, Telnet, SSH, and SNMP services are disabled.
This document describes how to perform the setup, management, and maintenance of the UAP in Standalone Mode.
For information about conguring the AP in Managed Mode by using the D-Link Unied Wireless Switch, see the User
Manual for the switch.
Before you power on a new UAP, review the following sections to check required hardware and software components,
client congurations, and compatibility issues. Make sure you have everything you need for a successful launch and
test of your new or extended wireless network.
The DWL-6600AP and DWL-8600AP are dual-radio access points and support the IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g,
and 802.11n modes. The DWL-2600AP and DWL-3600AP are single-radio access points and support the IEEE
802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, and 802.11n (2.4 GHz) modes. The DWL-3610AP is a single-radio access point that supports
both 2.4 GHz (IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11n) and 5 GHz (IEEE 802.11a, 802.11n, 802.11ac) modes.
The DWL-6610AP, DWL-8610AP, DWL-8710AP, and DWL-6620APS are dual radio access points and support all the
modes (IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n, and IEEE 802.11ac). The DWL-7620AP is a triradio access point which supports one 2.4GHz Radio (IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11n) and two 5GHz
Radios (IEEE 802.11a, 802.11n, 802.11ac).
This section contains the following topics:
•) “Administrator’s Computer Requirements” on page 11
•) “Wireless Client Requirements” on page 12
•) “Dynamic and Static IP Addressing on the AP” on page 13
•) “Installing the UAP” on page 13
•) “Basic Settings” on page 16
•) “Using the CLI to View the IP Address” on page 17
•) “Conguring the Ethernet Settings” on page 18
•) “Conguring IEEE 802.1X Authentication” on page 19
•) “Verifying the Installation” on page 20
•) “Conguring Security on the Wireless Access Point” on page 21
To manage the UAP by using the Web interface or by using the CLI through Telnet or SSH, the AP needs an IP
address. If you use VLANs or IEEE 802.1X Authentication (port security) on your network, you might need to congure
additional settings on the AP before it can connect to the network.
Note: The WLAN AP is not designed to function as a gateway to the Internet. To connect your
WLAN to other LANs or the Internet, you need a gateway device.
Administrator’s Computer Requirements
The following table describes the minimum requirements for the administrator’s computer for conguration and
administration of the UAP through a Web-based user interface (UI).
Required Software or Component Description
Serial or Ethernet Connection to the
Access Point
October 2017
The computer used to congure the rst access point must be connected
to the access point by a serial cable or an Ethernet cable.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 11
Page 12
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Required Software or Component Description
Wireless Connection to the Network After initial conguration and launch of the rst access point on your
new wireless network, you can make subsequent conguration changes
through the Administration Web pages using a wireless connection to the
internal network.
For wireless connection to the access point, your administration device will
need Wi-Fi capability similar to that of any wireless client:
•) Portable or built-in Wi-Fi client adapter that supports one or more of
the IEEE 802.11 modes in which you plan to run the access point.
•) Wireless client software congured to associate with the UAP.
Web Browser and Operating System Conguration and administration of the UAP is provided through a Web-
based user interface hosted on the access point.
We recommend using one of the following supported Web browsers to
access the access point Administration Web pages:
•) Microsoft
level for either major version)
•) Mozilla® Firefox version 3.5 or later
•) Safari 5 and later versions
The administration Web browser must have JavaScript™ enabled to
support the interactive features of the administration interface.
®
Internet Explorer® version 7.x or 8.x (with up-to-date patch
Section 2 - Getting Started
Note: DWL-3610AP and DWL-6610B1AP support the following web
browsers:
•) Microsoft® Internet Explorer® version 8.x or 9.x (with up-to-date patch
level for either major version)
•) Mozilla® Firefox version 26.0 or later
•) Chrome on Windows (for AP only) version 32.0 or later
Security Settings Ensure that security is disabled on the wireless client used to initially
congure the access point.
Table 2 - Requirements for the Administrator’s Computer
Wireless Client Requirements
The UAP provides wireless access to any client with a properly congured Wi-Fi client adapter for the 802.11 mode
in which the access point is running. The UAP supports multiple client operating systems. Clients can be laptop or
desktop computers, personal digital assistants (PDAs), or any other hand-held, portable or stationary device equipped
with a Wi-Fi adapter and supporting drivers.
To connect to the access point, wireless clients need the software and hardware described in the following table.
Required Component Description
Wi-Fi Client Adapter Portable or built-in Wi-Fi client adapter that supports one or more of the
IEEE 802.11 modes in which you plan to run the access point.
Wireless Client Software Client software, such as Microsoft Windows Supplicant, congured to
associate with the UAP.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 12
Page 13
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Required Component Description
Client Security Settings Security should be disabled on the client used to do initial conguration of
the access point.
If the Security mode on the access point is set to anything other than plain
text, wireless clients will need to set a prole to the authentication mode
used by the access point and provide a valid username and password,
certicate, or similar user identity proof. Security modes are Static WEP,
IEEE 802.1X, WPA with RADIUS server, and WPA-PSK.
For information about conguring security on the access point, see “Virtual
Access Point Settings” on page 50.
Table 3 - Requirements for Wireless Clients
Section 2 - Getting Started
Dynamic and Static IP Addressing on the AP
When you power on the access point, the built-in DHCP client searches for a DHCP server on the network in order
to obtain an IP Address and other network information. If the AP does not nd a DHCP server on the network, the AP
continues to use its default Static IP Address (10.90.90.91) until you re-assign it a new static IP address (and specify a
static IP addressing policy) or until the AP successfully receives network information from a DHCP server.
To change the connection type and assign a static IP address by using the CLI, see “Conguring the Ethernet
Settings” on page 18 or, by using the Web UI, see “Ethernet Settings” on page 36.
Caution! If you do not have a DHCP server on your internal network, and do not plan to use one,
the rst thing you must do after powering on the access point is change the connection type from
DHCP to static IP. You can either assign a new static IP address to the AP or continue using the
default address. We recommend assigning a new static IP address so that if you bring up another
WLAN AP on the same network, the IP address for each AP will be unique.
Recovering an IP Address
If you experience trouble communicating with the access point, you can recover a static IP address by resetting the AP
conguration to the factory defaults (see “Resetting the Factory Default Conguration” on page 86), or you can get
a dynamically assigned address by connecting the AP to a network that has a DHCP server.
Discovering a Dynamically Assigned IP Address
If you have access to the DHCP server on your network and know the MAC address of your AP, you can view the new
IP address associated with the MAC address of the AP.
If you do not have access to the DHCP server that assigned the IP address to the AP or do not know the MAC address
of the AP, you might need to use the CLI to nd out what the new IP address is. For information about how to discover
a dynamically assigned IP address, see “Using the CLI to View the IP Address” on page 17.
Installing the UAP
To access the Administration Web UI, you enter the IP address of the AP into a Web browser. You can use the default
IP address of the AP (10.90.90.91) to log on to the AP and assign a static IP address, or you can use a DHCP server
on you network to assign network information to the AP. The DHCP client on the AP is enabled by default.
To install the UAP, use the following steps:
1.) Connect the AP to an administrative PC by using a LAN connection or a direct-cable connection.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 13
Page 14
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
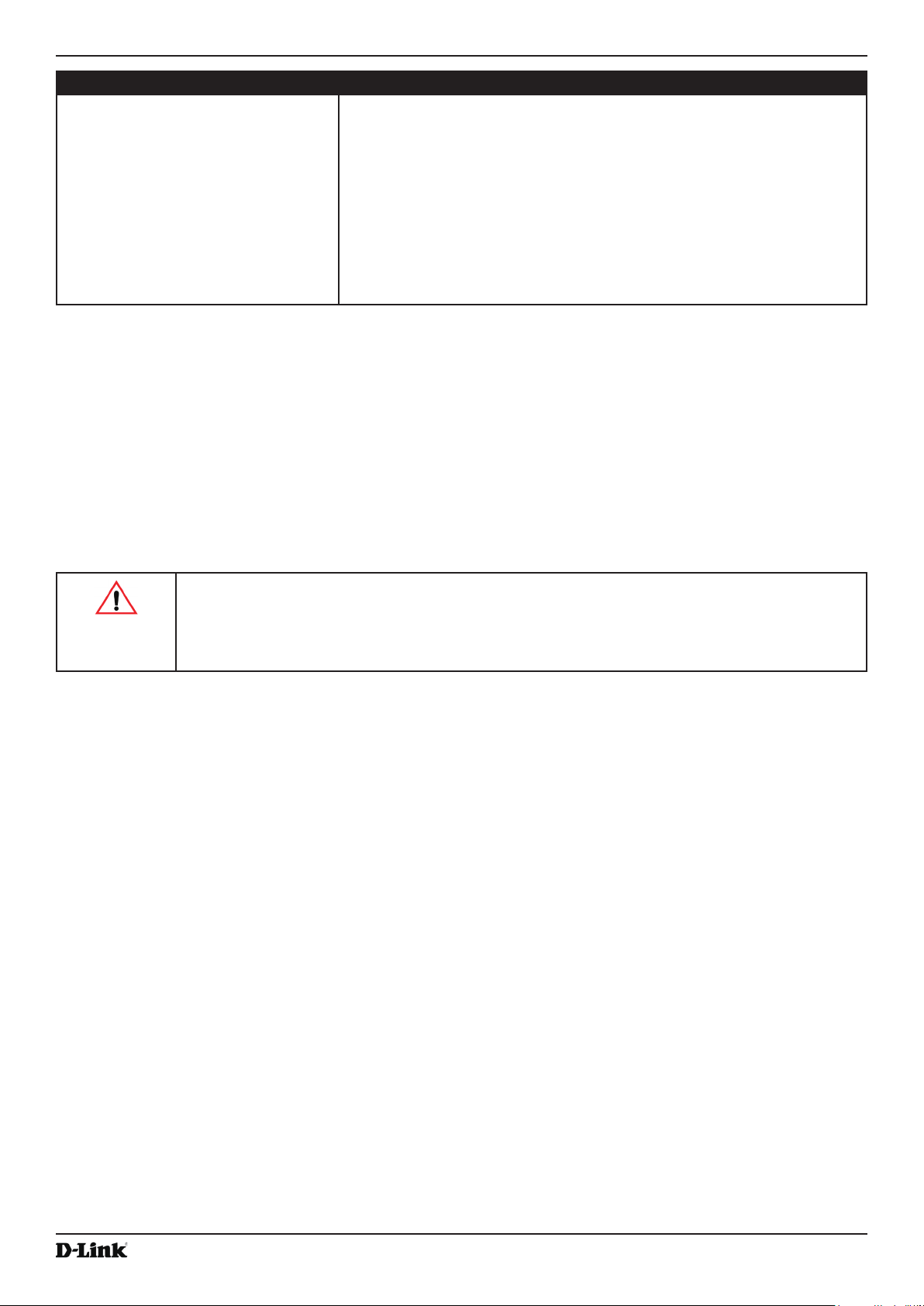
•) To use a LAN connection, connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the network port on the access point and
the other end to the same hub where your PC is connected, as shown in the following gure.
The hub or switch you use must permit broadcast signals from the access point to reach all other devices on
the network.
•) To use a direct-cable connection, connect one end of an Ethernet straight-through or crossover cable to the
network port on the access point and the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port on the PC, as shown in
the following gure. You can also use a serial cable to connect the serial port on the AP to a serial port on the
administrative computer.
Section 2 - Getting Started
For initial conguration with a direct Ethernet connection and no DHCP server, be sure to set your PC to a
static IP address in the same subnet as the default IP address on the access point. (The default IP address for
the access point is 10.90.90.91.)
If you use this method, you will need to recongure the cabling for subsequent startup and deployment of the
access point so that the access point is no longer connected directly to the PC but instead is connected to the
LAN (either by using a hub or directly).
Note: It is possible to detect access points on the network with a wireless connection. However,
we strongly advise against using this method. In most environments you may have no way
of knowing whether you are actually connecting to the intended AP. Also, many of the initial
conguration changes required will cause you to lose connectivity with the AP over a wireless
connection.
2.) Connect the power adapter to the power port on the back of the access point, and then plug the other end of the
power cord into a power outlet.
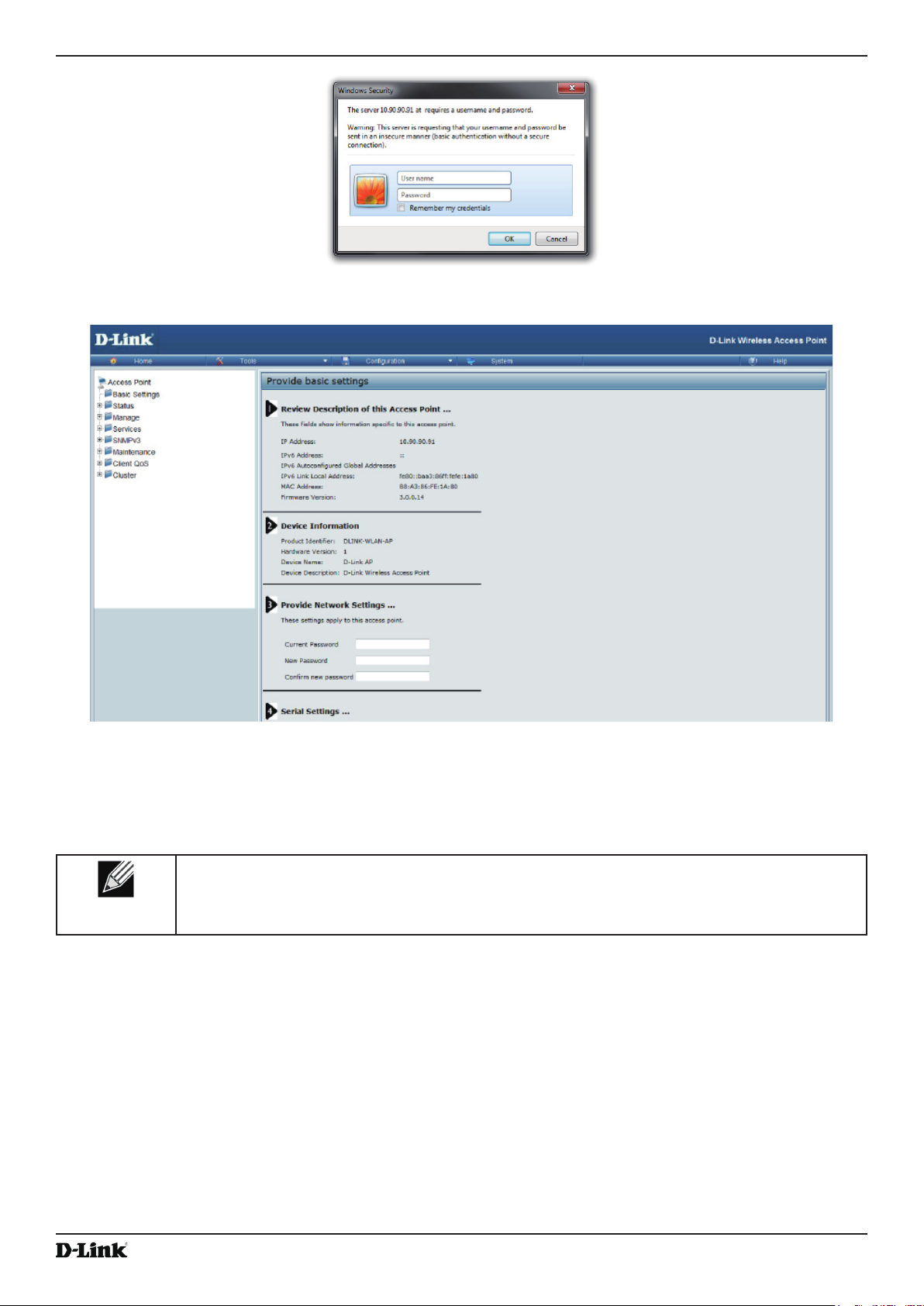
3.) Use your Web browser to log on to the UAP Administration Web pages.
•) If the AP did not acquire an IP address from a DHCP server on your network, enter 10.90.90.91 in the address
eld of your browser, which is the default IP address of the AP.
•) If you used a DHCP server on your network to automatically congure network information for the AP, enter the
new IP address of the AP into the Web browser.
•) If you used a DHCP server and you do not know the new IP address of the AP, use the following procedures to
obtain the information:
•) Connect a serial cable from the administrative computer to the AP and use a terminal emulation program to
access the command-line interface (CLI).
•) At the login prompt, enter admin for the user name and admin for the password. At the command prompt,
enter get management.
•) The command output displays the IP address of the AP. Enter this address in the address eld of your browser.
For a more detailed explanation about how to log on to the CLI by using the console port, see “Using the CLI
to View the IP Address” on page 24.
4.) When prompted, enter admin for the user name and admin for the password, then click Logon.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 14
Page 15
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
After you log in, the Basic Settings page for UAP administration is displayed, as the following gure shows.
Section 2 - Getting Started
Figure 2 - Web UI Login Prompt
Figure 3 - Provide Basic Settings
5.) Verify the settings on the Basic Settings page.
•) Review access point description and provide a new administrator password for the access point if you do not
want to use the default password, which is admin.
•) Click the Apply button to activate the wireless network with these new settings.
Note: The changes you make are not saved or applied until you click Apply. Changing some
access point settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system processes. If this happens,
wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that you change access point
settings when WLAN trafc is low.
For information about the elds and conguration options on the Basic Settings page, see “Basic Settings” on
page 16.
6.) If you do not have a DHCP server on the management network and do not plan to use one, you must change
the Connection Type from DHCP to Static IP.
You can either assign a new Static IP address to the AP or continue using the default address. We recommend
assigning a new Static IP address so that if you bring up another UAP on the same network, the IP address
for each AP will be unique. To change the connection type and assign a static IP address, see “Conguring the
Ethernet Settings” on page 18 (CLI) or “Ethernet Settings” on page 36 (Web).
7.) If your network uses VLANs, you might need to congure the management VLAN ID or untagged VLAN ID on
the UAP in order for it to work with your network.
For information about how to congure VLAN information, see “Conguring the Ethernet Settings” on page 18
(CLI) or “Ethernet Settings” on page 36 (Web).
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 15
Page 16
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
8.) If your network uses IEEE 802.1X port security for network access control, you must congure the 802.1X
supplicant information on the AP.
For information about how to congure the 802.1X user name and password, see “Conguring IEEE 802.1X
Authentication” on page 19.
Section 2 - Getting Started
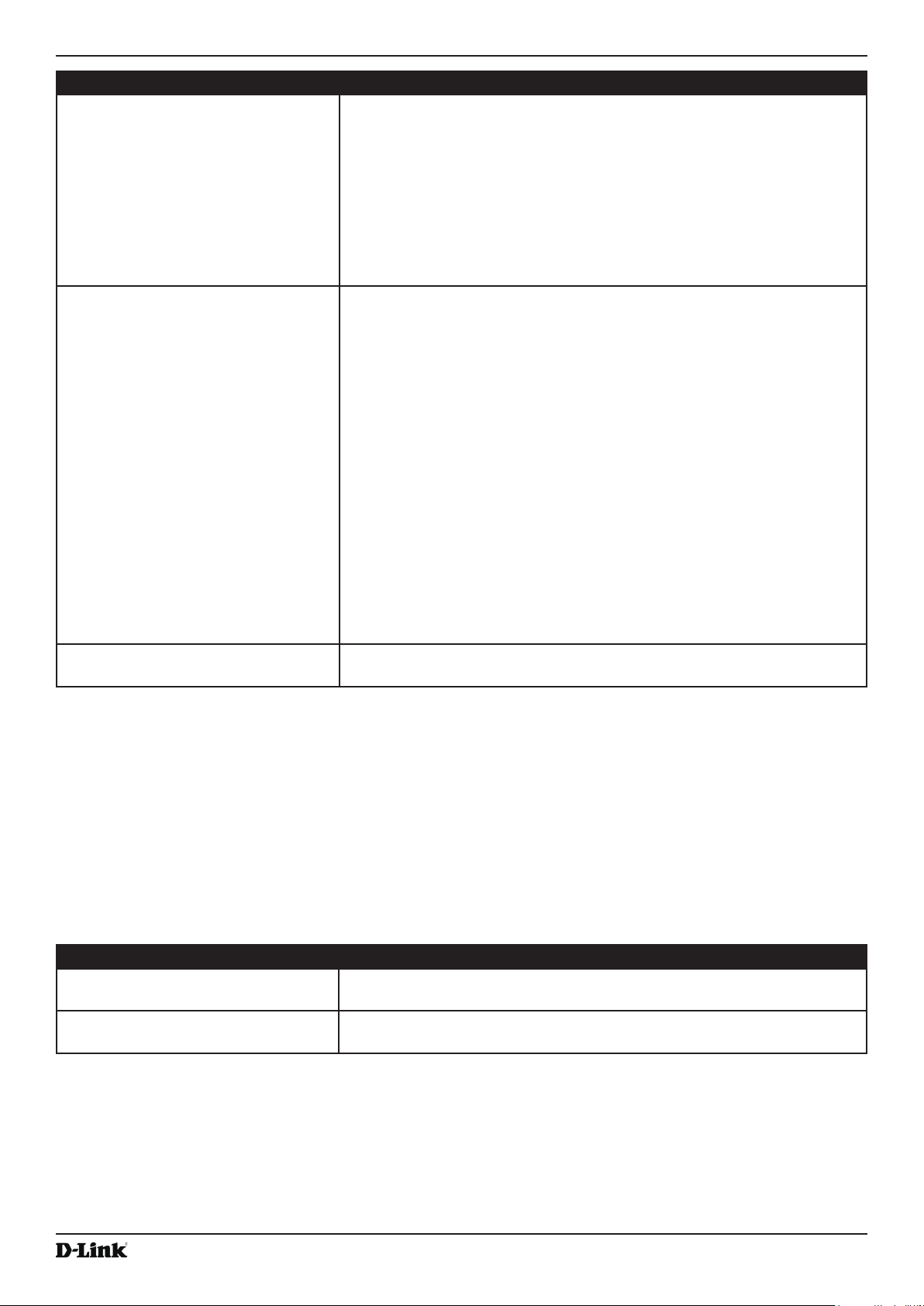
Basic Settings
From the Basic Settings page, you can view various information about the UAP, including IP and MAC address
information, and congure the administrator password for the UAP. The following table describes the elds and
conguration options on the Basic Settings page.
Field Description
IP Address Shows the IP address assigned to the AP. This eld is not editable on this page because
the IP address is already assigned (either by DHCP, or statically through the Ethernet
Settings page).
IPv6 Address Shows the IPv6 address assigned to the AP. This eld is not editable on this page because
the IP address is already assigned (either by DHCPv6, or statically through the Ethernet
Settings page).
IPv6 Address Status Shows the operational status of the static IPv6 address assigned to the management
interface of the AP. The possible values are Operational and Tentative.
IPv6 Autocongured Global
Addresses
IPv6 Link Local
Address
MAC Address Shows the MAC address of the AP. The address shown here is the MAC address
Firmware Version Shows version information about the rmware currently installed on the AP. As new
Model Displays the AP model number.
Product Identier Identies the AP hardware model.
Hardware Version Identies the AP hardware version.
Serial Number Shows the AP serial number.
Device Name Generic name to identify the type of hardware.
Device Description Provides information about the product hardware.
New Password Enter a new administrator password. The characters you enter are displayed as bullet
Shows each automatically-congured global IPv6 address for the management interface of
the AP.
Shows the IPv6 Link Local address, which is the IPv6 address used by the local physical
link. The link local address is not congurable and is assigned by using the IPv6 Neighbor
Discovery process.
associated with the management interface. This is the address by which the AP is known
externally to other networks.
versions of the WLAN AP rmware become available, you can upgrade the rmware on
your APs.
characters to prevent others from seeing your password as you type.
Conrm New
Password
October 2017
The administrator password must be an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. The
special characters are also supported.
Note: As an immediate rst step in securing your wireless network, we recommend that
you change the administrator password from the default.
Re-enter the new administrator password to conrm that you typed it as intended.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 16
Page 17

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Baud Rate Select a baud rate for the serial port connection. The baud rate on the AP must match the
baud rate on the terminal or terminal emulator to connect to the AP command-line interface
(CLI) by using a serial (console) connection.
The following baud rates are available:
•) 9600
•) 19200
•) 38400
•) 57600
•) 115200
System Name Enter a name for the AP. This name appears only on the Basic Settings page and is a
name to identify the AP to the administrator. Use up to 64 alphanumeric characters, for
example My AP.
System Contact Enter the name, e-mail address, or phone number of the person to contact regarding
issues related to the AP.
System Location Enter the physical location of the AP, for example Conference Room A.
Table 4 - Basic Settings Page
Section 2 - Getting Started
Connecting to the AP Web Interface by Using the IPv6 Address
To connect to the AP by using the IPv6 global address or IPv6 link local address, you must enter the AP address into
your browser in a special format.
Note: The following instructions and examples work with Microsoft Internet Explorer 7 (IE7) and
might not work with other browsers. For DWL-3610AP and DWL-6610B1AP, it will work with
Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 (IE8).
To connect to an IPv6 global address, add square brackets around the IPv6 address. For example, if the AP
global IPv6 address is 2520::230:abff:fe00:2420, type the following address into the IE7 address eld: http://
[2520::230:abff:fe00:2420].
To connect to the iPv6 link local address, replace the colons (:) with hyphens (-), add the interface number preceded
with an “s,” then add “.ipv6-literal.net.” For example, if the AP link local address is fe80::230:abff:fe00:2420, and the
Windows interface is dened as “%6,” type the following address into the IE7 address eld: http://fe80--230-abff-fe00-
2420s6.ipv6-literal.net.
Using the CLI to View the IP Address
The DHCP client on the UAP is enabled by default. If you connect the UAP to a network with a DHCP server, the
AP automatically acquires an IP address. To manage the UAP by using the Administrator UI, you must enter the IP
address of the access point into a Web browser.
If a DHCP server on your network assigns an IP address to the UAP, and you do not know the IP address, use the
following steps to view the IP address of the UAP:
1.) Using a null-modem cable, connect a VT100/ANSI terminal or a workstation to the console (serial) port.
If you attached a PC, Apple, or UNIX workstation, start a terminal-emulation program, such as HyperTerminal or
TeraTerm.
2.) Congure the terminal-emulation program to use the following settings:
•) Baud rate: 115200 bps
•) Data bits: 8
•) Parity: none
•) Stop bit: 1
•) Flow control: none
3.) Press the return key, and a login prompt should appear.
The login name is admin. The default password is admin. After a successful login, the screen shows the
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 17
Page 18
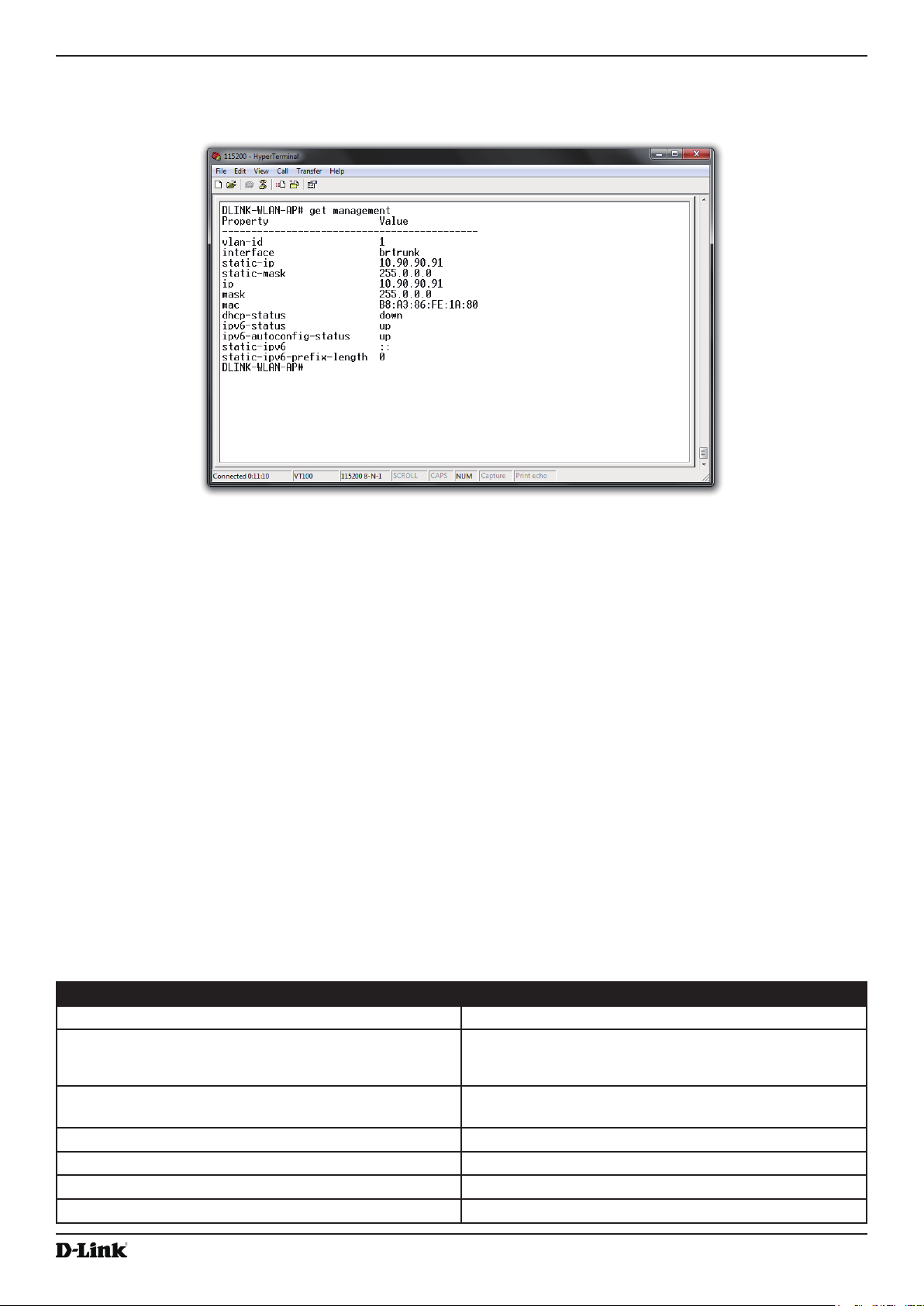
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
(Access Point Name)# prompt.
4.) At the login prompt, enter
Information similar to the following prints to the screen.
get management.
Section 2 - Getting Started
Figure 4 - Command Line Interface (CLI) Connection
Conguring the Ethernet Settings
The default Ethernet settings, which include DHCP and VLAN information, might not work for all networks.
By default, the DHCP client on the UAP automatically broadcasts requests for network information. If you want to
use a static IP address, you must disable the DHCP client and manually congure the IP address and other network
information.
The management VLAN is VLAN 1 by default. This VLAN is also the default untagged VLAN. If you already have
a management VLAN congured on your network with a different VLAN ID, you must change the VLAN ID of the
management VLAN on the access point.
For information about using the Web interface to congure the Ethernet settings, see “Ethernet Settings” on page
36. You can also use the CLI to congure the Ethernet settings, which the following section describes.
Using the CLI to Congure Ethernet Settings
Use the commands shown in the following table to view and set values for the Ethernet (wired) interface. For more
information about each setting, see the description for the eld in the following table.
Action Commands
Get the DNS Name
Set the DNS Name
Get Current Settings for the Ethernet (Wired) Internal
Interface
Set the management VLAN ID
View untagged VLAN information
Enable the untagged VLAN
Disable the untagged VLAN
October 2017
get host id
set host id <host_name>
For example:
set host id lab-ap
get management
set management vlan-id <1-4094>
get untagged-vlan
set untagged-vlan status up
set untagged-vlan status down
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 18
Page 19
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Action Commands
Set the untagged VLAN ID
View the connection type
Use DHCP as the connection type
Use a Static IP as the connection type
Set the Static IP address
set untagged-vlan vlan-id <1-4094>
get management dhcp-status
set management dhcp-status up
set management dhcp-status down
set management static-ip <ip_address>
For example:
set management static-ip 10.10.12.221
Set a Subnet Mask
set management static-mask <netmask>
For example:
set management static-mask 255.255.255.0
Set the Default Gateway
set static-ip-route gateway <ip_address>
For example:
set static-ip-route gateway 10.10.12.1
View the DNS Nameserver mode Dynamic= up
get host dns-via-dhcp
Manual=down
Set DNS Nameservers to Use Static IP Addresses
(Dynamic to Manual Mode)
set host dns-via-dhcp down
set host static-dns-1 <ip_address>
set host static-dns-2 <ip_address>
For example:
set host static-dns-1 192.168.23.45
Set DNS Nameservers to Use DHCP IP Addressing
set host dns-via-dhcp up
(Manual to Dynamic Mode)
Table 5 - CLI Commands for Ethernet Setting
Section 2 - Getting Started
In the following example, the administrator uses the CLI to set the management VLAN ID to 123 and to disable the
untagged VLAN so that all trafc is tagged with a VLAN ID.
DLINK-WLAN-AP# set management vlan-id 123
DLINK-WLAN-AP# set untagged-vlan status down
DLINK-WLAN-AP# get management
Property Value
-------------------------------------------vlan-id 123
interface brtrunk
static-ip 10.90.90.91
static-mask 255.0.0.0
ip 10.90.90.91
mask 255.0.0.0
mac 00:05:5E:80:70:00
dhcp-status down
ipv6-status up
ipv6-autocong-status up
static-ipv6 ::
static-ipv6-prex-length 0
DLINK-WLAN-AP# get untagged-vlan
Property Value
--------------vlan-id 1
status down
DLINK-WLAN-AP#
Conguring IEEE 802.1X Authentication
On networks that use IEEE 802.1X, port-based network access control, a supplicant (client) cannot gain access to
the network until the 802.1X authenticator grants access. If your network uses 802.1X, you must congure 802.1X
authentication information that the AP can supply to the authenticator.
If your network uses IEEE 802.1X see “Conguring IEEE 802.1X Authentication” on page 19 for information about
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 19
Page 20

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 2 - Getting Started
how to congure 802.1X by using the Web interface.
Using the CLI to Congure 802.1X Authentication Information
The following table shows the commands used to congure the 802.1X supplicant information using the CLI.
Action Command
View 802.1X supplicant settings
Enable 802.1X supplicant
Disable 802.1X supplicant
Set the 802.1X user name
Set the 802.1X password
Table 6 - CLI Commands for the 802.1X Supplicant
In the following example, the administrator enables the 802.1X supplicant and sets the user name to wlanAP and the
password to test1234.
DLINK-WLAN-AP# set dot1x-supplicant status up
DLINK-WLAN-AP# set dot1x-supplicant user wlanAP
DLINK-WLAN-AP# set dot1x-supplicant password test1234
DLINK-WLAN-AP# get dot1x-supplicant
Property Value
-------------------------status up
user wlanAP
eap-method md5
debug off
cert-present no
cert-exp-date Not Present
get dot1x-supplicant
set dot1x-supplicant status up
set dot1x-supplicant status down
set dot1x-supplicant user <name>
set dot1x-supplicant password <password>
DLINK-WLAN-AP#
Verifying the Installation
Make sure the access point is connected to the LAN and associate some wireless clients with the network. Once you
have tested the basics of your wireless network, you can enable more security and ne-tune the AP by modifying
advanced conguration features.
1.) Connect the access point to the LAN.
•) If you congured the access point and administrator PC by connecting both into a network hub, then your
access point is already connected to the LAN. The next step is to test some wireless clients.
•) If you congured the access point by using a direct cable connection from your computer to the access point,
do the following procedures:
•) Disconnect the cable from the computer and the access point.
•) Connect an Ethernet cable from the access point to the LAN.
•) Connect your computer to the LAN by using an Ethernet cable or a wireless card.
2.) Test LAN connectivity with wireless clients.
Test the UAP by trying to detect it and associate with it from some wireless client devices. For information about
requirements for these clients, see “Wireless Client Requirements” on page 12.
3.) Secure and congure the access point by using advanced features.
Once the wireless network is up and you can connect to the AP with some wireless clients, you can add in layers
of security, create multiple virtual access points (VAPs), and congure performance settings.
Note: The WLAN AP is not designed for multiple, simultaneous conguration changes. If more
than one administrator is logged onto the Administration Web pages and making changes to the
conguration, there is no guarantee that all conguration changes specied by multiple users will
be applied.
By default, no security is in place on the access point, so any wireless client can associate with it and access
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 20
Page 21

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
your LAN. An important next step is to congure security, as described in “Virtual Access Point Settings” on page
50.
Section 2 - Getting Started
Conguring Security on the Wireless Access Point
You congure secure wireless client access by conguring security for each virtual access point (VAP) that you
enable. You can congure up to 16 VAPs per radio that simulate multiple APs in one physical access point. By default,
only one VAP is enabled. For each VAP, you can congure a unique security mode to control wireless client access.
Each radio has 16 VAPs, with VAP IDs from 0-15. By default, only VAP 0 on each radio is enabled. VAP0 has the
following default settings:
•) VLAN ID: 1
•) Broadcast SSID: Enabled
•) SSID: dlink1
•) Security: None
•) MAC Authentication Type: None
•) Redirect Mode: None
All other VAPs are disabled by default. The default SSID for VAPs 1–15 is ”dlinkx” where x is the VAP ID.
To prevent unauthorized access to the UAP, we recommend that you select and congure a security option other than
None for the default VAP and for each VAP that you enable.
For information about how to congure the security settings on each VAP, see “Virtual Access Point Settings” on page
50.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 21
Page 22
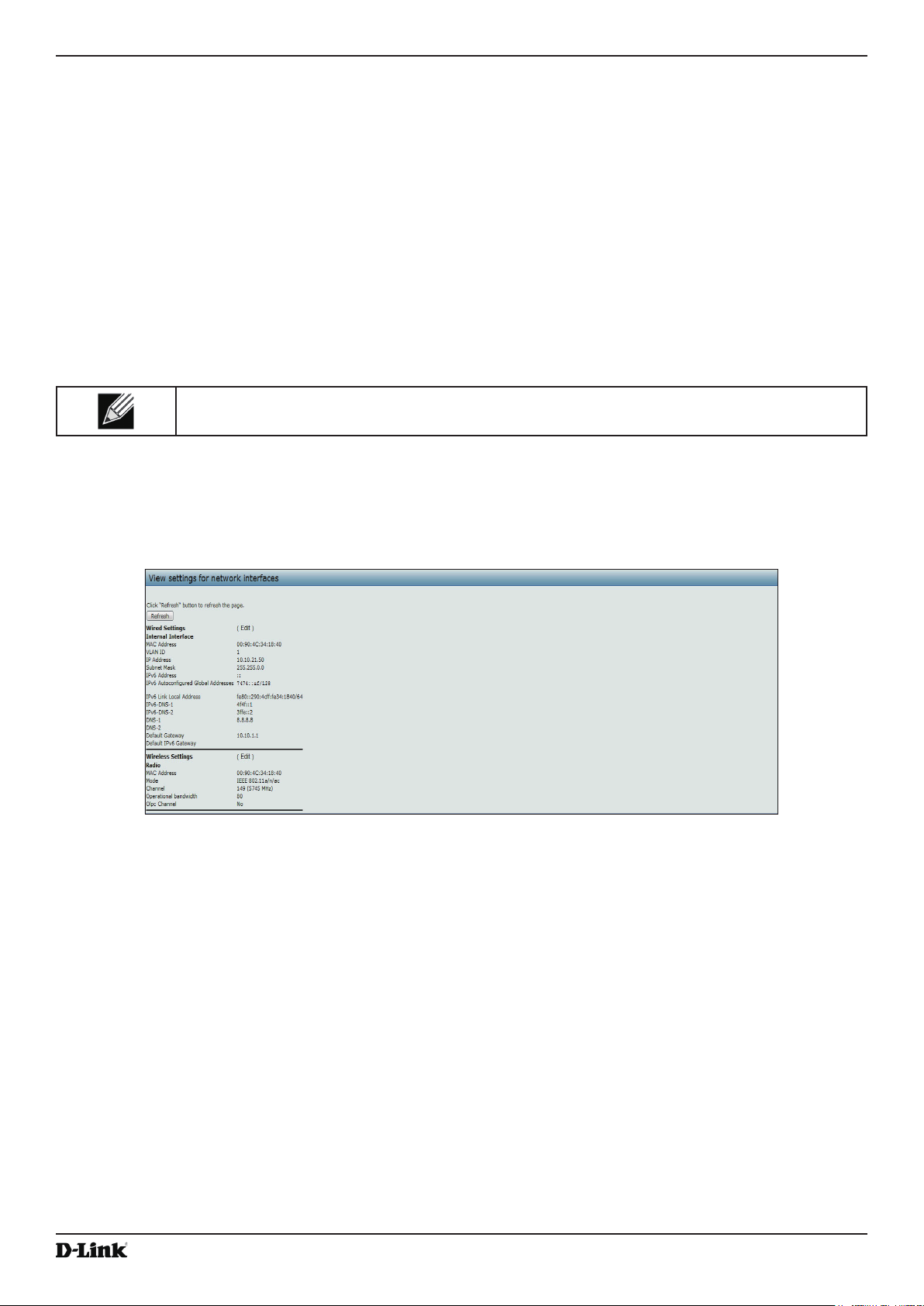
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
This section describes the information you can view from the tabs under the Status heading on the Administration
Web UI. This section contains the following subsections:
•) “Viewing Interface Status” on page 22
•) “Viewing Events” on page 23
•) “Viewing Transmit and Receive Statistics” on page 25
•) “Viewing Wireless Multicast Forwarding Statistics” on page 26
•) “Viewing TSPEC Client Associations” on page 27
•) “Viewing Rogue AP Detection” on page 29
•) “Viewing Managed AP DHCP Information” on page 32
•) “Viewing TSPEC Status and Statistics Information” on page 32
•) “Viewing TSPEC AP Statistics Information” on page 33
•) “Viewing Radio Statistics Information” on page 34
•) “Viewing Email Alert Operational Status” on page 35
Note: The web-based UI images show the DWL-8600AP administration pages. Pages for the
DWL-2600AP, DWL-3600AP, or DWL-3610AP will display information for one radio only.
Viewing Interface Status
To monitor Ethernet LAN (wired) and wireless LAN (WLAN) settings, click the Interfaces tab.
Figure 5 - Viewing Interface Status
This page displays the current settings of the UAP. It displays the Wired Settings and the Wireless Settings.
Wired Settings (Internal Interface)
The Internal interface includes the Ethernet MAC Address, Management VLAN ID, IP Address (IPv4 and IPv6),
Subnet Mask, and DNS information. To change any of these settings, click the Edit link. After you click Edit, you are
redirected to the Ethernet Settings page.
For information about conguring these settings, see “Conguring the Ethernet Settings” on page 18.
Wireless Settings
The Radio Interface includes the AeroScout™ Engine Communication status, Radio Mode and Channel. The
Wireless Settings section also shows the MAC address (read-only) associated with each radio interface.
To change the Radio Mode or Channel settings, click the Edit link. After you click Edit, you are redirected to the
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 22
Page 23
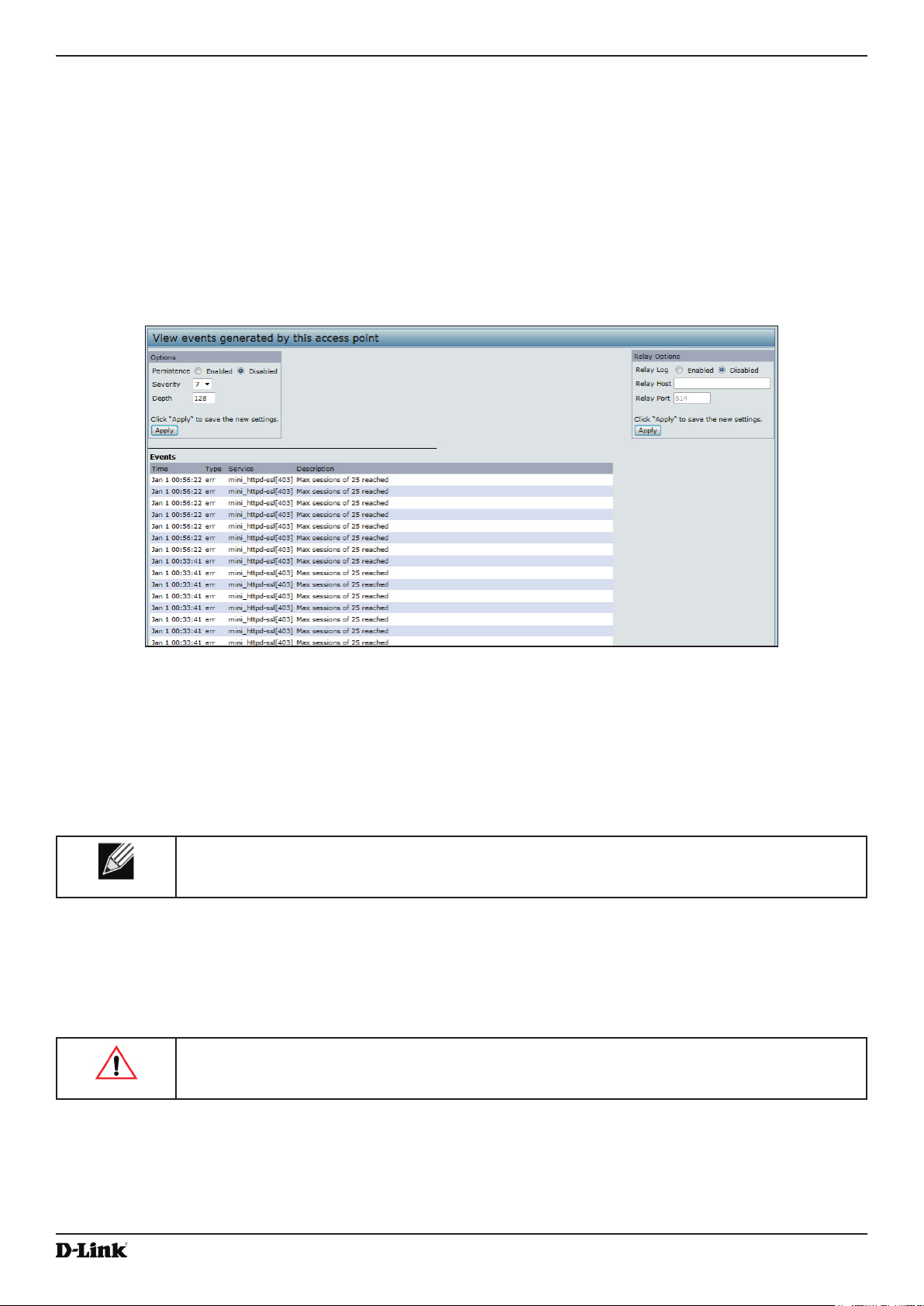
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Modify Wireless Settings page.
For information about conguring these settings, see “Wireless Settings” on page 38 and “Modifying Radio Settings”
on page 42.
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Events
The Events page shows real-time system events on the AP such as wireless clients associating with the AP and being
authenticated.
To view system events, click the Events tab.
Figure 6 - Viewing Events
From the Events page, you can perform the following tasks:
•) View the most recent, high-level events generated by this AP.
•) Enable and congure Persistent logging to write system event logs to non-volatile memory so that the events
are not erased when the system reboots.
•) Set a Severity Level to determine what category of log messages are displayed.
•) Set Depth to determine how many log messages are displayed in the Event log.
•) Enable a remote log relay host to capture all system events and errors in a Kernel Log.
Note: The AP acquires its date and time information using the network time protocol (NTP). This
data is reported in UTC format (also known as Greenwich Mean Time). You need to convert the
reported time to your local time.
Conguring Persistent Logging Options
If the system unexpectedly reboots, log messages can be useful to diagnose the cause. However, log messages are
erased when the system reboots unless you enable persistent logging.
Caution! Enabling persistent logging can wear out the ash (non-volatile) memory and degrade
network performance. You should only enable persistent logging to debug a problem. Make sure
you disable persistent logging after you nish debugging the problem.
To congure persistent logging on the Events page, set the persistence, severity, and depth options as described in
the following table, and then click Apply.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 23
Page 24

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Persistence Choose Enabled to save system logs to non-volatile memory so that the logs are not erased
when the AP reboots. Choose Disabled to save system logs to volatile memory. Logs in
volatile memory are deleted when the system reboots.
Severity Specify the severity level of the log messages to write to non-volatile memory. For example,
if you specify 2, critical, alert, and emergency logs are written to non-volatile memory. Error
messages with a severity level of 3 – 7 are written to volatile memory.
•) 0 — emergency
•) 1 — alert
•) 2 — critical
•) 3 — error
•) 4 — warning
•) 5 — notice
•) 6 — info
•) 7 — debug
Depth You can store up to 128 messages in non-volatile memory and 512 messages in volatile
memory. Once the number you congure in this eld is reached, the oldest log event is
overwritten by the new log event.
Table 7 - Logging Options
Note: To apply your changes, click Apply. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop
and restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity.
We recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Conguring the Log Relay Host for Kernel Messages
The Kernel Log is a comprehensive list of system events (shown in the System Log) and kernel messages such as
error conditions, like dropping frames.
You cannot view kernel log messages directly from the Administration Web UI for an AP. You must rst set up a remote
server running a syslog process and acting as a syslog log relay host on your network. Then, you can congure the
UAP to send syslog messages to the remote server.
Remote log server collection for AP syslog messages provides the following features:
•) Allows aggregation of syslog messages from multiple APs
•) Stores a longer history of messages than kept on a single AP
•) Triggers scripted management operations and alerts
To use Kernel Log relaying, you must congure a remote server to receive the syslog messages. The procedure to
congure a remote log host depends on the type of system you use as the remote host.
Note: The syslog process will default to use port 514. We recommend keeping this default port.
However, if you choose to recongure the log port, make sure that the port number you assign to
syslog is not being used by another process.
Enabling or Disabling the Log Relay Host on the Events Page
To enable and congure Log Relaying on the Events page, set the Log Relay options as described in the following
table, and then click Update.
Field Description
Relay Log Select Enabled to allow the UAP to send log messages to a remote host. Select Disabled
to keep all log messages on the local system.
Relay Host Specify the IP Address or DNS name of the remote log server.
Relay Port Specify the Port number for the syslog process on the Relay Host.
The default port is 514.
Table 8 - Log Relay Host
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 24
Page 25
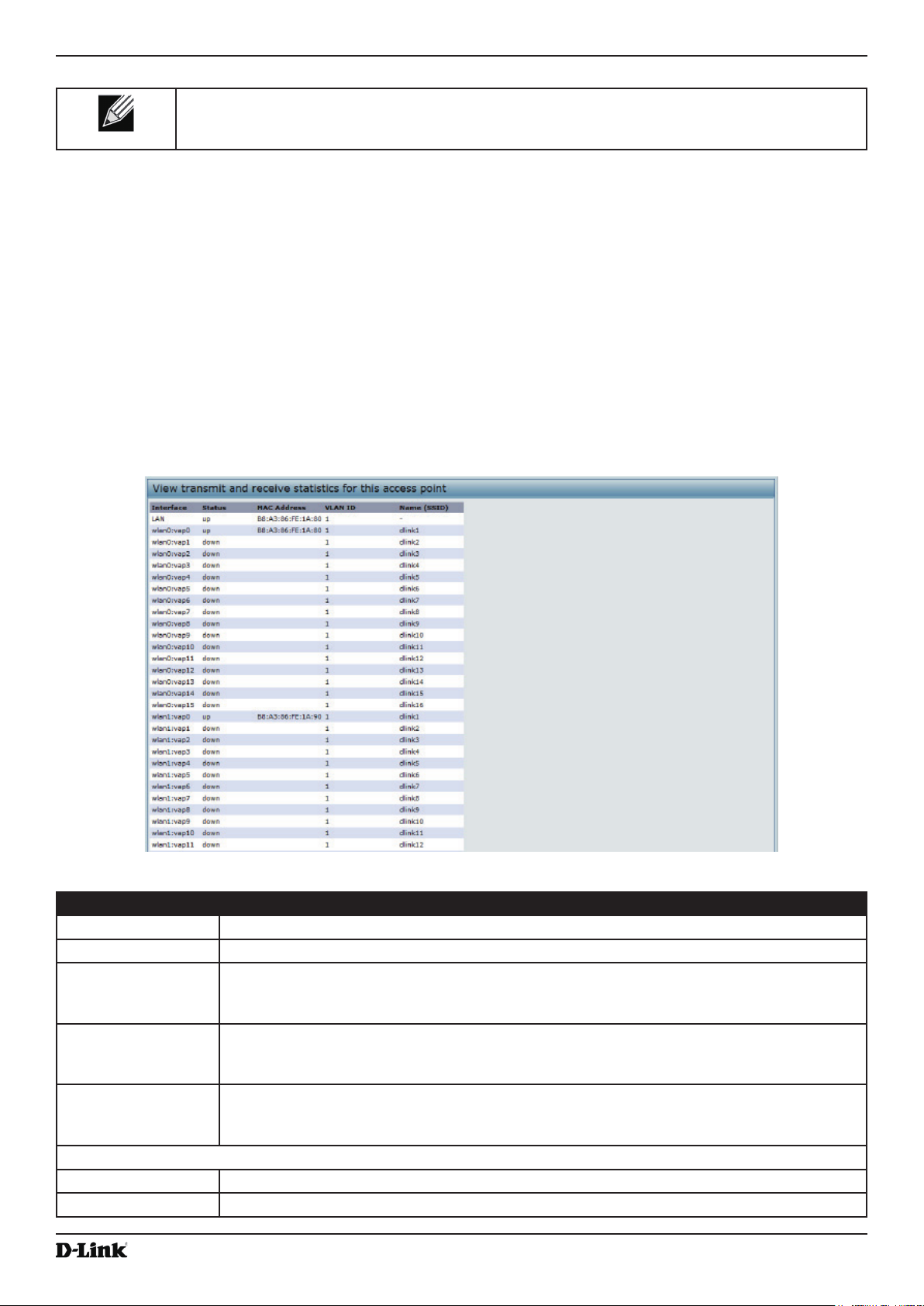
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Note: To apply your changes, click Apply. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop
and restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity.
We recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
If you enabled the Log Relay Host, clicking Apply will activate remote logging. The AP will send its kernel messages
real-time for display to the remote log server monitor, a specied kernel log le, or other storage, depending on how
you congured the Log Relay Host.
If you disabled the Log Relay Host, clicking Apply will disable remote logging.
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Transmit and Receive Statistics
The Transmit/Receive page provides some basic information about the current AP and a real-time display of the
transmit and receive statistics for the Ethernet interface on the AP and for the VAPs on all supported radio interfaces.
All transmit and receive statistics shown are totals since the AP was last started. If you reboot the AP, these gures
indicate transmit and receive totals since the reboot.
To view transmit and receive statistics for the AP, click the Transmit/Receive tab.
Figure 7 - Viewing Trafc Statistics
Field Description
Interface The name of the Ethernet or VAP interface.
Status Shows whether the interface is up or down.
MAC Address MAC address for the specied interface. The UAP has a unique MAC address for each
interface. Each radio has a different MAC address for each interface on each of its two
radios.
VLAN ID Virtual LAN (VLAN) ID.
You can use VLANs to establish multiple internal and guest networks on the same AP.
The VLAN ID is set on the VAP page. (See “Conguring Load Balancing” on page 64)
Name (SSID) Wireless network name. Also known as the SSID, this alphanumeric key uniquely identies a
wireless local area network.
The SSID is set on the VAP page. (See “Conguring Load Balancing” on page 64)
Transmit and Receive Information
Total Packets Indicates total packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received table) by this AP.
Total Bytes Indicates total bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received table) by this AP.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 25
Page 26

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Total Drop Packets Indicates total number of packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received table) by
this AP that were dropped.
Total Drop Bytes Indicates total number of bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received table) by
this AP that were dropped.
Errors Indicates total errors related to sending and receiving data on this AP.
Table 9 - Transmit/Receive
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Wireless Multicast Forwarding Statistics
The Wireless Multicast Forwarding Transmit and Receive Statistics page provides some basic information about the
current AP and a real-time display of the transmit and receive statistics for the Wireless Multicast Trafc interface on
the AP and for the VAPs on the radio interface. All transmit and receive statistics shown are totals since the AP was
last started. If you reboot the AP, these gures indicate transmit and receive totals since the reboot.
Figure 8 - Viewing WMF Transmit and Receive Statistics
To view transmit and receive statistics for the AP, click the Wireless Multicast Forwarding Transmit and Receive
Statistics tab.
Field Description
Network Shows which VAP the client is associated with. For example, an entry of wlan0vap2 means
the client is associated with Radio 1, VAP 2.
An entry of wlan0 means the client is associated with VAP 0 on Radio 1. An entry of wlan1
means the client is associated with VAP 0 on Radio 2.
Station Shows the MAC address of the associated wireless client.
Status The Authenticated and Associated Status shows the underlying IEEE 802.11 authentication
and association status, which is present no matter which type of security the client uses to
connect to the AP. This status does not show IEEE 802.1X authentication or association
status.
Some points to keep in mind with regard to this eld are:
•) If the AP security mode is None or Static WEP, the authentication and association
status of clients showing on the Client Associations page will be in line with what is
expected; that is, if a client shows as authenticated to the AP, it will be able to transmit
and receive data. (This is because Static WEP uses only IEEE 802.11 authentication.)
•) If the AP uses IEEE 802.1X or WPA security, however, it is possible for a client
association to show on this page as authenticated (via the IEEE 802.11 security) but
actually not be authenticated to the AP via the second layer of security.
From Station Shows the number of packets and bytes received from the wireless client and the number of
packets and bytes that were dropped after being received.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 26
Page 27

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
To Station Shows the number of packets and bytes transmitted from the AP to the wireless client and
the number of packets and bytes that were dropped upon transmission.
Table 10 - WMF Transmit and Receive Statistics Table
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Associated Wireless Client Information
To view the client stations associated with a particular access point, click the Client Associations tab.
Figure 9 - Viewing Client Association Information
The associated stations are displayed along with information about packet trafc transmitted and received for each
station.
The following describes the elds on the Client Associations page.
Field Description
Network Shows which VAP the client is associated with. For example, an entry of wlan0vap2 means
the client is associated with Radio 1, VAP 2.
An entry of wlan0 means the client is associated with VAP 0 on Radio 1. An entry of wlan1
means the client is associated with VAP 0 on Radio 2.
Station Shows the MAC address of the associated wireless client.
Status The Authenticated and Associated Status shows the underlying IEEE 802.11 authentication
and association status, which is present no matter which type of security the client uses to
connect to the AP. This status does not show IEEE 802.1X authentication or association
status.
Some points to keep in mind with regard to this eld are:
•) If the AP security mode is None or Static WEP, the authentication and association
status of clients showing on the Client Associations page will be in line with what is
expected; that is, if a client shows as authenticated to the AP, it will be able to transmit
and receive data. (This is because Static WEP uses only IEEE 802.11 authentication.)
•) If the AP uses IEEE 802.1X or WPA security, however, it is possible for a client
association to show on this page as authenticated (via the IEEE 802.11 security) but
actually not be authenticated to the AP via the second layer of security.
From Station Shows the number of packets and bytes received from the wireless client and the number of
packets and bytes that were dropped after being received.
To Station Shows the number of packets and bytes transmitted from the AP to the wireless client and
the number of packets and bytes that were dropped upon transmission.
Table 11 - Associated Clients
Viewing TSPEC Client Associations
The TSPEC Client Association Status and Statistics page provides some basic information about the client
associations status and a real-time display of the transmit and receive statistics for the TSPEC clients. All transmit and
receive statistics shown are totals since the client association started.
A TSPEC is a trafc specication that is sent from a QoS-capable wireless client to an AP requesting a certain
amount of network access for the trafc stream (TS) it represents. A trafc stream is a collection of data packets
identied by the wireless client as belonging to a particular user priority. An example of a voice trafc stream is a Wi-Fi
CERTIFIED™ telephone handset that marks its codec-generated data packets as voice priority trafc. An example of
a video trafc stream is a video player application on a wireless laptop that prioritizes a video conference feed from a
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 27
Page 28
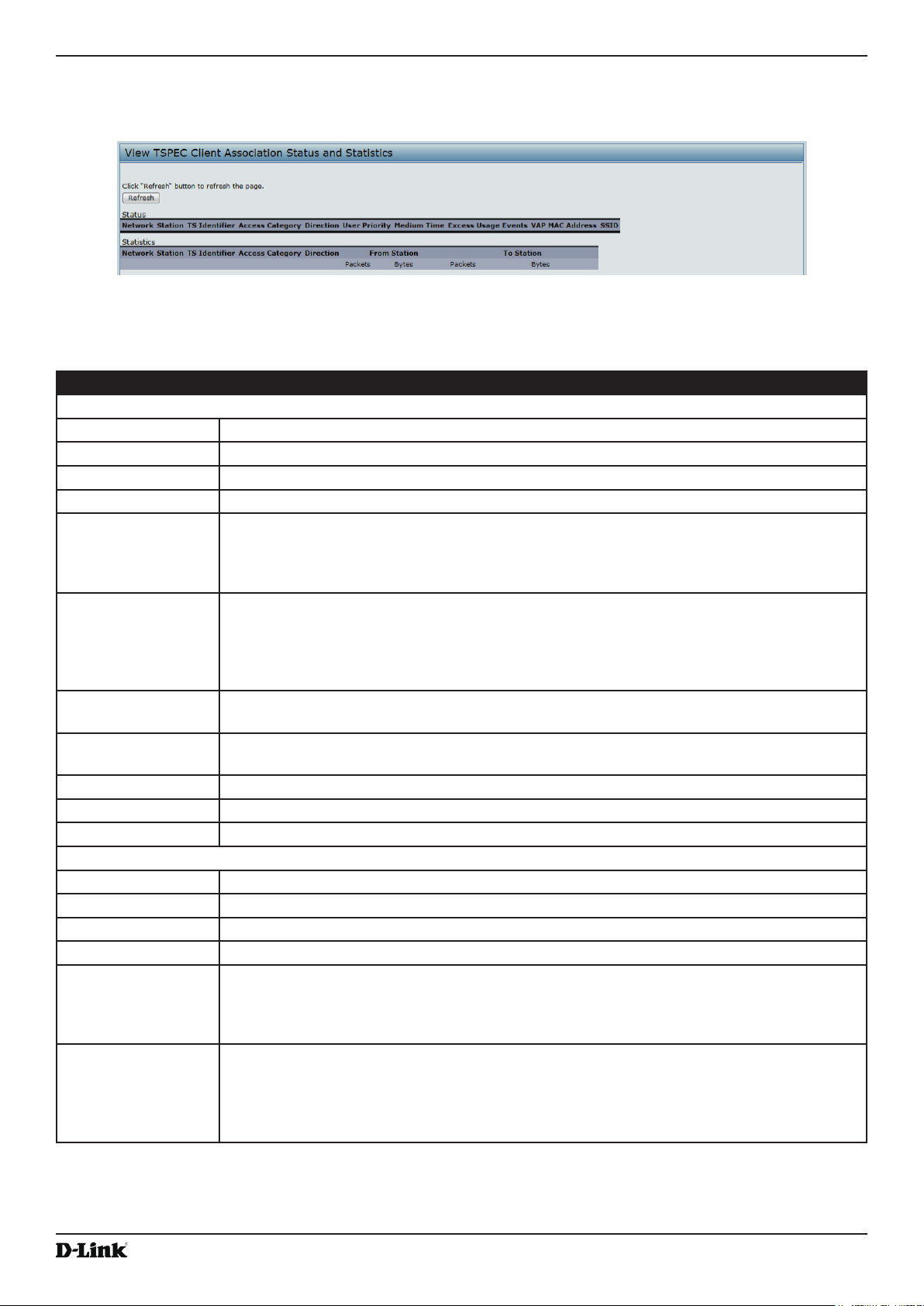
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
corporate server.
To view TSPEC client association statistics, click the TSPEC Client Associations tab.
Figure 10 - Viewing TSPEC Client Associations
The following table describes the information provided on the TSPEC Client Association Status and Statistics
page.
Field Description
Status
Network Radio interface used by the client.
Station Client station MAC address.
TS Identier TSPEC Trafc Session Identier (range 0-7).
Access Category TS Access Category (voice or video).
Direction The trafc direction for this TS. Direction can be:
•) uplink
•) downlink
•) bidirectional
User Priority The User Priority (UP) for this TS. The UP is sent with each packet in the UP portion of the
IP header. Typical values are:
•) 6 or 7 for voice
•) 4 or 5 for video
The value may differ depending on other priority trafc sessions.
Medium Time The time (in 32 microsecond per second units) that the TS trafc occupies the transmission
medium.
Excess Usage
Events
The number of times the client has exceeded the medium time established for its TSPEC.
Minor, infrequent violations are ignored.
VAP The Virtual Access Point associated with this TS client.
MAC Address The Virtual Access Point MAC address.
SSID The service set identier associated with this TS client.
Statistics
Network Radio interface used by the client.
Station Client station MAC address.
TS Identier TSPEC Trafc Session Identier (range 0-7).
Access Category TS Access Category (voice or video).
Direction The trafc direction for this TS. Direction can be:
•) uplink
•) downlink
•) bidirectional
From Station Shows the number of packets and bytes received from the wireless client and the number
of packets and bytes that were dropped after being received. Also shows the number of
packets:
•) in excess of an admitted TSPEC.
•) for which no TSPEC has been established when admission is required by the AP.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 28
Page 29
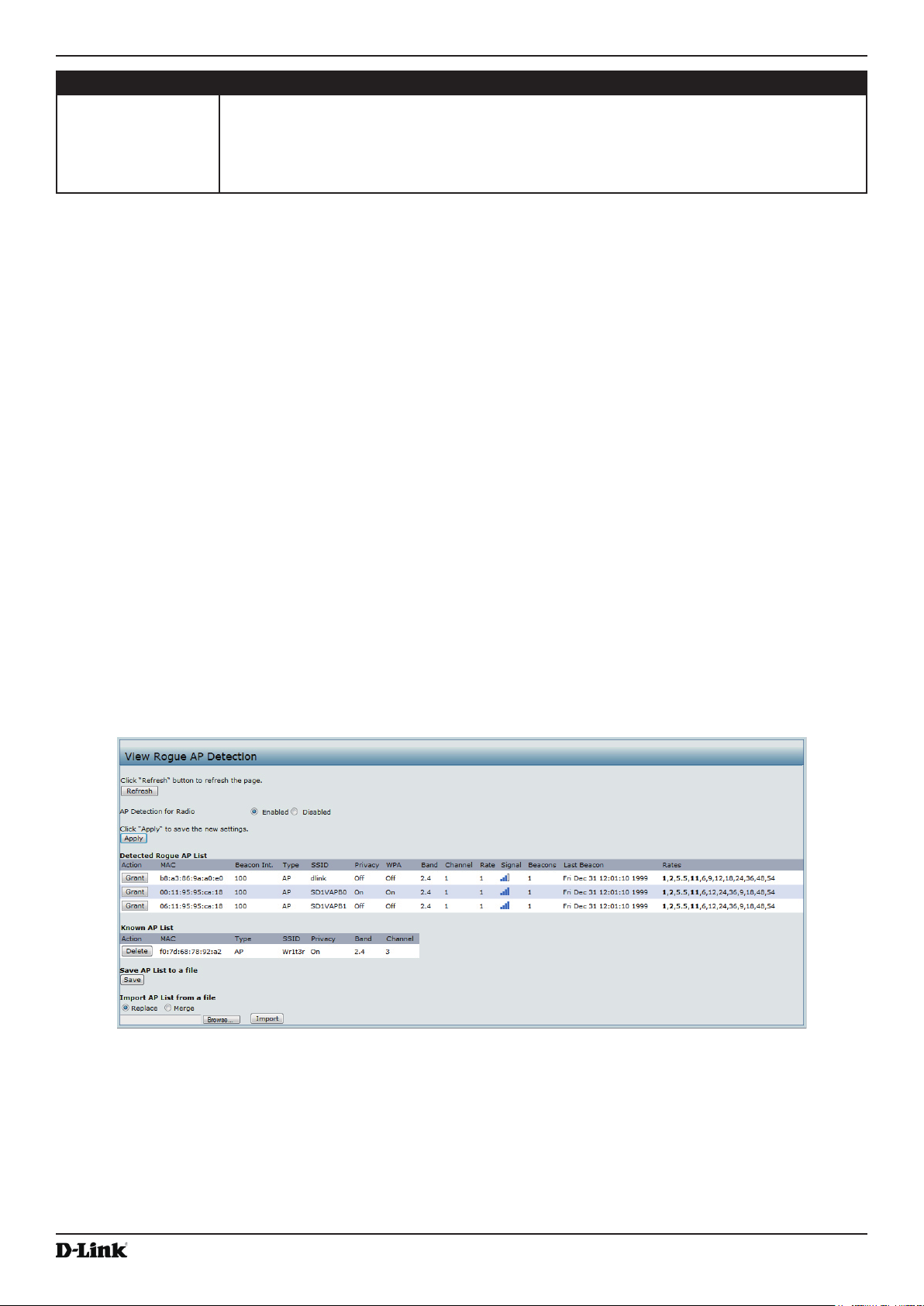
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
To Station Shows the number of packets and bytes transmitted from the AP to the wireless client and
the number of packets and bytes that were dropped upon transmission. Also shows the
number of packets:
•) in excess of an admitted TSPEC.
•) for which no TSPEC has been established when admission is required by the AP.
Table 12 - TSPEC Client Associations
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Link Integrity Monitoring
The UAP provides link integrity monitoring to continually verify its connection to each associated client. To do this,
the AP sends data packets to clients every few seconds when no other trafc is passing. This allows the AP to detect
when a client goes out of range, even during periods when no normal trafc is exchanged. The client connection
drops off the list within 300 seconds if these data packets are not acknowledged, even if no disassociation message is
received.
Viewing Rogue AP Detection
The status page to view Rogue AP Detection information provides real-time statistics for all APs within range of the
AP on which you are viewing the Administration Web pages. When AP detection is enabled, the radio will periodically
switch from its operating channel to scan other channels within the same band. Click Refresh to update the screen
and display the most current information.
The Rogue AP Detection page contains the following two lists:
•) Detected Rogue AP List — Lists all APs within range of the AP that have not been acknowledged as known APs.
•) Known AP List — Lists all APs within range of the AP that have been acknowledged as known APs either by
clicking the Grant button associated with an AP in the Detected Rogue AP List or by appearing in an imported
AP list.
To view information about other access points on the wireless network, click the Rogue AP Detection tab.
Figure 11 - Viewing Rogue and Known Access Points
You must enable the AP detection on a radio in order to collect information about other APs within range.
The following table describes the information provided on neighbouring access points.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 29
Page 30
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
AP Detection for
Radio
Detected Rogue AP List
Action Click Grant to move the AP from the Detected Rogue AP List to the Known AP List.
MAC Shows the MAC address of the neighbouring AP.
Radio The Radio eld indicates which radio detected the neighbouring AP:
Beacon Int. Shows the Beacon interval being used by this AP.
Type Indicates the type of device:
SSID The Service Set Identier (SSID) for the AP.
Privacy Indicates whether there is any security on the neighbouring device.
WPA Indicates whether WPA security is on or off for this AP.
Band This indicates the IEEE 802.11 mode being used on this AP. (For example, IEEE 802.11a,
Channel Shows the Channel on which the AP is currently broadcasting.
Rate Shows the rate (in megabits per second) at which this AP is currently transmitting.
Signal Indicates the strength of the radio signal emitting from this AP. If you hover the mouse
Beacons Shows the total number of beacons received from this AP since it was rst discovered.
Last Beacon Shows the date and time of the last beacon received from this AP.
Rates Shows supported and basic (advertised) rate sets for the neighbouring AP. Rates are shown
To allow the AP radios to perform neighbour AP detection and collect information about
neighbour APs, click Enabled.
To disable neighbour AP detection on the radios, click Disabled.
If you change the AP detection mode, click Update to save the new settings.
Note: The Detected Rouge AP and Known AP lists provide information. The DWL-x600AP
does not have any control over the APs on the list and cannot apply any security policies to
APs detected through the RF scan.
•) wlan0 (Radio One)
•) wlan1 (Radio Two)
Beacon frames are transmitted by an AP at regular intervals to announce the existence
of the wireless network. The default behaviour is to send a beacon frame once every 100
milliseconds (or 10 per second).
The Beacon Interval is set on the Radio page.(See “Modifying Radio Settings” on page
42)
•) AP indicates the neighbouring device is an AP that supports the IEEE 802.11 Wireless
Networking Framework in Infrastructure Mode.
•) Ad hoc indicates a neighbouring station running in Ad hoc Mode. Stations set to ad
hoc mode communicate with each other directly, without the use of a traditional AP.
Ad-hoc mode is an IEEE 802.11 Wireless Networking Framework also referred to as
peer-to-peer mode or an Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS).
The SSID is an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that uniquely identies a wireless
local area network. It is also referred to as the Network Name.
The SSID is set on the VAP page. (See “Conguring Load Balancing” on page 64)
•) Off indicates that the Security mode on the neighbouring device is set to None (no
security).
•) On indicates that the neighbouring device has some security in place.
•) Security is congured on the AP from the VAP page.
IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g.)
The number shown indicates the mode according to the following map:
•) 2.4 indicates IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n mode (or a combination of the modes)
•) 5 indicates IEEE 802.11a or 802.11n mode (or both modes)
The channel denes the portion of the radio spectrum that the radio uses for transmitting
and receiving.
The channel is set in Radio Settings. (See “Modifying Radio Settings” on page 42)
The current rate will always be one of the rates shown in Supported Rates.
pointer over the bars, a number appears and shows the strength in decibels (dB).
in megabits per second (Mbps).
All Supported Rates are listed, with Basic Rates shown in bold.
Rate sets are congured on the Radio Settings page. (See “Modifying Radio Settings” on
page 42)
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 30
Page 31

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Known AP List
Action An AP can appear in the Known AP List if it has been moved from the Detected Rogue AP
List by clicking the Grant button or if the MAC address of the AP appears in an AP list that
has been imported.
To move the AP from the Known AP List to the Detected Rogue AP List, click Delete.
Note: The Detected Rouge AP and Known AP lists provide information. The DWL-x600AP
does not have any control over the APs on the list and cannot apply any security policies to
APs detected through the RF scan.
MAC Shows the MAC address of the neighbouring AP.
Type Indicates the type of device:
•) AP indicates the neighbouring device is an AP that supports the IEEE 802.11 Wireless
Networking Framework in Infrastructure Mode.
•) Ad hoc indicates a neighbouring station running in Ad hoc Mode. Stations set to ad
hoc mode communicate with each other directly, without the use of a traditional AP.
Ad-hoc mode is an IEEE 802.11 Wireless Networking Framework also referred to as
peer-to-peer mode or an Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS).
SSID The Service Set Identier (SSID) for the AP.
The SSID is an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that uniquely identies a wireless
local area network. It is also referred to as the Network Name.
The SSID is set on the VAP page. (See “Conguring Load Balancing” on page 64)
Privacy Indicates whether there is any security on the neighboring device.
•) Off indicates that the Security mode on the neighbouring device is set to None (no
security).
•) On indicates that the neighbouring device has some security in place.
•) Security is congured on the AP from the VAP page.
Band This indicates the IEEE 802.11 mode being used on this AP. (For example, IEEE 802.11a,
IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g.)
The number shown indicates the mode according to the following map:
•) 2.4 indicates IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n mode (or a combination of the modes)
•) 5 indicates IEEE 802.11a or 802.11n mode (or both modes)
Channel Shows the Channel on which the AP is currently broadcasting.
The channel denes the portion of the radio spectrum that the radio uses for transmitting
and receiving.
The channel is set in Radio Settings. (See “Modifying Radio Settings” on page 42)
Table 13 - Rogue AP Detection
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Saving and Importing the Known AP List
To save the Known AP list to a le, click Save. The list contains the MAC addresses of all the APs that have been
added to the Known AP List. By default, the lename is Rogue1.cfg. You can use a text editor or Web browser to open
the le and view its contents.
Use the Import feature to import a list of Known APs from a saved list. The list might be from another DWL-x600AP or
created from a text le. If the MAC address of an AP appears in the Known AP List, it will not be detected as a rogue.
To import an AP List from a le, use the following steps:
1.) Choose whether to replace the existing Known AP list or add the entries in the imported le to the Known AP list.
•) Select the Replace option to import the list and replace the contents of the Known AP List.
•) Select the Merge option to import the list and add the APs in the imported le to the APs currently displayed in
the Known AP List.
2.) Click Browse and choose the le to import.
•) The le you want to import must be a plain-text le with .txt or .cfg extension. Entries in the le are MAC
addresses in hexadecimal format with each octet separated by colons, for example 00:11:22:33:44:55.
Separate entries with a single space. For the AP to accept the le, it must contain only MAC addresses.
3.) Click Import.
•) Once the import is completed, the screen refreshes and the MAC addresses of the APs in the imported le
appear in the Known AP List.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 31
Page 32

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Managed AP DHCP Information
The UAP can learn about D-Link Unied Wireless Switches on the network through DHCP responses to its initial
DHCP request. The Managed AP DHCP page displays the DNS names or IP addresses of up to four D-Link Unied
Wireless Switches that the AP learned about from a DHCP server on your network.
Figure 12 - Managed AP DHCP Information
For information about how to congure a DHCP server to respond to AP DHCP requests with the switch IP address
information, see the User Manual for the switch.
Viewing TSPEC Status and Statistics Information
The TSPEC Status and Statistics page provides:
•) Summary information about TSPEC sessions by radio
•) Summary information about TSPEC sessions by VAP
•) Real-time transmit and receive statistics for the TSPEC VAPs on all radio interfaces.
All of the transmit and receive statistics shown are totals since the AP was last started. If you reboot the AP, these
gures indicate transmit and receive totals since the reboot.
To view TSPEC status and statistics, click the TSPEC Status and Statistics tab.
Figure 13 - Viewing TSPEC Status and Statistics
The following table describes the information provided on TSPEC Status and Statistics page.
Field Description
AP and VAP Status
Interface Indicates the name of the Radio or VAP interface.
Access Category Indicates Current Access Category associated with this Trafc Stream (voice or video).
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 32
Page 33
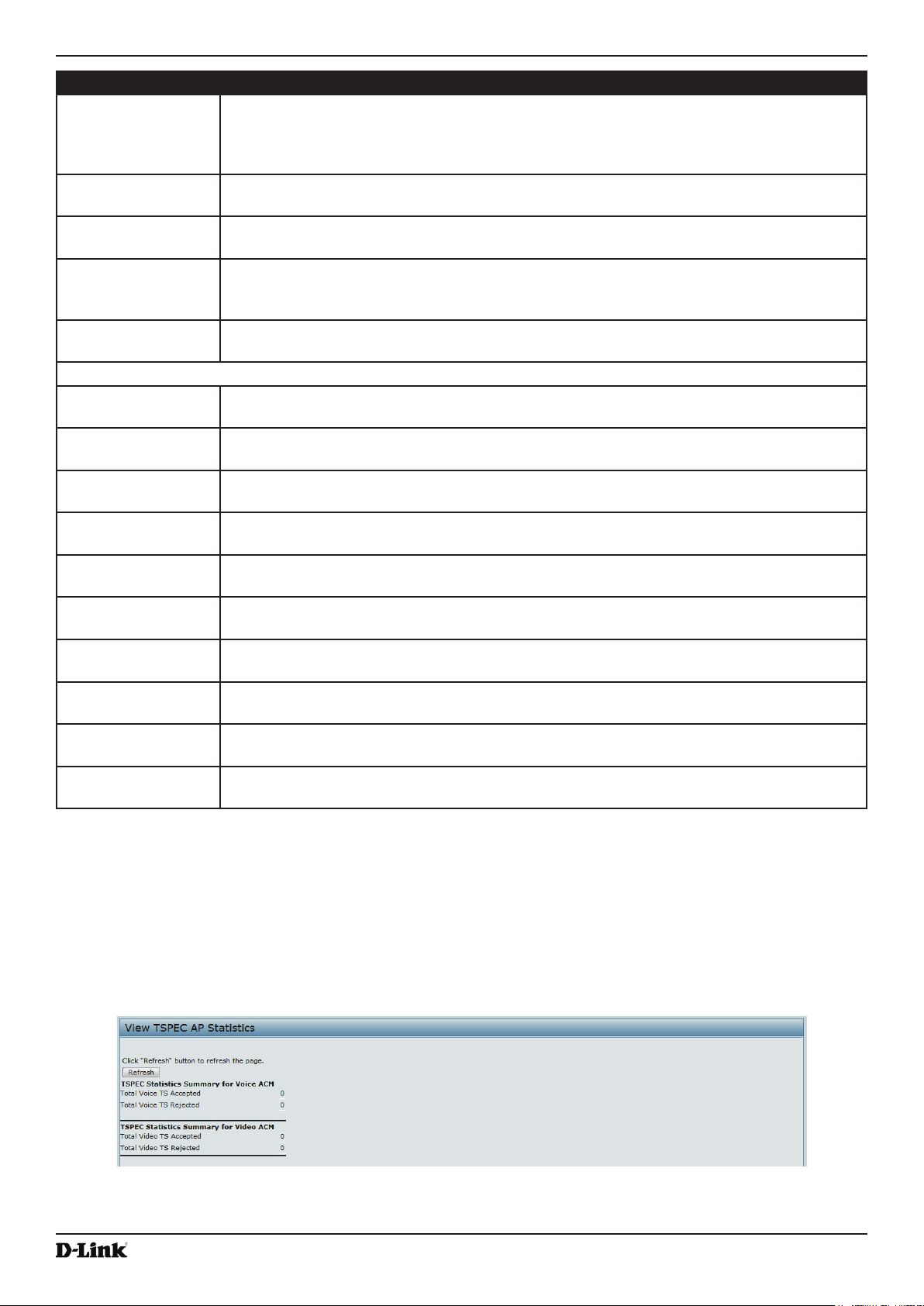
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Status Indicates whether the TSPEC session is enabled (up) or not (down) for the corresponding
Access Category.
Note: This is a conguration status (does not necessarily represent the current session
activity).
Active TS Indicates the number of currently active TSPEC Trafc Streams for this radio and Access
Category.
TS Clients Indicates the number of Trafc Stream clients associated with this radio and Access
Category.
Medium Time
Admitted
Medium Time
Unallocated
Transmit and Receive Statistics
Total Packets Indicates the total number of TS packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received
Total Bytes Indicates the total number of TS bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received
Total Voice Packets Indicates the total number of TS voice packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in
Total Voice Bytes Indicates the total TS voice bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received table) by
Total Video Packets Indicates the total number of TS video packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in
Total Video Bytes Indicates the total TS video bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received table) by
Total Best effort
Packets
Total Best effort
Bytes
Total Background
Packets
Total Background
Bytes
Time (in 32 microsecond per second units) allocated for this Access Category over the
transmission medium to carry data. This value should be less than or equal to the maximum
bandwidth allowed over the medium for this TS.
Time (in 32 microsecond per second units) of unused bandwidth for this Access Category.
table) by this Radio for the specied Access Category.
table) by this Radio for the specied Access Category.
Received table) by this AP for this VAP.
this AP for this VAP.
Received table) by this AP for this VAP.
this AP for this VAP.
Indicates the total number of TS best effort packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in
Received table) by this AP for this VAP.
Indicates the total TS best effort bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received
table) by this AP for this VAP.
Indicates the total number of TS background packets sent (in Transmit table) or received (in
Received table) by this AP for this VAP.
Indicates the total TS background bytes sent (in Transmit table) or received (in Received
table) by this AP for this VAP.
Table 14 - TSPEC Status and Statistics
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing TSPEC AP Statistics Information
The View TSPEC AP Statistics page provides information on the voice and video Trafc Streams accepted and
rejected by the AP.
To view TSPEC AP statistics, click the TSPEC AP Statistics tab.
Figure 14 - View TSPEC Status and Statistics
The following table describes the information provided on TSPEC AP Statistics page.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 33
Page 34

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
TSPEC Statistics
Summary for Voice
ACM
TSPEC Statistics
Summary for Video
ACM
TSPEC Statistics
Summary for Best
effort ACM
TSPEC Statistics
Summary for
Background ACM
Indicates the total number of accepted and the total number of rejected voice Trafc
Streams.
Indicates the total number of accepted and the total number of rejected video Trafc
Streams.
Indicates the total number of accepted and the total number of rejected best effort Trafc
Streams.
Indicates the total number of accepted and the total number of rejected background Trafc
Streams.
Table 15 - TSPEC AP Statistics
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Radio Statistics Information
The Radio Statistics page provides detailed information about the packets and bytes transmitted and received on the
radio interface of this access point.
Figure 15 - View Radio Statistics
The following table describes details about the Radio Statistics information.
Field Description
Radio Choose either radio 1 or radio 2 to view statistics for the selected radio
WLAN Packets
Received
WLAN Bytes
Received
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
WLAN Bytes
Receive Dropped
WLAN Packets
Transmit Dropped
WLAN Bytes
Transmit Dropped
Total packets received by the AP on this radio interface.
Total bytes received by the AP on this radio interface.
Total packets transmitted by the AP on this radio interface.
Total bytes transmitted by the AP on this radio interface.
Number of packets received by the AP on this radio interface that were dropped.
Number of bytes received by the AP on this radio interface that were dropped.
Number of packets transmitted by the AP on this radio interface that were dropped.
Number of bytes transmitted by the AP on this radio interface that were dropped.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 34
Page 35

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Fragments
Received
Fragments
Transmitted
Multicast Frames
Received
Multicast Frames
Transmitted
Duplicate Frame
Count
Failed Transmit
Count
Transmit Retry
Count
Multiple Retry
Count
RTS Success Count Count of CTS frames received in response to an RTS frame.
RTS Failure Count Count of CTS frames not received in response to an RTS frame.
ACK Failure Count Count of ACK frames not received when expected.
FCS Error Count Count of FCS errors detected in a received MPDU frame.
Frames Transmitted Count of each successfully transmitted MSDU.
WEP Undecryptable
Count
Count of successfully received MPDU frames of type data or management.
Number of transmitted MPDU with an individual address or an MPDU with a multicast
address of type Data or Management.
Count of MSDU frames received with the multicast bit set in the destination MAC address.
Count of successfully transmitted MSDU frames where the multicast bit is set in the
destination MAC address.
Number of times a frame is received and the Sequence Control eld indicates is a duplicate.
Number of times an MSDU is not transmitted successfully due to transmit attempts
exceeding either the short retry limit or the long retry limit.
Number of times an MSDU is successfully transmitted after one or more retries.
Number of times an MSDU is successfully transmitted after more than one retry.
Count of encrypted frames received and the key conguration of the transmitter indicates
that the frame should not have been encrypted or that frame was discarded due to the
receiving station not implementing the privacy option.
Table 16 - Radio Statistics Information
Section 3 - Viewing Access Point Status
Viewing Email Alert Operational Status
The Email Alert Operational Status page provides information about the email alerts sent based on the syslog
messages generated in the AP. To view the Email Alert Operational Status, click the Status > Email Alert Status tab.
To congure the email alerts, see “Conguring Email Alert” on page 76.
Figure 16 - Email Alert Operational Status
The following table describes details about the Email Alert Operational Status.
Field Description
Email Alert Status The Email Alert operational status The status is either Up or Down. The default is Down.
Number of Email
Sent
Number of Email
Failed
Time Since Last
Email Sent
The total number of email sent so far. The range is an unsigned integer of 32 bits. The
default is 0.
The total number of email failures so far. The range is an unsigned integer of 32 bits. The
default is 0.
The time since the last email was sent. Time format is used. The default is 00 days 00 hours
00 minutes 00 seconds. The UAP uses the system time to report the information. If an email
has not been sent since the device was reset, the status is not sent.
Table 17 - Email Alert Status
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 35
Page 36
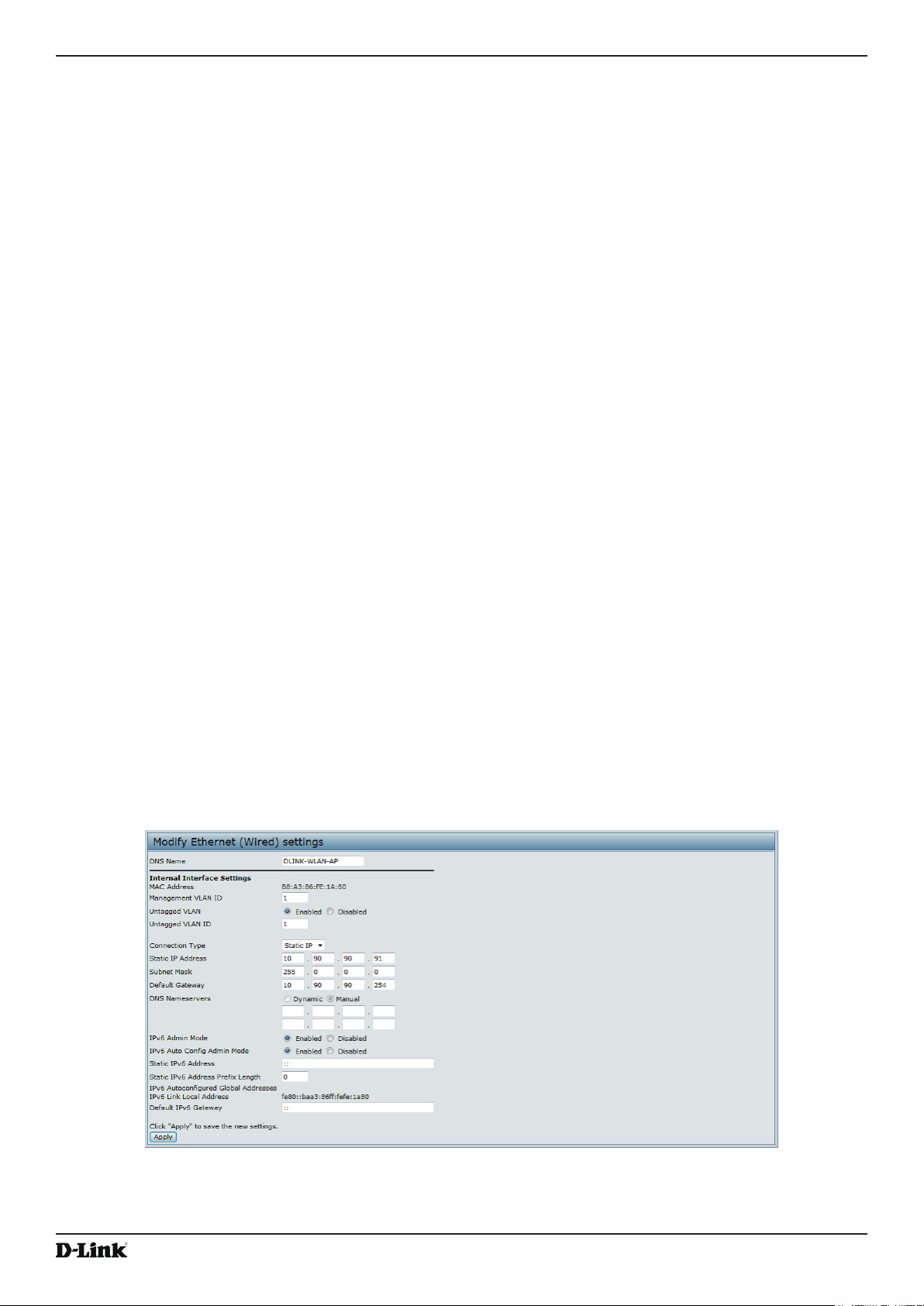
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
This section describes how to manage the UAP and contains the following subsections:
•) “Ethernet Settings” on page 36
•) “Wireless Settings” on page 38
•) “Modifying Radio Settings” on page 42
•) “Conguring Radio and VAP Scheduler” on page 47
•) “Scheduler Association Settings” on page 49
•) “Virtual Access Point Settings” on page 50
•) “Conguring Wireless Multicast Forwarding” on page 59
•) “Controlling Access by MAC Authentication” on page 63
•) “Conguring Load Balancing” on page 64
•) “Conguring 802.1X Authentication” on page 67
•) “Creating a Management Access Control List (ACL)” on page 68
The conguration pages for the features in this section are located under the Manage heading on the Administration
Web UI.
Ethernet Settings
The default wired interface settings, which include DHCP and VLAN information, might not work for all networks.
By default, the DHCP client on the UAP automatically broadcasts requests for network information. If you want to
use a static IP address, you must disable the DHCP client and manually congure the IP address and other network
information.
The management VLAN is VLAN 1 by default. This VLAN is also the default untagged VLAN. If you already have
a management VLAN congured on your network with a different VLAN ID, you must change the VLAN ID of the
management VLAN on the AP.
Management IPv6 settings describe the IPv6 conguration of Management Interface. Use this page to congure the
IPv6 admin mode, IPv6 auto-cong admin mode, connection type (DHCPv6 or Static IPv6 addressing) and DNS
servers. By default, the DHCPv6 client on the UAP automatically broadcasts requests for network information. If
you want to use a static IPv6 address, you must disable the DHCPv6 client and manually congure the Static IPv6
address and other network information.
To congure the LAN settings, click the Ethernet Settings tab.
Figure 17 - Modify Ethernet (Wired) settings
The following table describes the elds to view or congure on the Ethernet Settings page.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 36
Page 37
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Field Description
Hostname Enter a hostname for the AP. The hostname appears in the CLI prompt.
•) The hostname has the following requirements:
•) The length must be between 1 – 63 characters.
•) Upper and lower case characters, numbers, and hyphens are accepted.
•) The rst character must be a letter (a – z or A – Z), and the last character cannot be a
hyphen.
MAC Address Shows the MAC address for the LAN interface for the Ethernet port on this AP. This is a
read-only eld that you cannot change.
Management VLAN IDThe management VLAN is the VLAN associated with the IP address you use to access the
AP. The default management VLAN ID is 1.
Provide a number between 1 and 4094 for the management VLAN ID.
Untagged VLAN If you disable the untagged VLAN, all trafc is tagged with a VLAN ID.
By default all trafc on the UAP uses VLAN 1, which is the default untagged VLAN. This
means that all trafc is untagged until you disable the untagged VLAN, change the untagged
trafc VLAN ID, or change the VLAN ID for a VAP or client using RADIUS.
Untagged VLAN ID Provide a number between 1 and 4094 for the untagged VLAN ID. Trafc on the VLAN that
you specify in this eld will not be tagged with a VLAN ID.
Connection Type If you select DHCP, the UAP acquires its IP address, subnet mask, DNS, and gateway
information from a DHCP server.
If you select Static IP, you must enter information in the Static IP Address, Subnet Mask,
and Default Gateway elds.
Static IP Address Enter the static IP address in the text boxes. This eld is disabled if you use DHCP as the
connection type.
Subnet Mask Enter the Subnet Mask in the text boxes.
Default Gateway Enter the Default Gateway in the text boxes.
DNS Nameservers Select the mode for the DNS.
In Dynamic mode, the IP addresses for the DNS servers are assigned automatically via
DHCP. This option is only available if you specied DHCP for the Connection Type.
In Manual mode, you must assign static IP addresses to resolve domain names.
IPv6 Connection
Type
If you select DHCPv6, the UAP acquires its IPv6 address, DNS, and gateway information
from a DHCPv6 server.
If you select Static IPv6, you must enter information in the Static IPv6 Address, Prex
length, and Default Gateway elds.
IPv6 Admin Mode Enable or disable IPv6 management access to the AP
IPv6 Auto Cong
Admin Mode
Enable or disable IPv6 auto address conguration on the AP.
When IPv6 Auto Cong Mode is enabled, automatic IPv6 address conguration and gateway
conguration is allowed by processing the Router Advertisements received on the LAN port.
The AP can have multiple auto congured IPv6 addresses.
Static IPv6 Address Enter a static IPv6 address. The AP can have a static IPv6 address even if addresses have
already been congured automatically.
Static IPv6 Address
Enter the static IPv6 prex length, which is an integer in the range of 0 – 128.
Prex Length
IPv6 Autocongured
Global Addresses
IPv6 Link Local
Address
If the AP has been assigned one or more IPv6 addresses automatically, the addresses are
listed.
Shows the IPv6 Link Local address, which is the IPv6 address used by the local physical
link. The link local address is not congurable and is assigned by using the IPv6 Neighbor
Discovery process.
Default IPv6
Enter the default IPv6 gateway.
Gateway
IPv6 Domain
Nameservers
Select the mode for the DNS.
In Dynamic mode, the IPv6 addresses for the DNS servers are assigned automatically via
DHCPv6. This option is available only if DHCPv6 is selected for the Connection Type.
In Manual mode, you must assign static IPv6 addresses to resolve domain names.
Table 18 - Ethernet Settings
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 37
Page 38

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Note: After you congure the wired settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and
to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system
processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that
you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Note: Management IPv6 is available as a separate tab in few models of DWL.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
IPv6 Tunnel
The ISATAP (Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol) provides the support for encapsulating IPv6 packets
within IPv4 packets to allow transmission over IPv4 networks. This feature provides AP to act as an initiator of the
tunnel and will allow communication with remote IPv6 hosts. An ISATAP router acts as the end of the tunnel within the
network to help AP to auto-congure ISATAP tunnel interface.
From the IPv6 Tunnel page, you can enable, congure, and display ISATAP global operational and conguration
parameters.
Figure 18 - Modify IPv6 Tunnel Settings
Field Description
ISATAP Status Select Enable or Disable Administrative ISATAP tunnel status.
ISATAP Capable
Host
ISATAP Query
Interval
ISATAP Solicitation
Interval
ISATAP IPv6 Link
Local Address
ISATAP IPv6 Global
Address
Specify the IP Address or DNS name of the ISATAP router. The default value is isatap.
The number of seconds from 120-3600 between DNS queries (before the IP address of the
ISATAP router is known) for this tunnel. The interval can be a default value (120 seconds) or
a user dened interval.
The number of seconds from 120-3600 between ISATAP router solicitations messages,
when there is no active ISATAP router. The interval can be the default value (120 seconds)
or a user dened interval.
Displays link-local IPv6 address of ISATAP interface.
Displays global IPv6 address of ISATAP interface.
Table 19 - IPv6 Tunnel Settings
To apply your changes, click Update. Changing some settings might cause the AP to
stop and restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose
connectivity. We recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Wireless Settings
Wireless settings describe aspects of the local area network (LAN) related specically to the radio device in the
access point (802.11 Mode and Channel) and to the network interface to the access point (MAC address for access
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 38
Page 39

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
point and Wireless Network name, also known as SSID).
To congure the wireless interface, click the Manage > Wireless Settings tab.
Figure 19 - Modify Wireless Settings
The following table describes the elds and conguration options available on the Wireless Settings page.
Field Description
Country Select the country in which the AP is operating.
Wireless regulations vary from country to country. Make sure you select the correct country
code so that the AP complies with the regulations in your country. The country code
selection affects the radio modes the AP can support as well as the list of channels and
transmission power of the radio.
TSPEC Violation
Interval
Specify the time interval (in seconds) for the AP to report (through the system log and SNMP
traps) associated clients that do not adhere to mandatory admission control procedures.
Radio Interface Specify whether you want the radio interface on or off.
MAC Address Indicates the Media Access Control (MAC) addresses for the interface. Dual-radio APs have
a unique MAC address for each radio.
A MAC address is a permanent, unique hardware address for any device that represents
an interface to the network. The MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer. You cannot
change the MAC address. It is provided here for informational purposes as a unique
identier for an interface.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 39
Page 40

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Mode The Mode denes the Physical Layer (PHY) standard the radio uses.
Note: The modes available depend on the country code setting and the radio selected.
Select one of the following modes for radio 1:
•) IEEE 802.11a is a PHY standard that species operating in the 5 GHz U-NII band
using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). It supports data rates
ranging from 6 to 54 Mbps.
•) IEEE 802.11a/n operates in the 5 GHz ISM band and includes support for both
802.11a and 802.11n devices. IEEE 802.11n is an extension of the 802.11 standard
that includes multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology. IEEE 802.11n
supports data ranges of up to 248 Mbps and nearly twice the indoor range of 802.11
b, 802.11g, and 802.11a.
•) 5 GHz IEEE 802.11n is the recommended mode for networks with 802.11n devices
that operate in the 5 GHz frequency that do not need to support 802.11a devices.
IEEE 802.11n can achieve a higher throughput when it does not need to be
compatible with legacy devices (802.11a).
Select one of the following modes for radio 2:
•) IEEE 802.11b/g operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. IEEE 802.11b is an enhancement
of the initial 802.11 PHY to include 5.5 Mbps and 11 Mbps data rates. It uses direct
sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) or frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
as well as complementary code keying (CCK) to provide the higher data rates. It
supports data rates ranging from 1 to 11 Mbps. IEEE 802.11g is a higher speed
extension (up to 54 Mbps) to the 802.11b PHY. It uses orthogonal frequency division
multiplexing (OFDM). It supports data rates ranging from 1 to 54 Mbps.
•) IEEE 802.11b/g/n operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band and includes support for 802.11b,
802.11g, and 802.11n devices.
•) 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11n is the recommended mode for networks with 802.11n devices
that operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency that do not need to support 802.11b/g
devices. IEEE 802.11n can achieve a higher throughput when it does not need to be
compatible with legacy devices (802.11b/g).
•) IEEE 802.11a/n/ac: All the 802.11a, 802.11n and 802.11ac clients operating in the 5
GHz frequency can connect to the AP.
•) IEEE 802.11n/ac: 802.11n clients and 802.11ac clients operating in the 5-GHz
frequency can connect to the AP.
Channel Select the Channel.
The range of available channels is determined by the mode of the radio interface and the
country code setting. If you select Auto for the channel setting, the AP scans available
channels and selects a channel where no trafc is detected.
The Channel denes the portion of the radio spectrum the radio uses for transmitting and
receiving. Each mode offers a number of channels, depending on how the spectrum is
licensed by national and transnational authorities such as the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) or the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-R).
When automatic channel assignment is enabled on the Channel Management page for
Clustering, the channel policy for the radio is automatically set to static mode, and the Auto
option is not available for the Channel eld. This allows the automatic channel feature to set
the channels for the radios in the cluster.
Station Isolation To enable Station Isolation, select the check box directly beside it.
When Station Isolation is disabled, wireless clients can communicate with one another
normally by sending trafc through the AP.
When Station Isolation is enabled, the AP blocks communication between wireless clients
on the same radio and VAP. The AP still allows data trafc between its wireless clients and
wired devices on the network, across a WDS link, and with other wireless clients associated
with a different VAP, but not among wireless clients associated with the same VAP.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 40
Page 41

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
AeroScout™ Engine
Protocol Support
AeroScout Engine support provides location-based services for wireless networks. Specify
whether to enable support for the AeroScout protocol.
Options are Enabled or Disabled. The default is Disabled. When enabled, Aeroscout
devices are recognized and data is sent to an Aeroscout Engine (AE) for analysis. The AE
determines the geographical location of 802.11 capable devices, such as STAs, APs, and
AeroScout’s line of 802.11 enabled RFID devices, or tags. The AE communicates with APs
that support the AE protocol in order to collect information about the RF devices detected
by the APs. Using the AE protocol, D-Link supports direct communication between AE and
the APs. When operating in managed mode, the AE is congured with the IP address of
the managed access points from which it collects information. The Wireless Switch cannot
communicate with the AE.
For more information about the AeroScout protocol, see “Enabling AeroScout™ Engine
Support” on page 41.
Note: Only AeroScout tag hardware of types T2 and T3 are explicitly supported. Other tag
models are also supported only if their implementation of the AeroScout protocol conforms
to the AeroScout Engine - Access Point Interface Specication, version 2.1.
Note: AeroScout tags operate only in 802.11 b/g mode. Therefore, network administrators
who use the AeroScout tags must congure at least one radio on APs that are expected to
detect tags in either 802.11b/g or 802.11b/g/n mode. The radios congured in 2.4 GHz IEEE
802.11 mode or any of the 5GHz modes cannot detect AeroScout tags.
Note: The AE protocol allows access points to mark detected APs as rogue devices. The
D-Link APs do not support this feature and never report detected APs as rogues.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Table 20 - Wireless Settings
Note: After you congure the wireless settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and
to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system
processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that
you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Using the 802.11h Wireless Mode
For 802.11a radios, if the regulatory domain requires radar detection on the channel, the Dynamic Frequency
Selection (DFS) and Transmit Power Control (TPC) features of 802.11h are automatically activated.
There are a number of key points about the IEEE 802.11h standard:
•) 802.11h only works for the 802.11a band. It is not required for 802.11b or 802.11g.
•) If you are operating in an 802.11h enabled domain, the AP attempts to use the channel you assign. If the channel
has been blocked by a previous radar detection, or if the AP detects a radar on the channel, then the AP
automatically selects a different channel.
•) When 802.11h is enabled, the AP will not be operational in the 5GHz band for at least 60 seconds due to radar
scanning.
•) Setting up WDS links may be difcult when 802.11h is operational. This is because the operating channels of the
two APs on the WDS link may keep changing depending on channel usage and radar interference. WDS will
only work if both the APs operate on the same channel. For more information on WDS, see “Conguring Load
Balancing” on page 64.
Enabling AeroScout™ Engine Support
The AeroScout Engine (AE) is a software platform produced by AeroScout Inc. for location-based services. The AE
can determine the physical location of 802.11 capable AeroScout devices. The AE communicates with APs that have
the AE protocol enabled in order to collect information about the RF devices detected by the APs.
The DWS-4000 Series switch supports only direct communication between the AE and the APs. When operating
in managed mode, the AE is congured with the IP address of the managed access points from which it collects
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 41
Page 42
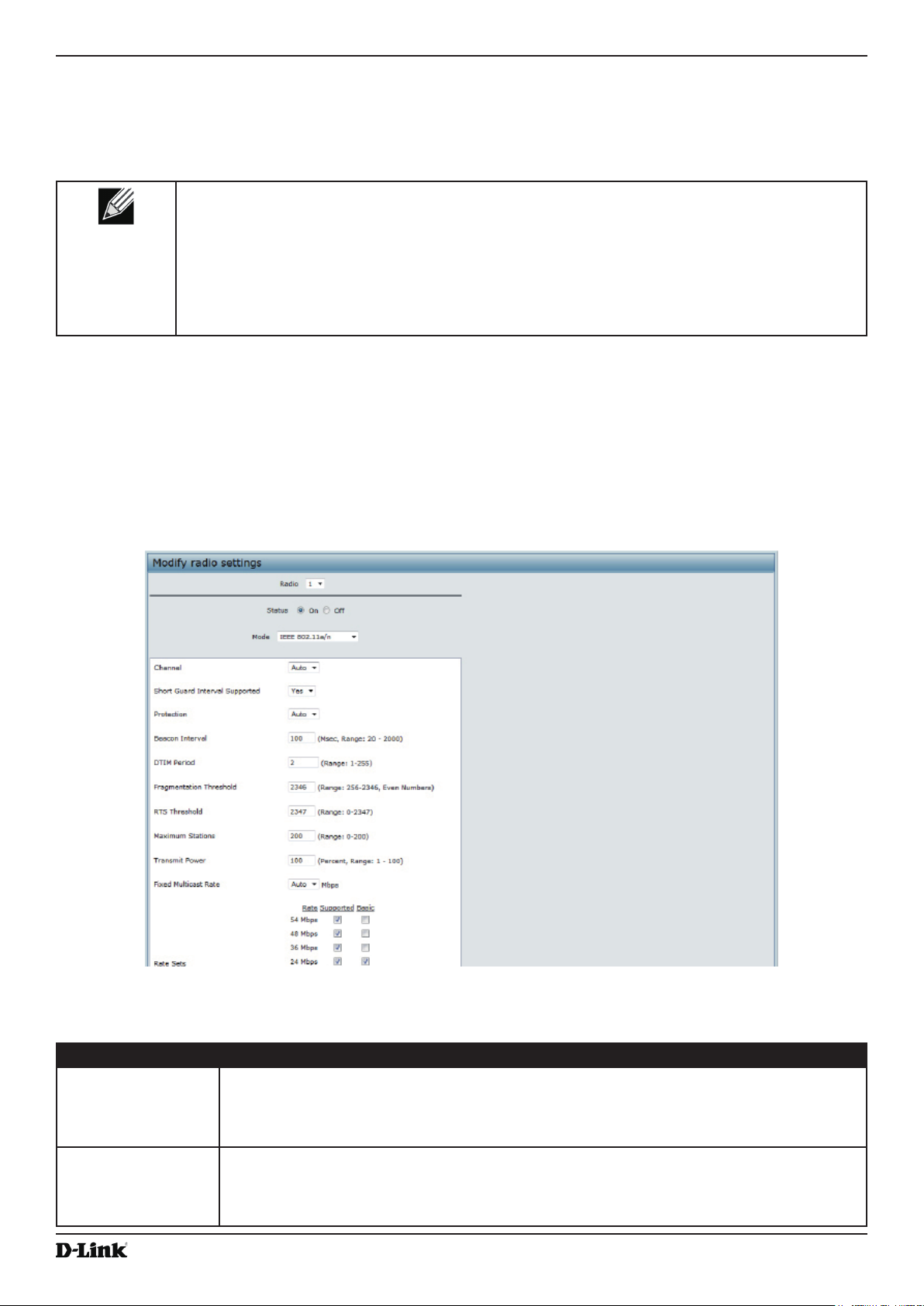
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
information. The DWS-4000 Series switch does not communicate with the AE.
AeroScout tags operate only in 802.11b/g mode. Therefore, network administrators who use the AeroScout tags must
congure at least one radio on APs that are expected to detect tags in either 802.11b/g or 802.11b/g/n mode. The
radios congured in 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11n mode cannot detect AeroScout tags.
Note: The following notes apply to AeroScout product and protocol support:
•) D-Link does not sell AeroScout products. Contact AeroScout for AeroScout hardware,
software or deployment information.
•) The AE protocol does not support any authentication or encryption between the AE server
and the access point.
•) The AE protocol requires radios to operate in promiscuous mode. This means that the AP
receives and processes all packets detected by the radios, as opposed to processing only
packets destined to the APs BSSID. This can affect AP throughput.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Modifying Radio Settings
Radio settings directly control the behaviour of the radio devices in the AP and its interaction with the physical
medium; that is, how and what type of electromagnetic waves the AP emits.
To specify radio settings, click the Radio tab in the Manage section.
Different settings will be displayed depending on the mode you select. All settings are described in the table below.
Figure 20 - Modify Radio Settings
The following table describes the elds and conguration options for the Radio Settings page.
Field Description
Radio Select Radio 1or Radio 2 to specify which radio to congure. The rest of the settings on this
page apply to the radio you select in this eld. Be sure to congure settings for both radios.
Radio 1 operates in the 5 GHz band (802.11a/n), and Radio 2 operates in the 2.4 GHz band
(802.11b/g/n).
Status (On/Off) Specify whether you want the radio on or off by clicking On or Off.
If you turn off a radio, the AP sends disassociation frames to all the wireless clients it is
currently supporting so that the radio can be gracefully shutdown and the clients can start
the association process with other available APs.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 42
Page 43

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Mode The Mode denes the Physical Layer (PHY) standard the radio uses.
Note: The modes available depend on the country code setting and the radio selected.
Select one of the following modes for radio 1:
•) IEEE 802.11a is a PHY standard that species operating in the 5 GHz U-NII band
using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). It supports data rates
ranging from 6 to 54 Mbps.
•) IEEE 802.11a/n operates in the 5 GHz ISM band and includes support for both
802.11a and 802.11n devices. IEEE 802.11n is an extension of the 802.11 standard
that includes multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology. IEEE 802.11n
supports data ranges of up to 248 Mbps and nearly twice the indoor range of 802.11
b, 802.11g, and 802.11a.
•) 5 GHz IEEE 802.11n is the recommended mode for networks with 802.11n devices
that operate in the 5 GHz frequency that do not need to support 802.11a devices.
IEEE 802.11n can achieve a higher throughput when it does not need to be
compatible with legacy devices (802.11a).
Select one of the following modes for radio 2:
•) IEEE 802.11b/g operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. IEEE 802.11b is an enhancement
of the initial 802.11 PHY to include 5.5 Mbps and 11 Mbps data rates. It uses direct
sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) or frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
as well as complementary code keying (CCK) to provide the higher data rates. It
supports data rates ranging from 1 to 11 Mbps. IEEE 802.11g is a higher speed
extension (up to 54 Mbps) to the 802.11b PHY. It uses orthogonal frequency division
multiplexing (OFDM). It supports data rates ranging from 1 to 54 Mbps.
•) IEEE 802.11b/g/n operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band and includes support for 802.11b,
802.11g, and 802.11n devices.
•) 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11n is the recommended mode for networks with 802.11n devices
that operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency that do not need to support 802.11b/g
devices. IEEE 802.11n can achieve a higher throughput when it does not need to be
compatible with legacy devices (802.11b/g).
•) IEEE 802.11a/n/ac: All the 802.11a, 802.11n and 802.11ac clients operating in the 5
GHz frequency can connect to the AP.
•) IEEE 802.11n/ac: 802.11n clients and 802.11ac clients operating in the 5 GHz
frequency can connect to the AP.
Channel Select the Channel.
The range of available channels is determined by the mode of the radio interface and the
country code setting. If you select Auto for the channel setting, the AP scans available
channels and selects a channel where no trafc is detected.
The channel denes the portion of the radio spectrum the radio uses for transmitting and
receiving. Each mode offers a number of channels, depending on how the spectrum is
licensed by national and transnational authorities such as the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) or the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-R).
When automatic channel assignment is enabled on the Channel Management page for
Clustering, the channel policy for the radio is automatically set to static mode, and the Auto
option is not available for the Channel eld. This allows the automatic channel feature to set
the channels for the radios in the cluster.
Channel Bandwidth
(802.11n and
802.11ac modes
only)
The 802.11n specication allows a 40 MHz wide channel in addition to the legacy 20 MHz
channel available with other modes. The 40 MHz channel enables higher data rates but
leaves fewer channels available for use by other 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz devices.
The 802.11ac specication allows an 80 MHz-wide channel in addition to the 20 MHz and 40
MHz channels.
Set the eld to 20 MHz to restrict the use of the channel bandwidth to a 20 MHz channel.
For the 802.11ac mode, set the eld to 40 MHz to prevent the radio from using the 80 MHz
channel bandwidth.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 43
Page 44

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Primary Channel
(802.11n modes
only)
DFS Support This eld is available only if the selected radio mode operates in the 5 GHz frequency.
Short Guard Interval
Supported
Multidomain
Regulatory Mode
STBC Mode This eld is available only if the selected radio mode includes 802.11n.
Protection The protection feature contains rules to guarantee that 802.11n transmissions do not cause
Beacon Interval Beacon frames are transmitted by an AP at regular intervals to announce the existence
This setting can be changed only when the channel bandwidth is set to 40 MHz. A 40 MHz
channel can be considered to consist of two 20 MHz channels that are contiguous in the
frequency domain. These two 20 MHz channels are often referred to as the Primary and
Secondary channels. The Primary Channel is used for 802.11n clients that support only a
20 MHz channel bandwidth and for legacy clients.
Select one of the following options:
•) Lower — Set the Primary Channel as the lower 20 MHz channel in the 40 MHz band.
•) Upper — Set the Primary Channel as the upper 20 MHz channel in the 40 MHz band.
For radios in the 5 GHz band, when DFS support is on and the regulatory domain requires
radar detection on the channel, the Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and Transmit
Power Control (TPC) features of 802.11h are activated.
DFS is a mechanism that requires wireless devices to share spectrum and avoid co-channel
operation with radar systems in the 5 GHz band. DFS requirements vary based on the
regulatory domain, which is determined by the country code setting of the AP.
This eld is available only if the selected radio mode includes 802.11n.
The guard interval is the dead time, in nanoseconds, between OFDM symbols. The guard
interval prevents Inter-Symbol and Inter-Carrier Interference (ISI, ICI). The 802.11n mode
allows for a reduction in this guard interval from the a and g denition of 800 nanoseconds
to 400 nanoseconds. Reducing the guard interval can yield a 10% improvement in data
throughput.
Select one of the following options:
•) Yes — The AP transmits data using a 400ns guard Interval when communicating with
clients that also support the short guard interval.
•) No — The AP transmits data using an 800ns guard interval.
This feature is congurable on a per radio basis. By default, it is enabled. Multidomain
Regulatory Mode (World Mode) causes the AP to broadcast which country it is operating in
as a part of its beacons and probe responses. This allows client stations to operate in any
country without re-conguration.
Disabling this feature prevents the country code setting from being broadcast in the
beacons. However, this only applies to radios congured to operate in the g band (2.4 GHz
band). For radios operating in the a band (5 GHz band), the AP software congures support
for 802.11h. When 802.11h is supported, the country code information is broadcast in the
beacons.
To enable Multidomain Regulatory Mode support, click Enabled.
To disable Multidomain Regulatory Mode support, click Disabled.
Space Time Block Coding (STBC) is an 802.11n technique intended to improve the reliability
of data transmissions. The data stream is transmitted on multiple antennas so the receiving
system has a better chance of detecting at least one of the data streams.
Select one of the following options:
•) On — The AP transmits the same data stream on multiple antennas at the same time.
•) Off — The AP does not transmits the same data on multiple antennas.
interference with legacy stations or APs. By default, these protection mechanisms are
enabled (Auto). With protection enabled, protection mechanisms will be invoked if legacy
devices are within range of the AP. This causes more overhead on every transmission,
which will impact performance. However, there is no impact on performance if there are no
legacy devices within range of the AP.
You can disable (Off) these protection mechanisms; however, when 802.11n protection is
off, legacy clients or APs within range can be affected by 802.11n transmissions. The 802.11
protection feature is also available when the mode is 802.11b/g. When protection is enabled
in this mode, it protects 802.11b clients and APs from 802.11g transmissions.
Note: This setting does not affect the ability of the client to associate with the AP.
of the wireless network. The default behaviour is to send a beacon frame once every 100
milliseconds (or 10 per second).
Enter a value from 20 to 2000 milliseconds.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 44
Page 45

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
DTIM Period Specify a DTIM period from 1 to 255 beacons.
The Delivery Trafc Information Map (DTIM) message is an element included in some
Beacon frames. It indicates which client stations, currently sleeping in low-power mode,
have data buffered on the AP awaiting pick-up.
The DTIM period you specify indicates how often the clients served by this AP should check
for buffered data still on the AP awaiting pickup.
The measurement is in beacons. For example, if you set this eld to 1, clients will check
for buffered data on the AP at every beacon. If you set this eld to 10, clients will check on
every 10th beacon.
Fragmentation
Threshold
RTS Threshold Specify a Request to Send (RTS) Threshold value between 0 and 2347.
Maximum Stations Specify the maximum number of stations allowed to access this AP at any one time.
Transmit Power Enter a percentage value for the transmit power level for this AP.
Fixed Multicast Rate Select the multicast trafc transmission rate you want the AP to support.
Frame-burst
Support
Legacy Rate Sets Check the transmission rate sets you want the AP to support and the basic rate sets you
Specify a number between 256 and 2,346 to set the frame size threshold in bytes.
The fragmentation threshold is a way of limiting the size of packets (frames) transmitted
over the network. If a packet exceeds the fragmentation threshold you set, the fragmentation
function is activated and the packet is sent as multiple 802.11 frames.
If the packet being transmitted is equal to or less than the threshold, fragmentation is not
used.
Setting the threshold to the largest value (2,346 bytes) effectively disables fragmentation.
Fragmentation plays no role when Aggregation is enabled.
Fragmentation involves more overhead both because of the extra work of dividing up and
reassembling of frames it requires, and because it increases message trafc on the network.
However, fragmentation can help improve network performance and reliability if properly
congured.
Sending smaller frames (by using lower fragmentation threshold) might help with some
interference problems; for example, with microwave ovens.
By default, fragmentation is off. We recommend not using fragmentation unless you suspect
radio interference. The additional headers applied to each fragment increase the overhead
on the network and can greatly reduce throughput.
The RTS threshold indicates the number of octets in an MPDU, below which an RTS/CTS
handshake is not performed.
Changing the RTS threshold can help control trafc ow through the AP, especially one
with a lot of clients. If you specify a low threshold value, RTS packets will be sent more
frequently. This will consume more bandwidth and reduce the throughput of the packet.
On the other hand, sending more RTS packets can help the network recover from
interference or collisions which might occur on a busy network, or on a network experiencing
electromagnetic interference.
You can enter a value between 0 and 200.
The default value, which is 100%, can be more cost-efcient than a lower percentage since
it gives the AP a maximum broadcast range and reduces the number of APs needed.
To increase capacity of the network, place APs closer together and reduce the value of the
transmit power. This helps reduce overlap and interference among APs. A lower transmit
power setting can also keep your network more secure because weaker wireless signals are
less likely to propagate outside of the physical location of your network.
Frame-burst Support boosts up the downstream throughput.
want the AP to advertise:
•) Rates are expressed in megabits per second.
•) Supported Rate Sets indicate rates that the AP supports. You can check multiple rates
(click a check box to select or de-select a rate). The AP will automatically choose the
most efcient rate based on factors like error rates and distance of client stations from
the AP.
•) Basic Rate Sets indicate rates that the AP will advertise to the network for the
purposes of setting up communication with other APs and client stations on the
network. It is generally more efcient to have an AP broadcast a subset of its
supported rate sets.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 45
Page 46
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
MCS (Data Rate)
Settings (802.11n
modes only)
This eld shows the Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) index values supported by the
radio. Each index can be enabled and disabled independently.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Broadcast/Multicast
Rate Limiting
DHCP Offer/ACK to
Unicast
Multicast to Unicast Enabling this feature will convert all multicast data stream to unicast stream and send to the
Forced Roaming Enabling this feature will detect and disconnect wireless clients based on the client RSSI. If
TSPEC Mode Regulates the overall TSPEC mode on the AP. The options are:
TSPEC Voice ACM
Mode
TSPEC Voice ACM
Limit
TSPEC Video ACM
Mode
TSPEC Video ACM
Limit
TSPEC BE ACM
Mode
TSPEC BE ACM
Limit
Enabling multicast and broadcast rate limiting can improve overall network performance by
limiting the number of packets transmitted across the network.
By default the Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limiting option is disabled. Until you enable
Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limiting, the following elds will be disabled:
•) Rate Limit - Enter the rate limit you want to set for multicast and broadcast trafc. The
limit should be greater than 1, but less than 50 packets per second. Any trafc that
falls below this rate limit will always conform and be transmitted to the appropriate
destination. The default and maximum rate limit setting is 50 packets per second.
•) Rate Limit Burst - Setting a rate limit burst determines how much trafc bursts can
be before all trafc exceeds the rate limit. This burst limit allows intermittent bursts of
trafc on a network above the set rate limit. The default and maximum rate limit burst
setting is 75 packets per second.
Enabling this feature will convert BOOTP replies from DHCP server to Unicast and send to
the requesting wireless client.
associated wireless clients.
the client RSSI falls below the roaming threshold value, the client will be disassociated.
Further association attempts will be monitored and disconnected 3 times if its RSSI is below
the threshold value. If still the client tries association 4th time, the association will be logged
and allowed to connect.
•) On — The AP handles TSPEC requests according to the TSPEC settings you
congure on the Radio page. Use this setting if the AP handles trafc from QoScapable devices, such as a Wi-Fi CERTIFIED phone.
•) Off — The AP ignores TSPEC requests from client stations. Use this setting if you do
not want to use TSPEC to give QoS-capable devices priority for time-sensitive trafc.
Regulates mandatory admission control (ACM) for the voice access category. The options
are:
•) On — A station is required to send a TSPEC request for bandwidth to the AP before
sending or receiving a voice trafc stream. The AP responds with the result of the
request, which includes the allotted medium time if the TSPEC was admitted.
•) Off — A station can send and receive voice priority trafc without requiring an admitted
TSPEC; the AP ignores voice TSPEC requests from client stations.
Specify an upper limit on the amount of trafc the AP attempts to transmit on the wireless
medium using a voice AC to gain access.
Regulates mandatory admission control for the video access category. The options are:
•) On — A station is required to send a TSPEC request for bandwidth to the AP before
sending or receiving a video trafc stream. The AP responds with the result of the
request, which includes the allotted medium time if the TSPEC was admitted.
•) Off — A station can send and receive video priority trafc without requiring an admitted
TSPEC; the AP ignores video TSPEC requests from client stations.
Specify an upper limit on the amount of trafc the AP attempts to transmit on the wireless
medium using a video AC to gain access.
Regulates mandatory admission control for the best effort access category. The options are:
• On-A station is required to send a TSPEC request for bandwidth to the AP before
sending or receiving a best effort trafc stream. The AP responds with the result of the
request, which includes the allotted medium time if the TSPEC was admitted.
• Off-A station can send and receive best effort priority trafc without requiring an admitted
TSPEC; the AP ignores best effort TSPEC requests from client stations.
Specify an upper limit on the amount of trafc the AP attempts to transmit on the wireless
medium using a best effort AC for stations roamed to this AP using Fast BSS Transition.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 46
Page 47
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
TSPEC BK ACM
Mode
TSPEC BK ACM
Limit
TSPEC AP Inactivity
Timeout
TSPEC Station
Inactivity Timeout
TSPEC Legacy
WMM Queue Map
Mode
Vht Features The purpose of this feature is to enable/disable Broadcom specic extensions in VHT for
Olpc Calibration
Period
Airtime Fairness The purpose of this is to enable/disable Airtime Fairness. This feature addresses the issue
Regulates mandatory admission control for the background access category. The options
are:
• On-A station is required to send a TSPEC request for bandwidth to the AP before
sending or receiving a background trafc stream. The AP responds with the result of the
request, which includes the allotted medium time if the TSPEC was admitted.
• Off-A station can send and receive background priority trafc without requiring an
admitted TSPEC; the AP ignores background TSPEC requests from client stations.
Specify an upper limit on the amount of trafc the AP attempts to transmit on the wireless
medium using a background AC for stations roamed to this AP using Fast BSS Transition.
Specify the amount of time for an AP to detect an downlink TS as idle before deleting it.
Specify the amount of time for an AP to detect an uplink TS as idle before deleting it.
Select Enable to allow intermixing of legacy trafc on queues operating as ACM.
Broadcom-to-Broadcom links. VHT feature enables support for 256QAM VHT rates not
specied by the 802.11ac Draft. The rates are all VHT LDPC mode, MCS 9 Nss 1 20Mhz,
MCS 9 Nss 2 20Mhz, MCS 6 Nss 3 80Mhz. The vht feature is supported for 802.11ac phy.
The purpose of this is to set Olpc Calibration Period which triggers a periodic calibration to
maintain output power same as target power for low power channels. The range of Olpc
Calibration Period is 10 to 20 minutes and ‘0’ is to disable the periodic calibration. This is
supported on 43431, 43460, and 43520 Radios.
of slower data transfers throttling the higher speed ones.
Table 21 - Radio Settings
Note: It is recommended not to require Admission Control for the access categories BE (Best
Effort) and BK (Background). Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart
system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We
recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Note: The following features are available only in DWL-3610AP and DWL-6610B1AP: DFS
Support, Frame-burst Support, DHCP Offer/ACK to Unicast, Multicast to Unicast, Forced Roaming,
TSPEC BE ACM Mode, TSPEC BE ACM Limit, TSPEC BK ACM Mode, TSPEC BK ACM Limit,
Vht Features, Olpc Calibration Period, and Airtime Fairness.
Use the Radio page to congure both Radio One and Radio Two. The settings on the page apply only to the radio
that you choose from the Radio drop-down list. After you congure settings for one of the radios, click Apply and then
select and congure the other radio. Be sure to click Apply to apply the second set of conguration settings for the
other radio.
Conguring Radio and VAP Scheduler
The Radio and VAP scheduler is a standalone DWL-x600AP feature. To congure the Radio and VAP scheduler,
select the Scheduler tab in the Manage section. The Radio and VAP Scheduler allows you to congure a rule with a
specic time interval for VAPs or radios to be operational, thereby automating the enabling or disabling of the VAPs
and Radios.
One of the ways you can use this feature is to schedule radios to operate only during the ofce working hours in order
to achieve security and reduce power consumption. You can also use the Scheduler to allow access to VAPs for
wireless clients only during specic times of day.
Each rule species the start time, end time and day (or days) of the week the radio or VAP can be operational. The
rules are periodic in nature and are repeated every week.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 47
Page 48

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
A valid rule must contain all of the following parameters:
•) Days of the Week.
•) Start Time (hour and minutes).
•) End Time (hour and minutes).
Only valid rules are added to the prole. Up to 16 rules are grouped together to form a scheduling prole. Any two
periodic rules time entries belonging to the same prole must not overlap. The time granularity for the schedules is
one minute. The DWL-x600AP supports up to 16 proles.
Figure 21 - Scheduler Conguration
Field Description
Global Scheduler
A global switch to enable or disable the scheduler feature. The default is Disable.
Mode
Scheduler Operational Status
Status The operational status of the Scheduler. The range is Up or Down. The default is Down.
Reason Provides additional information about the status. The reason can be one or more of the
following:
•) IsActive – Operational status is up.
•) CongDown – Operational status is down because global conguration is disabled.
•) TimeNotSet – Operational status is down because the AP time has not been set,
either manually or by specifying an NTP server to use.
•) ManagedMode– Operational status is down because the AP is in managed mode.
Scheduler Prole The Scheduler prole denes the list of proles names that can be associated to the VAP or
Radio conguration. Rules are associated with a named scheduler prole. You can dene up
to 16 scheduler prole names. By default, no proles are created.
The prole name can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters. Click Add to add the prole
name.
Rule Conguration Each scheduler prole may have up to 16 periodic rules. The list of parameters for each
periodic rule are described below.
Select Prole Select the prole name from the menu.
Set Schedule The day of the week. Range is: Daily, Weekday (Monday to Friday), Weekend (Saturday
and Sunday), Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday. The
default is Daily.
Start Time The time when the radio or VAP will be operationally enabled. The time is in HH:MM 24-hour
format. The range is <00-23>:<00-59>. The default is 00:00.
End Time The time when the radio or VAP will be operationally disabled. The time is in HH:MM 24-
hour format. The range is <00-23>:<00-59>. The default is 00:00.
Table 22 - Scheduler Conguration
After you select a prole from the Select Prole eld, the rules that have been added to the selected prole appear
in the table below the Rule Conguration area. When you add a new rule to a prole, it appears in the table. Use the
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 48
Page 49

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Modify Rule and Remove Rule buttons to manage the rules associated with a prole.
Use the following buttons to perform their respective tasks:
•) Add: To add a scheduler prole, specify the name of the prole in the appropriate eld and click Add.
•) Remove: To remove a scheduler prole, select it from the Select Prole eld in the Rule Conguration table and
click Remove.
•) Add Rule: After you congure the rule settings, click Add Rule to add the rule to the selected prole.
•) Modify Rule: To change an existing rule, select the rule, update the values in the Rule Conguration area, and
click Modify Rule.
•) Remove Rule: To delete a rule from a prole, select the rule and click Remove Rule.
•) Apply: After making any modications to the rules, click Apply to apply the changes and to save the settings.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Figure 22 - Scheduler Conguration (Modify Rule)
Click Apply to save the new conguration settings.
Note: After making any modications, you must click Apply to apply the changes and to save the
settings.
Scheduler Association Settings
For a Scheduler prole to take effect, you must associate it with at least one radio or VAP interface. To associate the
Scheduler proles, select the Scheduler Association tab in the Manage section. By default, there are no Scheduler
proles created, so no prole is associated to any radio or VAP. The Scheduler prole needs to be explicitly associated
to a radio or VAP conguration. Only one Scheduler prole can be associated to any radio or VAP conguration;
however, a single prole can be associated to multiple radios or VAPs. If the Scheduler prole associated with a VAP
or radio is deleted, then the associated prole to the VAP or radio is removed implicitly. If the radio is operationally
disabled, then all the VAPs associated to that radio are also operationally disabled irrespective of the VAP
conguration.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 49
Page 50

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Figure 23 - Scheduler Association Settings
Field Description
Radio Scheduler Prole Operational Status
1 or 2 From the menu, select the Scheduler prole to associate with Radio 1 or Radio 2.
Scheduler Prole From the menu, select the Scheduler prole to associate with the Radio.
Status The operational status of the Scheduler, which is either Up or Down.
VAP Scheduler Prole Operational Status
Radio From the menu, select Radio 1 or Radio 2 to associate the VAP Scheduler Prole.
VAP Identies the VAP associated with the rest of the information in the row.
0-15 or Scheduler
Prole
Operational Status The operational status of the Scheduler. The range is Up or Down.
From the menu, select the Scheduler prole to associate with the respective VAP.
Table 23 - Scheduler Association Settings
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Note: After you associate a Scheduler prole with a Radio interface or a VAP interface, you must
click Apply to apply the changes and to save the settings.
Virtual Access Point Settings
To change VAP 0 or to enable and congure additional VAPs, select the VAP tab in the Manage section.
VAPs segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of Ethernet VLANs.
VAPs simulate multiple APs in one physical AP. Each radio supports up to 16 VAPs.
For each VAP, you can customize the security mode to control wireless client access. Each VAP can also have
a unique SSID. Multiple SSIDs make a single AP look like two or more APs to other systems on the network.
By conguring VAPs, you can maintain better control over broadcast and multicast trafc, which affects network
performance.
You can congure each VAP to use a different VLAN, or you can congure multiple VAPs to use the same VLAN,
whether the VLAN is on the same radio or on a different radio. VAP0, which is always enabled on both radios, is
assigned to the default VLAN 1.
The AP adds VLAN ID tags to wireless client trafc based on the VLAN ID you congure on the VAP page or by using
the RADIUS server assignment. If you use an external RADIUS server, you can congure multiple VLANs on each
VAP. The external RADIUS server assigns wireless clients to the VLAN when the clients associate and authenticate.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 50
Page 51

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
You can congure up to four global IPv4 or IPv6 RADIUS servers. One of the servers always acts as a primary while
the others act as backup servers. The network type (IPv4 or IPv6) and accounting mode are common across all
congured RADIUS servers. You can congure each VAP to use the global RADIUS server settings, which is the
default, or you can congure a per-VAP RADIUS server set. You can also congure separate RADIUS server settings
for each VAP. For example, you can congure one VAP to use an IPv6 RADIUS server while other VAPs use the
global IPv4 RADIUS server settings you congure.
If wireless clients use a security mode that does not communicate with the RADIUS server, or if the RADIUS server
does not provide the VLAN information, you can assign a VLAN ID to each VAP. The AP assigns the VLAN to all
wireless clients that connect to the AP through that VAP.
Note: Before you congure VLANs on the AP, be sure to verify that the switch and DHCP server
the AP uses can support IEEE 802.1Q VLAN encapsulation.
To set up multiple VAPs, click Manage > VAP.
Figure 24 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings
The following table describes the elds and conguration options on the VAP page.
Field Description
RADIUS IP Address
Type
Specify the IP version that the RADIUS server uses.
You can toggle between the address types to congure IPv4 and IPv6 global RADIUS
address settings, but the AP contacts only the RADIUS server or servers for the address
type you select in this eld.
RADIUS IP Address
Enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address for the primary global RADIUS server. By default, each VAP
uses the global RADIUS settings that you dene for the AP at the top of the VAP page.
RADIUS IPv6
Address
When the rst wireless client tries to authenticate with the AP, the AP sends an
authentication request to the primary server. If the primary server responds to the
authentication request, the AP continues to use this RADIUS server as the primary server,
and authentication requests are sent to the address you specify.
If the IPv4 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected in the previous eld, enter the IP
address of the RADIUS server that all VAPs use by default, for example 192.168.10.23.
If the IPv6 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected, enter the IPv6 address of the
primary global RADIUS server, for example 2001:0db8:1234::abcd.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 51
Page 52

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
RADIUS IP or IPv6
Address 1–3
RADIUS Key Enter the RADIUS key in the text box.
RADIUS Key 1–3 Enter the RADIUS key associated with the congured backup RADIUS servers. The server
Enable RADIUS
Accounting
Enable RADIUS
FailThrough
Radio Select the radio to congure. VAPs are congured independently on each radio.
VAP You can congure up to 16 VAPs for each radio. VAP0 is the physical radio interface, so to
Enabled You can enable or disable a congured network.
VLAN ID When a wireless client connects to the AP by using this VAP, the AP tags all trafc from the
SSID Enter a name for the wireless network. The SSID is an alphanumeric string of up to 32
Enter up to three IPv4 or IPv6 addresses to use as the backup RADIUS servers. The eld
label is RADIUS IP Address when the IPv4 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected and
RADIUS IPv6 Address when the IPv6 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected.
If authentication fails with the primary server, each congured backup server is tried in
sequence. The IPv4 or IPv6 address must be valid in order for the AP to attempt to contact
the server.
The RADIUS Key is the shared secret key for the global RADIUS server. You can use up to
63 standard alphanumeric and special characters. The key is case sensitive, and you must
congure the same key on the AP and on your RADIUS server. The text you enter will be
displayed as “*” characters to prevent others from seeing the RADIUS key as you type.
at RADIUS IP Address-1 uses RADIUS Key-1, RADIUS IP Address-2 uses RADIUS Key-2,
and so on.
Select this option to track and measure the resources a particular user has consumed
such as system time, amount of data transmitted and received, and so on.
If you enable RADIUS accounting, it is enabled for the primary RADIUS server and all
backup servers.
Select this option to allow the secondary RADIUS server to authenticate wireless clients
if the authentication with the primary RADIUS server is unsuccessful, or if the primary
RADIUS server is unavailable.
disable VAP0, you must disable the radio.
•) To enable the specied network, select the Enabled option beside the appropriate
VA P.
•) To disable the specied network, clear the Enabled option beside the appropriate VAP.
If you disable the specied network, you will lose the VLAN ID you entered.
wireless client with the VLAN ID you enter in this eld unless you enter the untagged VLAN
ID or use a RADIUS server to assign a wireless client to a VLAN. The range for the VLAN ID
is 1 – 4094.
If you use RADIUS-based authentication for clients, you can optionally add the following
attributes to the appropriate le in the RADIUS or AAA server to congure a VLAN for the
client:
•) “Tunnel-Type”
•) “Tunnel-Medium-Type”
•) “Tunnel-Private-Group-ID”
The RADIUS-assigned VLAN ID overrides the VLAN ID you congure on the VAP page.
You congure the untagged and management VLAN IDs on the Ethernet Settings page. For
more information, see “Ethernet Settings” on page 36.
characters. You can use the same SSID for multiple VAPs, or you can choose a unique
SSID for each VAP.
Note: If you are connected as a wireless client to the same AP that you are administering,
resetting the SSID will cause you to lose connectivity to the AP. You will need to reconnect to
the new SSID after you save this new setting.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 52
Page 53

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Broadcast SSID Specify whether to allow the AP to broadcast the Service Set Identier (SSID) in its beacon
frames. The Broadcast SSID parameter is enabled by default. When the VAP does not
broadcast its SSID, the network name is not displayed in the list of available networks on
a client station. Instead, the client must have the exact network name congured in the
supplicant before it is able to connect.
•) To enable the SSID broadcast, select the Broadcast SSID check box.
•) To prohibit the SSID broadcast, clear the Broadcast SSID check box.
Note: Disabling the broadcast SSID is sufcient to prevent clients from accidentally
connecting to your network, but it will not prevent even the simplest of attempts by a hacker
to connect or monitor unencrypted trafc. Suppressing the SSID broadcast offers a very
minimal level of protection on an otherwise exposed network (such as a guest network)
where the priority is making it easy for clients to get a connection and where no sensitive
information is available.
Security Select one of the following Security modes for this VAP:
•) None
•) Static WEP
•) WPA Personal
•) IEEE 802.1X
•) WPA Enterprise
If you select a security mode other than None, additional elds appear. These elds are
explained below.
Note: The Security mode you set here is specically for this VAP.
MAC Authentication
Type
MFP (Management
Frame Protection)
You can congure a global list of MAC addresses that are allowed or denied access to
the network. The drop-down menu for this feature allows you to select the type of MAC
Authentication to use:
•) Disabled: Do not use MAC Authentication.
•) Local: Use the MAC Authentication list that you congure on the MAC Authentication
page.
•) RADIUS: Use the MAC Authentication list on the external RADIUS server.
For more information about MAC Authentication, see “Controlling Access by MAC
Authentication” on page 63.
Provides security for the otherwise unprotected and unencrypted 802.11 management
frames. This eld is visible only when wpa2 security and CCMP elds are enabled. Following
3 check box values can be congured for it.
• Not Required
• Capable
• Required
By default Not Required is selected. On selecting Required , Capable checkbox will be
selected and disabled.
Table 24 - Virtual Access Point Settings
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Note: After you congure the VAP settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and to save
the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system processes. If
this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that you change
AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
None (Plain-text)
If you select None as your security mode, no further options are congurable on the AP. This mode means that
any data transferred to and from the UAP is not encrypted. This security mode can be useful during initial network
conguration or for problem solving, but it is not recommended for regular use on the Internal network because it is
not secure.
Static WEP
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 53
Page 54

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a data encryption protocol for 802.11 wireless networks. All wireless stations and
APs on the network are congured with a static 64-bit (40-bit secret key + 24-bit initialization vector (IV)) or 128-bit
(104-bit secret key + 24-bit IV) Shared Key for data encryption.
Static WEP is not the most secure mode available, but it offers more protection than setting the security mode to None
(Plain-text) as it does prevent an outsider from easily snifng out unencrypted wireless trafc.
WEP encrypts data moving across the wireless network based on a static key. (The encryption algorithm is a stream
cipher called RC4.)
Figure 25 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (Static WEP)
Field Description
Transfer Key Index Select a key index from the drop-down menu. Key indexes 1 through 4 are available. The
default is 1.
The Transfer Key Index indicates which WEP key the AP will use to encrypt the data it
transmits.
Key Length Specify the length of the key by clicking one of the radio buttons:
•) 64 bits
•) 128 bits
Key Type Select the key type by clicking one of the radio buttons:
•) ASCII
•) Hex
WEP Keys You can specify up to four WEP keys. In each text box, enter a string of characters for each
key. The keys you enter depend on the key type selected:
•) ASCII — Includes upper and lower case alphabetic letters, the numeric digits, and
special symbols such as @ and #.
•) Hex — Includes digits 0 to 9 and the letters A to F.
Use the same number of characters for each key as specied in the Characters Required
eld. These are the RC4 WEP keys shared with the stations using the AP.
Each client station must be congured to use one of these same WEP keys in the same slot
as specied here on the AP.
Characters Required: The number of characters you enter into the WEP Key elds is
determined by the Key length and Key type you select. For example, if you use 128-bit
ASCII keys, you must enter 26 characters in the WEP key. The number of characters
required updates automatically based on how you set Key Length and Key Type.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 54
Page 55

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Authentication The authentication algorithm denes the method used to determine whether a client station
is allowed to associate with an AP when static WEP is the security mode.
Specify the authentication algorithm you want to use by choosing one of the following
options:
•) Open System authentication allows any client station to associate with the AP whether
that client station has the correct WEP key or not. This algorithm is also used in
plaintext, IEEE 802.1X, and WPA modes. When the authentication algorithm is set to
Open System, any client can associate with the AP.
Note: Just because a client station is allowed to associate does not ensure it can exchange
trafc with an AP. A station must have the correct WEP key to be able to successfully access
and decrypt data from an AP, and to transmit readable data to the AP.
•) Shared Key authentication requires the client station to have the correct WEP key in
order to associate with the AP. When the authentication algorithm is set to Shared
Key, a station with an incorrect WEP key will not be able to associate with the AP.
•) Both Open System and Shared Key. When you select both authentication
algorithms:
•) Client stations congured to use WEP in shared key mode must have a valid WEP
key in order to associate with the AP.
•) Client stations congured to use WEP as an open system (shared key mode not
enabled) will be able to associate with the AP even if they do not have the correct
WEP key.
Table 25 - Static WEP
Static WEP Rules
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
If you use Static WEP, the following rules apply:
•) All client stations must have the Wireless LAN (WLAN) security set to WEP, and all clients must have one of the
WEP keys specied on the AP in order to de-code AP-to-station data transmissions.
•) The AP must have all keys used by clients for station-to-AP transmit so that it can de-code the station
transmissions.
•) The same key must occupy the same slot on all nodes (AP and clients). For example if the AP denes abc123
key as WEP key 3, then the client stations must dene that same string as WEP key 3.
•) Client stations can use different keys to transmit data to the access point. (Or they can all use the same key, but
this is less secure because it means one station can decrypt the data being sent by another.)
•) On some wireless client software, you can congure multiple WEP keys and dene a client station “transfer
key index”, and then set the stations to encrypt the data they transmit using different keys. This ensures that
neighboring APs cannot decode each other’s transmissions.
•) You cannot mix 64-bit and 128-bit WEP keys between the access point and its client stations.
IEEE 802.1X
IEEE 802.1X is the standard dening port-based authentication and infrastructure for doing key management.
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) messages sent over an IEEE 802.11 wireless network using a protocol
called EAP Encapsulation Over LANs (EAPOL). IEEE 802.1X provides dynamically-generated keys that are
periodically refreshed. An RC4 stream cipher is used to encrypt the frame body and cyclic redundancy checking
(CRC) of each 802.11 frame.
This mode requires the use of an external RADIUS server to authenticate users. The AP requires a RADIUS server
capable of EAP, such as the Microsoft Internet Authentication Server. To work with Windows clients, the authentication
server must support Protected EAP (PEAP) and MSCHAP V2.
You can use any of a variety of authentication methods that the IEEE 802.1X mode supports, including certicates,
Kerberos, and public key authentication. You must congure the client stations to use the same authentication method
the AP uses.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 55
Page 56

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Figure 26 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (IEEE802.1X)
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Field Description
Use Global RADIUS
Server Settings
By default each VAP uses the global RADIUS settings that you dene for the AP at the top
of the VAP page. However, you can congure each VAP to use a different set of RADIUS
servers.
To use the global RADIUS server settings, make sure the check box is selected.
To use a separate RADIUS server for the VAP, clear the check box and enter the RADIUS
server IP address and key in the following elds.
RADIUS IP Address
Type
Specify the IP version that the RADIUS server uses.
You can toggle between the address types to congure IPv4 and IPv6 global RADIUS
address settings, but the AP contacts only the RADIUS server or servers for the address
type you select in this eld.
RADIUS IP Address
RADIUS IPv6
Address
Enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address for the primary RADIUS server for this VAP.
If the IPv4 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected in the previous eld, enter the IP
address of the RADIUS server that all VAPs use by default, for example 192.168.10.23. If
the IPv6 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected, enter the IPv6 address of the primary
global RADIUS server, for example 2001:0db8:1234::abcd.
RADIUS IP or IPv6
Address 1–3
Enter up to three IPv4 and/or IPv6 addresses to use as the backup RADIUS servers for this
VAP. The eld label is RADIUS IP Address when the IPv4 RADIUS IP Address Type option
is selected and RADIUS IPv6 Address when the IPv6 RADIUS IP Address Type option is
selected.
If authentication fails with the primary server, each congured backup server is tried in
sequence.
RADIUS Key Enter the RADIUS key in the text box.
The RADIUS Key is the shared secret key for the global RADIUS server. You can use up to
63 standard alphanumeric and special characters. The key is case sensitive, and you must
congure the same key on the AP and on your RADIUS server. The text you enter will be
displayed as “*” characters to prevent others from seeing the RADIUS key as you type.
RADIUS Key 1 – 3 Enter the RADIUS key associated with the congured backup RADIUS servers. The server
at RADIUS IP Address-1 uses RADIUS Key-1, RADIUS IP Address-2 uses RADIUS Key-2,
and so on.
Enable RADIUS
Accounting
Select this option to track and measure the resources a particular user has consumed
such as system time, amount of data transmitted and received, and so on.
If you enable RADIUS accounting, it is enabled for the primary RADIUS server and all
backup servers.
Enable RADIUS
FailThrough
Select this option to allow the secondary RADIUS server to authenticate wireless clients if
the authentication with the primary RADIUS server is unsuccessful, or if the primary RADIUS
server is unavailable.
Active Server Specify which congured RADIUS server to use as the active RADIUS server.
Broadcast Key
Refresh Rate
Enter a value to set the interval at which the broadcast (group) key is refreshed for clients
associated to this VAP (the default is 300).
The valid range is 0 – 86400 seconds. A value of 0 indicates that the broadcast key is not
refreshed.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 56
Page 57

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Session Key
Refresh Rate
Enter a value to set the interval at which the AP will refresh session (unicast) keys for each
client associated to the VAP.
The valid range is 0 – 86400 seconds. A value of 0 indicates that the broadcast key is not
refreshed.
Note: After you congure the security settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and to
save the settings.
Table 26 - IEEE 802.1X
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
WPA Personal
WPA Personal is a Wi-Fi Alliance IEEE 802.11i standard, which includes AES-CCMP and TKIP mechanisms. The
Personal version of WPA employs a pre-shared key (instead of using IEEE 802.1X and EAP as is used in the
Enterprise WPA security mode). The PSK is used for an initial check of credentials only.
This security mode is backwards-compatible for wireless clients that support the original WPA.
Figure 27 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (WPA Personal)
Field Description
WPA Versions Select the types of client stations you want to support:
•) WPA. If all client stations on the network support the original WPA but none support the
newer WPA2, then select WPA.
•) WPA2. If all client stations on the network support WPA2, we suggest using WPA2
which provides the best security per the IEEE 802.11i standard.
•) WPA and WPA2. If you have a mix of clients, some of which support WPA2 and others
which support only the original WPA, select both of the check boxes. This lets both
WPA and WPA2 client stations associate and authenticate, but uses the more robust
WPA2 for clients who support it. This WPA conguration allows more inter-operability,
at the expense of some security.
Cipher Suites Select the cipher suite you want to use:
•) TKIP
•) CCMP (AES)
•) TKIP and CCMP (AES)
Both TKIP and AES clients can associate with the AP. WPA clients must have one of the
following to be able to associate with the AP:
•) A valid TKIP key
•) A valid AES-CCMP key
Clients not congured to use a WPA Personal will not be able to associate with the AP.
Key The Pre-shared Key is the shared secret key for WPA Personal. Enter a string of at least 8
characters to a maximum of 63 characters. Acceptable characters include upper and lower
case alphabetic letters, the numeric digits, and special symbols such as @ and #.
Broadcast Key
Refresh Rate
Enter a value to set the interval at which the broadcast (group) key is refreshed for clients
associated to this VAP (the default is 300).
The valid range is 0–86400 seconds. A value of 0 indicates that the broadcast key is not
refreshed.
Table 27 - WPA Personal
October 2017
Note: After you congure the security settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and to
save the settings.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 57
Page 58
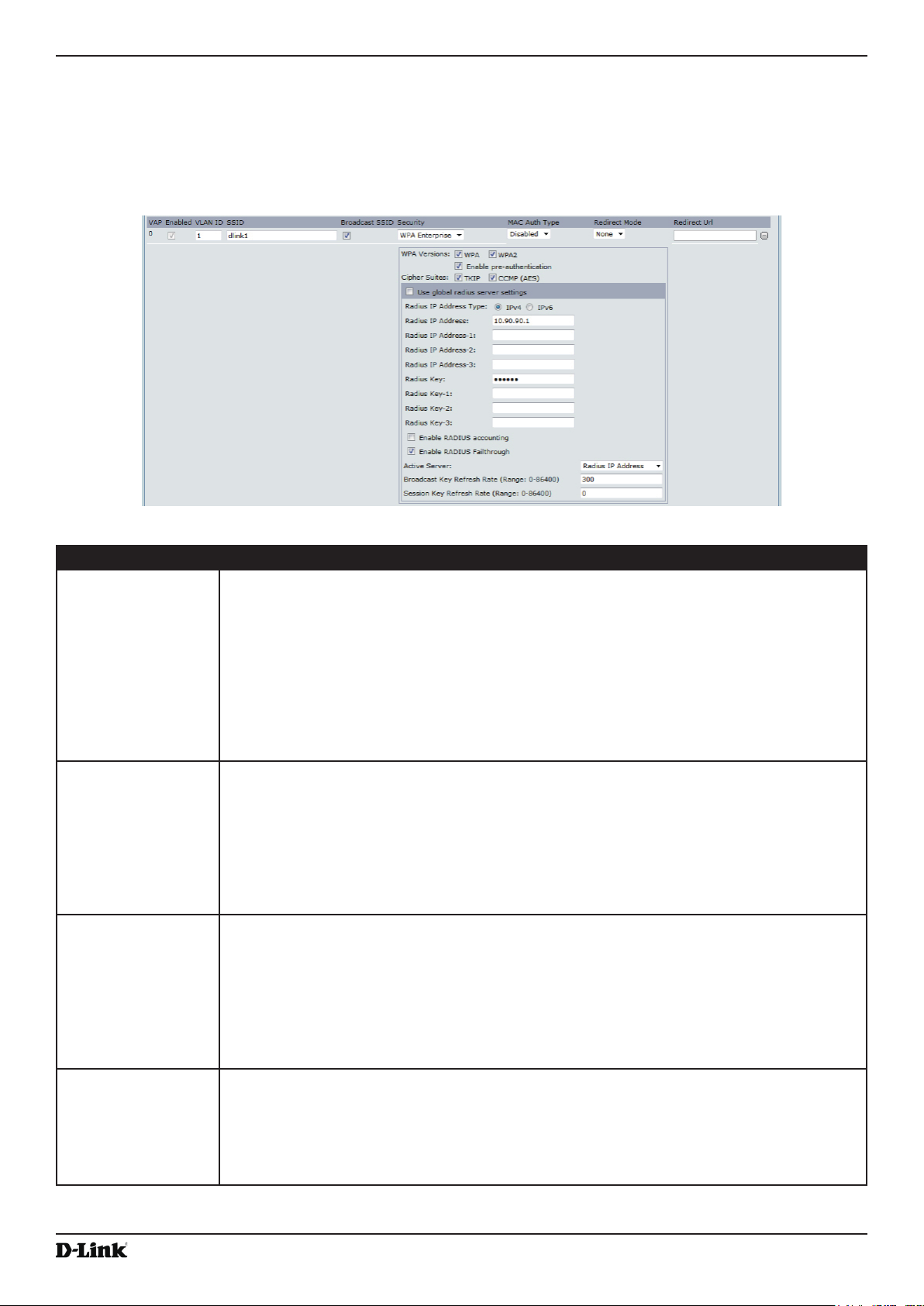
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
WPA Enterprise
WPA Enterprise with RADIUS is an implementation of the Wi-Fi Alliance IEEE 802.11i standard, which includes CCMP
(AES), and TKIP mechanisms. The Enterprise mode requires the use of a RADIUS server to authenticate users.
This security mode is backwards-compatible with wireless clients that support the original WPA.
Figure 28 - Modify Virtual Access Point Settings (WPA Enterprise)
Field Description
WPA Versions Select the types of client stations you want to support:
•) WPA. If all client stations on the network support the original WPA but none support the
newer WPA2, then select WPA.
•) WPA2. If all client stations on the network support WPA2, we suggest using WPA2
which provides the best security per the IEEE 802.11i standard.
•) WPA and WPA2. If you have a mix of clients, some of which support WPA2 and others
which support only the original WPA, select both WPA and WPA2. This lets both WPA
and WPA2 client stations associate and authenticate, but uses the more robust WPA2
for clients who support it. This WPA conguration allows more interoperability, at the
expense of some security.
Enable pre-
authentication
Cipher Suites Select the cipher suite you want to use:
Use Global RADIUS
Server Settings
If for WPA Versions you select only WPA2 or both WPA and WPA2, you can enable preauthentication for WPA2 clients.
Click Enable pre-authentication if you want WPA2 wireless clients to send preauthentication packet. The pre-authentication information will be relayed from the AP
the client is currently using to the target AP. Enabling this feature can help speed up
authentication for roaming clients who connect to multiple APs.
This option does not apply if you selected WPA for WPA Versions because the original WPA
does not support this feature.
•) TKIP
•) CCMP (AES)
•) TKIP and CCMP (AES)
By default both TKIP and CCMP are selected. When both TKIP and CCMP are selected,
client stations congured to use WPA with RADIUS must have one of the following:
•) A valid TKIP RADIUS IP address and RADIUS Key
•) A valid CCMP (AES) IP address and RADIUS Key
By default each VAP uses the global RADIUS settings that you dene for the AP at the top
of the VAP page. However, you can congure each VAP to use a different set of RADIUS
servers.
To use the global RADIUS server settings, make sure the check box is selected.
To use a separate RADIUS server for the VAP, clear the check box and enter the RADIUS
server IP address and key in the following elds.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 58
Page 59

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
RADIUS IP Address
Type
RADIUS IP Address
RADIUS IPv6
Address
RADIUS IP or IPv6
Address 1–3
RADIUS Key Enter the RADIUS key in the text box.
RADIUS Key 1–3 Enter the RADIUS key associated with the congured backup RADIUS servers. The server
Enable RADIUS
Accounting
Enable RADIUS
FailThrough
Active Server Specify which congured RADIUS server to use as the active RADIUS server.
Broadcast Key
Refresh Rate
Session Key
Refresh Rate
Specify the IP version that the RADIUS server uses.
You can toggle between the address types to congure IPv4 and IPv6 global RADIUS
address settings, but the AP contacts only the RADIUS server or servers for the address
type you select in this eld.
Enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address for the primary RADIUS server for this VAP.
If the IPv4 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected in the previous eld, enter the IP
address of the RADIUS server that all VAPs use by default, for example 192.168.10.23.
If the IPv6 RADIUS IP Address Type option is selected, enter the IPv6 address of the
primary global RADIUS server, for example 2001:0db8:1234::abcd.
Enter up to three IPv4 and/or IPv6 addresses to use as the backup RADIUS servers for this
VAP. The eld label is RADIUS IP Address when the IPv4 RADIUS IP Address Type option
is selected and RADIUS IPv6 Address when the IPv6 RADIUS IP Address Type option is
selected.
If authentication fails with the primary server, each congured backup server is tried in
sequence.
The RADIUS Key is the shared secret key for the global RADIUS server. You can use up to
63 standard alphanumeric and special characters. The key is case sensitive, and you must
congure the same key on the AP and on your RADIUS server. The text you enter will be
displayed as “*” characters to prevent others from seeing the RADIUS key as you type.
at RADIUS IP Address-1 uses RADIUS Key-1, RADIUS IP Address-2 uses RADIUS Key-2,
and so on.
Select this option to track and measure the resources a particular user has consumed
such as system time, amount of data transmitted and received, and so on.
If you enable RADIUS accounting, it is enabled for the primary RADIUS server and all
backup servers.
Select this option to allow the secondary RADIUS server to authenticate wireless clients
if the authentication with the primary RADIUS server is unsuccessful, or if the primary
RADIUS server is unavailable.
Enter a value to set the interval at which the broadcast (group) key is refreshed for clients
associated to this VAP (the default is 300).
The valid range is 0–86400 seconds. A value of 0 indicates that the broadcast key is not
refreshed.
Enter a value to set the interval at which the AP will refresh session (unicast) keys for each
client associated to the VAP.
The valid range is 0–86400 seconds. A value of 0 indicates that the broadcast key is not
refreshed.
Table 28 - WPA Enterprise
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Note: After you congure the security settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and to
save the settings.
Conguring Wireless Multicast Forwarding
The Wireless Multicast Forwarding provides an efcient way to forward the multicast trafc on the wireless medium
and overcomes the multicast transmission issues on WLAN using the repeated unicast of multicast frames. It
uses IGMP frames to keep track of participating group members, and multicast packets are transmitted only to the
interested members after unicast MAC conversion .
With WMF, the data transfer is more reliable as the frames are sent as unicast, and robust transmission is possible
as dynamic per station rate control can be done based on the link errors and noise conditions. The multicast group
members can be a STA end point. Streaming between STA devices will also be supported. The multicast streaming
server can be attached to any of the LAN ports.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 59
Page 60

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Figure 29 - Wireless Multicast Forwarding
Field Description
VAP •) You can congure up to 16 VAPs for each radio.
•) VAP0 is the physical radio interface, so to disable VAP0, you must disable the radio.
Enabled You can enable or disable a congured network. If you disable the specied network, you
will lose the VLAN ID you enabled
WMF-Enable Enable/Disable the WMF status in a VAP.
Table 29 - Wireless Multicast Forwarding
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Conguring the Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
The Wireless Distribution System (WDS) allows you to connect multiple UAPs. With WDS, APs communicate with one
another without wires in a standardized way. This capability is critical in providing a seamless experience for roaming
clients and for managing multiple wireless networks. It can also simplify the network infrastructure by reducing the
amount of cabling required. You can congure the AP in point-to-point or point-to-multipoint bridge mode based on the
number of links to connect.
In the point-to-point mode, the AP accepts client associations and communicates with wireless clients and other
repeaters. The AP forwards all trafc meant for the other network over the tunnel that is established between the APs.
The bridge does not add to the hop count. It functions as a simple OSI layer 2 network device.
In the point-to-multipoint bridge mode, one AP acts as the common link between multiple APs. In this mode, the
central AP accepts client associations and communicates with the clients and other repeaters. All other APs associate
only with the central AP that forwards the packets to the appropriate wireless bridge for routing purposes.
The UAP can also act as a repeater. In this mode, the AP serves as a connection between two APs that might be
too far apart to be within cell range. When acting as a repeater, the AP does not have a wired connection to the LAN
and repeats signals by using the wireless connection. No special conguration is required for the AP to function as a
repeater, and there are no repeater mode settings. Wireless clients can still connect to an AP that is operating as a
repeater.
Note: When you move an AP from Standalone Mode to Managed Mode, WDS is disabled.
In Managed Mode, you congure the AP by using the D-Link Unied Wireless Switch. The
Administrator UI, as well as Telnet, SSH, and SNMP access are disabled when the AP is in
Managed Mode.
To specify the details of trafc exchange from this access point to others, click the WDS tab.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 60
Page 61
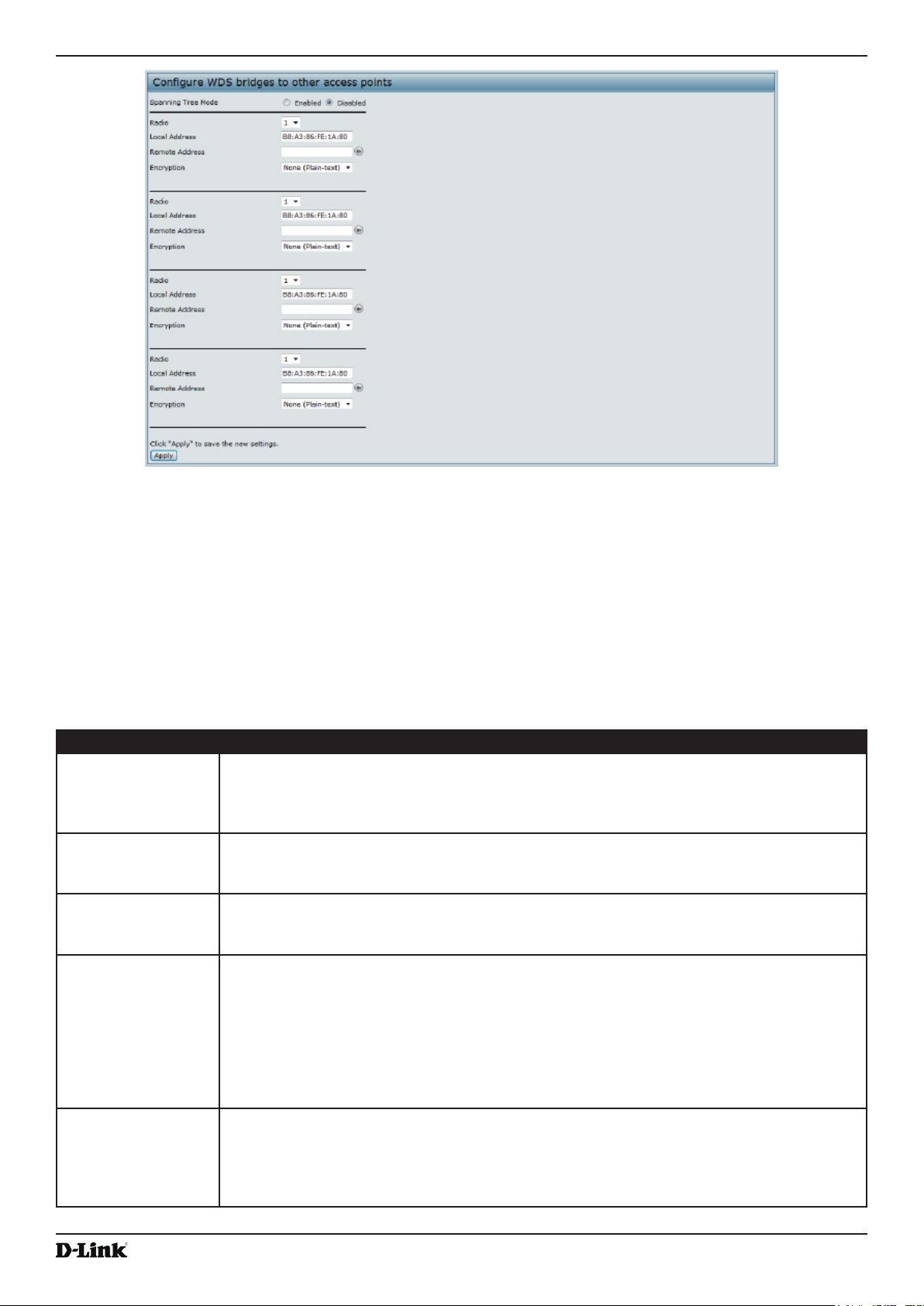
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Figure 30 - Congure WDS Bridges
Before you congure WDS on the AP, note the following guidelines:
•) When using WDS, be sure to congure WDS settings on both APs participating in the WDS link.
•) You can have only one WDS link between any pair of APs. That is, a remote MAC address may appear only
once on the WDS page for a particular AP.
•) Both APs participating in a WDS link must be on the same Radio channel and using the same IEEE 802.11
mode. (See “Modifying Radio Settings” on page 42 for information on conguring the Radio mode and
channel.)
•) When 802.11h is operational, setting up two WDS links can be difcult.
To congure WDS on this AP, describe each AP intended to receive handoffs and send information to this AP. For each
destination AP, congure the elds listed in the table below.
Field Description
Spanning Tree
Mode
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) prevents switching loops. STP is recommended if you
congure WDS links.
Select Enabled to use STP
Select Disabled to turn off STP links (not recommended)
Radio For each WDS link on a two-radio AP, select Radio One or Radio Two. The rest of the
settings for the link apply to the radio selected in this eld. The read-only Local Address will
change depending on which Radio you select in this eld.
Local Address Indicates the MAC addresses for this AP.
For each WDS link on a two-radio AP, the Local Address reects the MAC address for the
internal interface on the selected radio (Radio One on wlan0 or Radio Two on wlan1).
Remote Address Specify the MAC address of the destination AP; that is, the AP on the other end of the WDS
link to which data will be sent or handed-off and from which data will be received.
Click the drop-down arrow to the right of the Remote Address eld to see a list of all the
available MAC Addresses and their associated SSIDs on the network. Select the appropriate
MAC address from the list.
Note: The SSID displayed in the drop-down list is simply to help you identify the correct
MAC Address for the destination AP. This SSID is a separate SSID to that which you set for
the WDS link. The two do not (and should not) be the same value or name.
Encryption You can use no encryption, WEP, or WPA (PSK) on the WDS link.
If you are unconcerned about security issues on the WDS link you may decide not to set
any type of encryption. Alternatively, if you have security concerns you can choose between
Static WEP and WPA (PSK). In WPA (PSK) mode, the AP uses WPA2-PSK with CCMP
(AES) encryption over the WDS link.
Table 30 - WDS Settings
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 61
Page 62

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
If you select None as your preferred WDS encryption option, you will not be asked to ll in any more elds on the
WDS page. All data transferred between the two APs on the WDS link will be unencrypted.
Note: To disable a WDS link, you must remove the value congured in the Remote Address eld.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
WEP on WDS Links
The following table describes the additional elds that appear when you select WEP as the encryption type.
Field Description
Encryption WEP
WEP Select this option if you want to set WEP encryption on the WDS link.
Key Length If WEP is enabled, specify the length of the WEP key:
•) 64 bits
•) 128 bits
Key Type If WEP is enabled, specify the WEP key type:
•) ASCII
•) Hex
Characters
Required
WEP Key Enter a string of characters. If you selected ASCII, enter any combination of 0 – 9, a – z, and
Indicates the number of characters required in the WEP key.
The number of characters required updates automatically based on how you set Key Length
and Key Type.
A – Z. If you selected HEX, enter hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0 – 9 and a – f or
A – F). These are the RC4 encryption keys shared with the stations using the AP.
Table 31 - WEP on WDS Links
WPA/PSK on WDS Links
The following table describes the additional elds that appear when you select WPA/PSK as the encryption type.
Note: In order to congure WPA-PSK on any WDS link, VAP0 of the selected radio must be
congured for WPA-PSK or WPA-Enterprise.
Field Description
Encryption WPA (PSK)
SSID Enter an appropriate name for the new WDS link you have created. This SSID should be
different from the other SSIDs used by this AP. However, it is important that the same SSID
is also entered at the other end of the WDS link. If this SSID is not the same for both APs on
the WDS link, they will not be able to communicate and exchange data.
The SSID can be any alphanumeric combination.
Key Enter a unique shared key for the WDS bridge. This unique shared key must also be
entered for the AP at the other end of the WDS link. If this key is not the same for both APs,
they will not be able to communicate and exchange data.
The WPA-PSK key is a string of at least 8 characters to a maximum of 63 characters.
Acceptable characters include upper and lower case alphabetic letters, the numeric digits,
and special symbols such as @ and #.
Table 32 - WPA/PSK on WDS Links
October 2017
Note: After you congure the WDS settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and
to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system
processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that
you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 62
Page 63
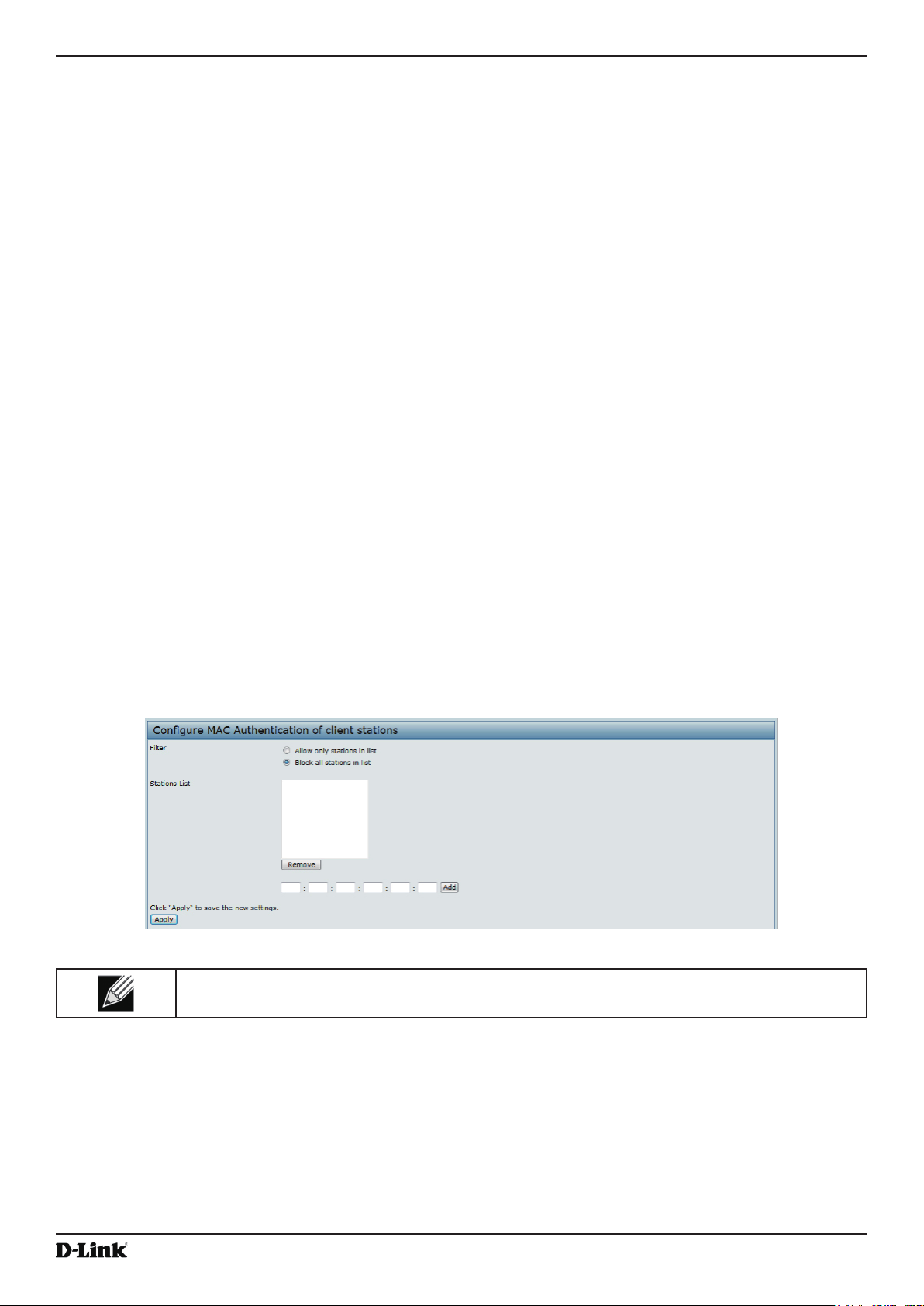
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Controlling Access by MAC Authentication
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a hardware address that uniquely identies each node of a network.
All IEEE 802 network devices share a common 48-bit MAC address format, usually displayed as a string of 12
hexadecimal digits separated by colons, for example 00:DC:BA:09:87:65. Each wireless network interface card (NIC)
used by a wireless client has a unique MAC address.
You can use the Administrator UI on the AP or use an external RADIUS server to control access to the network
through the AP based on the MAC address of the wireless client. This feature is called MAC Authentication or MAC
Filtering. To control access, you congure a global list of MAC addresses locally on the AP or on an external RADIUS
server. Then, you set a lter to specify whether the clients with those MAC addresses are allowed or denied access to
the network. When a wireless client attempts to associate with an AP, the AP looks up the MAC address of the client
in the local Stations List or on the RADIUS server. If it is found, the global allow or deny setting is applied. If it is not
found, the opposite is applied.
On the VAP page, the MAC Authentication Type setting controls whether the AP uses the station list congured
locally on the MAC Authentication page or the external RADIUS server. The Allow/Block lter setting on the MAC
Authentication page determines whether the clients in the station list (local or RADIUS) can access the network
through the AP. For more information about setting the MAC authentication type, see “Virtual Access Point Settings”
on page 50.
Conguring a MAC Filter and Station List on the AP
The MAC Authentication page allows you to control access to UAP based on MAC addresses. Based on how you
set the lter, you can allow only client stations with a listed MAC address or deny access to the stations listed.
When you enable MAC Authentication and specify a list of approved MAC addresses, only clients with a listed MAC
address can access the network. If you specify MAC addresses to deny, all clients can access the network except for
the clients on the deny list.
To enable ltering by MAC address, click the MAC Authentication tab.
Figure 31 - Congure MAC Authentication
Note: Global MAC Authentication settings apply to all VAPs on all supported radios.
The following table describes the elds and conguration options available on the MAC Authentication page.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 63
Page 64

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Filter To set the MAC Address Filter, select one of the following options:
•) Allow only stations in the list. Any station that is not in the Stations List is denied
access to the network through the AP.
•) Block all stations in list. Only the stations that appear in the list are denied access to
the network through the AP. All other stations are permitted access.
Note: The lter you select is applied to the clients in the station list, regardless of whether
that station list is local or on the RADIUS server.
Stations List This is the local list of clients that are either permitted or denied access to the network
through the AP. To add a MAC Address to the local Stations List, enter its 48-bit MAC
address into the lower text boxes, then click Add.
To remove a MAC Address from the Stations List, select its 48-bit MAC address, then click
Remove.
The stations in the list will either be allowed or denied access based on how you set the lter
in the previous eld.
Note: If the MAC authentication type for the VAP is set to Local, the AP uses the Stations
List to permit or deny the clients access to the network. If the MAC authentication type is set
to RADIUS, the AP ignores the MAC addresses congured in this list and uses the list that is
stored on the RADIUS server. The MAC authentication type is set on the VAP conguration
page.
Table 33 - MAC Authentication
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Note: After you congure local MAC Authentication settings, you must click Apply to apply the
changes and to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and
restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We
recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Conguring MAC Authentication on the RADIUS Server
If you use RADIUS MAC authentication for MAC-based access control, you must congure a station list on the
RADIUS server. The station list contains client MAC address entries, and the format for the list is described in the
following table.
RADIUS Server Attribute Description Value
User-Name (1) MAC address of the client station. Valid Ethernet MAC Address.
User-Password (2) A xed global password used to
lookup a client MAC entry.
Table 34 - RADIUS Server Attributes for MAC Authentication
NOPASSWORD
Conguring Load Balancing
You can set network utilization thresholds on the UAP to maintain the speed and performance of the wireless network
as clients associate and disassociate with the AP. The load balancing settings apply to all supported radios.
To congure load balancing and set limits and behaviour to be triggered by a specied utilization rate of the access
point, click the Load Balancing tab and update the elds shown in the following gure.
Figure 32 - Modify Load Balancing Settings
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 64
Page 65
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Load Balancing Enable or disable load balancing:
To enable load balancing on this AP, click Enable.
To disable load balancing on this AP, click Disable.
Utilization for No
New Associations
Provide the percentage of network bandwidth utilization allowed on the radio before the AP
stops accepting new client associations.
The default is 0, which means that all new associations will be allowed regardless of the
utilization rate.
Table 35 - Load Balancing
Note: After you congure the load balancing settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes
and to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system
processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that
you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Managed Access Point Overview
The UAP can operate in two modes: Standalone Mode or Managed Mode. In Standalone Mode, the UAP acts as
an individual AP in the network, and you manage it by using the Administrator Web User Interface (UI), CLI, or SNMP.
In Managed Mode, the UAP is part of the D-Link Unied Wired and Wireless System, and you manage it by using
the D-Link Unied Wireless Switch. If an AP is in Managed Mode, the Administrator Web UI, Telnet, SSH, and SNMP
services are disabled.
On the UAP, you can congure the IP addresses of up to four D-Link Unied Wireless Switches that can manage it. In
order to manage the AP, the switch and AP must discover each other. There are multiple ways for a switch to discover
an AP. Adding the IP address of the switch to the AP while it is in Standalone Mode is one way to enable switch-to-AP
discovery.
Transition Between Modes
Every 30 seconds, the D-Link Unied Wireless Switch sends a keepalive message to all of the access points it
manages. Each AP checks for the keepalive messages on the SSL TCP connection. As long as the AP maintains
communication with the switch through the keepalive messages, it remains in Managed Mode.
If the AP does not receive a message within 45 seconds of the last keepalive message, the AP assumes the switch
has failed and terminates its TCP connection to the switch, and the AP enters Standalone Mode.
Once the AP transitions to Standalone Mode, it continues to forward trafc without any loss. The AP uses the
conguration on the VAPs congured in VLAN Forwarding mode (the standard, non-tunneled mode).
While the AP is in Standalone Mode, you can manage it by using the Web interface or the CLI (through Telnet or
SSH).
For any clients that are connected to the AP through tunneled VAPs, the AP sends disassociate messages and
disables the tunneled VAPs.
As long as the Managed AP Administrative Mode is set to Enabled, the AP starts discovery procedures. If the AP
establishes a connection with a wireless switch, which may or may not be the same switch it was connected to
before, the switch sends the AP its conguration and the AP sends the wireless switch information about all currently
associated clients.
After the conguration from the switch is applied, the AP radio(s) restart. Client trafc is briey interrupted until the
radio(s) are up and the clients are re-associated.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 65
Page 66

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Conguring Managed Access Point Settings
To add the IP address of a D-Link Unied Wireless Switch to the AP, click the Managed Access Point tab under the
Manage heading and update the elds shown in the table below.
Figure 33 - Congure Managed AP Wireless Switch Parameters
Field Description
Managed AP
Administrative
Mode
Switch IP Address
(1-4)
Base IP Port The starting IP port number used by the wireless feature (in a range of 10 consecutive port
Pass Phrase Select the Edit option and enter a passphrase to allow the AP to authenticate itself with the
WDS Managed
Mode
WDS Managed
Ethernet Port
WDS Group
Password
Click Enabled to allow the AP and switch to discover each other. If the AP successfully
authenticates itself with a wireless switch, you will not be able to access the Administrator
UI.
Click Disabled to prevent the AP from contacting wireless switches.
Enter the IP address of up to four wireless switches that can manage the AP. You can
enter the IP address in dotted format or as an DNS name.
You can view a list of wireless switches on your network that were congured by using a
DHCP server.
The AP attempts to contact Switch IP Address 1 rst.
numbers). Only the rst number in the range is congurable. The default value is 57775
(through 57784).
Note: When the wireless Base IP Port number is changed on the switch, the wireless
feature is automatically disabled and re-enabled. The new value is not sent as part of the
global switch conguration in the cluster conguration distribution command; every switch in
the cluster must be congured independently with the new Wireless IP port number.
Note: When the wireless Base IP Port number is changed from its default value on the
switch, it must also be changed on the Access Points.
wireless switch. The passphrase must be between 8 and 63 characters.
To remove the password, select Edit, delete the existing password, and then click Apply.
You must congure the same passphrase on the switch.
Specify whether the AP will act as a Root AP or Satellite AP within the WDS group:
•) Root AP — Acts as a bridge or repeater on the wireless medium and communicates
with the switch via the wired link.
•) Satellite AP — Communicates with the switch via a WDS link to the Root AP. This
mode enables the Satellite AP to discover and establish WDS link with the Root AP.
Specify whether the Ethernet port is to be enabled or disabled when the AP becomes part
of a WDS group.
Password for WPA2 Personal authentication used to establish the WDS links. Only the
Satellite APs need this conguration. The Root APs get the password from the switch when
they become managed.
Table 36 - Managed Access Point
Note: After you congure the settings on the Managed Access Point page, you must click Apply
to apply the changes and to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop
and restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity.
We recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
If the UAP successfully authenticates with a D-Link Unied Wireless Switch, you will loose access to the AP through
the Administrator UI.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 66
Page 67

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Conguring 802.1X Authentication
On networks that use IEEE 802.1X, port-based network access control, a supplicant (client) cannot gain access to
the network until the 802.1X authenticator grants access. If your network uses 802.1X, you must congure 802.1X
authentication information that the AP can supply to the authenticator.
To congure the UAP 802.1X supplicant user name and password by using the Web interface, click the
Authentication tab and congure the elds shown in the table below.
Figure 34 - Modify 802.1X Supplicant Authentication Settings
Field Description
802.1X Supplicant Click Enabled to enable the Administrative status of the 802.1X Supplicant.
Click Disabled to disable the Administrative status of the 802.1X Supplicant.
EAP Method Select one of the following EAP methods to use for communication between the AP and the
authenticator:
•) MD5
•) PEAP
•) TLS
Username Enter the user name for the AP to use when responding to requests from an 802.1X
authenticator.
The user name can be 1 to 64 characters in length. ASCII printable characters are allowed,
which includes upper and lower case alphabetic letters, the numeric digits, and special
symbols such as @ and #.
Password Enter the password for the AP to use when responding to requests from an 802.1X
authenticator.
The password can be 1 to 64 characters in length. ASCII printable characters are allowed,
which includes upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special symbols such as @ and
#.
Certicate File
Status
Certicate File
Upload
Indicates whether a certicate le is present and when that certicate expires. It also
indicates when the HTTP SSL Certicate le will expire. The range is a valid date. If no
certicate le exists on the AP, the eld displays Not Present.
Upload a certicate le to the AP by using HTTP or TFTP:
•) HTTP — Browse to the location where the certicate le is stored and click Upload.
•) TFTP — Specify the IP address of the TFTP server where the certicate le is located
and provide the le name, including the le path, then click Upload.
Table 37 - IEEE 802.1X Supplicant Authentication
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 67
Page 68

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Note: After you congure the settings on the Authentication page, you must click Apply to apply
the changes and to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and
restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We
recommend that you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Section 4 - Managing the Access Point
Creating a Management Access Control List (ACL)
You can create an access control list (ACL) that lists up to ve IPv4 hosts and ve IPv6 hosts that are authorized to
access the AP management interface. If this feature is disabled, anyone can access the management interface from
any network client by supplying the correct AP username and password.
To create an access list, click the Management ACL tab.
Figure 35 - Congure Management Access Control Parameters
Field Description
Management ACL
Mode
IP Address (1–5) Enter up to ve IPv4 addresses that are allowed management access to the AP. Use
IPv6 Address (1–5) Enter up to ve IPv6 addresses that are allowed management access to the AP. Use the
Enable or disable the management ACL feature. At least one IPv4 address should be
congured before enabling Management ACL Mode. If enabled, only the IP addresses you
specify will have Web, Telnet, SSH, and SNMP access to the management interface.
dotted-decimal format (for example, 192.168.10.10).
standard IPv6 address format (for example 2001:0db8:1234::abcd).
Table 38 - Management ACL
Note: After you congure the settings, click Apply to apply the changes and to save the settings.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 68
Page 69
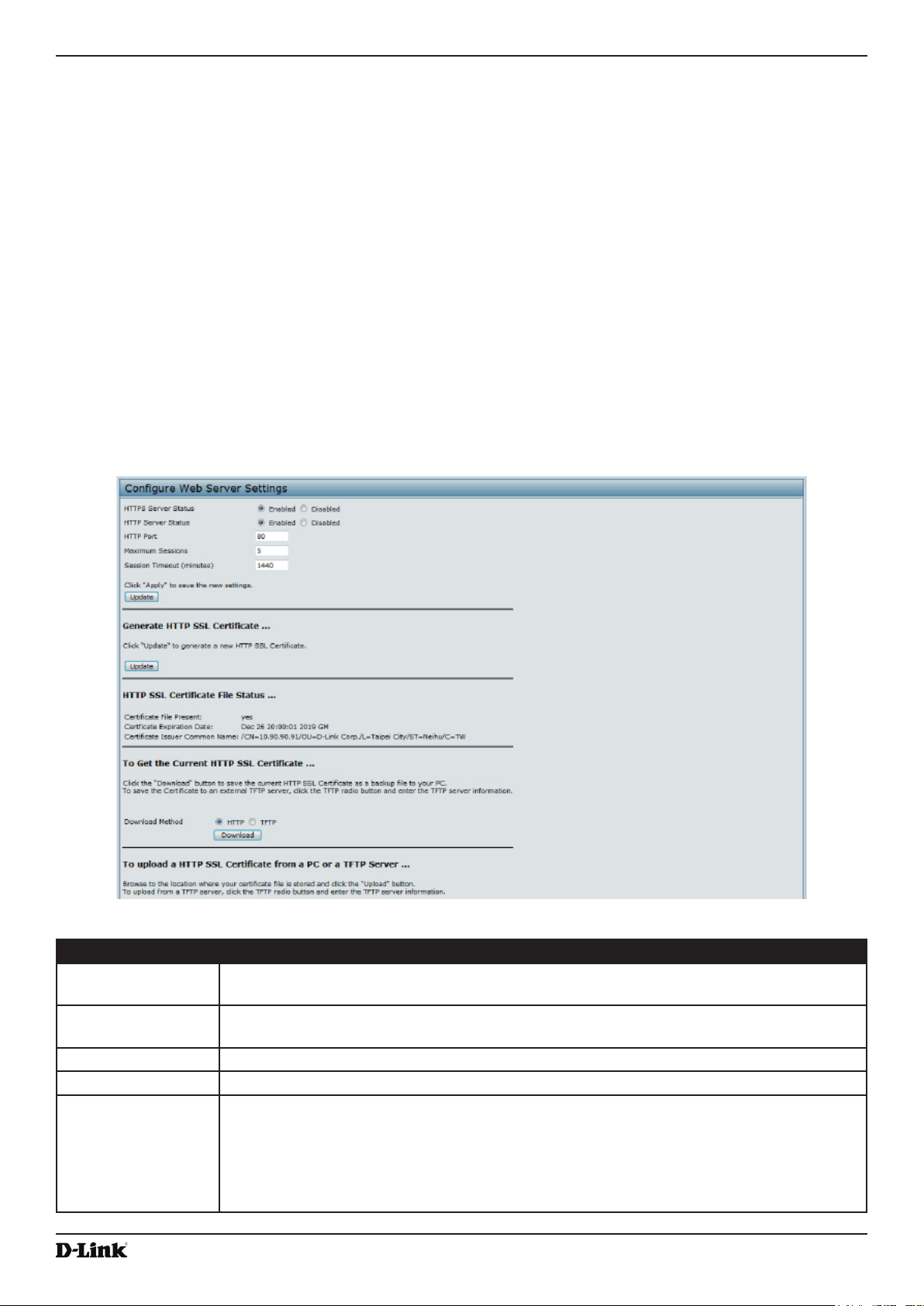
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
This section describes how to congure services on the UAP and contains the following subsections:
•) “Web Server Settings” on page 69
•) “Conguring SNMP on the Access Point” on page 70
•) “Setting the SSH Status” on page 72
•) “Setting the Telnet Status” on page 73
•) “Conguring DDP” on page 73
•) “Conguring Quality of Service” on page 73
•) “Conguring Email Alert” on page 76
•) “Enabling the Time Settings (NTP)” on page 78
Web Server Settings
The AP can be managed through HTTP or secure HTTP (HTTPS) sessions. By default both HTTP and HTTPS access
are enabled. Either access type can be disabled separately.
To congure Web server settings, click Web Server tab.
Figure 36 - Congure Web Server Settings
Field Description
HTTPS Server
Status
HTTP Server Status Enable or disable access through HTTP. This setting is independent of the HTTPS server
HTTP Port Specify the port number for HTTP trafc (default is 80).
HTTPS Port Specify the port number for HTTPS trafc (default is 443).
Maximum Sessions When a user logs on to the AP web interface, a session is created. This session is
October 2017
Enable or disable access through a Secure HTTP Server (HTTPS).
status setting.
maintained until the user logs off or the session inactivity timer expires.
Enter the number web sessions, including both HTTP and HTTPs, that can exist at the same
time. The range is 1–10 sessions. If the maximum number of sessions is reached, the next
user who attempts to log on to the AP web interface receives an error message about the
session limit.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 69
Page 70

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Session Timeout Enter the maximum amount of time, in minutes, an inactive user remains logged on to the
AP web interface. When the congured timeout is reached, the user is automatically logged
off the AP. The range is 1–1440 minutes (1440 minutes = 1 day).
Generate HTTP SSL Certicate
Generate HTTP SSL
Certicate
HTTP SSL Certicate File Status
HTTP SSL
Certicate File
Status
To Get the Current HTTP SSL Certicate
Download Method Save a copy of the current HTTP SSL certicate on a local system or TFTP server.
HTTP SSL
Certicate File
Server IP The IPv4 or IPv6 address of the TFTP server where the le will be downloaded. The default
To Upload an HTTP SSL Certicate from a PC or a TFTP Server
Upload Method and
HTTP SSL Certifcate
File
Server IP The IPv4 or IPv6 address of the TFTP server where the le is located. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Select this option to generate a new SSL certicate for the secure Web server. This should
be done once the access point has an IP address to ensure that the common name for the
certicate matches the IP address of the UAP. Generating a new SSL certicate will restart
the secure Web server. The secure connection will not work until the new certicate is
accepted on the browser. Click the Update button to generate the new SSL certicate.
Indicates whether a certicate le is present and species its expiration date and issuer
common name.
•) HTTP — Click Download and specify where to store the backup copy of the certicate
le.
•) TFTP — Provide a le name for the certicate le, including the le path, specify the
IP address of the TFTP server where the certicate le copy is to be stored, and then
click Download.
This eld is available when the selected download method is TFTP. Enter the lename of the
certicate. The lename is a 255-byte alphanumeric string. The default is Mini_httpd.pem.
is 0.0.0.0.
Upload a certicate le to the AP by using HTTP or TFTP:
•) HTTP — Browse to the location where the certicate le is stored and click Upload.
•) TFTP — Specify the IP address of the TFTP server where the certicate le is located
and provide the le name, including the le path, then click Upload.
Table 39 - Web Server Settings
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Note: Click Apply to apply the changes and to save the settings. If you disable the protocol you
are currently using to access the AP management interface, the current connection will end and
you will not be able to access the AP by using that protocol until it is enabled.
Conguring SNMP on the Access Point
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) denes a standard for recording, storing, and sharing information
about network devices. SNMP facilitates network management, troubleshooting, and maintenance. The AP supports
SNMP versions 1, 2, and 3. Unless specically noted, all conguration parameters on this page apply to SNMPv1 and
SNMPv2c only.
Key components of any SNMP-managed network are managed devices, SNMP agents, and a management system.
The agents store data about their devices in Management Information Bases (MIBs) and return this data to the SNMP
manager when requested. Managed devices can be network nodes such as APs, routers, switches, bridges, hubs,
servers, or printers.
The UAP can function as an SNMP managed device for seamless integration into network management systems such
as HP OpenView.
From the SNMP page under the Services heading, you can start or stop control of SNMP agents, congure community
passwords, access MIBs, and congure SNMP Trap destinations.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 70
Page 71
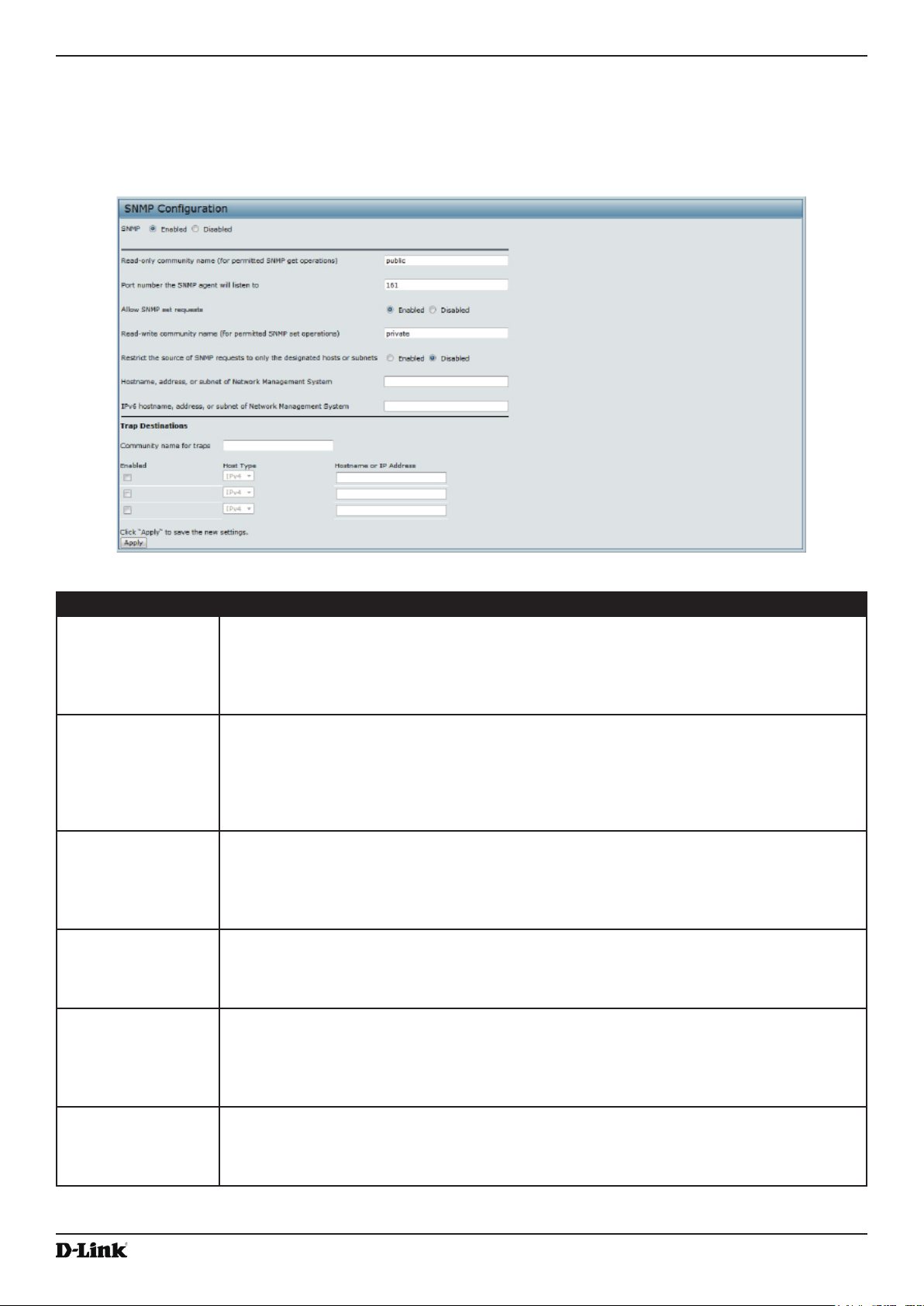
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
From the pages under the SNMPv3 heading, you can manage SNMPv3 users and their security levels and dene
access control to the SNMP MIBs. For information about how to congure SNMPv3 views, groups, users, and targets,
see “Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3” on page 80.
To congure SNMP, click the SNMP tab under the Services heading and update the elds described in the table
below.
Field Description
SNMP Enabled/
Disabled
You can specify the SNMP administrative mode on your network. By default SNMP is
enabled. To enable SNMP, click Enabled. To disable SNMP, click Disabled. After changing
the mode, you must click Apply to save your conguration changes.
Note: If SNMP is disabled, all remaining elds on the SNMP page are disabled. This is a
global SNMP parameter which applies to SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
Read-only
community name
(for permitted SNMP
get operations)
Enter a read-only community name. The valid range is 1-256 characters.
The community name, as dened in SNMPv2c, acts as a simple authentication mechanism
to restrict the machines on the network that can request data to the SNMP agent. The name
functions as a password, and the request is assumed to be authentic if the sender knows
the password.
The community name can be in any alphanumeric format.
Port number the
SNMP agent will
listen to
By default an SNMP agent only listens to requests from port 161. However, you can
congure this so the agent listens to requests on another port.
Enter the port number on which you want the SNMP agents to listen to requests. The valid
range is 1-65535.
Note: This is a global SNMP parameter that applies to SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
Allow SNMP set
requests
You can choose whether or not to allow SNMP set requests on the AP. Enabling SNMP
set requests means that machines on the network can execute conguration changes via
the SNMP agent on the AP to the D-Link System MIB. To enable SNMP set requests, click
Enabled. To disable SNMP set requests, click Disabled.
Read-write
community name
(for permitted SNMP
set operations)
If you have enabled SNMP set requests you can set a read-write community name. The
valid range is 1-256 characters.
Setting a community name is similar to setting a password. Only requests from the
machines that identify themselves with this community name will be accepted.
The community name can be in any alphanumeric format.
Restrict the source
of SNMP requests to
only the designated
You can restrict the source of permitted SNMP requests.
To restrict the source of permitted SNMP requests, click Enabled.
To permit any source submitting an SNMP request, click Disabled.
hosts or subnets
Figure 37 - SNMP Conguration
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 71
Page 72

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Hostname,
address or subnet
of Network
Management
System
IPv6 Hostname
or IPv6 subnet
of Network
Management
System
Community name
for traps
Host Type Specify whether the enabled host is an IPv4 host or an IPv6 host.
Hostname or IP
address
Specify the IPv4 DNS hostname or subnet of the machines that can execute get and set
requests to the managed devices. The valid range is 1-256 characters.
As with community names, this provides a level of security on SNMP settings. The SNMP
agent will only accept requests from the hostname or subnet specied here.
To specify a subnet, enter one or more subnetwork address ranges in the form
mask_length
Both formats address/mask and address/mask_length are supported. Individual hosts
can be provided for this, i.e. IP Address or Hostname. For example, if you enter a range of
192.168.1.0/24 this species a subnetwork with address 192.168.1.0 and a subnet mask of
255.255.255.0.
The address range is used to specify the subnet of the designated NMS. Only machines
with IP addresses in this range are permitted to execute get and set requests on the
managed device. Given the example above, the machines with addresses from 192.168.1.1
through 192.168.1.254 can execute SNMP commands on the device. (The address
identied by sufx .0 in a subnetwork range is always reserved for the subnet address, and
the address identied by .255 in the range is always reserved for the broadcast address).
As another example, if you enter a range of 10.10.1.128/25 machines with IP addresses
from 10.10.1.129 through 10.10.1.254 can execute SNMP requests on managed devices. In
this example, 10.10.1.128 is the network address and 10.10.1.255 is the broadcast address.
126 addresses would be designated.
Specify the IPv6 DNS hostname or subnet of the machines that can execute get and set
requests to the managed devices.
Enter the global community string associated with SNMP traps. The valid range is 1-256
characters.
Traps sent from the device will provide this string as a community name.
The community name can be in any alphanumeric format. Special characters are not
permitted.
Enter the DNS hostname of the computer to which you want to send SNMP traps. The valid
range is 1-256 characters.
An example of a DNS hostname is: snmptraps.foo.com. Since SNMP traps are sent
randomly from the SNMP agent, it makes sense to specify where exactly the traps should
be sent. You can add up to a maximum of three DNS hostnames. Ensure you select the
Enabled check box beside the appropriate hostname.
where address is an IP address and mask_length is the number of mask bits.
Table 40 - SNMP Settings
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
address/
Note: After you congure the SNMP settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and
to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system
processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that
you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Setting the SSH Status
Secure Shell (SSH) is a program that provides access to the DWL-x600AP CLI from a remote host. SSH is more
secure than Telnet for remote access because it provides strong authentication and secure communications over
insecure channels. From the SSH page, you can enable or disable SSH access to the system.
Figure 38 - Set SSH Status
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 72
Page 73

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
SSH Status Choose to either enable or disable SSH access to the AP CLI:
•) To permit remote access to the AP by using SSH, click Enabled.
•) To prevent remote access to the AP by using SSH, click Disabled.
Table 41 - SSH Settings
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Setting the Telnet Status
Telnet is a program that provides access to the DWL-x600AP CLI from a remote host. From the Telnet page, you can
enable or disable Telnet access to the system.
Figure 39 - Set Telnet Status
Field Description
Telnet Status Choose to either enable or disable Telnet access to the AP CLI:
•) To permit remote access to the AP by using Telnet, click Enabled.
•) To prevent remote access to the AP by using Telnet, click Disabled.
Table 42 - Telnet Settings
Conguring DDP
DDP (D-Link Discover Protocol) supports basic command (IP, factory reset, F/W upgrade, etc.) to setting UAP, and
user can use DNA (D-Link Network Assistance) to congure basic setting. From the DDP page, you can enable or
disable DDP daemon to the system.
Figure 40 - DDP Status Conguration
Field Description
DDP Status Choose to either enable or disable DDP access to the AP CLI:
•) To start DDP daemon, click Enabled.
•) To stop DDP daemon, click Disabled.
Table 43 - DDP Settings
Conguring Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) provides you with the ability to specify parameters on multiple queues for increased
throughput and better performance of differentiated wireless trafc like Voice-over-IP (VoIP), other types of audio,
video, and streaming media, as well as traditional IP data over the UAP.
Conguring QoS on the UAP consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different types of wireless trafc,
and effectively specifying minimum and maximum wait times (through Contention Windows) for transmission. The
settings described here apply to data transmission behavior on the AP only, not to that of the client stations.
AP Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) Parameters affect trafc owing from the AP to the client station.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 73
Page 74

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Station Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) Parameters affect trafc owing from the client station to the
A P.
The default values for the AP and station EDCA parameters are those suggested by the Wi-Fi Alliance in the WMM
specication. In normal use these values should not need to be changed. Changing these values will affect the QoS
provided.
Note: On the DWL-6600AP, DWL-8600AP, DWL-6610AP, DWL-8610AP, and DWL-8710AP
devices, the QoS settings apply to both radios, but the trafc for each radio is queued
independently.
To set up queues for QoS, click the QoS tab under the Services heading and congure settings as described in the
table below.
Figure 41 - Modify QoS Queue Parameters
Field Description
Radio Select the radio with the QoS settings to view or congure.
EDCA Template Possible options are: Default, Optimized for Voice, and Custom.
AP EDCA Parameters
Queue Queues are dened for different types of data transmitted from AP-to-station:
•) Data 0 (Voice) — High priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive data such as
VoIP and streaming media are automatically sent to this queue.
•) Data 1(Video) — High priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue.
•) Data 2 (Best Effort) — Medium priority queue, medium throughput and delay. Most
traditional IP data is sent to this queue.
•) Data 3 (Background) — Lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk data that
requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this queue (FTP
data, for example).
AIFS (Inter-Frame
Space)
The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing (AIFS) species a wait time for data frames. The wait
time is measured in slots. Valid values for AIFS are 1 through 255.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 74
Page 75

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
cwMin (Minimum
Contention Window)
cwMax (Maximum
Contention Window)
Max. Burst Length The Max. Burst Length is an AP EDCA parameter and only applies to trafc owing from
Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Settings
Wi-Fi MultiMedia
(WMM)
Station EDCA Parameters
Queue Queues are dened for different types of data transmitted from station-to-AP:
AIFS (Inter-Frame
Space)
This parameter is input to the algorithm that determines the initial random back off wait time
(window) for retry of a transmission.
The value specied for Minimum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a
range from which the initial random back off wait time is determined.
The rst random number generated will be a number between 0 and the number specied
here.
If the rst random back off wait time expires before the data frame is sent, a retry counter
is incremented and the random back off value (window) is doubled. Doubling will continue
until the size of the random back off value reaches the number dened in the Maximum
Contention Window.
Valid values for cwMin are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for cwMin
must be lower than the value for cwMax.
The value specied for the Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds)
for the doubling of the random back off value. This doubling continues until either the data
frame is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached.
Once the Maximum Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a
maximum number of retries allowed is reached.
Valid values for cwMax are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for cwMax
must be higher than the value for cwMin.
the AP to the client station.
This value species (in milliseconds) the maximum burst length allowed for packet bursts
on the wireless network. A packet burst is a collection of multiple frames transmitted without
header information. The decreased overhead results in higher throughput and better
performance.
Valid values for maximum burst length are 0.0 through 999.
Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM) is enabled by default. With WMM enabled, QoS prioritization and
coordination of wireless medium access is on. With WMM enabled, QoS settings on the
UAP control downstream trafc owing from the AP to client station (AP EDCA parameters)
and the upstream trafc owing from the station to the AP (station EDCA parameters).
Disabling WMM deactivates QoS control of station EDCA parameters on upstream trafc
owing from the station to the AP.
With WMM disabled, you can still set some parameters on the downstream trafc owing
from the AP to the client station (AP EDCA parameters).
To disable WMM extensions, click Disabled.
To enable WMM extensions, click Enabled.
•) Data 0 (Voice) — Highest priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive data such as
VoIP and streaming media are automatically sent to this queue.
•) Data 1(Video) — Highest priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue.
•) Data 2 (Best Effort) — Medium priority queue, medium throughput and delay. Most
traditional IP data is sent to this queue.
•) Data 3 (Background) — Lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk data that
requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this queue (FTP
data, for example).
The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing (AIFS) species a wait time for data frames. The wait
time is measured in slots. Valid values for AIFS are 1 through 255.
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 75
Page 76

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
cwMin (Minimum
Contention Window)
cwMax (Maximum
Contention Window)
TXOP Limit The TXOP Limit is a station EDCA parameter and only applies to trafc owing from the
Other QoS Settings
No
Acknowledgement
APSD Select On to enable Automatic Power Save Delivery (APSD), which is a power management
This parameter is used by the algorithm that determines the initial random back off wait
time (window) for retry of a data transmission during a period of contention for Unied
Access Point resources. The value specied here in the Minimum Contention Window is
the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back off wait time
will be determined. The rst random number generated will be a number between 0 and the
number specied here. If the rst random back off wait time expires before the data frame
is sent, a retry counter is incremented and the random back off value (window) is doubled.
Doubling will continue until the size of the random back off value reaches the number
dened in the Maximum Contention Window.
The value specied here in the Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in
milliseconds) for the doubling of the random back off value. This doubling continues until
either the data frame is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached.
Once the Maximum Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a
maximum number of retries allowed is reached.
client station to the AP. The Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) is an interval of time, in
milliseconds, when a WME client station has the right to initiate transmissions onto the
wireless medium (WM) towards the Unied Access Point. The TXOP Limit maximum value is
65535.
Select On to specify that the AP should not acknowledge frames with QosNoAck as the
service class value.
method. APSD is recommended if VoIP phones access the network through the AP.
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Note: After you congure the QoS settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and to save
the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system processes. If
this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that you change
AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
Table 44 - QoS Settings
Conguring Email Alert
The Email Alert feature allows the AP to automatically send email messages when an event at or above the congured
severity level occurs. Use the Email Alert Conguration page to congure mail server settings, to set the severity level
that triggers alerts, and to add up to three email addresses where urgent and non-urgent email alerts are sent.
Note: Email alert is operationally disabled when the AP transitions to managed mode.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 76
Page 77

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Figure 42 - Email Alerts Conguration
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Field Description
Email Alert Global Conguration
Admin Mode Globally enable or disable the Email Alert feature on the AP. By default, email alerts are
disabled.
From Address Specify the email address that appears in the From eld of alert messages sent from the AP,
for example dlinkAP23@foo.com. The address can be a maximum of 255 characters and
can contain only printable characters. By default, no address is congured.
Log Duration This duration, in minutes, determines how frequently the non-critical messages are sent to
the SMTP Server. The range is 30-1440 minutes. The default is 30 minutes.
Urgent Message
Severity
Congures the severity level for log messages that are considered to be urgent. Messages
in this category are sent immediately. The security level you select and all higher levels are
urgent:
•) Emergency indicates system is unusable. It is the highest level of severity.
•) Alert indicates action must be taken immediately.
•) Critical indicates critical conditions.
•) Error indicates error conditions.
•) Warning indicates warning conditions.
•) Notice indicates normal but signicant conditions.
•) Info indicates informational messages.
•) Debug indicates debug-level messages.
Non Urgent Severity Congures the severity level for log messages that are considered to be non-urgent.
Messages in this category are collected and sent in a digest form at the time interval
specied by the Log Duration eld. The security level you select and all levels up to, but not
including the lowest Urgent level are considered non-urgent. Messages below the security
level you specify are not sent via email.
See the Urgent Message eld description for information about the security levels.
Email Alert Mail Server Conguration
Mail Server Address Specify the IP address or hostname of the SMTP server on the network.
Mail Server Security Specify whether to use SMTP over SSL (TLSv1) or no security (Open) for authentication
with the mail server. The default is Open.
Mail Server Port Congures the TCP port number for SMTP. The range is a valid port number from 0 to
65535. The default is 25, which is the standard port for SMTP.
Username Specify the user name to use when authentication with the mail server is required. The user
name is a 64-byte character string with all printable characters. The default is admin.
Password Specify the password associated with the user name congured in the previous eld.
Email Alert Message Conguration
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 77
Page 78
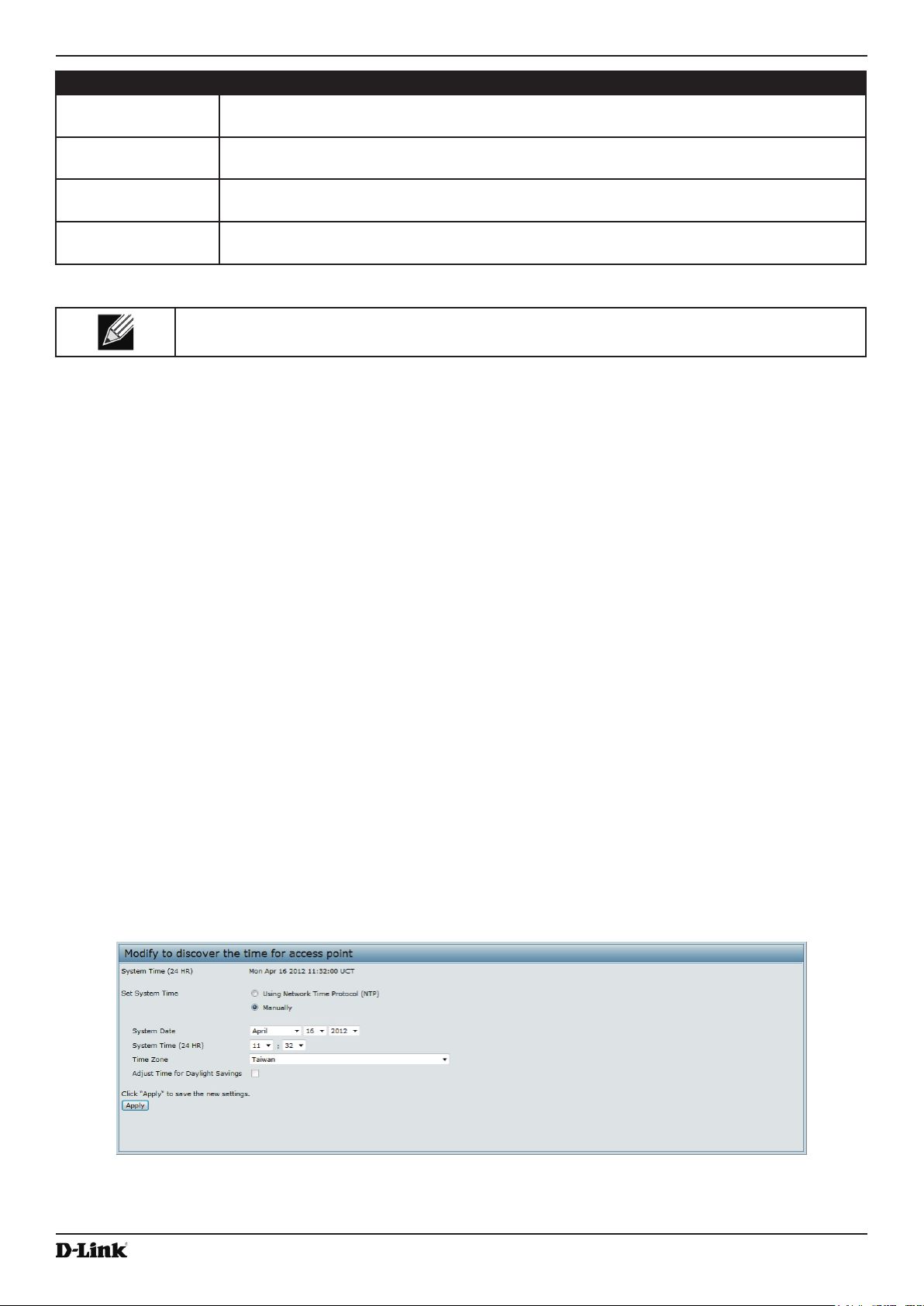
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Field Description
To Address 1 Congure the rst email address to which alert messages are sent. The address must be a
valid email address. By default, no address is congured.
To Address 2 Optionally, congure the second email address to which alert messages are sent. The
address must be a valid email address. By default, no address is congured.
To Address 3 Optionally, congure the third email address to which alert messages are sent. The address
must be a valid email address. By default, no address is congured.
Email Subject Specify the text to be displayed in the subject of the email alert message. The subject can
contain up to 255 alphanumeric characters. The default is Log message from AP.
Table 45 - Email Alert Conguration
Note: After you congure the Email Alert settings, click Apply to apply the changes and to save
the settings.
To validate the congured email server credentials, click Test Mail. You can send a test email once the email server
details are congured.
The following text shows an example of an email alert sent from the AP to the network administrator:
From: AP-192.168.2.10@mailserver.com
Sent: Wednesday, July 08, 2011 11:16 AM
To: administrator@mailserver.com
Subject: log message from AP
TIME Priority Process Id Message
Jul 8 03:48:25 info login[1457] root login on ‘ttyp0’
Jul 8 03:48:26 info mini_http-ssl[1175] Max concurrent connections of 20 reached
Enabling the Time Settings (NTP)
Use the Time Settings page to specify the Network Time Protocol (NTP) server to use to provide time and date
information to the AP or to congure the time and date information manually.
NTP is an Internet standard protocol that synchronizes computer clock times on your network. NTP servers transmit
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC, also known as Greenwich Mean Time) to their client systems. NTP sends periodic
time requests to servers, using the returned time stamp to adjust its clock. The timestamp is used to indicate the date
and time of each event in log messages.
See http://www.ntp.org for more information about NTP.
To set the system time either manually or by specifying the address of the NTP server for the AP to use, click the
Services > Time Settings (NTP) tab and update the elds as described in the table below.
October 2017
Figure 43 - Time Settings (NTP)
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 78
Page 79

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 5 - Conguring Access Point Services
Field Description
Set System Time NTP provides a way for the AP to obtain and maintain its time from a server on the network.
Using an NTP server gives your AP the ability to provide the correct time of day in log
messages and session information.
Choose to use a network time protocol (NTP) server to determine the system time, or set the
system time manually:
•) To permit the AP to poll an NTP server, click Using Network Time Protocol (NTP).
•) To prevent the AP from polling an NTP server, click Manually.
NTP Server (Use
NTP)
If NTP is enabled, specify the NTP server to use.
You can specify the NTP server by hostname or IP address, although using the IP address
is not recommended as these can change more readily.
If you specify a hostname, note the following requirements:
•) The length must be between 1 – 63 characters.
•) Upper and lower case characters, numbers, and hyphens are accepted.
•) The rst character must be a letter (a–z or A–Z), and the last character cannot be a
hyphen.
System Date
Specify the current month, day, and year.
(Manual
conguration)
System Time
(Manual
Specify the current time in hours and minutes. The system uses a 24-hour clock, so 6:00 PM
is congured as 18:00.
conguration)
Time Zone Select your local time zone from the menu. The default is USA (Pacic).
Adjust Time for
Daylight Savings
Select to have the system adjust the reported time for Daylight Savings Time (DST). When
this eld is selected, elds to congure Daylight Savings Time settings appear.
DST Start (24 HR) Congure the date and time to begin Daylight Savings Time for the System Time.
DST End (24 HR) Congure the date and time to end Daylight Savings Time for the System Time.
DST Offset
Select the number of minutes to offset DST. The default is 60 minutes.
(minutes)
Table 46 - NTP Settings
Note: After you congure the Time settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes and
to save the settings. Changing some settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system
processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that
you change AP settings when WLAN trafc is low.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 79
Page 80
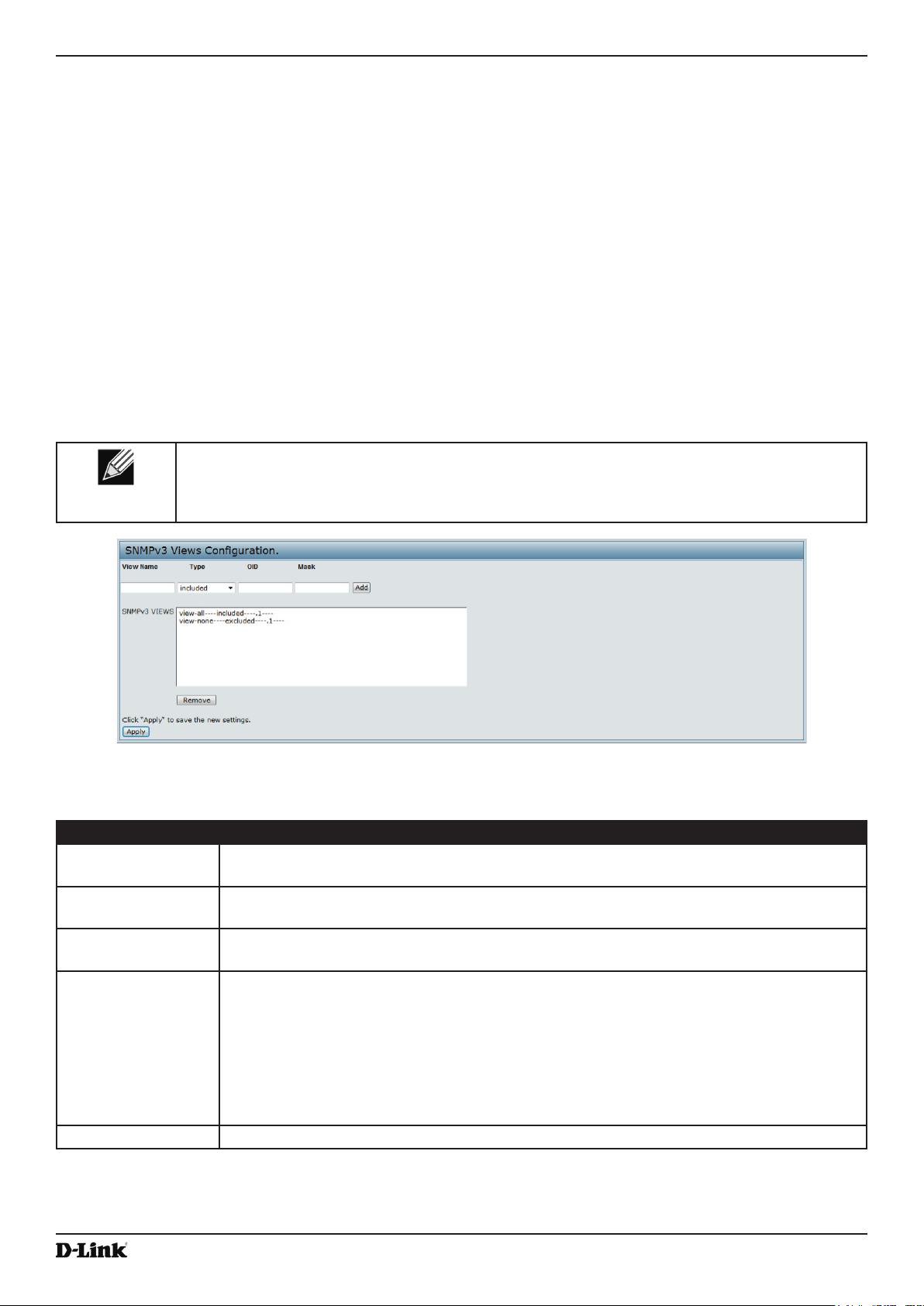
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3
Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3
This section describes how to congure the SNMPv3 settings on the UAP and contains the following subsections:
•) “Conguring SNMPv3 Views” on page 80
•) “Conguring SNMPv3 Groups” on page 81
•) “Conguring SNMPv3 Users” on page 82
•) “Conguring SNMPv3 Targets” on page 83
Conguring SNMPv3 Views
A MIB view is a combination of a set of view subtrees or a family of view subtrees where each view subtree is a
subtree within the managed object naming tree. You can create MIB views to control the OID range that SNMPv3
users can access.
A MIB view called “all” is created by default in the system. This view contains all management objects supported by
the system.
Note: If you create an excluded view subtree, create a corresponding included entry with the
same view name to allow subtrees outside of the excluded subtree to be included. For example, to
create a view that excludes the subtree 1.3.6.1.4, create an excluded entry with the OID 1.3.6.1.4.
Then, create an included entry with OID .1 with the same view name.
Figure 44 - SNMPv3 Views Conguration
The following table describes the elds you can congure on the SNMPv3 Views page.
Field Description
View Name Enter a name to identify the MIB view.
View names can contain up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
Type Species whether to include or exclude the view subtree or family of subtrees from the MIB
view.
OID Enter an OID string for the subtree to include or exclude from the view.
For example, the system subtree is specied by the OID string .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.
Mask The OID mask is 47 characters in length. The format of the OID mask is xx.xx.xx (.)... or
xx:xx:xx.... (:) and is 16 octets in length. Each octet is 2 hexadecimal characters separated
by either . (period) or : (colon). Only hex characters are accepted in this eld. For example,
OID mask FA.80 is 11111010.10000000.
A family mask is used to dene a family of view subtrees. The family mask indicates which
sub-identiers of the associated family OID string are signicant to the family’s denition.
A family of view subtrees allows control access to one row in a table, in a more efcient
manner.
SNMPv3 Views This eld shows the MIB views on the UAP. To remove a view, select it and click Remove.
Table 47 - SNMPv3 Views
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 80
Page 81

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Note: After you congure the SNMPv3 Views settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes
and to save the settings.
Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3
Conguring SNMPv3 Groups
SNMPv3 groups allow you to combine users into groups of different authorization and access privileges.
By default, the UAP has two groups:
•) RO — A read-only group using authentication and data encryption. Users in this group use an MD5 key/
password for authentication and a DES key/password for encryption. Both the MD5 and DES key/passwords
must be dened. By default, users of this group will have read only access to the default all MIB view, which can
be modied by the user.
•) RW — A read/write group using authentication and data encryption. Users in this group use an MD5 key/
password for authentication and a DES key/password for encryption. Both the MD5 and DES key/passwords
must be dened. By default, users of this group will have read and write access to the default all MIB view,
which can be modied by the user.
RW and RO groups are dened by default.
Note: The UAP supports maximum of eight groups.
To dene additional groups, navigate to the SNMPv3 Groups page and congure the settings that the table below
describes.
Figure 45 - SNMPv3 Groups Conguration
Field Description
Name Specify a name to use to identify the group. The default group names are RW and RO.
Group names can contain up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
Security Level Select one of the following security levels for the group:
•) noAuthentication-noPrivacy — No authentication and no data encryption (no
security).
•) Authentication-noPrivacy — Authentication, but no data encryption. With this security
level, users send SNMP messages that use an MD5 key/password for authentication,
but not a DES key/password for encryption.
•) Authentication-Privacy — Authentication and data encryption. With this security level,
users send an MD5 key/password for authentication and a DES key/password for
encryption.
For groups that require authentication, encryption, or both, you must dene the MD5 and
DES key/passwords on the SNMPv3 Users page.
Write Views Select the write access to management objects (MIBs) for the group:
•) write-all — The group can create, alter, and delete MIBs.
•) write-none — The group is not allowed to create, alter, or delete MIBS.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 81
Page 82

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Read Views Select the read access to management objects (MIBs) for the group:
•) view-all — The group is allowed to view and read all MIBs.
•) view-none — The group cannot view or read MIBs.
SNMPv3 Groups This eld shows the default groups and the groups that you have dened on the AP. To
remove a group, select the group, and click Remove.
Table 48 - SNMPv3 Groups
Note: After you congure the SNMPv3 Groups settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes
and to save the settings.
Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3
Conguring SNMPv3 Users
From the SNMPv3 Users page, you can dene multiple users, associate the desired security level to each user, and
congure security keys.
For authentication, only MD5 type is supported, and for encryption only DES type is supported. There are no default
SNMPv3 users on the UAP.
Figure 46 - SNMPv3 User Conguration
The following table describes the elds to congure SNMPv3 users.
Field Description
Name Enter the user name to identify the SNMPv3 user.
User names can contain up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
Group Map the user to a group. The default groups are RWAuth, RWPriv, and RO. You can dene
additional groups on the SNMPv3 Groups page.
Authentication Type Select the type of authentication to use on SNMP requests from the user:
•) MD5 — Require MD5 authentication on SNMPv3 requests from the user.
•) None — SNMPv3 requests from this user require no authentication.
Authentication Key If you specify MD5 as the authentication type, enter a password to enable the SNMP agent
to authenticate requests sent by the user.
The passphrase must be between 8 and 32 characters in length.
Encryption Type Select the type of privacy to use on SNMP requests from the user:
•) DES — Use DES encryption on SNMPv3 requests from the user.
•) None — SNMPv3 requests from this user require no privacy.
Encryption Key If you specify DES as the privacy type, enter a key to use to encrypt the SNMP requests.
The passphrase must be between 8 and 32 characters in length.
SNMPv3 Users This eld shows the users that you have dened on the AP. To remove a user, select the
user and click Remove.
Table 49 - SNMPv3 Users
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 82
Page 83
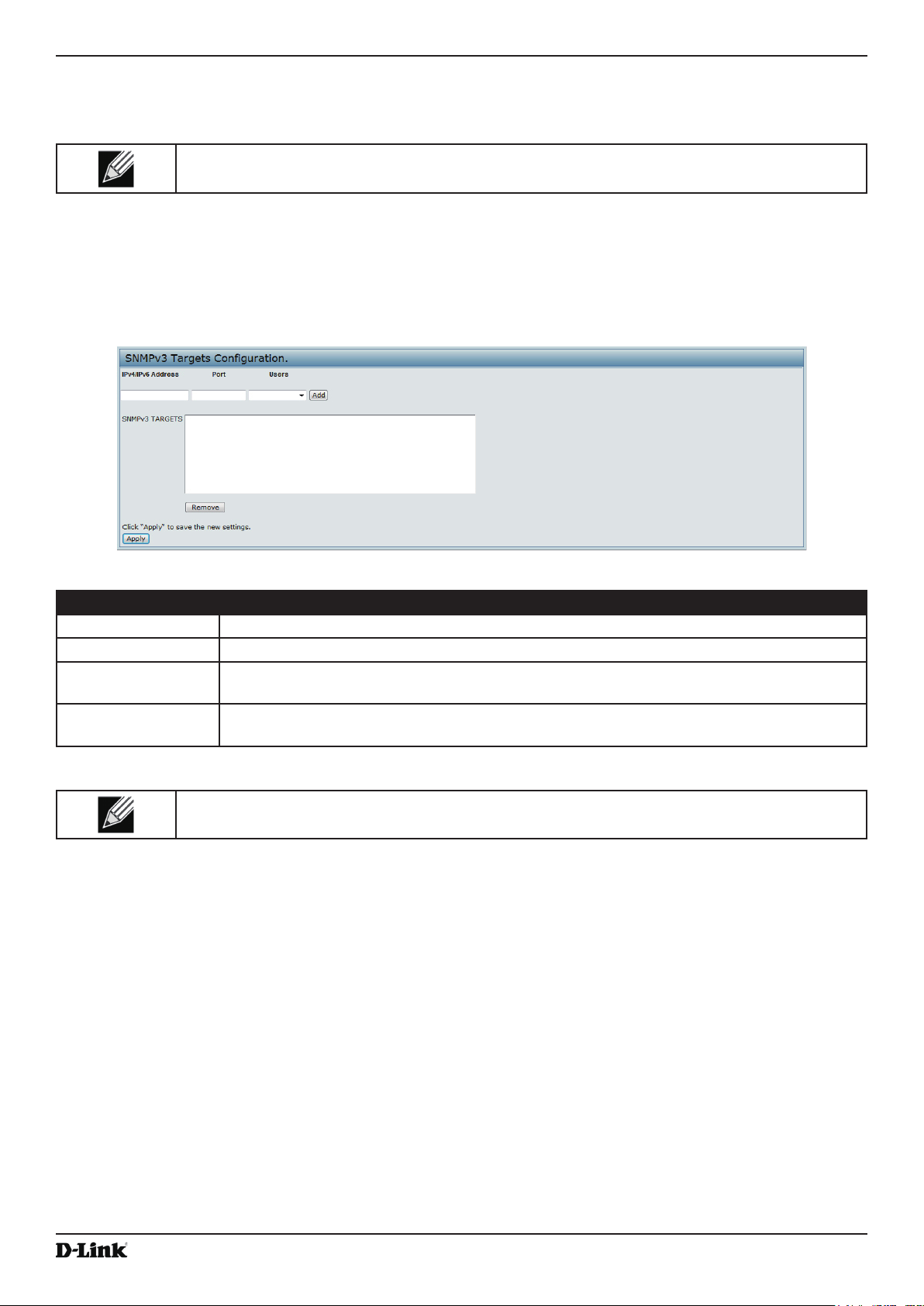
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Use the buttons on the page to perform the following tasks:
•) Add: Add the new user to the SNMPv3 users table.
•) Remove: Remove the selected user from the SNMPv3 users table.
•) Update: Apply and save the changed SNMPv3 user settings.
Note: After you congure the SNMPv3 Users settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes
and to save the settings.
Section 6 - Conguring SNMPv3
Conguring SNMPv3 Targets
SNMPv3 Targets send “inform” messages to the SNMP manager. Each target is identied by a target name and
associated with target IP address, UDP port, and SNMP user name.
Figure 47 - SNMPv3 Targets Conguration
Field Description
IPv4/IPv6 Address Enter the IP address of the remote SNMP manager to receive the target.
Port Enter the UDP port to use for sending SNMP targets.
Users Select the name of the SNMP user to associate with the target. To congure SNMP users,
see “Conguring SNMPv3 Users” on page 82.
SNMPv3 Targets This eld shows the SNMPv3 Targets on the UAP. To remove a target, select it, and click
Remove.
Table 50 - SNMPv3 Targets
Note: After you congure the SNMPv3 Target settings, you must click Apply to apply the changes
and to save the settings.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 83
Page 84

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
This section describes how to maintain the UAP.
From the UAP Administrator UI, you can perform the following maintenance tasks:
•) “Saving the Current Conguration to a Backup File” on page 84
•) “Restoring the Conguration from a Previously Saved File” on page 85
•) “Rebooting the Access Point” on page 86
•) “Performing AP Maintenance” on page 86
•) “Resetting the Factory Default Conguration” on page 86
•) “Upgrading the Firmware” on page 86
•) “Packet Capture Conguration and Settings” on page 88
•) “Support Information Conguration and Settings” on page 92
Saving the Current Conguration to a Backup File
The AP conguration le is in XML format and contains all of the information about the AP settings. You can download
the conguration le to a management station to manually edit the content or to save as a back-up copy.
You can use HTTP or TFTP to transfer les to and from the UAP. After you download a conguration le to the
management station, you can manually edit the le, which is in XML format. Then, you can upload the edited
conguration le to apply those conguration settings to the AP.
Use the following steps to save a copy of the current settings on an AP to a backup conguration le by using TFTP:
1.) Select TFTP for Download Method.
Figure 48 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Save (TFTP)
2.) Enter a name (1 to 255 characters) for the backup le in the Conguration File eld, including the .xml le
name extension and the path to the directory where you want to save the le.
3.) Enter the Server IP address of the TFTP server.
4.) Click Download to save a copy of the le to the TFTP server.
Use the following steps to save a copy of the current settings on an AP to a backup conguration le by using HTTP:
1.) Select HTTP for Download Method.
2.) Click the Download button.
October 2017
Figure 49 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Save (HTTP)
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 84
Page 85

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
A dialog box displays verifying the download.
Figure 50 - Conrmation Prompt
3.) To proceed with the download, select OK.
A dialog box opens allowing you to view or save the le.
4.) Select the Save File option and select OK.
5.) Use the le browser to navigate to the directory where you want to save the le, and click OK to save the le.
You can keep the default le name (cong.xml) or rename the backup le, but be sure to save the le with an
.xml extension.
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Restoring the Conguration from a Previously Saved File
You can use HTTP or TFTP to transfer les to and from the UAP. After you download a conguration le to the
management station, you can manually edit the le, which is in XML format. Then, you can upload the edited
conguration le to apply those conguration settings to the AP.
Use the following procedures to restore the conguration on an AP to previously saved settings by using TFTP:
1.) Select TFTP for Upload Method.
Figure 51 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Restore (TFTP)
2.) Enter a name (1 to 255 characters) for the backup le in the Filename eld, including the .xml le name
extension and the path to the directory that contains the conguration le to upload.
3.) Enter the IP address of the TFTP server in the Server IP eld.
4.) Click the Restore button.
The AP reboots. A reboot conrmation dialog and follow-on rebooting status message displays. Please wait for
the reboot process to complete, which might take several minutes.
The Administration Web UI is not accessible until the AP has rebooted.
Use the following steps to save a copy of the current settings on an AP to a backup conguration le by using HTTP:
1.) Select HTTP for Upload Method.
October 2017
Figure 52 - Manage this Access Point’s Conguration - Restore (HTTP)
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 85
Page 86

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
2.) Use the Browse button to select the le to restore.
3.) Click the Restore button.
A File Upload or Choose File dialog box displays.
4.) Navigate to the directory that contains the le, then select the le to upload and click Open.
(Only those les created with the Backup function and saved as .xml backup conguration les are valid to use
with Restore; for example,
5.) Click the Restore button.
A dialog box opens verifying the restore.
6.) Click OK to proceed.
The AP reboots. A reboot conrmation dialog and follow-on rebooting status message displays. Please wait for
the reboot process to complete, which might take several minutes.
The Administration Web UI is not accessible until the AP has rebooted.
ap_cong.xml.)
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Rebooting the Access Point
On the Maintenance > Conguration page, you can reboot the UAP for maintenance purposes and for
troubleshooting measures.
Figure 53 - Rebooting the Access Point
Performing AP Maintenance
From the Maintenance page, you can reset the AP to its factory default settings or reboot the AP.
Figure 54 - Performing AP Maintenance
Resetting the Factory Default Conguration
If you are experiencing problems with the UAP and have tried all other troubleshooting measures, click Reset. This
restores factory defaults and clears all settings, including settings such as a new password or wireless settings. You
can also use the reset button on the back panel to reset the system to the default conguration.
Rebooting the Access Point
For maintenance purposes or as a troubleshooting measure, you can reboot the UAP. To reboot the AP, click the
Reboot button on the Conguration page.
Upgrading the Firmware
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 86
Page 87

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
As new versions of the UAP rmware become available, you can upgrade the rmware on your devices to take
advantage of new features and enhancements. The AP uses a TFTP client for rmware upgrades. You can also use
HTTP to perform rmware upgrades.
After you upload new rmware and the system reboots, the newly added rmware becomes the primary image. If the
upgrade fails, the original rmware remains as the primary image.
Note: When you upgrade the rmware, the access point retains the existing conguration
information.
Use the following steps to upgrade the rmware on an access point by using TFTP:
1.) Select TFTP for Upload Method.
Figure 55 - Manage Firmware (TFTP)
2.) Enter a name (1 to 255 characters) for the image le in the Image Filename eld, including the path to the
directory that contains the image to upload.
For example, to upload the ap_upgrade.tar image located in the /share/builds/ap directory, enter /
share/builds/ap/ap_upgrade.tar
in the Image Filename eld.
The rmware upgrade le supplied must be a tar le. Do not attempt to use bin les or les of other formats for
the upgrade; these types of les will not work.
3.) Enter the Server IP address of the TFTP server.
4.) Click Upgrade.
Upon clicking Upgrade for the rmware upgrade, a popup conrmation window is displayed that describes the
upgrade process.
5.) Click OK to conrm the upgrade and start the process.
Note: The rmware upgrade process begins once you click Upgrade and then OK in the pop-up
conrmation window.
The upgrade process may take several minutes during which time the access point will be unavailable. Do not
power down the access point while the upgrade is in process. When the upgrade is complete, the access point
restarts. The AP resumes normal operation with the same conguration settings it had before the upgrade.
6.) To verify that the rmware upgrade completed successfully, check the rmware version shown on the Upgrade
page (or the Basic Settings page). If the upgrade was successful, the updated version name or number is
indicated.
Use the following steps to upgrade the rmware on an access point by using HTTP:
1.) Select HTTP for Upload Method.
Figure 56 - Manage Firmware (HTTP)
2.) If you know the path to the new rmware image le, enter it in the Image Filename eld. Otherwise, click the
Browse button and locate the rmware image le.
The rmware upgrade le supplied must be a tar le. Do not attempt to use bin les or les of other formats for
the upgrade; these types of les will not work.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 87
Page 88

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
3.) Click Upgrade to apply the new rmware image.
Upon clicking Upgrade for the rmware upgrade, a popup conrmation window is displayed that describes the
upgrade process.
4.) Click OK to conrm the upgrade and start the process.
Note: The rmware upgrade process begins once you click Upgrade and then OK in the popup
conrmation window.
The upgrade process may take several minutes during which time the access point will be unavailable. Do not
power down the access point while the upgrade is in process. When the upgrade is complete, the access point
restarts. The AP resumes normal operation with the same conguration settings it had before the upgrade.
5.) To verify that the rmware upgrade completed successfully, check the rmware version shown on the Upgrade
page (or the Basic Settings page). If the upgrade was successful, the updated version name or number is
indicated.
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Packet Capture Conguration and Settings
Wireless packet capture operates in two modes:
•) Capture le mode.
•) Remote capture mode.
For capture le mode, captured packets are stored in a le on the Access Point. The AP can transfer the le to a TFTP
server. The le is formatted in pcap format and can be examined using tools such as Wireshark and OmniPeek.
®
For remote capture mode, the captured packets are redirected in real time to an external PC running the Wireshark
tool.
The AP can capture the following types of packets:
•) 802.11 packets received and transmitted on radio interfaces. Packets captured on radio interfaces include the
802.11 header.
•) 802.3 packets received and transmitted on the Ethernet interface.
•) 802.3 packets received and transmitted on the internal logical interfaces such as VAPs and WDS interfaces.
From the Packet Capture Conguration and Settings page, you can:
•) View the current packet capture status.
•) Congure packet capture parameters.
•) Congure packet le capture.
•) Congure a remote capture port.
•) Download a packet capture le.
October 2017
Figure 57 - Packet Capture Conguration & Settings
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 88
Page 89

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Packet Capture Status
Packet Capture Status allows you to view the status of packet capture on the AP.
Figure 58 - Packet Capture Status
The following table describes information the packet capture status elds display.
Field Description
Current Capture
Status
Packet Capture
Time
Packet Capture File
Size
Shows whether packet capture is running or stopped.
Shows elapsed capture time.
Shows the current capture le size.
Table 51 - Packet Capture Status
Packet Capture Parameter Conguration
Packet Capture Conguration allows you to congure parameters that affect how packet capture functions on the radio
interfaces.
Figure 59 - Packet Capture Conguration
The following table describes the elds to congure the packet capture.
Field Description
Capture Beacons Enable to capture the 802.11 beacons detected or transmitted by the radio.
Promiscuous
Capture
Client Filter Enable Enable to use the WLAN client lter to capture only frames that are transmitted to, or
Client Filter MAC
Address
Enable to place the radio in promiscuous mode when the capture is active.
In promiscuous mode the radio receives all trafc on the channel, including trafc that is not
destined to this AP. While the radio is operating in promiscuous mode, it continues serving
associated clients. Packets not destined to the AP are not forwarded.
As soon as the capture is completed, the radio reverts to non-promiscuous mode operation.
received from a WLAN client with a specied MAC address.
Specify a MAC address for WLAN client ltering.
Note: The MAC lter is active only when capture is performed on an 802.11 interface.
Table 52 - Packet Capture Conguration
October 2017
Note: Changes to packet capture conguration parameters take affect after packet capture is
restarted. Modifying the parameters while the packet capture is running doesn’t affect the current
packet capture session. In order to begin using new parameter values, an existing packet capture
session must be stopped and re-started.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 89
Page 90

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Packet File Capture
In Packet File Capture mode the AP stores captured packets in the RAM le system.
Upon activation, the packet capture proceeds until one of the following occurs:
•) The capture time reaches congured duration.
•) The capture le reaches its maximum size.
•) The administrator stops the capture.
During the capture, you can monitor the capture status, elapsed capture time, and the current capture le size. This
information can be updated, while the capture is in progress, by clicking Refresh.
Figure 60 - Packet File Capture
The following table describes the elds to congure the packet capture status.
Field Description
Capture Interface Select an AP Capture Interface name from the drop-down menu. AP capture interface
names are eligible for packet capture are:
•) brtrunk - Linux bridge interface in the AP
•) eth0 - 802.3 trafc on the Ethernet port.
•) wlan0 - VAP0 trafc on radio 1.
•) wlan1 - VAP0 trafc on radio 2.
•) radio1 - 802.11 trafc on radio 1.
•) radio2 - 802.11 trafc on radio 2.
•) wlan0vap1 to wlan0vap15. Trafc on the specied VAP on Radio 1.
•) wlan1vap1 to wlan1vap 15. Trafc on the specied VAP on Radio 2.
•) wlan0wds0 to wlan0wds3. Trafc on the specied WDS interface.
Capture Duration Specify the time duration in seconds for the capture (range 10 to 3600).
Max Capture File
Size
Specify the maximum allowed size for the capture le in KB (range 64 to 4096).
Table 53 - Packet File Capture
Remote Packet Capture
Remote Packet Capture allows you to specify a remote port as the destination for packet captures. This feature works
in conjunction with the Wireshark network analyzer tool for Windows. A packet capture server runs on the AP and
sends the captured packets via a TCP connection to the Wireshark tool.
A Windows PC running the Wireshark tool allows you to display, log, and analyze captured trafc.
When the remote capture mode is in use, the AP doesn’t store any captured data locally in its le system.
Your can trace up to ve interfaces on the AP at the same time. However, you must start a separate Wireshark session
for each interface. You can congure the IP port number used for connecting Wireshark to the AP. The default port
number is 2002. The system uses 5 consecutive port numbers starting with the congured port for the packet capture
sessions.
If a rewall is installed between the Wireshark PC and the AP, these ports must be allowed to pass through the
rewall. The rewall must also be congured to allow the Wireshark PC to initiate TCP connection to the AP.
To congure Wireshark to use the AP as the source for captured packets, you must specify the remote interface in the
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 90
Page 91

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
“Capture Options” menu. For example to capture packets on an AP with IP address 192.168.1.10 on radio 1 using the
default IP port, specify the following interface:
rpcap://192.168.1.10/radio1
To capture packets on the Ethernet interface of the AP and VAP0 on radio 1 using IP port 58000, start two Wireshark
sessions and specify the following interfaces:
rpcap://192.168.1.10:58000/eth0
rpcap://192.168.1.10:58000/wlan0
When you are capturing trafc on the radio interface, you can disable beacon capture, but other 802.11 control frames
are still sent to Wireshark. You can set up a display lter to show only:
•) Data frames in the trace
•) Trafc on specic BSSIDs
•) Trafc between two clients
Some examples of useful display lters are:
•) Exclude beacons and ACK/RTS/CTS frames:
!(wlan.fc.type_subtype == 8 || wlan.fc.type == 1)
•) Data frames only:
wlan.fc.type == 2
•) Trafc on a specic BSSID:
wlan.bssid == 00:02:bc:00:17:d0
•) All trafc to and from a specic client:
wlan.addr == 00:00:e8:4e:5f:8e
In remote capture mode, trafc is sent to the PC running Wireshark via one of the network interfaces. Depending on
where the Wireshark tool is located the trafc can be sent on an Ethernet interface or one of the radios. In order to
avoid a trafc ood caused by tracing the trace packets, the AP automatically installs a capture lter to lter out all
packets destined to the Wireshark application. For example if the Wireshark IP port is congured to be 58000 then the
following capture lter is automatically installed on the AP:
not portrange 58000-58004.
Enabling the packet capture feature impacts performance of the AP and can create a security issue (unauthorized
clients may be able to connect to the AP and trace user data). The AP performance is negatively impacted even if
there is no active Wireshark session with the AP. The performance is negatively impacted to a greater extent when
packet capture is in progress.
Due to performance and security issues, the packet capture mode is not saved in NVRAM on the AP; if the AP resets,
the capture mode is disabled and the you must re-enable it in order to resume capturing trafc. Packet capture
parameters (other than mode) are saved in NVRAM.
In order to minimize performance impact on the AP while trafc capture is in progress, you should install capture lters
to limit which trafc is sent to the Wireshark tool. When capturing 802.11 trafc, large portion of the captured frames
tend to be beacons (typically sent every 100ms by all Access Points). Although Wireshark supports a display lter for
beacon frames, it does not support a capture lter to prevent the AP from forwarding captured beacon packets to the
Wireshark tool. In order to reduce performance impact of capturing the 802.11 beacons, you can disable the capture
beacons mode.
The remote packet capture facility is a standard feature of the Wireshark tool for Windows.
Note: Remote packet capture is not standard on the Linux version of Wireshark; the Linux version
doesn’t work with the AP.
Wireshark is an open source tool and is available for free; it can be downloaded from http://www.wireshark.org.
Figure 61 - Remote Packet Capture
The following table describes the elds to congure the packet capture status.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 91
Page 92

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Remote Capture
Port
Specify the remote port to use as the destination for packet captures. (range 1 to 65530).
Note: For DWL-XX10AP models, the port range is from 1025 to 65530.
Table 54 - Remote Packet Capture
Section 7 - Maintaining the Access Point
Packet Capture File Download
Packet Capture File Download allows you to download the capture le by TFTP to a congured TFTP server or by
HTTP(S) to a PC. The captured packets are stored in le /tmp/apcapture.pcap on the AP. A capture is automatically
stopped when the capture le download command is triggered.
Because the capture le is located in the RAM le system, it disappears if the AP is reset.
Figure 62 - Packet Capture File Download
The following table describes the elds to congure the packet capture status.
Field Description
Use TFTP to
download the
capture le
TFTP Server
Filename
Server IP When using TFTP to download the le, specify the IP address of the TFTP server.
Select or clear this option to determine whether to use TFTP or HTTP(S) to download the
capture le:
•) To download the le by using TFTP, select this option and complete the additional
elds.
•) To download the le by using HTTP or HTTPS, clear this option and click Download to
browse to the location where the le is to be saved.
When using TFTP to download the le, specify a name for the packet capture le, including
the .pcap le name extension and the path to the directory where you want to save the le.
Table 55 - Packet Capture File Download
Support Information Conguration and Settings
The Support Information page provides a way to gather the diagnostic/troubleshooting information about the AP
beyond what is available through the Web UI.
Note: DWL-2600AP, DWL-3600AP, DWL-6600AP, DWL-6700AP, DWL-8600AP do not support this function.
Figure 63 - Support Information
Field Description
Download To download the diagnostic information for support, click “Download” button.
Table 56 - Support Information
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 92
Page 93
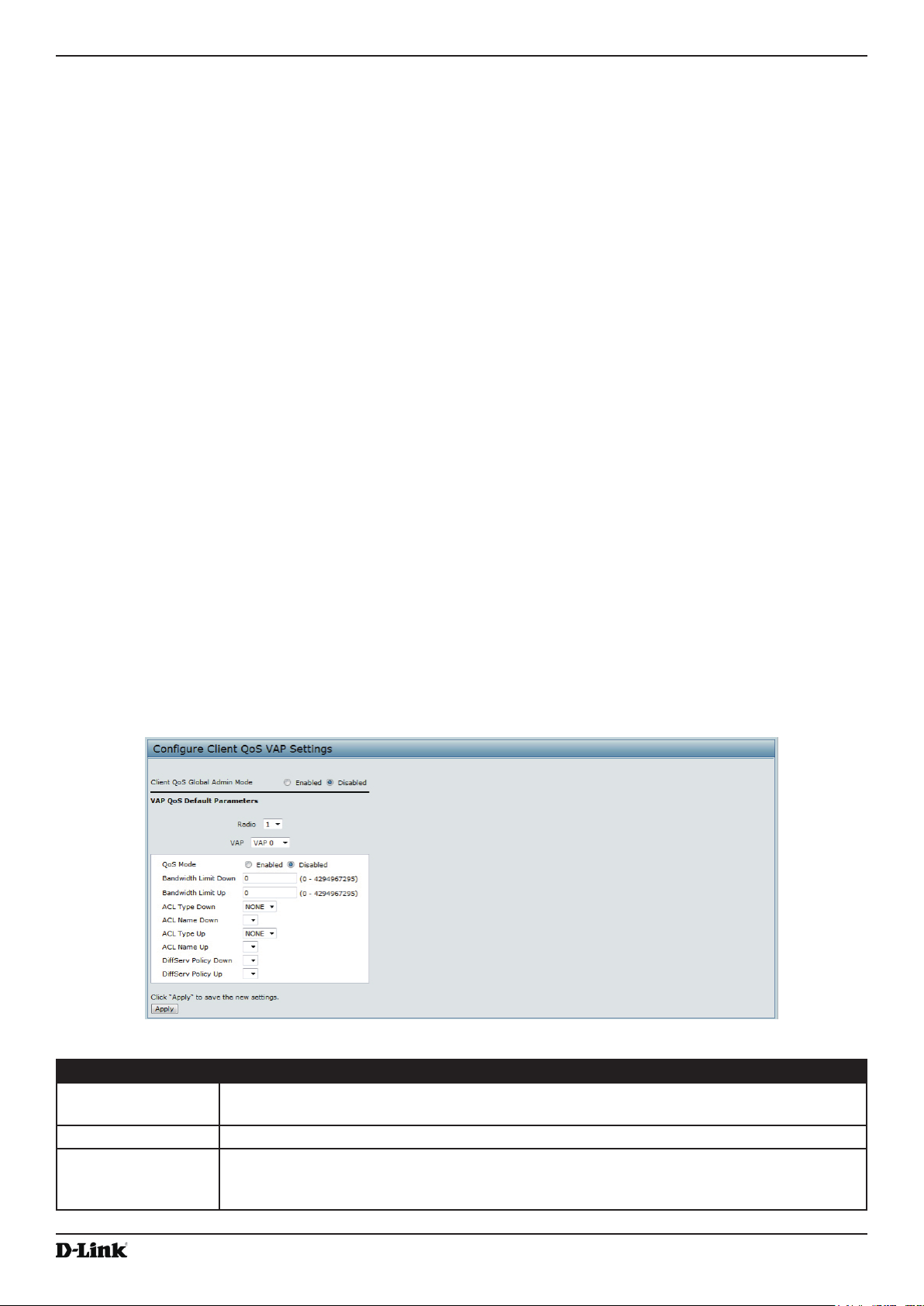
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
This section describes how to congure QoS settings that affect trafc from the wireless clients to the AP. By using the
UAP Client QoS features, you can limit bandwidth and apply ACLs and DiffServ policies to the wireless interface. If a
VAP uses WPA Enterprise security to authenticate clients, you can congure the RADIUS server to provide per-client
QoS information.
This section describes the following features:
•) “Conguring VAP QoS Parameters” on page 93
•) “Managing Client QoS ACLs” on page 94
•) “Creating a DiffServ Class Map” on page 100
•) “Creating a DiffServ Policy Map” on page 105
•) “Conguring RADIUS-Assigned Client QoS Parameters” on page 107
Conguring VAP QoS Parameters
The client QoS features on the UAP provide additional control over certain QoS aspects of wireless clients that
connect to the network, such as the amount of bandwidth an individual client is allowed to send and receive. To control
general categories of trafc, such as HTTP trafc or trafc from a specic subnet, you can congure ACLs and assign
them to one or more VAPs.
In addition to controlling general trafc categories, Client QoS allows you to congure per-client conditioning of various
micro-ows through Differentiated Services (DiffServ). DiffServ policies are a useful tool for establishing general microow denition and treatment characteristics that can be applied to each wireless client, both inbound and outbound,
when it is authenticated on the network.
From the VAP QoS Parameters page, you can enable the Client QoS feature, specify client bandwidth limits, and
select the ACLs and DiffServ policies to use as default values for clients associated with the VAP when the client does
not have their own attributes dened by a RADIUS server.
To congure the Client QoS administrative mode and to congure the QoS settings for a VAP, click the VAP QoS
Parameters tab.
Figure 64 - Congure Client QoS VAP Settings
Field Description
Client QoS Global
Admin Mode
Radio For dual-radio APs, select Radio 1 or Radio 2 to specify which radio to congure.
VAP Specify the VAP that will have the Client QoS settings that you congure.
October 2017
Enable or disable Client QoS operation on the AP.
Changing this setting will not affect the WMM settings you congure on the QoS page.
The QoS settings you congure for the selected VAP will not affect clients that access the
network through other VAPs.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 93
Page 94

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Client QoS Mode Enable or disable QoS operation on the VAP selected in the VAP menu.
QoS must be enabled globally (from the Client QoS Global Admin Mode eld) and on the
VAP ( QoS Mode eld) for the Client QoS settings to be applied to wireless clients.
Bandwidth Limit
Down
Bandwidth Limit Up Enter the maximum allowed client transmission rate to the AP in bits per second. The valid
ACL Type Down Select the type of ACL to apply to trafc in the outbound (down) direction, which can be one
ACL Name Down Select the name of the ACL applied to trafc in the outbound (down) direction.
ACL Type Up Select the type of ACL to apply to trafc in the inbound (up) direction, which can be one of
ACL Name Up Select the name of the ACL applied to trafc entering the AP in the inbound (up) direction.
DiffServ Policy
Down
DiffServ Policy Up Select the name of the DiffServ policy applied to trafc sent to the AP in the inbound (up)
Enter the maximum allowed transmission rate from the AP to the wireless client in bits per
second. The valid range is 0 – 429496000 bits/sec.
The value you enter must be a multiple of 8000 bits/sec, in other words, the value must be
n × 8000 bits/sec, where n = 0, 1, 2, 3... If you attempt to set the limit to a value that is not
a multiple of 8000 bits/sec, the conguration will be rejected. A value of 0 means that the
bandwidth maximum limit is not enforced in this direction.
range is 0 – 4294967295 bps.
The value you enter must be n × 8000 bits/sec, where n = 0, 1, 2, 3... If you attempt to set
the limit to a value that is not a multiple of 8000 bits/sec, the conguration will be rejected. A
value of 0 means that the bandwidth maximum limit is not enforced in this direction.
of the following:
•) IPv4: The ACL examines IPv4 packets for matches to ACL rules
•) IPv6: The ACL examines IPv6 packets for matches to ACL rules
•) MAC: The ACL examines layer 2 frames for matches to ACL rules
After switching the packet or frame to the outbound interface, the ACL’s rules are checked
for a match. The packet or frame is transmitted if it is permitted, and discarded if it is denied.
the following:
•) IPv4: The ACL examines IPv4 packets for matches to ACL rules
•) IPv6: The ACL examines IPv6 packets for matches to ACL rules
•) MAC: The ACL examines layer 2 frames for matches to ACL rules
When a packet or frame is received by the AP, the ACL’s rules are checked for a match. The
packet or frame is processed if it is permitted, and discarded if it is denied.
Select the name of the DiffServ policy applied to trafc from the AP in the outbound (down)
direction.
direction.
Table 57 - VAP QoS Parameters
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
Managing Client QoS ACLs
ACLs are a collection of permit and deny conditions, called rules, that provide security by blocking unauthorized
users and allowing authorized users to access specic resources. ACLs can block any unwarranted attempts to reach
network resources.
The UAP supports up to 50 IPv4, IPv6, and MAC ACLs.
IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs
IP ACLs classify trafc for Layers 3 and 4.
Each ACL is a set of up to 10 rules applied to trafc sent from a wireless client or to be received by a wireless client.
Each rule species whether the contents of a given eld should be used to permit or deny access to the network.
Rules can be based on various criteria and may apply to one ore more elds within a packet, such as the source or
destination IP address, the source or destination L4 port, or the protocol carried in the packet.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 94
Page 95

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
MAC ACLs
MAC ACLs are Layer 2 ACLs. You can congure the rules to inspect elds of a frame such as the source or
destination MAC address, the VLAN ID, or the Class of Service 802.1p priority. When a frame enters or exits the AP
port (depending on whether the ACL is applied in the up or down direction), the AP inspects the frame and checks the
ACL rules against the content of the frame. If any of the rules match the content, a permit or deny action is taken on
the frame.
ACL Conguration Process
Congure ACLs and rules on the Client QoS ACL page (steps 1–5), and then apply the rules to a specied VAP on
the AP QoS Parameters page (step 6).
Use the following general steps to congure ACLs:
1.) Specify a name for the ACL.
2.) Select the type of ACL to add.
3.) Add the ACL.
4.) Add new rules to the ACL.
5.) Congure the match criteria for the rules.
6.) Apply the ACL to one or more VAPs.
To congure an ACL, click the Client QoS ACL tab.
The elds to congure ACL rules appear only after you have created an ACL. The following image shows the
conguration of a new rule for the IPv4 ACL named acl1. The rule prevents HTTP trafc from all clients in the
192.168.20.0 network from being forwarded.
Figure 65 - Congure Client QoS ACL Settings
The following table describes the elds available on the Client QoS ACL page.
Field Description
ACL Conguration
ACL Name Enter a name to identify the ACL. The name can contain from 1 – 31 alphanumeric
characters. Spaces are not allowed.
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
October 2017
Page 95
Page 96

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
ACL Type Select the type of ACL to congure:
•) IPv4
•) IPv6
•) MAC
IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs control access to network resources based on Layer 3 and Layer 4
criteria. MAC ACLs control access based on Layer 2 criteria.
ACL Rule Conguration
ACL Name - ACL
Type
Rule To congure a new rule to add to the selected ACL, select New Rule. To add an existing rule
Action Species whether the ACL rule permits or denies an action.
Match Every Indicates that the rule, which either has a permit or deny action, will match the frame or
IPv4 ACL
Protocol Select the Protocol eld to use an L3 or L4 protocol match condition based on the value of
Source IP Address Select this eld to require a packet’s source IP address to match the address listed here.
Wild Card Mask Species the source IP address wildcard mask.
Select the ACL to congure with the new rule. The list contains all ACLs added in the ACL
Conguration section.
to an ACL or to modify a rule, select the rule number.
When an ACL has multiple rules, the rules are applied to the packet or frame in the order in
which you add them to the ACL. There is an implicit deny all rule as the nal rule.
•) When you select Permit, the rule allows all trafc that meets the rule criteria to enter or
exit the AP (depending on the ACL direction you select). Trafc that does not meet the
criteria is dropped.
•) When you select Deny, the rule blocks all trafc that meets the rule criteria from
entering or exiting the AP (depending on the ACL direction you select). Trafc that
does not meet the criteria is forwarded unless this rule is the nal rule. Because there
is an implicit deny all rule at the end of every ACL, trafc that is not explicitly permitted
is dropped.
packet regardless of its contents.
If you select this eld, you cannot congure any additional match criteria. The Match Every
option is selected by default for a new rule. You must clear the option to congure other
match elds.
the IP Protocol eld in IPv4 packets or the Next Header eld of IPv6 packets.
Once you select the eld, choose the protocol to match by keyword or enter a protocol ID.
Select From List
Select one of the following protocols from the list:
•) IP
•) ICMP
•) IGMP
•) TCP
•) UDP
Match to Value
To match a protocol that is not listed by name, enter the protocol ID.
The protocol ID is a standard value assigned by the IANA. The range is a number from
0–255.
Enter an IP address in the appropriate eld to apply this criteria.
The wild card masks determines which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A wild card
mask of 255.255.255.255 indicates that no bit is important. A wildcard of 0.0.0.0 indicates
that all of the bits are important. This eld is required when Source IP Address is checked.
A wild card mask is, in essence, the inverse of a subnet mask. For example, to match the
criteria to a single host address, use a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0. To match the criteria to a
24-bit subnet (for example 192.168.10.0/24), use a wild card mask of 0.0.0.255.
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 96
Page 97

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Source Port Select this eld to include a source port in the match condition for the rule. The source port
is identied in the datagram header.
Once you select the eld, choose the port name or enter the port number.
Select From List
Select the keyword associated with the source port to match:
•) ftp
•) ftpdata
•) http
•) smtp
•) snmp
•) telnet
•) tftp
•) www
Each of these keywords translates into its equivalent port number.
Match to Port
Enter the IANA port number to match to the source port identied in the datagram header.
The port range is 0 – 65535 and includes three different types of ports:
•) 0 – 1023: Well Known Ports
•) 1024 – 49151: Registered Ports
•) 49152 – 65535: Dynamic and/or Private Ports
Destination IP
Address
Wild Card Mask Species the destination IP address wildcard mask.
Destination Port Select this eld to include a destination port in the match condition for the rule. The
IP DSCP To use IP DSCP as a match criteria, select the check box and select a DSCP value
Select this eld to require a packet’s destination IP address to match the address listed
here. Enter an IP address in the appropriate eld to apply this criteria.
The wild card masks determines which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A wild card
mask of 255.255.255.255 indicates that no bit is important. A wildcard of 0.0.0.0 indicates
that all of the bits are important. This eld is required when Source IP Address is checked.
A wild card mask is in essence the inverse of a subnet mask. For example, to match the
criteria to a single host address, use a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0. To match the criteria to a
24-bit subnet (for example 192.168.10.0/24), use a wild card mask of 0.0.0.255.
destination port is identied in the datagram header.
Once you select the eld, choose the port name or enter the port number.
Select From List
Select the keyword associated with the destination port to match:
•) ftp
•) ftpdata
•) http
•) smtp
•) snmp
•) telnet
•) tftp
•) www
Each of these keywords translates into its equivalent port number.
Match to Port
Enter the IANA port number to match to the destination port identied in the datagram
header. The port range is 0 – 65535 and includes three different types of ports:
•) 0 – 1023: Well Known Ports
•) 1024 – 49151: Registered Ports
•) 49152 – 65535: Dynamic and/or Private Ports
keyword or enter a DSCP value to match. You can select only one service type (DSCP, IP
Precedence or TOS bits) to use for match criteria.
Select from List
Select from a list of DSCP types.
Match to Value
Enter a DSCP Value to match (0 – 63).
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 97
Page 98

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
IP Precedence Select this option and enter a value to use the packet’s IP Precedence value in the IP
header as match criteria. You can select only one service type (DSCP, IP Precedence or
TOS bits) to use for match criteria.
The IP Precedence range is 0 – 7.
IP TOS Bits Select this option and enter a value to use the packet’s Type of Service bits in the IP header
as match criteria. You can select only one service type (DSCP, IP Precedence or TOS bits)
to use for match criteria.
The IP TOS eld in a packet is dened as all eight bits of the Service Type octet in the IP
header. The TOS Bits value is a two-digit hexadecimal number from 00 to ff.
The high-order three bits represent the IP precedence value. The high-order six bits
represent the IP Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) value.
IP TOS Mask Enter an IP TOS mask value to identify the bit positions in the TOS Bits value that are used
for comparison against the IP TOS eld in a packet.
The TOS Mask value is a two-digit hexadecimal number from 00 to ff, representing an
inverted (i.e. wildcard) mask. The zero-valued bits in the TOS Mask denote the bit positions
in the TOS Bits value that are used for comparison against the IP TOS eld of a packet. For
example, to check for an IP TOS value having bits 7 and 5 set and bit 1 clear, where bit 7
is most signicant, use a TOS Bits value of a0 and a TOS Mask of 00. This is an optional
conguration.
IPv6 ACL
Protocol Select the Protocol eld to use an L3 or L4 protocol match condition based on the value of
the IP Protocol eld in IPv4 packets or the Next Header eld of IPv6 packets.
Once you select the eld, choose the protocol to match by keyword or enter a protocol ID.
Select From List
Select one of the following protocols from the list:
•) IP
•) ICMP
•) IPv6
•) ICMPv6
•) IGMP
•) TCP
•) UDP
Match to Value
To match a protocol that is not listed by name, enter the protocol ID.
The protocol ID is a standard value assigned by the IANA. The range is a number from
0–255.
Source IPv6
Address
Source IPv6 Prex
Length
Select this eld to require a packet’s source IPv6 address to match the address listed here.
Enter an IPv6 address in the appropriate eld to apply this criteria.
Enter the prex length of the source IPv6 address.
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 98
Page 99

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
Source Port Select this option to include a source port in the match condition for the rule. The source port
is identied in the datagram header.
Once you select the eld, choose the port name or enter the port number.
Select From List
Select the keyword associated with the source port to match:
•) ftp
•) ftpdata
•) http
•) smtp
•) snmp
•) telnet
•) tftp
•) www
Each of these keywords translates into its equivalent port number.
Match to Port
Enter the IANA port number to match to the source port identied in the datagram header.
The port range is 0 – 65535 and includes three different types of ports:
•) 0 – 1023: Well Known Ports
•) 1024 – 49151: Registered Ports
•) 49152 – 65535: Dynamic and/or Private Ports
Destination IPv6
Address
Destination IPv6
Prex Length
Destination Port Select this option to include a destination port in the match condition for the rule. The
IPv6 Flow Label Flow label is 20-bit number that is unique to an IPv6 packet. It is used by end stations to
IPv6 DSCP To use IPv6 DSCP as a match criteria, select the check box and select a DSCP value
MAC ACL
Select this eld to require a packet’s destination IPv6 address to match the address listed
here. Enter an IPv6 address in the appropriate eld to apply this criteria.
Enter the prex length of the destination IPv6 address.
destination port is identied in the datagram header.
Once you select the eld, choose the port name or enter the port number.
Select From List
Select the keyword associated with the destination port to match:
•) ftp
•) ftpdata
•) http
•) smtp
•) snmp
•) telnet
•) tftp
•) www
Each of these keywords translates into its equivalent port number.
Match to Port
Enter the IANA port number to match to the destination port identied in the datagram
header. The port range is 0 – 65535 and includes three different types of ports:
•) 0 – 1023: Well Known Ports
•) 1024 – 49151: Registered Ports
•) 49152 – 65535: Dynamic and/or Private Ports
signify quality-of-service handling in routers (range 0 to 1048575).
keyword or enter a DSCP value to match. You can select only one service type (DSCP, IP
Precedence or TOS bits) to use for match criteria.
Select from List
Select from a list of DSCP types.
Match to Value
Enter a DSCP Value to match (0 – 63).
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 99
Page 100

Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Field Description
EtherType Select the EtherType eld to compare the match criteria against the value in the header of
an Ethernet frame.
Select an EtherType keyword or enter an EtherType value to specify the match criteria.
Select from List Select
Select one of the following protocol types:
•) appletalk
•) arp
•) ipv4
•) ipv6
•) ipx
•) netbios
•) pppoe
Match to Value
Enter a custom protocol identier to which packets are matched. The value is a four-digit
hexadecimal number in the range of 0600 – FFFF.
Class of Service Select this eld and enter an 802.1p user priority to compare against an Ethernet frame.
The valid range is 0 – 7. This eld is located in the rst/only 802.1Q VLAN tag.
Source MAC
Address
Source MAC Mask Select this eld and enter the source MAC address mask specifying which bits in the source
Destination MAC
Address
Destination MAC
Mask
VLAN ID Select this eld and enter the VLAN IDs to compare against an Ethernet frame.
Select this eld and enter the source MAC address to compare against an Ethernet frame.
MAC to compare against an Ethernet frame.
A 0 indicates that the address bit is signicant, and an f indicates that the address bit is to be
ignored. A MAC mask of 00:00:00:00:00:00 matches a single MAC address.
Select this eld and enter the destination MAC address to compare against an Ethernet
frame.
Enter the destination MAC address mask specifying which bits in the destination MAC to
compare against an Ethernet frame.
A 0 indicates that the address bit is signicant, and an f indicates that the address bit is to be
ignored. A MAC mask of 00:00:00:00:00:00 matches a single MAC address.
This eld is located in the rst/only 802.1Q VLAN tag.
Table 58 - ACL Conguration
Section 8 - Conguring Client Quality of Service (QoS)
After you set the desired rule criteria, click Apply. To delete an ACL, select the Delete ACL option and click Apply.
Creating a DiffServ Class Map
The Client QoS feature contains Differentiated Services (DiffServ) support that allows trafc to be classied into
streams and given certain QoS treatment in accordance with dened per-hop behaviours.
Standard IP-based networks are designed to provide best effort data delivery service. Best effort service implies that
the network delivers the data in a timely fashion, although there is no guarantee that it will. During times of congestion,
packets may be delayed, sent sporadically, or dropped. For typical Internet applications, such as e-mail and le
transfer, a slight degradation in service is acceptable and in many cases unnoticeable. However, on applications with
strict timing requirements, such as voice or multimedia, any degradation of service has undesirable effects.
By classifying the trafc and creating policies that dene how to handle these trafc classes, you can make sure that
time-sensitive trafc is given precedence over other trafc.
The UAP supports up to 50 Class Maps.
October 2017
Unied Access Point Administrator’s Guide
Page 100
 Loading...
Loading...