D-Link DSL-2730E User Manual

DSL-2730E
User Manual

User Manual
Contents
1 Introduction ........................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Safety Precautions ................................................................................ 1
1.2 LEDs and Interfaces .............................................................................. 1
1.3 System Requirements ........................................................................... 3
1.4 Features ................................................................................................ 3
2 Hardware Installation ......................................................................................... 5
3 About the Web Configuration ............................................................................. 7
3.1 Access the Router ................................................................................. 7
3.2 Status ..................................................................................................... 8
3.3 Setup ................................................................................................... 10
3.3.1 WAN Configuration ................................................................... 13
3.3.1.1 WAN .............................................................................. 13
3.3.1.2 Automatically PVC ........................................................ 18
3.3.1.3 ATM Setting................................................................... 19
3.3.1.4 ADSL Setting ................................................................. 20
3.3.2 LAN ........................................................................................... 21
3.3.2.1 LAN ............................................................................... 21
3.3.2.2 DHCP ............................................................................ 23
3.3.2.3 DHCP Static .................................................................. 27
3.3.2.4 DHCP Filter ................................................................... 28
3.3.2.5 LAN IPv6 ....................................................................... 29
3.3.3 WLAN ....................................................................................... 31
3.3.3.1 Basic Settings ............................................................... 31
3.3.3.2 Security ......................................................................... 33
3.3.3.3 Multi-BSSID .................................................................. 36
3.3.3.4 Access Control .............................................................. 38
3.3.3.5 Advanced ...................................................................... 38
3.3.3.6 WPS .............................................................................. 40
3.4 Advanced ............................................................................................. 41
3.4.1 Route ........................................................................................ 42
3.4.1.1 Static Route ................................................................... 42
3.4.1.2 IPv6 Static Route .......................................................... 43
3.4.1.3 RIP ................................................................................ 44
3.4.2 NAT ........................................................................................... 46
i

User Manual
3.4.2.1 DMZ .............................................................................. 46
3.4.2.2 Virtual Server ................................................................ 46
3.4.2.3 ALG ............................................................................... 48
3.4.2.4 NAT Exclude IP ............................................................. 48
3.4.2.5 Port Trigger ................................................................... 49
3.4.3 QoS ........................................................................................... 51
3.4.4 CWMP ...................................................................................... 53
3.4.5 Port Mapping ............................................................................ 55
3.4.6 Others ....................................................................................... 60
3.4.6.1 Bridge Setting ............................................................... 60
3.4.6.2 Client Limit .................................................................... 61
3.4.6.3 Tunnel ........................................................................... 61
3.4.6.4 Others ........................................................................... 63
3.5 Service ................................................................................................. 63
3.5.1 IGMP ......................................................................................... 63
3.5.1.1 IGMP Proxy ................................................................... 64
3.5.1.2 IGMP MLD .................................................................... 64
3.5.2 UPnP ........................................................................................ 65
3.5.3 SNMP ....................................................................................... 65
3.5.4 DNS .......................................................................................... 66
3.5.4.1 DNS .............................................................................. 67
3.5.4.2 IPv6 DNS ...................................................................... 67
3.5.5 DDNS ........................................................................................ 68
3.6 Firewall ................................................................................................ 69
3.6.1 MAC Filter ................................................................................. 70
3.6.2 IP/Port Filter .............................................................................. 70
3.6.2.1 IP/Port Filter .................................................................. 70
3.6.2.2 IPv6/Port Filter .............................................................. 71
3.6.3 Parent Control........................................................................... 73
3.6.4 ACL ........................................................................................... 74
3.6.4.1 ACL ............................................................................... 74
3.6.4.2 IPv6 ACL ....................................................................... 77
3.6.5 DoS ........................................................................................... 80
3.6.6 MAC Spoofing ........................................................................... 81
3.7 Maintenance ........................................................................................ 82
3.7.1 Update ...................................................................................... 82
ii

User Manual
3.7.1.1 Firmware Update .......................................................... 82
3.7.1.2 Backup/Restore ............................................................ 83
3.7.2 Password .................................................................................. 84
3.7.3 Reboot ...................................................................................... 85
3.7.4 Time .......................................................................................... 85
3.7.5 Log ............................................................................................ 87
3.7.6 Diagnostics ............................................................................... 87
4 Q&A .................................................................................................................. 88
iii

User Manual
1 Introduction
The device supports multiple line modes. It provides four 10/100 base-T Ethernet
interfaces at the user end. The device provides high-speed ADSL2+ broadband
connection to the Internet or Intranet for high-end users, such as net bars and
office users. It provides high performance access to the Internet.
The device supports WLAN access, such as WLAN AP or WLAN device, to the
Internet. It complies with IEEE 802.11, 802.11b/g/n specifications, WEP, WPA, and
WPA2 security specifications.
1.1 Safety Precautions
Follow the following instructions to prevent the device from risks and damage
caused by fire or electric power:
Use volume labels to mark the type of power.
Use the power adapter packed within the device package.
Pay attention to the power load of the outlet or prolonged lines. An
overburden power outlet or damaged lines and plugs may cause electric
shock or fire accident. Check the power cords regularly. If you find any
damage, replace it at once.
Proper space left for heat dissipation is necessary to avoid damage caused
by overheating to the device. The long and thin holes on the device are
designed for heat dissipation to ensure that the device works normally. Do
not cover these heat dissipation holes.
Do not put this device close to a place where a heat source exists or high
temperature occurs. Avoid the device from direct sunshine.
Do not put this device close to a place where it is over damp or watery. Do
not spill any fluid on this device.
Do not connect this device to any PCs or electronic products, unless our
customer engineer or your broadband provider instructs you to do this,
because any wrong connection may cause power or fire risk.
Do not place this device on an unstable surface or support.
1.2 LEDs and Interfaces
1
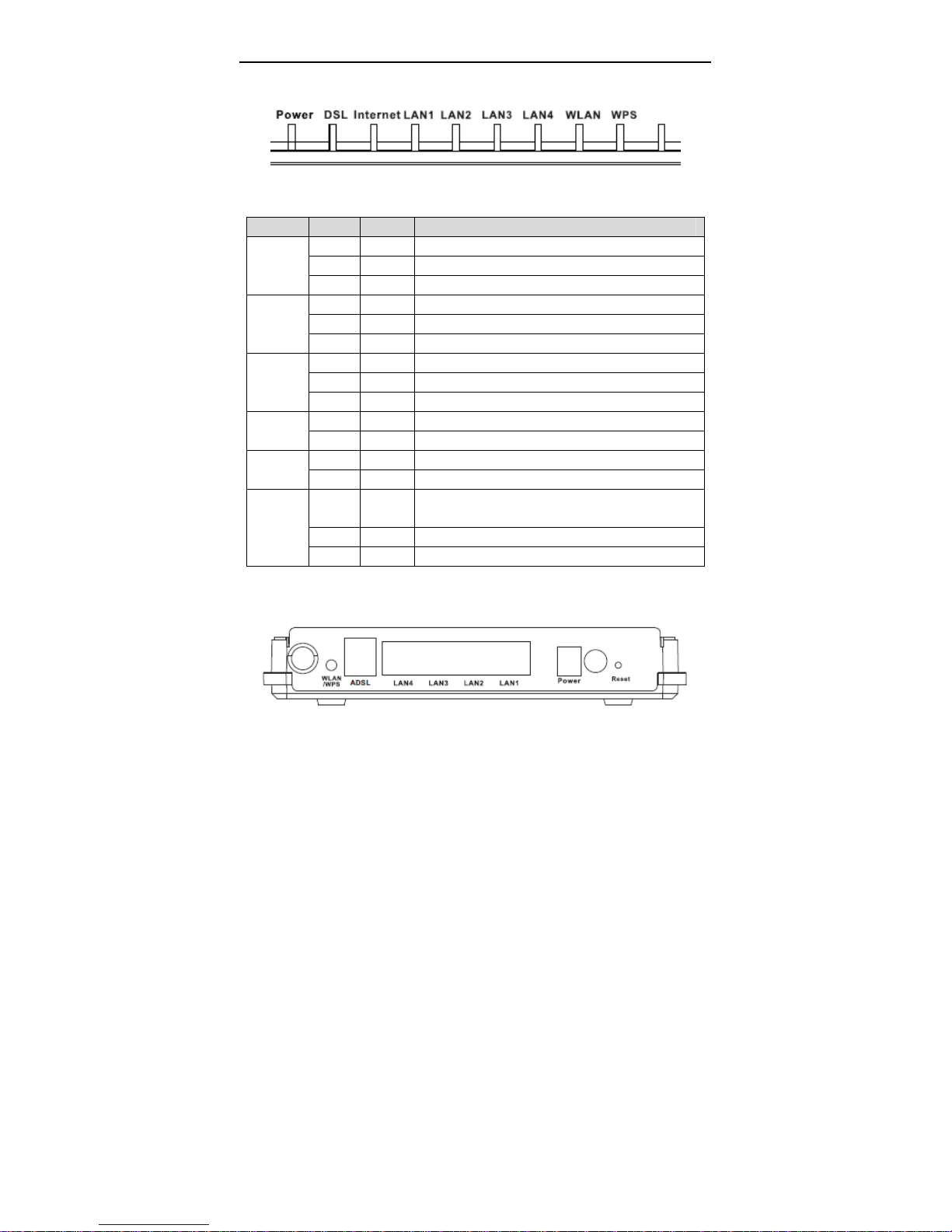
User Manual
Front Panel
The following table describes the LEDs of the device.
LEDs Color Status Description
Green On The initialization of the device is successful.
Power
DSL
INT
WiFi
LAN1~4
WPS
Green Off The device is powered off.
Red On POST Fail
Green On DSL link up / link synchronized.
Green Off Link disconnection.
Green Blinks Link training / DSL link not synchronized.
Green On Successful PPP session.
Red On Failure PPP session (1 minitue after link up).
Green Off Before DSL link up.
Green On The WLAN connection has been activated.
Green Off The WLAN connection is not activated.
Green On The LAN connection is nomal and activated.
Green Off The LAN interface is disconnected.
Green Blinks
Green Off WPS is idle.
Green On WPS negotiate succefully
WPS is triggered, and is waiting for client to
negotiate.
Rear Panel
2

User Manual
The following table describes the interfaces and buttons of the device:
Interface Description
Reset to the factory default configuration. Keep the device
Reset
On/Off Power switch, power on or power off the device.
Power
LAN1~4
DSL
WLAN/WPS
powered on, and insert a needle into the hole for 3 seconds,
then release it. The deivce is reset to the factory default
configuration.
Power interface, for connecting to the power adapter of 12V
DC, 0.5A.
RJ-45 interface, for connecting to the Ethernet interface of a
PC or the Ethenet devices through an Ethernet cable.
RJ-11 interface, for connecting to the ADSL interface or a
splitter through a telephone cable.
Press the button between 1s and 6s to enable WLAN
function.
Press the button for more than 6s to enable WPS (Wi-Fi
Protected Setup) function.
1.3 System Requirements
Recommended system requirements are as follows:
Service subscriber
10 Base T/100 Base T Ethernet card
Hub or switch (attached to several PCs through one of Ethernet interfaces
on the device)
Operating system: Windows 98 SE, Windows 2000, Wndows ME, Windows
XP, Windows Vista, Window 7
Internet Explorer V5.0 or higher, Netscape V4.0 or higher, or FireFox 1.5 or
higher
1.4 Features
The device supports the following features:
Various line modes (line auto-negotiation)
3

User Manual
External PPPoE dial-up access
Internal PPPoE/PPPoA dial-up access
1483B/1483R/MER access
Multiple PVCs (eight at most)
A single PVC with multiple sessions
Multiple PVCs with multiple sessions
Auto PVC
DHCP server
IPv4/IPv6
NAT/NAPT
ALG
TR-069
SNMP
Static route
Firmware upgrading through Web, TFTP, or FTP
Resetting to the factory defaults through Reset button or Web
DNS relay
Virtual server
Two-level passwords and usernames
Web interface
Telnet CLI
System status display
PPP session PAP/CHAP
IP/Port filter
Remote access control
Line connection status test
Remote management (Telnet; HTTP )
Backup and restoration of configuration file
IP quality of service (QoS)
Universal plug and play (UPnP)
WLAN with high-speed data transmission rate, compatible with IEEE
802.11b/g/n, 2.4 GHz compliant equipment
4
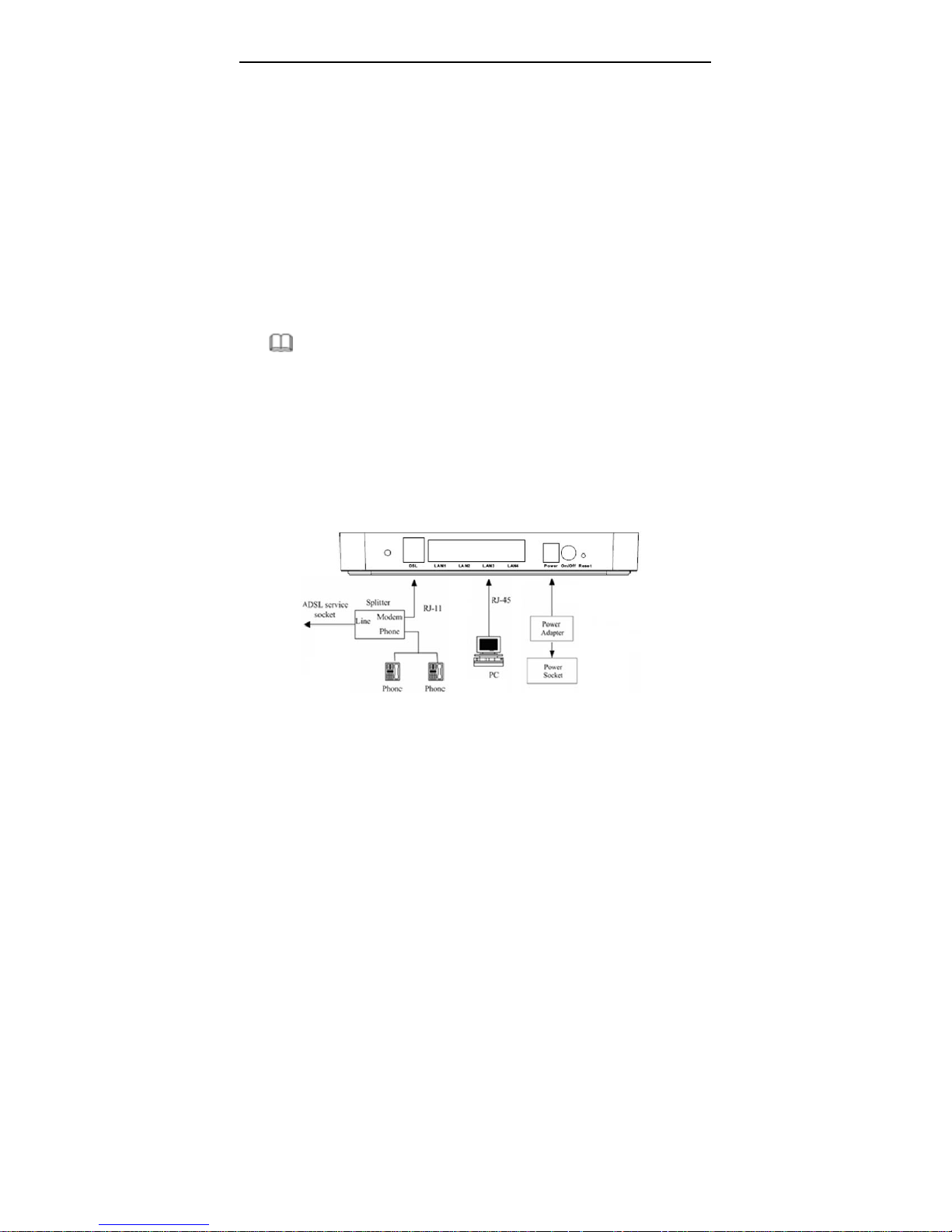
User Manual
2 Hardware Installation
Step 1 Connect the DSL interface of the router and the Modem interface of
the splitter through a telephone cable. Connect the phone to the Phone
interface of the splitter through a cable. Connect the incoming line to the
Line interface of the splitter.
The splitter has three interfaces:
Line: Connect to a wall phone jack (RJ-11 jack)
Modem: Connect to the ADSL jack of the device
Phone: Connect to a telephone set.
Step 2 Connect the LAN interface of the modem with the network card of the
PC through an Ethernet line (MDI/MDIX).
Note:
Use twisted-pair cables to connect with the hub or Switch.
Step 3 Plug the power adapter to the wall outlet and then connect the other
end of it to the Power interface of the modem.
Connection 1
Figure1 displays the application diagram for the connection of the modem, PC,
splitter, and telephone sets, when no telephone set is placed before a splitter.
This type of connection is recommended.
Figure 1 Connection diagram (no telephone set is placed before the splitter)
5
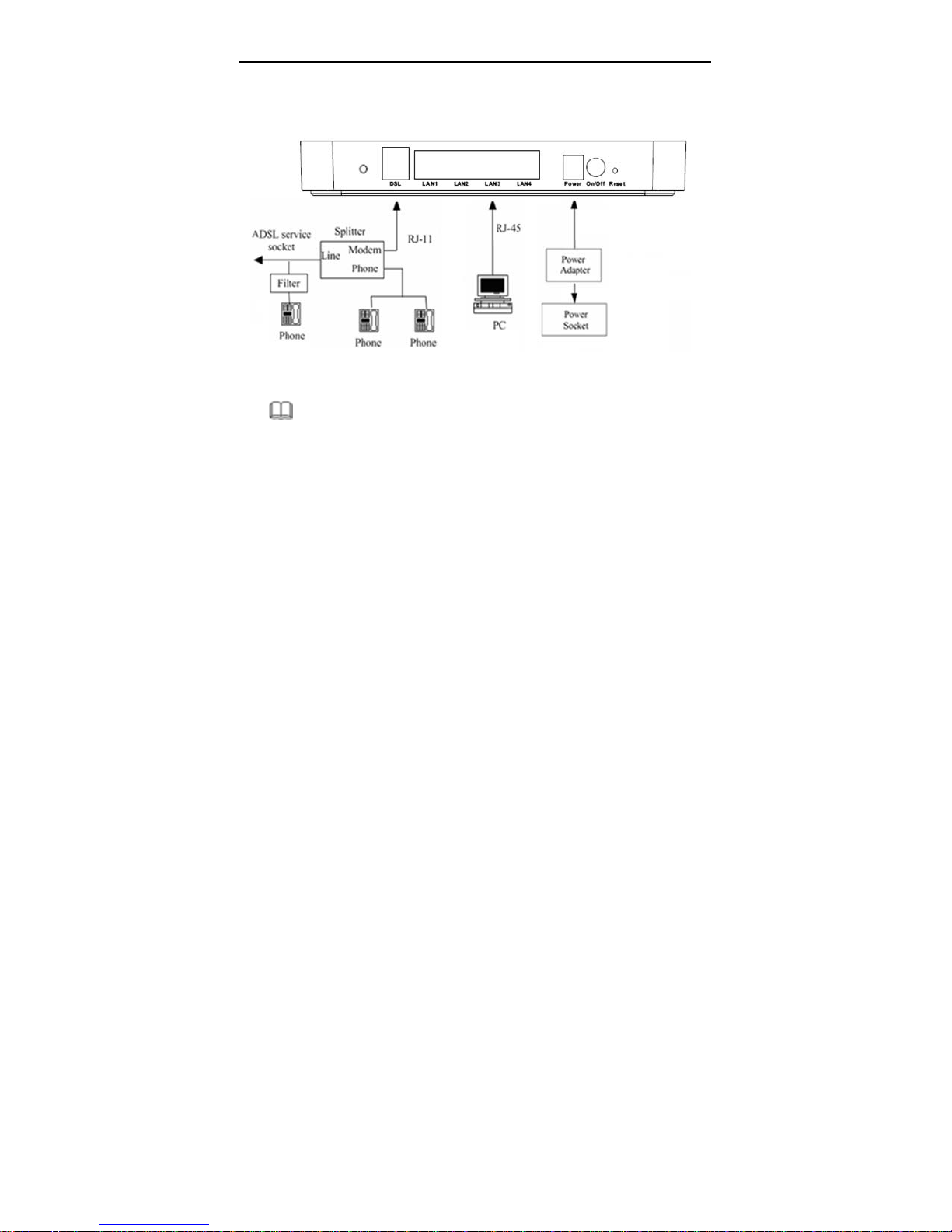
User Manual
Connection 2
Figure 2 displays the connection when the telephone set is placed before a
splitter.
Figure 2 Connection diagram (a telephone set is plac ed be fo re the splitter)
Note:
In actual application, it is recommended to following connection 1. When
connection 2 is used, the filter must be installed close to the telephone cable.
See Figure2. Do not use the splitter to replace the filter.
Installing a telephone directly before the splitter may lead to a failure of
connection between the modem and the device of LAN side, or cannot access
into the Internet, or slow the connection speed. If you really need to add a
telephone set before the splitter, you have to add a microfilter before connecting
to a telephone set. Do not connect several telephones before the splitter. Do not
connect several telephones with the microfilter.
6
User Manual
3 About the Web Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the router by using the Web-based
configuration utility.
3.1 Access the Router
The following is the detailed description of accesing the router for the first time.
Configure the IP address of the PC as 192.168.1.X (2~254), netmask as 255.
255.255.0. Open the Internet Explorer (IE) browser and enter
http://192.168.1.1.In the Login page that is displayed, enter the username and
password.
The username and password of the super user are tmadmin and
tmadmin
The username and password of the common user are tmuser and
tmuser.
If you log in as a super user, you will see the Device Info page as shown below
appears. You can check the basic settings of the modem, such as firmware
version, upstream speed, downstream speed, LAN MAC address, LAN IP
address, DHCP server status. You can also view the basic status of WAN and
DNS server.
7
User Manual
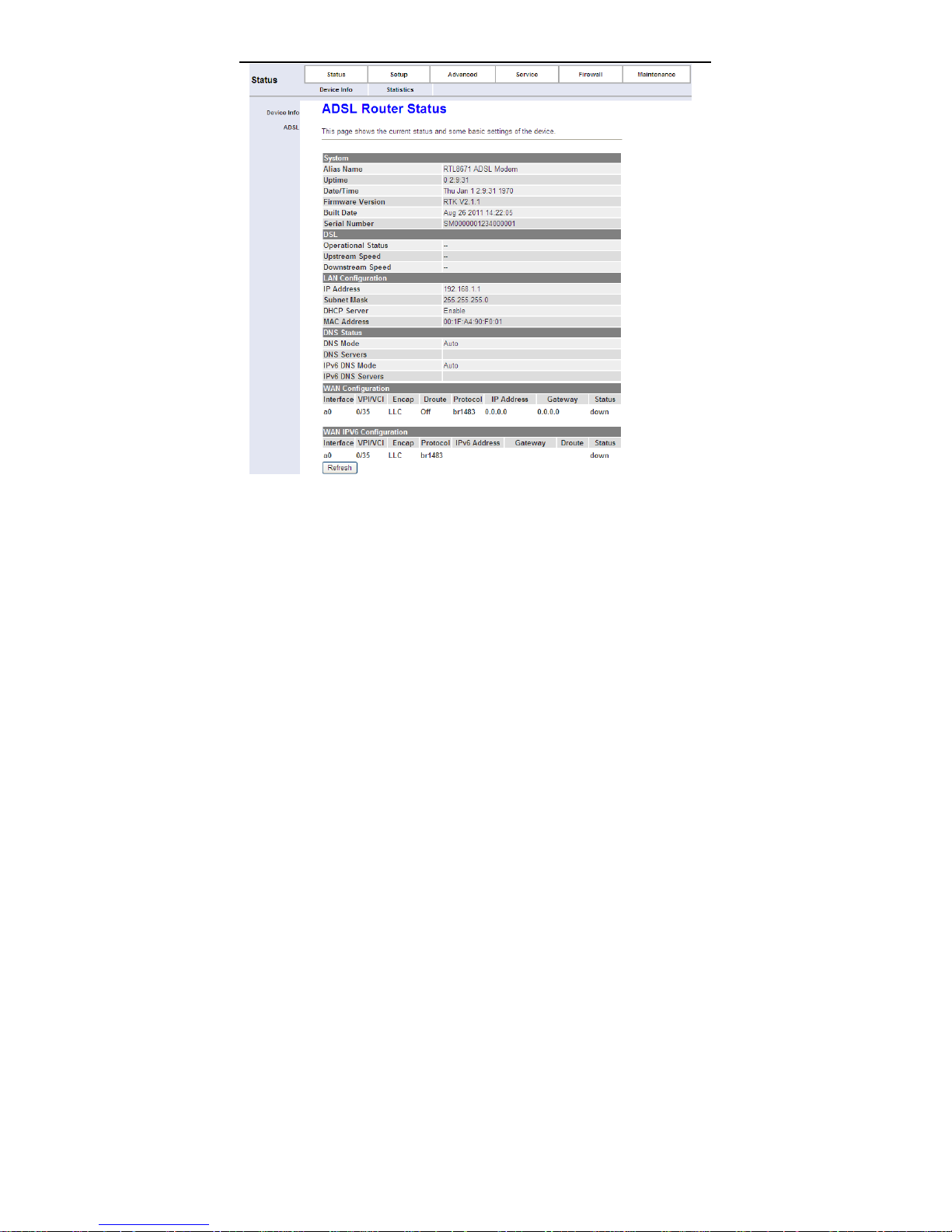
3.2 Status
The tab Status contains Device Info and Statistics. Click Status > Device
Info > ADSL, the following page appears. You can see the router settings such
as the Adsl Line Status, Vendor ID and Firmware Version.
8

User Manual
Click Status > Statistics, the following page appears. In this page, you can view
the statistics of each network port.
9

User Manual
3.3 Quick Setup
In the navigation bar, click Quick Setup. The tab Quick Setup contains a simple
way to setup WAN, and WLAN.
Quick Setup provided 3 simple steps to setup the connection. Below is an
example on each step.
10

User Manual
3.3.1 Step 1
The following table describes the parameters of this page.
Field Description
Your Streamyx Username ID
Streamyx ID
Streamyx Password Your Streamyx Password
Connection Type You can choose LLC or VC-Mux.
Protocal You can choose PPPoE, PPPoA or Bridge
Enable IPv6
Address Type You can choose DHCP or Static
Static IP (Static Only) Your Streamyx Static IP
Subnet Mask Your Static Static IP Subnet Mask
After proper settings, click Next and the following page appears.
username@streamyx
username@tmnet
You can choose to enable IPv6.
(Only when you are inform by your ISP)
11

User Manual
3.3.2 Step 2
The following table describes the parameters of this page.
Field Description
Wireless ID Your Wireless SSID/Name
Encryption
Network Key
After proper settings, click Next and the following page appears.
You can choose WEP Encryption or WPA
Encryption
Your Wireless Security Key, your wireless
device should use the same key for
connection.
WEP : Must be 13 Characters
WPA : Range 8~63 Characters
12

User Manual
3.3.3 Step 3
You can check on the key-in info:
Click on Prev if you need to change any things.
Click on Apply changes to confirm the changes (The changes will be
applied immediately).
Click on Cancel to cancel the setup.
3.4 Setup
In the navigation bar, click Setup. The tab Setup contains WAN, LAN and
WLAN.
3.4.1 WAN Configuration
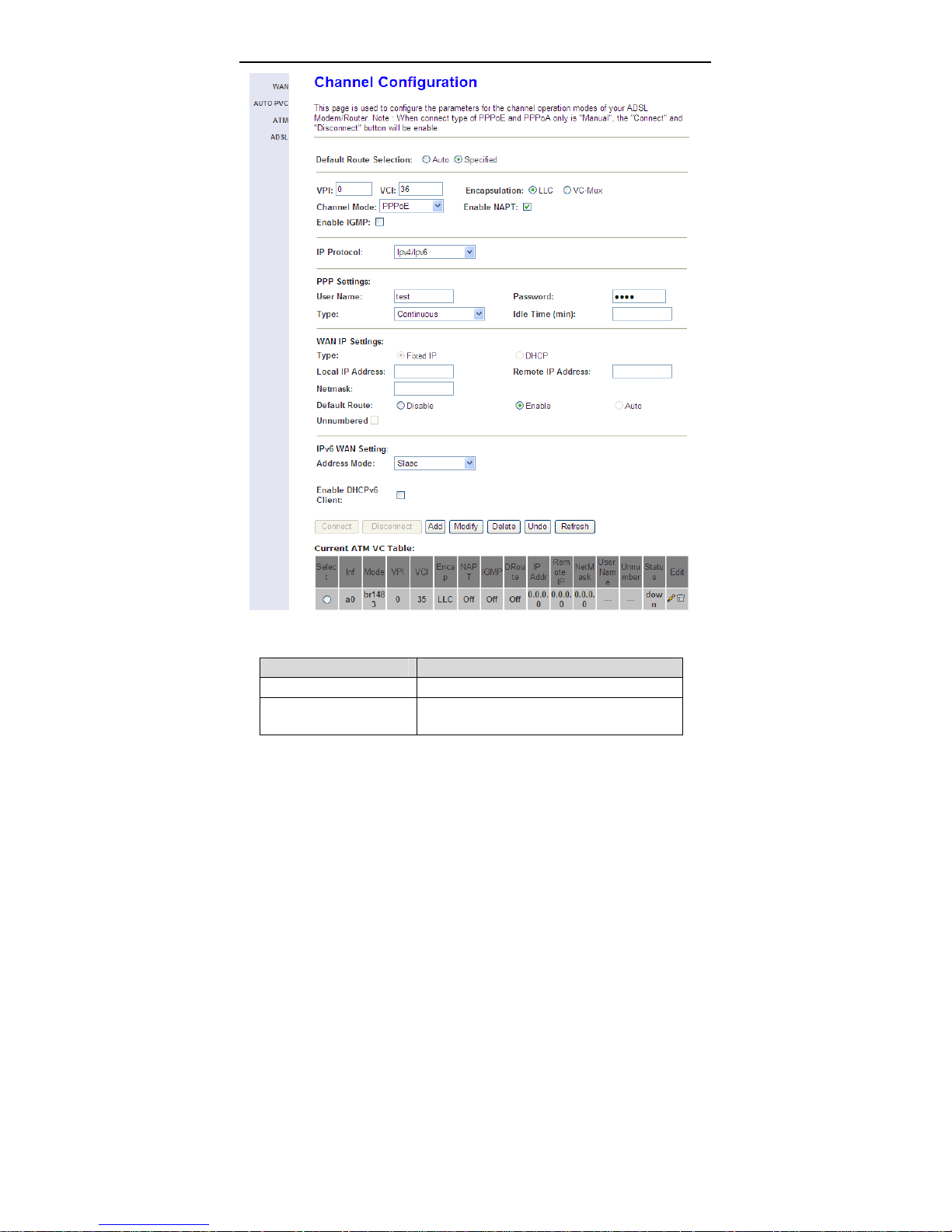
3.4.1.1 WAN
Choose Setup > WAN > WAN and the page shown in the following figure
appears.
In this page, you can configure WAN interface of your router.
13
User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page.
Field Description
Default Route Selection You can select Auto or Specified.
VPI
The virtual path between two points in an
ATM network, ranging from 0 to 255.
14

User Manual
Field Description
The virtual channel between two points in an
VCI
Encapsulation You can choose LLC and VC-Mux.
Channel Mode
Enable NAPT
Enabel IGMP
IP Protocol
PPP Settings
User Name
Password
Type
Idle Time (min)
WAN IP Settings
Type
ATM network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to
31 are reserved for known protocols)
You can choose 1483 Bridged, 1483 MER,
PPPoE, PPPoA, 1483 Routed or IPoA.
Select it to enable Network Address Port
Translation (NAPT) function. If you do not
select it and you want to access the Internet
normally, you must add a route on the uplink
equipment. Otherwise, the access to the
Internet fails. Normally, it is enabled.
You can enable or disable Internet Group
Management Protocol (IGMP) function.
Select this interface support ipv4/ipv6, ipv4 or
ipv6.
Enter the correct user name for PPP dial-up,
which is provided by your ISP.
Enter the correct password for PPP dial-up,
which is provided by your ISP.
You can choose Continuous, Connect on
Demand or Manual.
If set the type to Connect on Demand, you
need to enter the idle timeout time. Within the
preset minutes, if the router does not detect
the flow of the user continuously, the router
automatically disconnects the PPPoE
connection.
You can choose Fixed IP or DHCP.
If select Fixed IP, you should enter the
local IP address, remote IP address and
subnet mask.
15
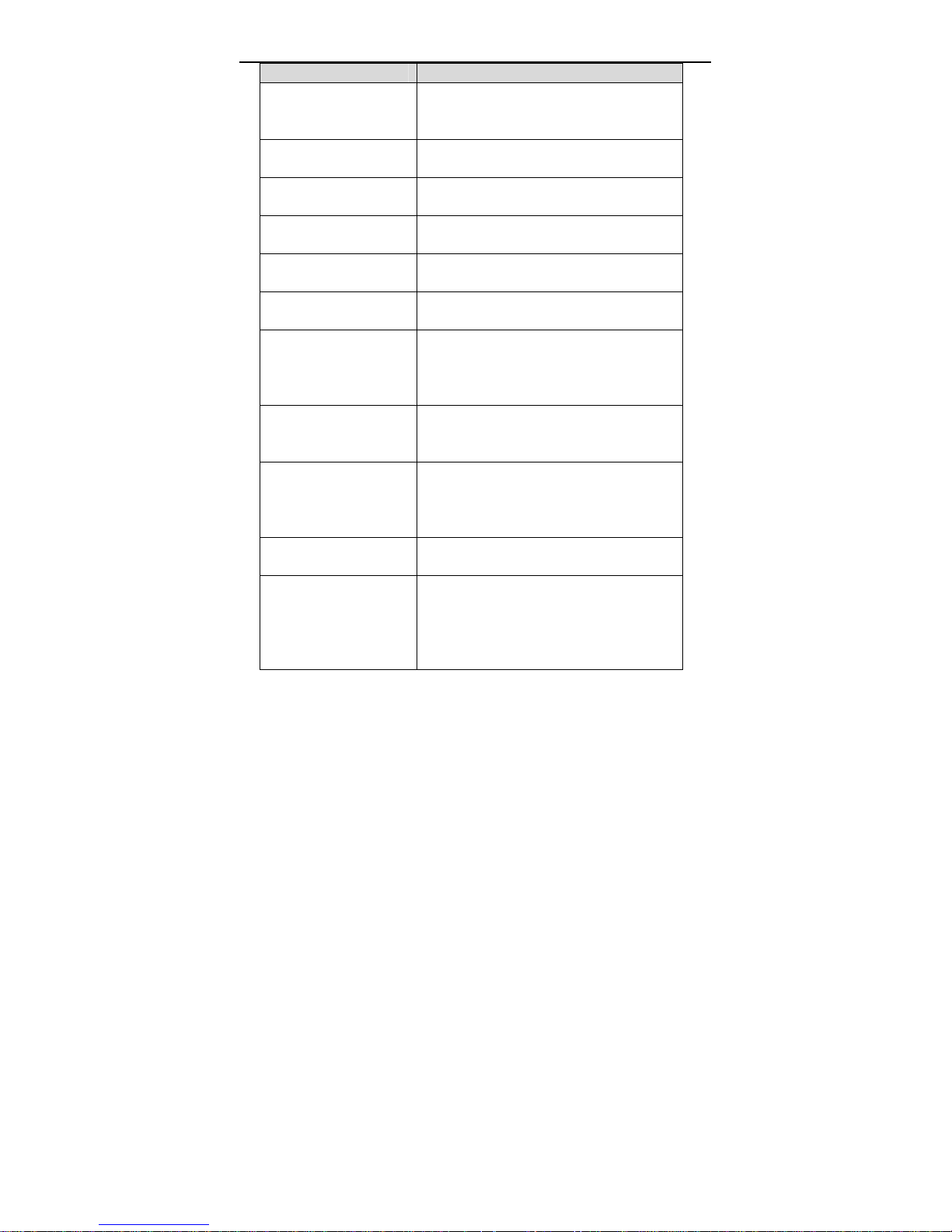
User Manual
Field Description
If select DHCP, the router is a DHCP
client, the WAN IP address is assigned
by the remote DHCP server.
Local IP Address
Netmask
Unnumbered
IPv6 WAN Setting
Address Mode
Enable DHCPv6 Client
Add
Modify
Delete
Current ATM VC T able
After proper settings, click Add and the following page appears.
Enter the IP address of WAN interface
provided by your ISP.
Enter the subnet mask of the local IP
address.
Select this checkbox to enable IP
unnumbered function.
Set ipv6 wan setting if this interface support
ipv6
Select this interface support Slaac or Static to
generate wan ipv6 addresses.
Enable or disable dhcpv6 client on this
interface, if enable, user can specify if the
dhcpv6 client request Address or request
Prefix.
After configuring the parameters of this page,
click it to add a new PVC into the Current
ATM VC Table.
Select a PVC in the Current ATM VC Table,
then modify the parameters of this PVC. After
finishing, click it to apply the settings of this
PVC.
Select a PVC in the Current ATM VC Table,
and then click Delete to delete it
This table shows the existed PVCs. It shows
the interface name, channel mode, VPI/VCI,
encapsulation mode, local IP address,
remote IP address and other information. The
maximum item of this table is eight.
16
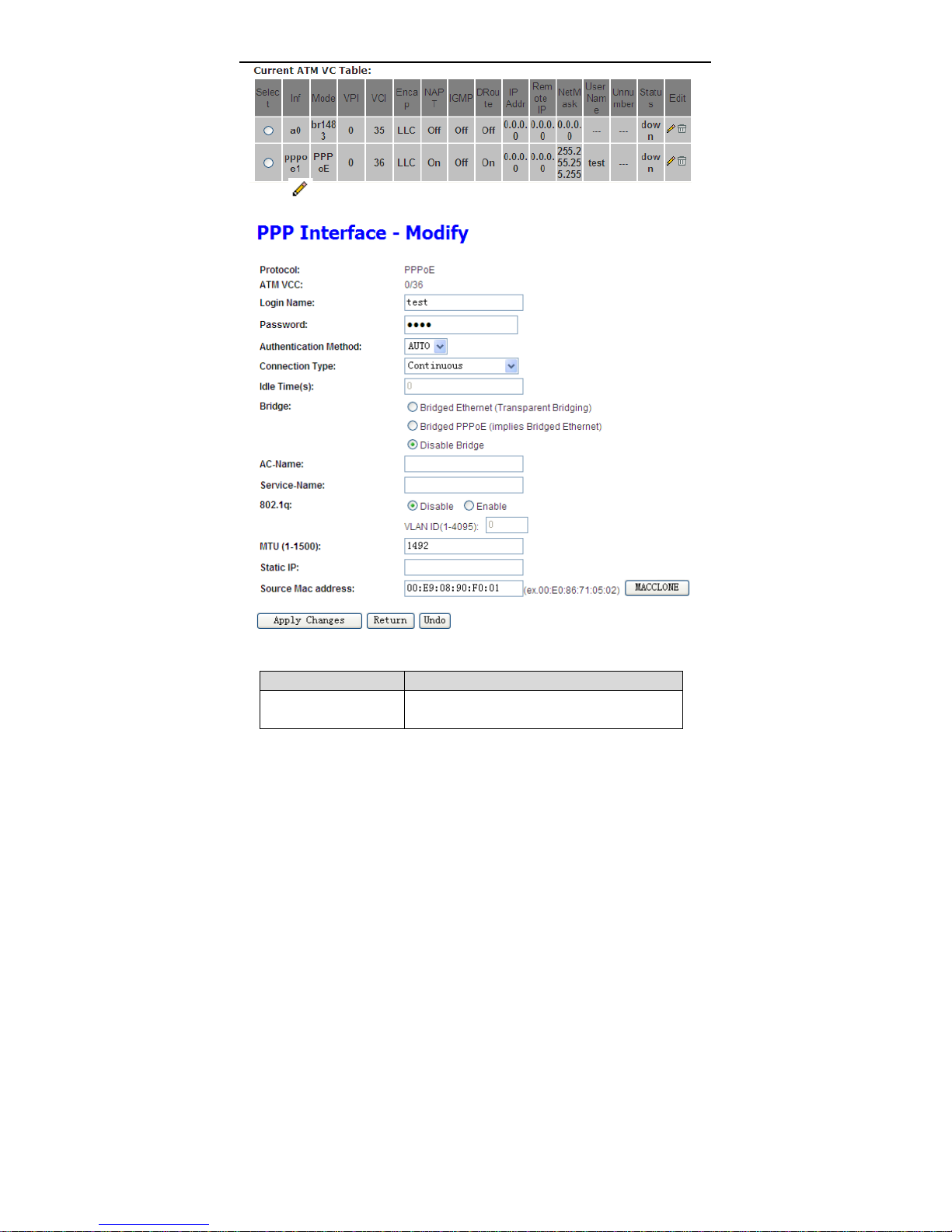
User Manual
Click
this page, you can configure parameters of this PPPoE PVC.
in the PPPoE mode, the page shown in the following figure appears. In
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page.
Field Description
Protocol It displays the protocol type used for this WAN
connection.
17

User Manual
Field Description
ATM VCC The ATM virtual circuit connection assigned for
this PPP interface (VPI/VCI).
Login Name The user name provided by your ISP.
Password The password provided by your ISP.
Authentication Method You can choose AUTO, PAP or CHAP.
Connection Type You can choose Continuous, Connect on
Demand or Manual.
Idle Time (s) If choose Connect on Demand, you need to
enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset
minutes, if the router does not detect the flow of
the user continuously, the router automatically
disconnects the PPPoE connection.
Bridge You can select Bridged Ethernet, Bridged
PPPoE or Disable Bridge.
AC-Name The accessed equipment type.
Service-Name The service name.
802.1q You can select Disable or Enable. After enable
it, you need to enter the VLAN ID. The value
ranges from 1 to 4095.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page
temporarily.
Return Click it to return to the Channel Configuration
page.
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
Source Mac address The MAC address you want to clone.
MAC Clone Click it to enable the MAC Clone function with
the MAC address that is configured.
3.4.1.2 Automatically PVC
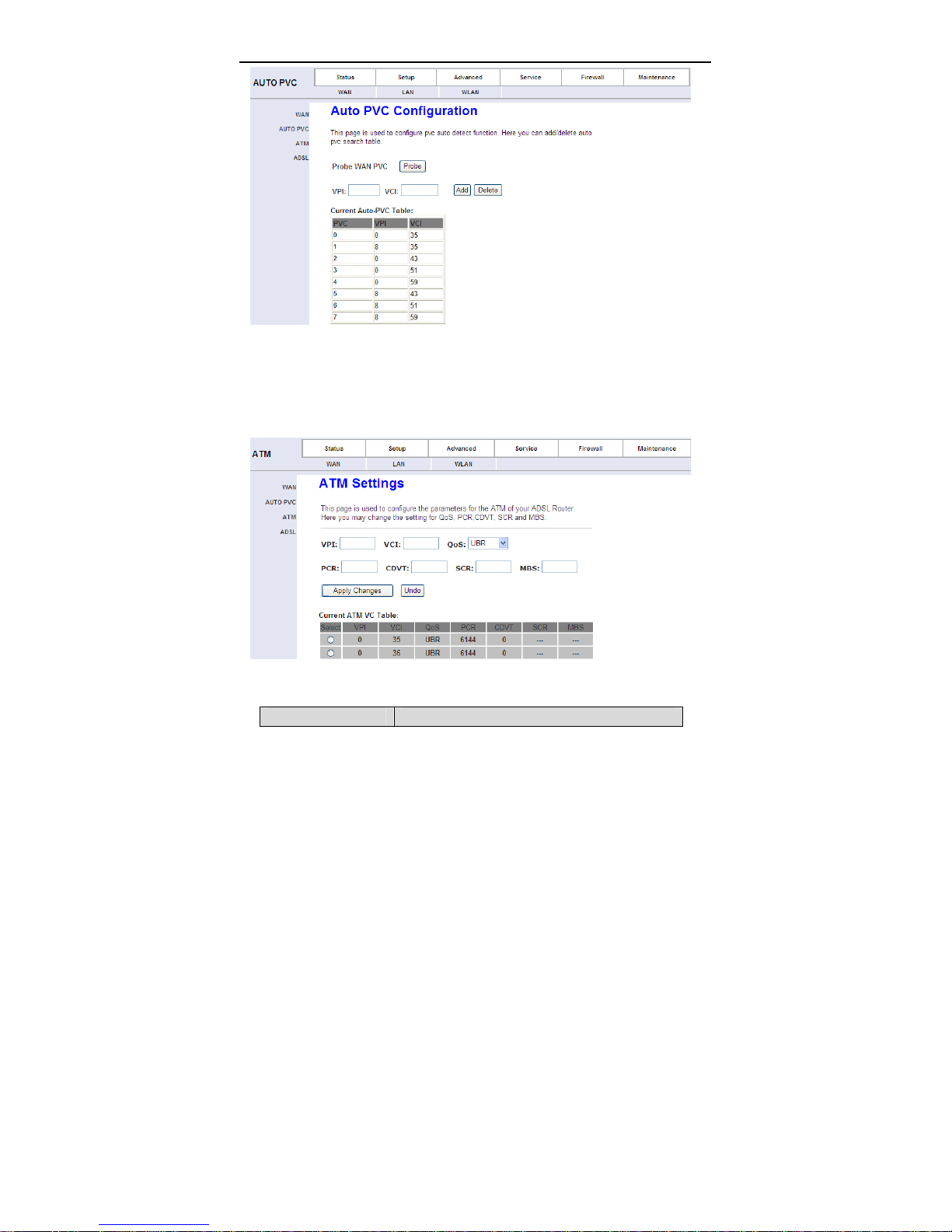
Click Auto PVC in the left pane, page shown in the following figure appears. In
this page, you can get PVC automatically through detecting function, and add or
delete the PVC that you do not want.
18
User Manual
3.4.1.3 ATM Setting
Click AT M Setti ng in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can configure the parameters of the ATM, including
QoS, PCR, CDVT, SCR and MBS.
The following table describes the parameters of this page.
Field Description
19
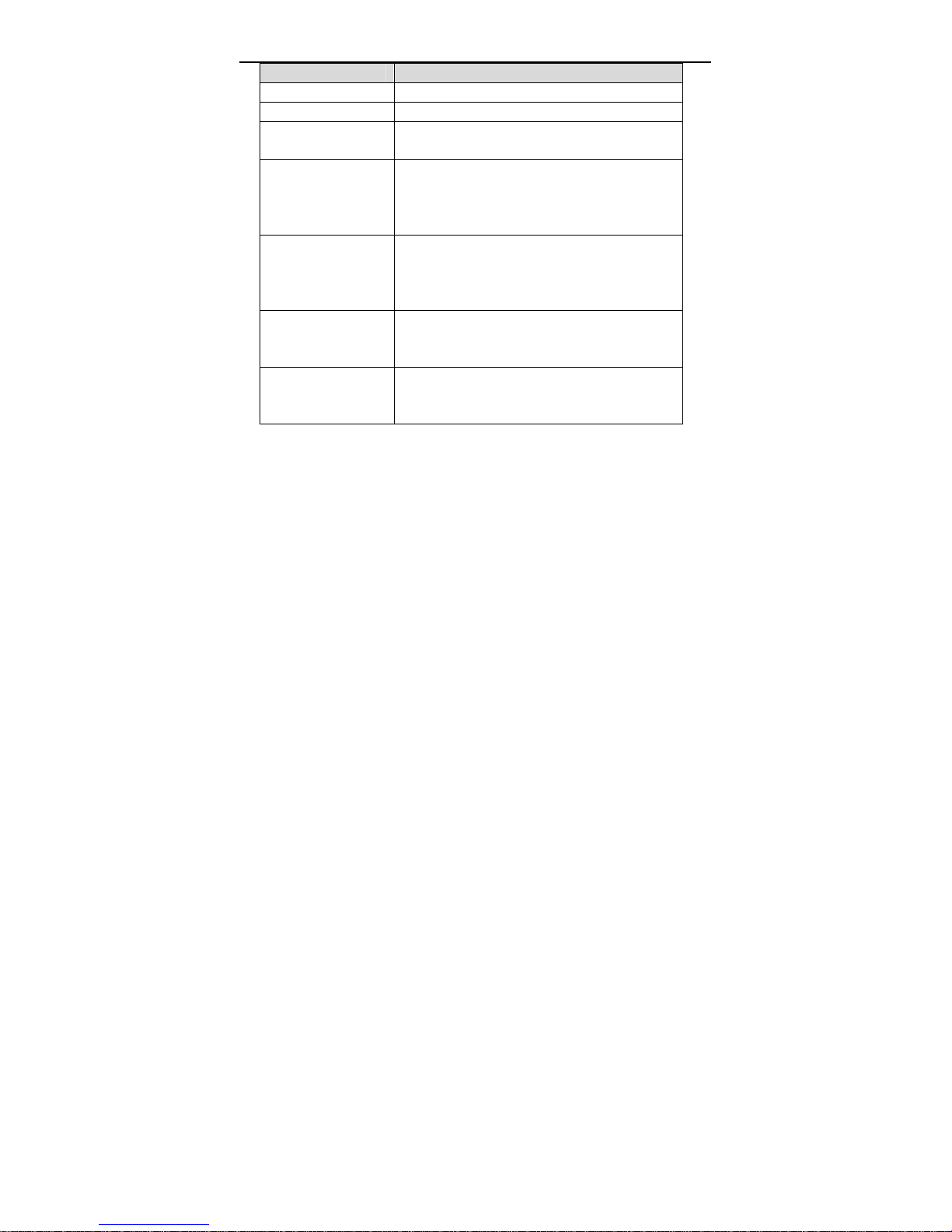
User Manual
Field Description
VPI The virtual path identifier of the ATM PVC.
VCI The virtual channel identifier of the ATM PVC.
QoS The QoS category of the PVC. You can choose
UBR, CBR, rt-VBR or nrt-VBR.
PCR Peak cell rate (PCR) is the maximum rate at
which cells can be transmitted along a connection
in the ATM network. Its value ranges from 1 to
65535.
CDVT Cell delay variation tolerance (CDVT) is the
amount of delay permitted between ATM cells (in
microseconds). Its value ranges from 0 to
4294967295.
SCR Subtain cell rate (SCR) is the maximum rate tha t
traffic can pass over a PVC without the risk of cell
loss. Its value ranges from 0 to 65535.
MBS Maximum burst size (MBS) is the maximum
number of cells that can be transmitted at the
PCR. Its value ranges from 0 to 65535.
3.4.1.4 ADSL Setting
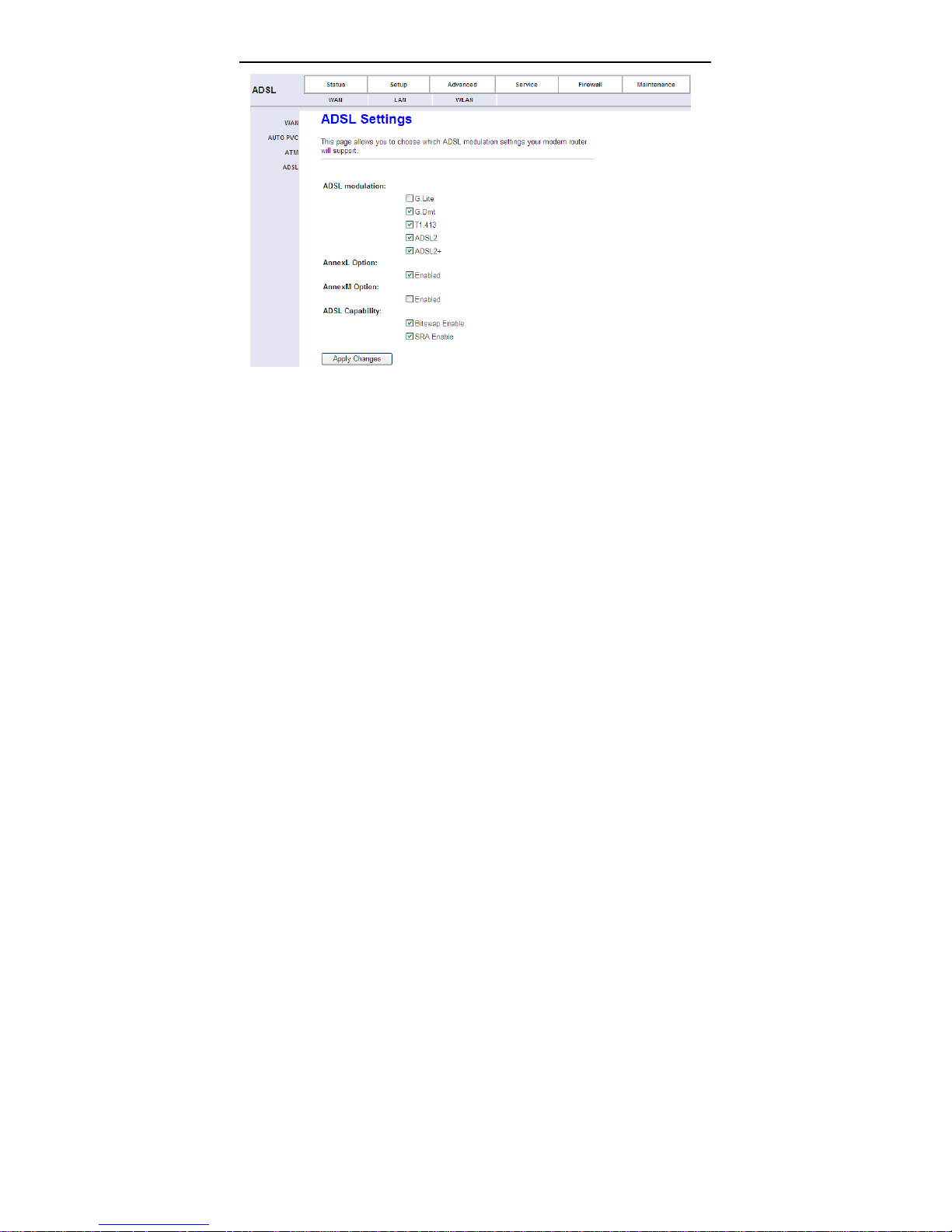
Click ADSL Setting in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can select the DSL modulation. Generally you need to
remain this factory default settings. The router negotiates the modulation modes
with the DSLAM.
20
User Manual
3.4.2 LAN
3.4.2.1 LAN
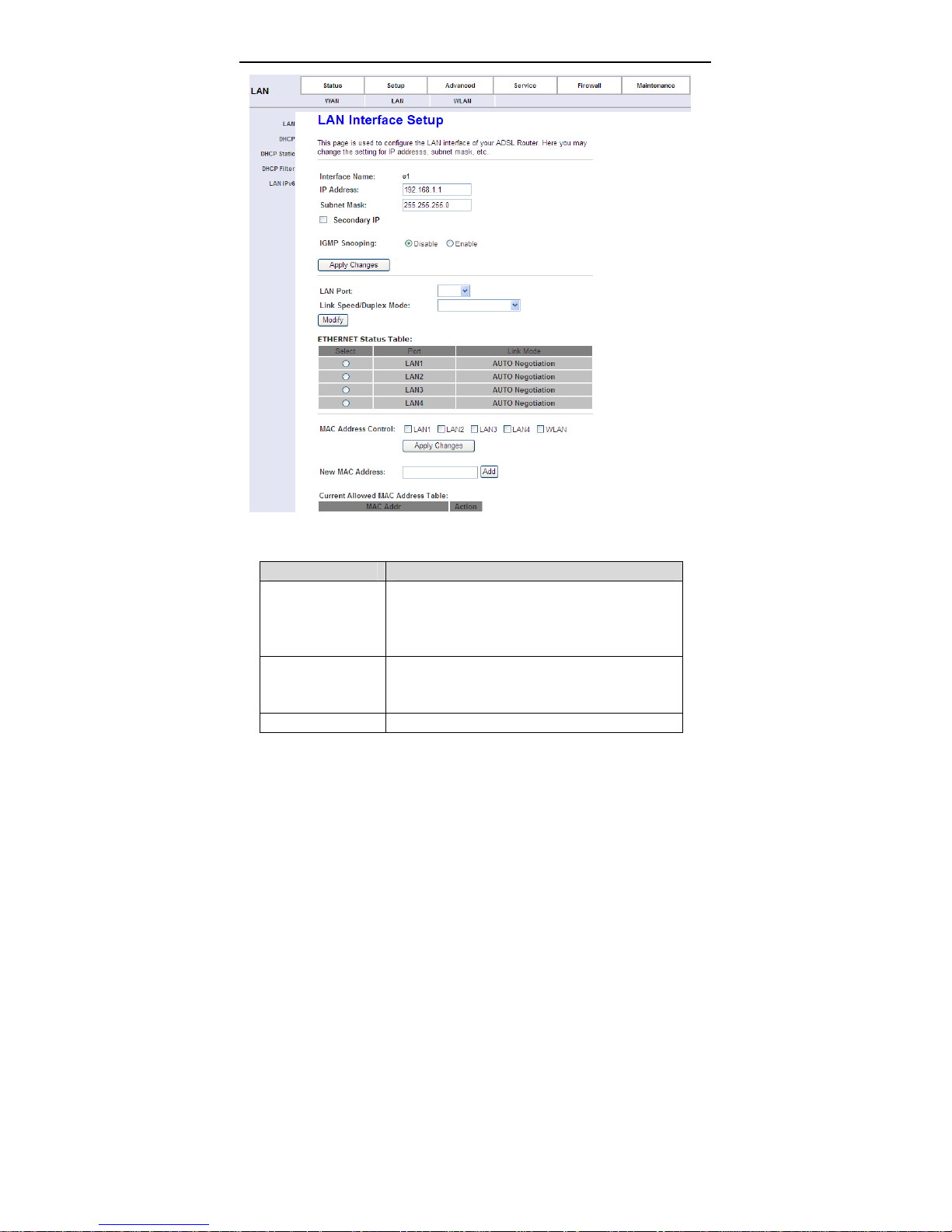
Click LAN in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
In this page, you can change IP address of the router. The default IP address is
192.168.1.1, which is the private IP address of the router.
21
User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page.
Field Description
Enter the IP address of LAN interface. It is
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Secondary IP Select it to enable the secondary LAN IP address.
recommended to use an address from a block that
is reserved for private use. This address block is
192.168.1.1- 192.168.255.254.
Enter the subnet mask of LAN interface. The range
of subnet mask is from
255.255.0.0-255.255.255.254.
22
User Manual
Field Description
The two LAN IP addresses must be in the different
network.
LAN Port
Link Speed/Duplex
Mode
Modify
Ethernet Status
Table
MAC Address
Control
New MAC Address A MAC address to be added.
Current Allowed
MAC Address
Table
You can choose the LAN interface you want to
configure.
You can select the following modes from the
drop-downlist:100Mbps/FullDuplex,100Mbps/Half
Duplex,10Mbps/FullDuplex,10Mbps/Half Duplex
and Auto Negotiation.
Select the index from Ethernet status table, and
then click modify.
It shows the current Ethernet status list.
Select the LAN interface on which you want to run
MAC Address Control.
It shows the current allowed MAC address list.
3.4.2.2 DHCP
Click DHCP in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
23

User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page.
Field Description
If set to DHCP Server, the router can assign IP
DHCP Mode
IP Pool Range
Pool Size It allows the size machines that can be set up
Show Client
Default Gateway Enter the default gateway of the IP address pool.
Max Lease Time
addresses, IP default gateway and DNS Servers to
the host in Windows95, Windows NT and other
operation systems that support the DHCP client.
It specifies the first IP address in the IP address pool.
The router assigns IP address that base on the IP
pool range to the host.
Click it, the Active DHCP Client Table appears. It
shows IP addresses assigned to clients.
The lease time determines the period that the host
retains the assigned IP addresses before the IP
24
 Loading...
Loading...