Page 1
DI-304
ISDN/DSL Router
User’s Guide
Third Edition (DEC 2004)
DI304..…A3
Printed in Taiwan
RECYCLABLE
Page 2

Copyright Statement
Copyright ©2002 D-Link Corporation
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used
to make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without
permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems Inc., as stipulated by the
United States Copyright Act of 1976.
Trademarks
D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc.
All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in
a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void your authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference in which case
the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Page 3

Limited Warranty
Hardware:
D-Link warrants each of its hardware products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials under
normal use and service for a period commencing on the date of purchase from D-Link or its Authorized
Reseller and extending for the length of time stipulated by the Authorized Reseller or D-Link Branch Office
nearest to the place of purchase.
This Warranty applies on the condition that the product Registration Card is filled out and returned to a
D-Link office within ninety (90) days of purchase. A list of D-Link offices is provided at the back of this
manual, together with a copy of the Registration Card.
If the product proves defective within the applicable warranty period, D-Link will provide repair or
replacement of the product. D-Link shall have the sole discretion whether to repair or replace, and
replacement product may be new or reconditioned. Replacement product shall be of equivalent or better
specifications, relative to the defective product, but need not be identical. Any product or part repaired by
D-Link pursuant to this warranty shall have a warranty period of not less than 90 days, from date of such
repair, irrespective of any earlier expiration of original warranty period. When D-Link provides replacement,
then the defective product becomes the property of D-Link.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting a D-Link office within the applicable warranty period, and
requesting a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number. If a Registration Card for the product in
question has not been returned to D-Link, then a proof of purchase (such as a copy of the dated purchase
invoice) must be provided. If Purchaser's circumstances require special handling of warranty correction, then
at the time of requesting RMA number, Purchaser may also propose special procedure as may be suitable to
the case.
After an RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged securely in the original or other
suitable shipping package to ensure that it will not be damaged in transit, and the RMA number must be
prominently marked on the outside of the package. The package must be mailed or otherwise shipped to
D-Link with all costs of mailing/shipping/insurance prepaid. D-Link shall never be responsible for any
software, firmware, information, or memory data of Purchaser contained in, stored on, or integrated with any
product returned to D-Link pursuant to this warranty.
Any package returned to D-Link without an RMA number will be rejected and shipped back to Purchaser at
Purchaser's expense, and D-Link reserves the right in such a case to levy a reasonable handling charge in
addition mailing or shipping costs.
Software:
Warranty service for software products may be obtained by contacting a D-Link office within the applicable
warranty period. A list of D-Link offices is provided at the back of this manual, together with a copy of the
Registration Card. If a Registration Card for the product in question has not been returned to a D-Link office,
then a proof of purchase (such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice) must be provided when requesting
warranty service. The term "purchase" in this software warranty refers to the purchase transaction and
resulting license to use such software.
D-Link warrants that its software products will perform in substantial conformance with the applicable
product documentation provided by D-Link with such software product, for a period of ninety (90) days from
the date of purchase from D-Link or its Authorized Reseller. D-Link warrants the magnetic media, on which
D-Link provides its software product, against failure during the same warranty period. This warranty applies
to purchased software, and to replacement software provided by D-Link pursuant to this warranty, but shall
not apply to any update or replacement which may be provided for download via the Internet, or to any update
which may otherwise be provided free of charge.
D-Link's sole obligation under this software warranty shall be to replace any defective software product with
product which substantially conforms to D-Link's applicable product documentation. Purchaser assumes
responsibility for the selection of appropriate application and system/platform software and associated
reference materials. D-Link makes no warranty that its software products will work in combination with any
hardware, or any application or system/platform software product provided by any third party, excepting only
such products as are expressly represented, in D-Link's applicable product documentation as being
compatible. D-Link's obligation under this warranty shall be a reasonable effort to provide compatibility, but
D-Link shall have no obligation to provide compatibility when there is fault in the third-party hardware or
software. D-Link makes no warranty that operation of its software products will be uninterrupted or
absolutely error-free, and no warranty that all defects in the software product, within or without the scope of
D-Link's applicable product documentation, will be corrected.
D-Link Offices for Registration and Warranty Service
The product's Registration Card, provided at the back of this manual, must be sent to a D-Link office. To
obtain an RMA number for warranty service as to a hardware product, or to obtain warranty service as to a
Page 4

software product, contact the D-Link office nearest you. An address/telephone/fax/e-mail/Web site list of
D-Link offices is provided in the back of this manual.
Page 5

Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
1. Bitte lesen Sie sich diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den spätern Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen. Vervenden Sie keine Flüssig- oder
Aerosolreiniger. Am besten dient ein angefeuchtetes Tuch zur Reinigung.
4. Um eine Beschädigung des Gerätes zu vermeiden sollten Sie nur Zubehörteile verwenden, die vom
Hersteller zugelassen sind.
5. Das Gerät is vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sichern Stand zu achten. Ein Kippen oder Fallen könnte
Verletzungen hervorrufen. Verwenden Sie nur sichere Standorte und beachten Sie die Aufstellhinweise
des Herstellers.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen zur Luftzirkulation die das Gerät vor Überhitzung schützt. Sorgen Sie
dafür, daß diese Öffnungen nicht abgedeckt werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Die Netzanschlußsteckdose muß aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit einen Schutzleiterkontakt
haben.
10. Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen kann. Es sollete auch nichts auf der
Leitung abgestellt werden.
11. Alle Hinweise und Warnungen die sich am Geräten befinden sind zu beachten.
12. Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten Sie es vom Stromnetz trennen.
Somit wird im Falle einer Überspannung eine Beschädigung vermieden.
13. Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät gelangen.
Dies könnte einen Brand bzw. Elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
14. Öffnen Sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit nur von
authorisiertem Servicepersonal geöffnet werden.
15. Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen und von einer qualifizierten
Servicestelle zu überprüfen:
a – Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sint beschädigt.
b – Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c – Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
d – Wenn das Gerät nicht der Bedienungsanleitung ensprechend funktioniert oder Sie mit Hilfe dieser
Anleitung keine Verbesserung erzielen.
e – Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f – Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
16. Bei Reparaturen dürfen nur Orginalersatzteile bzw. den Orginalteilen entsprechende Teile verwendet
werden. Der Einsatz von ungeeigneten Ersatzteilen kann eine weitere Beschädigung hervorrufen.
17. Wenden Sie sich mit allen Fragen die Service und Repartur betreffen an Ihren Servicepartner. Somit
stellen Sie die Betriebssicherheit des Gerätes sicher.
18. Zum Netzanschluß dieses Gerätes ist eine geprüfte Leitung zu verwenden, Für einen Nennstrom bis 6A
und einem Gerätegewicht grőßer 3kg ist eine Leitung nicht leichter als H05VV-F, 3G, 0.75mm2
einzusetzen
Page 6

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................. 1
Product Features ................................................................................................ 1
Ease of Installation.................................................................1
Built-in Switch....................................................................... 2
ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) ..........................................2
Dial On Demand ....................................................................2
Bandwidth On Demand..........................................................2
Full Network Management ....................................................2
PPP Security ..........................................................................2
RIP-1/RIP-2 ........................................................................... 2
DHCP Support (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) ...... 2
Networking Compatibility .....................................................3
Firmware Upgrade (TFTP) Server......................................... 3
Web (HTTP) Server...............................................................3
Remote Access Server (RAS)................................................3
Domain Name Server (DNS) Proxy ......................................3
Telnet Terminal Server ..........................................................3
Built-in Flash ROM ............................................................... 3
Point-to-Point over Ethernet (PPPoE) Client Support...........3
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) Client Support ...4
Firewall ..................................................................................4
Remote Management .............................................................4
Applications for your DI-304 ............................................................................. 4
Internet Access....................................................................... 4
Network Address Translation (NAT) .................................... 4
LAN-to-LAN Enterprise Connections...................................4
Remote Dial-In Server ...........................................................4
What This Manual Covers .................................................................................. 5
What This Manual Doesn’t Cover...................................................................... 6
Other Resources ................................................................................................. 6
Packing List ........................................................................................................ 6
Additional Installation Requirements................................................................. 6
INSTALLATION & SETUP ................................................................................7
Before You Start.................................................................................................. 7
Ordering Your ISDN Line........................................................7
The DI-304 Front Panel ..................................................................................... 8
The DI-304 Rear Panel....................................................................................... 9
Hardware Installation ...................................................................................... 10
Connecting the Power Adapter ............................................10
Connecting to the Ethernet ..................................................10
Page 7

Connecting to an ISDN BRI Line........................................11
Connecting to a DSL/Cable Modem.................................... 11
Setting Up a Management PC.............................................. 12
Checking the Network IP Configuration .............................12
Configuring the TCP/IP Protocol ........................................13
Checking TCP/IP Settings ................................................... 15
Using the Smart Start Wizard ..............................................16
Using the Web Configurator................................................20
BASIC CONFIGURATION AND INTERNET ACCESS............................................ 24
Changing the Administrator Password ................................24
Configuring Ethernet TCP/IP Address and DHCP Server ..24
Configuring the ISDN Interface ..........................................26
Internet Access Setup............................................................. 26
ISDN Dial-up Internet Access ...............................................28
Dialing to Dual ISPs ............................................................ 29
DSL/Cable Modem Internet Access.......................................31
Using PPTP with a DSL Modem......................................... 33
Using a Static IP with a DSL/Cable Modem .......................34
Configuring ISDN Dial Backup ..........................................36
REMOTE ACCESS........................................................................................ 37
Remote Dial-In Access...........................................................37
Creating an Access Account for a Dial-in User...................38
LAN-to-LAN Access .............................................................40
Activating the Dial-In Capability ........................................41
Creating a LAN-to-LAN Dialer Profile...............................42
ADVANCED SETUP ......................................................................................47
Enabling the Remote Activation Function.............................47
Call Control Setup ...............................................................48
PPP/MP Dial-Out Setup.......................................................48
Bandwidth On Demand (BOD) Setup ................................. 49
Call Schedule Setup ...............................................................50
NAT Setup..............................................................................50
Static Route Setup ..................................................................54
IP Filter/Firewall Setup ..........................................................55
SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...............................................................................63
Online Status ..........................................................................63
Time Setup ............................................................................. 65
Management Setup.................................................................65
Diagnostic Tools ....................................................................67
Reboot System........................................................................73
Firmware Upgrade..................................................................74
PPENDIX A – TROUBLESHOOTING AND FAQS............................................. 75
A
Page 8

Using the Telnet Terminal Commands .................................. 75
Viewing Call Logs .................................................................76
Viewing ISDN Logs ............................................................77
Viewing PPP Logs ...............................................................77
Viewing WAN Logs ............................................................77
FAQs................................................................................................................. 78
APPENDIX B – BASIC IP CONCEPTS ............................................................ 79
IP Addresses ..................................................................................................... 79
IP Network Classes ................................................................ 80
Subnet Mask...................................................................................................... 81
APPENDIX C – IP PROTOCOL AND PORT NUMBERS.......................................82
IP Protocol Numbers ........................................................................................ 82
IP Port Numbers............................................................................................... 82
APPENDIX D - TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS .................................................. 83
INDEX ........................................................................................................ 85
Page 9

Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of a D-Link DI-304 remote access router with
integrated Ethernet switch and ISDN TA. No larger than an ordinary modem, your
router offers inexpensive yet complete telecommunications and internetworking
solutions for your home or branch office. It is ideal for applications such as
Internet/intranet access, Wide Area Networking, Electronic Commerce, and Remote
Network Access.
This complete solution also includes remote dial-in user support, an Internet singleuser account (Network Address Translation) option, extensive network management
capabilities, and solid security features.
The DI-304 provides multiple users with efficient and reliable access over a single
ISDN BRI, DSL line, or Cable Modem (Dynamic IP is not supported) service to the
Internet and corporate LAN for using E-mail, sharing documents, Web surfing, file
transfers, etc. Moreover, the provision of a built-in four-port Fast Ethernet Switch
and one Uplink port may give cost-effective workgroup connectivity over Ethernet.
In addition to improving the productivity of employee, flexible telecommuting
access, and affordable management cost, the DI-304 accommodates room
for business growth from 4 computers or more.
The broadband access protocol supports PPPoE, PPTP, and Static IP. These
protocols comply with worldwide Ethernet-based DSL/Cable Modem standards.
The Router provides seamless migration from ISDN to a broadband connection for
multiple SOHO users and easy usage of ISDN for backup-dial and/or remote access
while concurrently using the DSL/Cable modem connection.
PPPoE/PPTP allows users on the LAN interface to setup a dial-on-demand DSL
connection sharing the same IP account, and paying for only one connection. The
idle-time out function prevents wasted connection charges by shutting down the
connection when it is idle. No PPPoE/PPTP client software is required for the
computers.
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Product Features
The DI-304 router is packed with features that give it the flexibility to provide a
complete networking solution for almost any small to medium-sized office
environment.
Ease of Installation
Your DI-304 is a self-contained unit that is quick and easy to install. Physically, it
resembles an external modem; however, it is a combination ISDN router and
1
Page 10

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
Ethernet switch, and it uses twisted-pair Ethernet cables to connect to the host
network.
Built-in Switch
A dual-speed NWay switch, the DI-304 provides four ports for connecting network
end nodes—single-user computers, servers, bridges, other routers, etc.—through
standard “straight-through” twisted-pair cables and one port for making an “uplink”
connection to another hub or switch through the same type of straight-through cable
used to connect end nodes.
ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
Using a standard S/T the DI-304 supports DSS1 ISDN switches. The two ISDN Bchannels can be used independently for two destinations, or they can be bundled
together for one high-bandwidth connection supporting bandwidth-on-demand.
Dial On Demand
The Dial On Demand feature allows a DI-304 to automatically place a call to a
Remote Node whenever there is traffic coming from any workstation on the LAN
(Local Area Network) to that remote site.
Bandwidth On Demand
Bandwidth-on-Demand (BOD) for ISDN Interface: As the ISDN BRI interface has
two independent B channels, the BOD mechanism allows you to automatically
add/drop a B channel according to data traffic throughput.
Full Network Management
The DI-304 incorporates SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) support
and menu-driven network management via a Telnet connection or an embedded
Web configuration program.
PPP Security
The DI-304 supports PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP
(Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol).
RIP-1/RIP-2
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Support: Used in most LAN-to-LAN
applications. The RIP protocol exchanges routing information between routers.
DHCP Support (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows IP addresses to be
automatically and dynamically assigned to hosts on your network.
2
Page 11

Networking Compatibility
The DI-304 is compatible with remote access products from other companies such
as Ascend, Cisco, and 3Com. Additionally, Microsoft Windows 95, 98, 2000, and
Windows NT remote access capability are all supported.
Firmware Upgrade (TFTP) Server
Using this server and the Firmware Upgrade Utility software, you may easily
upgrade to the latest firmware whenever enhanced features are added.
Web (HTTP) Server
A Web browser is the most common tool used to surf the Internet. You may use
Microsoft Internet Explorer or any Netscape browser to configure the Router. It’s as
easy as surfing a Website.
Remote Access Server (RAS)
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
RAS provides remote dial-in access services for home workers, branch offices, or
telecommuters. DI-304 routers offer 10 dial-in user profiles, including an
authentication mechanism through CHAP/PAP and Calling Line Identification
(CLID), secure callback functions, and 16 Lan-to-Lan Dialer Profiles.
Domain Name Server (DNS) Proxy
The DNS proxy maintains a DNS cache, including a mapping table between domain
names and IP addresses. The proxy also remembers DNS query packets sent through
the router and saves them into its own DNS cache. For enhanced speed, when a
DNS query packet enters the router, the proxy searches its local DNS cache. If
matched, the router sends an answer to the host that sent the DNS query packet.
Only unmatched DNS queries require querying a WAN Domain Name Server.
Telnet Terminal Server
The Telnet User Interface (TUI) is an efficient method of configuring and managing
routers. It utilizes a traditional command-line user interface and is mainly for
advanced configuration, management, and troubleshooting.
Built-in Flash ROM
The Flash ROM memory saves the router firmware and configurations, even after
power down.
Point-to-Point over Ethernet (PPPoE) Client Support
If you are a DSL user, the router has a built-in PPPoE client for establishing
a DSL link connection with the ISP. There is no need to install a further PPPoE
driver on your computers.
3
Page 12

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) Client Support
Some DSL modems (e.g. Alcatel modems) only provide a PPTP local connection for
an end user computer. The DI-304 has a built-in PPTP client for establishing a DSL
link transport protocol for your entire local network. There is no need to install a
PPTP driver on your computers.
Firewall
In addition to the built-in NAT mechanism, the Router features another powerful
firewall to protect your local network or to deny specified local users access to
unauthorized network services.
Remote Management
The system manager can remotely manage the routers through an ISDN remote dialin, ISDN, or DSL WAN interface.
Applications for your DI-304
Some applications for the DI-304 include:
Internet Access
Your DI-304 supports TCP/IP protocol, which is the language used for the Internet.
It is also compatible with access servers manufactured by major vendors such as
Cisco and Ascend.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
For small office environments, the DI-304 allows multiple users on the LAN to
access the Internet concurrently through a single Internet account. This provides
Internet access to everyone in the office for the price of a single user.
NAT address mapping can also be used to link two IP domains via a LAN-to-LAN
connection.
LAN-to-LAN Enterprise Connections
The DI-304 can dial to or answer calls from another remote access router connected
to a different LAN. The DI-304 supports TCP/IP and has the capability to bridge
any Ethernet protocol.
Remote Dial-In Server
The DI-304 allows Remote Dial-in Users to dial in and gain access to your LAN.
This feature enables users that have workstations with remote access capabilities,
e.g., Windows 98, to dial in using an ISDN terminal adapter (TA) to access the
network resources without physically being in the office.
4
Page 13

What This Manual Covers
This manual is divided into thirteen parts.
♦ Chapter One, “Introduction,” describes many of the
technologies implemented in the DI-304 as well as product
features, etc.
♦ Chapter Two, “Installation and Setup,” is designed as a step-
by-step guide to installing the router. In addition, descriptions
of the front panel and rear panel are provided.
♦ Chapter Three, “Basic Configuration and Internet Access,”
provides detailed explanations for basic setup and Internet
access setup. It also covers ISDN dial-up Internet access and
DSL/cable modem Internet access.
♦ Chapter Four, “Remote Access,” provides an introduction to
remote access, including remote dial-in access and LAN-toLAN access.
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
♦ Chapter Five, “Advanced Setup,” describes how to enable the
remote activation function, and configure the BOD
parameters, as well as information relating to NAT setup and
IP filter and firewall setup.
♦ Chapter Six, “System Management,” gives detailed
explanations of online status and management setup, as well
as information pertaining to diagnostic tools and rebooting the
system.
♦ Appendix A, “Troubleshooting and FAQ,” includes some of
the most Frequently Asked Questions.
♦ Appendix B, “Basic IP Concepts,” contains a brief of some
fundamental IP concepts.
♦ Appendix C, “IP Protocol and Port Numbers,” lists many
commonly used IP settings.
♦ Appendix D, “Technical Specifications,” lists specifications
about the DI-304 ISDN router.
Regardless of the application, it is important that you follow the steps outlined in
Chapters 2, “Installation and Setup,” to correctly connect your DI-304 to your LAN.
You can then refer to other chapters of the manual depending on your specific
installation requirements.
5
Page 14

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
What This Manual Doesn’t Cover
This manual assumes that you know how to use your computer and are familiar with
your communications software. If you have questions about using either one, refer
to the manual for the product.
Other Resources
For more information about your DI-304 check the following sources:
♦ Quick Start Guide.
♦ Support disk containing Router Tools.
Packing List
Before proceeding further, check all items received with your DI-304 against this
list to make sure nothing is missing. The complete package should include:
♦ One DI-304 ISDN router.
♦ One power adapter.
♦ One Ethernet LAN cable.
♦ One ISDN cable with RJ-45 connectors.
♦ One hard copy of the Quick Installation Guide.
♦ One hard copy of the User’s Guide.
♦ One User’s Guide on CD-ROM
Additional Installation Requirements
In addition to the contents of your package, there are other hardware and software
requirements you need before you can install and use your router. These
requirements include:
♦ An ISDN line.
♦ Ethernet connection(s) to your computer(s).
After the router has been successfully connected to your network, you can make
future changes to the configuration using a Telnet client application.
6
Page 15

Installation & Setup
Before You Start
♦ Use only the power adapter supplied by D-Link Corporation (18 VAC 1A).
Using an incorrectly rated power adapter will result in damage to the router.
♦ Know the type of interface provided by your ISP or telecom. The standard model
only supports the ISDN BRI S/T-interface. If you are an ISDN U-interface user,
you need to order a U-interface model. If you are an ISDN S/T-interface user,
you should have an NT-1 or NT-1 plus provided by your ISP or telecom. Also,
make sure the ISDN line is available.
♦ In case of emergency, unplug the power adapter first.
♦ Locate the device in a clean location. Do not block the ventilating slots on the
rear panel.
♦ Cables must be attached to the correct ports; to do otherwise may result in
damage to the router. Keep cables away from walkways.
♦ If you use S/T-interface, do not extend the ISDN line greater than 100 meters
from the NT-1 (NT-1 plus) box and the router.
♦ If you use DSL/Cable, check that your subscribed DSL/Cable modem supports
the Ethernet interface for connecting to your PC. If not, you will be unable to
connect it to the router.
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Ordering Your ISDN Line
If you do not have an ISDN line installed already, we suggest that you order it from
your telephone company as soon as possible to avoid the long waiting period
common when ordering a new line. Use the information in this section to place the
order. If you have already installed your ISDN line, you can check the following
section to make sure that you can use all the features of your DI-304.
1. Contact your local telephone company’s ISDN Ordering Center.
2. Make sure DSS1 switches are available since these are the only switch types
currently supported by the DI-304.
3. When the telephone company installs your ISDN line, be sure to obtain the
following information:
◊ ISDN switch type.
◊ ISDN telephone number(s).
7
Page 16

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
Before you set up the router, you need to know the default settings of the DI-304 as
shown below:
Factory Default Settings:
Default IP Network Settings:
IP Address: 192.168.0.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
DHCP Server: Enabled
Start IP Address: 192.168.0.100
IP Pool Counts: 100
DNS Server IP Address
- Primary IP Address: empty
- Secondary IP Address: empty
Web Configurator:
Username: admin
- Password: <blank>
Note: Blank means no password required.
Telnet Console:
Password: <blank>
Note: Blank means no password required.
Management from the Internet: Not allowed
Remote Dial-In Server: Disable
IP: 192.168.0.200.
The following section outlines how to connect your DI-304 to your LAN and ISDN
line. Refer to the diagrams below to identify all of the ports on your device when
you make connections.
The DI-304 Front Panel
Names and descriptions of your router’s front panel LEDs are given below:
8
Page 17
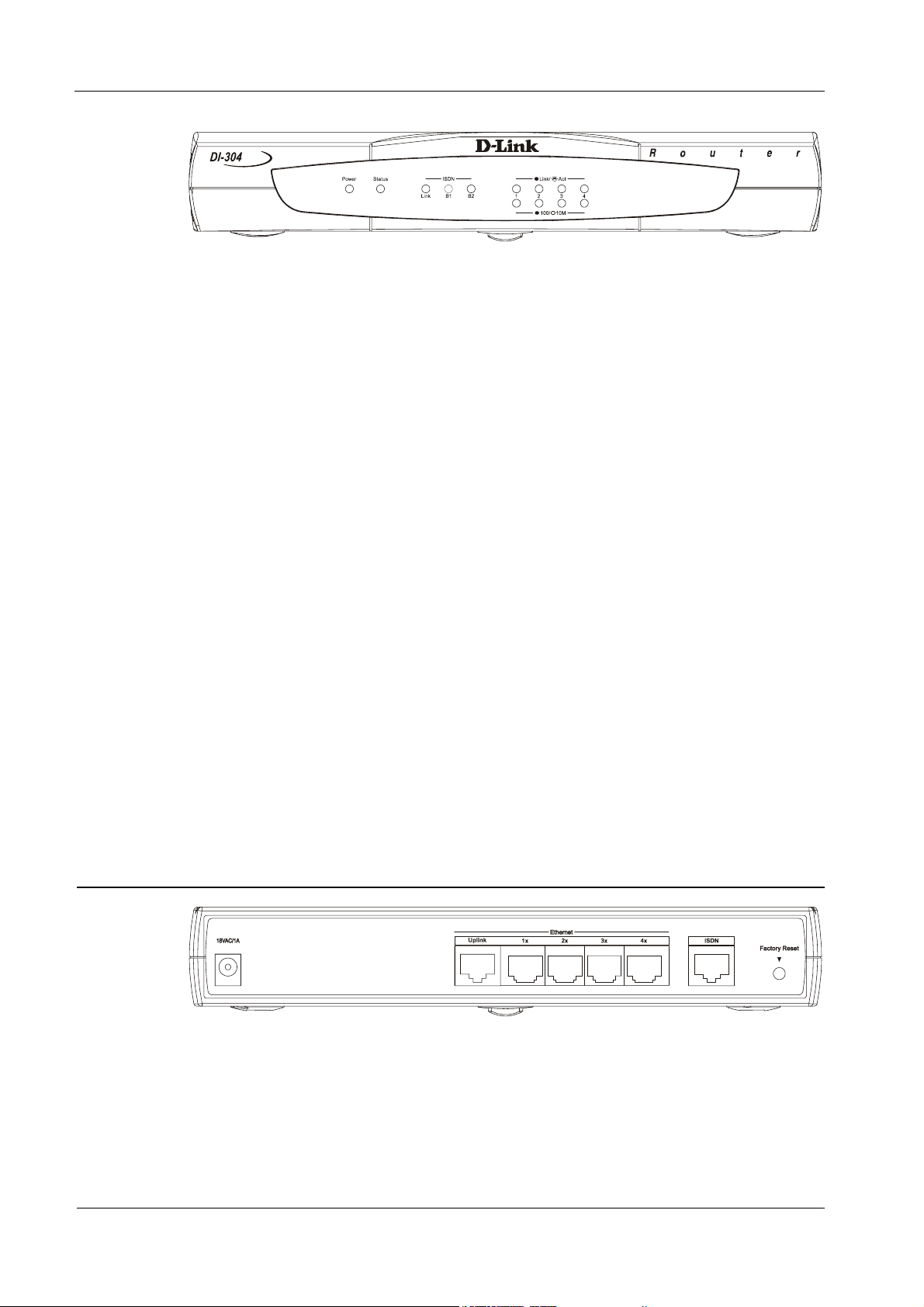
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
DI-304
♦ POWER— Comes on as soon as you connect the router to the power
adapter and plug the power adapter into a suitable AC outlet.
♦ STATUS— Should be blinking if the router is functioning properly.
♦ ISDN – LINK— Indicates that the router has an ISDN line connected to
the ISDN interface and it has been successfully initialized.
Note: On some NT1 boxes, the LINK indicator will go off when the ISDN line has
been idle for a while. When the router is dialing or answering a call, it should
be on again.
♦ ISDN – B1 and B2— On if there is an active ISDN session on that
channel or if that channel is making or receiving a call.
♦ LINK/ACT – 1 through 4 — These indicators light up when a port is
connected to a powered-on Ethernet/Fast Ethernet station. The LEDs
blink when information is transmitted or received on a port.
♦ 100/10M – 1 through 4 — These indicators light up when a port is
operating at 100Mbps. Otherwise, if this indicator is dark and the
corresponding LINK indicator is lit, then the port is operating at
10Mbps.
The DI-304 Rear Panel
DI-304
9
Page 18

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
The DI-304 has a power jack, an uplink port, four RJ-45 ports, an ISDN port on the
rear panel, and a factory reset button. Please note that only the D-Link supplied
power adapter should be connected to the power jack.
♦ POWER — This socket is an 18 volt, 750mA power input jack. If the
power adapter included with the router has been lost or misplaced,
please ensure that the replacement adapter meets both the voltage and
amperage requirements.
♦ ETHERNET – The Ethernet ports function as a normal, dual speed
NWay Ethernet switch.
♦ Uplink – This port is used to connect the router to another
switch or hub using a straight-through twisted-pair cable.
When the Uplink port is used, Port 1x is unavailable.
♦ Ports 1x to 4x – These four ports can be used to connect
end-stations to the router using straight-through cables.
♦ ISDN – This socket is used to connect the ISDN line to either an NT-1
or directly to the ISDN wall jack, depending on the type of service
delivered by your phone company.
♦ Factory Reset :
Press and hold the button. Then switch on your DI-304.
The Status LED flashes.
To reset the DI-304 to the factory settings: Press and hold the button for
5 seconds when the unit is switched on. The Status LED will flash more
quickly – at this moment, release the button and the router is reset to its
factory settings.
Hardware Installation
Connecting the Power Adapter
1. Connect the power adapter to the electrical outlet in the wall and to the power
jack on the rear panel of the router.
2. The Act LED should be blinking once every 2 seconds.
Connecting to the Ethernet
A. Connecting to PCs:
1. Attach the Ethernet cable to any P1 ~ P4 port.
10
Page 19

2. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to your PCs' installed network
interface card (NIC).
3. The LED indicators at both the Ethernet port and the NIC should be ON.
Note: If the Ethernet cable is not long enough to reach your PCs, purchase a longer
straight-through Cat. 5 UTP or STP Ethernet cable.
B. Connecting to an External Ethernet Hub:
1. Attach the Ethernet cable to the Uplink port.
2. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the external Ethernet hub or
switch.
3. The LED indicators on both the Uplink port and the external Ethernet hub
or switch should be ON.
Note: If the Ethernet cable is not long enough to reach the external hub/switch,
purchase a longer straight-through 10BASE-T Ethernet cable, or connect two
shorter cables to create a cable of sufficient length.
Connecting to an ISDN BRI Line
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
A. S/T-Interface Model
1. Locate the ISDN cable.
2. Plug one of the RJ-45 connectors on the cable into the ISDN port on the
rear panel of the router.
3. Plug the other end of the cable into any of the NT-1 (or NT1 plus) S/Tinterface ports.
B. U-Interface Model
1. Locate the ISDN cable.
2. Plug one of the RJ-45 connectors on the cable into the ISDN port on the
rear panel of the router.
3. Plug the other end of the cable into the ISDN wall outlet.
Connecting to a DSL/Cable Modem
The router supports connection of a DSL modem via an Ethernet interface only.
Non-Ethernet interface DSL modems, such as USB and ATMF-25, will not be
supported.
11
Page 20

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
1. Attach the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port of the DSL/Cable modem.
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the P1 to P4 port.
3. If the port’s LED is not bright, please change the direct cable to cross cable.
The hardware installation is now complete. The following sections will guide you
through setting up your management PC and connecting to the Web Configurator.
Setting Up a Management PC
The Router has a built-in HTTP (Web) server for configuration. Before you use the
router to access the Internet, you should set up a management PC to log into the
router for further configuration. The management PC may be configured with a
fixed or dynamically assigned IP address. For a fixed IP address, use an IP address
from a 192.168.0.0/24 network, such as 192.168.0.2. For the dynamic IP address,
you need to set the PC as a DHCP client, and then restart or renew the network
settings. The DHCP server embedded in the router is enabled by default so the PC
will then be assigned an IP address and related settings by the router. The following
examples are for a Microsoft Windows 95/98 machine set to use a dynamic IP
address. For other operating systems, please refer to the OS user manuals.
Checking the Network IP Configuration
The following explains how to setup the Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) in Windows 95/98. For more detailed information on TCP/IP
setup, refer to the Windows 95/98 help files. For other operating systems refer to the
user manuals.
1. On the desktop, right-click Network Neighborhood. Click Properties. The
Network window will open:
12
Page 21
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Your particular system may differ from the window shown here. Check if you have
an Ethernet Network Interface card (NIC) installed. If not, refer to the installation
documentation from the NIC card manufacturer and install the card and drivers.
If you have installed the NIC card,
1. Click the Add button. The Select Network Component
Type dialog box will open. This box has four options: Client, Adapter,
Protocol, and Service.
2. Select Protocol and click the Add button. The Select Network Protocol
dialog box will open.
3. Select Microsoft in the left scrolling window, then select TCP/IP on the
right, and click OK. It will return to the Network dialog box.
Configuring the TCP/IP Protocol
1. On the Network dialog box Configuration card, select TCP/IP and then click
Properties. The TCP/IP Properties dialog box will open.
13
Page 22
DI-304ISDN Remote Router
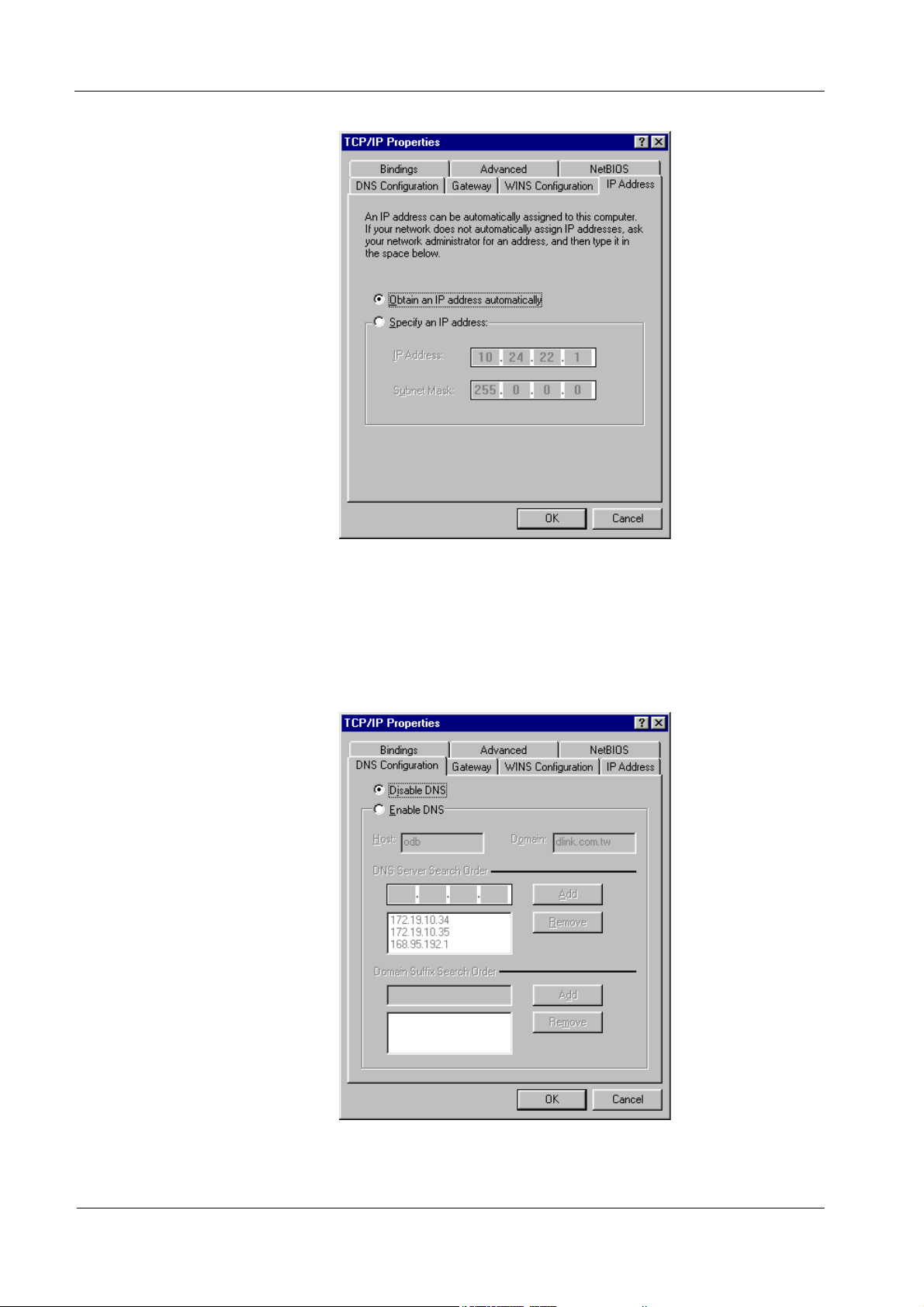
2. On the IP Address tab, click Obtain an IP address automatically. As the
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server built into the router is enabled
by default, your computer will get an IP address, subnet mask, and other related IP
network settings from the router.
3. On the DNS Configuration tab, click Disable DNS.
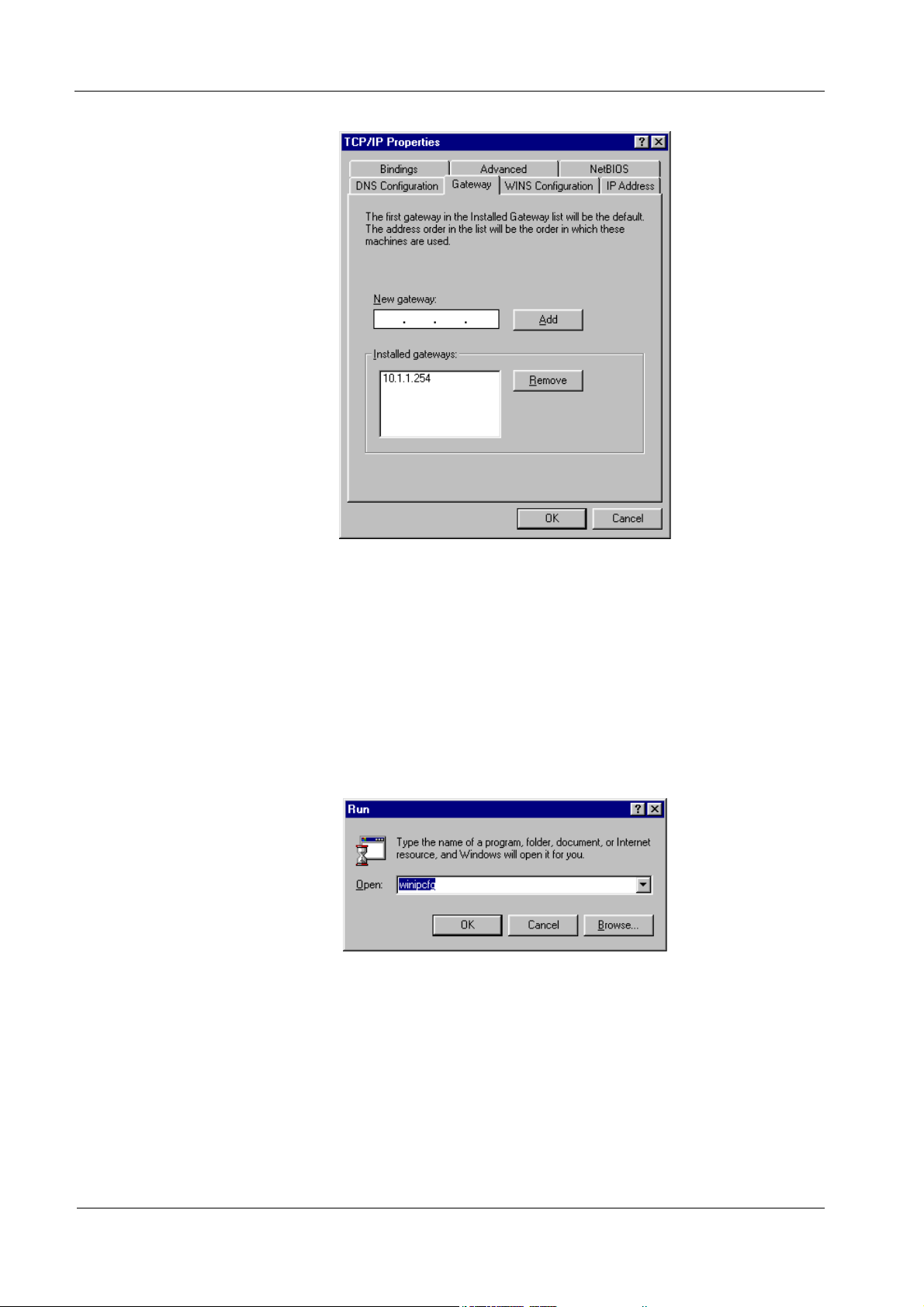
4. Click the Gateway tab.
14
Page 23
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
5. Make the New gateway and Installed gateways fields blank and click OK. A
dialog box will pop up asking you to restart the PC. Click Yes.
Checking TCP/IP Settings
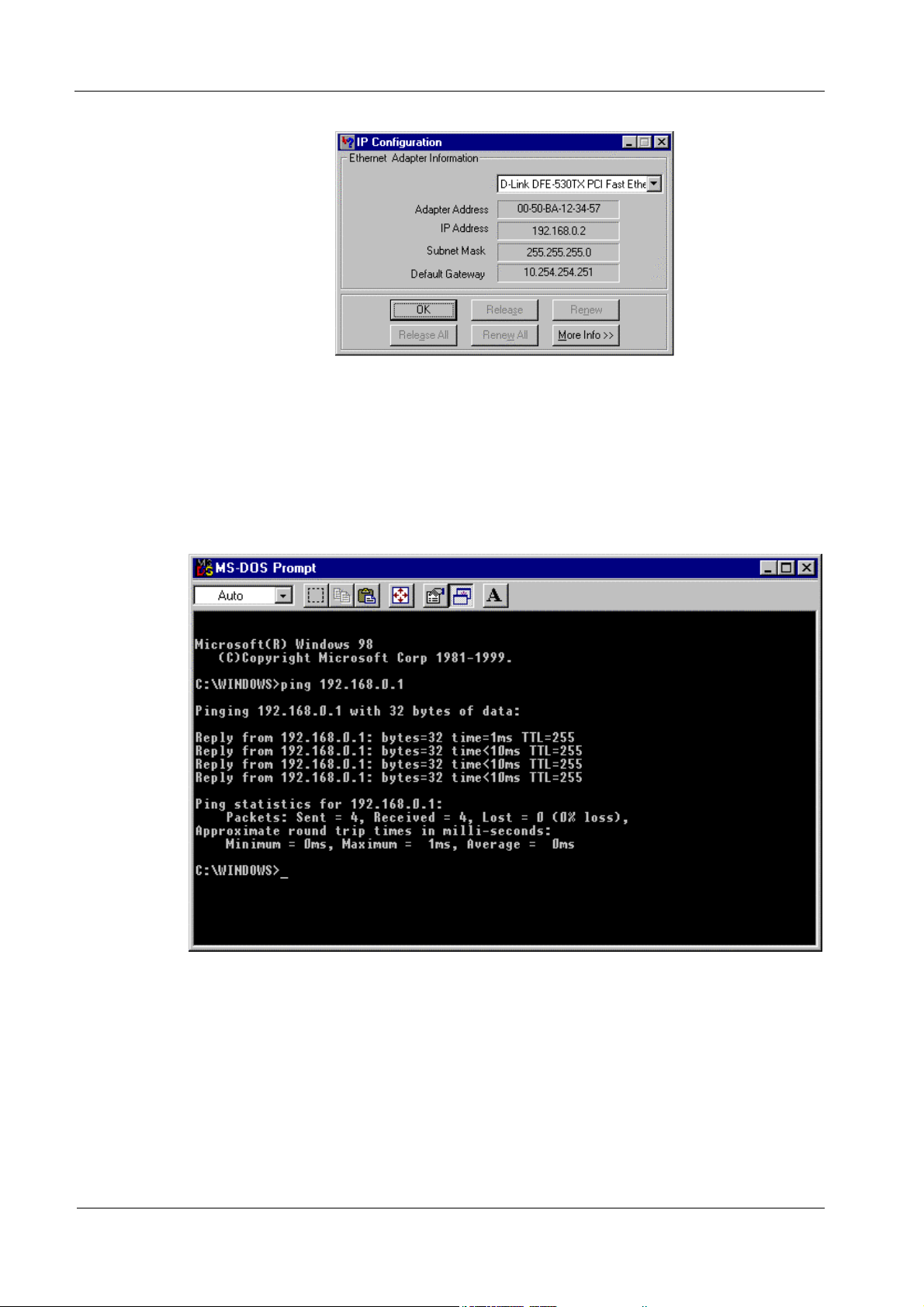
1. After completing the previous steps, click Start → Run. Click the Gateway tab
and type winipcfg. The IP Configuration window will open. If the PC does not
show an IP address in the 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.254 range, click the Release
button to release the current configuration. Wait a few seconds and click Renew to
get a new IP configuration from the router.
15
Page 24
DI-304ISDN Remote Router
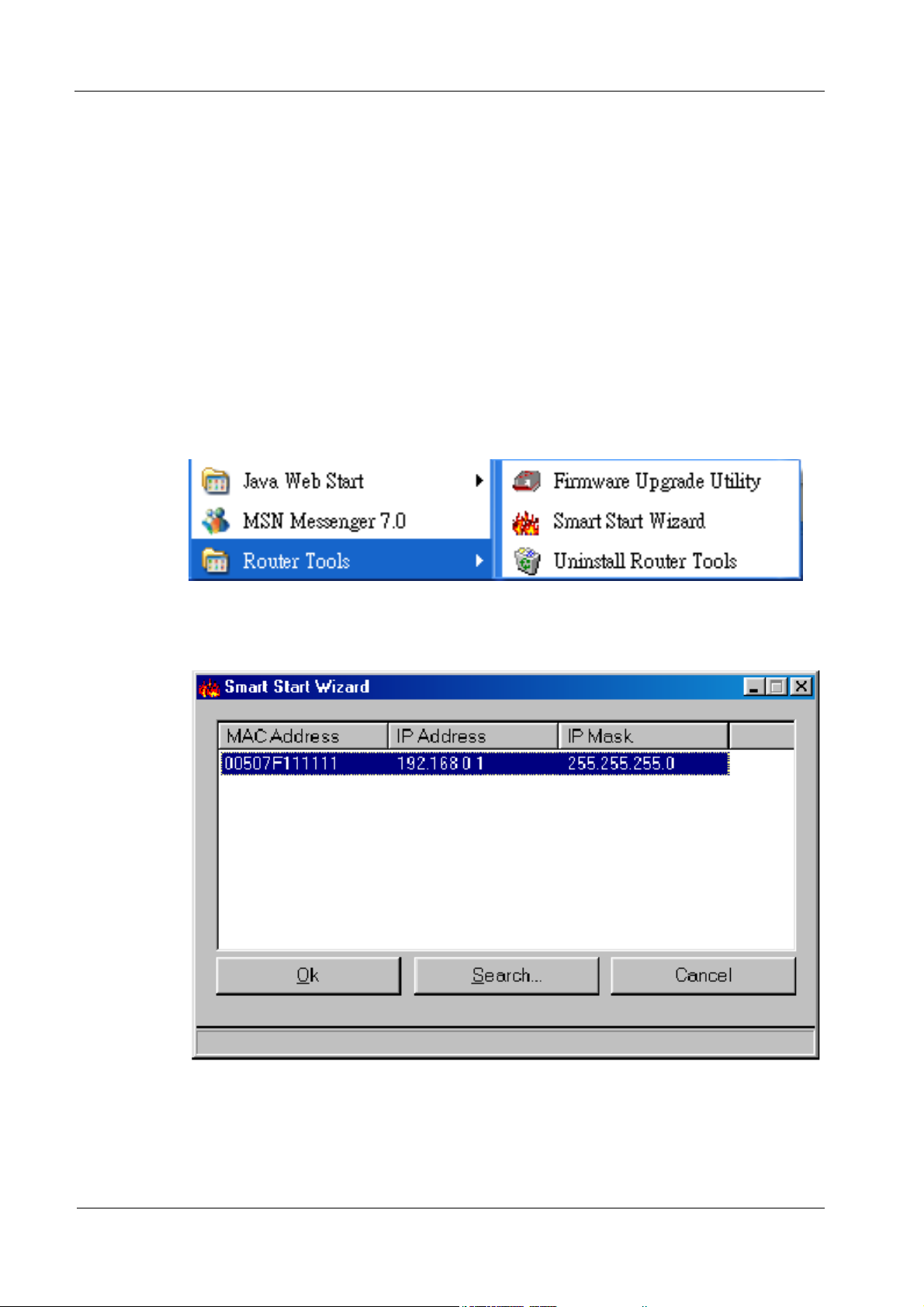
2. If the IP configuration is correct, you will be able to use the Ping diagnostic utility
built in Microsoft Windows to Ping the router. Click Start → Programs → MS-
DOS Prompt. A command mode window will open. Type ping 192.168.0.1 (default
IP of the router) to diagnose the network connectivity. If both hardware and
software are correct, your computer will receive a response from the router as shown
on the next page. If not, verify that the Ethernet cable is connected to the router
properly and the Ethernet port LED on the front panel is lit.
Using the Smart Start Wizard
The Smart Start Wizard will guide you to the Web Configurator or Telnet
Terminal (command-line based management). Also, if the network you currently
installed is not located in the 192.168.0.x IP range, the wizard will find the router
and change the router's default IP address and IP mask to match the current network.
If you are familiar with using a Web browser (Microsoft Internet Explorer, Netscape
Communicator, etc.) or Telnet client software, you may jump directly to the next
section. We suggest you use the most up-to-date version of your Web browser.
16
Page 25
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Installing the Router Tools
1. Insert the CD supplied with the router into the CD-ROM drive. The auto-run CD
will display the main menu.
Note: If auto-run fails to start the installation program, click autostart.exe on the
root directory of the CD to start the program.
2. Click Router Tools for install. The Router Tools utilities include Firmware
Upgrade Utility, Smart Start Wizard, and Uninstall Router Tools.
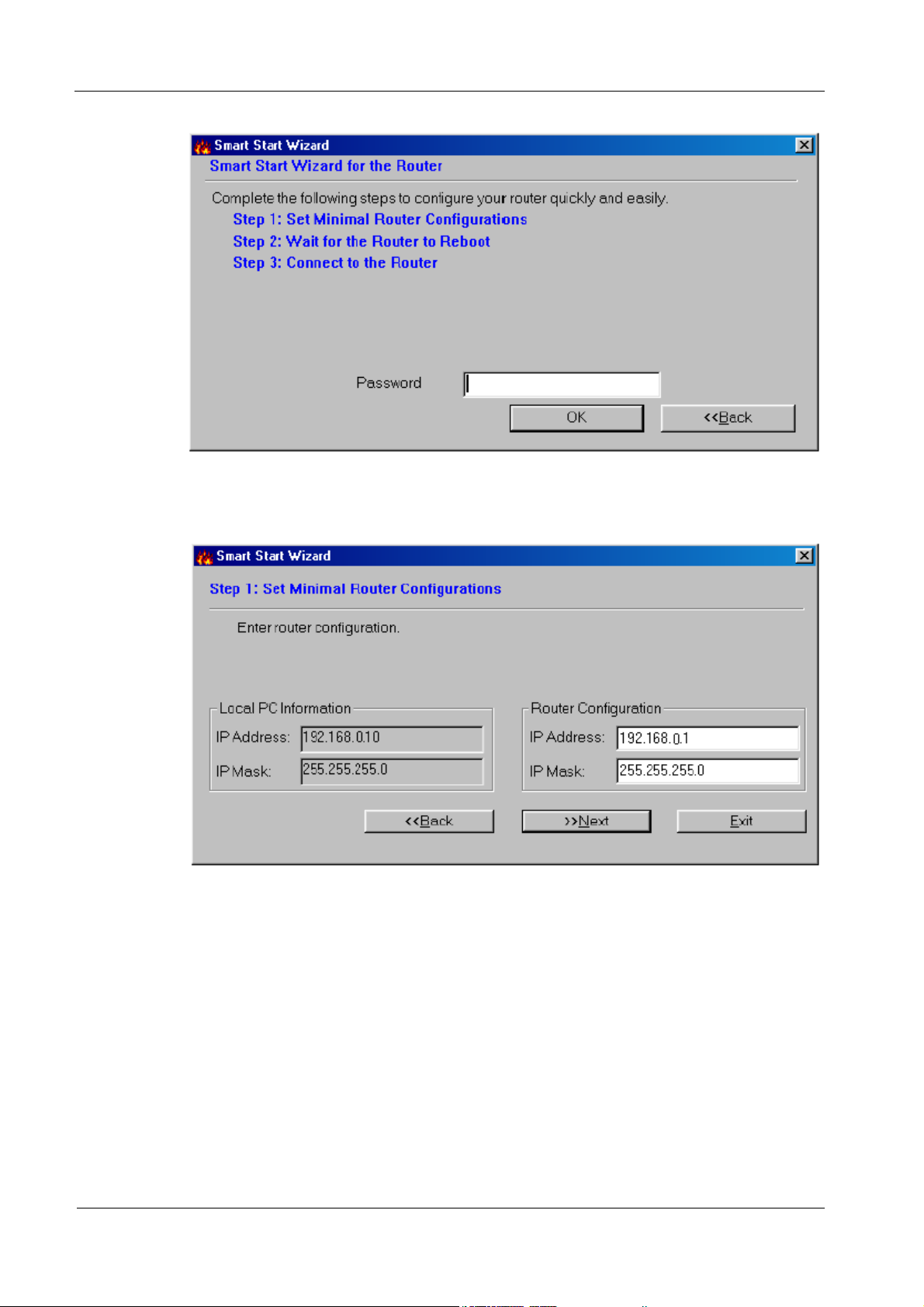
Using the Wizard
1. Click Start → Programs → Router Tools → Smart Start Wizard.
2.
The following screen will open.
2. Click Search to find the router on your network.
3. Click OK to go to the login password screen.
17
Page 26
DI-304ISDN Remote Router
4. If this is the first time you setup the router, do not enter any password. Click OK
to go to the next screen.
The screen shows read-only IP and IP mask settings for the PC you are using, and
also the IP Address and IP Mask settings for the router. Here you may change the
settings of the router to match your current network environment, or keep the default
settings.
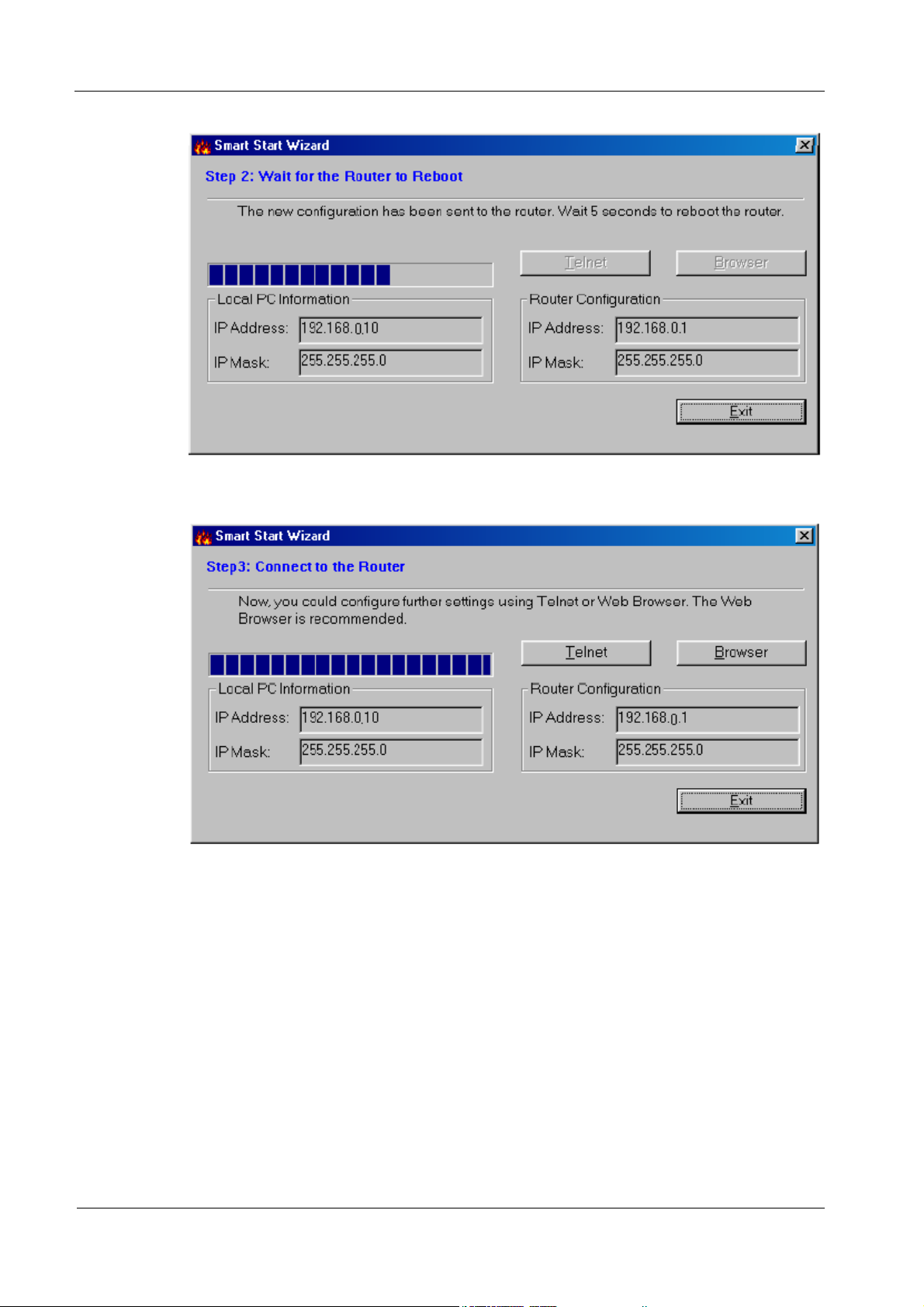
5. Click Next to update the settings of the router.
18
Page 27
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
6. Wait for a few seconds. The Telnet and the Browser will be clear (see below).
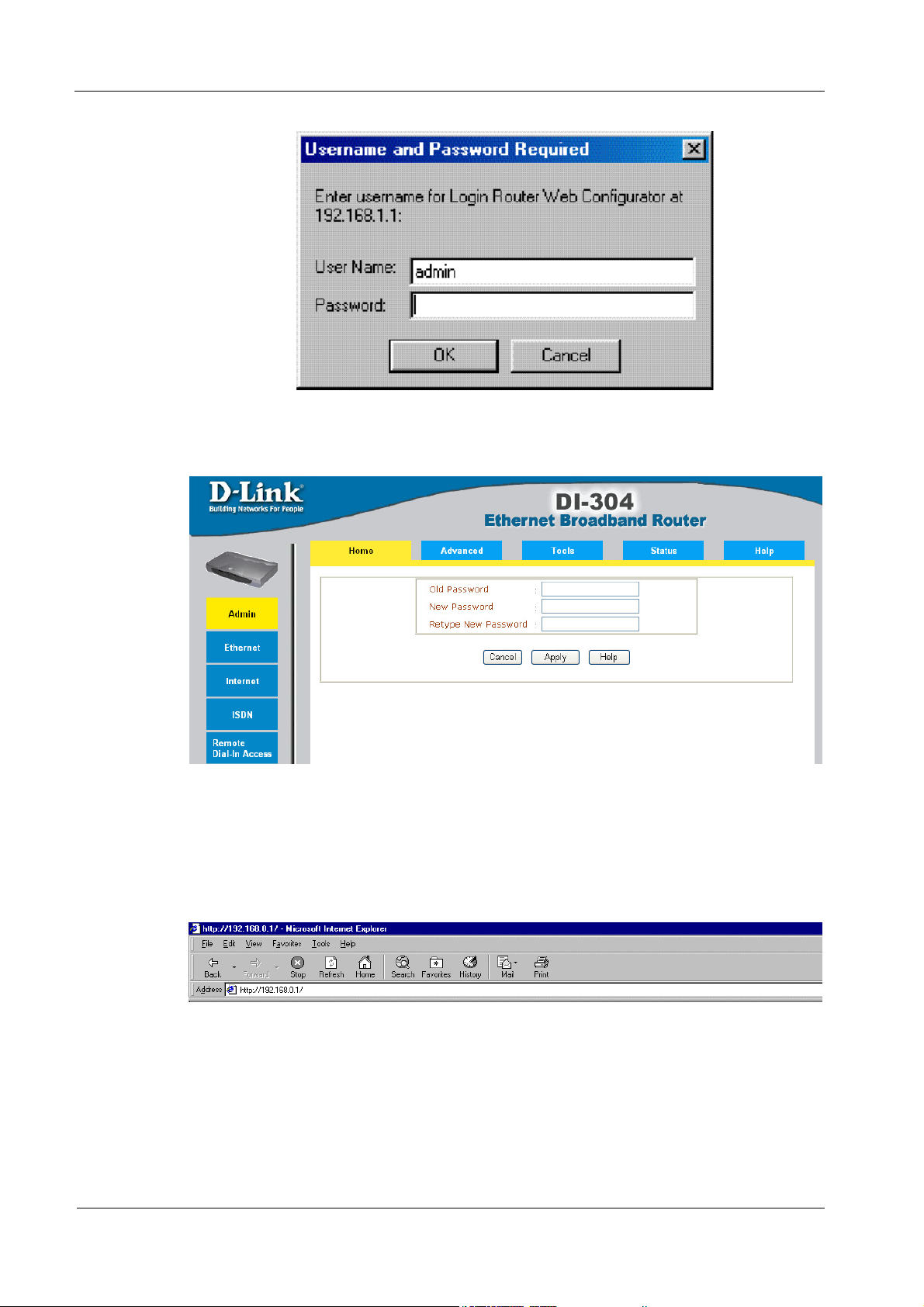
If the IP address and IP Mask of your PC and the router are not located at the same
subnet, please renew your PC's IP address using winipcfg.exe on
Windows95/98/ME or ipconfig.exe on Windows NT/2000. As the browser has been
launched, the following pop-up window will ask for User Name and Password.
19
Page 28
DI-304ISDN Remote Router
Enter admin as the User Name and leave the Password field blank. The Web
Configurator will open.
Using the Web Configurator
Connecting to the Web Configurator via a Web Browser
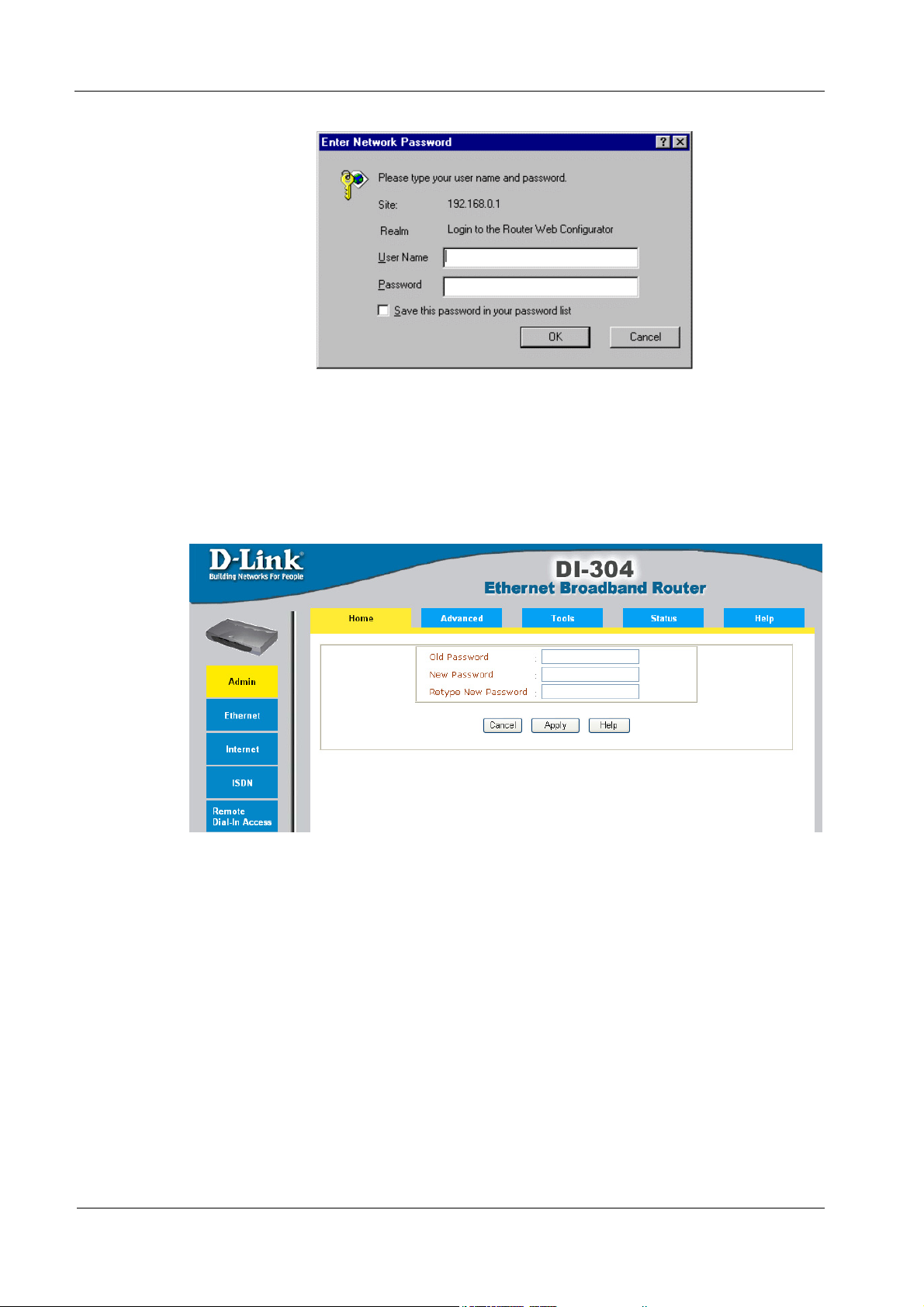
1. Launch the Web browser. Enter http://192.168.0.1 into the browser Address
window and press the Enter key.
2. An authentication dialog box will open.
20
Page 29
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
3. If this is the first time you setup the router, type admin as the User Name and
leave the Password field blank. Click OK.
4. The Web Configurator Setup Main Menu will open. On the main page, Model,
Firmware Version, Build Date/Time, and LAN MAC (Hardware) Address
information will be displayed.
Overview of the Web Configurator
The Setup Main Menu (see above figure) consists of five groups: Home, Advanced,
Tools, Status, and Help. The following will describe the outline for each
configuration menu.
Home (Setup First):
1. Admin Setup:
Sets/changes the administrator password.
2. Ethernet Setup:
Modifies the router's IP address and DHCP server settings.
3. Internet Access Setup: (required for Internet access)
21
Page 30

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
4. ISDN Setup:
5. Remote Dial-In Access Setup:
Advanced Setup:
The following settings are for advanced configurations only. These items do not
need to be configured for standard Internet access.
1. Dynamic DNS
Supports the Dynamic DNS function.
2. Call Control Setup:
3. Call Schedule Setup:
Supports totals 15 profiles for call schedule usage.
4. NAT (Network Address Translation) Setup:
5. Radius Client
This menu can be used to setup this router as a Radius client.
6. Static Route Setup:
7. Remote Dial-in User Setup:
8. LAN-to-LAN Dialer Profile Setup
9. Firewall Setup
System Management:
Usually the router functions as a border router for SOHO or home
networking so you must enter settings here to enable access to the Internet.
ISDN users need to select a country code. Sets some ISDN
numbering settings, e.g. MSN numbers and Own (Calling) numbers.
Remote access or LAN-to-LAN remote access settings are made here.
Sets bandwidth-on-demand (BOD) parameters for the MP (Multiple link
PPP) protocol. Also, some call control parameters may be set here.
Sets NAT configurations, such as Port Redirection, etc.
This menu has 10 routing rules for static routing usage. Here you may
add/delete or activate/deactivate any static route.
This menu supports 10 remote dial-in accounts for remote access
applications. You can manage these dial-in accounts under the setup menu.
The LAN-to-LAN Dialer Profiles are different from last setup menu. Here up
to 16 LAN to LAN profiles can be set for access to up to 16 remote networks
via an ISDN line. These profiles have dial-out/dial-in/static route functions.
The router has a powerful built-in firewall. Up to 84 Call Filter and Data
Filter rules may be set.
22
Page 31

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
1. Syslog Setup
The router can be setup as a syslog client.
2. Time Setup:
Sets time information for the router.
3. Configuration Back/Restore
Router configuration can be saved in a single file for restoration later.
4. Management Setup
This allows you to grant or limit access rights to manage the router. Also,
you may set HTTP or Telnet ports to specific port numbers of your choice.
5. Reboot System
You can restart the router with the default configuration or with the current
running configuration.
6. Firmware Upgrade (TFTP Server)
Enables the TFTP server for firmware upgrades.
Status:
1. Online Status
Click this item to view the current online status and statistics of the system.
2. Diagnostic Tools.
Diagnostic tools offers useful tools to diagnose the router or your network,
e.g. view ARP table, routing table, NAT port map, DHCP server status, last
triggered packet, etc.
Help:
Help file can be accessed here.
Note: You should now have some basic concepts on how to setup and
configure the router. The following chapters will explain each setup menu
and related settings in more detail.
23
Page 32

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
Basic Configuration and Internet Access
Basic Setup (Setup First)
This group includes Administrator Password Setup, Ethernet TCP/IP and
DHCP Setup, and ISDN Setup.
Changing the Administrator Password
On first setup the router requires no password. However, for security reasons, we
strongly recommend that you set an administrator password for the router. If you do
not set a password for the router, any user can access the setting of the router and
make changes randomly from local network or the Internet.
Click Administrator Password Setup, the following screen will open.
♦ Old Password – If this is the first time you enter this menu, leave this
field blank.
♦ New Password – Enter an administrator password.
♦ Retype New Password – Type the password again to confirm.
Configuring Ethernet TCP/IP Address and DHCP Server
The Router has four Ethernet ports for connecting to the local Ethernet network and
external broadband device (i.e. DSL modem/router or Cable modem). There are two
sets of IP address settings for the Ethernet. The first IP address/net mask is for
private users or NAT users, and the second IP address/subnet mask is for public
users or pure router (not NAT) user. To allow access of public users you need to
subscribe a globally reachable subnet from your ISP.
For example, for some ISDN dial-up access, the ISP will assign a few public IP
addresses for your local network usage. You could use one IP address for your
router; the second IP address/subnet mask should be configured using the public IP
24
Page 33

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
address. Other local PCs should set the router IP address as the default gateway.
When the ISDN connection to the ISP has been established, each local PC will
directly route to the Internet. Also, you could use the first IP address/subnet mask to
connect to other private users (PCs). These user's IP addresses will be translated to
the second IP address by the router and sent out via ISDN.
Router IP Network Configuration:
For NAT Usage
♦ 1st IP Address – Private IP address for connecting to a local private
network (Default: 192.168.0.1).
♦ 1st Subnet Mask – Subnet mask for the local private network (Default:
255.255.255.0/24).
For IP Routing Usage – (Default: Disable)
♦ Enable – Enable the 2nd IP address settings.
♦ Disable – Disable the 2nd IP address settings.
♦ 2nd IP Address – Set a public IP address.
♦ 2nd Subnet Mask – Set a subnet mask for the public IP address.
DHCP Server Configuration:
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol can automatically dispatch related IP settings
to any local user configured as a DHCP client. The DHCP server supports up to 253
users (PCs) on the local network.
♦ Activate – (Default: Yes)
♦ Yes – Enable the DHCP server.
♦ No – Disable the DHCP server.
♦ Start IP Address – Set the start IP address of the IP address pool.
♦ IP Pool Counts – Set the number of IPs in the IP address pool.
♦ Gateway IP Address – Set the Gateway IP address.
♦ DNS Server IP Address – (Default: None) DNS stands for Domain
Name System. Every Internet host must have a unique IP address. They
may also have an easy-to-remember name such as www.dlink.com.tw.
The DNS server converts this name into its equivalent IP address.
♦ Primary IP Address – Set the IP address of the primary DNS server.
25
Page 34

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
♦ Secondary IP Address – Set the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
If you leave both Primary IP and Secondary IP Address fields blank, the router will
assign its own IP address to local users as a DNS proxy server and maintain a DNS
cache. If the IP address of a Domain Name is already in the DNS cache, the router
will resolve the Domain Name immediately. Otherwise, the router forwards the
DNS query packet to the external DNS server by establishing a WAN (e.g. ISDN or
DSL/Cable) connection.
Configuring the ISDN Interface
♦ Country Code – Set the correct country code for proper function on your
local ISDN network.
♦ Own Number – Set your ISDN number. The number you entered in this
field will be carried with every outgoing call to the users you called.
♦ MSN Numbers for the Router – "MSN Numbers" means that the router
is able to accept number-matched incoming calls. The router provides
three MSN number fields. Note that MSN services must be subscribed to
from your local telecom. By default, MSN function is disabled (i.e. leave
the MSN number fields blank) under which all incoming calls will be
accepted without number matching. Click OK to return to the Main
Setup Menu.
Internet Access Setup
For most users, Internet access is the primary application. The following sections
will explain more details of ISDN dial-up access and broadband access setup. When
you click Internet Access Setup within the Quick Setup group, the following setup
page will be shown.
26
Page 35

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Five methods are available for Internet Access:
♦ Dialing to Single ISP – If you want to access the Internet via a single
ISP, click here.
♦ Dialing to Dual ISP – If you have more than one ISP, click here to set up
two ISP dialup profiles. You will be able to dial to both ISPs at the same
time. This is mainly for those ISPs who do not support Multiple link PPP
(ML-PPP). In such cases dialing to two ISPs can increase the bandwidth
utilization of the ISDN line to 128kbps data speed.
♦ PPPoE – This is for most DSL modem users. All local users can share
one PPPoE connection to access the Internet.
♦ PPTP – Some DSL service providers supply a special DSL modem (e.g.
Alcatel's DSL modem). This kind of modem only supports the PPTP
tunnel method to access the Internet. In these cases, you create a PPTP
tunnel that carries a PPP session and terminates on the DSL modem. Once
the tunnel has been established, this kind of DSL modem will forward the
PPP session to the ISP. As long as the PPP session is connected, all the
local users will be able to share this PPP session to access to the Internet.
♦ Static IP – If you have obtained public IP address from DSL, Leased-
Line or Cable (static IP only) service provider, select Static IP to setup
your Internet Access mode.
27
Page 36

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
ISDN Dial-up Internet Access
Dialing to a Single ISP
ISP Access Setup
♦ ISP Name – Enter your ISP name.
♦ Dial Number – Enter the ISDN access number provided by your ISP.
♦ Username – Enter the username provided by your ISP.
♦ Password – Enter the password provided by your ISP.
♦ Require ISP Callback (CBCP) – If your ISP supports the callback
function, check "Require ISP Callback (CBCP)" to enable the Callback
Control Protocol during PPP negotiations.
♦ Scheduler (1-15) – Enter up to 4 index numbers for calls that have been
previously configured on the Call Schedule Setup windows (under
Advanced Setup).
PPP/MP Setup
♦ Link Type – There are four link types:
◊ Link Disable - Disable the ISDN dial-out function.
◊ Dialup 64Kbps - Use one ISDN B channel for Internet access.
◊ Dialup 128Kbps - Use both ISDN B channels for Internet access.
◊ Dialup BOD -BOD stands for bandwidth-on-demand. The router
will use only one B channel under low traffic situations. Once the
single B channel bandwidth is filled, the other B channel will be
dialed automatically. For more detailed BOD parameter settings,
refer to the Advanced Setup group→ Call Control and PPP/MP
Setup.
◊ None not included.
♦ PPP Authentication – There are two types of authentication:
◊ PAP Only - Set the PPP session to use the PAP protocol to
negotiate the username and password with the ISP.
28
Page 37

♦ Idle Timeout – Idle timeout means the router will disconnect after being
IP Address Assignment Method (IPCP)
♦ Fixed IP and Fixed IP Address – In most environments you should not
Dialing to Dual ISPs
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
◊ PAP or CHAP - Set the PPP session to use the PAP or CHAP
protocols to negotiate the username and password with the ISP.
idle for a preset amount of time. The default is 180 seconds. If you set the
time to 0, the ISDN connection will remain always connected to the ISP.
change the default settings as most ISPs provide a dynamic IP address for
the router when it connects to the ISP. If your ISP provides a fixed IP
address, check Yes and enter the assigned IP address in the Fixed IP
Address field.
Most configuration parameters are the same as last section. This page provides an
"Enable Dual ISPs Function" check box and adds a secondary ISP Setup section.
Check the box and enter the second ISP information.
ISP Access Setup
♦ ISP Name – Enter the Internet Service Provider Name.
♦ Username – Enter the username obtained from your ISP provider.
♦ Password – Enter the password obtained from your ISP provider.
PPP/MP Setup
♦ Link Type – You have three selections:
◊ Link Disable – Disables the ISDN dial-out function.
◊ Dialup 128Kbps – Uses both ISDN B channels for Internet access.
29
Page 38

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
IP Address Assignment Method (ICPC)
◊ Dialup BOD – BOD stands for bandwidth-on-demand. The router
will use only one B channel under low traffic situations. Once the
single B channel bandwidth is filled, the other B channel will be
dialed automatically. For more detailed BOD parameter settings,
refer to the Advanced Setup group > Call Control and PPP/MP
Setup.
♦ PPP Authentication – Two types of authentication
◊ PAP Only - Set the PPP session to use the PAP protocol to
negotiate the username and password with the ISP.
◊ PAP or CHAP - Sets the PPP session to use the PAP or CHAP
protocols to negotiate the username and password with the ISP.
♦ Fixed IP and Fixed IP Address – In most environments you should not
change the default settings as most ISPs provide a dynamic IP address for
the router when it connects to the ISP. If your ISP provides a fixed IP
address, check Yes and enter the assigned IP address in the Fixed IP
Address field.
30
Page 39

DSL/Cable Modem Internet Access
Before you connect a broadband access device, e.g. a DSL/Cable modem, to the
router, you need to know what kind of Internet access is provided by your ISP.
The following paragraphs deal with three widely used broadband access services.
These are PPPoE Client, PPTP Client, and Static IP for DSL/Cable Modem. In
most cases, you will get a DSL/Cable modem from the broadband access service
provider. The router is connected behind the broadband device and works as a NAT
or IP router for broadband and ISDN connections.
In addition to broadband access capabilities, the ISDN port can do dial backup, or
provide remote access and remote management functions to support more flexible
network connectivity. The following application scenario shows that the head office
is capable of getting on to the Internet through the DI-304 and a broadband device
and connecting to the branch office via an ISDN network simultaneously.
Using PPPoE with a DSL Modem
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Click Internet Access Setup → PPPoE to enter the setup page.
31
Page 40

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
PPPoE Setup
ISP Access Setup
ISDN Dial Backup Setup
PPP/MP Setup
♦ PPPoE Link – Check Enable to enable the PPPoE client protocol.
♦ ISP Name – Enter the ISP name.
♦ Username – Enter the ISP supplied username.
♦ Password – Enter the ISP supplied password.
♦ Scheduler (1-15) – Enter up to 4 index numbers for calls that have been
previously configured on the Call Schedule Setup windows (under
Advanced Setup).
♦ Dial Backup Mode –There are three options:
◊ None - Disable the backup function.
◊ Packet Trigger - The backup line is disconnected until a packet
from a local host triggers the router to establish a connection.
◊ Always On - If the broadband connection is no longer available,
the backup line will automatically connect and stay Always On
until the broadband connection is recovered.
♦ PPP Authentication – Select PAP or CHAP for widest compatibility.
♦ Always On - If the broadband connection is no longer available, the
backup line will automatically connect and stay Always On until the
broadband connection is recovered.
♦ Idle Timeout – Idle timeout means the router will disconnect after being
idle for a preset amount of time. The default is 180 seconds. If you set the
time to 0, the PPP session will not terminate itself.
♦ Fixed IP – Check No (Dynamic IP) unless your ISP has provided you
with a static IP address.
32
Page 41

♦ Fixed IP Address – If your ISP has provided you with a static IP address
enter it here.
IP Address Assignment Method (IPCP)
♦ Fixed IP – Check No (Dynamic IP) unless your ISP has provided you
with a static IP address.
♦ Fixed IP Address – If you ISP has provided you with a static IP address
enter it here.
Click OK.
Using PPTP with a DSL Modem
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
PPTP Setup
♦ PPTP Link – Check Enable to enable a PPTP client to establish a tunnel
to a DSL/Cable modem.
♦ PPTP Server IP Address – Specify the IP address of the PPTP-enabled
DSL/Cable modem. Refer to the user manual of the PPTP-enabled
DSL/Cable modem.
Click Internet Access Setup → PPTP to enter the setup page. The following
setup page is just for example. Your DSL/Cable service should provide the
exact settings.
ISP Access Setup
♦ ISP Name – Enter the ISP name.
♦ Username – Enter the ISP supplied username.
♦ Password – Enter the ISP supplied password.
33
Page 42

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
♦ Scheduler (1-15) – Enter up to 4 index numbers for calls that have been
previously configured on the Call Schedule Setup windows (under
Advanced Setup).
ISDN Dial Backup Setup
♦ Dial Backup Mode – Select None to disable this feature or select Packet
Trigger to activate this feature.
PPP Setup
♦ PPP Authentication – Select PAP or CHAP for widest compatibility.
♦ Idle Timeout – Idle timeout means the router will disconnect after being
idle for a preset amount of time. The default is 180 seconds. If you set the
time to 0, the PPP session will not terminate itself.
♦ Fixed IP – Check No (Dynamic IP) unless your ISP has provided you
with a static IP address.
♦ Fixed IP Address – If your ISP has provided you with a static IP address
enter it here.
Using a Static IP with a DSL/Cable Modem
Select this access mode if you receive a fixed public IP address or a public subnet
from your DSL or Cable ISP. In most cases, a Cable ISP will provide a fixed public
IP, while a DSL ISP will provide a public subnet. You must enable IP Routing
Usage, and enter the fixed public IP or choose one public IP from the public subnet
for Ethernet TCP/IP Setup.
34
Page 43

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Click Ethernet to enable the “For IP Routing Usage” and type in the IP
address/subnet mask:
Click Internet Access Setup → Static IP to enter the setup page.
Access Control
♦ Broadband Access – Select Enable to turn on the broadband access
capability.
♦ Gateway IP Address – Enter the IP address from DSL service provider
as Router IP address or the fixed IP gateway IP address.
ISDN Dial Backup Setup
♦ Dial Backup Mode – Select None to disable this feature or select Packet
Trigger to activate this feature, or select always on to recover connection.
Note: The router should be restarted to allow the settings to take effect.
35
Page 44

DI-304ISDN Remote Router
Configuring ISDN Dial Backup
♦ ISDN Dial Backup Setup – There are three options:
◊ None - Disable the backup function.
◊ Packet Trigger - The backup line is disconnected until a packet
from a local host triggers the router to establish a connection.
◊ Always On - If the broadband connection is no longer available,
the backup line will automatically connect and stay Always On until
the broadband connection is recovered.
♦ Dial Backup Mode – There are three options:
◊ None - Disable the backup function.
◊ Packet Trigger - The backup line is disconnected until a packet
from a local host triggers the router to establish a connection.
◊ Always On - If the broadband connection is no longer available,
the backup line will automatically connect and stay Always On until
the broadband connection is recovered.
To start ISDN Dial Backup function, you must create a dial backup profile. Click
Internet Access Setup → Dialing to a Single ISP to setup the backup profile.
36
Page 45

Remote Access
This chapter explains the capabilities of remote access of the Router. Use the
following setup links on the Setup Main Menu to setup remote access functions.
The term "Remote Access" covers two types of remote access. The first, "Remote
Dial-In Access" means the router allows normal ISDN TA users or NAT routers (IP
sharing routers) to dial into the router for sharing the network resources of the local
network, or to surf the Internet via a broadband device. The other remote access
function, "LAN-to-LAN Access," provides a solution to connect two independent
LANs for mutual sharing of network resources. For example, the head office
network can access the branch office network, and vice versa.
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Quick Setup
>> Remote Dial-In Access Setup
Advanced Setup
>> Remote Dial-In User Setup
>> LAN-to-LAN Dialer Profile Setup
Remote Dial-In Access
Activating Remote Dial-In
In the Quick Setup group of the Setup Main Menu, click Remote Dial-In Access
Setup to enter the setup page.
Dial-In Access Control
♦ Dial-In Service – Click Enable to allow dial-in service. Note that if you
click Disable, the router will not accept any in-coming ISDN calls.
37
Page 46

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
PPP/MP Setup
♦ Dial-In PPP Authentication – There are two choices:
◊ PAP - Selecting this option will force the router to authenticate
dial-in users with the PAP protocol.
◊ PAP or CHAP - Selecting this option means the router will
attempt to authenticate dial-in users with the CHAP protocol first. If
the dial-in user does not support this protocol, it will fall back to use
the PAP protocol for authentication.
♦ Mutual Authentication (PAP) – Enable this only if the connecting router
requires mutual authentication. By default, the option is set to No.
♦ Username – Enter the mutual Authentication username.
♦ Password – Enter the mutual Authentication password.
IP Address Assignment for Dial-In Users
♦ Start IP Address – Enter a start IP address to be assigned to the dial-in
PPP connection. You should choose an IP address from the local private
network. For example, if the local private network is
192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0, you can choose 192.168.1.200 to be the Start
IP Address. Because one ISDN BRI has two independent data channels
(B-channels), it is possible to allow two dial-in users at the same time.
The first dial-in user would be assigned the start IP address and the
second would be assigned the start IP address plus 1. Click OK.
Creating an Access Account for a Dial-in User
After activating the dial-in capability, you must create an access account for each
dial-in user. From the Advanced Setup menu, click Remote Dial-In User Setup to
open the page shown below. The router provides 10 access accounts for dial-in
users.
♦ Set to Factory Default – Clicking here will clear all dial-in user
accounts.
38
Page 47

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
♦ Index: Click one of the index numbers to open an individual setup page
and enter the detail setting for each account.
♦ Dial-In Username – The “???” means the access account has not set up
yet. If an access account has been configured, the username will be
shown.
♦ Status – The symbol "v" means the account is active, "x" means inactive.
Click the index number of an account to open an individual setup page for
detail setting.
User Account and Authentication
♦ Check to enable the user account – Check this item to activate the
individual user account.
♦ Username – Specify a username for the specific dial-in user.
♦ Password – Specify a password for the specific dial-in user.
♦ Idle Timeout – Default setting is 300 seconds. When a dial-in connection
has been idled longer than the time limit, the router will drop the
connection.
♦ Check to enable CLID authentication – For extra security, enables the
option to allow the dial-in user to call only from a specific number. CLID
stands for Calling Line Identification.
♦ Peer ISDN Number – If CLID authentication has been enabled, enter the
dial-in user's ISDN number.
Callback Function
The callback function provides a callback service for the dial-in user. The router
owner will be charged the connection fee by the telecom.
♦ Check to enable the Callback function – Enable the callback function.
♦ Specify the callback number – This option is for extra security. Once
enabled, the router will only call back to the specified ISDN number
defined in the next parameter, Callback Number.
39
Page 48

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
♦ Callback Number – If the previous option has been enabled, enter the
♦ Check to enable Callback Budget Control – Enable the callback budget
♦ Callback Budget (Unit: minutes) – By default, the callback function has
LAN-to-LAN Access
dial-in user's ISDN line number here.
control.
a 30-minute time restriction. The budget will be decreased automatically
per callback connection. Once the callback budget has been exhausted,
the callback mechanism will be disabled automatically.
The following sections are based on the network layout above to describe how to set
up a LAN-to-LAN profile to connect two private networks. In the above network
layout, the private network of the head office is 192.168.1.0/24 and the off-site
branch office network is 192.168.2.0/24.
Before you begin to setup a LAN-to-LAN profile for each network, you should
gather the information shown in the following table.
Head Office Branch Office
Network ID 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.0/24
Router IP /Subnet mask 192.168.1/24 192.168.2.1/24
Assigned IP for dial-in
192.168.1.200 192.168.2.200
connection
Access Account UN: head; PW: head UN: branch; PW: branch
ISDN line number 1000 2000
Callback function Disable Disable
40
Page 49

Activating the Dial-In Capability
In the Quick Setup group of the Setup Main Menu, click Remote Dial-In
Access Setup to enter the setup page. See the Remote Dial-In Access section earlier
in this chapter for a full explanation of the fields on this page.
Head Office:
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
The IP range of the Head Office network is 192.168.1.0/24. The settings should be
as below:
♦ Dial-In Service – Enable
♦ Start IP Address – 192.168.1.200.
Branch Office:
41
Page 50

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
The IP range of the Branch Office network is 192.168.2.0/24, the settings should be
as below:
♦ Dial-In Service – Enable
♦ Start IP Address – 192.168.2.200
Creating a LAN-to-LAN Dialer Profile
After enabling the Dial-in service, you must create a LAN-to-LAN profile
for each network. From the Advance Setup menu, click LAN-to-LAN
Dialer Profile to enter the setup page displayed below.
42
Page 51

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
The router provides 16 LAN-to-LAN profiles for connecting to up to
16 different remote networks.
♦ Set to Factory Default – Clicking here will clear all the LAN-to-LAN
profiles.
♦ Index – Click a number in the Index to open a detailed settings page for
each profile.
♦ Name – Indicate the name of the LAN-to-LAN profile. The symbol "???"
means the profile is available.
♦ Status – Indicate the status of the individual profiles. The symbol "v"
means the profile is active and "x" means it is inactive.
Click an index number to open an individual LAN-to-LAN profile settings page.
Each LAN-to-LAN profile includes 4 subgroups: Common Settings, Dial-Out
Settings, Dial-In Settings, and TCP/IP Network Settings. The following will explain
every subgroup in detail.
43
Page 52

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Common Settings
♦ Profile Name – Specify a name for the remote network.
♦ Enable this profile – Check here to activate this profile.
♦ Call Direction – Specify the allowed call direction for this profile.
♦ Idle Timeout – Default setting is 300 seconds. When a connection of a
Dial-Out Settings
♦ Username – Specify a username for authentication by the remote router.
♦ Password – Specify a password for authentication by the remote router.
♦ Dial Number – Specify the destination ISDN number for dialup.
♦ Scheduler (1-15) – Enter up to 4 index numbers for calls that have been
♦ Link Type – Indicate the dial-out link type.
♦ PPP Authentication – Specify the authentication method. Normally set
♦ VJ Compression – VJ Compression means TCP/IP protocol header
♦ Callback Function (CBCP) – The callback function is implemented by
Dial-In Settings
♦ Username – Specify an username to authenticate the dial-in router.
♦ Password – Specify a password to authenticate the dial-in router.
♦ Enable CLID Authentication – Limit the dial-in router to be called from
◊ Both - allow access of both outgoing and incoming calls.
◊ Dial-Out - allow access of outgoing calls only.
◊ Dial-In - allow access of incoming calls only.
profile has been idled longer than the time limit, the router will drop the
connection.
previously configured on the Call Schedule Setup windows (under
Advanced Setup).
◊ Disable: Deactivate the dial-out action.
◊ 64kbps: Specify the outgoing connection speed is restricted to
64kbps (one B-channel).
◊ 128k bps: Specify the outgoing connection speed is 128kbps (two
B-channels).
◊ BOD: Specify the link type to be dynamic bandwidth control
(Bandwidth-on-Demand).
to PAP/CHAP for the widest compatibility.
compression. Normally set to "On" to improve band-width utilization.
the CBCP protocol that is one of the PPP protocol suite.
◊ Require Remote to Callback - Inactive by default. When active,
the router exchanges connection information with the remote router
and requires the remote router to call back to make a connection.
◊ Provide ISDN Number to Remote - In some cases, the remote
router requires the ISDN number for calling back. Check here to
allow the local router to send the ISDN number to the remote router.
The remote router owner will be charged the connection fee by the
telecom.
a specific ISDN number.
44
Page 53

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
♦ Peer ISDN Number – If CLID Authentication is enabled, enter the
remote router's ISDN number in this field
♦ Link Type – Refer to Dial-Out Settings.
♦ PPP Authentication – Refer to Dial-Out Settings.
♦ VJ Compression – Refer to Dial-Out Settings.
♦ Callback Function (CBCP) – Checking here allows this router to accept
requests from a remote router for call back.
◊ Enable Callback Function - Checking here to enable this function.
The router owner will be charged the connection fee by the telecom.
◊ Use the Following Number to Callback:
- Callback Number: Check here and enter a callback number
for the router to call.
- Callback Budget: Specify a time budget for the callback
function. By default the budget is set to zero, which means no
call back attempt will work.
TCP/IP Network Settings
The following settings are required for proper LAN-to-LAN operation.
♦ My WAN IP – In most cases you may accept the default value (0.0.0.0)
in this field. The router will then get a WAN IP address from the remote
router during the IPCP negotiation phase. If the WAN IP address is fixed
by remote, specify the fixed IP address here.
♦ Remote Gateway IP –In most cases please accept the default value
(0.0.0.0) in this field.
♦ Remote Network IP – Specify the network identification of the remote
network. For example, 192.168.1.0 is a network identification of a class-C
subnet with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 (/24).
♦ Remote Network Mask – Specify the subnet mask of the remote
network.
♦ RIP Direction – The option specify the direction of RIP (Routing
Information Protocol) packets through the ISDN WAN connection.
♦ RIP Version – Select the RIP protocol version. Specify Ver. 2 for
greatest compatibility.
♦ For NAT operation, treat remote sub-net as – Toggle between Private
IP and Public IP.
For the example listed in this section, the LAN-to-LAN Dialer profile should be
configured as below:
Head Office:
45
Page 54

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Branch Office:
46
Page 55

Advanced Setup
This chapter explains the remaining options available in Advanced Setup:
Advanced Setup
>> Call Control and PPP/MP Setup
>> Call Schedule Setup
>> NAT Setup
>> Static Route Setup
>> IP Filter/Firewall Setup
Click Call Control and PPP/MP Setup to open the setup page displayed below.
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Enabling the Remote Activation Function
Some applications require the router to be remotely activated, or dial up to the ISP
using the ISDN interface. For instance, if you are a user who accesses the Internet
via ISDN from home, usually the dialup connection is idle when you are not at
home. You may want to get some files from home while you are working in the
office. This function allows you to make a phone call to the router and ask it to dial
up to the ISP. Then you can access your home network to retrieve the files. Of
course, you have to have a fixed IP address and expose some internal network
resources, such as FTP, WWW etc.
47
Page 56

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Click Call Control and PPP/MP Setup and specify a phone number in the Remote
Activation field.
Call Control Setup
Dial Retry and Dial Delay Interval
These two parameters set global settings for ISDN dialup access.
♦ Dial Retry – Specify the dial retry counts per triggered packet. A
♦ Dial Delay Interval – Specify the interval between dialup retries. By
Remote Activation
If the router accepts a call from the number 12345678, it will disconnect
immediately and dial to the ISP. Note that Internet Access Setup → Dialing to a
Single ISP should be preset properly.
triggered packet is any packet whose destination is outside the local
network. The default setting is no dial retry. If set to 5, for each triggered
packet, the router will dial 5 times until it is connected to the ISP or
remote access router.
default, the interval is 0 seconds.
PPP/MP Dial-Out Setup
Basic Setup
Select according to the ISP service type subscribed to and enter parameters
according to the setup you entered for Remote Access Setup in Chapter 4.
48
Page 57

Bandwidth On Demand (BOD) Setup
BOD stands for bandwidth-on-demand for Multiple Link PPP (ML-PPP or MP).
Click Call Control and PPP/MP Setup to see the following settings.
These parameters are activated when you set the Link Type to Dialup BOD.
Usually the ISDN will use one B channel to access the Internet or remote network
when you use the Dialup BOD link type. The router will use the parameters here to
make a decision on when to activate/drop the additional B channel. Note that cps
(characters-per-second) measures the total link utilization.
♦ High Water Mark and High Water Time – These parameters specify
the conditions under which the second channel will be activated. When
the utilization of the first connected channel goes over the High Water
Mark and past the High Water Time, the additional channel will be
activated. The link speed will then be 128kbps (two B channels).
♦ Low Water Mark and Low Water Time – These parameters specify the
conditions under which the second channel will be dropped. When the
utilization of two B channels is under the Low Water Mark and past the
High Water Time, the additional channel will be dropped. The link speed
will be 64kbps (one B channel).
Note: If you are not familiar with the operation of ISDN and ML-PPP, be wary of
changing the default values.
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
49
Page 58

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Call Schedule Setup
NAT Setup
Users are allowed to designate up to 15 scheduled calls, which the router will be
able to receive based on the information filled out in the page below. Please note,
however, that no more than 4 calls can be scheduled at one time (see the Scheduler
(1-15) parameter located under Quick Setup → Internet Access Setup for a Single
ISP among other places in the Setup Main Menu).
Usually you will use the router as a NAT-enabled router. NAT stands for Network
Address Translation. It means the router gets one (in Single ISP, PPPoE, PPTP) or
two (in Dual ISPs mode) globally re-routable IP addresses from the ISP. Local hosts
will use private network IP addresses defined by RFC-1918 to communicate with
the router. The router translates the private network addresses to a globally routable
IP address that is then used to access the Internet. The following explains NAT
features for specific applications.
Click NAT Setup to open the setup page. On the page you will see the private IP
address definitions defined in RFC-1918. Usually we use the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet
for the router.
Configure Port Redirection Table
50
Page 59

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Exposing Internal Servers to the Public Domain
The Port Redirection Table may be used to expose internal servers to the public
domain or to directly assign a specific port number to internal hosts. External hosts
or domain can specify port numbers to access internal network services, such as
FTP, WWW, etc.
The following example shows how an internal FTP server is exposed to the public
domain. The internal FTP server is running on the local host addressed as
192.168.1.10.
51
Page 60

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
As shown above, the Port Redirection Table provides 10 port-mapping entries for
internal hosts.
♦ Service Name – Specify the name for the specific network service.
♦ Protocol – Specify the transport layer protocol that supports TCP and
♦ Public Port – Specify which port should be redirected to the internal
♦ Private IP – Specify the private IP address of the internal host offering
♦ Private Port – Specify the private port number of the service offered by
♦ Active – Check here to activate the port-mapping entry.
DMZ Host Setup
Click DMZ Host Setup to open the setup page. The DMZ Host settings allow a
defined internal user to be exposed to the Internet to use some special-purpose
applications such as Netmeeting, Internet games, etc.
♦ DMZ Enable – Check to enable the DMZ Host function.
♦ DMZ Host IP – Enter the IP address of DMZ host.
UDP options.
host.
the service.
the internal host.
52
Page 61

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Open Ports Setup
Click Open Ports Setup to open the following setup page.
Fill in the appropriate information for each open port table entry and click OK to let
the changes take effect.
53
Page 62

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Well-known Port Number List
This page provides some well-known port numbers for your reference.
Static Route Setup
This menu contains 10 routing rules for static routing usage. You may add/delete or
activate/deactivate any static route.
54
Page 63

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Click on the desired index number from 1 to 10 on the window above.
IP Filter/Firewall Setup
The IP Filter/Firewall function helps to prevent your local network against attack
from outside. It also provides a method of restricting users on the local network
from accessing the Internet. Additionally, it can filter out specific packets to trigger
the router to place an outgoing connection.
An Overview of the Firewall
The IP Filter/Firewall includes two types of filter: Call Filter and Data Filter. The
former is designed to block or allow IP packets that will trigger the router to
establish an outgoing connection. The latter is designed to block or allow which
kind of IP packets are allowed to pass through the router when the WAN connection
has been established. It works like this: when an outgoing packet is routed to the
WAN, the IP Filter will decide if the packet should be forwarded to the Call Filter or
Data Filter. If the WAN connection has not been established, the packet will enter
the Call Filter. If the packet is not allowed to trigger router dialing, it will be
dropped. Otherwise, it will initiate a call to establish the WAN connection.
If the WAN connection of the router has been established, the packet will pass
through the Data Filter. Packets match the block rule will be dropped and the
contrary will be sent to the WAN interface. Alternatively, if an incoming packet
enters from the WAN interface, it will pass through the Data Filter directly. If the
packets match the block rule, it will be dropped. Otherwise, it will be sent to the
internal LAN. The filter architecture is shown as below.
55
Page 64

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
The Following sections will explain more about IP Filter/Firewall Setup using Web
Configurator. The Filter has 12 filter sets with 7 filter rules for each set. There are a
total of 84 filter rules for the IP Filter/Firewall Setup. By default, the Call Filter
rules are defined in filter set 1 and the Data Filter rules are defined in filter set 2.
♦ General Setup – Some general settings are in the setup link.
♦ Filter Setup – Here there are 12 filter sets for IP Filter configurations.
♦ Set to Factory Default – Click here to restore the filter rules to default
values.
56
Page 65

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
General Setup
On the General Setup page you can enable/disable the Call Filter or Data Filter and
assign a Start Filter Set for each, configure the log settings, and set the MAC
address for duplicate packets.
♦ Call Filter – Check Enable to activate the Call Filter function. Assign a
start filter set for Call Filter.
♦ Data Filter – Check Enable to activate the Data Filter function. Assign a
start filter set for Data Filter.
♦ Log Flag – For troubleshooting purpose, you need to specify the filter log
here.
◊ None - The log function is inactive.
◊ Block - All blocked packets will be logged.
◊ Pass - All passed packets will be logged.
◊ No Match - The log function will record all packets that are
unmatched.
Note: The filter log will be displayed on the Telnet terminal when you type the "log
-f" command.
♦ MAC Address for Packet Duplication – Logged packets may also be
logged to another location via Ethernet. If you want to duplicate logged
packets from the router to another network device, you must enter the
MAC address (HEX Format) of the other devices. Enter "0" to disable the
feature. It will be helpful under Ethernet switch environment.
57
Page 66

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Editing the Filter Sets
♦ Comments – Enter filter set comments/description. Its maximum length
is 22 characters.
♦ Filter Rule – Click a button numbered "1" ~ "7" to edit the filter rule.
♦ Active – Enable or disable the filter rule.
♦ Next Filter Set – Specify the next filter set to link to after the current
filter set. Be aware of the sequence of the link and avoid any possible
loop among the filter sets.
The following setup pages show the default settings for Call Filter and Data Filter.
You will see the Call Filter set is assigned to Set 1 and the Data Filter set to Set 2.
58
Page 67

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Editing the Filter Rules
Click the Filter Rule index button to enter the Filter Rule setup page for each filter.
The following explains each configurable item in detail.
59
Page 68

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
♦ Comments – Enter filter set comment/description. Its maximum length is
♦ Check to enable the Filter Rule – Enable the filter rule.
♦ Pass or Block – Specify the action to be taken when packets match the
14 characters.
rule.
◊ Block Immediately - Packets matching the rule will be dropped
immediately.
◊ Pass Immediately - Packets matching the rule will be passed
immediately.
◊ Block If No Further Match - A packet matching the rule and that
does not match further rules, will be dropped.
◊ Pass If No Further Match - A packet matching the rule,
and that does not match further rules, will pass through.
♦ Branch to Other Filter Set – If the packet matches the filter rule, the
next filter rule will branch to the specified filter set.
♦ Duplicate to LAN – If you want to log the matched packets to another
network device, check this box to enable it. The MAC Address is defined
in General Setup → MAC Address for Packet Duplication.
♦ Log – Check this box to enable the log function. Use the Telnet command
"log -f" to view the logs.
♦ Direction – Set the direction of packet flow. For the Call Filter, this
setting is irrelevant.
IN: Specify the rule for filtering incoming packets.
OUT: Specify the rule for filtering outgoing packets.
♦ Protocol – Specify the protocol(s) this filter rule will apply to.
60
Page 69

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
♦ IP Address – Specify a source and destination IP address for this filter
rule to apply to. Placing the symbol "!" before a particular IP Address will
prevent this rule from being applied to that IP address. It is equal to the
logical NOT operator.
♦ Subnet Mask – Specify the Subnet Mask for the IP Address column for
this filter rule to apply to.
♦ Operator – The operator column specifies the port number settings. If the
Start Port is empty, the Start Port and the End Port column will be
ignored. The filter rule will filter out any port number.
= : If the End Port is empty, the filter rule will set the port
number to be the value of the Start Port. Otherwise, the
port number ranges between the Start Port and the End
Port (including the Start Port and the End Port).
!= : If the End Port is empty, the port number is not equal
to the value of the Start Port. Otherwise, this port number
is not between the Start Port and the End Port (including
the Start Port and End Port).
> : Specify the port number is larger than the Start Port
(includes the Start Port).
< : Specify the port number is less than the Start Port
(includes the Start Port).
♦ Keep State – also may be quoted as SPI (stateful packets inspection), is a
mechanism used to drop the invalid incoming packets. When checked,
protocol information about the TCP/UDP/ICMP communication sessions
will be kept by the IP Filter/Firewall (the Firewall Protocol option
requires that TCP or UDP or TCP/UDP or ICMP be selected for this to
operate correctly).
♦ Source Route – When checked, the IP options of source routing will be
applied for the rule. In general please do not enable this option for higher
security policy.
♦ Fragments – Specify a fragmented packets action.
◊ Don't Care - Specify no fragment options in the filter rule.
◊ Unfragmented - Apply the rule to unfragmented packets.
◊ Fragmented - Apply the rule to fragmented packets.
◊ Too Short - Apply the rule only to packets that are too short to
contain a complete header.
Some fragmented packets are malicious so it may be necessary to
hinder the fragmented packets for higher security policies.
Restricting Unauthorized Internet Services
This section will show a simple example to restrict access of WWW from certain
locations. In this example, we assume the IP address of the access-restricted user is
192.168.1.10. The filter rule is created in the Data Filter set and is shown as below.
61
Page 70

DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
62
Page 71

System Management
This chapter will show you how to manage your router using the System
Management tools shown below:
System Management
>> Online Status
>> Time Setup
>> Management Setup
>> Diagnostic Tools
>> Reboot System
>> Firmware Upgrade (TFTP Server)
DI-304/DI-304M ISDN Remote Router
Online Status
Click Online Status to open the Online Status page. The example shown in the next
page has both ISDN B1 and B2 channel active and also a Static IP connection.
The Online Status page contains three subgroups: ISDN Status, LAN Status, and
WAN Status.
ISDN Status
Shows the connection status of B1, B2, and D channel, including ISP dialup, active
remote dial-in user, or LAN-to-LAN connection.
63
Page 72

♦ Active Connection – Shows the ISP, active remote dial-in user, or LAN-
to-LAN profile name and also the IP address for each B channel.
♦ TX Pkts – Total numbers of transmitted IP packets sent during this
connection session.
♦ TX Rate – Transmission rate for outgoing data. The unit is characters per
second (cps).
♦ RX Pkts – Total number of received IP packets received during this
connection session.
♦ RX Rate – Reception rate for ingoing data. The unit is characters per
second (cps).
♦ Up Time – Connection time. The format is HH:MM:SS where HH means
hours, MM means minutes, and SS means seconds.
♦ AOC – The Advice of Charge (AOC) service allows you to view
information concerning charges for a call.
♦ Drop B1 – Click to disconnect the B1 channel.
♦ Drop B2 – Click to disconnect the B2 channel.
LAN Status
♦ IP Address – IP address of the LAN interface.
♦ TX Packets – Total number of transmitted IP packets send since the
router was powered on.
♦ RX Packets – Total number of transmitted IP packets received since the
router was powered on.
WAN Status
♦ Mode – Indicates which broadband access mode is active. Depending
upon the broadband access mode, you may see Static IP, PPTP, or PPPoE.
♦ GW IP Address – Indicates the gateway IP address.
♦ IP Address – The 2nd IP Address of Ethernet or the IP address of WAN
interface that is from PPTP/PPPoE connection.
♦ TX Packets – Total number of transmitted IP packets sent during this
connection session.
♦ TX Rate – Transmission rate for outgoing data. The unit is characters per
second (cps).
♦ RX Packets – Total number of transmitted IP packets received during
this connection session.
♦ RX Rate – Reception rate for ingoing data. The unit is characters per
second (cps).
♦ Up Time – Connection time. The format is HH:MM:SS where HH means
hour, MM means minute, and SS means second.
♦ Drop PPPoE or PPTP – Click to disconnect the PPPoE or PPTP
connection.
Page 73

Time Setup
Click Time Setup to open a page that allows you to make configuration changes to
the time setup.
Management Setup
By default, the router may be configured and managed with any Telnet client or
Web browser running on any operating system. There is no requirement for
additional software or utilities. However, for some specific environments, you may
want to change the server port numbers for the built-in Telnet or HTTP server,
create access lists to protect the router, or reject system administrator login from the
Internet.
Click Management Setup. The following setup page will display.
Page 74

Management Access Control
♦ Allow management from the Internet – Check to allow system
administrators to login from the Internet. The default setting is "not
allowed".
♦ Disable PING from the Internet – Check to prevent Ping capability
from the Internet.
Access List
You may specify that the system administrator can only login from a specific host or
network defined in the list. A maximum of three IPs/subnet masks may be entered.
♦ List IP – Specifies an IP address allowed to login to the router.
♦ Subnet Mask – Specifies a subnet mask allowed to login to the router.
Management Port Setup
♦ Default Ports – Check to use standard port numbers for the Telnet and
HTTP servers.
♦ User Defined Ports – Check and enter user-defined port numbers for the
Telnet and HTTP servers.
SNMP Setup
♦ Enable SNMP Agent – Check to enable SNMP agent and then fill out
the appropriate information for the Get Community, Set Community,
Manager Host IP, Trap Community, Notification Host IP, and a Trap
Timeout.
Page 75

Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools provide useful tools for viewing or diagnosing the router. Click
Diagnostic Tools to enter the following page.
ISDN/PPPoE/PPTP Diagnostics
♦ Refresh – To obtain the latest information, click here to reload the page.
ISDN
♦ ISDN Link Status – If the link is active, this field will show up.
Otherwise, it shows down.
Page 76

♦ Dial ISDN – Clicking here causes the router to dial to the preset ISP.
Click Internet Access Setup → Dial to a Single ISP to configure dial-up
settings.
♦ Activity – Displays the connection name for each B channel. If the B
channel is idle, it will show Idle.
◊ Drop B1 - Click to disconnect the B1 channel.
◊ Drop B2 - Click to disconnect the B2 channel.
Broadband Access
♦ Broadband Access Mode/Status – Displays the broadband access mode
and status. If the broadband connection is active, it will show PPPoE,
PPTP, or Static IP depending on which access mode is enabled. If the
connection is idle, it will show "- - -".
♦ WAN IP Address – The WAN IP address for the active connection.
♦ Dial PPPoE or PPTP – Click to force the router to establish a PPPoE or
PPTP connection.
♦ Drop PPPoE or PPTP – Click to force the router to disconnect the
current active PPPoE or PPTP connection.
Triggered Dial-out Packet Header
Triggered Dial-out Packet Header shows the last IP packet header that triggers the
router to dial out.
♦ Refresh – Click to reload the page.
View Routing Table:
Click View Routing Table to view the router's routing table.
Page 77

The table provides current IP routing information held in the router. To the left of
each routing rule you will see a key. These keys are defined as:
C --- Directly connected.
S --- Static route.
R --- RIP.
* --- Default route.
To the right of each routing rule you will see an interface identifier:
IF0 --- Local LAN interface.
IF1 --- ISDN B1 channel.
IF2 --- ISDN B2 channel.
View ARP Cache Table:
Click View ARP Cache Table to view the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
cache held in the router. The table shows a mapping between an Ethernet hardware
address (MAC Address) and an IP address.
Page 78

View DHCP Assigned IP Addresses
View DHCP Assigned IP Addresses provides information on IP address
assignments. This information is helpful in diagnosing network problems, such as IP
address conflicts, etc.
Page 79

View NAT Port Redirection Running Table
If you have configured Port Redirection (under NAT Setup), click to verify that
your settings are correct for redirecting specific port numbers to specified internal
users.
View NAT Active Sessions Table
As the router is getting on the Internet through the built-in NAT engine, click View
NAT Active Sessions Table to see which active outgoing sessions are online.
Page 80

Each line across the screen indicates an active session. The following information is
displayed:
♦ Private IP, Port – The internal user's (PC's) IP address and port number.
♦ #Pseudo Port – The public port number.
♦ Peer IP, Port – The peer user's (PC's) IP address and port number.
♦ Ifno – Stands for interface number. The definition is listed below:
◊ 0 --- LAN interface.
◊ 1 --- B1 interface.
◊ 2 --- B2 interface.
♦ Status – Stands for the NAT mapping status. The status is defined below:
◊ 0 --- Idle.
◊ 1 --- Connecting.
◊ 2 --- Connected.
◊ 3 --- Interface linking.
SysLog Setting
Page 81

Reboot System
The Web Configurator may be used to restart your router. Click Reboot System to
open the following setup page.
There is two reboot options: Using current configuration and Using factory
default configuration. If you want to reboot the router using current running
configurations, check Using current configuration and click OK. To reset the
router's settings to default values, check Using factory default configuration and
click OK.
The router will take 3 to 5 seconds to reboot the system.
Page 82

Firmware Upgrade
Before upgrading your router firmware, you must install the Router Tools. The
Firmware Upgrade Utility is included in the tools. The following steps will guide
you through the process of upgrade. Note that the examples below use Windows OS.
1. Download the latest firmware from D-Link’s Website.
2. Use Web Configurator to enable the Firmware Upgrade function. Click
Firmware Upgrade (TFTP Server) to open the following screen. Click OK to
enable the function.
3. Click Start → Programs → Router Tools → Firmware Upgrade Utility to
launch the Firmware Upgrade Utility.
The Router IP field will show the IP address of your router. Click Browse to select
the new firmware file. Click Upgrade. The upgrade status will be shown on the
progress bar.
Page 83

Appendix A – Troubleshooting and FAQs
The following section explains how to use Telnet terminal commands to diagnose
your network problems via the built-in debug tool. Our examples use Windows
Telnet client software. If you are a Mac user, you should install third-party Telnet
client software on your computer. By default, the Linux has a built-in Telnet client.
Using the Telnet Terminal Commands
Click Start → Run and type Telnet 192.168.0.1 in the Open box as below. Note
that the IP address in the example is the default address of the Router. If you have
changed the default, enter the current IP address of the router.
Click OK. The Telnet terminal will open. If an administrator password has not been
assigned, follow the on-screen instructions to assign one.
After assigning a password, type a question mark (?). You will see all the possible
Telnet commands.
Page 84

Command Help
If you are not familiar with these commands, type the command followed by a
question mark (?). For example, the ip command is a first level command. Type ip ?
to get next level commands as shown below.
Recall Commands
The Telnet terminal also provides a method to recall the command history. Use the
Up and Down arrow keys on your keyboard to recall previous commands.
Quitting the Telnet Terminal
Enter quit or exit to quit the Telnet terminal.
Viewing Call Logs
The Call log provides a simple method for troubleshooting the call setup or WAN
connection problems. By default, the router records WAN connection messages.
This information can be helpful in diagnosing WAN connection problems. If you do
not understand the content, you can easily save the log and send it to a support
technician.
The steps are:
Page 85

1. Login to the Telnet terminal.
2. Type log -F c to clear all call logs.
3. Ping to any outside host to trigger the router to dial from your PC.
4. Type log -c to display the latest call log.
Viewing ISDN Logs
To capture messages exchanged on the ISDN interface, clear all ISDN logs before
you start capturing the new log.
The steps are:
1. Login to the Telnet terminal.
2. Type log -F w to clear all ISDN logs.
3. Ping to any outside host to trigger the router to dial from your PC.
4. Type log -i to display the latest ISDN log. To display all ISDN logs saved in the
log buffer, type log -i -t.
Detailed ISDN log example:
The above example shows detailed D-channel SETUP messages only. Note that all
ISDN D-channel messages will be displayed when you type the log -i -t command.
To use the command, you will get to know whether the ISDN connection could be
established or not. Note that if you cannot read the details, please save these
messages in file and attach to support technician.
Viewing PPP Logs
To view PPP logs, type log -p.
The steps are:
1. Login to the Telnet terminal.
2. Type log -F w to clear all PPP logs.
3. Ping to any outside host to trigger the router to dial from your PC.
4. Type log -p to display the latest PPP log. To display all PPP logs, use the log -p -t
command.
The PPP log is useful in solving communication problems for normal ISDN dialup,
or PPPoE and PPTP dialup via a DSL modem.
Viewing WAN Logs
To view all WAN logs including ISDN D-channel and PPP/PPPoE/PPTP messages,
the simplest way is to type log -w -t.
The steps are:
1. Login to the Telnet terminal.
2. Type "log -F w" to clear all PPP/PPPoE/PPTP and ISDN logs.
3. Ping to any outside host to trigger the router to dial from your PC.
4. Type "log -w" to display the latest WAN log. If you want to display all WAN
logs, use the log –w –t command.
Page 86

FAQs
The following section covers answers for some frequently asked questions.
1. What is the default administrator password to login to the router?
A: By default, you do not need a password to login to the router. However, for
security reasons, you should assign a password to protect your router against
misusage and hacker attack.
2. What is the default IP address of the router?
A: The default IP address is 192.168.0.1 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
3. Why does the router dial out very often?
A: Examine the packets that trigger the router to dial out. Login to the Web
Configurator and click Diagnostic Tools → Triggered Dial-out Packet Header.
You will see the triggered packet contents. Report the results to technical support by
e-mail or telephone.
4. Why can't I connect to the Web Configurator?
A: Remove the proxy server settings in your Web browser.
5. Why can I ping to outside hosts but can not access Internet Websites?
A: Check if the Primary and the Secondary DNS servers have been correctly setup
on your PC. You should have received the DNS server settings from your ISP. If
your PC is running a DHCP client, remove any DNS IP address settings since the
router will assign the DNS settings to the DHCP-client-enabled PC.
6. How many IP addresses can the DHCP server of the router assign to local
PCs?
A: The built-in DHCP server can support 253 IP addresses for local network usage.
Page 87

Appendix B – Basic IP Concepts
This appendix describes some basic IP concepts, the TCP/IP addressing scheme and
show how to assign IP Addresses.
When setting up the router, you must make sure all ports to be utilized on the router
have valid IP addresses. Even if you will not use the ISDN or WAN ports, you
should, at the very least, make sure the LAN port is assigned a valid IP address. This
is required for telnet, in-band SNMP management, and related functions such as
“trap” handling and TFTP firmware download.
IP Addresses
The Internet Protocol (IP) was designed for routing data between network sites all
over the world, and was later adapted to allow routing between networks (often
referred to as “subnets”) within any site. IP includes a system by which a unique
number can be assigned to each of the millions of networks and each of the
computers on those networks. Such a number is called an IP address.
To make IP addresses easy to understand, the originators of IP adopted a system of
representation called “dotted decimal” or “dotted quad” notation. Below are
examples of IP addresses written in this format:
201.202.203.204 189.21.241.56 125.87.0.1
Each of the four values in an IP address is the ordinary decimal (base 10)
representation of a value that a computer can handle using eight “bits” (binary digits
— 1s and 0s). The dots are simply convenient visual separators.
Zeros are often used as placeholders in dotted decimal notation; 189.21.241.56 can
therefore also appear as 189.021.241.056.
IP networks are divided into three classes on the basis of size. A full IP address
contains a network portion and a “host” (device) portion. The network and host
portions of the address are different lengths for different classes of networks, as
shown in the table below.
Page 88

Networks attached to the Internet are assigned class types that determine the
maximum number of possible hosts per network. The previous figure illustrates how
the net and host portions of the IP address differ among the three classes. Class A is
assigned to networks that have more than 65,535 hosts; Class B is for networks that
have 256 to 65534 hosts; Class C is for networks with less than 256 hosts.
IP Network Classes
Class Maximum
Number of
Networks in
Class
A 126 1(.0.0.0) to 126(.0.0.0) 16,777,214
B 16,382 128.1(.0.0) to 191.254(.0.0) 65,534
C 2,097,150 192.0.1(.0) to 223.255.254(.0) 254
Network Addresses (Host
Portion in Parenthesis)
Maximum
Number of
Hosts per
Network
Note: All network addresses outside of these ranges (Class D and E) are either
reserved or set aside for experimental networks or multicasting.
When an IP address's host portion contains only zero(s), the address identifies a
network and not a host. No physical device may be given such an address.
The network portion must start with a value from 1 to 126 or from 128 to 223. Any
other value(s) in the network portion may be from 0 to 255, except that in class B
the network addresses 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.0.0 are reserved, and in class C the
network addresses 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.0 are reserved.
The value(s) in the host portion of a physical device's IP address can be in the range
of 0 through 255 as long as this portion is not all-0 or all-255. Values outside the
range of 0 to 255 can never appear in an IP address (0 to 255 is the full range of
integer values that can be expressed with eight bits).
The network portion must be the same for all the IP devices on a discrete physical
network (a single Ethernet LAN, for example, or a WAN link). The host portion
must be different for each IP device — or, to be more precise, each IP-capable port
or interface — connected directly to that network.
Page 89

The network portion of an IP address will be referred to in this manual as a network
number; the host portion will be referred to as a host number.
To connect to the Internet or to any private IP network that uses an Internet-assigned
network number, you must obtain a registered IP network number from an Internetauthorized network information center. In many countries you must apply through a
government agency, however they can usually be obtained from your Internet
Service Provider (ISP).
If your organization's networks are, and will always remain, a closed system with no
connection to the Internet or to any other IP network, you can choose your own
network numbers as long as they conform to the above rules.
If your networks are isolated from the Internet, e.g. only between your two branch
offices, you can assign any IP Addresses to hosts without problems. However, the
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three
blocks of IP Addresses specifically for private (stub) networks:
Class Beginning Address Ending Address
A 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255
B 172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255
C 192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255
It is recommended that you choose private network IP Addresses from the above
list. For more information on address assignment, refer to RFC 1597, Address
Allocation for Private Internets and RFC 1466, Guidelines for Management of IP
Address Space.
Subnet Mask
In the absence of subnetworks, standard TCP/IP addressing may be used by
specifying subnet masks as shown below.
Subnet mask settings other than those listed above add significance to the
interpretation of bits in the IP address. The bits of the subnet mask correspond
directly to the bits of the IP address. Any bit an a subnet mask that is to correspond
to a net ID bit in the IP address must be set to 1.
IP Class Subnet Mask
Class A 255.0.0.0
Class B 255.255.0.0
Class C 255.255.255.0
Page 90

Appendix C – IP Protocol and Port
Numbers
Common Internet service protocols and IP port numbers.
IP Protocol Numbers
Protocol # Protocol Name Description
1 ICMP Internet Control Message [RFC792]
2 IGMP Internet Group Management [RFC1112]
6 TCP Transmission Control [RFC793]
8 EGP Exterior Gateway Protocol [RFC888,DLM1]
9 IGP any private interior gateway [IANA]
17 UDP User Datagram [RFC768,JBP]
46 RSVP Reservation Protocol [Bob Braden]
88 EIGRP EIGRP [CISCO,GXS]
115 L2TP Layer Two Tunneling Protocol [Aboba]
(used by Cisco for their IGRP)
IP Port Numbers
Service TCP UDP Notes
FTP 21 File Transfer
Telnet 23
SMTP 25 Simple Mail Transfer
DNS 53 53 Domain Name Server
Finger 79
WWWHTTP 80 World Wide Web HTTP
POP3 110 Post Office Protocol – Version 3
137 137 NetBios Name Service
138 138 NetBios Datagram Service
139 139 NetBios Session Service
SNMP 161
SNMP Trap 162
Page 91

Appendix D - Technical Specifications
General
Ports
Number of Ports:
4 LAN ports
1 Uplink port
1 WAN port
LED Readout
Power
Status
ISDN Link, B1, B2
LAN Link/Act, 10/100M, 1, 2, 3, 4
LAN
Standard IEEE 802.3/802.3u
LAN Protocol CSMA/CD
Data Transfer Rates 10/100Mbps auto-negotiation
Network Cables
10BASE-T:
2-pair UTP Cat.3, 4, 5
(100m max. length)
100BASE-TX:
2-pair UTP Cat. 5
(100m max. length)
ISDN
Standard PPP/Multi-link PPP
ISDN Protocols
ISDN speeds ISDN BRI: up to 128,000bps
ISDN Interface
1 ISDN BRI port: 64Kbps B channel x 2
ISDN network Compatibility
ISDN switch type DSS1
Data Compression
Routing
IP Packet Routing TCP/IP with RIP-1 and RIP-2, static routes
Other Protocols
Management
SNMP MIB-II
Security
Physical & Environmental
DC Input:
External DC power adapter
Power Consumption 12W max.
RJ-45
RJ-45
ISDN BRI S/T
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm screened twisted-pair
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm screened twisted-pair
Standard BRI S/T
16Kbps D channel x 1
Hi/fn LZS (Stac)
UDP, TCP, NAT, DHCP, BAP/BACP, ICMP,
IGMP
PAP, CHAP, MS CHAP
Administrative password through Telnet only
Firewall filtering
16-18VAC, 1.0A
Page 92

Ventilation Fanless
Operating Temperature 0 - 50 C (32 - 122 F)
Storage Temperature -25 - 55 C (-13 - 131 F)
Humidity 5% - 95% non-condensing
Dimensions 22.4cm x 13.2cm x 3.5cm
Emissions (EMI) CE,C-Tick
Telecom CTR-3
Safety UL/CSA/TUV, C-Tick (for power adapter)
Page 93

Index
Adapter, Installation & Setup page 7
Bandwidth On Demand. See BOD
BOD, 2
Challenge Handshake Authentication
Protocol. See CHAP
CHAP, 2
Configuration , 25
Dial On Demand, 2
Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol, 3
Front panel LED’s, 9
installation, 1
Internet, 4
IP Addresses, 79
IP Concepts, 79
IP Network Classes, 80
IP Port Numbers, 82
IP Protocol, 82
IP Protocol Numbers, 82
ISDN, 10
Lan, 2
LAN, 2, 5, 6, 9
Local Area Network. See LAN
Management, 25
network management, 2
PAP, 2
Password Authentication Protocol.
See PAP
Remote Dial-in Users, 1, 5
Remote Node, 1, 2
RS-232, 2
Simple Network Management
Protocol. See SNMP
Single User Account, 1, 5
SNMP, 2
STP, 91
SUA. See Single User Account
Subnet Mask, 81
TCP/IP, 4, 5, 79
Telecommuting, 5
Telnet, 2, 7, 61
UTP, 82
, 11
Page 94

International Offices
U.S.A
17595 Mt. Herrmann Street
Fountain Valley, CA. 92708
TEL: 714-885-6000
FAX: 866-743-4905
URL: www.dlink.com
Canada
2180 Winston Park Drive
Oakville, Ontario, L6H 5W1
Canada
TEL: 1-905-8295033
FAX: 1-905-8295223
URL: www.dlink.ca
Europe (U. K.)
th
Floor, Merit House
4
Edgware Road, Colindale
London NW9 5AB
U.K.
TEL: 44-20-8731-5555
FAX: 44-20-8731-5511
URL: www.dlink.co.uk
Germany
Schwalbacher Strasse 74
D-65760 Eschborn
Germany
TEL: 49-6196-77990
FAX: 49-6196-7799300
URL: www.dlink.de
France
Le Florilege #.2, Allee de la Fresnerie
78330 Fontenay le Fleury
France
TEL: 33-1-30238688
FAX: 33-1-30238689
URL: www.dlink-france.fr
Netherlands
Weena 290
3012 NJ Rotterdam
Netherlands
Tel: +31-10-282-1445
Fax: +31-10-282-1331
URL: www.dlink-benelux.com
Belgium
Rue des Colonies 11
B-1000 Brussels
Belgium
Tel: +32(0)2 517 7111
Fax: +32(0)2 517 6500
URL: www.dlink-benelux.com
Italy
Via Nino Bonnet n. 6/b
20154 – Milano,
Italy
TEL: 39-02-2900-0676
FAX: 39-02-2900-1723
URL: www.dlink.it
Sweden
P.O. Box 15036, S-167 15 Bromma
Sweden
TEL: 46-(0)8564-61900
FAX: 46-(0)8564-61901
URL: www.dlink.se
Denmark
Naverland 2, DK-2600
Glostrup, Copenhagen,
Denmark
TEL: 45-43-969040
FAX: 45-43-424347
URL:www.dlink.dk
Norway
Karihaugveien 89
1086 Oslo
Norway
TEL: +47 23 89 71 89
FAX: +47-22-309085
URL: www.dlink.no
Finland
Pakkalankuja 7A
01510 Vantaa,
Finland
TEL : +358-9-2707 5080
FAX: + 358-9-2707 5081
URL: www.dlink.fi
Iberia
C/Sabino De Arana,
56 Bajos
08028 Barcelona
TEL: 34 93 4090770
FAX: 34 93 4910795
URL: www.dlinkiberia.es
Singapore
1 International Business Park
#03-12 The Synergy
Singapore 609917
TEL: 65-6774-6233
FAX: 65-6774-6322
URL: www.dlink-intl.com
Australia
1 Giffnock Avenue,
North Ryde, NSW 2113
Australia
TEL: 61-2-8899-1800
FAX: 61-2-8899-1868
URL: www.dlink.com.au
India
D-Link House, Kurla Bandra Complex Road,
Off CST Road, Santacruz (East), Mumbai -
400098.
India
TEL: 91-022-26526696/56902210
FAX: 91-022-26528914
URL: www.dlink.co.in
Middle East (Dubai)
P.O.Box: 500376
Office No.:103, Building:3
Dubai Internet City
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel:+971-4-3916480
Fax:+971-4-3908881
URL: www.dlink-me.com
Turkey
Maslak Ayazaga Yolu
No: 2 Kat :5
Ayazaga-Istanbul
TURKEY
TEL: 0090 212 289 56 59
FAX: 0090 212 289 76 06
URL: www.dlink.com.tr
Egypt
19 El-Shahed Helmy, El Masri
Al-Maza, Heliopolis
Cairo,Egypt.
TEL:+202 414 4295
FAX:+202 415 6704
URL: www.dlink-me.com
Israel
11 Hamanofim Street
Ackerstein Towers, Regus Business Center
P.O.B 2148, Hertzelia-Pituach 46120.
Israel
TEL: +972-9-9715700
FAX: +972-9-9715601
URL: www.dlink.co.il
LatinAmerica
Isidora Goyeechea 2934 of 702,
Las Condes
Santiago – Chile S.A.
TEL: 56-2-232-3185
FAX: 56-2-232-0923
URL: www.dlink.cl
Brasil
Av das Nacoes Unidas,
11857 - 14 - andar - cj 141/142
Brooklin Novo
Sao Paulo - SP - Brazil
CEP 04578-000
TEL: +55 11 55039320
FAX: +55 11 55039322
URL: www.dlinkbrasil.com.br
South Africa
Einstein Park II
Block B
102-106 Witch-Hazel Avenue
Highveld Technopark
Centurion
Gauteng
Republic of South Africa
TEL: 27-12-665-2165
FAX: 27-12-665-2186
URL: www..d-link.co.za
Russia
Grafsky per., 14, floor 6
Moscow
129626 Russia
TEL: 7-095-744-0099
FAX: 7-095-744-0099 #350
URL: www.dlink.ru
China
No.202,C1 Building, Huitong Office Park,
No.71, Jianguo Road, Chaoyang District,
Beijing,
100025, China.
TEL +86-10-58635800
FAX: +86-10-58635799
URL: www.dlink.com.cn
Taiwan
2F, No. 119, Pao-Chung Rd.
Hsin-Tien, Taipei
Tai wan
TEL: 886-2-2910-2626
FAX: 886-2-2910-1515
URL: www.dlinktw.com.tw
Headquarters
2F, No. 233-2, Pao-Chiao Rd.
Hsin-Tien, Taipei
Tai wan
TEL: 886-2-2916-1600
FAX: 886-2-2914-6299
URL: www.dlink.com.tw
Page 95

Registration Card
Print, type or use block letters.
Your name: Mr./Ms_____________________________________________________________________________
Organization: ________________________________________________ Dept. ____________________________
Your title at organization: ________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: ______________ _________________________ Fax:___________________________ _____________
Organization's full address: ______________________________________________________________________
__________________________ ___________________________________________ _______________________
Country: _____________________________________________________________________________________
Date of purchase (Month/Day/Year): _______________________________________________________________
Product Model Product Serial No. * Product installed in type of
computer (e.g., Compaq 486)
(* Applies to adapters only)
Product was purchased from:
Reseller's name: ______________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: ______________ _________________________ Fax:___________________________ _____________
Reseller's full address: _________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
Answers to the following questions help us to support your product:
1. Where and how will the product primarily be used?
Home Office Travel Company Business Home Business Personal Use
2. How many employees work at installation site?
1 employee 2-9 10-49 50-99 100-499 500-999 1000 or more
3. What network protocol(s) does your organization use ?
XNS/IPX TCP/IP DECnet Others_____________________________
4. What network operating system(s) does your organization use ?
D-Link LANsmart Novell NetWare NetWare Lite SCO Unix/Xenix PC NFS 3Com 3+Open
Banyan Vines DECnet Pathwork Windows NT Windows NTAS Windows '95
Others__________________________________________
5. What network management program does your organization use ?
D-View HP OpenView/Windows HP OpenView/Unix SunNet Manager Novell NMS
NetView 6000 Others________________________________________
6. What network medium/media does your organization use ?
Fiber-optics Thick coax Ethernet Thin coax Ethernet 10BASE-T UTP/STP
100BASE-TX 100BASE-T4 100VGAnyLAN Others_________________
7. What applications are used on your network?
Desktop publishing Spreadsheet Word processing CAD/CAM
Database management Accounting Others_____________________
8. What category best describes your company?
Aerospace Engineering Education Finance Hospital Legal Insurance/Real Estate Manufacturing
Retail/Chainstore/Wholesale Government Transportation/Utilities/Communication VAR
System house/company Other________________________________
9. Would you recommend your D-Link product to a friend?
Yes No Don't know yet
10.Your comments on this product?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
* Product installed in
computer serial No.
Page 96

 Loading...
Loading...